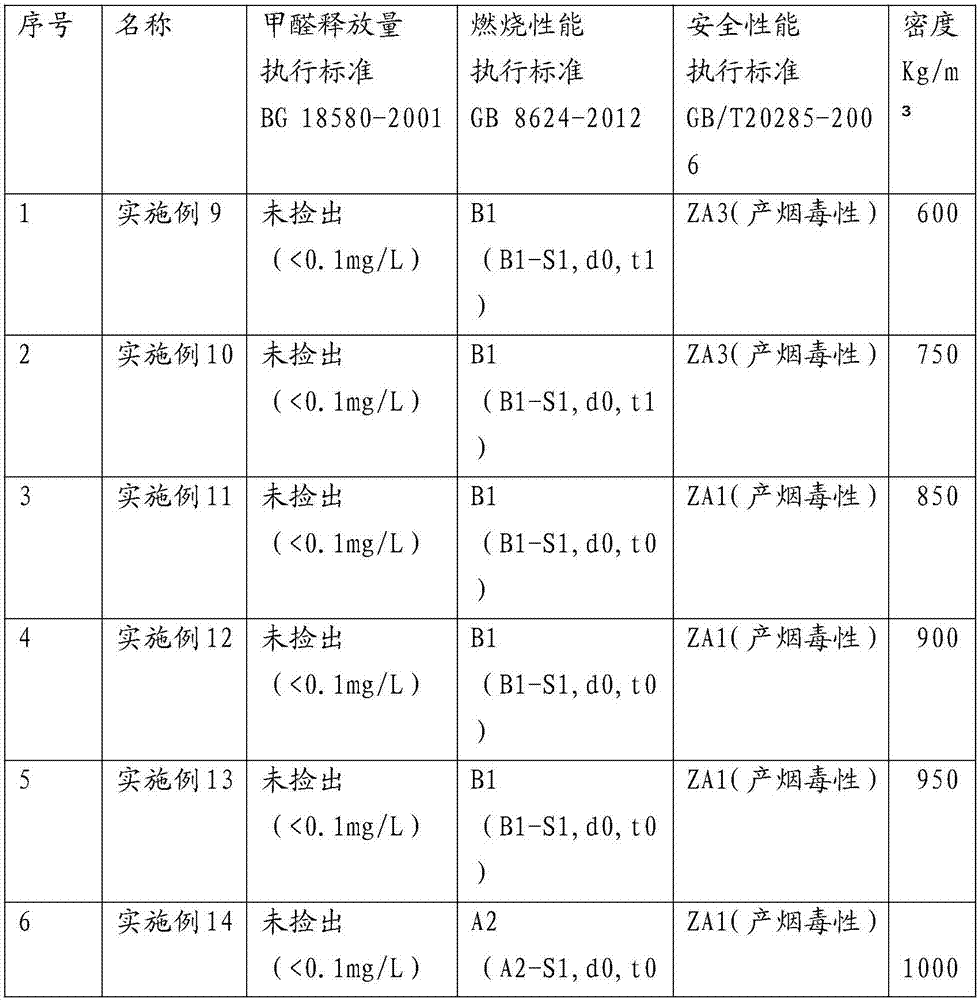
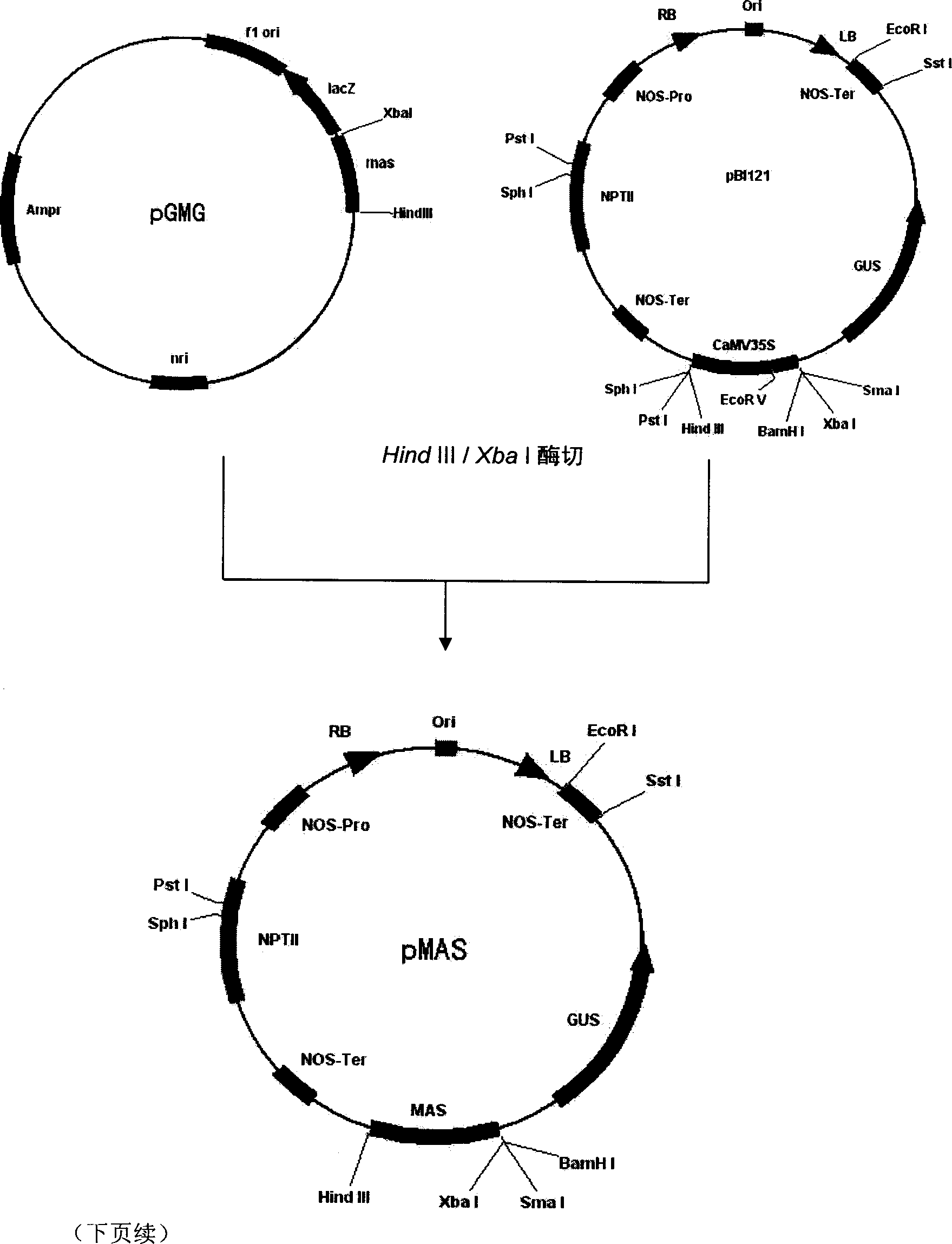
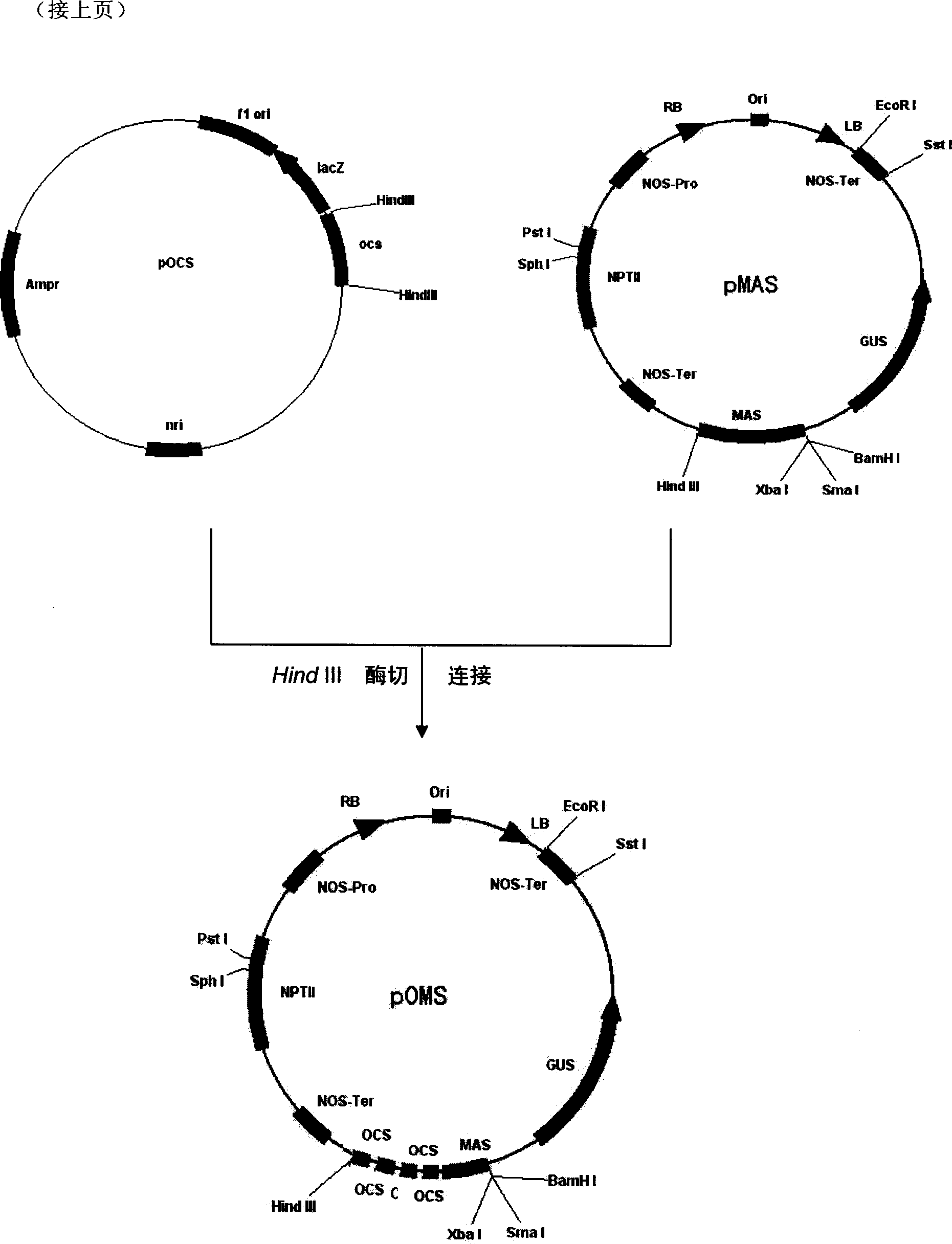
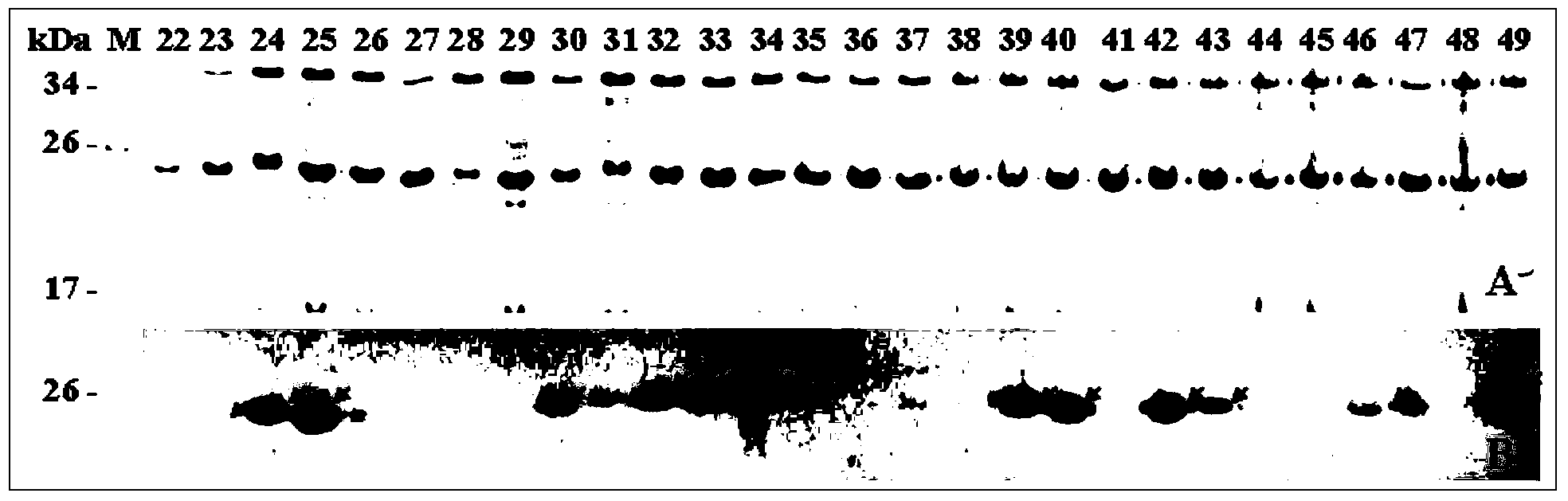Patents
Literature
43 results about "Core fragment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Core Fragment. Core Fragment is a type of ore that glows red and is found very deep underground on all planet types except moons or barren planets. This ore is abundant near the core of a planet. This ore can be found without mining on garden planets as all garden planets have old mines that contain core fragments.
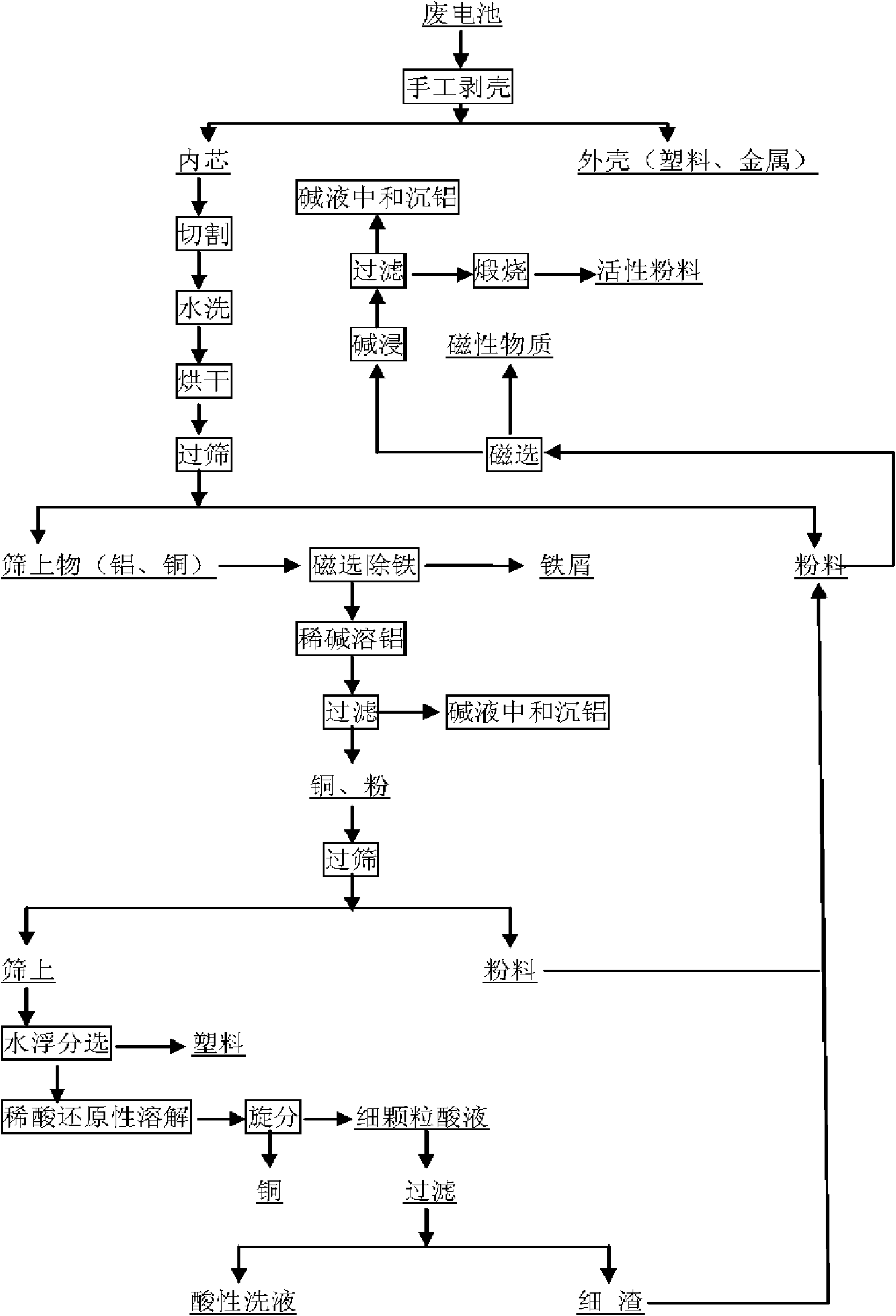
Method for efficiently recovering active materials of positive poles in waste lithium batteries
InactiveCN101599563AWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementCycloneElectrical battery
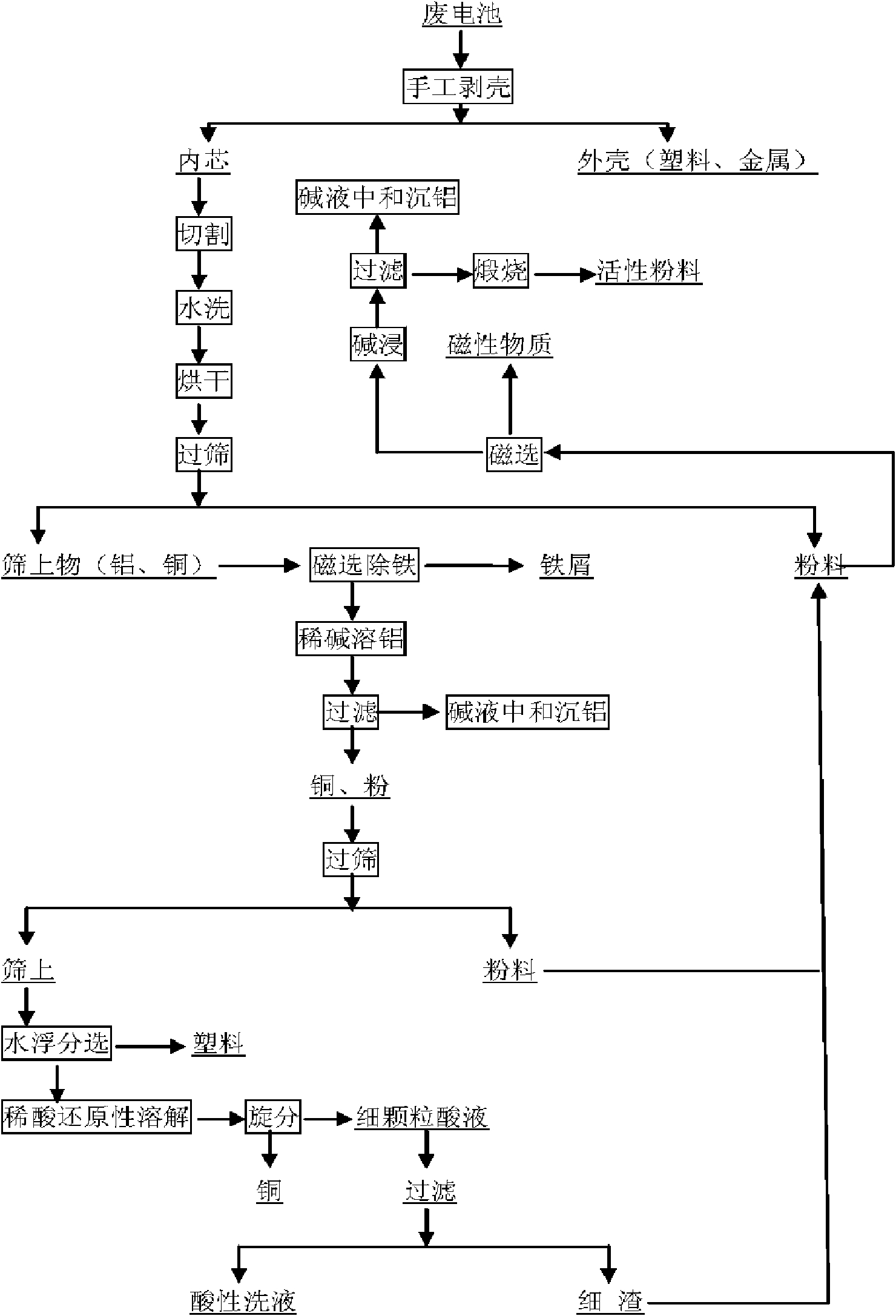
The invention discloses a method for efficiently recovering active materials of positive poles in waste lithium batteries, which is mainly characterized by adding crushed electrical core fragments into hot water, stirring the mixture, and performing first vibration screening after the filtration and drying to separate most of an active material; dissolving aluminum foil through alkaline leaching after an oversize part is magnetically separated, adjusting the pH value of an alkaline leaching filtrate by dilute acid and ammonium bicarbonate solution, and recovering aluminum; performing second vibration screening after the filtration and drying to separate a residual powder material; and placing the oversize part into water for water cyclone separation, dumping to remove an upper-layer plastic diaphragm, then using dilute sulfuric acid and sodium thiosulfate solution to wash a copper sheet to ensure that carbon powder and active powder which are adhered to the copper sheet are loosened and fall off, making the powder float on an upper layer through cyclone separation after the washing, mixing the powder and the active powders obtained by two screenings, using NaOH solution to soak the mixture after the magnetic separation, calcining the alkali-leached active powder material after the filtration and drying, and taking the active powder material as active powder for subsequent treatment. The use of the method can ensure that the recovery rates of copper and aluminum in waste lithium ion batteries reach 98.5 percent and 97 percent respectively, and the recovery rate of the active materials is about 99 percent.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Electric pencil sharpener
An electric pencil sharpener comprises a wasteful shaving prevention mechanism for separating the rotatable cutting blade from the pencil a pencil-core tip adjustment mechanism for adjusting the diameter of the shaved pencil-core tip, and a core fragment removal mechanism for removing any broken off pencil-core fragment remaining in the electric pencil sharpener. The wasteful shaving prevention mechanism includes the cutting blade, a cutter shaft and a plate and is structured to separate the cutting blade from the pencil when sharpening if finished. The pencil-core tip adjustment mechanism includes a pencil-core tip adjustment dial, a rotatable pencil-core tip adjustment screw, a gear shaft, a connecting rod, a plate and a stop. The core fragment removal mechanism includes a button, a gear shaft, a connecting rod, a plate and a stop. An electric pencil sharpener that further incorporates a pencil diameter adapter is also provided.
