Patents
Literature
558 results about "Absorbing element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, an absorbing element (or annihilating element) is a special type of element of a set with respect to a binary operation on that set. The result of combining an absorbing element with any element of the set is the absorbing element itself. In semigroup theory, the absorbing element is called a zero element because there is no risk of confusion with other notions of zero. In this article the two notions are synonymous.
Controlled artificial intervertebral disc implant
ActiveUS20050251260A1Reduce the amount requiredProlong lifeBone implantJoint implantsMedicineAxial compression
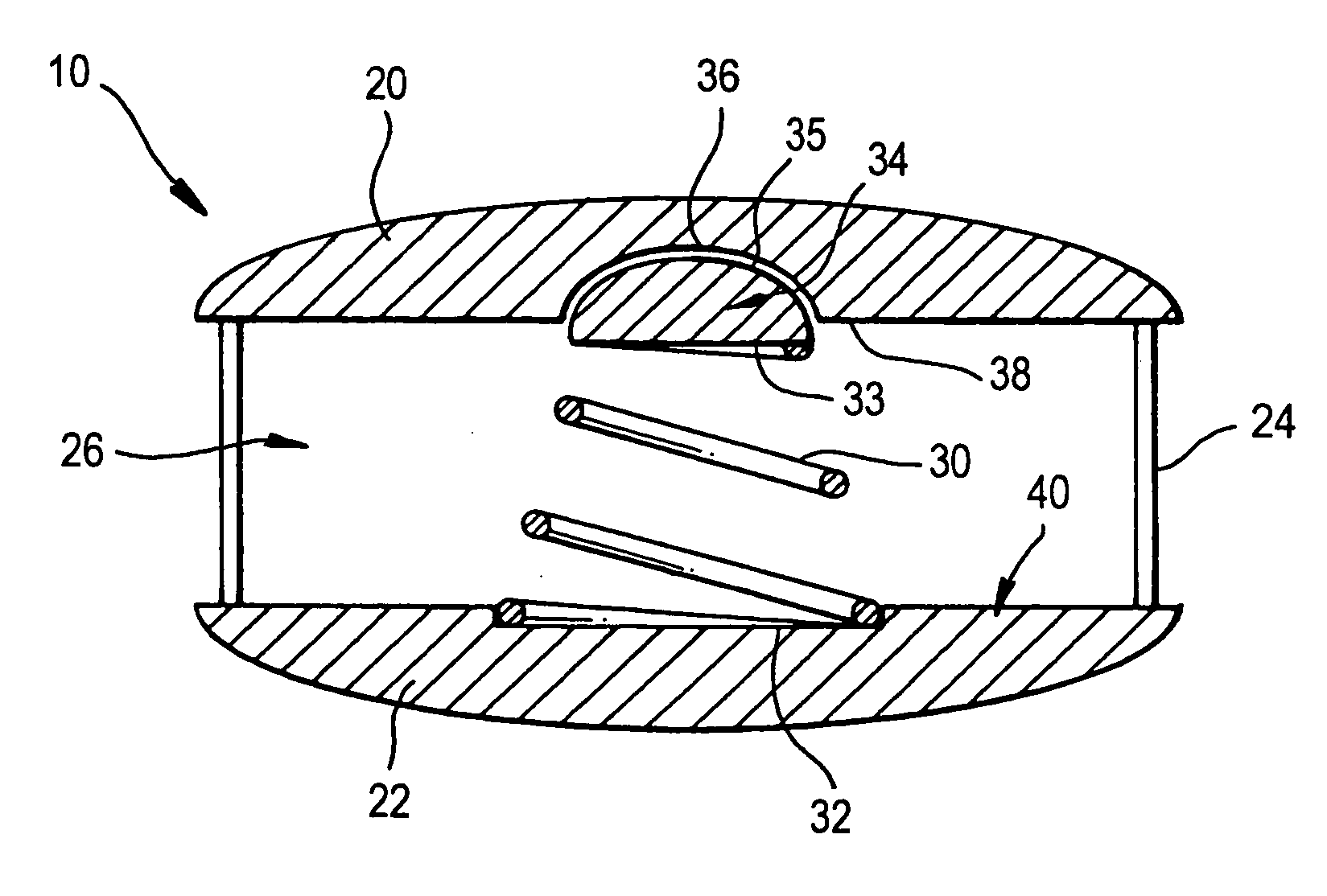
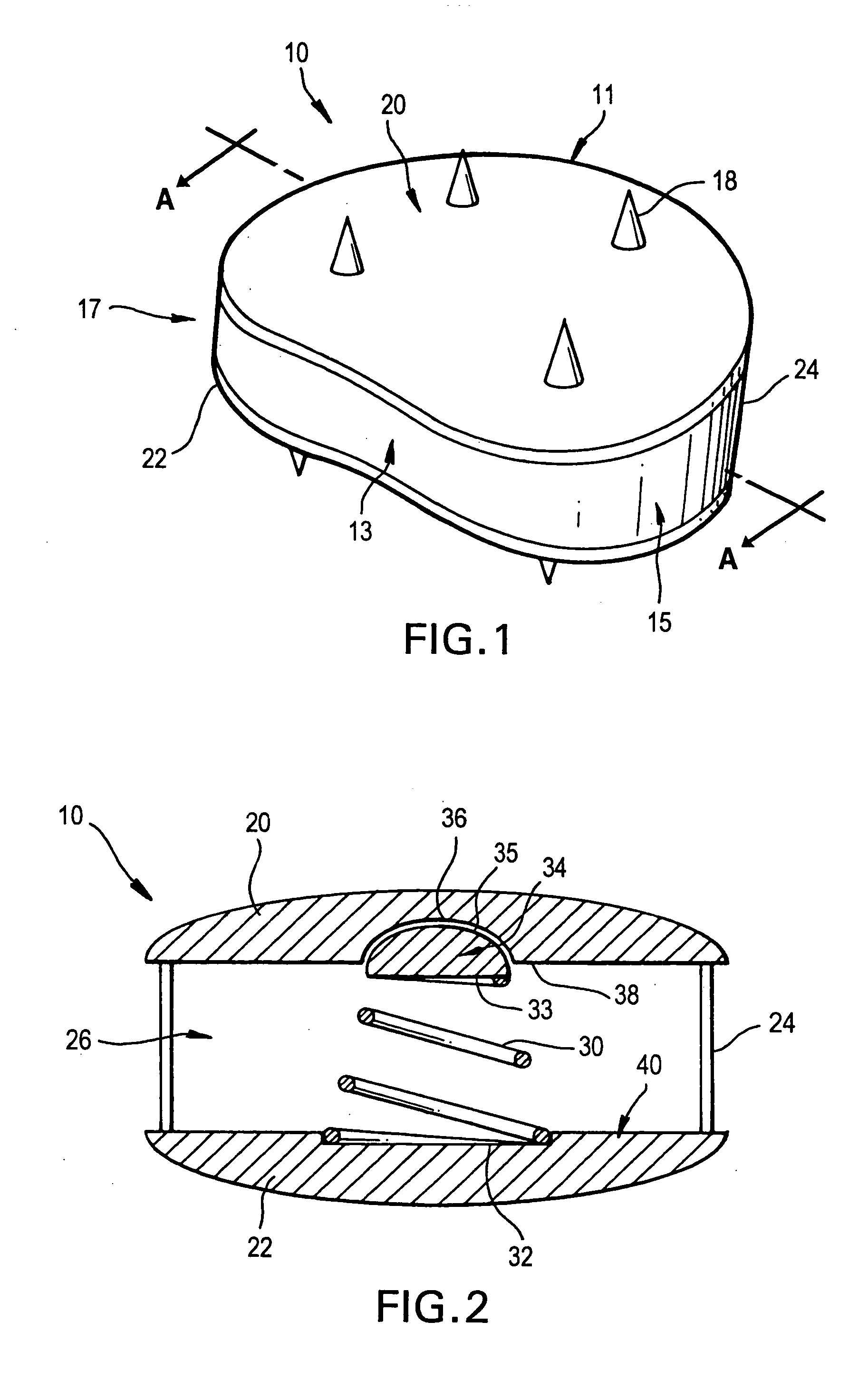
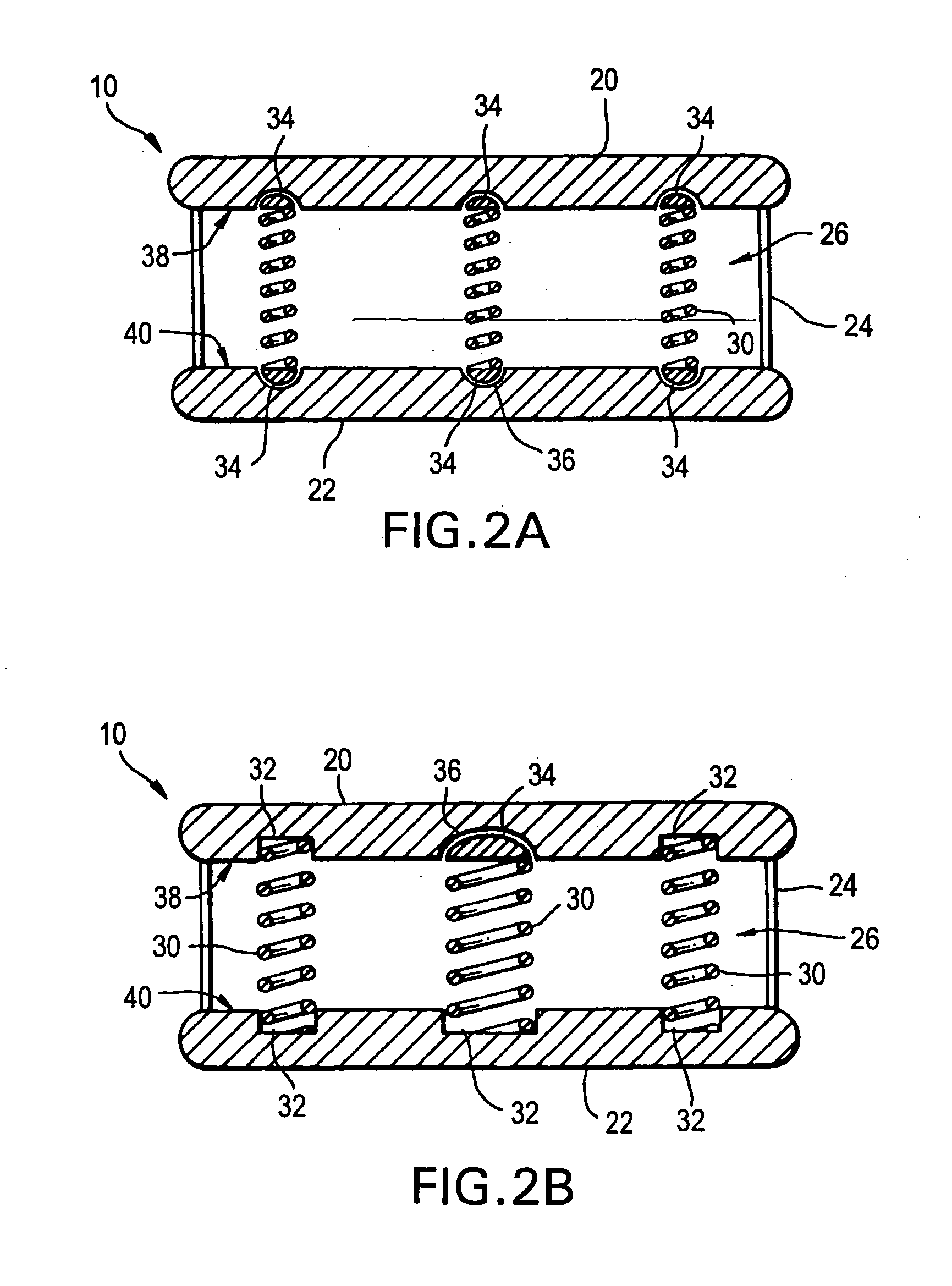
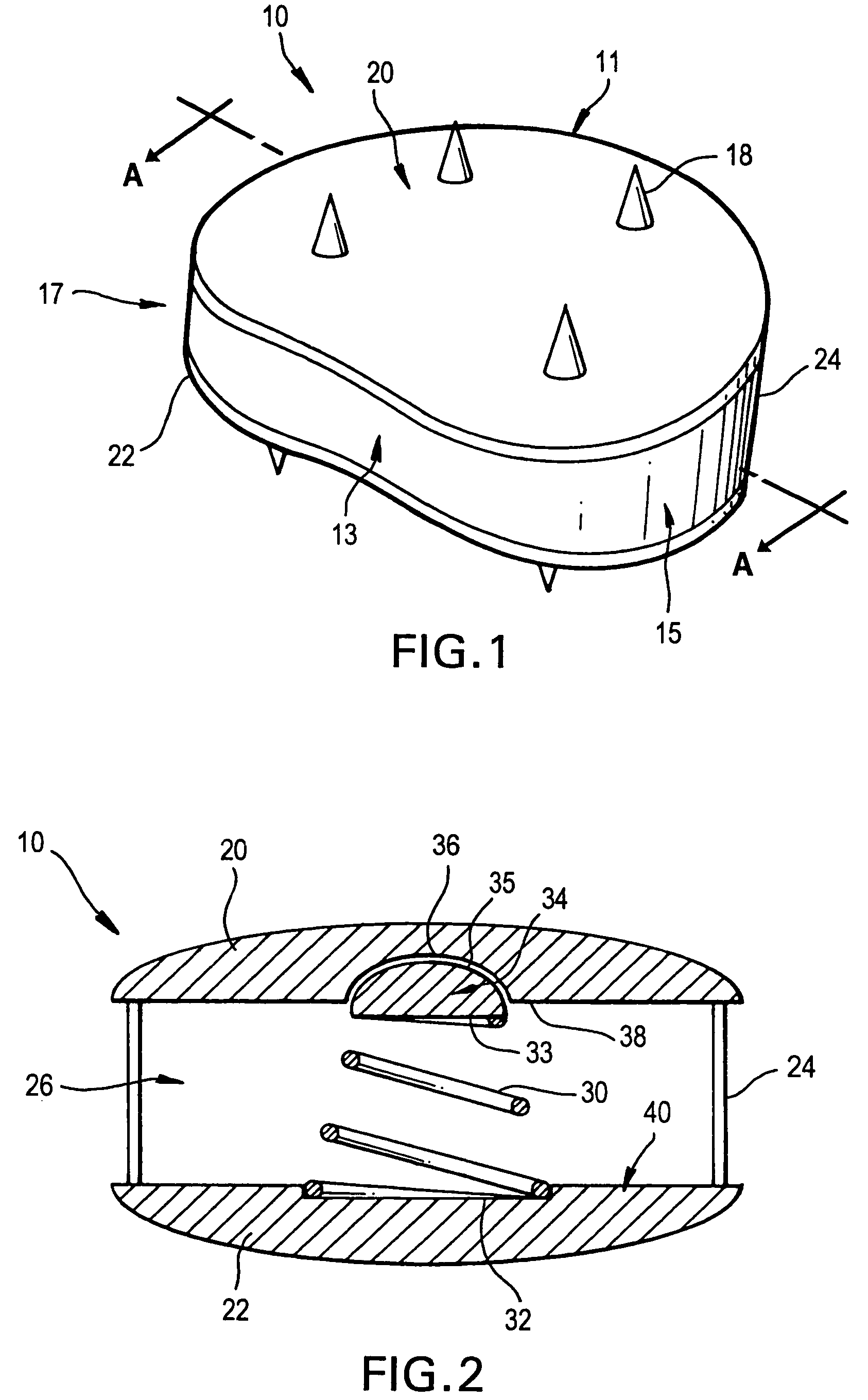
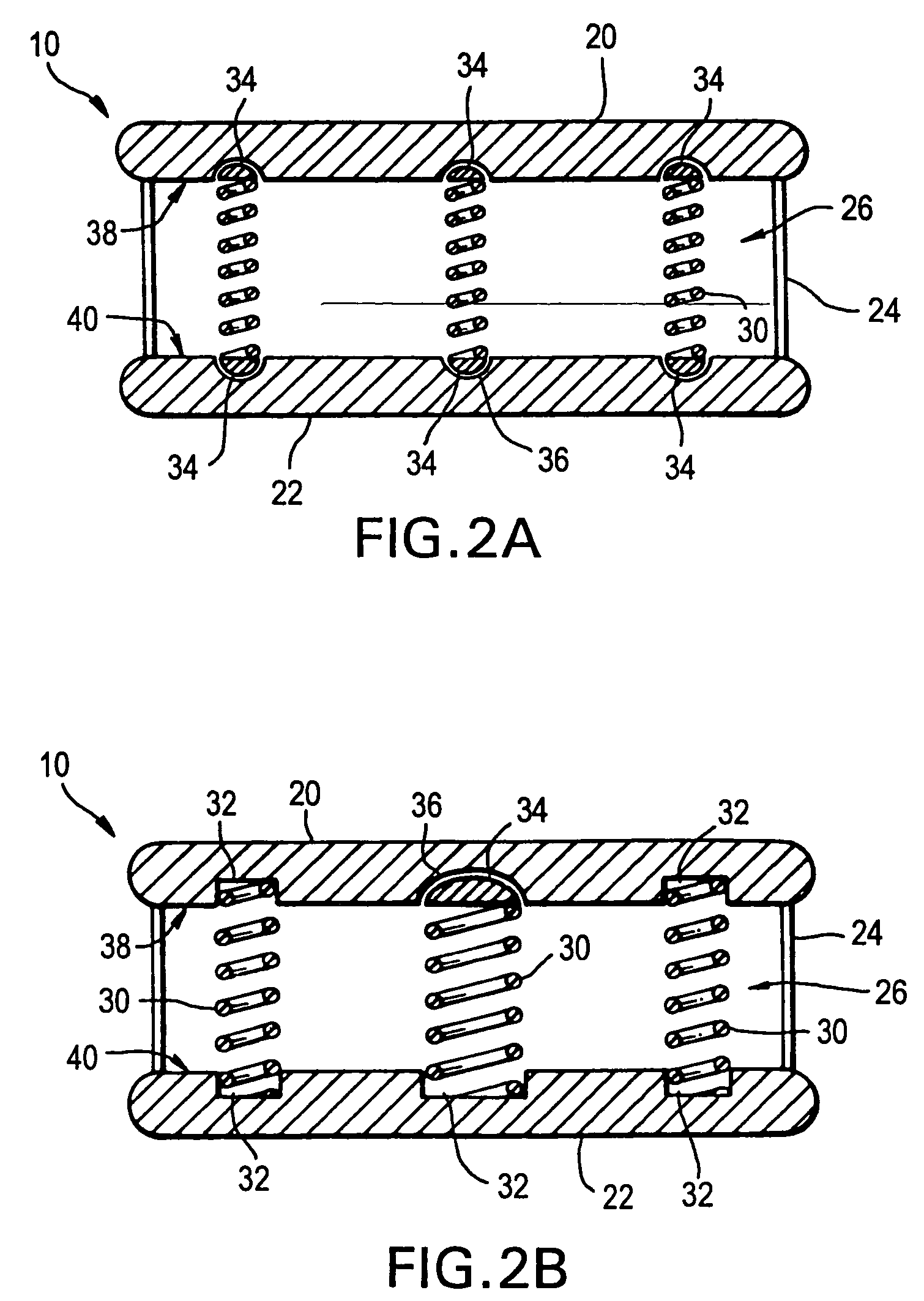
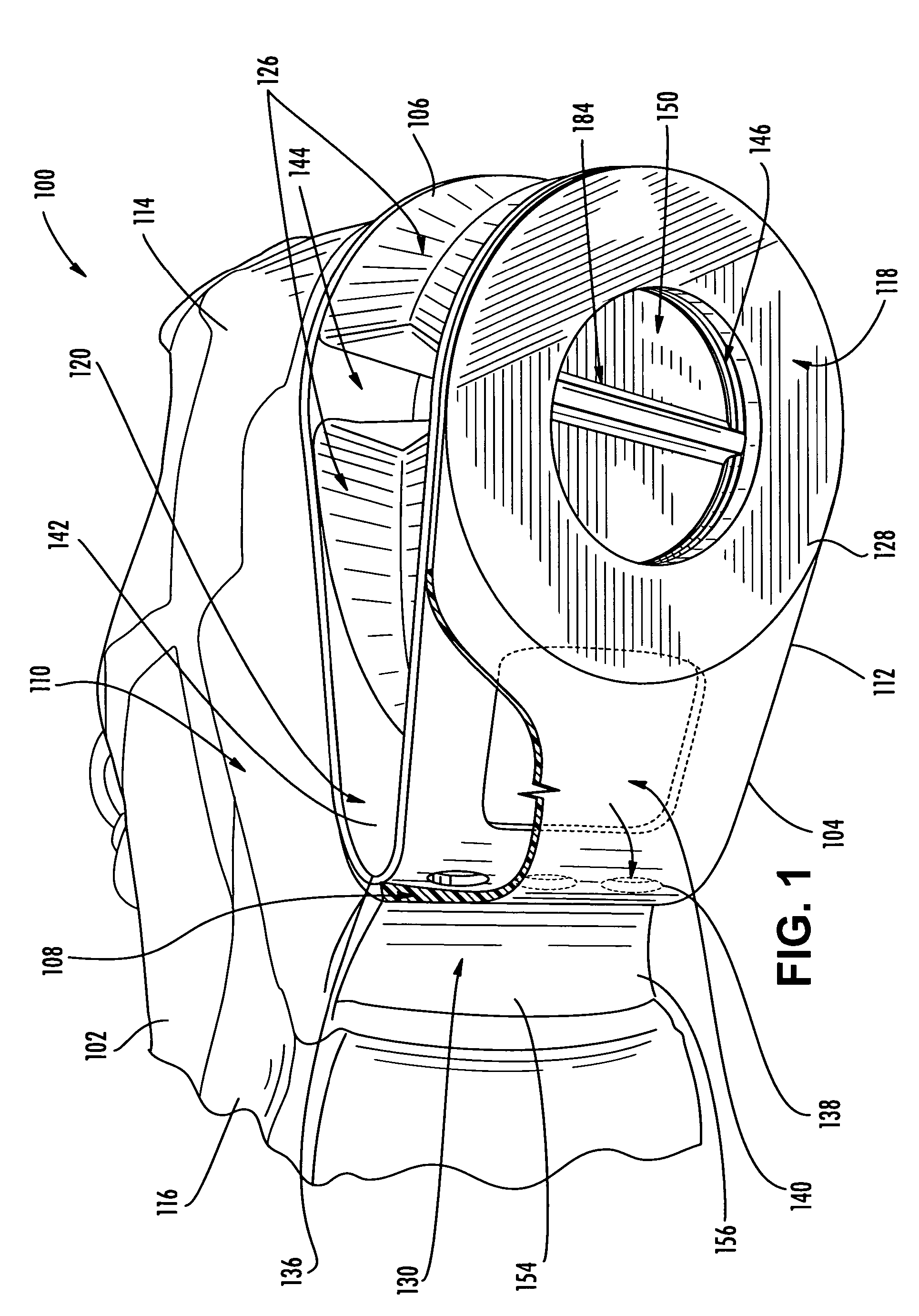
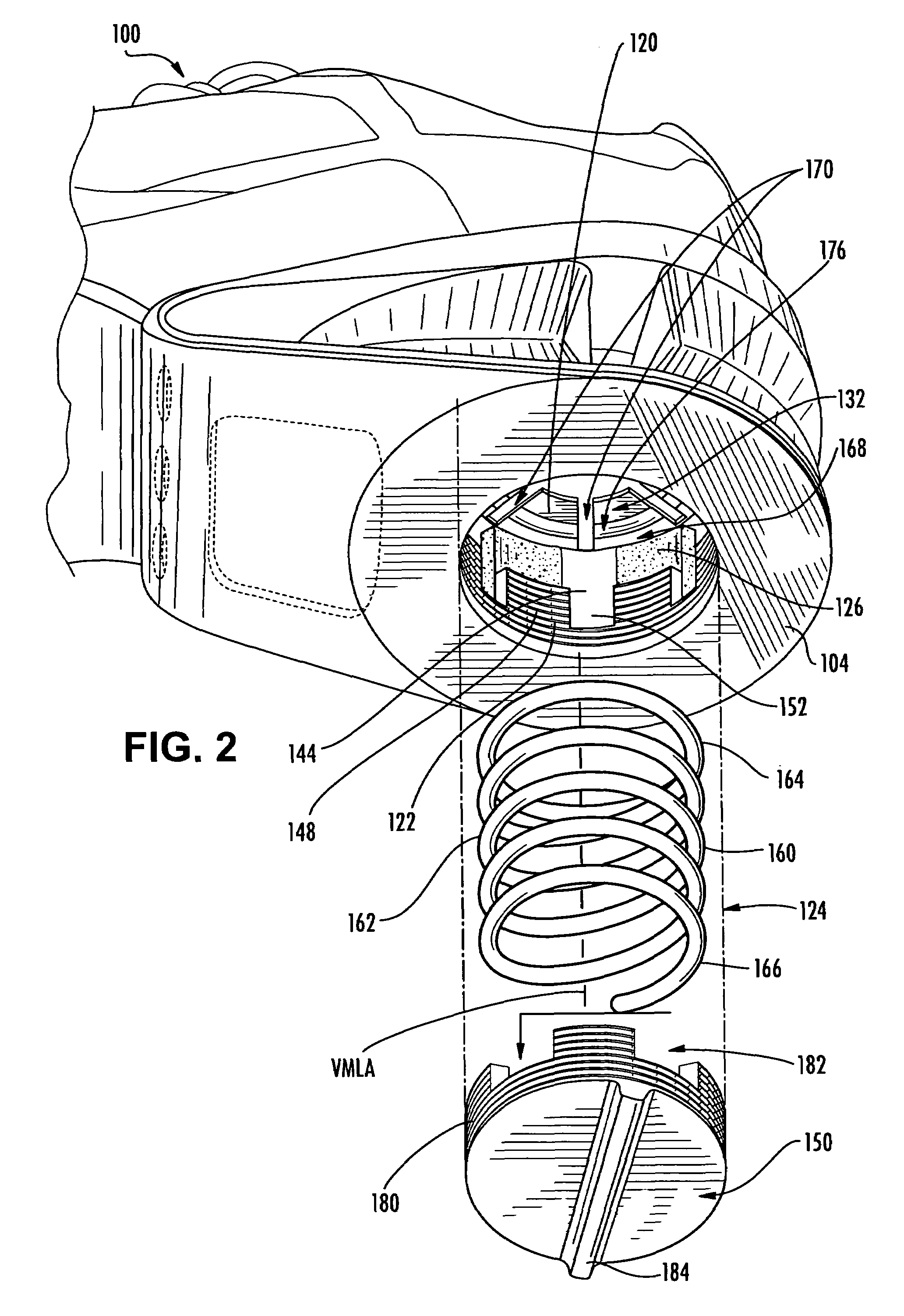
The invention relates to an artificial intervertebral disc for placement between adjacent vertebrae. The artificial intervertebral disc is preferably designed to restore disc height and natural disc curvature, allow for a natural range of motion, absorb shock and provide resistance to motion and axial compression. Furthermore, the intervertebral disc may be used in the cervical, the thoracic, or the lumbar regions of the spine. The artificial intervertebral disc may include either singularly or in combination: an interior including at least one spring member preferably incorporating a arcuate surface member, a flexible core, the flexible core preferably being a slotted core, a ring spring, a winged leaf spring, or a leaf spring, or The articulating member preferably being attached to one of the endplate by an intermediate shock absorbing element.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Controlled artificial intervertebral disc implant
The invention relates to an artificial intervertebral disc for placement between adjacent vertebrae. The artificial intervertebral disc is preferably designed to restore disc height and natural disc curvature, allow for a natural range of motion, absorb shock and provide resistance to motion and axial compression. Furthermore, the intervertebral disc may be used in the cervical, the thoracic, or the lumbar regions of the spine. The artificial intervertebral disc may include either singularly or in combination: an interior including at least one spring member preferably incorporating a arcuate surface member, a flexible core, the flexible core preferably being a slotted core, a ring spring, a winged leaf spring, or a leaf spring, or The articulating member preferably being attached to one of the endplate by an intermediate shock absorbing element.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Golf club head
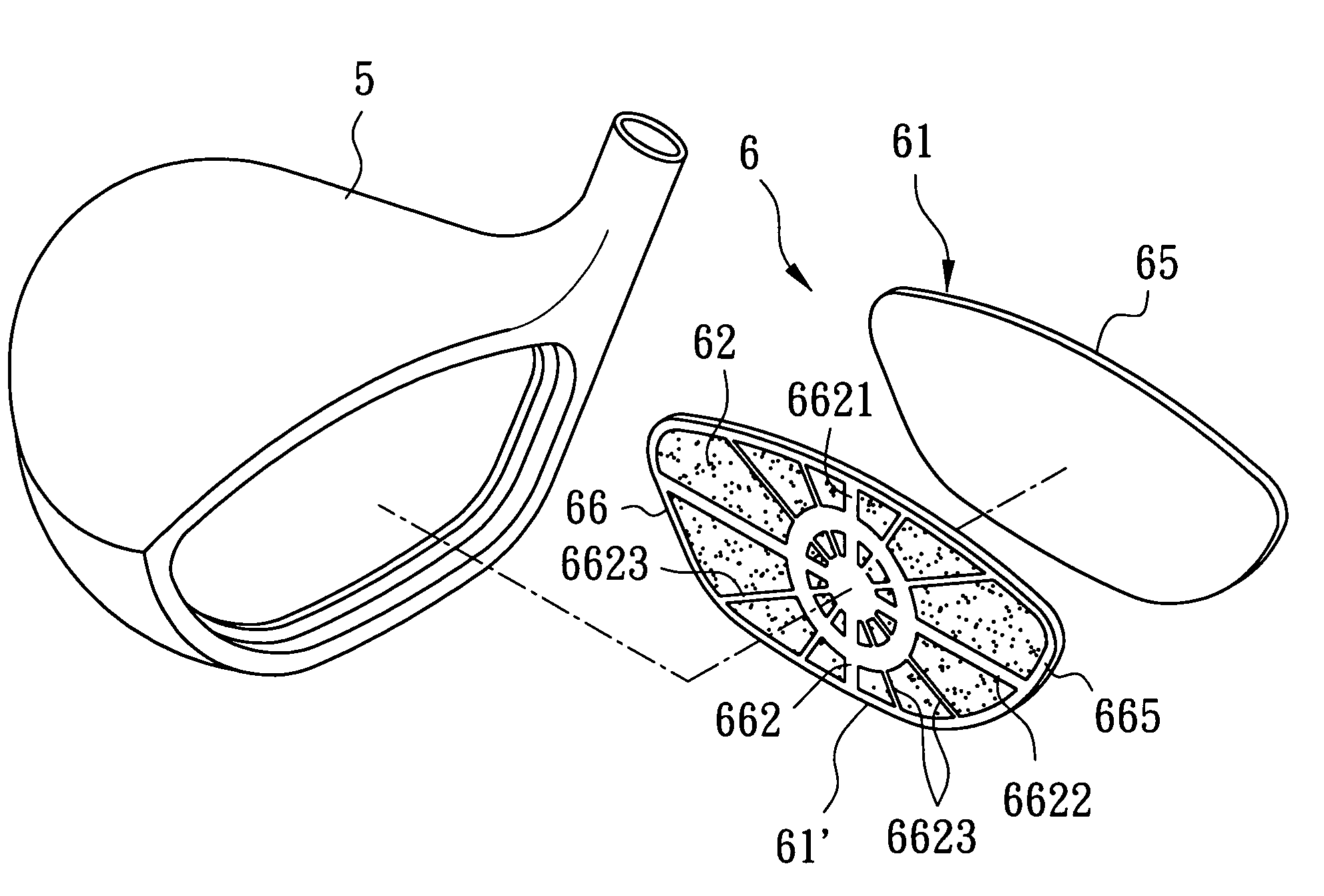
A golf club head includes a head body having a front opening, a striking plate member covering the front opening, and at least one vibration-absorbing element. The striking plate member includes a striking face with a striking zone, and a back face opposite to the striking face and having a receiving groove. The vibration-absorbing element is disposed in the receiving groove.
