Patents
Literature
154results about How to "Short focal length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
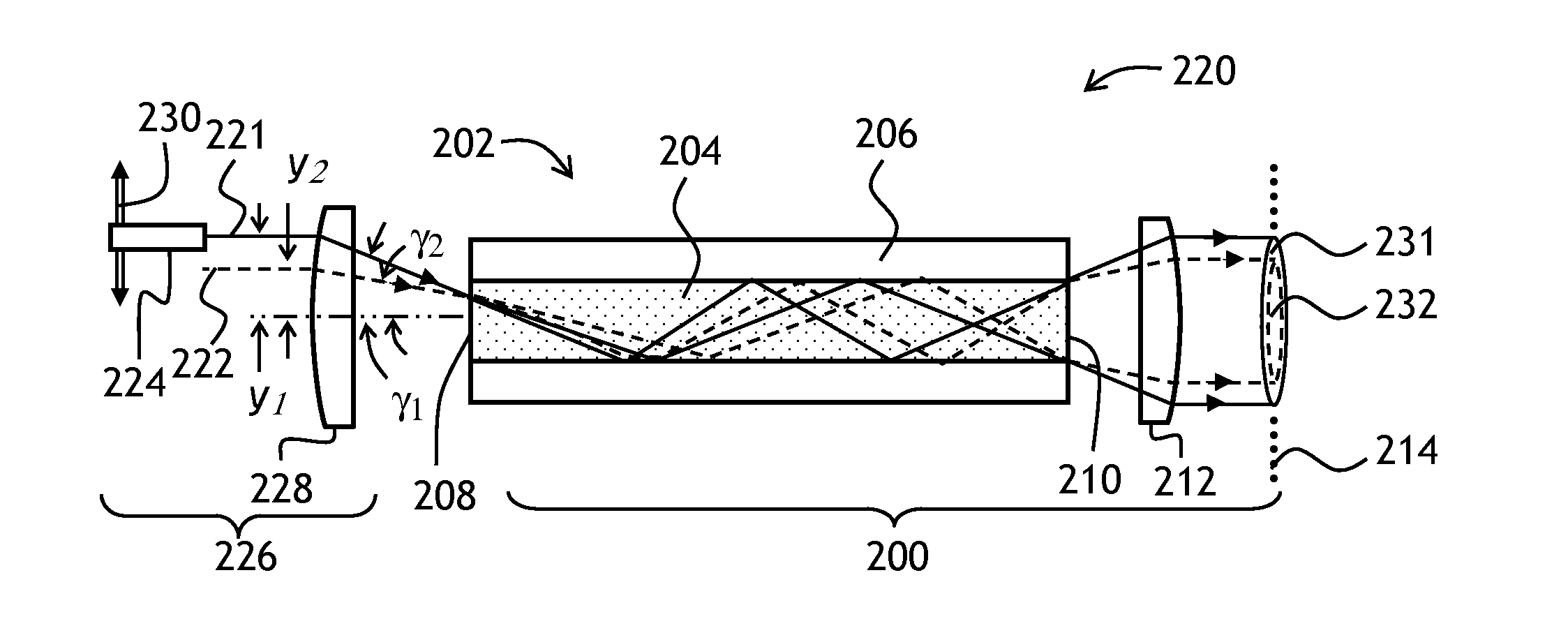
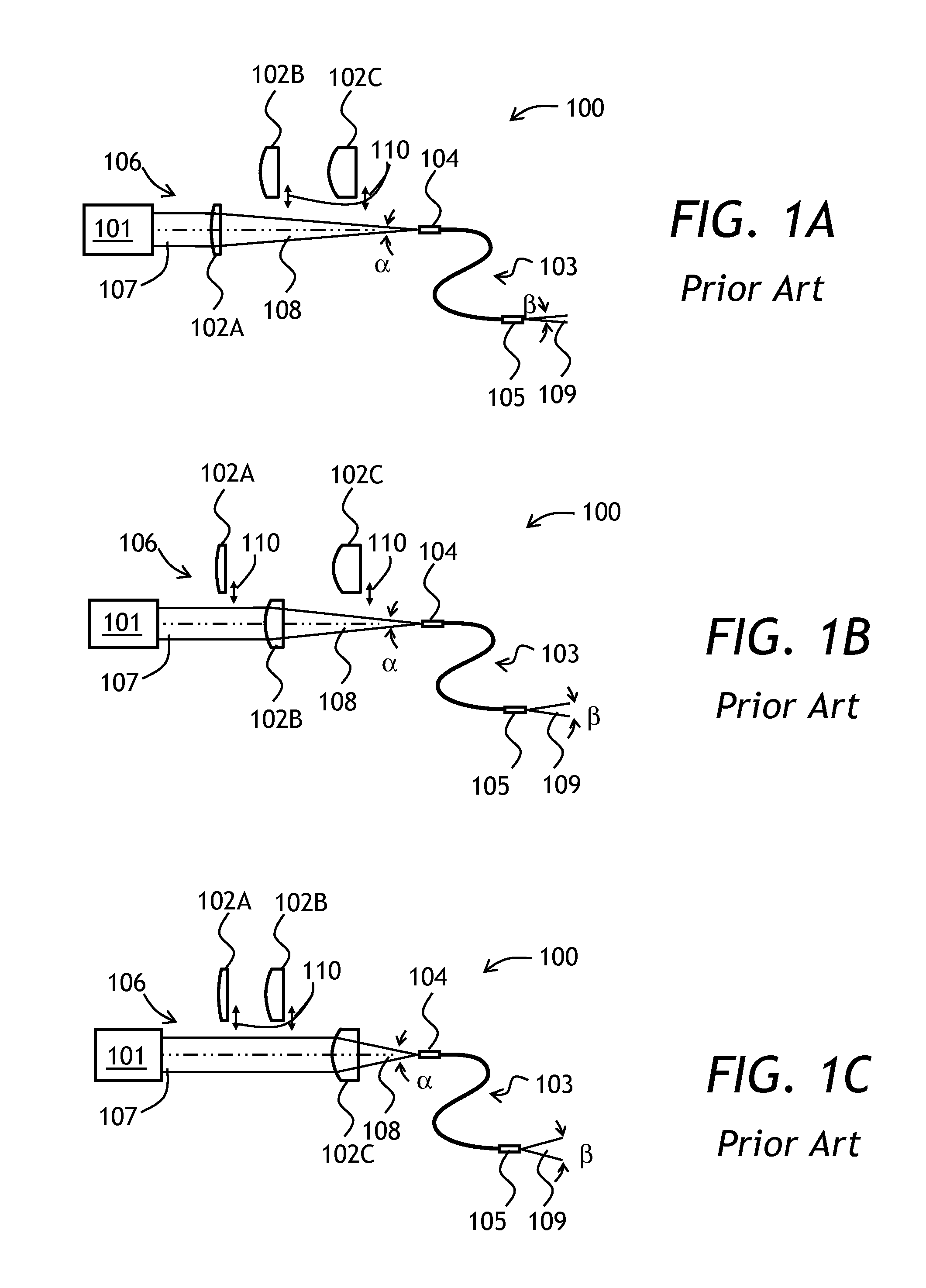
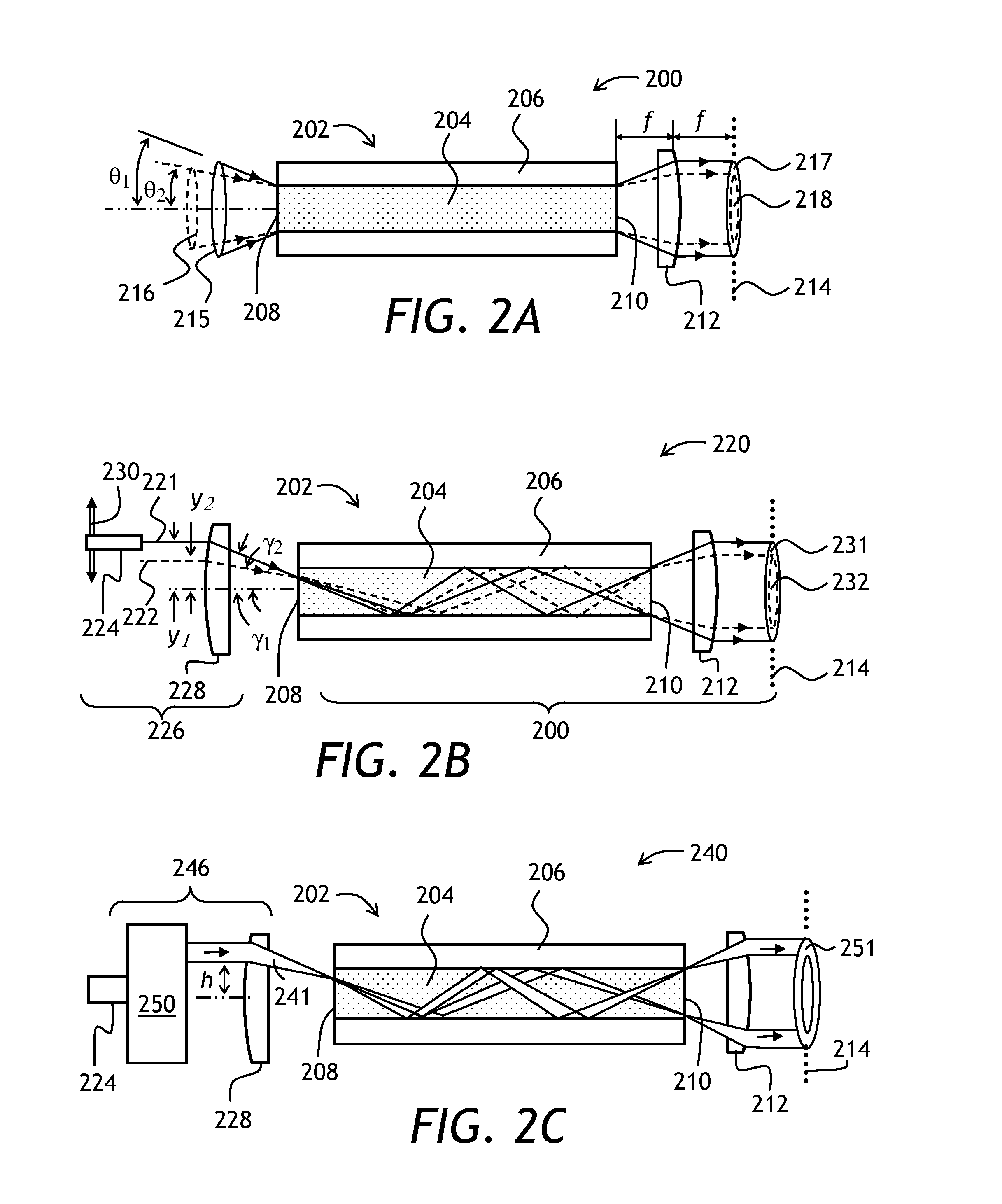
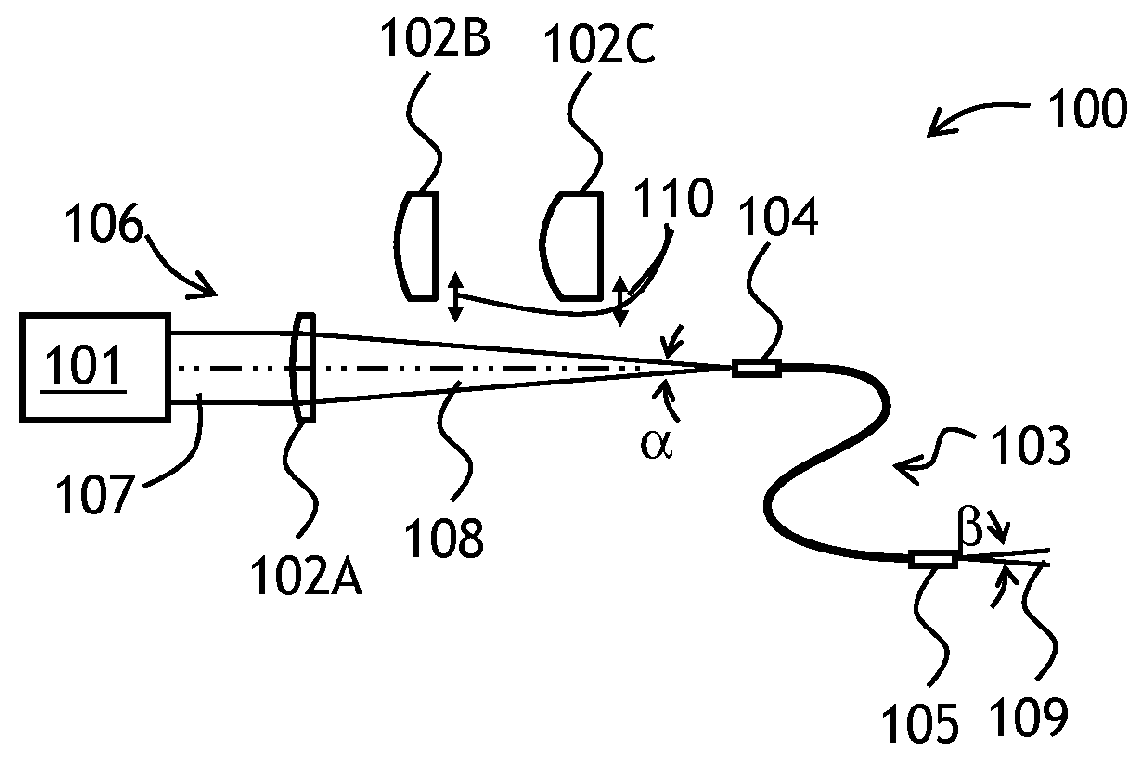
Varying beam parameter product of a laser beam
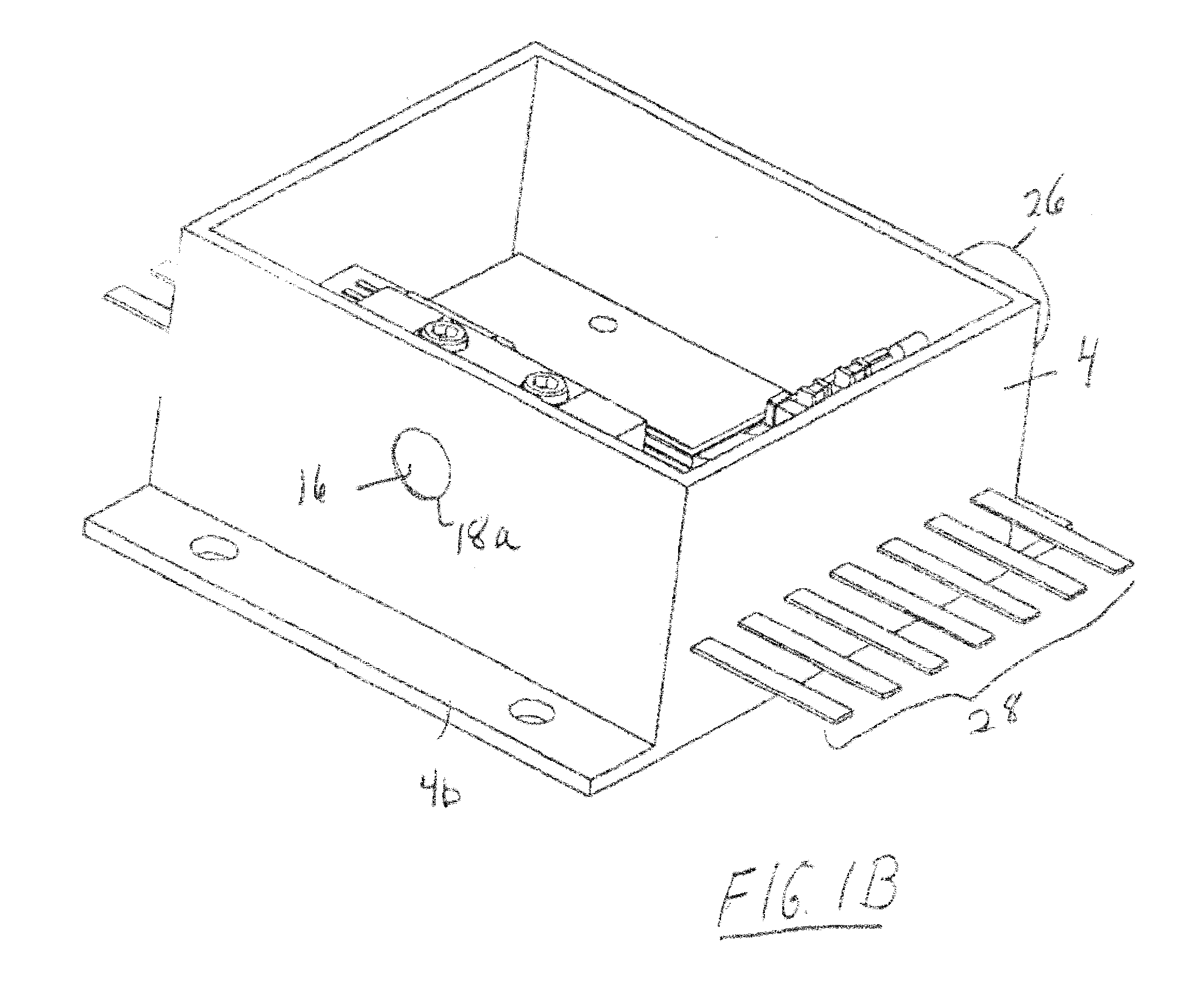
ActiveUS20130148925A1Short focal lengthClear processLaser detailsCoupling light guidesLaser processingLight beam
An optical delivery waveguide for a material laser processing system includes a small lens at an output end of the delivery waveguide, transforming laser beam divergence inside the waveguide into a spot size after the lens. By varying the input convergence angle and / or launch angle of the laser beam launched into the waveguide, the output spot size can be continuously varied, thus enabling