Owner:KTF
An electric pencil sharpener
The invention provides an electric pencil sharpener with all functions of a wasteful shaving prevention mechanism, a pencil-core tip adjustment mechanism, a core fragment removal mechanism and a pencil diameter adapter. In the electric pencil sharpener composed of a main body cover, a drive mechanism passing the power, a transfer mechanism for the rotating operation, a cutting mechanism with a rotating cutting blade of the rotating cutting the pencil, a wasteful shaving prevention mechanism for separating the rotatable cutting blade from the pencil, a pencil-core tip adjustment mechanism for adjusting the diameter of the shaved pencil-core tip, and a core fragment removal mechanism for removing any broken off pencil-core fragment remaining in the electric pencil sharpener. The wasteful shaving prevention mechanism includes the cutting blade, a cutter shaft and a plate and is structured to separate the cutting blade from the pencil when sharpening if finished. The pencil-core tip adjustment mechanism includes a pencil-core tip adjustment dial, a rotatable pencil-core tip adjustment screw, a gear shaft, a connecting rod, a plate and a stop. The core fragment removal mechanism includes a button, a gear shaft, a connecting rod, a plate and a stop.
Owner:KTF
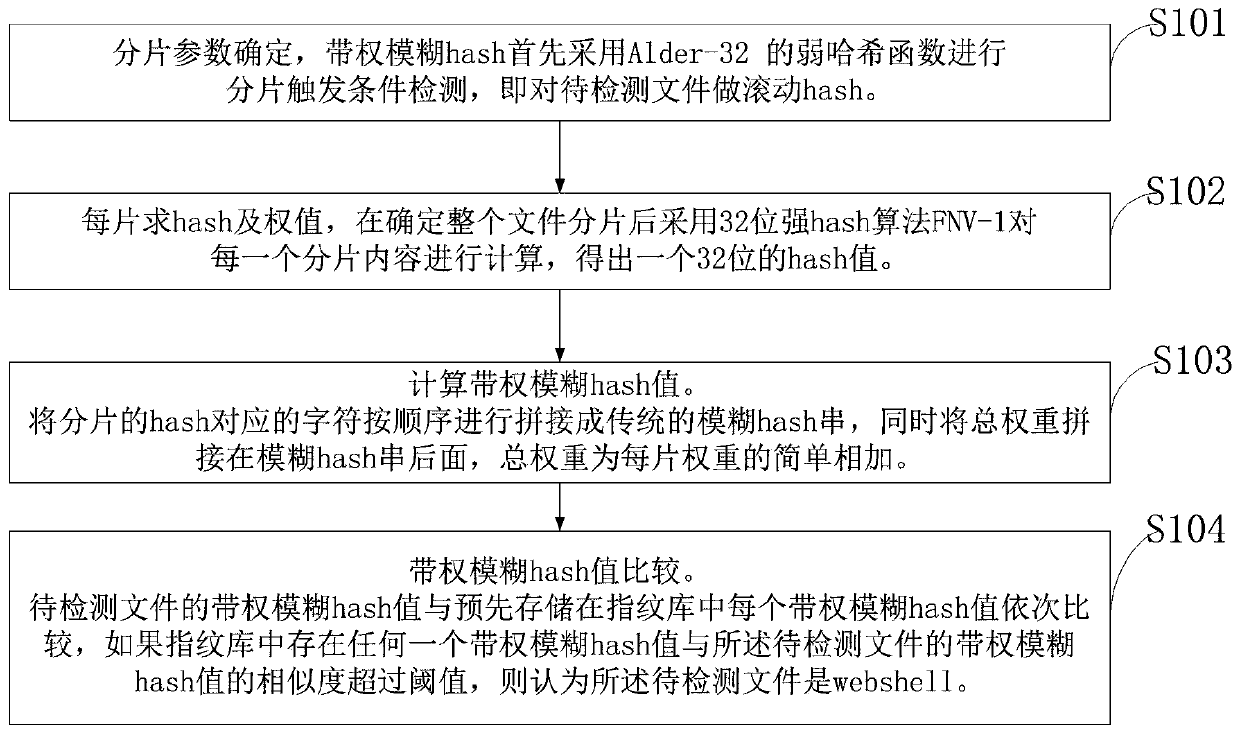
Webshell detection method based on weighted fuzzy hash
ActiveCN110034921AImprove detection accuracyAccommodates large variations in sizeEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesTheoretical computer scienceData mining
The invention belongs to the technical field of network space security, and discloses a webshell detection method and system based on a weighted fuzzy hash algorithm. A file to be detected is fragmented, the hash and weight of each fragment are solved, the weight is given to each fragment, the core fragment with the danger function is provided with a large weight, the information entropy of each fragment is considered at the same time, and the larger the information entropy value is, the smaller the given weight is; the hash of each fragment is spliced into a fuzzy hash string, and a total weight value is calculated to obtain a weighted fuzzy hash value; and the weighted fuzzy hash value of the to-be-detected file is compared with the weighted fuzzy hash value of each webshell pre-stored in the fingerprint database in sequence. Compared with a traditional fuzzy Hash algorithm, the method can effectively adapt to the situation that the size of a detected object changes greatly, has goodadaptability, greatly improves the detection accuracy of a variety sample, and improves the anti-interference performance.
Owner:NAT COMP NETWORK & INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT CENT
Flame-retardance formaldehyde-free industrial hemp straw fiberboard and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN107322745AWith flame retardant functionClear componentsDomestic articlesFlat articlesSolventFiberboard
The invention provides a flame-retardance formaldehyde-free industrial hemp straw fiberboard. The fiberboard comprises raw materials of industrial hemp straw all-straw core fragments and flame-retardance adhesive being 18-48 weight% of the fragments; and the fiberboard is prepared by such steps as cold pressing and curing. Aiming at a hot pressing process and a method for applying solvent adhesive in traditional fiberboard manufacturing, the flame-retardance formaldehyde-free industrial hemp straw fiberboard is prepared by using a cold pressing process and special flame-retardance formaldehyde-free adhesive. Compared with a traditional fiberboard preparation method, the method has the advantages of simple process, low energy consumption and no environmental pollution; and compared a wood fiberboard, the obtained product has such characteristics as flame retardance, low smoke, no irritation, no poison, no formaldehyde, bacteria resistance, insect resistance, water resistance, high strength and possession of both medium density and high density.
Owner:洪家敏
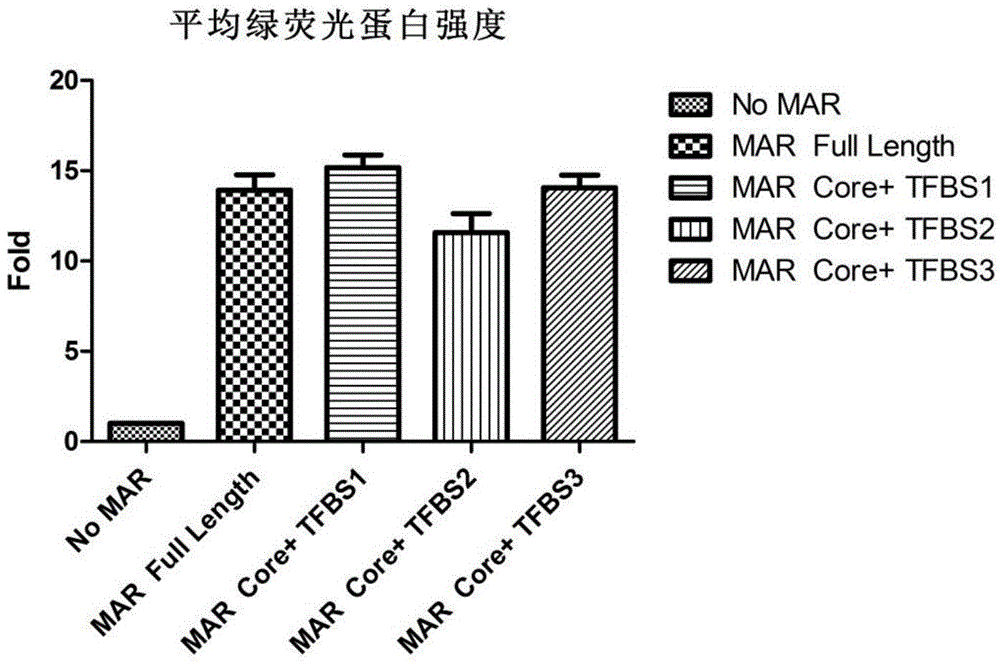
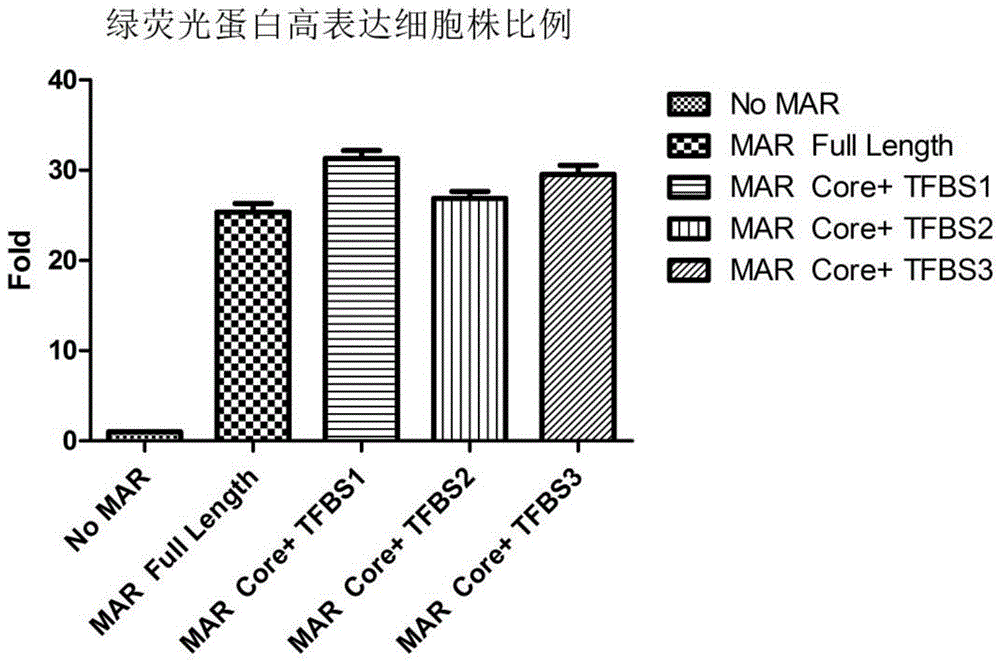
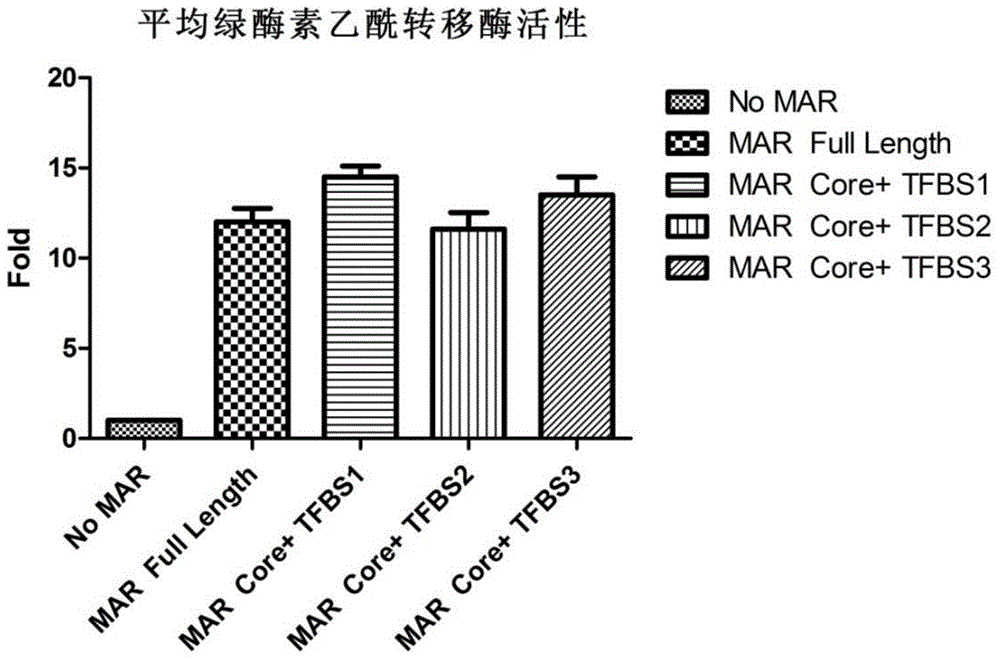
Novel MAR (matrix attachment region) core fragment-containing animal cell expression vector
ActiveCN104975009AHigh expressionImprove stabilityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceMammalian cell
The invention discloses a novel MAR (matrix attachment region) core fragment-containing animal cell expression vector. The nucleotide base sequence of the MAR core fragment of the recombinant expression vector is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, SEQ ID No.2 or SEQ ID No. 3. The expression vector disclosed by the invention can effectively increase the yield of protein in mammalian cells and reduce production cost.