Owner:O TA PRECISION IND
Optoelectronic device incorporating an interference filter
InactiveUS20050117623A1Optical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionOptical cavityResonance
A novel class of optoelectronic devices incorporate an interference filter. The filter includes at least two optical cavities. Each of the cavities localizes al least one optical mode. The optical modes localized at two cavities are at resonance only at one or at a few discrete selective wavelengths. At resonance, the optical eigenmodes contain one mode having a zero intensity at a node position between the two cavities, where this position shifts as a function of the wavelength. A non-transparent element, which is preferably an absorbing element, a scatterer, or a reflector, is placed between two cavities. At a discrete selective wavelength, when the node of the optical mode matches with the non-transparent element, the filter is transparent for light. At other wavelengths, the filter is not transparent for light. This allows for the construction of various optoelectronic devices showing a strongly wavelength-selective operation.
Owner:INNOLUME
Vehicular rearview mirror element having a display-on-demand display
InactiveUS7543947B2Reduce material costsGood optical performanceMirrorsAntiglare equipmentDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
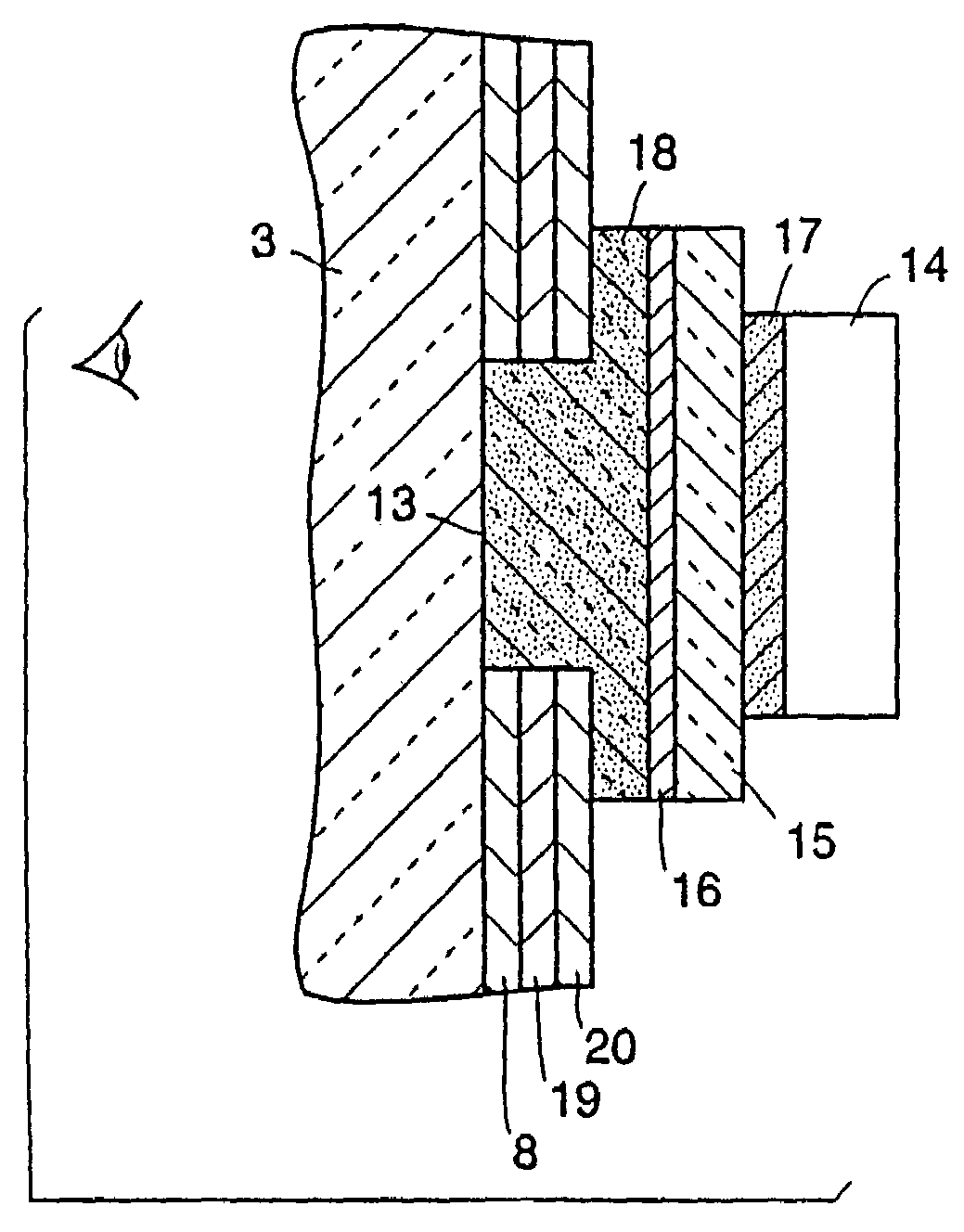
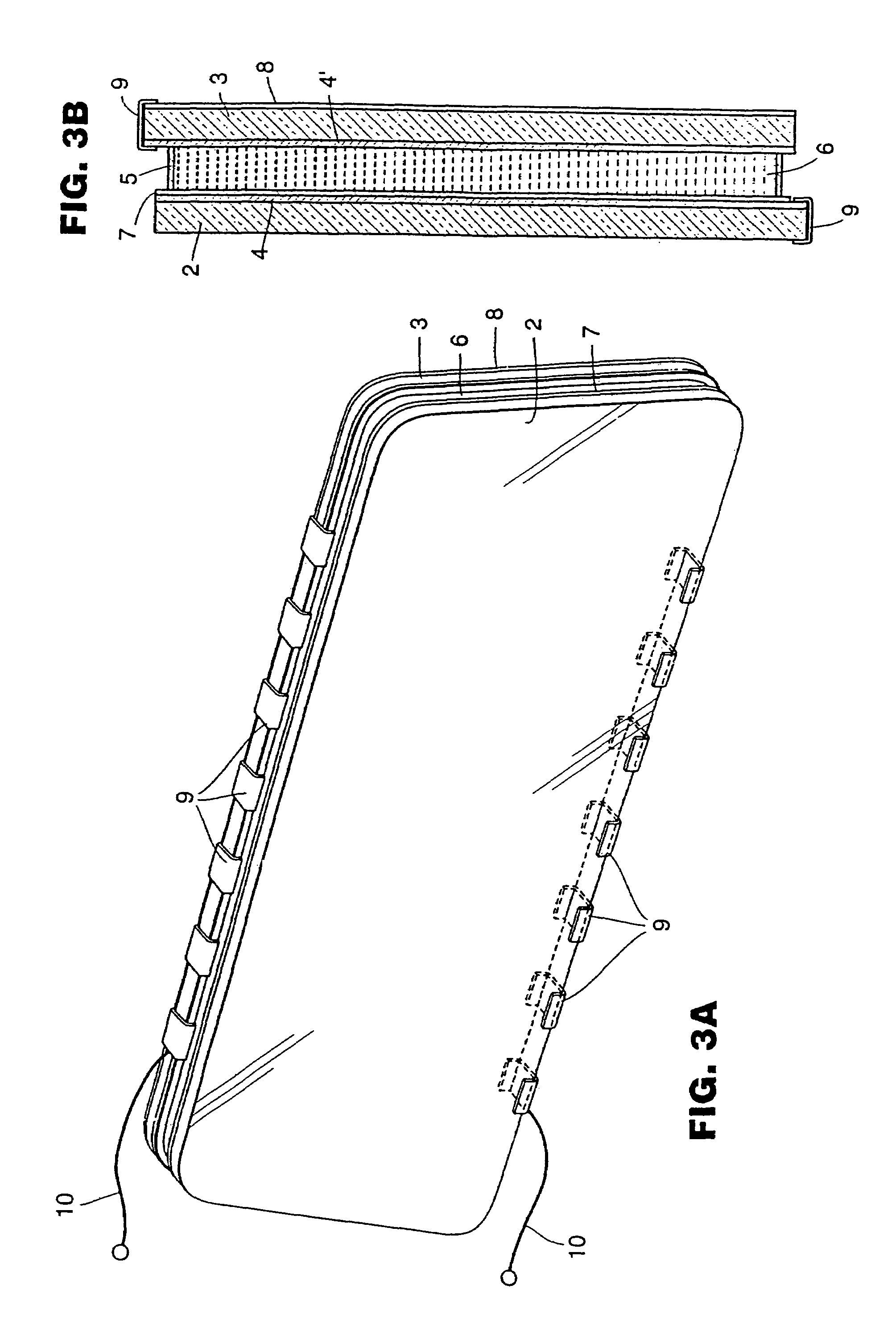
A rearview mirror element for a motor vehicle includes a light transmitting substrate having a visible light reflecting and visible light transmitting mirror reflector disposed on a surface thereof. A display-on-demand display device is disposed behind the substrate such that light emitted by the display device when powered passes through both the light transmitting substrate and the mirror reflector. The display device exhibits, when powered during day time driving conditions, a display luminance of at least about 60 foot lamberts. When not emitting light, the disposition of the display device to the rear of the light transmitting substrate is not substantially distinguishable to the driver of the equipped vehicle when viewing the mirror element. To the rear of the light transmitting substrate is rendered substantially opaque by a light absorbing element that is disposed at least adjacent to where, and except at where, the display device is disposed therebehind.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
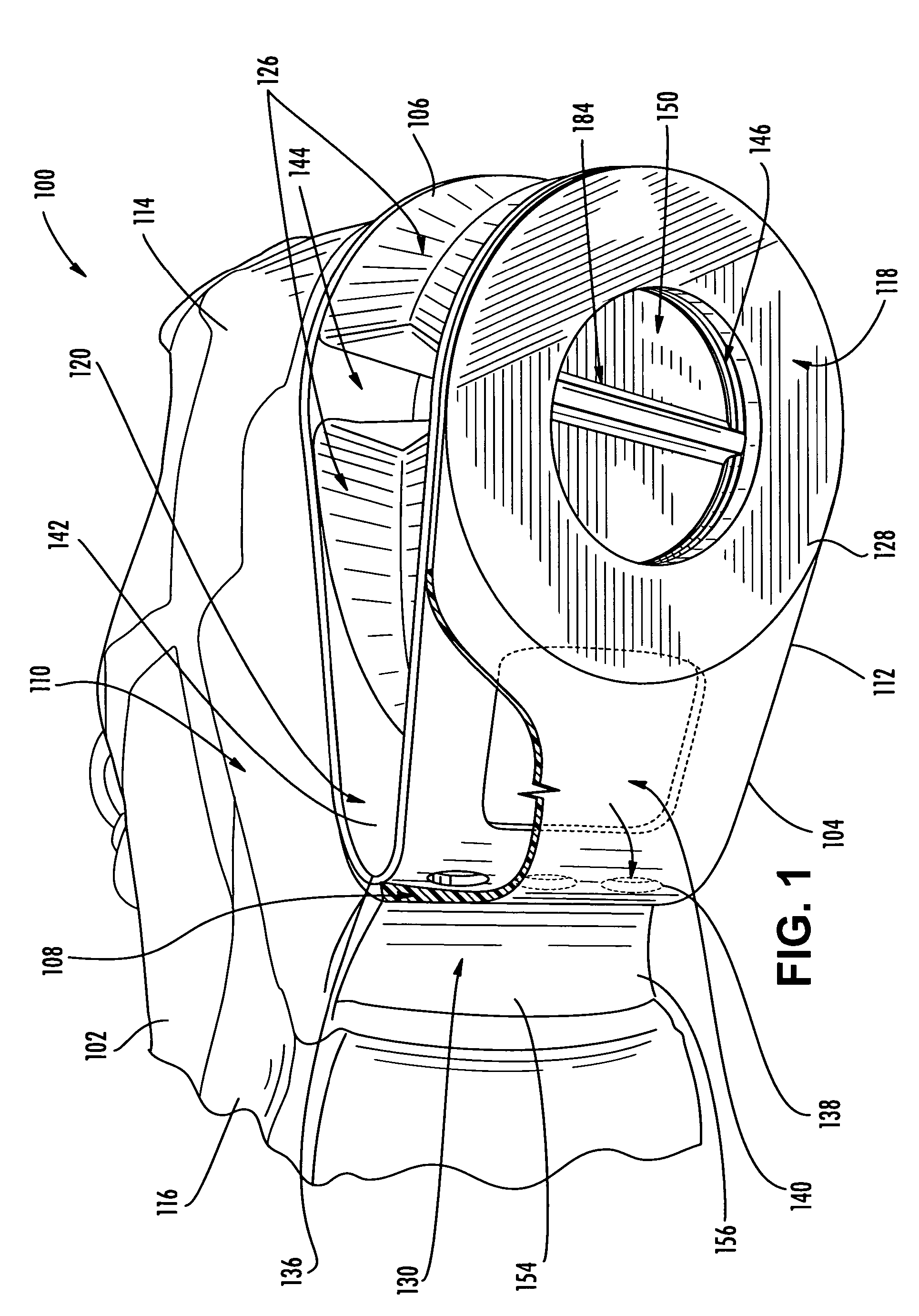
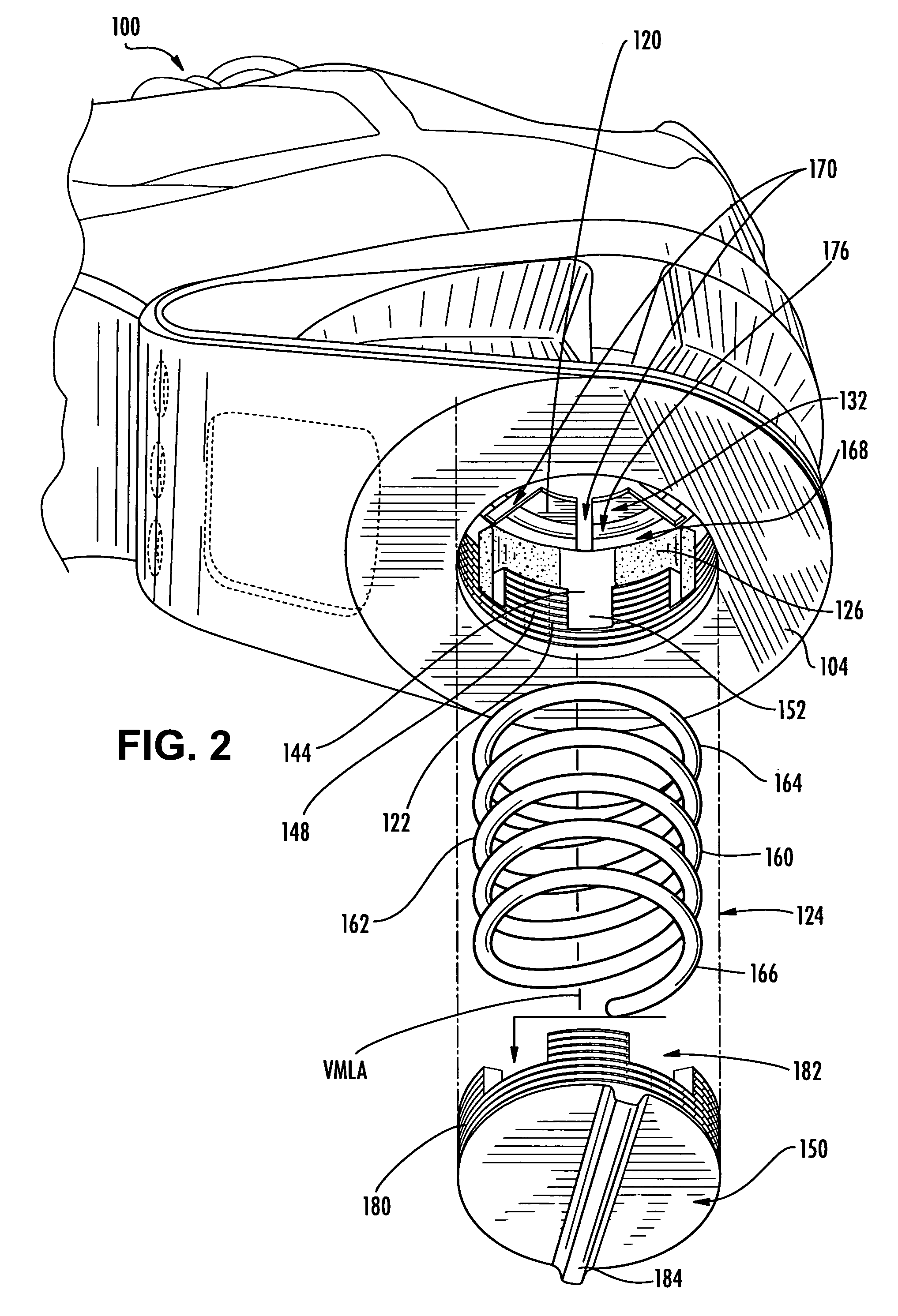
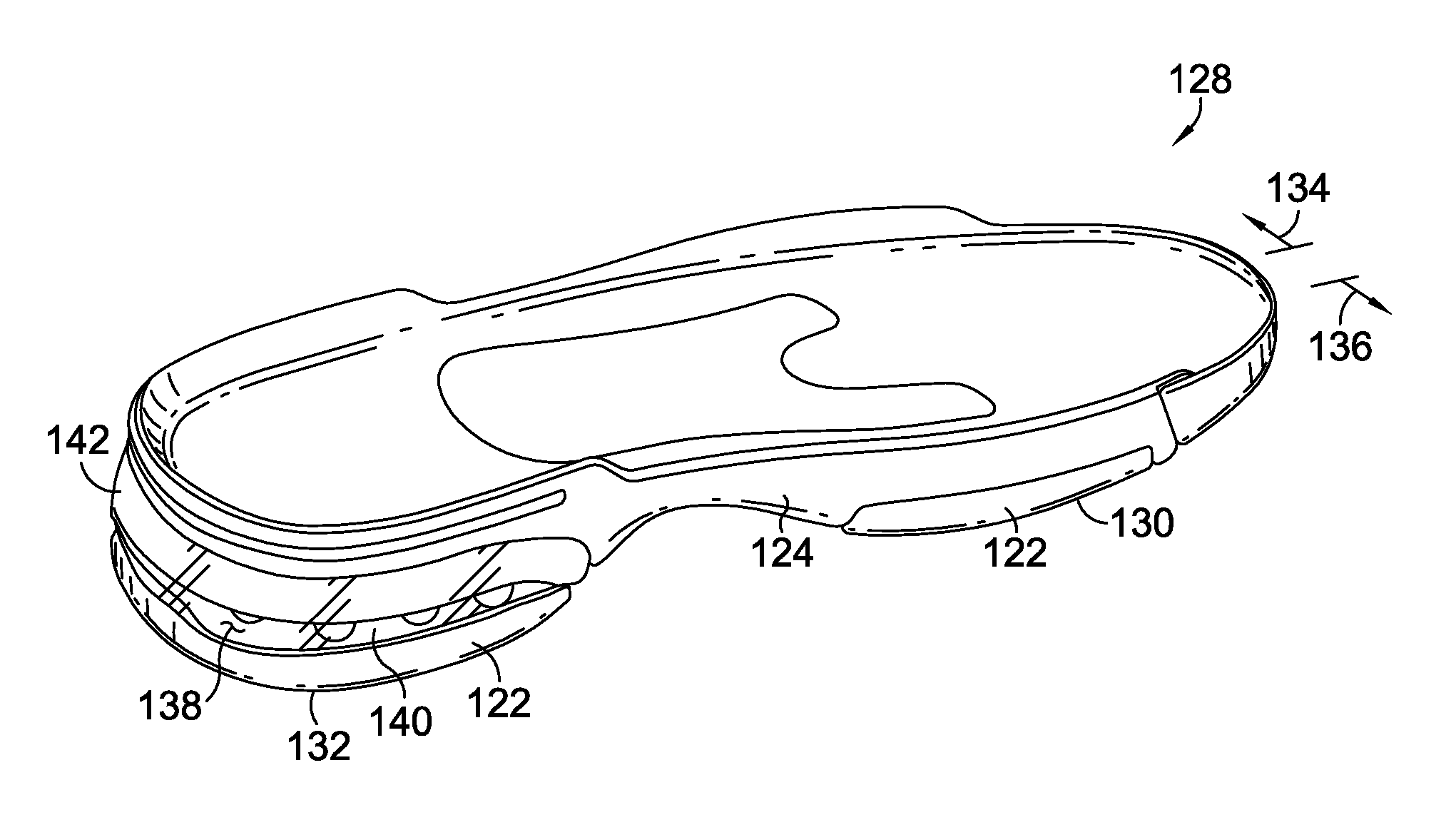
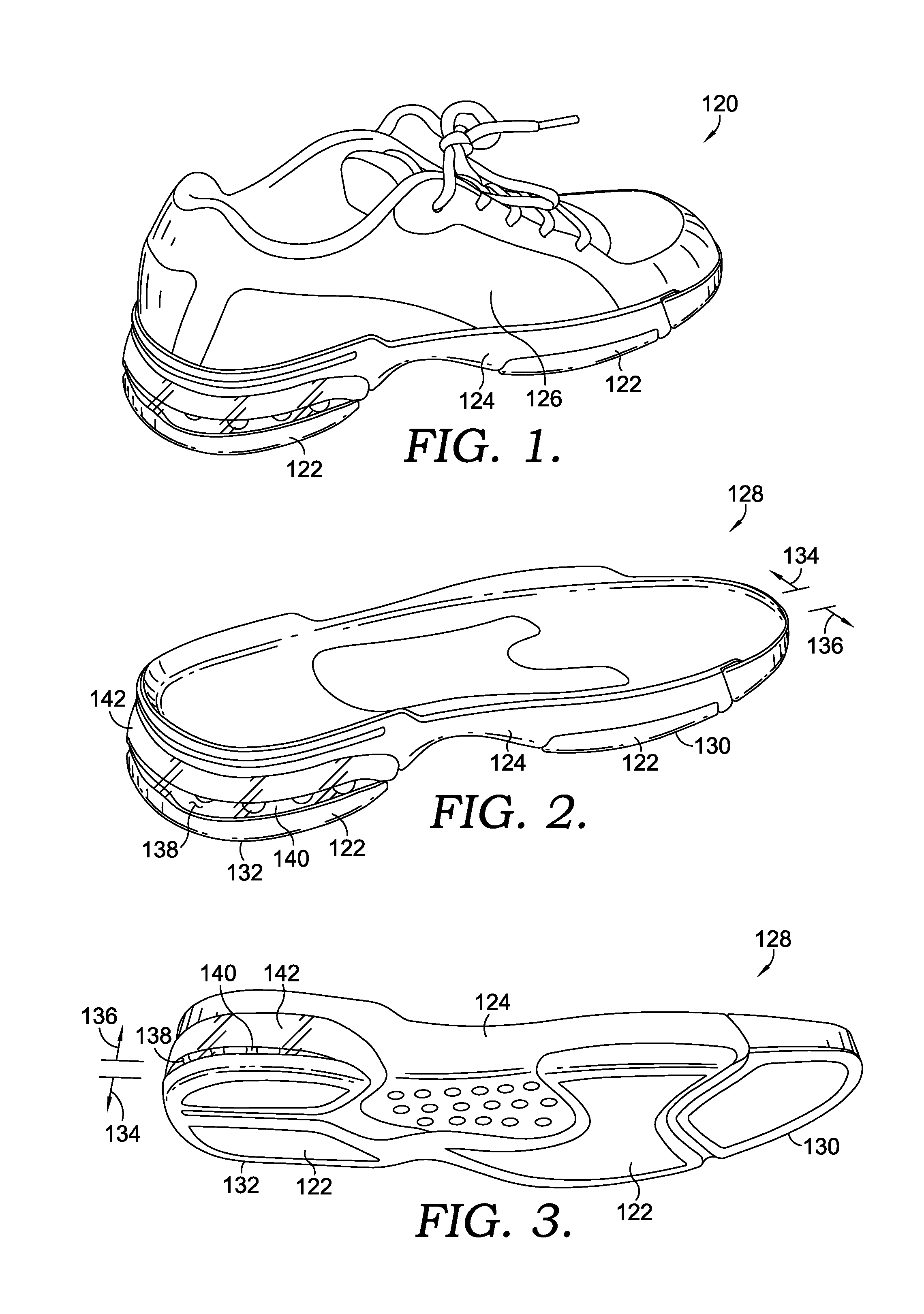
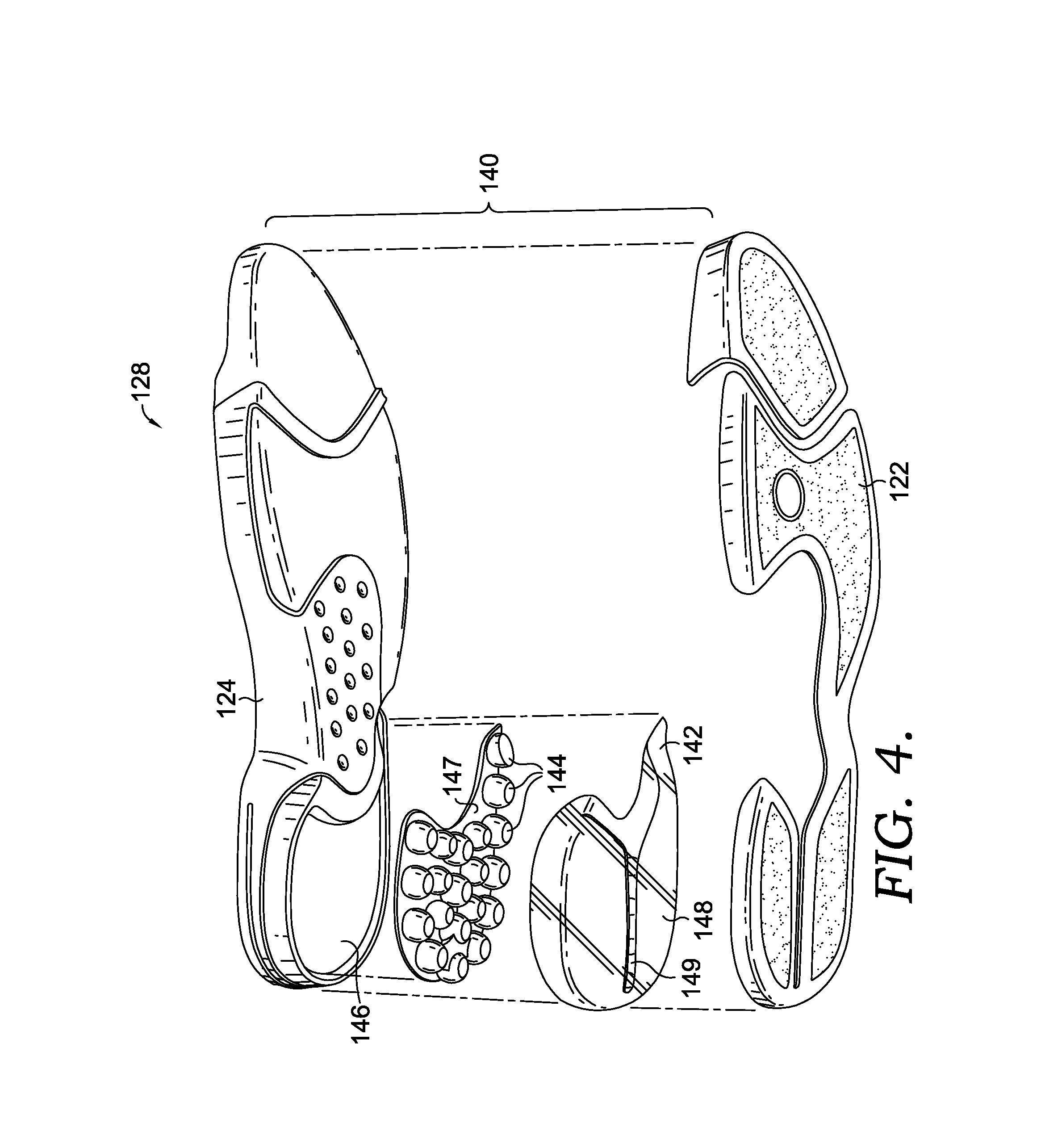
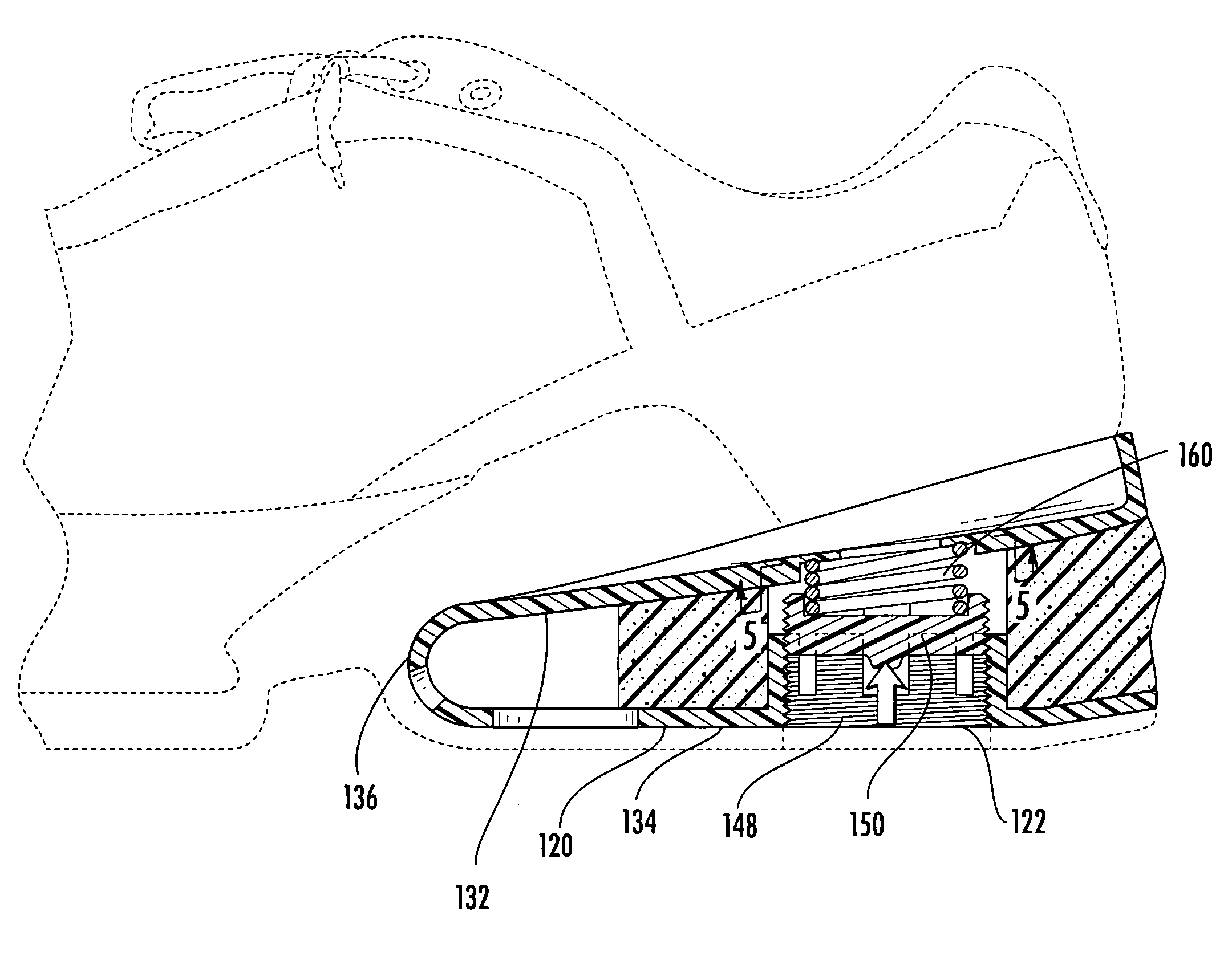
Athletic shoe with removable resilient element
An athletic shoe is provided with a selectively adjustable shock-absorbing element. In one preferred aspect, a plate is provided with a plurality of independently moveable portions in contact with the shock-absorbing element. In another aspect, a plate is provided at an angle relative to a coil spring. A method is provided for adjusting a shock-absorbing spring.
