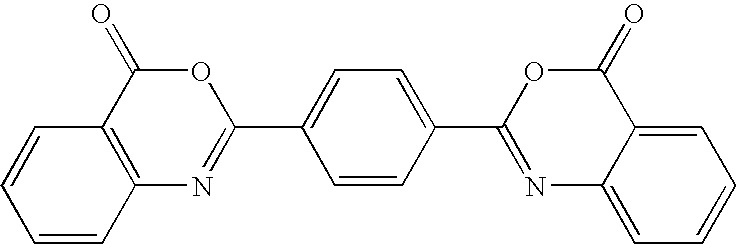
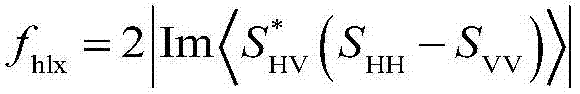Patents
Literature
107 results about "Diffuse scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diffuse scattering is the scattering that arises from any departure of the material structure from that of a perfectly regular lattice. One can think of it as the signal that arises from disordered structures, and it appears in experimental data as scattering spread over a wide q-range (diffuse).
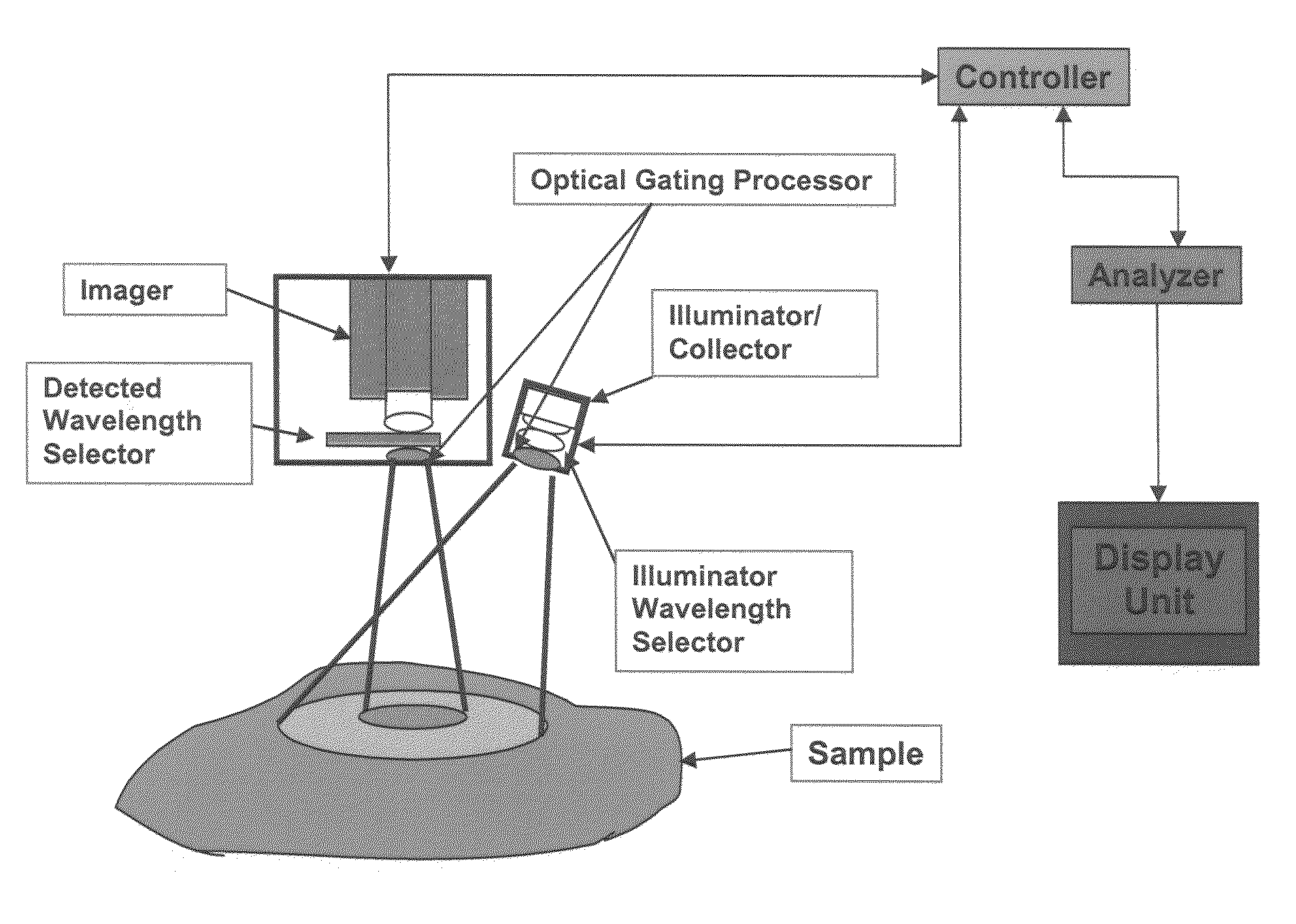
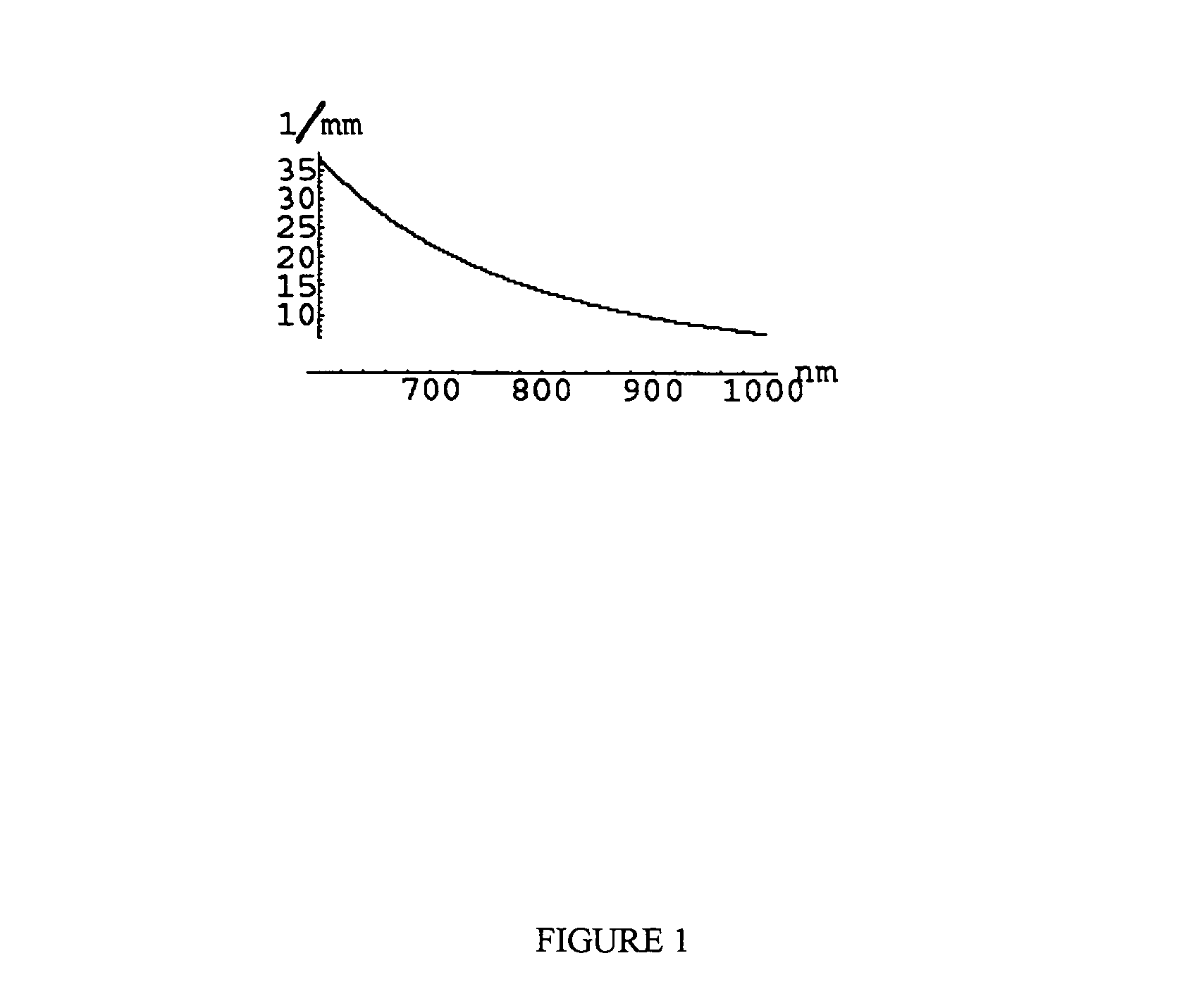
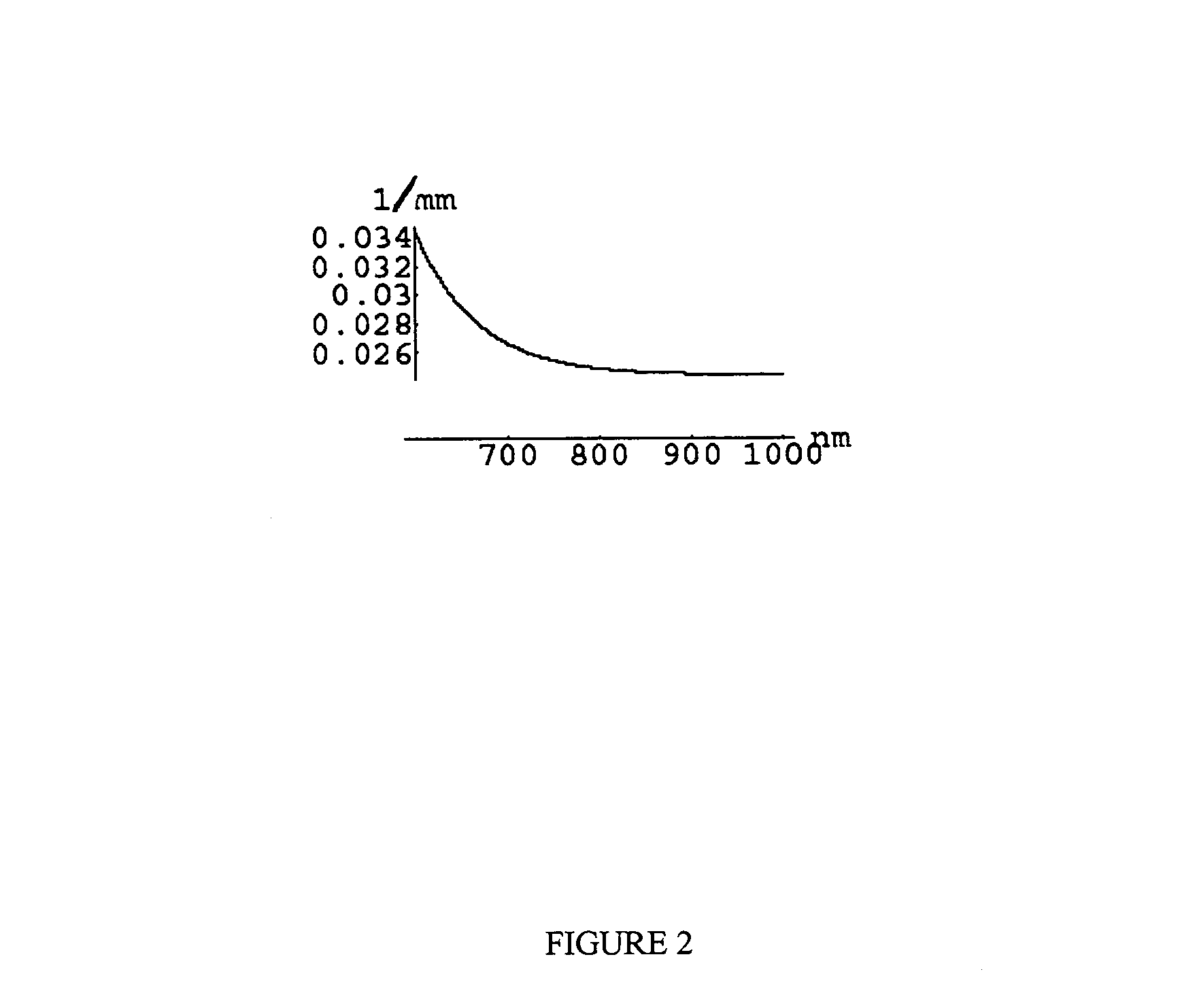
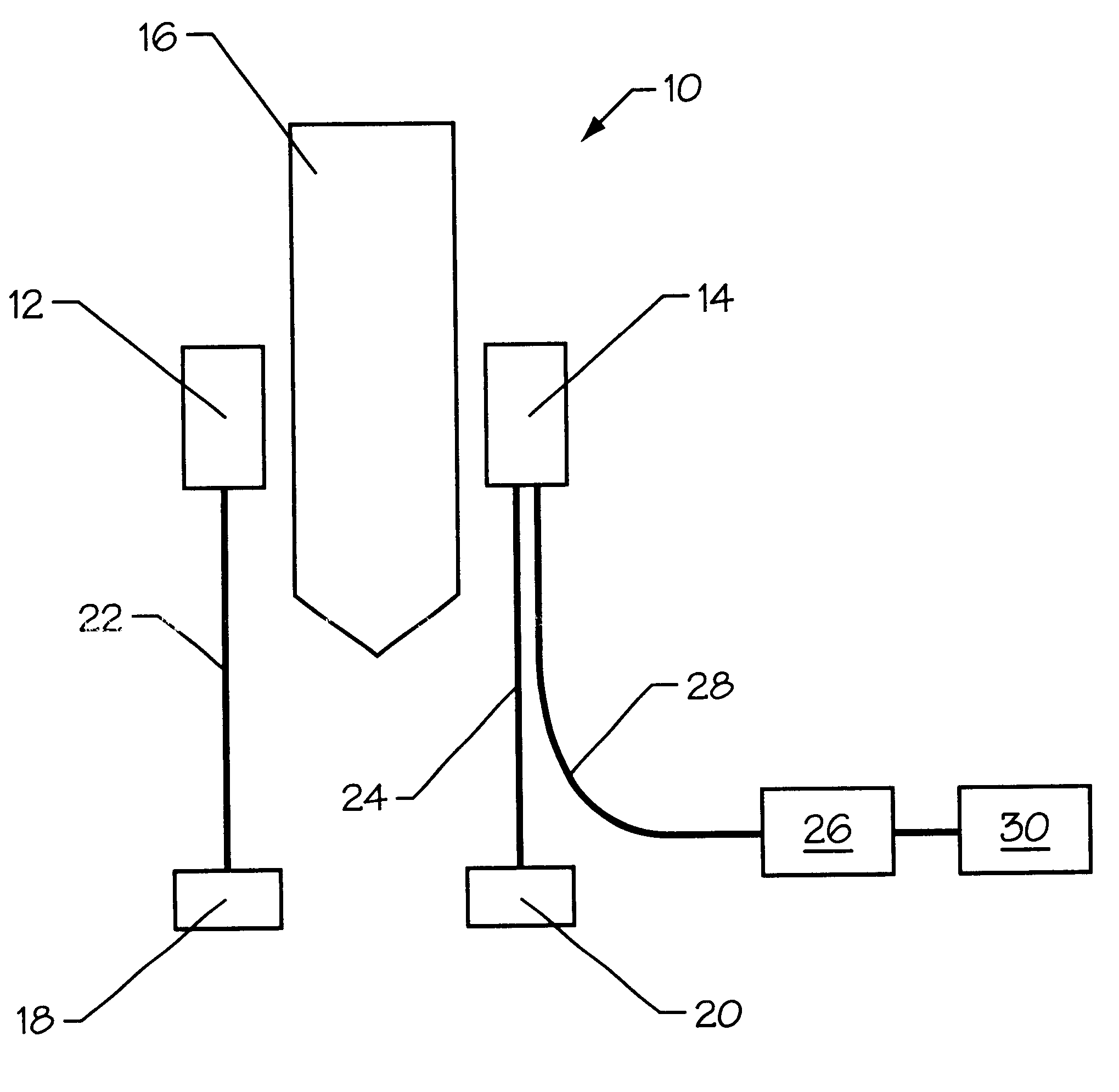
Multispectral imaging for quantitative contrast of functional and structural features of layers inside optically dense media such as tissue
InactiveUS20050273011A1Easy to measureImprove analysisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTelevision system detailsCalorescenceWavelength
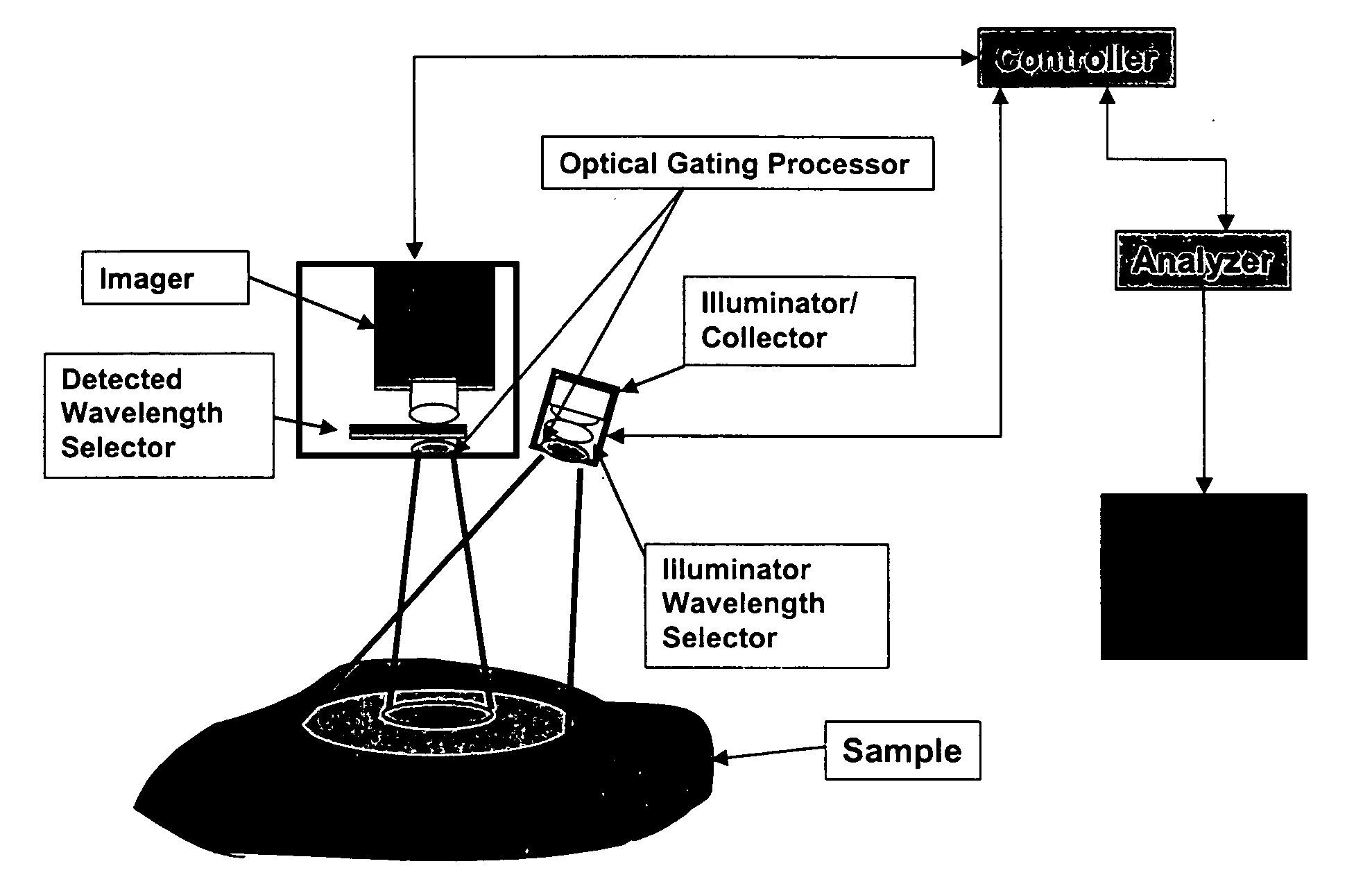
A method for the evaluation of target media parameters in the visible and near infrared is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a light source, an illuminator / collector, optional illumination wavelength selector, an optional light gating processor, an imager, detected wavelength selector, controller, analyzer and a display unit. The apparatus illuminates an in situ sample of the target media in the visible through near infrared spectral region using multiple wavelengths and gated light. The sample absorbs some of the light while a large portion of the light is diffusely scattered within the sample. Scattering disperses the light in all directions. A fraction of the deeply penetrating scattered light exits the sample and may be detected in an imaging fashion using wavelength selection and an optical imaging system. The method extends the dynamic range of the optical imager by extracting additional information from the detected light that is used to provide reconstructed contrast of smaller concentrations of chromophores. The light detected from tissue contains unique spectral information related to various components of the tissue. Using a reiterative calibration method, the acquired spectra and images are analyzed and displayed in near real time in such a manner as to characterize functional and structural information of the target tissue.
