Patents
Literature
651 results about "Neutron detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
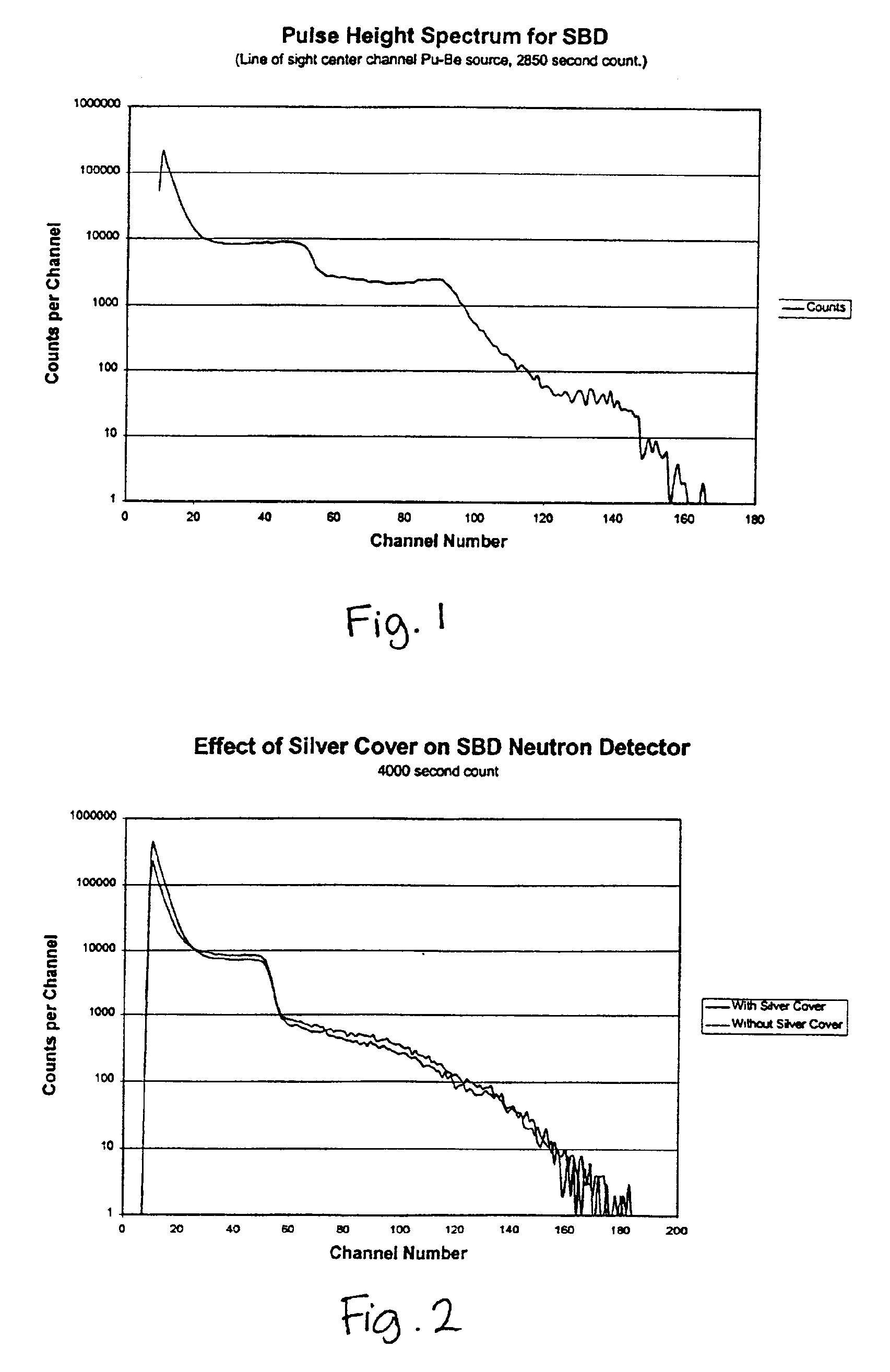
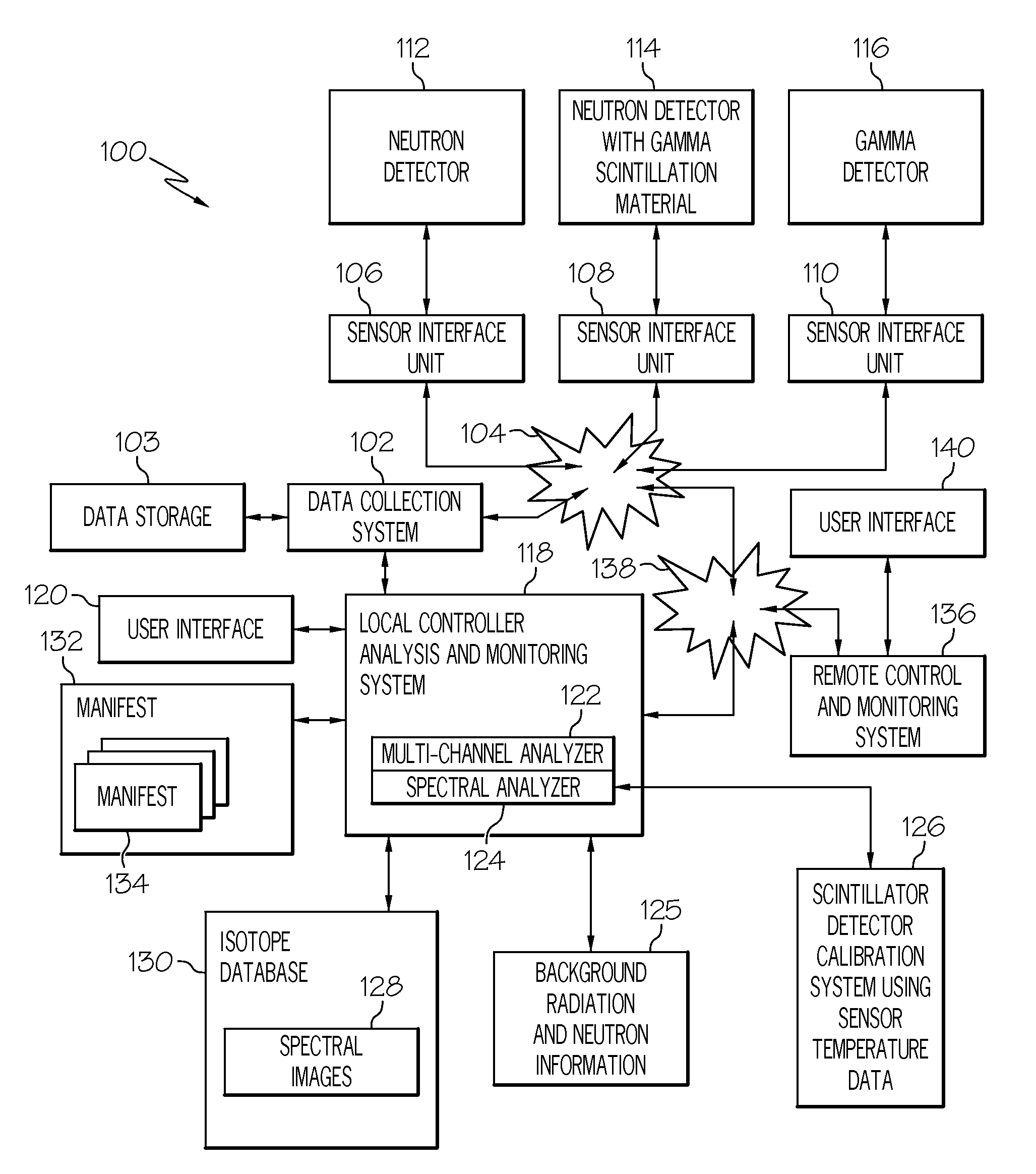
Neutron detection is the effective detection of neutrons entering a well-positioned detector. There are two key aspects to effective neutron detection: hardware and software. Detection hardware refers to the kind of neutron detector used (the most common today is the scintillation detector) and to the electronics used in the detection setup. Further, the hardware setup also defines key experimental parameters, such as source-detector distance, solid angle and detector shielding. Detection software consists of analysis tools that perform tasks such as graphical analysis to measure the number and energies of neutrons striking the detector.
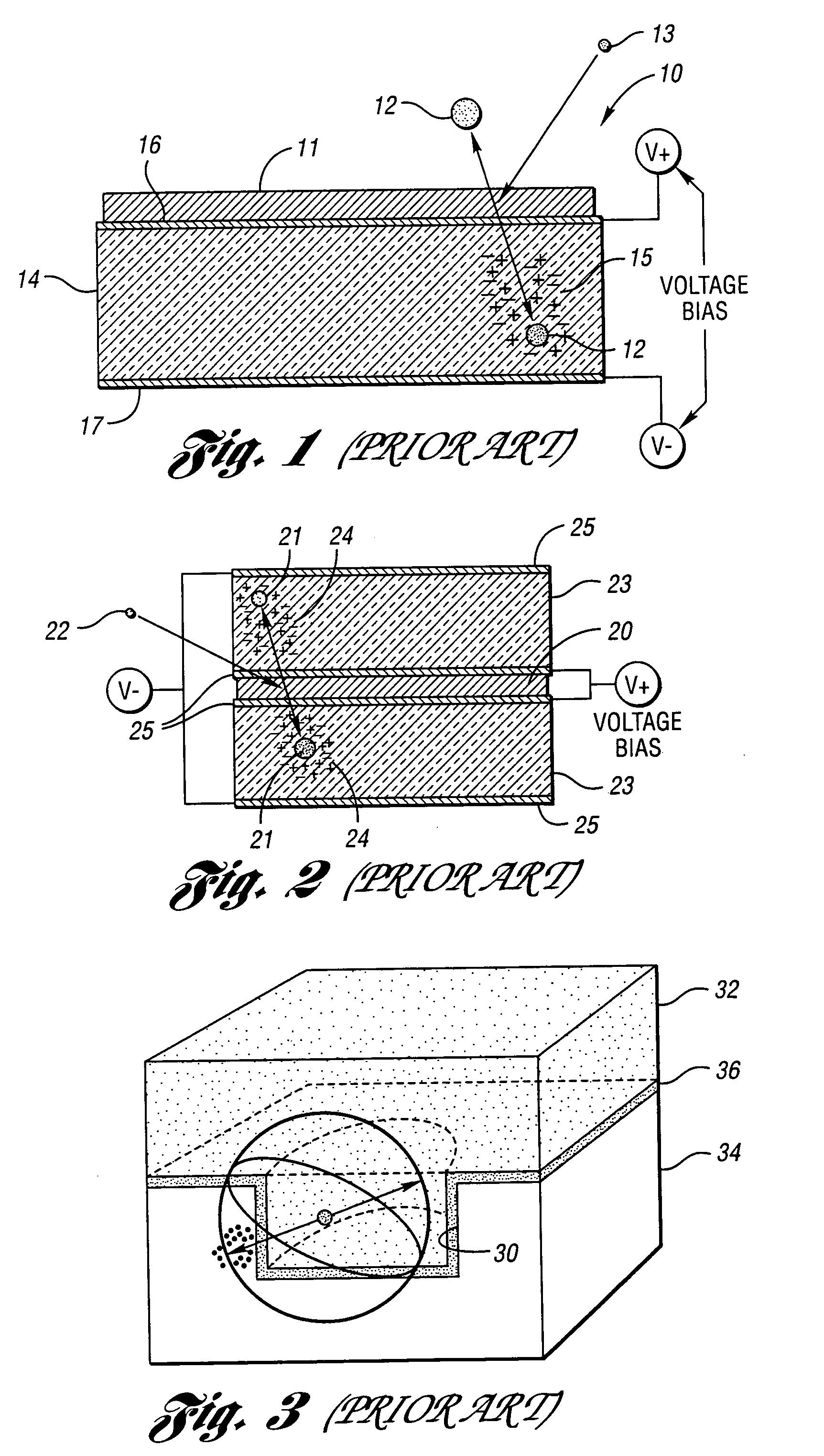
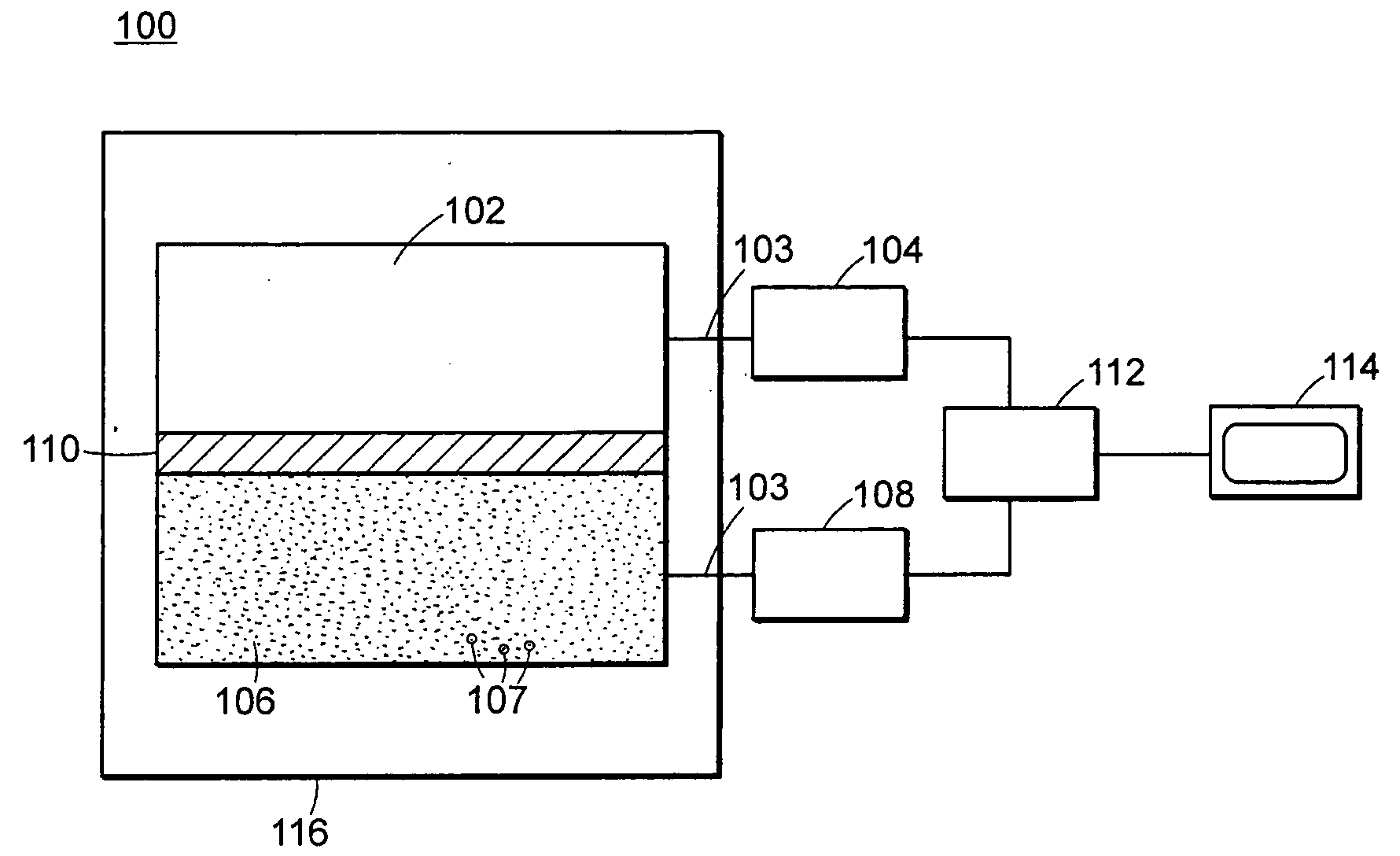
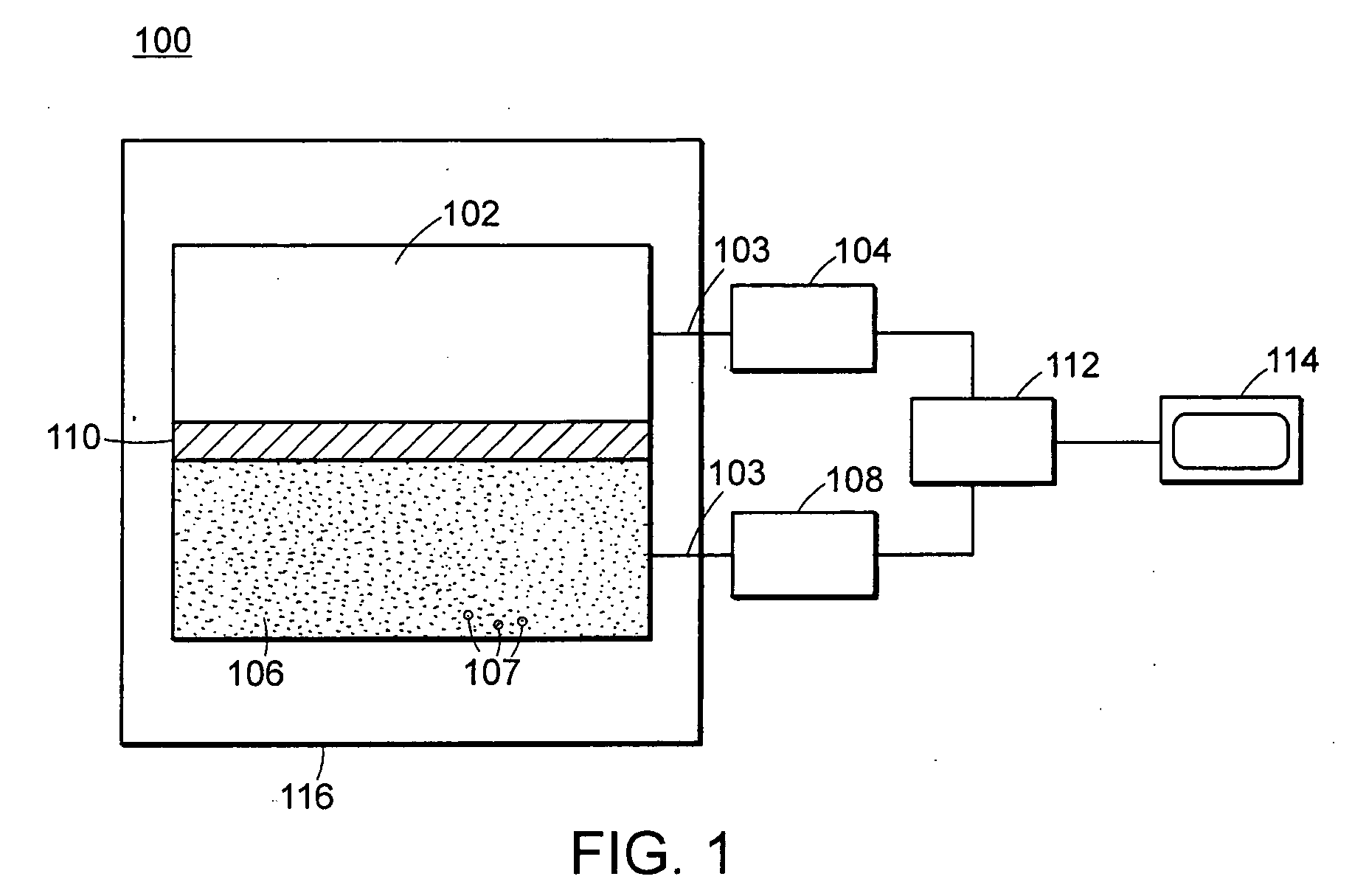
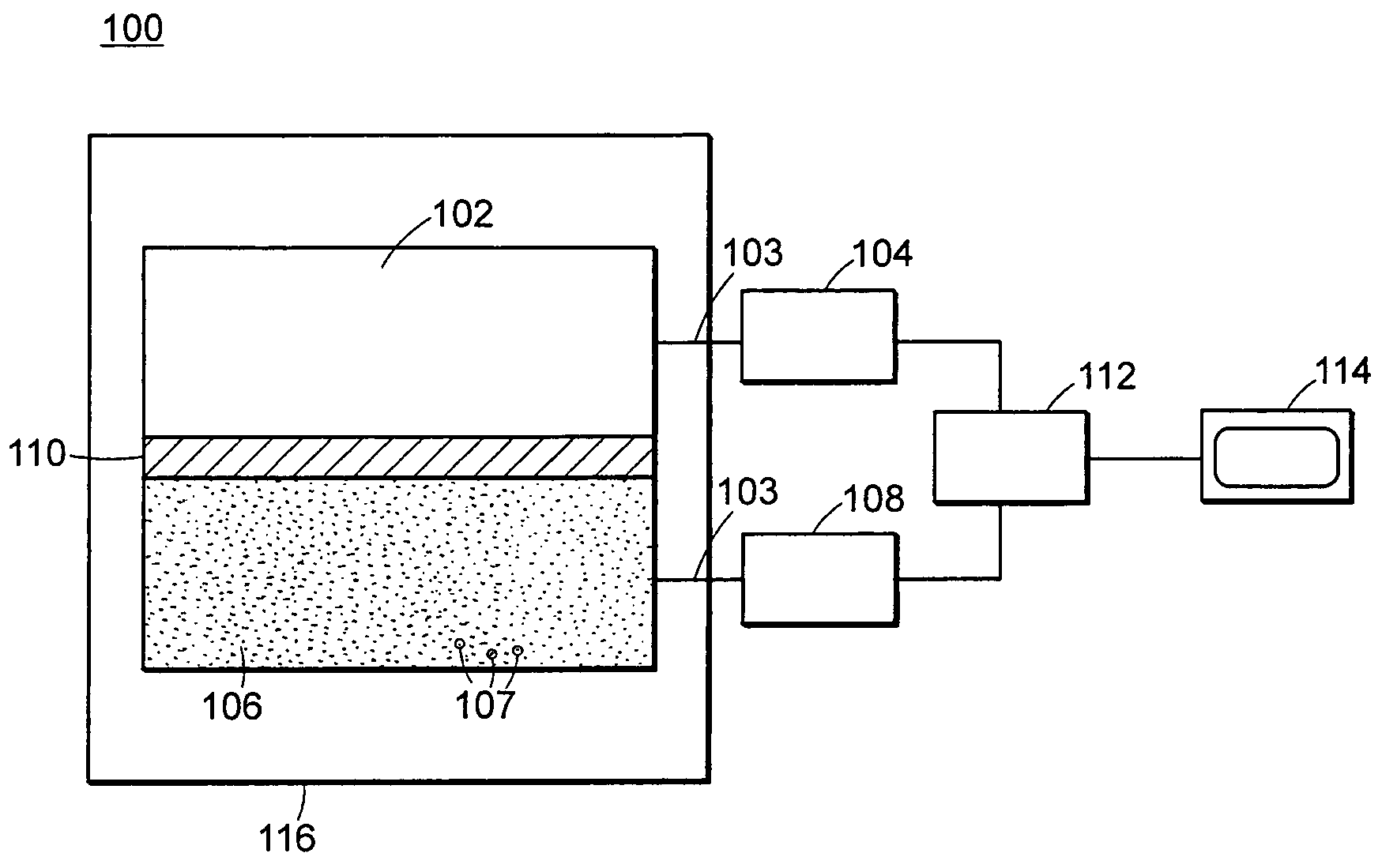
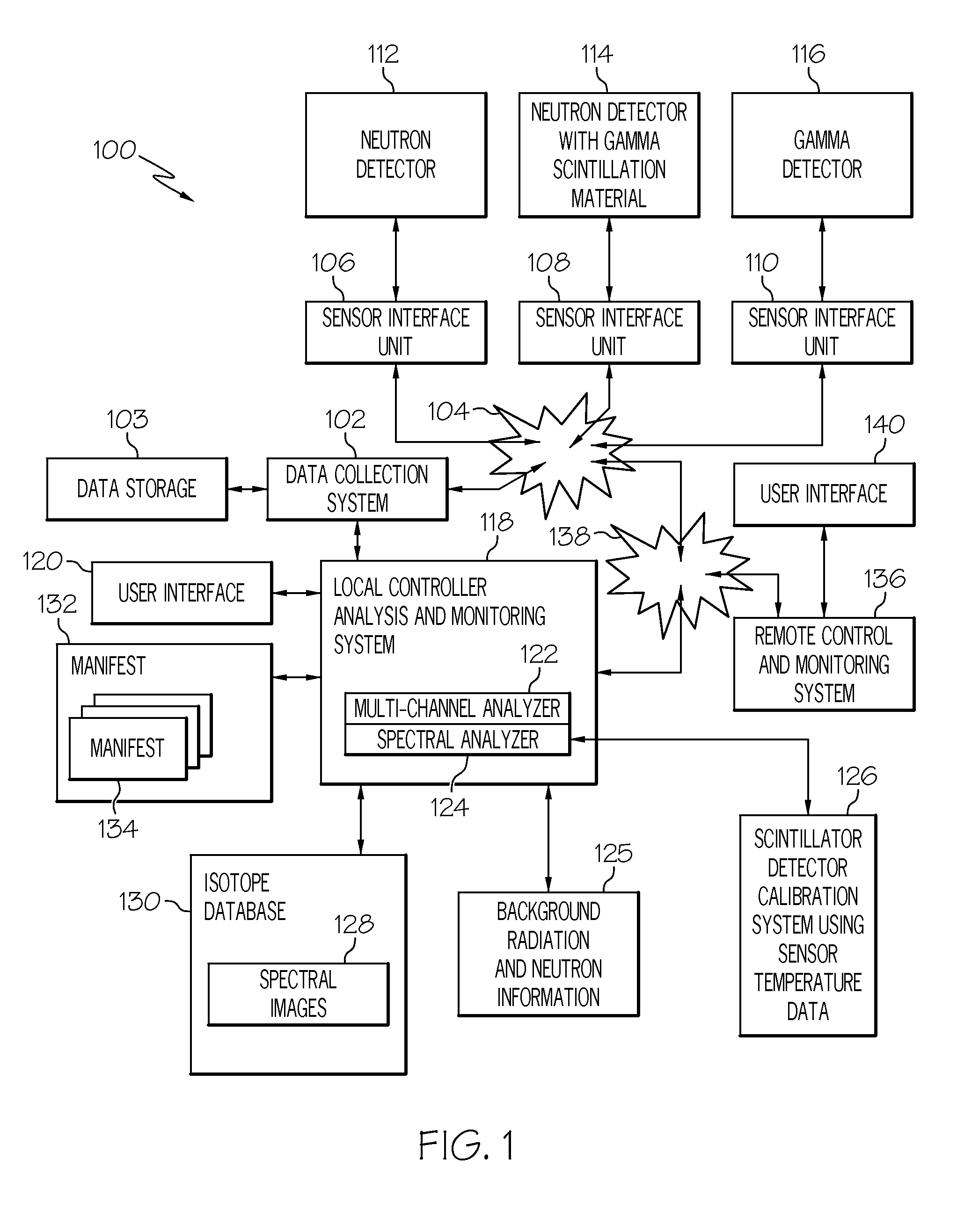
Method and system for high energy, low radiation power X-ray imaging of the contents of a target
ActiveUS7453987B1Affordable enhanced detectionReduce system costX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSoft x rayHigh energy
The systems and methods described herein automatically detect, highlight and identify high-Z materials in volume concentrations of approximately 100 cm3 or greater utilizing single and / or dual energy sources with x-ray and neutron detectors. The methods and systems described herein are applied to the imaging of containerized cargo and cargo vehicles. Pursuant to the described systems and methods, radiation powers are orders of magnitude lower than those used in the conventional systems. By reducing the radiation power by a factor of, for example, 100 or more, the shielding requirements for the system are greatly reduced, alignment requirements can be significantly relaxed and system components can be lighter weight and more modular. Consequently, system costs are reduced.