Owner:SUNSHINE GUOJIAN PHARMA (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Method for efficiently recovering active materials of positive poles in waste lithium batteries
InactiveCN101599563BWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementElectrical batteryFiltration
The invention discloses a method for efficiently recovering active materials of positive poles in waste lithium batteries, which is mainly characterized by adding crushed electrical core fragments into hot water, stirring the mixture, and performing first vibration screening after the filtration and drying to separate most of an active material; dissolving aluminum foil through alkaline leaching after an oversize part is magnetically separated, adjusting the pH value of an alkaline leaching filtrate by dilute acid and ammonium bicarbonate solution, and recovering aluminum; performing second vibration screening after the filtration and drying to separate a residual powder material; and placing the oversize part into water for water cyclone separation, dumping to remove an upper-layer plastic diaphragm, then using dilute sulfuric acid and sodium thiosulfate solution to wash a copper sheet to ensure that carbon powder and active powder which are adhered to the copper sheet are loosened and fall off, making the powder float on an upper layer through cyclone separation after the washing, mixing the powder and the active powders obtained by two screenings, using NaOH solution to soak the mixture after the magnetic separation, calcining the alkali-leached active powder material after the filtration and drying, and taking the active powder material as active powder for subsequent treatment. The use of the method can ensure that the recovery rates of copper and aluminum in waste lithium ion batteries reach 98.5 percent and 97 percent respectively, and the recovery rate of the active materials is about 99 percent.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
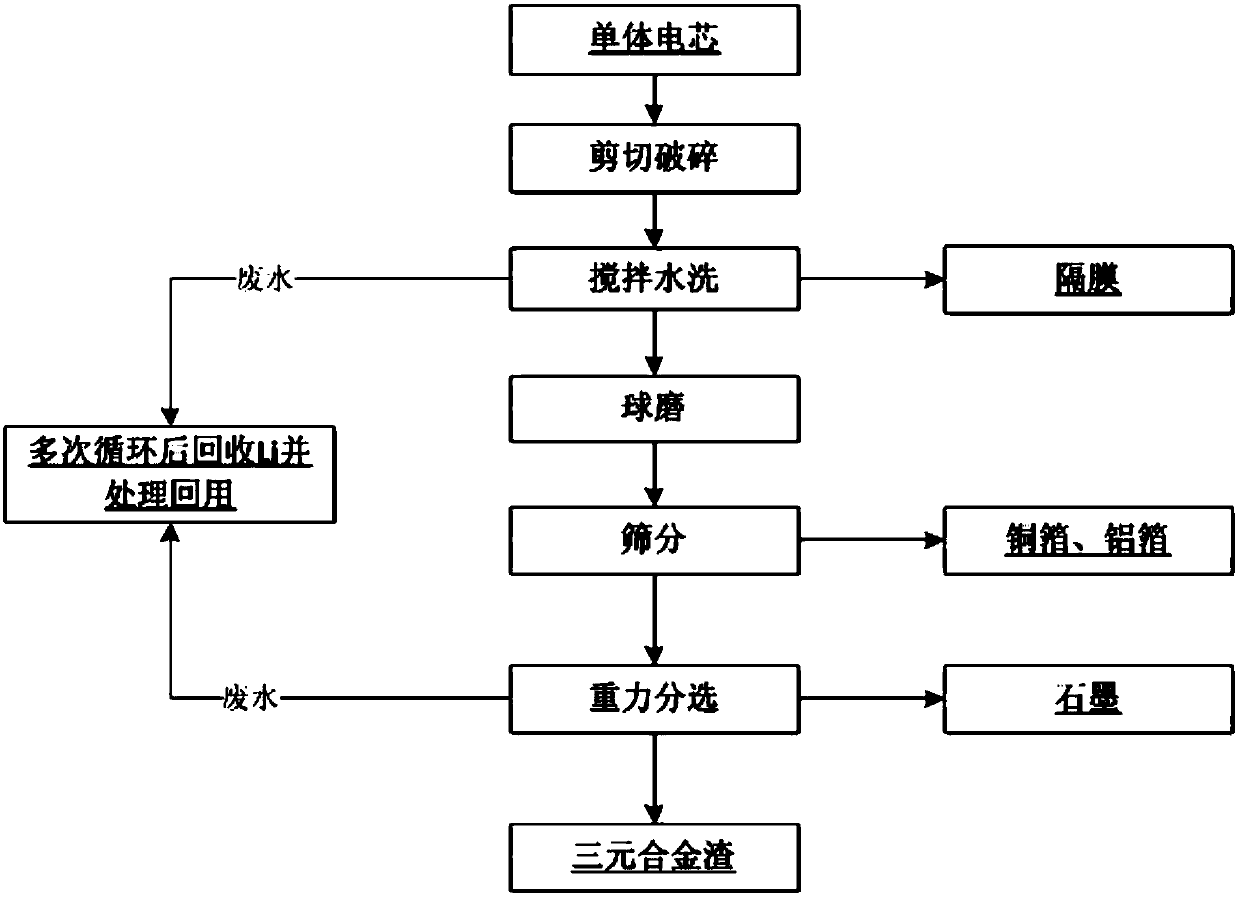
Technology for recycling valuable metal from electric core of waste tertiary power battery
ActiveCN107689465AAchieve recyclingReduce consumptionWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementAlloyEngineering
The invention discloses a technology for recycling valuable metal from an electric core of a waste tertiary power battery. The technology comprises the following steps of (1) shearing and crushing theelectric core under the water protection condition, and enabling electrolyte to enter into water; (2) washing the crushed electric core fragments in a water tank, removing a diaphragm, and further washing to remove electrolyte residue; (3) filtering the electric core fragments after water washing, performing ball milling, and separating tertiary material and graphite from a copper coil and an aluminum coil; (4) enabling a screen net to screen the copper coil and the aluminum coil; performing gravity sorting on the matters under the screen by a rocking bed to remove graphite, so as to obtain tertiary alloy residue; (5) recycling the shearing, crushing and washing water for multiple times, separating out lithium by a precipitation method, and sending into a water treatment plant to treat and recycle. The technology has the advantage that the difference between physical properties of the tertiary material and other components in the power battery is utilized, the environment-friendly physical sorting technology is adopted, the usable components are gradually separated, and the electrolyte is simultaneously treated, so that all valuable metal elements in the tertiary power battery canbe recycled.
Owner:有研资源环境技术研究院(北京)有限公司
Core confirming method for development degree of reservoir cracks
ActiveCN107064454ASure objectiveThe method works wellEarth material testingComputer sciencePerformed Imaging
The invention relates to a core confirming method for the development degree of reservoir cracks. The method comprises the following steps: 1) jointing cores; 2) summarizing and recognizing the characteristics of natural cracks; 3) performing imaging logging calibration; 4) finally confirming the natural cracks; and 5) judging the development degree of the cracks. The invention is specific to the reservoir cracks; the natural cracks are confirmed according to two data of the core and imaging logging, so that the confirmation of the natural cracks is more objective; furthermore, the splicing resetting is performed on the core fragments according to the invention, so that the quantity statistics of the natural cracks of the core can more objectively reflect the quantity of practical reservoir cracks, especially, the reservoir with abnormal development of the cracks and serious core segment; the method has a better effect; besides, the development degree of reservoir cracks confirmed according to the invention can avoid the common industrial misunderstanding that a same crack is mistakenly recorded as multiple cracks under the influence of mutual cutting of the cracks.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
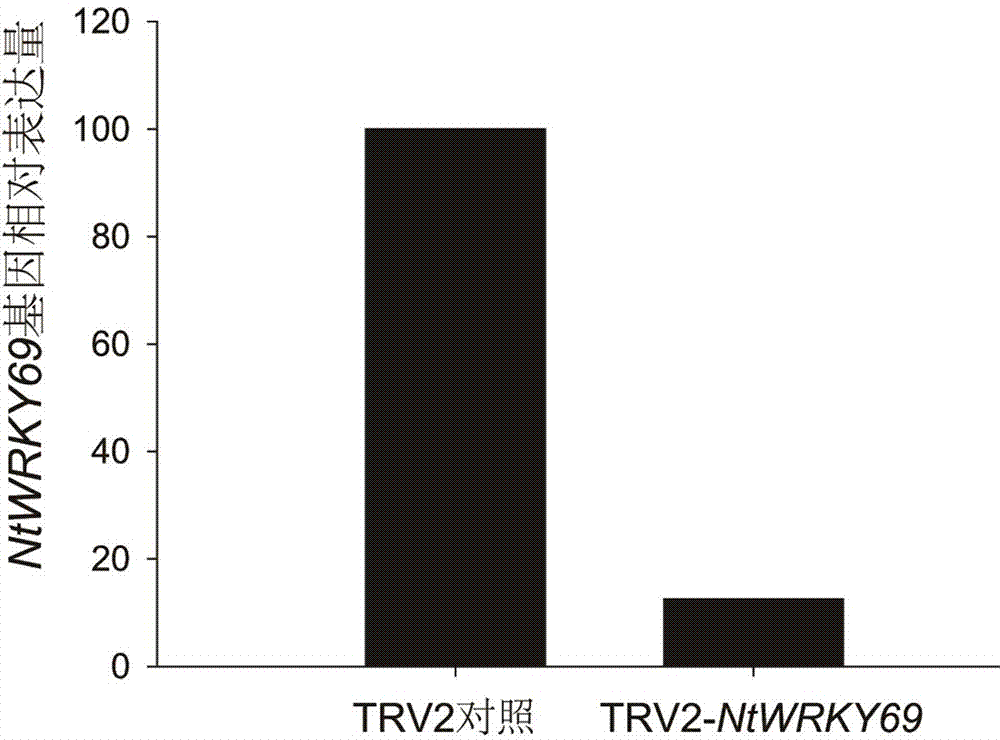
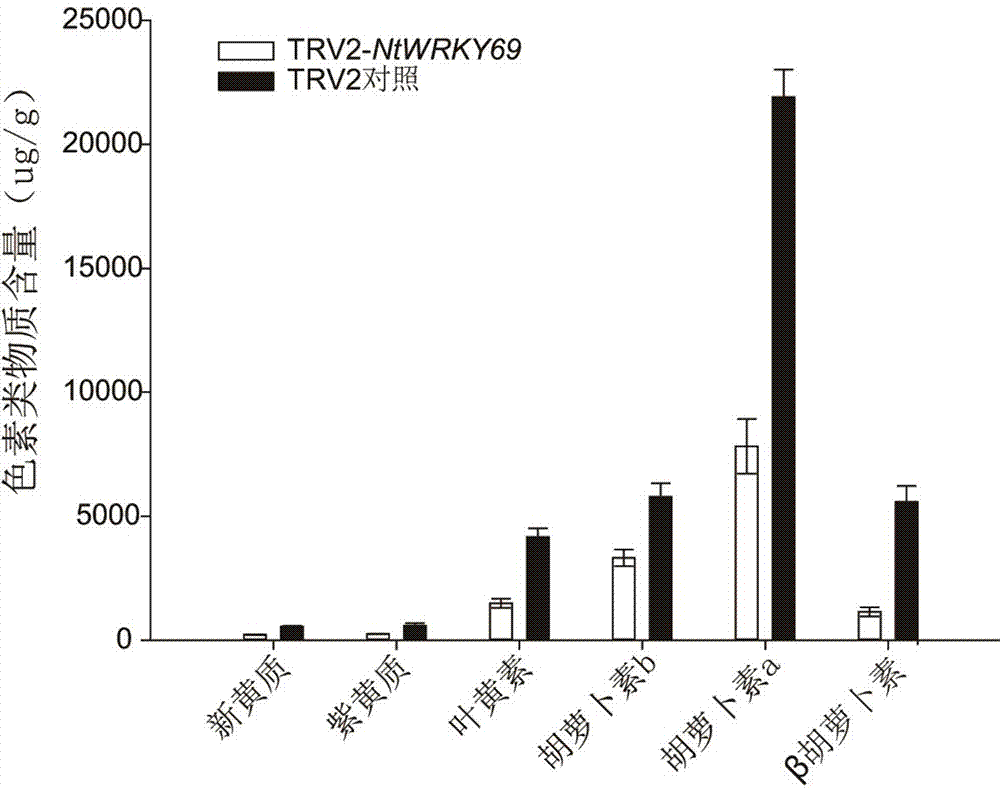
NtWRKY69 gene affecting tobacco pigment content and application of NtWRKY69 gene
ActiveCN107177604AReduced content of pigmentsPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology engineering and particularly relates to an NtWRKY69 gene affecting tobacco pigment content and an application of the NtWRKY69 gene. The gene comprises a 918bp base with the base sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, wherein 80th-600th nucleotides are specific core fragments. Through cloning of the NtWRKY69 gene of tobacco and analysis of corresponding protein, the gene is found to play important roles in regulating tobacco pigment synthesis ways and be highly correlated with the content of pigments in plant leaves. Further, by the aid of a virus mediated gene silencing technology, after the NtWRKY69 gene is silent, the content of the pigments in new transgenic plants is obviously reduced. By means of the characteristic, a new strategy and path can be provided for gene engineering breeding of the tobacco or breeding of other new plant varieties.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Pressurized water reactor spent fuel element indirect neutron CT imaging device
ActiveCN105023622AAvoid influenceGuaranteed accuracyNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringPressurized water reactorEngineering
The invention relates to a nuclear material detection device. The invention provides a pressurized water reactor spent fuel element indirect neutron CT imaging device. The device realizes a 3D nondestructive test on a pressurized water reactor spent fuel element. The device comprises a spent fuel element motion control device and a conversion screen exposure device. The spent fuel element motion control device comprises a spent fuel element motion controller and a shield housing. The conversion screen exposure device comprises a neutron convert screen, a neutron convert screen channel, a neutron beam channel and a neutron convert screen motion controller. The neutron beam channel is provided with a spent fuel element inlet. The imaging device realizes a 3D nondestructive test on a pressurized water reactor spent fuel element, can acquire complete detection information of defects such as spent fuel element core fragment morphology, core inner particle distribution and a housing breaking state, and can provide forceful guarantee for quality detection and performance improvement of a pressurized water reactor spent fuel element in China.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
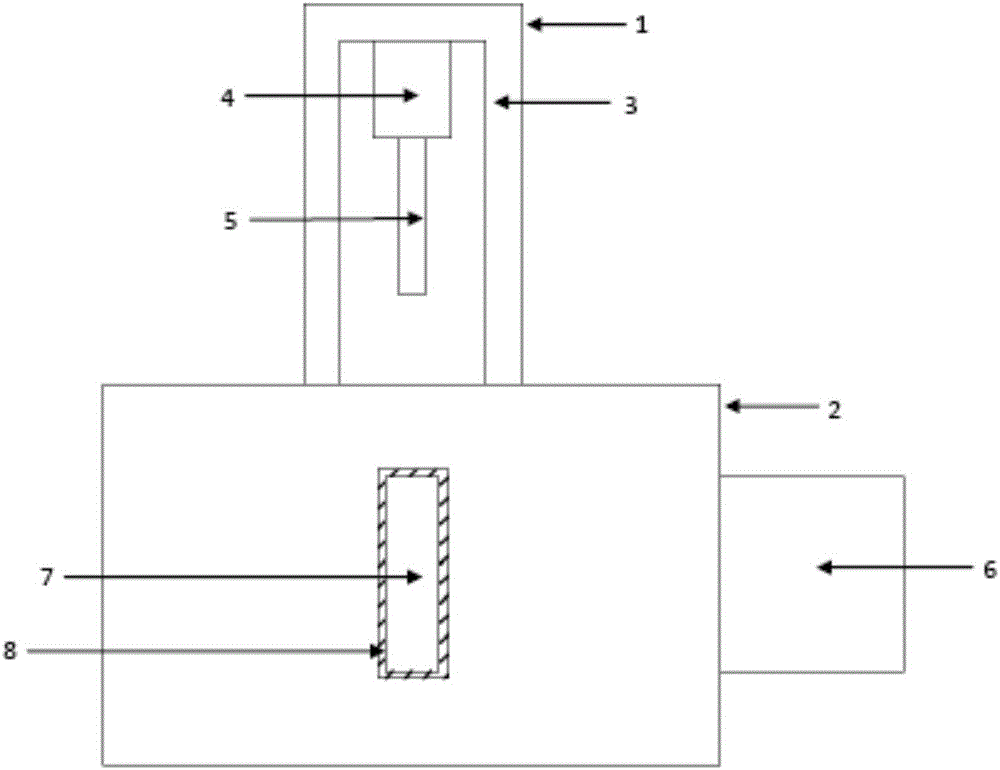
Preparation method for allochroic sensor used for rapid identification and early diagnosis of IgA nephrosis
InactiveCN105223193ASimple methodHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorNephrosisDiagnosis early
The invention discloses a preparation method for an allochroic sensor used for rapid identification and early diagnosis of IgA nephrosis. The preparation method includes obtaining stable butadiyne-type vesicle dispersoid by using a film method or an injection method; dissolving a probe agglutinin in a buffer having pH of 6-8, adding the agglutinin into the butadiyne-type vesicle dispersoid in mol ratio of 1:1 to 1:5; modifying the surface of butadiyne-type vesicle by the agglutinin in the solution in a physical absorption or chemical coupling manner at the temperature of 4-37 DEG C to obtain a tool having a specific recognition function for N-acetylgalactosamine in serum wherein N-acetylgalactosamine is the core fragment of the IgA1 marker having abnormal O-glycosylation. The preparation method is simple, rapid, accuracy and economy, and the price of the product is far lower than that of the like product. The preparation method for an allochroic sensor is used for popularizing the rapid identification, early diagnosis and general examination of IgA nephrosis.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Mounting structure of amorphous alloy transformer
ActiveCN102664088AReduce vibrationTo avoidTransformers/reacts mounting/support/suspensionTransformers/inductances coolingFuel tankEngineering
The invention discloses a mounting structure of an amorphous alloy transformer. The mounting structure of the amorphous alloy transformer comprises an oil tank and a transformer body of the amorphous alloy transformer which is arranged in the oil tank and comprises an upper clamp. The oil tank comprises a tank cover and a tank body, a plurality of fixing plates are connected to the upper end face of the tank cover by means of evenly distribution, a plurality of right-angled bridge plates in one-to-one correspondence with the fixing plates are fixed on the top face of the upper clamp, the lower end face of each of the fixing plates butts against the tope face of the upper clamp of the transformer body through a first cushion, and a second cushion is arranged between the side face of each of the fixing plates and a vertical portion of the corresponding bridge plate and is connected to the bridge plate through a connecting piece. By the mounting structure of the amorphous alloy transformer, corresponding vibration of the transformer body due to electromotive force produced by a coil is reduced when the transformer is short-circuited unexpectedly, and no-load loss increasing and core fragments caused by extra-stress produced by vibration of the transformer can be prevented effectively.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHIXIN ELECTRIC AMORPHOUS +4
Mytilus coruscus multi-drug resistance protein Abcc -- novel marine biological pollution detection marker
InactiveCN109336959AStrong specificitySensitive biological responseMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMytilus coruscusMolecular level
The invention discloses a mytilus coruscus multi-drug resistance protein Abcc. The multi-drug resistance protein Abcc is a cloned gene, which is obtained by cloning a gene core fragment of mytilus coruscus Abcc by a gene cloning technology. The invention also discloses a novel marine biological pollution detection marker, which uses mytilus coruscus as a biological sample for detecting marine pollution, and uses the mytilus coruscus multi-drug resistance protein Abcc as a detection marker for marine pollution. The relative expression amount of a multi-drug resistance protein Abcc gene of the mytilus coruscus multi-drug resistance protein Abcc is the highest in digestive glands and gills, and a PCR reaction system for cloning can ensure the specificity of an amplification reaction and improve the PCR amplification efficiency. The detection marker provided by the invention has strong specificity, can directly take target cells or target molecules in organisms as reaction endpoints to carry out sensitive biological reactions at the molecular level, and has an early warning effect on marine pollutant exposure and toxicity effects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Assembly device and method for horizontal body of dry amorphous alloy transformer
InactiveCN103093951AImprove consistencyImprove assembly efficiencyInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureGeneral assemblyLow voltage
The invention discloses assembly device and method for a horizontal body of a dry amorphous alloy transformer. The assembly method includes: opening an upper yoke of a core which is horizontal, allowing three-phase high and low voltage coils to penetrate through the upper yoke respectively, and closing the upper yoke of the core. Compared with vertical installation of the core, the method causes few core fragments during core opening and closing, and prevents the core fragments from falling into a small gap between the core and a guard plate. The requirement for single-point grounding between the core and the guard plate is guaranteed exactly. Technical performance indexes of products are well uniform. Compared with the general assembly process, the assembly method enables general assembly staff to be halved and general assembly efficiency to be doubled, so that production efficiency is improved greatly and product performance is stable. Tests show that the assembly method is evidently effective, product quality and production efficiency are improved greatly, and product performance is stable.
