Patents
Literature
74 results about "Neutron imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neutron imaging is the process of making an image with neutrons. The resulting image is based on the neutron attenuation properties of the imaged object. The resulting images have much in common with industrial X-ray images, but since the image is based on neutron attenuating properties instead of X-ray attenuation properties, some things easily visible with neutron imaging may be very challenging or impossible to see with X-ray imaging techniques (and vice versa).
Neutron source detection camera
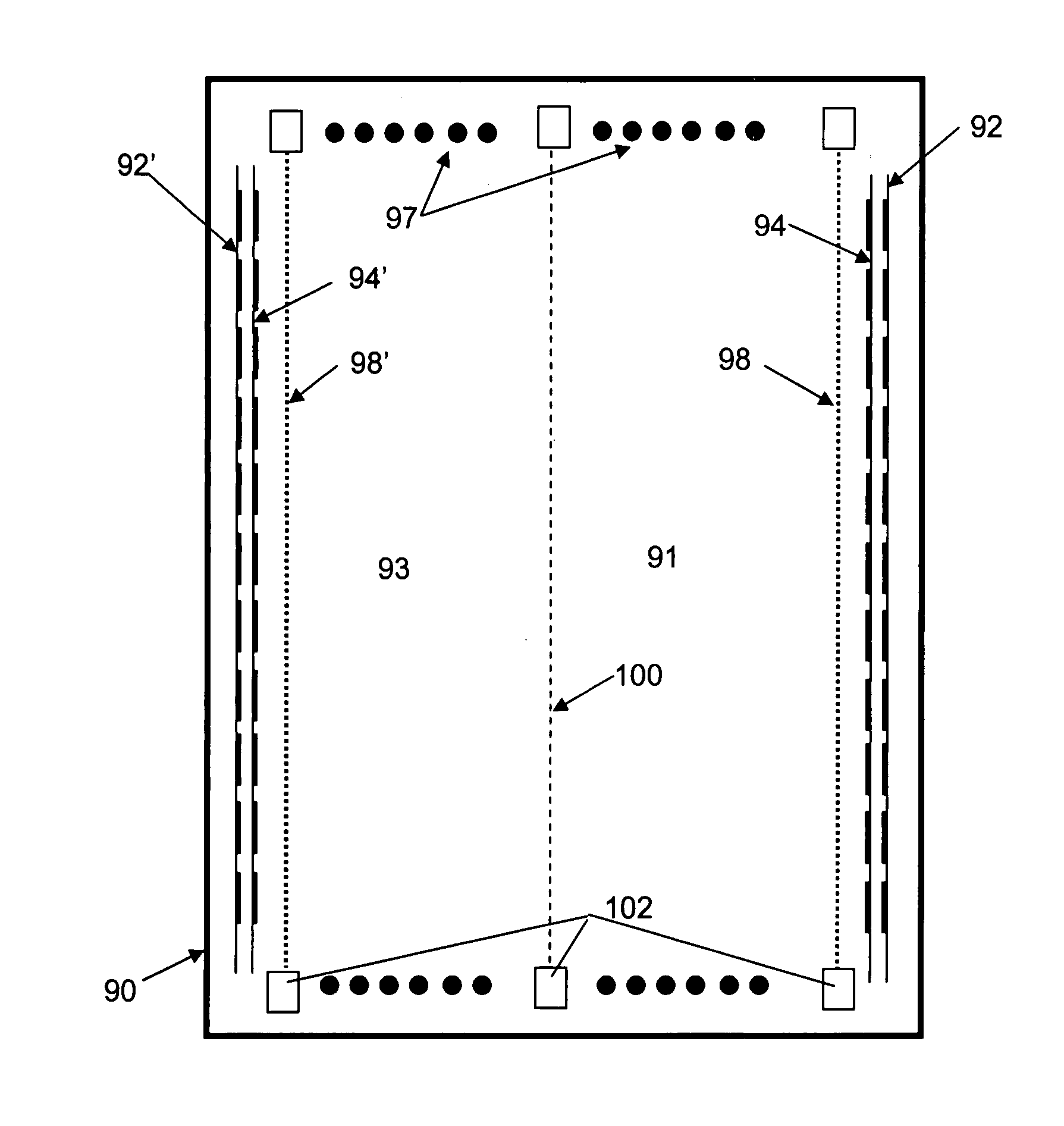
InactiveUS20060017000A1Measurement with semiconductor devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionImaging equipment
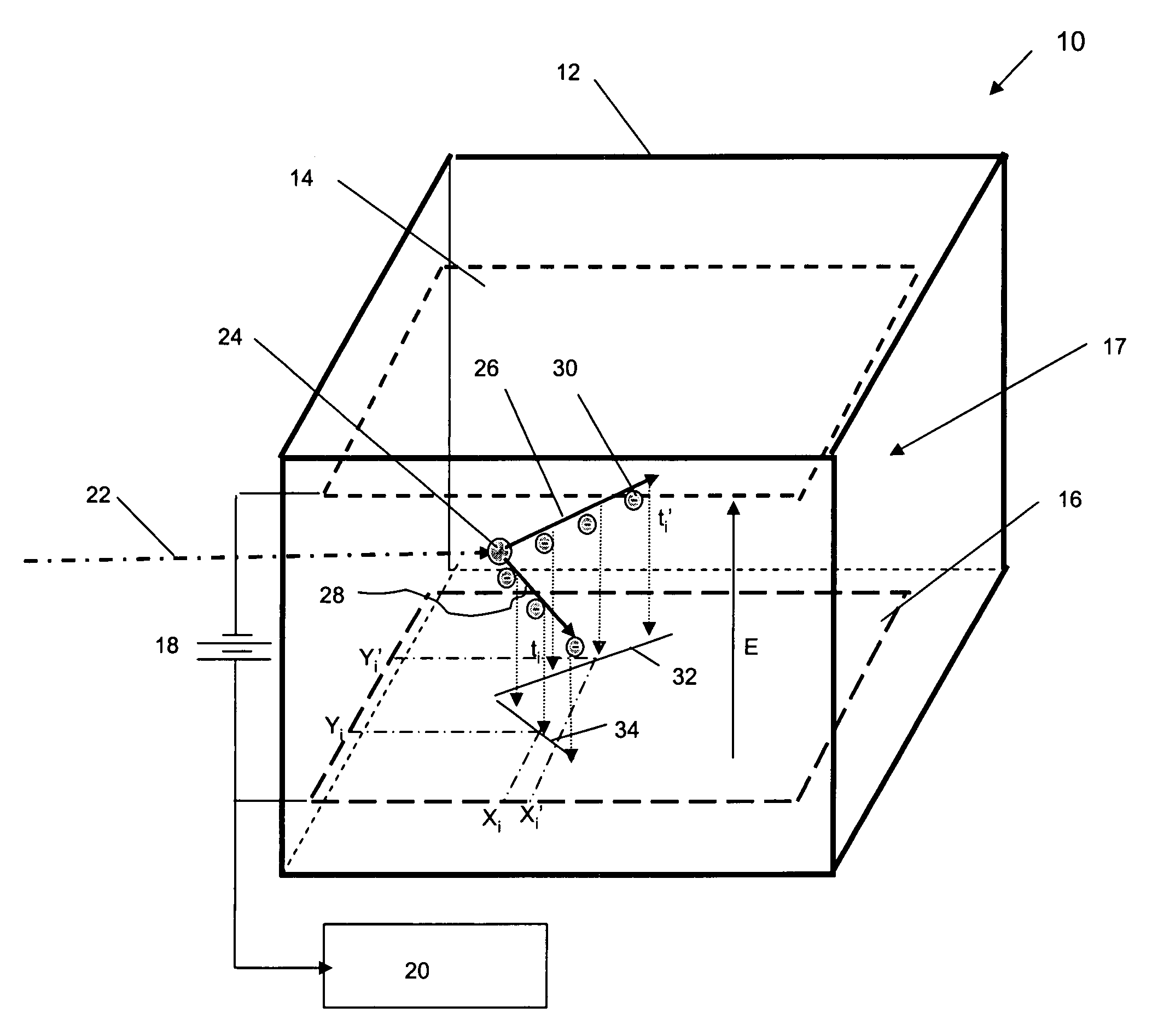
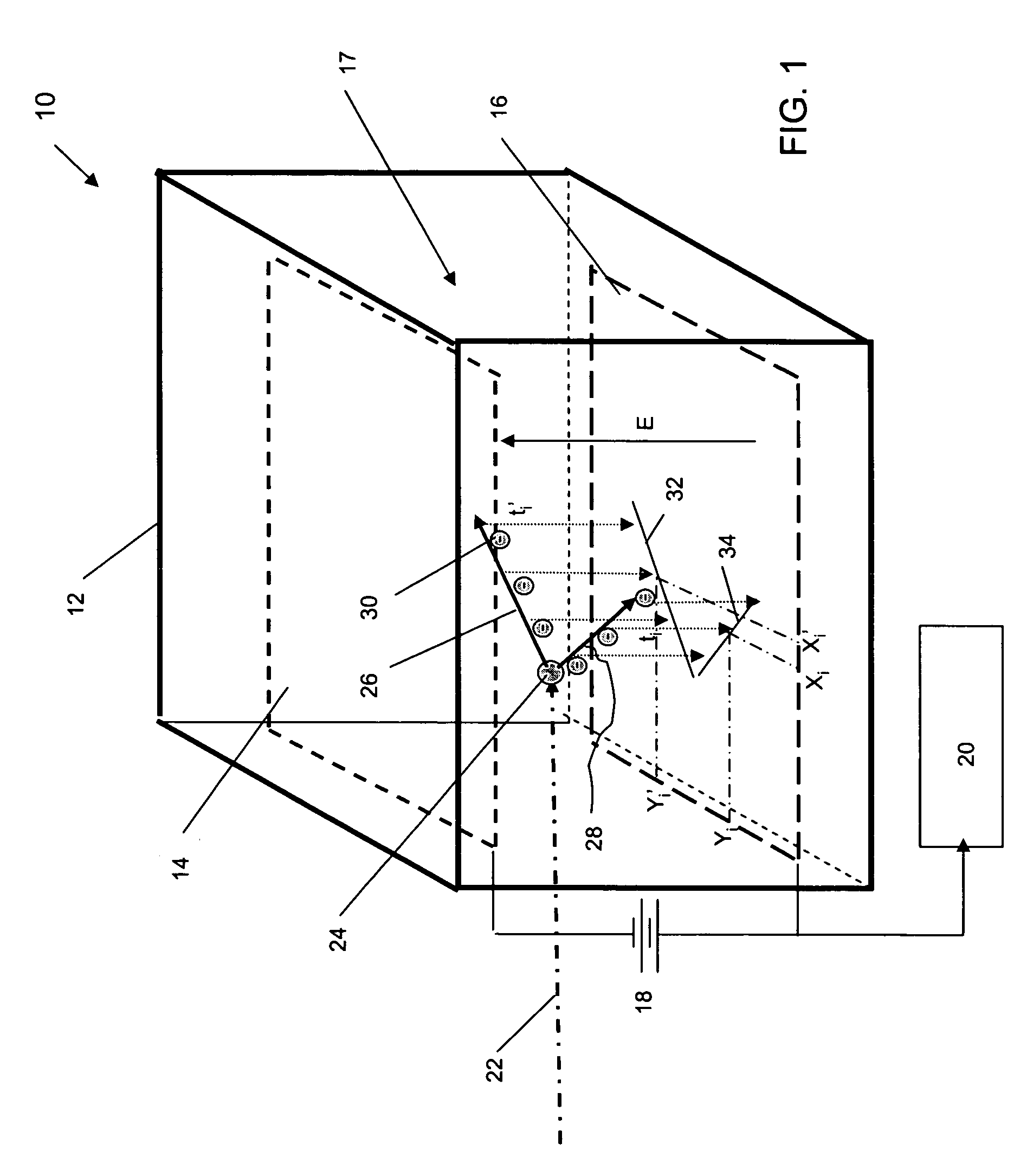
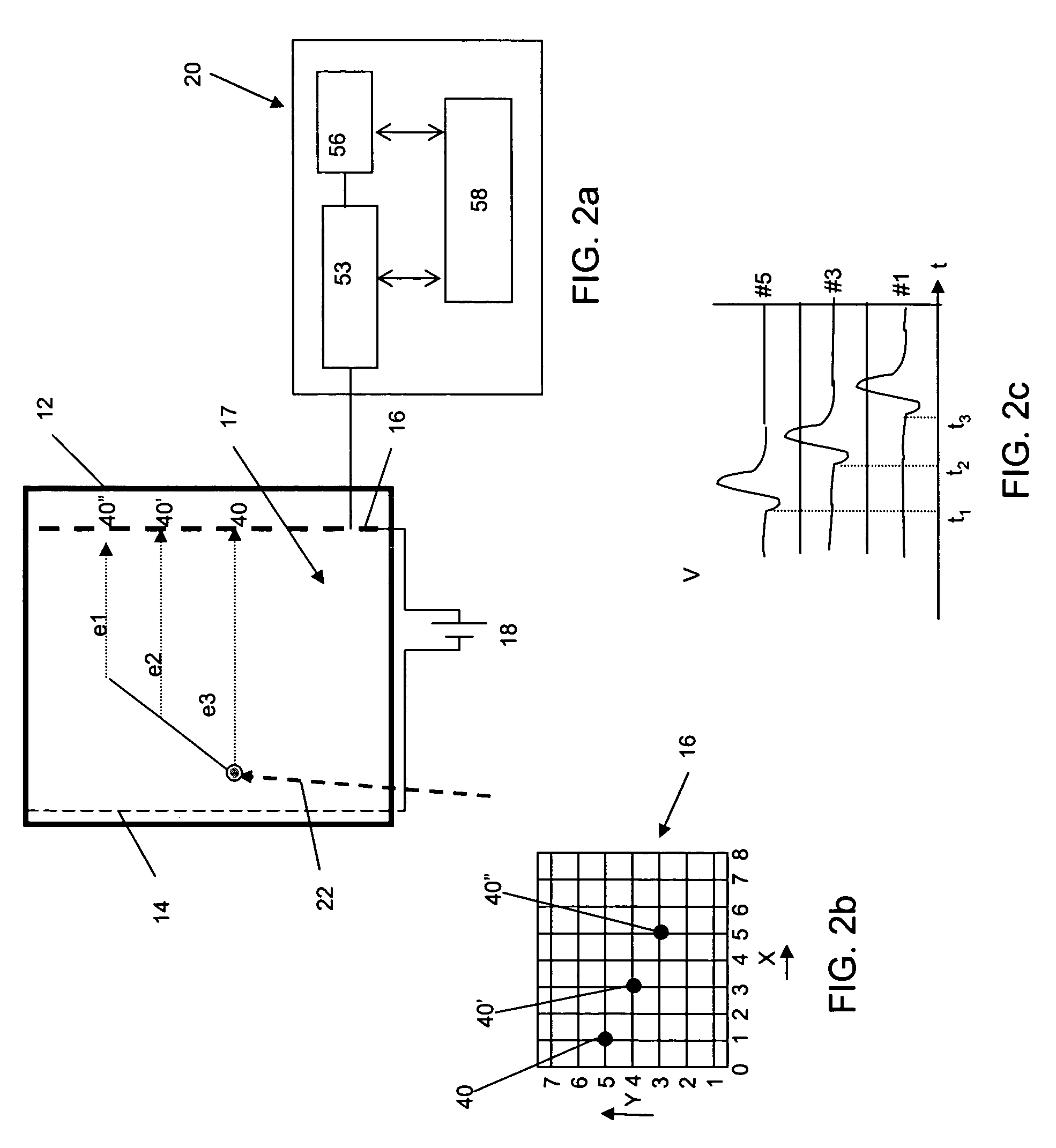
A neutron imaging apparatus for obtaining an image of the general shape of a neutron emitting source and a bearing of the source relative to the apparatus, the apparatus comprising a chamber comprising a gas with a high probability of interacting with low energy neutrons, releasing collision products that maintain the neutron momentum, and generating ionization particles. The chamber comprises an electrode for providing an electronic signal indicative of the impact location of ionization particles on the electrode and a field to drift the ionization particles to the electrode. A readout indicates the location and time of impact of each ionization particle on the electrode; a memory stores a plurality of the electronic signals; and a computer receives and analyzes the signals and impact times and indicates the location of the source of neutrons by using back projection algorithms to calculate three-dimensional vectors indicative of the neutron path directions.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
