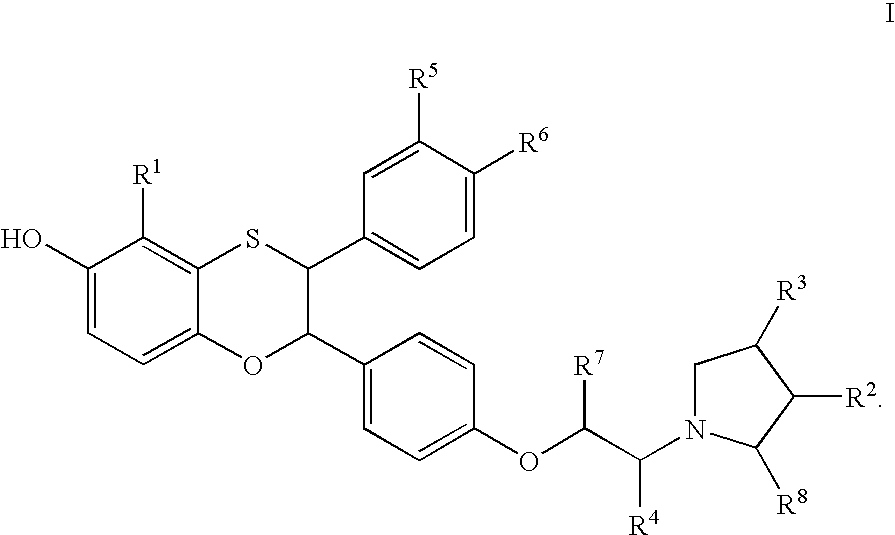
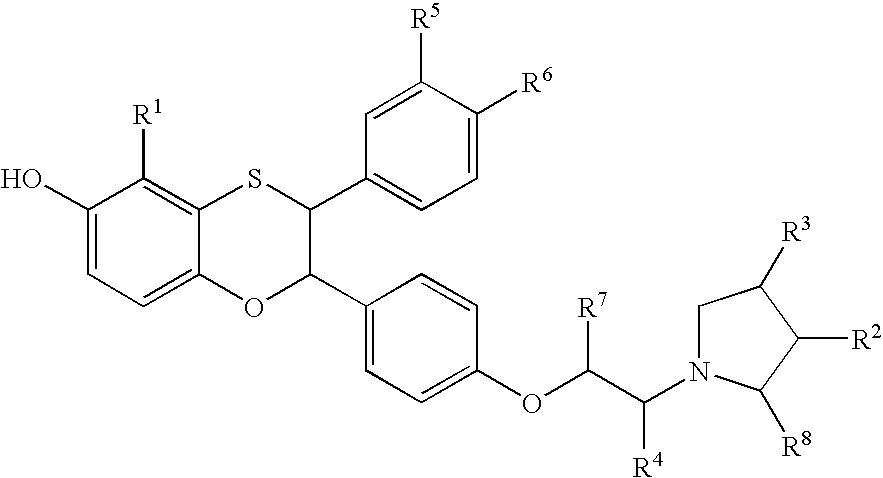
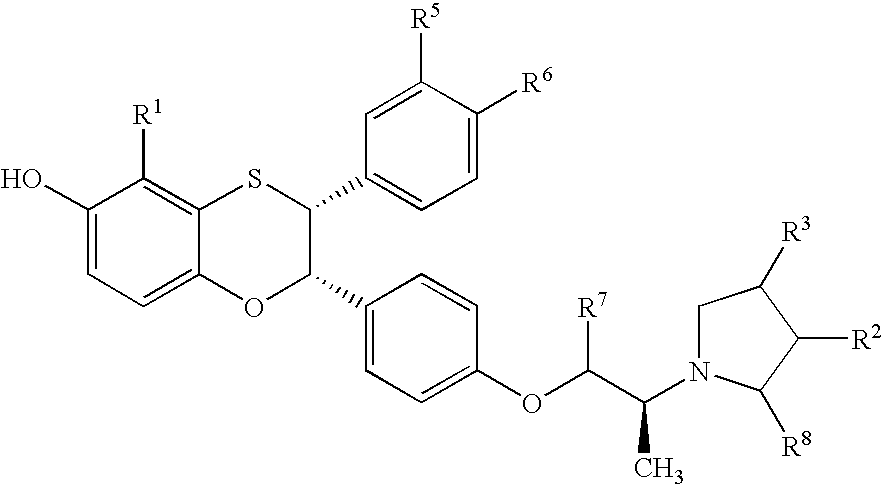
Patents
Literature
564 results about "Leiomyocyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods and systems for the inhibition of vascular hyperplasia
InactiveUS6210393B1Limited extentQuick layeringUltrasound therapyStentsSmooth muscleVascular proliferation
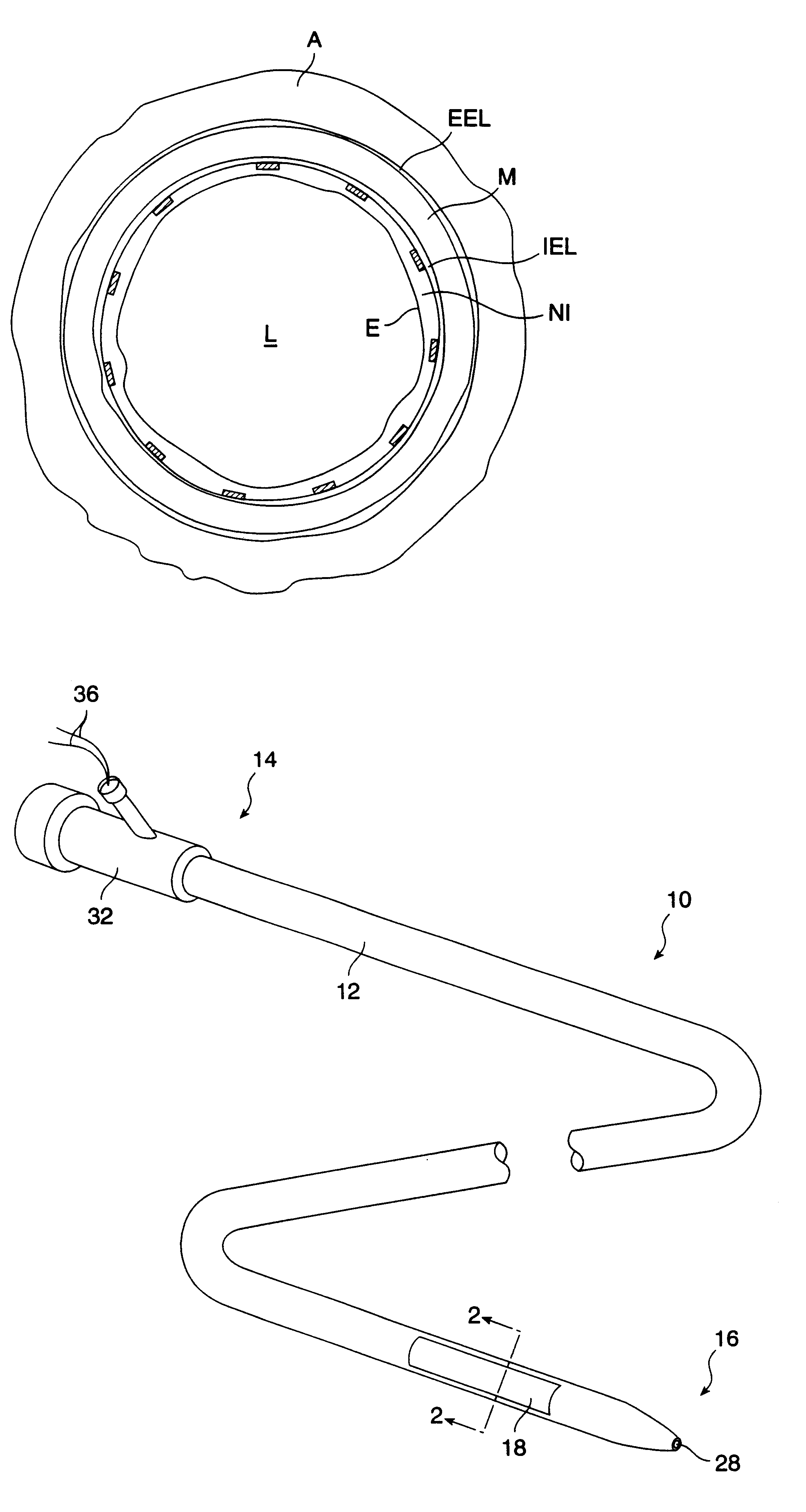
Post-interventional neointimal hyperplasia in arteries is treated by the application of ultrasonic energy. Usually, an intravascular catheter having an interface surface is positioned at a target site in the artery which has previously been treated. The interface surface is vibrationally excited to apply energy to the arterial wall in a manner which inhibits smooth muscle cell proliferation in the neointimal layer.
Owner:PHARMASONICS
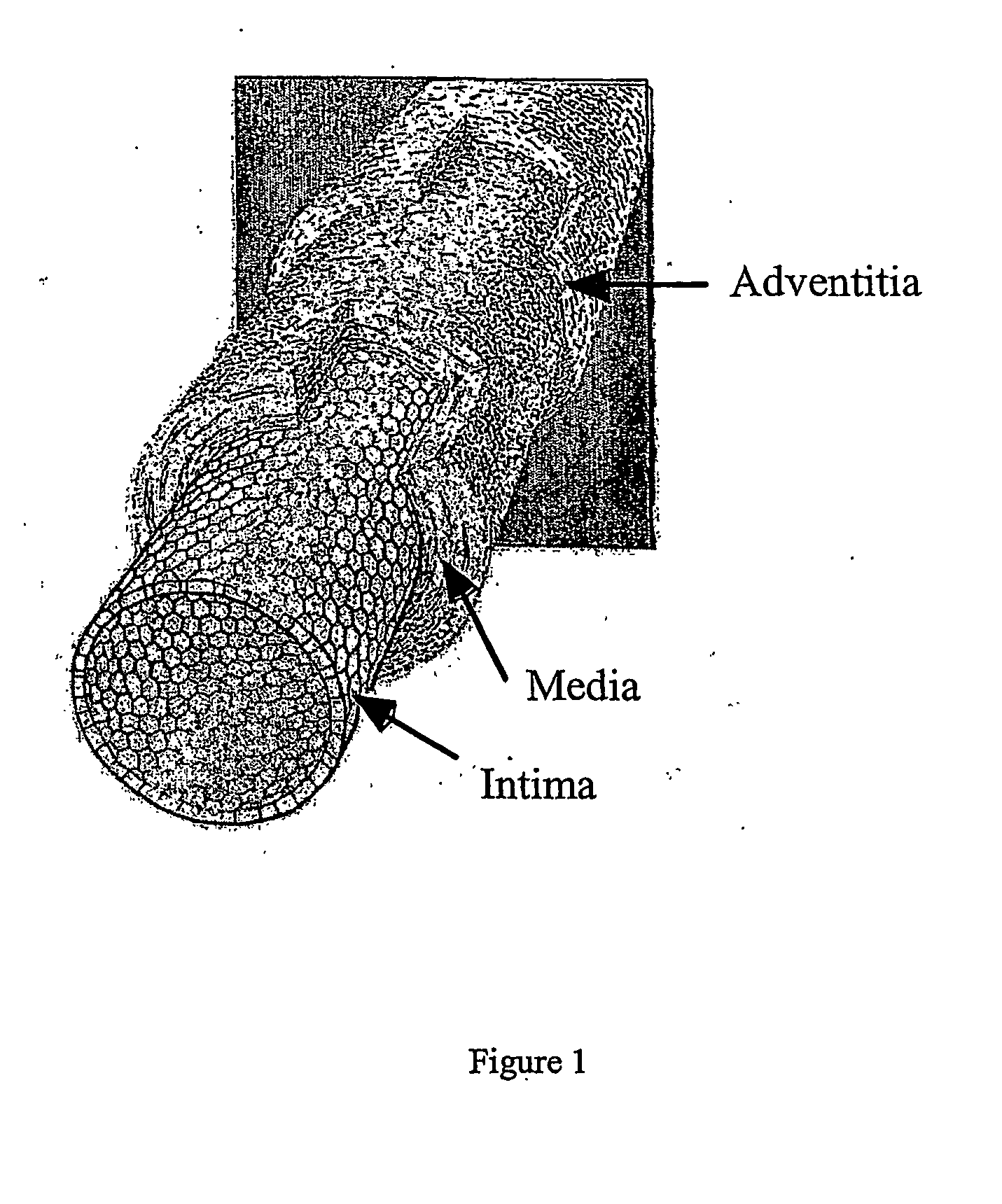
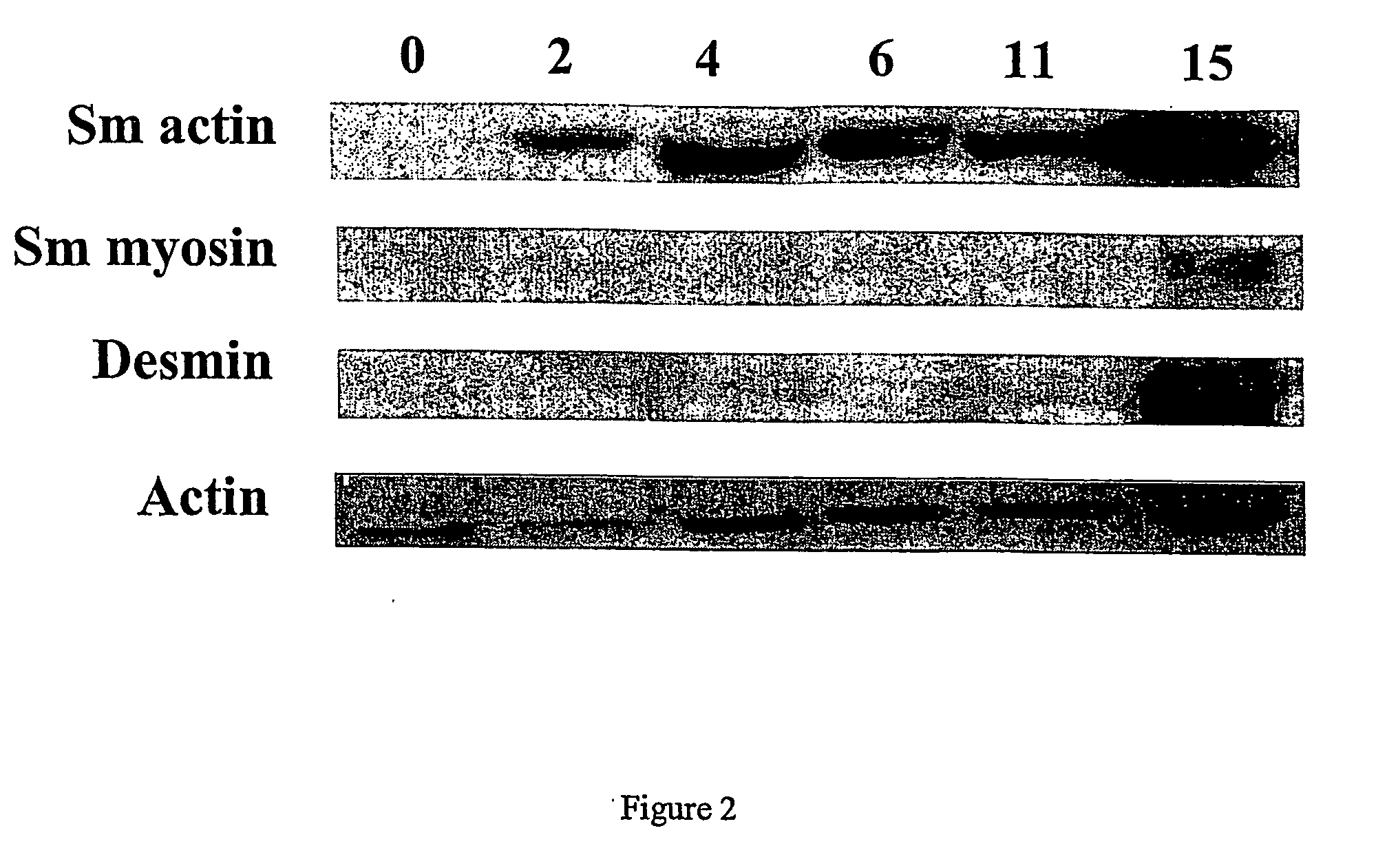
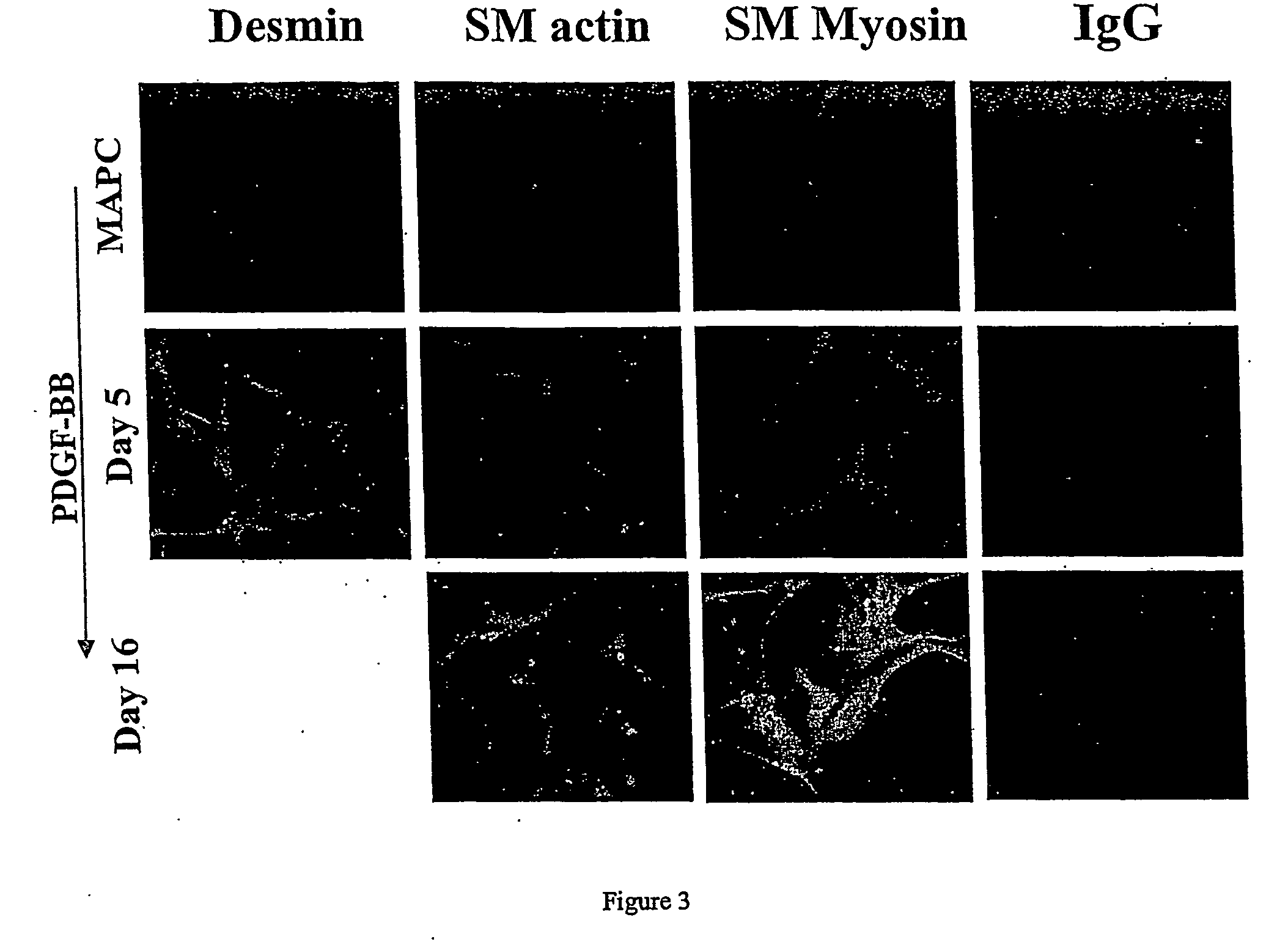
Methods and compositions for smooth muscle reconstruction
This invention also provides a purified or isolated population of ADSCs that can differentiate into a cell of the leiomyogenic lineage, e.g., smooth muscle or skeletal muscle. In yet another aspect, the population additionally can be differentiated into a lineage selected from the group consisting of osteogenic, adipogenic, chondrogenic, myogenic and neuronal. This invention further provides a composition comprising a substantially homogeneous expanded population of smooth muscle cells. This invention provides a composition comprising a substantially homogeneous expanded population of skeletal muscle cells. Also provided herein is an isolated composition comprising a purified adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC) or progeny of said ADSC and an effective amount of laminin or heparin, effective to induce leiomyogenic differentiation. Diagnositic and therapeutic uses for these compositions are provided herein.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
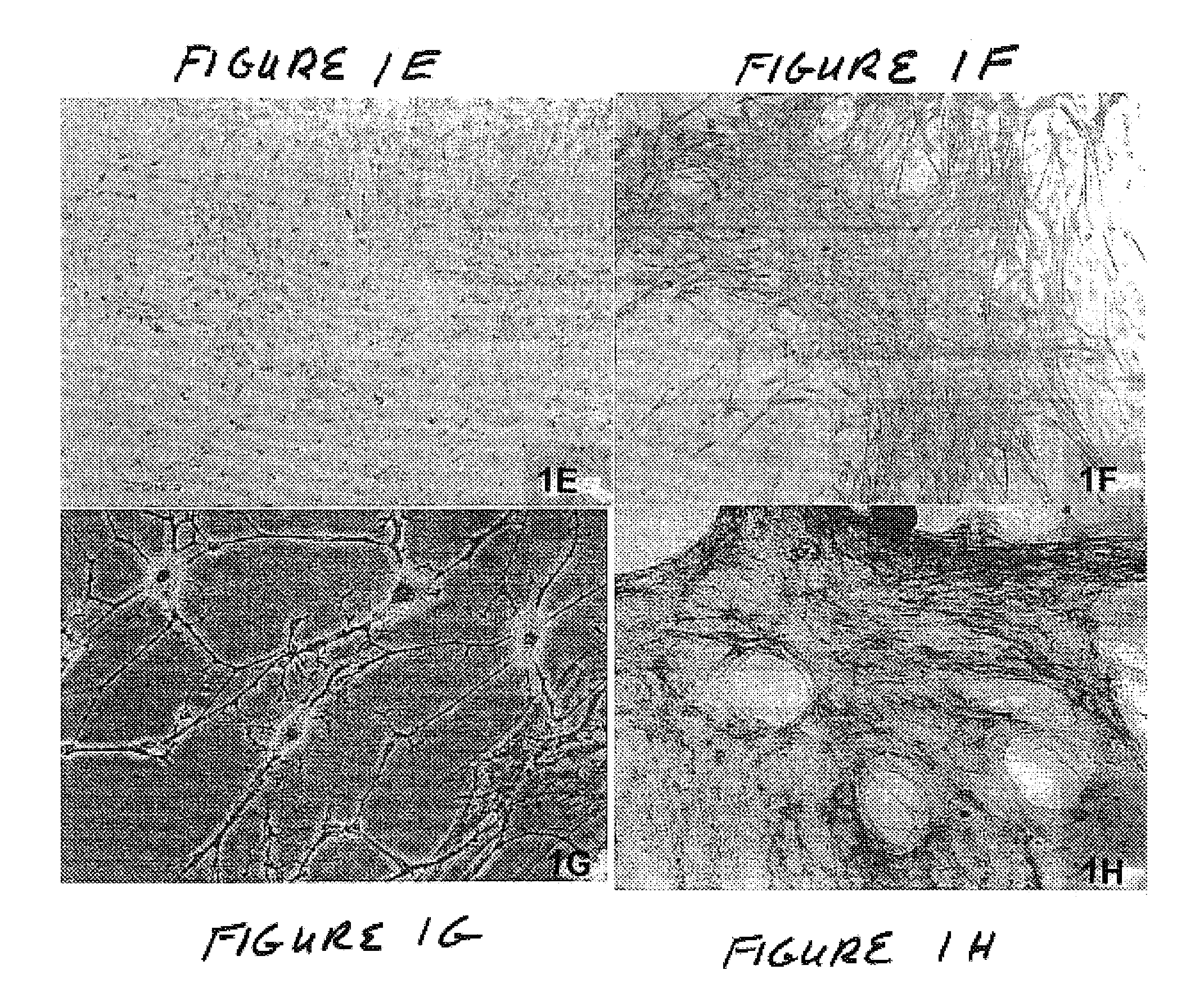
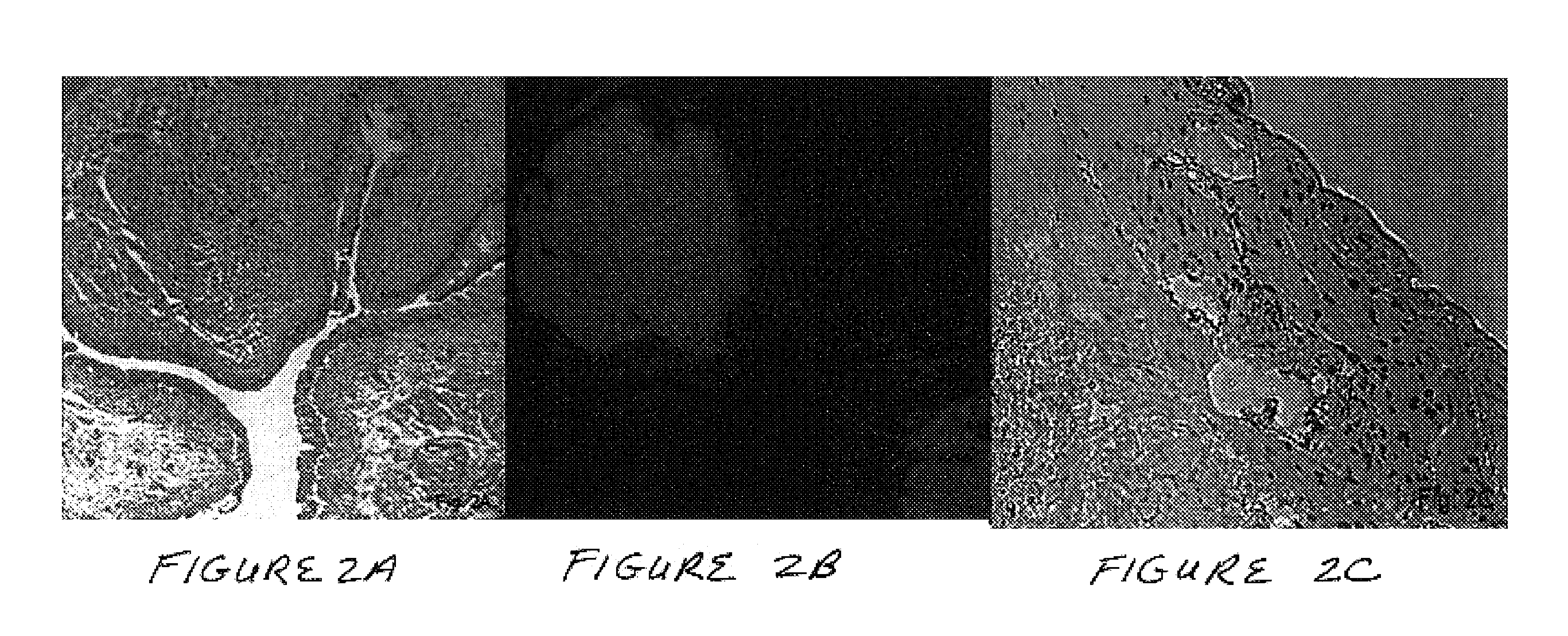
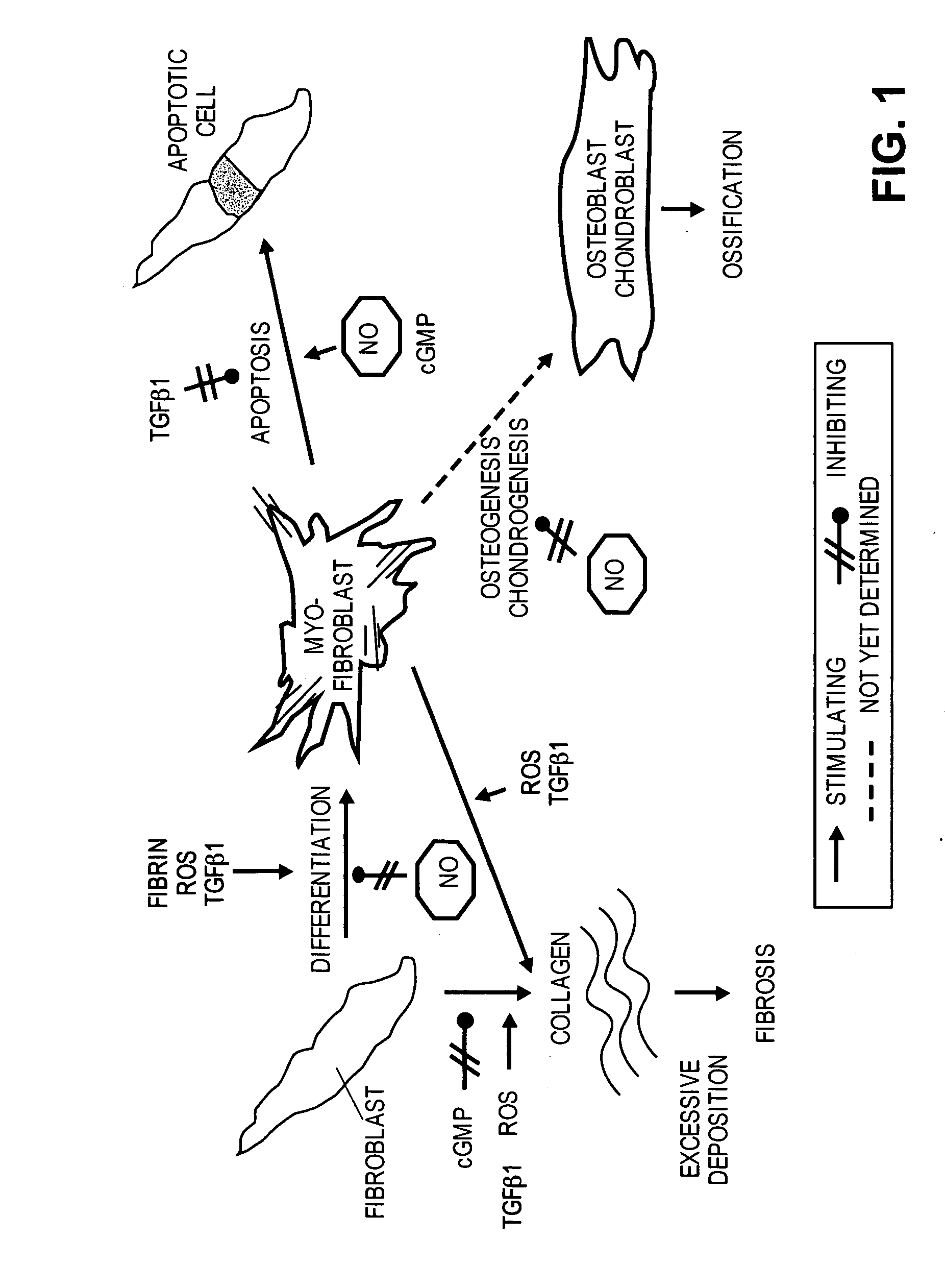
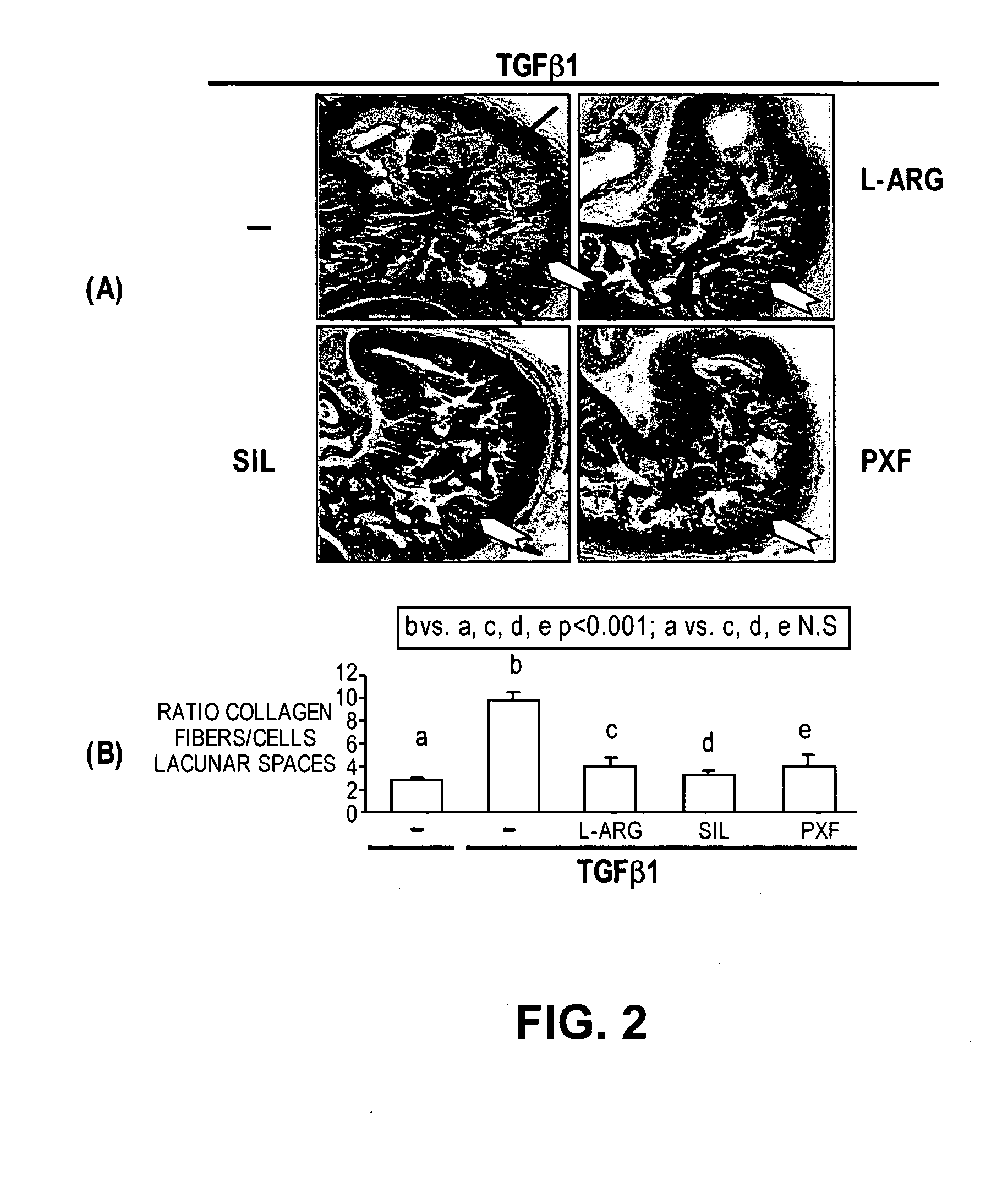
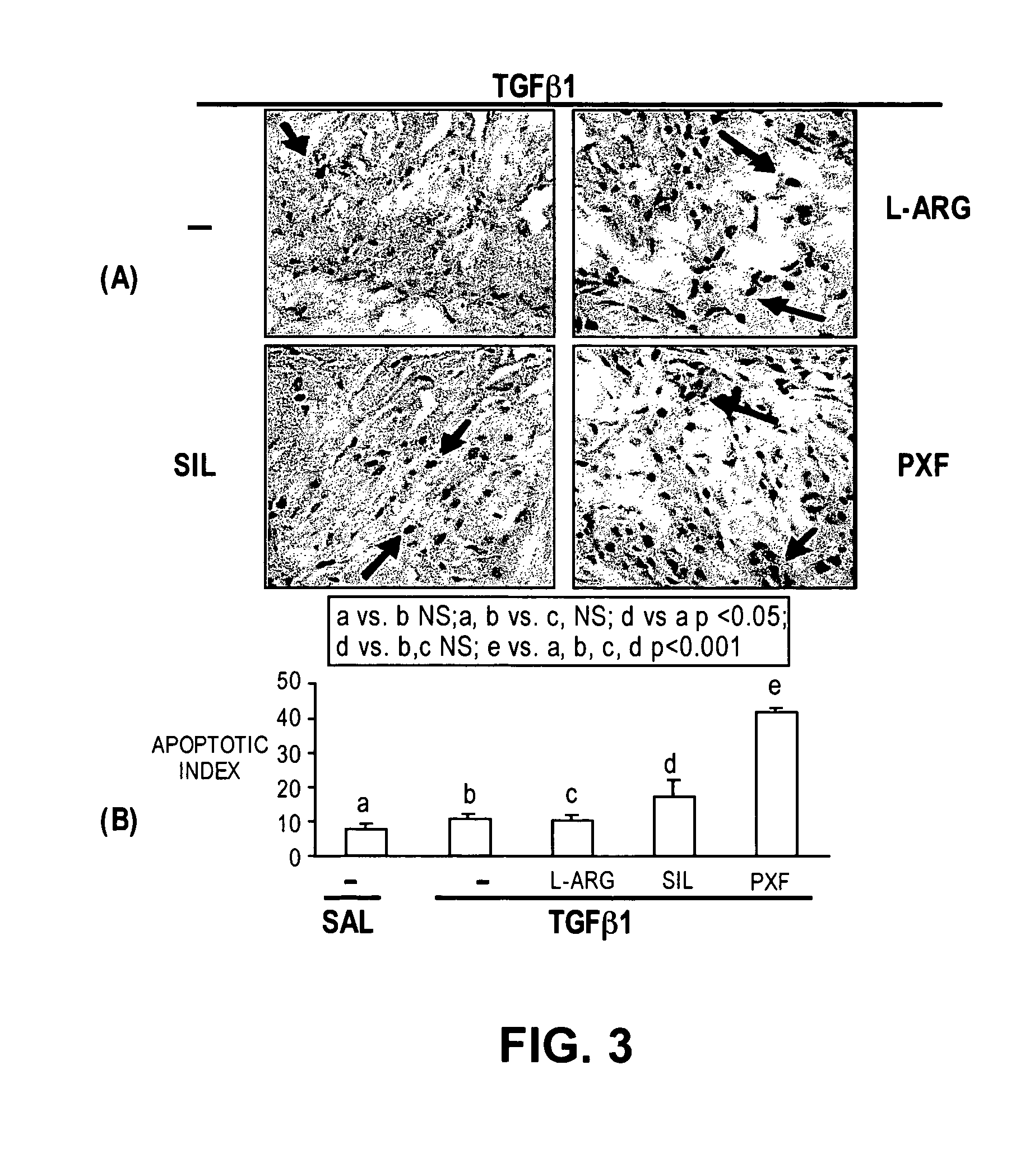
Methods of use of inhibitors of phosphodiesterases and modulators of nitric oxide, reactive oxygen species, and metalloproteinases in the treatment of peyronie's disease, arteriosclerosis and other fibrotic diseases
ActiveUS20050085486A1Increasing NO levelReduce expressionBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismFemale Sexual Arousal DisorderCyclase