Owner:AKEVA
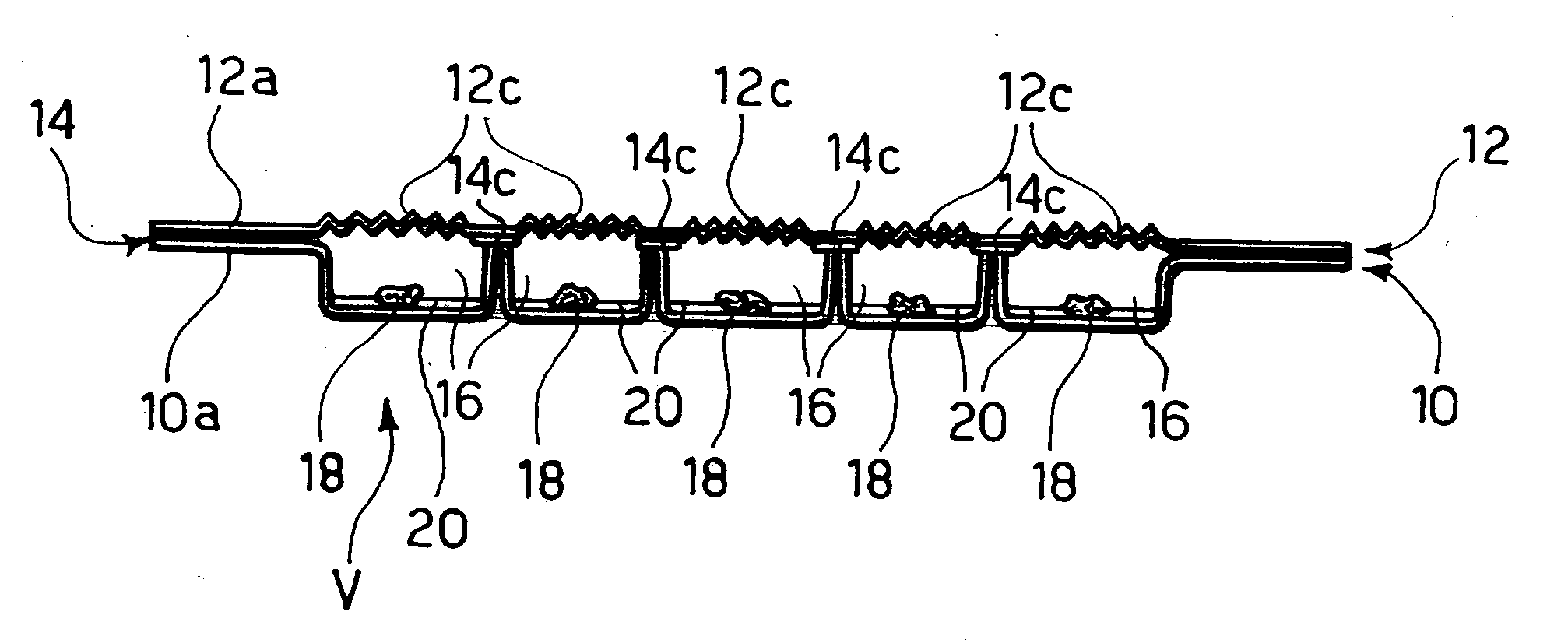
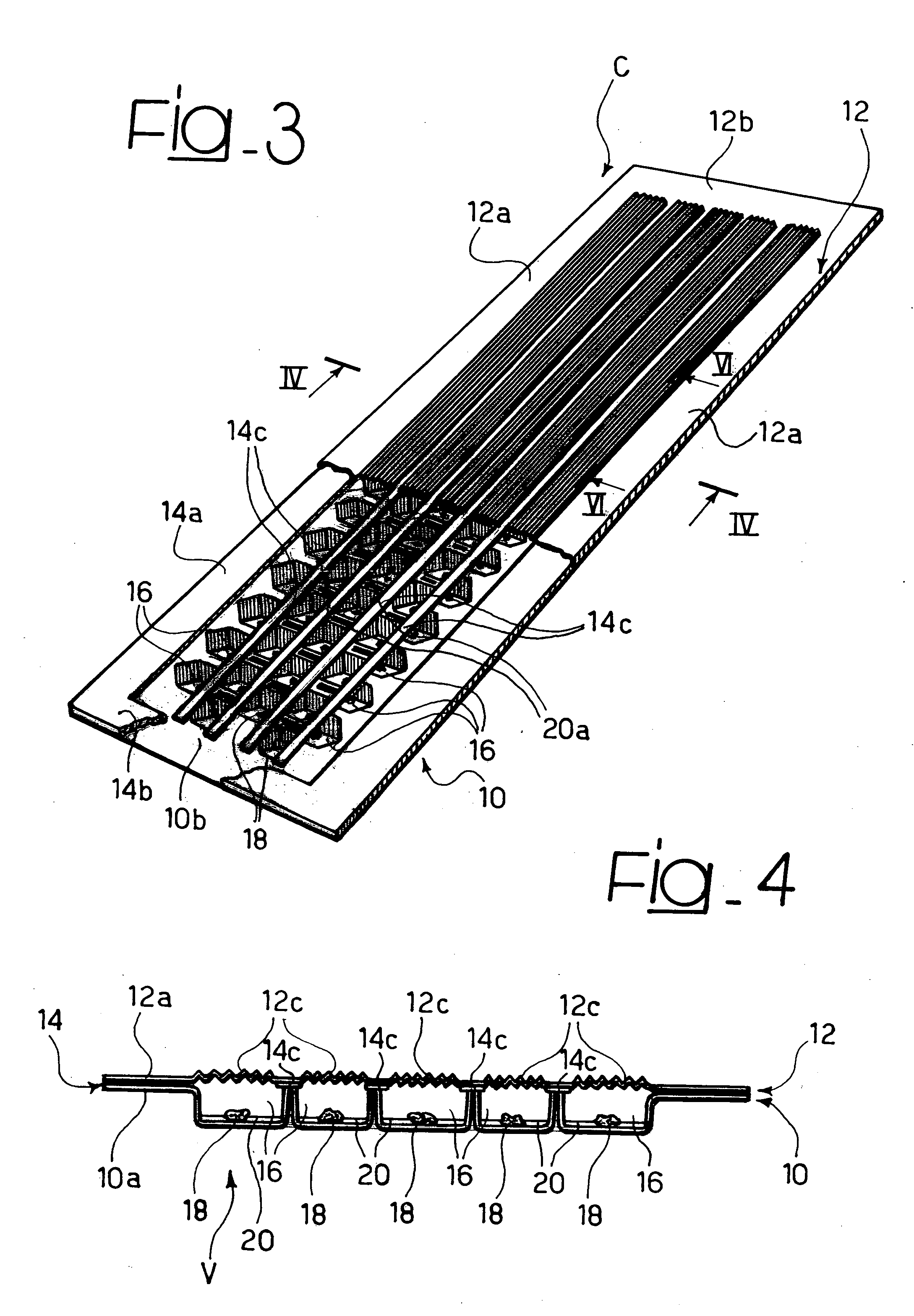
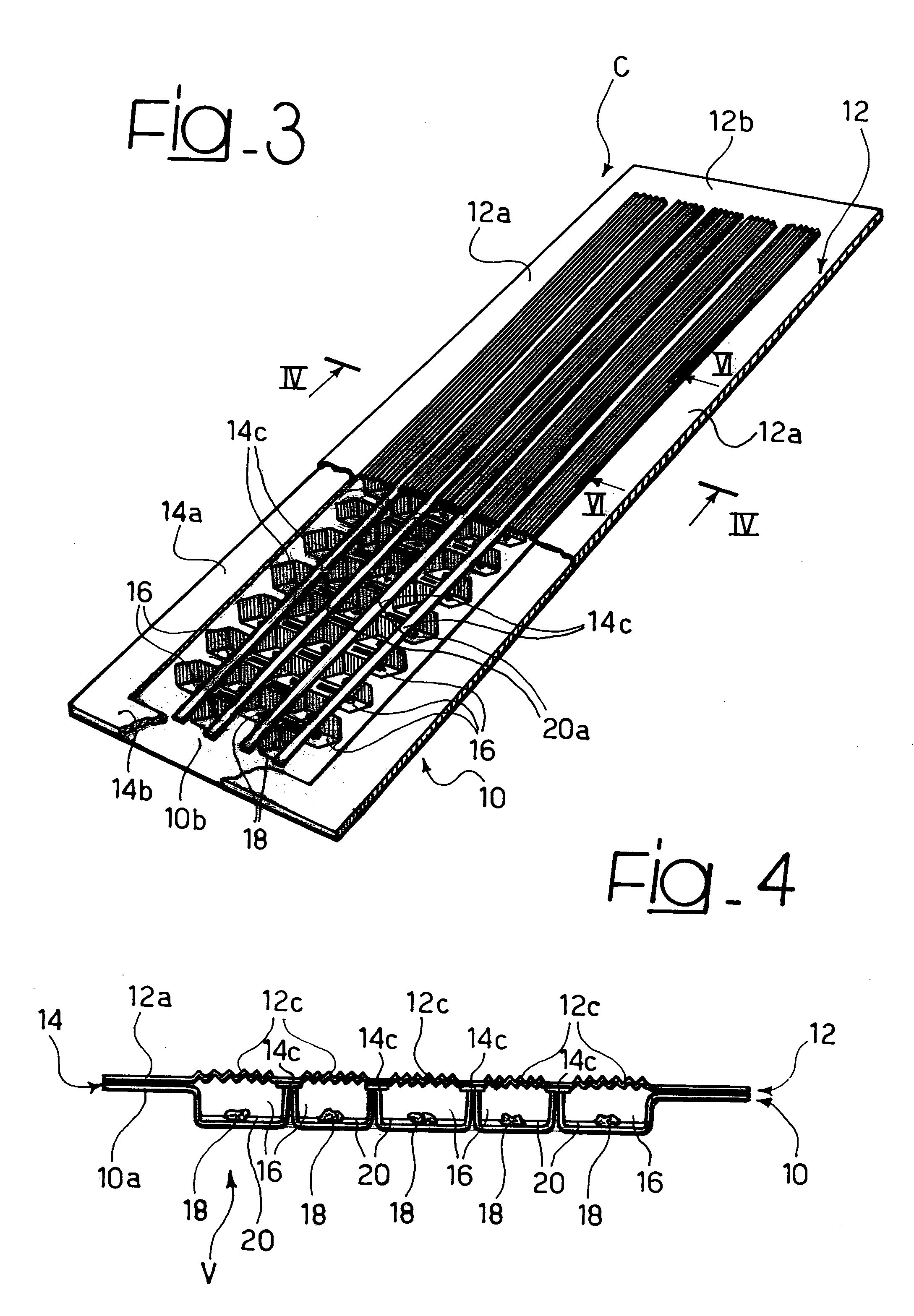
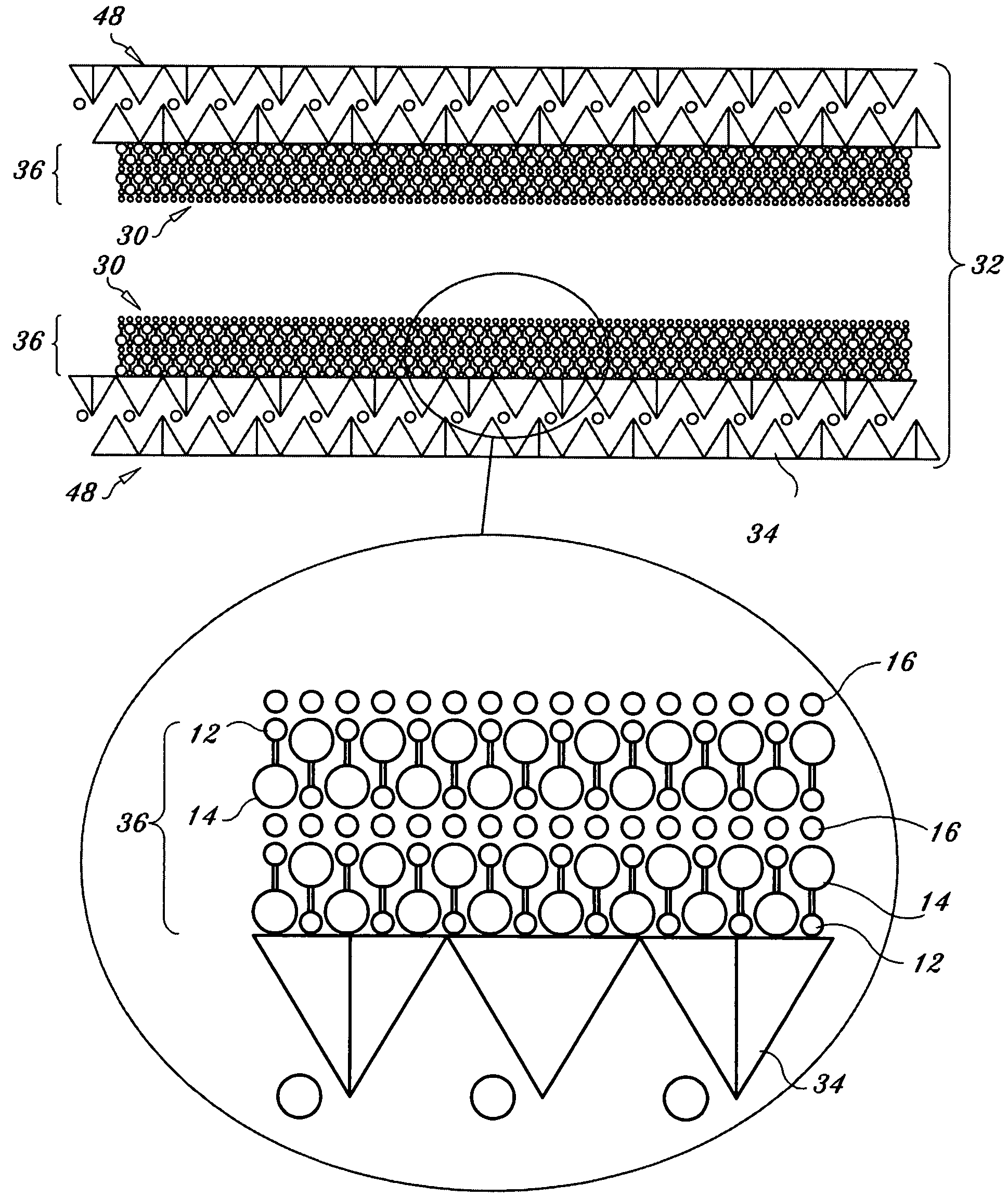
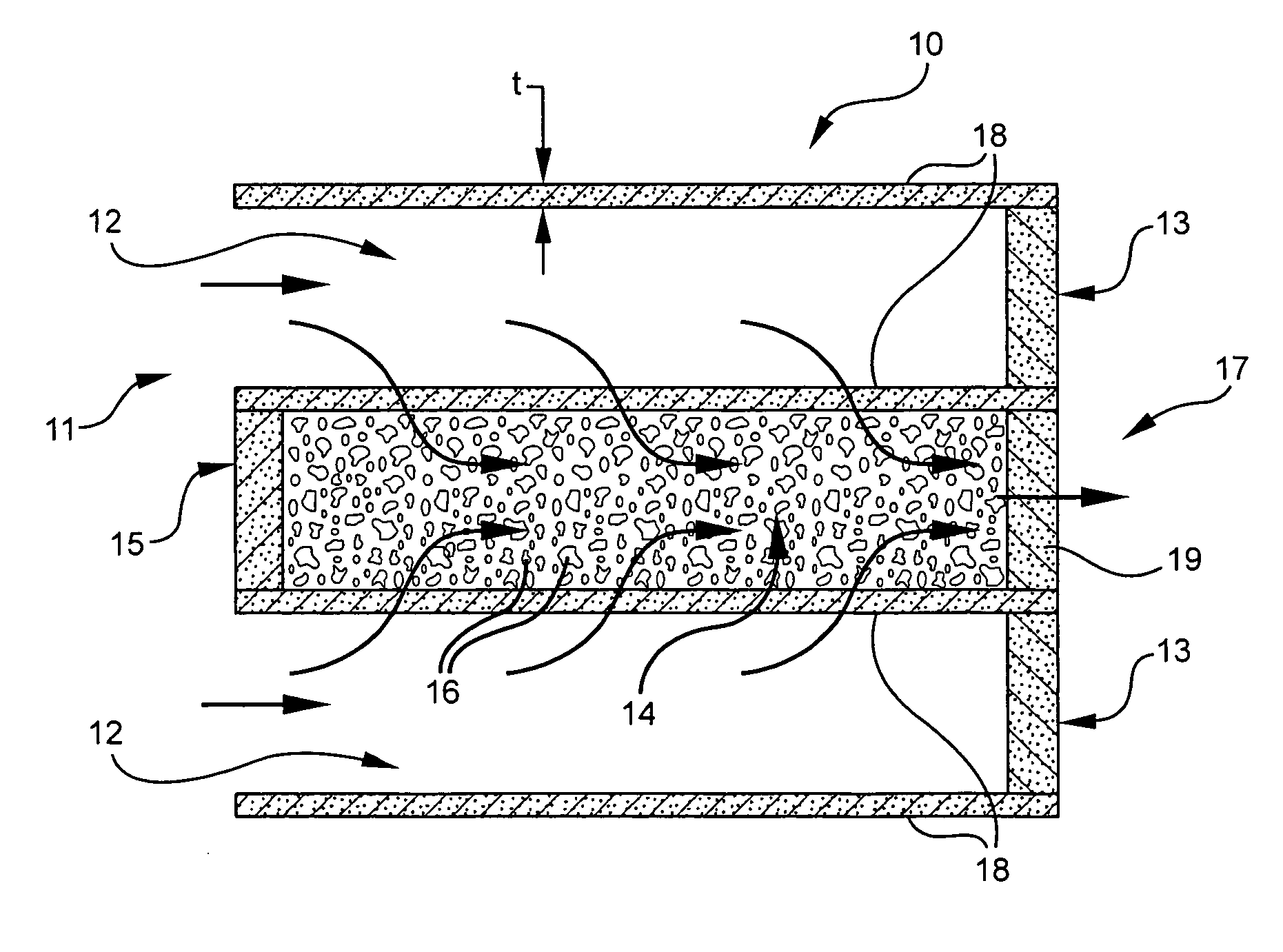
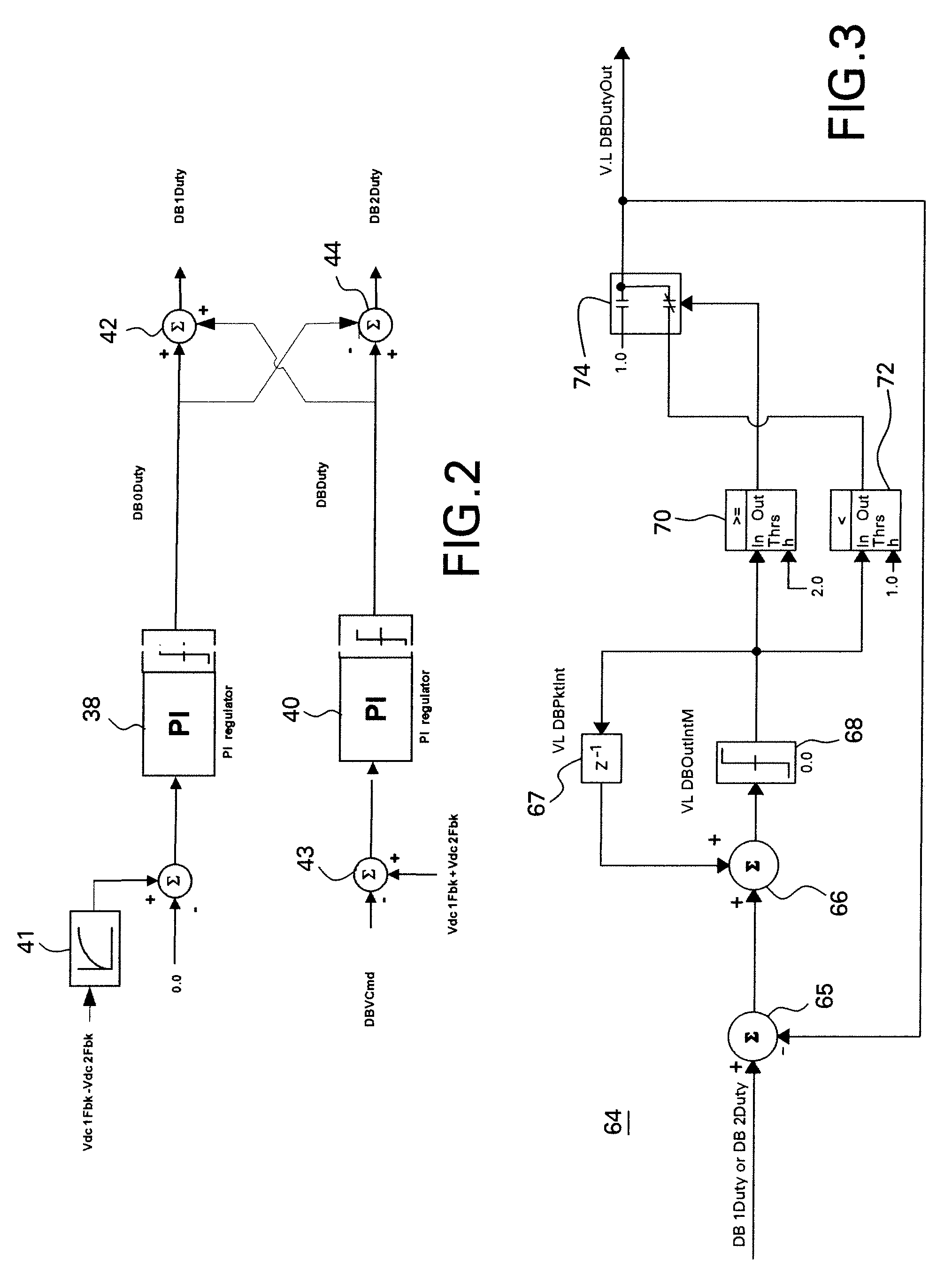
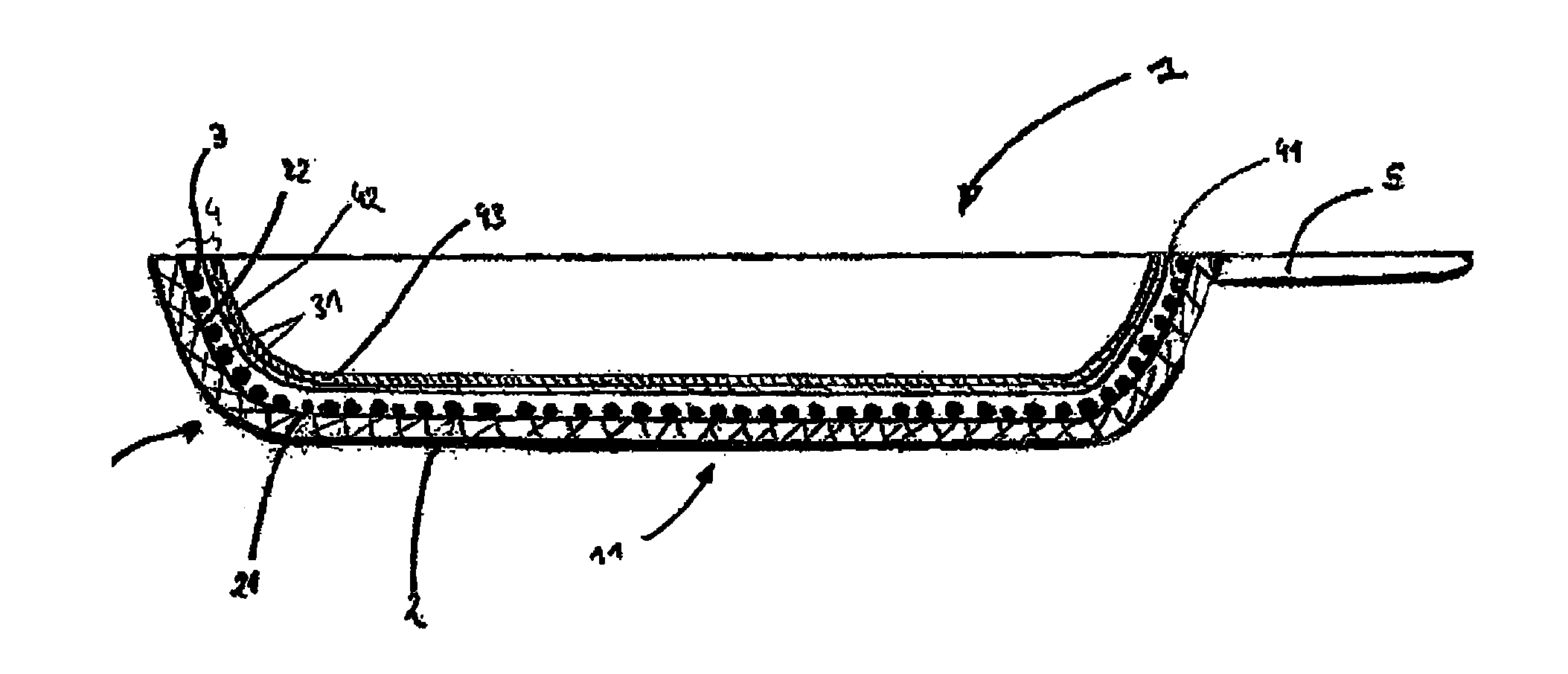
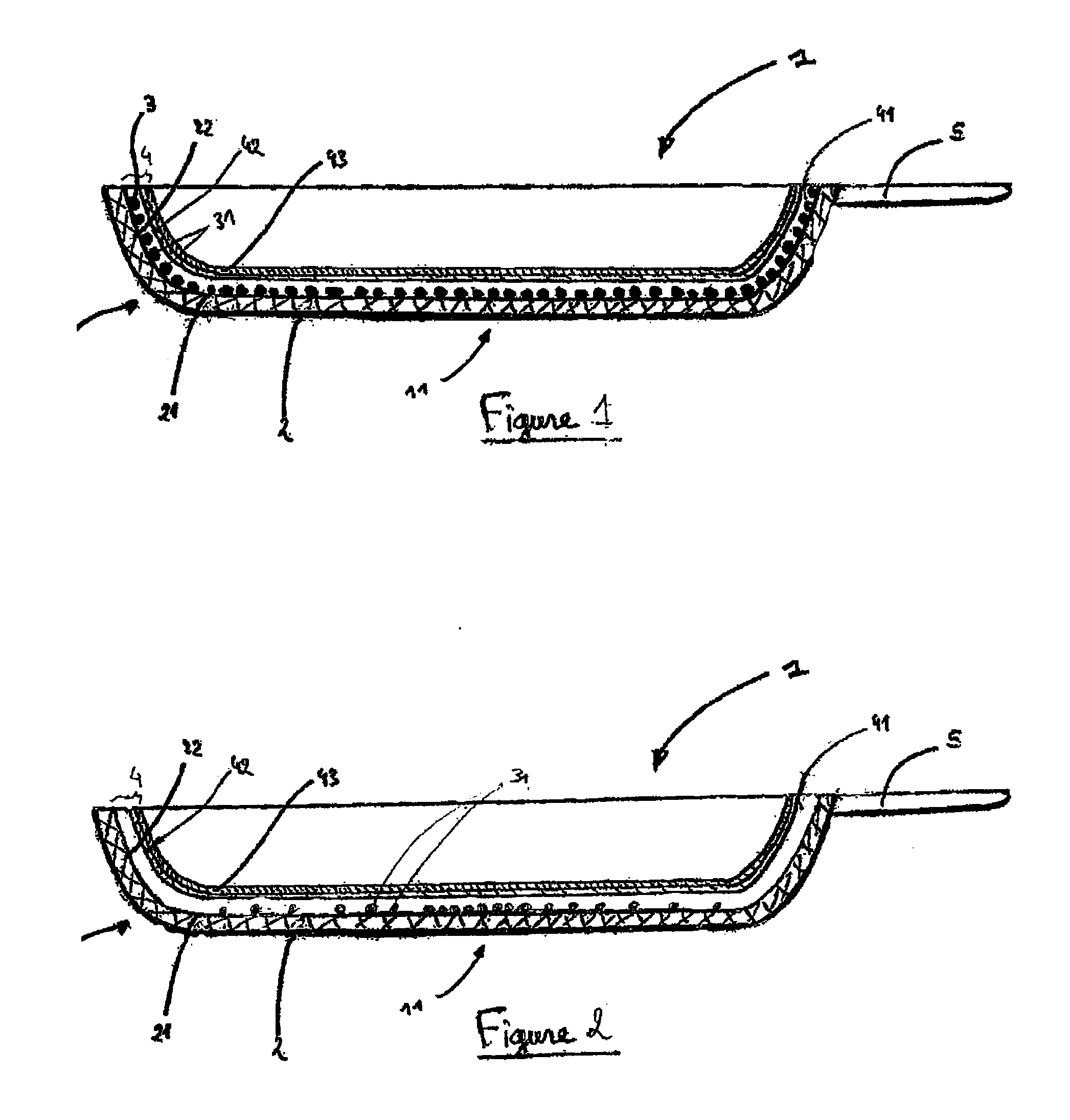
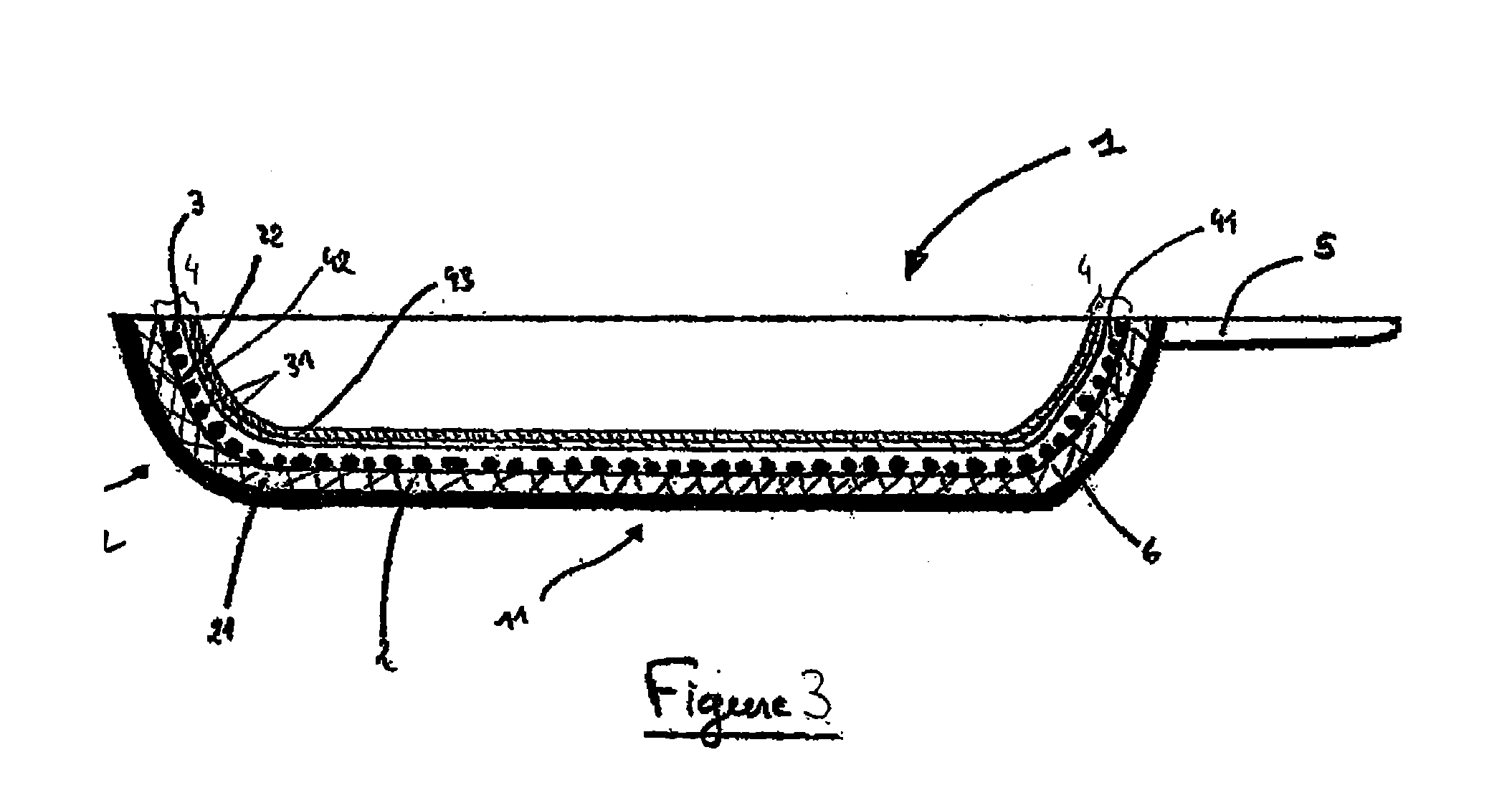
Absorbing element for sanitary products, having expandable pockets containing superabsorbent material and manufacturing process
An absorbent element for the absorption of body fluids in sanitary articles comprises a first layer of sheet material presenting an array of hollowed formations (16) with respective mouth parts, as well as masses (18) of superabsorbent material that is able to expand as a result of the absorption of body fluid, which are set in the aforesaid hollowed formations (16). A second layer of sheet material (12) is applied on the first layer of sheet material (10) so as to cover the mouth parts of the hollowed formations (16). At least one of the layers of sheet material (10, 12) is permeable to body fluids to enable the body fluids themselves to penetrate into the hollowed formations and be absorbed by the masses of superabsorbent material (18) that expand in the hollowed formations (16), creating a first level of absorption of body fluids. The second layer of sheet material (12) is compliant in an area corresponding to the mouth parts of the hollowed formations (16) and enables further expansion of said masses of superabsorbent material (18) beyond said hollowed formations (16) so as to create a second level of absorption of body fluids. The first layer (10) and the second layer (12) of sheet material are connected to one another by adhesive formations (14c) that leave the mouth parts of the hollowed formations (16) at least partially free.