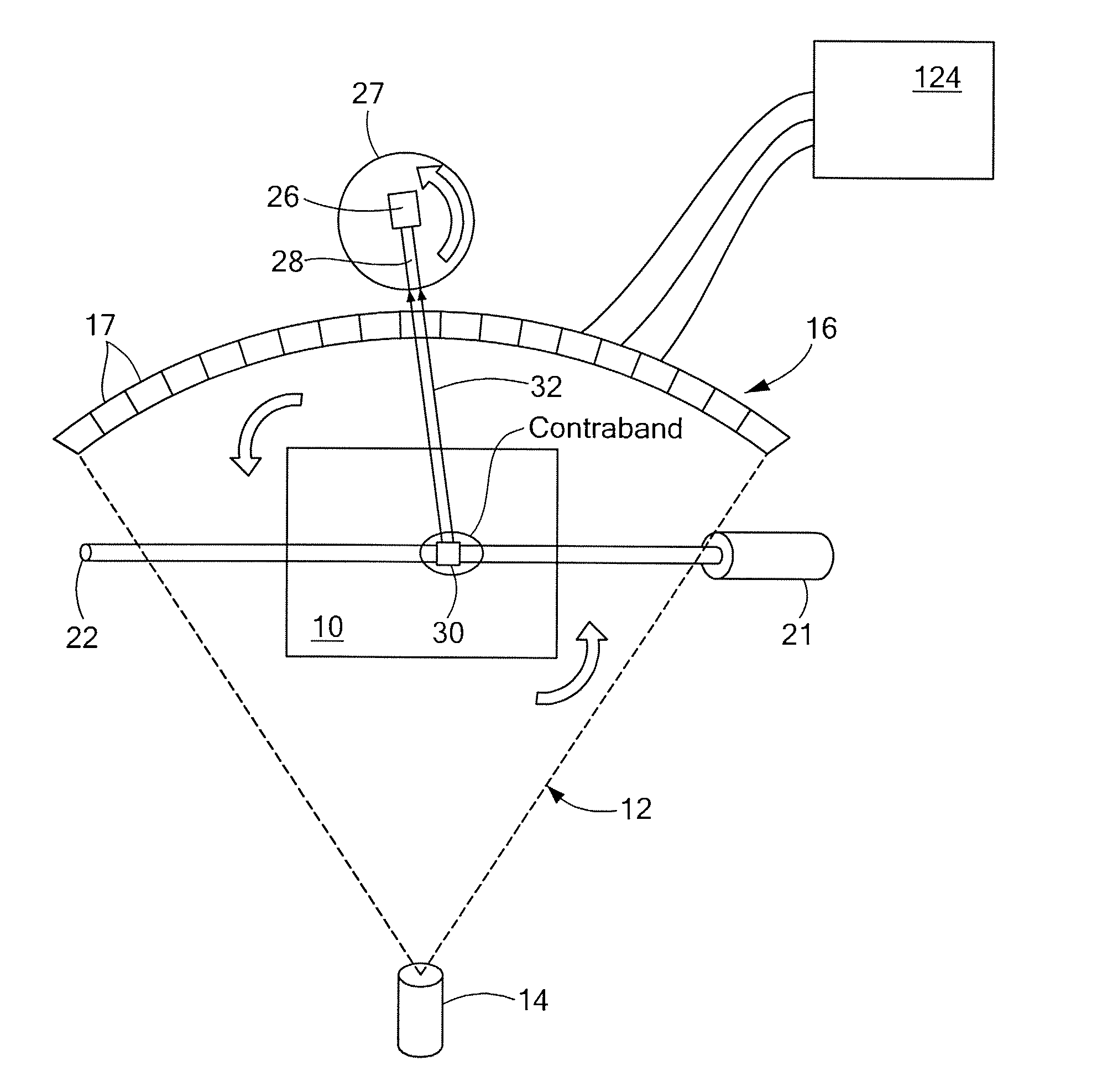
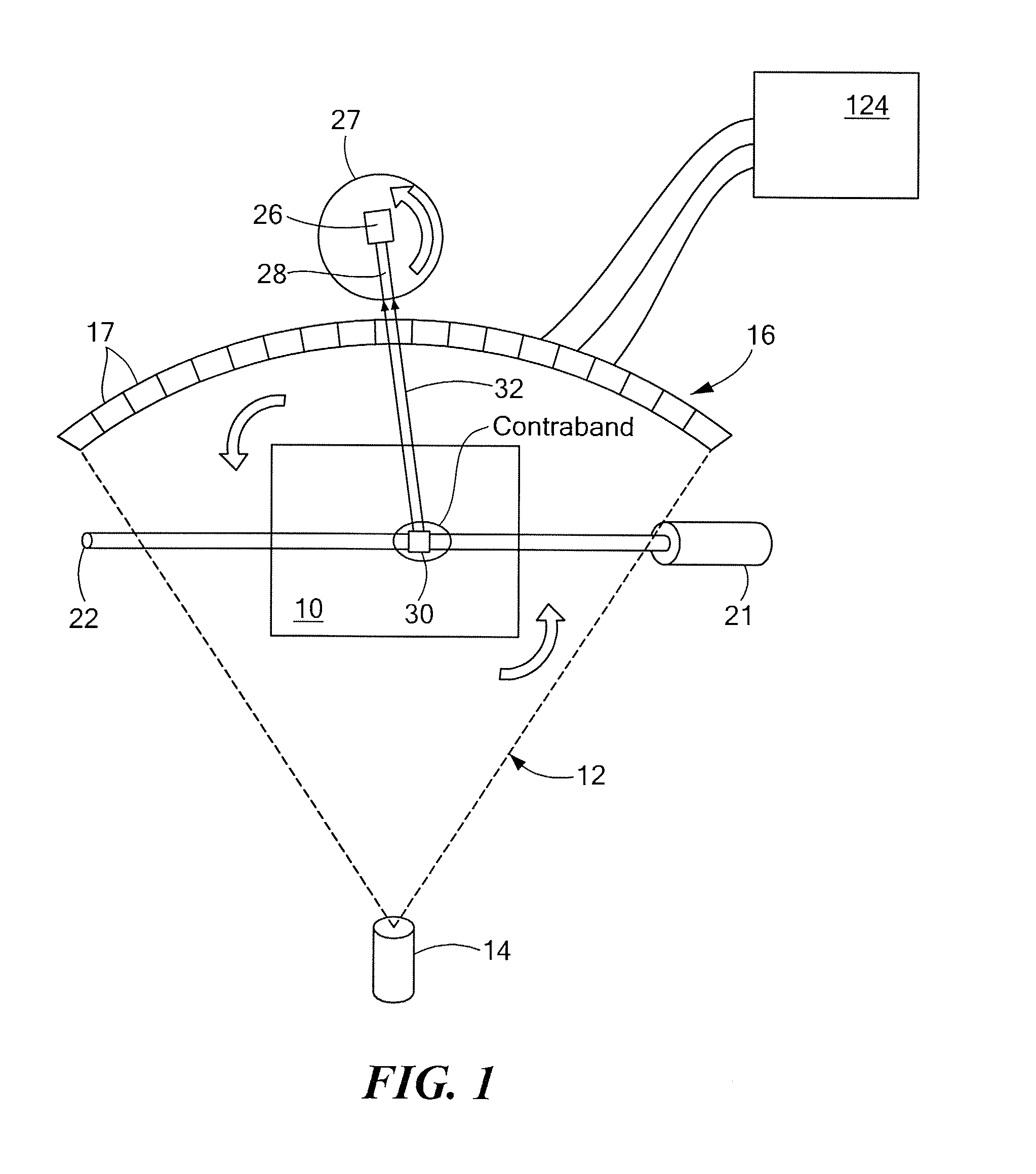
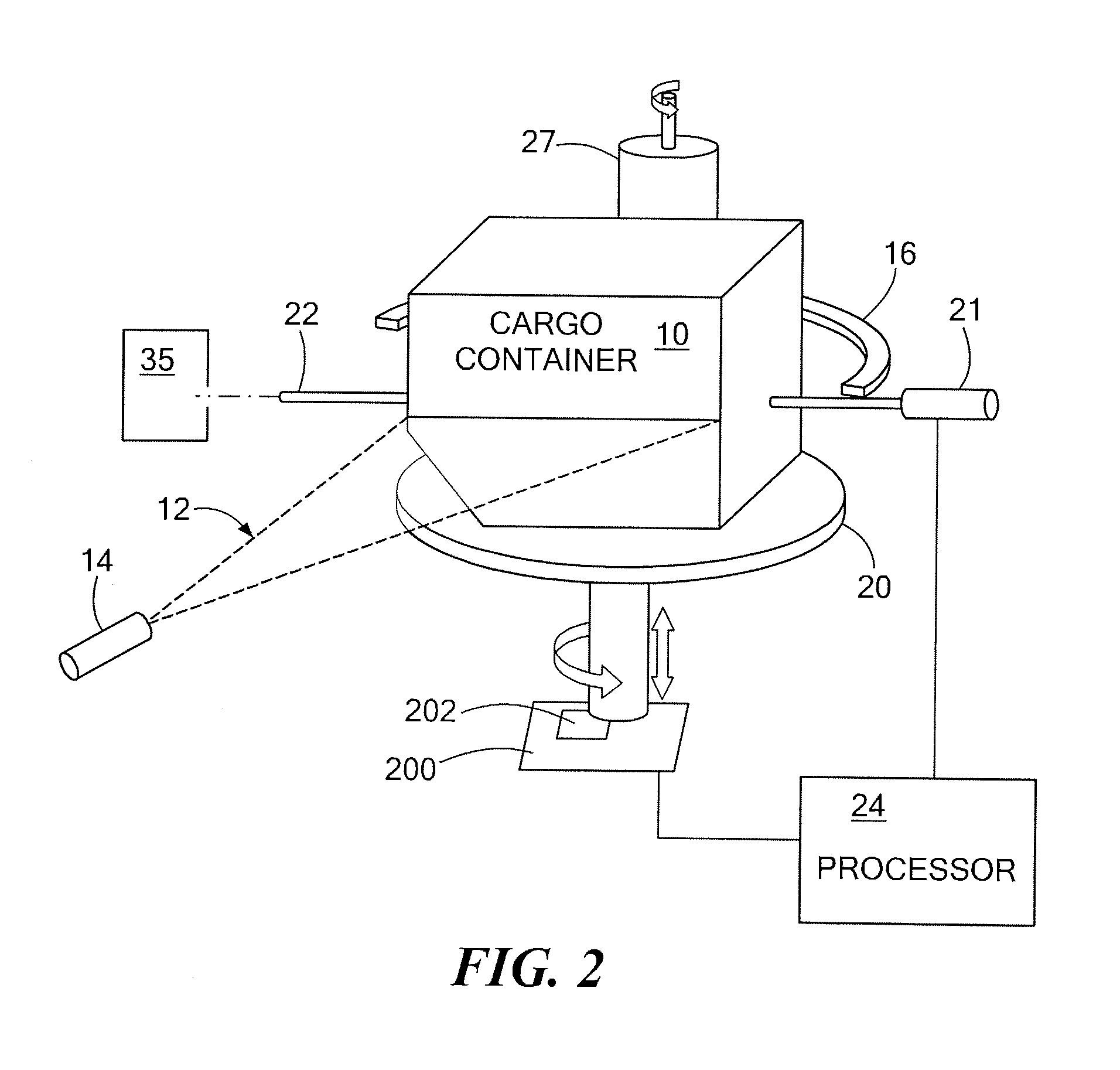
Combined X-ray CT/neutron material identification system
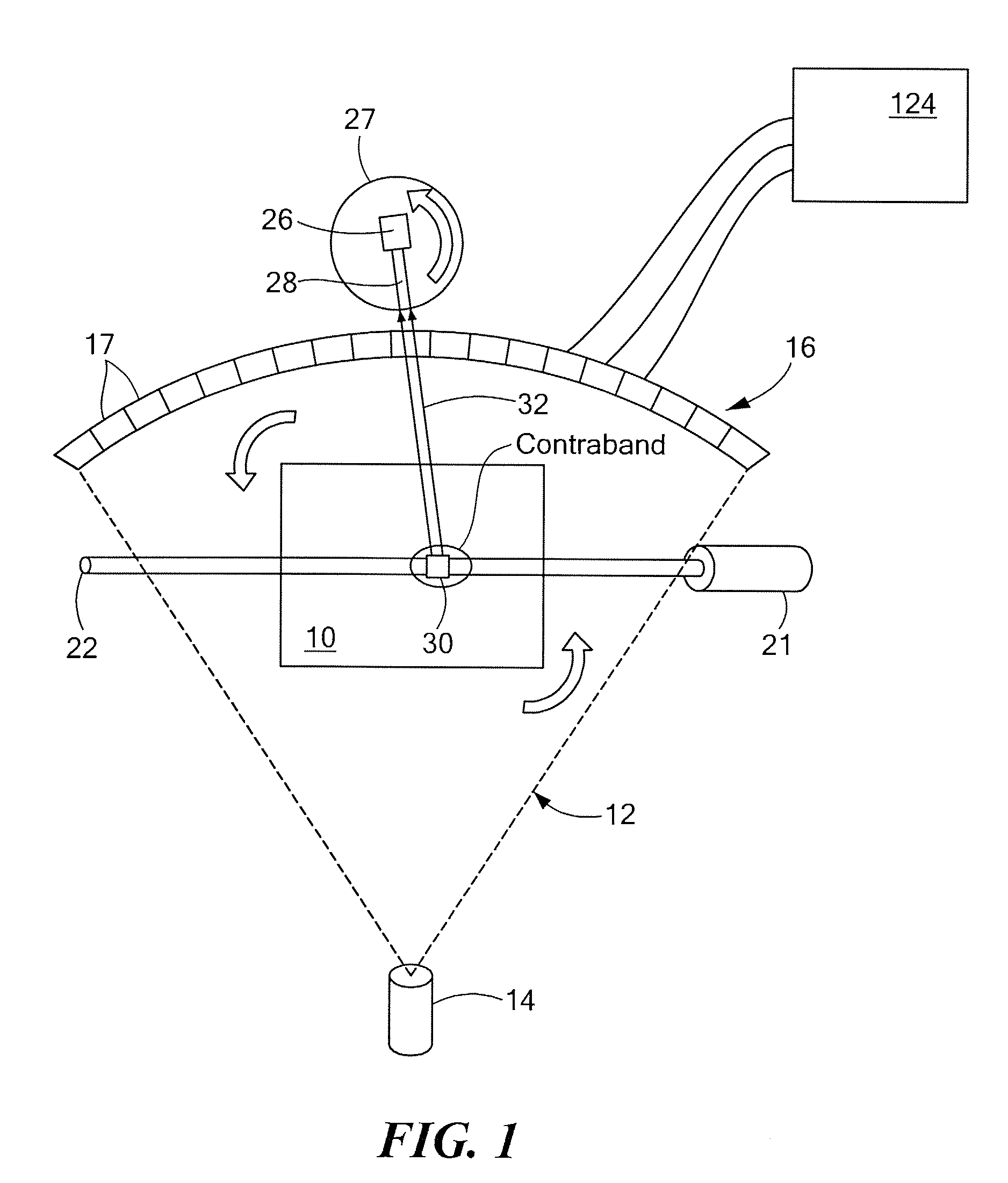
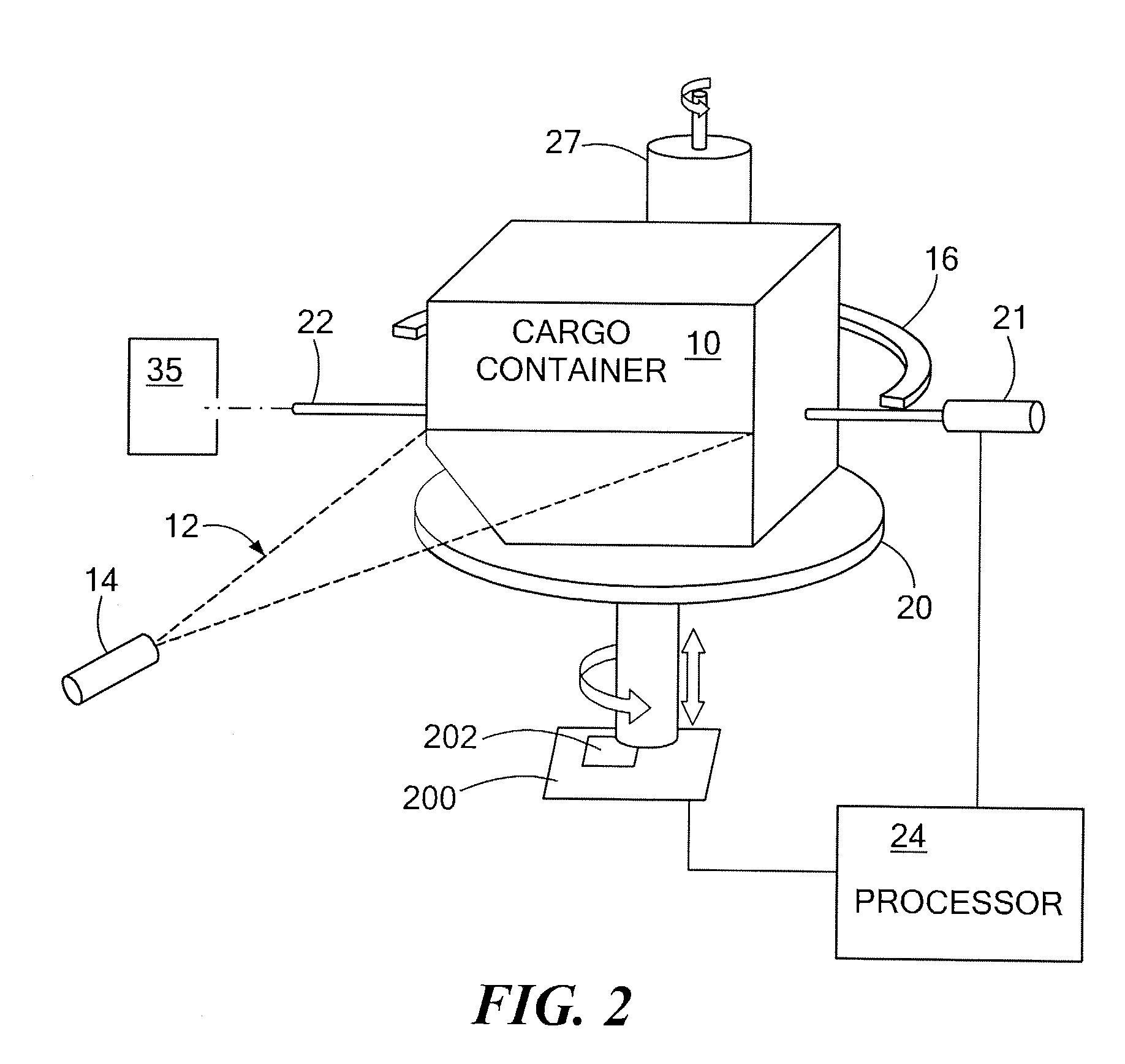
A system and methods for identifying contents of an enclosure such as an air cargo container. A three-dimensional image indicative of at least one of the CT number and the density of contents of the enclosure is obtained using penetrating radiation such as x-rays. If one or more suspect regions are identified among contents of the enclosure, a collimated neutron beam is activated to traverse each suspect region and fluorescent emission from the suspect region is detected, allowing material within the suspect region to be characterized based at least on the detected fluorescent emission. Additionally, the collimated neutron beam may be employed for neutron imaging of the contents of the enclosure.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
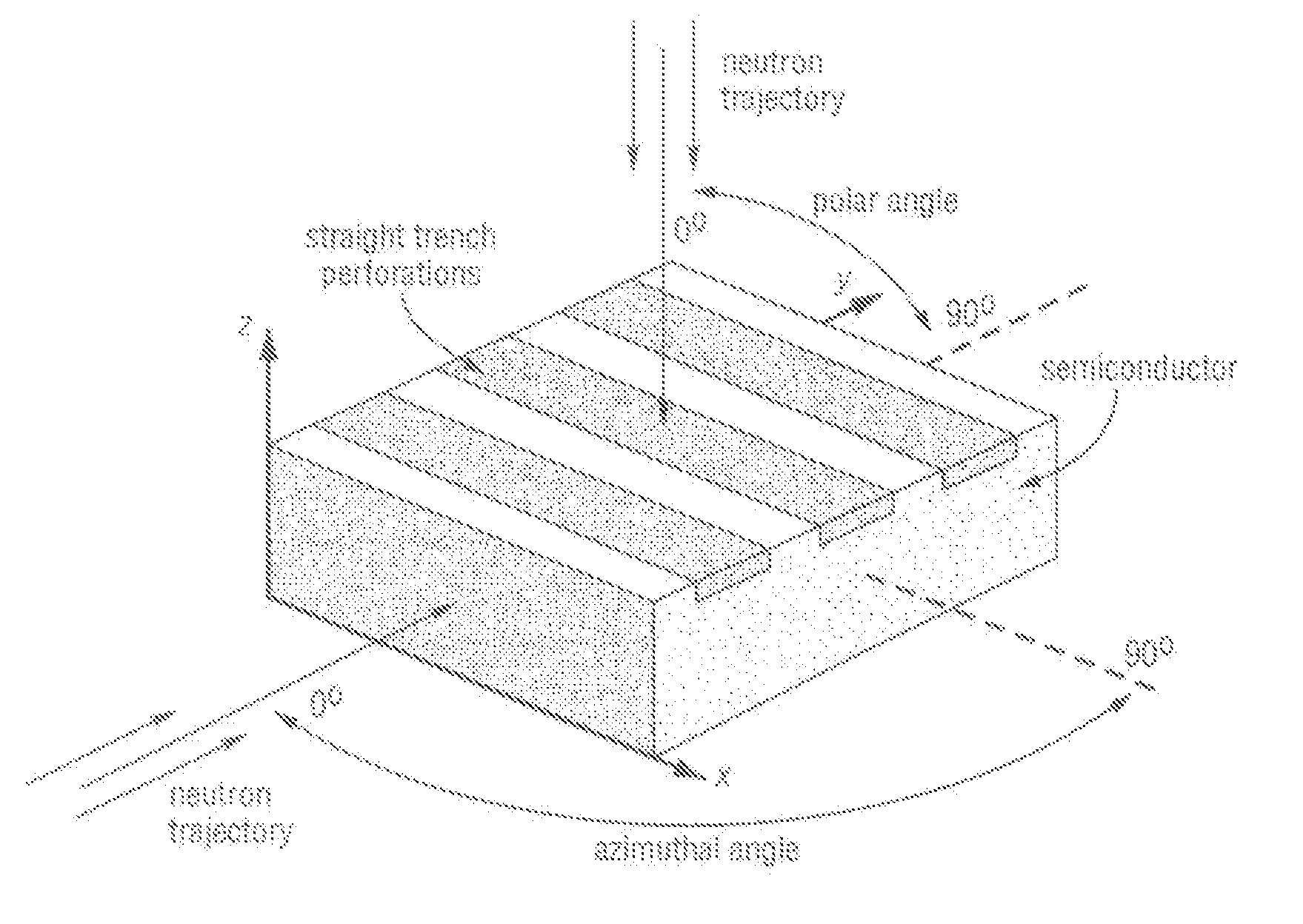
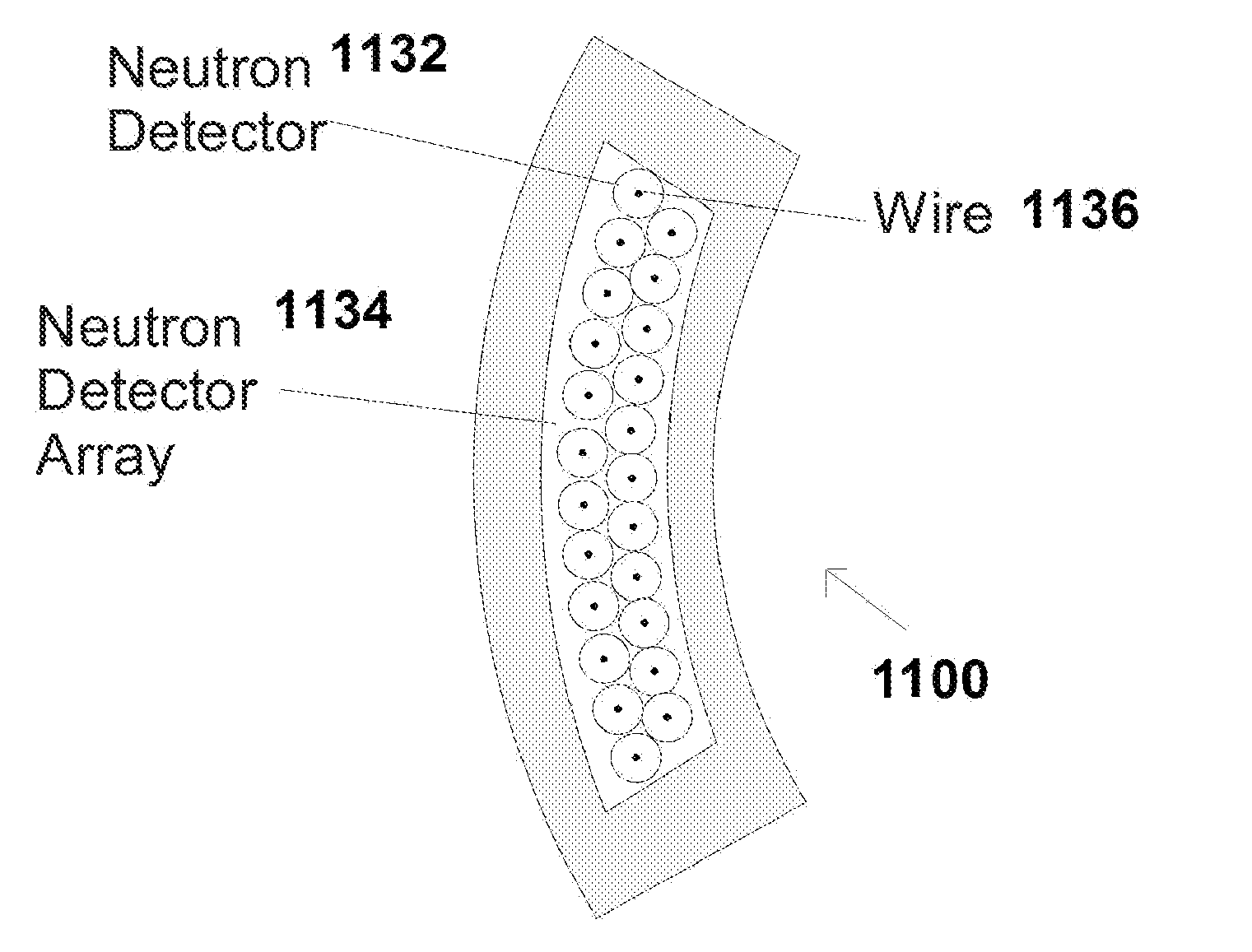
Non-streaming high-efficiency perforated semiconductor neutron detectors, methods of making same and measuring wand and detector modules utilzing same
ActiveUS20090302231A1Reliable designTotal current dropMeasurement with semiconductor devicesDosimetersNeutron imagingComputer module
Non-streaming high-efficiency perforated semiconductor neutron detectors, method of making same and measuring wands and detector modules utilizing same are disclosed. The detectors have improved mechanical structure, flattened angular detector responses, and reduced leakage current. A plurality of such detectors can be assembled into imaging arrays, and can be used for neutron radiography, remote neutron sensing, cold neutron imaging, SNM monitoring, and various other applications.