Owner:LEIDOS
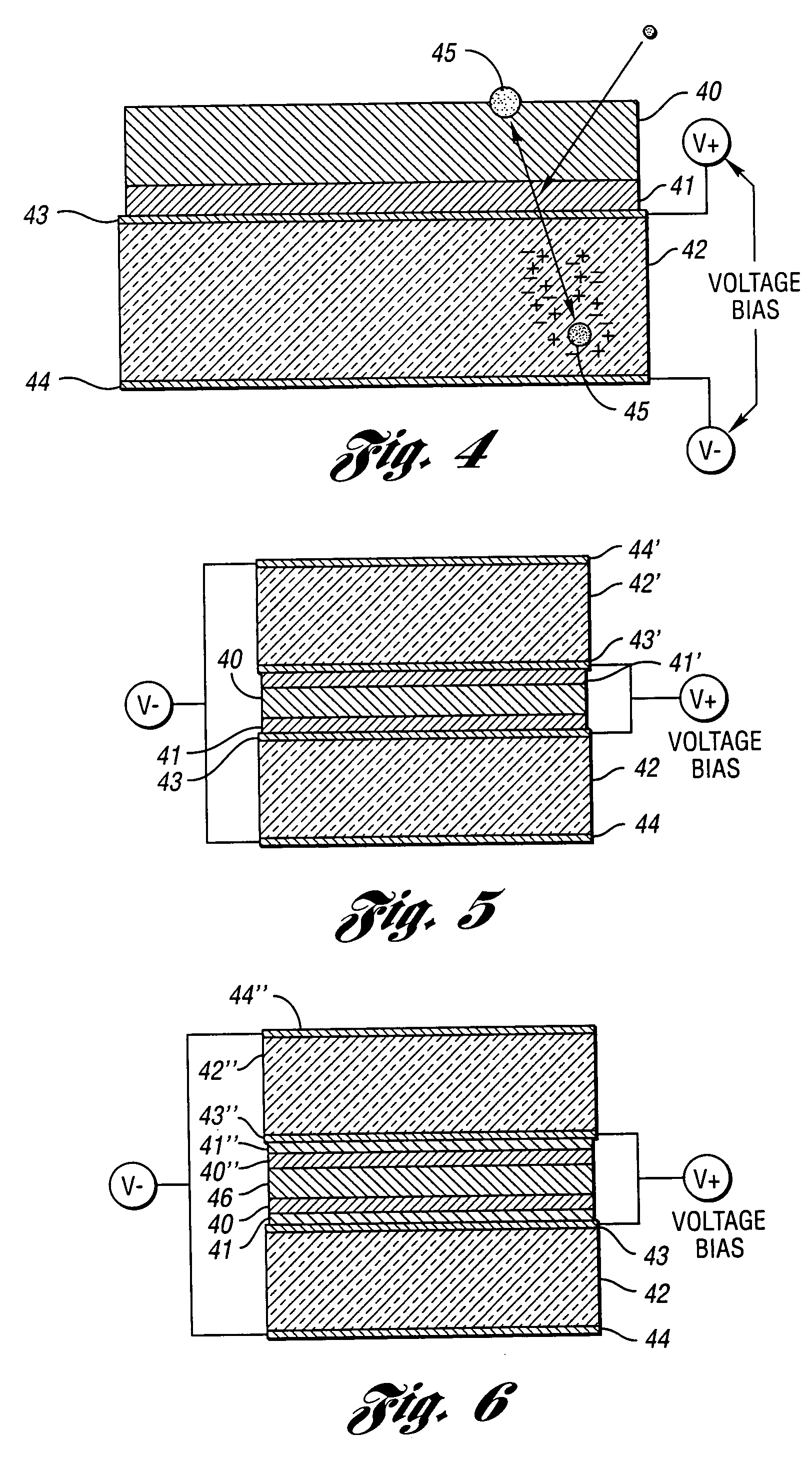
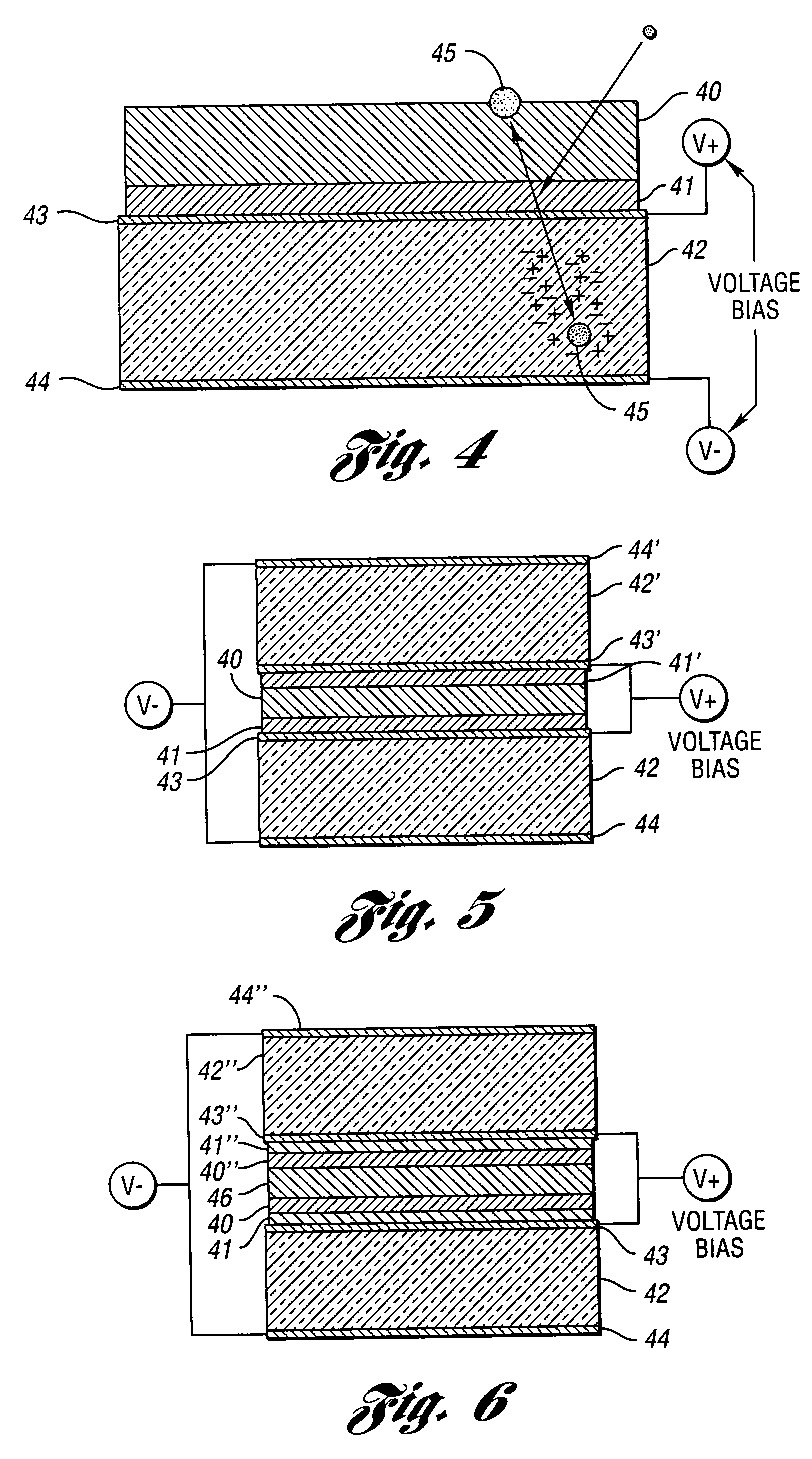
High-efficiency neutron detectors and methods of making same
ActiveUS20050258372A1Efficient detectionThin and compactMeasurement with semiconductor devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansRoom temperatureReactive material
Neutron detectors, advanced detector process techniques and advanced compound film designs have greatly increased neutron-detection efficiency. One embodiment of the detectors utilizes a semiconductor wafer with a matrix of spaced cavities filled with one or more types of neutron reactive material such as 10B or 6LiF. The cavities are etched into both the front and back surfaces of the device such that the cavities from one side surround the cavities from the other side. The cavities may be etched via holes or etched slots or trenches. In another embodiment, the cavities are different-sized and the smaller cavities extend into the wafer from the lower surfaces of the larger cavities. In a third embodiment, multiple layers of different neutron-responsive material are formed on one or more sides of the wafer. The new devices operate at room temperature, are compact, rugged, and reliable in design.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
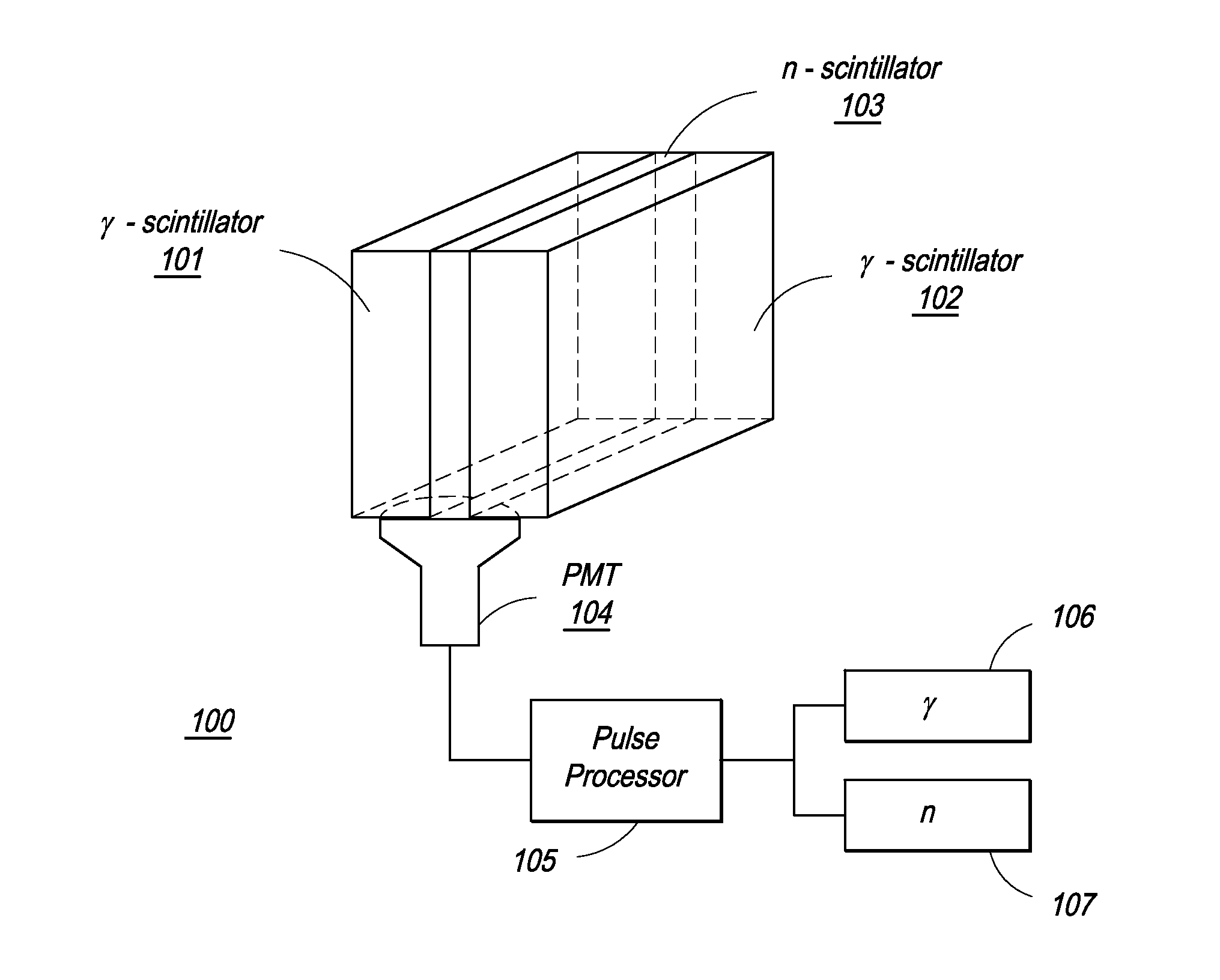
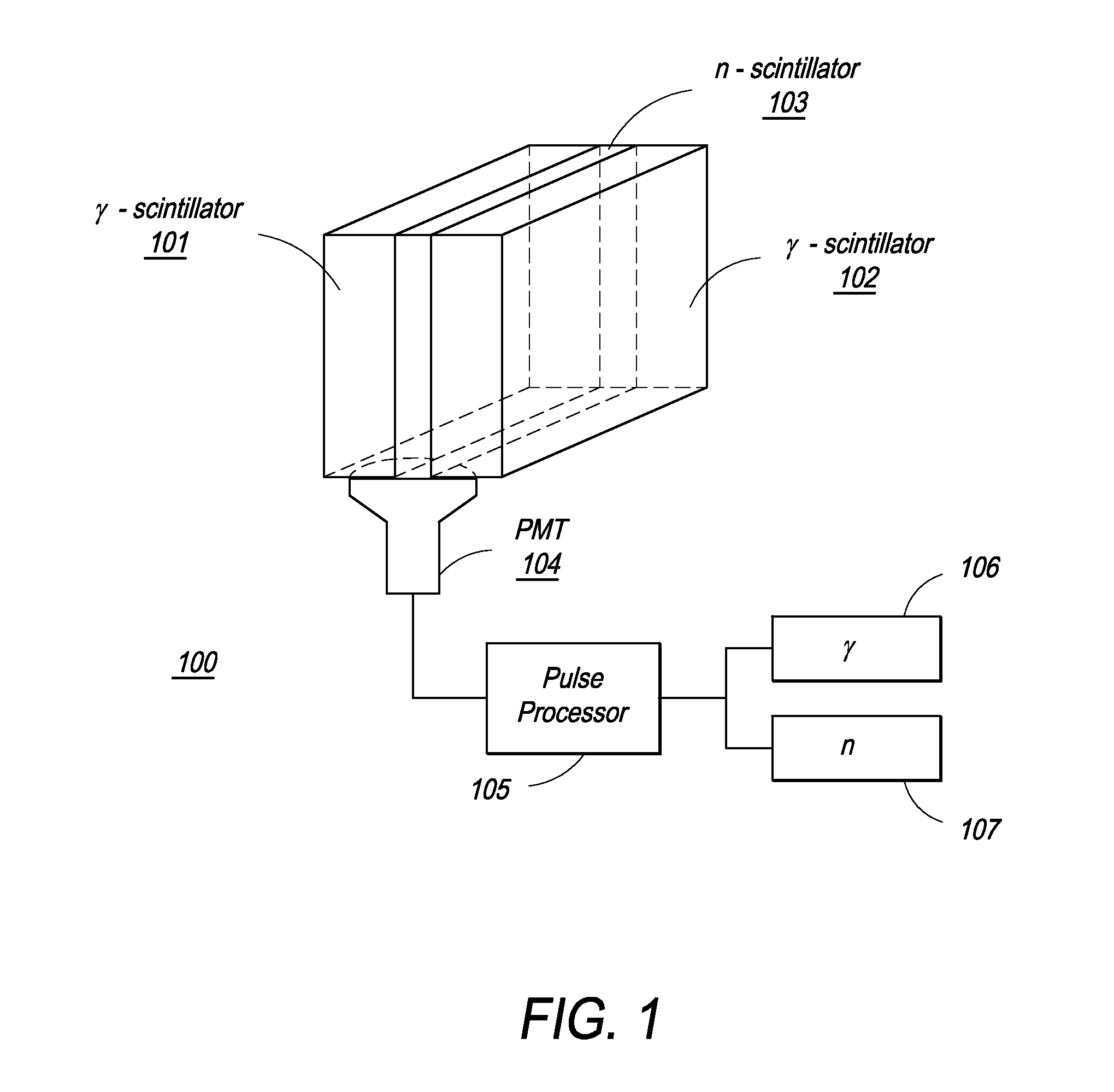
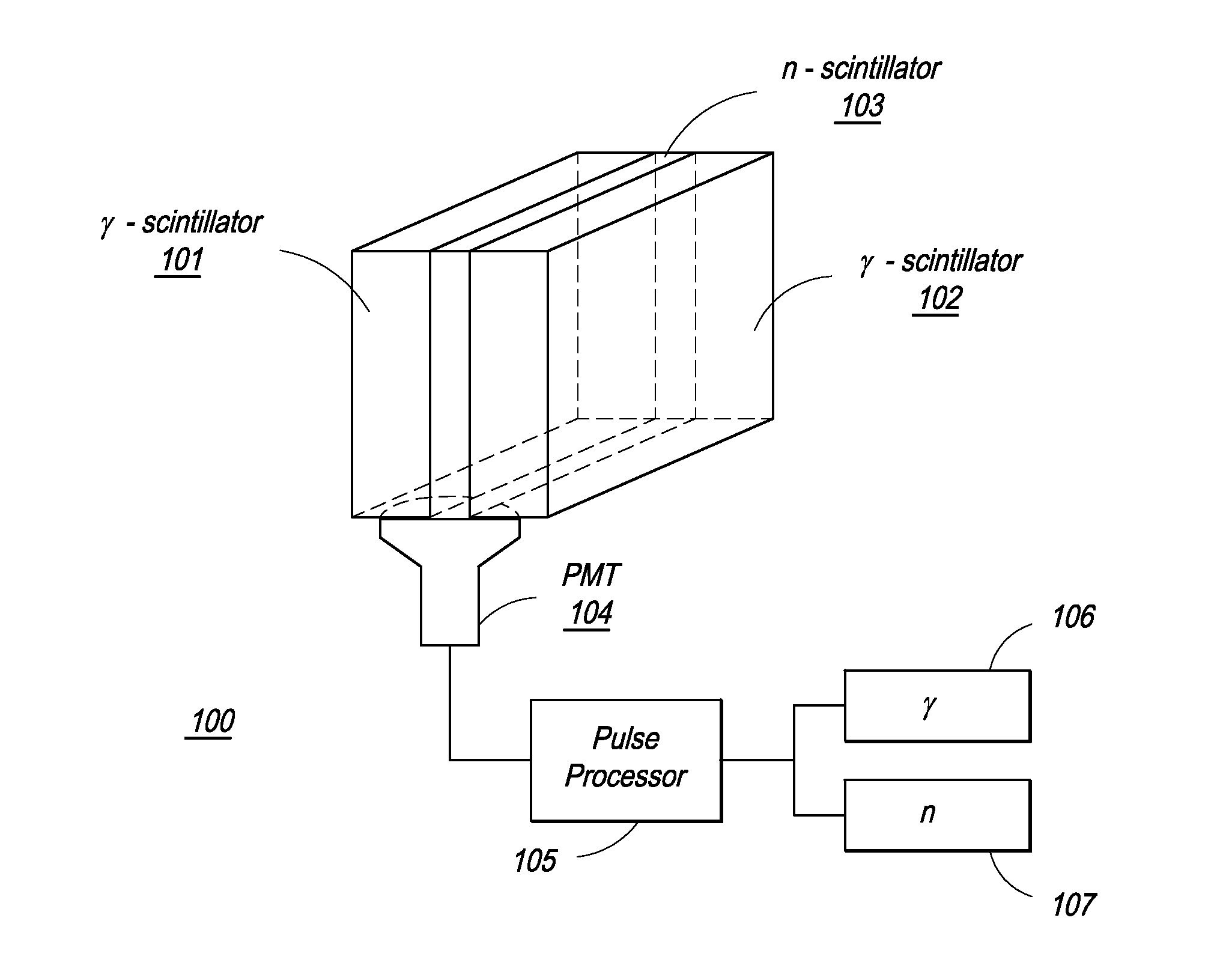
Composite Gamma-Neutron Detection System
ActiveUS20110204243A1Avoid cross contaminationMultiplier cathode arrangementsMeasurement with scintillation detectorsHeavy particleLight guide
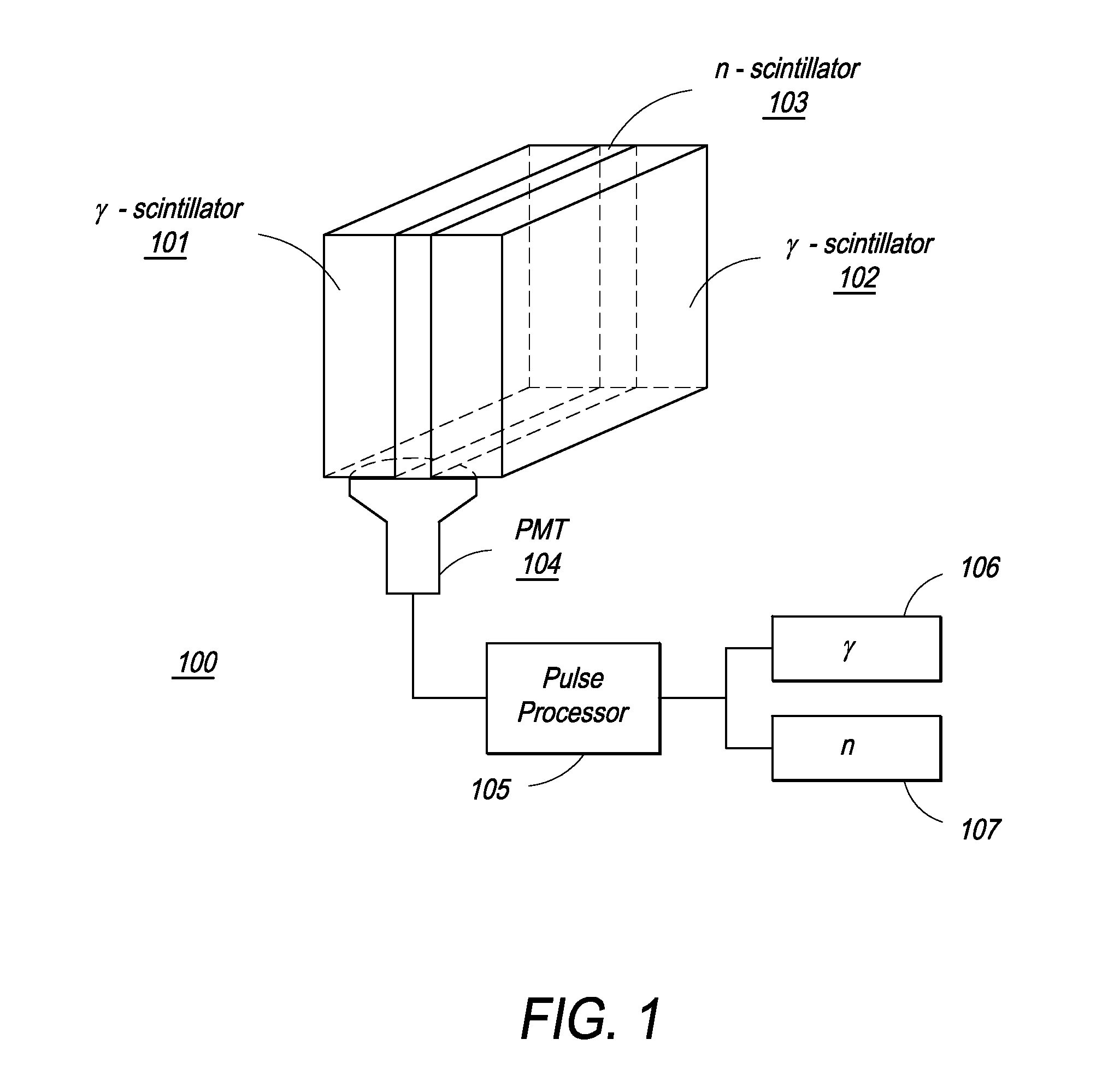
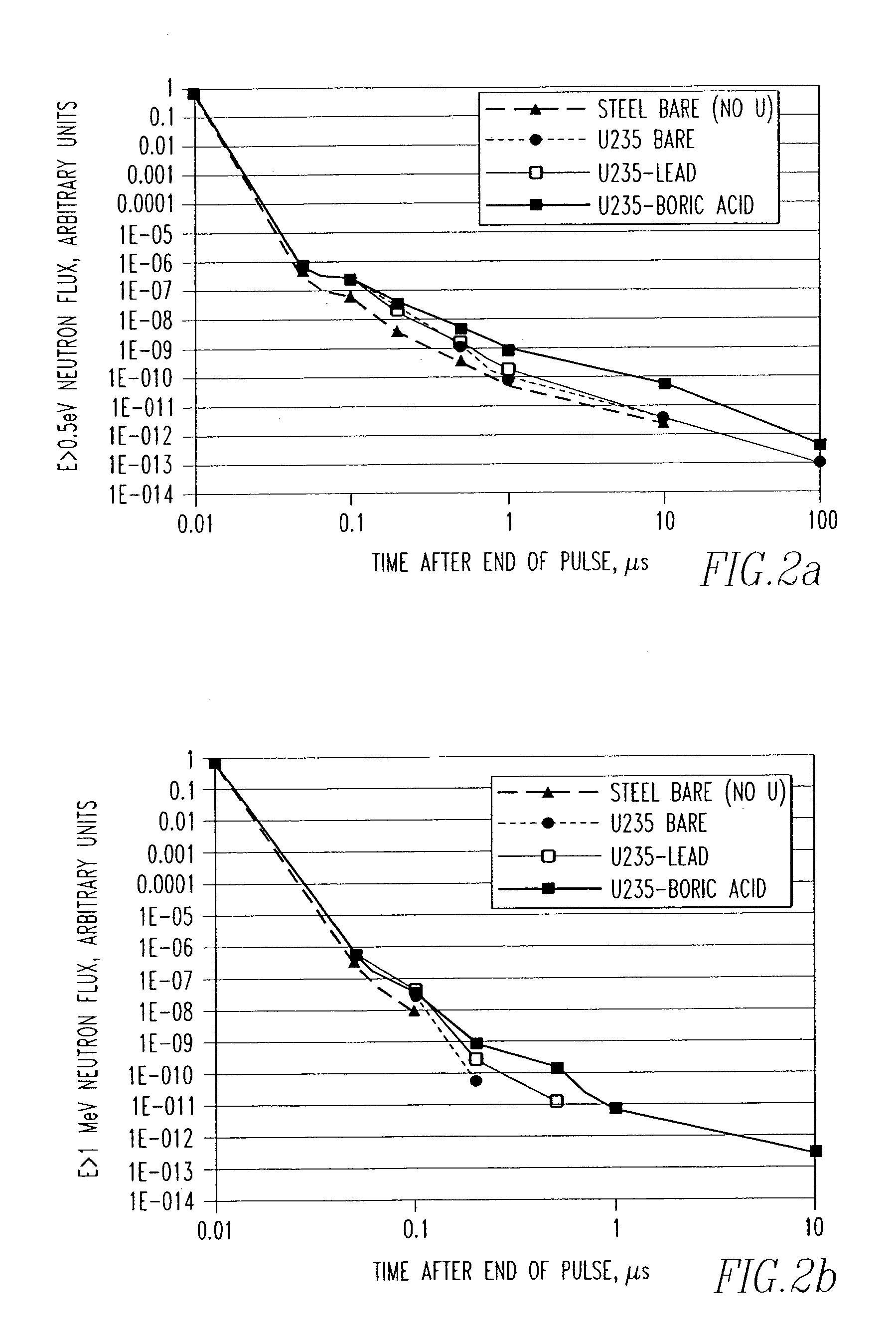
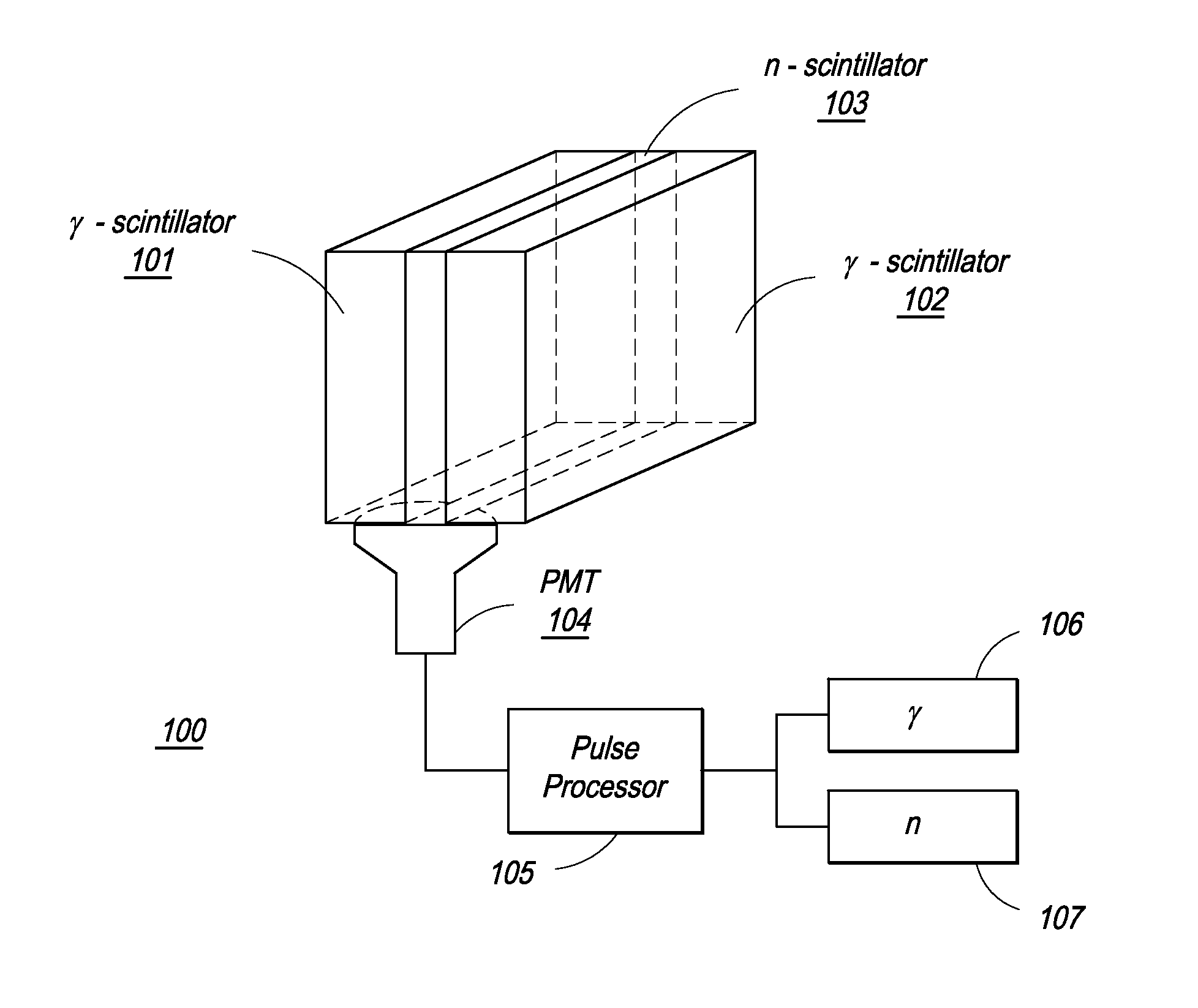
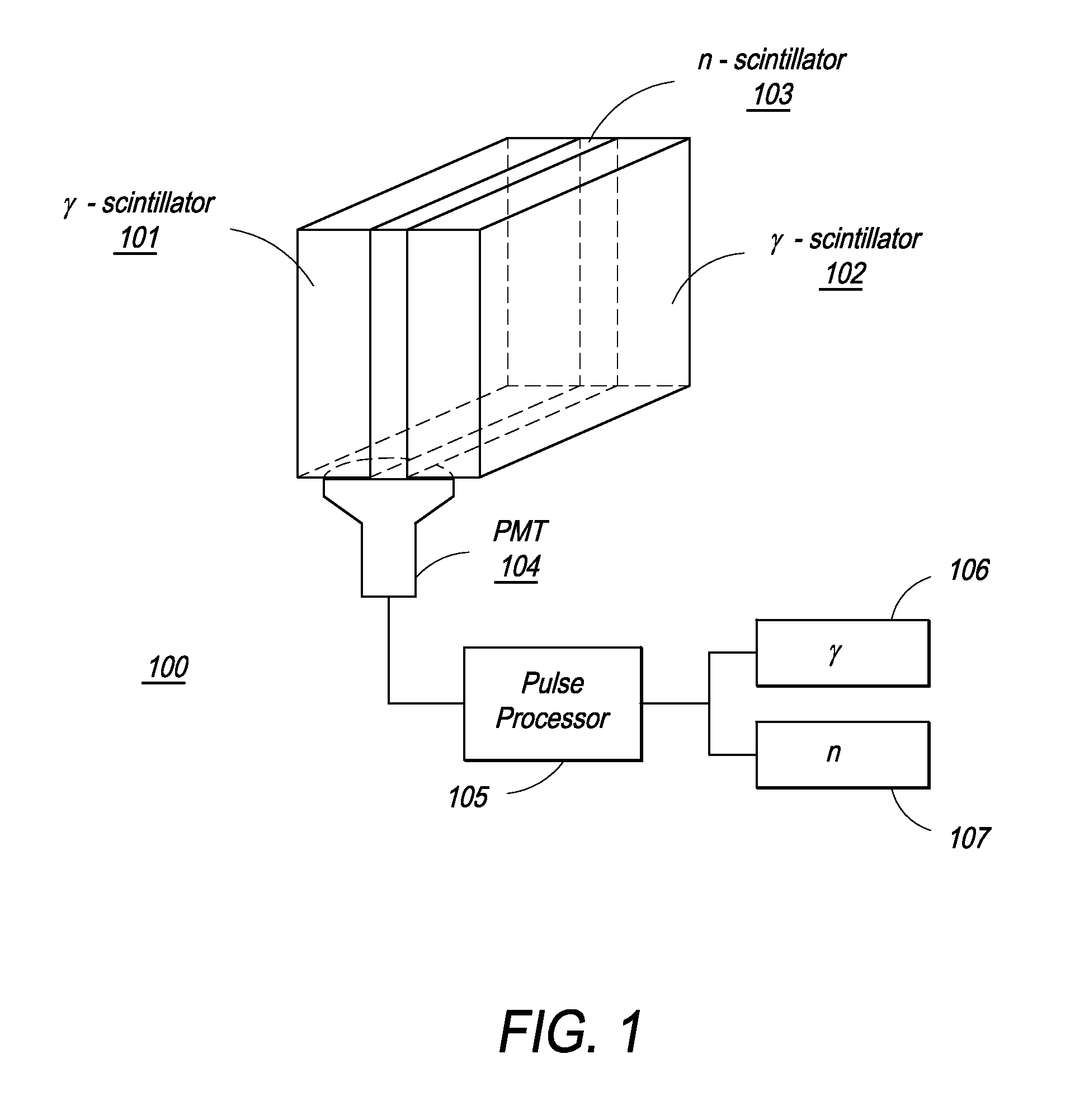
The present invention provides a gamma-neutron detector based on mixtures of thermal neutron absorbers that produce heavy-particle emission following thermal capture. The detector consists of one or more thin screens embedded in transparent hydrogenous light guides, which also serve as a neutron moderator. The emitted particles interact with the scintillator screen and produce a high light output, which is collected by the light guides into a photomultiplier tube and produces a signal from which the neutrons are counted. Simultaneous gamma-ray detection is provided by replacing the light guide material with a plastic scintillator. The plastic scintillator serves as the gamma-ray detector, moderator and light guide. The neutrons and gamma-ray events are separated employing Pulse-Shape Discrimination (PSD). The detector can be used in several scanning configurations including portal, drive-through, drive-by, handheld and backpack, etc.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Directional Neutron Detector