Owner:FAMECCANICA DATA SPA
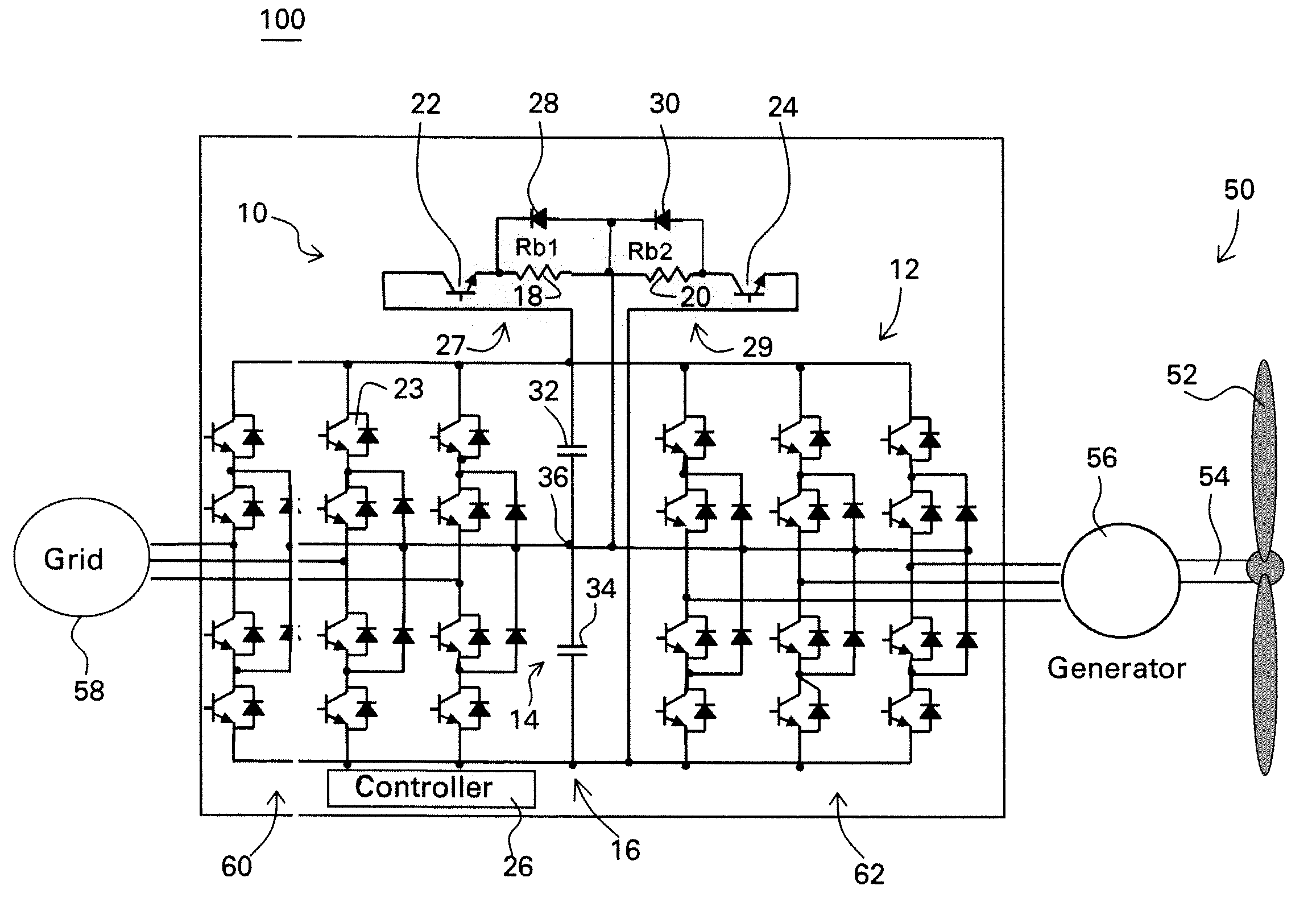
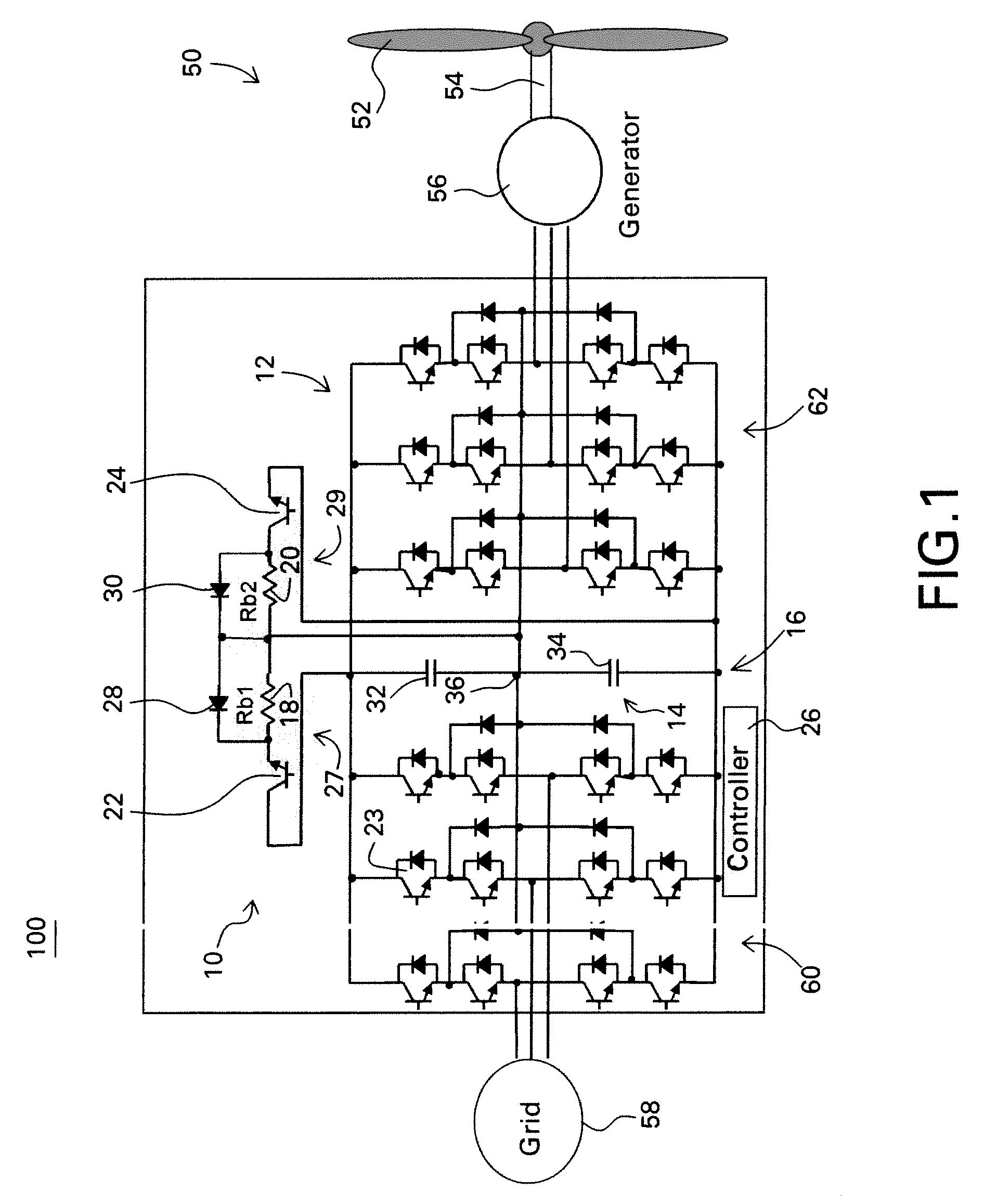
Protective circuit and method for multi-level converter
ActiveUS7573732B2Efficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsControl signalEngineering
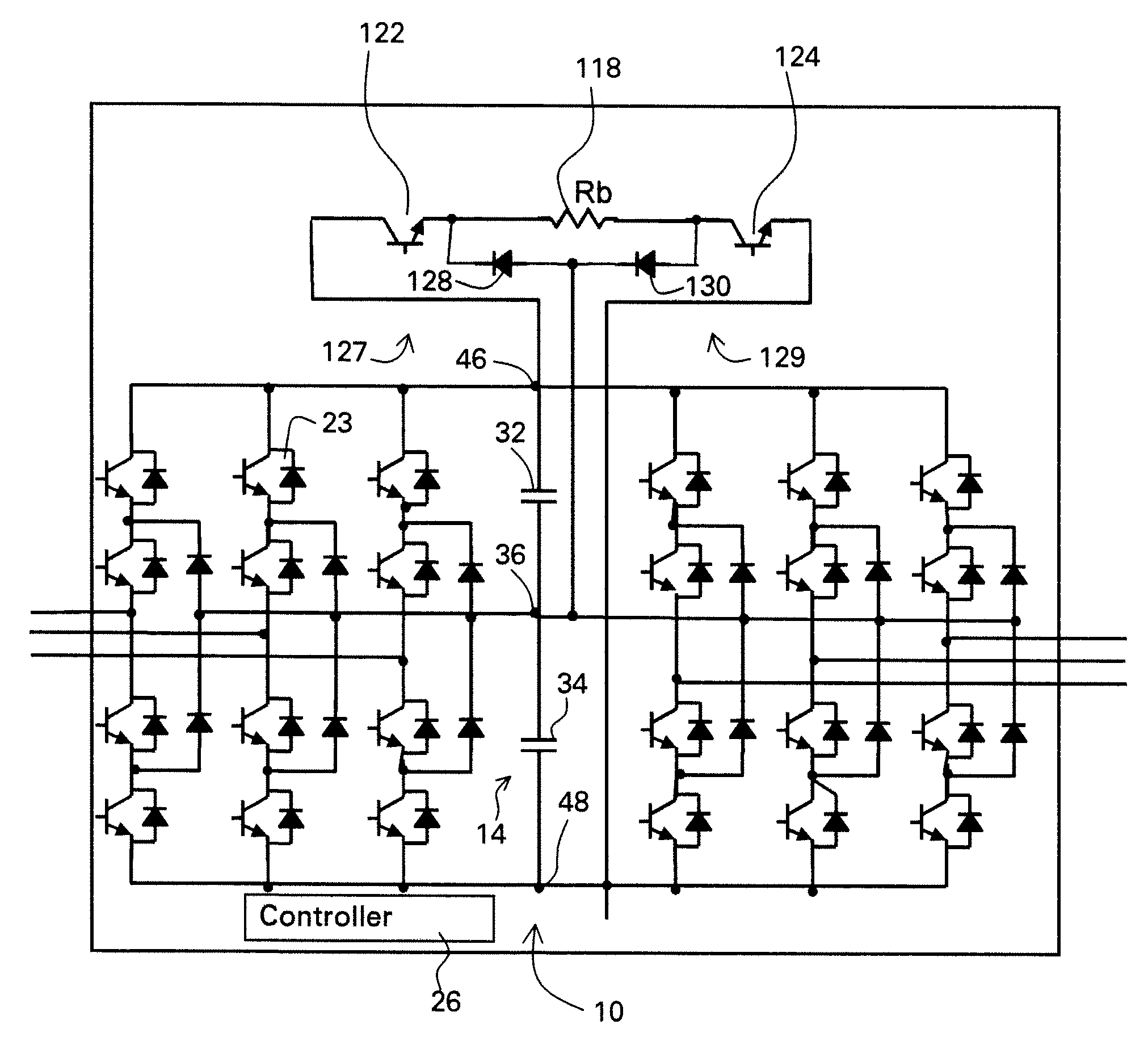
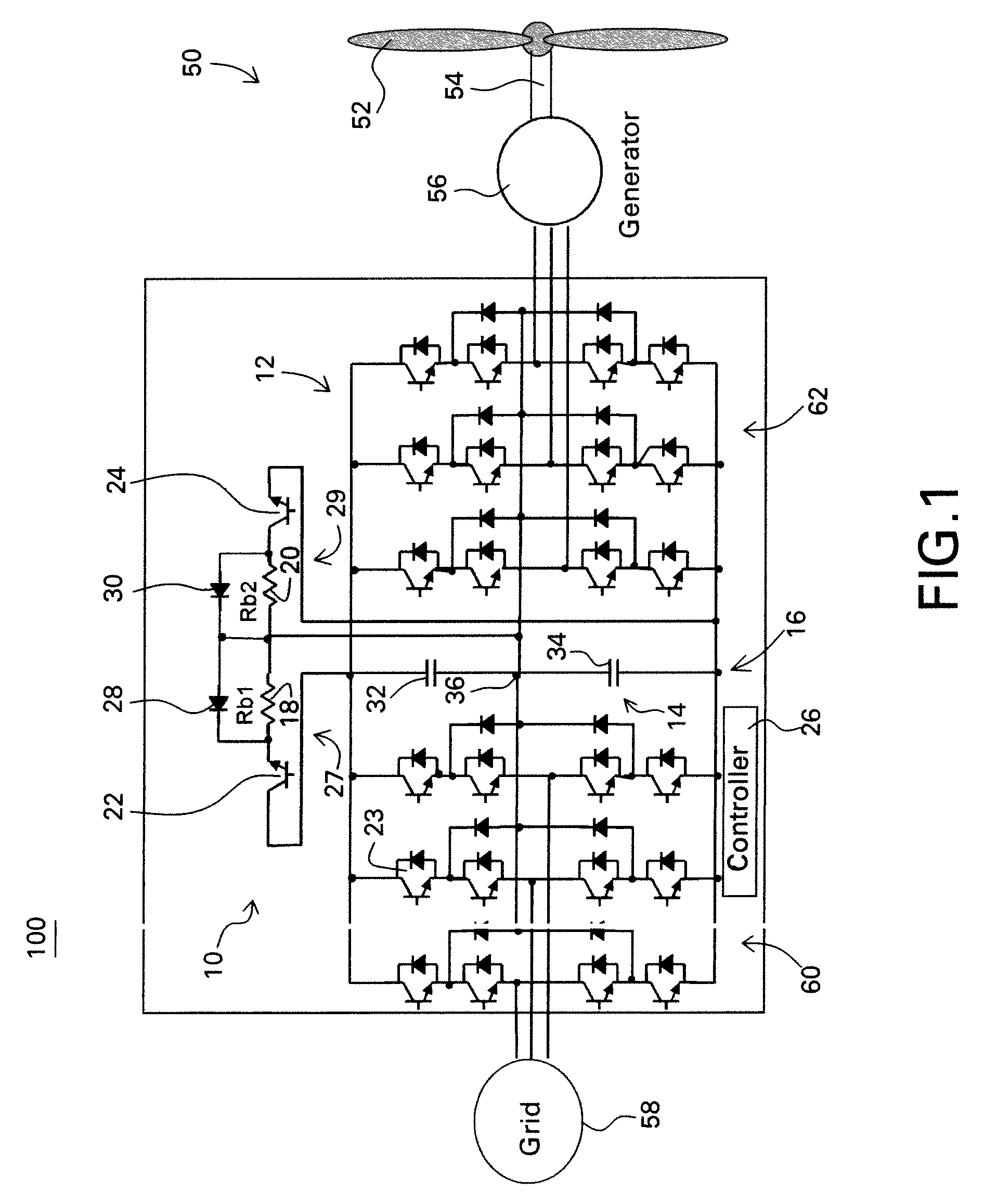
A protective circuit for a multi-level converter including a DC link capacitor bank includes: an energy absorbing element; switches, wherein at least two of the switches each couple the energy absorbing element to the capacitor bank; and a controller configured to provide control signals to the switches to selectively actuate the switches to enable control of energy dissipation and to enable control of voltage balance on the capacitor bank of the multi-level converter.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Athletic shoe with removable resilient element
An athletic shoe is provided with a selectively adjustable shock-absorbing element. In one preferred aspect, a plate is provided with a plurality of independently moveable portions in contact with the shock-absorbing element. In another aspect, a plate is provided at an angle relative to a coil spring. A method is provided for adjusting a shock-absorbing spring.
Owner:AKEVA
Absorbing element for sanitary products, having expandable pockets containing superabsorbent material and manufacturing process
ActiveUS8633347B2Easy to understandLaminationLamination apparatusManufacturing technologyEngineering
An absorbent element for the absorption of body fluids in sanitary articles comprises a first layer of sheet material presenting an array of hollowed formations (16) with respective mouth parts, as well as masses (18) of superabsorbent material that is able to expand as a result of the absorption of body fluid, which are set in the aforesaid hollowed formations (16). A second layer of sheet material (12) is applied on the first layer of sheet material (10) so as to cover the mouth parts of the hollowed formations (16). At least one of the layers of sheet material (10, 12) is permeable to body fluids to enable the body fluids themselves to penetrate into the hollowed formations and be absorbed by the masses of superabsorbent material (18) that expand in the hollowed formations (16), creating a first level of absorption of body fluids. The second layer of sheet material (12) is compliant in an area corresponding to the mouth parts of the hollowed formations (16) and enables further expansion of said masses of superabsorbent material (18) beyond said hollowed formations (16) so as to create a second level of absorption of body fluids. The first layer (10) and the second layer (12) of sheet material are connected to one another by adhesive formations (14c) that leave the mouth parts of the hollowed formations (16) at least partially free.
Owner:FAMECCANICA DATA SPA
Inhaler and atomizing assembly thereof
InactiveUS20160278163A1Prolonging life useImprove atomization efficiencyMedical devicesTobacco devicesEngineeringAbsorbing element
An inhaler and an atomizing assembly thereof are provided. The liquid reservoir is sealed before use, such that the liquid stored in the liquid reservoir will not be volatile, thus prolonging the life use of the inhaler. In addition, since the liquid conducting element is located between the liquid reservoir and the liquid absorbing element, the liquid in the liquid reservoir can be more fluently directed to the liquid absorbing element by capillary force, thus increasing the atomizing efficiency.
Owner:SHENZHEN SMOORE TECH LTD
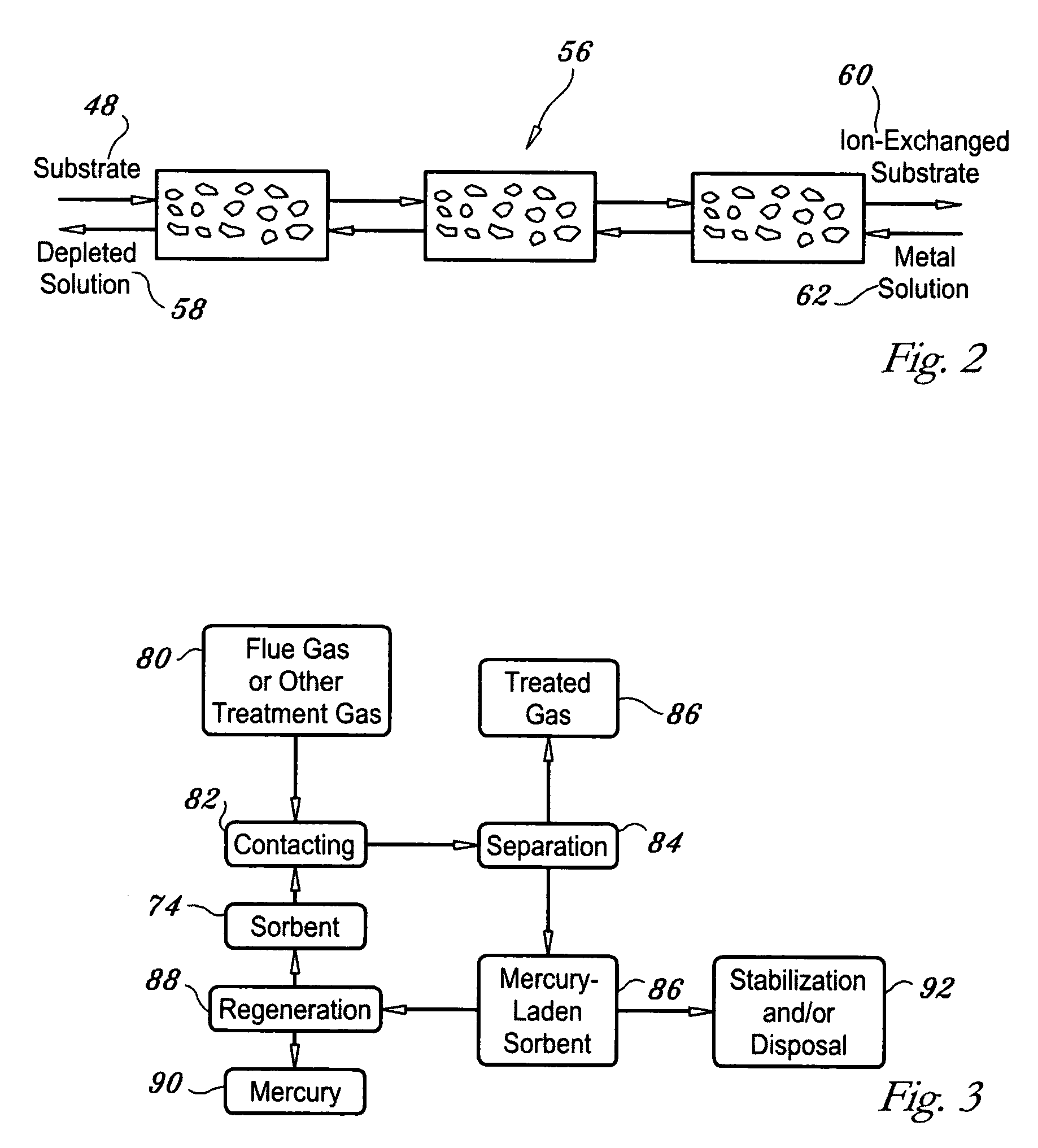
Regenerable high capacity sorbent for removal of mercury from flue gas
InactiveUS7288499B1Low costLower performance requirementsInorganic chemistryGas treatmentSorbentManganese
A regenerable, high-capacity sorbent for removal of mercury from flue gas and processes and systems for making and using the sorbent. A phyllosilicate substrate, for example vermiculite or montmorillinite, acts as an inexpensive support to a thin layer for a polyvalent metal sulfide, ensuring that more of the metal sulfide is engaged in the sorption process. The sorbent is prepared by ion exchange between the silicate substrate material and a solution containing one or more of a group of polyvalent metals including tin (both Sn(II) and Sn(IV)), iron (both Fe(II) and Fe(III)), titanium, manganese, zirconium and molybdenum, dissolved as salts, to produce an exchanged substrate. Controlled reaction of a sulfide ion source with the one or more polyvalent metals that are exchanged on the silicate substrate produces the sorbent. The sorbent is used to absorb elemental mercury or oxidized mercury species such as mercuric chloride from flue gas containing acid gases (e.g., SO2, NO and NO2, and HCl) and other gases over a wide range of temperatures.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ENERGY SERVICES
Localization of a radioactive source
InactiveUS7952079B2High sensitivityImprove efficiencySurgical navigation systemsMaterial analysis by optical meansRadioactive sourceAbsorbing element
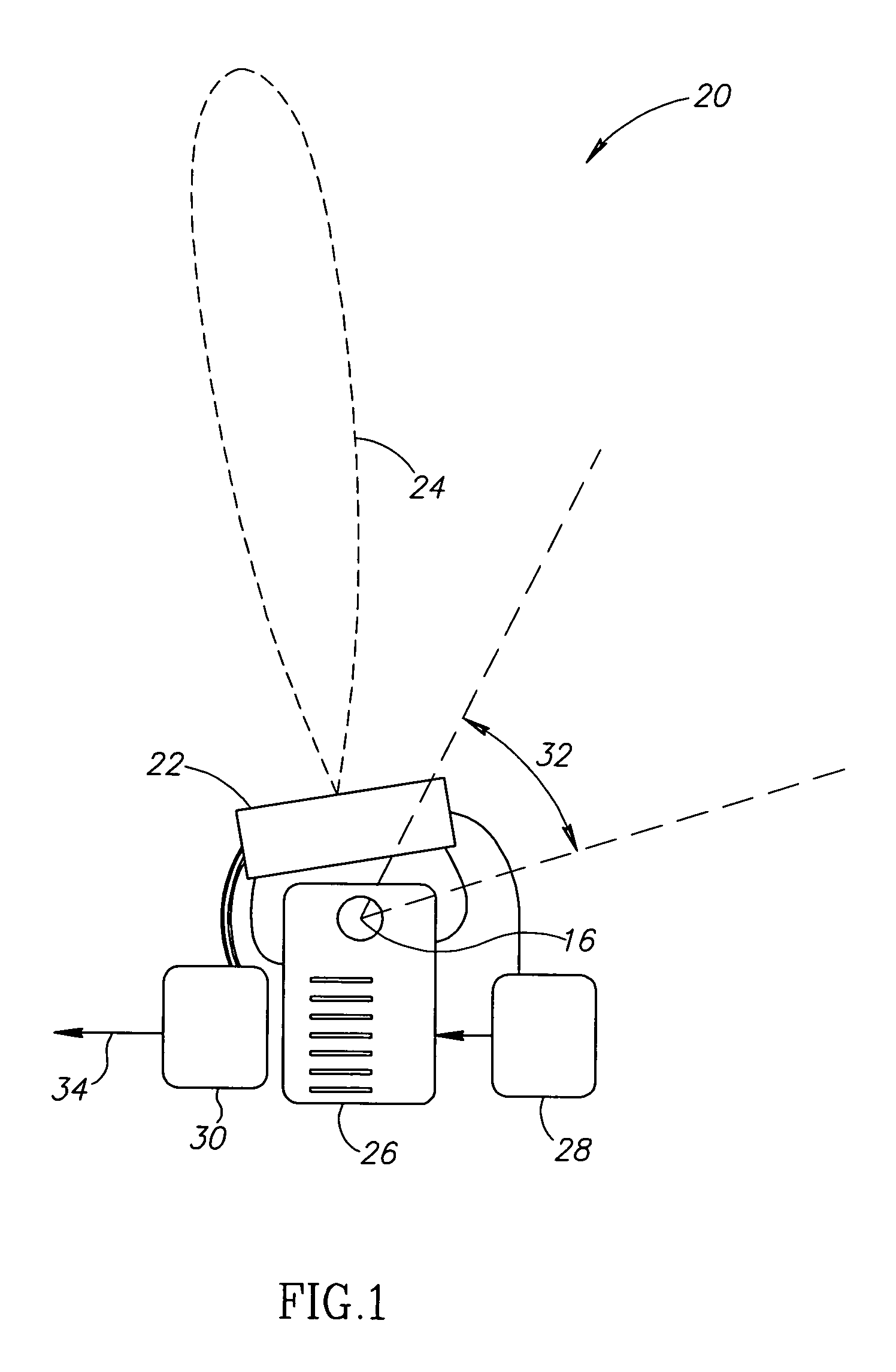
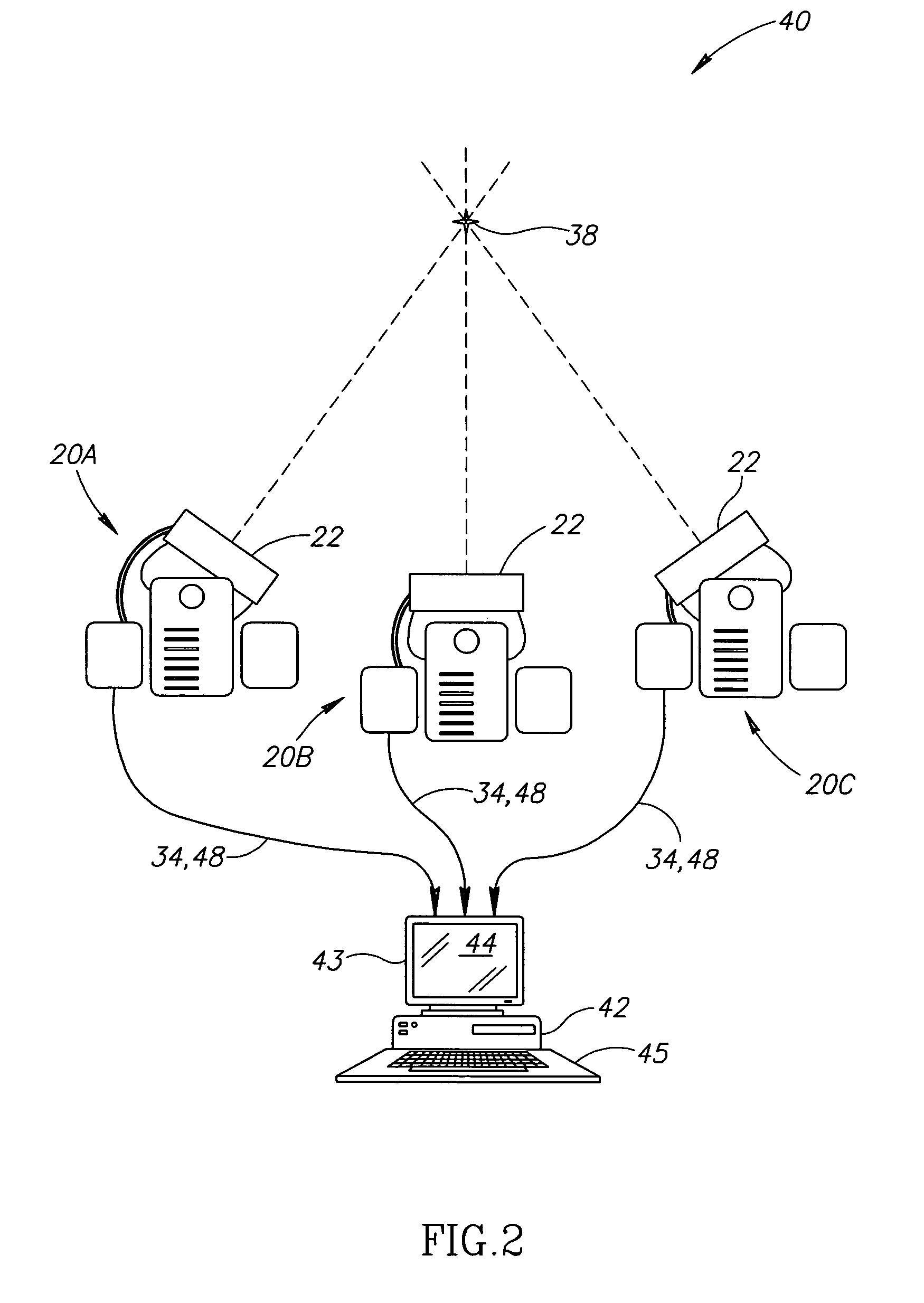
An angle-responsive sensor, comprising:a radiation detector adapted to detect ionizing radiation;at least one radiation absorbing element arranged to block radiation from reaching said detector in a manner dependent on a relative orientation of a radiation source, said detector and said element, said detector and said element defining an aim for said sensor; andcircuitry coupled to said detector and which generates an output signal which varies as a function of said relative orientation,wherein said detector and said element are arranged to have a working volume of at least 10 cm in depth and having an angular width, such that said signal defines an accuracy of better than 3 mm within one standard deviation, over said working volume.