The present methods and compositions are of use for treatment of conditions involving fibrosis, such as Peyronie's disease plaque, penile corporal fibrosis, penile veno-occlusive dysfunction, Dupuytren's disease nodules, vaginal fibrosis, clitoral fibrosis, female sexual arousal disorder, abnormal wound healing, keloid formation, general fibrosis of the kidney, bladder, prostate, skin, liver, lung, heart, intestines or any other localized or generalized fibrotic condition, vascular fibrosis, arterial intima hyperplasia, atherosclerosis, arteriosclerosis, restenosis, cardiac hypertrophy, hypertension or any condition characterized by excessive fibroblast or smooth muscle cell proliferation or deposition of collagen and extracellular matrix in the blood vessels and / or heart. In certain embodiments, the compositions may comprise a PDE-4 inhibitor, a PDE-5 inhibitor, a compound that elevates cGMP and / or PKG, a stimulator of guanylyl cyclase and / or PKG, a combination of a compound that elevates cGMP, PKG or NO with an antioxidant that decreases ROS, or a compound that increases MMP activity.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
Engineered blood vessels
The present invention relates to engineered blood vessels and methods of making such vessels using matrices comprising endothelial and smooth muscle cells, or cells capable of differentiating into endothelial and smooth muscle cell lineages (e.g., stem cells, or the progenitors thereof).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Production of tissue engineered heart valves
ActiveUS20060253192A1Avoid it happening againMore of their natural flexibilityHeart valvesNanoinformaticsProgenitorSmooth muscle
The invention is directed to methods for preparing artificial heart valves by preconditioning a matrix seeded with endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells differentiated from isolated progenitor cells. These cell seeded matrices are exposed to fluid conditions that mimic blood flow through the heart to produce tissue engineered heart valves that are analogous to native heart valves.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Apparatus and method for delivery of mitomycin through an eluting biocompatible implantable medical device
InactiveUS7396538B2Increase the diameterPrevent proliferationStentsOrganic active ingredientsQuinoneDrug release rate
The present invention is an apparatus and a method for delivery of mitomycin through an eluting biocompatible implantable medical device. A biocompatible drug release matrix comprises a biocompatible drug release matrix and a drug incorporated into the biocompatible drug release matrix. The drug has antibiotic and anti-proliferative properties and is an analogue related to the quinone-containing alkylating agents of a mitomycin family. The drug is initially released from the biocompatible drug release matrix at a faster rate followed by a release at a slower rate. The drug release rate maintains tissue level concentrations of the drug for at least two weeks after implantation of the medical device. The present invention provides a coating for a vascular prosthesis that elutes the drug at a controlled rate to inhibit proliferation of smooth muscle cells causing restenosis.