Owner:APOGEE BIODIMENSIONS
Image registration system and method
InactiveUS6658282B1Reassembled accuratelyMotion compensationSurgical instrument detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringLight spotReference image
An apparatus for registering a series of video images of a spherical or quasi-spherical surface subject to movement relies on projecting at least four diffusely scattering spots of light on the surface in a preferred angular manner, and monitoring the movement of images of the light spots relative to a reference image of the light spots.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Piezoelectric/electrostrictive ceramics sintered body and method of calculating diffuse scattering intensity ratio
InactiveUS20100019624A1Easy accessPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSymmetry reductionLattice plane
An alkali niobate-based piezoelectric / electrostrictive ceramics sintered body including, as a main crystal phase, a perovskite type oxide containing at least one type of element selected from the group consisting of Li, Na and K as A site constituent elements and at least one type of element selected from the group consisting of Nb and Ta as B site constituent elements. The number of lattice-strained layers of the piezoelectric / electrostrictive ceramics sintered body is preferably small. A diffuse scattering intensity ratio, which is a ratio of an intensity of diffuse scattering by a lattice-strained layer present near a domain wall to a sum of an X-ray diffraction intensity of a first lattice plane and that of a second lattice plane different in interplanar spacing from the first lattice plane due to crystallographic symmetry reduction is preferably 0.5 or lower.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
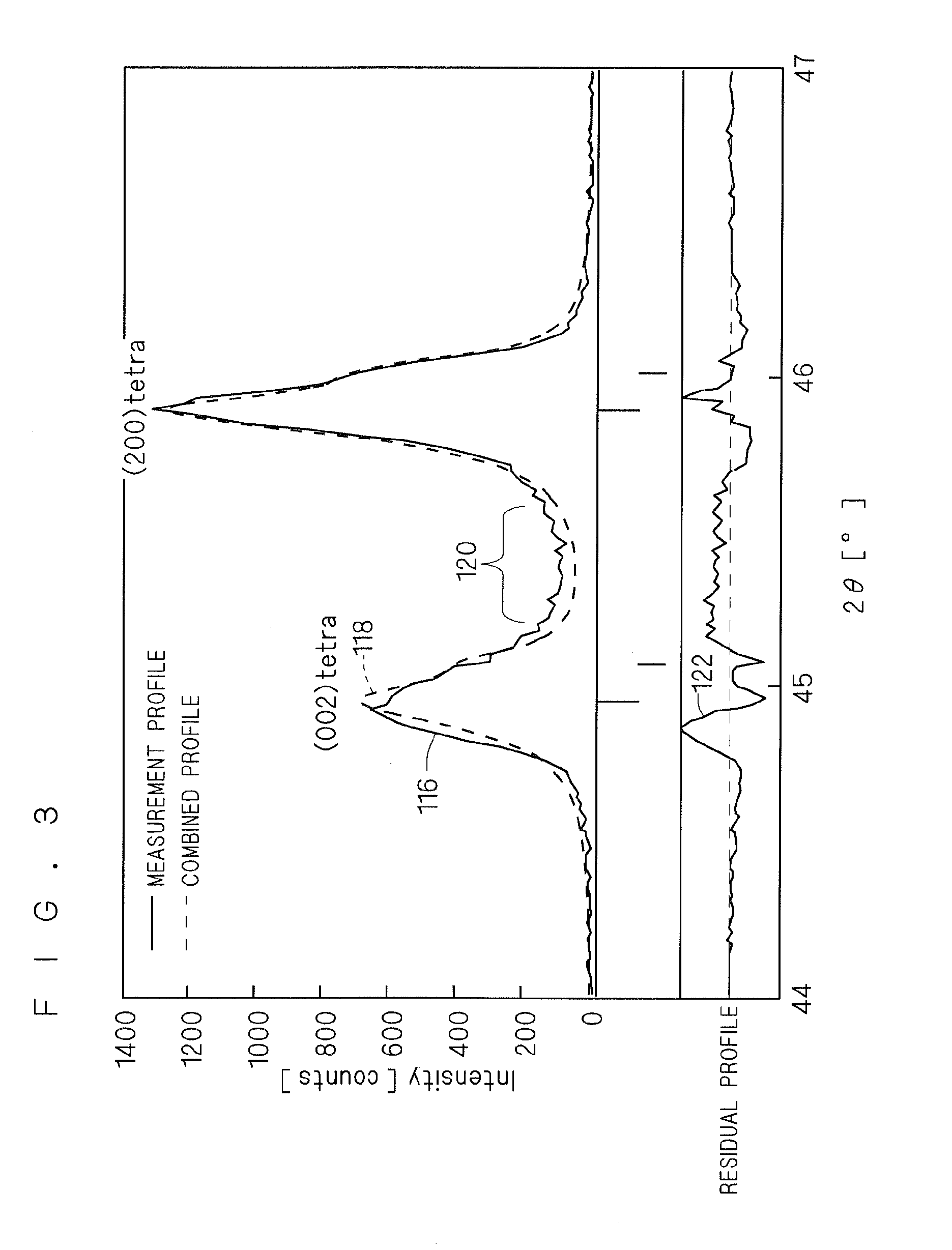
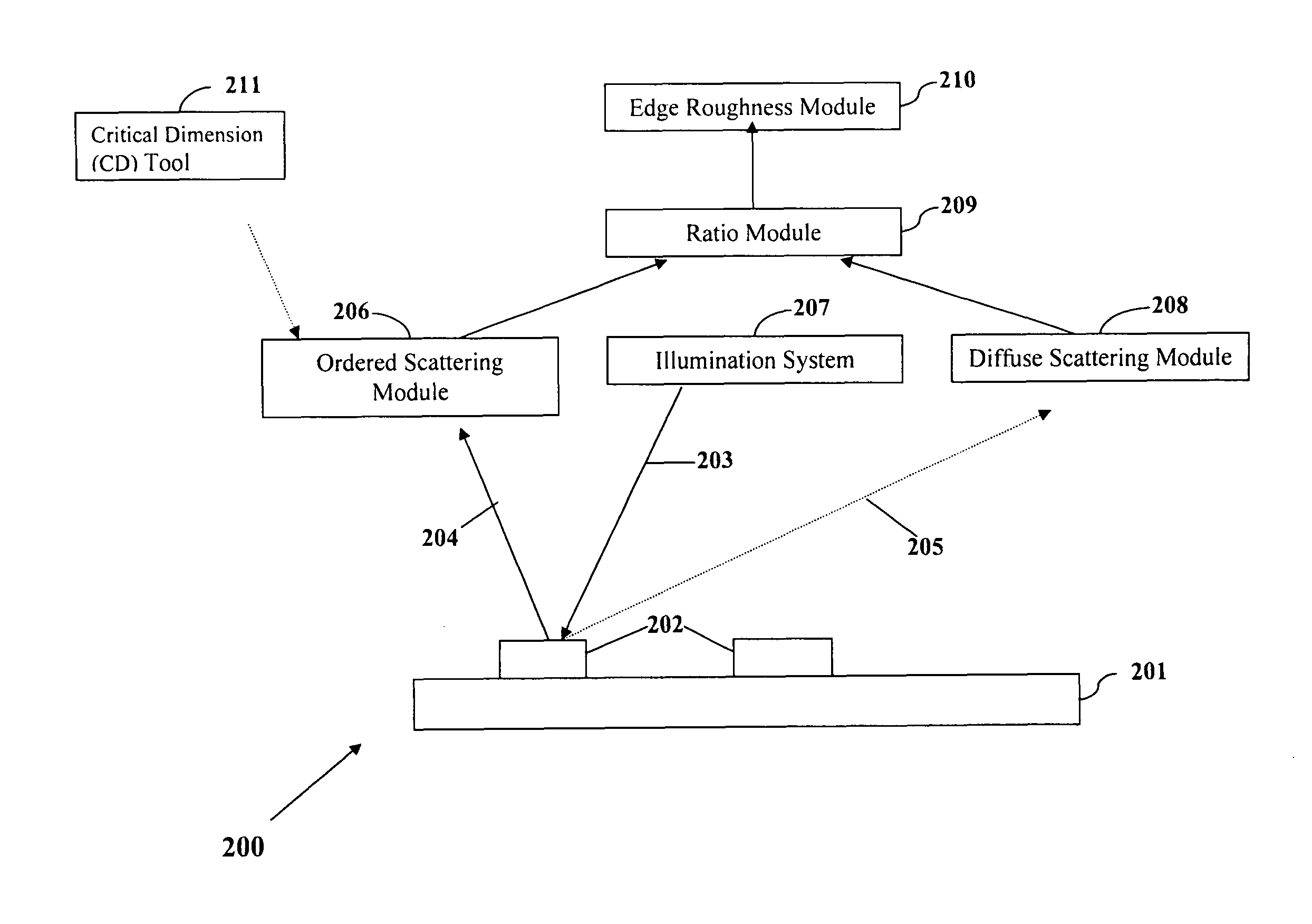
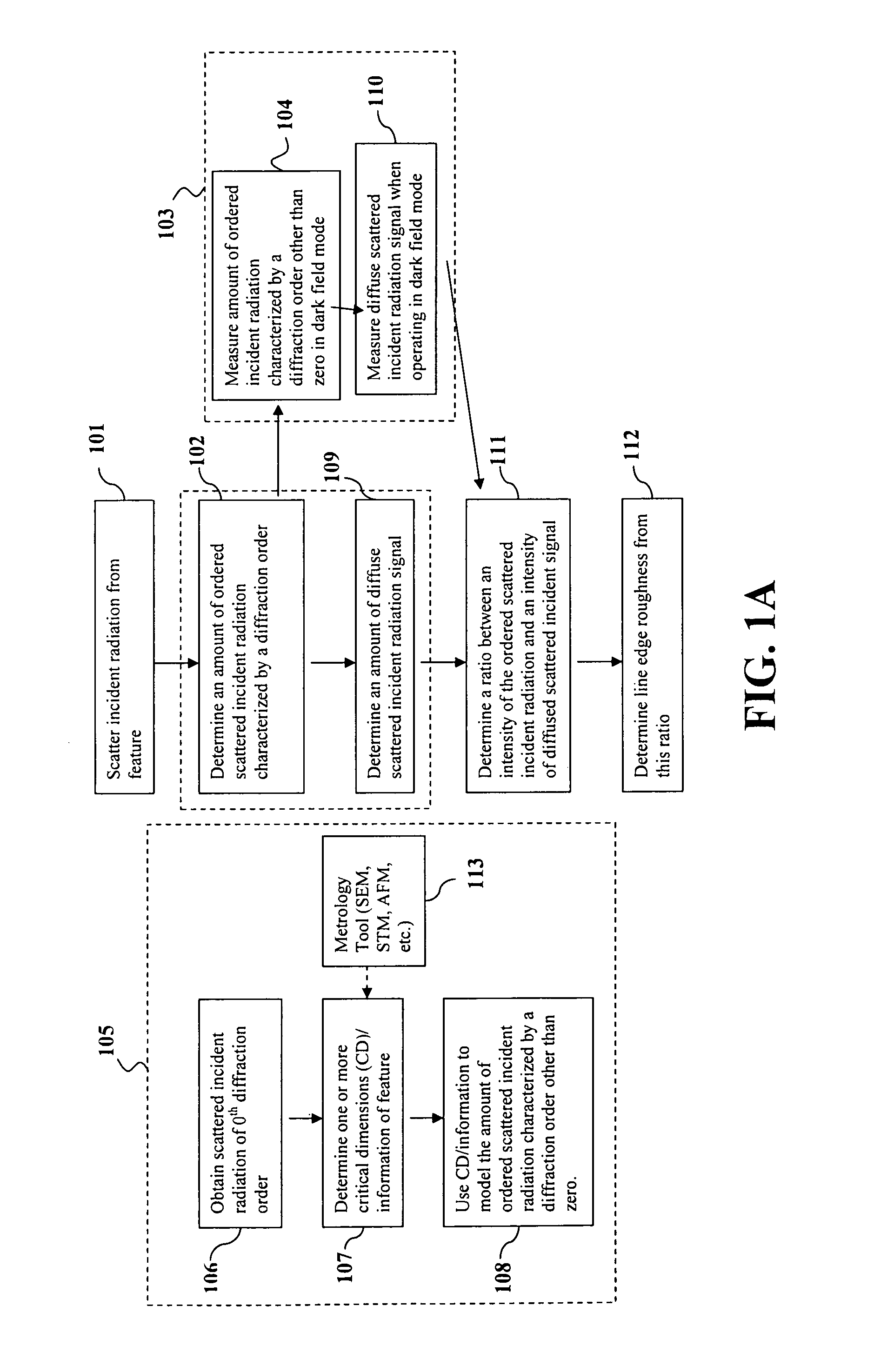
Bright and dark field scatterometry systems for line roughness metrology
Line edge roughness or line width roughness of a feature on a sample may be determined from incident radiation scattered from the feature. An amount of ordered scattered radiation characterized by a discrete diffraction order is determined and a diffuse scattered radiation signal is measured. A ratio between an intensity of the ordered scattered incident radiation and an intensity of the diffuse scattered radiation signal is determined. The line edge roughness or line width roughness is determined from the ratio.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Multispectral imaging for quantitative contrast of functional and structural features of layers inside optically dense media such as tissue
InactiveUS7920908B2Improved measurement and analysisImprove dynamic rangeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTelevision system detailsImaging modalitiesMultispectral image
A method for the evaluation of target media parameters in the visible and near infrared is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a light source, an illuminator / collector, optional illumination wavelength selector, an optional light gating processor, an imager, detected wavelength selector, controller, analyzer and a display unit. The apparatus illuminates an in situ sample of the target media in the visible through near infrared spectral region using multiple wavelengths and gated light. The sample absorbs some of the light while a large portion of the light is diffusely scattered within the sample. Scattering disperses the light in all directions. A fraction of the deeply penetrating scattered light exits the sample and may be detected in an imaging fashion using wavelength selection and an optical imaging system. The method extends the dynamic range of the optical imager by extracting additional information from the detected light that is used to provide reconstructed contrast of smaller concentrations of chromophores. The light detected from tissue contains unique spectral information related to various components of the tissue. Using a reiterative calibration method, the acquired spectra and images are analyzed and displayed in near real time in such a manner as to characterize functional and structural information of the target tissue.
Owner:APOGEE BIODIMENSIONS
Refractive index based detector system for liquid chromatography
InactiveUS6377341B1Easy to carryCheap constructionComponent separationPhase-affecting property measurementsOn columnAnalyte
An apparatus and method for on-column analysis in flash chromatography. The detection scheme utilizes refractive index changes as analytes move through an illuminated region of a chromatography column. The column packing material is a diffuse scattering medium when the refractive index of the solvent is significantly different than that of the packing material. The magnitude of the signal depends on the degree to which the refractive index mismatch is changed as an analyte passes through the illuminated region. This detection scheme provides a simple, inexpensive means for monitoring the end of a flash chromatography column to determine the exit time of the species of interest, thus greatly reducing the post-column analysis time. Additionally, the detector is movable along the length of the column, offering the potential to monitor separations as they occur.