Owner:NAVOTEK MEDICAL
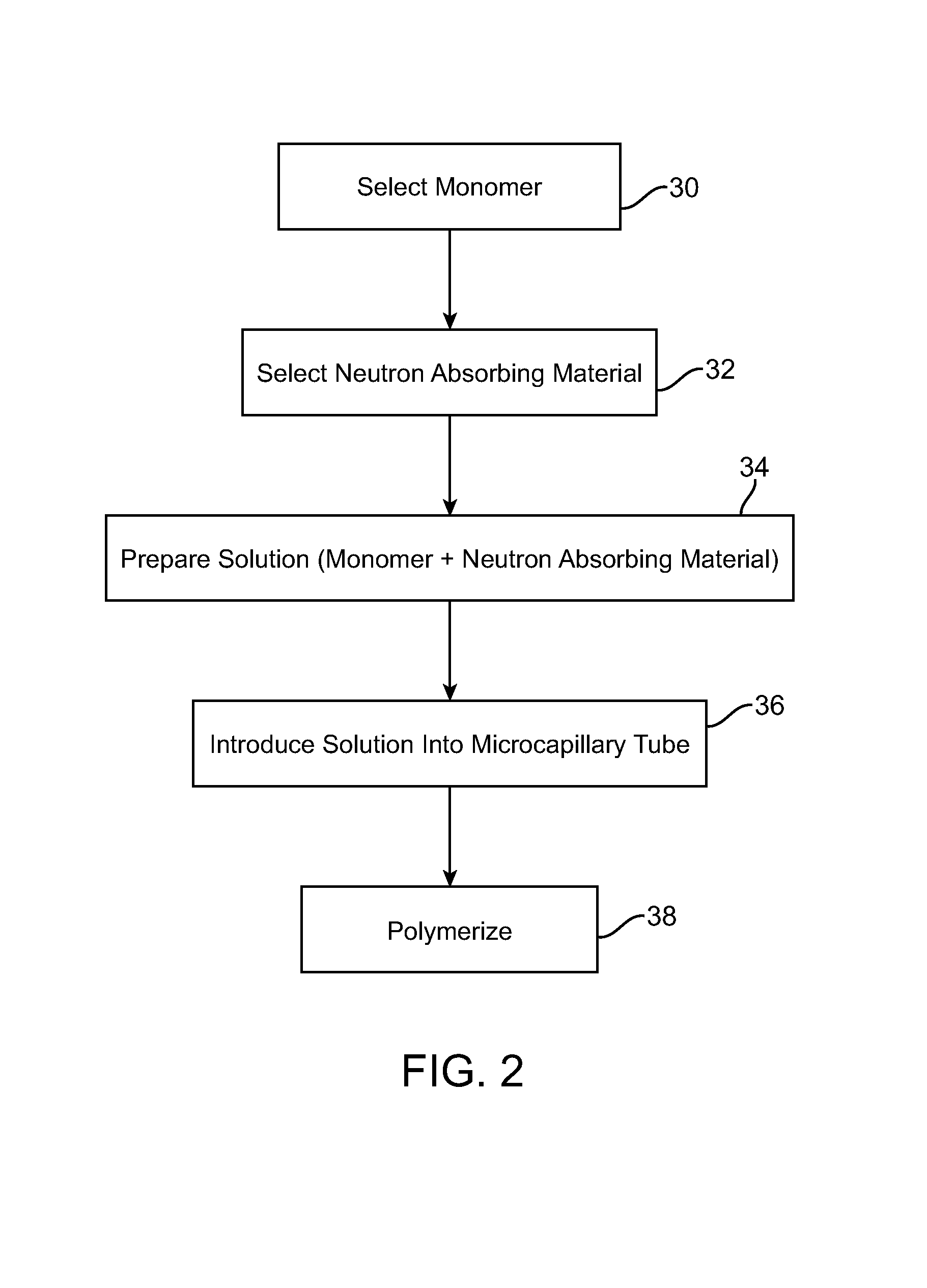
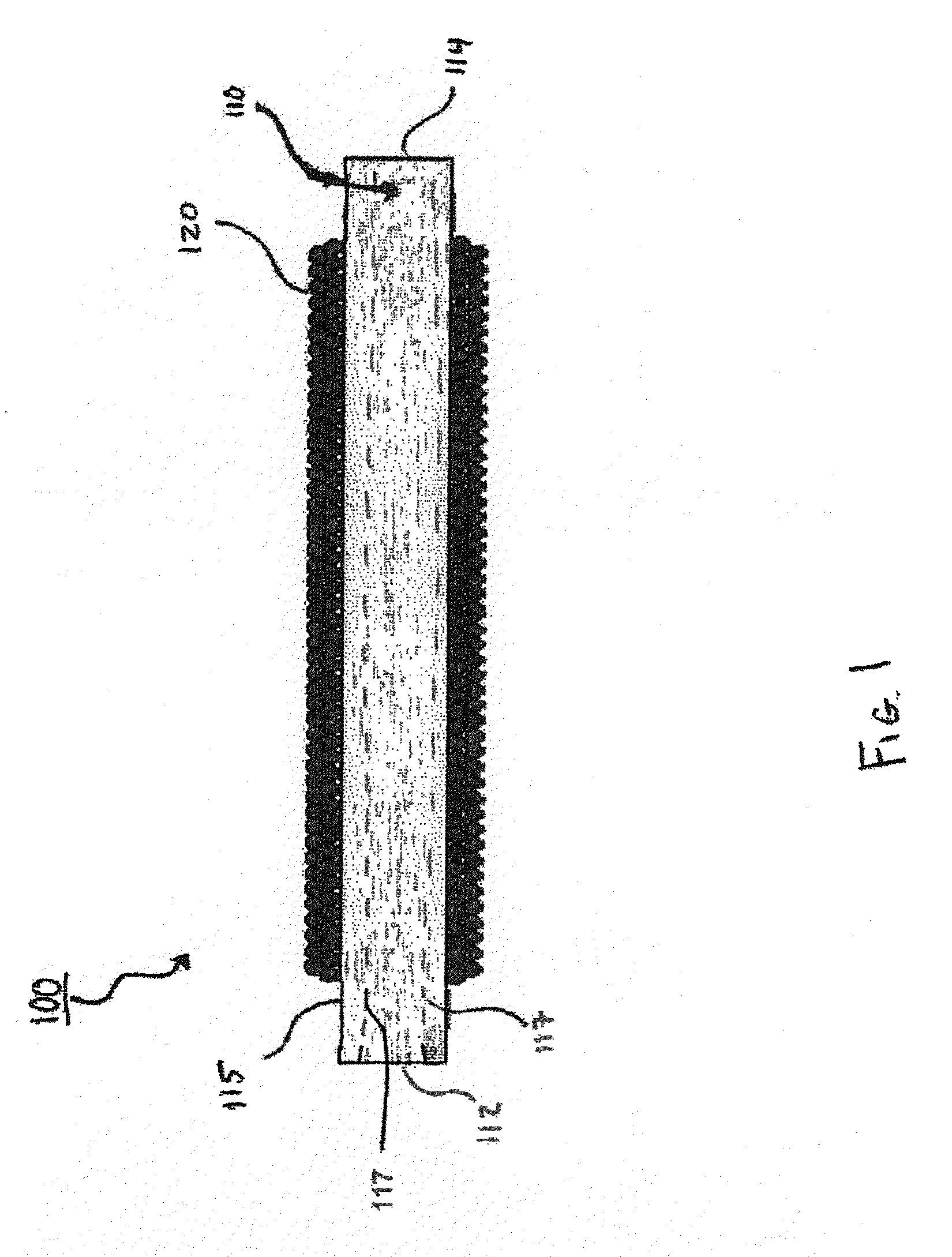
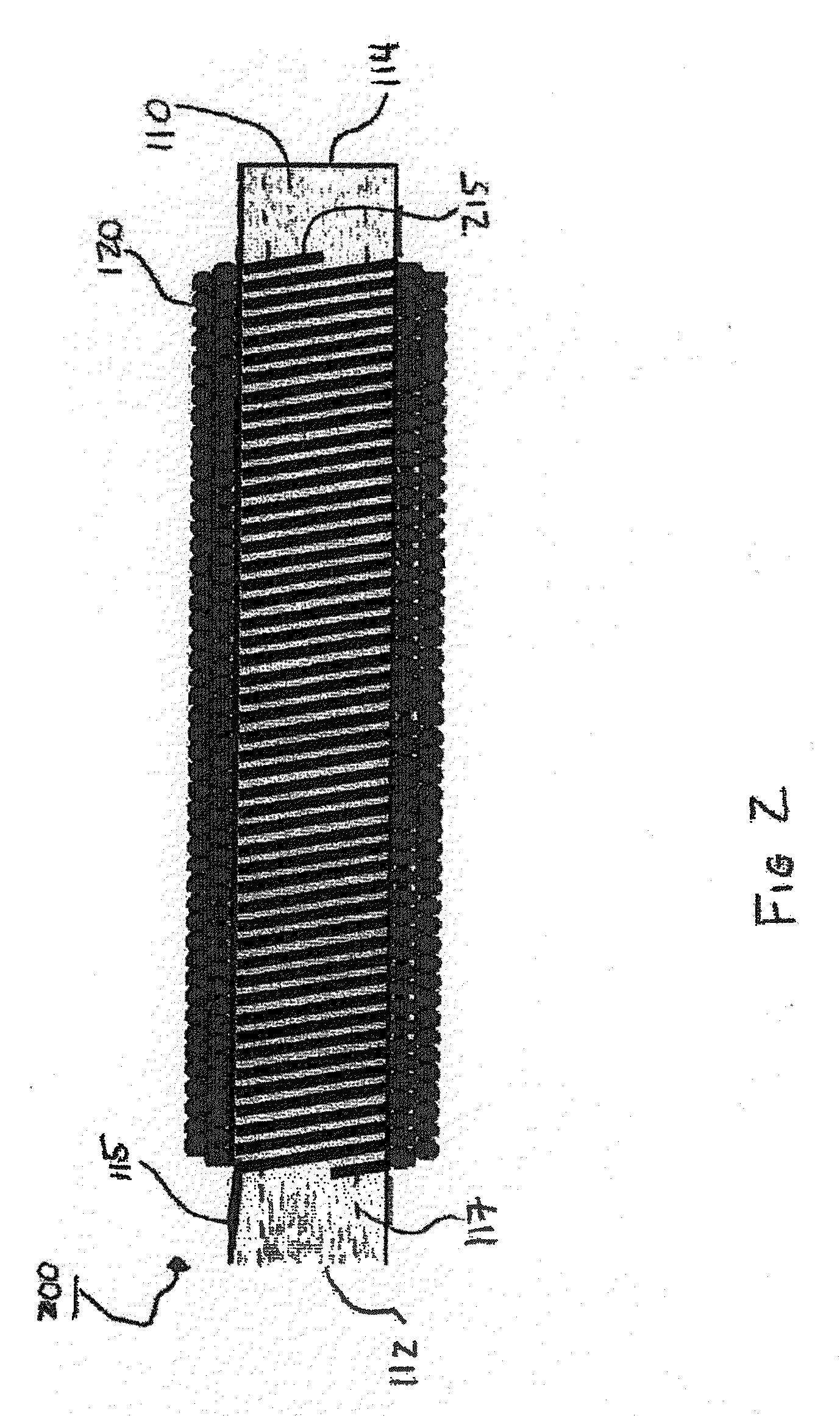
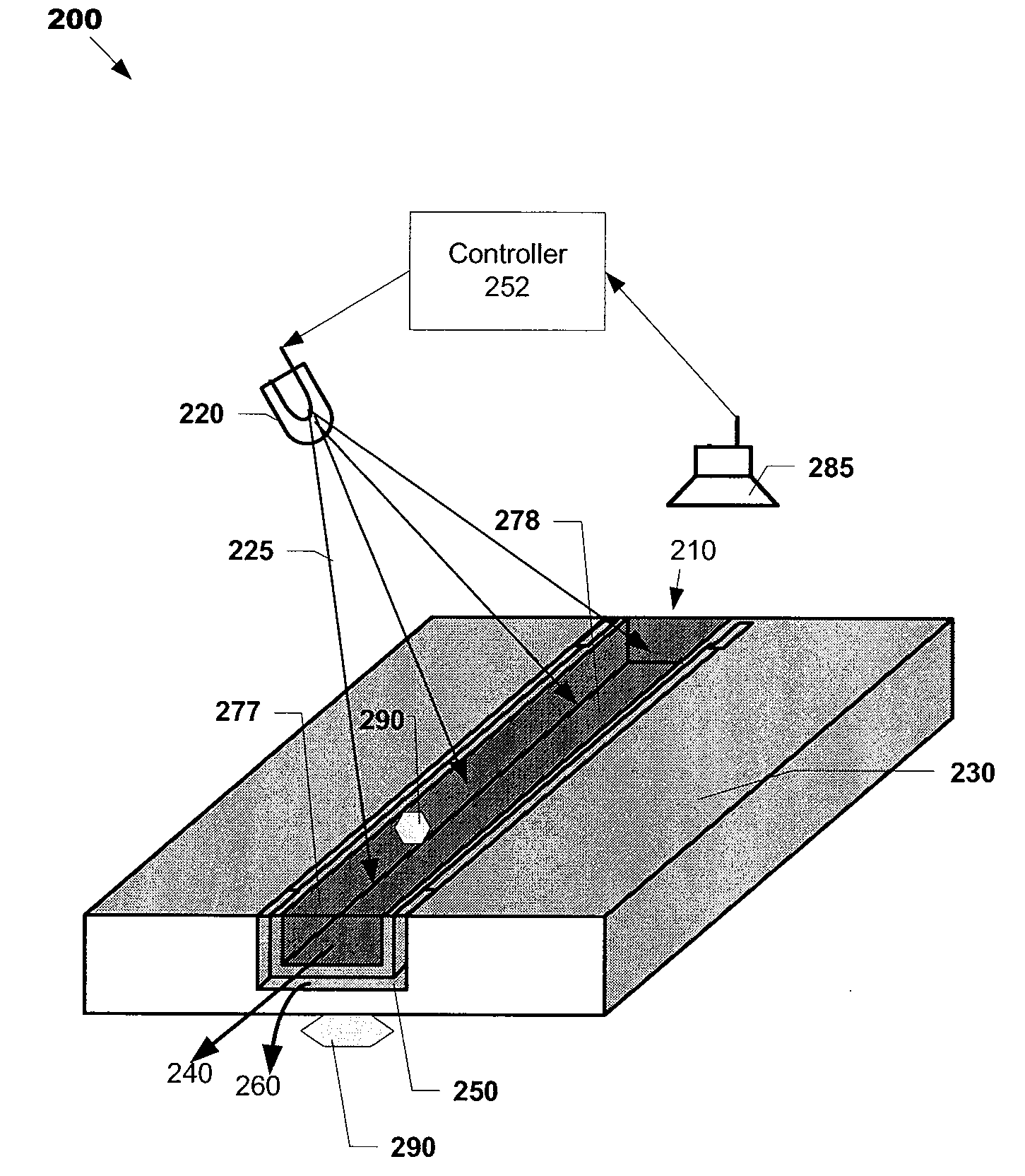
Neutron detectors and related methods
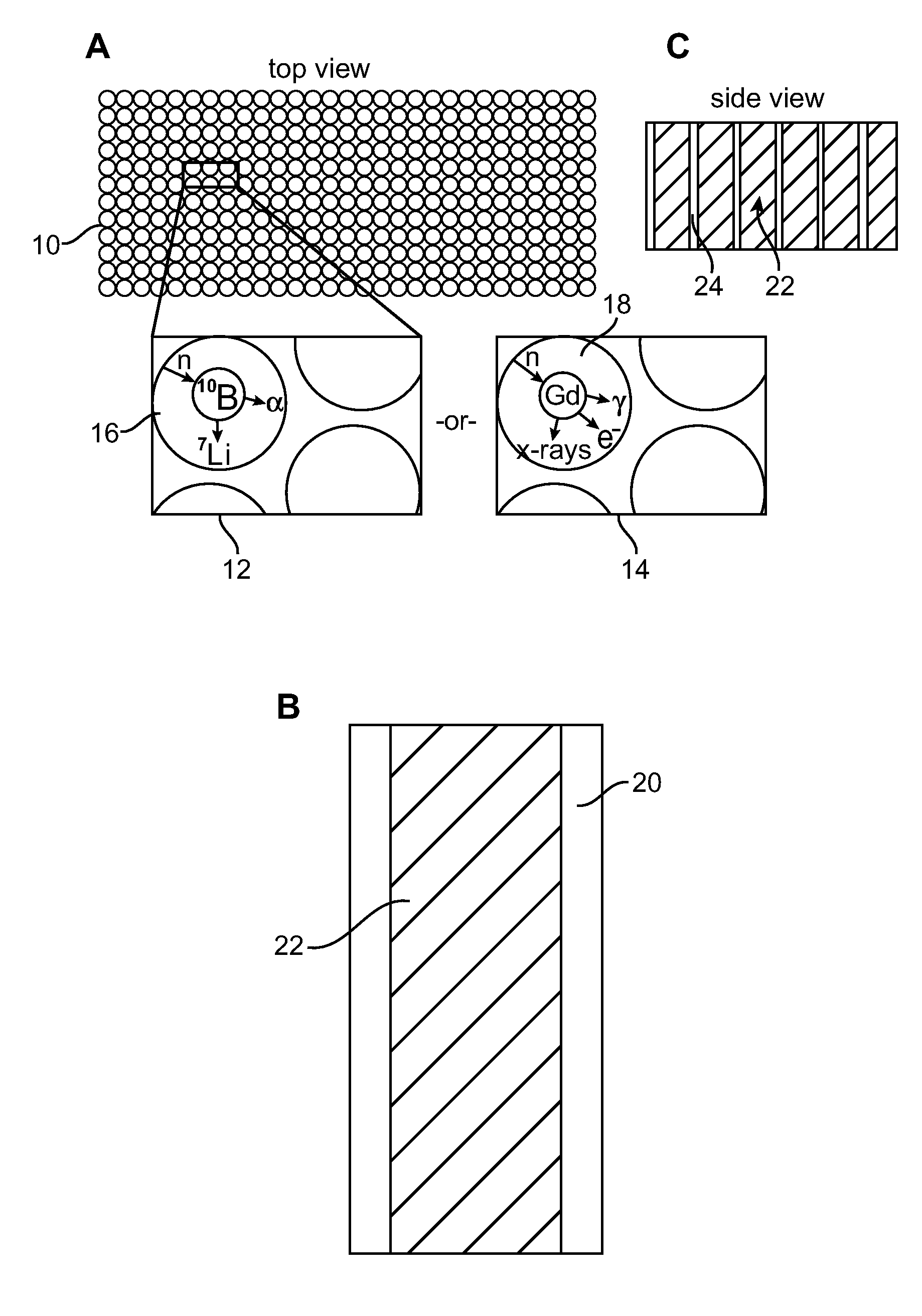
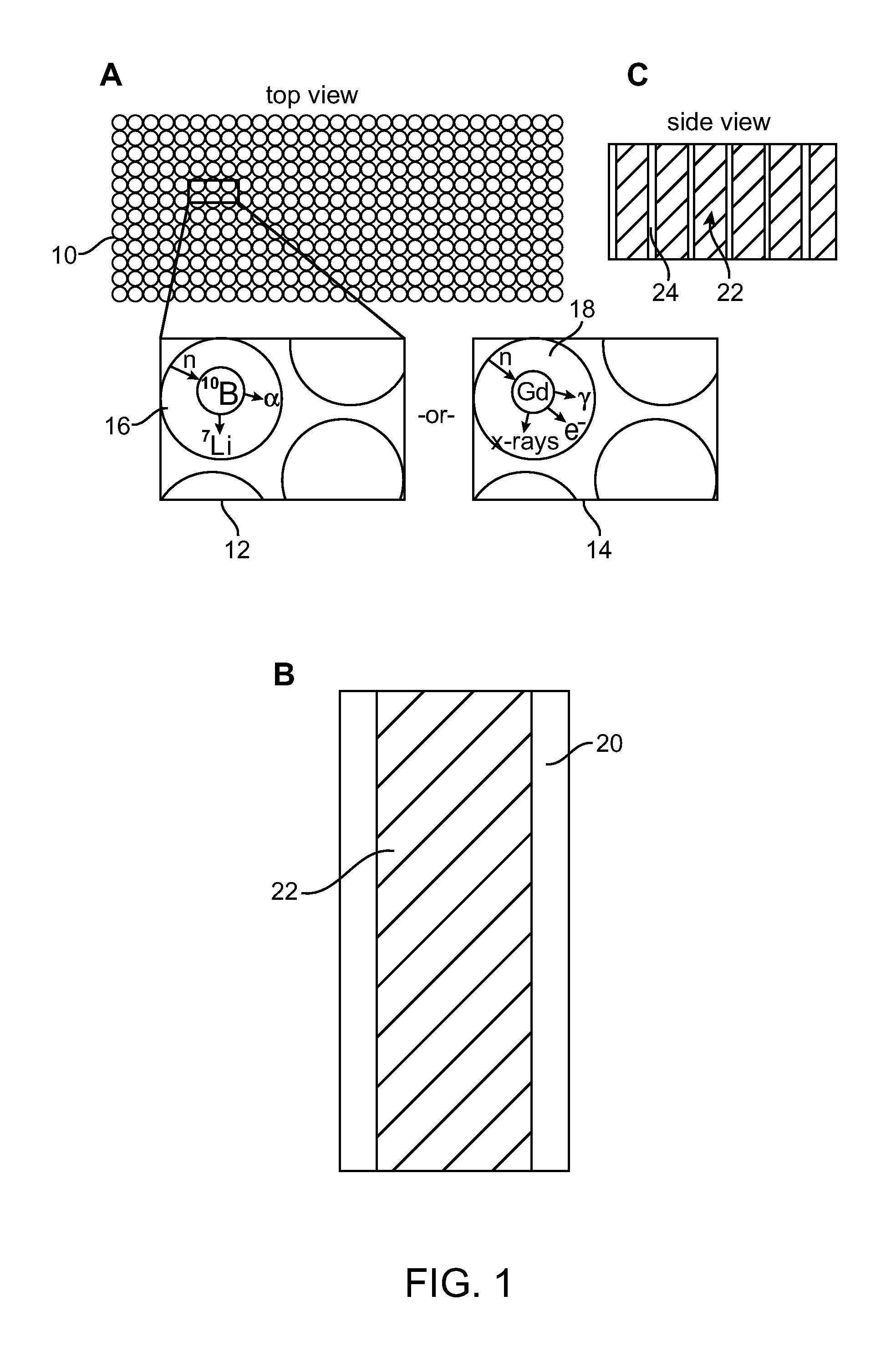
ActiveUS7372041B1Sacrificing spatial resolutionImprove detection efficiencyMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansScintillatorBiology
The present invention relates generally to neutron detecting scintillators and related methods and devices. A neutron detecting scintillator includes a plurality of microcapillary tubes loaded with a scintillator composition comprising a plastic scintillator and a neutron absorbing material. The present invention additionally provides methods of producing a neutron detecting scintillator having a plurality of microcapillary tubes loaded with a scintillator composition comprising a plastic scintillator and a neutron absorbing material. The method includes preparing a solution comprising a monomer and a neutron absorbing element, introducing the solution into a microcapillary tube of the plurality, and polymerizing the solution within the microcapillary tube.
Owner:RADIATION MONITORING DEVICES
Solar receiver utilizing carbon nanotube infused coatings
A solar receiver includes a heat absorbing element having an outer surface and an inner surface opposite the outer surface and a first coating including a carbon nanotube-infused fiber material in surface engagement with and at least partially covering the outer surface of the heat absorbing element. Solar radiation incident onto the first coating is received, absorbed, and converted to heat energy, and the heat energy is transferred from the first coating to the heat absorbing element. A multilayer coating for a solar receiver device includes a first coating that includes a CNT-infused fiber material and an environmental coating disposed on the first coating.
Owner:APPL NANOSTRUCTURED SOLUTIONS LLC
System and method for rapid thermal cycling
ActiveUS20080176289A1More rapid thermal cyclingImage enhancementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
At least one exemplary embodiment is directed to an apparatus that includes a microfluidic channel and at least one energy absorbing element, where the energy absorbing element is configured to absorb at least a portion of an incident electromagnetic radiation. The absorption of the radiation by the energy absorbing element varies the temperature of a sample in the microfluidic channel.