InactiveUS20090014662A1Easy to distinguishMinimize the cross-talk with adjacent fibersMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberSensor array
A directional neutron detector consisting of very thin plastic scintillation fibers and optically coupled to a photo-sensor array, where the directionality of Neutrons is estimated from the sequence of fibers traversed by the scattered protons and energy deposited in each one of them . Several fabrication methods of the large thin fiber arrays are described.
Owner:SUHAMI AVRAHAM
Neutron and gamma ray monitor
ActiveUS20070272874A1Easy to detectMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionLight guide
An apparatus for selective radiation detection includes a neutron detector that facilitates detection of neutron emitters, e.g. plutonium, and the like; a gamma ray detector that facilitates detection of gamma ray sources, e.g., uranium, and the like. The apparatus comprises a first light guide, optically coupled to a first optical detector; a second light guide, optically coupled to a second optical detector a sheet of neutron scintillator, opaque for incoming optical photons, said sheet of neutron scintillator sandwiched between the first and the second light guides. The second light guide comprises a gamma ray scintillator material.
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
Neutron and gamma ray monitor
ActiveUS7525101B2Easy to detectMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansNeutron emissionLight guide
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
High-efficiency neutron detectors and methods of making same
ActiveUS7164138B2Many timesThin and compactMeasurement with semiconductor devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansRoom temperatureReactive material
Neutron detectors, advanced detector process techniques and advanced compound film designs have greatly increased neutron-detection efficiency. One embodiment of the detectors utilizes a semiconductor wafer with a matrix of spaced cavities filled with one or more types of neutron reactive material such as 10B or 6LiF. The cavities are etched into both the front and back surfaces of the device such that the cavities from