Owner:INDEVR +1
Matt, thermoformable, IR-reflective polyester film
InactiveUS20060008641A1Produced cost-effectivelyGood orientationSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsPolyesterPolyethylene terephthalate glycol
Biaxially oriented polyester films formed from a crystallizable polyester having increased diethylene glycol content and / or increased polyethylene glycol content, and / or increased isophthalic acid content, preferably polyethylene terephthalate. The films of the invention further include at least one IR-reflective pigment and one UV stabilizer. The inventive films feature adjustable mattness, diffuse scattering power for visible light, high light transmittance and IR reflectance and good thermoformability, and are suitable for thermally protective coatings or thermally protective packaging.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POLYESTER FILM
Laser projection system
InactiveCN106707671AVariety of divergence anglesImprove display qualityProjectorsOptical elementsDivergence angleLight beam
The invention discloses a laser projection system comprising a laser light source which emits laser beams of at least one color. The transmission light path of the laser beams includes a light homogenizing part which is used for receiving and homogenizing the laser beams; a light valve which is used for receiving the laser beams homogenized by the light homogenizing part and modulating the laser beams; a diffuse scattering phase plate which is arranged at the light incident surface side of the light homogenizing part and can increase the divergence angle of the beams; and a moving diffuser which is arranged at the light emergent surface side of the light homogenizing part and can greatly enhance the generation number of random phases, wherein the position of the moving diffuser is the object plane position of the light valve and the human eye integration effect is performed on the generated random phases so that the speckle effect of the projection frame can be weakened or eliminated to the greatest extent, and thus the speckle elimination effect and the display quality of the projection frame can be greatly enhanced.
Owner:HISENSE
Organic-inorganic hybrid film with photoconductive property and total reflection characteristic and preparation method thereof
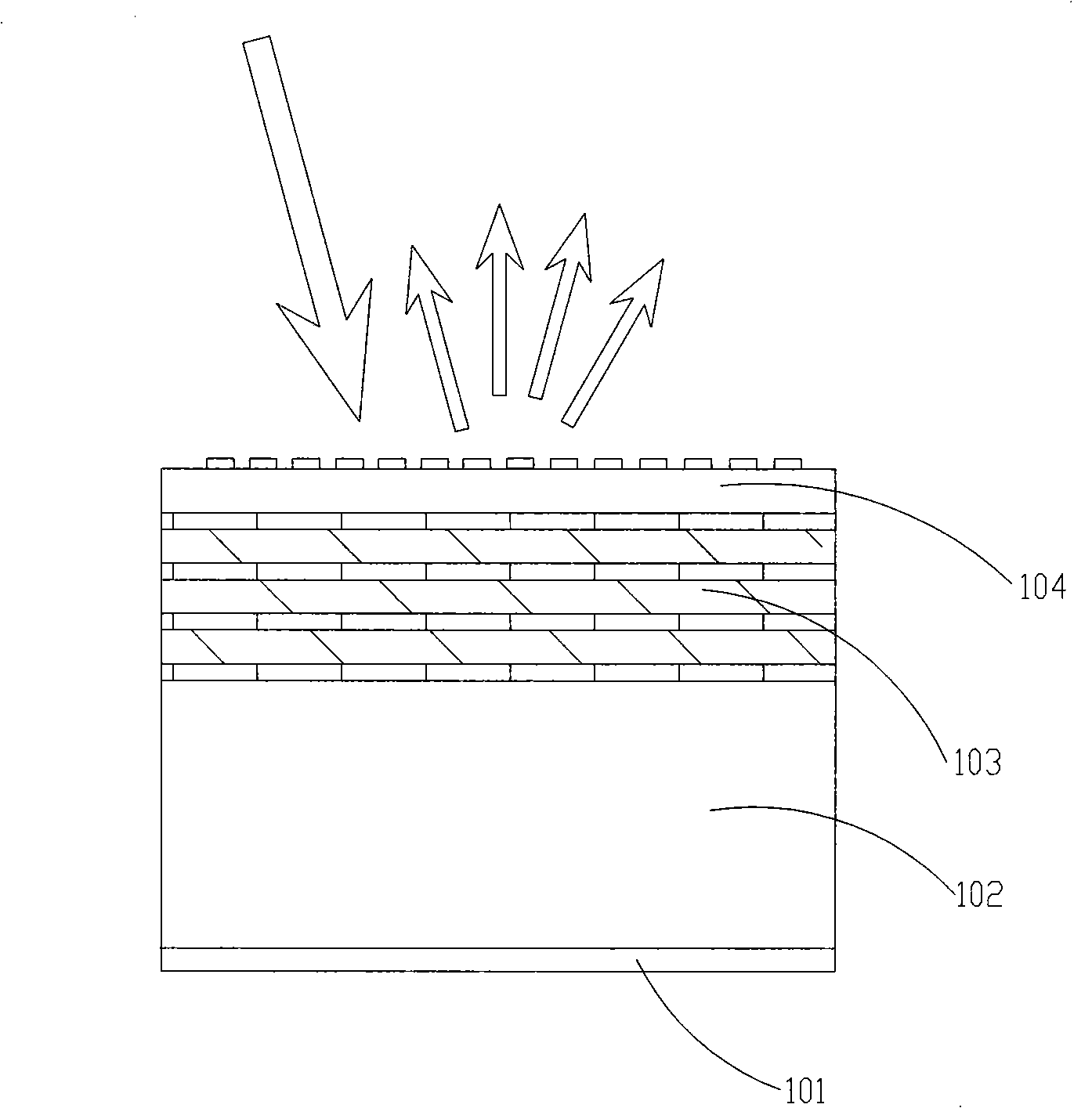
The invention discloses an organic-inorganic hybrid film which comprises a light reflection layer, a photoconductive layer and a light diffusion layer or a photodiffusion layer arranged on the photoconductive layer, wherein the refractive index of the light diffusion layer or the photodiffusion layer is larger than that of the photoconductive layer, and the refractive index of photoconductive layer is larger than that of the light reflection layer. The film also comprises a substrate which is arranged under the light reflection layer, and the refractive index of the light reflection layer is larger than that of the substrate. The organic-inorganic hybrid film has the optical characteristics of photoconduction, total reflection and diffuse scattering, high mechanical strength and thicknessof 0.01-0.08mm. The total reflection characteristic of the film can effectively improve the utilization ratio of a backlight source; and a light guide plate and a reflecting plate in a traditional backlight module are combined into a whole, thereby achieving the purpose of thinness.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus for measuring quality of laser beam
InactiveCN1800794AInstantaneous and accurate measurementAccurate measurementPhotometryLight spotOptoelectronics
The quality measurement device for laser beam comprises: a focusing lens, an attenuation sheet of a diffuse scattering board, a CCD to collect light spot, a computer with high-speed collection card, and a light splitter contained a first plate with inner surface of 100% reflectivity and a second plate with inner surface of 90~99% reflectivity both 45Deg parallel laid in light path. Wherein, there is a malposition m between two plates and an antireflection coating on outer surface of the second plate. This invention can measure accurately for Gauss beam or non-Gauss beam with power-in-barrel ratio method, and has simple structure with well stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polarimetric SAR multi-component target decomposition method
InactiveCN105445712AImproved scattered powerImprove object detectionWave based measurement systemsRough surfaceDecomposition
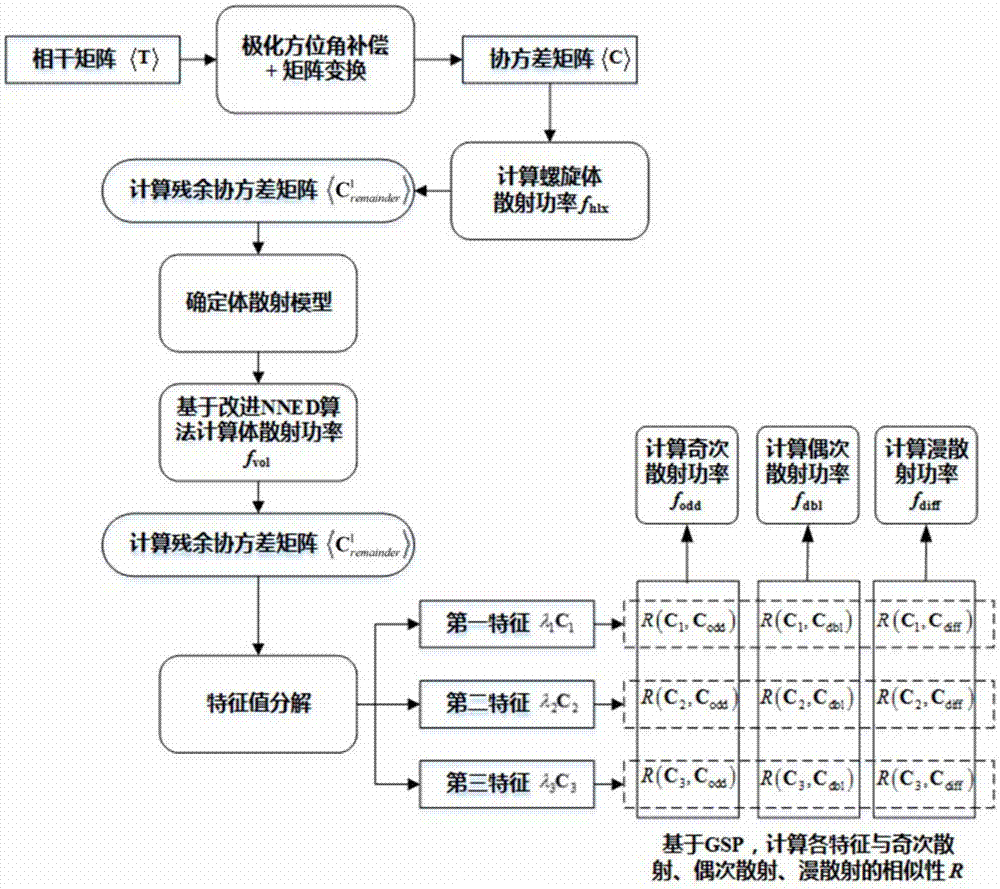
The invention provides a polarimetric SAR multi-component target decomposition method. According to the method, an additional diffuse scattering mechanism which may come from a terrain or rough surface is added as a fifth decomposition component on the basis of a previous four-component decomposition algorithm, namely, the linear weighted sum of five scattering components (odd scattering, even scattering, volume scattering, helicoid scattering and diffuse scattering) decomposed from a fully-polarimetric SAR coherence matrix T or covariance matrix C. The power of volume scattering is solved by an improved NNED method, and the contribution values of odd scattering, even scattering and diffuse scattering are directly solved by adopting corresponding odd scattering, even scattering and diffuse scattering models of a Pauli matrix directly and using a generalized similarity parameter GSP and eigenvalue decomposition. The novel method provided by the invention is conductive to improving the terrain classification accuracy of polarimetric SAR data.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
Brightness enhancing film and film based diffuser for improved illumination uniformity of displays
InactiveUS20110037736A1Diffusing elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
An optical device has a first film (200) that has a first side and a second side. When illuminated by light (204) at the first side, the first film is characterized by a first fraction of broadly diffused transmitted light (206) and a second fraction of narrowly diffused transmitted light (208). A second film (202) is disposed to the second side of the first film. The second film has at least one free surface that diverts light. In some embodiments, the first film has a diffuse scattering optical density between 0.5 and 3. The device finds use in spreading and making light uniform in a backlight in a display such as a liquid crystal display.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Apparatus for measuring liquid material component content by near-infrared spectrum
InactiveCN1948951AInformativeImprove detection accuracyScattering properties measurementsReference sampleCollection system