Owner:CANON US LIFE SCIENCES INC
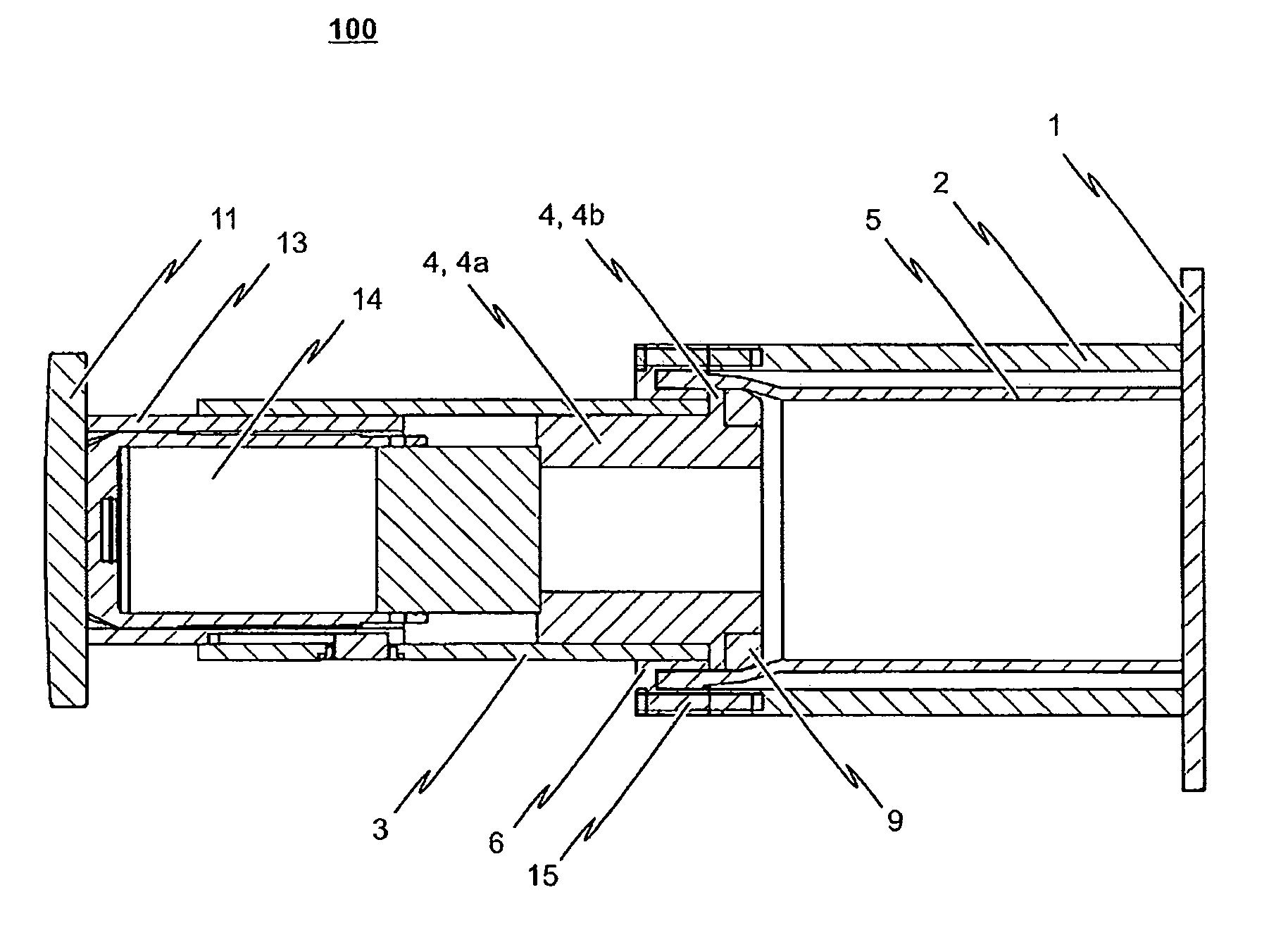
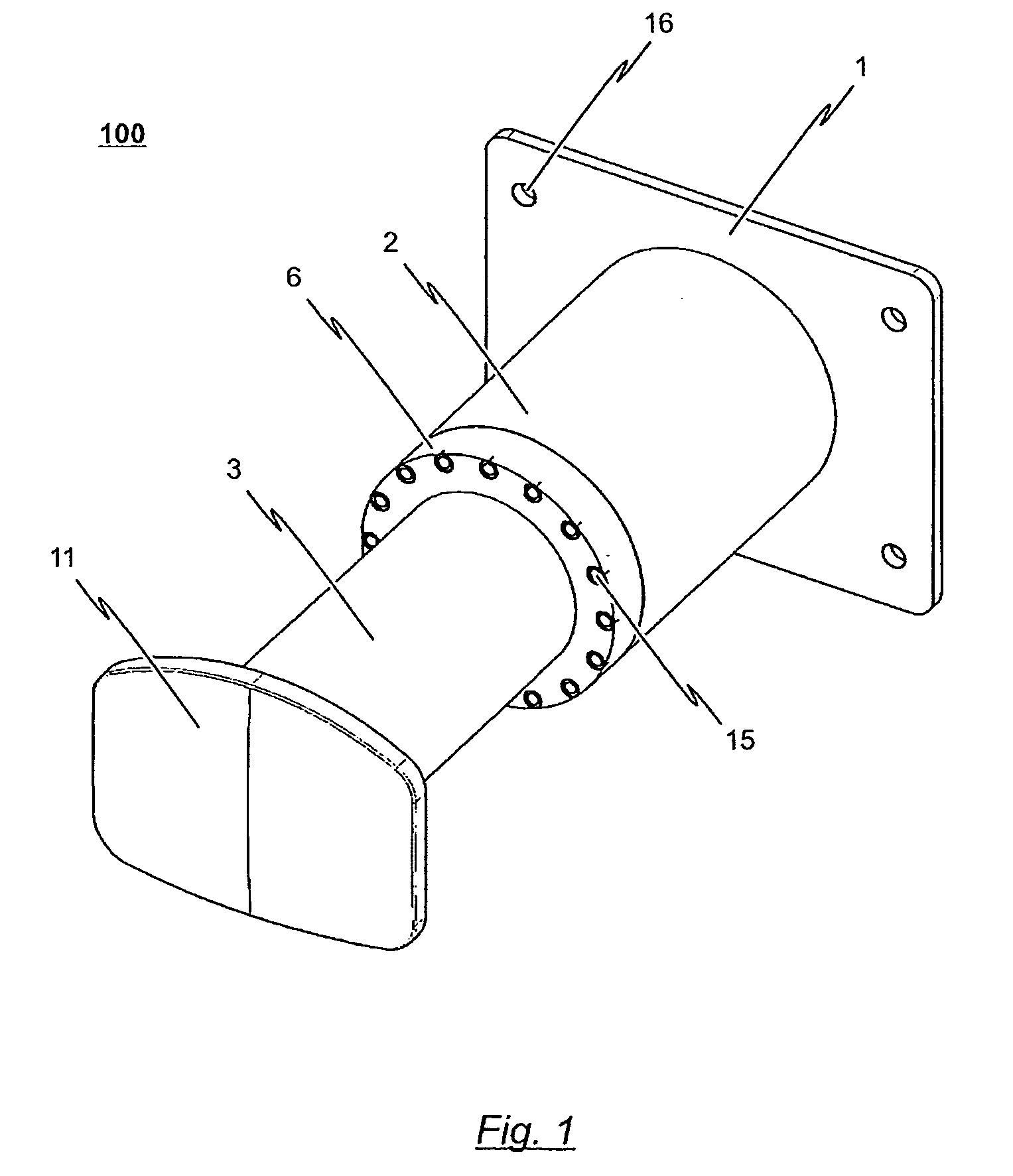
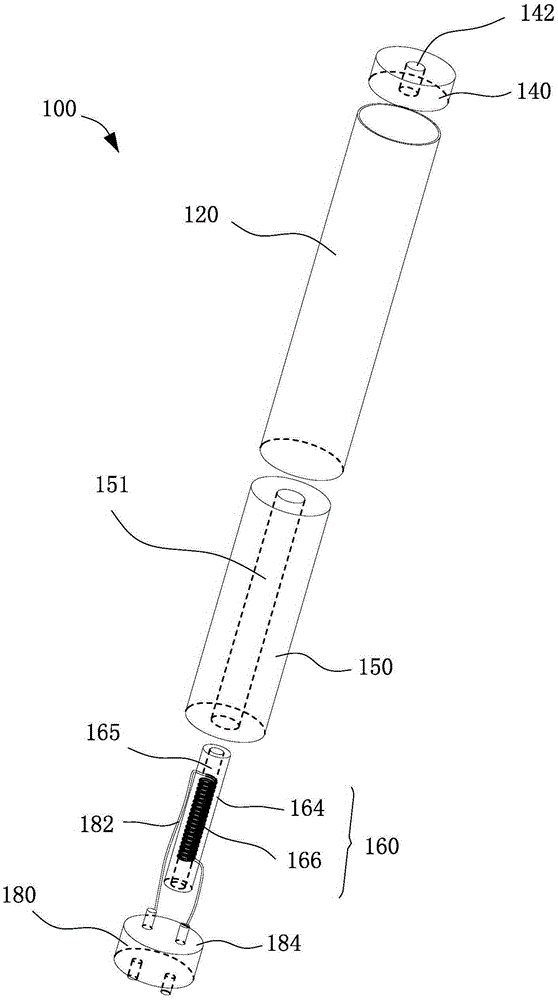
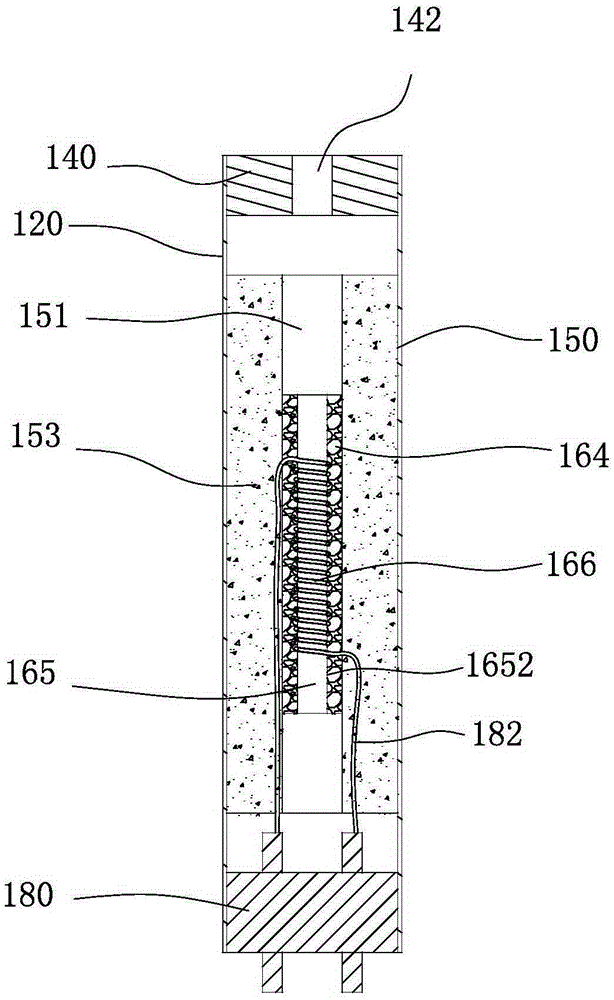
Shock absorber
InactiveUS20090065462A1Protection from damageBuffer carsClimate change adaptationEnergy absorptionEngineering
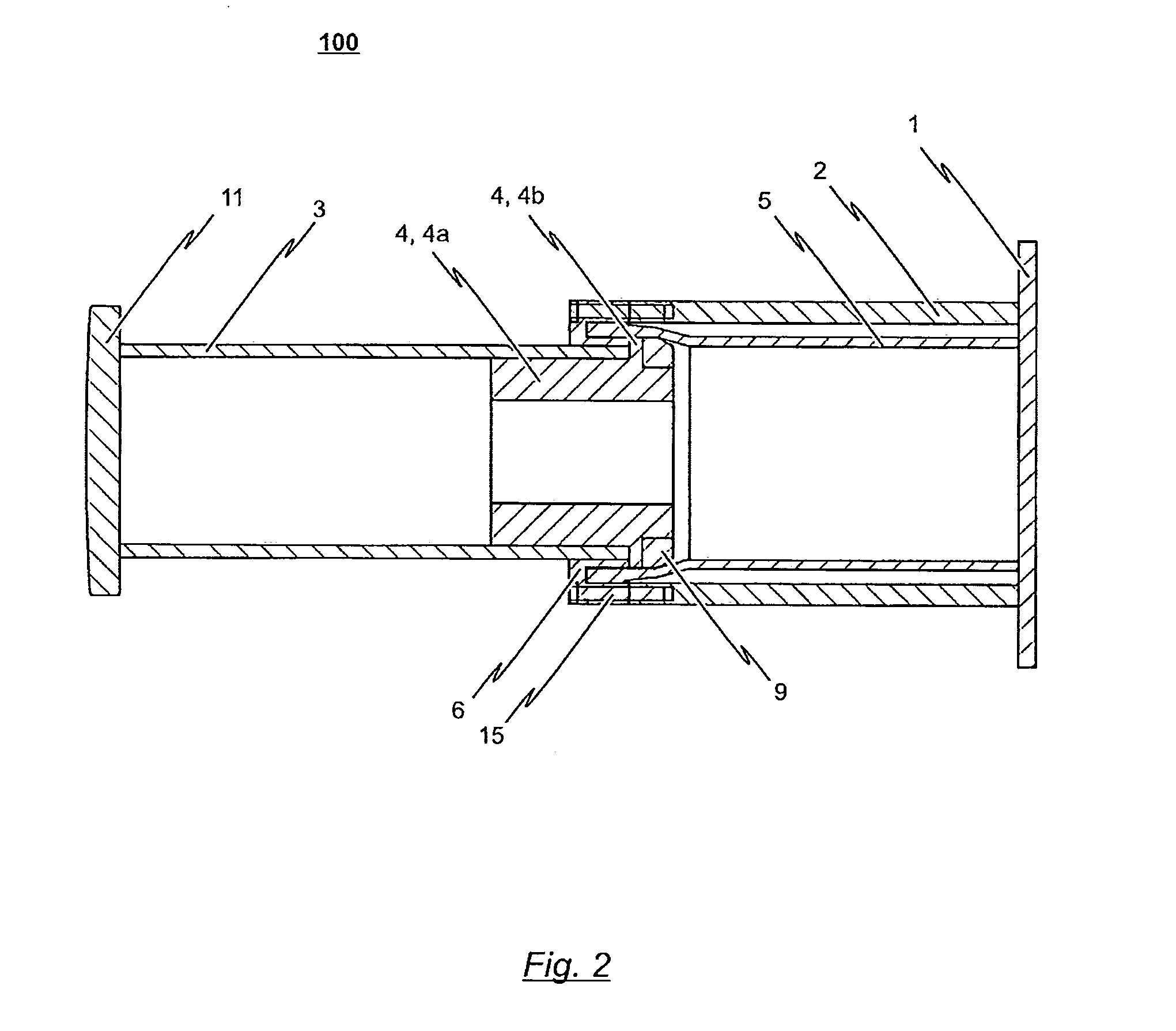
The invention relates to a shock absorber (100), in particular for use as an additional irreversible shock-absorbing stage together with a component for transferring force. In order to achieve the reliable dissipating of high impact energies, a shock absorber (100) comprising the following is indicated in accordance with the invention: a base plate (1); a force-transferring element (3) having a tensioning element (4); an energy-absorbing element in the form of a deformation tube (5) which is connected by a first end section to the base plate (1); and a connecting element (6) for the disengageable connecting of the force-transferring element (3) to a second end section of the deformation tube (5), wherein the connecting element (6) is pressed against the tensioning element (4) such that the deformation tube (5) is braced between the tensioning element (4) and the base plate (1) without play.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
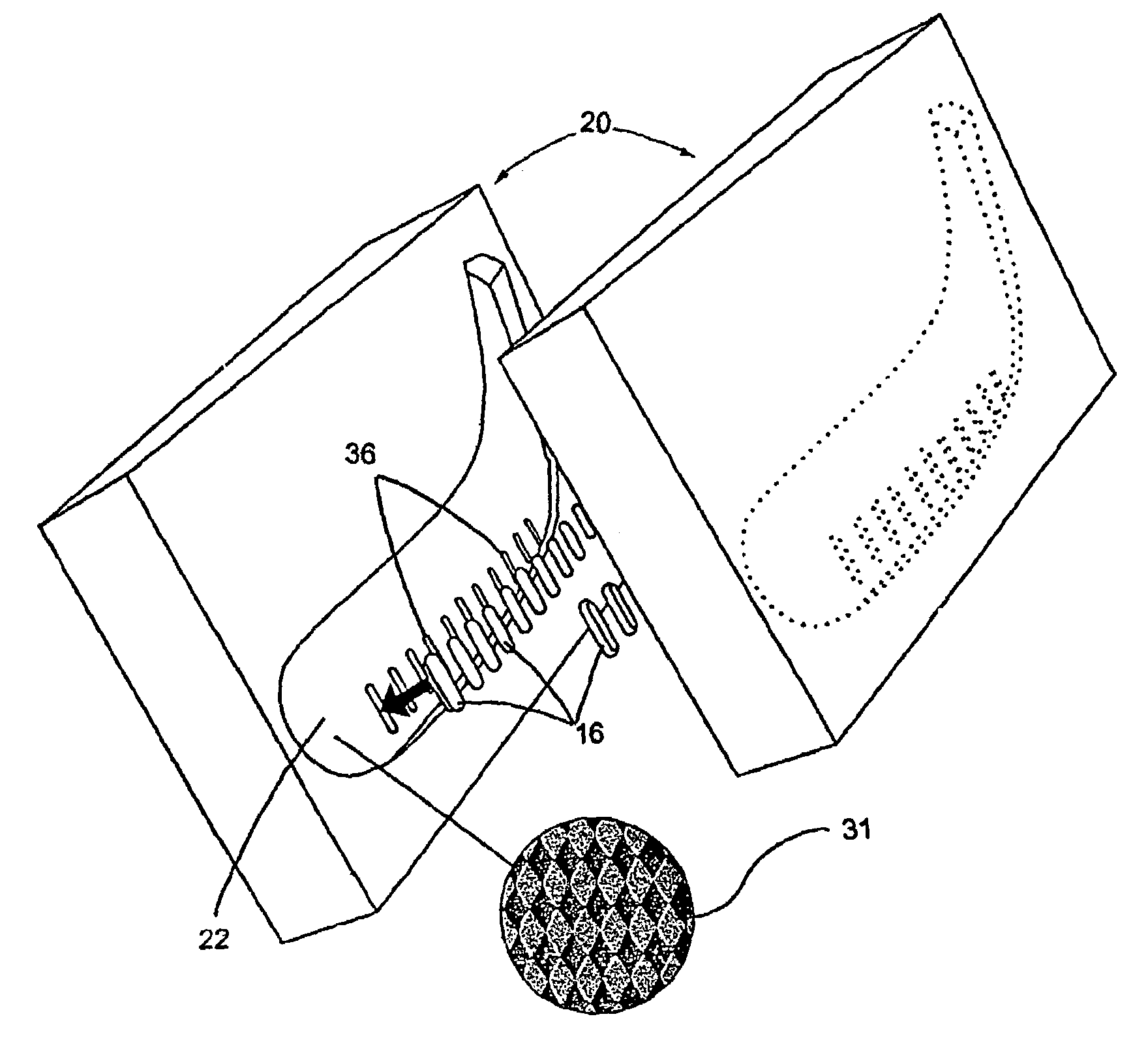
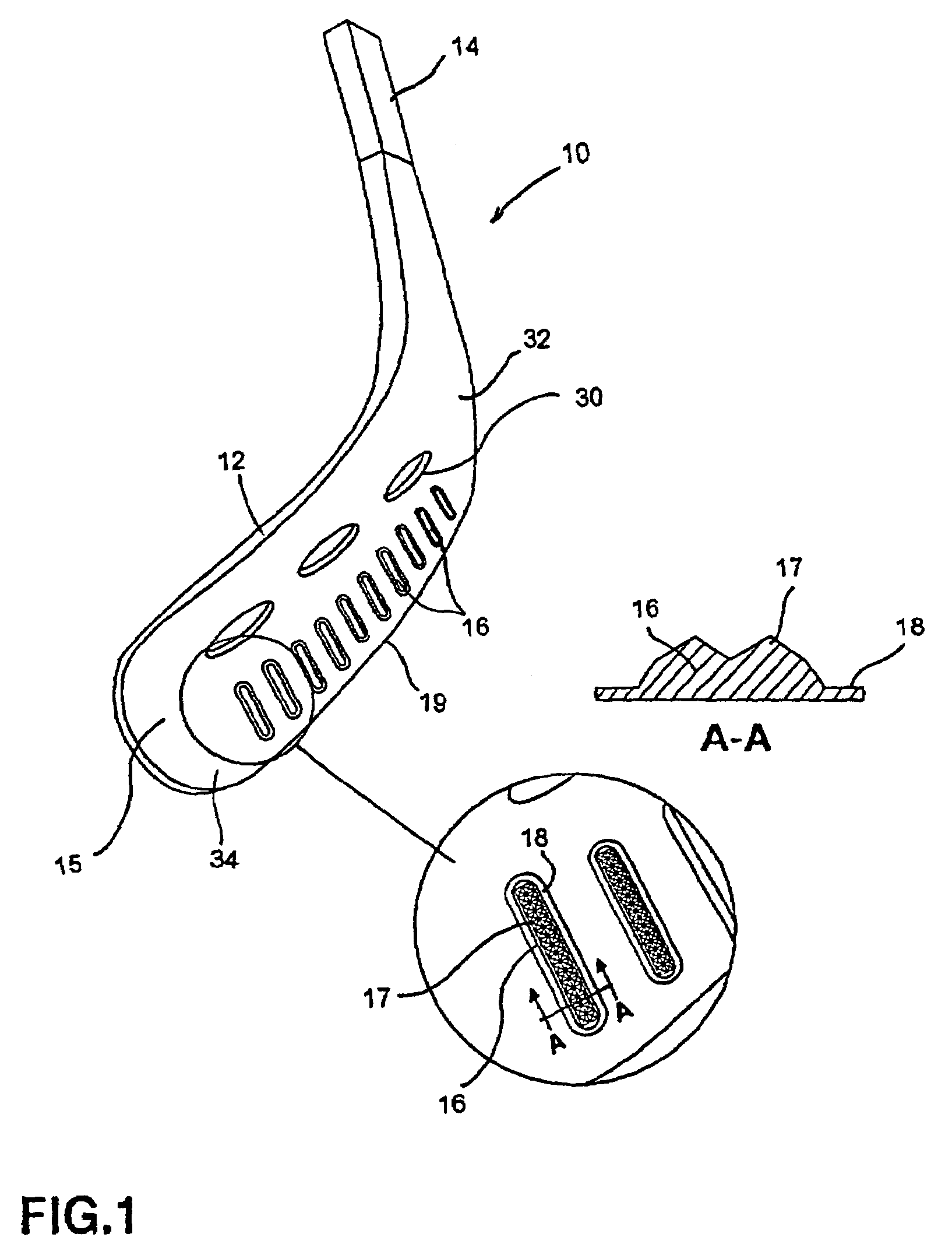
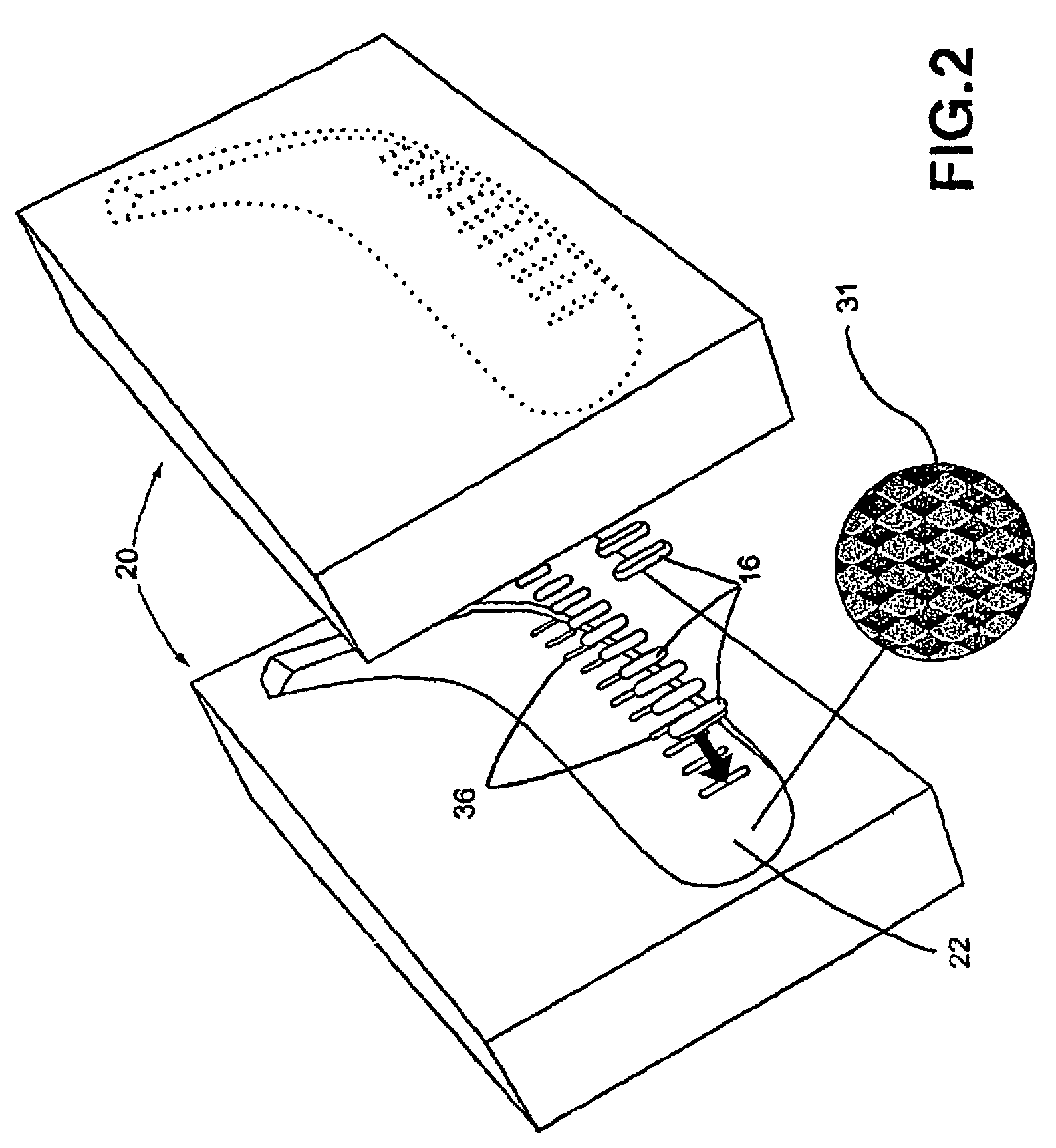
Blade for hockey stick or the like
A composite hockey stick blade having molded outer surfaces defining a rough surface finish on a portion the outer surfaces. The molded outer surface of the blade adapted to enhance friction between the blade and a puck. The blade may also comprise shock-absorbing elements embedded into the molded outer surfaces of the blade.
Owner:PAGOTTO JOHN
Localization of a Radioactive Source
InactiveUS20090127459A1Reduce biological effectHigh sensitivitySurgical navigation systemsMaterial analysis by optical meansRadioactive wasteRadioactive source
An angle-responsive sensor, comprising:a radiation detector adapted to detect ionizing radiation;at least one radiation absorbing element arranged to block radiation from reaching said detector in a manner dependent on a relative orientation of a radiation source, said detector and said element, said detector and said element defining an aim for said sensor; andcircuitry coupled to said detector and which generates an output signal which varies as a function of said relative orientation,wherein said detector and said element are arranged to have a working volume of at least 10 cm in depth and having an angular width, such that said signal defines an accuracy of better than 3 mm within one standard deviation, over said working volume.
Owner:NAVOTEK MEDICAL
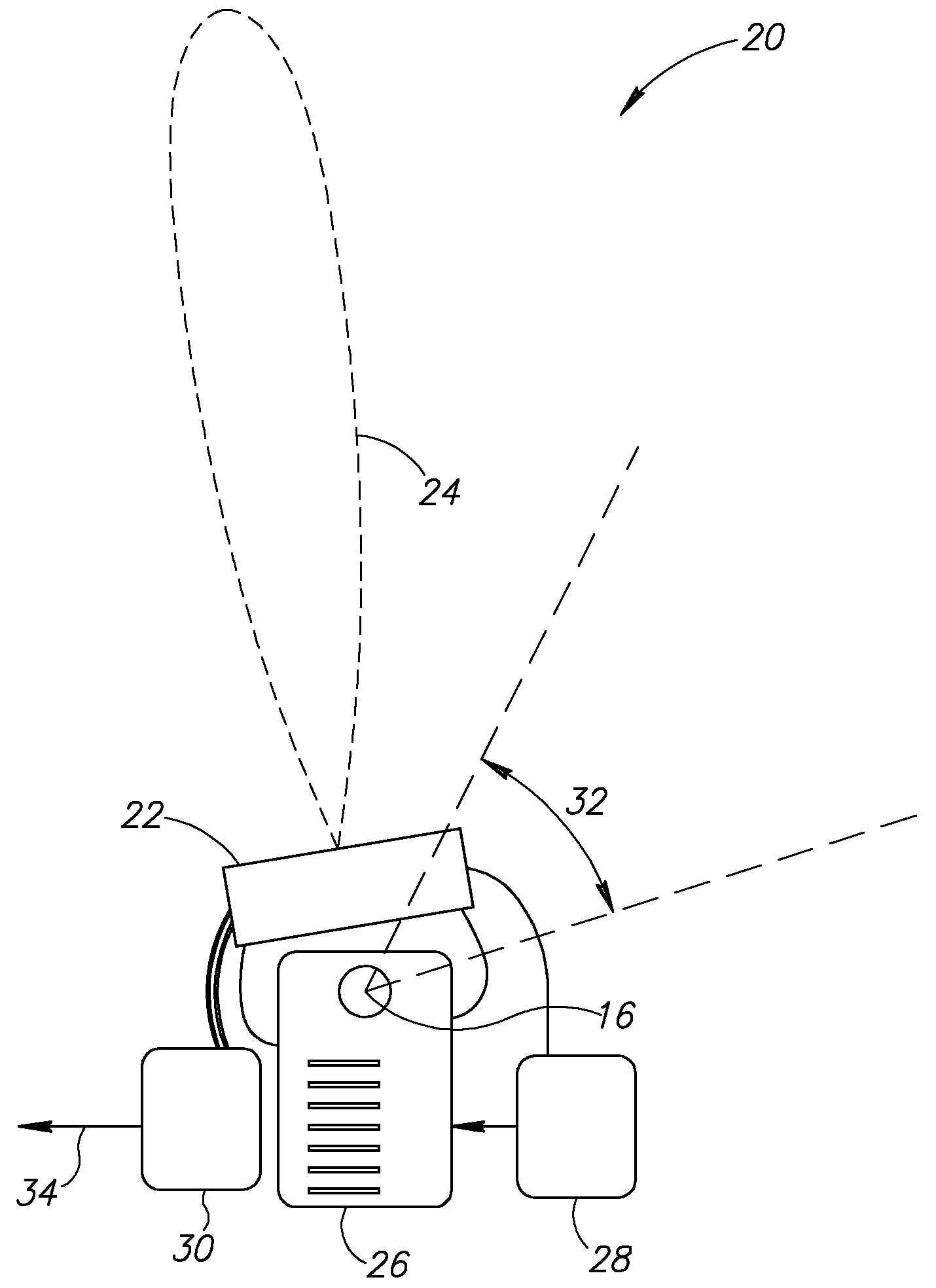
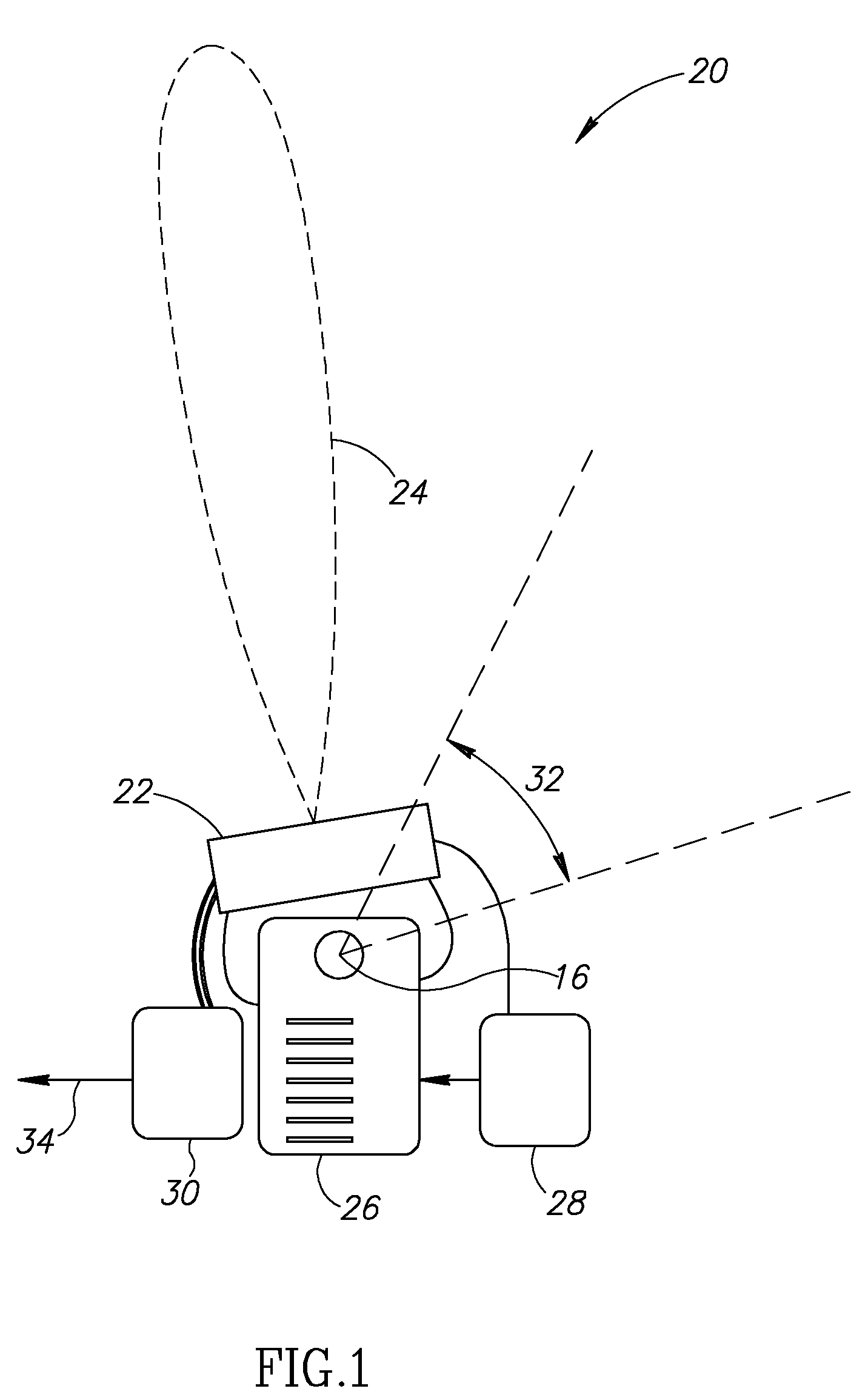
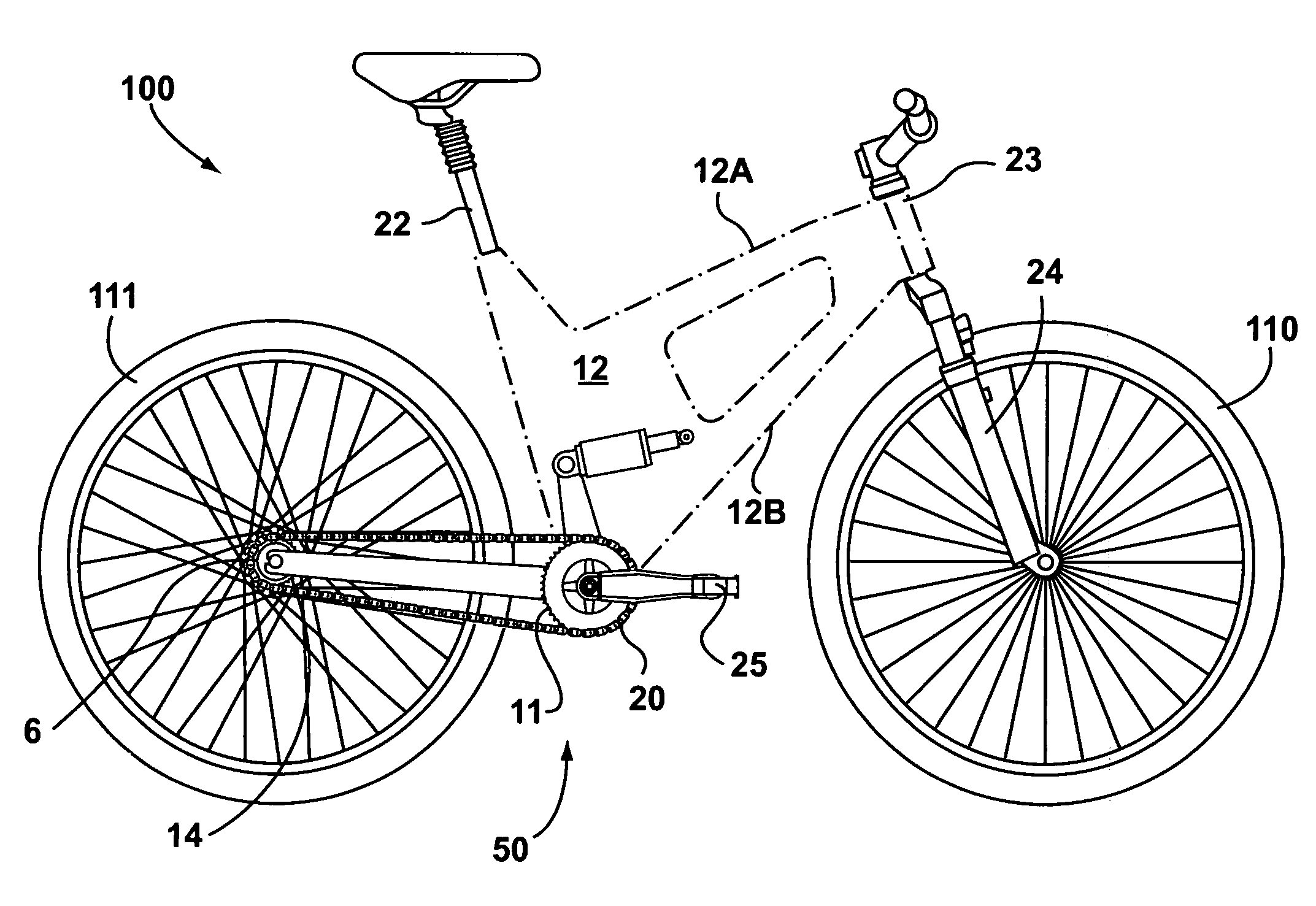
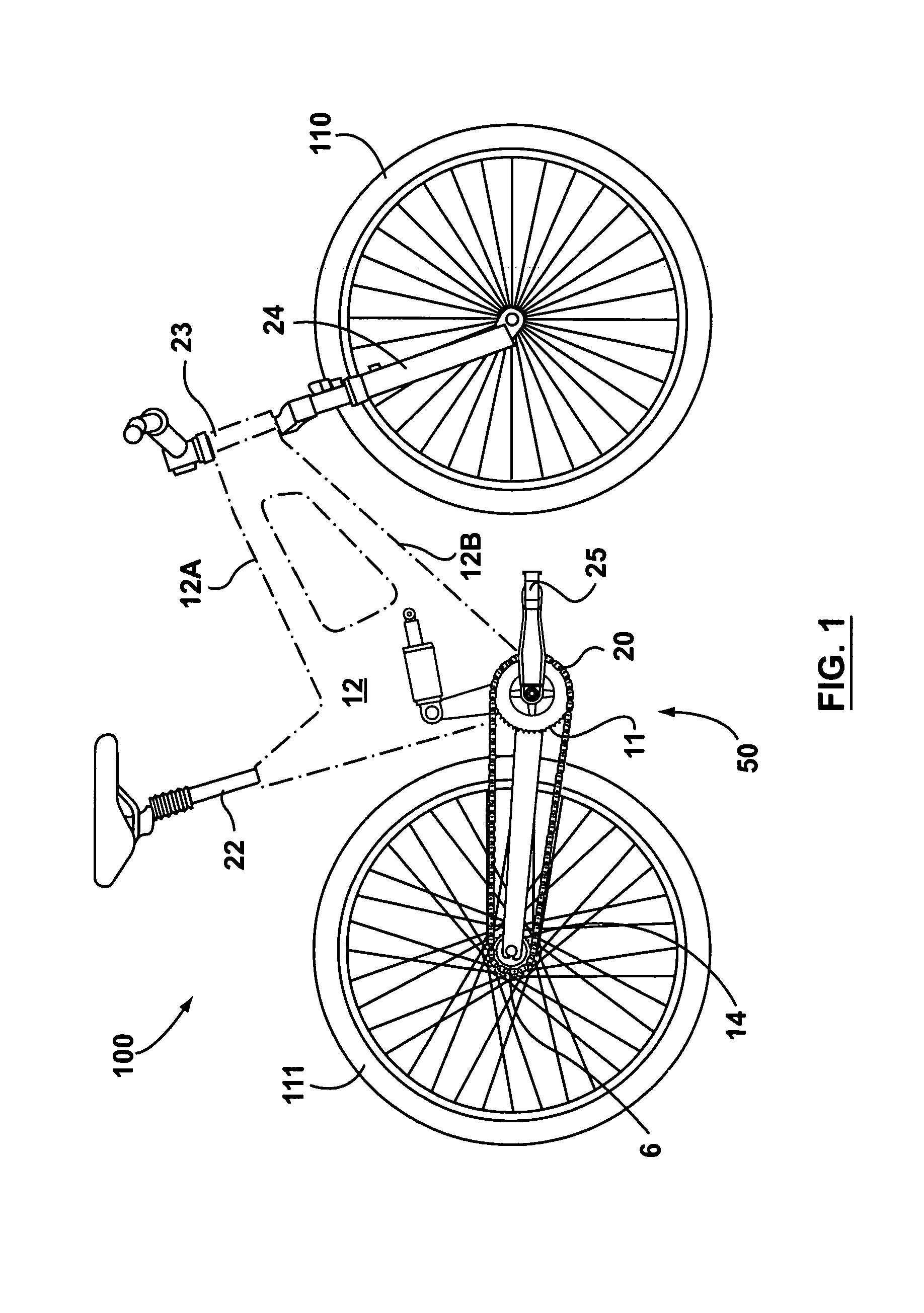
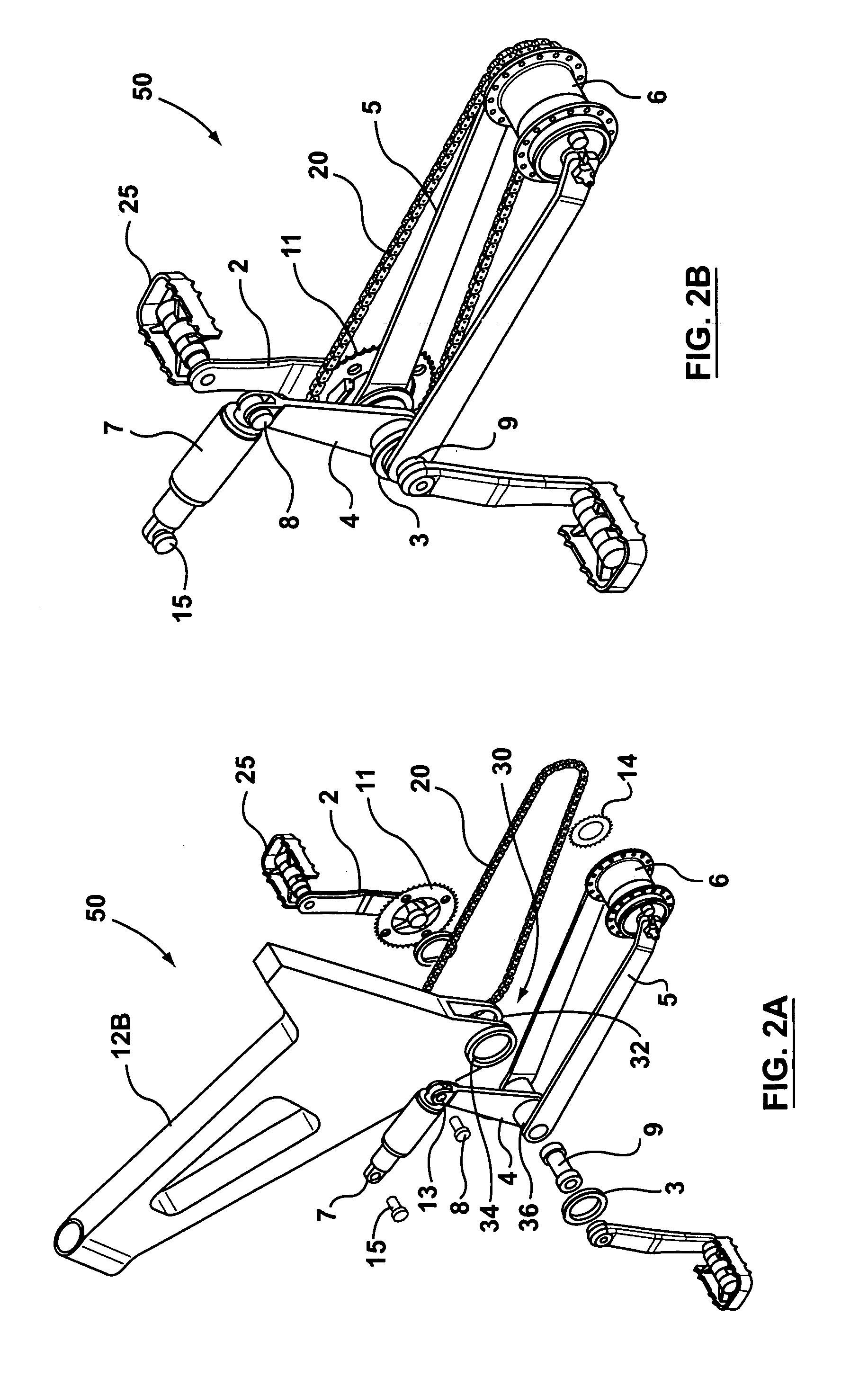
Cantilever rear suspension for a bicycle
ActiveUS7104562B2Reduce unwanted playIncrease surface areaPassenger cyclesChildren cyclesRotational axisEngineering
A bicycle is equipped with a rear wheel suspension having a swing arm with one or more generally cantilevered side arms, which are capable of withstanding bending and torsional loads and isolating said loads from the rider. A bottom portion of the bicycle frame includes a pedal sleeve. A pedal or crank assembly rotates within the pedal sleeve about a rotational axis with a fixed location relative to the frame. The swing arm is pivotally secured to the frame for movement about the rotational axis. A shock-absorbing element is connected between the swing arm and the frame.