a continuous and real-time laser spot size adjustment on the workpiece, without having to replace the delivery waveguide or a process head. A divergence of the laser beam can also be adjusted dynamically and in concert with the spot size.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Varying beam parameter product of a laser beam
An optical delivery waveguide for a material laser processing system includes a small lens at an output end of the delivery waveguide, transforming laser beam divergence inside the waveguide into a spot size after the lens. By varying the input convergence angle and / or launch angle of the laser beam launched into the waveguide, the output spot size can be continuously varied, thus enabling a continuous and real-time laser spot size adjustment on the workpiece, without having to replace the delivery waveguide or a process head. A divergence of the laser beam can also be adjusted dynamically and in concert with the spot size.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Device, image processing device and method for optical imaging
ActiveUS8629930B2Short focal lengthReduction of building lengthTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingGrating
An optical device for imaging is disclosed having at least one micro lens field with at least two micro lenses and one image sensor with at least two image detector matrices. The at least two image detector matrices each include a plurality of image detectors and there is an allocation between the image detector matrices and the micro lenses, so that each micro lens together with an image detector matrix forms an optical channel. The center points of the image detector matrices are shifted laterally by different distances, with respect to centroids, projected onto the image detector matrices, of the micro lens apertures of the associated optical channels, so that the optical channels have different partially overlapping detection areas and so that an overlapping area of the detection areas of two channels is imaged onto the image detector matrices offset with respect to an image detector raster of the image detector matrices. Further, an image processing device and a method for optical imaging are described.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Effective method to improve sub-micron color filter sensitivity
ActiveUS20050242271A1High sensitivityLong focal lengthTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesColor gelPhotodiode
An image sensor device and method for forming said device are described. The image sensor structure comprises a substrate with