one side surround the cavities from the other side. The cavities may be etched via holes or etched slots or trenches. In another embodiment, the cavities are different-sized and the smaller cavities extend into the wafer from the lower surfaces of the larger cavities. In a third embodiment, multiple layers of different neutron-responsive material are formed on one or more sides of the wafer. The new devices operate at room temperature, are compact, rugged, and reliable in design.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
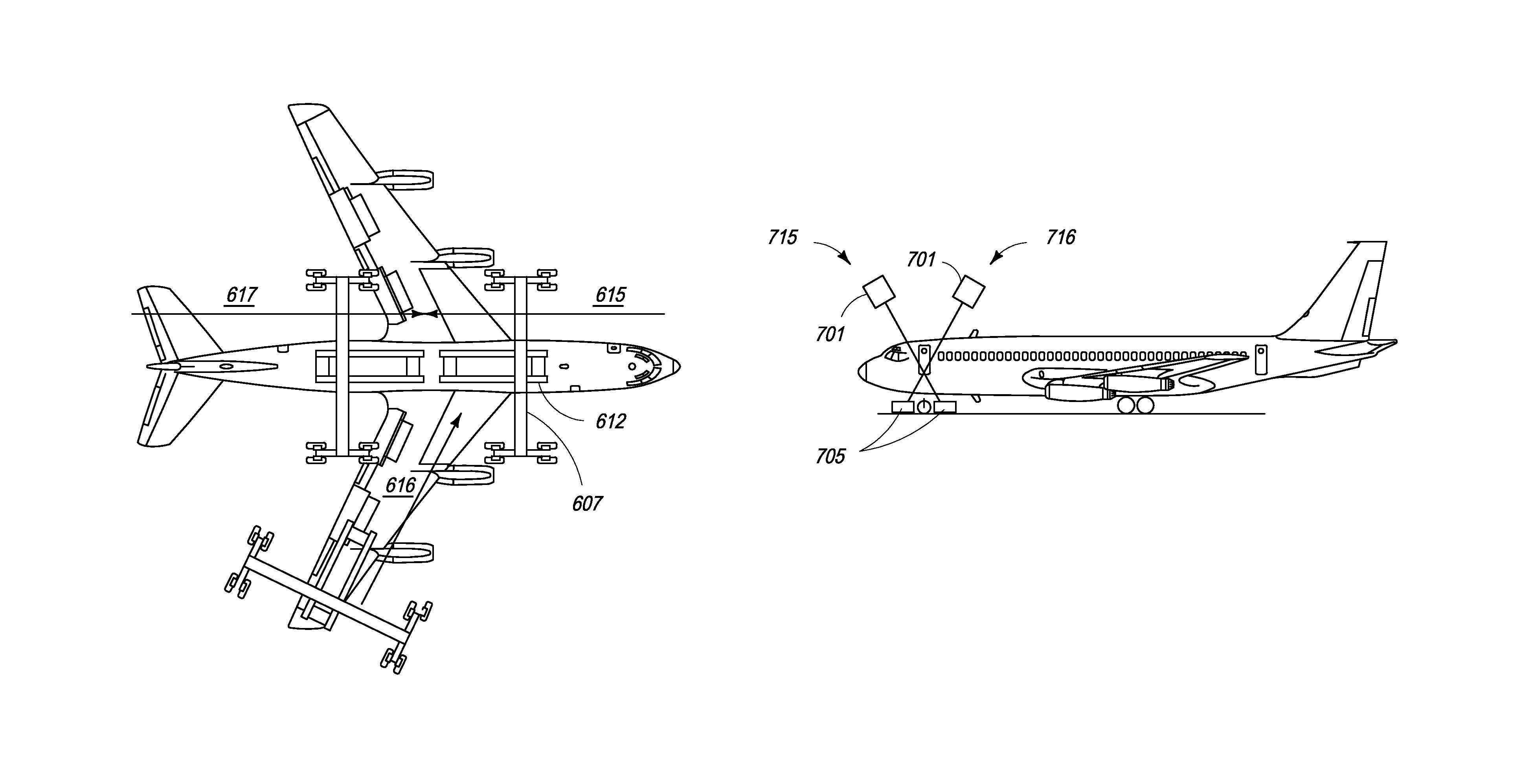
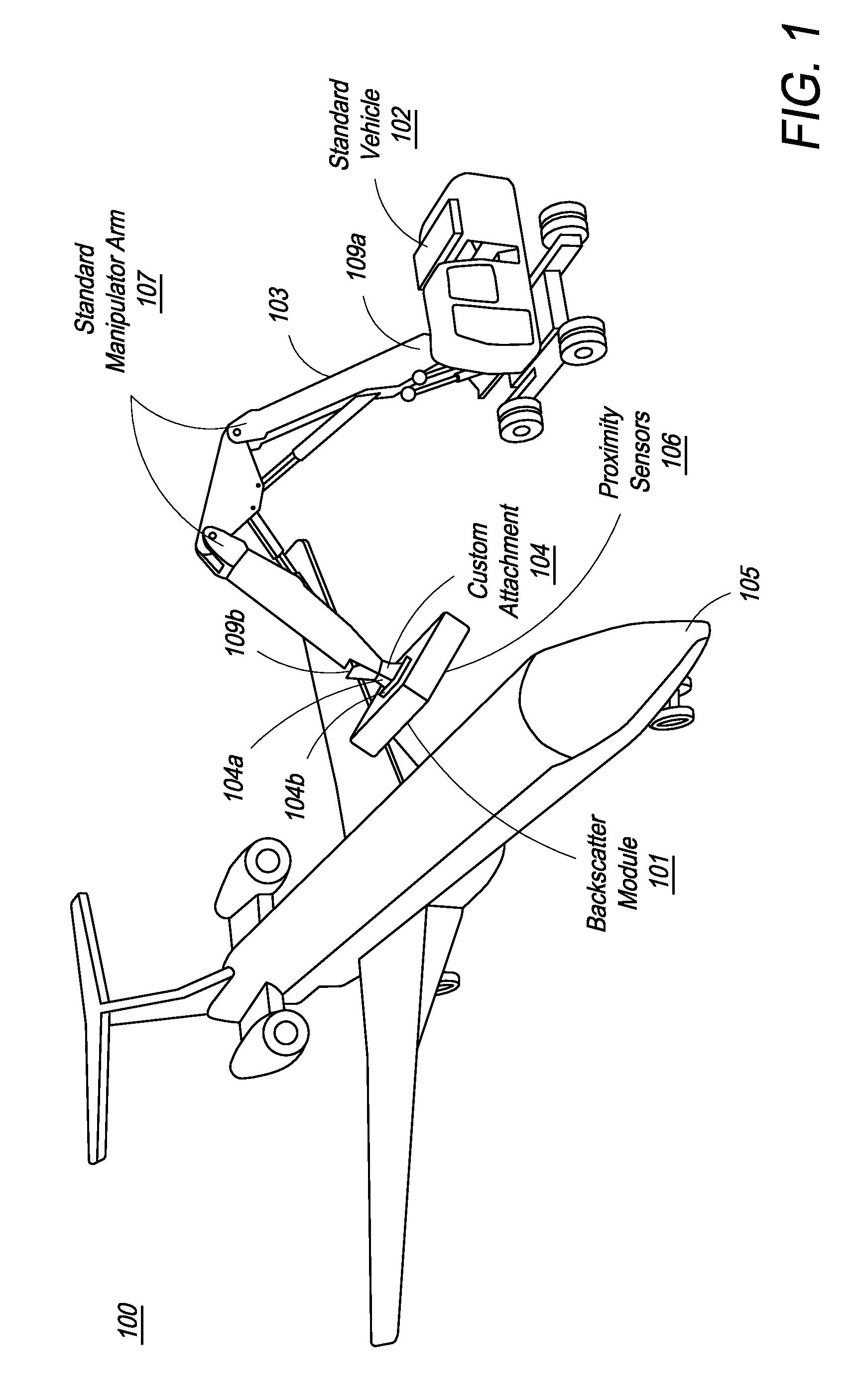
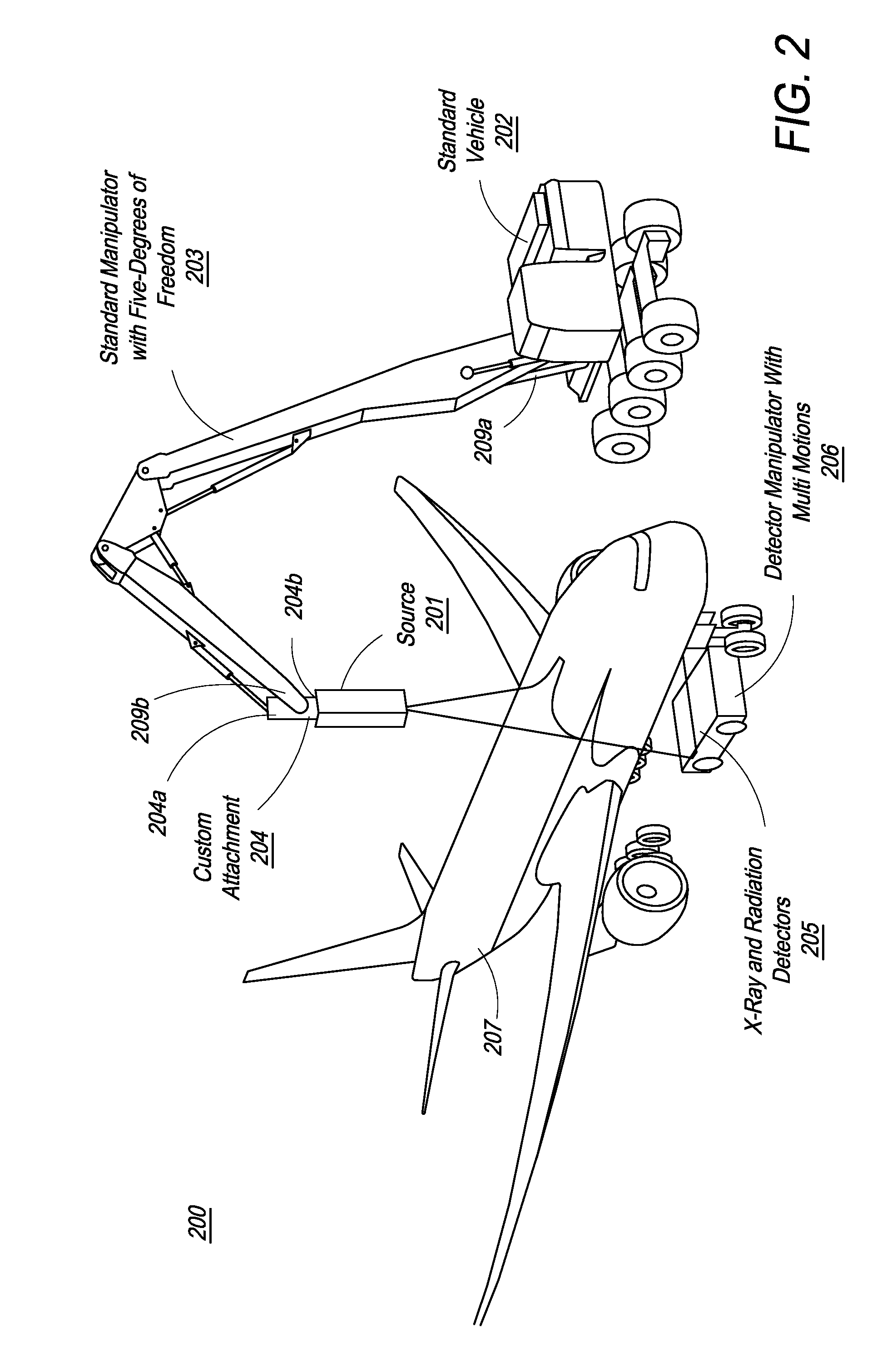
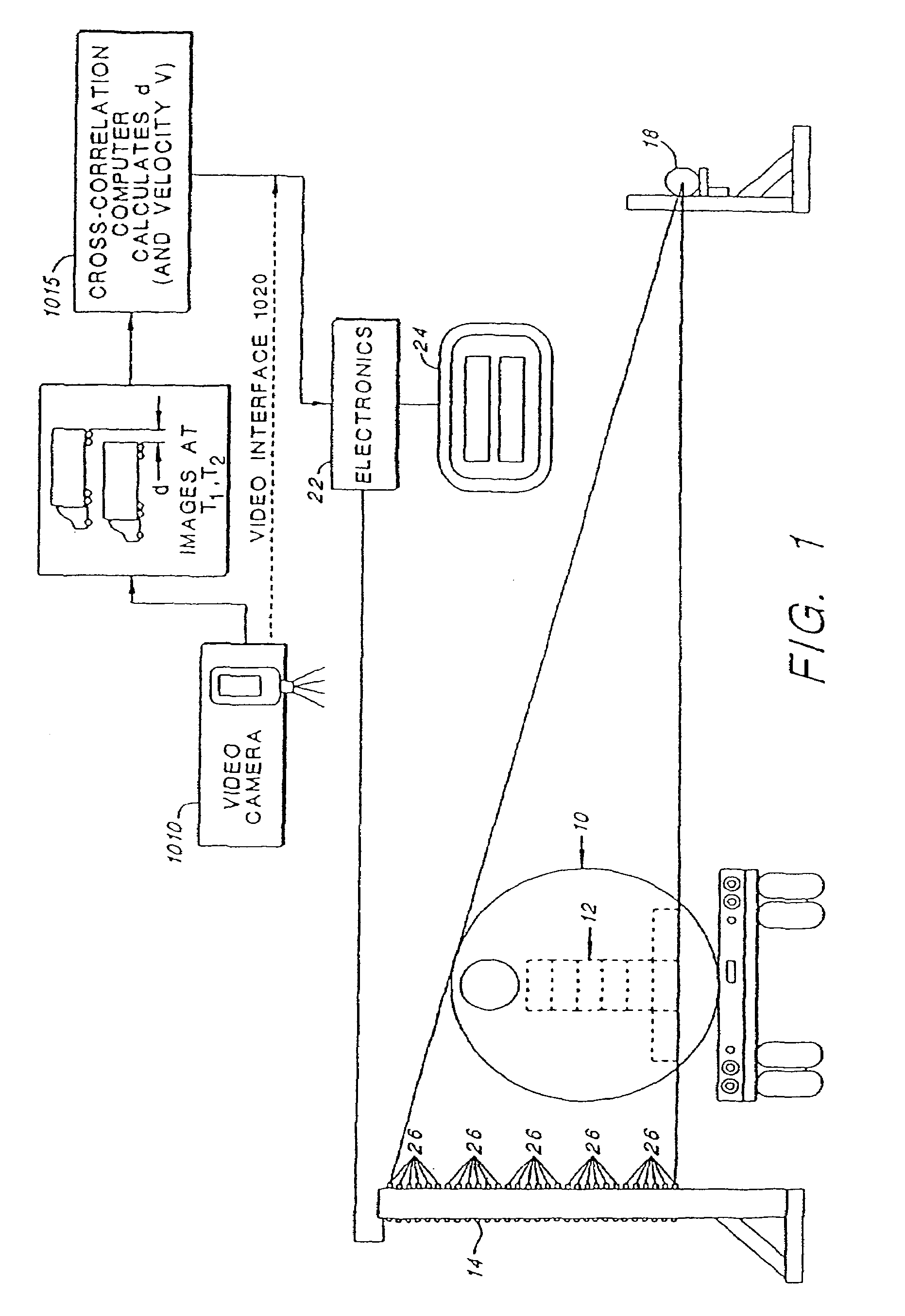
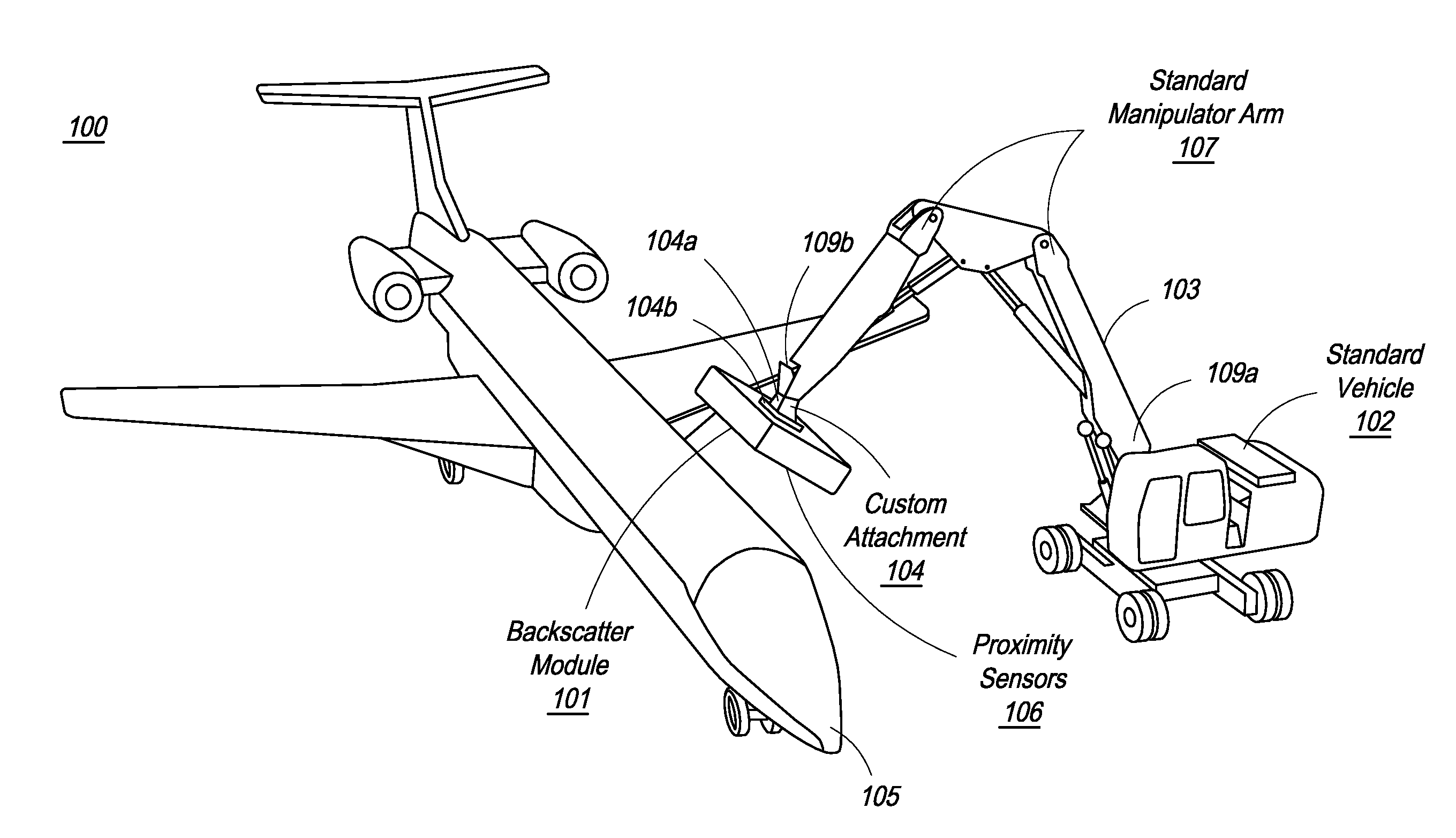
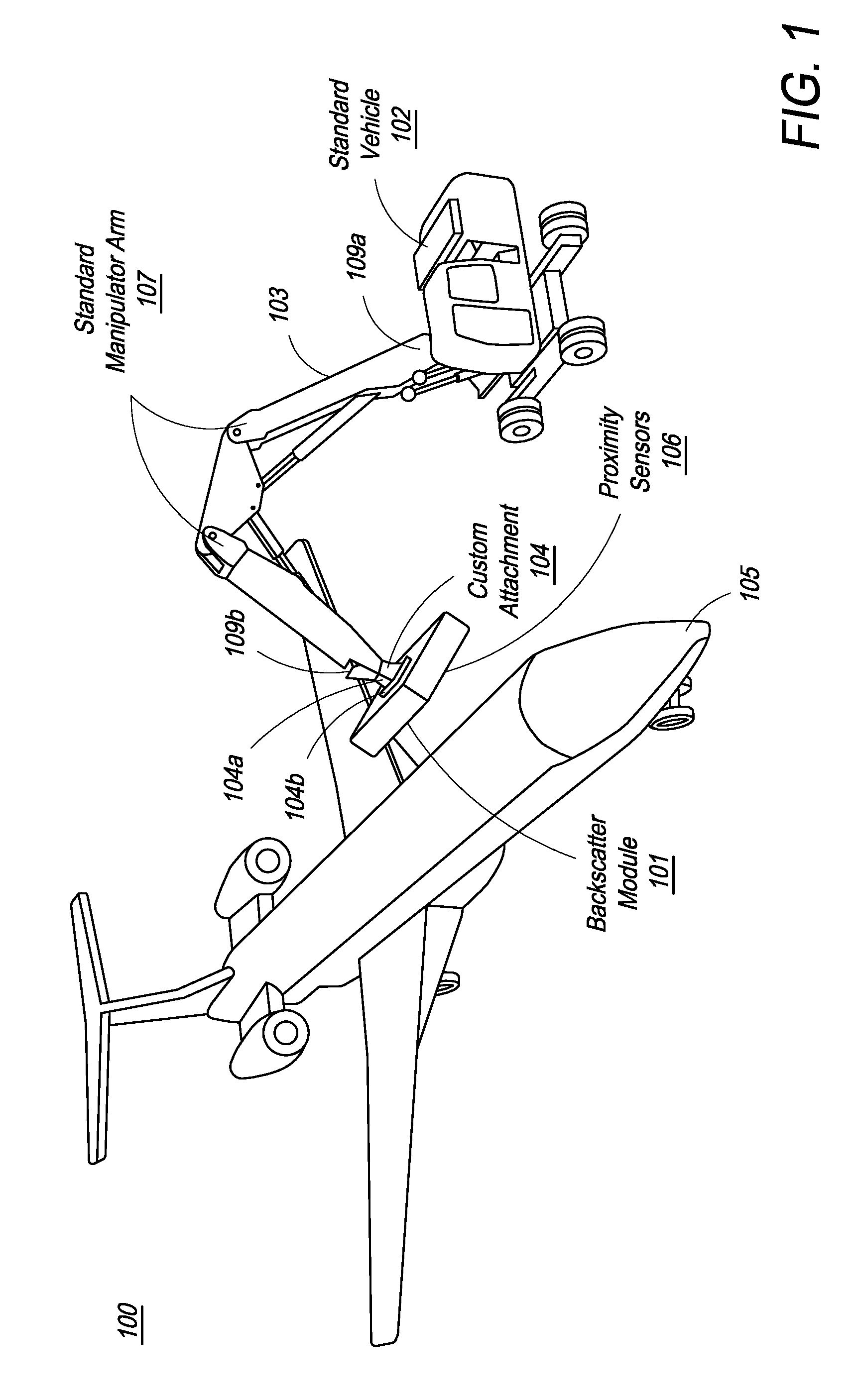
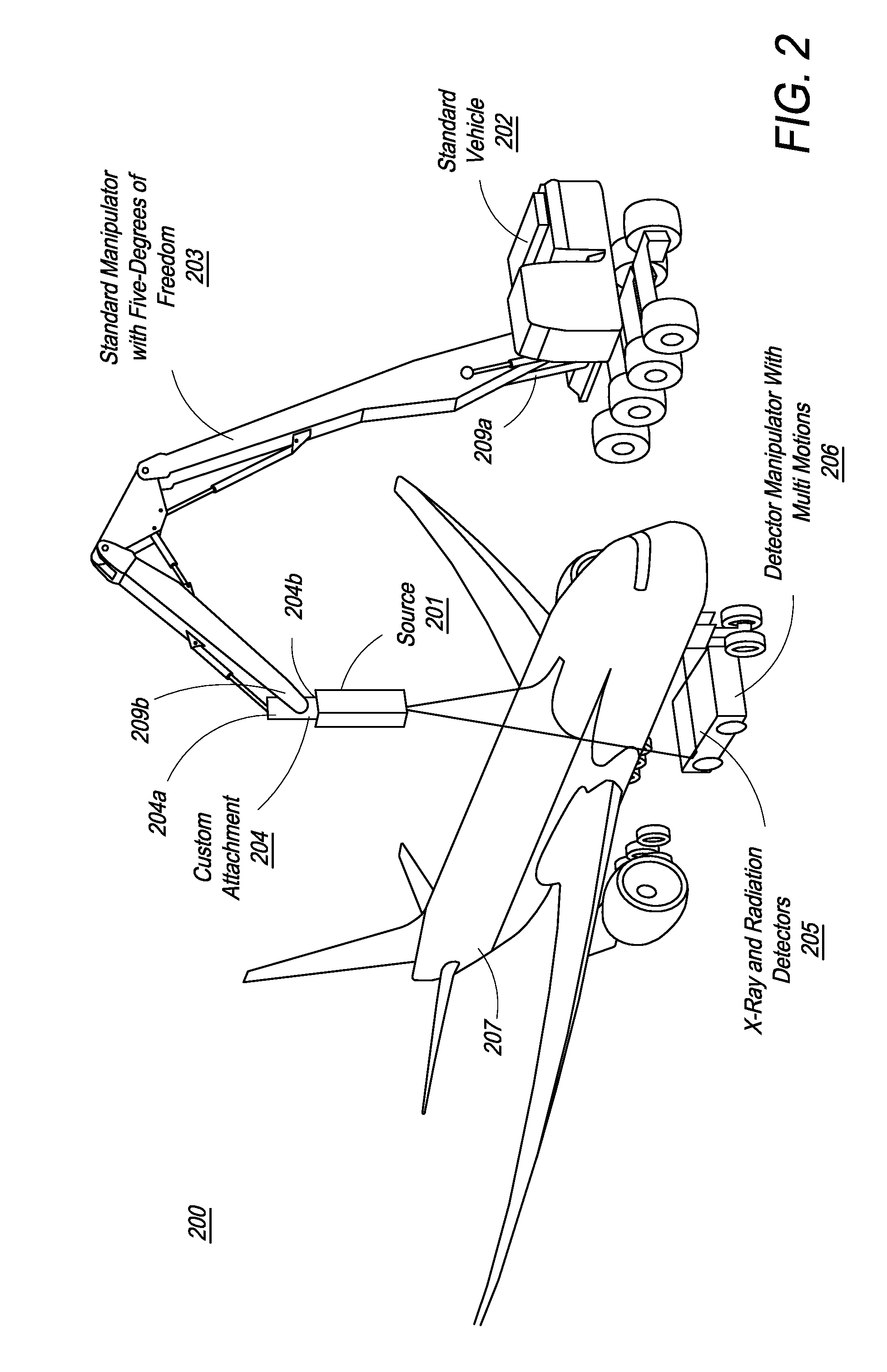
Mobile aircraft inspection system
A system for scanning aircraft for concealed threats is provided. The system comprises a vehicle and a manipulator arm attached with a scanning head that can be maneuvered in multiple directions to completely scan an aircraft from the outside. The system uses transmission based X-ray detection, backscatter based X-ray detection or a combination thereof, in various embodiments. The system also includes gamma-ray and neutron detectors, for detection of nuclear and radioactive materials.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Nonintrusive method for the detection of concealed special nuclear material
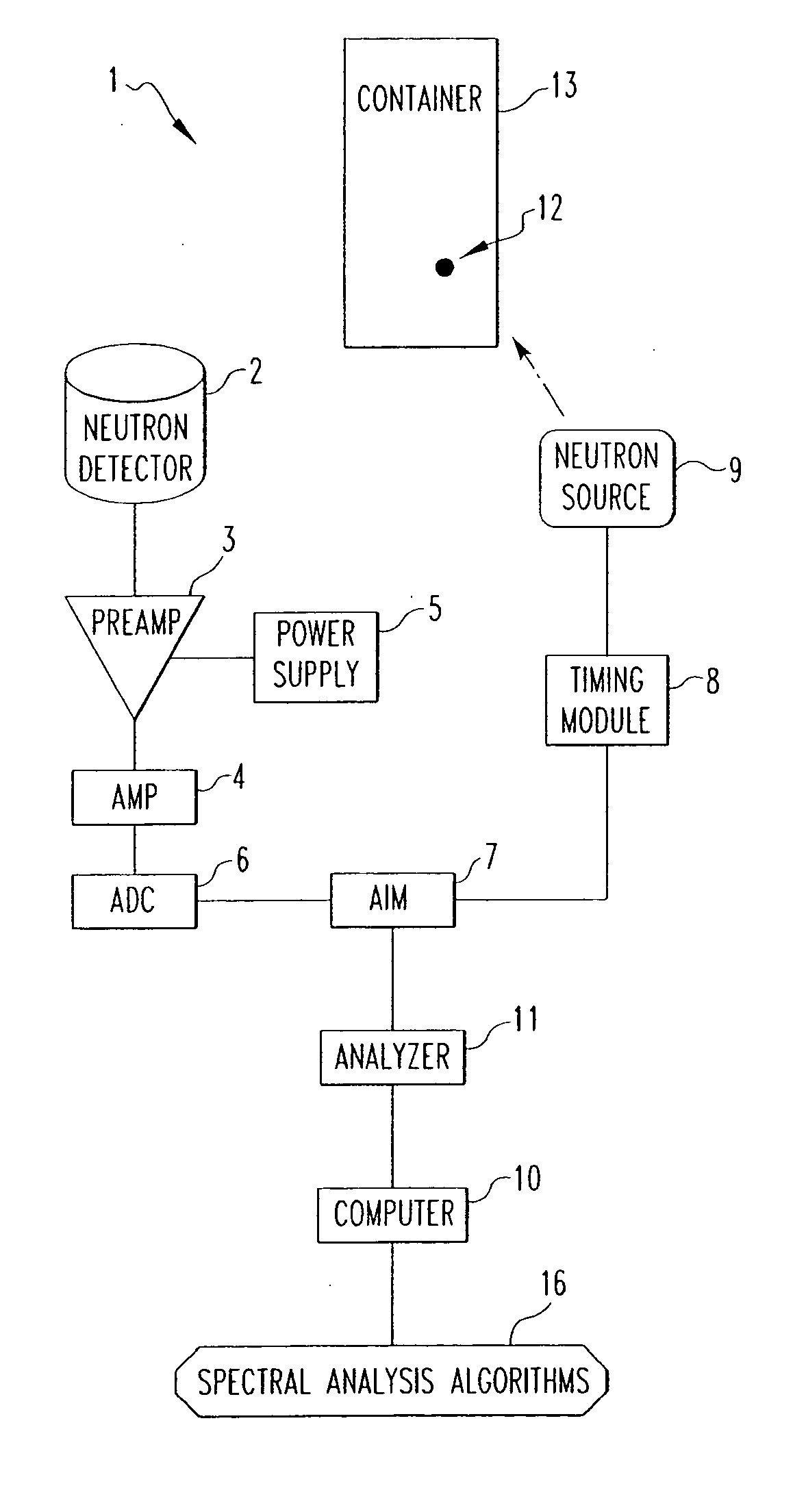
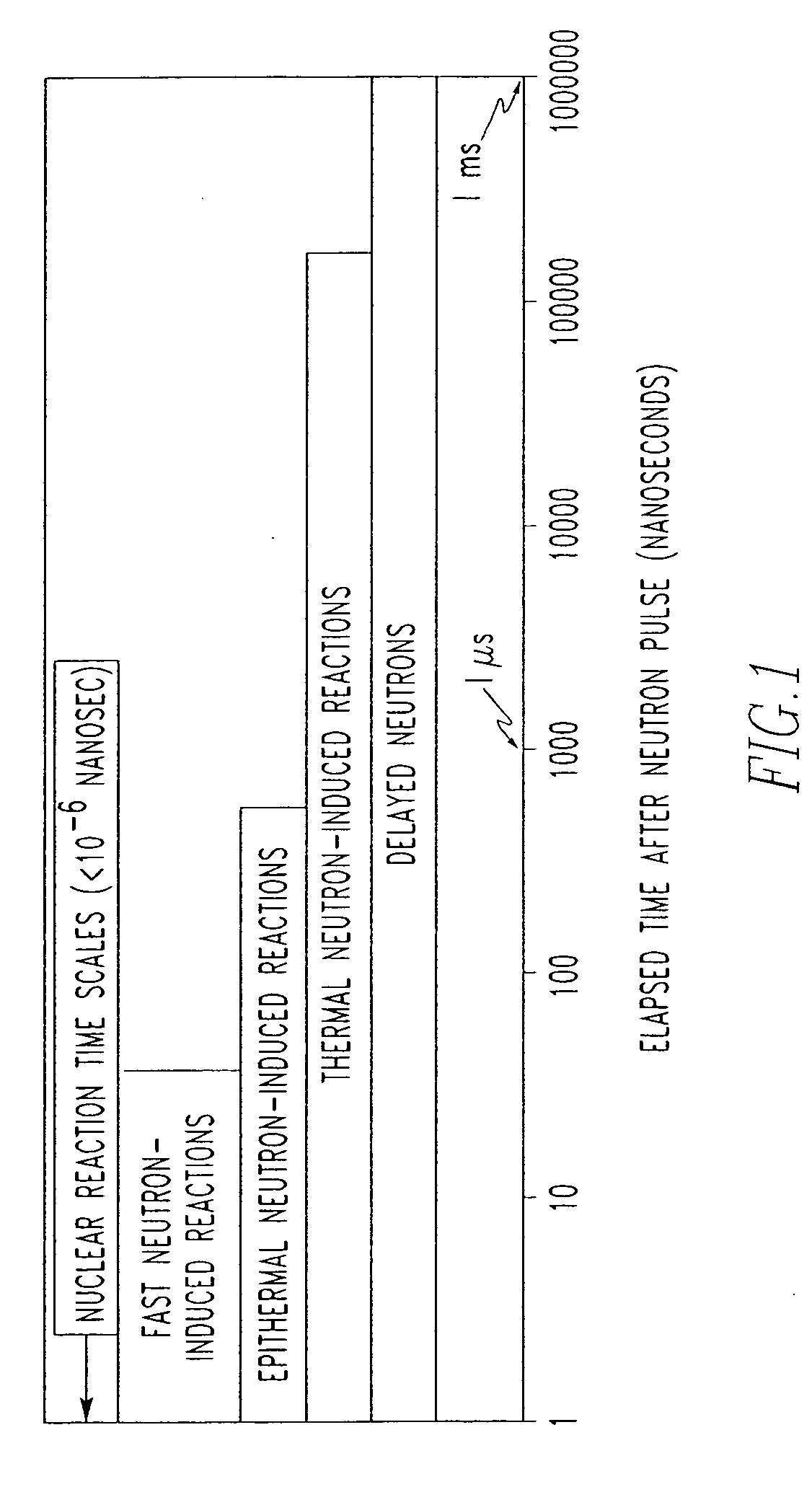
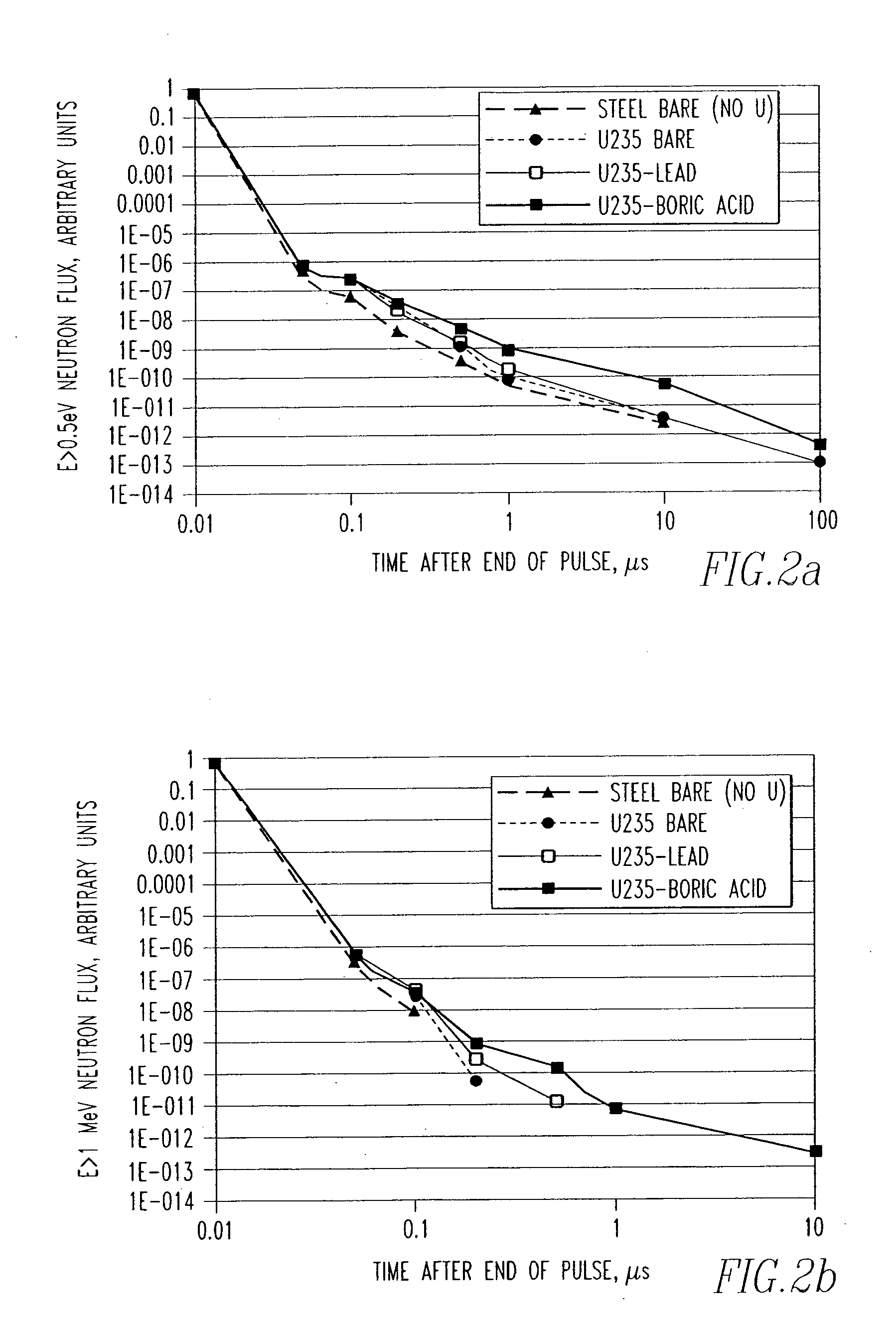
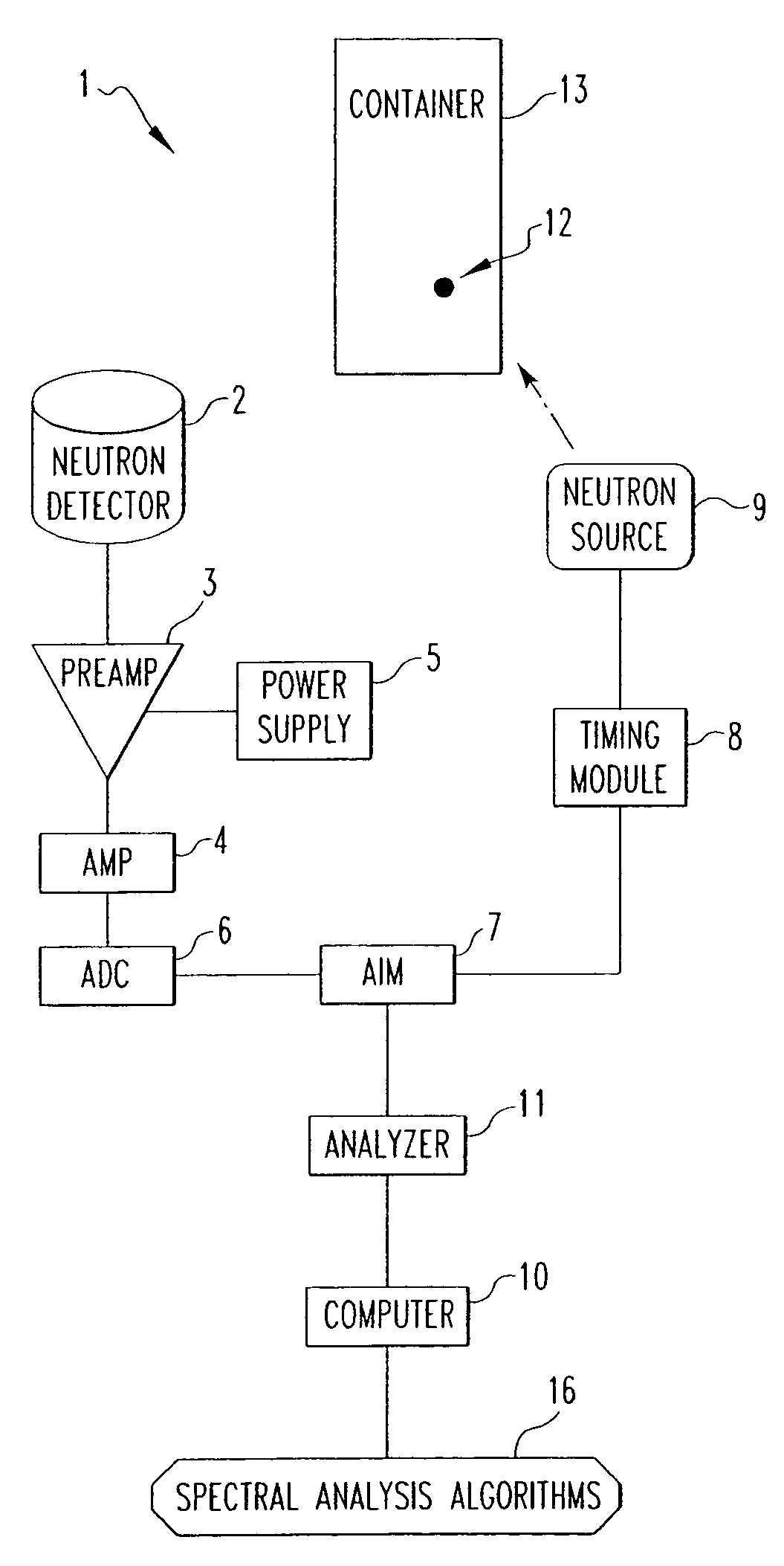
ActiveUS20050220247A1Overcome problemsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear monitoringNeutron pulseRadiation damage
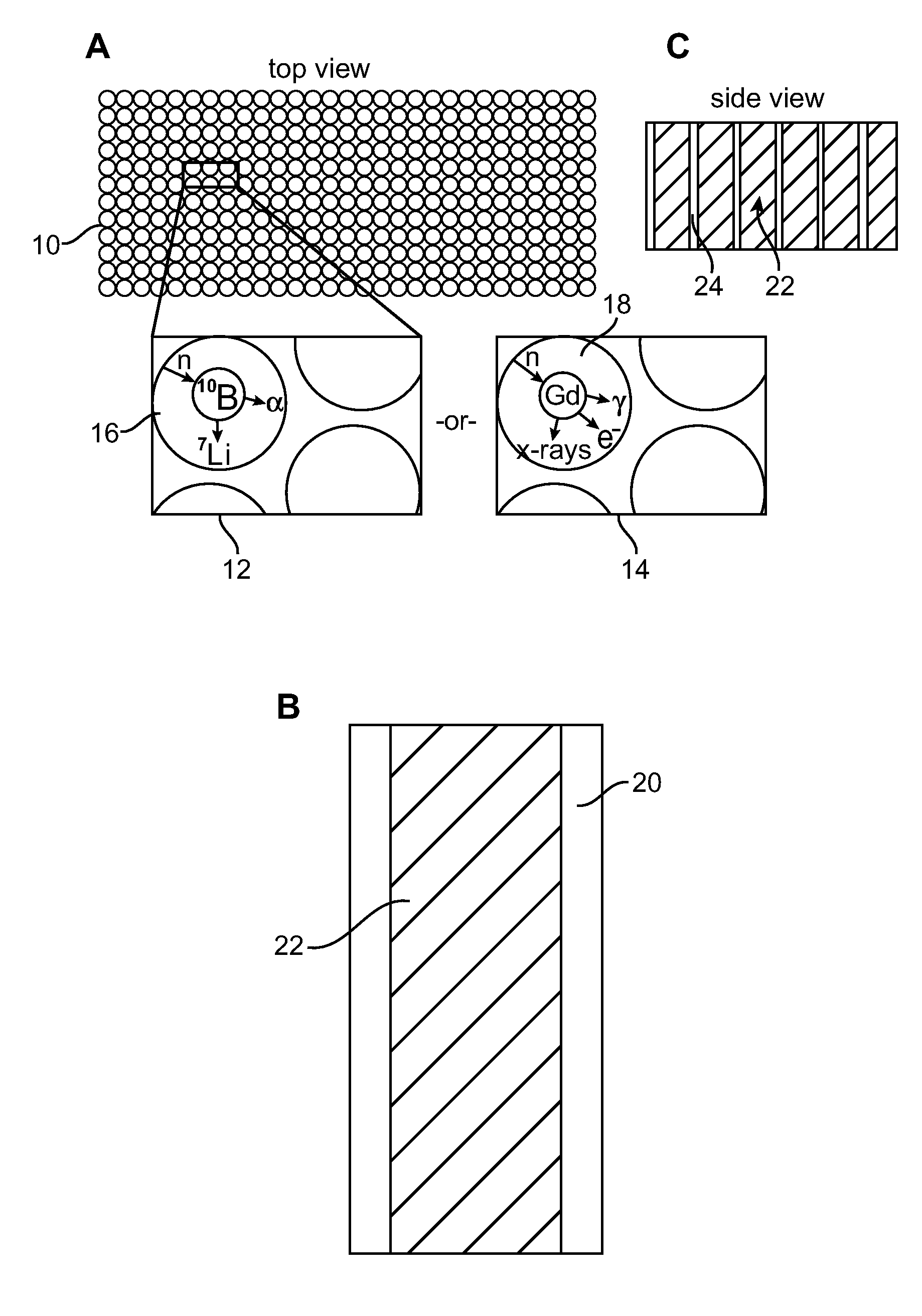
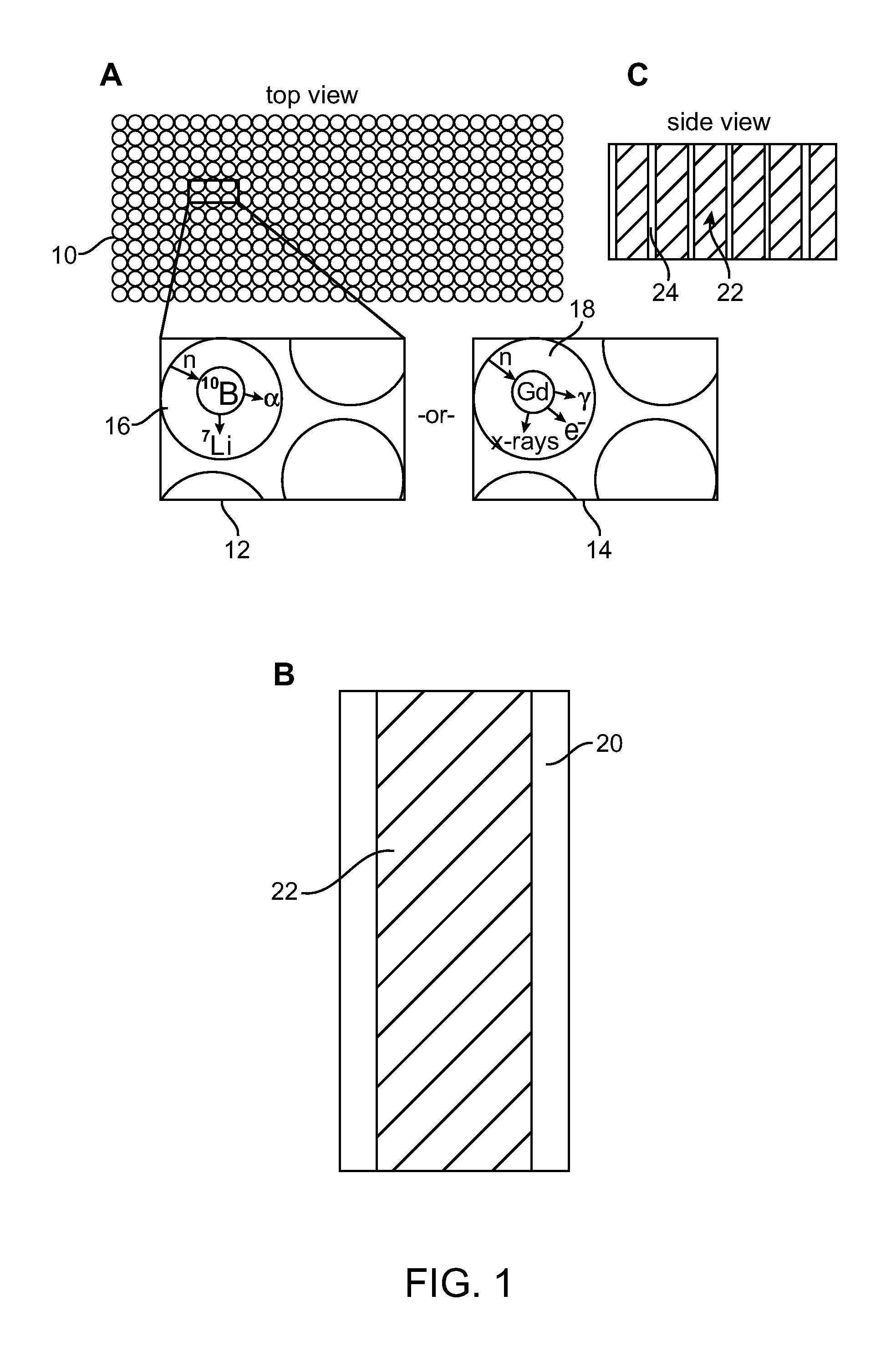
A method and associated apparatus for detecting concealed fissile, fissionable or special nuclear material in an article, such as a shipping container, is provided. The article is irradiated with a source of fast neutrons, and fast neutrons released by the fissile or fissionable material, if present, are detected between source neutron pulses. The method uses a neutron detector that can detect and discriminate fast neutrons in the presence of thermal neutrons and gamma radiation. The detector is able to process high count rates and is resistant to radiation damage, and is preferably a solid state neutron detector comprised of silicon carbide.