Owner:SHANGHAI SUPERCONDUCTOR ENERGY EQUIP
Process for culturing brownness resistant sweet potatoes utilizing gene engineering technology
InactiveCN1699574AReduced expression levelImprove qualityFermentationHorticulture methodsAntisense RNAGene engineering
The invention provides a process for culturing brownness resistant sweet potatoes utilizing gene engineering technology, which relates to the achievement of yam polyphenol oxidase gene core fragments and the process of cultivating brown trans-gene yam by employing antisense RNA technology, and the method comprises cloning polyphenol oxidase gene core fragment from yam, constructing plant highly effective antisense expression carrier, and leading into agrolbacterium and genetically transforming the yam.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
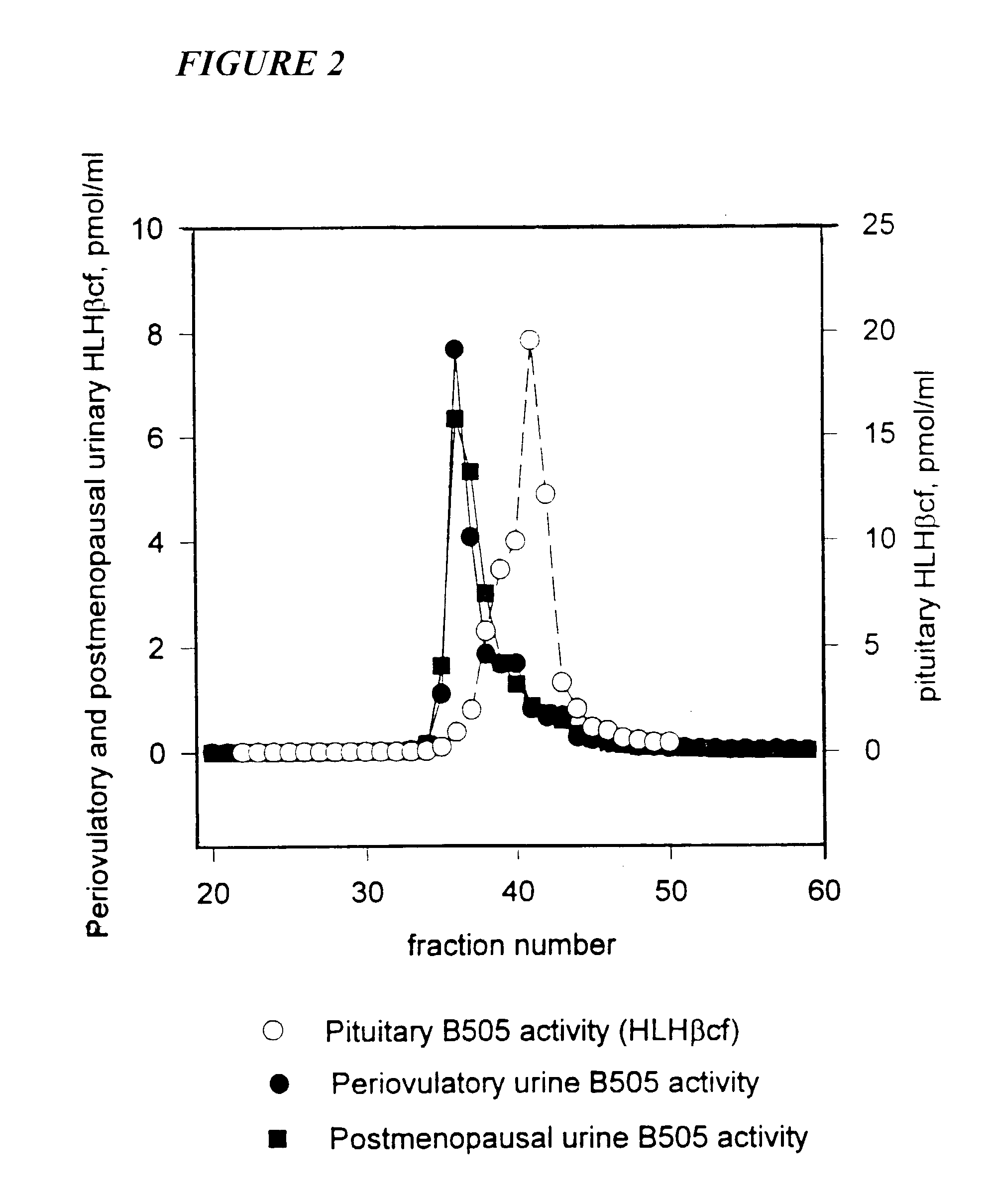
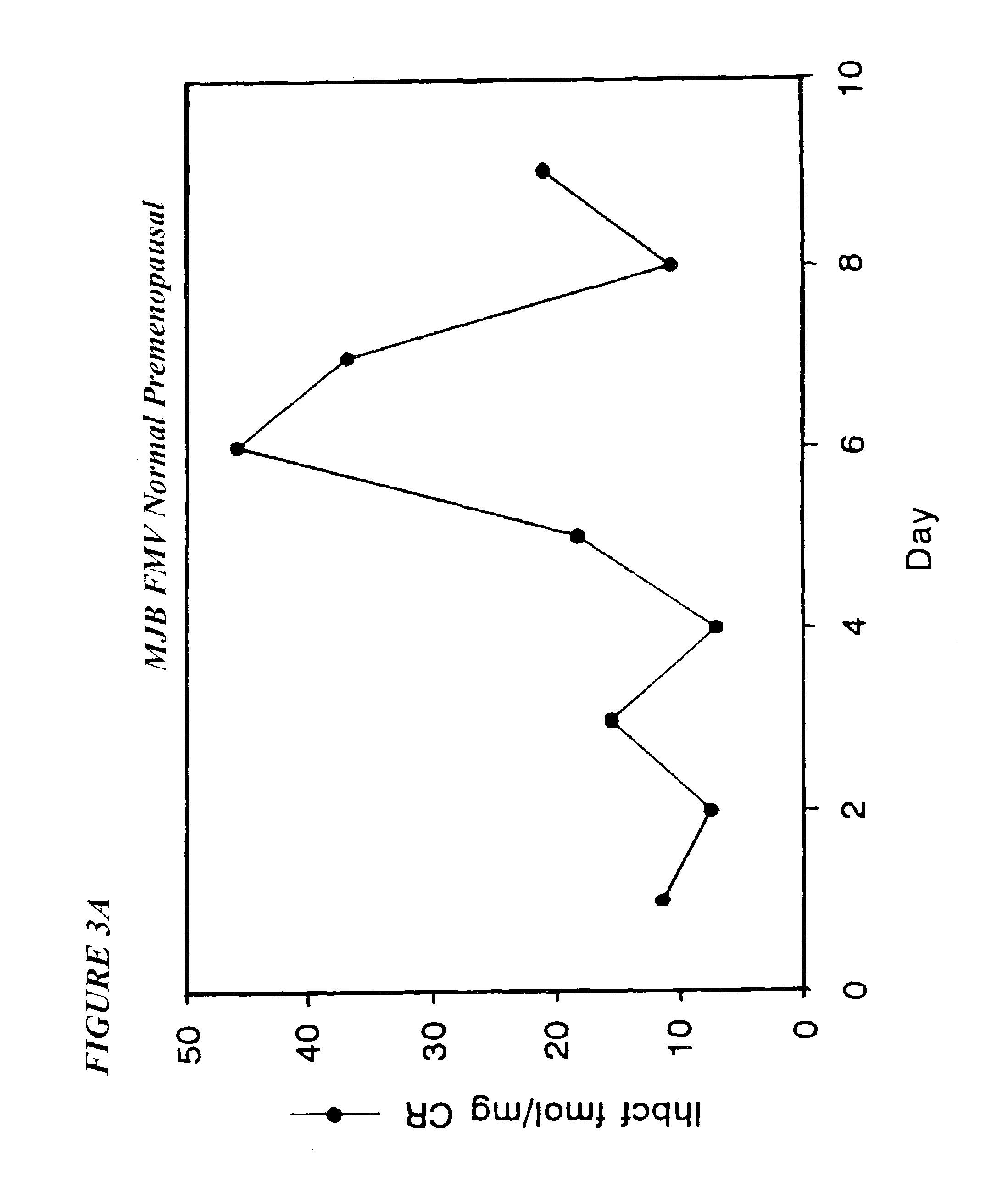
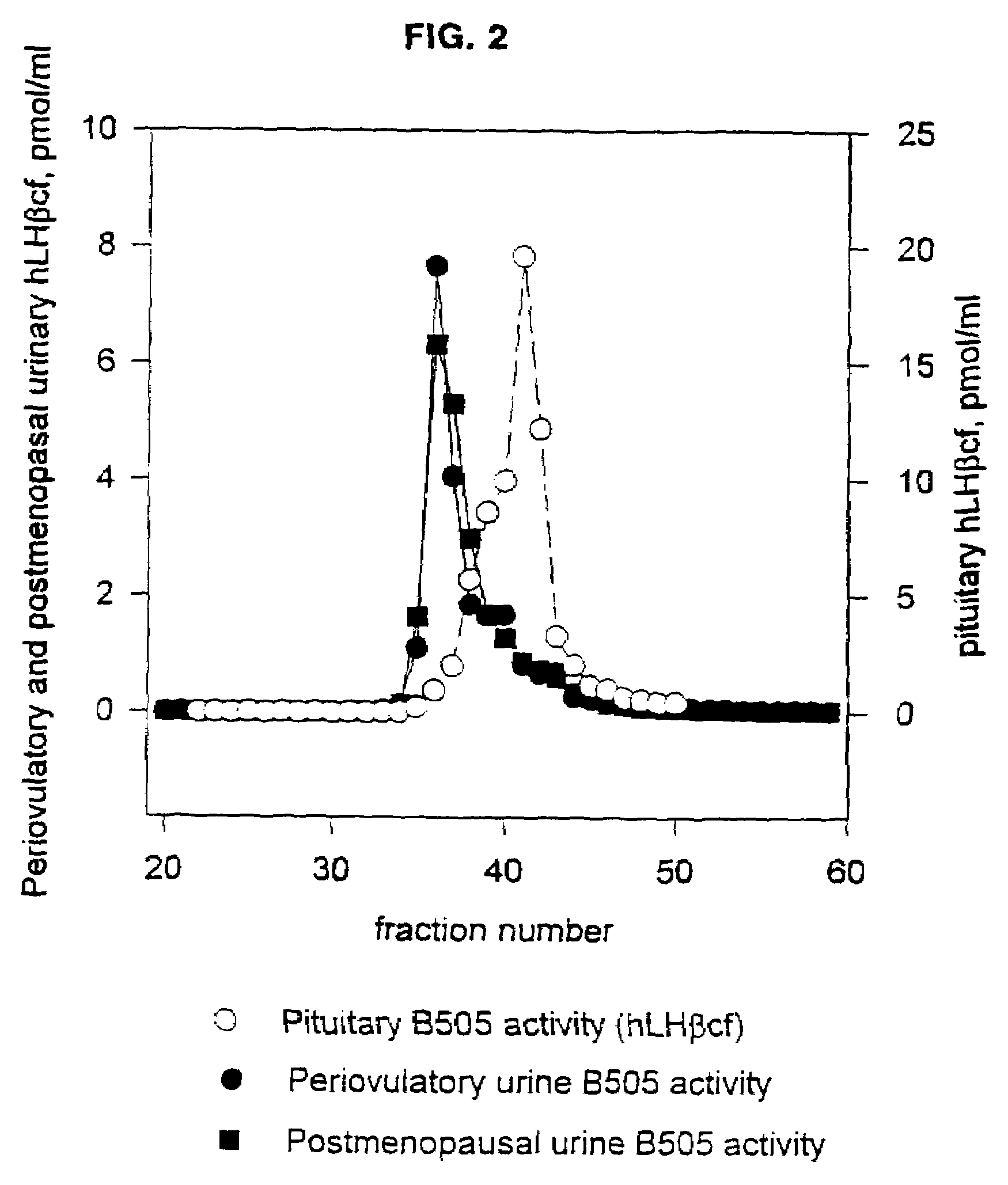
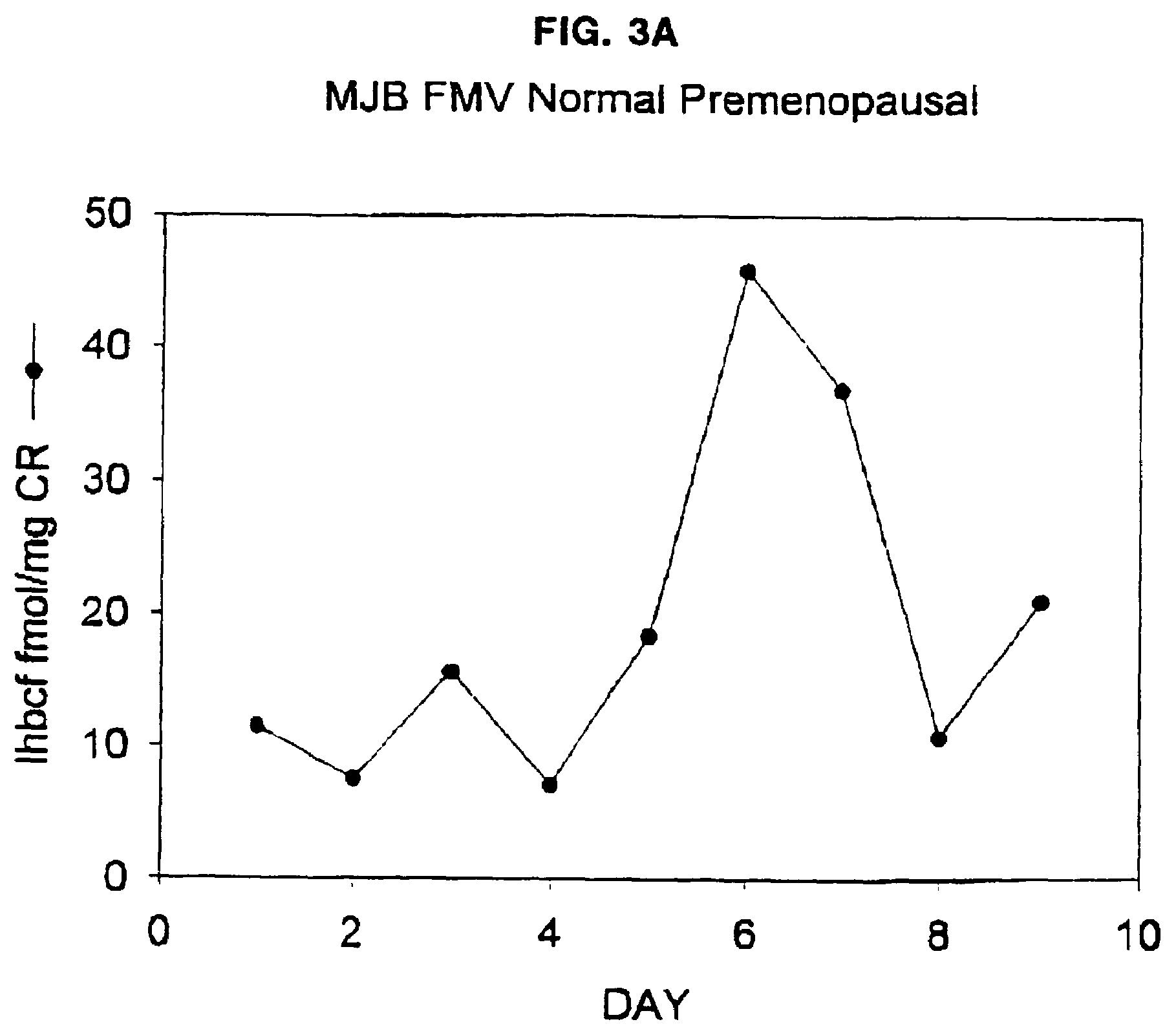
Methods and reagents for determining the amount of hLHbeta core fragment in a sample
InactiveUS7655410B2Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsDisease diagnosisBiologyCore fragment
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
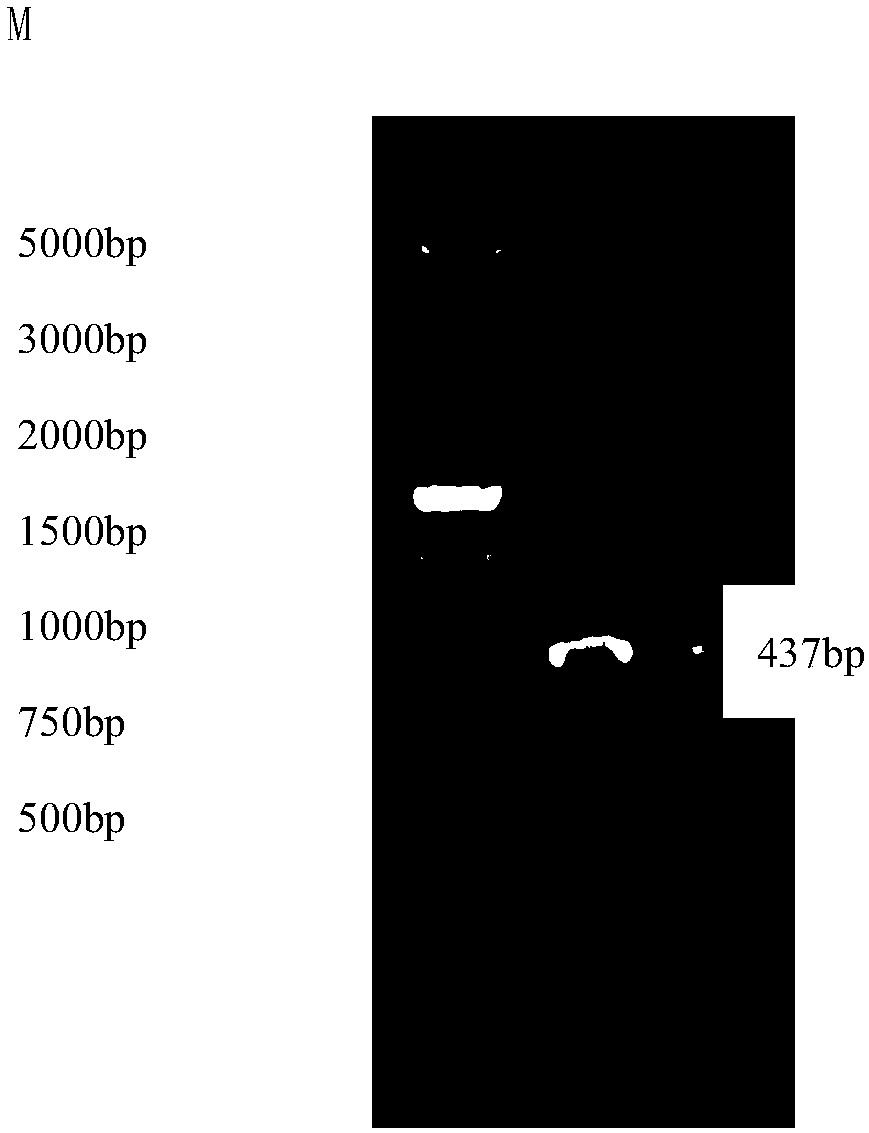
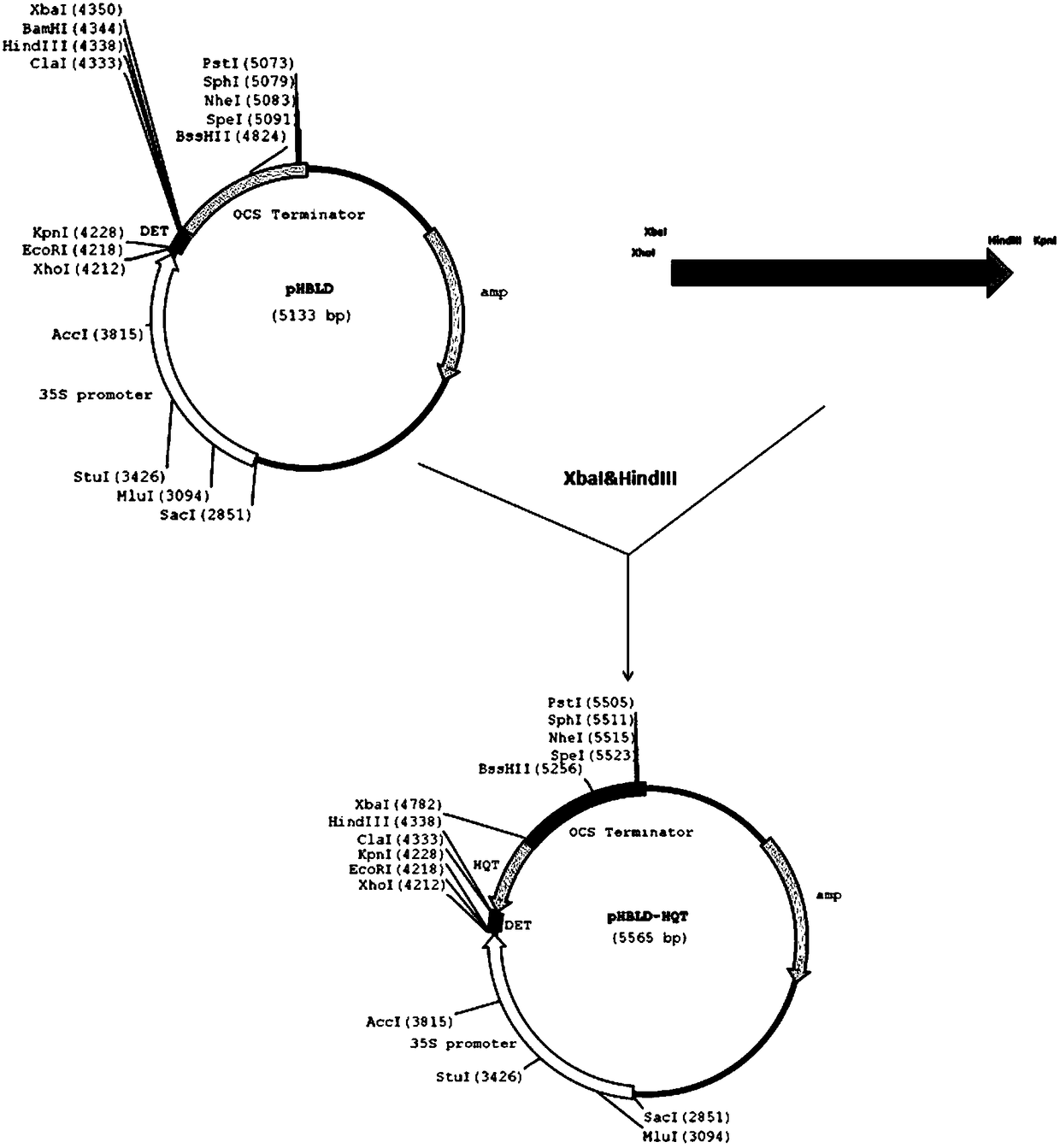
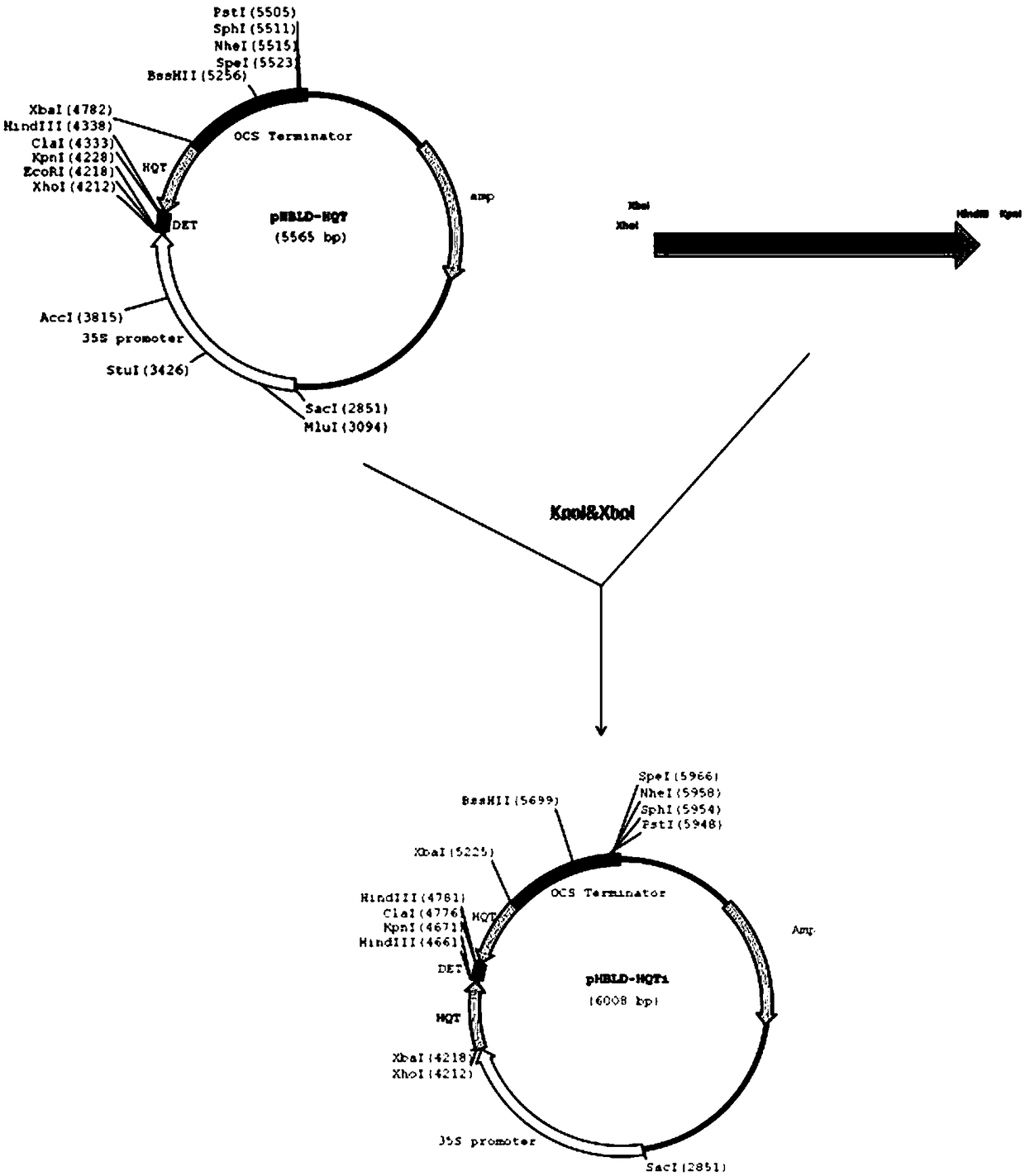
Cultivated eggplant SmHQT gene core fragment, RNAi expression vector and application thereof
InactiveCN108165555AReduce contentReduce browningBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChlorogenic acidCultivar
The invention discloses a cultivated eggplant SmHQT gene core fragment, an RNAi expression vector containing the same, and construction and application of the cultivated eggplant SmHQT gene core fragment. The cultivated eggplant SmHQT gene core fragment is shown in SEQ ID NO.3. According to the cultivated eggplant SmHQT gene core fragment, a cultivated eggplant variety with reduced chlorogenic acid synthesis through silent SmHQT gene, the purpose of reducing browning of pulp of cultivated eggplant, and a new cultivated variety has a good market prospect and economic value.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