Owner:KANSAS STATE UNIV RES FOUND
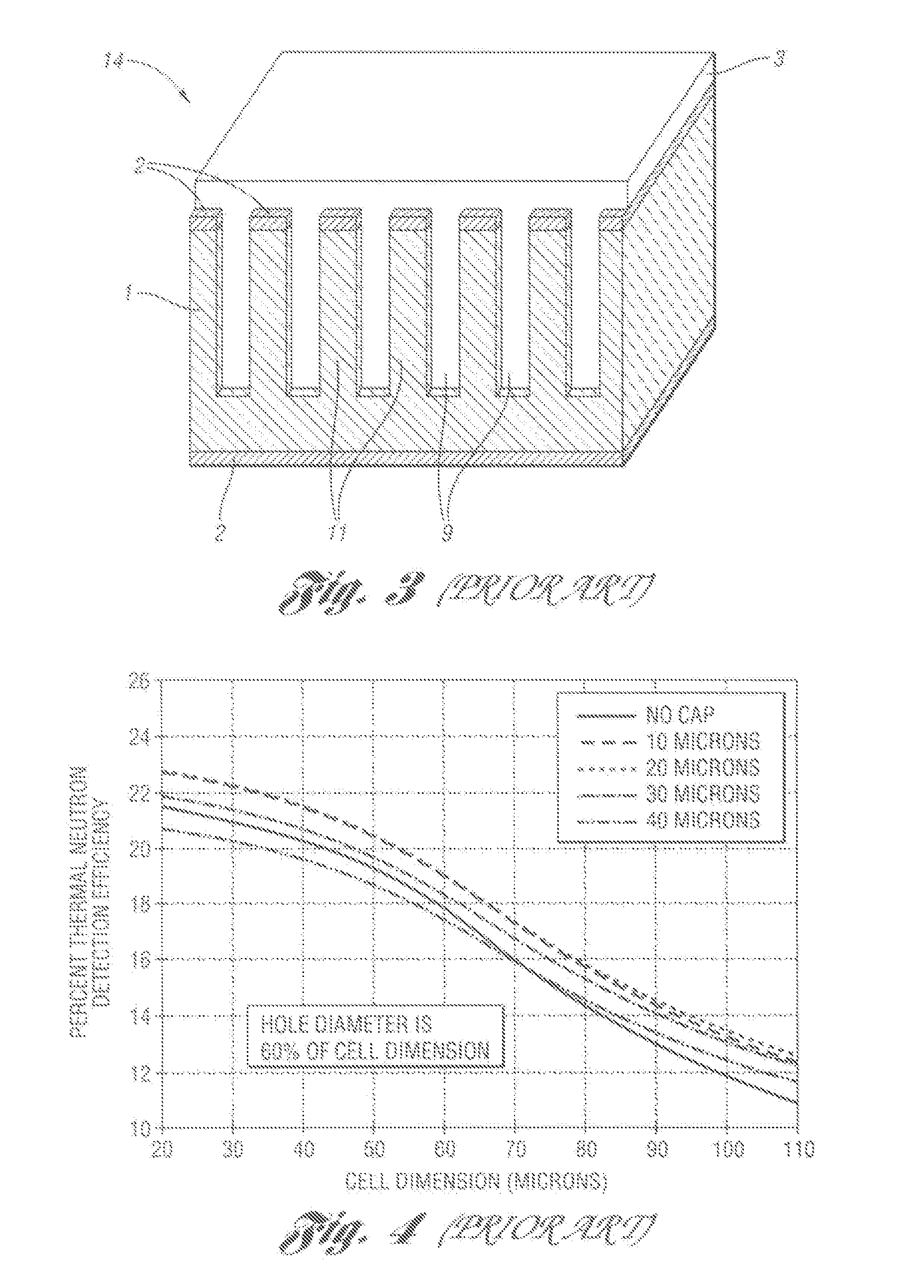
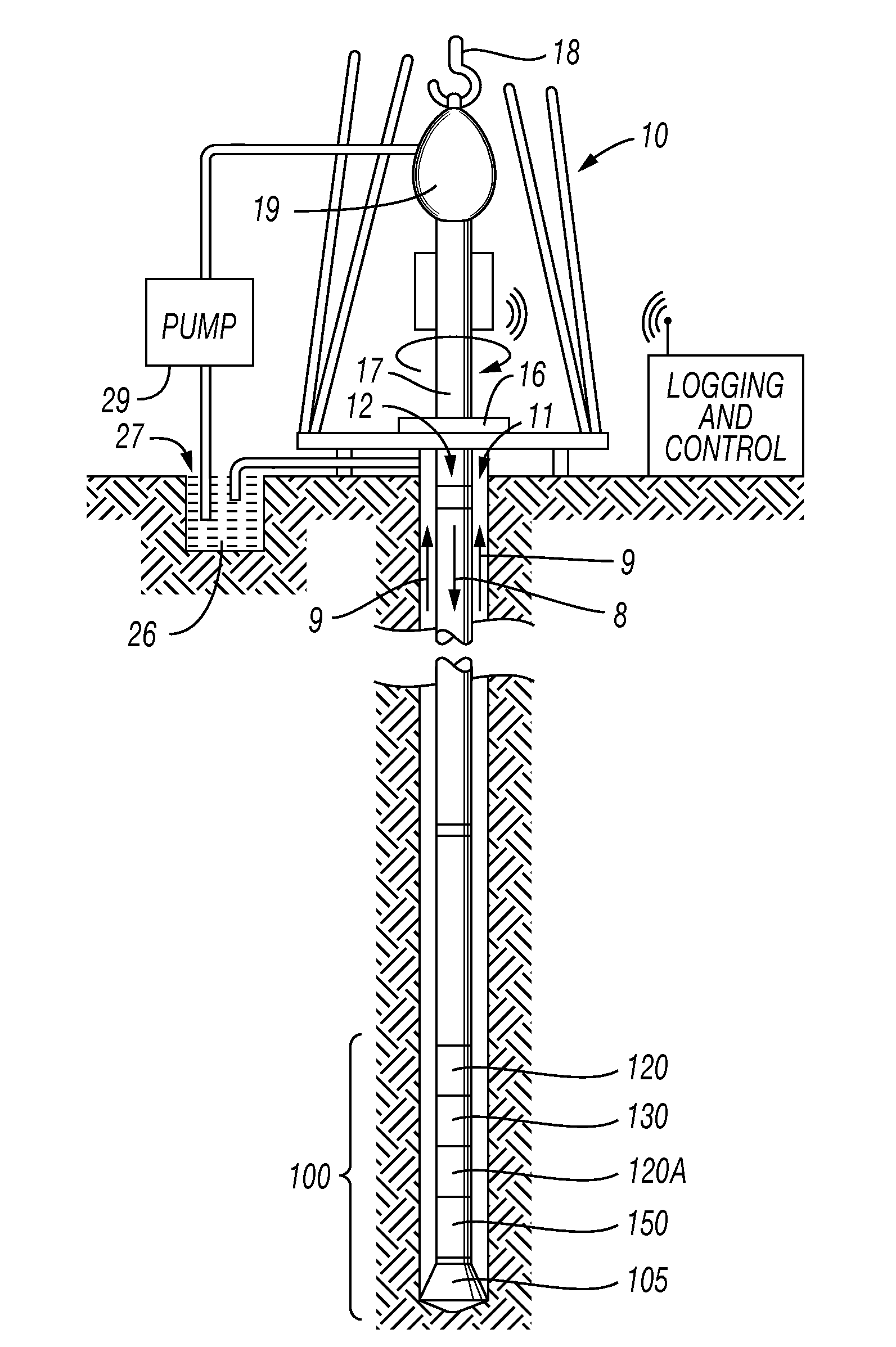
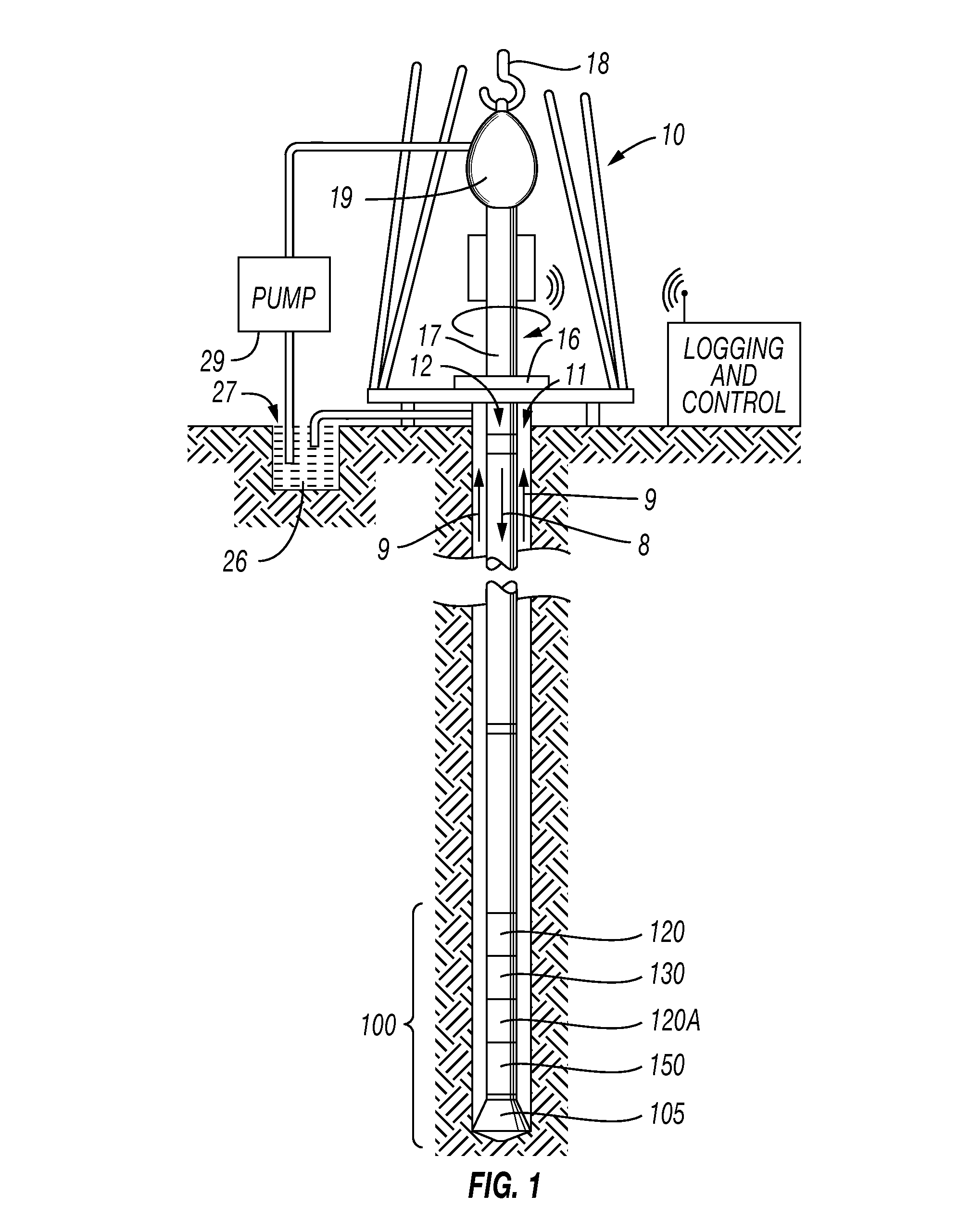
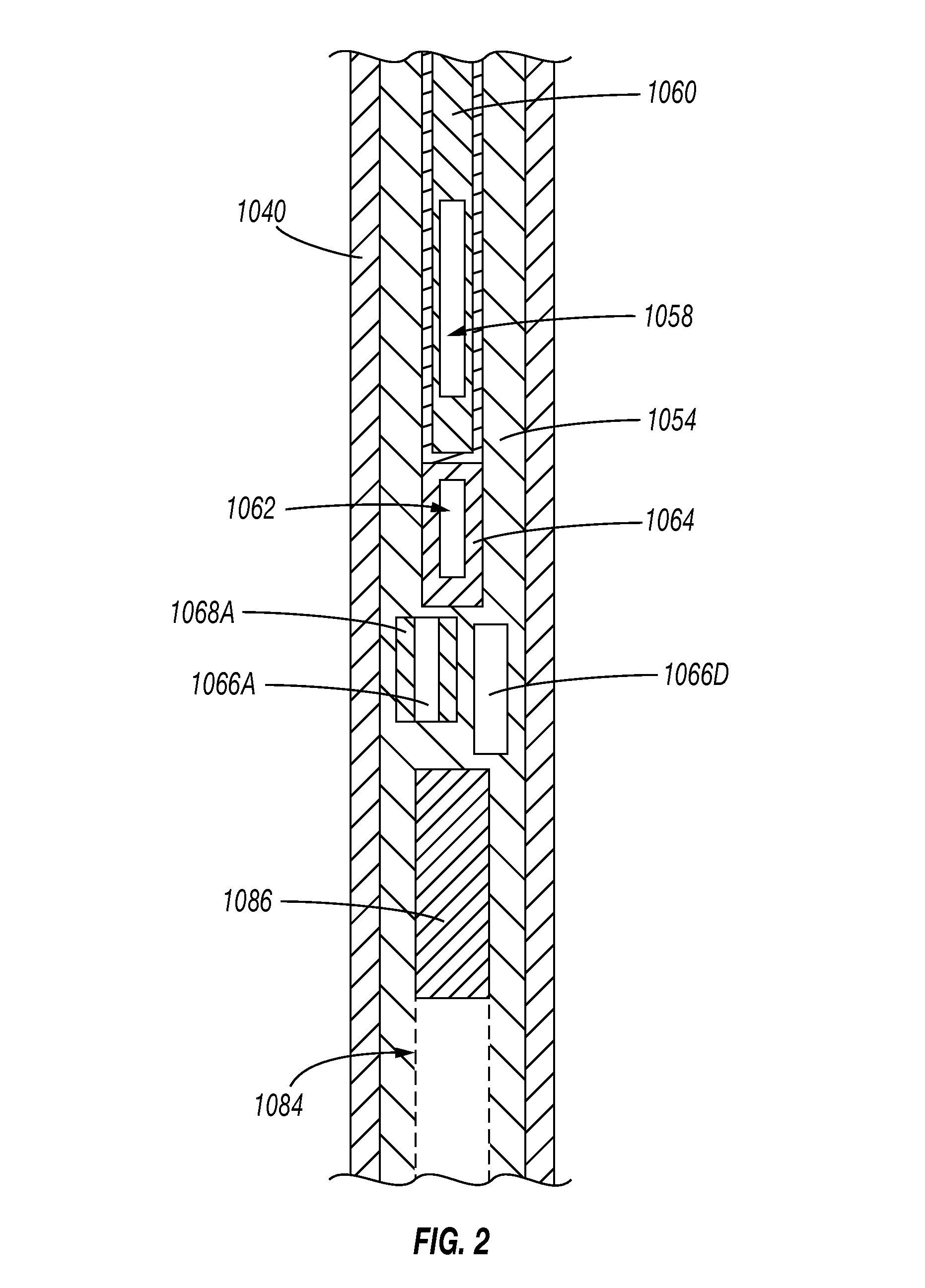
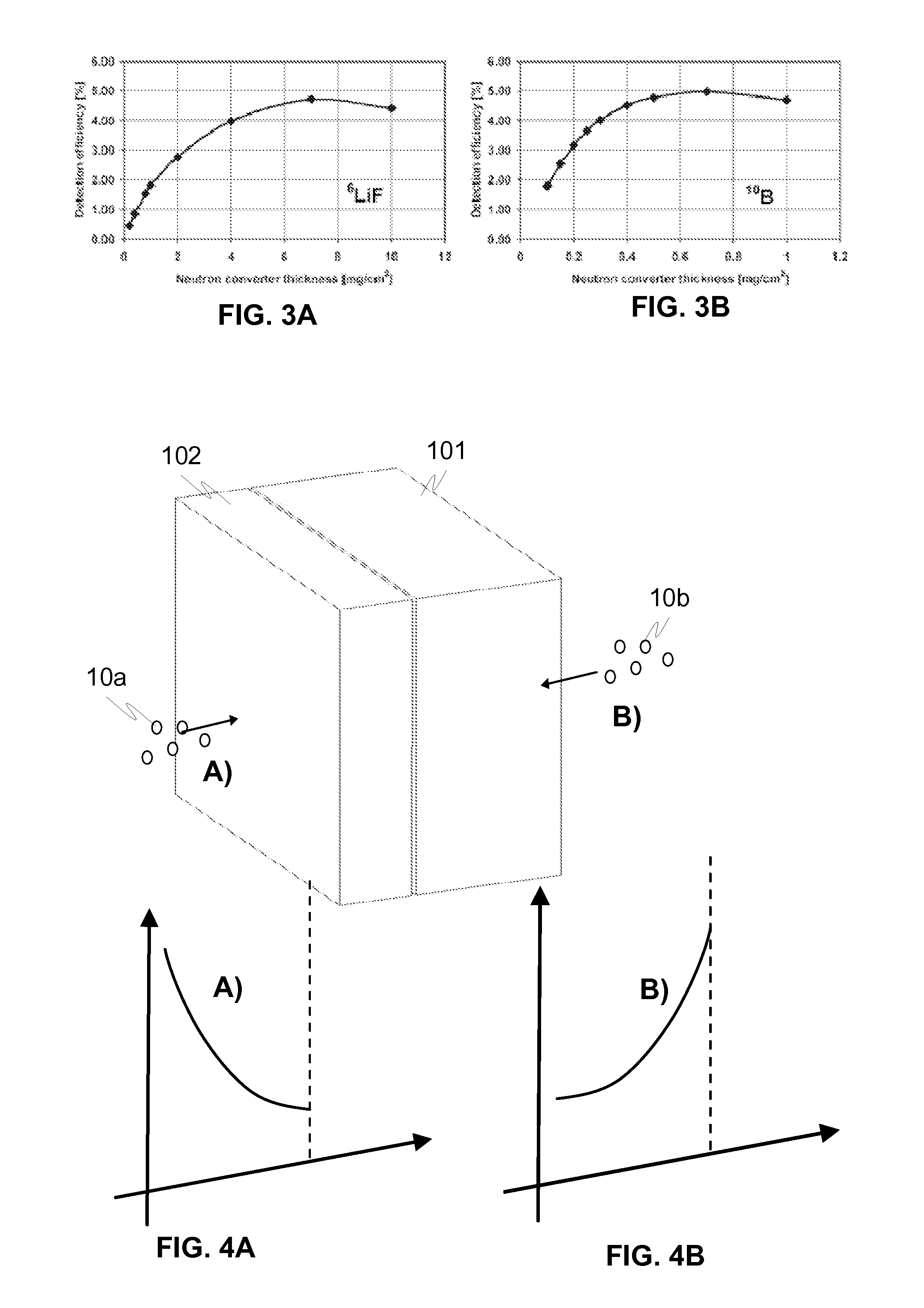
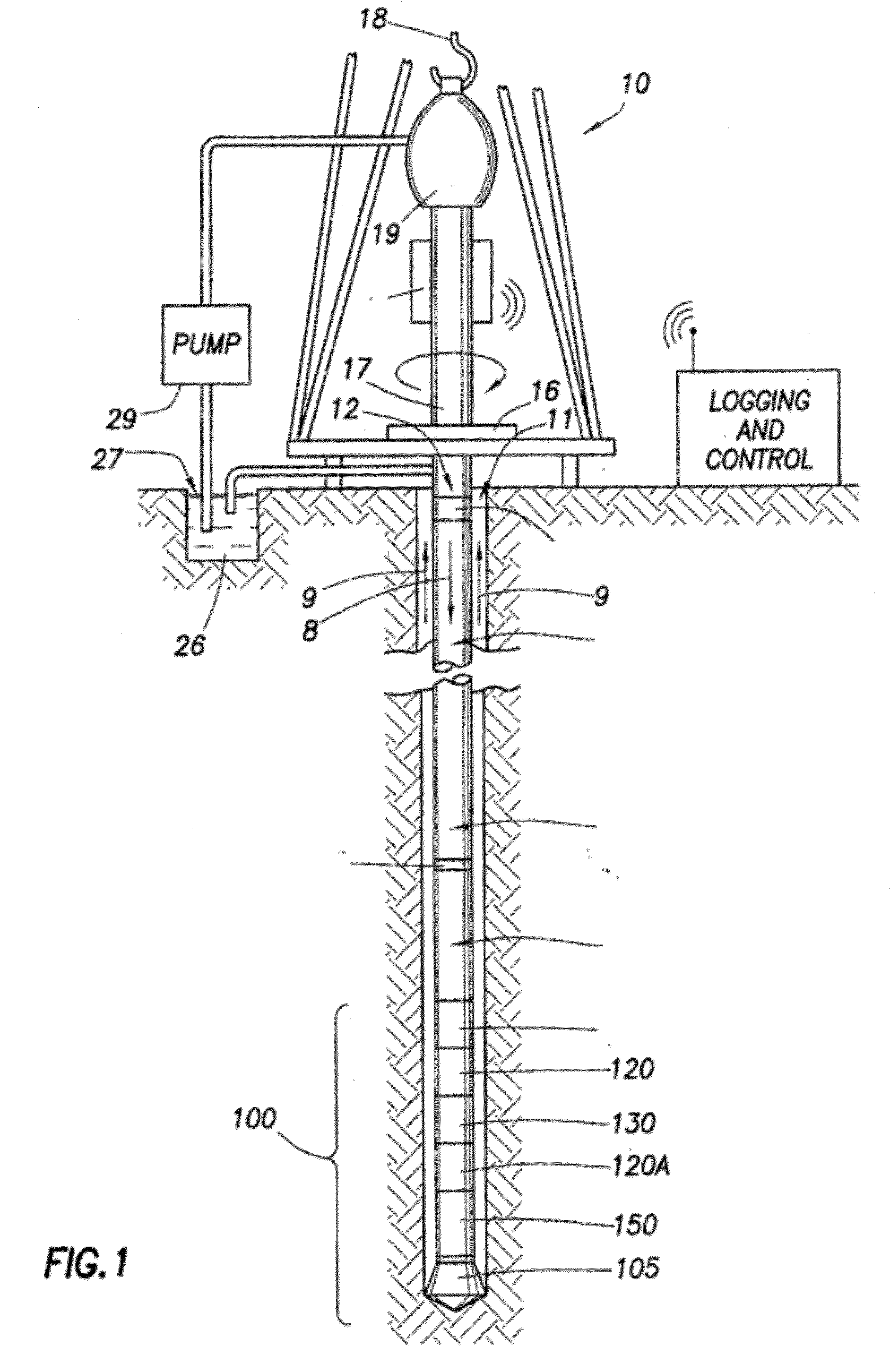
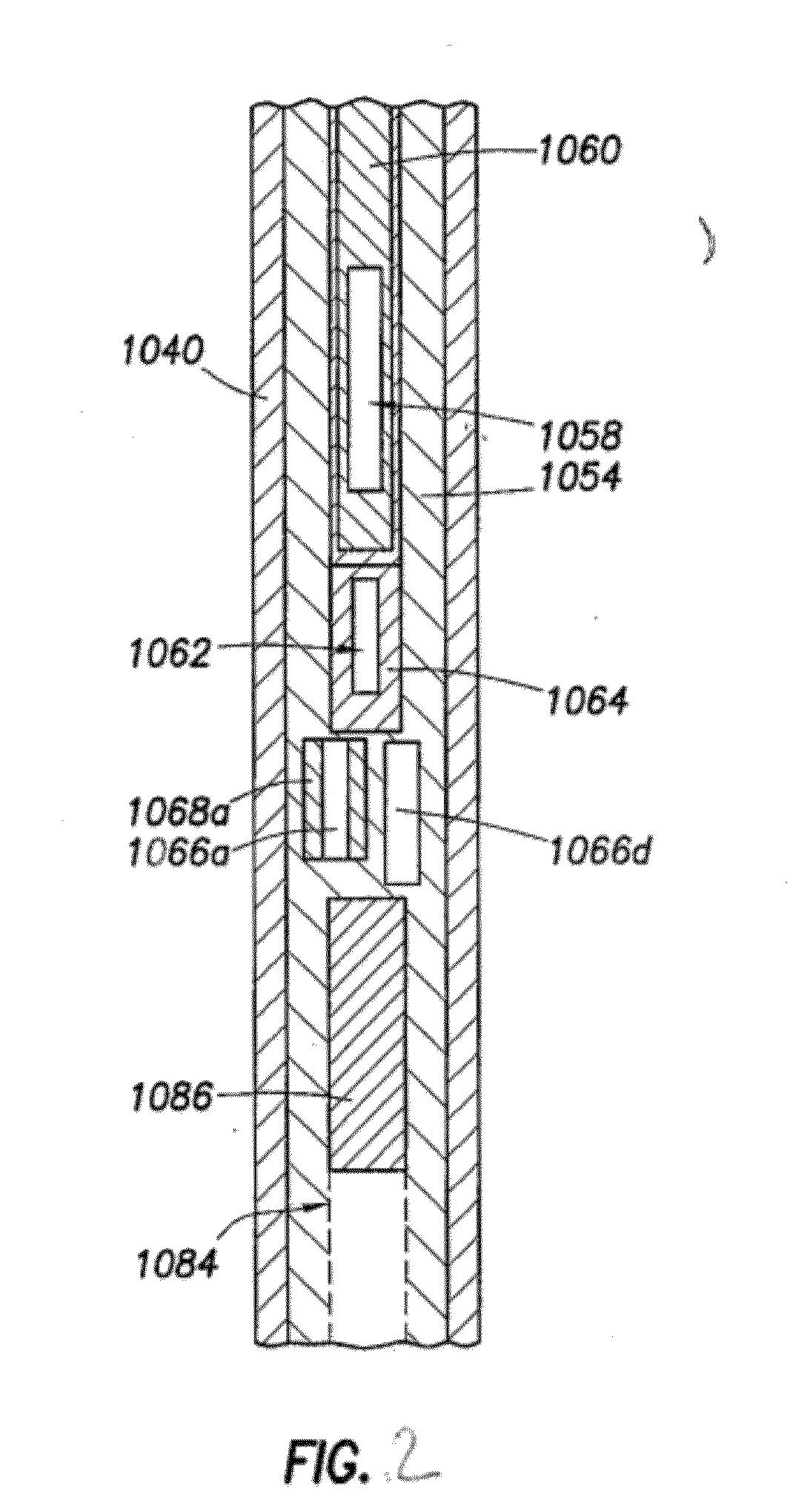
Non-rotating logging-while-drilling neutron imaging tool
A method and apparatus for obtaining neutron images of a rock formation are provided. The neutron images can be obtained from a tool in a logging-while-drilling system but which need not rotate to obtain neutron data from a plurality of azimuthal orientations.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Non-streaming high-efficiency perforated semiconductor neutron detectors, methods of making same and measuring wand and detector modules utilizing same
ActiveUS7855372B2Total current dropEfficient detectionMeasurement with semiconductor devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron imagingSemiconductor detector
Owner:KANSAS STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Ultra thin neutron detector, method for manufacturing the neutron detector and neutron imaging apparatus
InactiveUS8022369B2Mitigate such drawbackQuick collectionMeasurement with semiconductor devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansGamma photonElectricity
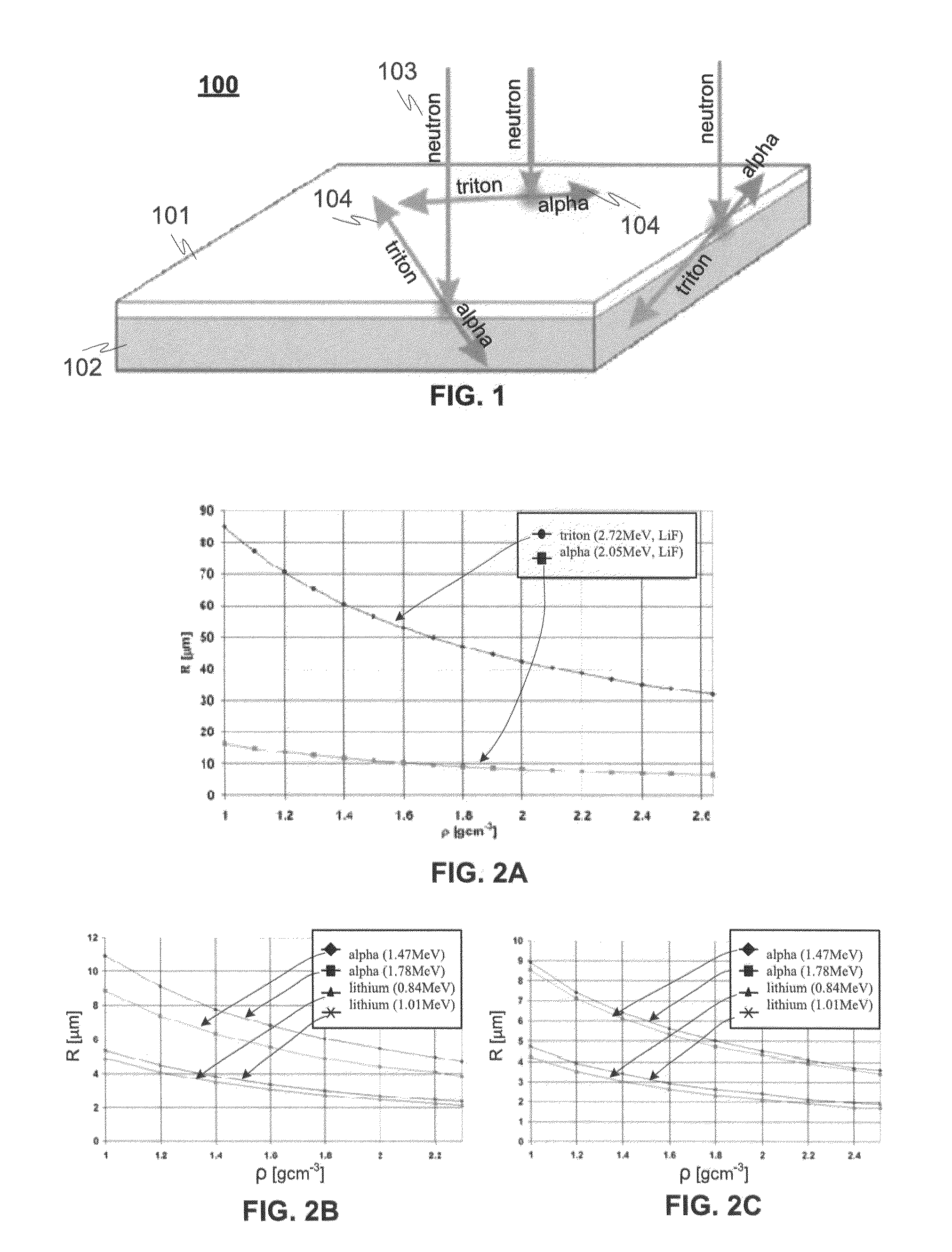
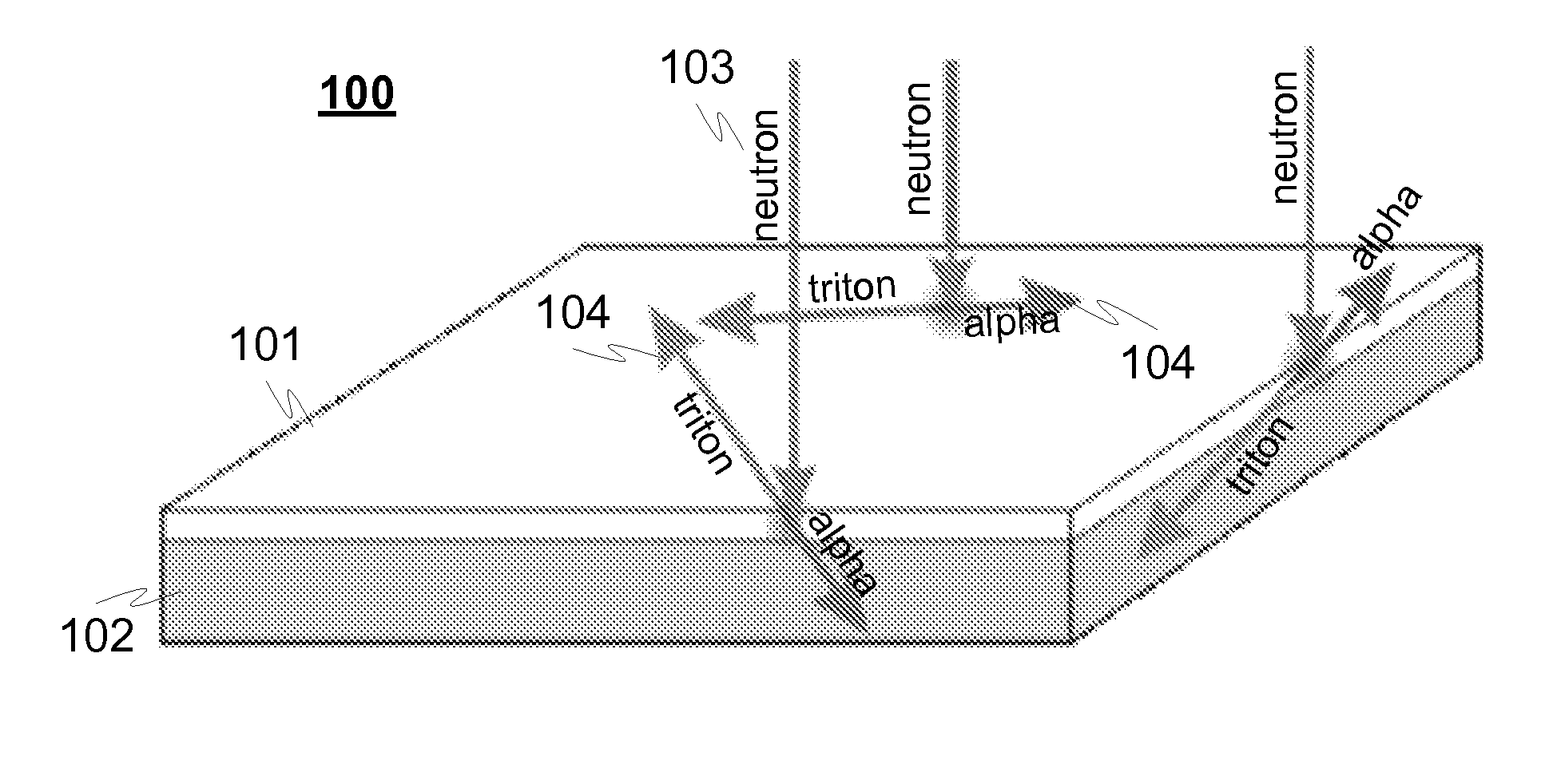
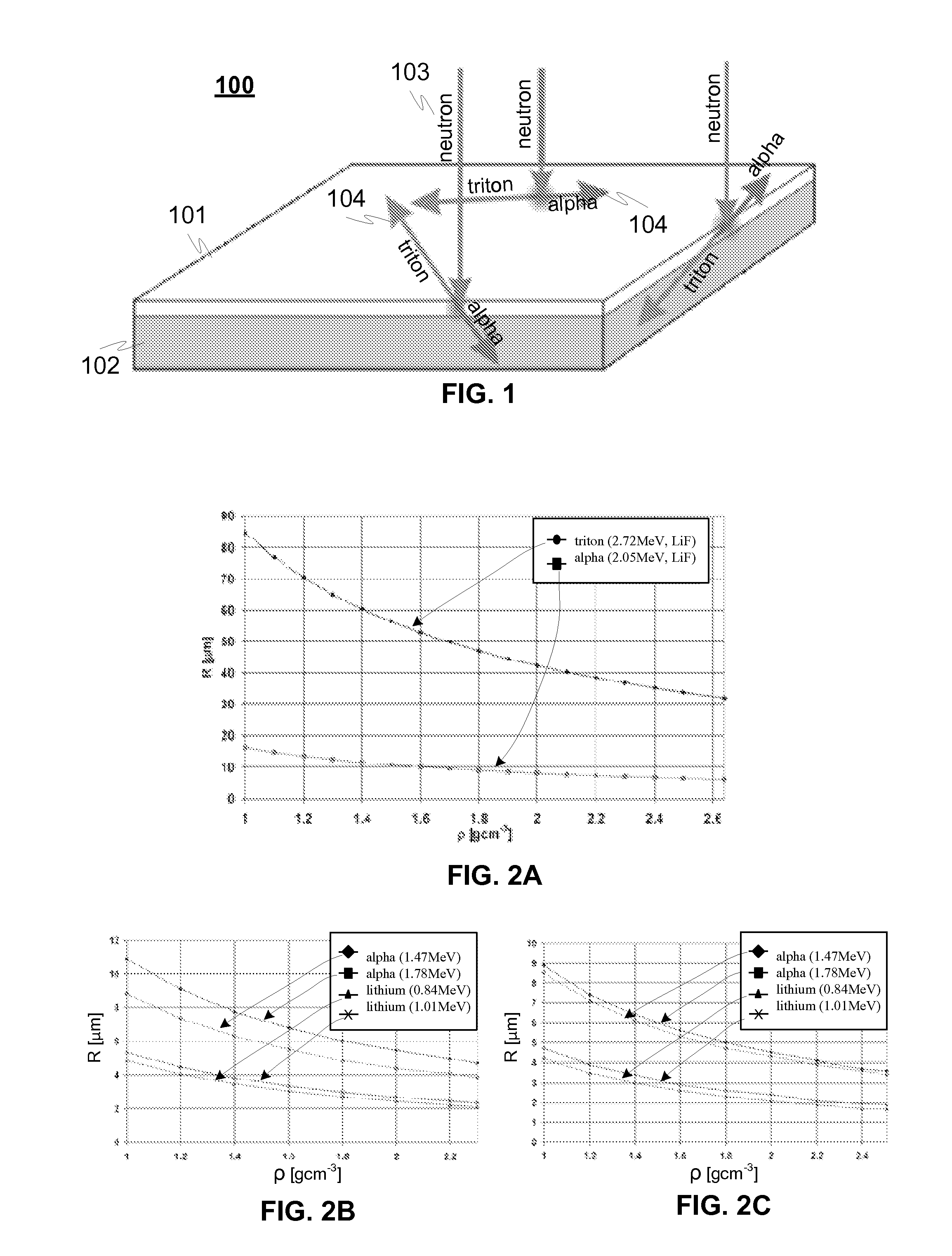
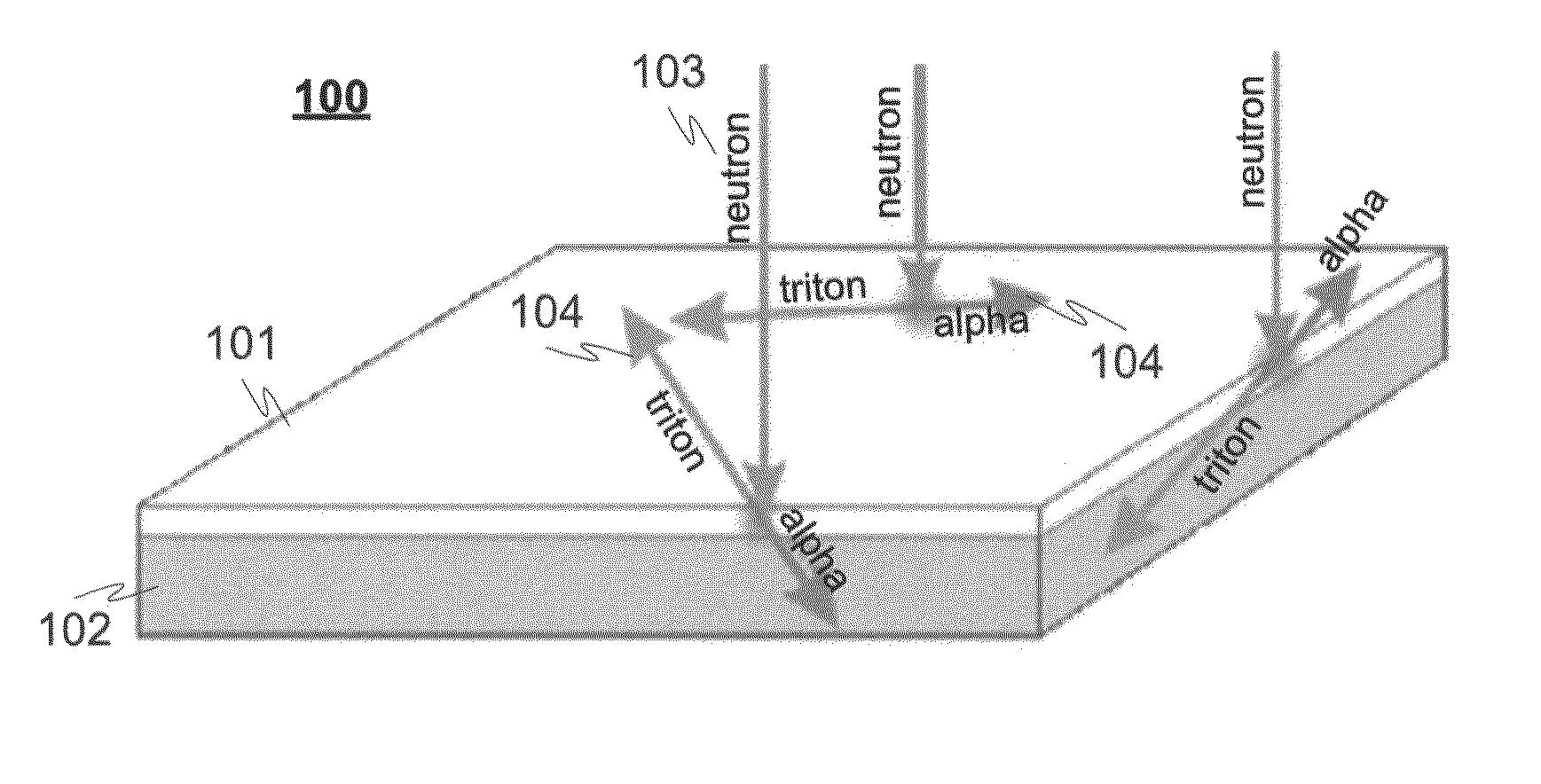
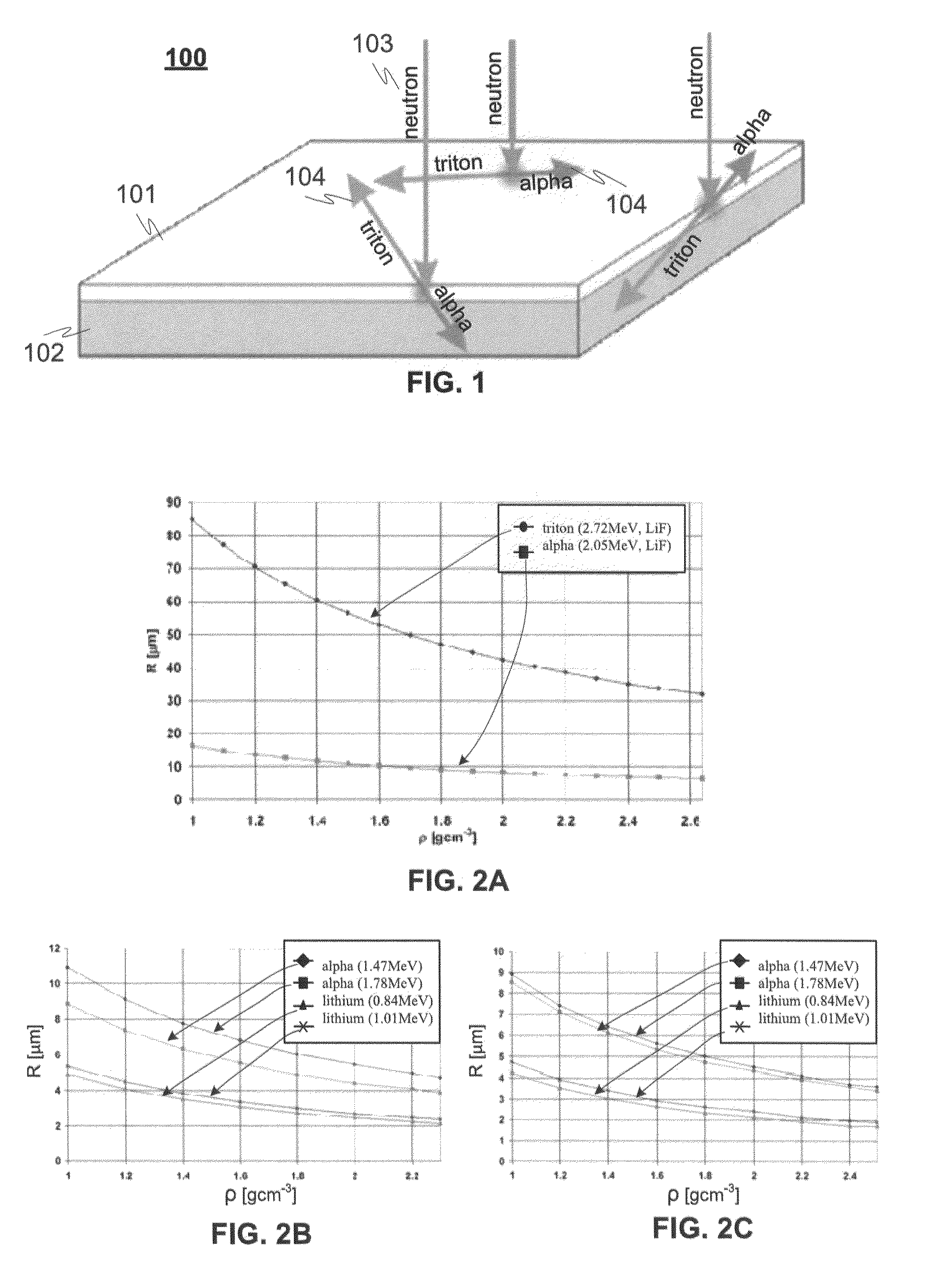
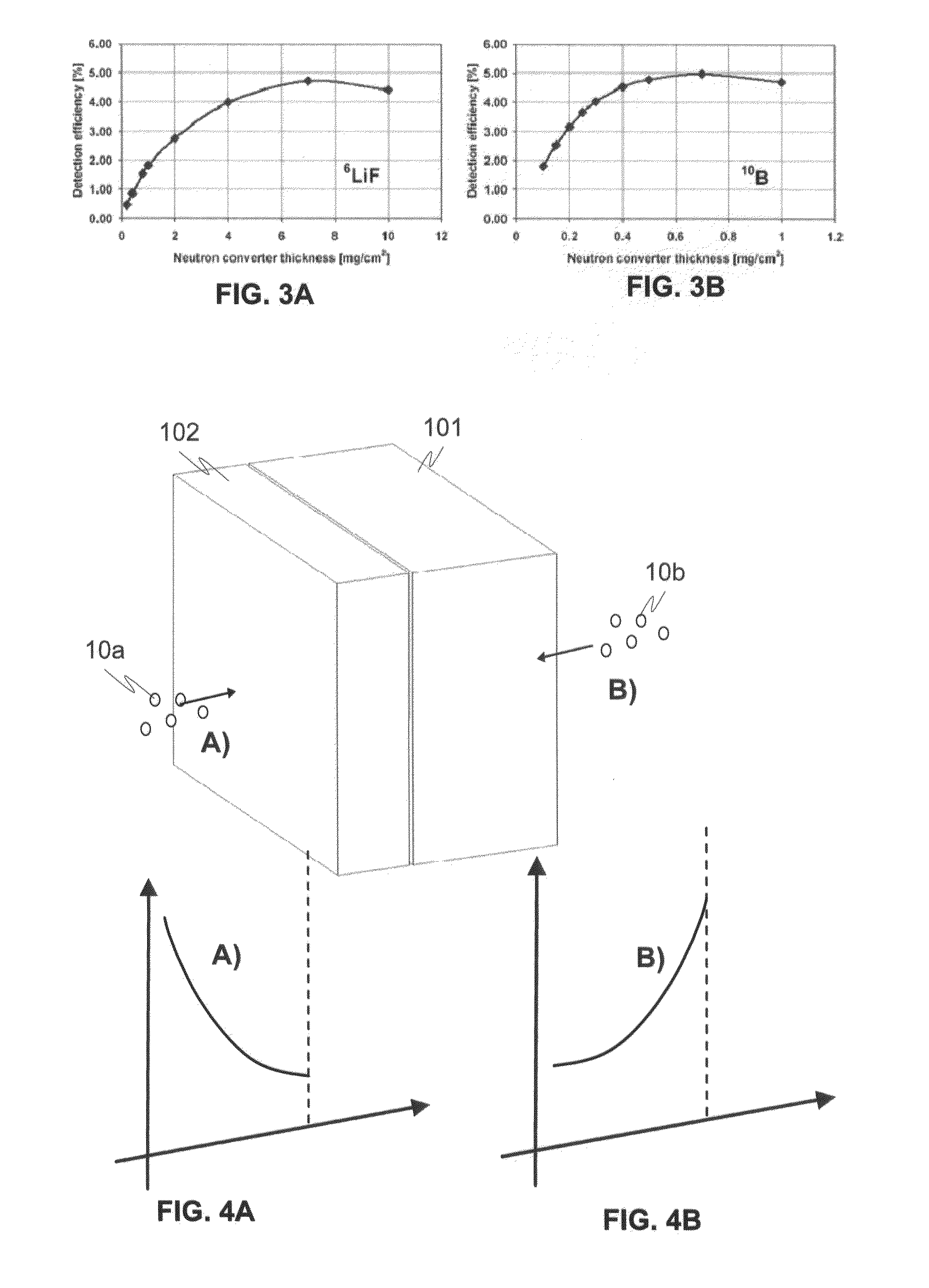
A detector (100) for detecting neutrons includes a neutron reactive material (102) adapted to interact with neutrons to be detected and release ionizing radiation reaction products in relation to the interactions with neutrons. The detector also includes a first semiconductor element (101) being coupled with the neutron reactive material (102) and adapted to interact with the ionizing radiation reaction