Owner:ENDOVASCULAR DEVICES INC
Tissue equivalents
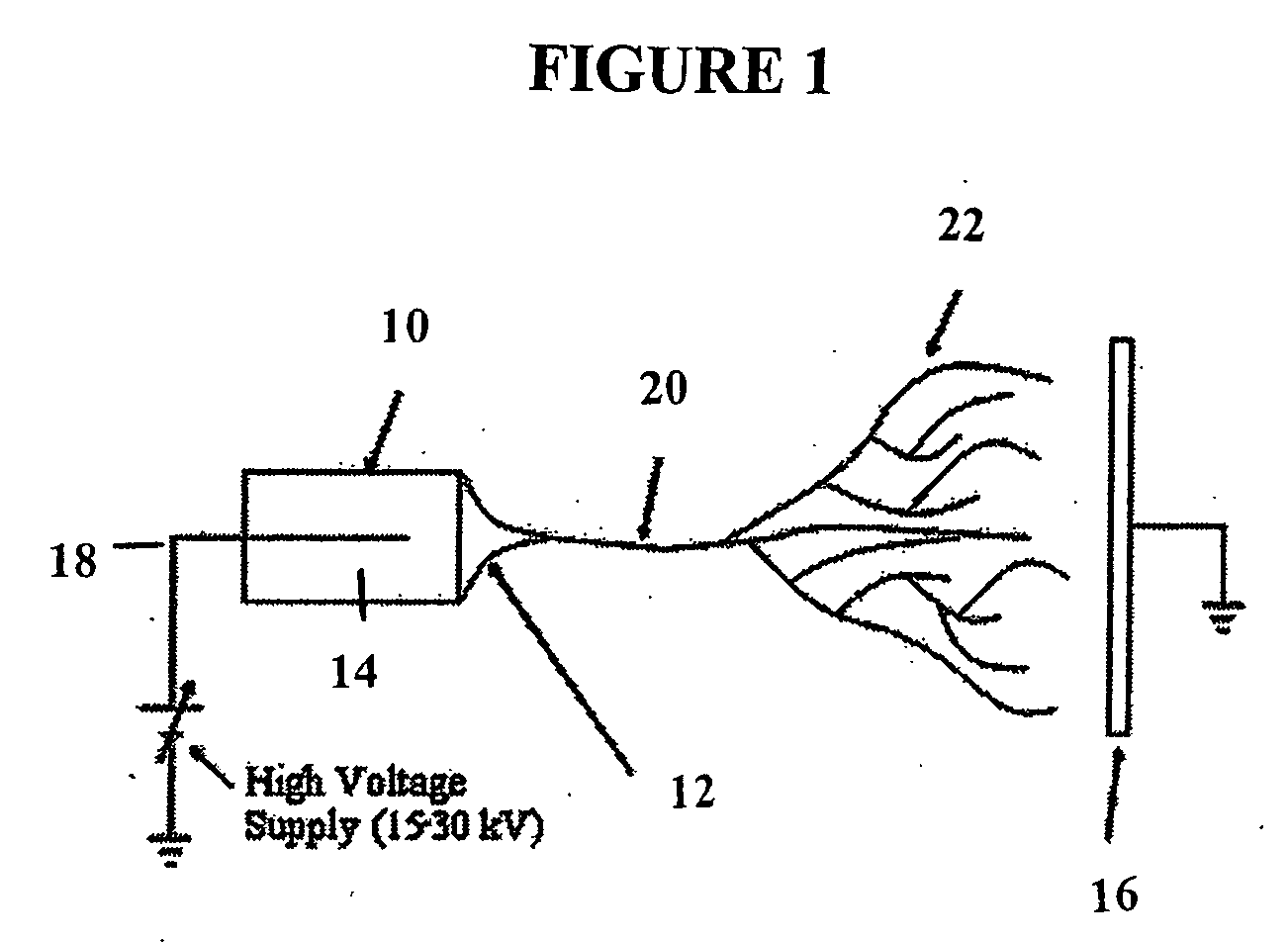
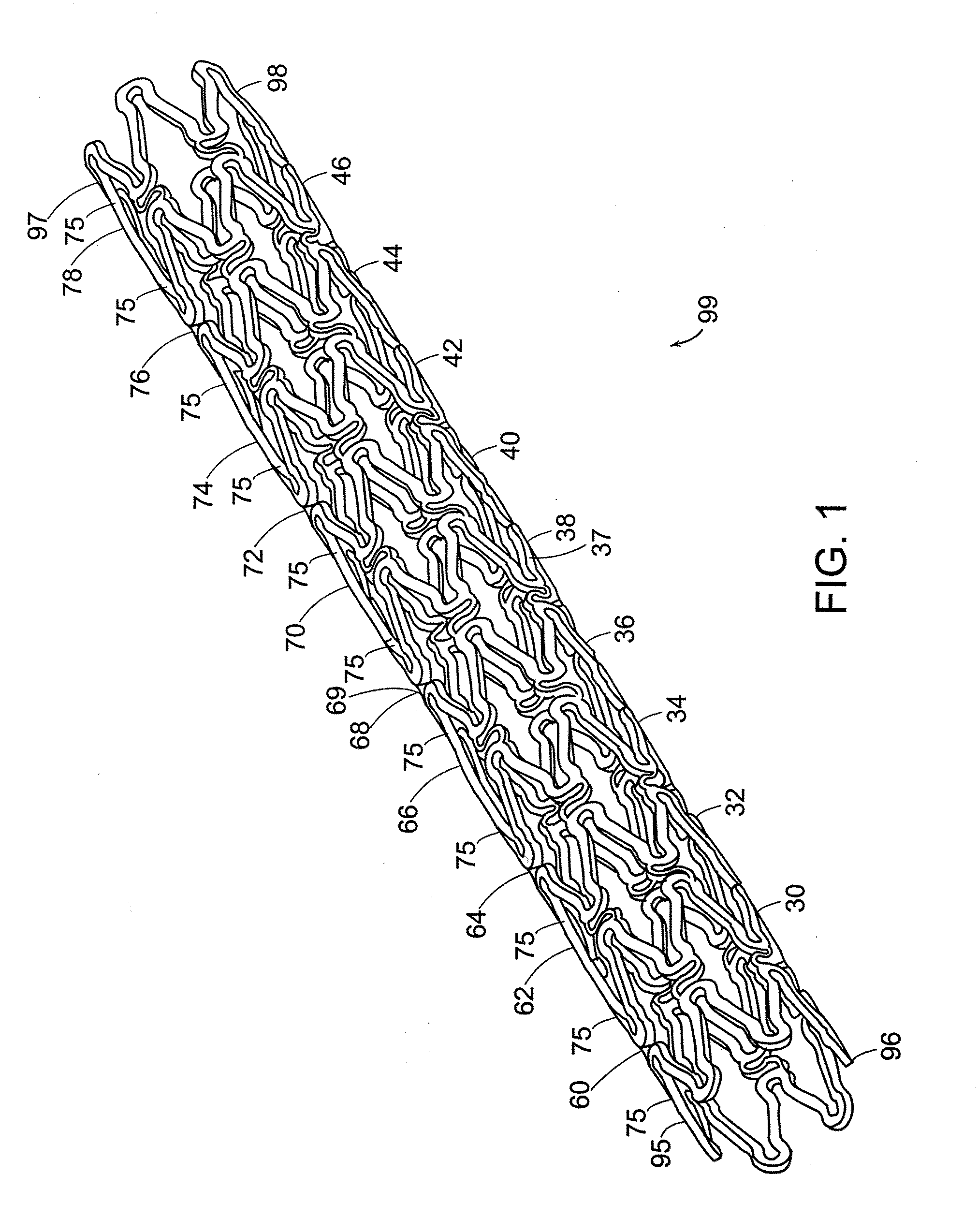
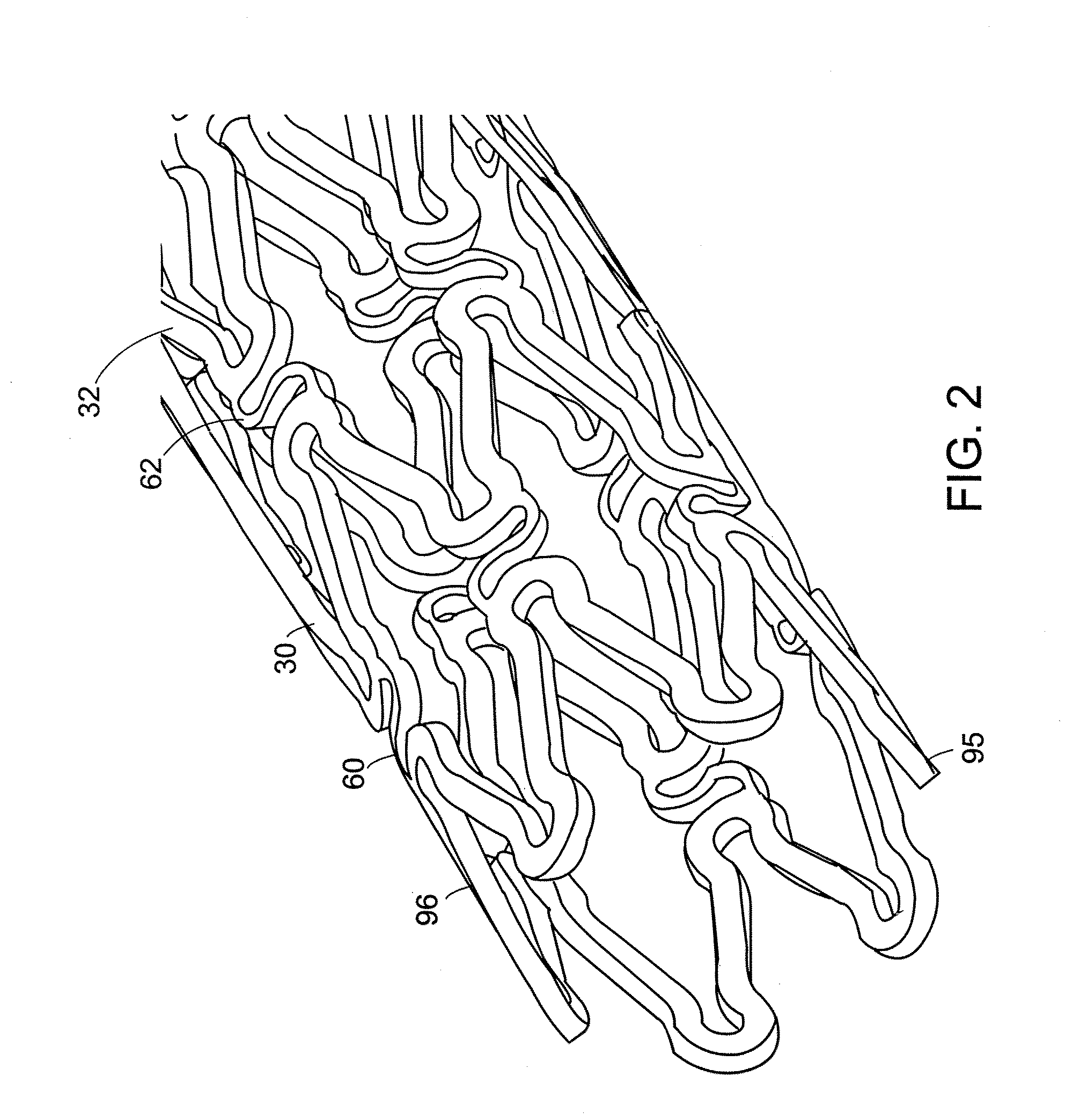
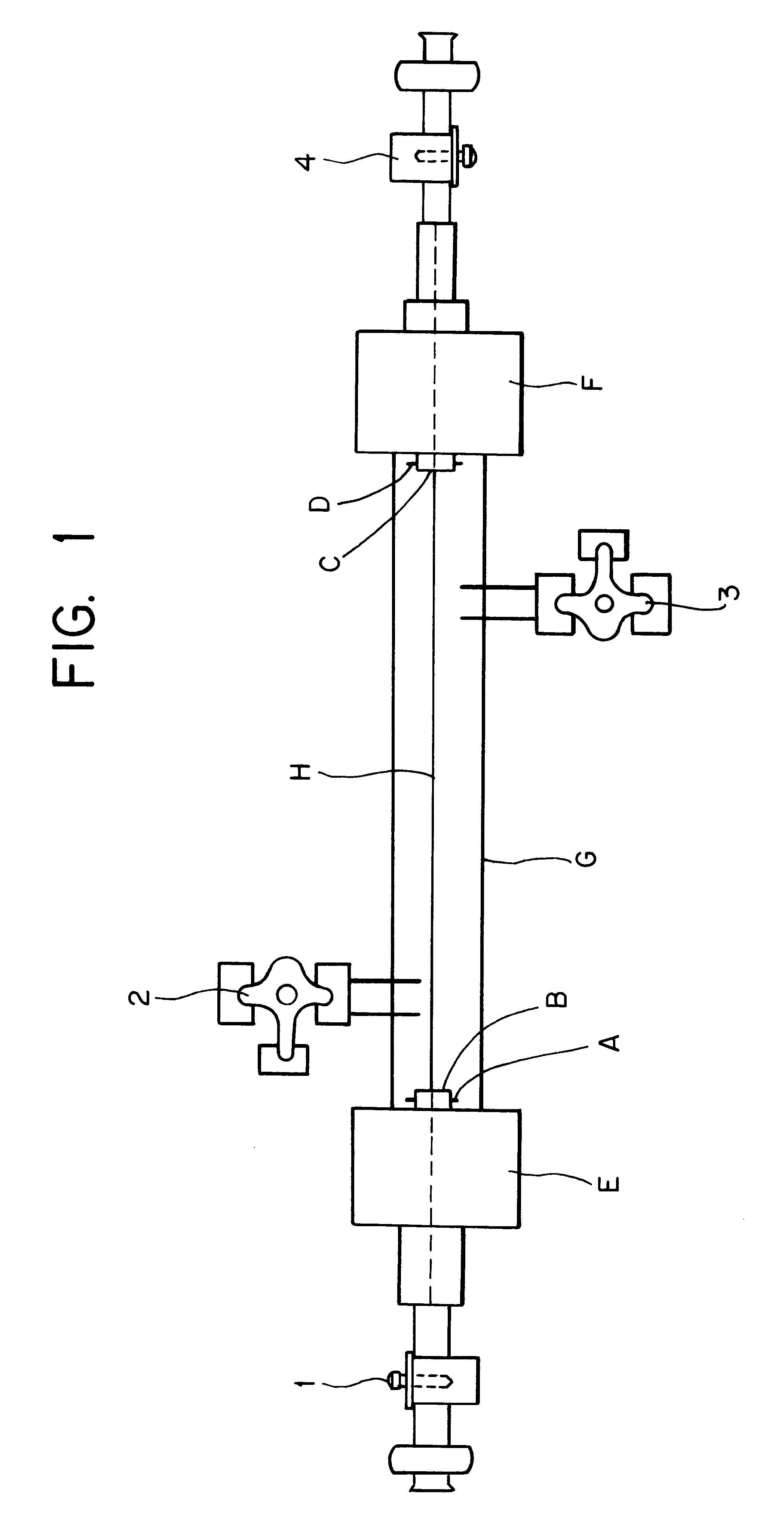
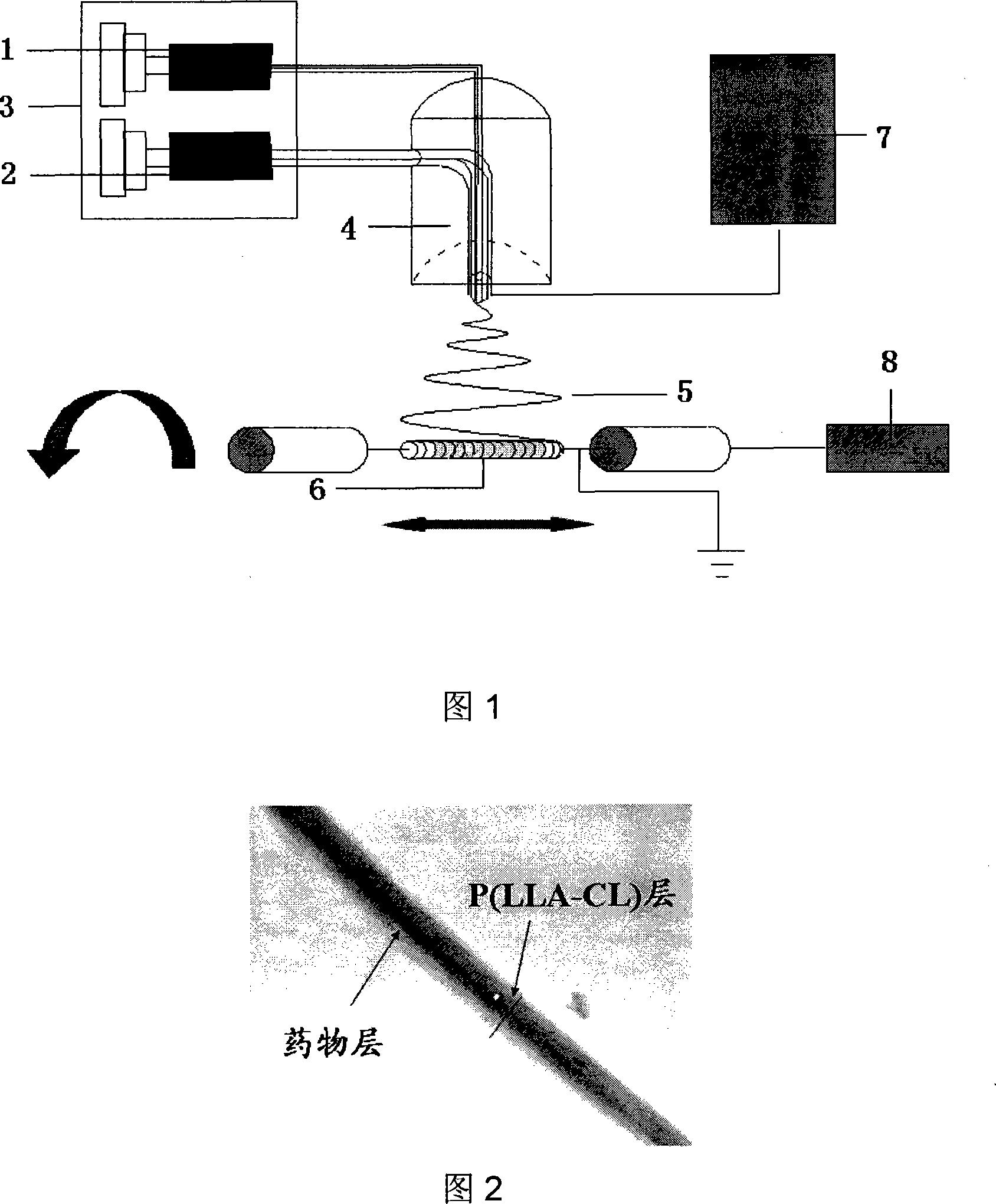
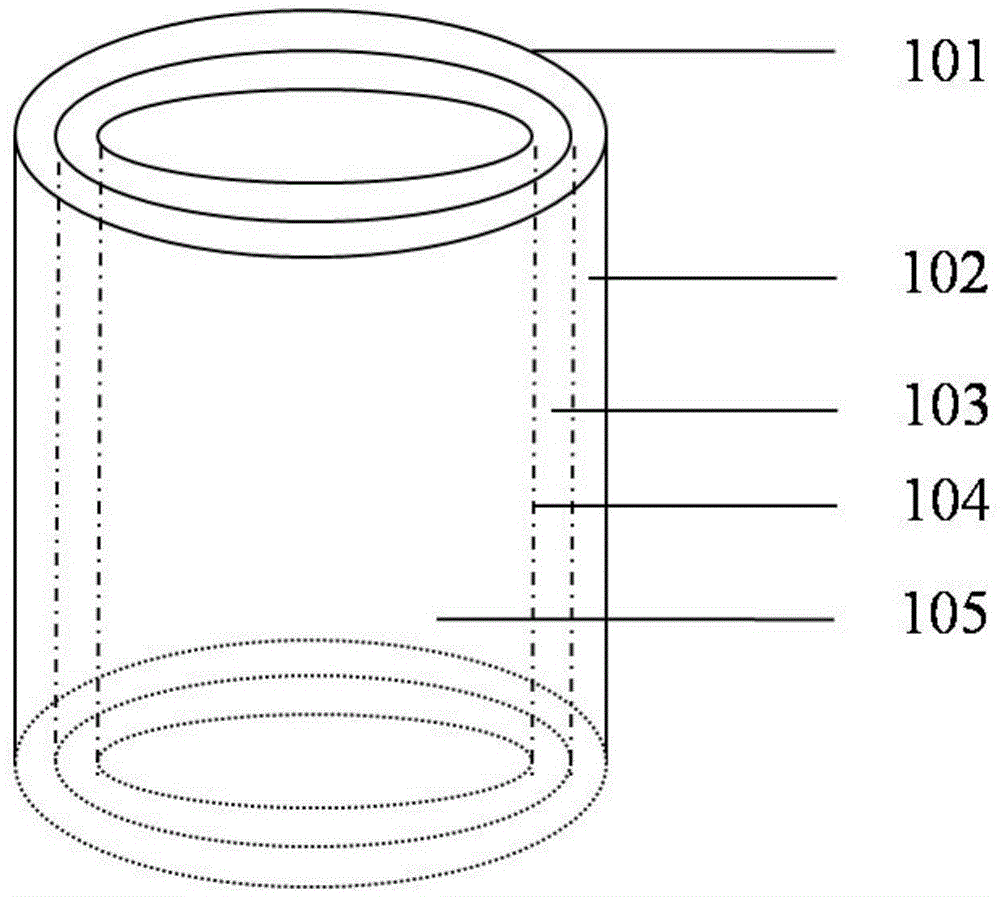
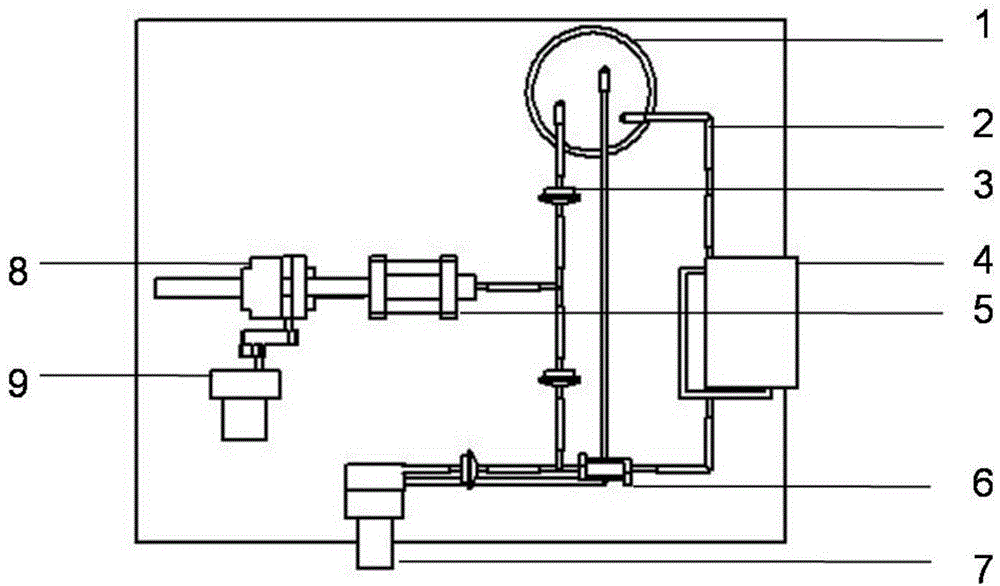
InactiveUS6197296B1Easy pretreatmentPrevent thrombosisBiocideTissue cultureLeiomyocytePhases of clinical research
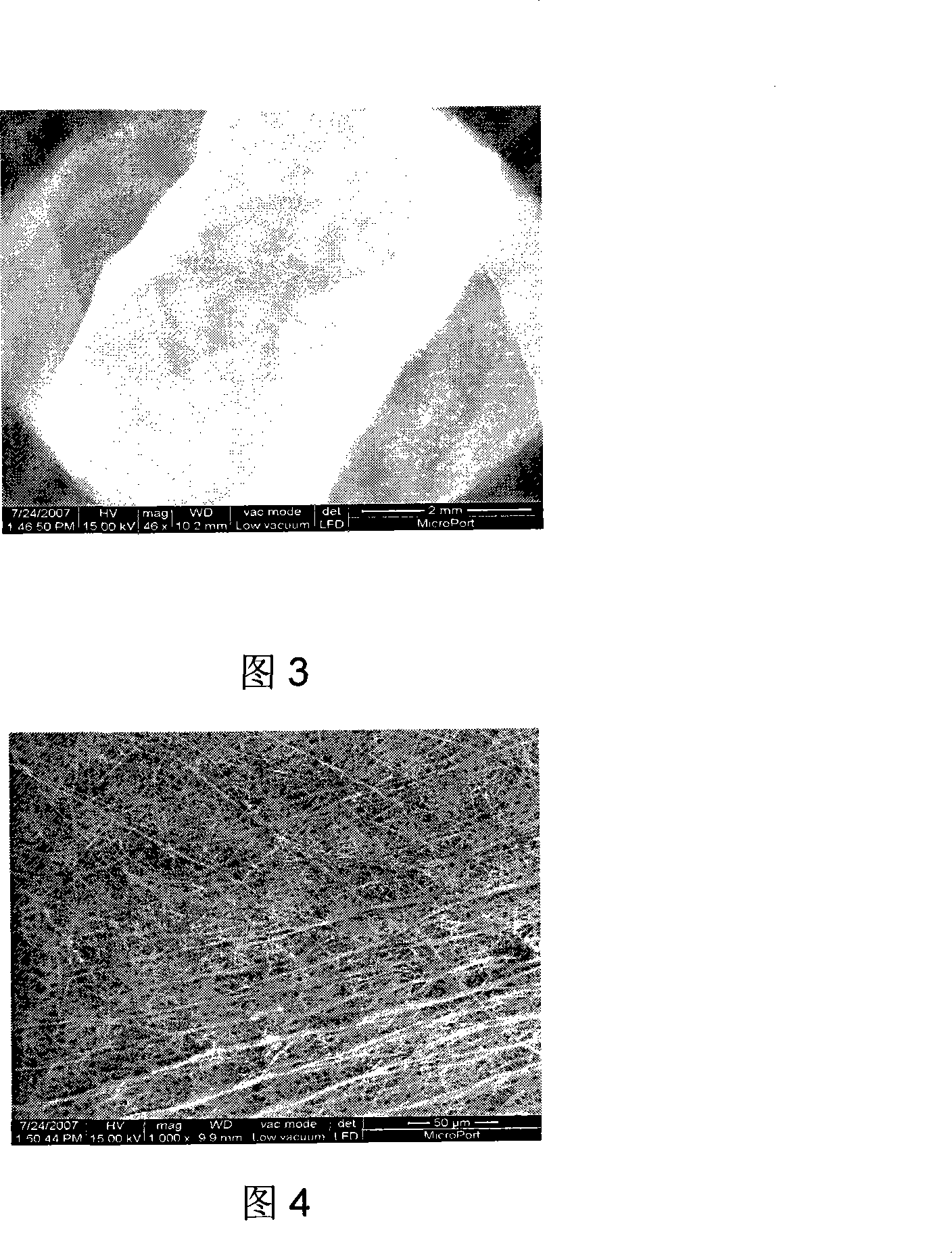
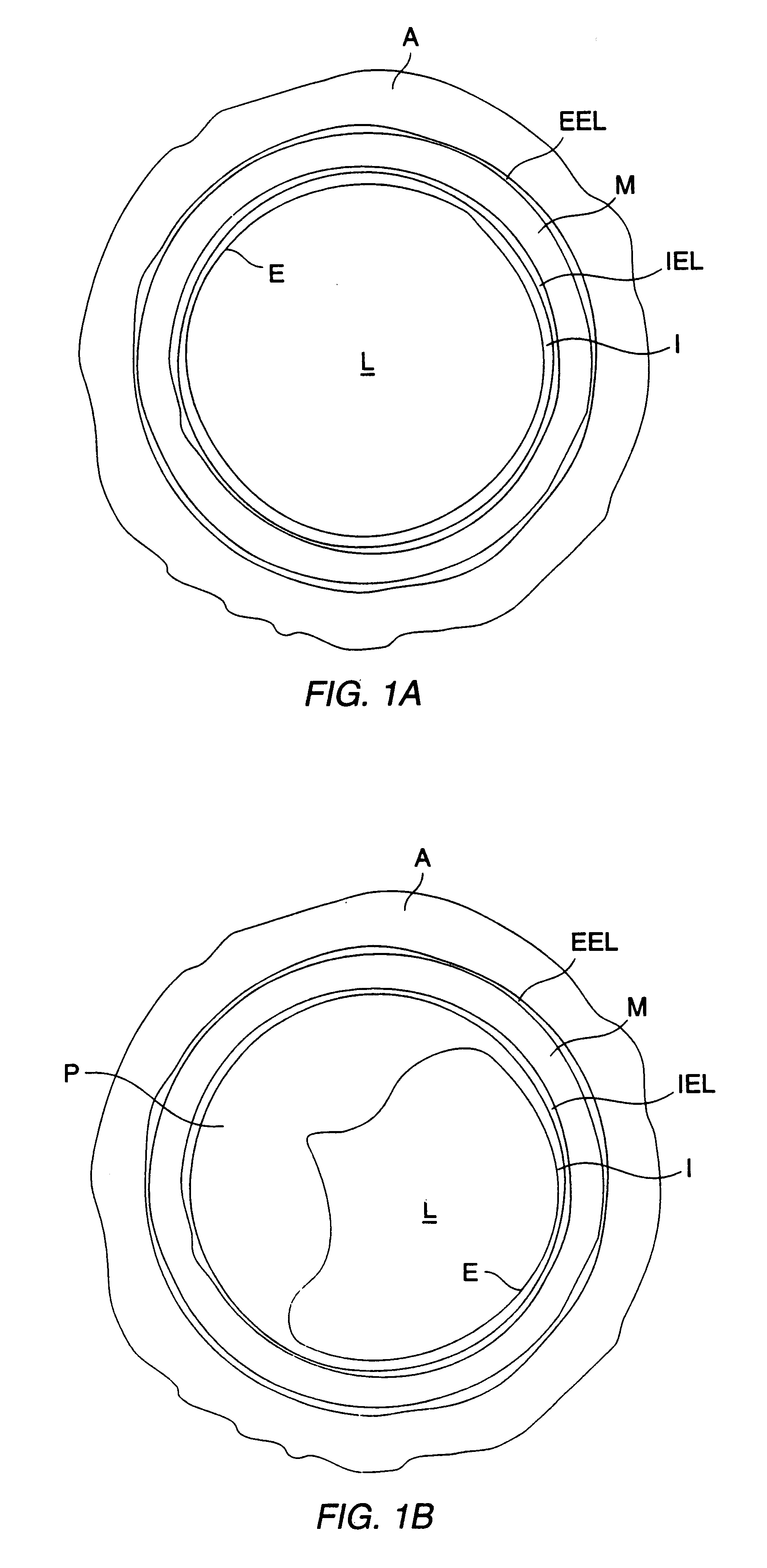
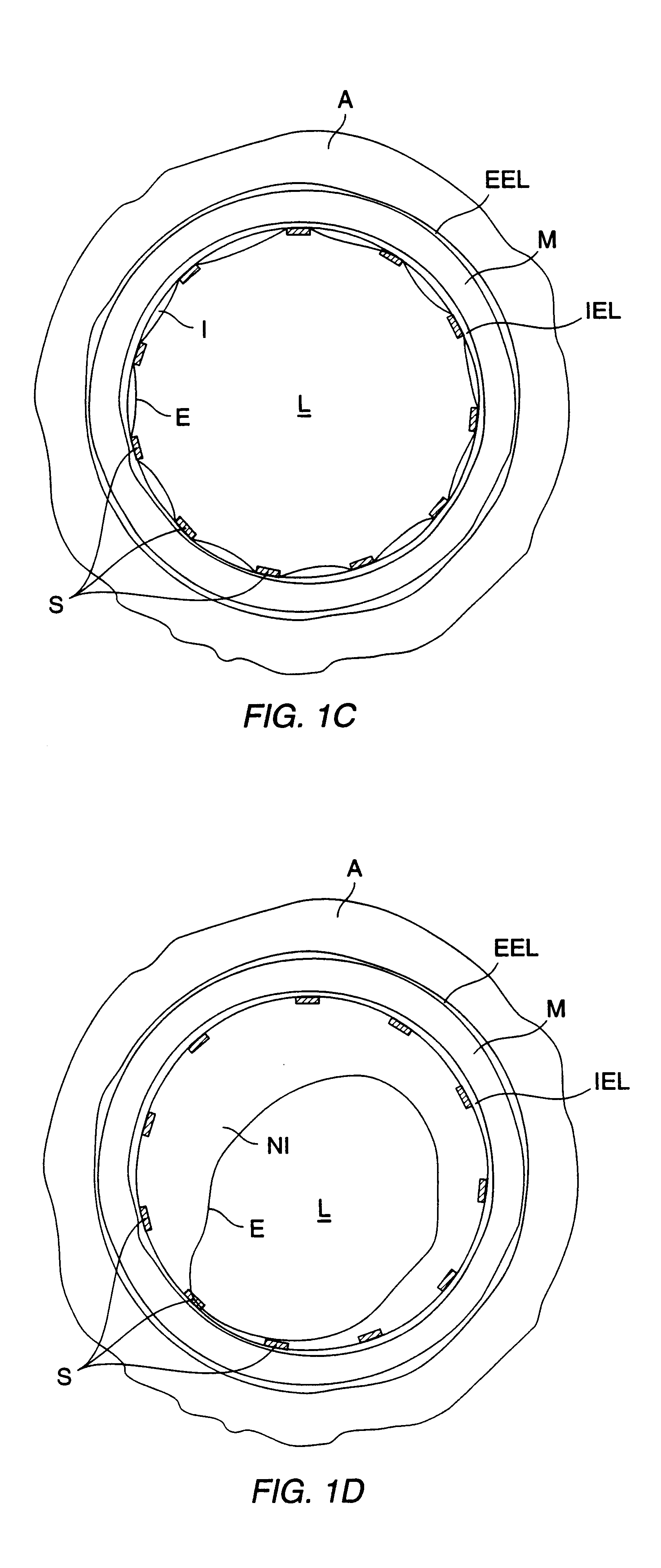
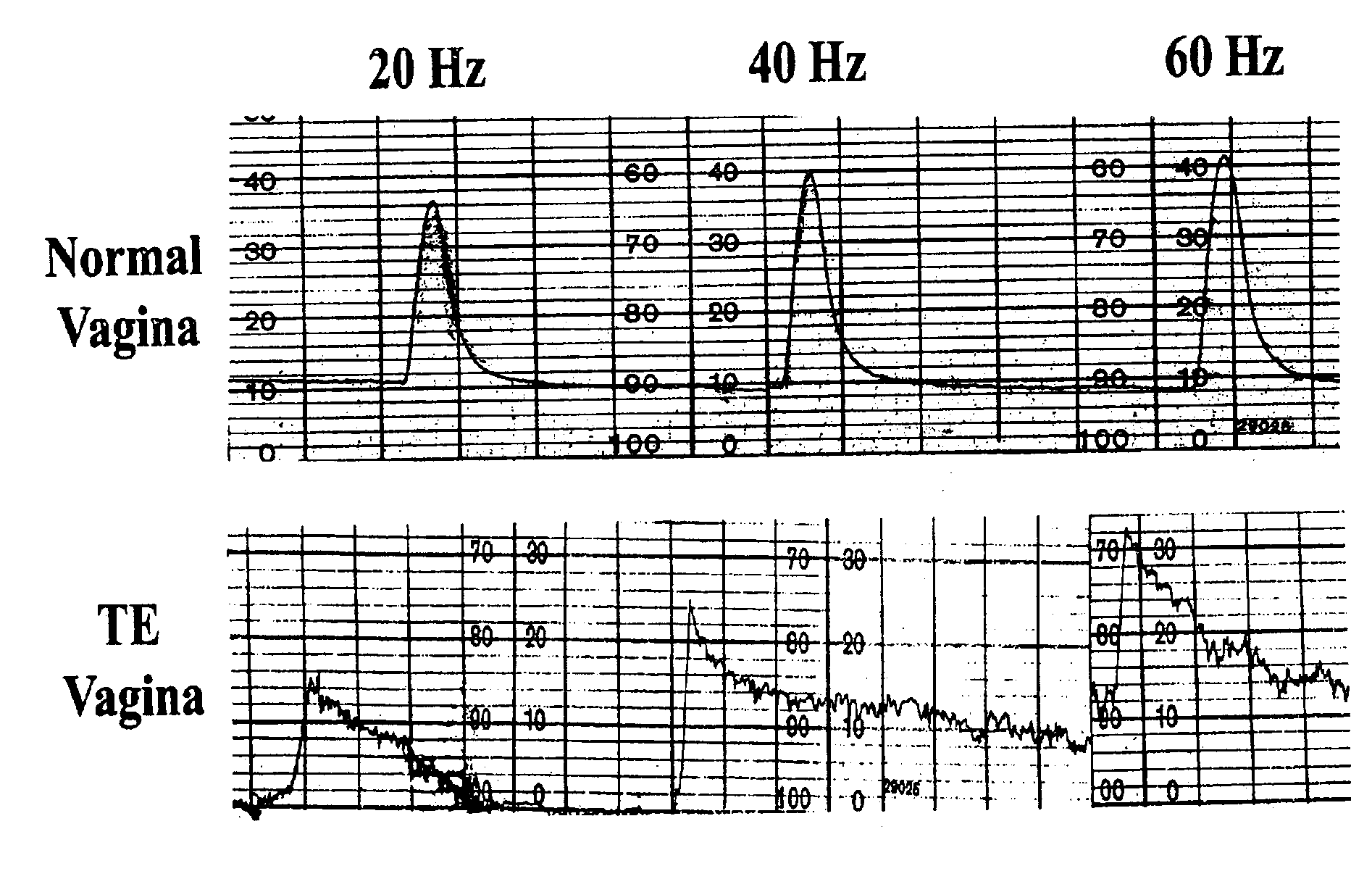
A method of forming a tissue equivalent is described. A length of polyester tube is threaded over a mandrel (H) and attached at either end by clips at A and D. A block (F) is then screwed into place. The polyester is then pre-soaked by injecting through Tap (2) an acidified collagen solution for approximately one hour. After a suitable period of time the excess solution is aspirated off. Following this stage, a second, alkaline solution is injected into the apparatus which contains smooth muscle cells (SMC). Thus, neutralisation of the collagen impregnated within the fabric of the tube occurs leading to spontaneous fibrillogenesis within the interstices of the cloth, eliminating the risk of delamination. The apparatus is then incubated. The collagen contracts down onto the fabric tube and the cell-impregnated gel becomes incorporated into the presoaked collagen. The pre-impregnated collagen and the collagen provided in the aqueous mixture contract down as one into a coherent whole with the SMC. The tissue equivalent is then lined with endothelial cells and the apparatus again incubated and fed at increasing intraluminal pressures applied either statically or dynamically. This is believed to cause the vessel to become preconditioned to the pressure it will work under as an implant. This allows organization of the basement membrane which in turn promotes EC attachment and theoretically prevents smooth muscle cell hyperplasia.