Owner:GINGL MANFRED
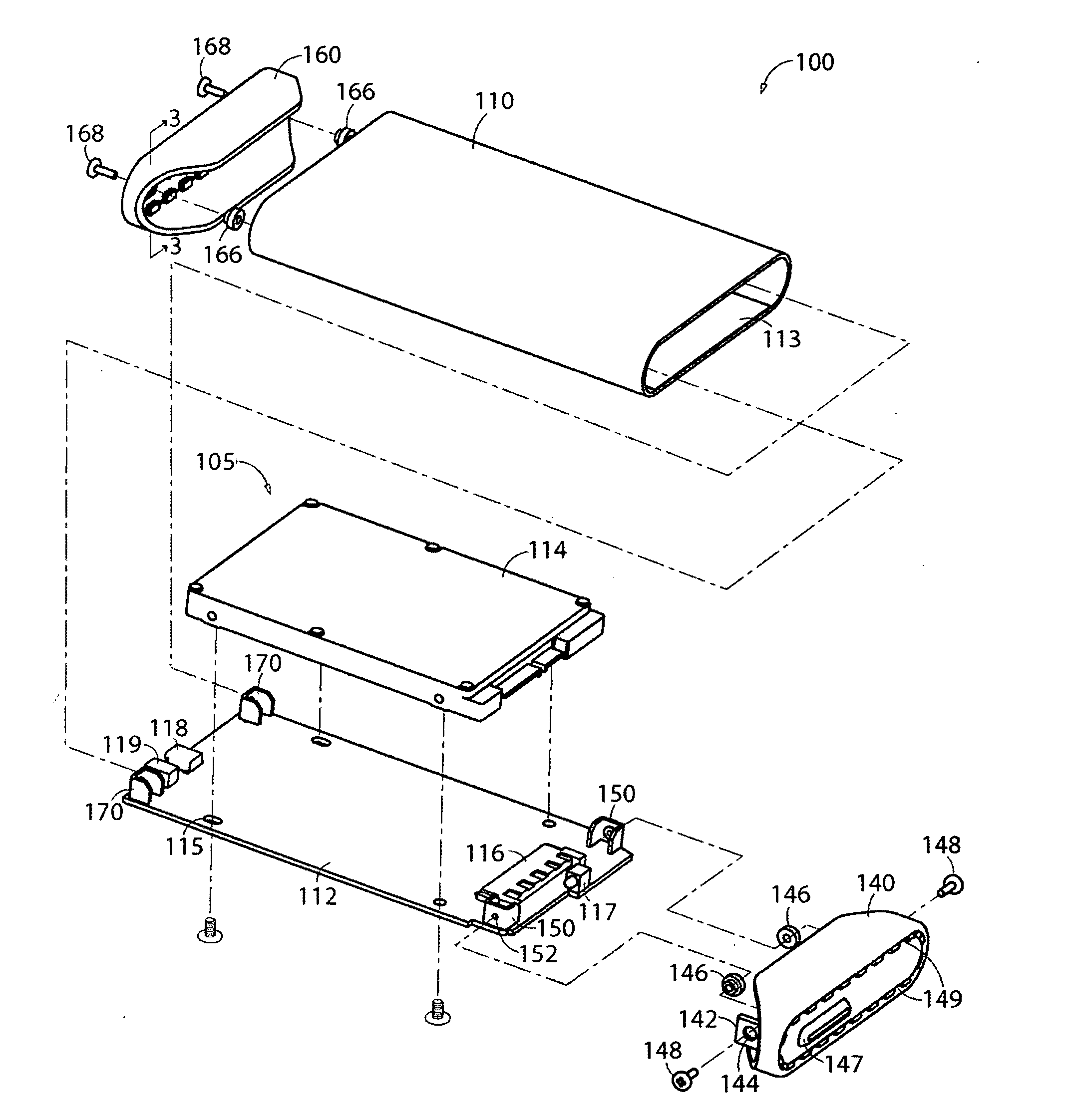
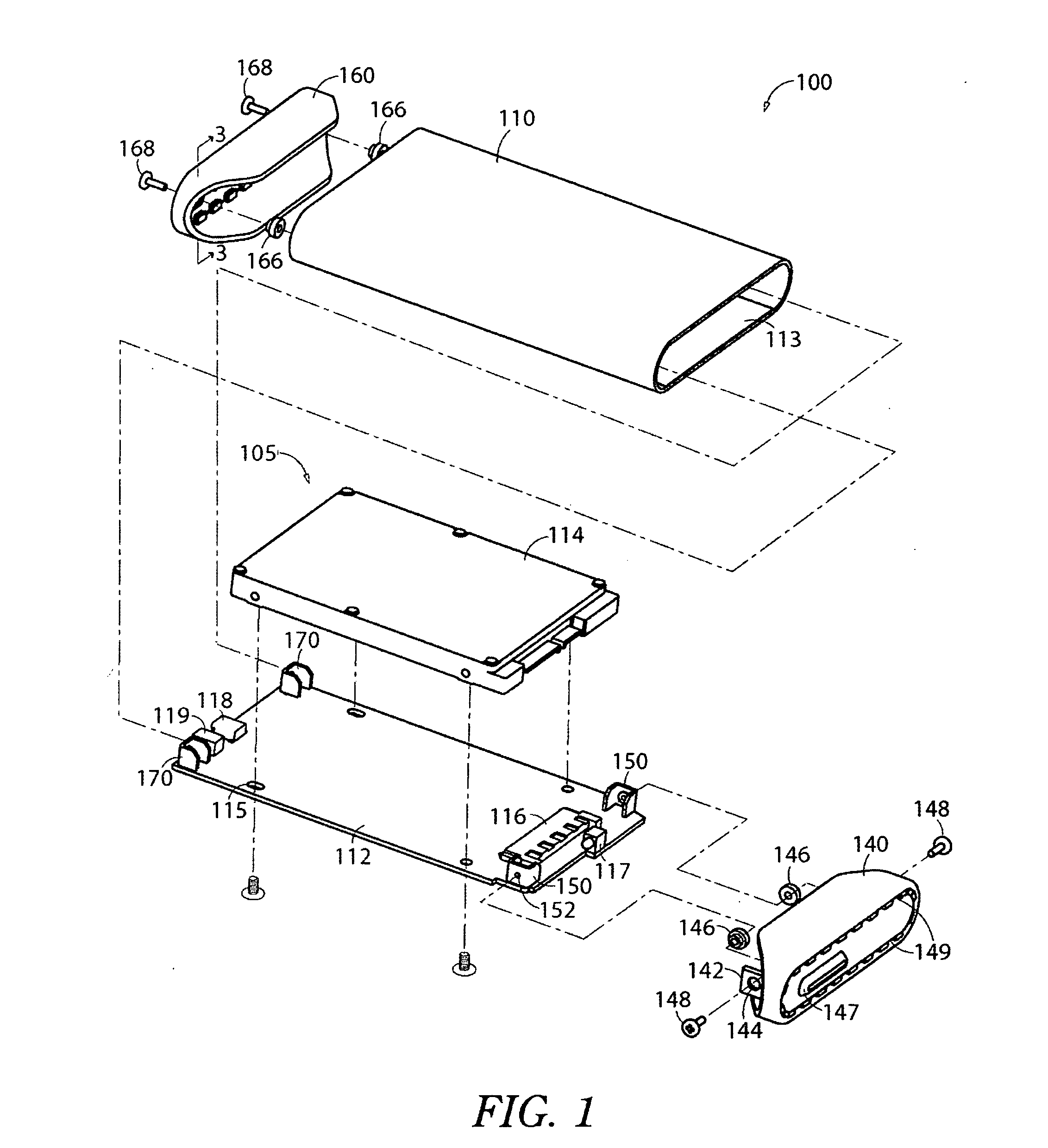
Apparatus to protect shock-sensitive devices and methods of assembly
InactiveUS20080158808A1Digital data processing detailsUndesired vibrations/sounds insulation/absorptionPrinted circuit boardBiomedical engineering
At least one shock-sensitive device is mounted within an enclosure using a shock-absorbing element as an exclusive point of contact between the shock-sensitive device and the enclosure. The shock-sensitive device may comprise a disk drive and / or a printed circuit board. The enclosure may comprise an end cap having at least one mounting bracket or flange to receive the shock-absorbing element. The shock-sensitive device may comprise a mounting tab to receive a fastener, wherein one end of the fastener is received in the mounting tab, and wherein the other end of the fastener is received in the shock-absorbing element. The shock-absorbing element may comprise a resilient material such as rubber, silicone, urethane, or foam. In an embodiment, the end cap may include ventilation holes.
Owner:TOSHIBA AMERICAN INFORMATION SYST INC
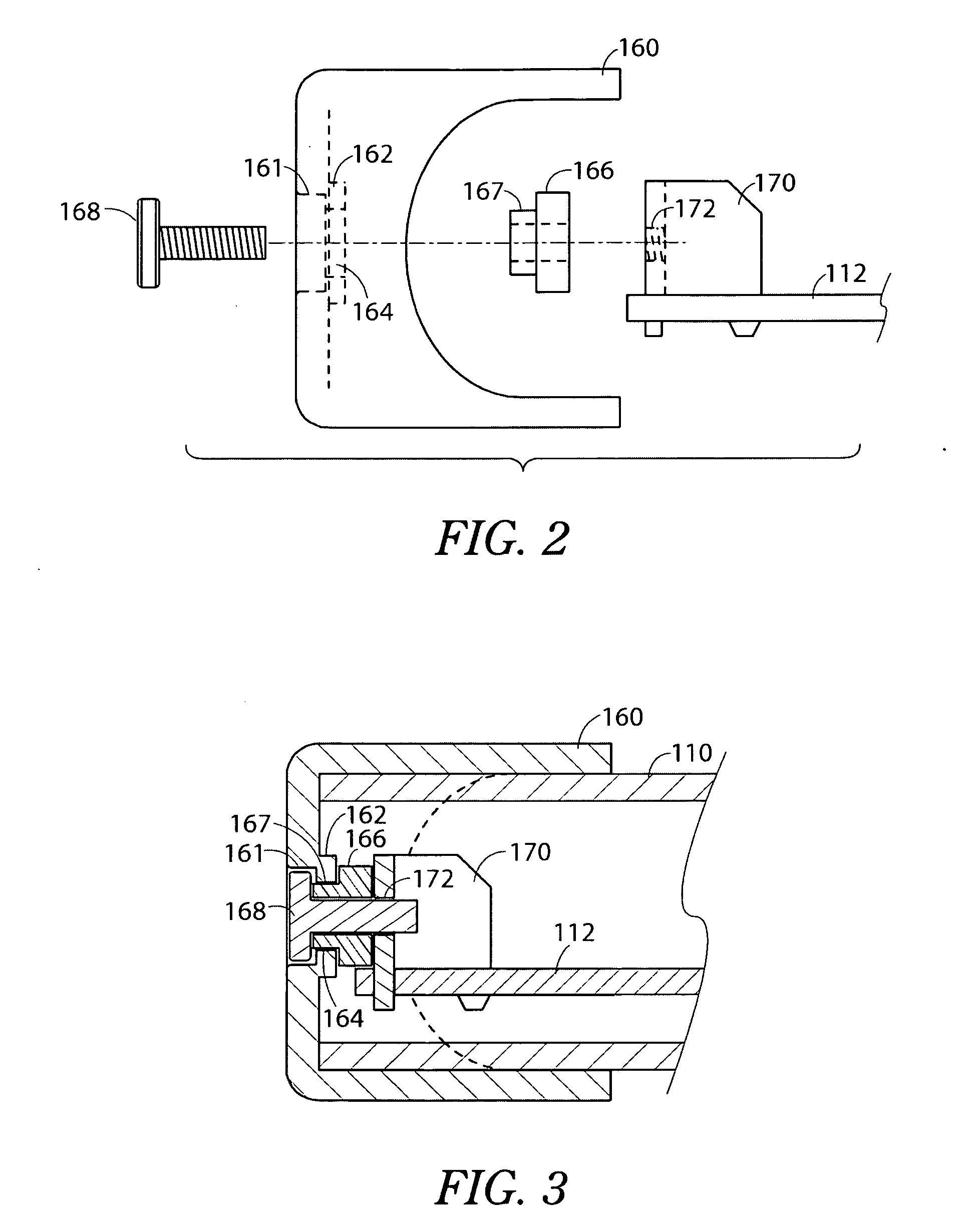
Adjustable steering column for motor vehicles
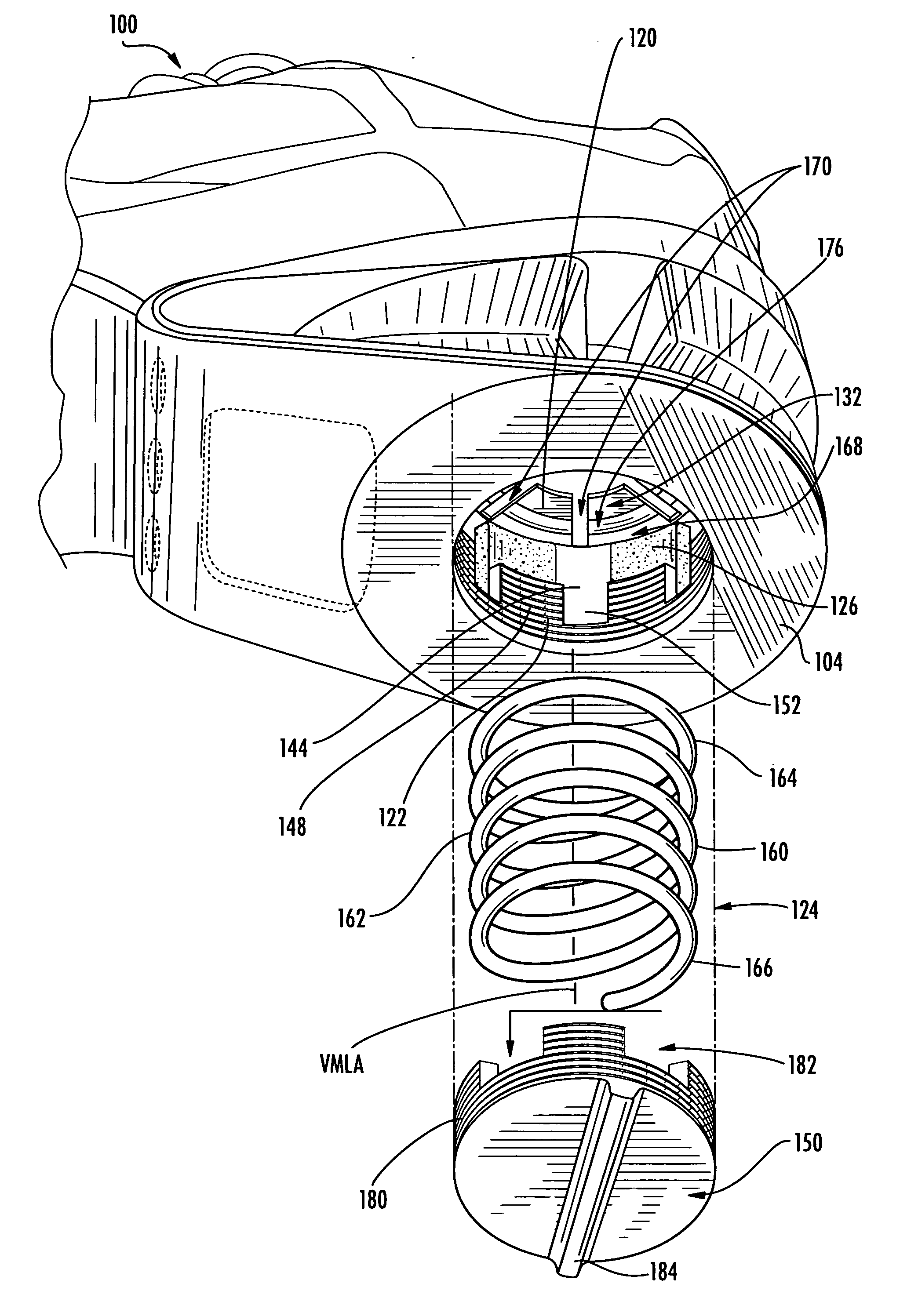
An adjustable steering column for a motor vehicle has a support assembly intended to be fixed to a chassis of a vehicle, a tubular body slidably mounted in the support assembly, adjustment and locking devices able to switch from a state of a adjusting the position of the tubular body in the support assembly to a state of immobilizing the tubular body in a desired adjusted position within the support assembly, a plastically deformable energy-absorbing element collaborating with a deformation member secured to the tubular body so that it undergoes plastic deformation as the tubular body retracts inside the support assembly following an impact transmitted to the tubular body when the adjustment and locking devices are in the locked state and a ratchet mechanism for securing the plastically deformable element to the support assembly during plastic deformation of the plastically deformable element.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH AUTOMOTIVE STEERING VENDOME SAS
Nearinfrared-ray absorbing galss, element, light filter and their production method and copper-contained glass
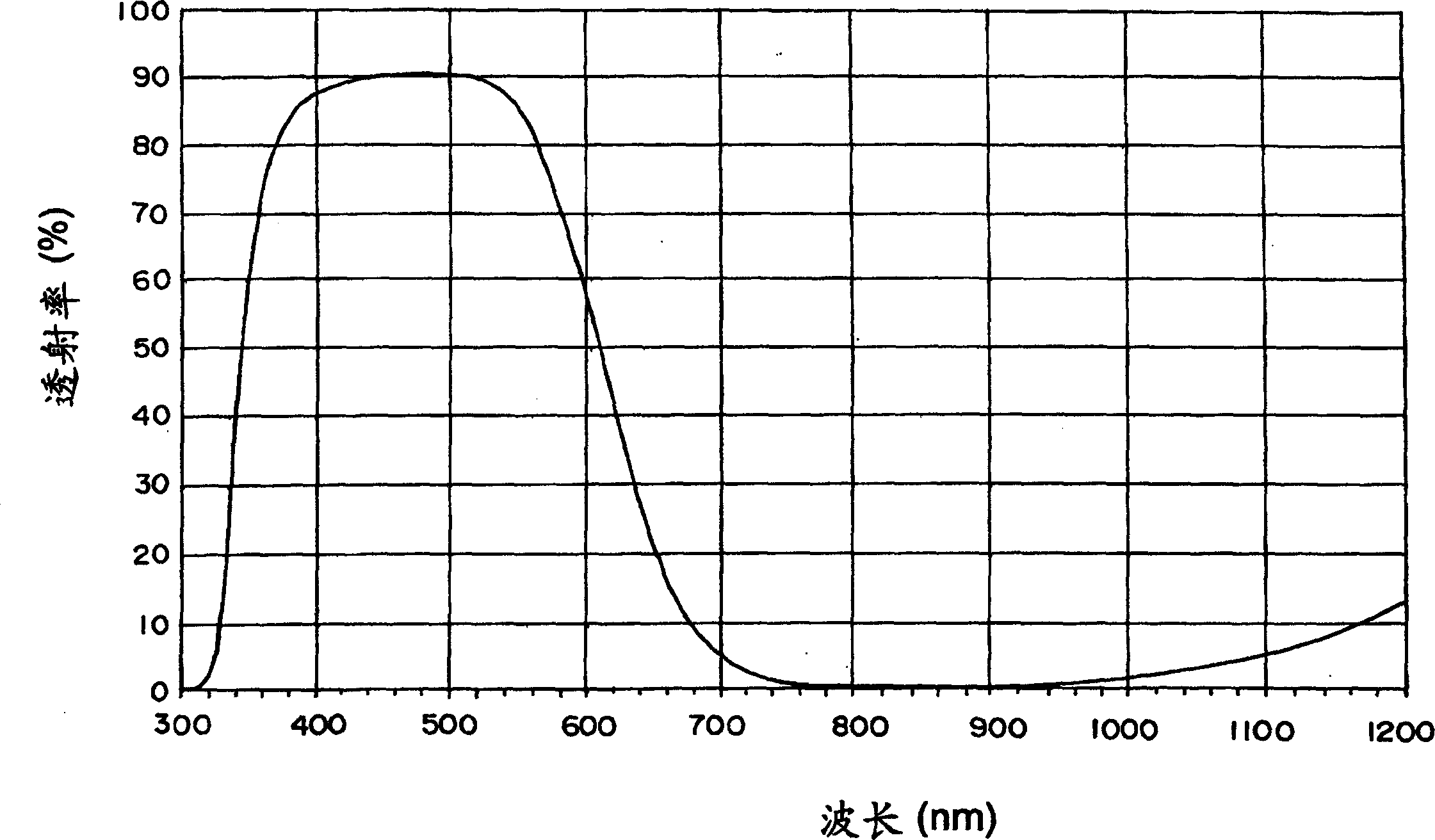
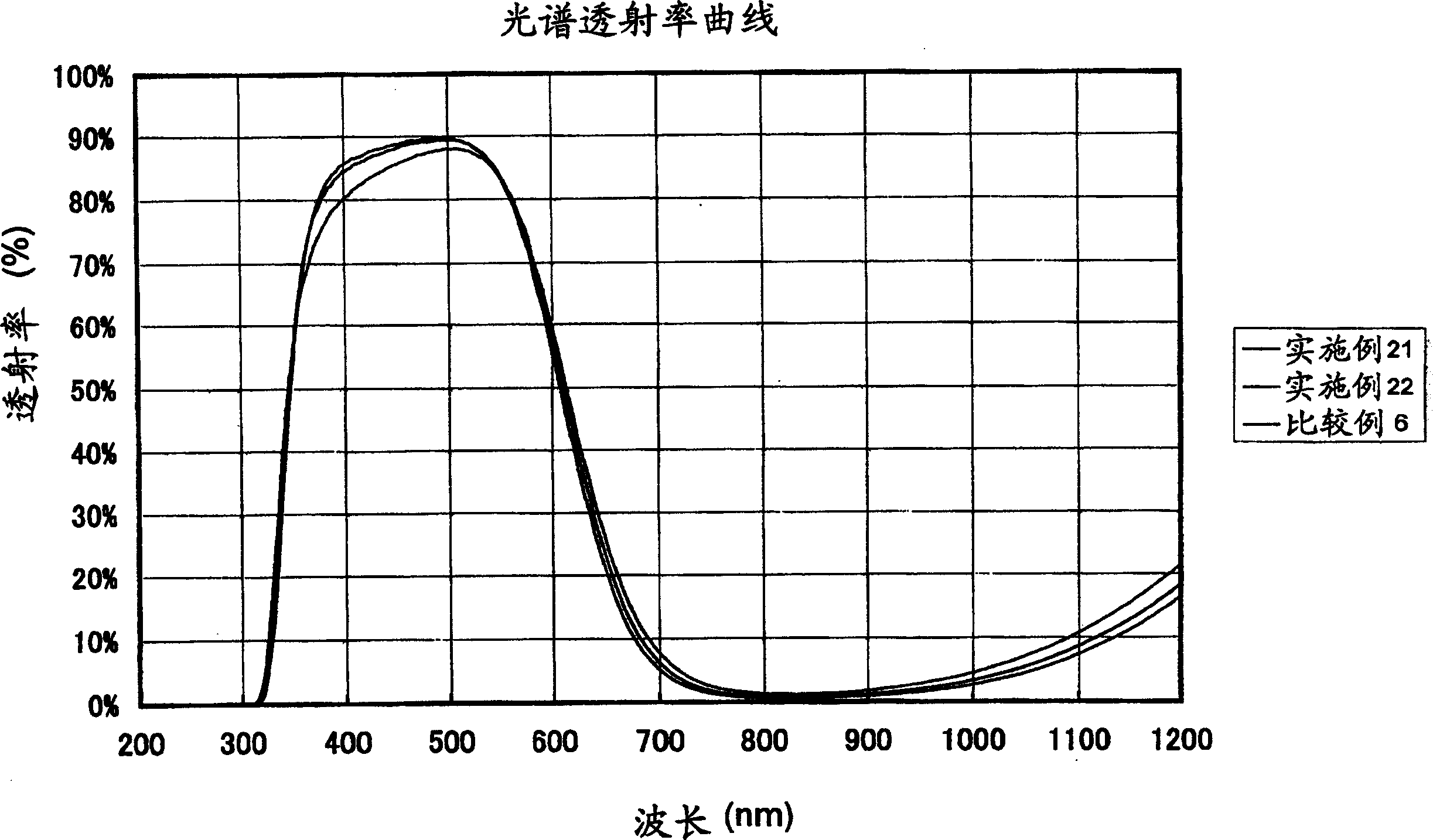
InactiveCN1508087AGood color sensitivity correction characteristicsIncreasing the thicknessOptical filtersSpectral transmittanceThinning
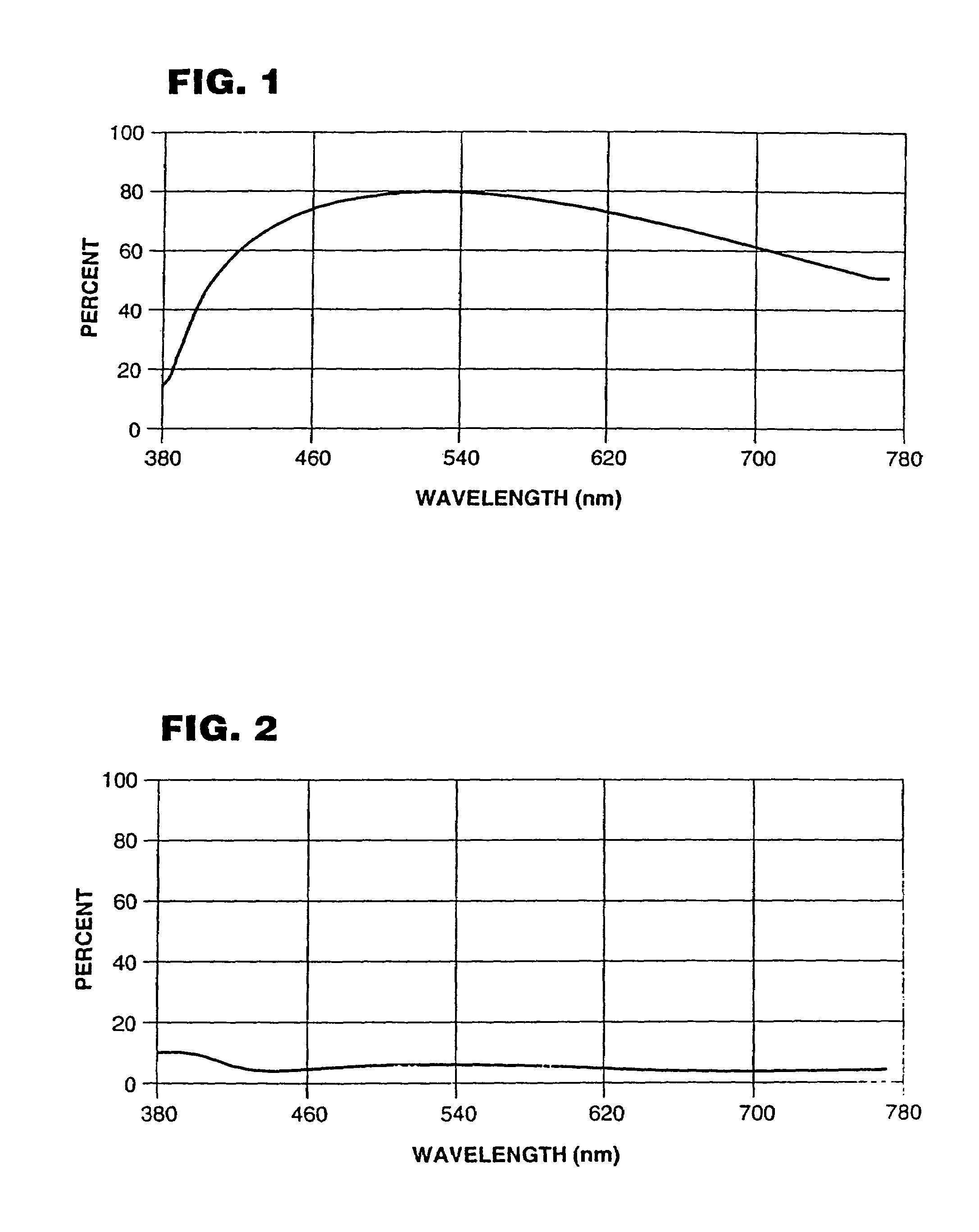
Provided are near-infrared light-absorbing glass in which good color compensating characteristics are maintained even without containing harmful arsenic, permitting the thinning of the glass, and having good weatherability and forming properties; a near-infrared light-absorbing element comprised of such glass; a near-infrared light-absorbing filter employing such glass. Also provided, at low cost, are near-infrared light-absorbing glass permitting good color compensating, a near-infrared light-absorbing element comprised of such glass, and a near-infrared light-absorbing filter comprising such elements. The glass comprises cationic components with a certain composition as well as F<-> and O<2-> as anionic components. Alternatively, the glass is near-infrared light-absorbing glass, wherein the glass exhibits properties, based on a thickness of 0.5 mm, in the spectral transmittance of wavelengths of 400 to 700 nm, that wavelength, at which a 50 percent transmittance is exhibited, is less than 630 nm, transmittance at a wavelength longer than said wavelength is less than 50 percent, transmittance at a wavelength shorter than said wavelength is higher than 50 percent and the viscosity at a liquid phase temperature is 0.5 Pa.s or more. The near-infrared light-absorbing element is comprised of such glass. The near-infrared light-absorbing filter comprises a glass plate comprised of such glass. Alternatively, the glass is comprised of fluorophosphate glass or phosphate glass, and comprises 0.1 weight percent or more of copper based on CuO, 0.005 to 0.5 weight percent of iron based on Fe2O3, 0.01 to 1 weight percent of antimony based on Sb2O3, and no arsenic.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Electronic cigarette and manufacturing method of atomizing component thereof
The invention relates to an electronic cigarette and a manufacturing method of an atomizing component thereof. The electronic cigarette comprises a liquid storage device, the atomizing component and a power source component, the liquid storage device is used for storing cigarette liquid, the atomizing component is contained in a shell and comprises a liquid absorbing element and a heating element, the liquid absorbing element is connected with the liquid storage device and made of porous ceramic and comprises a liquid absorbing face used for absorbing the cigarette liquid and an atomizing surface, the heating element is embedded inside the liquid absorbing element, the edge of the heating element is internally tangent with the atomizing surface, the heating element is used for converting the cigarette liquid absorbed by the liquid absorbing element into smoke, and the power source component is contained in the shell, connected with the atomizing component and used for powering the heating element.