The invention relates to near infrared spectral measurement fluent material component content device. It is made up of light source, optical splitting system, diffuse scattering light collecting system, sample cell, reference sample cell, pervious reflection sample cell, photoelectric sensor, reference photoelectric sensor, amplifier, A / D converter, light beam splitter, standard white plate, temperature sensor, control module, spectroscopic data register, scaling reference register, computation module, result output module which is set in thermostat. The invention can increase measuring precision, ensure sample information content abundant, gain sample various components and contents at the same time. The device has little volume, simple operation and maintenance which can be suited for on site real time measurement.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Determining biological tissue optical properties via integrating sphere spatial measurements
InactiveUS20100284014A1Optical properties of biological tissue is readily determinedRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryOptical propertyAcquisition apparatus
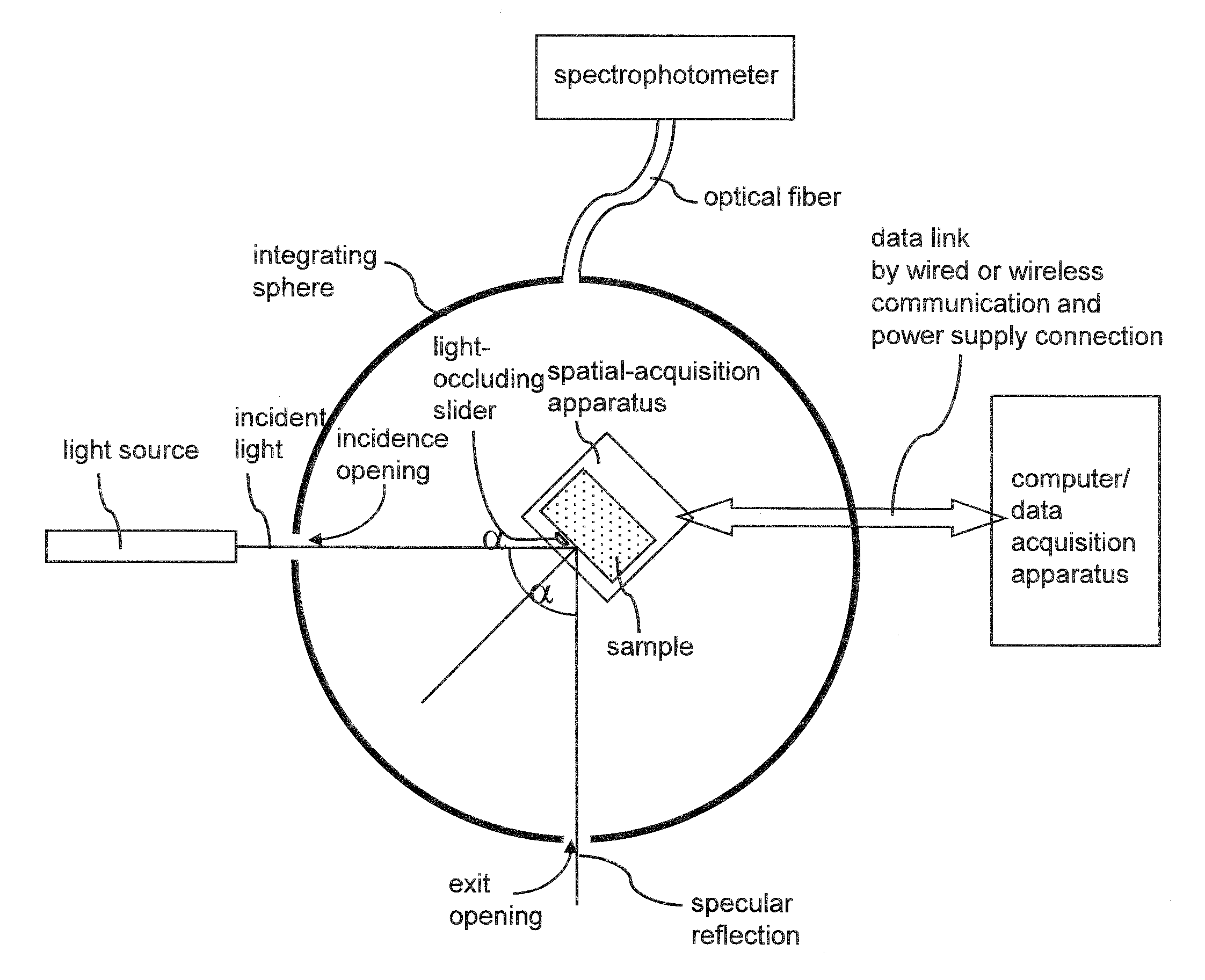
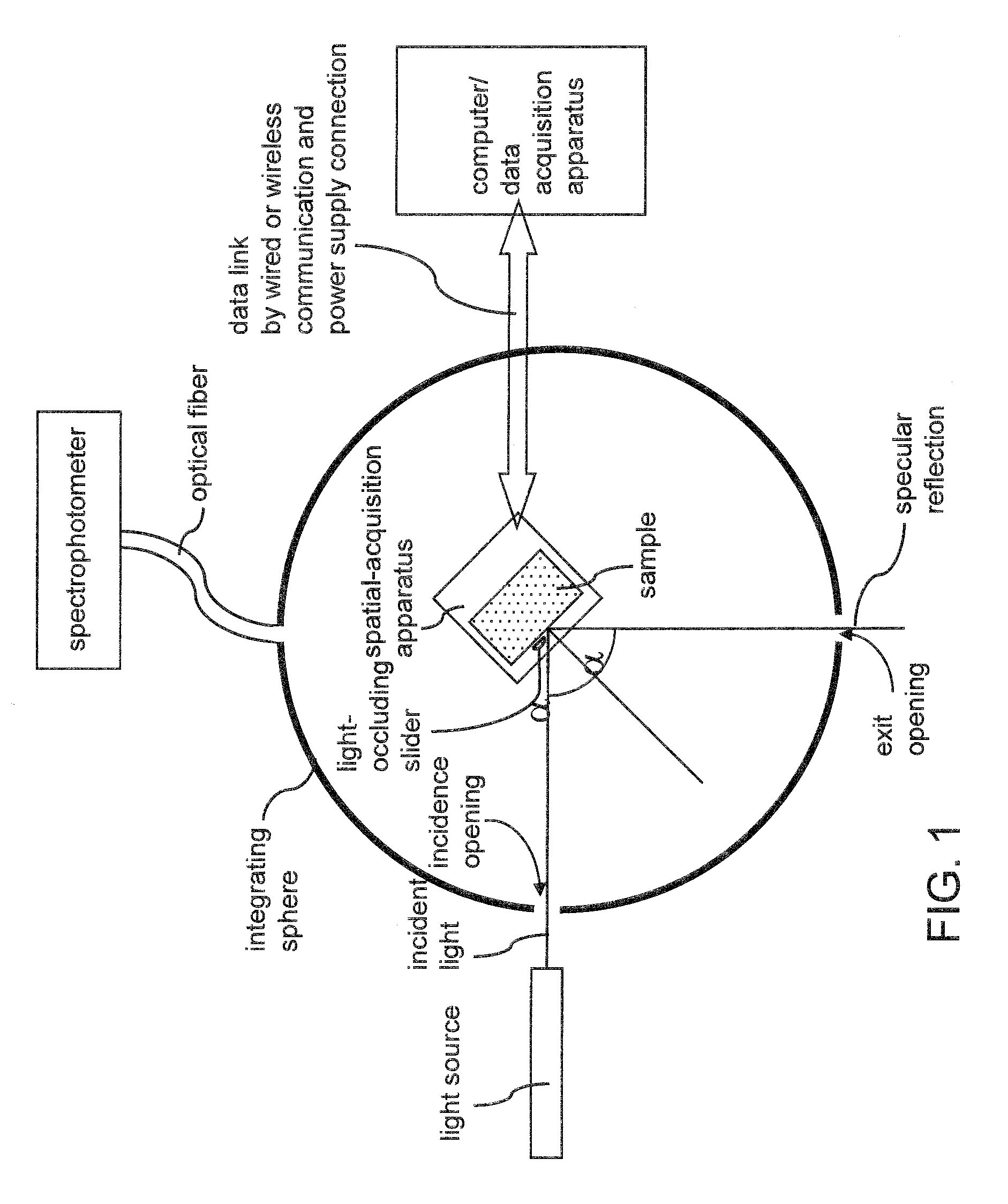
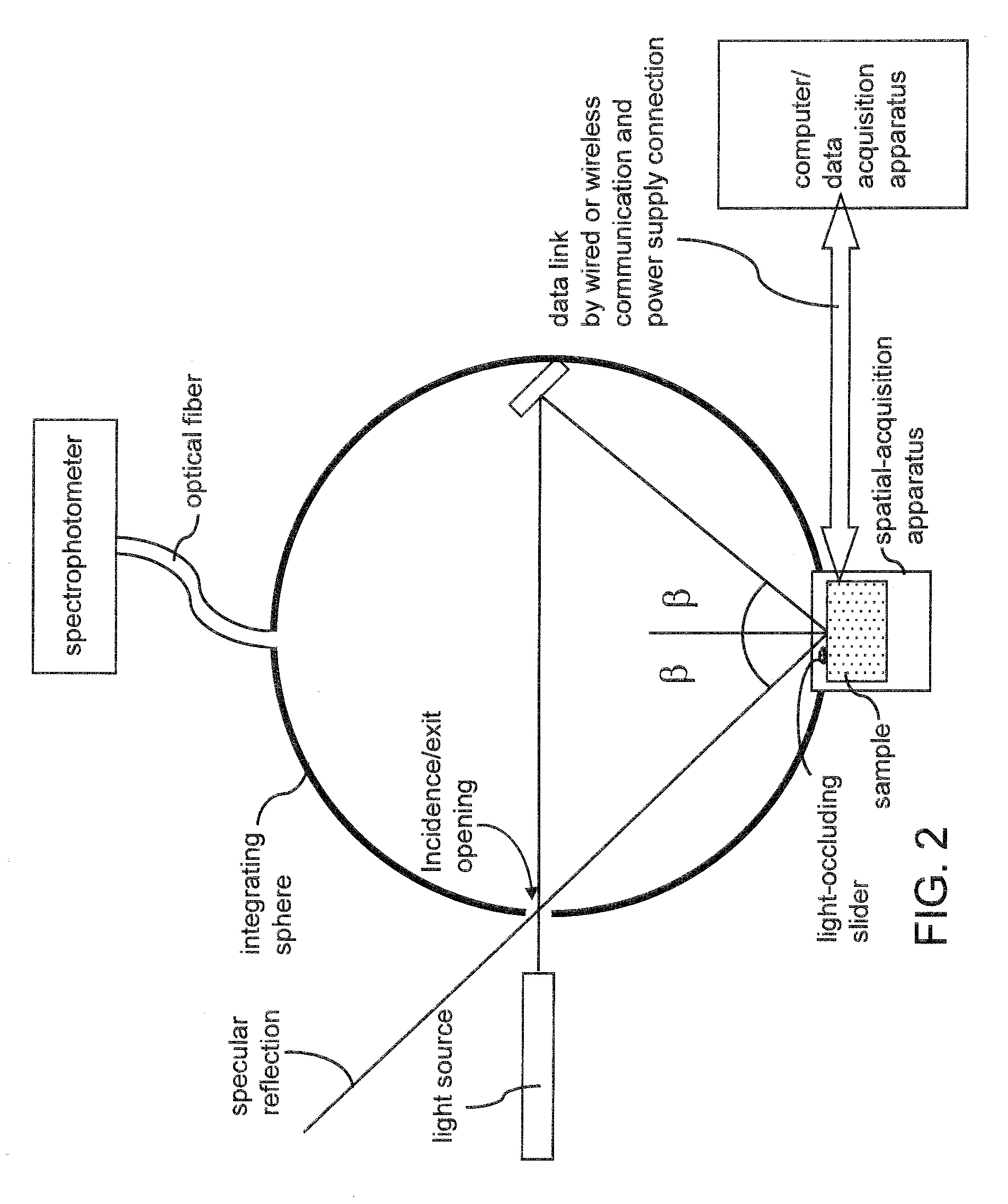
An optical sample is mounted on a spatial-acquisition apparatus that is placed in or on an enclosure. An incident beam is irradiated on a surface of the sample and the specular reflection is allowed to escape from the enclosure through an opening. The spatial-acquisition apparatus is provided with a light-occluding slider that moves in front of the sample to block portions of diffuse scattering from the sample. As the light-occluding slider moves across the front of the sample, diffuse light scattered into the area of the backside of the light-occluding slider is absorbed by back side surface of the light-occluding slider. By measuring a baseline diffuse reflectance without a light-occluding slider and subtracting measured diffuse reflectance with a light-occluding slider therefrom, diffuse reflectance for the area blocked by the light-occluding slider can be calculated.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Multilayer, matt, thermoformable, IR-reflective polyester film
InactiveUS7189451B2Synthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsPolyesterPolyethylene terephthalate glycol
Owner:MITSUBISHI POLYESTER FILM
Measuring Device for the Shortwavelentgh X Ray Diffraction and a Method Thereof
ActiveUS20080095311A1Improve measurable thicknessEasy to operateMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionMeasurement deviceMirror reflection
The present utility model relates to the field of X-ray diffraction technology. With different combinations, the X-ray diffractometer in the utility model is enabled to have functions of powder diffraction measurement, double crystal diffraction measurement, mirror reflection measurement and diffuse scattering measurement, thus becoming a multi-functional X-ray diffractometer. Further, the X-ray diffractometer is fully automatic in operation, with data collection being under the control of a microcomputer; and is suitable for microstructure analysis of materials, especially for microstructure analysis of solid film materials. The X-ray diffractometer has convenient operation and stable performance, and the technical parameters thereof may meet a general demand in the research of epitaxial film. Also, the X-ray diffractometer is low in cost, and may provide experience for the reconstruction of a diffractometer of the same kind.
Owner:SOUTHWEST TECH & ENG INST
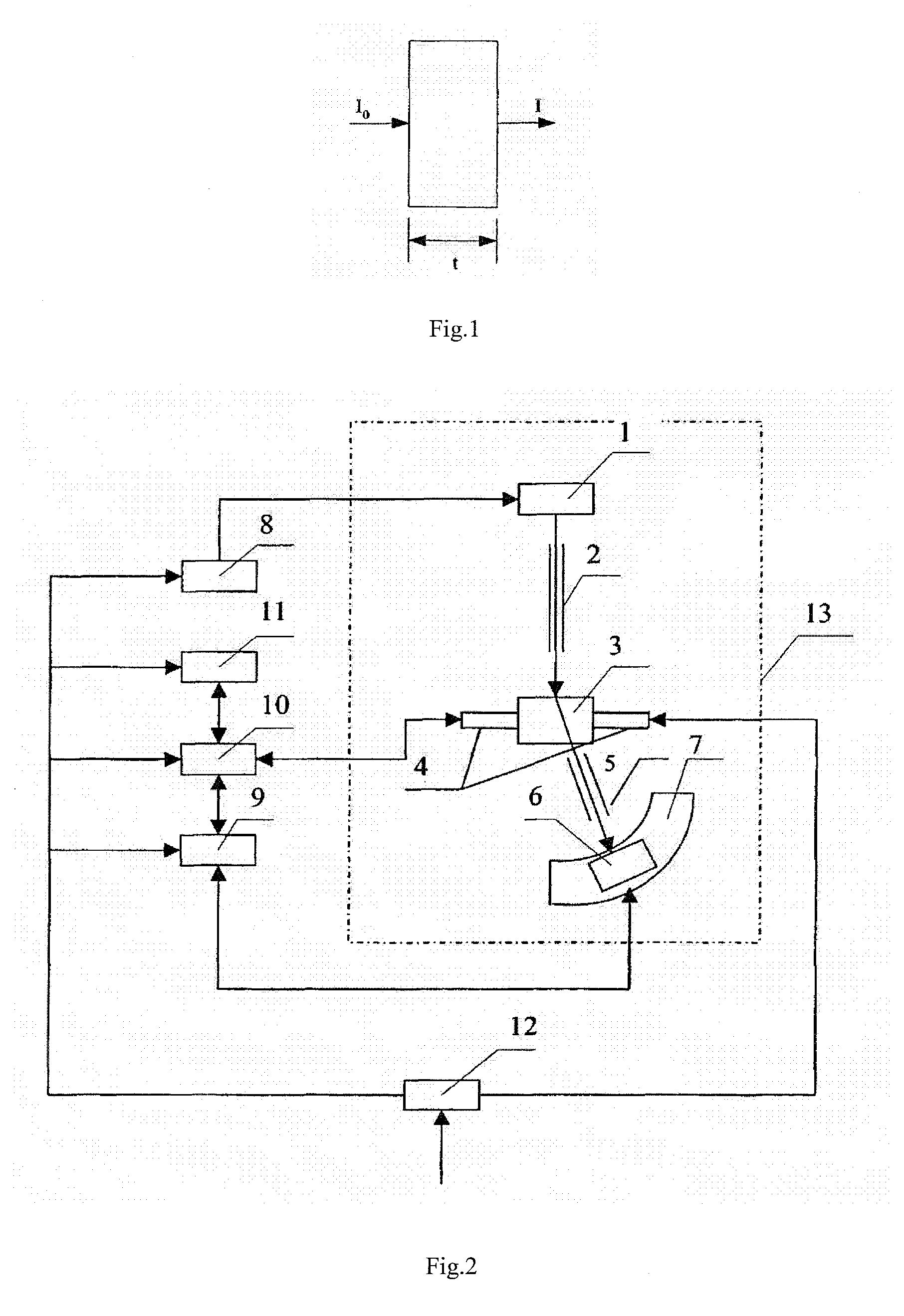
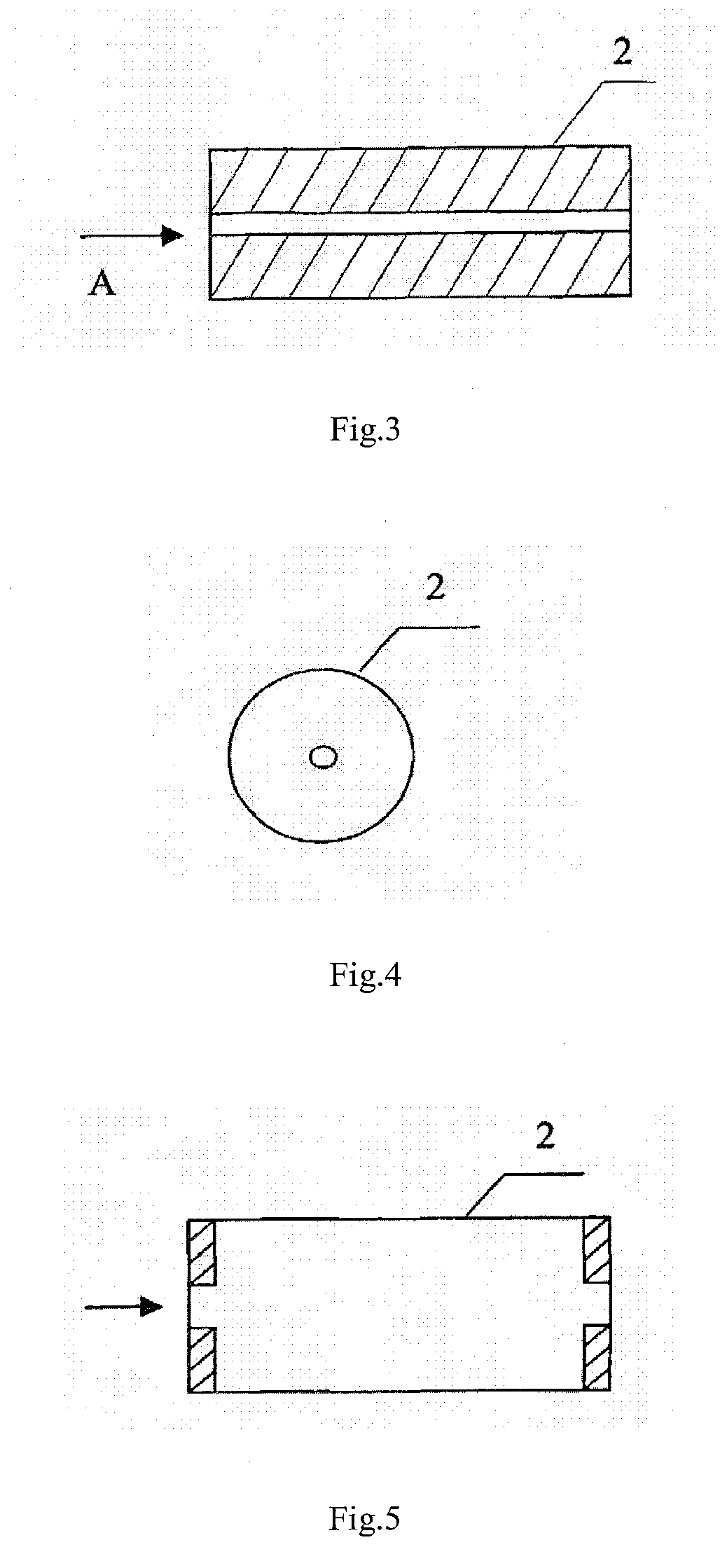
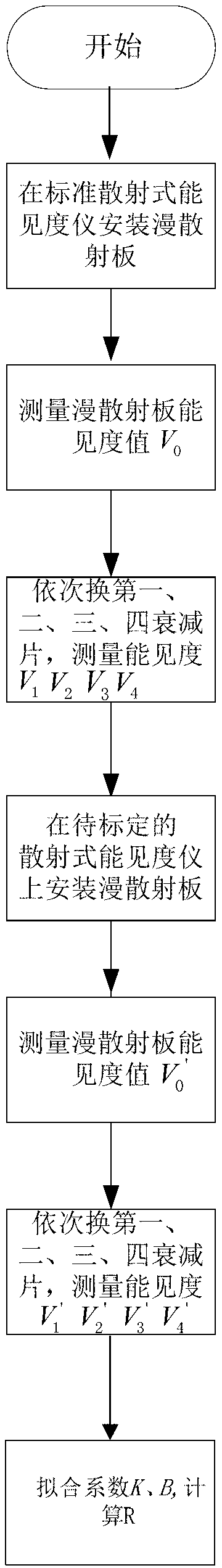
Calibrating method of forward scattering type visibility meter
ActiveCN103278478AProne to errorQuick calibrationScattering properties measurementsUltrasound attenuationForward scatter
The invention discloses a calibrating method of a forward scattering type visibility meter. The calibrating method is characterized in that a plurality of standard measuring points of the forward scattering type visibility meter in a full scale are quantitatively simulated through combination of a diffuse scattering board and attenuation sheets with different transmittances, and a coefficient of the forward scattering type visibility meter is modified by using a modifier formula, and therefore, the forward scattering type visibility meter is calibrated. The calibrating method is applied to the calibration after the forward scattering type visibility meters are produced in batch and used for a long time; the coefficient of the forward scattering type visibility meter can be accurately, conveniently and rapidly modified, and thus the accuracy and consistency of the forward scattering type visibility meter are improved, and the difficulty that the forward scattering type visibility meter can not be rapidly and accurately calibrated indoors is solved. The calibrated forward scattering type visibility meter and a standard meter are experimentally compared, the measurement error of the visibility within 10kilometers is less than 10 percent, the measurement error of the visibility of more than 10 kilometers is less than 20 percent, and the forward scattering type visibility meter accords with the requirement of accuracy in requirements of functions and specifications of forward scattering type visibility meters issued by the China Meteorological Administration.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Controlled diffuse scattering for displays
A display device comprising a pixel, where the pixel includes: (a) a polar fluid that is at least one of colored and black, (b) a non-polar fluid that is at least one of transparent and translucent, (c) a first substrate, (d) a second substrate arranged relative to the first substrate to define a channel occupied by the polar fluid and the non-polar fluid, wherein at least one of the polar fluid and the non-polar fluid is visible through at least one of the first substrate and the second substrate, (e) a reflector having a plurality of features, comprising at least one of concavities and projections, that alter an angle of reflected light from a specular reflection to provide the appearance of at least one of a diffuse reflection and a non-metallic reflection, where the reflector includes a hydrophobic coating causing the polar fluid that is at least one of colored and black to be non-wetting to the hydrophobic coating in the presence of the non-polar fluid, the display device also including a plurality of electrodes configured to cause repositioning of the polar fluid in the channel to displace at least a first portion of the non-polar fluid and a voltage source, where repositioning of the polar fluid occurs as a unified volume to retard reduced light reflection from the reflector in a portion of the channel where the polar fluid has been repositioned.