Owner:TISSUEMED LTD
Enriched stem cell and progenitor cell populations, and methods of producing and using such populations
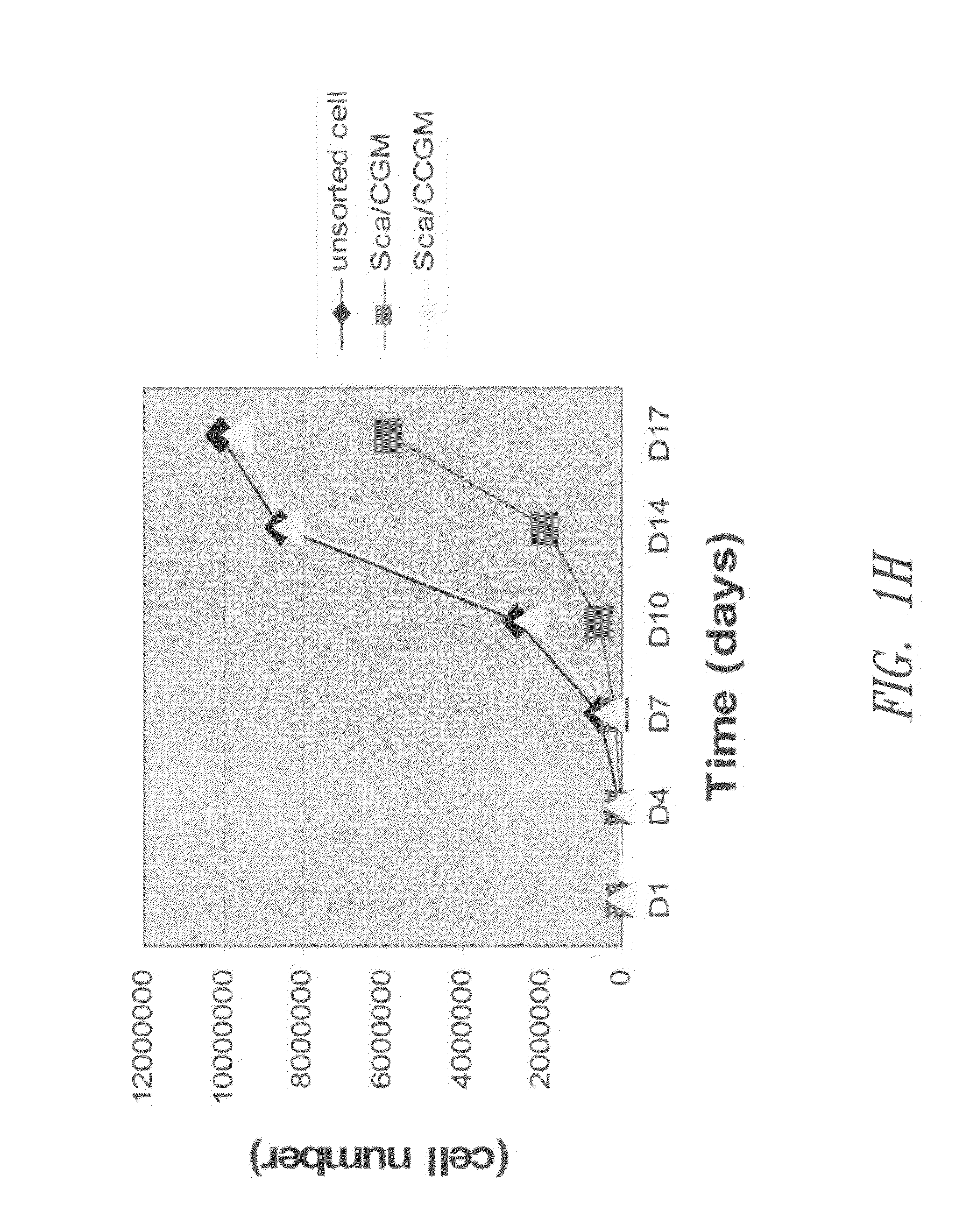
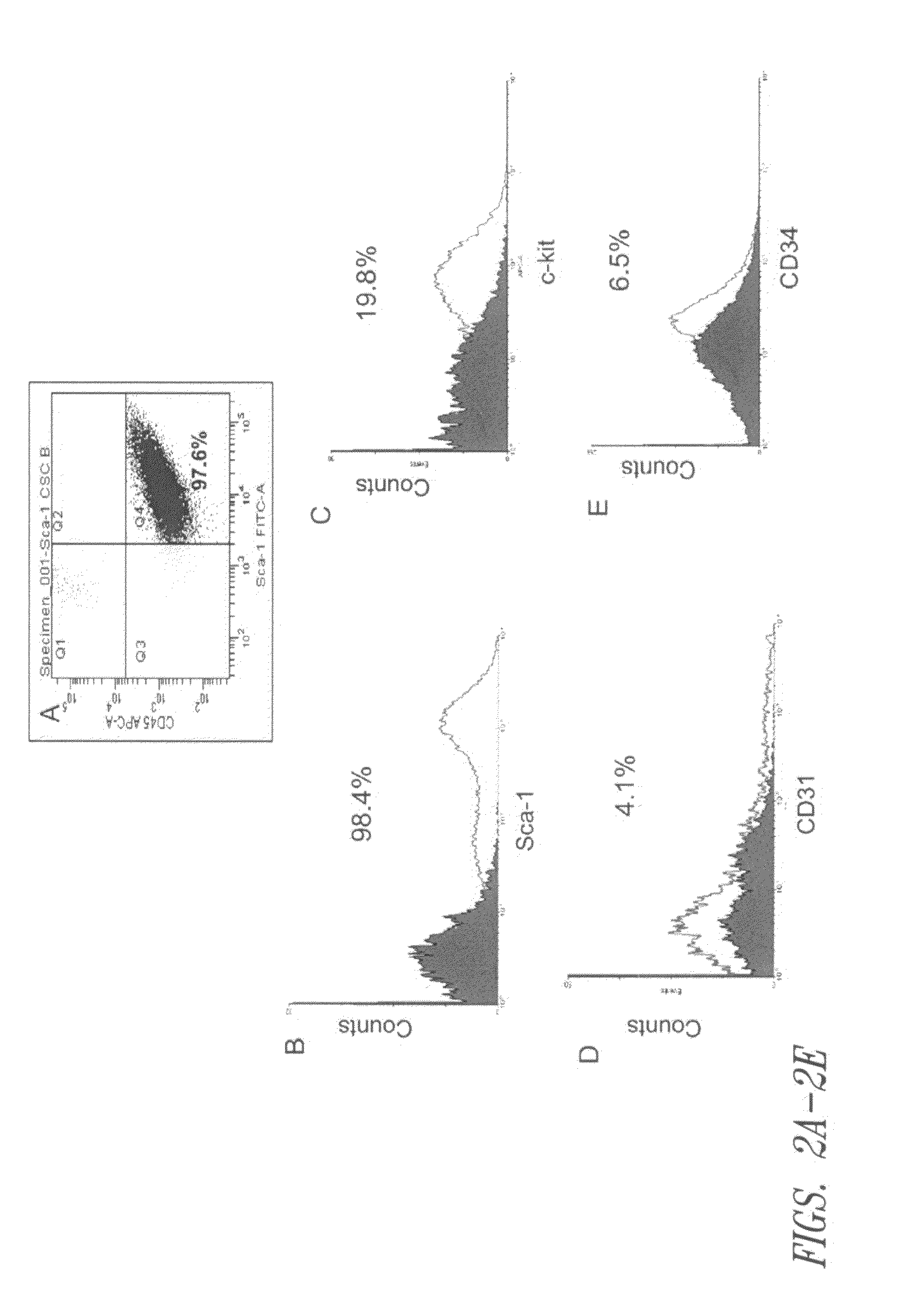
The present invention provides a novel method to isolate and expand pure progenitor / stem cells from a primary tissue explant, which produces a population enriched in multipotent functional progenitor / stem cells free of contaminating fibroblasts and other cell types. Cardiac progenitor / stem cells isolated by this method maintain their self-renewal and clonogenic character in vitro and differentiate into normal cells in myocardium, including cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells, after transplantation into ischemic hearts. The present invention also includes substantially pure populations of multipotent progenitor / stem cells, e.g., cardiac progenitor / stem cells, and their use to treat and prevent diseases and injuries, including those resulting from myocardial infarction.
Owner:KECK GRADUATE INST A UNIV OF THE STATE OF CALIFORNIA
Drug-eluting stents coated with P2Y12 receptor antagonist compound
InactiveUS20060122143A1Prevent restenosisPrevent thrombosisBiocideSugar derivativesPercent Diameter StenosisThrombus
The present invention provides a P2Y12 receptor antagonist compound-eluting stent, wherein the stent is coated with one or more P2Y12 receptor antagonist compounds or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate, or hydrate thereof. When the stent is placed in a narrowed or damaged arterial vessel, a therapeutically effective amount of the P2Y12 receptor antagonist compound is eluted continuously from the stent to the local environment of the stent. The P2Y12 receptor antagonist compound-eluting stents are useful in preventing thrombosis and restenosis, and are effective in inhibiting the contraction of vascular smooth muscle cells, inhibiting cell proliferation, and reducing inflammation.
Owner:INSPIRE PHARMA +1
Estrogen receptor modulators
The present invention relates to compounds and derivatives thereof, their synthesis, and their use as estrogen receptor modulators. The compounds of the instant invention are ligands for estrogen receptors and as such may be useful for treatment or prevention of a variety of conditions related to estrogen functioning including: bone loss, bone fractures, osteoporosis, cartilage degeneration, endometriosis, uterine fibroid disease, hot flashes, increased levels of LDL cholesterol, cardiovascular disease, impairment of cognitive functioning, cerebral degenerative disorders, restenosis, gynecomastia, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, obesity, incontinence, and cancer, in particular of the breast, uterus and prostate.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Micro-structured and nano-structured surfaces on biodegradable polymers
In embodiments of the present invention, a biodegradable / biodegradable polymer film may be used as a scaffold for tissue engineering scaffolds for engineering organized organs, such as vascular grafts, for example. In one embodiment, an ultraviolet (UV) resin made from a diacrylated biodegradable oligomer is molded into a flexible scaffold having cavities and / or channels. Channel / cavity size may be on the order of micrometers and / or nanometers, and thus the walls may have high aspect ratios. Smooth muscle cells may be deposited in the channels and because of the high aspect ratios, the cells may align along the channels / cavities as confluence is reached.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Tissue engineered blood vessels and apparatus for their manufacture
InactiveUS7112218B2Eliminate the problemBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBursting strengthFiber
The invention is a tissue engineered blood vessel (TEBV) made from a cultured fibroblast sheet rolled into a multilayer vessel which has sufficient burst strength to withstand physiological blood pressure without the inclusion of smooth muscle cells or synthetic scaffolding. The TEBV is made in a bioreactor having an enclosed chamber, a sheet growth module, a rollable mandrel, and a clamp for holding the sheet to the mandrel for rolling.