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
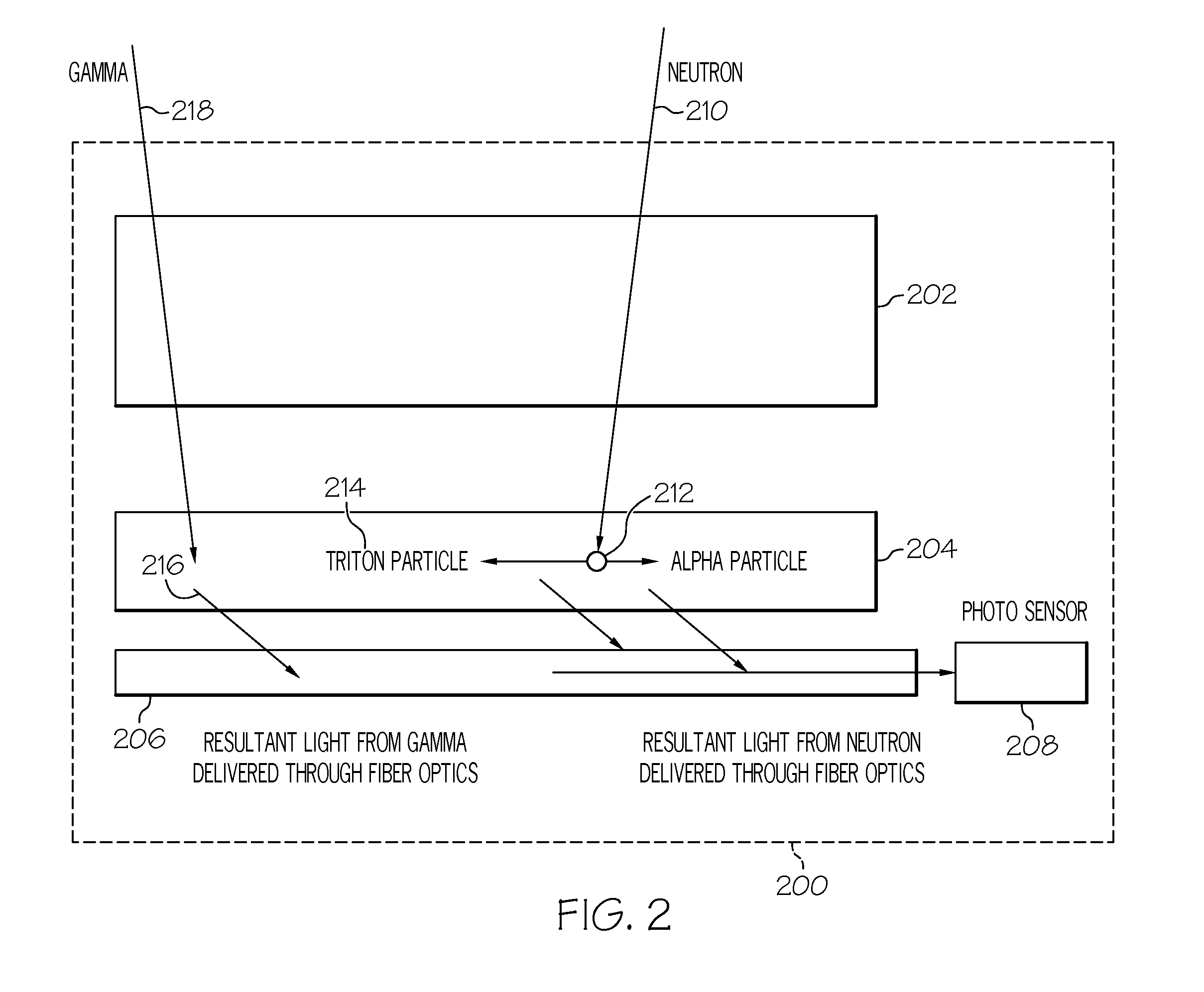
Neutron detector using neutron absorbing scintillating particulates in plastic
InactiveUS20050135535A1Low costIncrease in sizeMeasurement with scintillation detectorsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentParticulatesNinetieth percentile
A neutron detector composed of a matrix of scintillating particles imbedded in a lithiated glass is disclosed. The neutron detector detects the neutrons by absorbing the neutron in the 6Li isotope which has been enriched from the natural isotopic ratio to a commercial ninety five percent. The utility of the detector is optimized by suitably selecting scintillating particle sizes in the range of the alpha and the triton. Nominal particle sizes are in the range of five to twenty five microns depending upon the specific scintillating particle selected.
Owner:NEUTRON SCI
Neutron detectors and related methods
ActiveUS7372041B1Sacrificing spatial resolutionImprove detection efficiencyMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansScintillatorBiology
The present invention relates generally to neutron detecting scintillators and related methods and devices. A neutron detecting scintillator includes a plurality of microcapillary tubes loaded with a scintillator composition comprising a plastic scintillator and a neutron absorbing material. The present invention additionally provides methods of producing a neutron detecting scintillator having a plurality of microcapillary tubes loaded with a scintillator composition comprising a plastic scintillator and a neutron absorbing material. The method includes preparing a solution comprising a monomer and a neutron absorbing element, introducing the solution into a microcapillary tube of the plurality, and polymerizing the solution within the microcapillary tube.
Owner:RADIATION MONITORING DEVICES
Neutron detector with layered thermal-neutron scintillator and dual function light guide and thermalizing media
ActiveUS20050224719A1Shorten speedKinetic energy is lostMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansHydrogenFluorescence
A broad spectrum neutron detector has a thermal neutron sensitive scintillator film interleaved with a hydrogenous thermalizing media. The neutron detector has negligible sensitivity to gamma rays and produces a strong and unambiguous signal for virtually all neutrons that interact with the hydrogenous volume. The interleaving of the layers of thermal neutron sensitive phosphors helps ensure that all parts of the thermalizing volume are highly sensitive.
Owner:LEIDOS
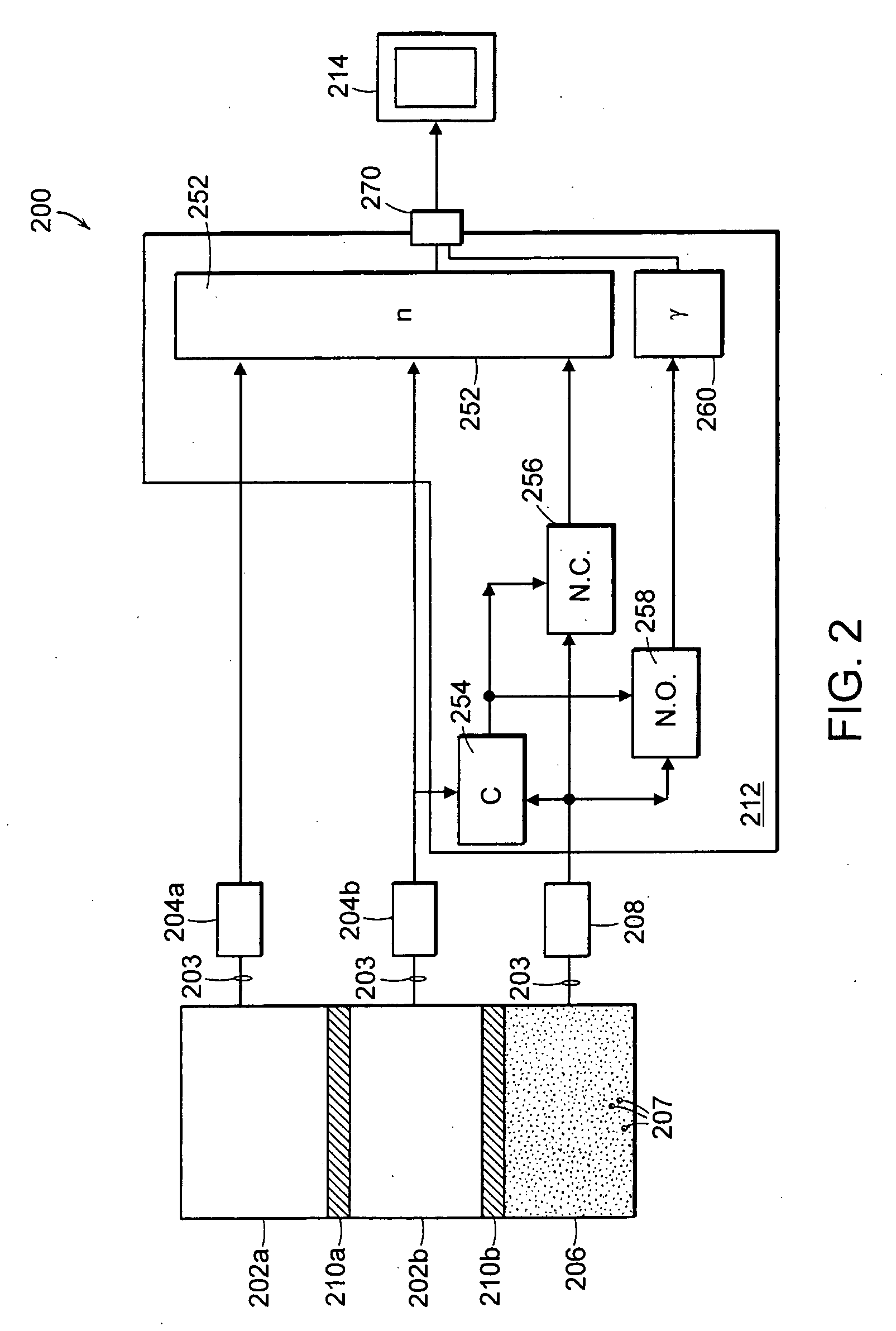
System and method for target inspection using discrete photon counting and neutron detection
Described herein is system for the inspection of a target object. The system may include a gamma radiation source, a gamma detector and an image processor coupled to the gamma detector. When the inspection system is operating in a first active mode for imaging a target object, the gamma radiation source directs radiation at a target object, the radiation passes through the target object, and the image processor images the target object based on an output of the gamma detector. When the dual-mode system is operating in a second passive mode for imaging a target object, the target object is scanned by a neutron detector for radiation that is emitted by the target object, the emitted radiation from the target object is detected by the neutron detector and an indicator indicates the presence of the emitted radiation.
Owner:LEIDOS INC
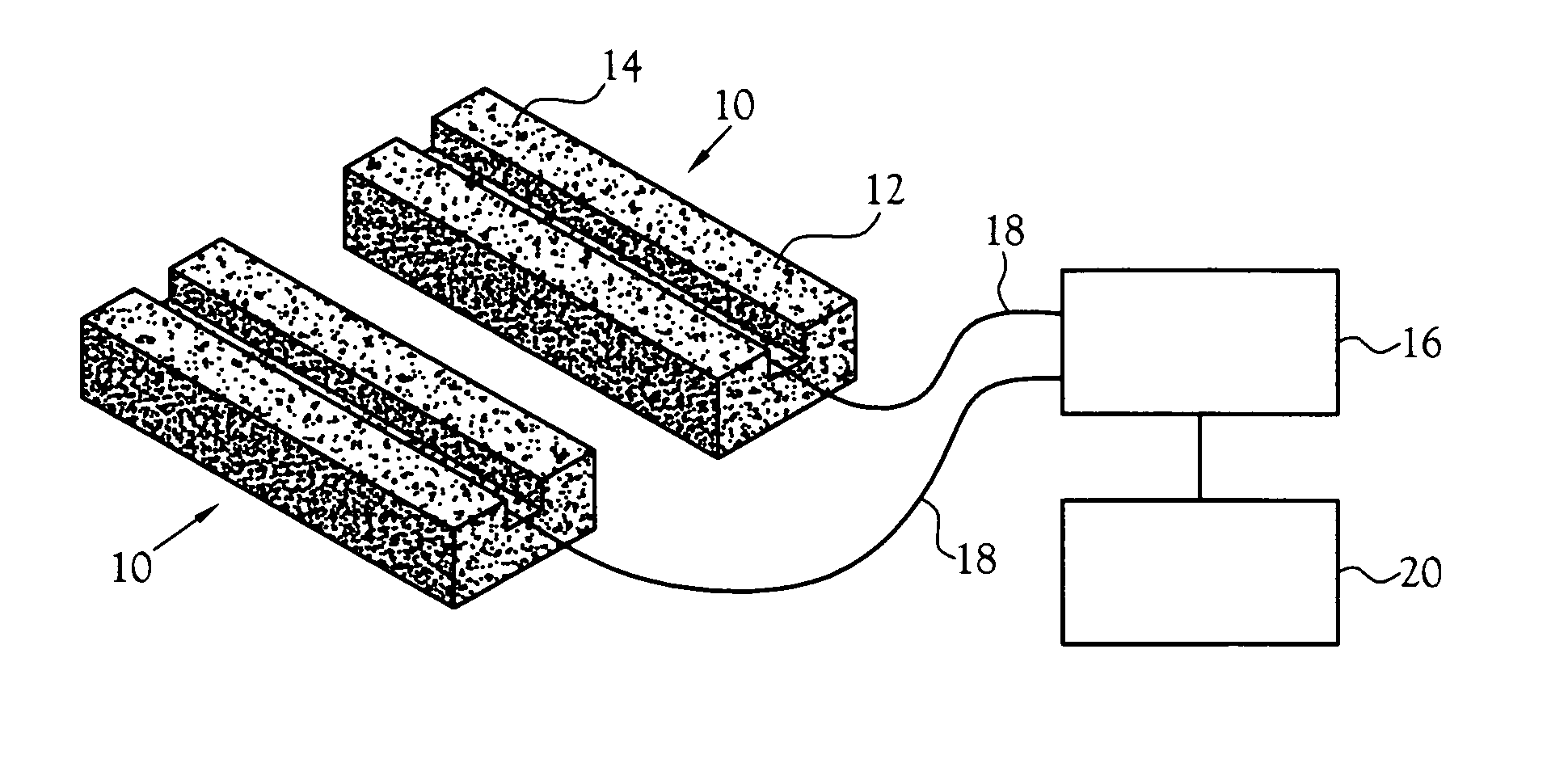
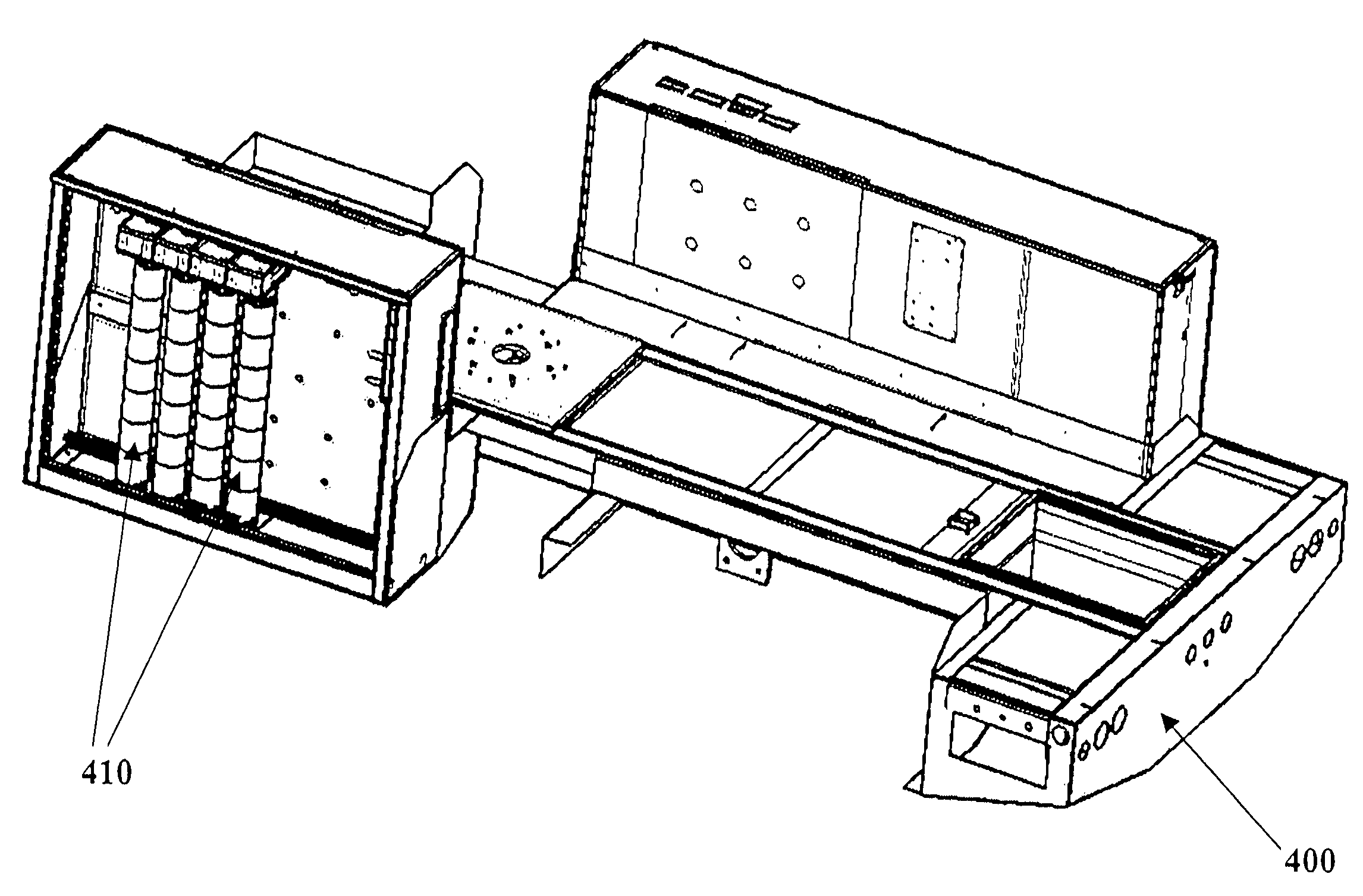
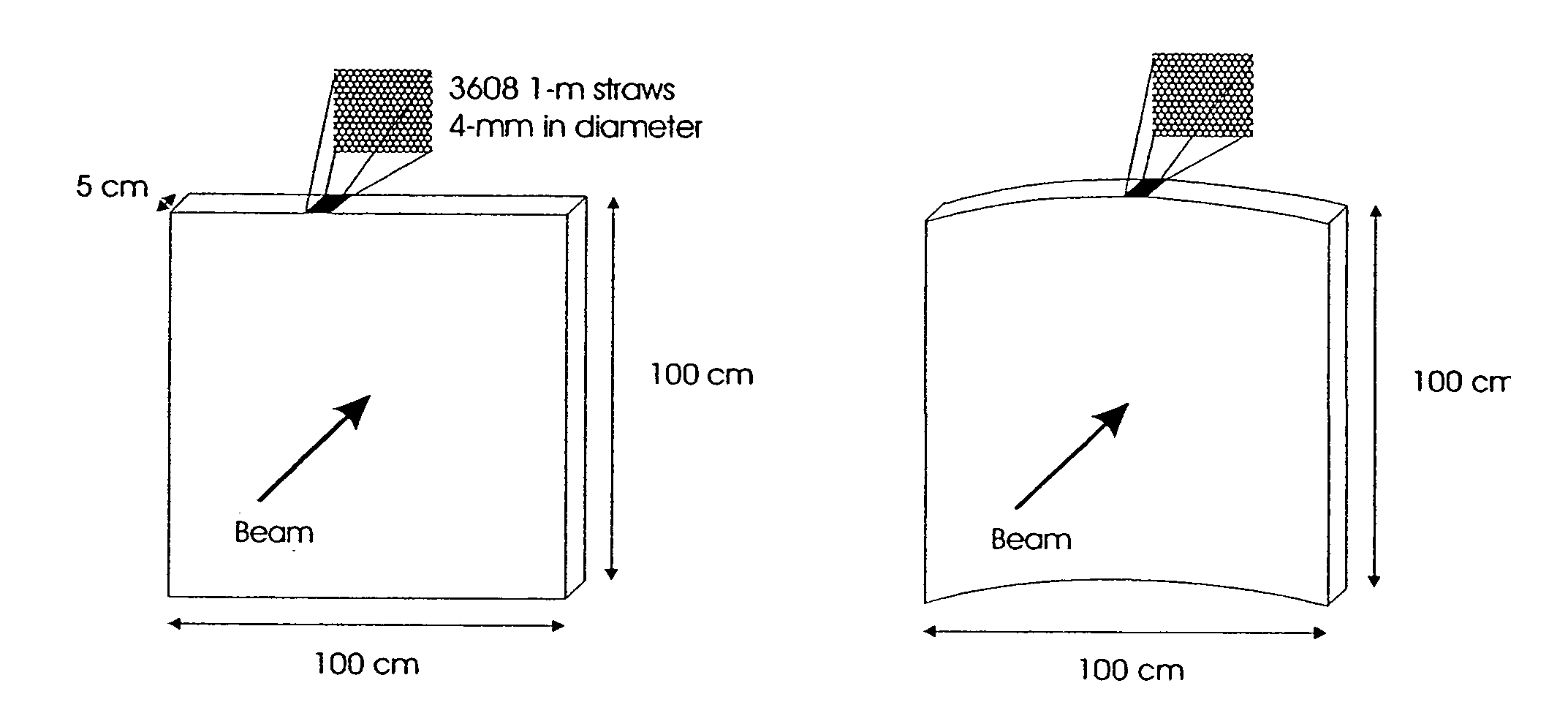
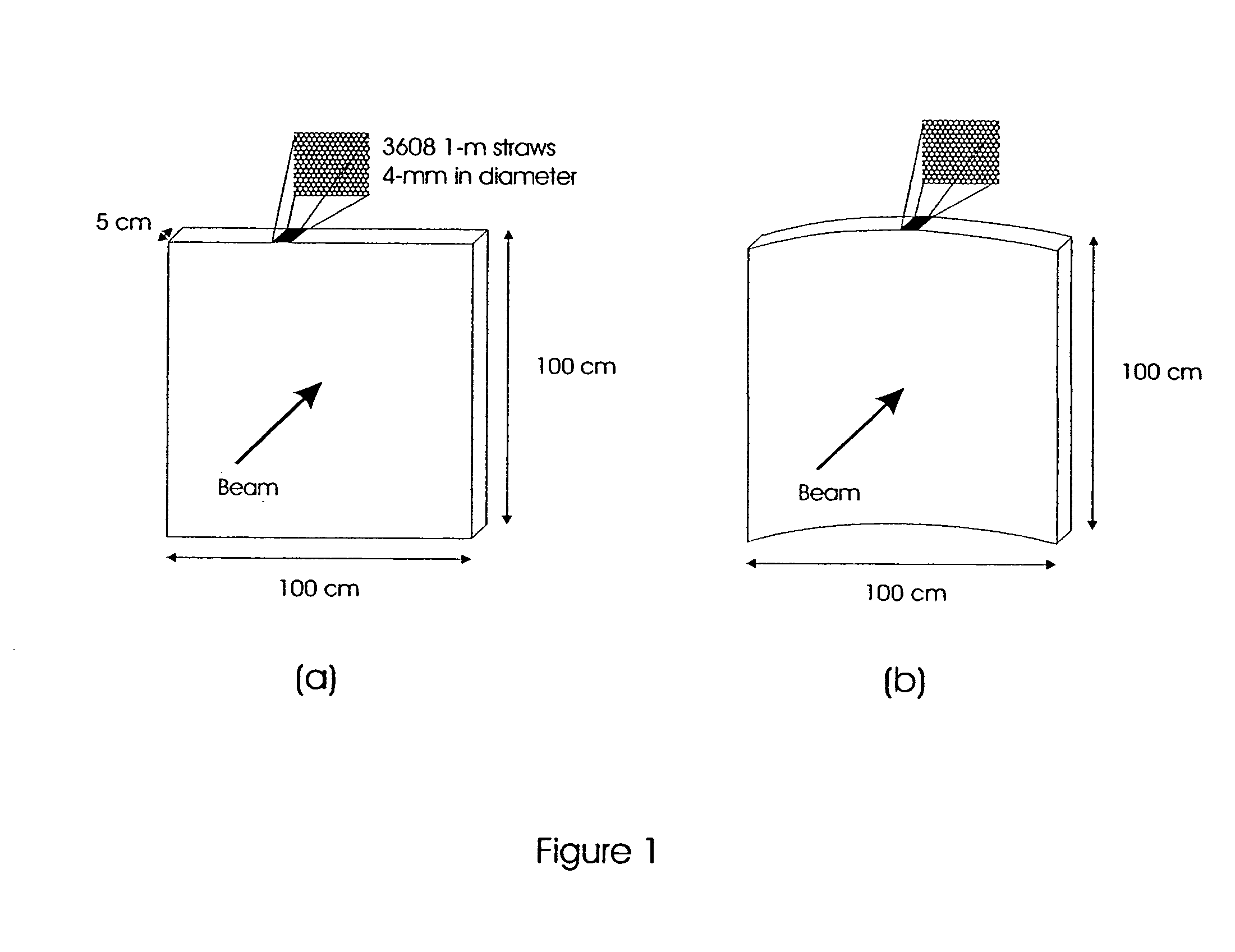
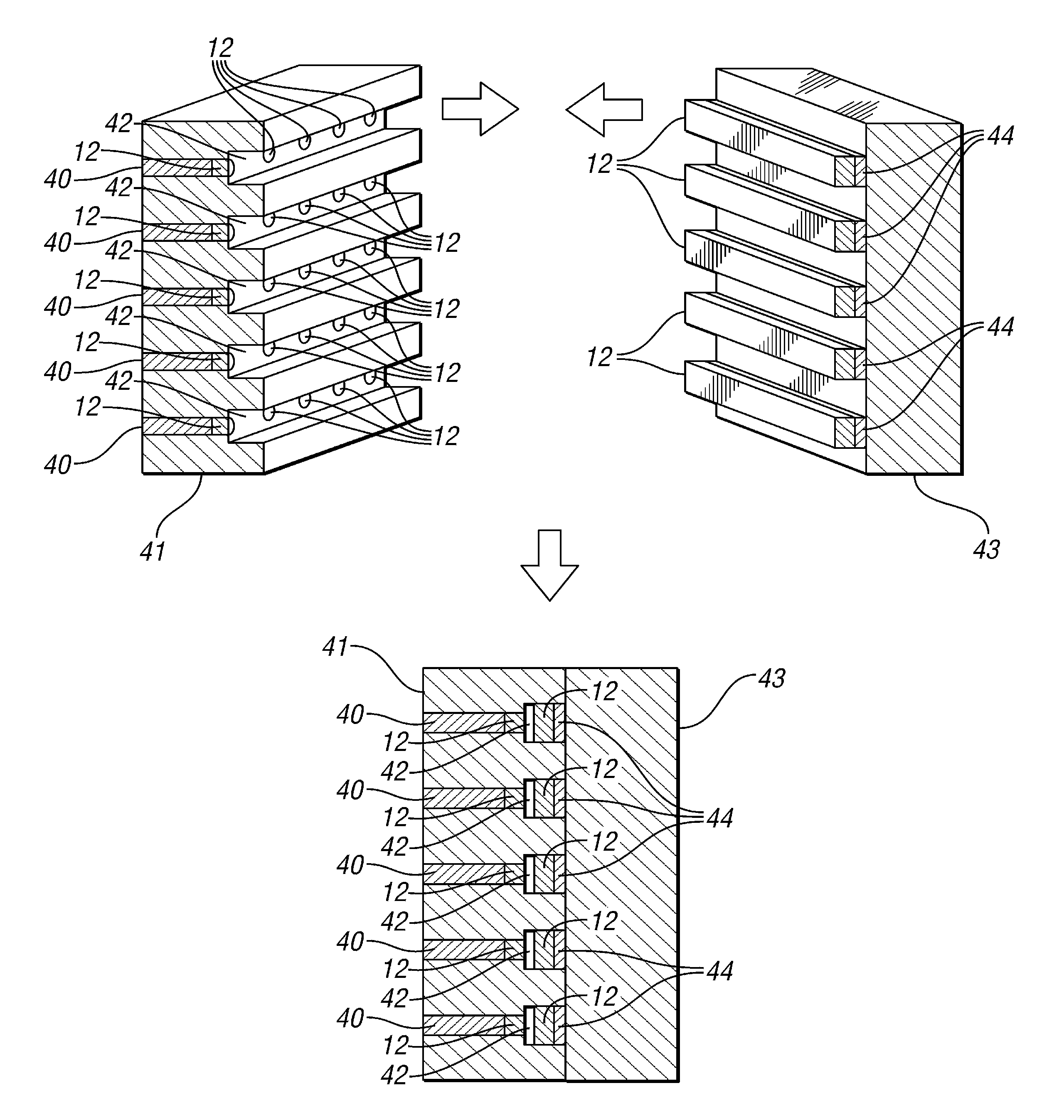
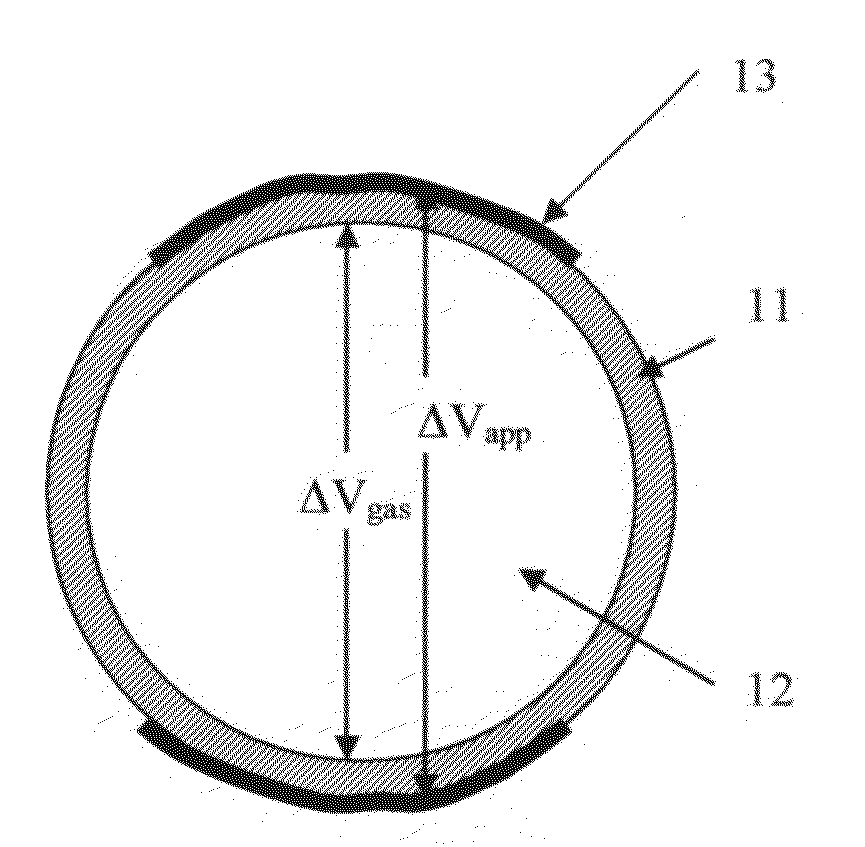
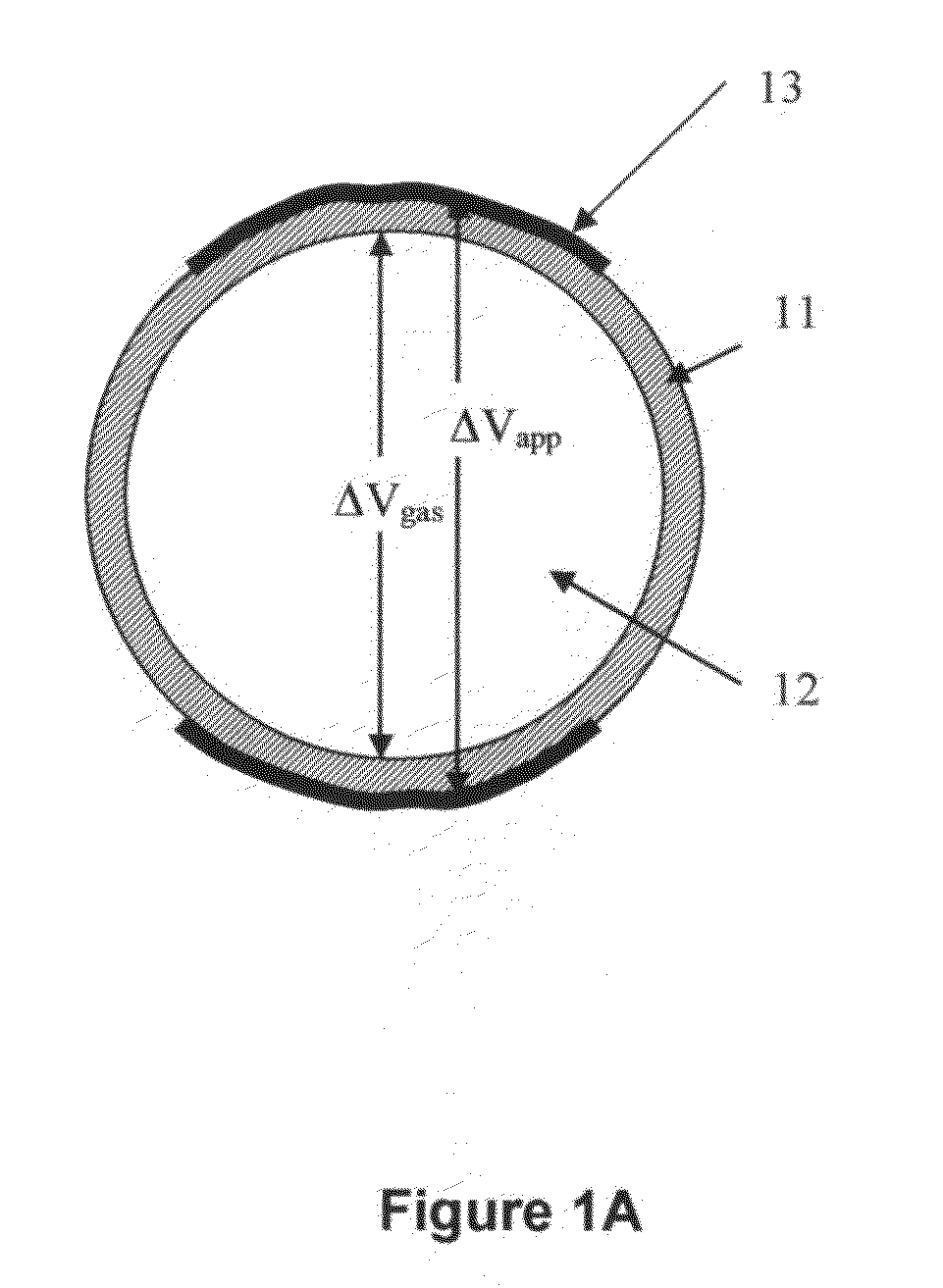
Boron coated straw neutron detector