Owner:DEAN KENNETH A +2
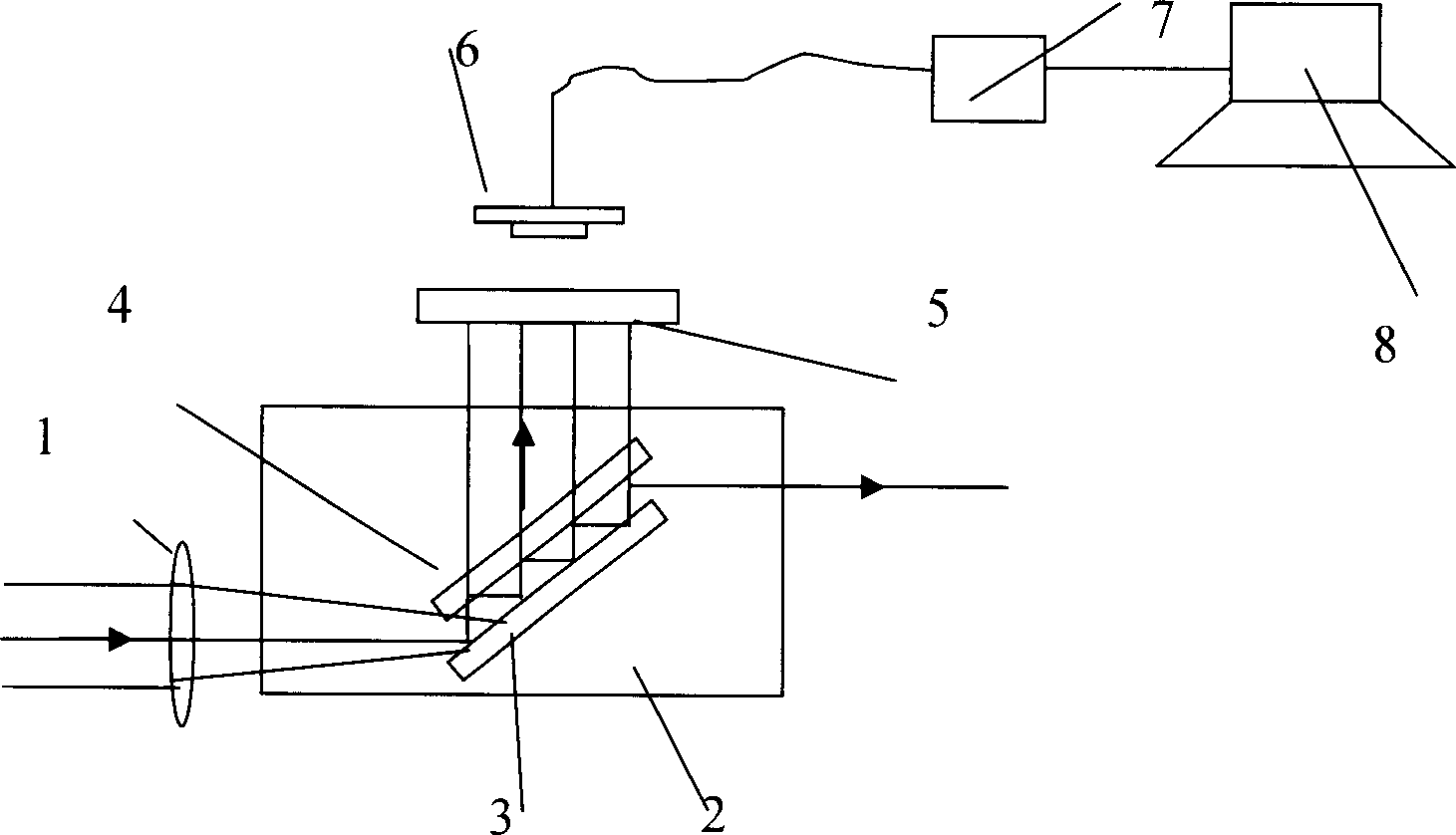
Plane optical component surface quality rapid detecting device and method
ActiveCN109975319ARealize multi-axis linkageRealize real-time monitoringScattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationBeam splitterLight energy
The invention relates to a plane optical component surface quality rapid detecting device and method. The device comprises a photoelectric detector 1, a photoelectric detector 2 and a two-dimensionalrotation system, wherein the photoelectric detector 1 is combined with a beam splitter and is placed in a detected light path so as to measure incident light energy; the photoelectric detector 2 is fixed in an inner detecting hole of an integrating sphere to measure scattered light energy; and the two-dimensional rotation system is used for fixing a component to be tested and is installed on an XYguide rail to achieve multi-axis linkage of the component to be tested. A measuring principle is characterized in that a detection light beam emitted by a laser light source successively passes through the beam splitter, a laser beam expander, and a high reflection mirror, and is projected into the tested component through an integrating sphere incidence hole so as to form scattered light; a mirror portion of the scattered light leaves the integrating sphere through an integrating sphere emitting / sample hole and is collected by a light collector; and a diffuse scattering portion of the scattered light is reflected multiple times in the integrating sphere to form uniform light, which is measured by the photoelectric detector 2. The detecting device can realize rapid detection of a grade ofdefects on the surface of the plane optical component.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
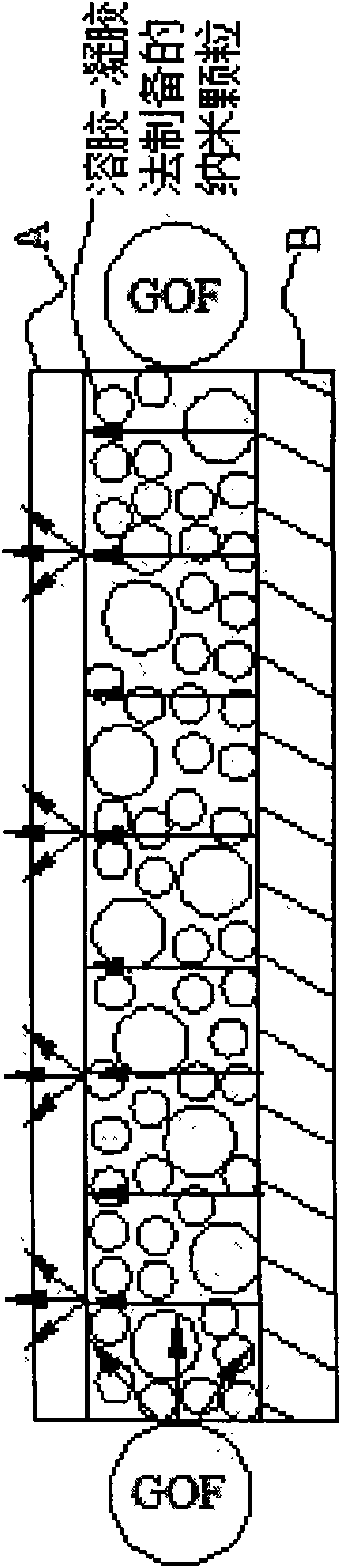
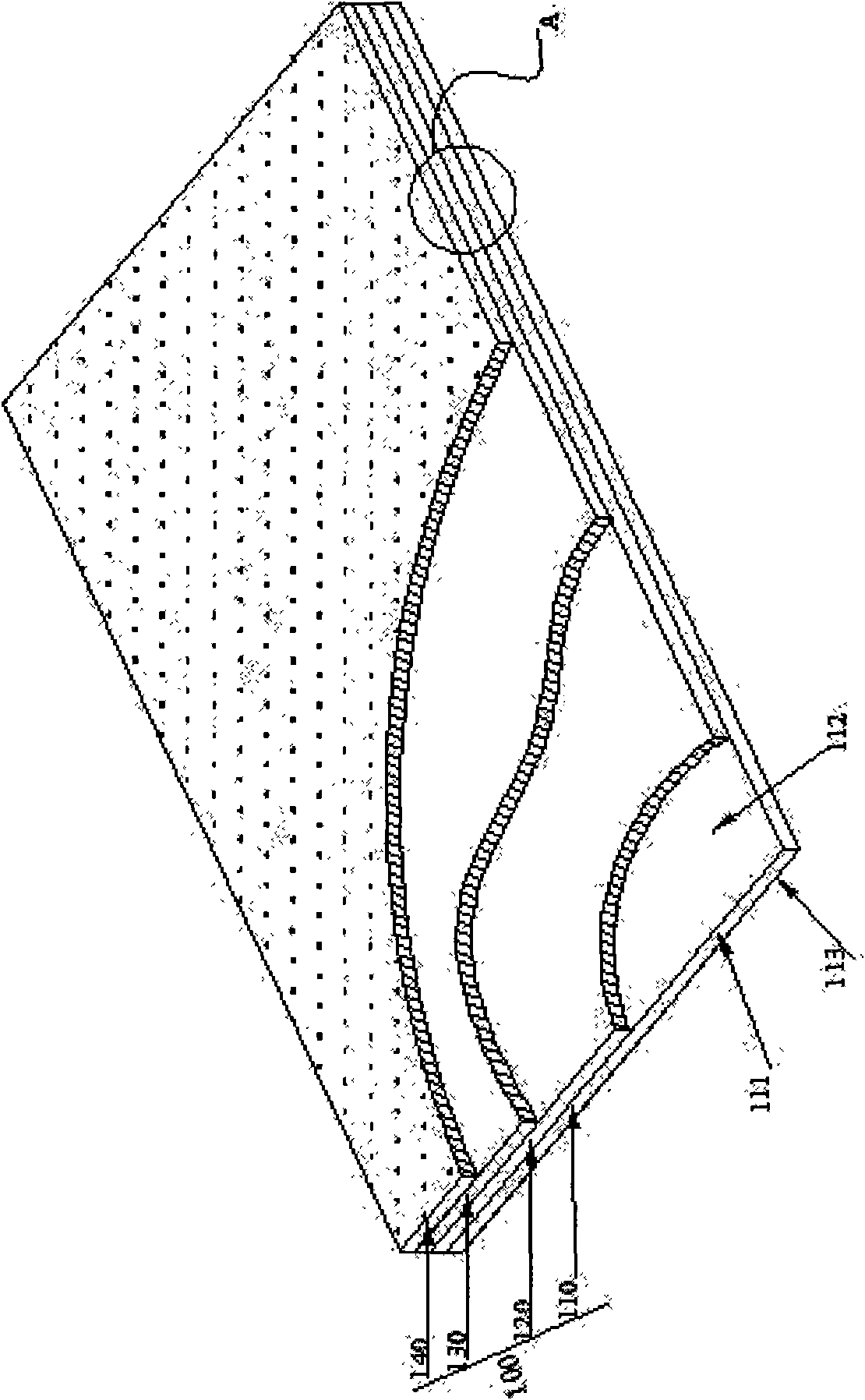
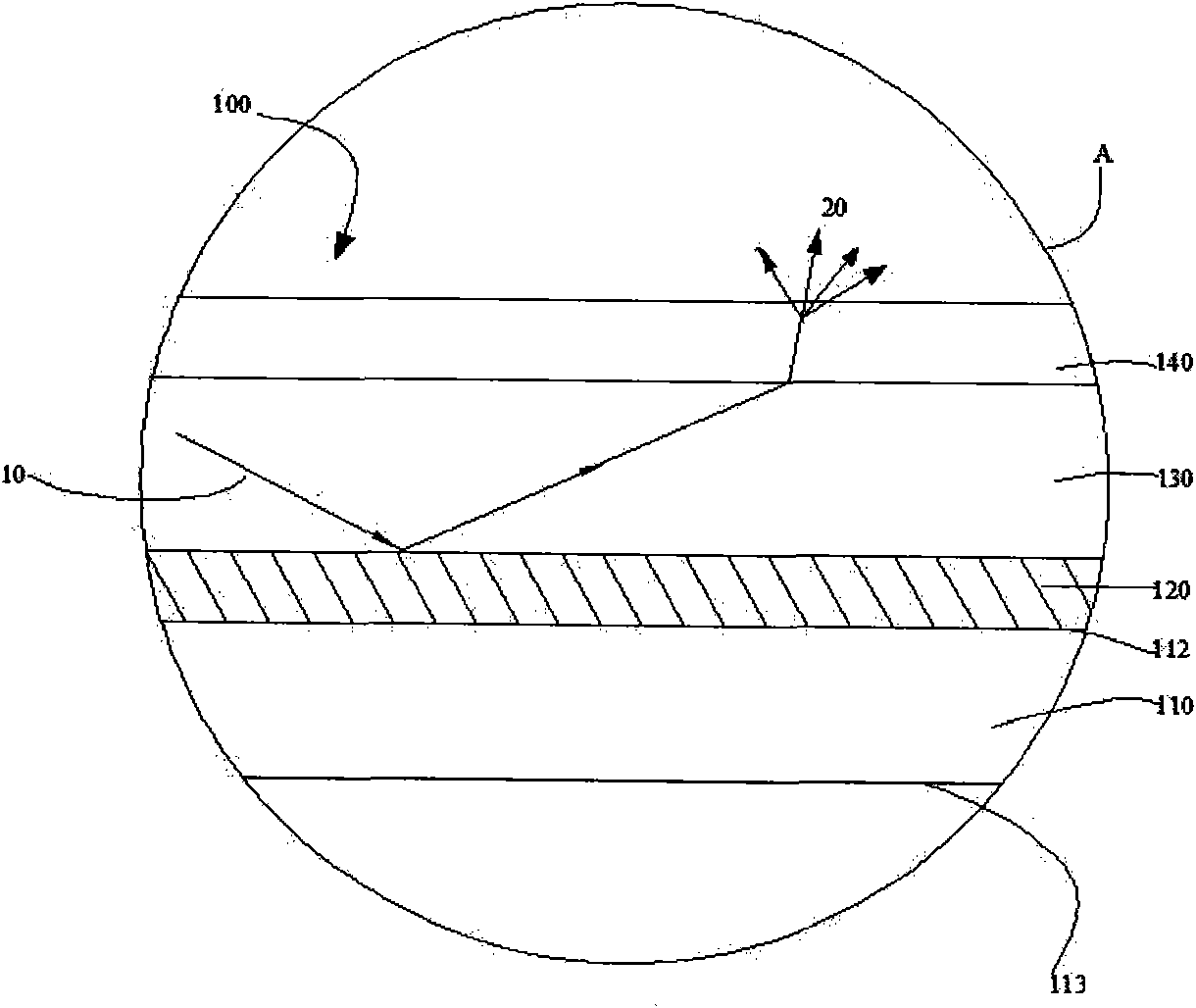
Diffuse scattering polyethylene greenhouse membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108081719AWith dripping functionLife SynchronizationSynthetic resin layered productsPlant protective coveringsThermal insulationGreenhouse
The invention relates to a diffuse scattering polyethylene greenhouse membrane and a preparation method thereof. The diffuse scattering polyethylene greenhouse membrane comprises an outer layer, a middle layer and an inner layer. The outer layer is a greenhouse membrane dripping layer, the middle layer is a greenhouse membrane thermal insulation layer and the inner layer is a greenhouse membrane long-life layer. The outer layer contains 6-7wt% of diffuse scattering master batches. The middle layer contains 2-3wt% of diffuse scattering master batches. The inner layer contains 1-2wt% of diffusescattering master batches. The diffuse scattering polyethylene greenhouse membrane has a dripping function and a diffuse scattering function and has a life the same to that of the agricultural membrane. The preparation method of the diffuse scattering polyethylene greenhouse membrane is scientific, reasonable, simple and easy.
Owner:SHANDONG QINGTIAN PLASTIC IND
Laser tracker with two measuring function alities
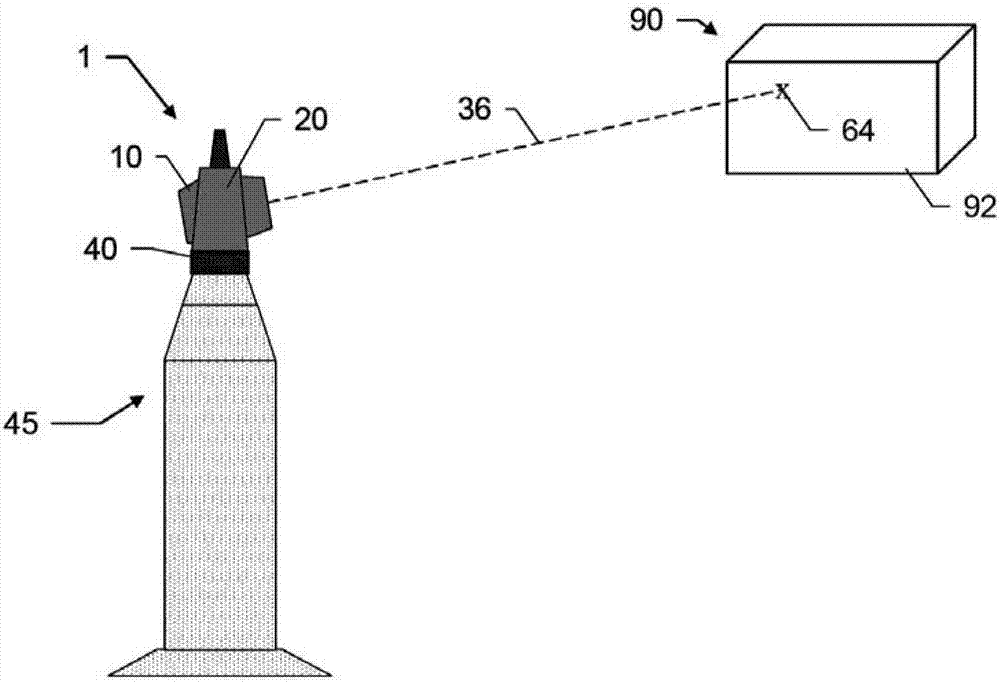
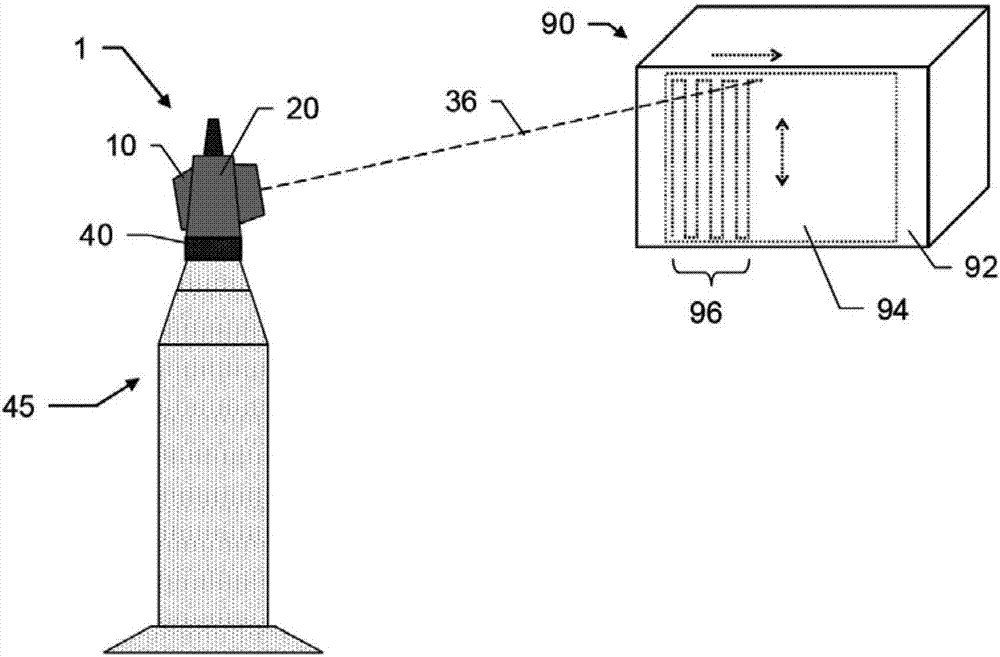
ActiveCN107192380AReduce complexityReduce structural complexityActive open surveying meansUsing optical meansBeam sourceLight beam
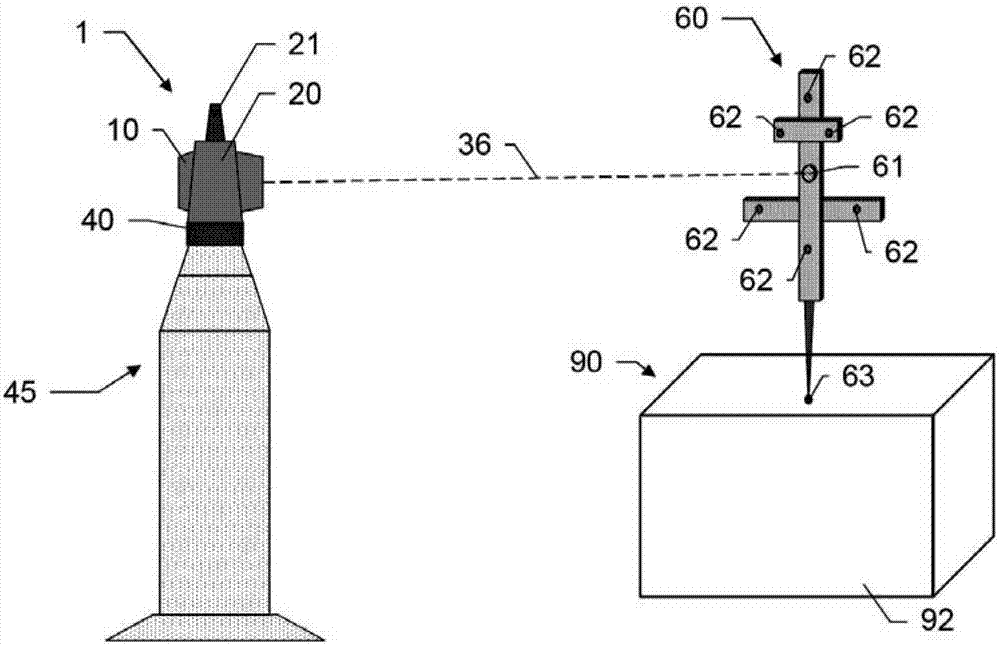
A laser tracker with two measuring function alities. A laser tracker (1) for determining the industrial coordinate position of the target (61, 64), wherein the laser tracker (1) comprises at least: a control and evaluation unit, a base (40) and a beam guide unit (10), means for detecting the rotation angle of the beam guide unit with respect to the base, and means having at least a first beam source (30) and a first optical distance measuring unit (2) of a first detection unit(12).The distance measurement unit (2) and the control and evaluation unit are designed to implement the first measurement function and the second measurement function; for this purpose, at least one element of the distance measuring unit (2) is designed for dual use in both the first measurement function and the second measurement function. The first measurement function is designed for the coordinate position determination of the retroreflective target (61), and the second measurement function is designed for the coordinate position determination for the diffuse scattering target (64).