photodiodes, an interconnect structure formed on the substrate, a color filter layer above the interconnect structure, a first microlens array, an overcoat layer, and a second microlens array. A key feature is that a second microlens has a larger radius of curvature than a first microlens. Additionally, each first microlens and second microlens is a flat convex lens. Thus, a thicker second microlens with a short focal length is aligned above a thinner first microlens having a long focal length. A light column that includes a first microlens, a second microlens and a color filter region is formed above each photodiode. A second embodiment involves replacing a second microlens in each light column with a plurality of smaller second microlenses that focus light onto a first microlens.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
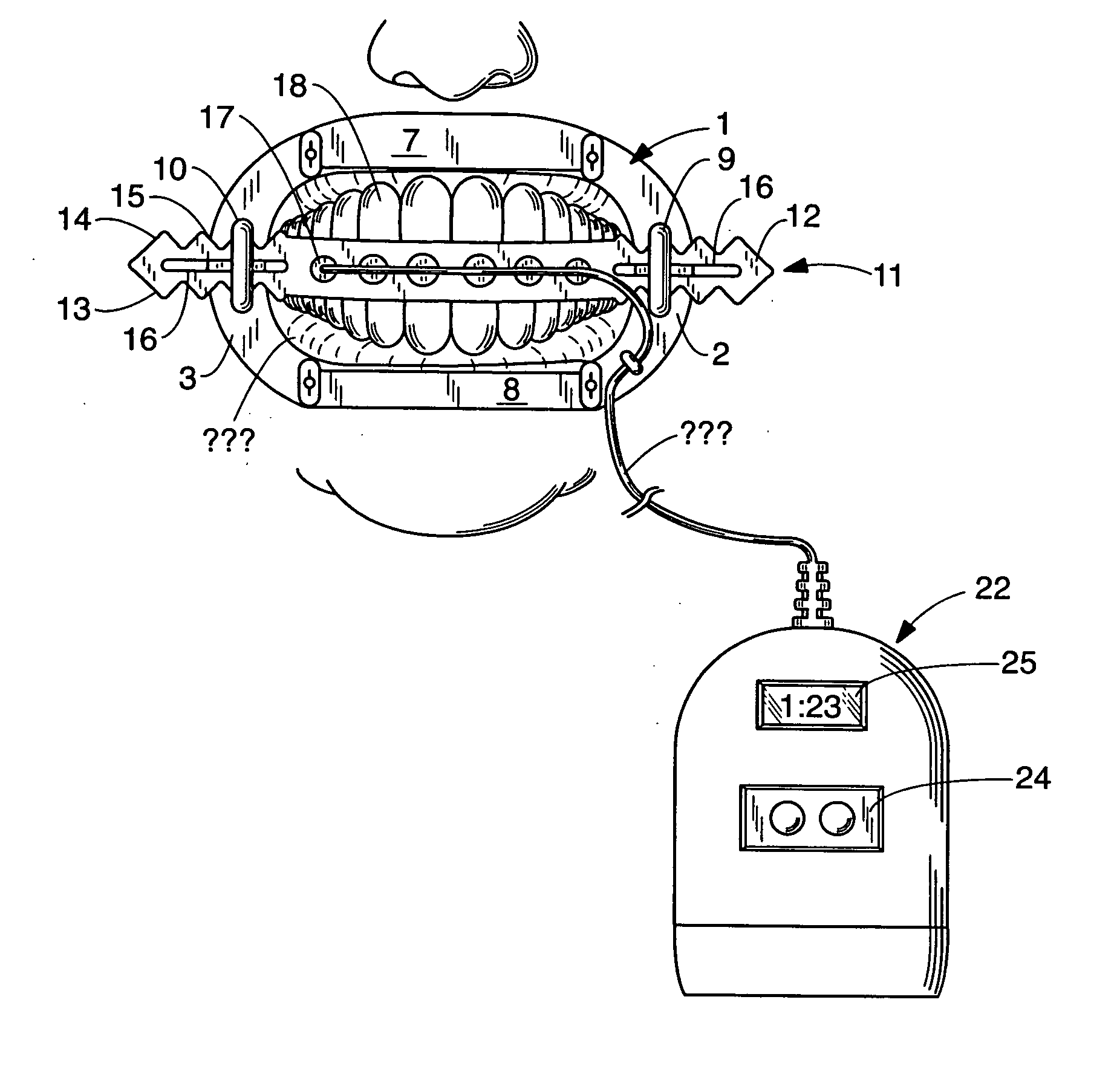