ActiveUS7002159B2Sensitive to radiationImpression capsElectric discharge tubesElectronCharge division
A neutron detector technology based on 10B thin film conversion of neutrons and detection of neutron capture reaction products in a counter gas within a thin straw tube detector body is described. This neutron detector is based on gas-filled thin wall straw tubes, modified for the conversion of neutrons in a very thin coating, or layer, of 10B, applied for example as a sputter-coated film of 10B4C, that lines the interior, or inside of the straw tube surface; and the subsequent detection of the neutron reaction products in the counter gas. One embodiment of this invention employs a closely-packed array of 10B4C-lined straw tubes employing a very thin and therefore high efficiency 10B4C layer, hence removing the barrier to efficient neutron capture reaction product escape while still providing for efficient neutron capture by providing a plurality of very thin 10B converters, each individual converter element providing efficient reaction product escape. Using such densely packed straw tube detectors of small diameter, a reasonable stack depth allows a high neutron detection efficiency to be achieved on the 1–10Å wavelength range of thermal neutrons. The position of each interacting neutron can be accurately obtained with for example, resistive charge division readout combined with straw decoding electronics to determine the identity of the struck straw.
Owner:PROPORTIONAL TECH
Gas-filled neutron detectors having improved detection efficiency
ActiveUS20120217406A1Improves neutron detection efficiencyIncrease the amount of neutron reactive materialMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansSemi solidReactive material
Surfaces or surface portions incorporated into gas-filled neutron detectors are coated with and / or composed of at least partially, neutron reactive material. The surfaces may be flat or curved fins or plates, foils, porous or filamentary material, or semi-solid material or aerogel. The incorporation of the extended surfaces coated with or composed of neutron reactive material increases the neutron detection efficiency of the gas-filled detectors over conventional coated designs. These surfaces or surface portions increase the amount of neutron reactive material present in the detector over conventional coated designs and, as a result, increase the neutron detection efficiency. The surfaces can be made of conductive, semiconductive or insulative materials. The surfaces are arranged such that they do not detrimentally detract from the main function of a gas-filled detector with particular attention to gas-filled proportional detectors.
Owner:MCGREGOR DOUGLAS S
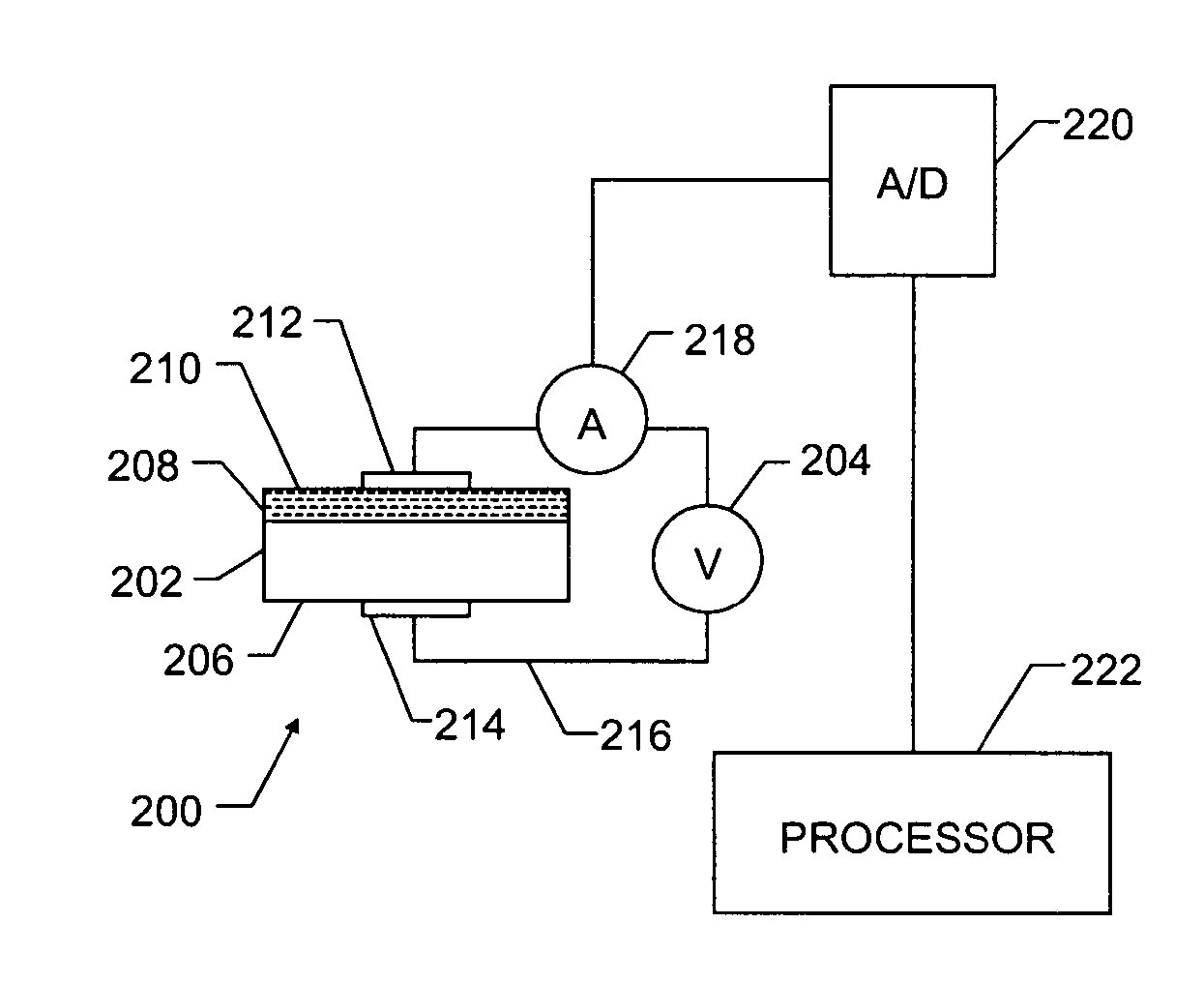
Neutron detector for downhole use
InactiveUS20040178337A1Measurement with semiconductor devicesNuclear radiation detectionNuclear engineeringBoron
A tool for measuring formation properties in situ. The tool includes a solid state neutron detector and a neutron source disposed on a drill string or wireline. The detector includes a boron carbon surface deposited on a substrate, and the surface can be multi-planar or curved for allowing sensitivity in more than one direction.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Neutron detector with layered thermal-neutron scintillator and dual function light guide and thermalizing media
ActiveUS7244947B2Shorten speedKinetic energy is lostMeasurement with semiconductor devicesMeasurement with scintillation detectorsHydrogenLight guide
A broad spectrum neutron detector has a thermal neutron sensitive scintillator film interleaved with a hydrogenous thermalizing media. The neutron detector has negligible sensitivity to gamma rays and produces a strong and unambiguous signal for virtually all neutrons that interact with the hydrogenous volume. The interleaving of the layers of thermal neutron sensitive phosphors helps ensure that all parts of the thermalizing volume are highly sensitive.