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
Fast neutron imaging method and system based on time-of-flight method
InactiveCN103245680AIncrease the lengthOvercoming the lack of clarityMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Neutron imaging
The invention relates to a fast neutron imaging technology, and in particular relates to a fast neutron imaging method and system based on a time-of-flight method. The method comprises the steps that: a plurality of scintillant units form a scintillant array to enable the scintillant array to be coupled with a position sensitive detector; the whole coupled detector array is arranged away from a neutron source; a sample is arranged close to the neutron source; the measurement is performed by using the neutron time-of-flight method; interference factors are eliminated by using a conforming method to obtain effective counting on each scintillant unit detector; and the effective counting on each scintillant unit detector is arrayed to obtain a two-dimensional image in which only acting source neutrons acts. The method and the system adopt a detector array design mode, so that the detection efficiency is improved; and the time-of-flight method measurement mode can effectively remove scattered sample neutrons, an environment diffuse scattering background and a gamma background, and a signal-to-noise ratio is increased.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
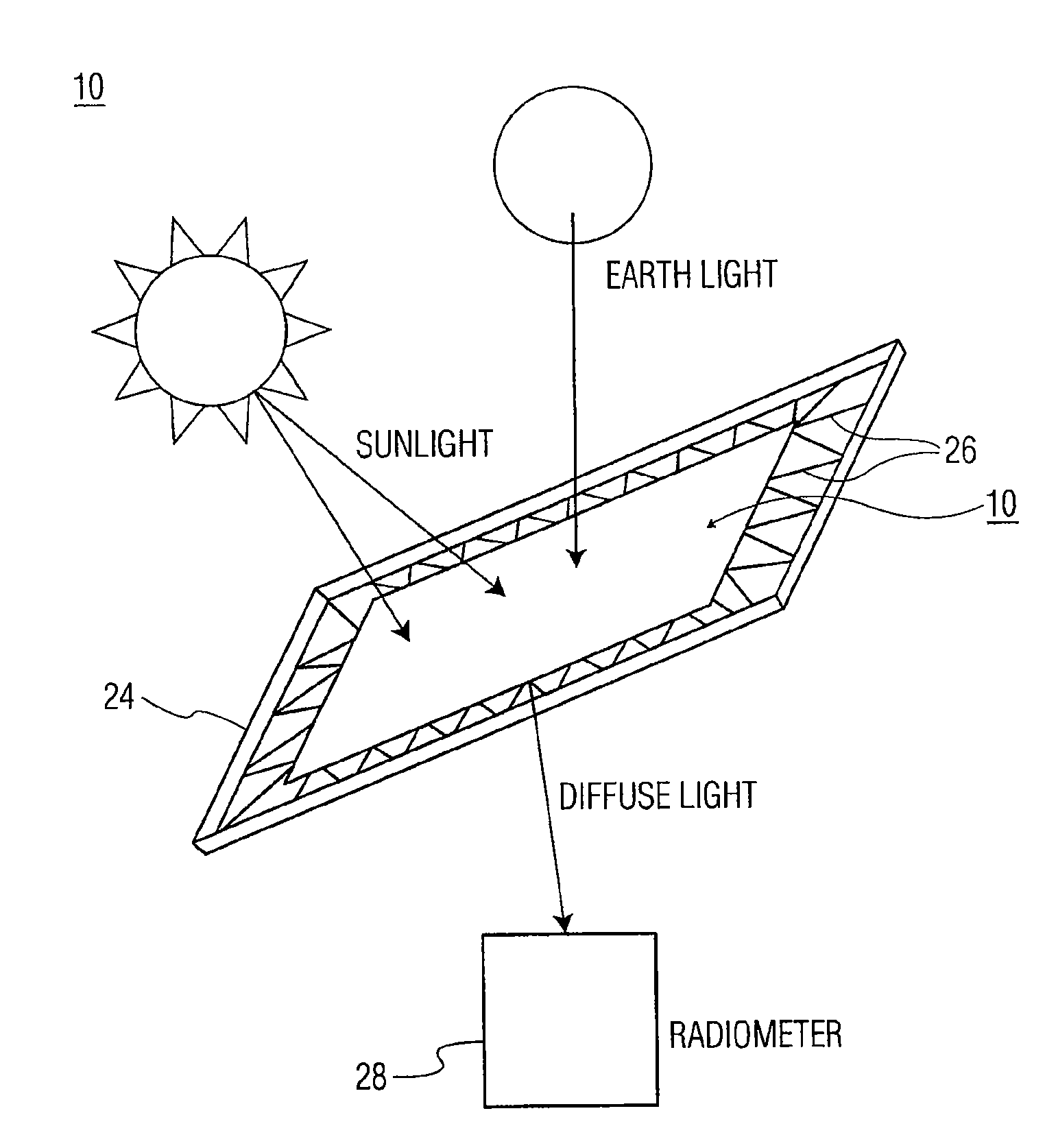
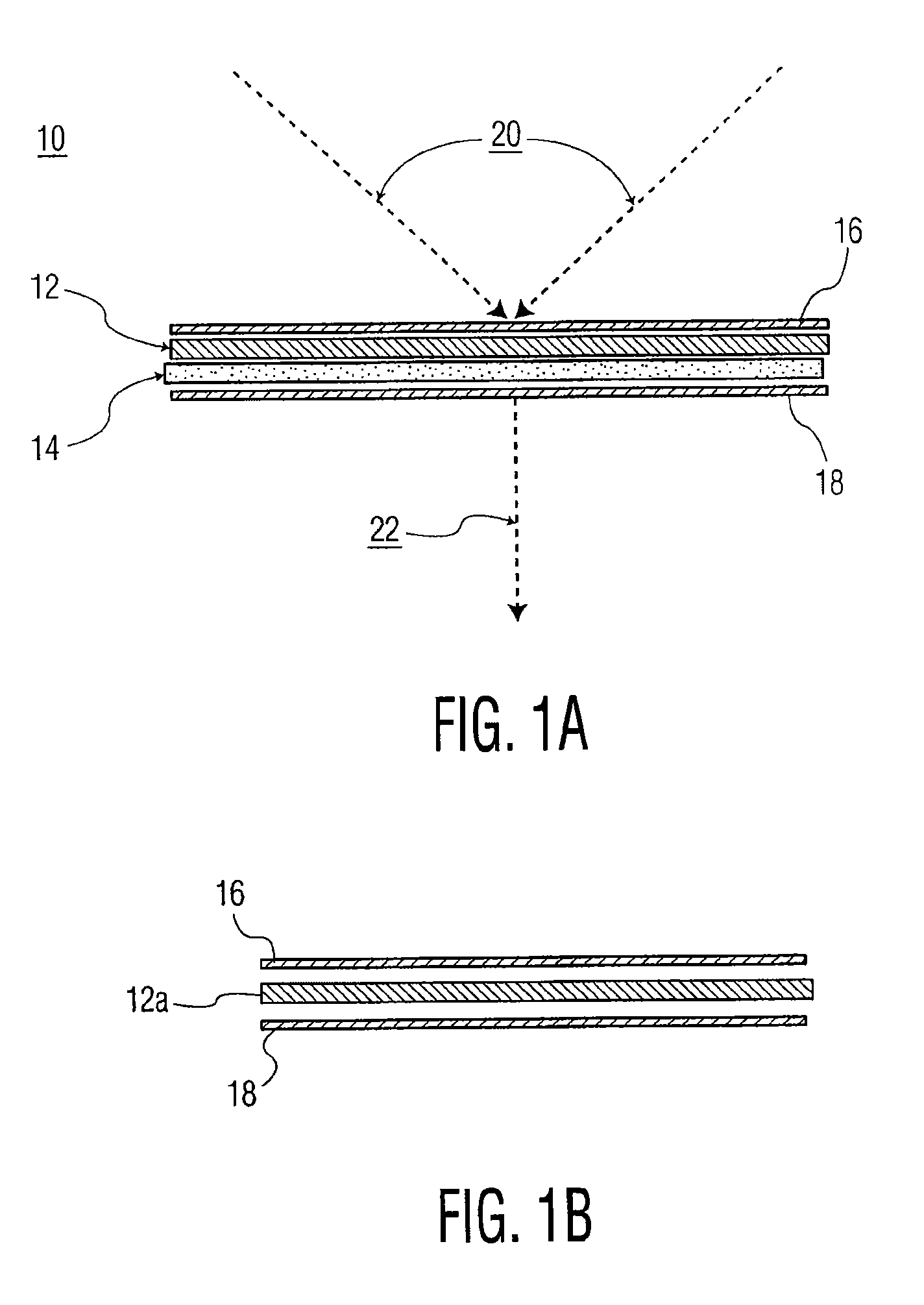
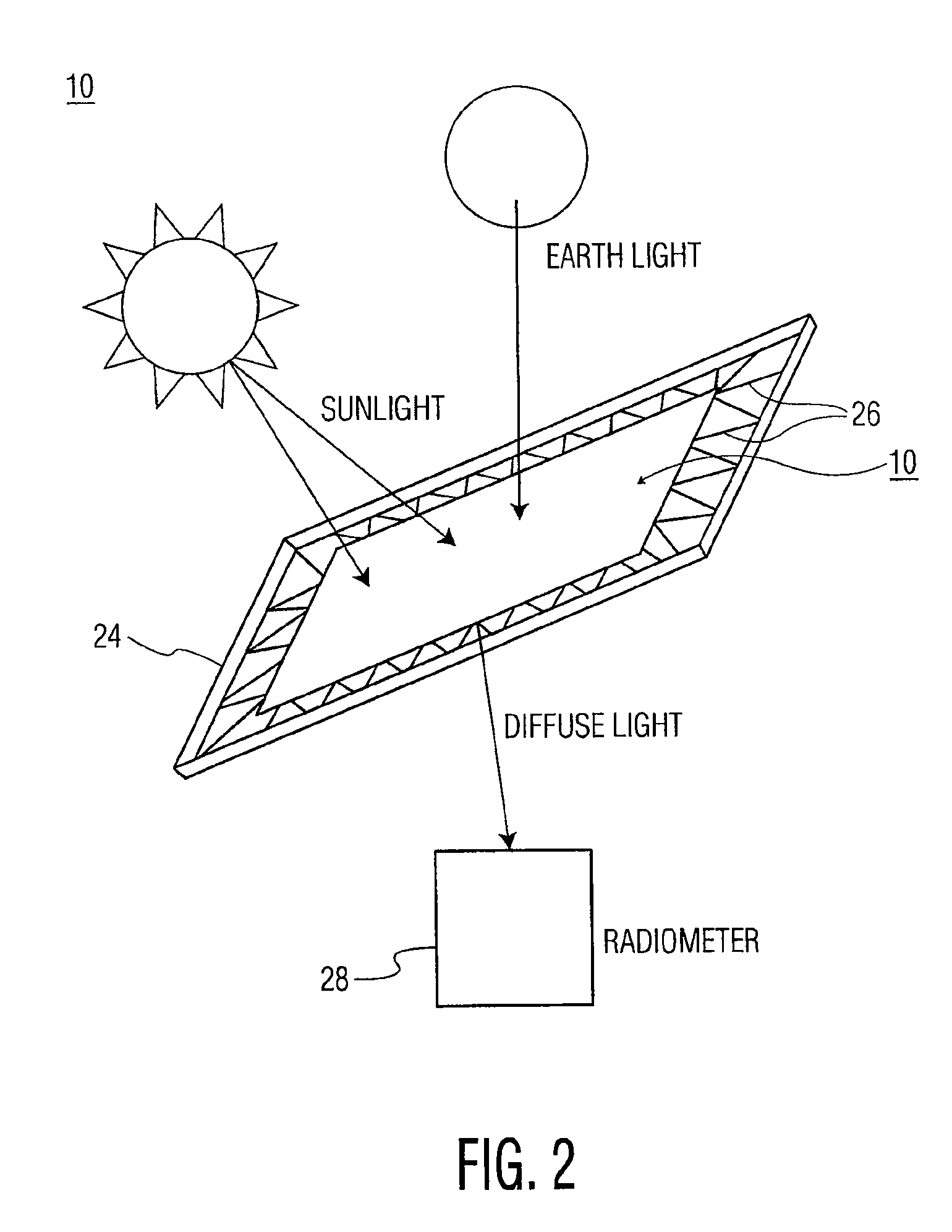
Transmissive diffuser with a layer of polytetrafluoroethylene on the output surface for use with an on-orbit radiometric calibration
A flux diffuser for radiometrically calibrating an imaging sensor using the sun as a calibration light source, the flux diffuser including a fiberglass cloth having input and output surfaces. The input surface receives solar irradiance, and the output surface provides diffused scattered light to a radiometer. A layer of mylar may be disposed on top of the input surface. A layer of PTFE or Spectralon™ may be disposed on top of the output surface, and another layer of mylar may be disposed on top of the layer of PTFE or Spectralon™.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Diffuse scattering film, preparation method thereof and use thereof
ActiveCN108570178AHigh light transmittanceHigh hazeClimate change adaptationGreenhouse cultivationGreenhouseOptical transmittance
The present invention provides a diffuse scattering film, a preparation method thereof and use thereof. The film includes a transparent polymer and organic light scattering particles uniformly distributed in the transparent polymer. The mass of the organic light scattering particles is not more than 5 wt% of the mass of the transparent polymer. The diffuse scattering film can effectively prevent leaves of crops in a greenhouse from being burnt when the light is too strong while maintaining high light transmittance and maintaining excellent illumination, and can ensure that the back of leaves can receive diffused light emitted by the film, thus increasing the photosynthesis efficiency of crops.