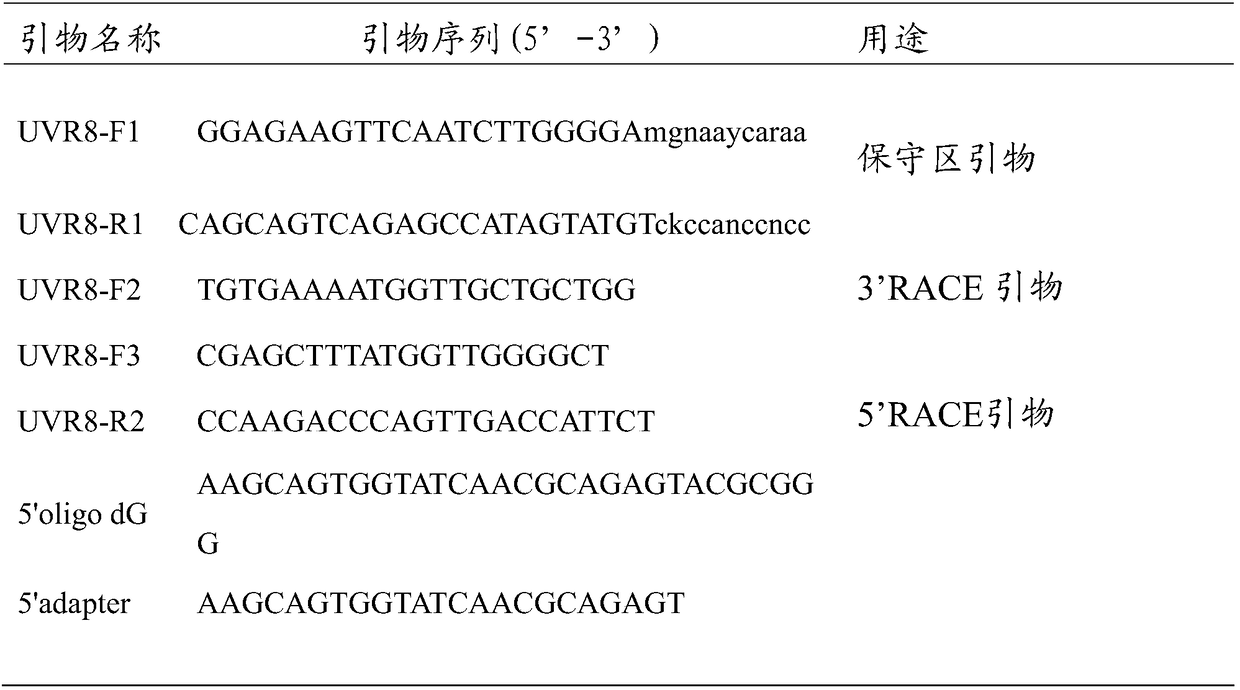
Purple sweet potato ultraviolet receptor UVR8 gene and cloning method thereof
InactiveCN108103072AFull sequence cloningFast and accurate full sequenceMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesConserved sequenceComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention provides a purple sweet potato ultraviolet receptor UVR8 gene and a cloning method thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the purple sweet potato ultraviolet receptor UVR8 gene is shown as SEQ NO. 4; the cloning method of the purple sweet potato ultraviolet receptor UVR8 gene comprises the following steps: (1) synthesizing a cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) first chain; (2) carrying out homologous cloning on a UVR8 conserved sequence; (3) amplifying a 3' end of UVR8; (4) amplifying a 5' end of the UVR8; (5) splicing the sequence. By adopting the method provided by the invention, species with a relatively close genetic relationship are not needed and the cloning of a core fragment can be finished through designing various merged basic groups only if a homologous gene exists; the method is also applicable to gene cloning of other plants. In 5' end cloning, a process that a phosphoric acid group of mRNA (messenger Ribonucleic Acid) is removed through phosphorylase and ligase is connected with a connector linker primer is not needed; howeverbut, 3 to 5 C are added at the 3' end in an RNA reverse transcription process according to properties of M-MuLV reverse transcriptase; then 3 to 5 G are added at the tail end of a designed primer and are matchedfoe matching with the designed primerC and the reverse transcription process is finished. The method is simple and convenient, the time and cost are saved and the success rate is relatively high.
