Bionic vascularized soft tissue with multilayer vascular structure and preparation method thereof
A bionic blood vessel and vascular structure technology, applied in the field of bionic vascularized soft tissue and its preparation, can solve the problems of low efficiency and complex biological factor regulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
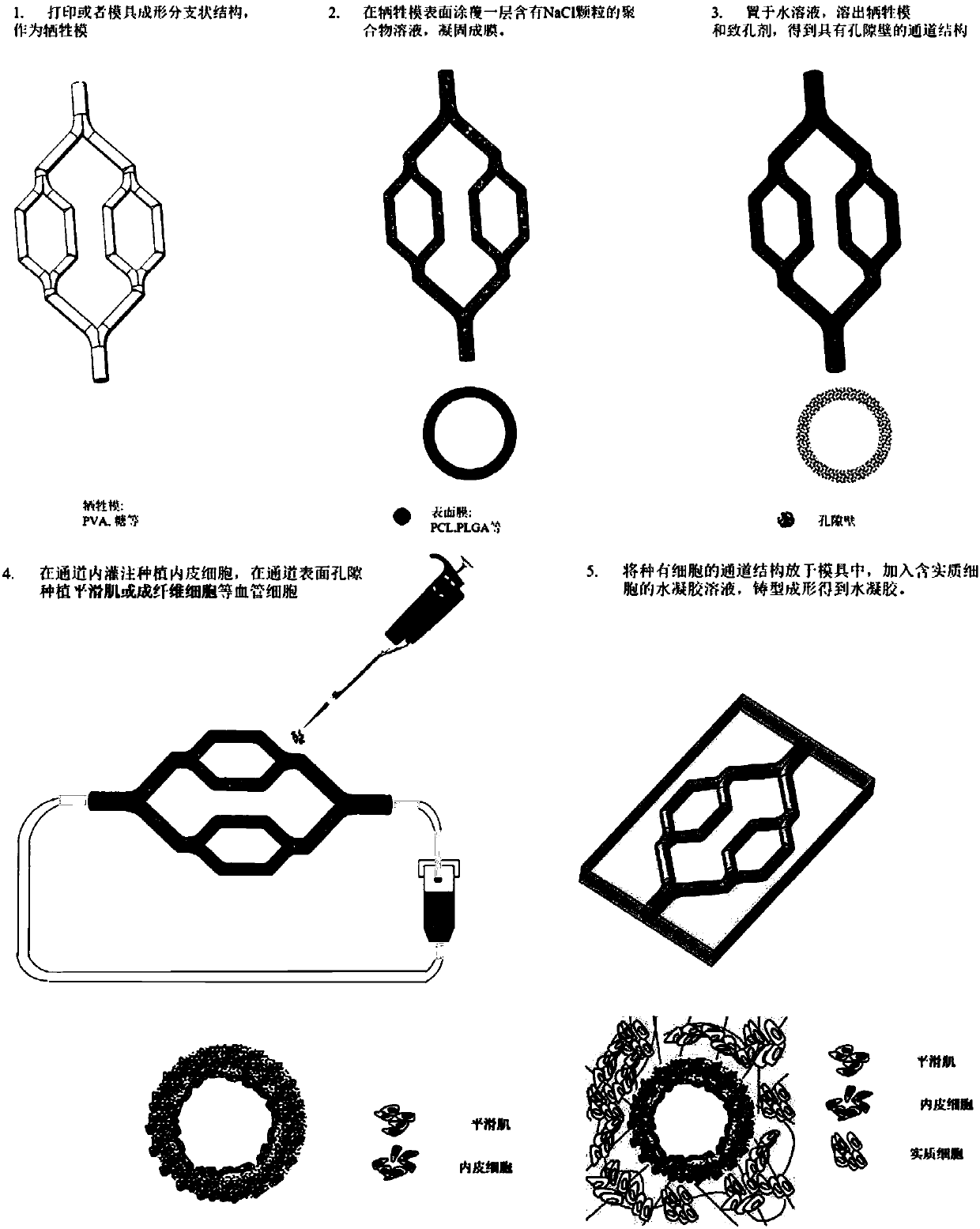
[0046] figure 1 A schematic diagram of the preparation method for constructing a biomimetic vascularized soft tissue with a multi-layered vascular structure in a hydrogel provided by the present invention, including the following steps:
[0047] 1) Obtain a sacrificial mold with a branched structure by casting or 3D printing; as figure 1 Step 1 in;
[0048] 2) Coating or spraying the polymer solution mixed with a porogen on the surface of the above-mentioned branched structure, solidifying to form a film, such as figure 1 Step 2 in;
[0049] 3) Place the structure obtained in step 2) in an aqueous solution, dissolve the sacrificial mold and porogen, and obtain a vessel-like channel structure with a certain wall thickness and surface pores, such as figure 1 Step 3 in;
[0050] 4) Plant endothelial cells in the channel to simulate the endothelial layer of the vascular structure; plant cells such as smooth muscle cells or fibroblasts in the surface pores of the channel struct...
Embodiment 1
[0057] Example 1. Preparation of biomimetic vascularized soft tissue with multi-layered vascular structure
[0058] Polylactic acid (PLA, molecular weight 50,000, viscosity 1.5 dL / g) was dissolved in chloroform (CHCl 3 ), prepare a polylactic acid (PLA) solution with a concentration of 50 mg / mL, and add sodium chloride (NaCl) particles (with a diameter of 75±25 μm), wherein sodium chloride (NaCl):polylactic acid (PLA)=8:2 (wt%), uniformly stirred to obtain a polylactic acid (PLA) solution containing sodium chloride (NaCl).
[0059] Add the gelatin (Gelatin, 15k~25kDa, 0.15g / ml) solution into the syringe nozzle of the extrusion 3D printing device at 37°C, generate a printing path according to the preset structure, and print at 4°C to form a two-level branch Morphological structure (500-1500 μm in diameter). The surface of the printed structure was uniformly coated with a polylactic acid (PLA) solution containing sodium chloride (NaCl), and air-dried for 12 hours to obtain a p...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Example 2. Preparation of bionic vascularized soft tissue with multi-layered vascular structure
[0063] Dissolve polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer (PLGA, the molar ratio of polylactic acid (PLA) to polyglycolic acid (PGA) is 75:25, viscosity is 0.93dl / g) in 1,4 dioxane (1, 4-dioxane), prepare a solution of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer with a concentration of 20 mg / mL, and add sodium chloride (NaCl) particles (with a diameter of 100±25-μm), wherein sodium chloride (NaCl): polylactic acid Glycolic acid copolymer (PLGA)=7:3 (wt%), uniformly stirred to obtain a polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer (PLGA) solution containing sodium chloride (NaCl).
[0064] Mix sucrose, maltose, and glucose uniformly at a mass ratio of 1:12:2, put them into the nozzle cavity of the melt extrusion printing equipment, and heat and melt at 130°C, and control the continuous extrusion of the nozzle by air pressure. Set the structure to generate a printing path, and form a st...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com