Owner:JIANGSU YONGXIN MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Method and device for detecting roughness of inner surface of micro-pore
InactiveCN103615992AImprove detection efficiencyEnables parallel measurementsUsing optical meansRough surfaceLinear relationship
The invention provides a method and device for detecting the roughness of the inner surface of a micro-pore. The method comprises the steps that diffuse scattering luminous fluxes of different positions modulated through the rough surface intensity are collected so that the roughness can be evaluated; a non-linear relationship exists between the ratio of voltages generated by two sets of luminous fluxes and the roughness, a micro-pore with the known roughness is calibrated, the micro-pore to be detected is compared with a calibration value, and then the roughness of the micro-pore to be detected is detected. By the adoption of the method and device for detecting the roughness of the inner surface of the micro-pore, the problem that a sensor cannot extend into the micro-pore in the prior art is solved, the angle of the sensor can be changed flexibly and conveniently, the measurement accuracy is high, and efficiency is high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Reflection type substrate
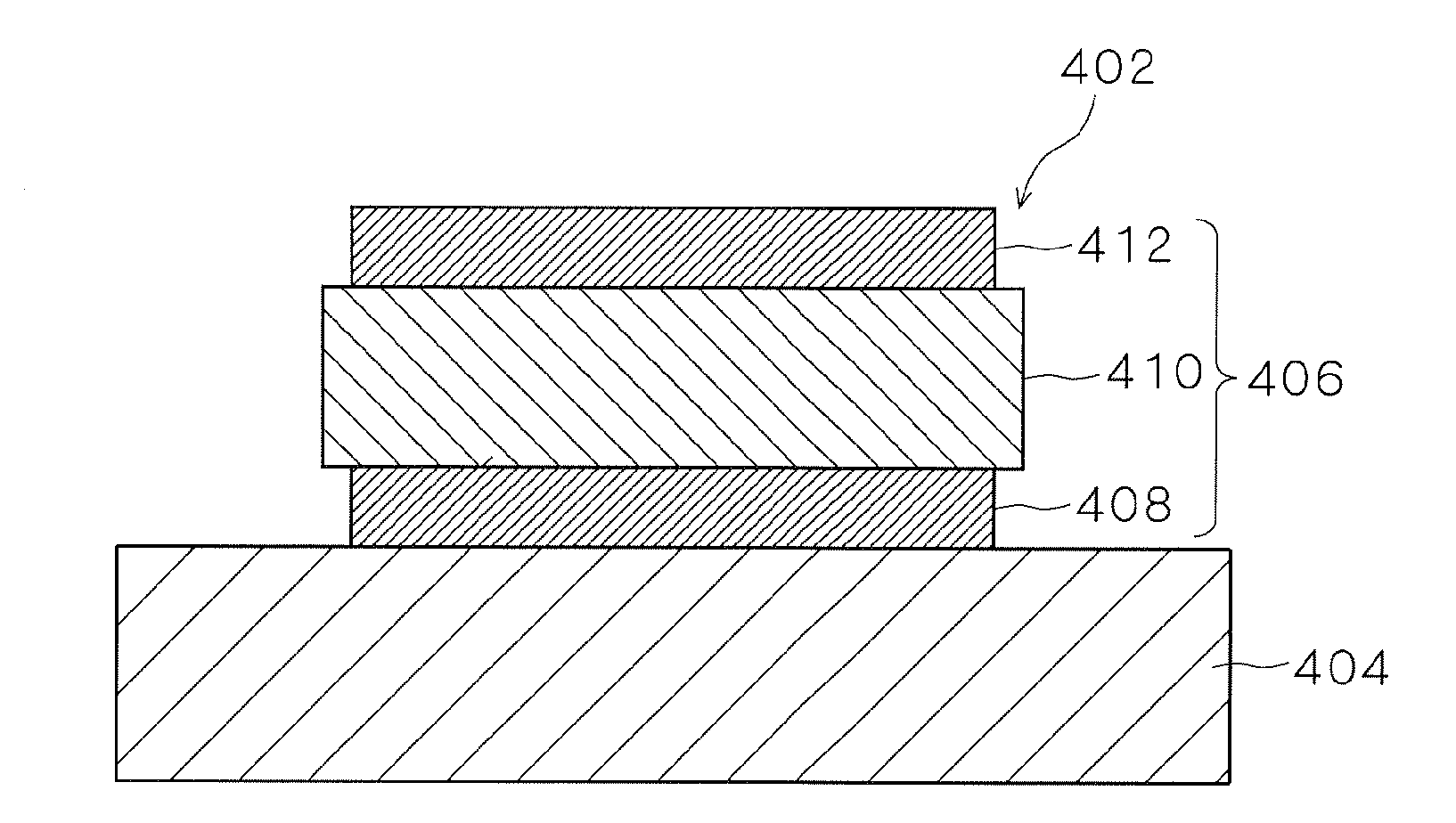
ActiveCN101323879ASmall sizeGuaranteed CompatibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingHigh signal intensityFluorescence
The invention discloses a reflection-typed substrate which is a specular reflection-typed substrate for a biochip applied to the biological field, comprising a base and a chemical modification layer supporting and combining with biological molecules on the base; a film layer for reducing the diffuse scattering of a fluorescence signal is arranged between the base and the chemical modification layer supporting and combining with the biological molecules. In a condition that the chemical modification layer supporting and combining with the biological molecules of the reflection-typed substrate ensures combination capability between the substrate and the biological molecules (the combination capability is enhanced by the chemical modification layer to a certain extent), the arrangement of the film layer for reducing the diffuse scattering of the fluorescence signal further promotes the strength and flexibility of the signal when the biochip is used for detection, solves the situation that on a solid medium, the fluorescence signal scatters in a diffuse way towards each direction, causes the fluorescence signal of the marked biological molecules to reflect directionally and a biological signal with high contrast ratio, high signal strength and high flexibility to be obtained at a signal collection end (a photoelectric magnification tube (PMT) and matrix of charge coupled device (CCD)) of scanning equipment.
Owner:张波
Device and method for the optical detection of objects
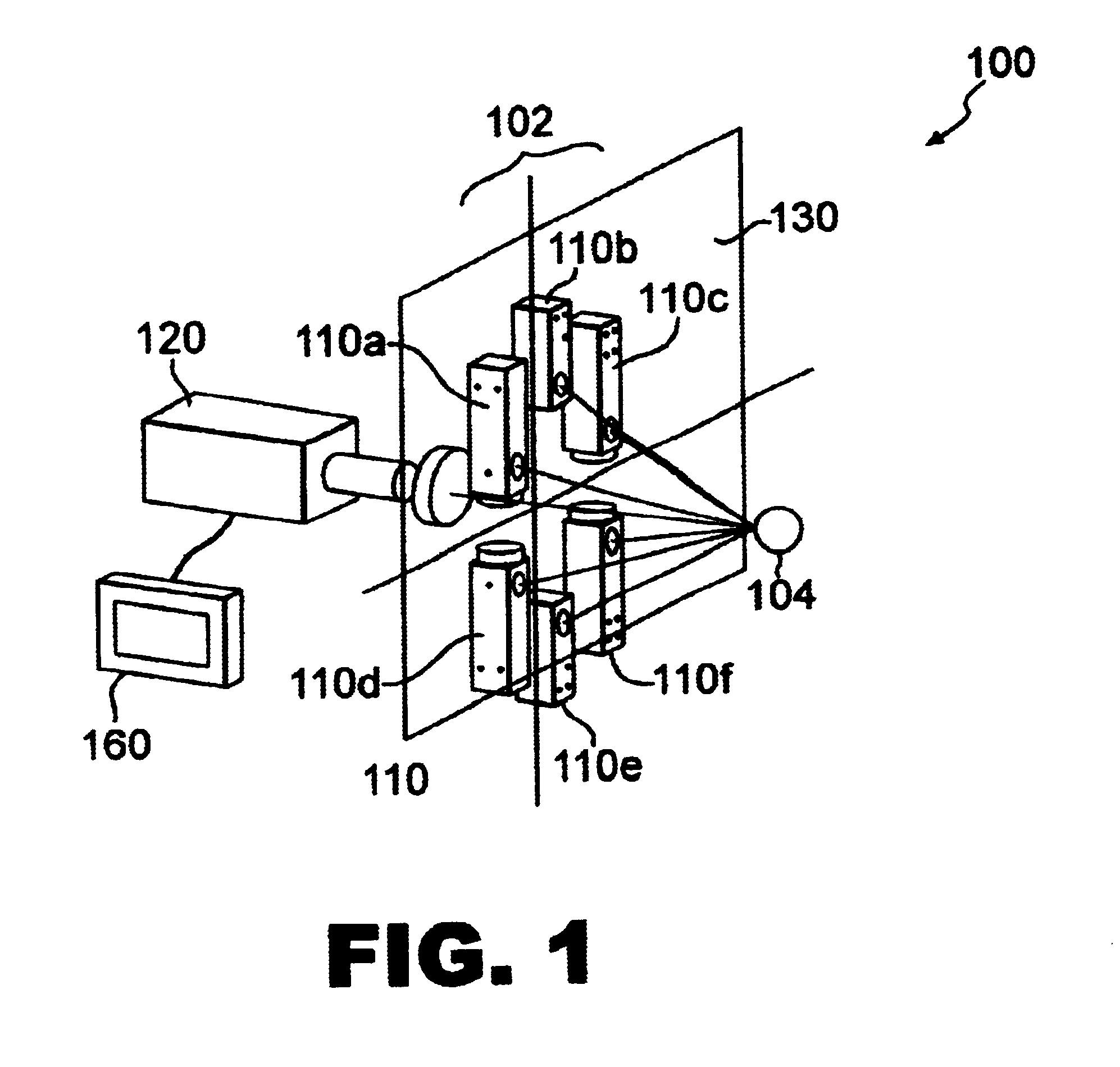
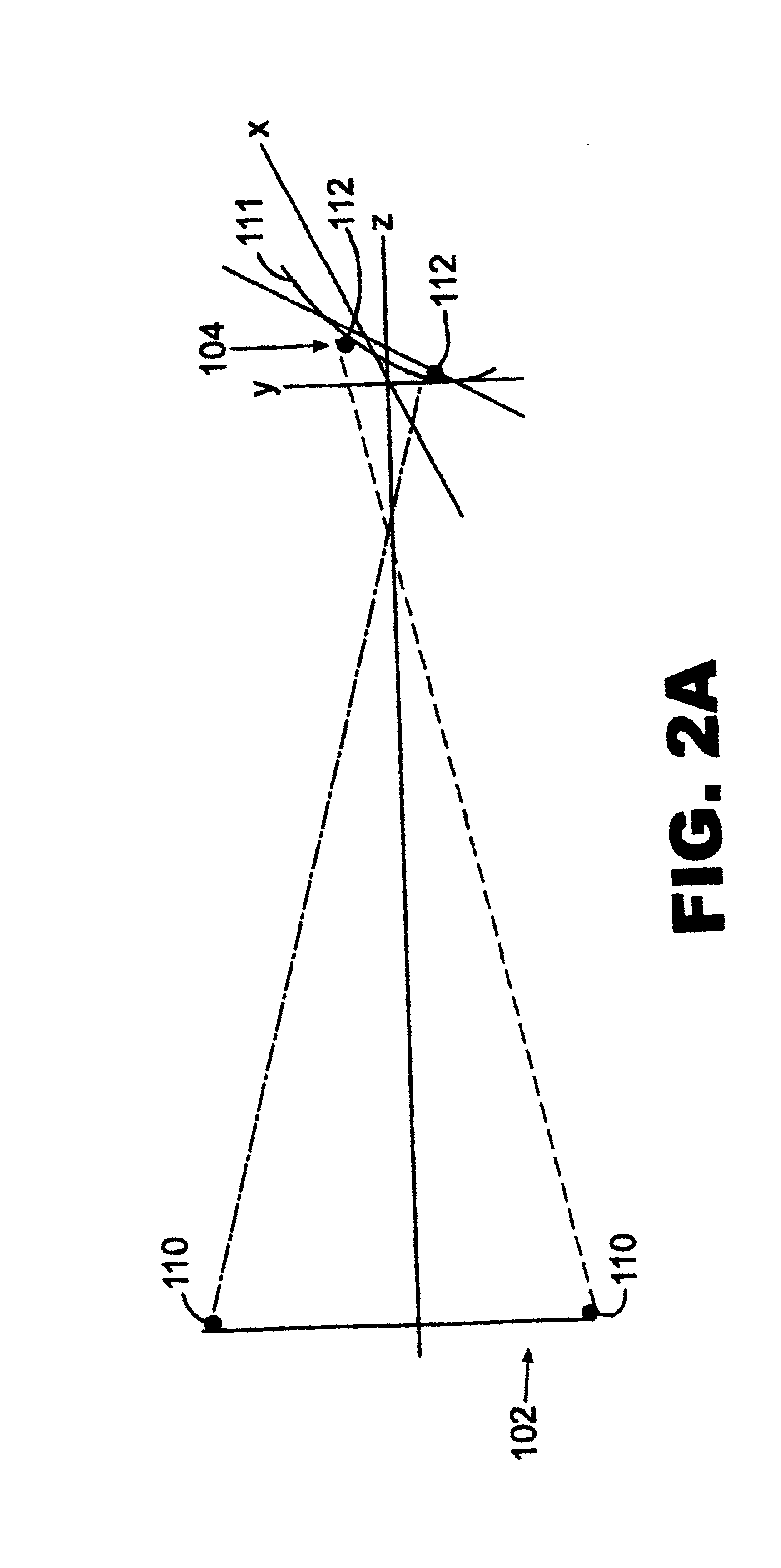
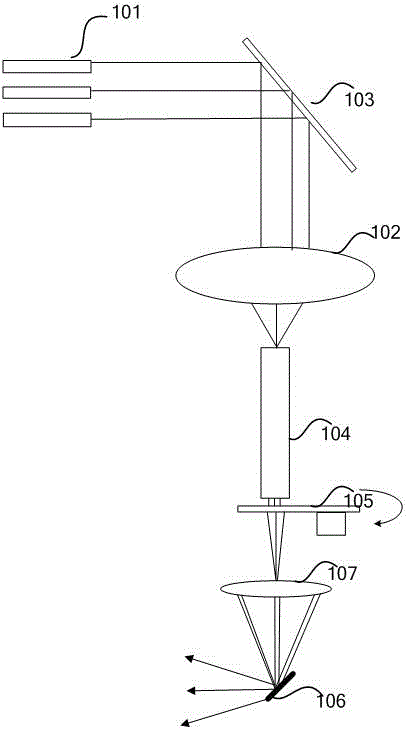
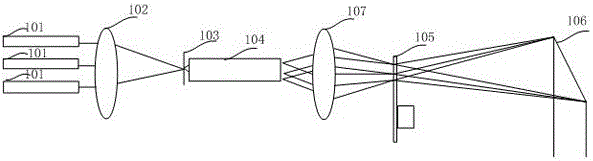
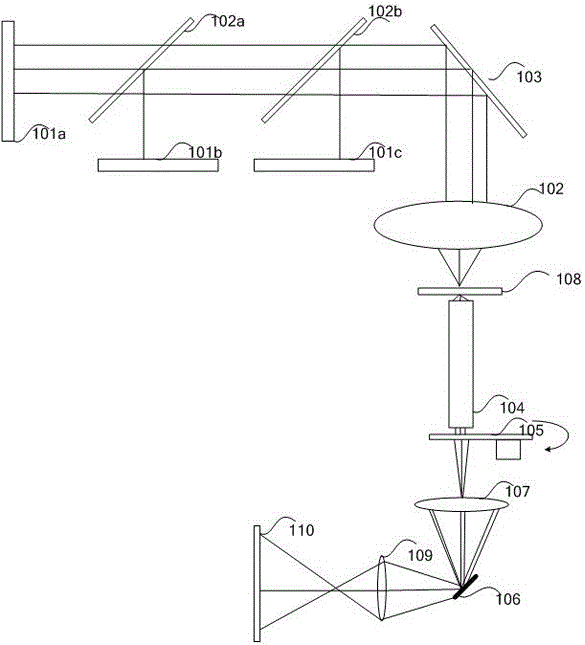
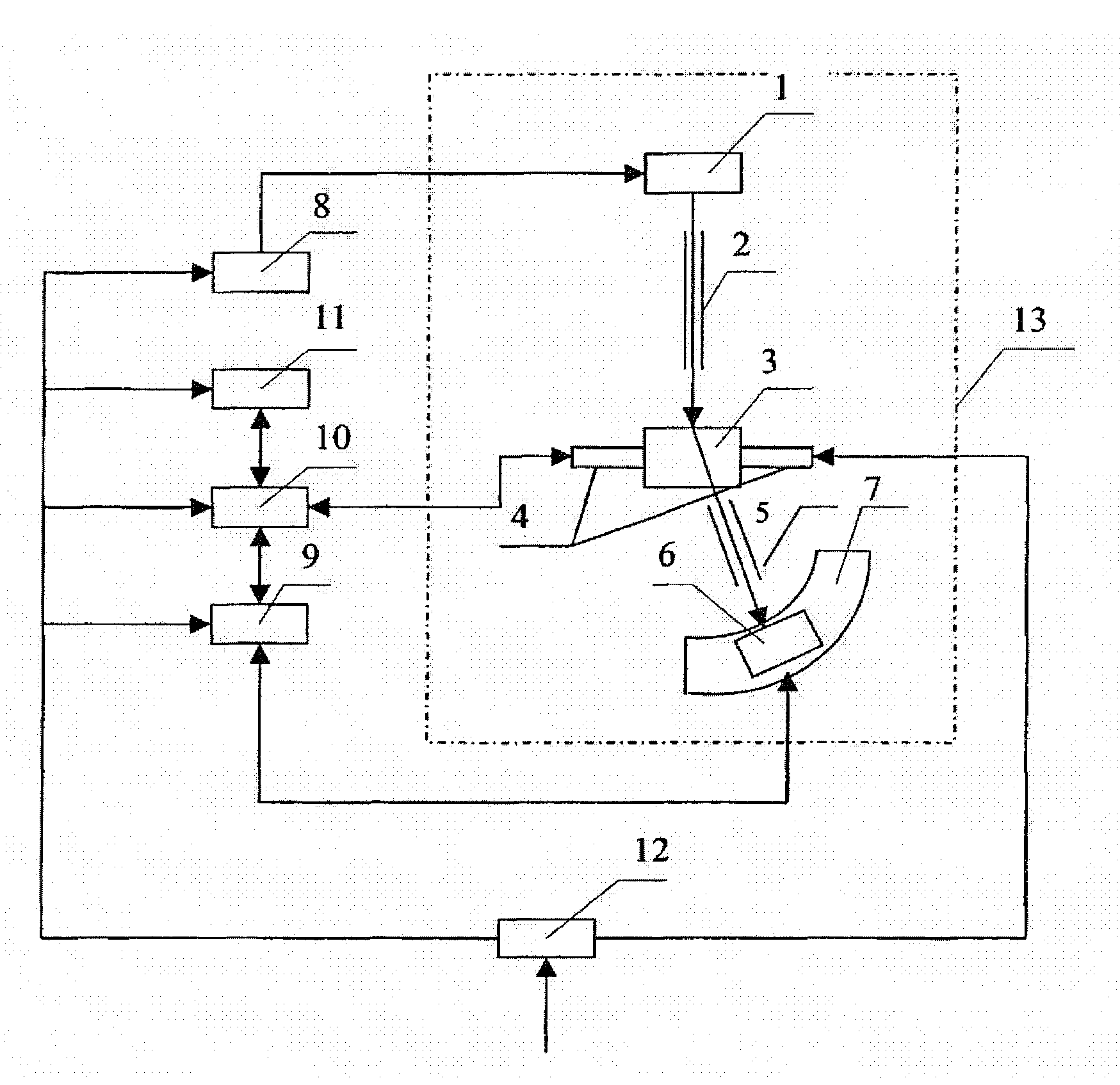
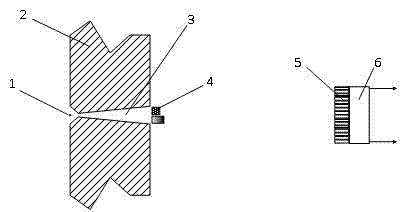
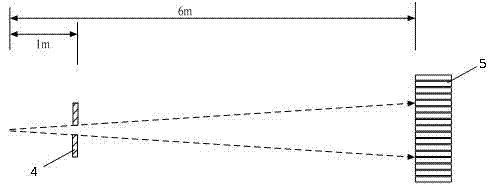
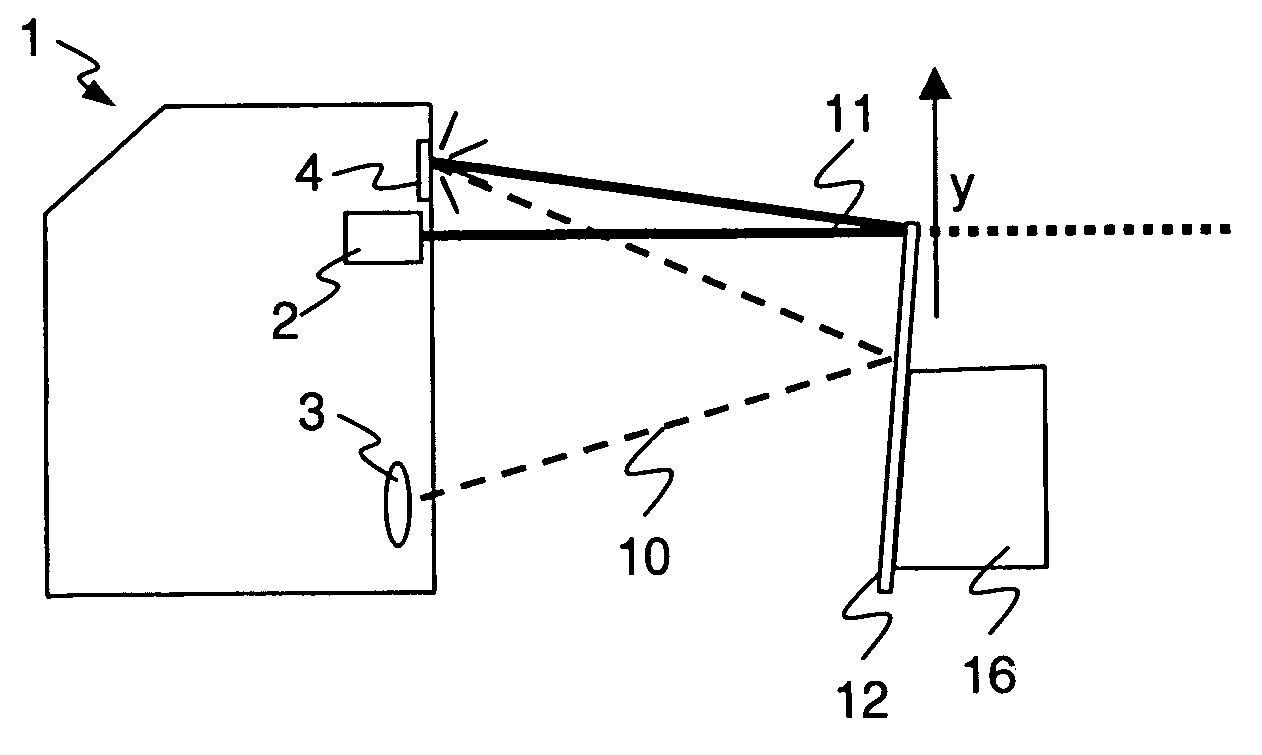
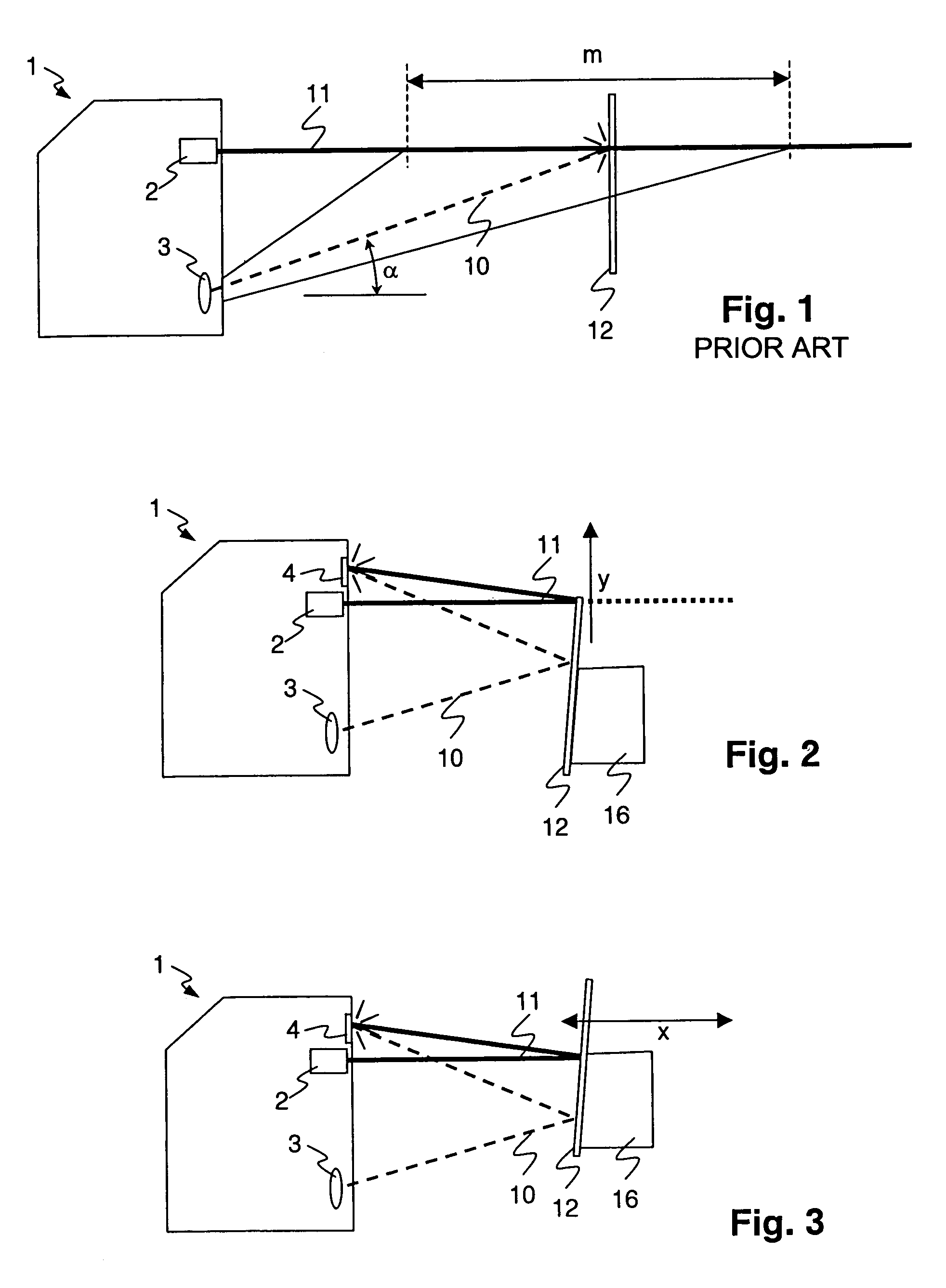