Owner:CROP RES INST OF FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Preparation method of core fragment rIFN (interferon)-alpha1of recombinant chicken IFN-alpha
InactiveCN102321630ASmall molecular weightInhibition of value addedFermentationInterferonsIfn alphaNewcastle disease virus NDV
The invention relates to a preparation method of a core fragment rIFN (interferon)-alpha1 of recombinant chicken IFN-alpha, which comprises the following steps that: chicken spleen RNA (ribonucleic acid) is extracted, and is subjected to reverse transcription into cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid), and the cDNA is used as a template; a nested PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method is adopted, firstly, an outer primer capable of amplifying the chicken full-length gene of IFN-alpha is used for the first round of amplification, and then a self-designed inner primer is used for amplifying corresponding subcloned IFN-alpha1 encoding gene to obtain the core fragment rIFN-alpha1 of the recombinant chicken IFN-alpha. For the core fragment rIFN-alpha1 of recombinant chicken IFN-alpha, the detection of the anti-Newcastle disease virus activity of chicken IFN-alpha1 on BHK-21 cells is carried out, indicating that the highest activity unit of the chicken rIFN-alpha1 is up to 4.32*103U.mg <-1>; and the detection of the anti-Newcastle disease virus activity of chicken IFN-alpha1 is carried out by utilizing SPF (specific pathogen free) chicken embryos cultured virus, indicating that the antiviral activity is higher.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
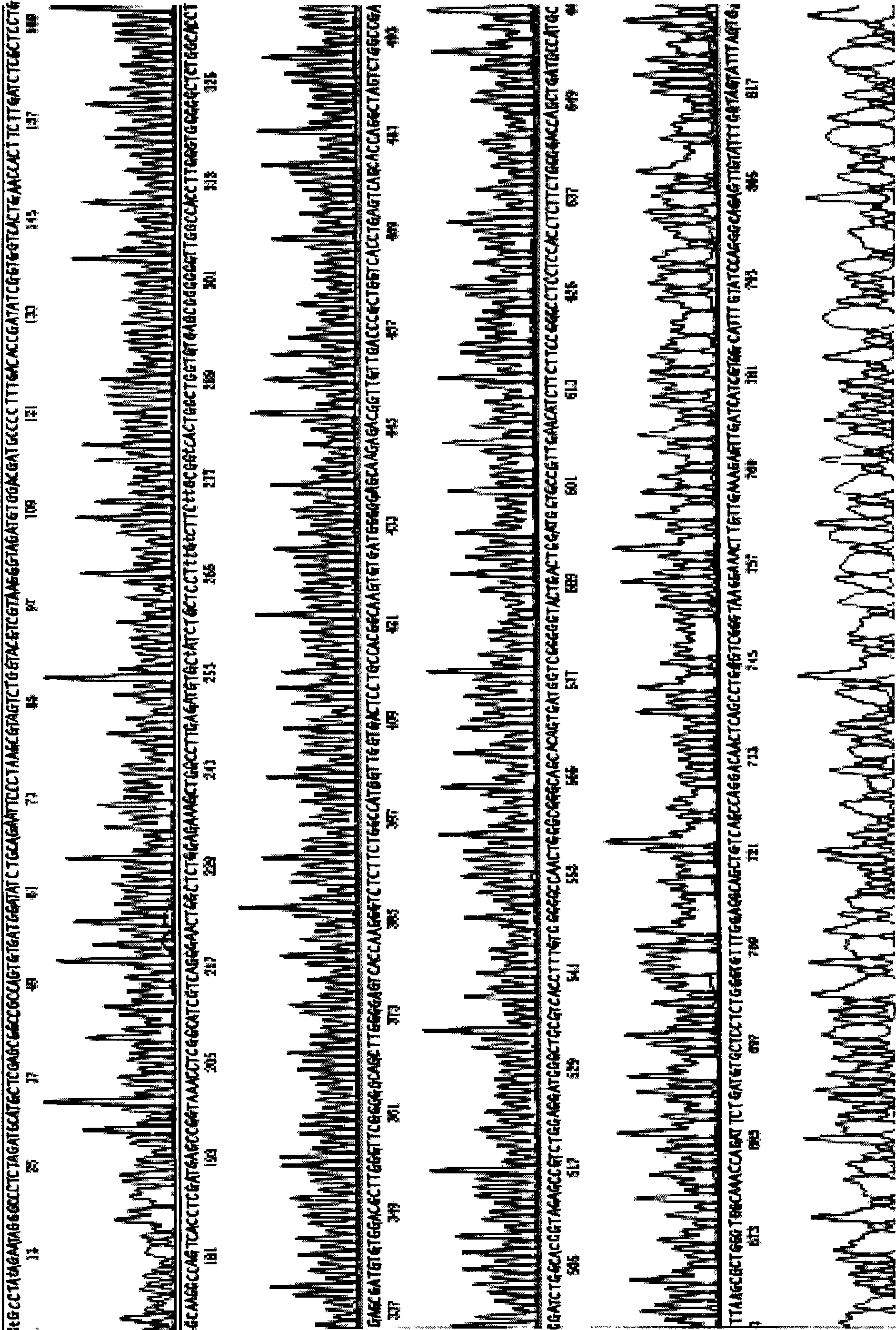
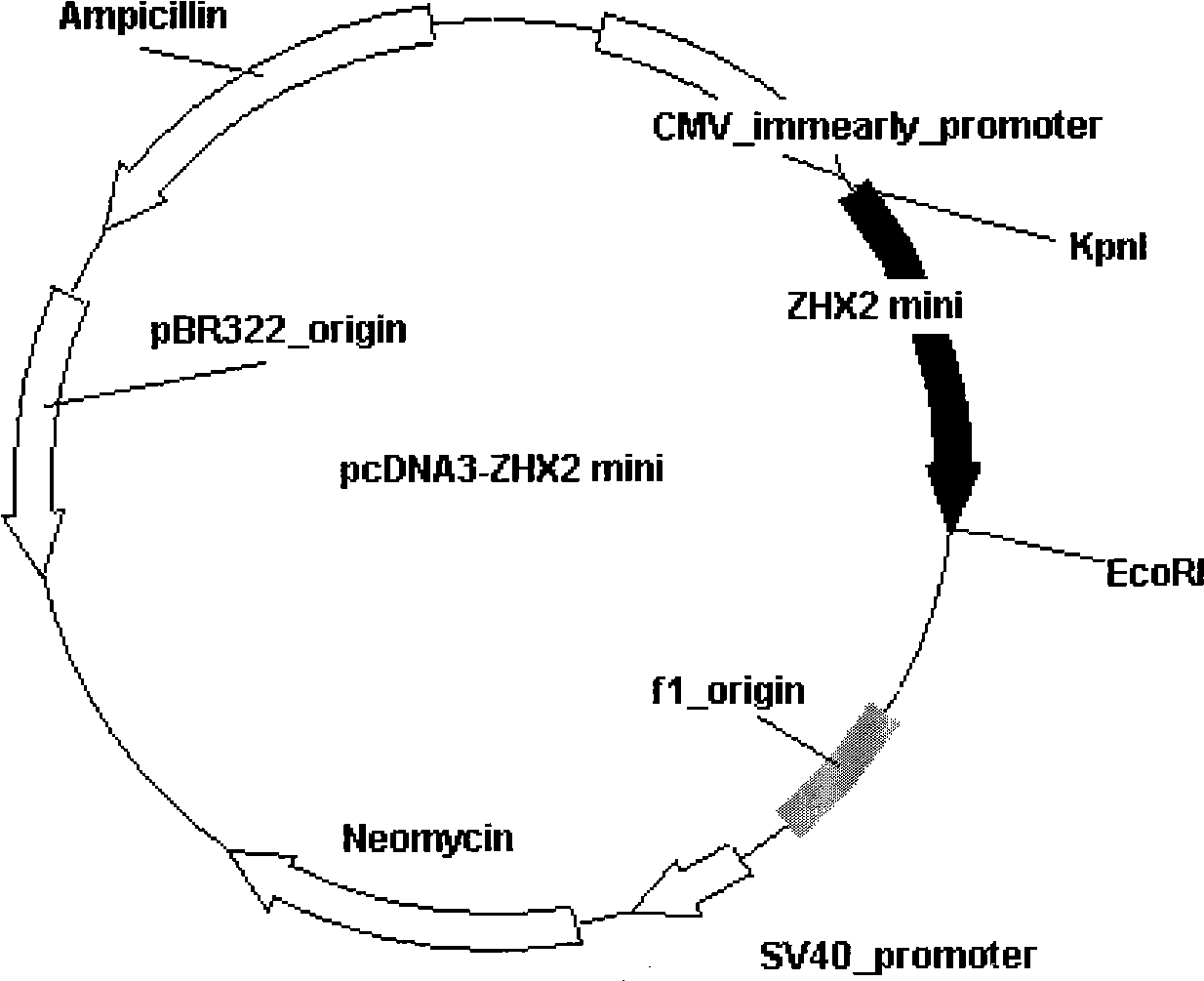
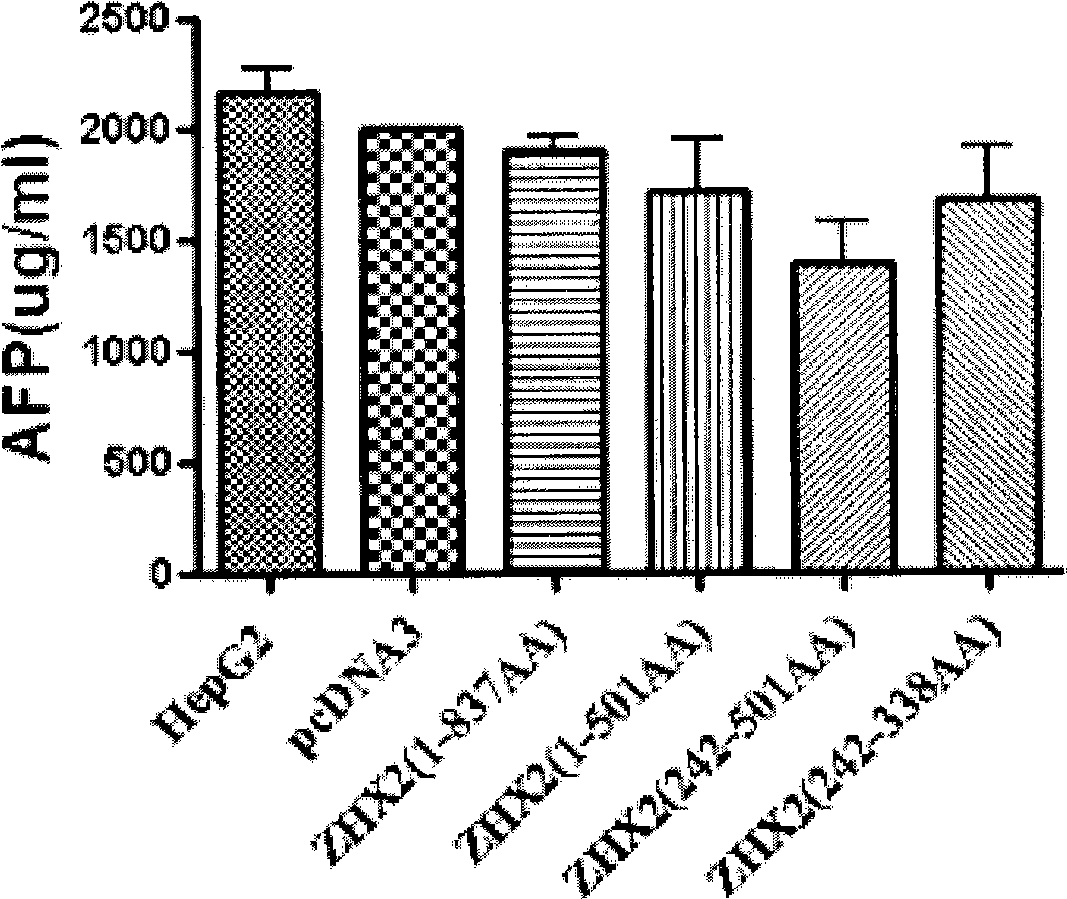
Core fragment of human ZHX2 transcription factor and application thereof
InactiveCN101532019AGrowth inhibitionInhibition of colony formation abilityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideFactor ii
The invention relates to a functional fragment of a human ZHX2 transcription factor and application thereof, which belong to the technical field of gene engineering. A core fragment of the human ZHX2 transcription factor has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1; and protein encoded by the core fragment has an amino sequence shown in SEQ ID No.2. The invention also relates to an expression vector containing the core fragment and a construction method thereof, and application of products in inhibiting the growth of human liver cancer cells. The invention provides a way with attractive application prospect for treating hepatocellular carcinoma, and provides an evidence for the development of novel medicaments.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
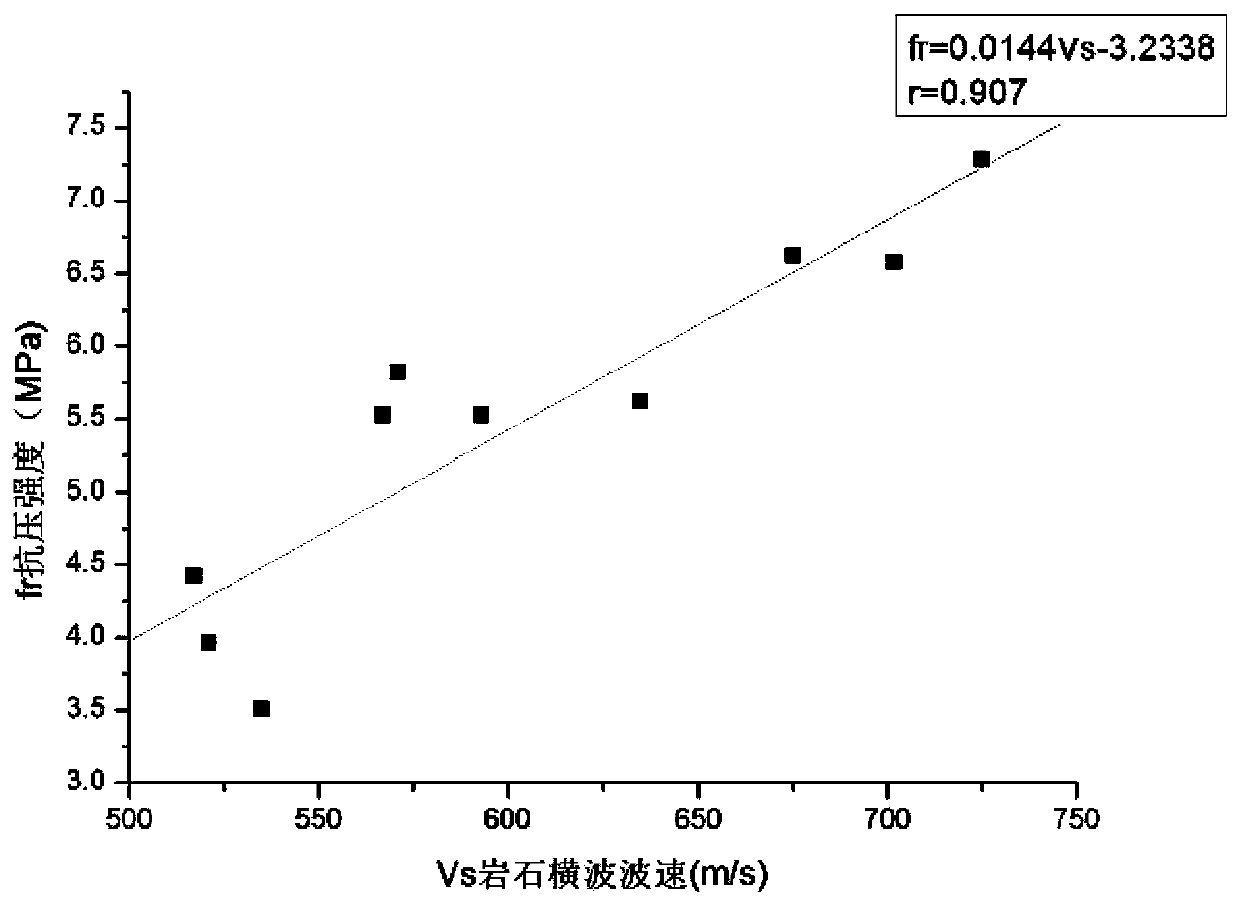
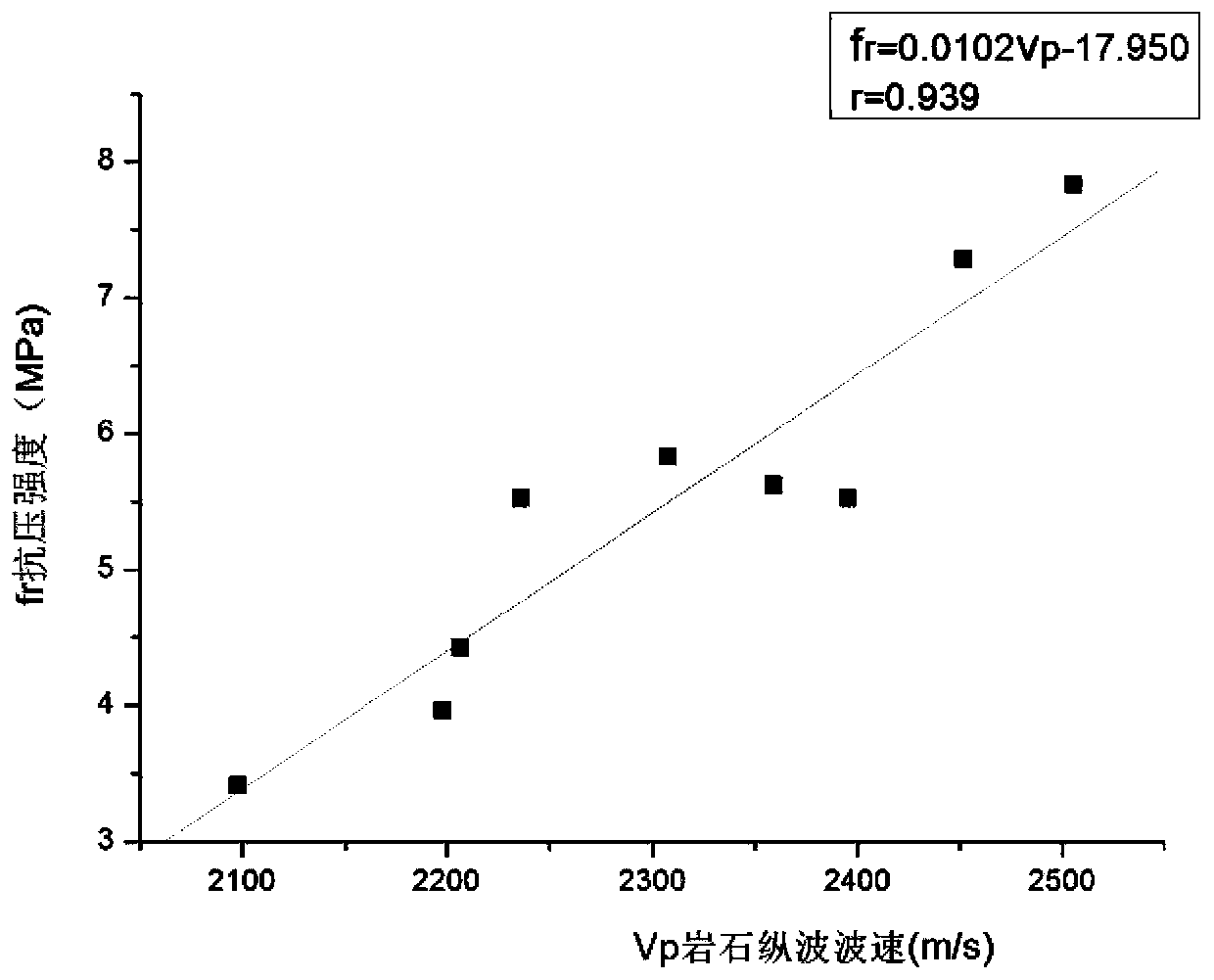
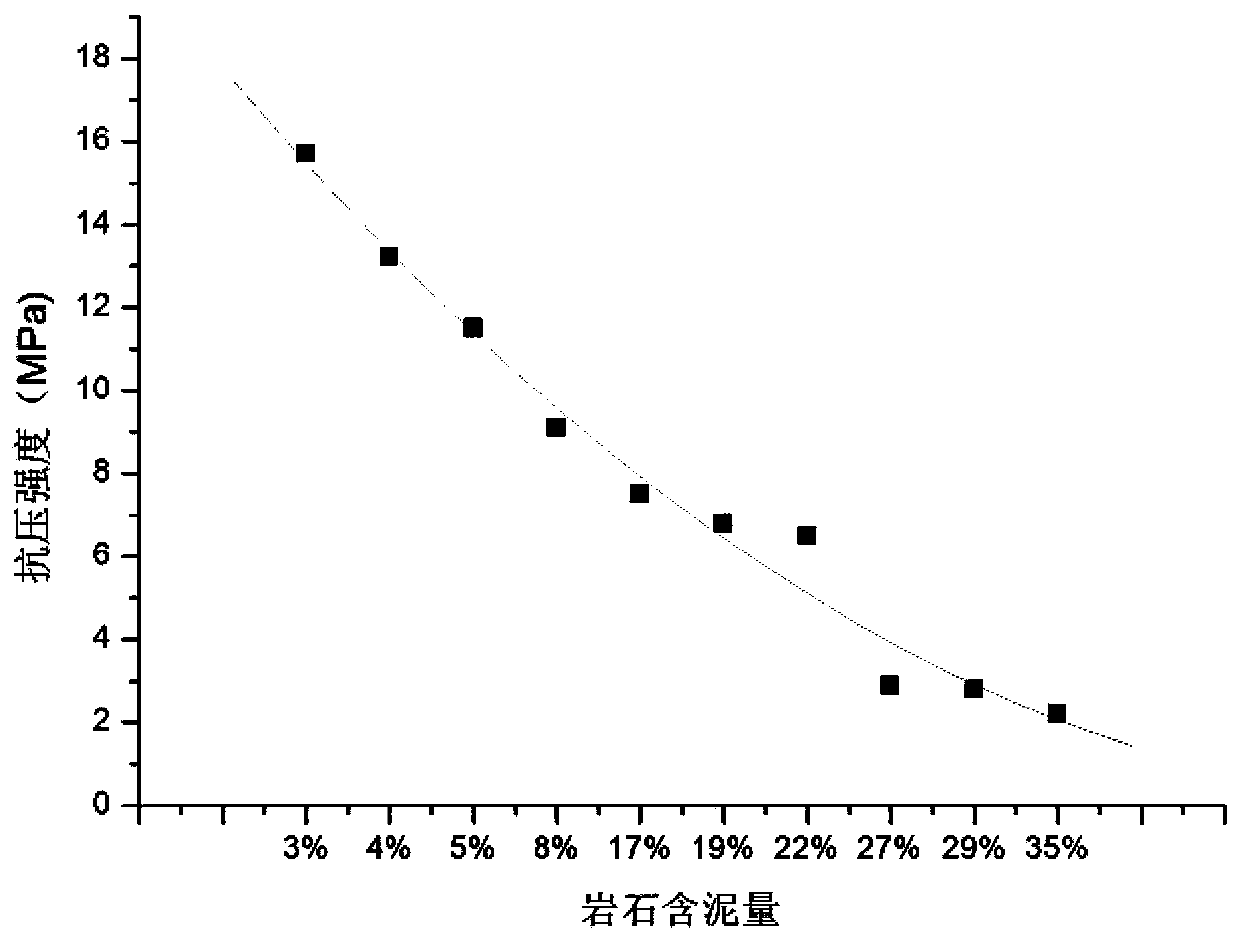
Method for predicting compressive strength of argillaceous siltstone
ActiveCN110361264ASave manpower and material resourcesAccurate dataAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesRock coreLongitudinal wave
The invention relates to a method for predicting the compressive strength of an argillaceous siltstone. The method comprises: step one, after taking out a rock core in a surveying hole, carrying out testing of a transverse wave velocity Vs and a longitudinal wave velocity Vp timely in the core in the hole and conveying the taken core to a lab timely to carry out indoor core acoustic wave testing;step two, observing comparison of longitudinal wave velocities Vp and Vp' and transverse wave velocities Vs and Vs' of the core in a same depth zone in the surveying hole and the indoor space; step three, carrying out compression testing on the core; step four, carrying out sediment content testing on core fragments after compression resistance; step five, analyzing the correlation between the sediment content and the compressive strength fr and analyzing correlation of the compressive strength, the transverse wave velocity Vs and the longitudinal wave velocity Vp of the core; step six, makingcorresponding relation maps of the transverse wave velocity Vs, the longitudinal wave velocity Vp, the sediment content and the compressive strength fr respectively; step seven, establishing a prediction formula fprediction; and step eight, establishing a corrected compressive strength correction formula fcorrection.