products and provide electrical charges proportional to the energy of the ionizing radiation reaction products. In addition electrodes are arranged in connection with the first semiconductor element (101) for providing charge collecting areas (106) for collecting the electrical charges and to provide electrically readable signal proportional to the collected electrical charges. The thickness of the first semiconductor element (101) is adapted to be electrically and / or physically so thin that it is essentially / practically transparent for incident photons, such as background gamma photons.
Owner:RAKKATEC OY
Neutron detector with neutron converter, method for manufacturing the neutron detector and neutron imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20110095194A1Mitigate such drawbackEfficient detectionMeasurement with semiconductor devicesVacuum evaporation coatingNeutron converterElectricity
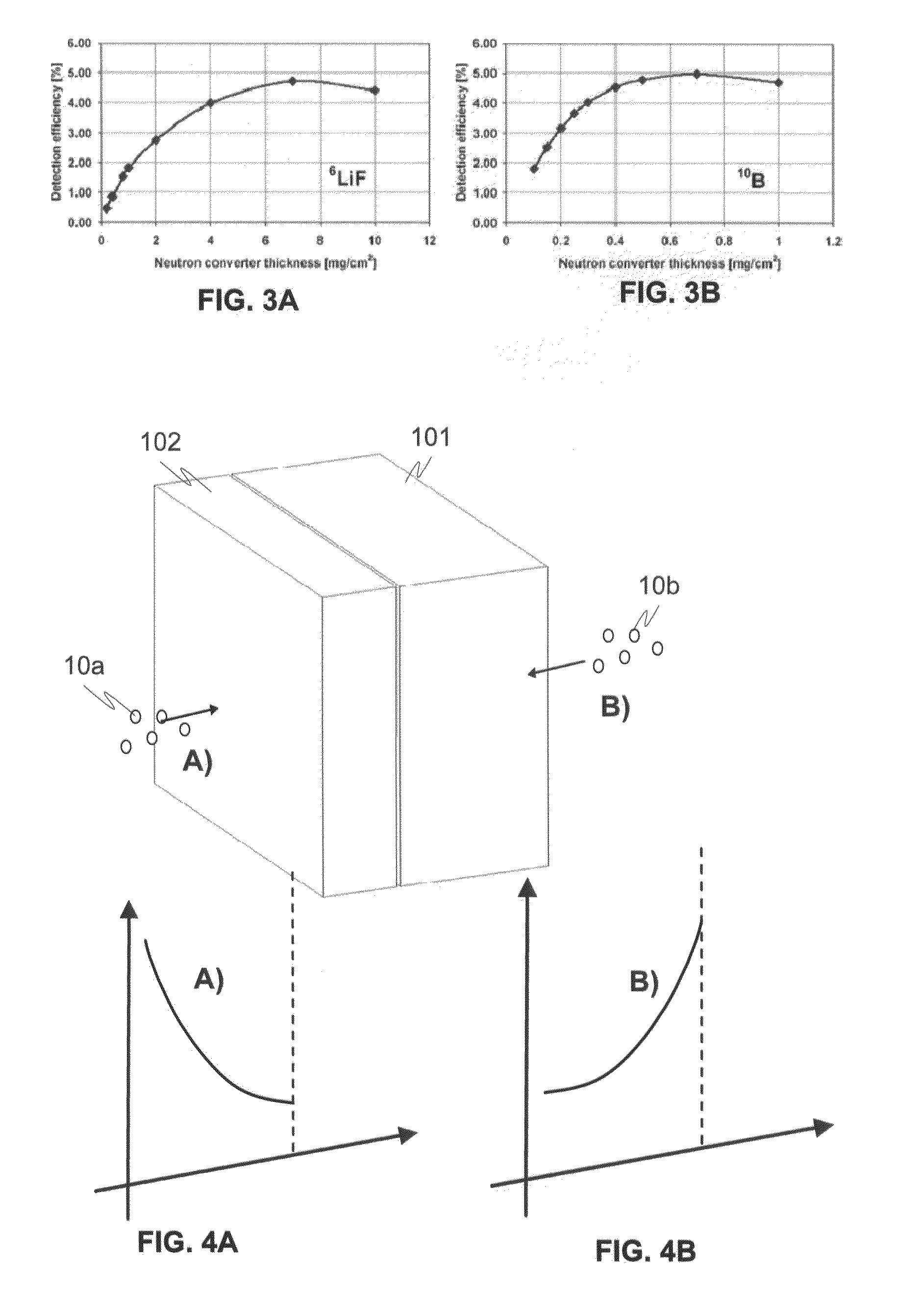
A detector for detecting neutrons includes a neutron reactive material interacting with neutrons to be detected and releasing ionizing radiation reaction products in relation to the interactions. It also includes a first semiconductor element being coupled with the neutron reactive material and adapted to interact with the ionizing radiation reaction products and provide electrical charges proportional to the energy of the ionizing radiation reaction products. In addition electrodes are arranged in connection with the first semiconductor element for providing charge collecting areas for collecting the electrical charges and to provide electrically readable signal proportional to the collected electrical charges. In the detector the neutron reactive material is arranged so that the incident neutrons to be detected interact with the neutron reactive material essentially in the portion nearest to the charge collecting areas provided by the electrodes in the first semiconductor element to which the neutron reactive material is coupled with.