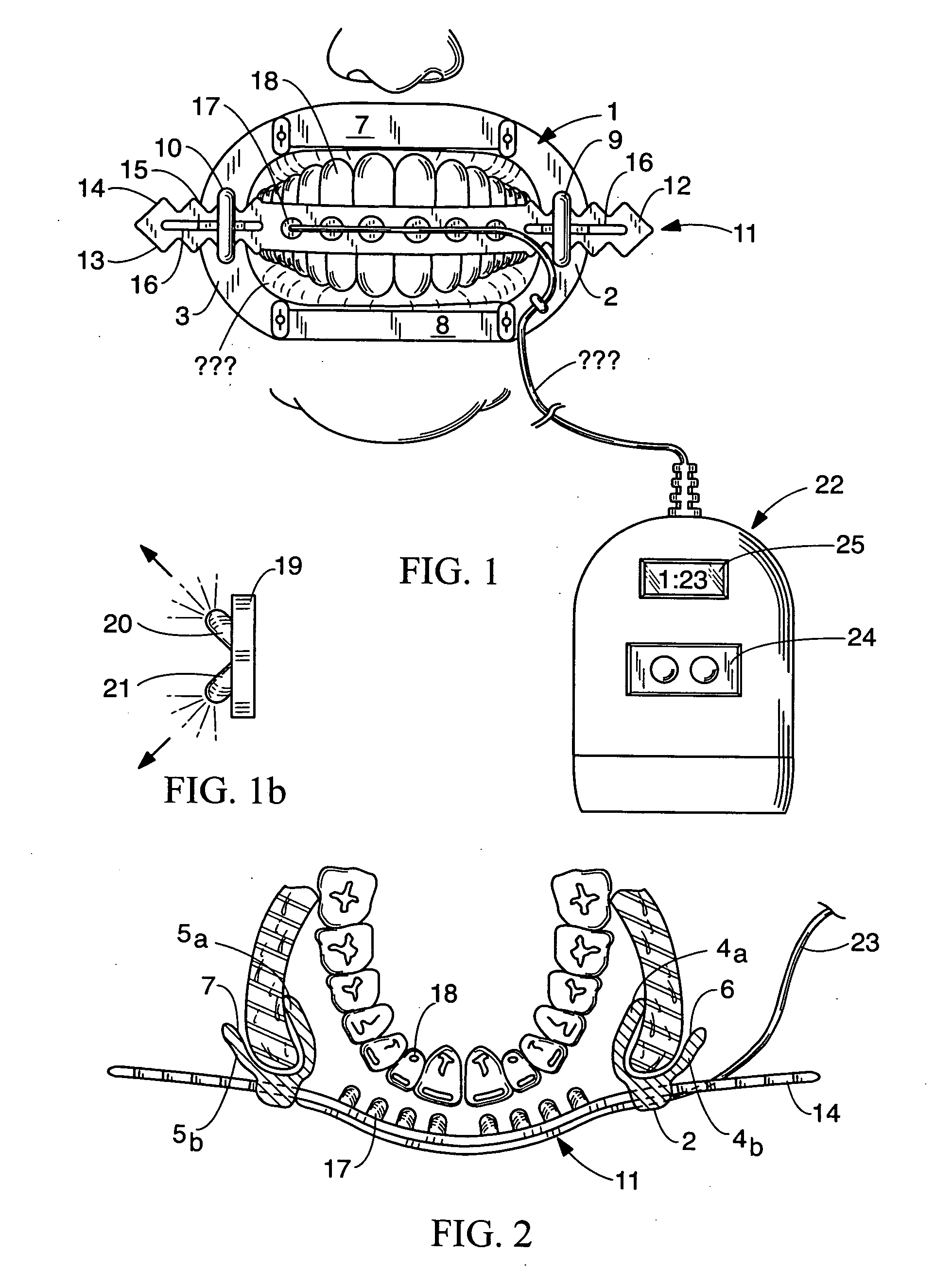
Tooth whitening device
InactiveUS20060003284A1Simple processEasily toleratedDental toolsLip/mouth protectorsHead movementsElectricity
The invention is a locally mounted light source for light activation of tooth whitening compositions. A support in the form of a bridge attached to a retractor or as part of a mouth guard has integral therewith, a small and lightweight light source, such as could be provided by one or more high-intensity LED's, though other light sources could be used. The light source may be in the form of an array, powered by either a direct electrical connection to a power supply or by battery power, for example, with a battery pack worn by the user. The light source is thus located in proximity to the tooth surfaces regardless of head movement or orientation, increasing user mobility and comfort.