Owner:SHENZHEN SMOORE TECH LTD
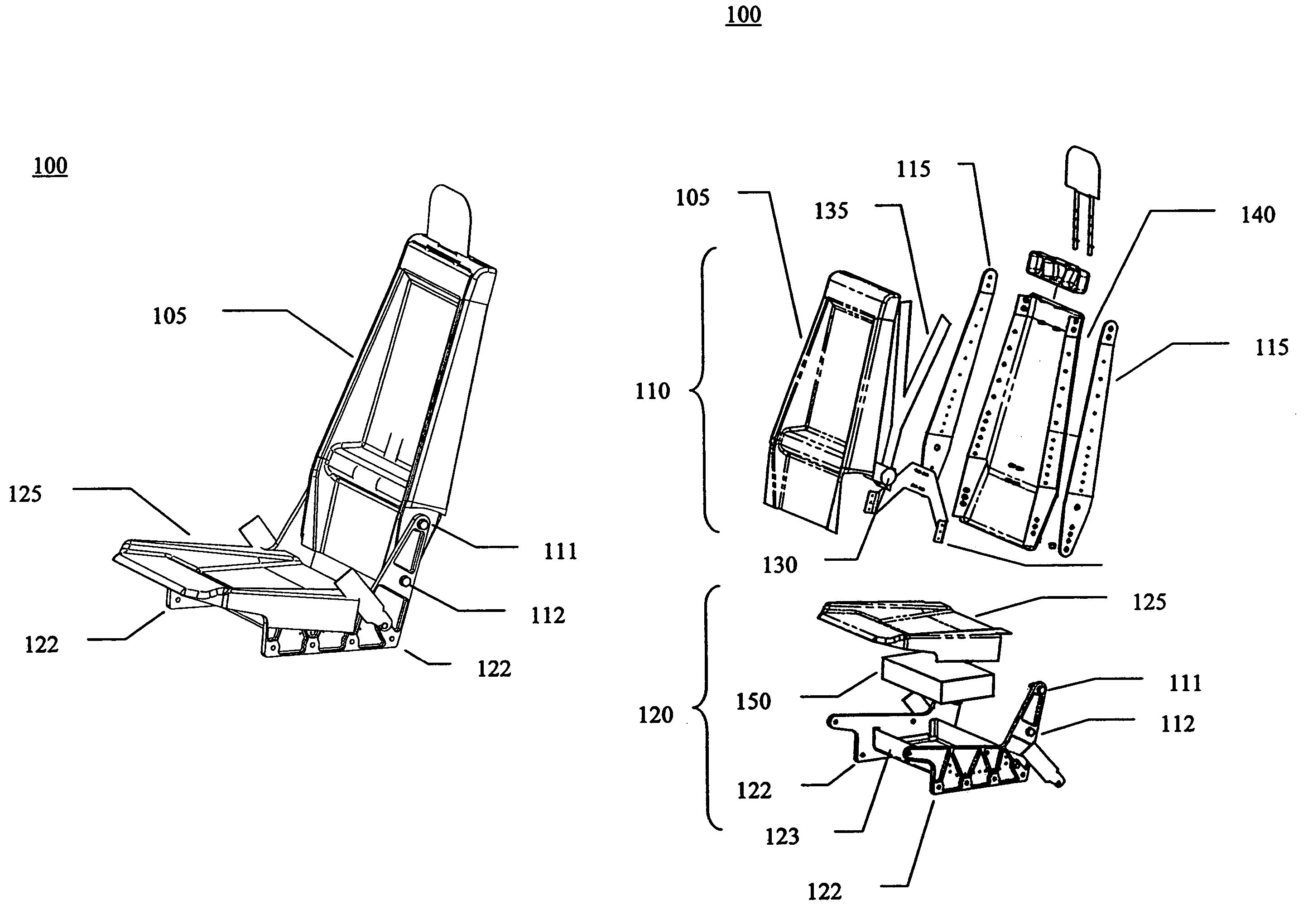
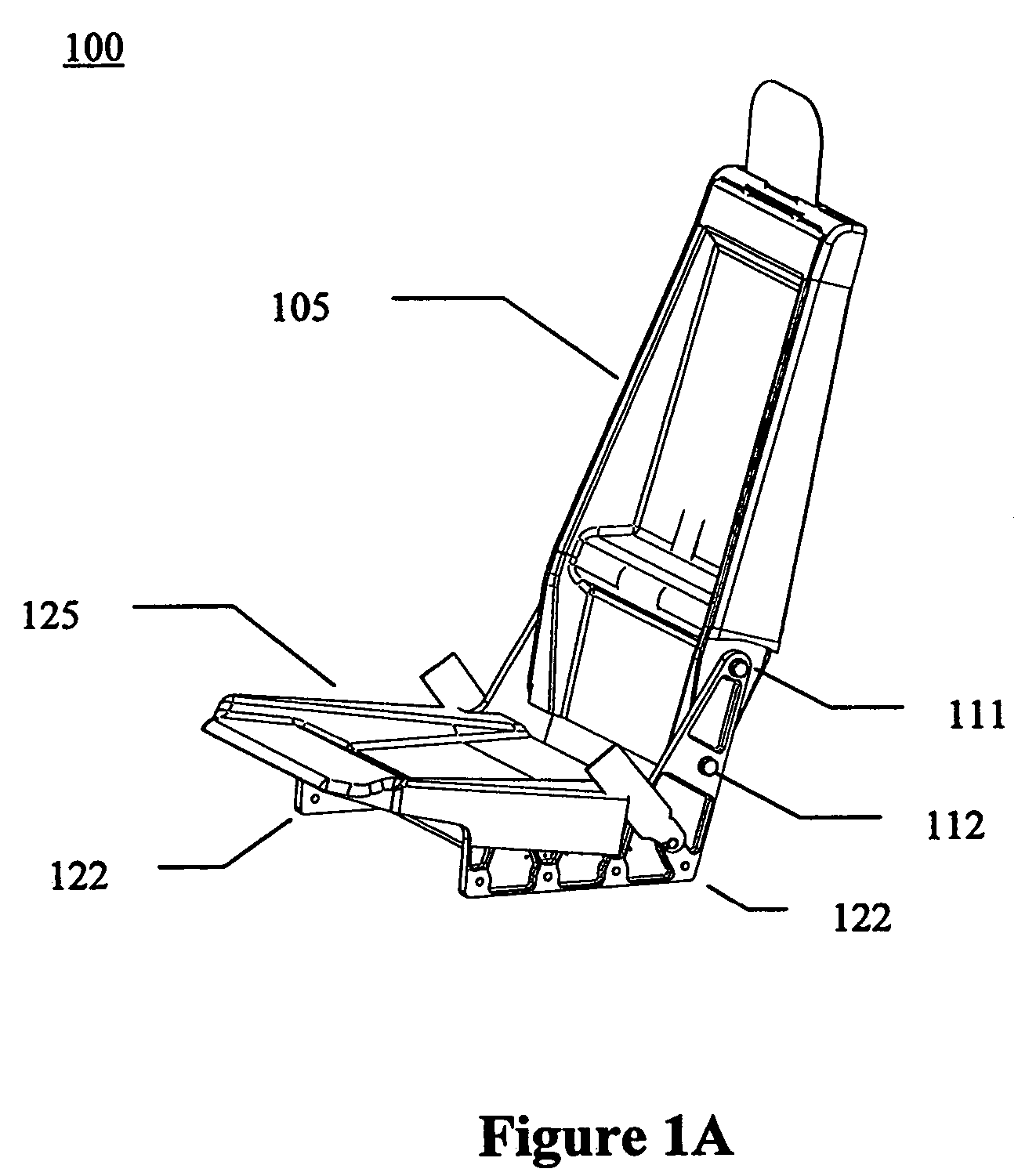
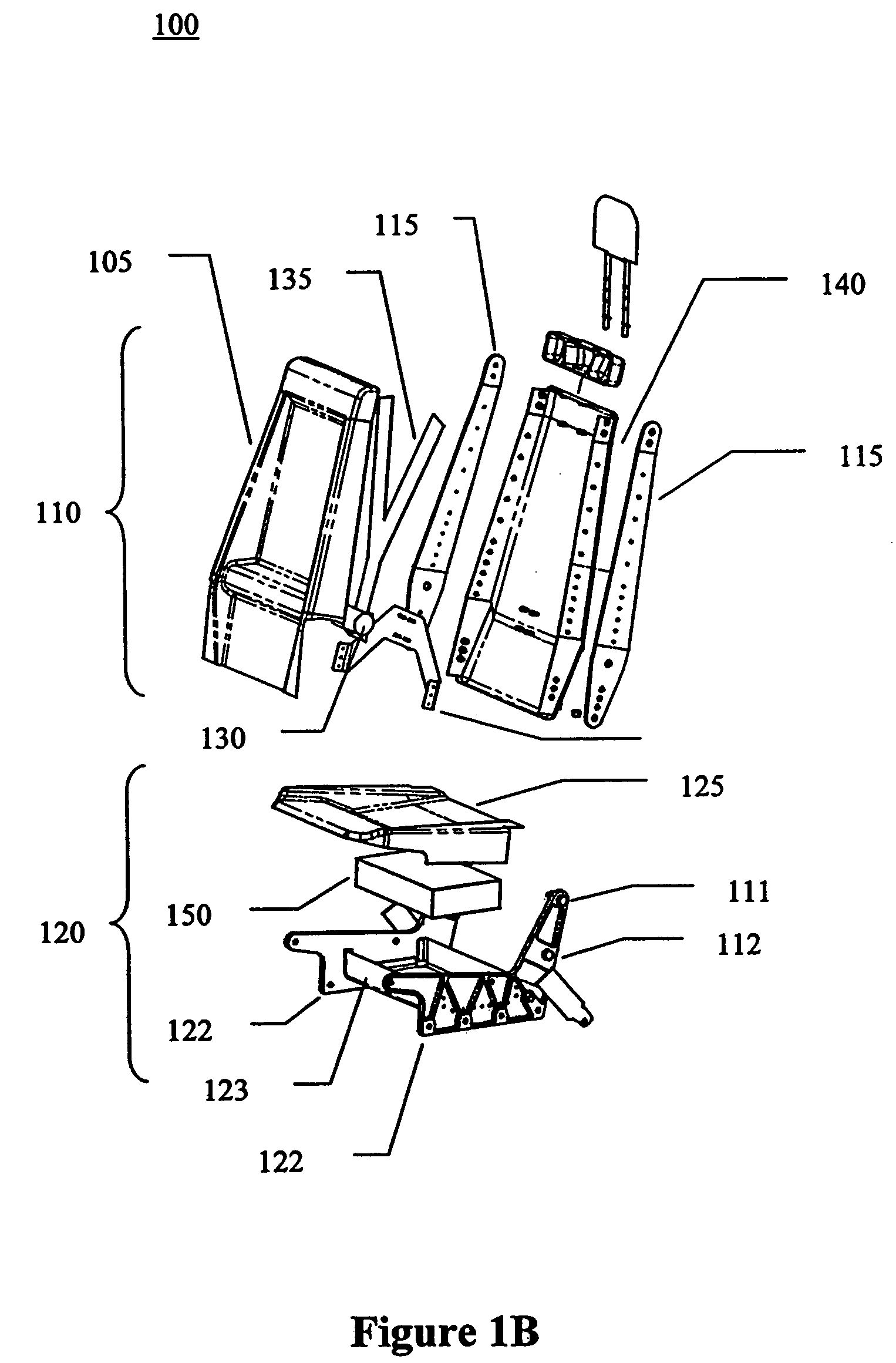
Hybrid composite-metal energy absorbing seat
InactiveUS7083230B2Design/aesthetic flexibilityVehicle seatsSupports/holding devicesEnergy absorptionEngineering
A hybrid composite-metal energy absorbing seat is described. According to one embodiment, an aircraft seat includes a seat base assembly and a seat back assembly. The seat base assembly includes multiple rigid metal seat base side frame elements joined by a lower seat pan, an energy absorbing element placed on the lower seat pan to deform and absorb downward energy in a crash, and a contoured seat pan whose sides extend past the seat base side frame elements and deform to absorb downward energy in a crash. The seat back assembly is attached to the seat base assembly and includes multiple rigid metal seat back side frame elements joined by a contoured composite seat back. The rigid metal seat back side frame elements absorb forward crash load energy by permanently deforming during a severe forward crash load. The contoured composite seat back provides design / aesthetic flexibility.
Owner:TRITON AEROSPACE
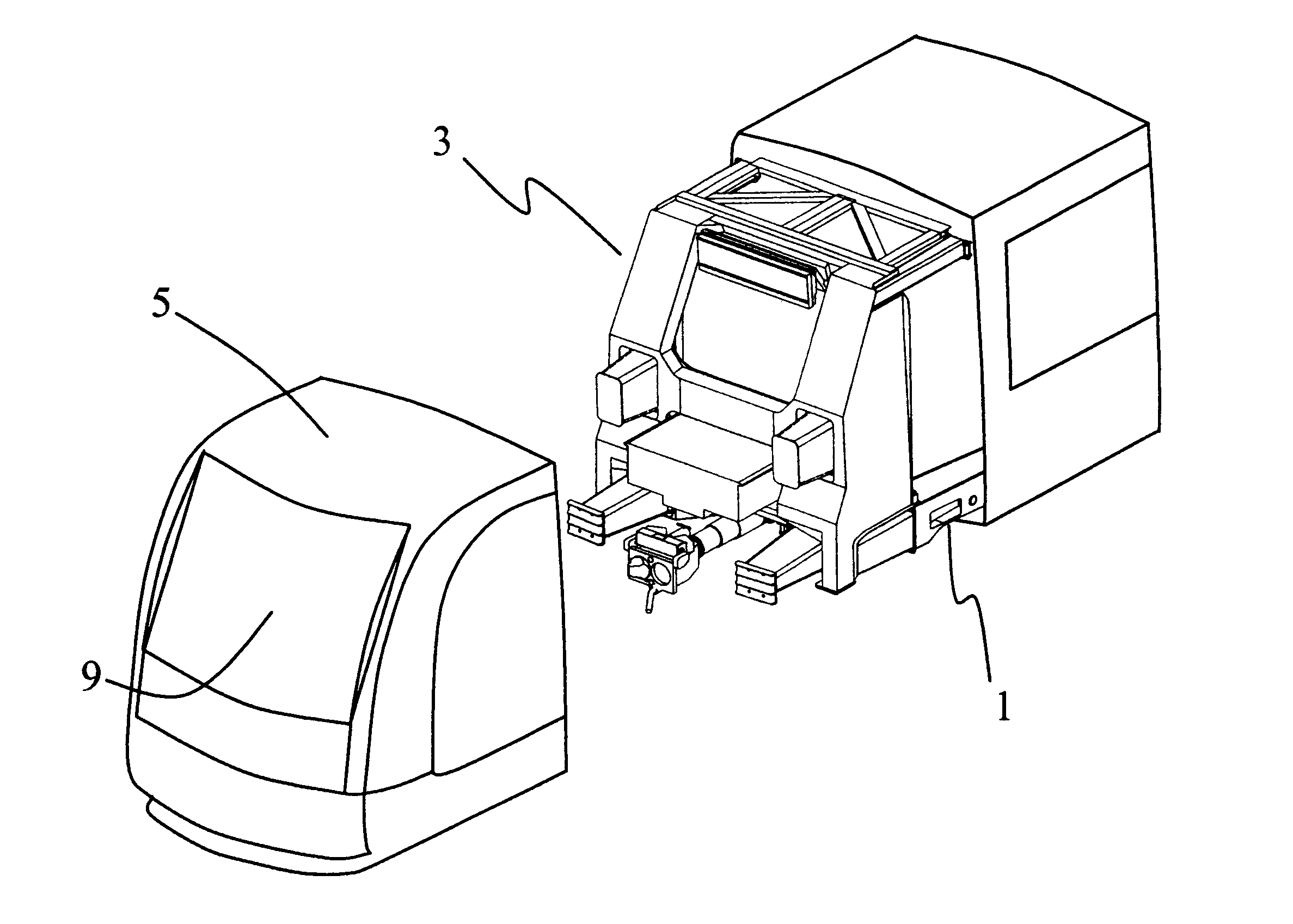
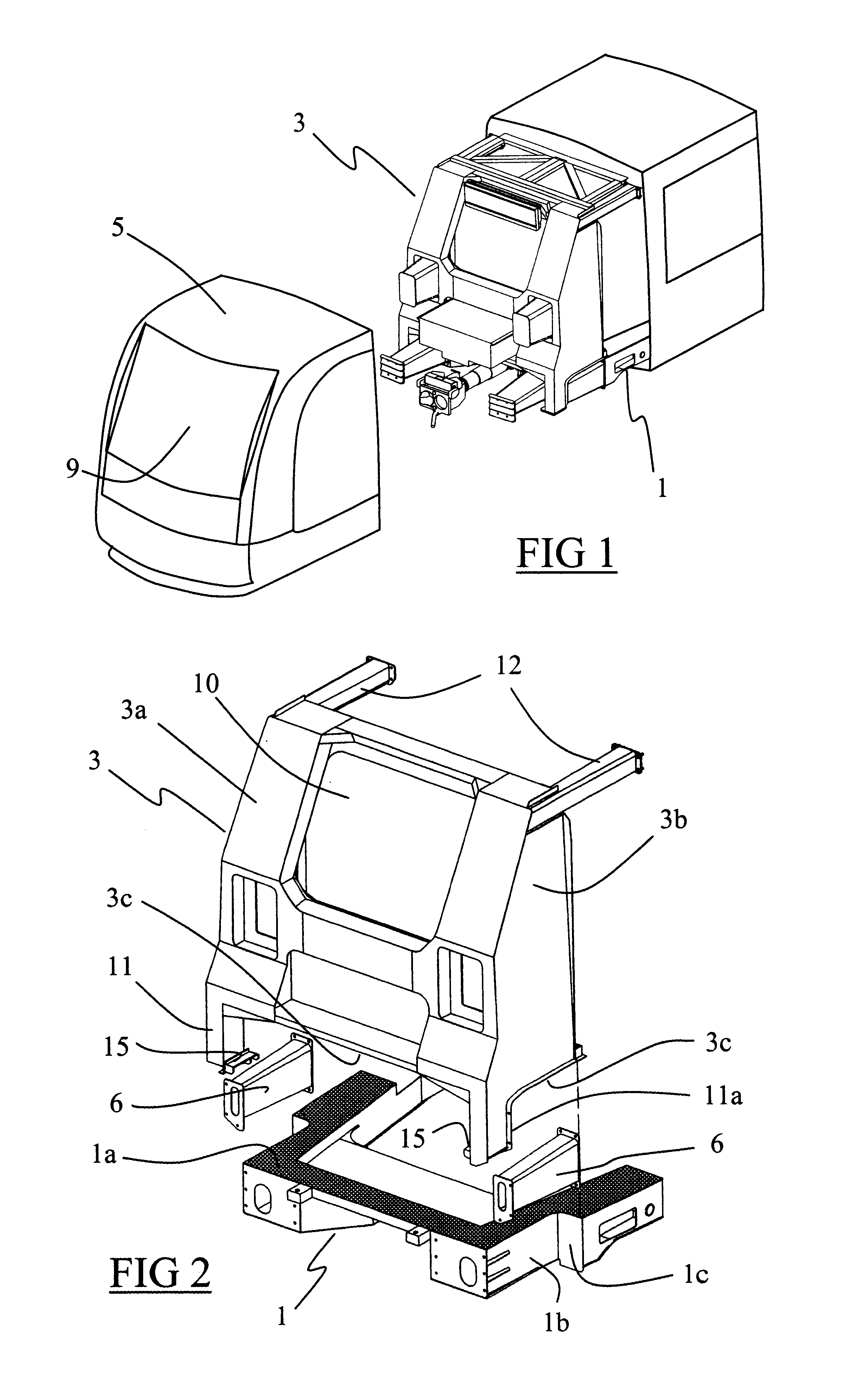
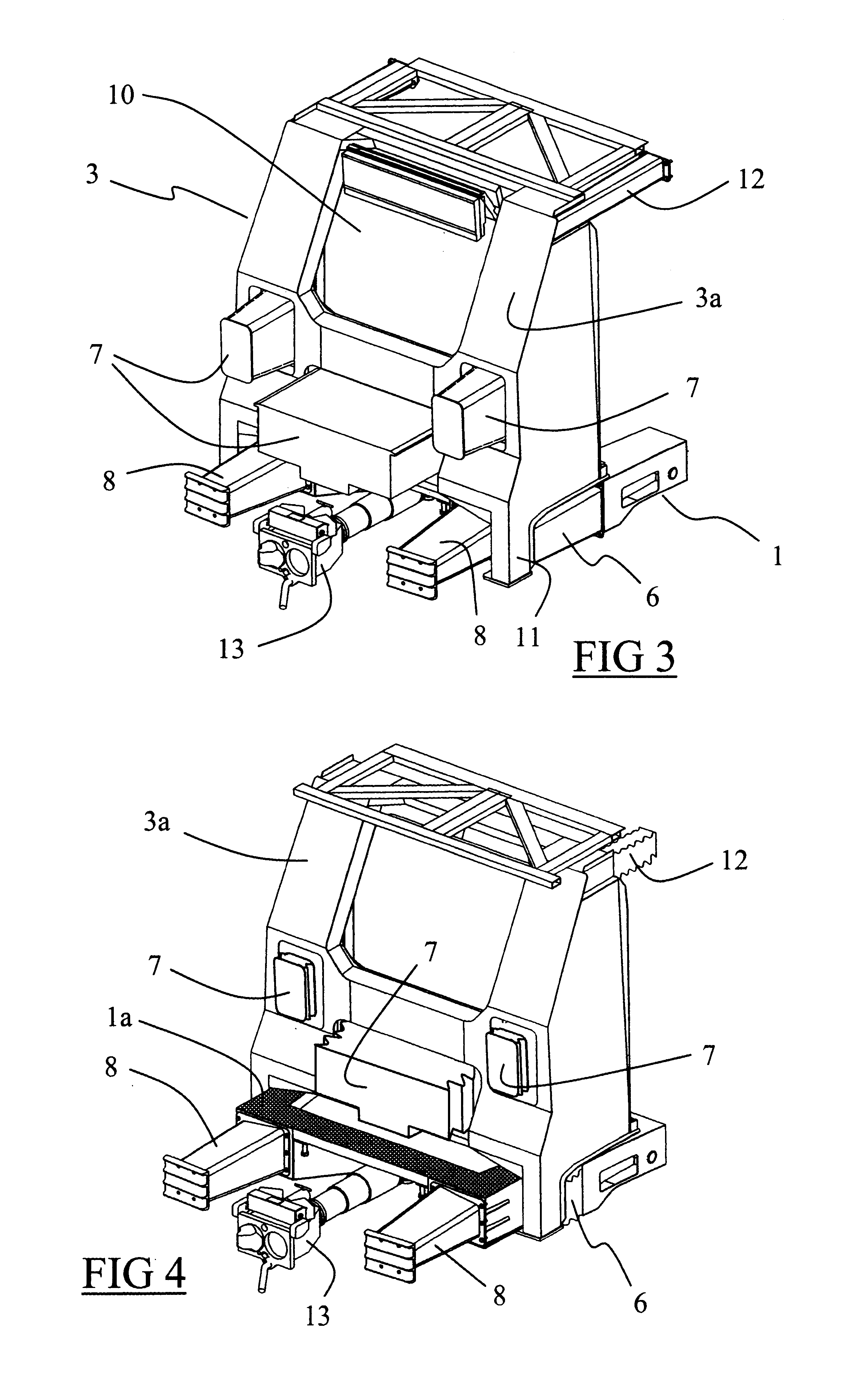
Rail vehicle having a driver's cab provided with an energy-absorbing structure adapted to cope with a collision above the frame of the vehicle
InactiveUS6561105B2Simple and inexpensive to implementMitigate such drawbackVehicle seatsRailway wheel guards/bumpersEnergy absorptionEngineering
Owner:ALSTOM TRANSPORT TECH SAS
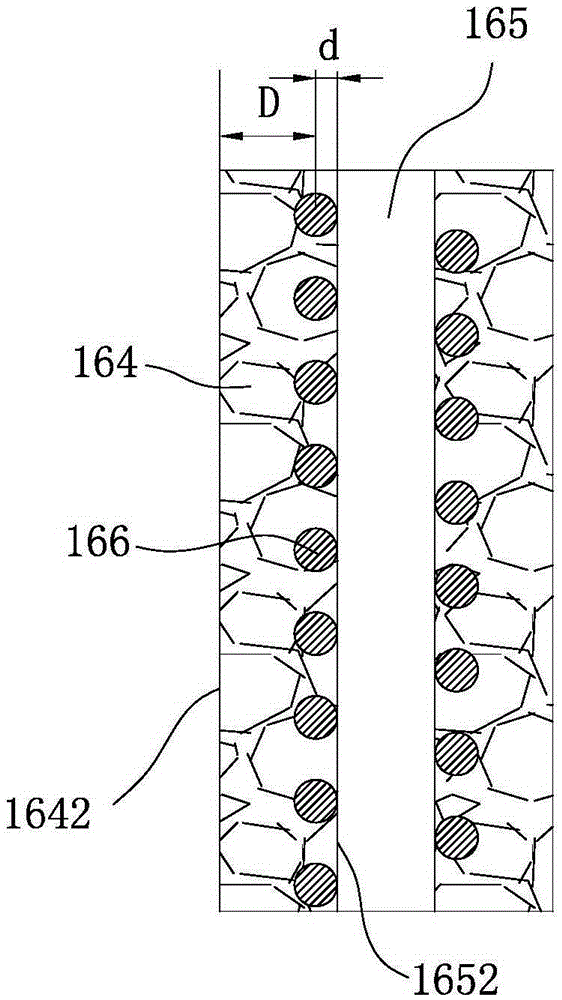
Ceramic wall-flow filter including heat absorbing elements and methods of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20060191248A1Large heat capacitySmall wall thicknessCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulatesHeat capacity
A ceramic wall-flow filter for filtering particulate matter from gases and methods for manufacturing such wall-flow filters are disclosed. The filter includes an array of porous ceramic walls defining a pattern of end-plugged inlet and outlet cells, and heat absorbing elements disposed within at least some of the outlet cells such that a bulk heat capacity of the outlet cells is greater than a bulk capacity of the inlet cells. The heat absorbing elements increase a bulk heat capacity of the filter without substantially interfering with a flow of gas through the porous ceramic walls by allowing thinner walls. According to the method, during the step of extruding or thereafter, heat absorbing elements are formed within at least some of the outlet cells such that a heat capacity of the outlet cells is greater than the inlet cells.
Owner:CORNING INC
Protective circuit and method for multi-level converter
ActiveUS20080291708A1Efficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsControl signalEngineering
A protective circuit for a multi-level converter including a DC link capacitor bank includes: an energy absorbing element; switches, wherein at least two of the switches each couple the energy absorbing element to the capacitor bank; and a controller configured to provide control signals to the switches to selectively actuate the switches to enable control of energy dissipation and to enable control of voltage balance on the capacitor bank of the multi-level converter.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Article with a ceramic coating and method for producing such an article using a laser
InactiveUS20110198358A1Low melting pointPoint becomes highCooking-vessel materialsRadiation applicationsCeramic coatingLength wave
An article comprising a metal support with two opposing faces at least one of which is covered by a discontinuous ceramic coating. Said coating has a softening point above the melting point of the support and has at least one absorbing element for the laser radiation at a wavelength of the order of 1 μm, being at least 1% of the weight of said coating. The invention further relates to a method for producing said article.
Owner:SEB SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com