Owner:FINPHYS
Non-rotating logging-while-drilling neutron imaging tool
A method and apparatus for obtaining neutron images of a rock formation are provided. The neutron images can be obtained from a tool in a logging-while-drilling system but which need not rotate to obtain neutron data from a plurality of azimuthal orientations.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Combined X-Ray CT/Neutron Material Identification System
InactiveUS20070286339A1X-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationAir cargoX-ray
Combined X-Ray CT / Neutron Material Identification System A system and methods for identifying contents of an enclosure such as an air cargo container. A three-dimensional image indicative of at least one of the CT number and the density of contents of the enclosure is obtained using penetrating radiation such as x-rays. If one or more suspect regions are identified among contents of the enclosure, a collimated neutron beam is activated to traverse each suspect region and fluorescent emission from the suspect region is detected, allowing material within the suspect region to be characterized based at least on the detected fluorescent emission. Additionally, the collimated neutron beam may be employed for neutron imaging of the contents of the enclosure.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & ENG INC
X-ray and neutron imaging
InactiveUS20030081724A1Short focal lengthLaser detailsElectrode and associated part arrangementsSoft x rayX-ray
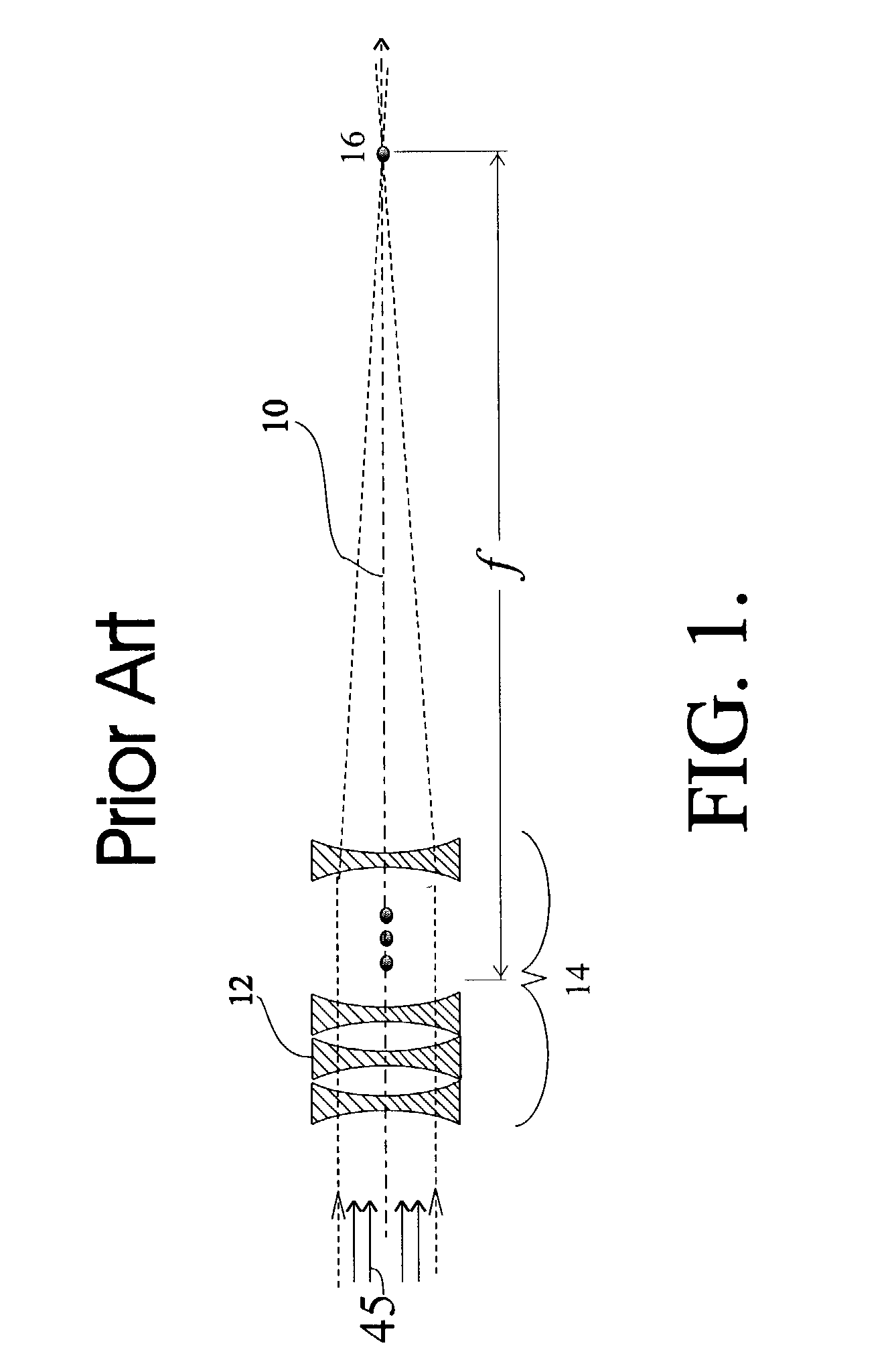
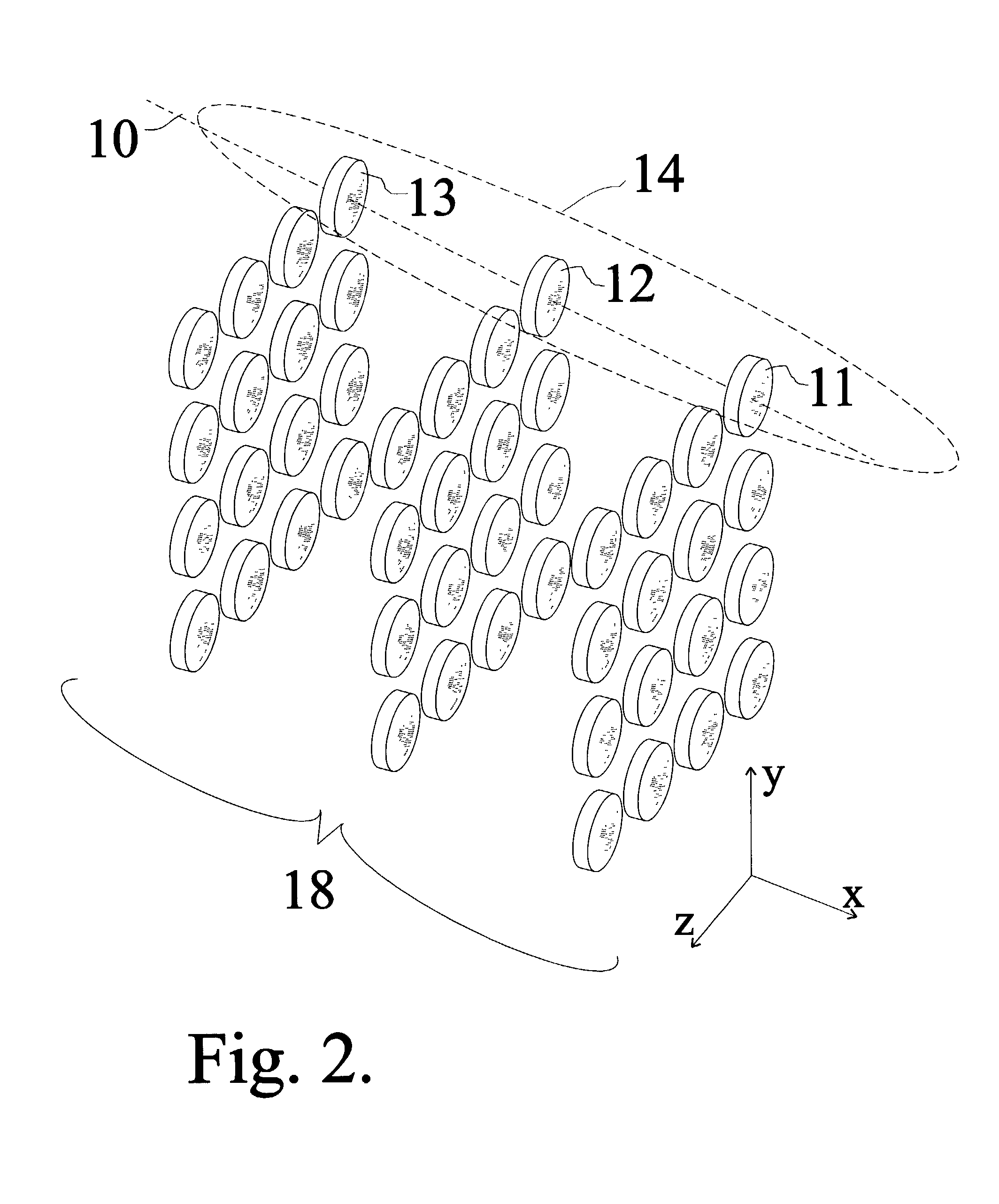
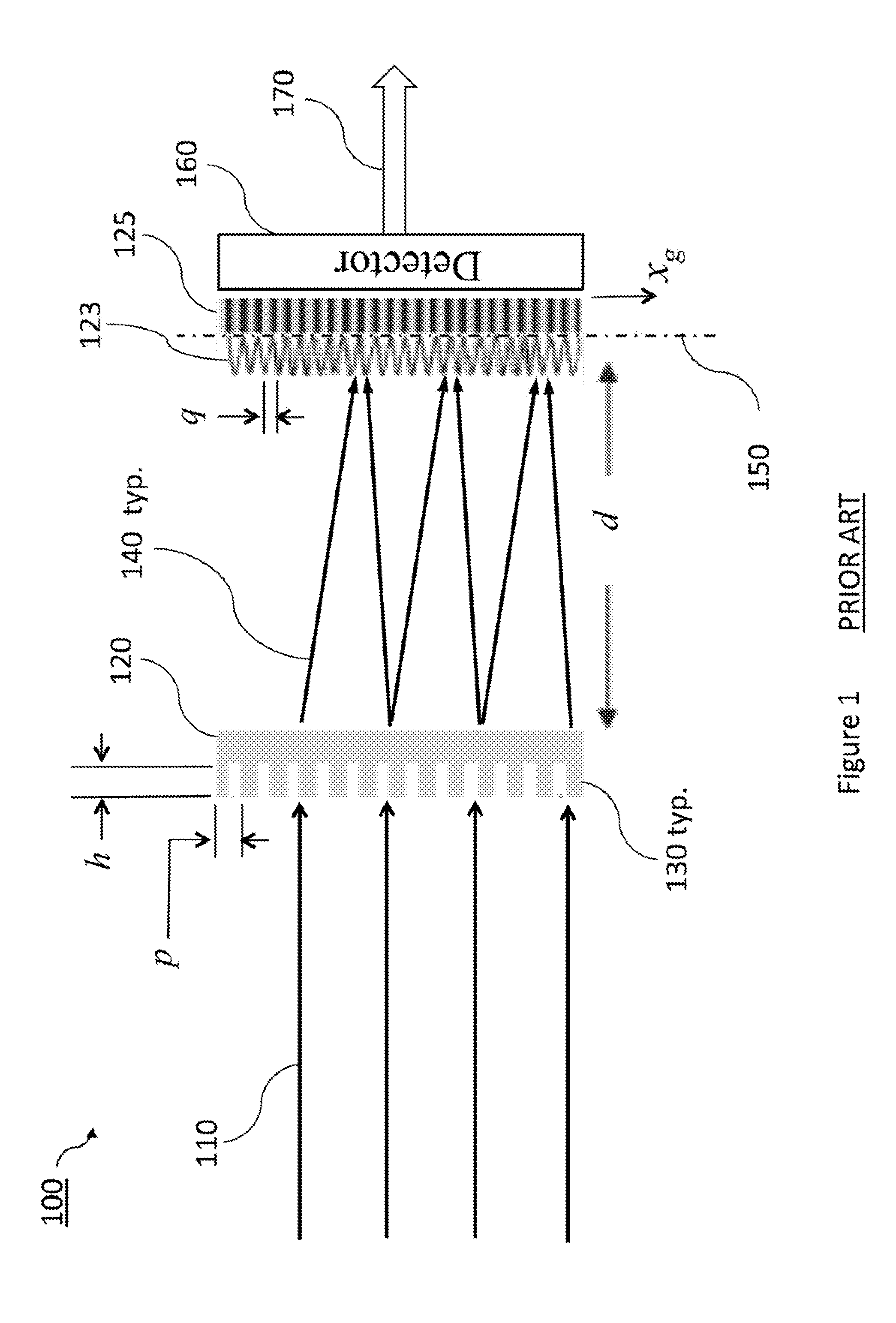
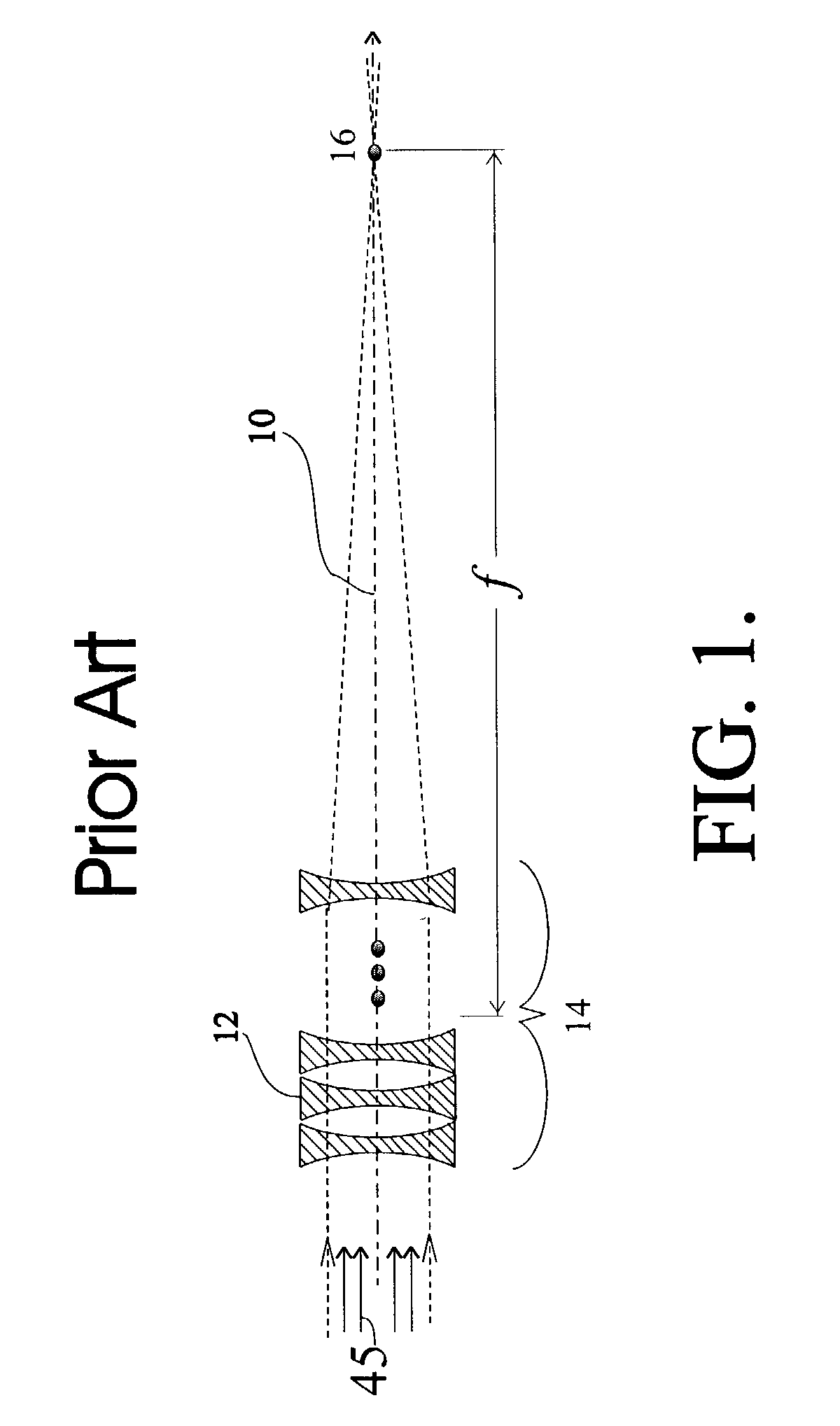
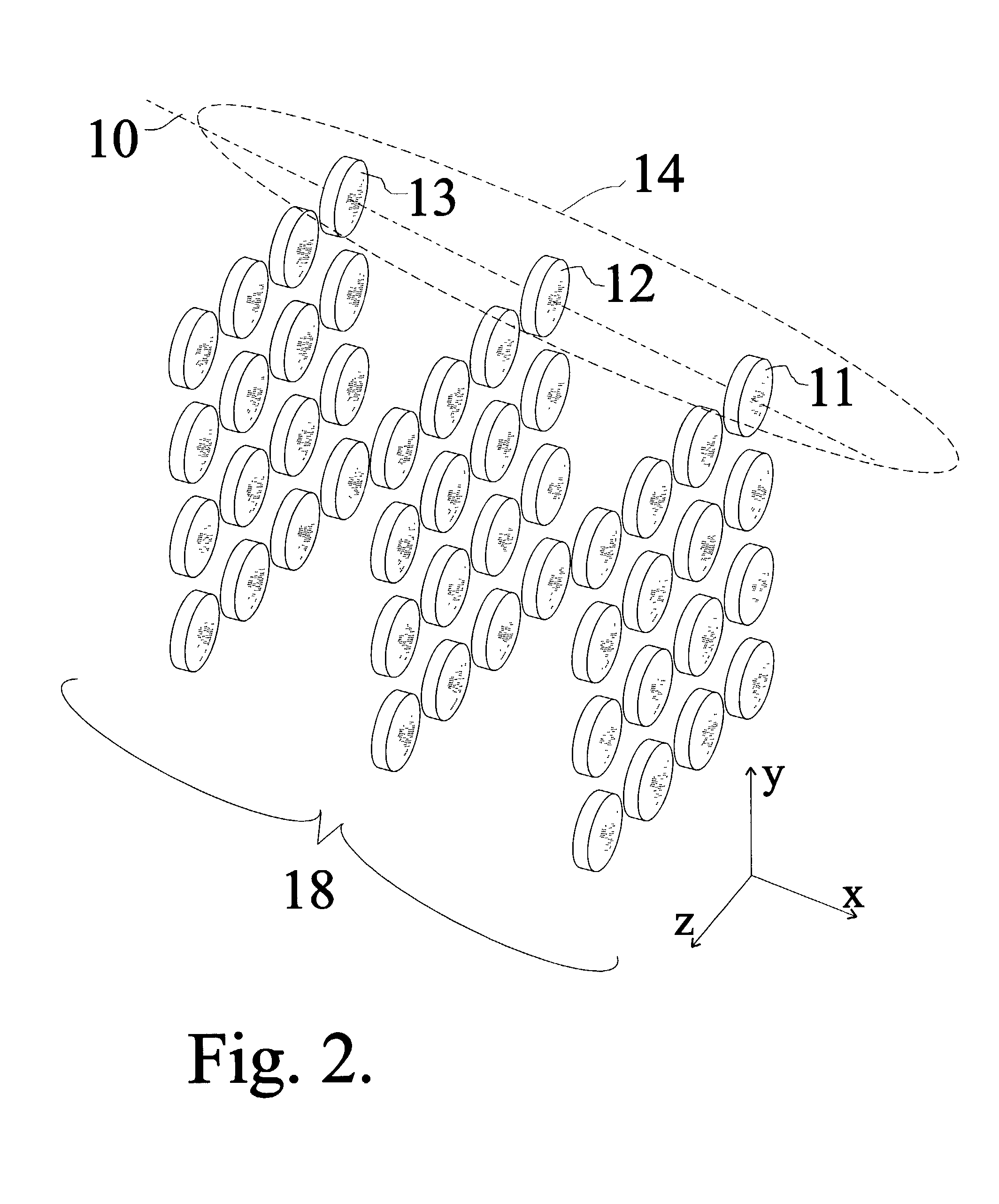
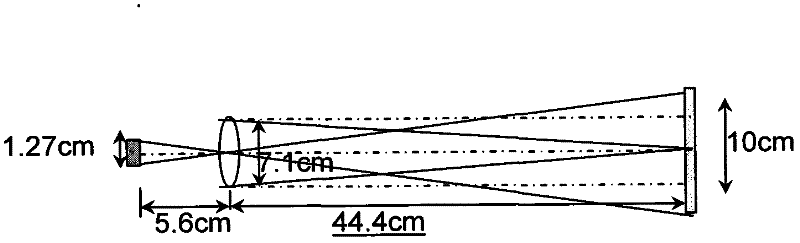
An x-ray or neutron apparatus for the transmission of x-ray or neutron images is described, which includes x-ray- or neutron-three-dimensional (3-D) arrays or mosaics, including a plurality of x-ray or neutron lenses positioned so that they form a two-dimensional (2-D) mosaic of compound refractive lenses to provide a plurality of separate x-ray or neutron paths between an object and an image at an x-ray- or neutron-detector. The apparatus is so constructed that it permits separate parts of an object to be imaged such that a total composite image is formed from these various parts. An imaging apparatus of the detection of carcinoma in breast tissue is formed using such an apparatus. Methods of microscopy and imaging are obtained using this apparatus.
Owner:ADELPHI TECH INC
Phase-sensitive two-dimensional neutron shearing interferometer and hartmann sensor
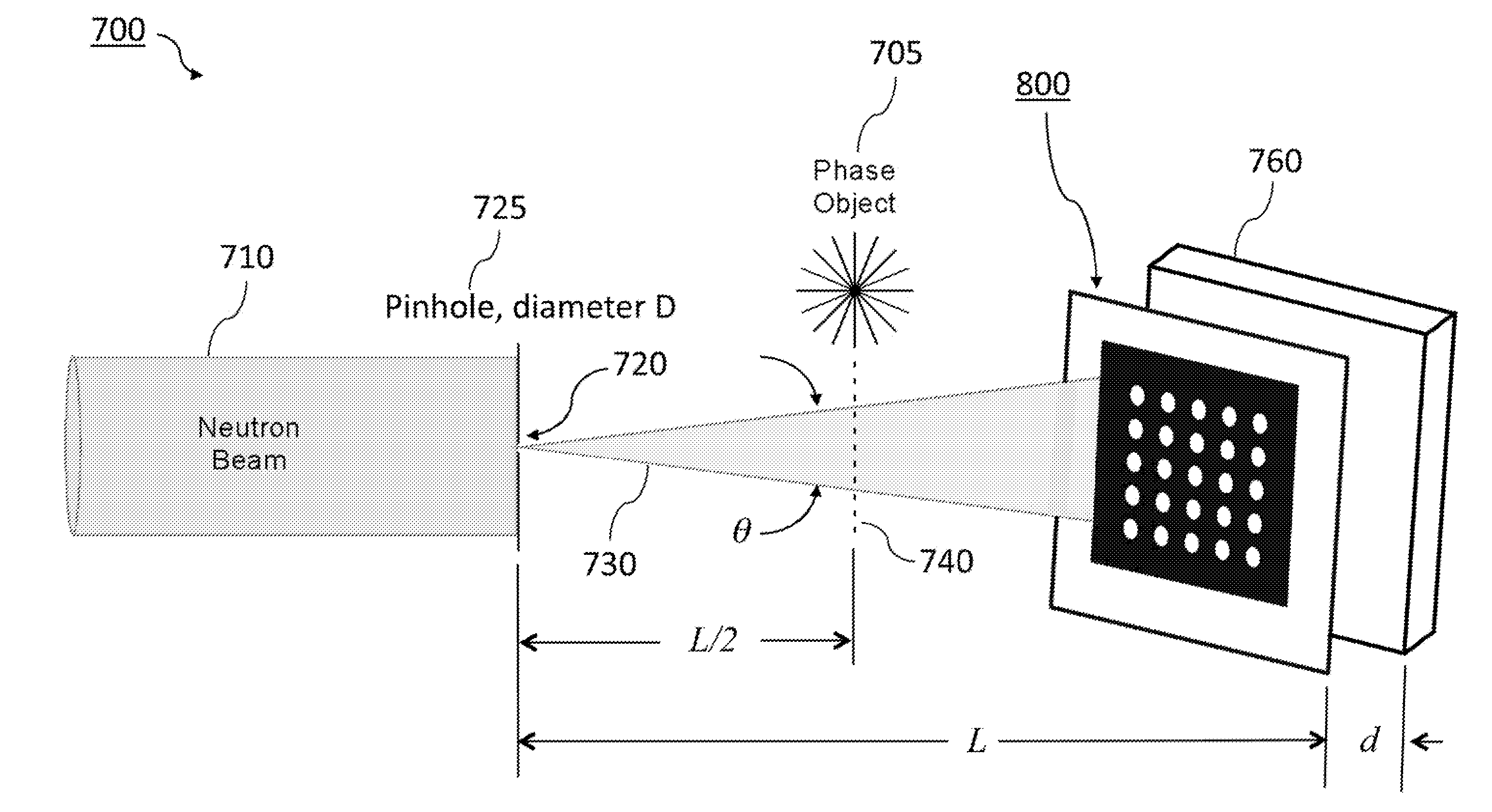
A neutron imaging system detects both the phase shift and absorption of neutrons passing through an object. The neutron imaging system is based on either of two different neutron wavefront sensor techniques: 2-D shearing interferometry and Hartmann wavefront sensing. Both approaches measure an entire two-dimensional neutron complex field, including its amplitude and phase. Each measures the full-field, two-dimensional phase gradients and, concomitantly, the two-dimensional amplitude mapping, requiring only a single measurement.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Method of Producing an Elongate Implant Containing a Structurally Encoded Pin Through Electrical Discharge Machining
ActiveUS20180064507A1Process economyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical furnitureDiagnostic Radiology ModalityElectric discharge
An implant and method for manufacturing an implant comprising an implant body defining a longitudinal axis and a structurally encoded pin contained within the implant body and aligned substantially along the longitudinal axis, the structurally encoded pin having a shape or surface characteristics discernable by an imaging modality such as x-ray, fluoroscopy, computed tomography, electromagnetic radiation, ultrasound, visible light, UV light, magnetic resonance imaging, positron emission tomography and neutron imaging, from outside the implant body, the shape or surface characteristics representing structurally encoded data. The structurally encoded pin is encoded via an electric discharge machining process.
Owner:KIESER BRIAN +2
Ultra thin neutron detector, method for manufacturing the neutron detector and neutron imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20110095193A1Mitigate such drawbackFast charge collectionMeasurement with semiconductor devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansGamma photonElectricity
A detector (100) for detecting neutrons includes a neutron reactive material (102) adapted to interact with neutrons to be detected and release ionizing radiation reaction products in relation to the interactions with neutrons. The detector also includes a first semiconductor element (101) being coupled with the neutron reactive material (102) and adapted to interact with the ionizing radiation reaction products and provide electrical charges proportional to the energy of the ionizing radiation reaction products. In addition electrodes are arranged in connection with the first semiconductor element (101) for providing charge collecting areas (106) for collecting the electrical charges and to provide electrically readable signal proportional to the collected electrical charges. The thickness of the first semiconductor element (101) is adapted to be electrically and / or physically so thin that it is essentially / practically transparent for incident photons, such as background gamma photons.