Owner:LEIDOS
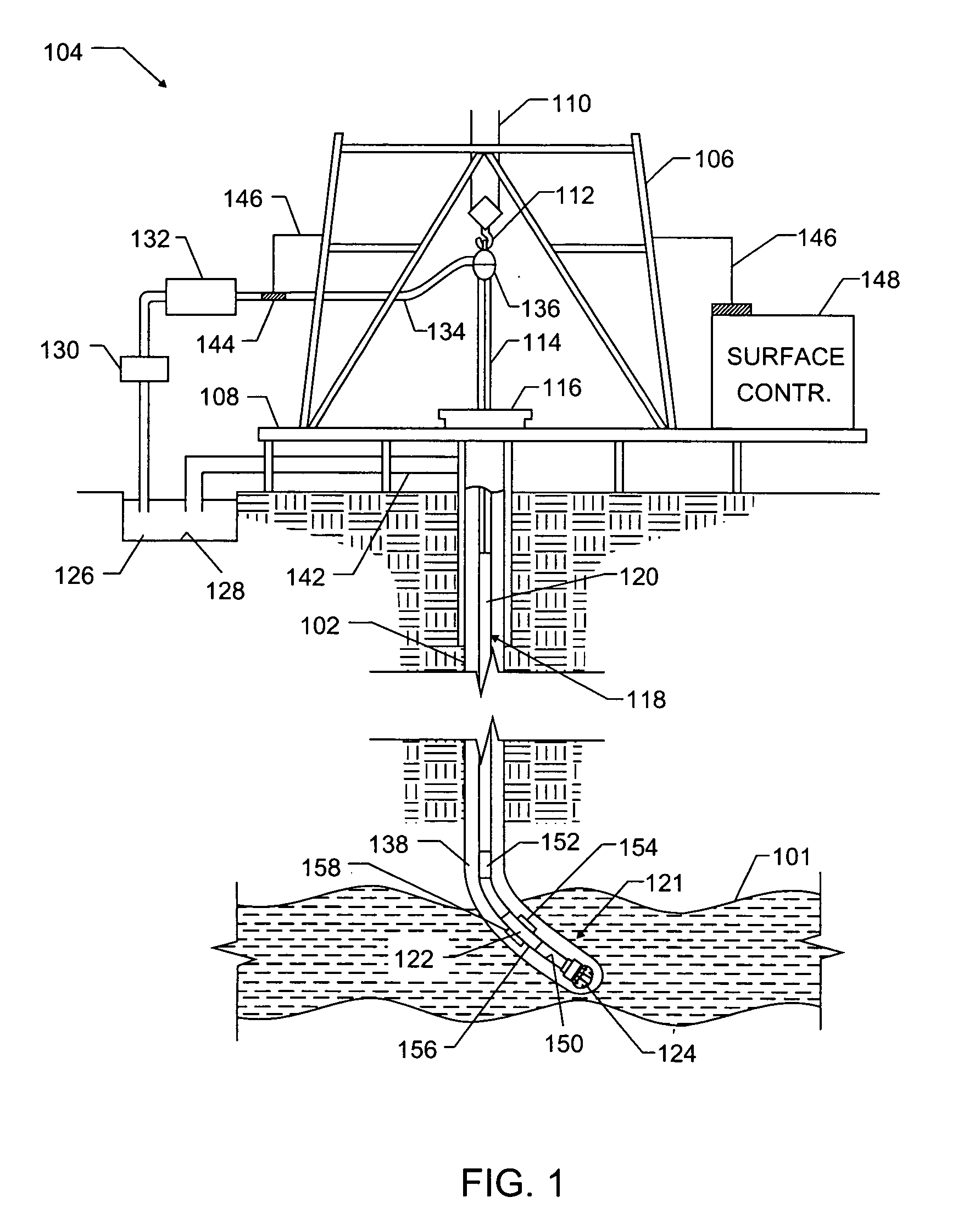
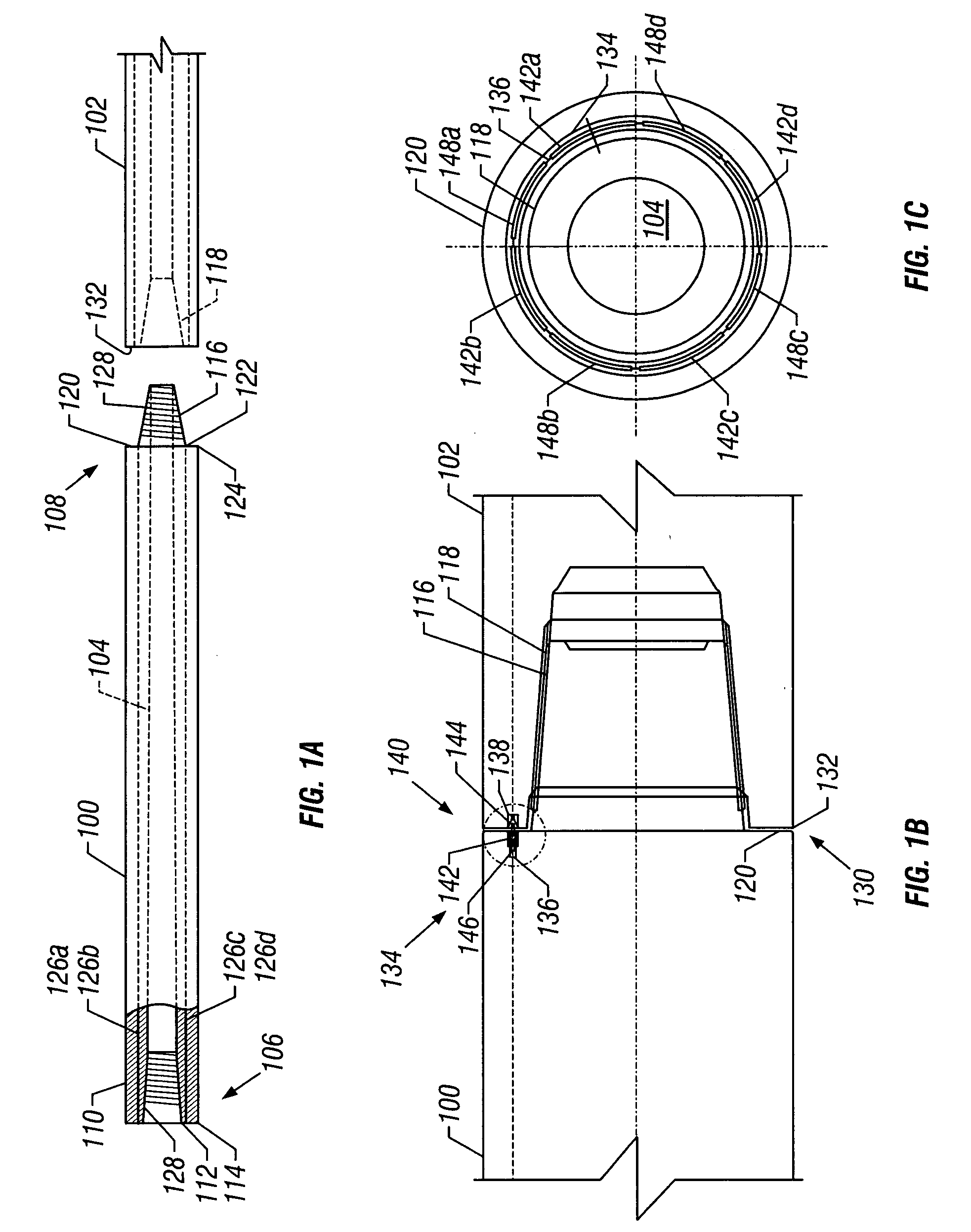
Well logging apparatus and method for measuring formation properties
A logging tool includes an elongated body housing a neutron source and at least one neutron detector positioned along one side of the neutron source. Some embodiments of the logging tool include at least one gamma ray detector longitudinally separated from and to one end of the neutron source, and may be used to make simultaneous gamma ray and neutron logging measurements. In some embodiments, the logging tool also includes a (n, 2n)-neutron shield positioned to one end of the neutron detector, longitudinally between the neutron detector and the neutron source.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Mobile Aircraft Inspection System
A system for scanning aircraft for concealed threats is provided. The system comprises a vehicle and a manipulator arm attached with a scanning head that can be maneuvered in multiple directions to completely scan an aircraft from the outside. The system uses transmission based X-ray detection, backscatter based X-ray detection or a combination thereof, in various embodiments. The system also includes gamma-ray and neutron detectors, for detection of nuclear and radioactive materials.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
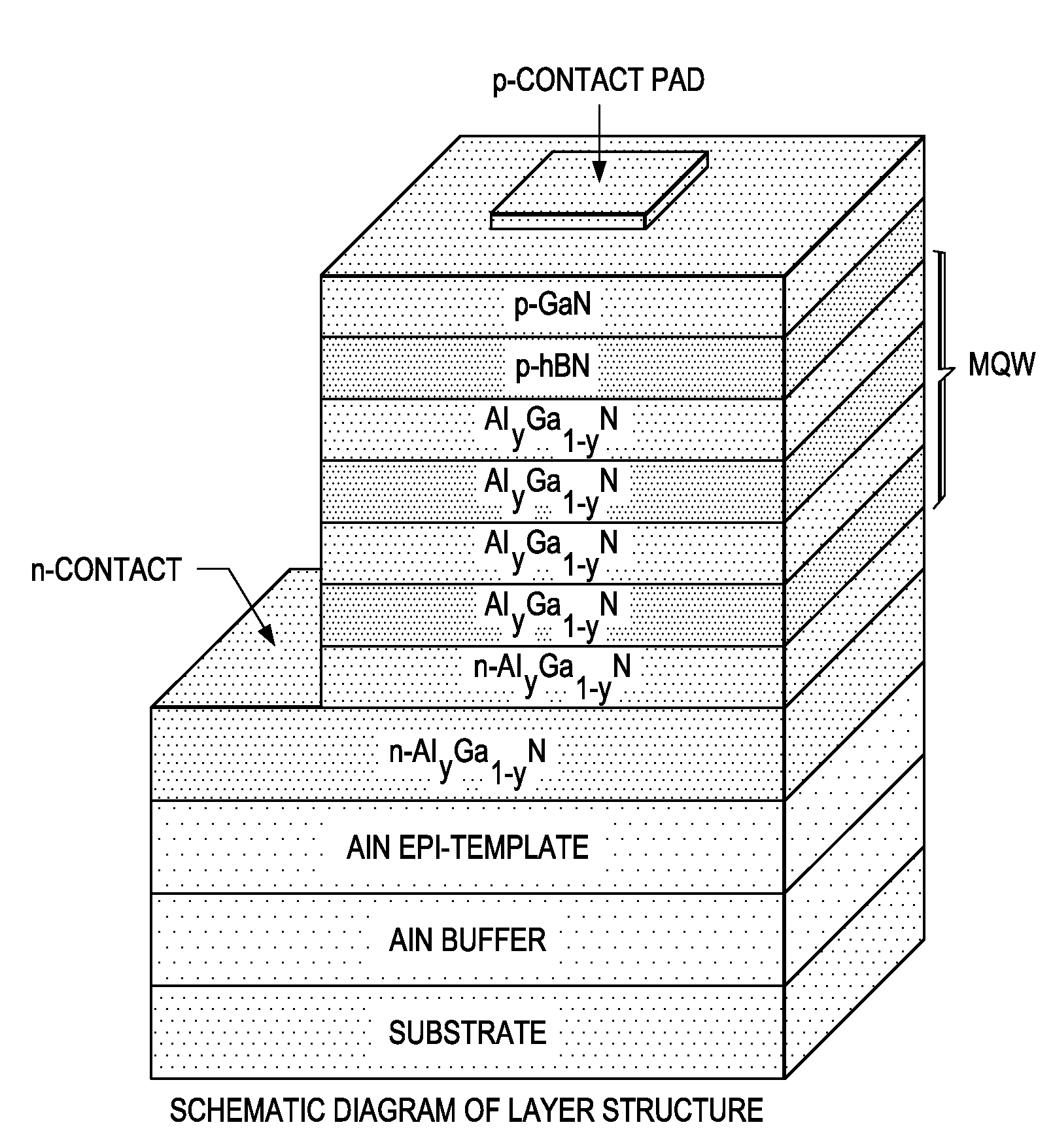
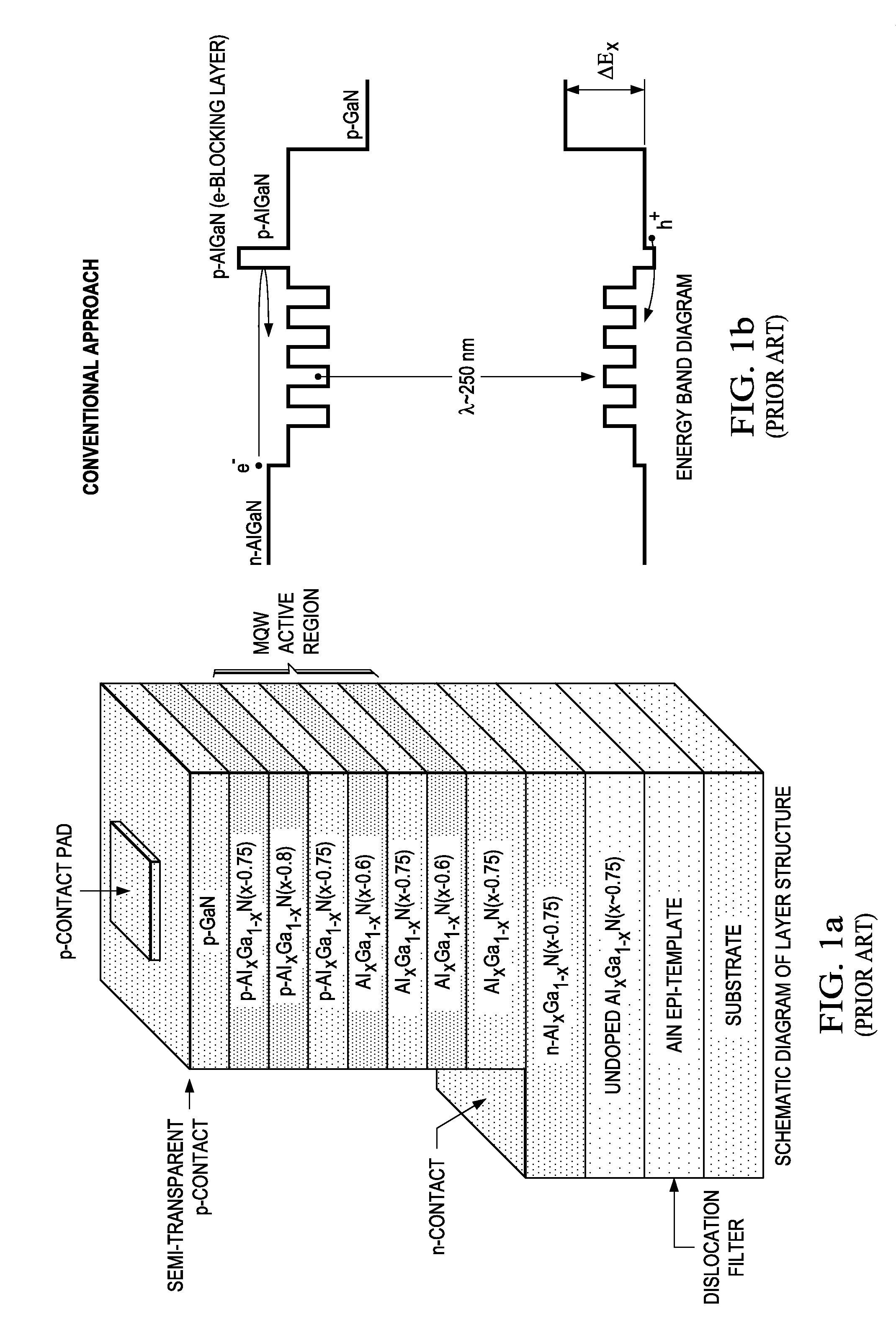
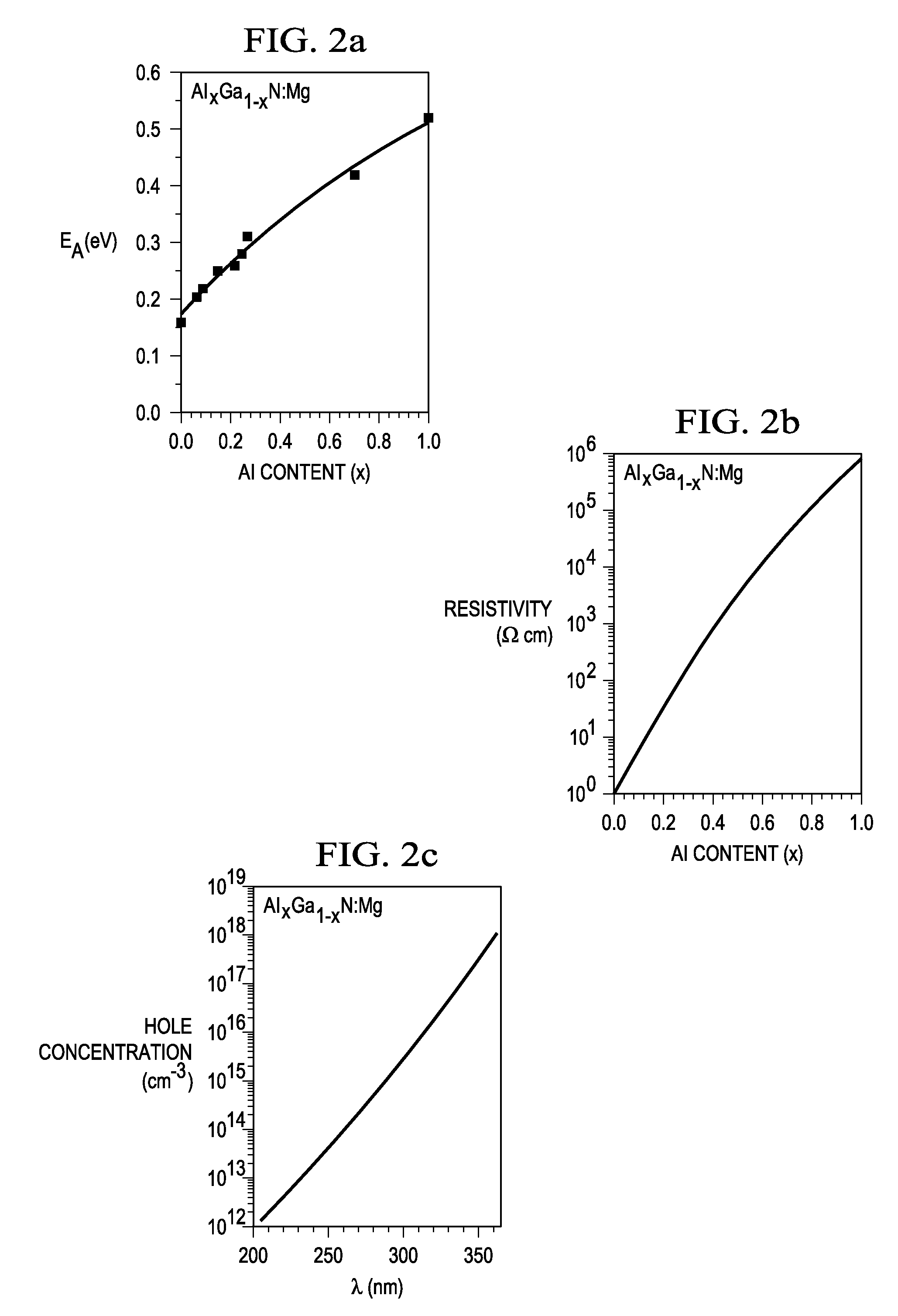
Structures and Devices Based on Boron Nitride and Boron Nitride-III-Nitride Heterostructures
InactiveUS20130292685A1Revolutionize neutron detectionImprove abilitiesFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionHexagonal boron nitride
The present invention relates to optoelectronic device layer structures, light emitting devices, and detectors based upon heterostructures formed between hexagonal boron nitride (hNB) and III-nitrides, and more particularly, to heterojunction devices capable of emitting and detecting photons in the ultraviolet (UV) and extremely ultraviolet (RUV) spectral range. The present invention also relates to neutron detectors based on epitaxially grown hBN thin films (or epitaxial layers) and hBN stacked thin films (or epitaxial layers) to satisfy the thickness required for capturing all incoming neutrons.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST
Composite gamma-neutron detection system
ActiveUS8389941B2Avoid cross contaminationMultiplier cathode arrangementsMeasurement with scintillation detectorsHeavy particleLight guide
The present invention provides a gamma-neutron detector based on mixtures of thermal neutron absorbers that produce heavy-particle emission following thermal capture. The detector consists of one or more thin screens embedded in transparent hydrogenous light guides, which also serve as a neutron moderator. The emitted particles interact with the scintillator screen and produce a high light output, which is collected by the light guides into a photomultiplier tube and produces a signal from which the neutrons are counted. Simultaneous gamma-ray detection is provided by replacing the light guide material with a plastic scintillator. The plastic scintillator serves as the gamma-ray detector, moderator and light guide. The neutrons and gamma-ray events are separated employing Pulse-Shape Discrimination (PSD). The detector can be used in several scanning configurations including portal, drive-through, drive-by, handheld and backpack, etc.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Nonintrusive method for the detection of concealed special nuclear material
ActiveUS7151815B2Conversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear monitoringNeutron pulseRadiation damage
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC CORP
Composite gamma-neutron detection system
InactiveUS20140197321A1Avoid cross contaminationMeasurement with scintillation detectorsPhotometryHeavy particleLight guide
The present invention provides a gamma-neutron detector based on mixtures of thermal neutron absorbers that produce heavy-particle emission following thermal capture. The detector consists of one or more thin screens embedded in transparent hydrogenous light guides, which also serve as a neutron moderator. The emitted particles interact with the scintillator screen and produce a high light output, which is collected by the light guides into a photomultiplier tube and produces a signal from which the neutrons are counted. Simultaneous gamma-ray detection is provided by replacing the light guide material with a plastic scintillator. The plastic scintillator serves as the gamma-ray detector, moderator and light guide. The neutrons and gamma-ray events are separated employing Pulse-Shape Discrimination (PSD). The detector can be used in several scanning configurations including portal, drive-through, drive-by, handheld and backpack, etc.
Owner:BENDAHAN JOSEPH +1
Composite Gamma-Neutron Detection System
ActiveUS20140042330A1Improve efficiencyEasy constructionMultiplier cathode arrangementsMeasurement with scintillation detectorsHeavy particlePhotomultiplier
The present invention provides a gamma-neutron detector based on mixtures of thermal neutron absorbers that produce heavy-particle emission following thermal capture. In one configuration, B-10 based detector is used in a parallel electrode plate geometry that integrates neutron moderating sheets, such as polyethylene, on the back of the electrode plates to thermalize the neutrons and then detect them with high efficiency. The moderator can also be replaced with plastic scintillator sheets viewed with a large area photomultiplier tube to detect gamma-rays as well. The detector can be used in several scanning configurations including portal, drive-through, drive-by, handheld and backpack, etc.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Neutron detector utilizing sol-gel absorber and activation disk
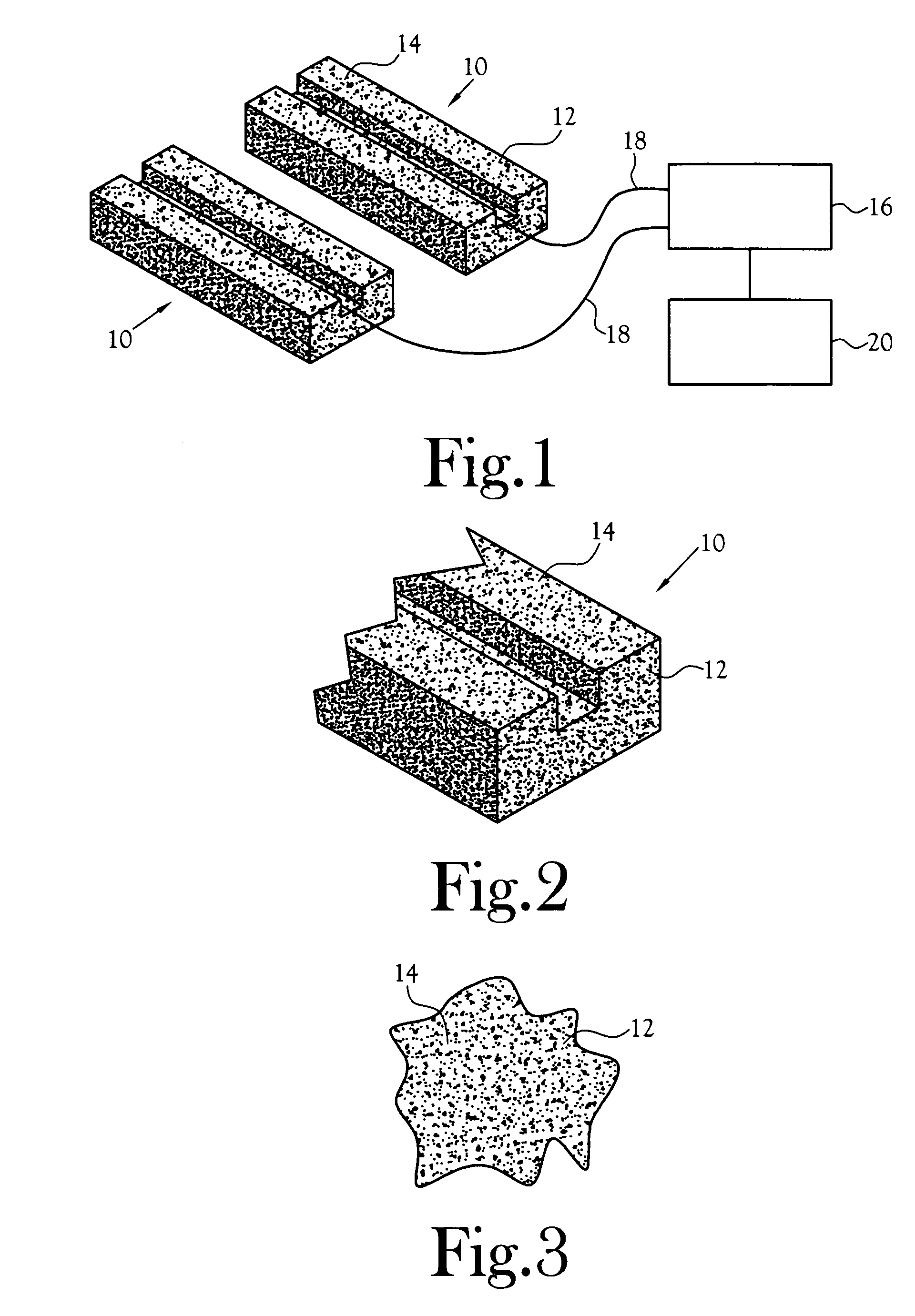
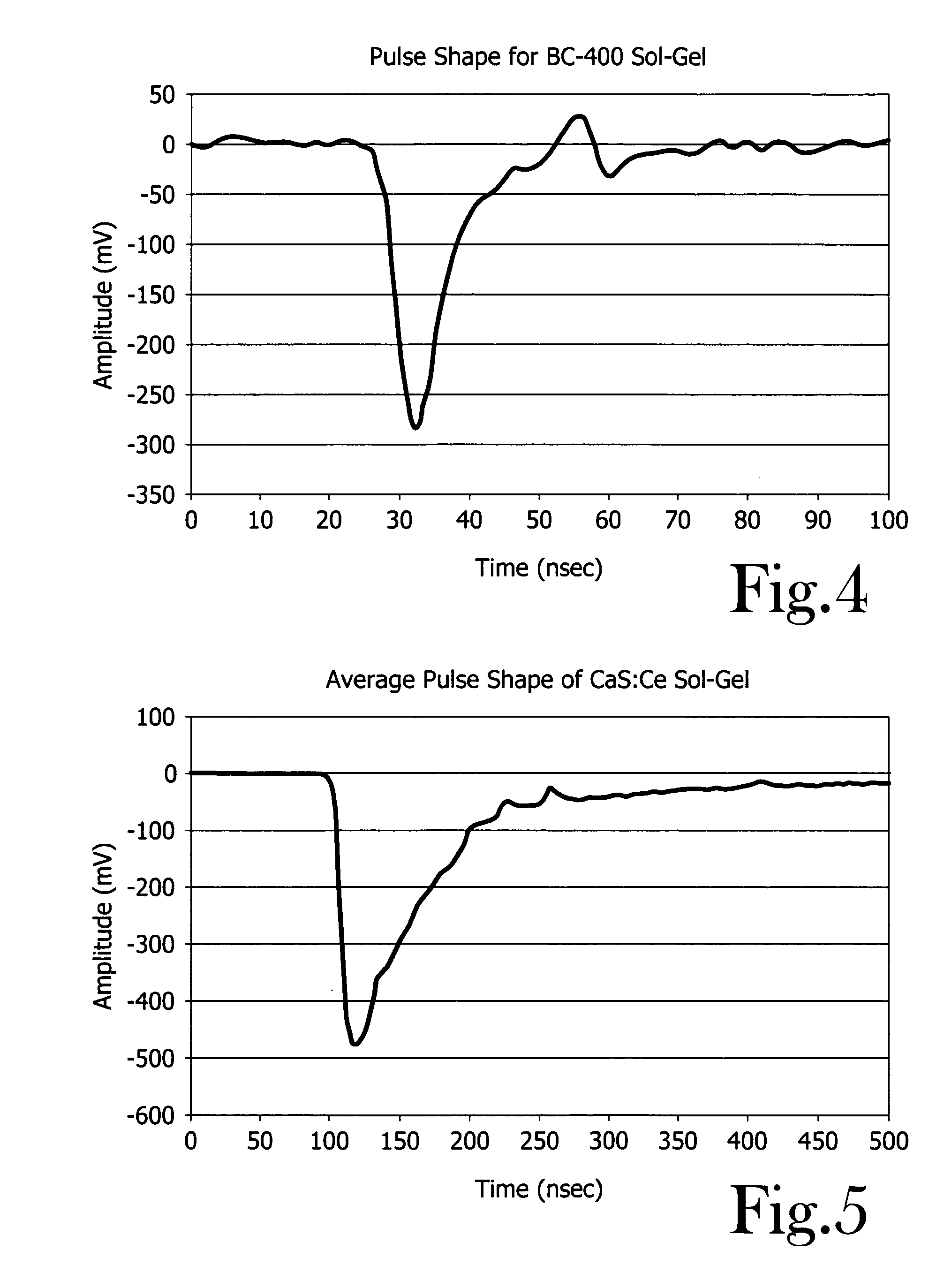
InactiveUS6876711B2Simple and inexpensive conversionStrong differentiation abilityMeasurement with semiconductor devicesGlass dosimetersPrompt neutronBiological activation
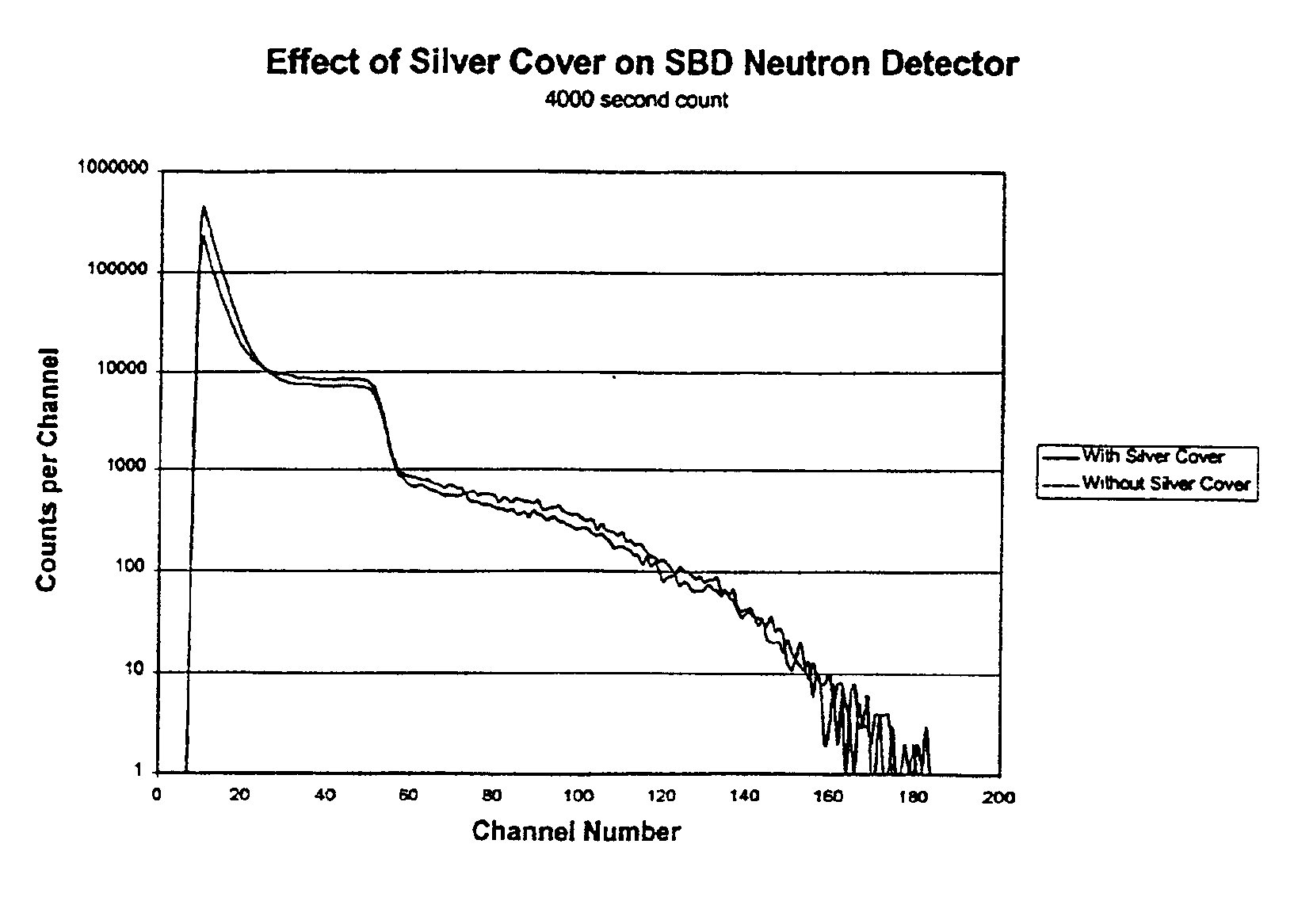
A neutron detector utilizing a sol-gel absorber incorporating a fissionable material and an activation disk. Preferably utilizing Li-6 and B-10 as fissionable material and Ag-109 as activation disk material for increased sensitivity and better differentiation of thermal versus prompt neutrons and neutrons versus other radiation fragments.