Owner:NIGHTINGALE INC
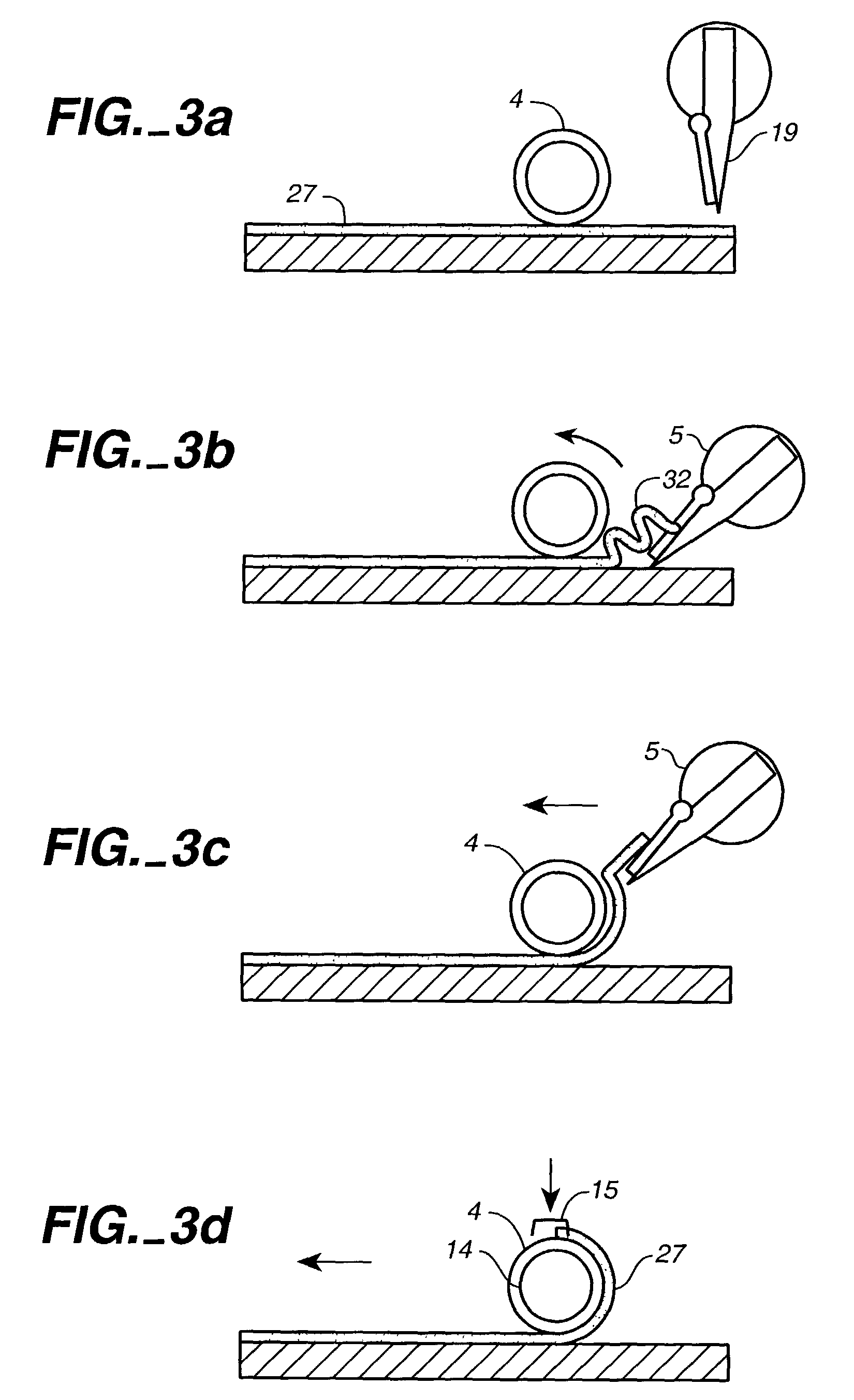
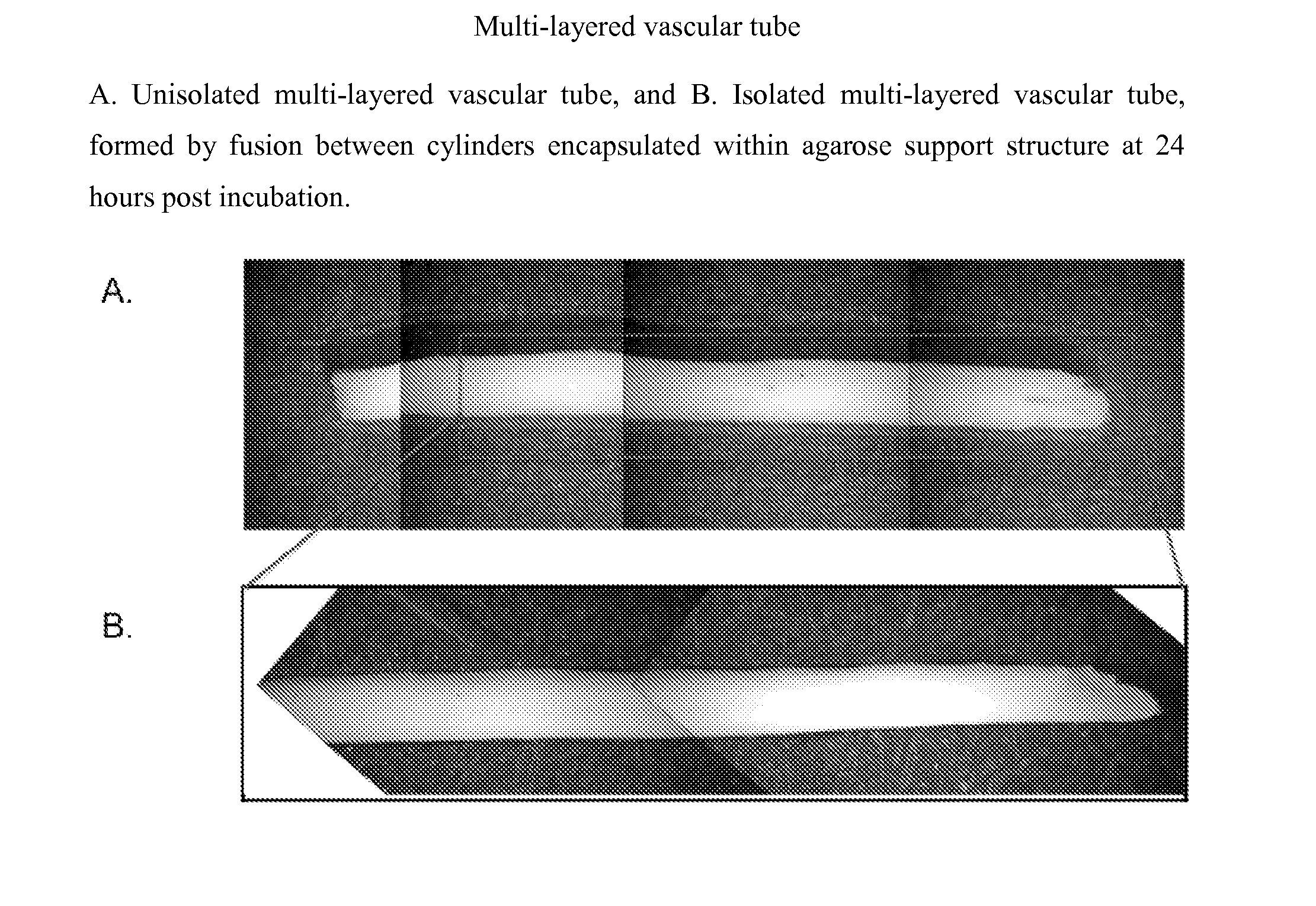
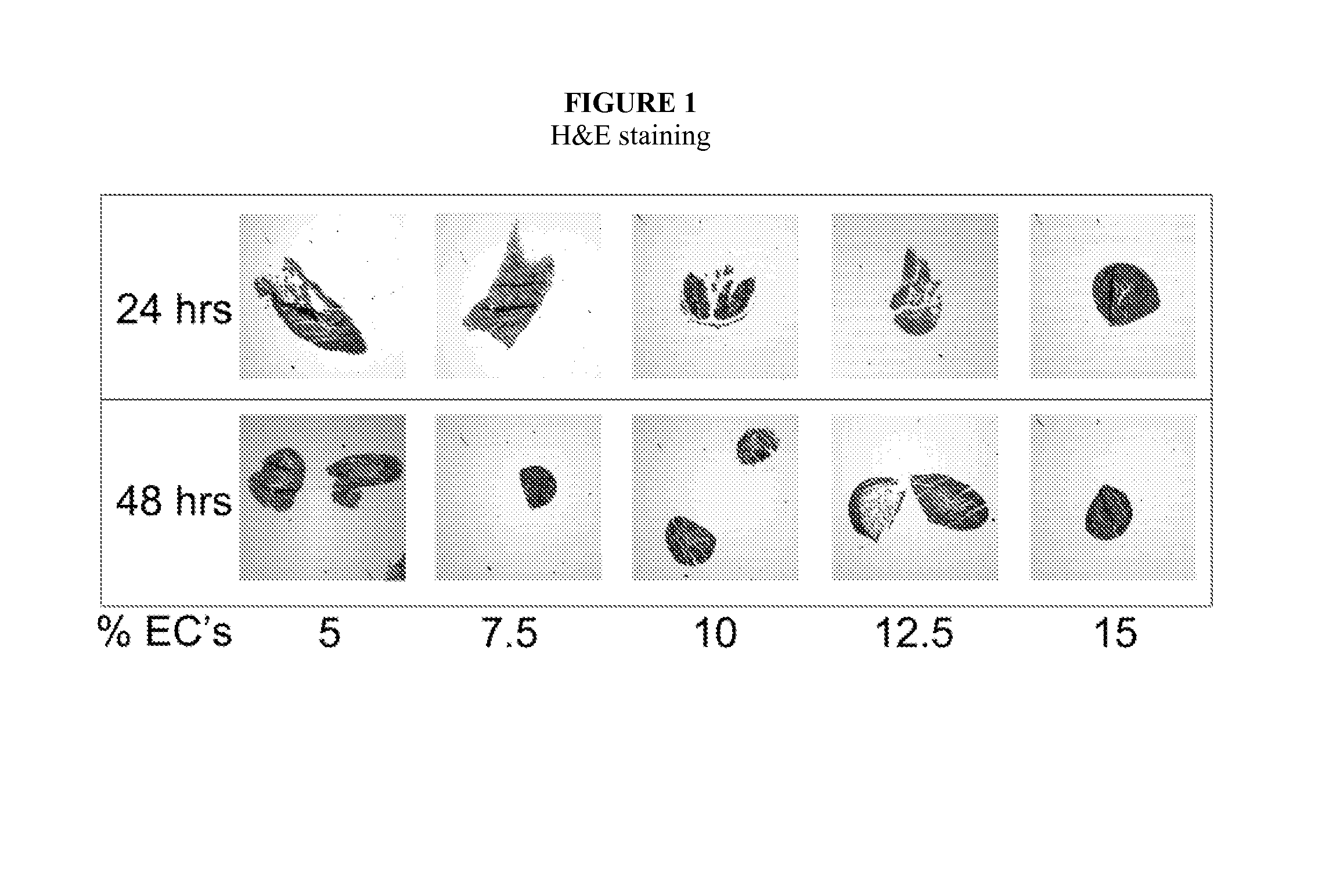
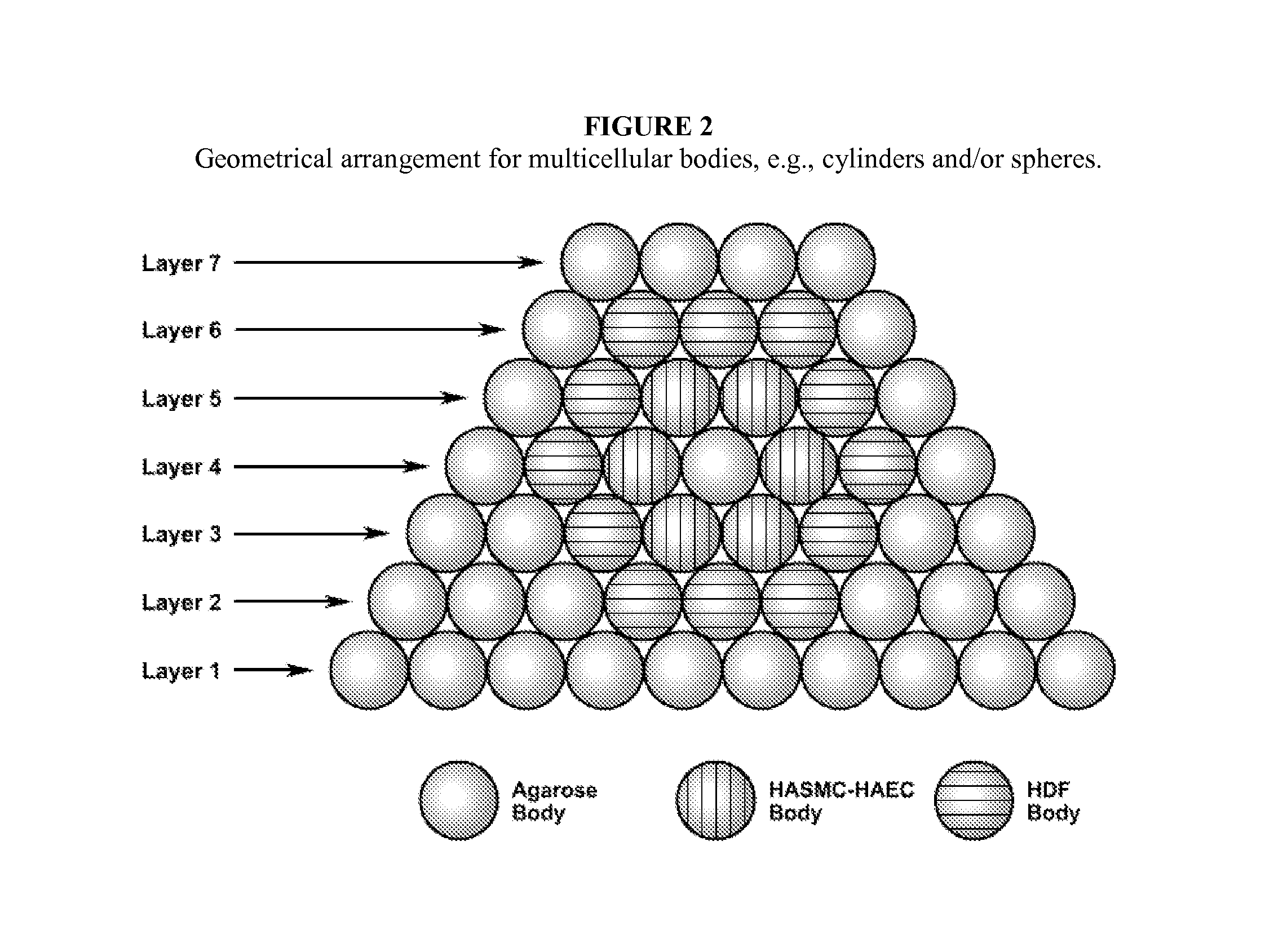
Multilayered vascular tubes
InactiveUS20130345794A1High burst resistanceUniform thicknessMetabolism disorderAnti-incontinence devicesSmooth muscleFibroblast
Described herein are engineered multilayered vascular tubes comprising at least one layer of differentiated adult fibroblasts, at least one layer of differentiated adult smooth muscle cells, wherein any layer further comprises differentiated adult endothelial cells, wherein said tubes have the following features: (a) a ratio of endothelial cells to smooth muscle cells of about 1:99 to about 45:55; (b) the tube is compliant; (c) the internal diameter of the tube is about 6 mm or smaller; (d) the length of the tube is up to about 30 cm; and (e) the thickness of the tube is substantially uniform along a region of the tube; provided that the engineered multilayered vascular tube is free of any pre-formed scaffold. Also described herein are methods of forming said tubes and uses for said tubes including methods for treating patients, comprising providing such a tube into to a patient in need thereof.