Owner:湖南化工地质工程勘察院有限责任公司
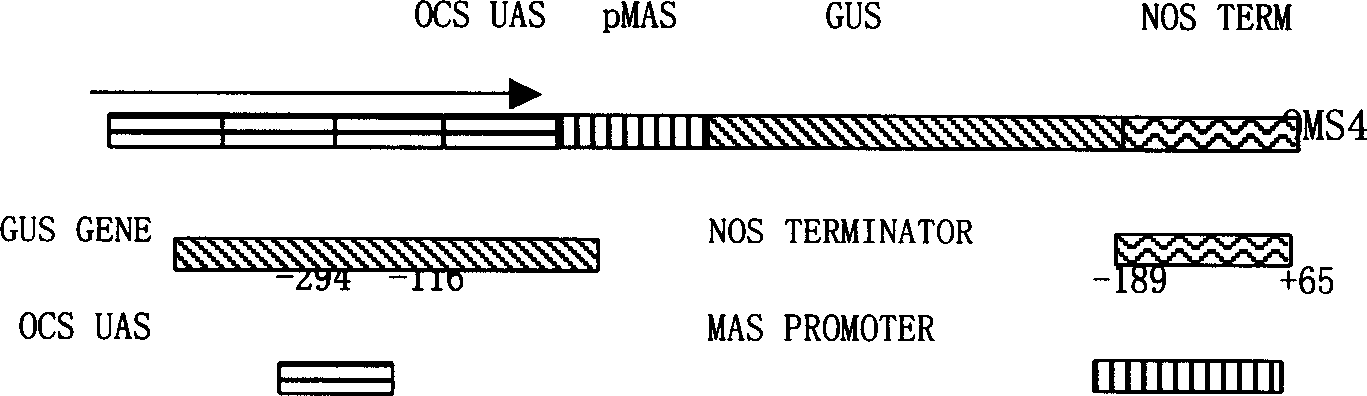
Superstrong fusion promoter, fusion method and use thereof
InactiveCN1401775AIncrease productionVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationNicotiana tabacumPlant genetic engineering
A ultrastrong fusion promoter oms4, its expression vector and its application in transgenic tobacco are disclosed. Said oms 4 promoter is constructed with 4 copied ocs enhensers by cyclically forward linking them to the core fragment of mas promoter. The oms4 promoter can be used to replace the 35S promoter in expression vector pBI121 of plant for constructing pOMS4. Its advantage is high expression level of exogenous gene gus in tobacco (increased by 23-47 times).
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
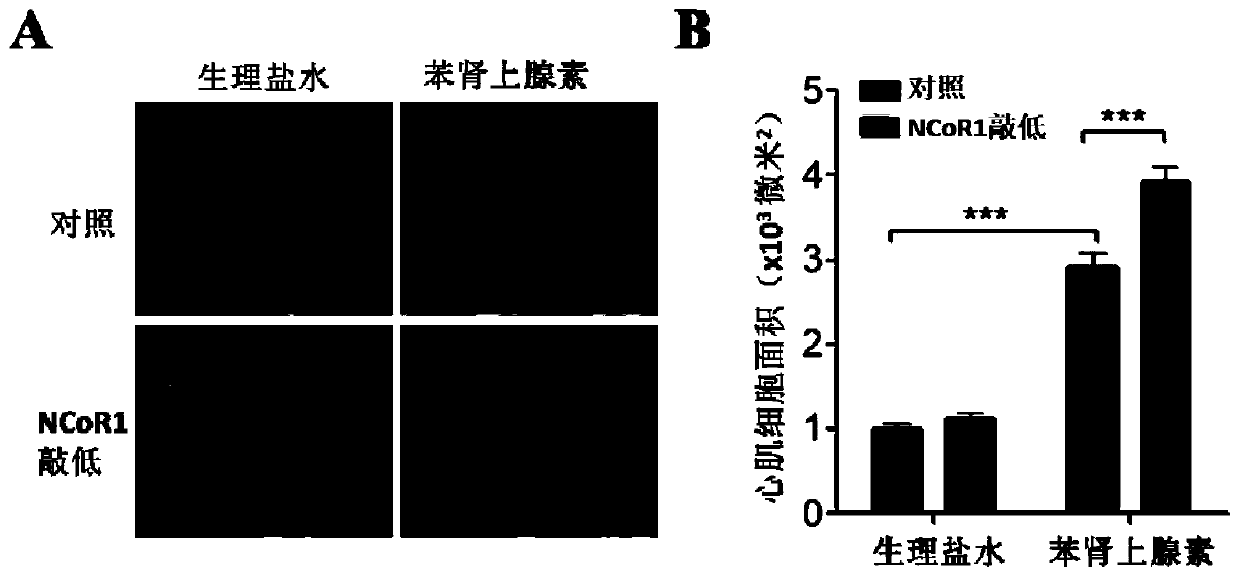
Polynucleotide and application of same in diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases
InactiveCN109810981AOrganic active ingredientsMedical automated diagnosisCardiac dysfunctionPressure overload
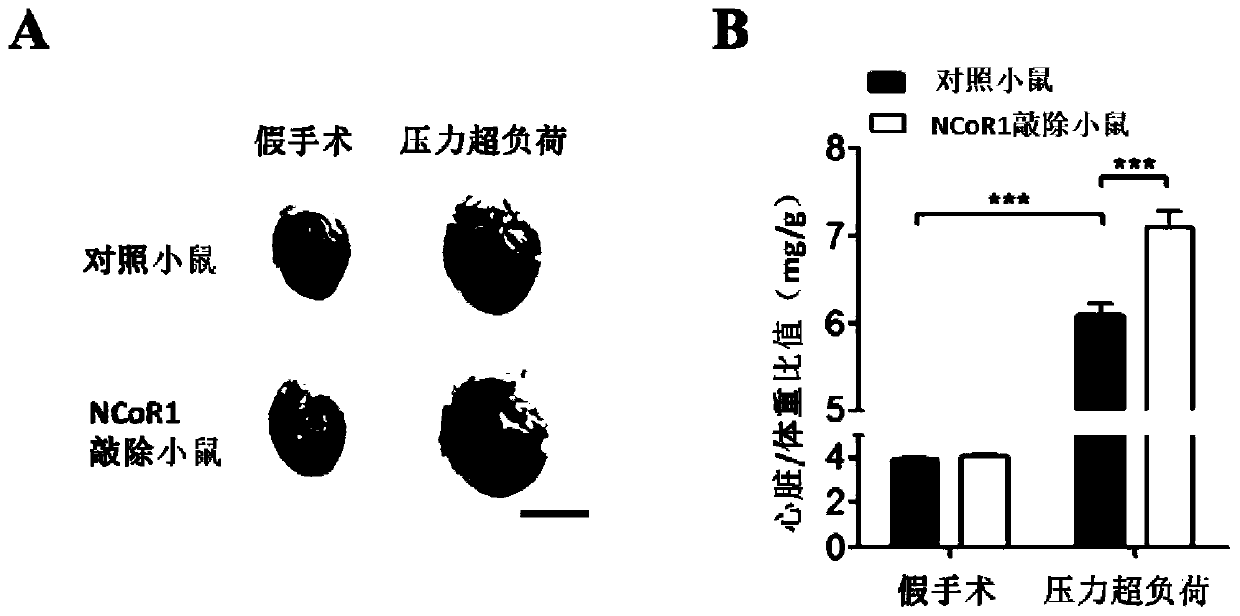
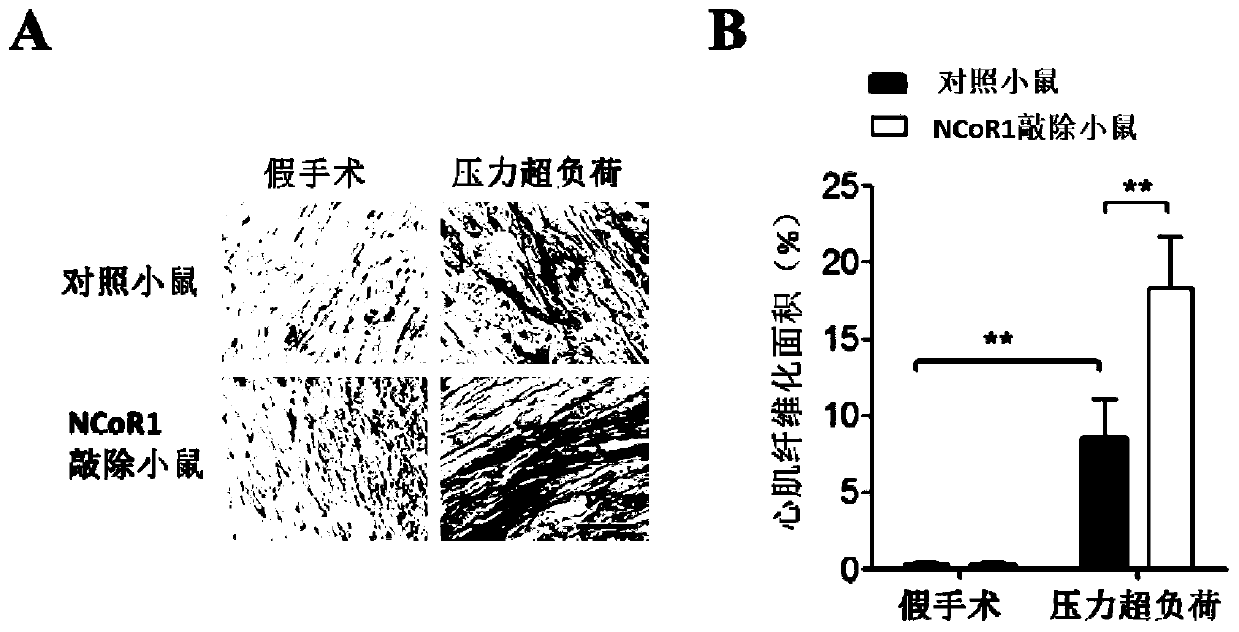
The invention discloses polynucleotide having the sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The polynucleotide or a vector provided by the invention carries NCoR1 or an RIDs core fragment in the NCoR1, and can significantly alleviate the cardiovascular diseases, such as cardiac hypertrophy and cardiac dysfunction, caused by pressure overload after cell transduction; it is verified that the expression ofthe NCoR1 in myocardial tissues of patients and mice suffering from the cardiac hypertrophy is increased and the NCoR1 can be used as a biomarker for diagnosis of the cardiac hypertrophy.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Diagnostic kit for predicting the onset of menopause
InactiveUS7229781B2Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsDisease diagnosisMenopause AgeCore fragment
The present invention provides methods to quantitate the hLHβ core fragment in a sample. The present invention now makes it possible to evaluate the metabolism of hLH in premenopausal, perimenopausal and postmenopausal women and to distinguish between normal and abnormal physiological states.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
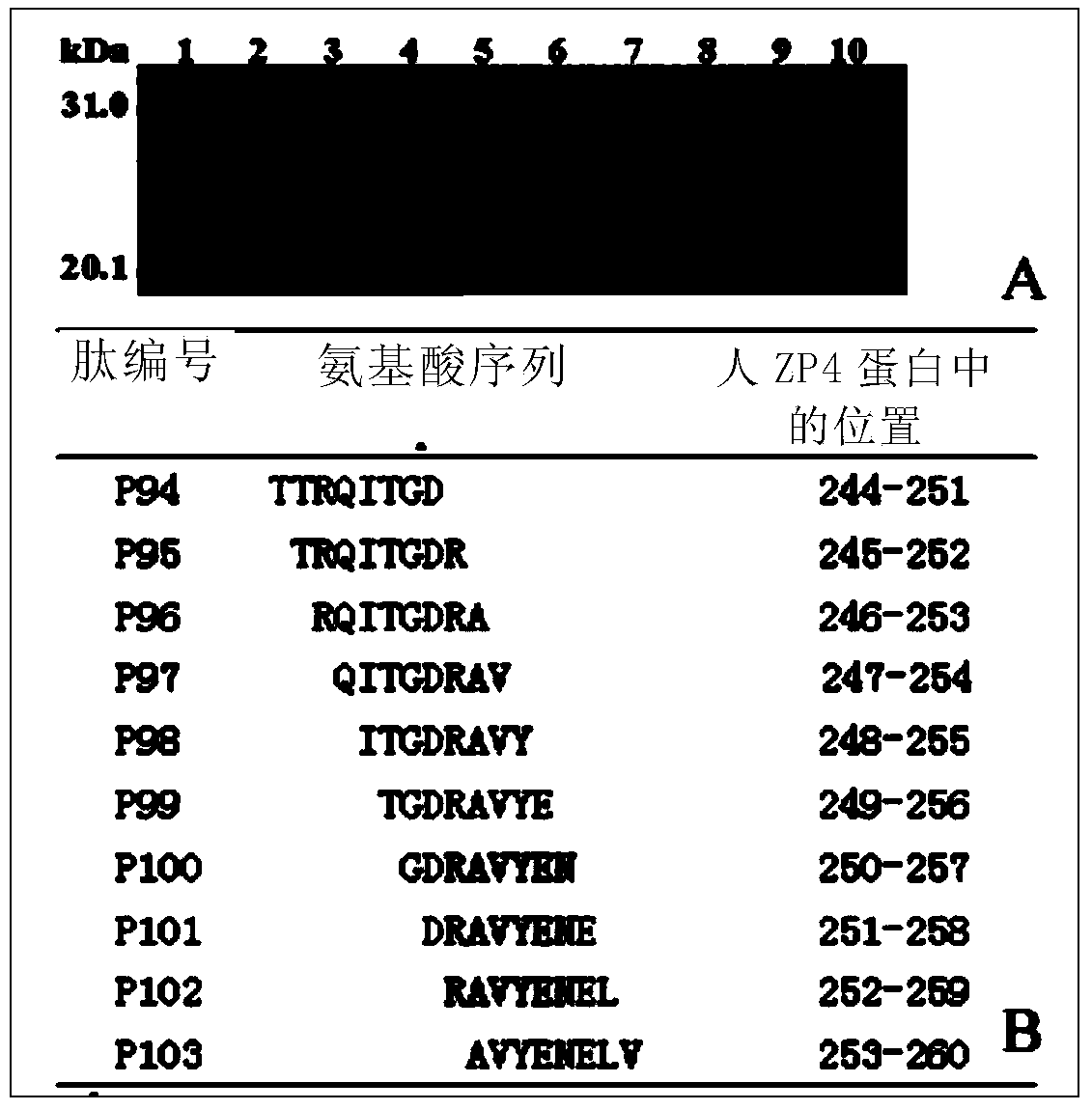
Epitope peptide in human spawn ZP (zona pellucida) protein 4 and application of epitope peptide
InactiveCN103524601AClear and reliable color rendering resultsPositive clone method is simplePeptidesBiological testingAutoimmune responsesAmino acid
The invention discloses an epitope peptide in human spawn ZP protein 4 and an application of the epitope peptide, and particularly relates to a short peptide separated from human spawn ZP protein-4 (a human ZP protein 4 227-463 bit). The formula I of the short peptide is shown as follows: X1-X-X2 (the formula I), and the following characteristics are met: a), the X in the formula I is 6-7 amino acid core fragments; b), the number sum of the X1 and the X2 in the formula I is smaller than or equal to 2; c), the sequences of the core fragments are selected from SEQ ID NO.: 1-6; and d), the short peptide is provided with activity combined with an anti-human ZP 4C antibody, wherein the '-' expresses a peptide link or a peptide joint. The epitope peptide can be combined and applied to detection of the existence or content of various antibodies of anti-human ZP 4 protein in a sample, so that women's sterility caused by ZP autoimmunity can be diagnosed at high specificity and high sensitivity; and besides, the epitope peptide can also be used for preparing recombination human ZP multi-epitope-peptide contraceptive vaccine with safe and effective advantages.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PLANNED PARENTHOOD RES +1
A device and method for assembling a horizontal body of a dry-type amorphous alloy transformer
InactiveCN103093951BImprove consistencyImprove assembly efficiencyInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureGeneral assemblyLow voltage
The invention discloses assembly device and method for a horizontal body of a dry amorphous alloy transformer. The assembly method includes: opening an upper yoke of a core which is horizontal, allowing three-phase high and low voltage coils to penetrate through the upper yoke respectively, and closing the upper yoke of the core. Compared with vertical installation of the core, the method causes few core fragments during core opening and closing, and prevents the core fragments from falling into a small gap between the core and a guard plate. The requirement for single-point grounding between the core and the guard plate is guaranteed exactly. Technical performance indexes of products are well uniform. Compared with the general assembly process, the assembly method enables general assembly staff to be halved and general assembly efficiency to be doubled, so that production efficiency is improved greatly and product performance is stable. Tests show that the assembly method is evidently effective, product quality and production efficiency are improved greatly, and product performance is stable.