Owner:RAKKATEC OY
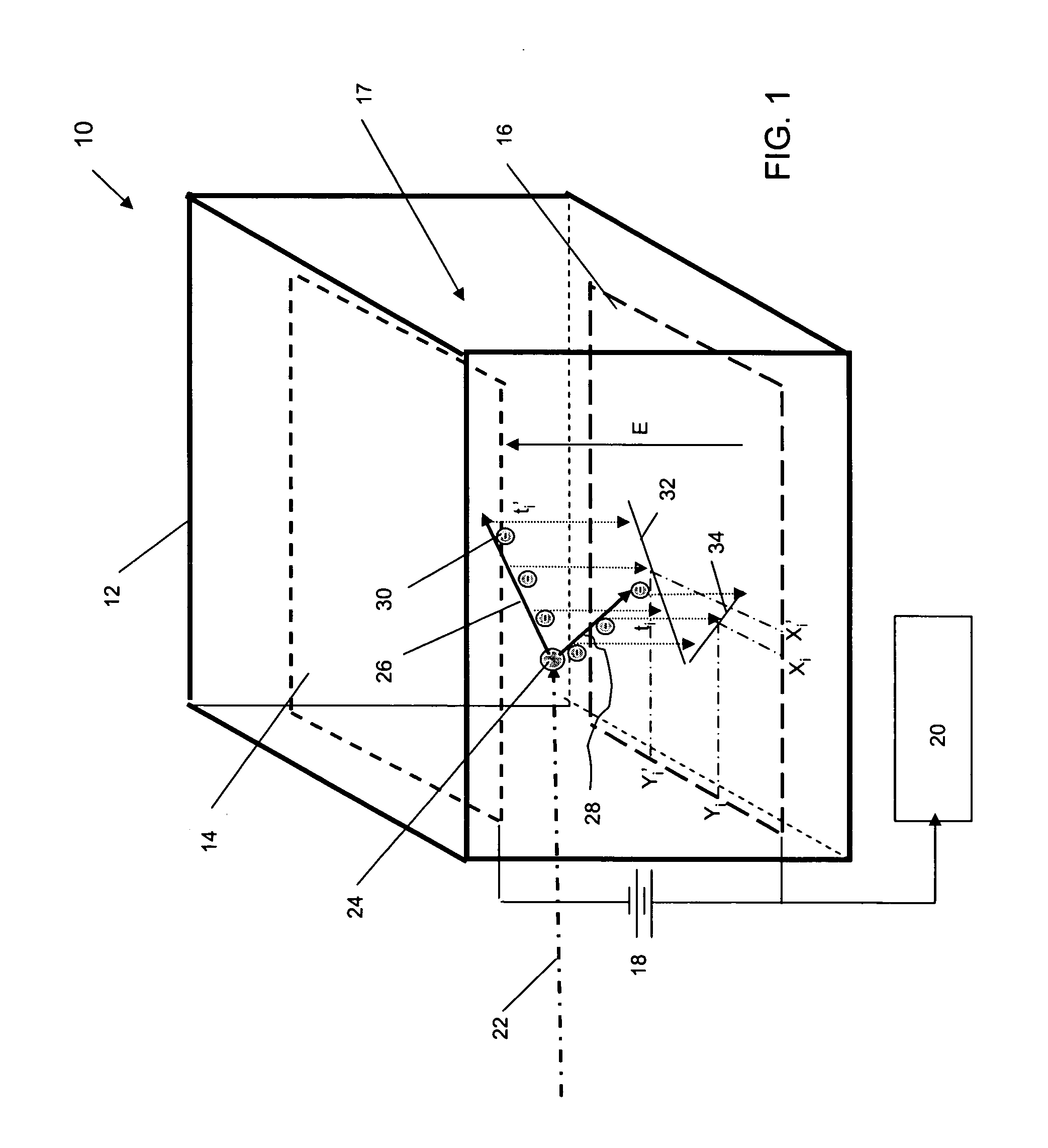
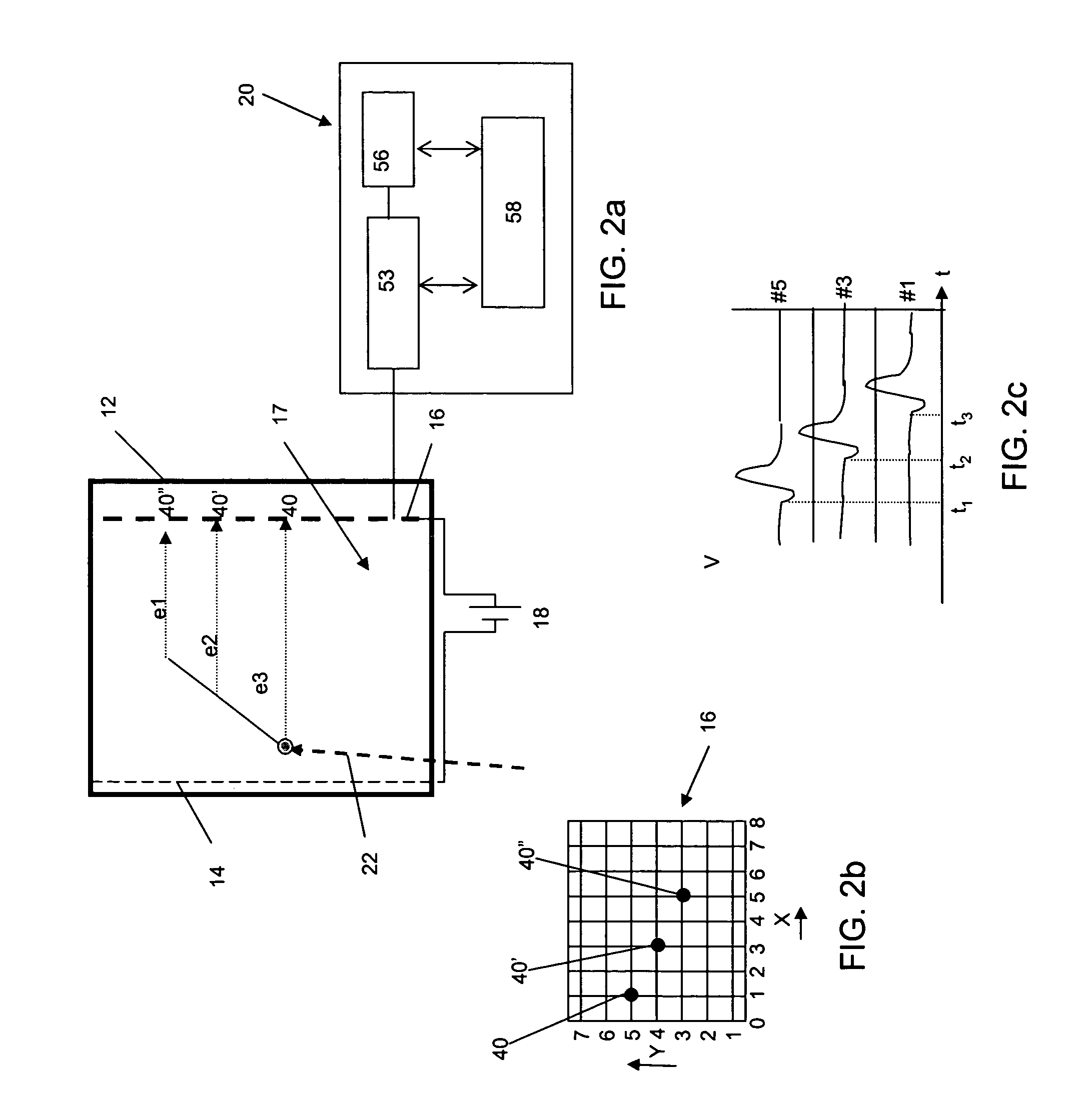
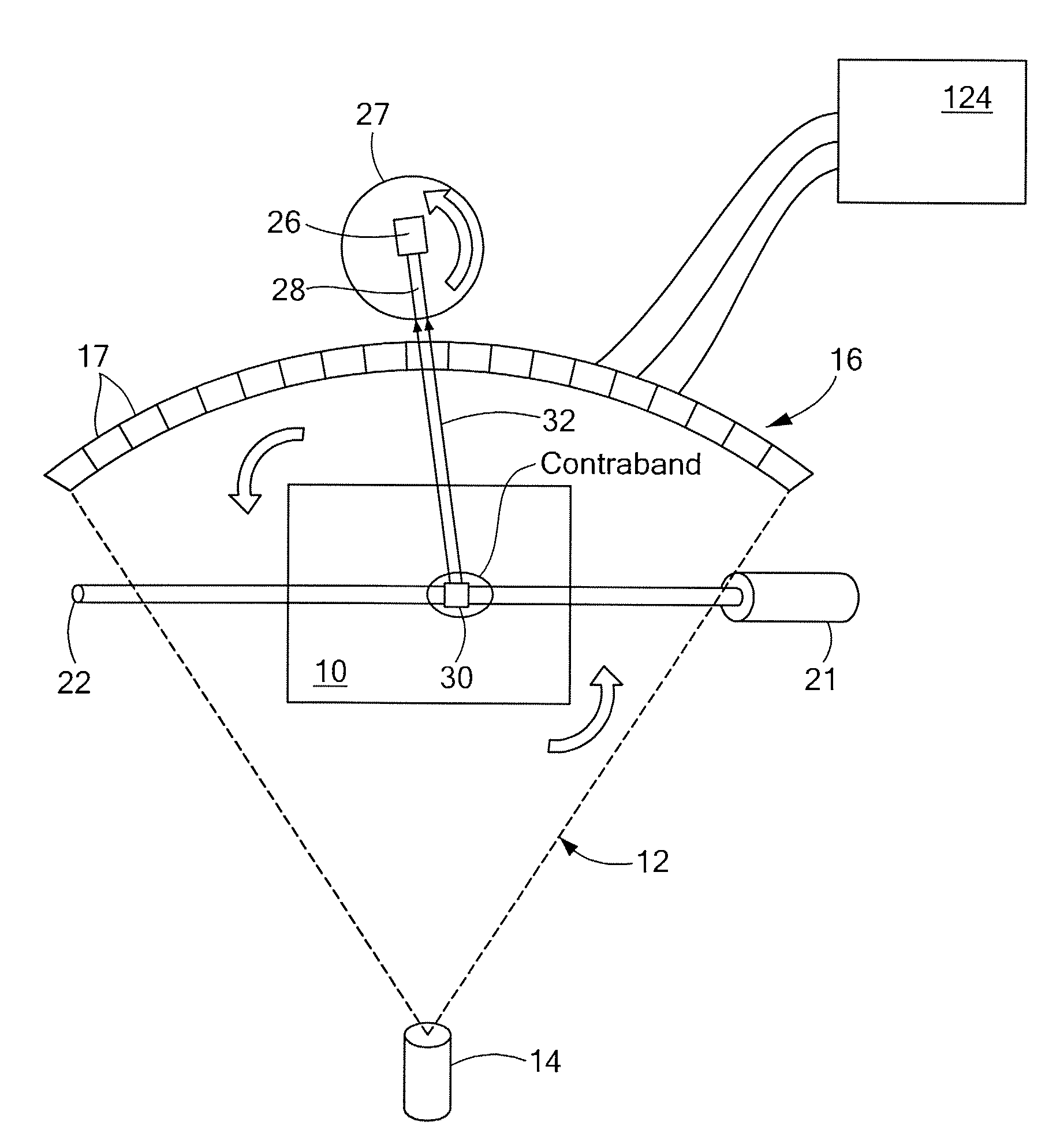
Neutron source detection camera
InactiveUS7049603B2Material analysis by optical meansX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentNeutron emissionMomentum
A neutron imaging method for obtaining an image of the general shape of a neutron emitting source and a bearing of the source relative to an apparatus comprising a chamber comprising a gas with a high probability of interacting with low energy neutrons, releasing collision products that maintain the neutron momentum, and generating ionization particles. The chamber comprises an electrode for providing an electronic signal indicative of the impact location of ionization particles on the electrode and a field to drift the ionization particles to the electrode. A readout indicates the location and time of impact of each ionization particle on the electrode; a memory stores a plurality of the electronic signals; and a computer receives and analyzes the signals and impact times and indicates the location of the source of neutrons by using back projection algorithms to calculate three-dimensional vectors indicative of the neutron path directions.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
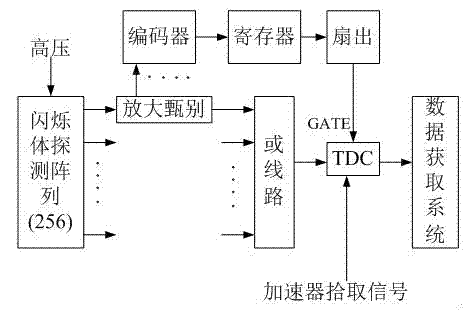
Fast neutron imaging method and system based on time-of-flight method
InactiveCN103245680AIncrease the lengthOvercoming the lack of clarityMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Neutron imaging
The invention relates to a fast neutron imaging technology, and in particular relates to a fast neutron imaging method and system based on a time-of-flight method. The method comprises the steps that: a plurality of scintillant units form a scintillant array to enable the scintillant array to be coupled with a position sensitive detector; the whole coupled detector array is arranged away from a neutron source; a sample is arranged close to the neutron source; the measurement is performed by using the neutron time-of-flight method; interference factors are eliminated by using a conforming method to obtain effective counting on each scintillant unit detector; and the effective counting on each scintillant unit detector is arrayed to obtain a two-dimensional image in which only acting source neutrons acts. The method and the system adopt a detector array design mode, so that the detection efficiency is improved; and the time-of-flight method measurement mode can effectively remove scattered sample neutrons, an environment diffuse scattering background and a gamma background, and a signal-to-noise ratio is increased.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
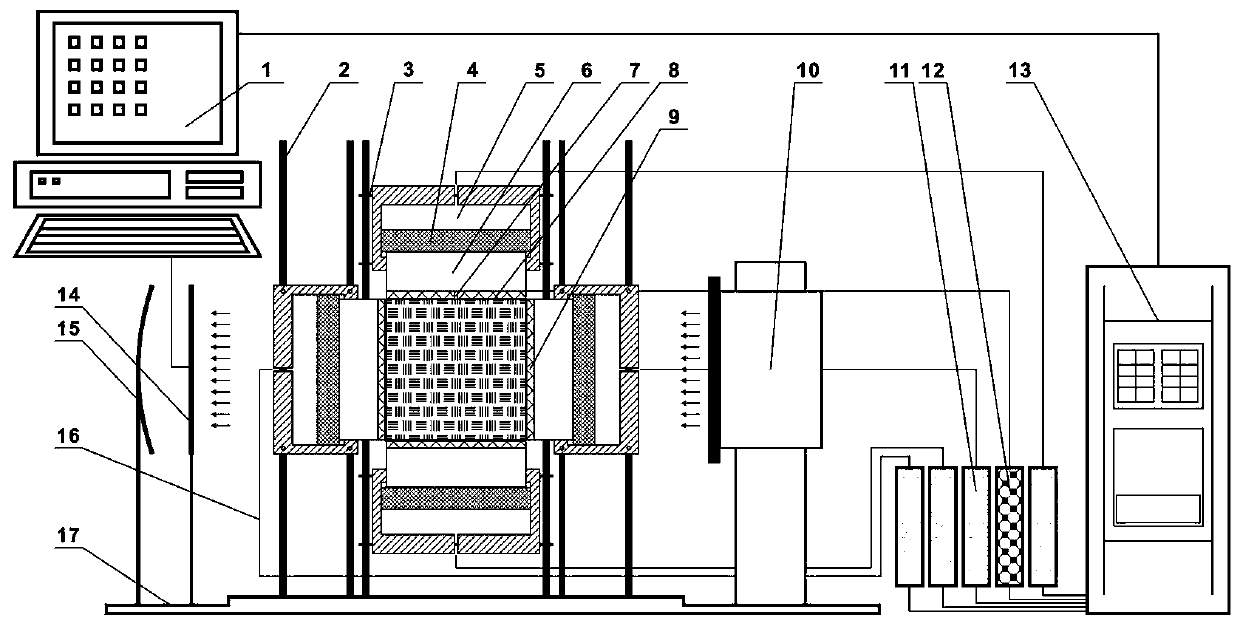
Oil and gas reservoir fracturing crack expansion simulation dynamic monitoring system and method
ActiveCN109827848AOvercoming the disadvantages of real-time monitoring of fracture expansionSolve the problem of dynamic real-time monitoringMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesAcoustic emissionDynamic monitoring
The invention discloses an oil and gas reservoir fracturing crack expansion simulation dynamic monitoring system and method. According to the system and method, a piston is utilized to hydraulically load a rock test piece; and the extension and expansion behavior of a fracturing crack is dynamically monitored by means of the real-time imaging function of a neutron camera system. The neutron camerasystem is introduced into a fracturing physical simulation process, and therefore, the defect that a traditional acoustic emission technology and a fluorescent tracer method fail to realize real-timemonitoring during the expansion research of a fracturing crack, and difficulty in the dynamic real-time monitoring of the extension and expansion of the fracturing crack can be eliminated, and the real-time coordination of rock true triaxial technology and neutron imaging technology is realized. The system and method are of great significance for studying the formation and extension law of the fracturing crack under a true triaxial stress state.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Fast neutron imaging system
ActiveCN109507719AMeet imaging requirementsImprove detection efficiencyMeasurement with scintillation detectorsSilicon photomultiplierElectron multiplication
The invention provides a fast neutron imaging system. The fast neutron imaging system comprises a neutron conversion screen, a mirror, an image detector, an optical adjustment frame, a camera obscura,a shielding module and a computer control system, wherein the neutron conversion screen, the mirror, the image detection and the optical adjustment frame are arranged in the camera obscura, and the shielding module is arranged at one side, facing a neutron beam, of the camera obscura; the neutron conversion screen comprises a neutron-proton conversion layer, a proton energy selection layer, an electron multiplication layer and a fluorescent layer; the image detector adopts a silicon photomultiplier tube array or an image enhancement CCD camera; the optical adjustment frame comprises a first translation stage and a second translation stage; one end of the first translation stage is provided with the mirror, the other end of the first translation stage is connected with a second translationstage, and the second translation stage is provided with the image detector opposite to the mirror; the computer control system remotely controls the movement of the first translation stage and second translation stage. The fast neutron imaging system has the advantages that the structure is simple and compact, and the imaging requirements of different views fields and resolutions can be met.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Small neutron source and preparing method thereof
The invention provides a small neutron source and a preparing method of the small neutron source, and particularly relates to the technical field where field-induced ion emission is adopted to generate neutrons. The small neutron source and the preparing method aim to solve the problems that a traditional neutron source is large in size, inconvenient to use, high in cost, limited in application and the like. According to the neutron source, by means of the characteristic of a small radius of curvature of one-dimensional nanostructured materials like a carbon nano tube, the one-dimensional nanostructured materials like the carbon nano tube are used as a field-induced ion emission electrode. By exerting a voltage on a gate electrode, huge negative electricity field intensity is formed near the tip of one-dimensional structures like CNTs, so that deuterium gas or tritium gas is ionized into ions, the ions are speeded up and bombard target materials rich in deuterium or tritium elements, and therefore the ions are recombined and released. The neutron source is simple in structure, small in size, low in cost, free of influence of radiation, convenient to use and the like, and can be widely applied to neutron imaging, element analysis, instrument adjustment, neutron verification and the like.
Owner:广州市昊志影像科技有限公司
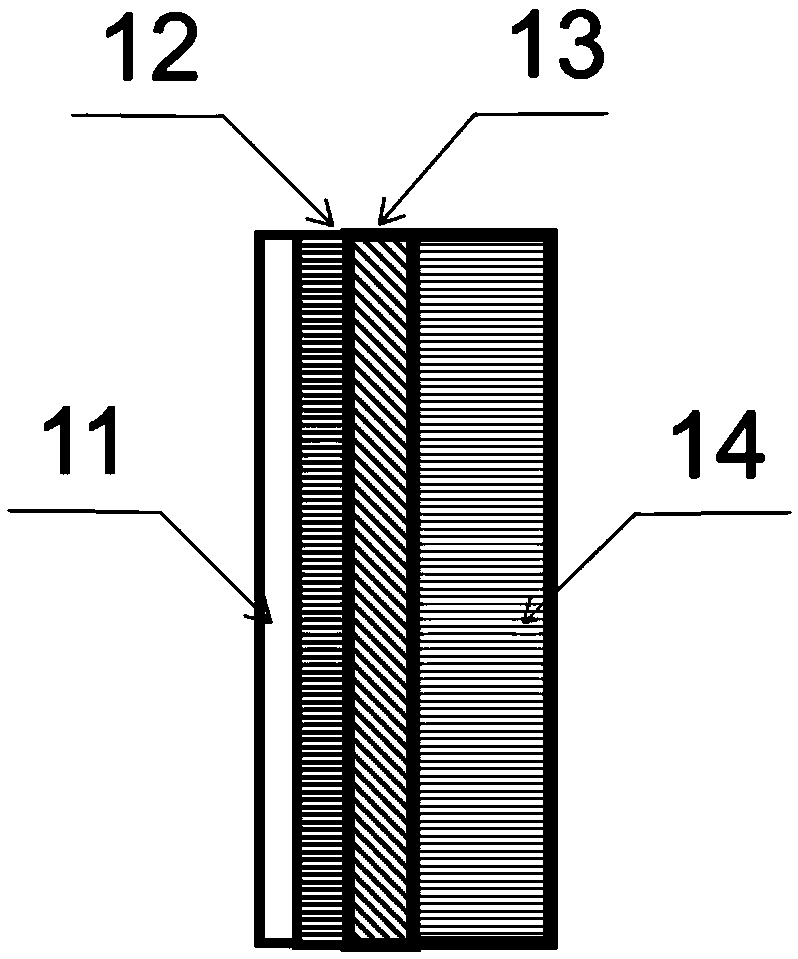
Flicker-wavelength-shifting optical fiber and fast neutron conversion screen
InactiveCN102183812AImprove detection efficiencyHigh resolutionCladded optical fibreMeasurement with scintillation detectorsGeneration processLuminous intensity
The invention discloses a flicker-wavelength-shifting optical fiber and a fast neutron conversion screen, belonging to the field of fast neutron imaging. The optical fiber disclosed by the invention sequentially comprises a core layer, a covering layer and a reflection film from inside to outside, wherein the core layer is a wavelength-shifting optical fiber, the covering layer is a hydrogen-containing organic matter doped with fluorescent powder, and the wavelength-shifting optical fiber of the core layer can absorb light emitted by the fluorescent powder of the covering layer and emit secondary photons. In the fast neutron conversion screen disclosed by the invention, a screen surface is formed by a plurality of sections of optical fiber end faces obtained by arraying optical fibers with equal lengths. Compared with the prior art, the invention ensures that the thickness of the conversion screen can be greatly improved, fast neutron detection efficiency can be increased by over 10 times compared with the common ZnS screen; and the reflection film on the outer layer can enhance the light-emitting strength of the conversion screen and effectively increase the resolution rate of the conversion screen. The invention has a matured generation process and can realize commercialized volume production.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
X-ray and neutron imaging
An x-ray or neutron apparatus for the transmission of x-ray or neutron images is described, which includes x-ray- or neutron-three-dimensional (3-D) arrays or mosaics, including a plurality of x-ray or neutron lenses positioned so that they form a two-dimensional (2-D) mosaic of compound refractive lenses to provide a plurality of separate x-ray or neutron paths between an object and an image at an x-ray- or neutron-detector. The apparatus is so constructed that it permits separate parts of an object to be imaged such that a total composite image is formed from these various parts. An imaging apparatus of the detection of carcinoma in breast tissue is formed using such an apparatus. Methods of microscopy and imaging are obtained using this apparatus.