Owner:WALLACE STEVEN A +1
Dual modality detection system of nuclear materials concealed in containers
ActiveUS20080191140A1Small footprintMinimal false alarmMeasurement with semiconductor devicesMeasurement with scintillation detectorsGamma detectionNeutron detection
Dual modality detection devices and methods are provided for detecting nuclear material, the devices include a neutron detector including multiple neutron detection modules; and a gamma detector including multiple gamma detection modules, where the multiple neutron detection modules and the multiple gamma detection modules are integrated together in a single unit to detect simultaneously both gamma rays and neutrons.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Composite solid-state scintillators for neutron detection
InactiveUS7105832B2Improve efficiencyPhotosensitive materialsMeasurement with scintillation detectorsSilicon dioxideElectron
Applicant's present invention is a composite scintillator for neutron detection comprising a matrix material fabricated from an inorganic sol-gel precursor solution homogeneously doped with a liquid scintillating material and a neutron absorbing material. The neutron absorbing material yields at least one of an electron, a proton, a triton, an alpha particle or a fission fragment when the neutron absorbing material absorbs a neutron. The composite scintillator further comprises a liquid scintillating material in a self-assembled micelle formation homogeneously doped in the matrix material through the formation of surfactant-silica composites. The scintillating material is provided to scintillate when traversed by at least one of an electron, a proton, a triton, an alpha particle or a fission fragment. The scintillating material is configured such that the matrix material surrounds the micelle formation of the scintillating material. The composite scintillator is fabricated and applied as a thin film on substrate surfaces, a coating on optical fibers or as a glass material.
Owner:U T RES FOUND +1
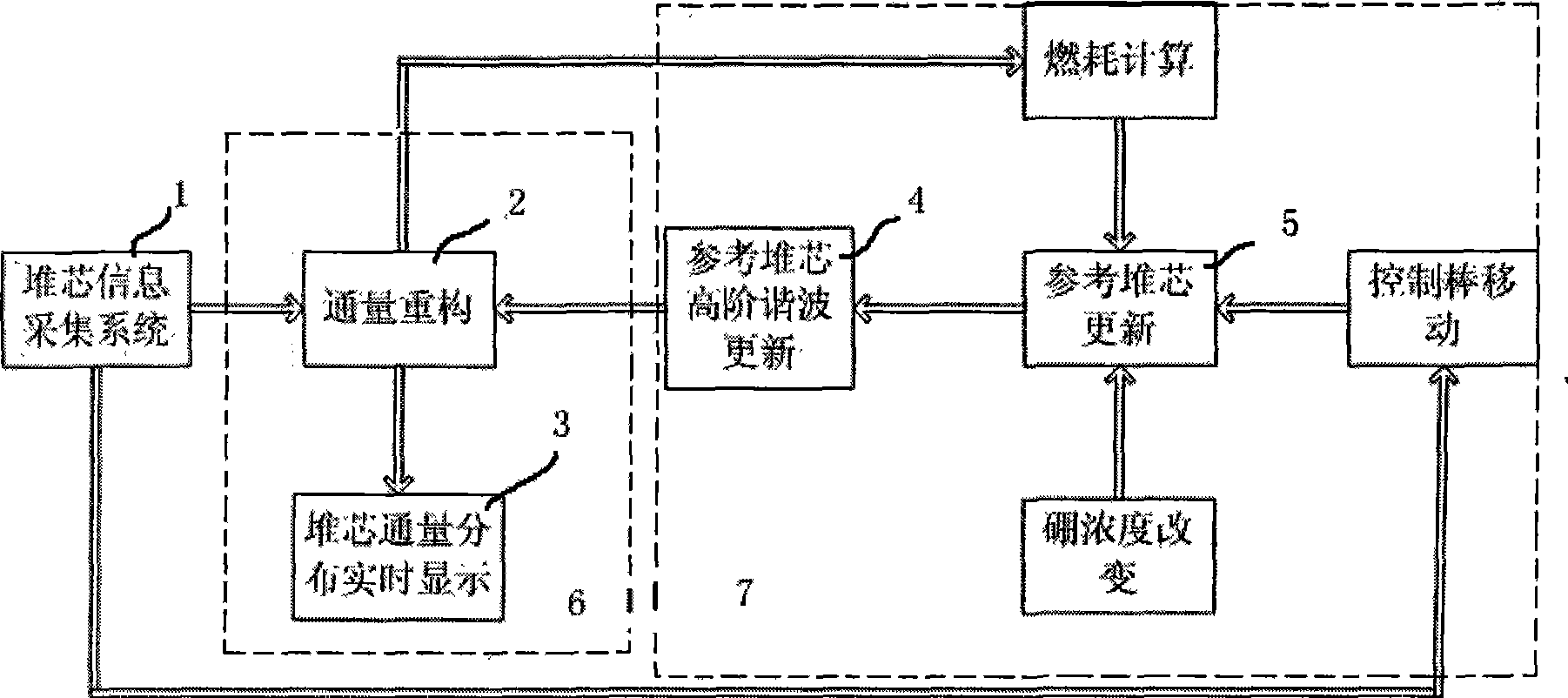
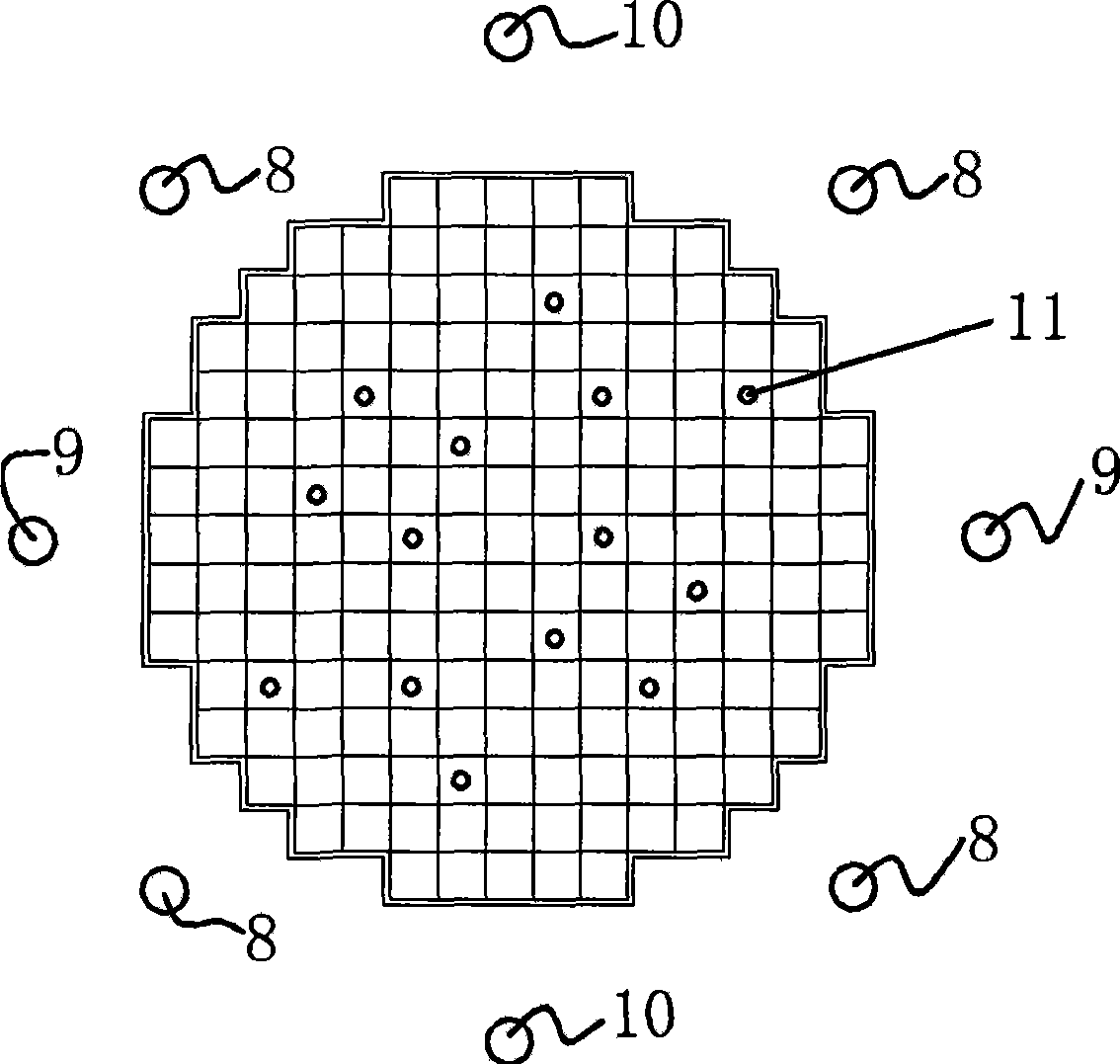
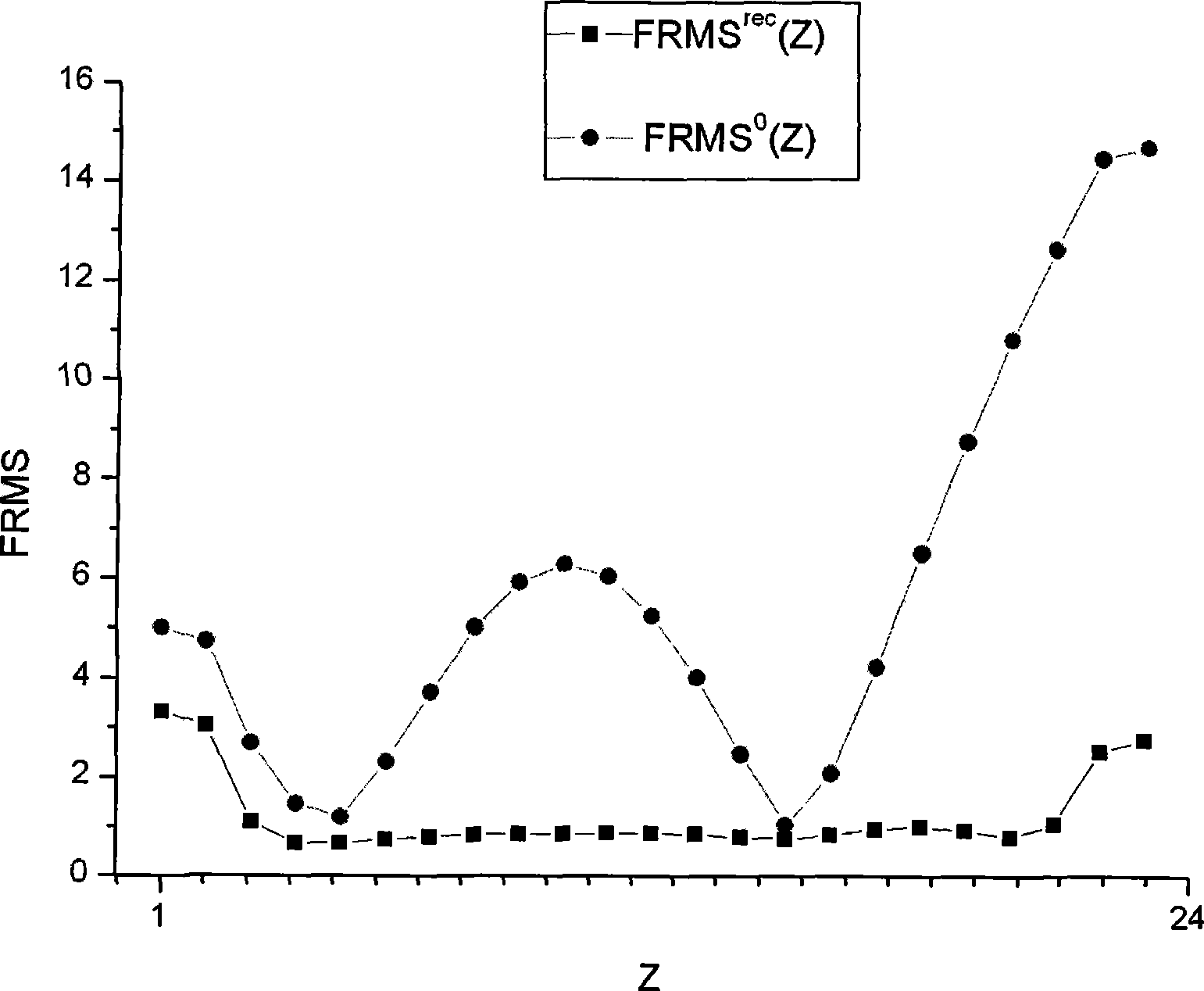
Method for on-line monitoring neutron flux distribution of nuclear reactor core
InactiveCN101399091AEasy to implementLow costNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear reactor coreNuclear reactor
The invention relates to the nuclear reactor core power monitoring field and discloses a method for online monitoring the neutron flux distribution of the reactor core. The method bases on M1 internal neutron detectors and M2 external neutron detectors which are arranged on the reactor. According to a reference reactor core model of a renewal reactor that MPhi is equal to (1 / k) FPhi, higher order harmonics are solved. Then, reading data of the internal neutron detectors and the external neutron detectors are combined. The neutron flux distribution in the core of a real reactor is reconstructed online.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
High performance neutron detector with near zero gamma cross talk
InactiveUS20100224783A1Eliminate outside light interferenceIncrease the number ofMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberRadioactive agent
A scintillator system is provided to detect the presence of fissile material and radioactive material. One or more neutron detectors are based on 6LiF mixed in a binder medium with scintillator material, and are optically coupled to one or more wavelength shifting fiber optic light guide media that have a tapered portion extending from the scintillator material to guide light from the scintillator material to a photosensor at the tapered portion. An electrical output of the photosensor is connected to an input of a first pre-amp circuit designed to operate close to a pulse shape and duration of a light pulse from the scintillator material, without signal distortion. The scintillator material includes a set of scintillation layers connected to the wavelength shifting fiber optic light guide media that guide light to the photosensor. Moderator material is applied around the set of scintillation layers increasing detector efficiency.
Owner:INNOVATIVE AMERICAN TECH
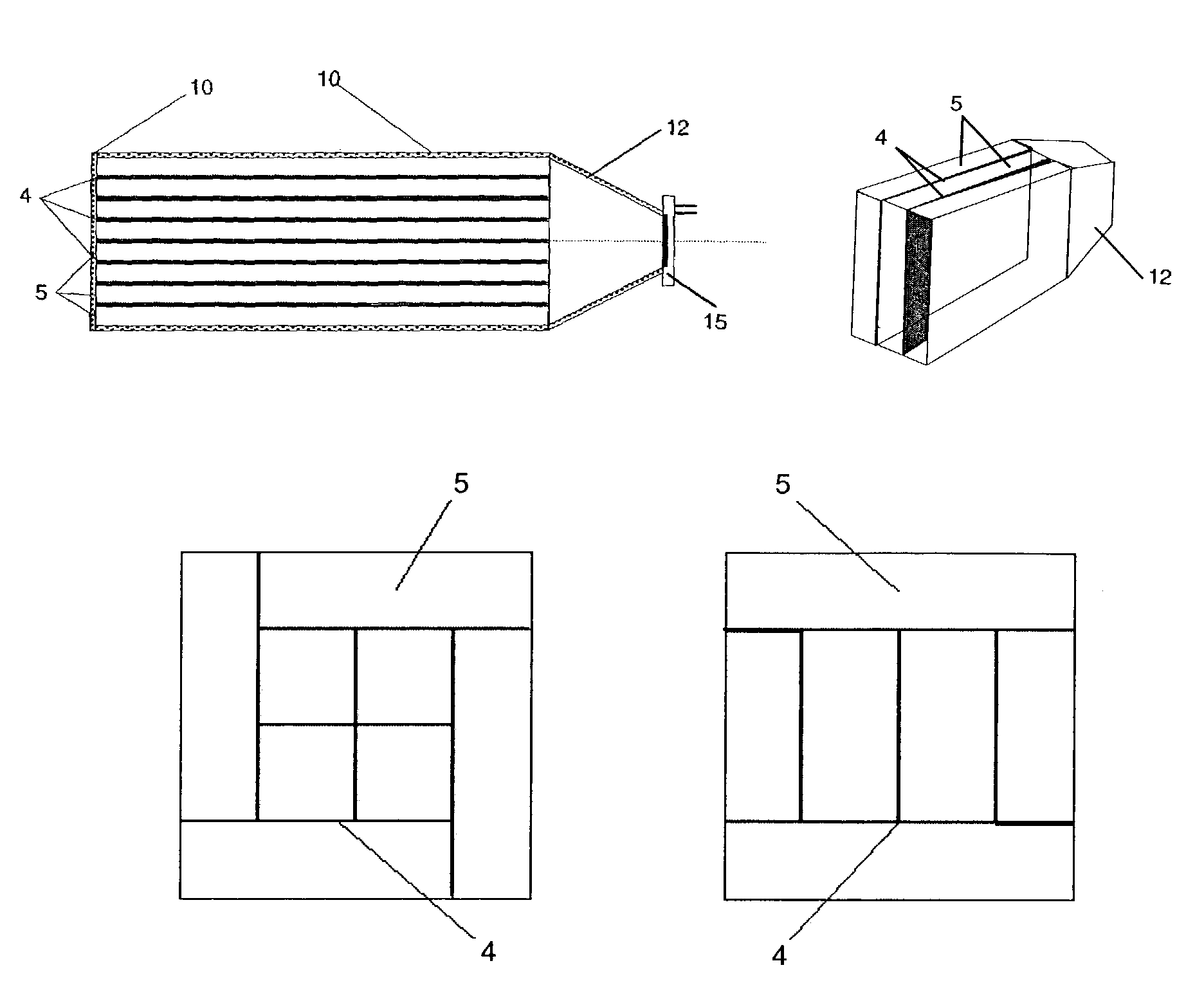
Neutron detector
InactiveUS20100019164A1Discrimination capability is not loweredEasy to useElectric discharge tubesMeasurement with scintillation detectorsLight spectrumNeutron detection
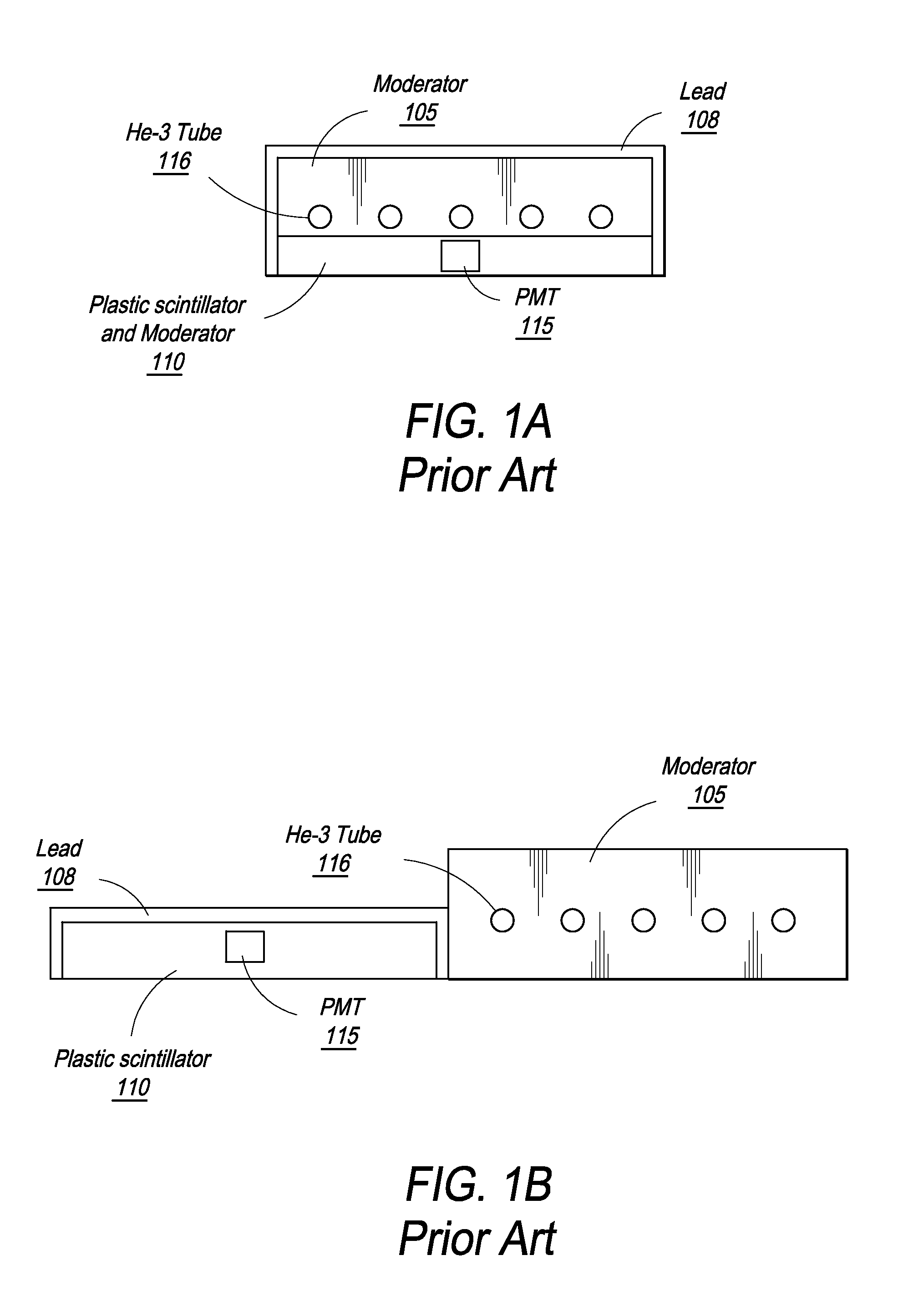
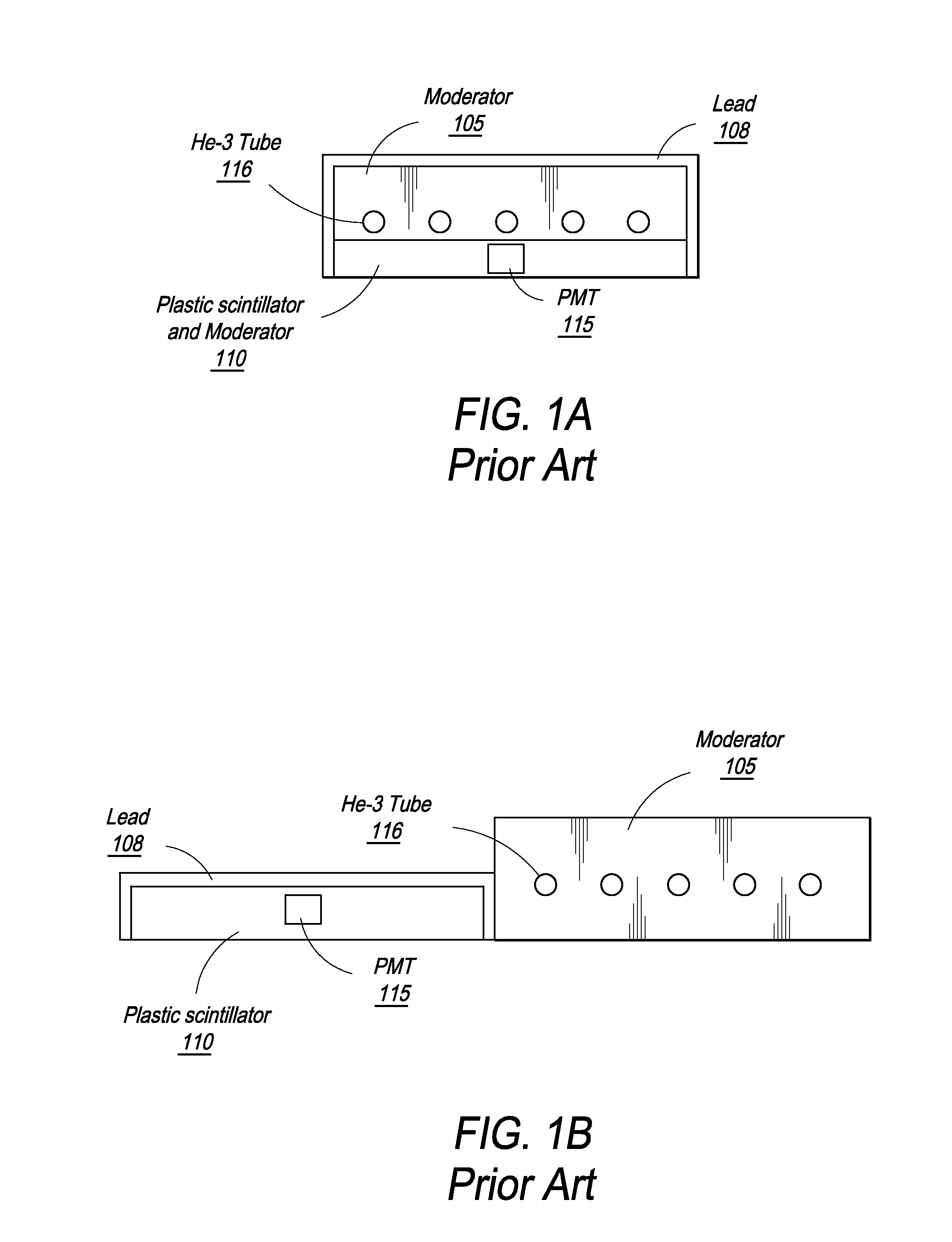
A neutron detector has a volume of neutron moderating material and a plurality of individual neutron sensing elements dispersed at selected locations throughout the moderator, and particularly arranged so that some of the detecting elements are closer to the surface of the moderator assembly and others are more deeply embedded. The arrangement captures some thermalized neutrons that might otherwise be scattered away from a single, centrally located detector element. Different geometrical arrangements may be used while preserving its fundamental characteristics. Different types of neutron sensing elements may be used, which may operate on any of a number of physical principles to perform the function of sensing a neutron, either by a capture or a scattering reaction, and converting that reaction to a detectable signal. High detection efficiency, an ability to acquire spectral information, and directional sensitivity may be obtained.
Owner:MATERIALS INNOVATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com