Owner:SHANGHAI SUPERCONDUCTOR ENERGY EQUIP
Process for culturing brownness resistant sweet potatoes utilizing gene engineering technology
InactiveCN100374567CReduced expression levelImprove qualityFermentationHorticulture methodsAntisense RNAGene engineering
The invention provides a process for culturing brownness resistant sweet potatoes utilizing gene engineering technology, which relates to the achievement of yam polyphenol oxidase gene core fragments and the process of cultivating brown trans-gene yam by employing antisense RNA technology, and the method comprises cloning polyphenol oxidase gene core fragment from yam, constructing plant highly effective antisense expression carrier, and leading into agrolbacterium and genetically transforming the yam.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
An indirect neutron ct imaging device for spent fuel components of pressurized water reactors
ActiveCN105023622BRealize 3D non-destructive testingExpand the amount of non-destructive testing informationNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringPressurized water reactorNeutron imaging
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
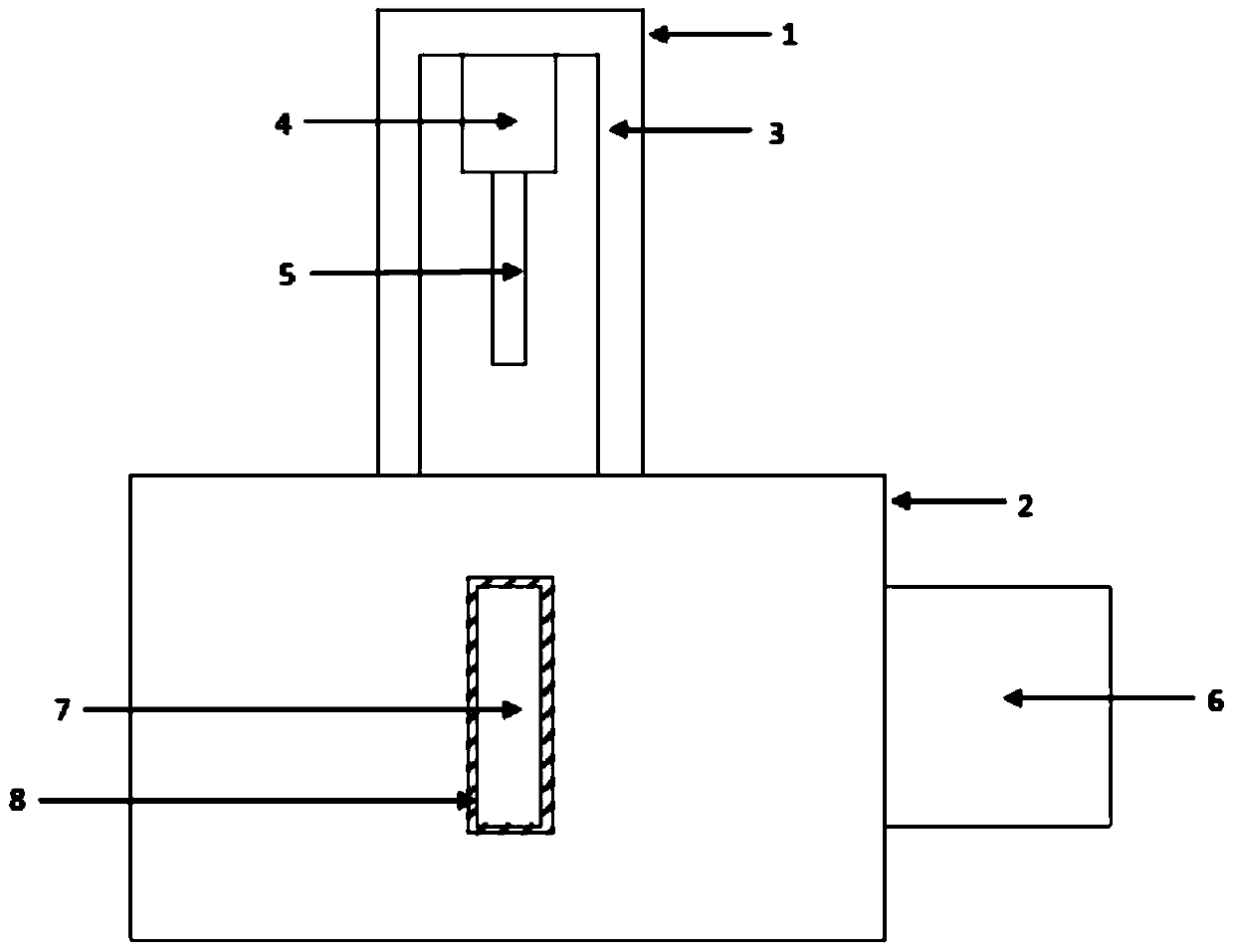
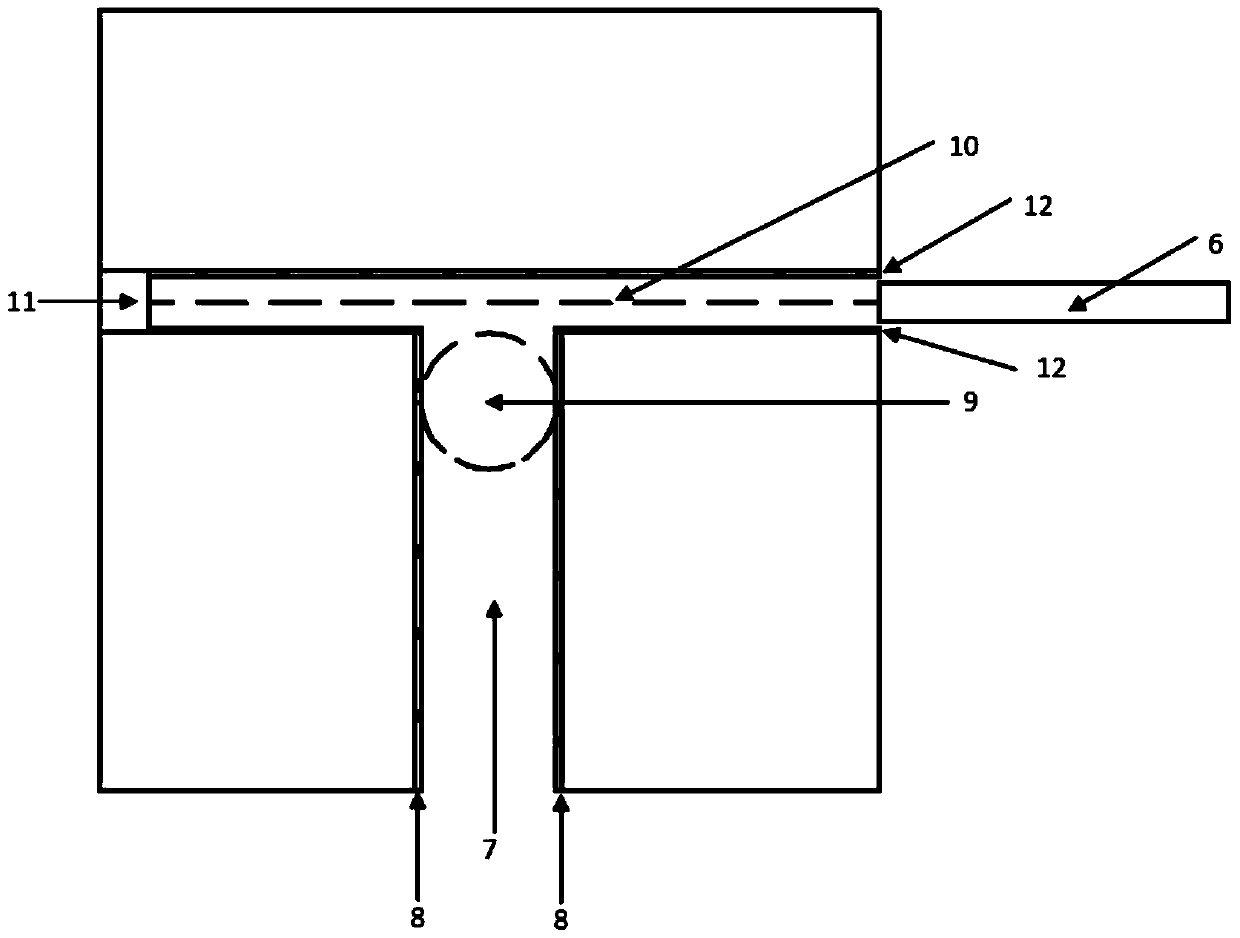
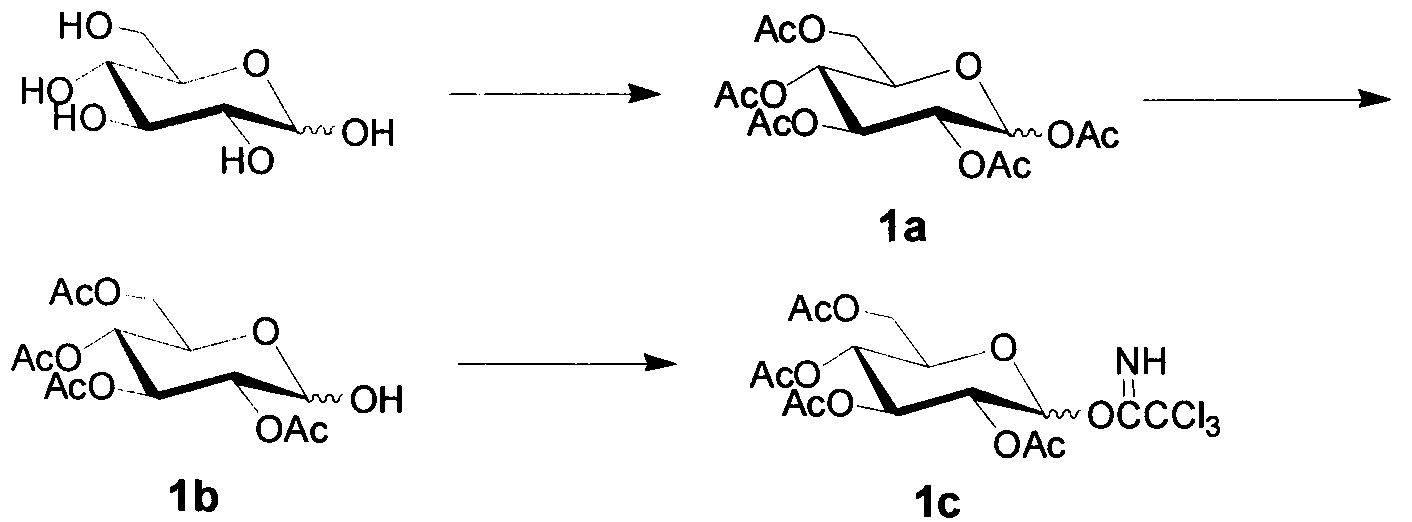
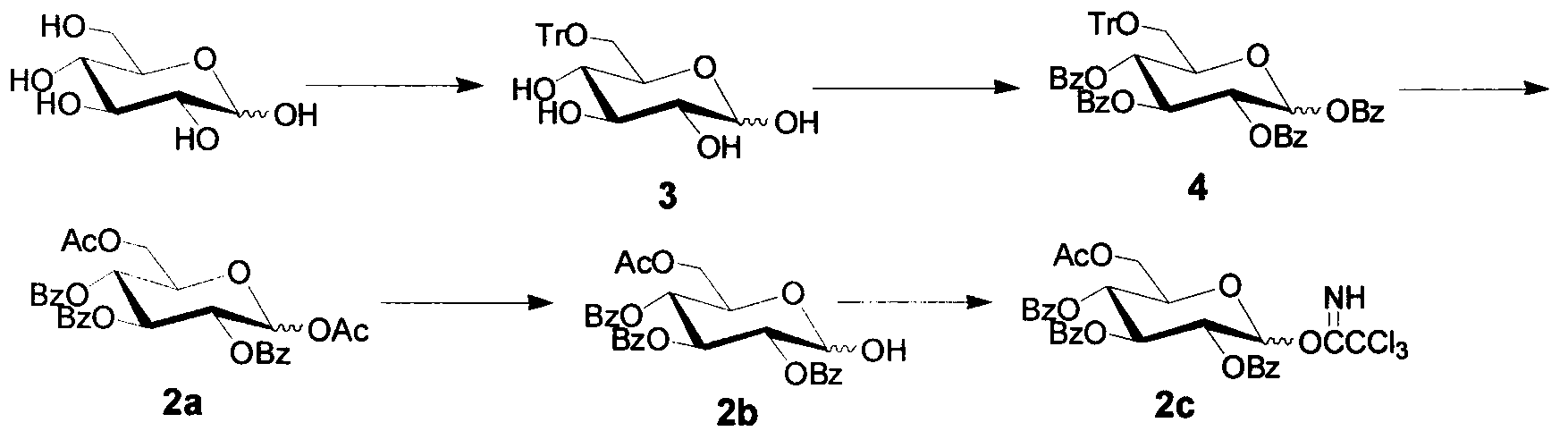
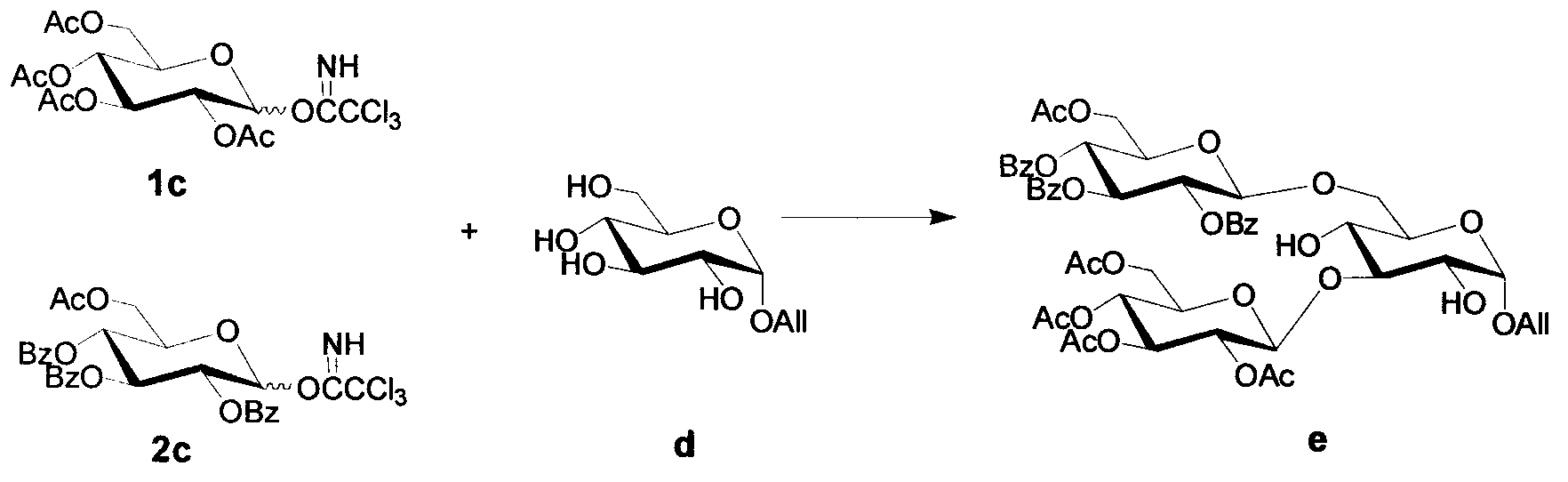
Simple synthetic method of plant immunoactivator core fragment glucose trisaccharide
The invention discloses a simple synthetic method of plant immunoactivator core fragment glucose trisaccharide, and belongs to the field of oligosaccharide preparation. The method can be used for synthesizing glucose trisaccharide branched at the 3, 6 positions, which is a core fragment with immunoloregulation effect, antineoplastic effect, anti-inflammatory effect, and antibiotic effect; the glucose trisaccharide is obtained by one-step coupling of an acylated Schmidt reagent used as a glycosyl donor, and an allyl-alpha-D-glucopyranoside used as a receptor. The method of the invention is characterized by concise synthetic route, simple operation, easy product crystallization and purification, and suitability for large-scale preparation.
Owner:NANJING LAIKEXING BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com