Owner:ADELPHI TECH INC
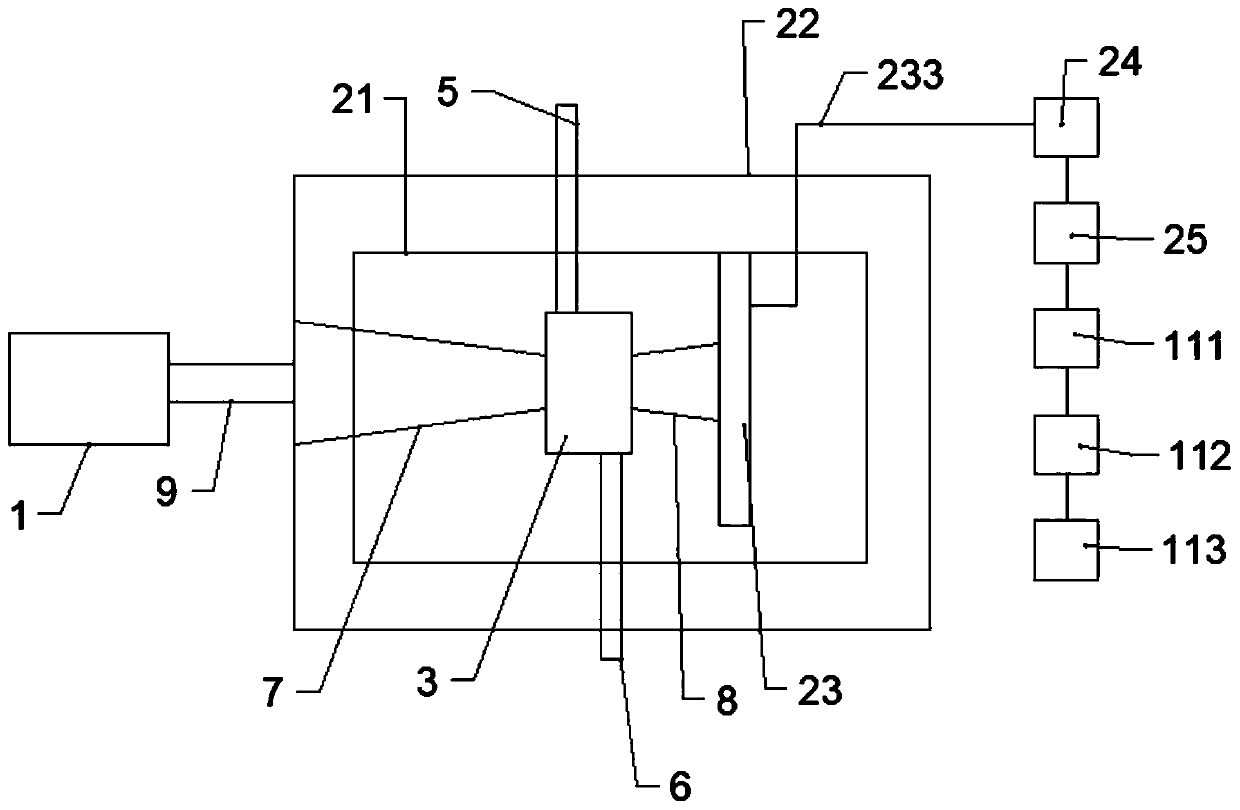
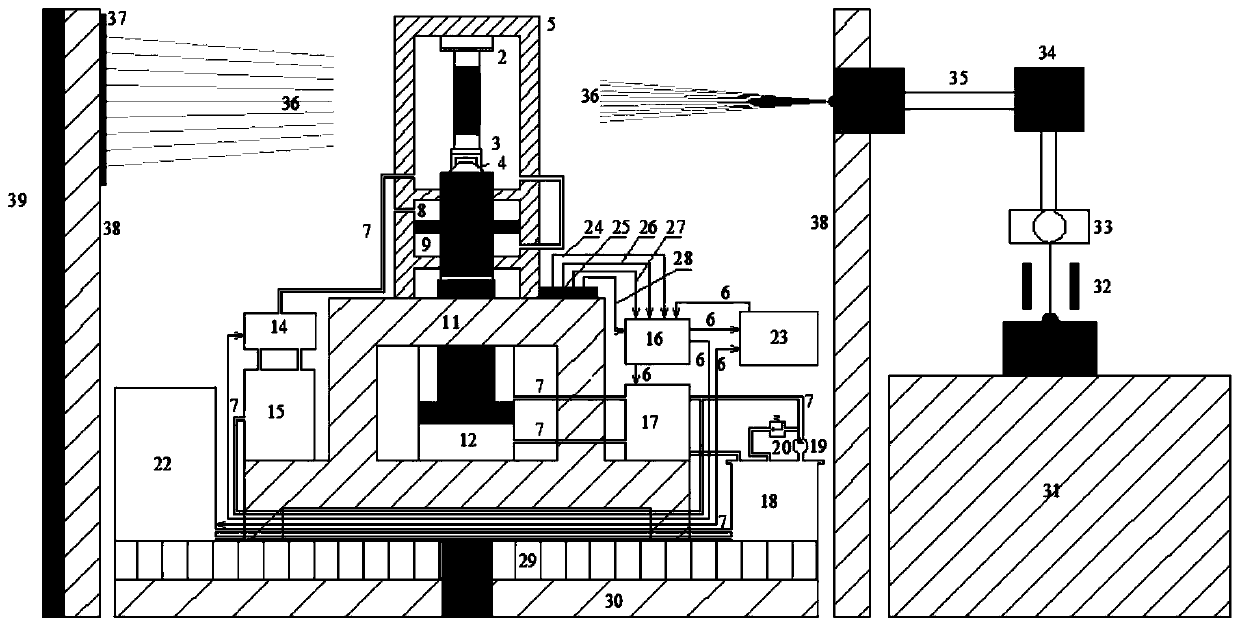
Neutron generation equipment, neutron imaging equipment and imaging method
The invention discloses neutron generation equipment, neutron imaging equipment and an imaging method. The equipment comprises neutron generation equipment, a neutron detector, a data acquisition circuit and data processing equipment, wherein the neutron generation equipment is used for generating continuous energy spectrum neutron beams; the neutron detector is used for receiving neutron beams which penetrate through a checked object and used for obtaining electric signals; the data acquisition circuit is coupled with the neutron detector and is used for converting the electric signals into digital signals; the data processing equipment is coupled with the data acquisition circuit and used for obtaining images of the checked object in different energy spectrum neutrons on the basis of the digital signals. By adopting the scheme, the continuous energy spectrum neutron beams can be generated, so that images of the checked object in different energy neutrons can be obtained by using a time-of-flight method, and the detection sensitivity can be improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
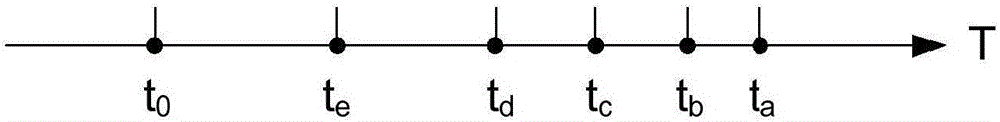
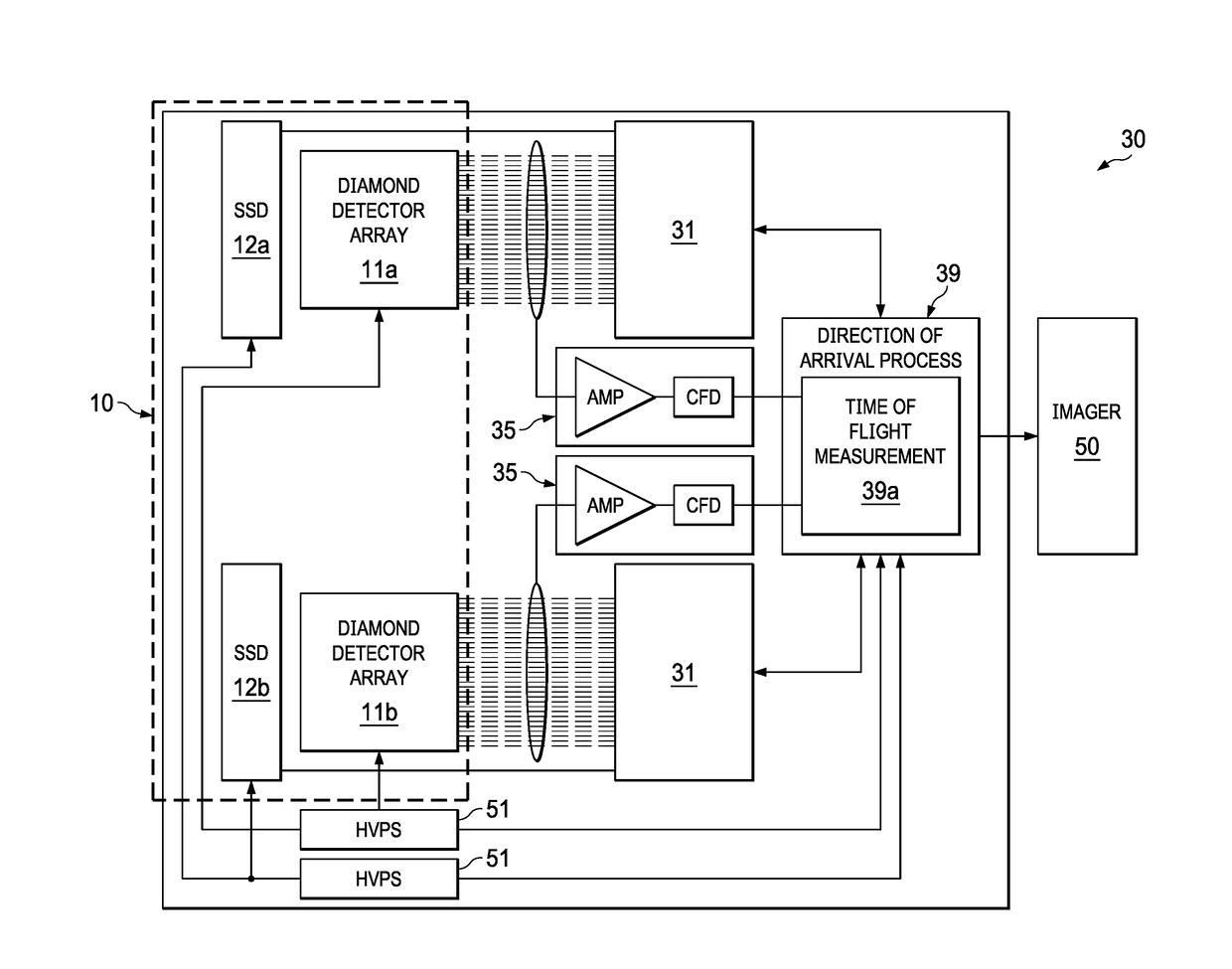
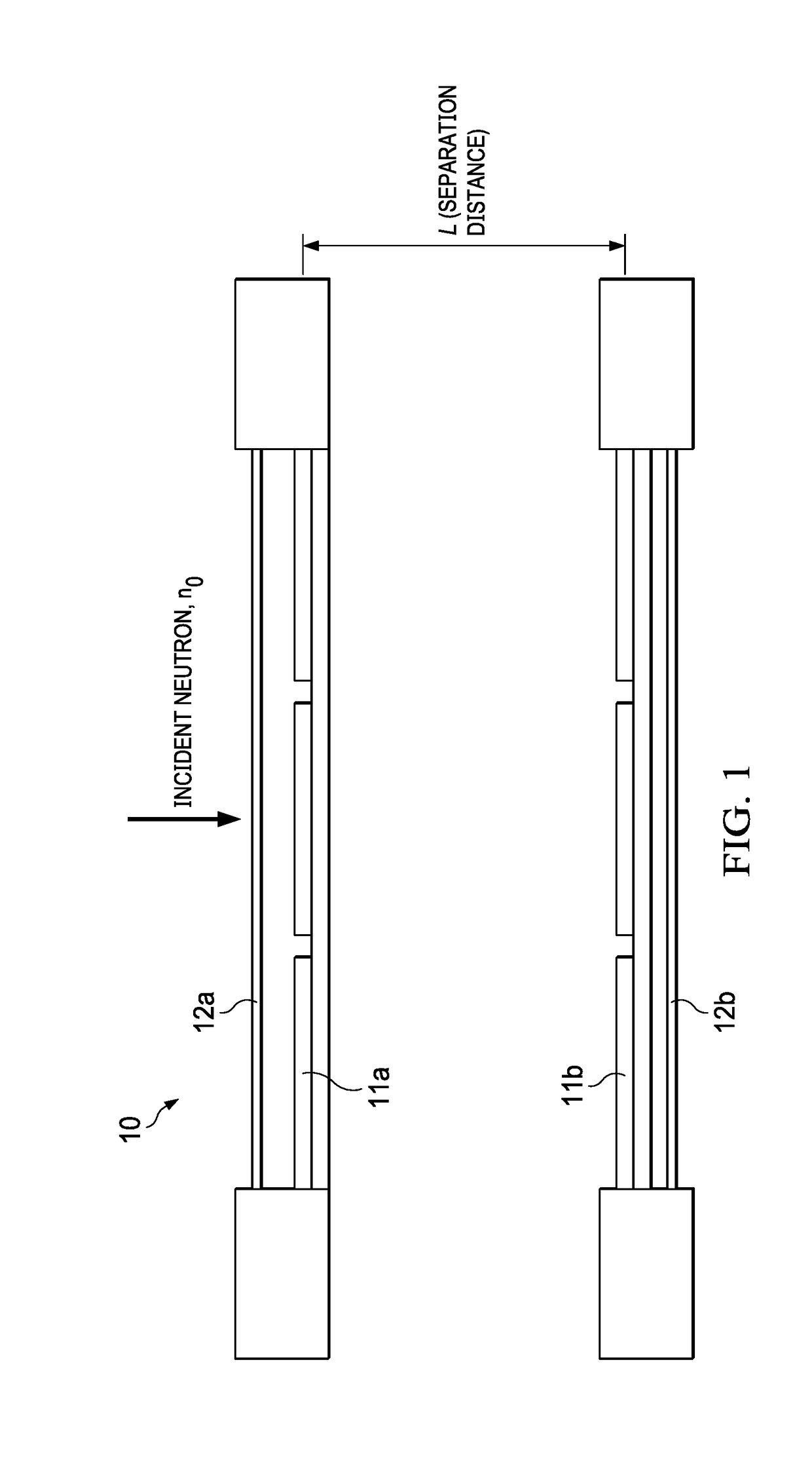
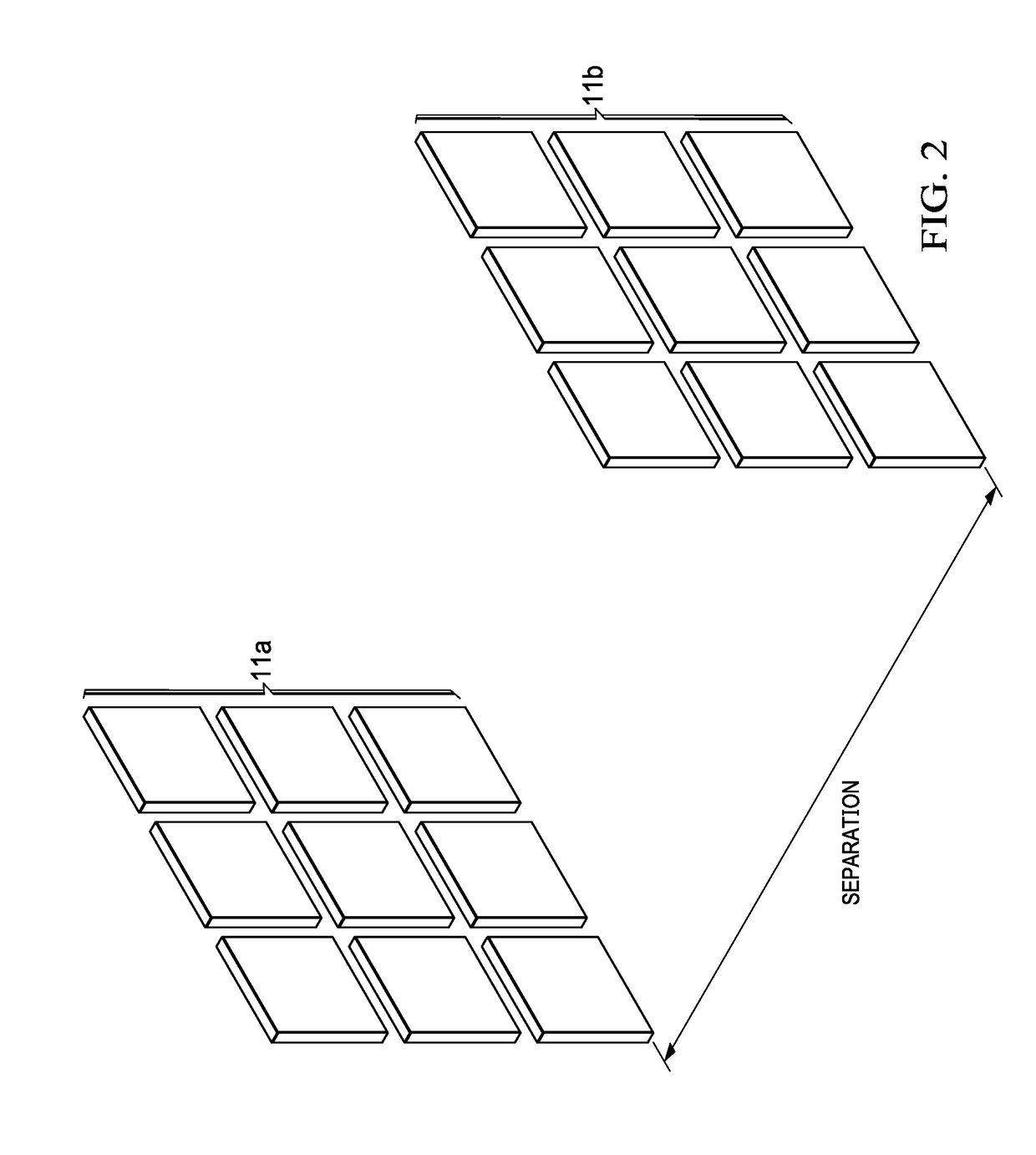
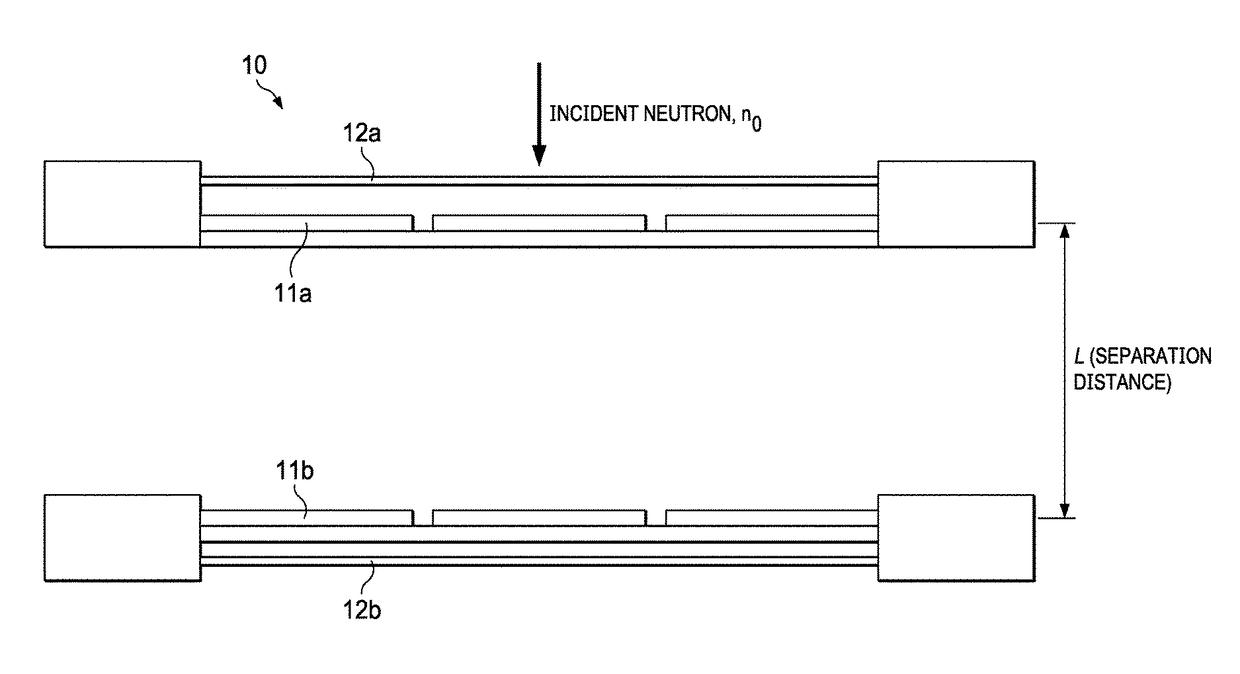
Neutron Imager With Spaced Diamond Detector Arrays
ActiveUS20180120460A1Measurement with semiconductor devicesMeasurement by spectrometryPulse heightNeutron imaging
A neutron detector system, with a detector having a pair of spaced diamond detector layers, sandwiched between outer silicon layers. In response to incident neutrons, the detector system measures pulse heights and response times, and from those measurements, calculates the carbon recoil energy and time of flight of scattered neutrons. This data is further used to calculate a “direction cone”, which represents the approximate angle of arrival of the incident neutron. These direction cones can be used to image neutron events.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
High-safety neutron detection device
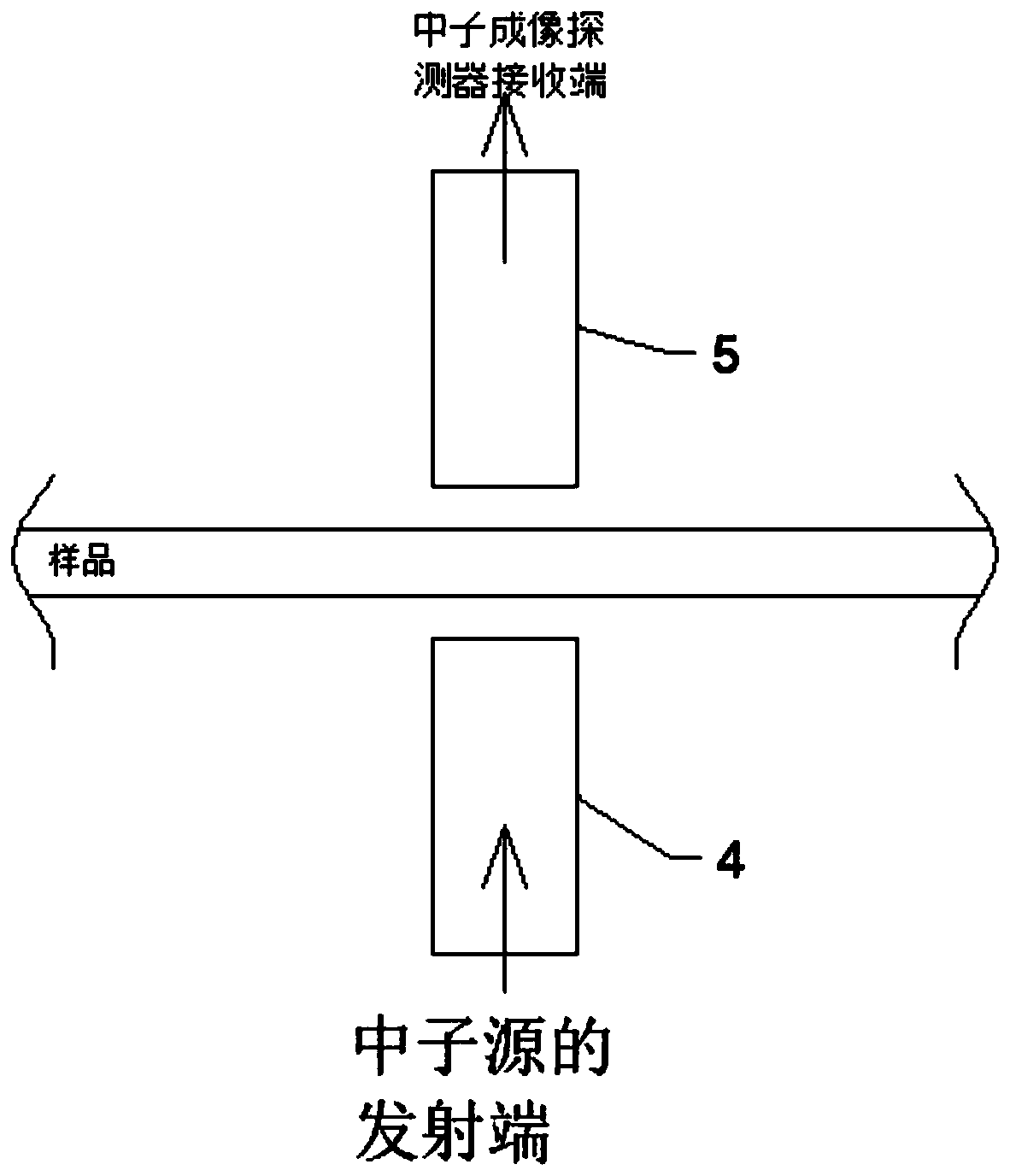
PendingCN109884096AImprove securityMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationNeutron emissionNeutron imaging
The invention discloses a high-safety neutron detecting device. The high-safety neutron detecting device comprises a neutron emission source, a neutron shielding box, a sample receiving box, and a neutron imaging detector; the sample receiving box is arranged inside the neutron shielding box; an upper end of the sample receiving box is connected with a liquid adding tube, and a lower end of the sample receiving box is connected with a liquid discharging tube; the sample receiving box is spaced from the inner side wall of the neutron shielding box; a radiation shielding medium is filled betweenthe neutron shielding box and the sample receiving box; the left side of the sample receiving box is provided with a neutron incident tube; the right end of the neutron incident tube is connected tothe outer wall of the sample receiving box, and the left end of the neutron incident tube is passed out from the left side wall of the neutron shielding box; a neutron exit tube is arranged on the right side of the sample receiving box; the left end of the neutron exit tube is connected to the outer wall of the sample receiving box, and the right end of the neutron exit tube is passed out from theright side wall of the neutron shielding box; the neutron emission source is connected to the left end of the neutron incident tube; and the neutron imaging detector is connected to the right end ofthe neutron exit tube.
