Primers for specific gene of Escherichia coli and detection method of Escherichia coli
An Escherichia coli and specific gene technology, applied in the biological field of Escherichia coli, can solve the problems of serious cross-reaction, easy contamination of immunological methods, inability to detect damaged bacteria and dead bacteria, etc., and achieves sensitive and specific test results, convenient and fast detection, Detect quick and cheap effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
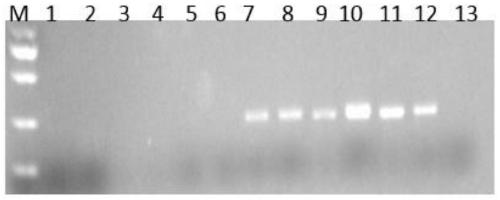
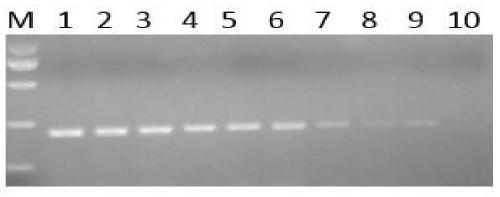
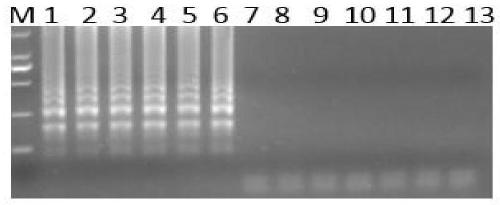
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1: Specific target gene screening and primer design
[0036] 1. Local BLAST analysis
[0037] Download the whole genome sequence of Escherichia coli from NCBI (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / genome / ), perform a local BLAST search on the local nucleic acid database, and obtain the comparison results of each sequence fragment of the strain with the database .
[0038] 2. BLAST reconfirmation
[0039] Using the online BLAST function, 2 strategies were used to confirm their species specificity and species identification availability. One strategy is to exclude the target strain during BLAST, and the results show that those without any similar sequences are the specific genes of the target strain; the second strategy is to search within the target strain when BLAST is used, and the results return a large number of similar sequences to the target strain The consensus sequences of different strains of the species. Combine the two strategies, and finally find out the t...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2: the establishment of detection method
[0043] 1. Extraction of DNA
[0044] (1) Use the bacterial genomic DNA mini-extraction kit of Beijing Zhuangmeng International Biogene Technology Co., Ltd. for extraction and recovery, the steps are as follows:
[0045] ①Take 5mL of bacterial culture solution, centrifuge at 12,000rpm for 1 minute, and aspirate the supernatant as much as possible.
[0046] ② Add 500 μL of cell suspension to the centrifuge tube with the bacterial pellet left, use a pipette or vortex shaker to thoroughly suspend the bacterial cell pellet, and incubate at 37°C for 30 minutes. Mix by inversion several times every 10 minutes. Centrifuge at 12,000rpm for 2 minutes, and try to suck up the supernatant.
[0047] ③Add 225 μL buffer A to the cell pellet and shake until the cell is completely suspended.
[0048] ④Add 6 μL RNaseA solution to the tube, shake for 15 seconds, and place at room temperature for 5 minutes.
[0049] ⑤ Add 10 μL of p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com