Owner:ORGANOVO
Hydrogel providing cell-specific ingrowth
InactiveUS20050119762A1Facilitate cell-specific ingrowthEncourage adherenceSurgeryPharmaceutical containersCross-linkCell specific
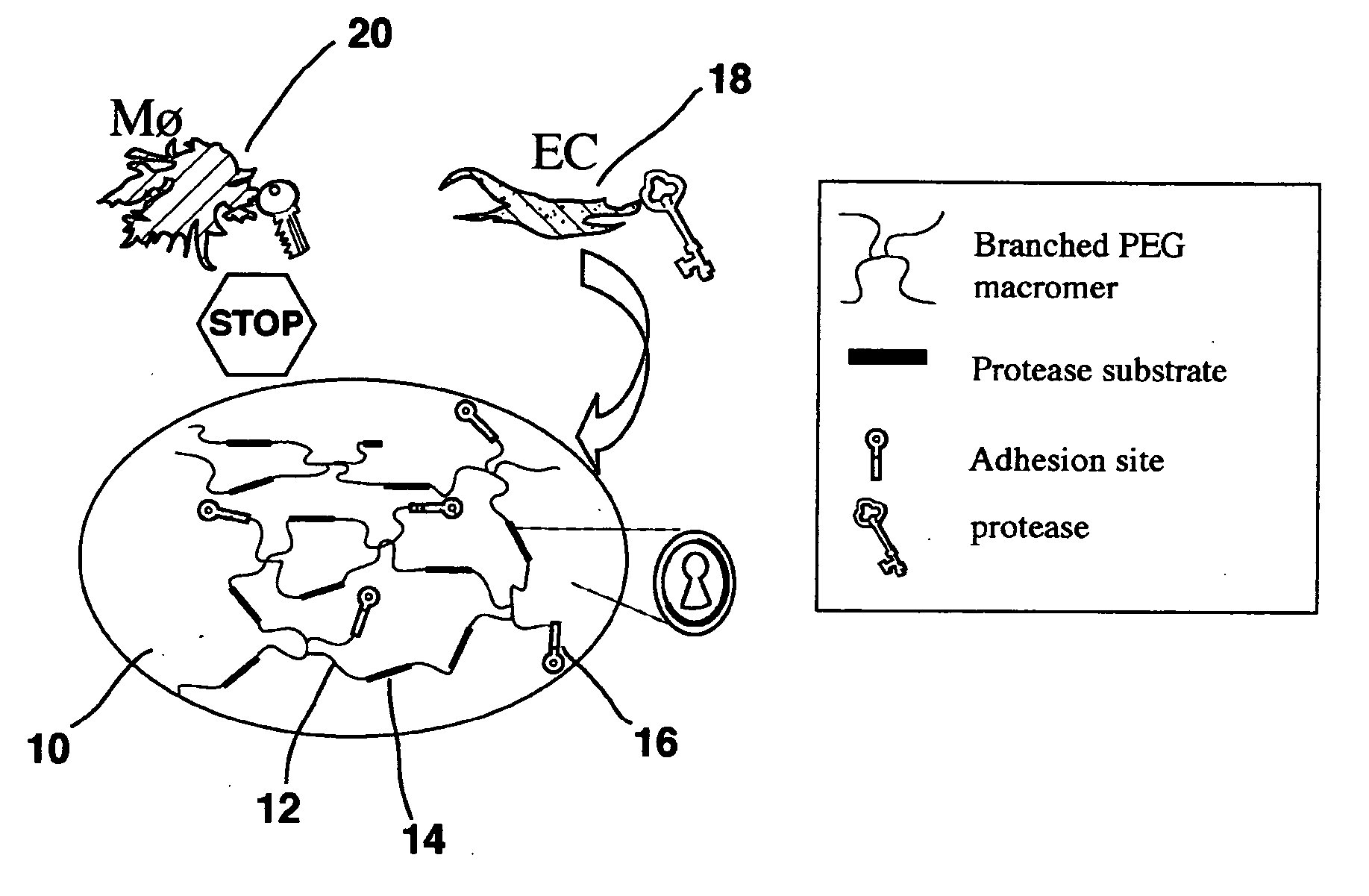
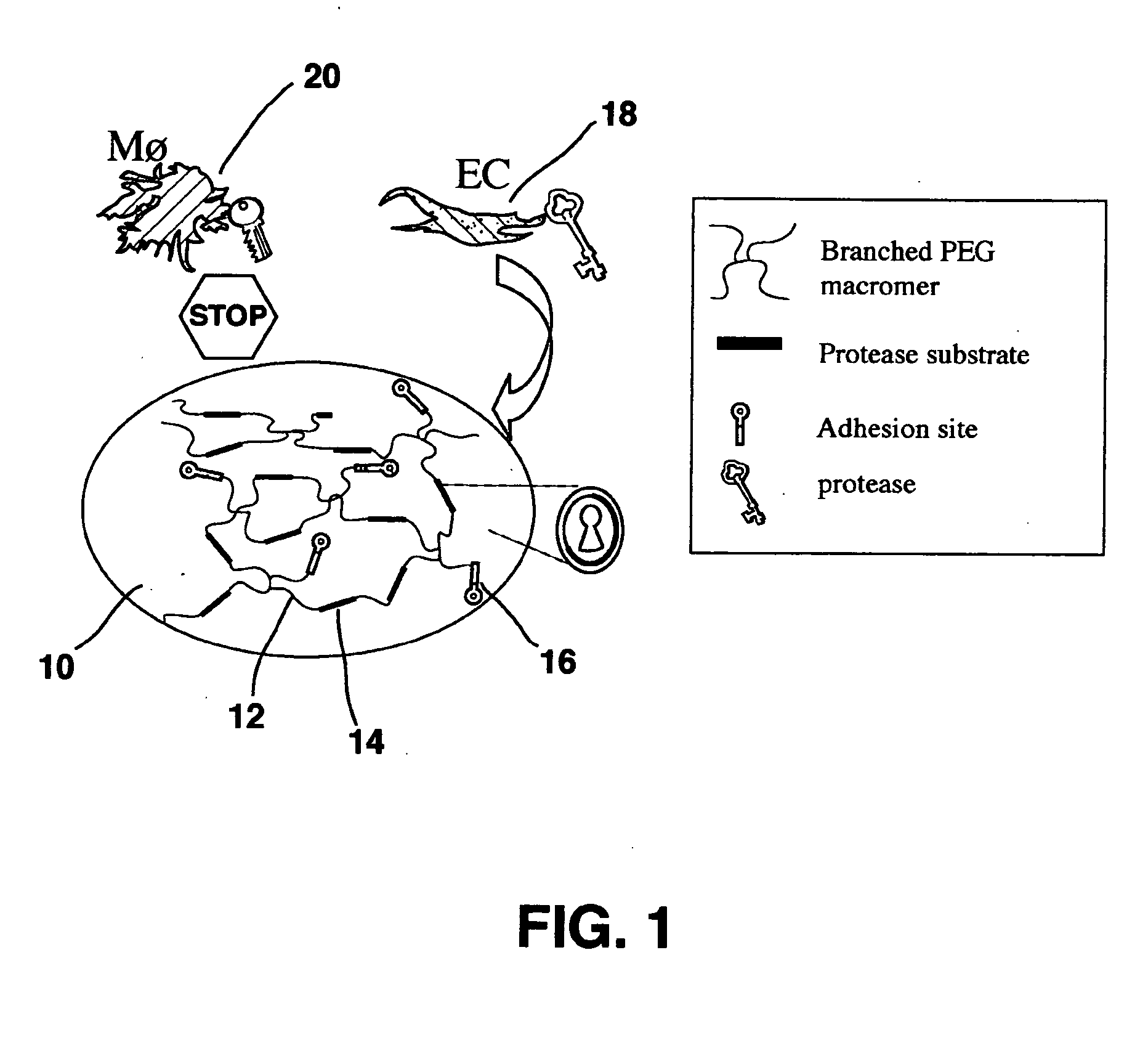
A polymeric biomaterial that facilitates cell-specific ingrowth. The polymeric biomaterial encourages the ingrowth of cell types while reducing the ingrowth of undesirable cell types. This activity encourages proper integration of prosthetic implants or scaffolds utilizing this biomaterial by discouraging encapsulation or the accumulation of inflammatory cells such as macrophages, while encouraging infiltration by desirable cells such as endothelial or smooth muscle cells. Short peptide sequences are included in a polymeric biomaterial that result in complementary activities. Peptide sequences that are specifically cleaved by proteases found within preferred cells are used to cross-link the biomaterial and lead to degradation by those cells. Peptide sequences taken from proteins involved in cell adhesion can also be attached to the biomaterial to encourage adhesion by preferred cells. Combined use of both peptides in the polymeric biomaterial provides both specific adhesion and selective ingrowth.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Bionic vascularized soft tissue with multilayer vascular structure and preparation method thereof
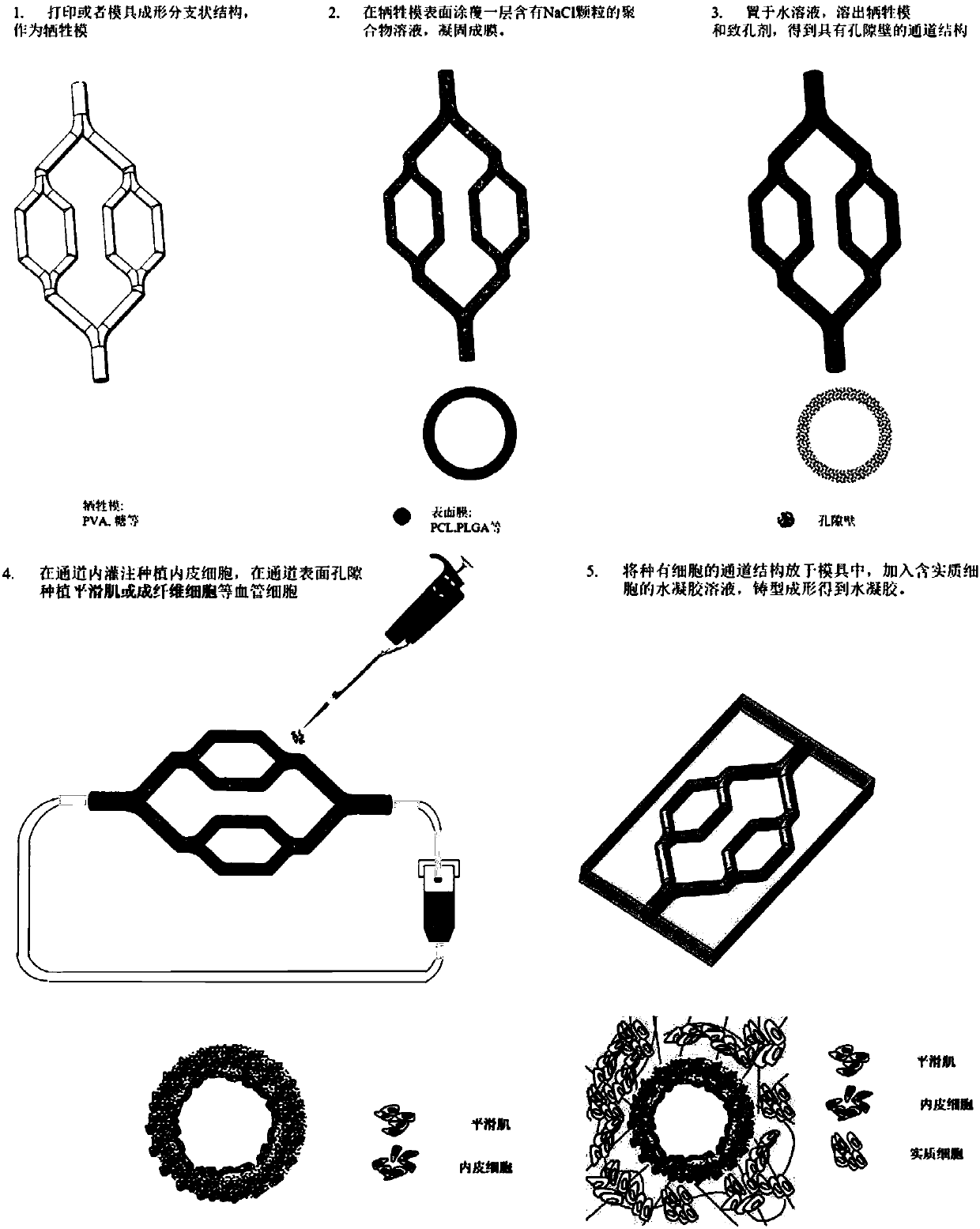
ActiveCN107693846AAdditive manufacturing apparatusEducational modelsPolymer thin filmsPolymer solution
The invention discloses a bionic vascularized soft tissue with a multilayer vascular structure and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of: employing a moulding process or 3D printing way to obtain a sacrificial membrane with a branched structure; coating or spraying a polymer solution containing a pore-foaming agent on the surface of the sacrificial membrane toobtain a polymer film; removing the treated sacrificial membrane of the structure and the pore-foaming agent to obtain a vascular channel-like structure with surface pores; conducting perfusion planting of endothelial cells in the channel of the vascular channel-like structure; planting smooth muscle cells or fibroblasts in the surface pores of the vascular channel-like structure; and placing thetreated vascular channel-like structure in a mold, adding an aquogel solution containing parenchymal cells, and conducting moulding so as to obtain the bionic vascularized soft tissue. The method provided by the invention can construct bionic blood vessels with a multilayer structure in artificial tissues.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
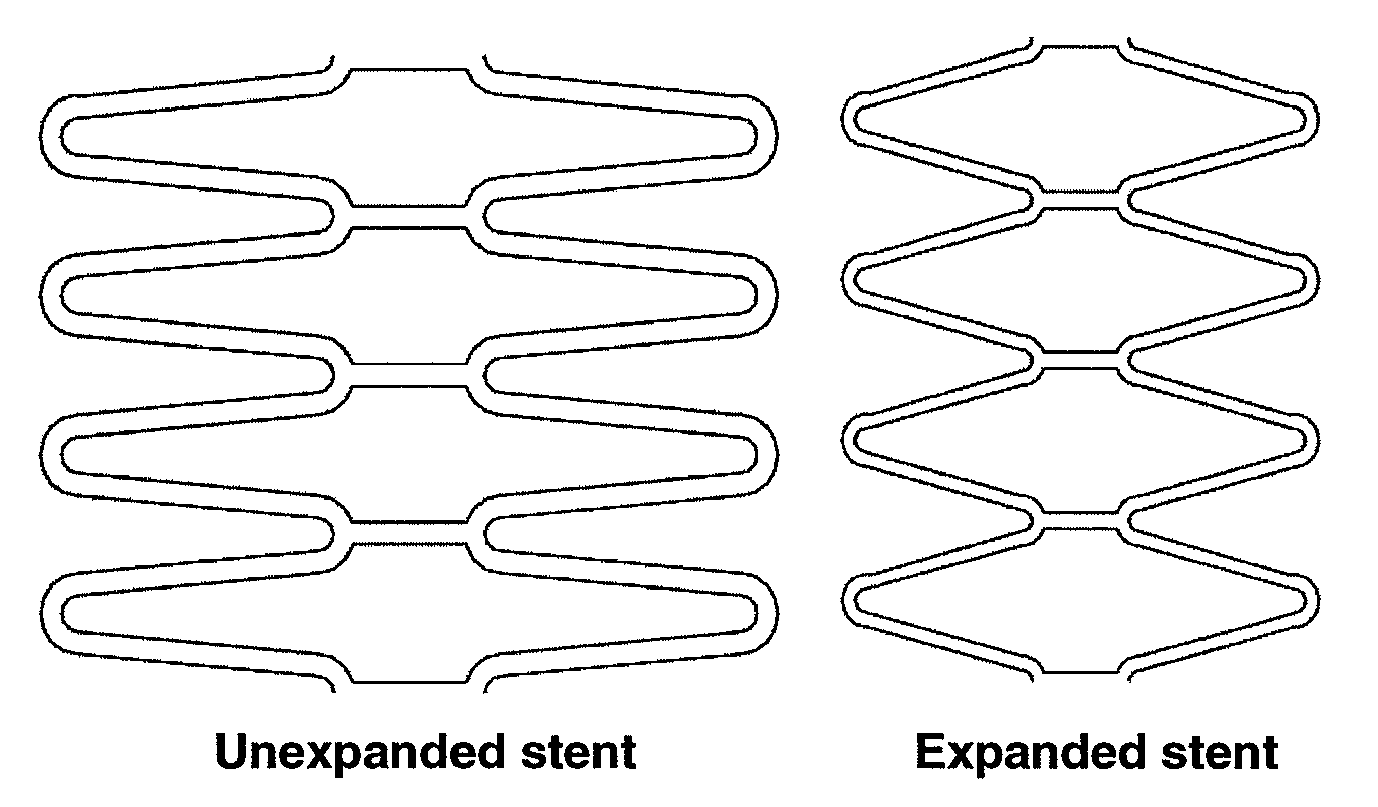
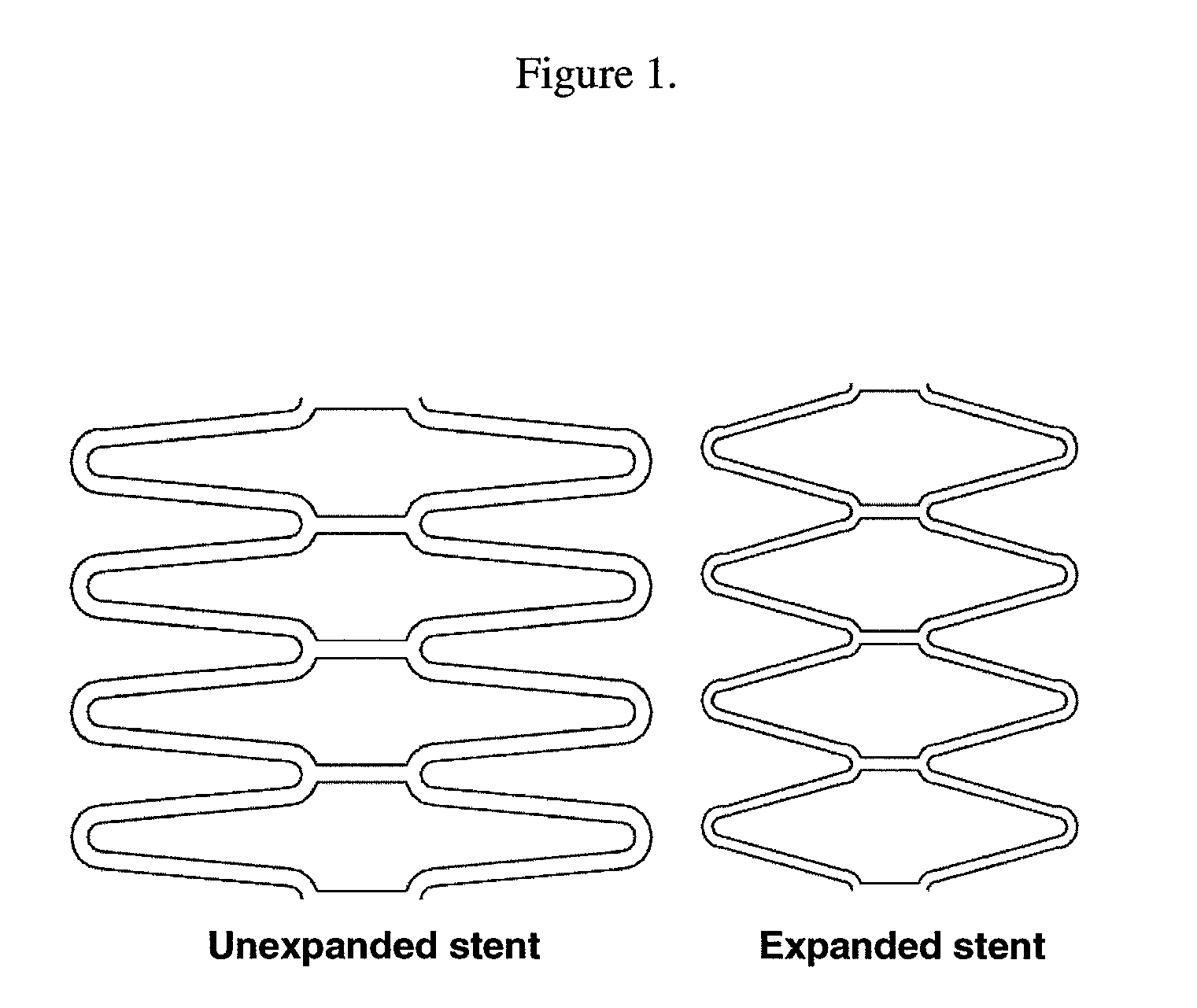
Matrix Coated Stent
InactiveUS20110172763A1Promote endothelializationSimplifying device manufacture and loadingStentsSurgeryBiocompatibility TestingDisease progression
The present invention relates generally to a drug eluting stent containing metallic surfaces modified in microsphere metallic matrix structure and methods for making same. More specifically, the invention relates to an expandable and implantable vascular stent having at least one matrix layer that promotes improved cellular adhesion properties for healing promotion healing and long term biocompatibility. In the case of coronary stents, the metallic matrix layer promotes re-endothelialization at sites of stent implantation, improves overall healing, and reduces inflammation and intimal disease progression. The microsphere metallic matrix layer may be optionally loaded with one or more therapeutic agent to further improve the function of the implanted stent and further augment clinical efficacy and safety. The active compounds are selected primarily for their anti-proliferative, immunosuppressive, and anti-inflammatory activities, among other properties, which prevent, in part, smooth muscle cell proliferation and promote endothelial cell growth.