Owner:广东太微加速器有限公司
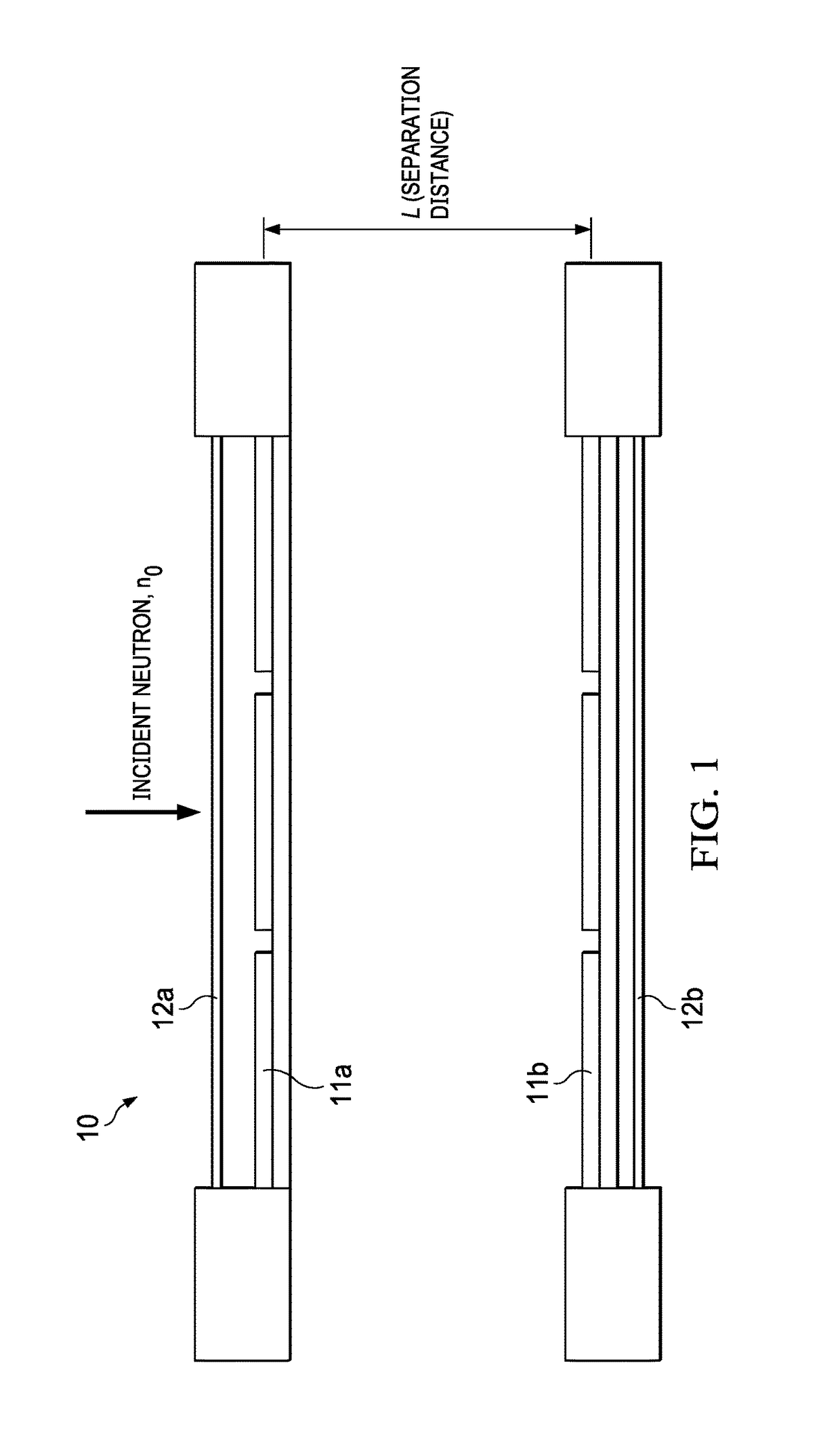
Neutron imager with spaced diamond detector arrays
ActiveUS9958560B1Measurement with semiconductor devicesMeasurement by spectrometryPulse heightNeutron imaging
A neutron detector system, with a detector having a pair of spaced diamond detector layers, sandwiched between outer silicon layers. In response to incident neutrons, the detector system measures pulse heights and response times, and from those measurements, calculates the carbon recoil energy and time of flight of scattered neutrons. This data is further used to calculate a “direction cone”, which represents the approximate angle of arrival of the incident neutron. These direction cones can be used to image neutron events.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Neutron detector with neutron converter, method for manufacturing the neutron detector and neutron imaging apparatus
InactiveUS8263940B2Mitigate such drawbackEfficient detectionMeasurement with semiconductor devicesVacuum evaporation coatingNeutron converterElectricity
A detector for detecting neutrons includes a neutron reactive material interacting with neutrons to be detected and releasing ionizing radiation reaction products in relation to the interactions. It also includes a first semiconductor element being coupled with the neutron reactive material and adapted to interact with the ionizing radiation reaction products and provide electrical charges proportional to the energy of the ionizing radiation reaction products. In addition electrodes are arranged in connection with the first semiconductor element for providing charge collecting areas for collecting the electrical charges and to provide electrically readable signal proportional to the collected electrical charges. In the detector the neutron reactive material is arranged so that the incident neutrons to be detected interact with the neutron reactive material essentially in the portion nearest to the charge collecting areas provided by the electrodes in the first semiconductor element to which the neutron reactive material is coupled with.
Owner:FINPHYS
Neutron detection device capable of realizing accurate detection
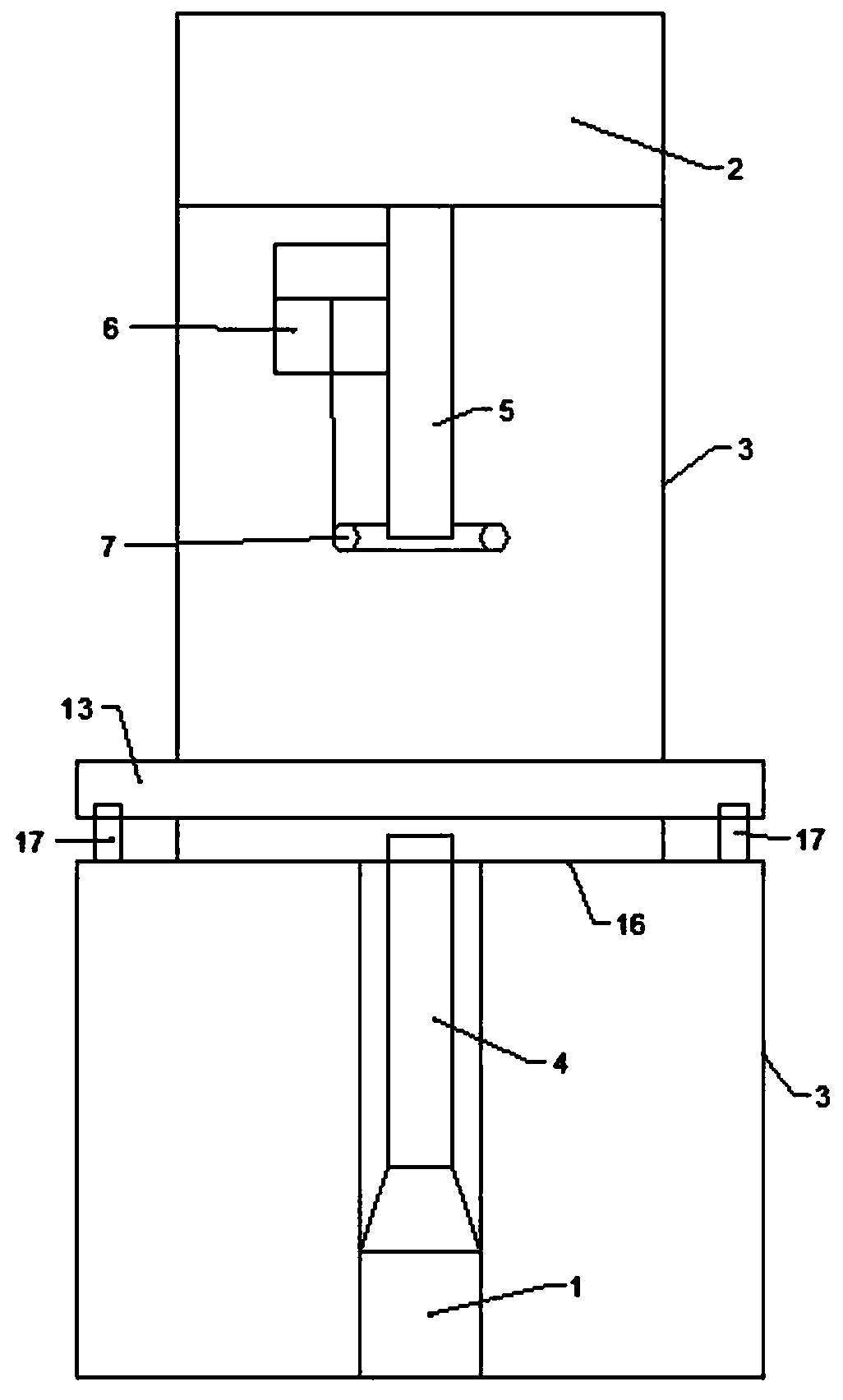
PendingCN109884095APlay the role of confining the neutron beamReduce the impactMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationNeutron emissionNeutron imaging
The invention discloses a neutron detection device capable of realizing accurate detection. The neutron detection device comprises a neutron emission source, a sample placement frame and a neutron imaging detector; the neutron imaging detector is arranged above the neutron emission source; the sample placement frame is arranged between the neutron emission source and the neutron imaging detector;the neutron detection device further comprises a rack; the neutron emission source, the sample placement rack and the neutron imaging detector are arranged on the rack; a first shielding tube is vertically arranged on an emission hole of the neutron emission source; a second shielding tube is vertically arranged on an incidence hole of the neutron imaging detector; the first shielding tube and thesecond shielding tube are arranged in an up-and-down telescopic mode; a marking mechanism is arranged on the second shielding tube; the marking mechanism comprises a driving air cylinder and a pressing ring; the pressing ring and the second shielding tube are coaxially and radially arranged at intervals; the driving air cylinder is fixedly connected to the second shielding tube; the driving air cylinder can drive the pressing ring to move up and down; the outer surface of the pressing ring is coated with a layer of sponge soaked with ink; and the sample placement frame can be adjusted in position in the front-back direction and the left-right direction.
Owner:广东太微加速器有限公司
Neutron imaging method for natural gas hydrate sediment triaxial mechanical test
PendingCN110567814AIncrease cold neutron contentRealize digital image outputMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesResponse processImage resolution
The invention provides a method capable of carrying out high-precision imaging on an internal structure of a natural gas hydrate sediment triaxial mechanical test. The method is characterized in thatthe distinction degree of natural gas hydrate, natural gas and water molecules is enhanced, the imaging resolution of the internal structure of natural gas hydrate sediment is improved and high-precision imaging of the structure in the natural gas hydrate triaxial mechanical test process is achieved by reducing the energy of neutron beams and improving the mass attenuation coefficient of neutron beams based on the fact that the molecular structure size of hydrate is close to the wavelength of cold neutrons. By means of the method, the creep and relaxation rules in the natural gas hydrate sample forming and decomposing process can be obtained, and the dynamic response process of reservoir stability after natural gas hydrate development can be known easily. The method is characterized in that the distinction degree of natural gas hydrate, natural gas and water molecules is enhanced, the imaging resolution is improved and high-precision imaging of the natural gas hydrate dynamic gatheringand dispersing process is realized by reducing the energy of neutron beams and improving the mass attenuation coefficient of neutron beams based on the fact that the molecular structure size of hydrate is close to the wavelength of cold neutrons.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Neutron detector and neutron image sensor
InactiveCN101171530AHigh detection sensitivityImprove time resolutionMeasurement with semiconductor devicesSuperconductor devicesElectricityNeutron imaging
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
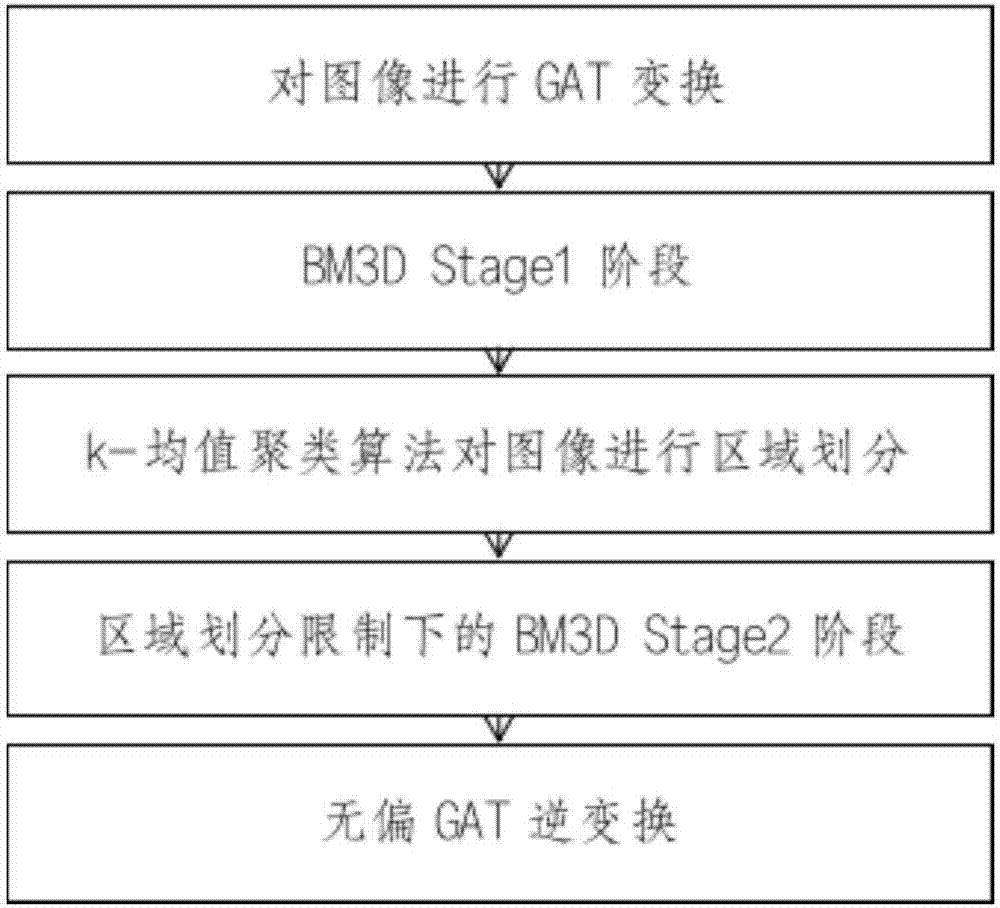
Image restoration method suitable for neutron imaging system image and based on Gauss-Poisson hybrid noise model
InactiveCN107169932ATroubleshoot bad matchesPreserve edge featuresImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMixed noise
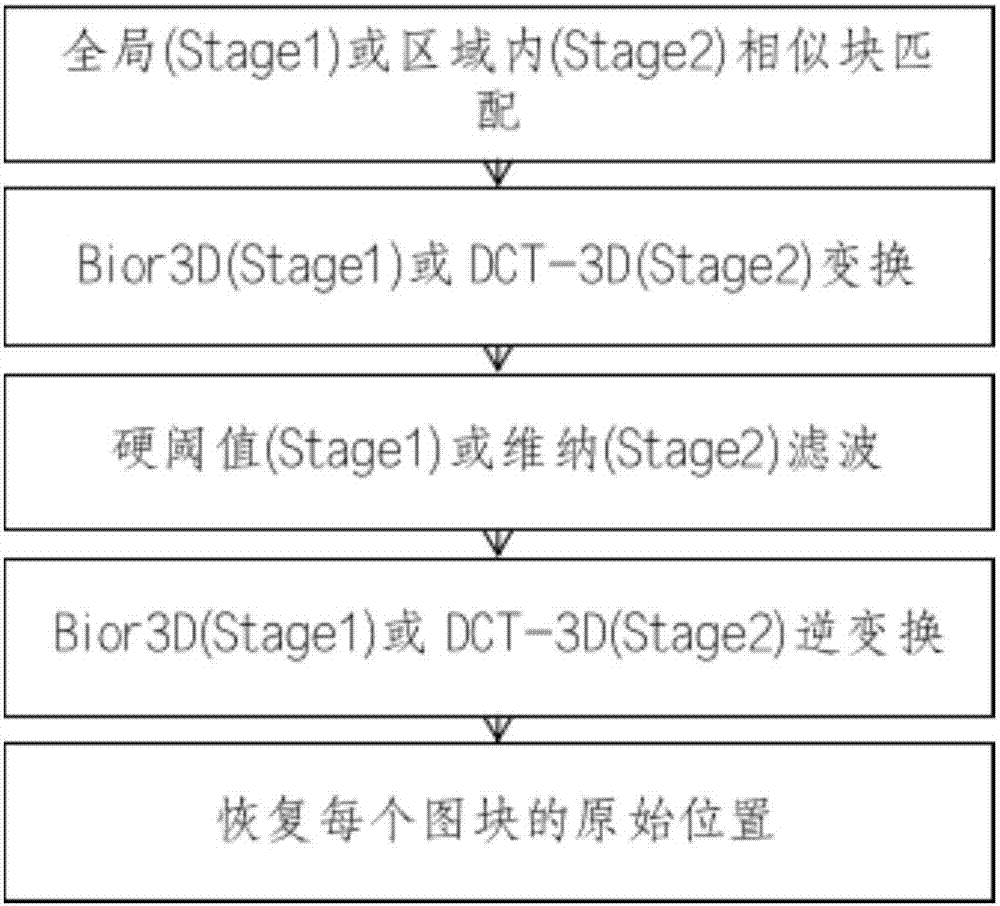
The invention discloses an image restoration method suitable for a neutron imaging system image and based on a Gauss-Poisson hybrid noise model. According to the method, an image with Gauss-Poisson hybrid noise is transformed into a Gaussian white noise image through GAT transformation, a regional limitation BM3D algorithm is used to process the image obtained after transformation, and then unbiased GAT inverse transformation is performed on the obtained image to obtain a final de-noised image. Through the method, a Lloyd algorithm is used to perform regional division on the image, similar blocks of BM3D Stage2 are matched and limited in the same region, and the problems that through a traditional BM3D method, when Gaussian noise variance is large, object edge information is seriously lost in a filtering process, and an object edge in an image after de-noising is fuzzy are solved. Compared with a traditional BM3D algorithm, through the de-noising method, a restored image, with a better visual effect, of an image subjected to strong Gauss-Poisson hybrid noise interference can be obtained, object edge information is reserved more completely, and a higher PSNR value is obtained.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
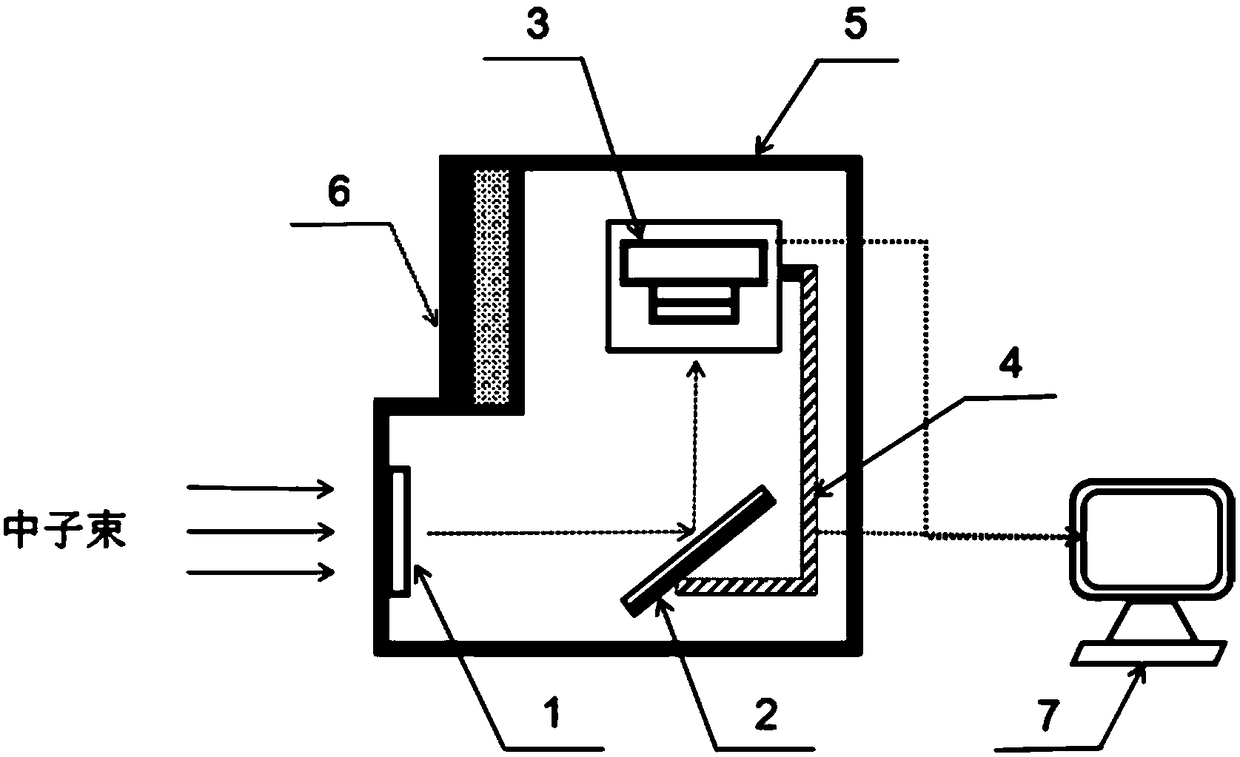
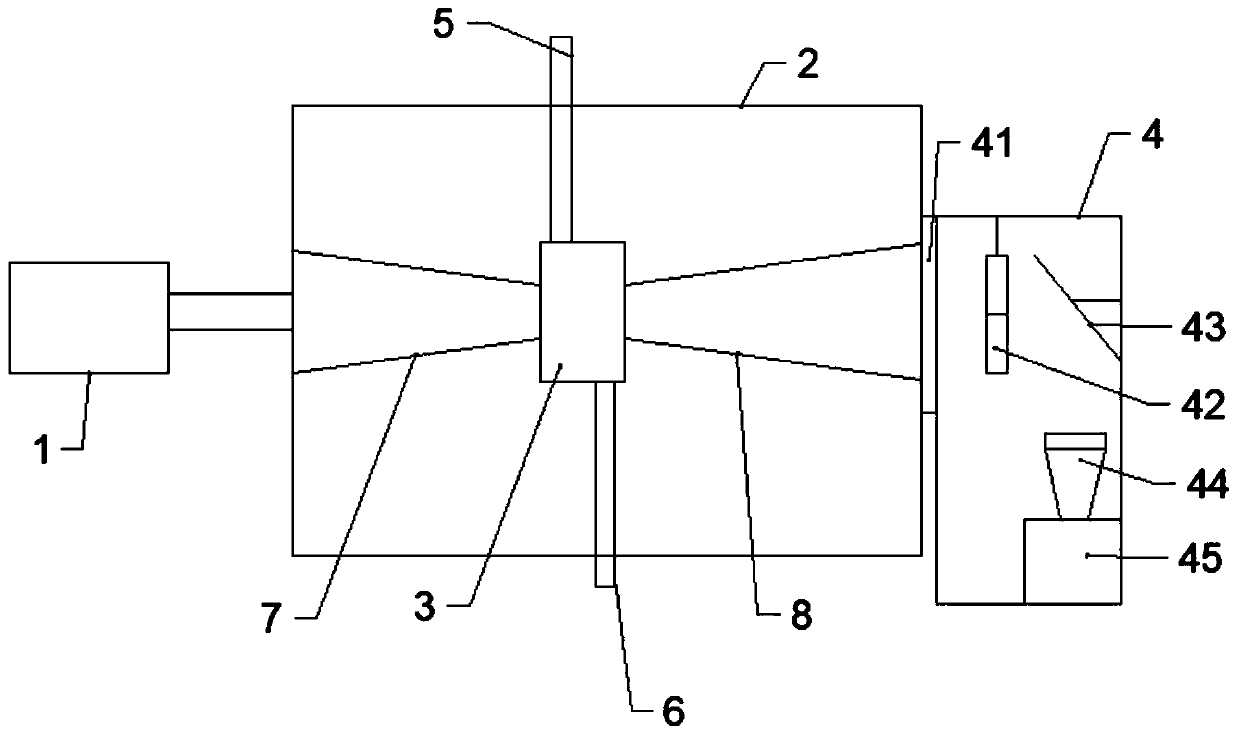
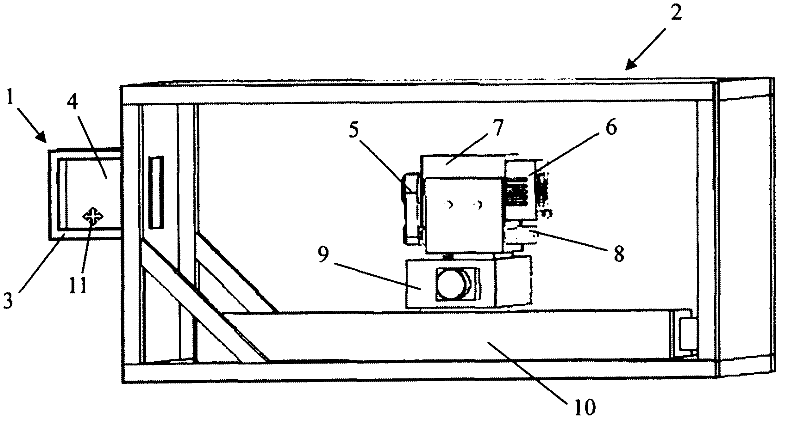
High-speed neutron photographing device
ActiveCN102243433AGuaranteed self-adjusting measurementsSimplify the shield structureHigh-speed photographyFocusing aidsCamera lensCMOS
The invention relates to a neutron imaging technology, in particular to a high-speed neutron photographing device which structurally comprises a neutron conversion cavity and a detection cavity, wherein the neutron conversion cavity is provided with a scintillation screen for converting a neutron image into a visible image, and a plane mirror for refracting visible light to the detection cavity is arranged at the rear side of the scintillation screen; the detection cavity is internally provided with a lens and a high-speed CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Transistor) camera; the lens and the high-speed CMOS camera are wholly arranged in a shielding lead box, the lens faces to a visible light incident direction, and a translation platform capable of driving the lens and the high-speed CMOS camera to move wholly is arranged in the detection cavity. The high-speed neutron photographing device provided by the invention can respond to different view field ranges and resolution requirements and can be used for performing automatic focusing on different object distances so as to guarantee automatic regulation and measurement of online belts.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com