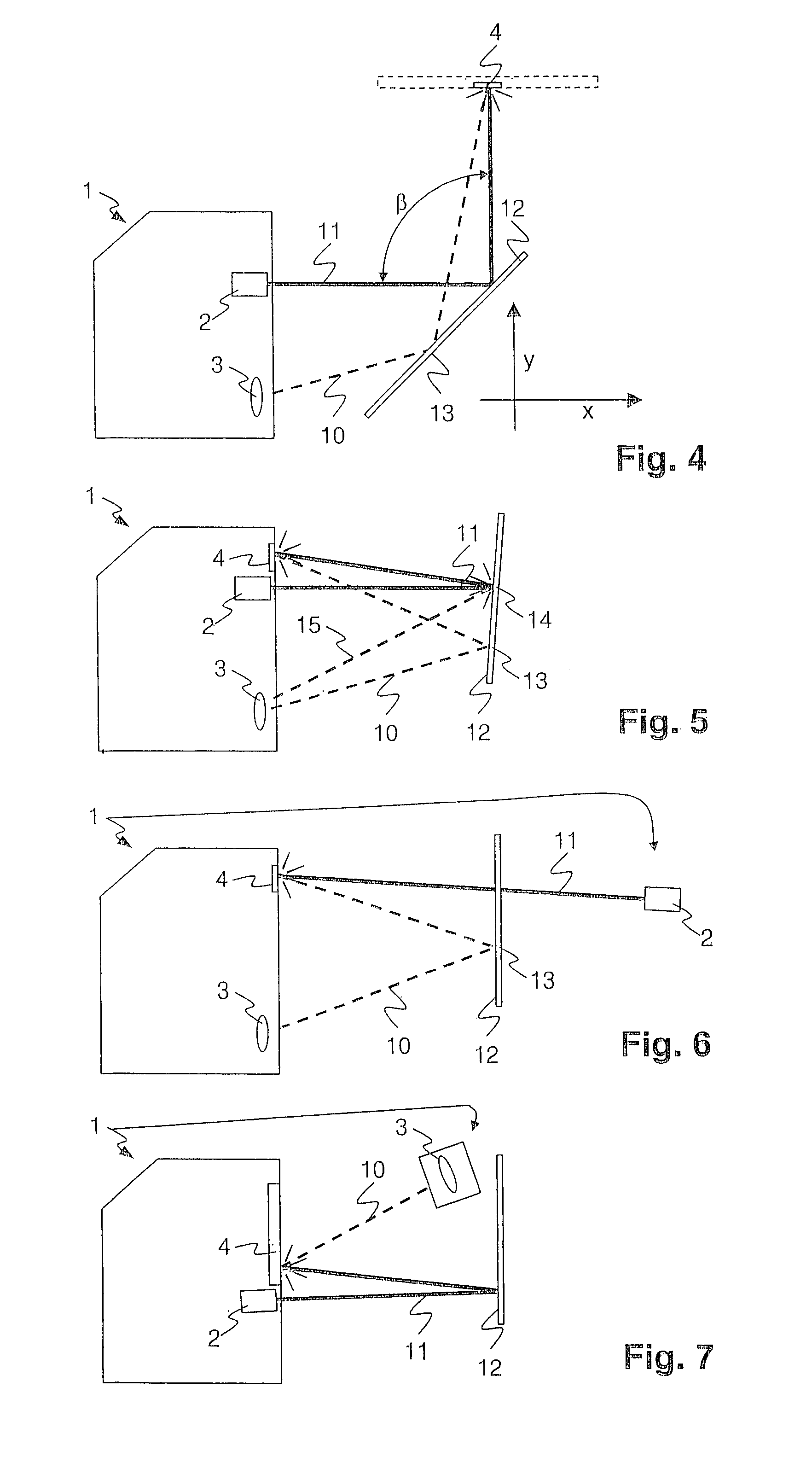
InactiveUS7046378B2Easy to adjustPrecise alignmentOptical rangefindersUsing optical meansSpecular reflectionDiffuse scattering
A method and a device for the optical distance measurement and for the optical detection of objects with an at least partially specular reflective surface (12) wherein light through the specular reflective surface (12) and a diffuse scattering at a reflector (4) is directed to light receiving means and detected there.
Owner:BAUMER ELECTRIC
Asymmetric millimeter wave and submillimeter wave wireless channel simulation method
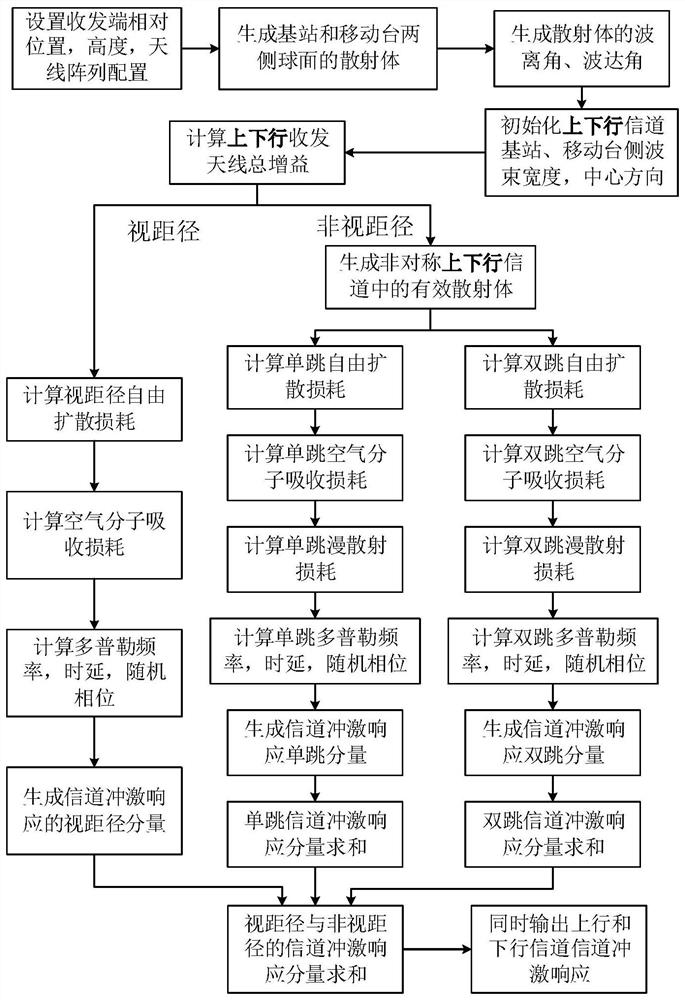
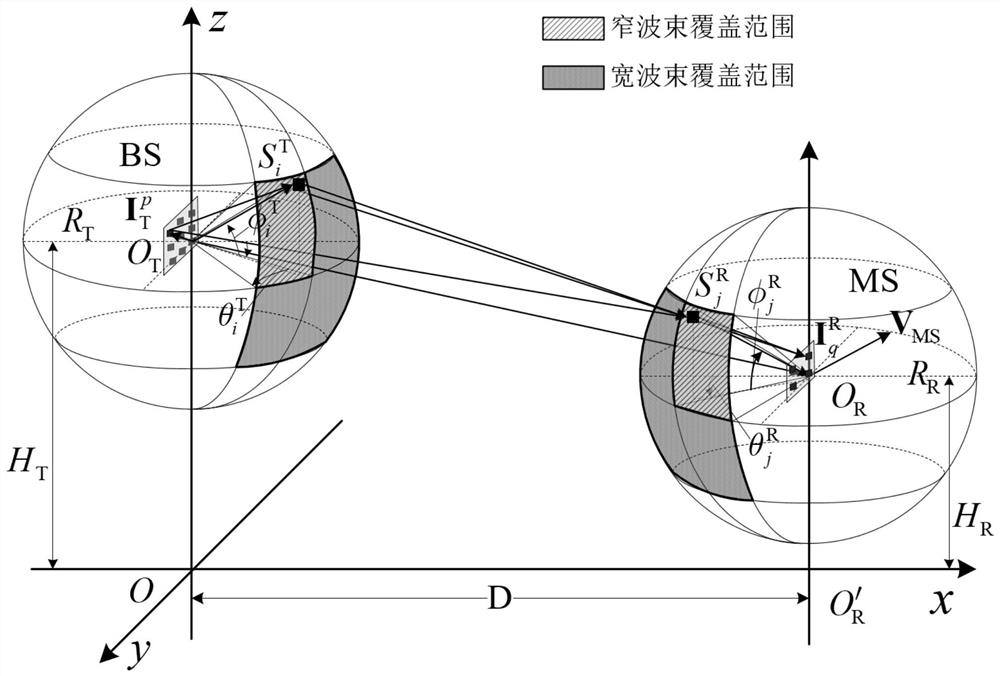
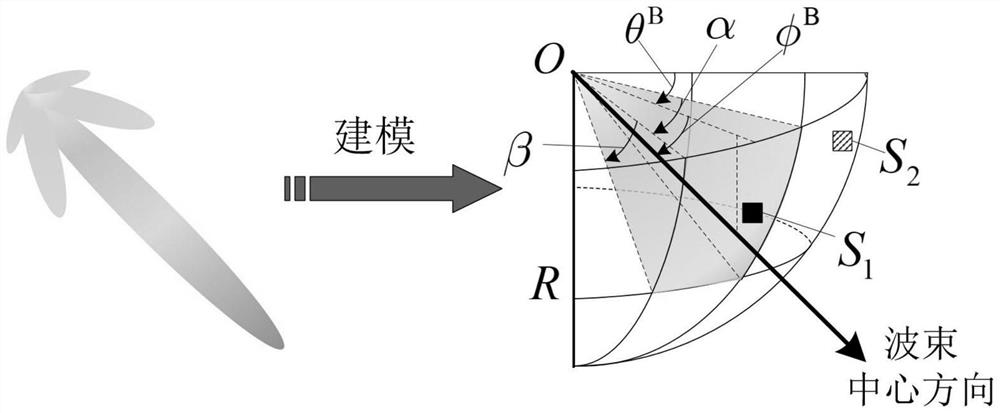
ActiveCN113364544ARealize simulationReduce complexityTransmission monitoringCommunications systemChannel impulse response
The invention discloses an asymmetric millimeter wave and submillimeter wave outdoor channel simulation method, and relates to the field of wireless communication. According to the method, the characteristic that the channel distribution environment shows asymmetry is fully considered, the millimeter wave and submillimeter wave channel simulation method is designed, and millimeter wave and submillimeter wave wireless channel impulse response and parameters under the asymmetry condition can be generated through adoption of the method. Channel impulse response is divided into a sight distance path, a single hop and a double hop by combining the propagation characteristics of air molecule absorption and rough surface diffuse scattering of millimeter waves and submillimeter waves, so that parameter description and channel simulation of uplink and downlink channels are accurately realized. And moreover, the correlation of the asymmetric uplink and downlink channels is fully utilized, so that the complexity of channel response and channel parameter generation is effectively reduced, and the practicability of the method in system simulation verification application is enhanced. The method can be applied to design and deployment of an asymmetric millimeter wave and submillimeter wave communication system, and theoretical and model bases are provided.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Matt, thermoformable, IR-reflective polyester film
InactiveUS7189452B2Synthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsPolyesterPolyethylene terephthalate
Biaxially oriented polyester films formed from a crystallizable polyester having increased diethylene glycol content and / or increased polyethylene glycol content, and / or increased isophthalic acid content, preferably polyethylene terephthalate. The films of the invention further include at least one IR-reflective pigment and one UV stabilizer. The inventive films feature adjustable mattness, diffuse scattering power for visible light, high light transmittance and IR reflectance and good thermoformability, and are suitable for thermally protective coatings or thermally protective packaging.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POLYESTER FILM
Thin film temperature measurement using optical absorption edge wavelength
ActiveUS8786841B2Precise and real-time measurementRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationLength waveSemiconductor
Owner:K SPACE ASSOCS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com