Owner:STERLING VASCULAR SYST
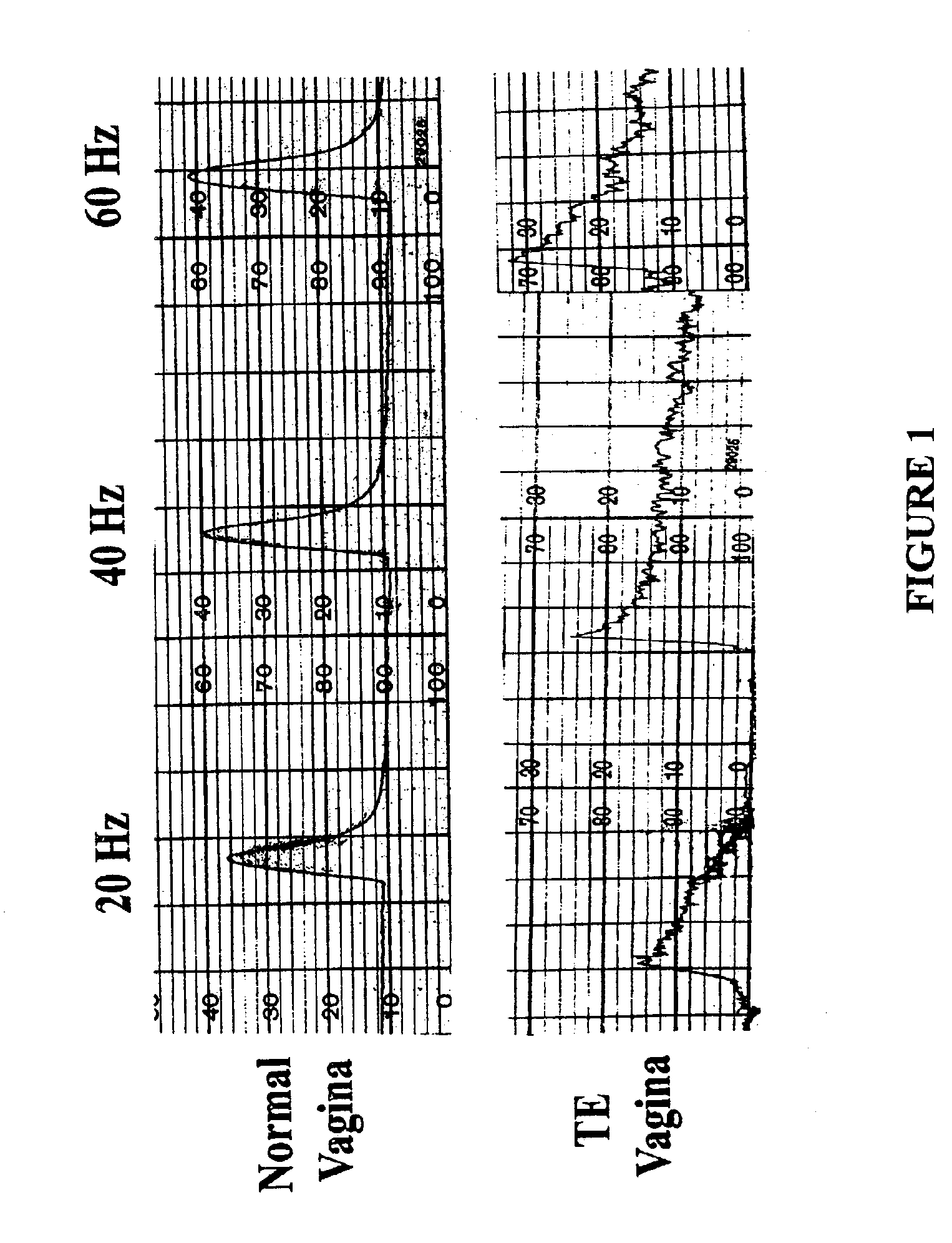
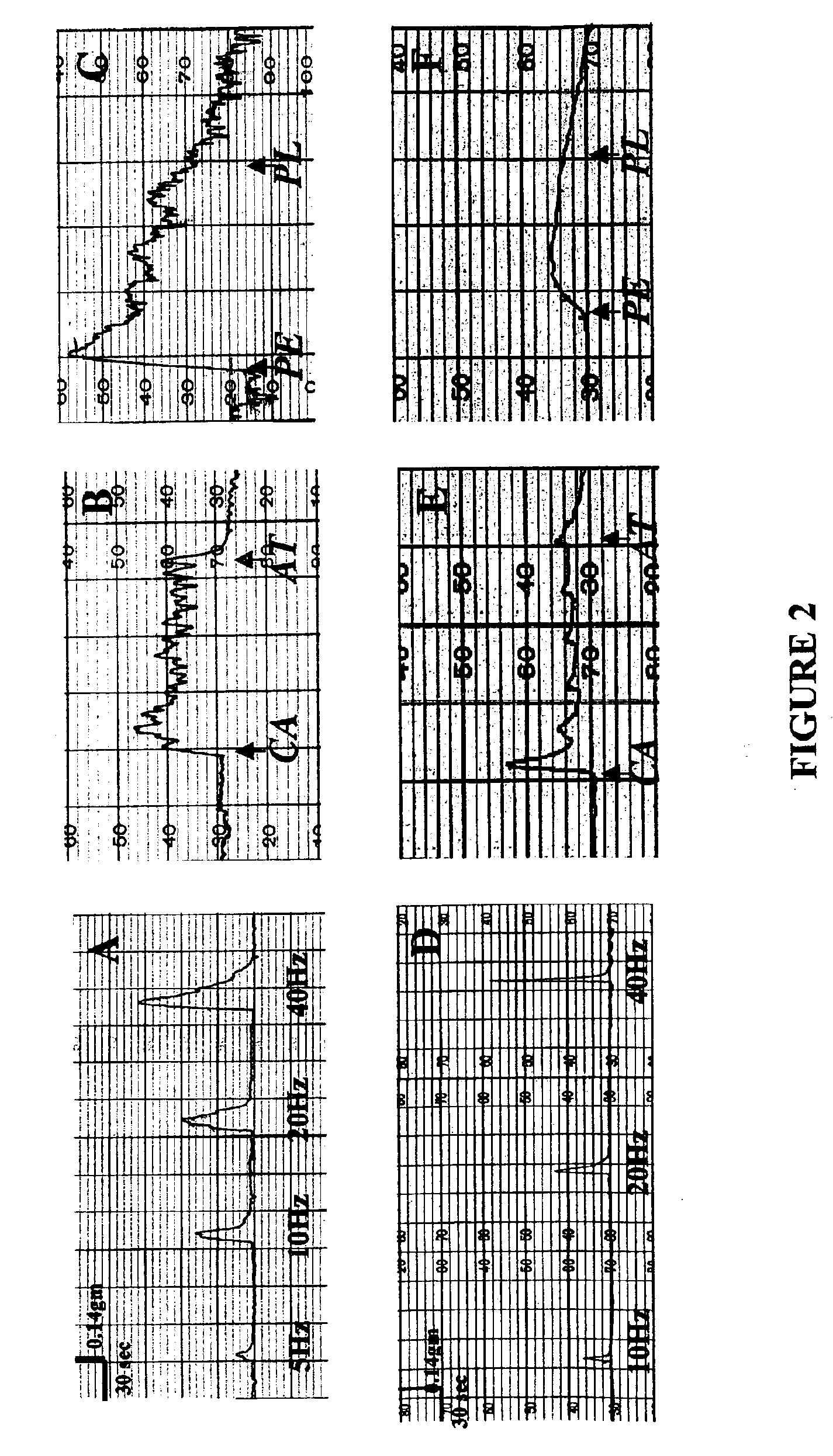
Tissue engineered uterus
The invention is directed to compositions and methods for reconstructing artificial female reproductive organs. The constructs and methods of the invention can be used for ameliorating congenital malformations and disorders of female reproductive tract using tissue engineered female reproductive organs, such as the uterus, vagina, cervix, and fallopian tubes. These tissue engineered female reproductive organs can be generated by perfusing cultured cell populations derived from cells of the female reproductive tissues, such as uterine, vaginal, cervical, fallopian tube epithelial cells as well as smooth muscle cells.
Owner:ATALA ANTHONY J
Coated devices and method of making coated devices that reduce smooth muscle cell proliferation and platelet activity
ActiveUS20100331965A1Extensive treatmentRemarkable effectStentsSurgeryAtherosclerosis preventionLeiomyocyte
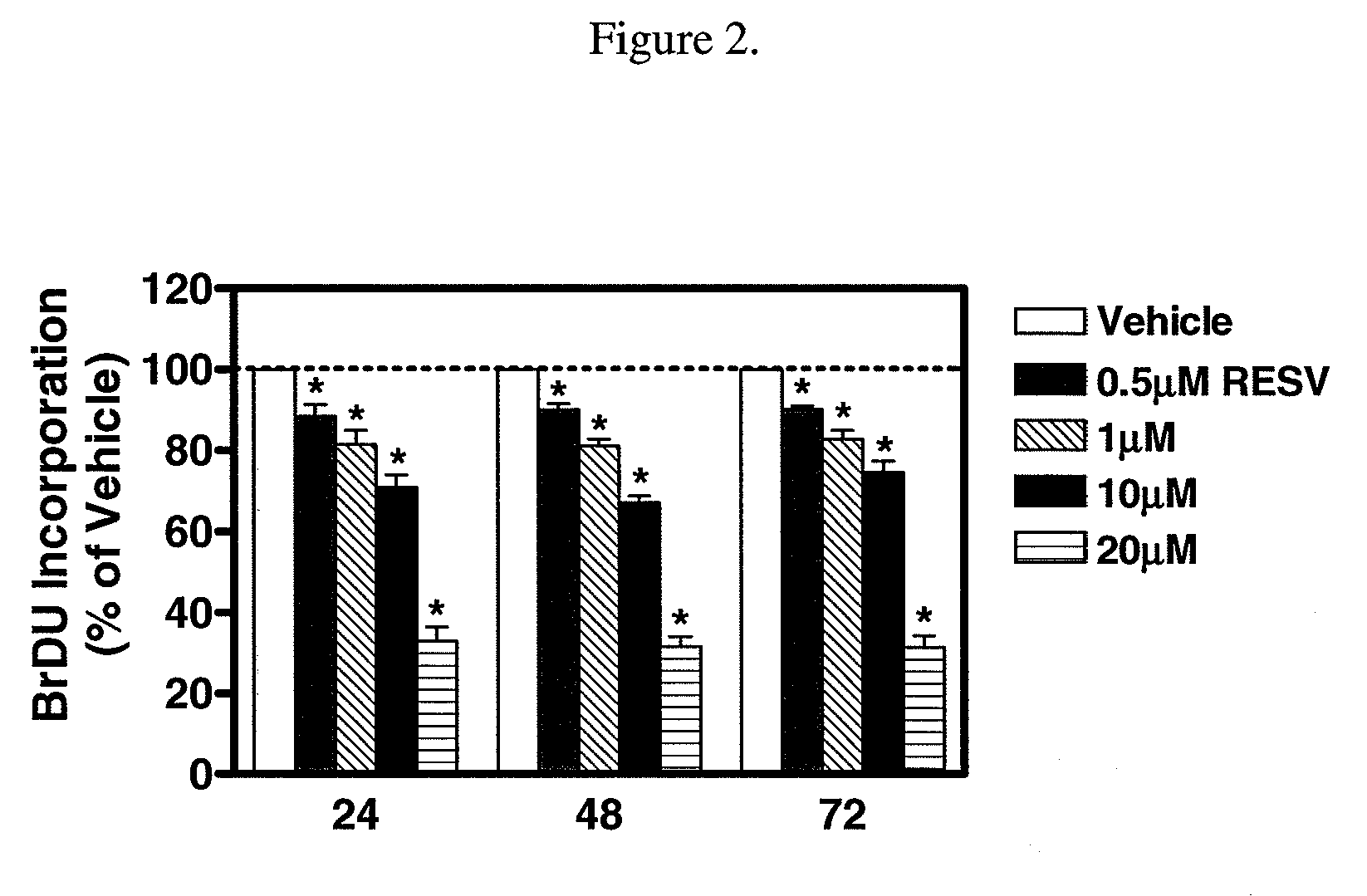
The present invention relates generally to the maintenance of blow flood using drug eluting stents and / or other coated medical devices to increased length of time of blood flow. Further, the present invention relates to drug-releasing coated devices for reducing smooth muscle cell proliferation and platelet activity to further limit restenosis utilizing resveratrol and quercetin, polyphenols that are linked to the cardioprotection of red wine consumption. The present invention also provides products and methods for treating or preventing atherosclerosis, stenosis, restenosis, smooth muscle cell proliferation, platelet cell activation and other clotting mechanisms, occlusive disease, or other abnormal lumenal cellular proliferation condition in a location within the body of a patient.
Owner:NANOCOPOEIA +1
Selective estrogen receptor modulators
InactiveUS7157604B2Urea derivatives preparationBiocideHormone Receptor ModulatorsPercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention relates to compounds and derivatives thereof, their synthesis, and their use as estrogen receptor modulators. The compounds of the instant invention are ligands for estrogen receptors and as such may be useful for treatment or prevention of a variety of conditions related to estrogen functioning including: bone loss, bone fractures, osteoporosis, cartilage degeneration, endometriosis, uterine fibroid disease, hot flashes, increased levels of LDL cholesterol, cardiovascular disease, impairment of cognitive functioning, cerebral degenerative disorders, restenosis, gynecomastia, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, obesity, incontinence, and cancer, in particular of the breast, uterus and prostate.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Methods and compositions for smooth muscle reconstruction
This invention also provides a purified or isolated population of ADSCs that can differentiate into a cell of the leiomyogenic lineage, e.g., smooth muscle or skeletal muscle. In yet another aspect, the population additionally can be differentiated into a lineage selected from the group consisting of osteogenic, adipogenic, chondrogenic, myogenic and neuronal. This invention further provides a composition comprising a substantially homogeneous expanded population of smooth muscle cells. This invention provides a composition comprising a substantially homogeneous expanded population of skeletal muscle cells. Also provided herein is an isolated composition comprising a purified adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC) or progeny of said ADSC and an effective amount of laminin or heparin, effective to induce leiomyogenic differentiation. Diagnositic and therapeutic uses for these compositions are provided herein.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Target
The present invention relates to an isolated target sequence. The target sequence is a splice variant of PDE5 called a PDE5a1, a component of which is presented as SEQ ID No 1. The identified target sequence of the present invention may be used to as a target to identify agents (such as modulators) useful in the prevention and / or treatment of a disease associated with scarring and / or fibrosis or to selectively identify smooth muscle cells and myofibroblasts and myoepithelial cells in samples of normal and diseased tissue from individuals.
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
Biological artificial blood vessel capable of in vivo capturing endothelial ancestral cell
ActiveCN101066477AAddressing Compliance MismatchesResolve thrombosisImmobilised enzymesPharmaceutical containersAntigenThrombus
The present invention relates to preparation of biological artificial blood vessel capable of in vivo capturing endothelial ancestral cell, and features that the biological artificial blood vessel may be prepared with composite blood vessel material or homogeneous or heterogeneous blood vessel with the antigen eliminated and through surface modification. The biological artificial blood vessel may be used as tissue engineering blood vessel rack, on which smooth muscle cell and / or endothelial cell may be planted. The biological artificial blood vessel of the present invention has excellent mechanical performance and anticoagulant property, and may be in different calibers. It may be in vivo reshaped and in vivo induced to plant endothelial ancestral cell. It can antagonize intravascular thrombogenesis and inhibit the pathological proliferation of smooth muscle cell to avoid angiostenosis and blood vessel blocking.
Owner:广州宏畅生物科技有限公司
Well-based flow system for cell culture
InactiveUS20110091930A1Improve throughputImproved fluidic routingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSmooth muscle3D cell culture
A well-based flow system for cell culture is described which provides for flow of culture containing compounds for drug screening to be exposed to cells seeded on a membrane. The flow of medium may be planar or radial and means are provided for the removal of waste media through fluid outlets in fluid communication with the assay well plates through conduits. Methods of using the system for cell culture and drug toxicity screening are also provided including coculturing cells such as hepatocytes, stem cells, fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells and selectively exposing cells to test compounds.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Preparation method of shell core fibre tectorial membrana endovascular stent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a shell core fiber covered endovascular stent graft. The steps are as follows: firstly, a polymer is dissolved in adaptive dissolvent to obtain solution with a certain concentration; secondly, medicine or an artificial polymer and medicine, and a bio-active element are dissolved in the adaptive dissolvent to obtain solution or suspension liquid; thirdly, the solution of the polymer and the medicine or the solution or suspension liquid of the medicine or bio-active element are respectively filled in two injectors, the speed of a micro injection pump, the voltage of an electrostatic generator and the distance of a receiving device are adjusted, fiber is obtained through the static spinning preparation, and the fiber is received as a tube shape or film shape structure; fourthly, the endovascular stent graft is fixed on a revolution axle, through the revolution of the endovascular stent graft, the static spinning fiber are directly received as fibrous membrane covered on the endovascular stent graft. The invention can effectively prevent smooth muscle cells from hyperplasia in the stent graft or from narrowing in the stent graft caused by the other functions, and the shell core fiber for the medicine loading can slowly release the medicine to attain the purpose of curing.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing composite artificial blood vessel stent by combined electro-spinning with knitting technique
InactiveCN101264349AIncrease growth activityNot easy to embolismStentsSurgeryTextile technologyHuman body
The invention relates to a preparation method of compound artificial blood vessel support by electrostatic textile and weave technology, which can be described as follows: 6% to 10% (g / ml) polymer spinning solution is prepared; under the control of electrostatic spinning parameter, the prepared solution is used to make nano fiber with electrostatic textile technology; the nano fiber is collected by a roller collecting device to be the inner layer of a tubular support; the fiber materials are woven into tubular form by making use of the textile equipment to be the outer layer of the tubular support; the electrostatically textile inner layer and the woven outer layer are compounded together with the method of hot shaping or coating; with the adoption of biocompatible implant technology, human endothelial cells are implanted on the inner layer of the support and human smooth muscle cells are implanted on the outer layer of the support; after cell culture, the blood support is completed. The preparation method of compound artificial blood vessel support through electrostatic textile and weave technology has the advantages of simplification and time-saving effect, fine growth activity of the prepared artificial blood vessel after being implanted into human body; besides, the smooth muscle can grow along and into the fiber, and adaptability adjustment can be made to the blood vessel according to the condition of the host, leaving less liability for embolization.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Use of one or more elements from the group containing yttrium, neodymium and zirconium and pharmaceutical compositions containing said elements
A method of treating a patient includes the medical use of one or more of the elements from the group yttrium, neodymium and zirconium, pharmaceutical formulations which contain said elements and implants which are at least region-wise made up of such formulations. It has been found inter alia that a formulation containing one or more of the elements has an action of inhibiting the proliferation of human smooth muscle cells.
Owner:BIOTRONIK VI PATENT
Artificial blood vessel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105983134APromote proliferationHigh mechanical strengthPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingCell layerAnti coagulation
The invention relates to an artificial blood vessel and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of organ preparing and biological materials. The artificial blood vessel comprises an outer cortex layer, a fibroblast layer, a smooth muscle cell layer, an endothelial cell layer and an inner cavity. The orderly distribution of the endothelial cell layer, the smooth muscle cell layer, the fibroblast layer and the outer cortex layer in the three-dimensional space is achieved through the comprehensive technology of plasma spraying, electric spraying, electrospinning, reverse molding and 3D printing, the anti-coagulation performance of the artificial blood vessel is enhanced through anti-coagulation factors, step-by-step induced differentiation of stem cells in the artificial blood vessel is achieved through a growth factor controlled-release method, the artificial blood vessel is cultured through a pulsation reactor and made to simulate natural animal blood vessels on the structure and the function, and a corresponding substitute is provided for blood vessel transplanting and repairing. The artificial blood vessel is also applicable to other tubular tissue and organs such as the oesophagus, the trachea, the ovarian duct, the bile duct, the urethra and the bladder.
Owner:刘畅
System and method for in vitro blood vessel modeling
ActiveUS20110053207A1Reduce non-physiological shear stressMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresCell layerVascular pathology
The present invention provides an in vitro blood vessel model for investigation of drug induced vascular injury and other vascular pathologies. The in vitro blood vessel model provides two channels separated by a porous membrane that is coated on one side by an endothelial cell layer and is coated on the other side by a smooth muscle cell layer, wherein said model is susceptible to the extravasation of red blood cells across said porous membrane due to drug induced vascular injury.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY +1
Inhibition of proteasomes to prevent restenosis
InactiveUS20040116329A1Peptide/protein ingredientsBoron compound active ingredientsSmooth musclePercent Diameter Stenosis
Restenosis of blood vessels after angioplasty is achieved by preventing of cell proliferation, particularly of smooth muscle cells, in blood vessel walls by inhibiting the ubiquitin-proteasome protein degradation pathway. The inhibition is accomplished by administering to the cells in the blood vessel walls a compound, e.g., a protein or small molecule, capable of inhibiting the ubiquitin-proteasome protein degradation pathway. The inhibiting compound is preferably administered by coating the compound on a stent and implanting the stent in the blood vessel after angioplasty.
Owner:MEDSTAR RES INST
Enriched stem cell and progenitor cell populations, and methods of producing and using such populations
InactiveUS8017389B2BiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementIschemic heartFirst myocardial infarction
The present invention provides a novel method to isolate and expand pure progenitor / stem cells from a primary tissue explant, which produces a population enriched in multipotent functional progenitor / stem cells free of contaminating fibroblasts and other cell types. Cardiac progenitor / stem cells isolated by this method maintain their self-renewal and clonogenic character in vitro and differentiate into normal cells in myocardium, including cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells, after transplantation into ischemic hearts. The present invention also includes substantially pure populations of multipotent progenitor / stem cells, e.g., cardiac progenitor / stem cells, and their use to treat and prevent diseases and injuries, including those resulting from myocardial infarction.
Owner:KECK GRADUATE INST A UNIV OF THE STATE OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com