Owner:PROFESSIONAL DENTAL TECH
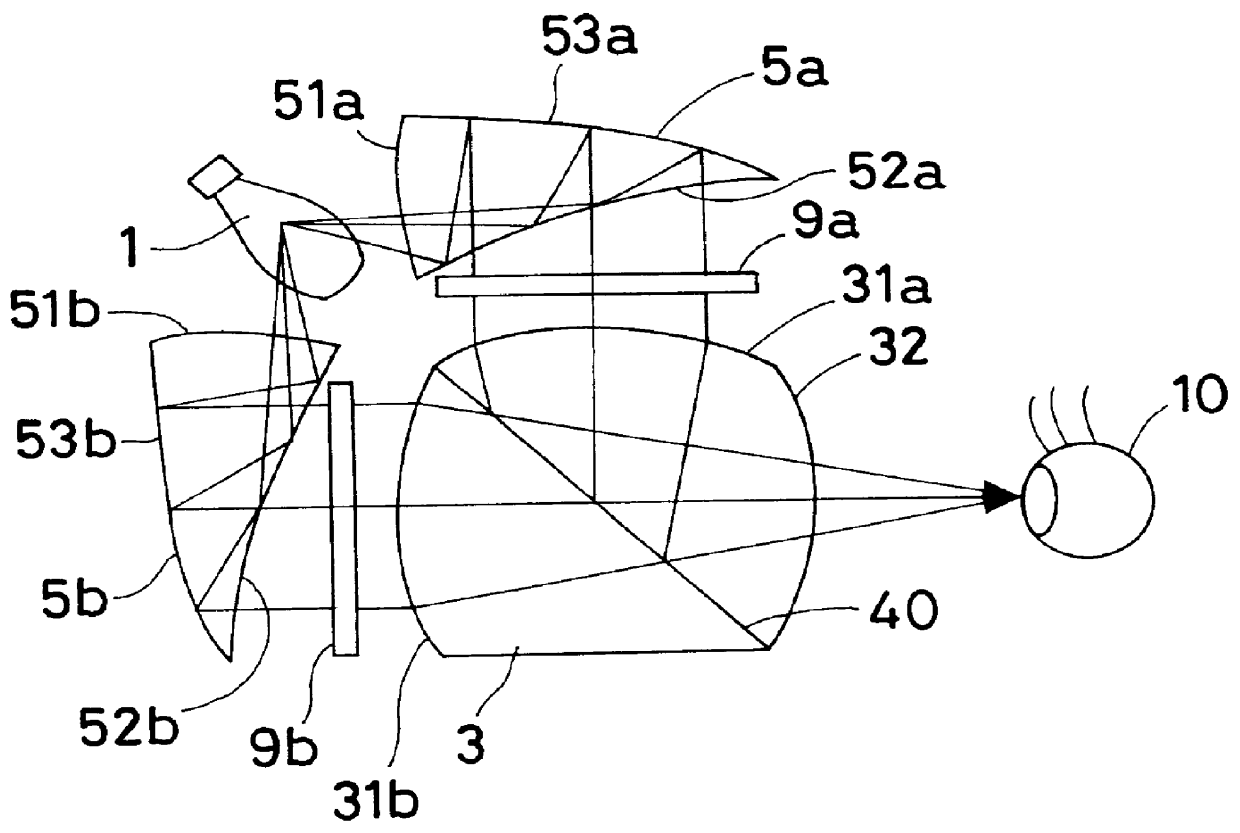
Resolution enhancing image display apparatus
InactiveUS6130784AClear and beautiful imageHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage resolutionVirtual image
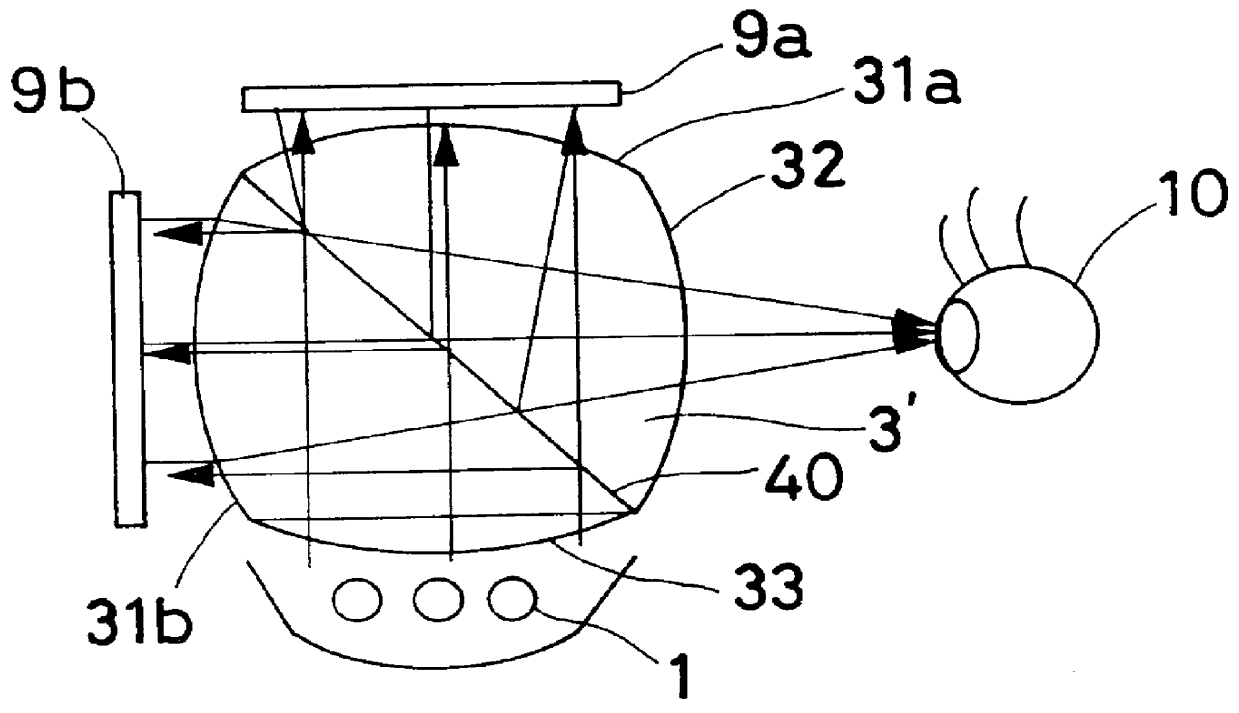
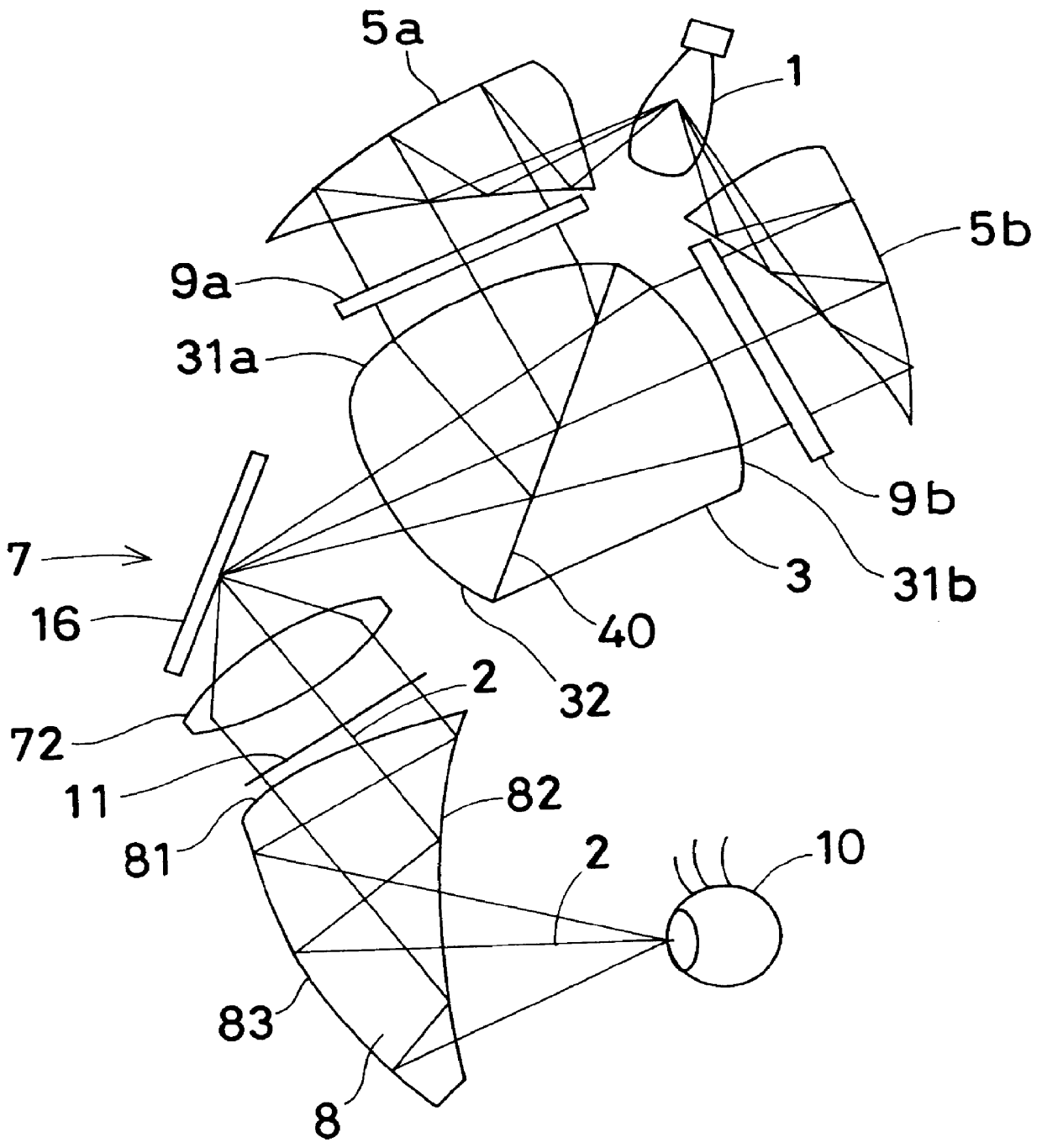
An image display apparatus that presents an observer an image of higher resolution than the original resolution of an image display device used, thereby allowing the observer to view a clear and beautiful image. An illuminating optical system (5) illuminates an image display device with illuminating light from a light source (1). The image display device displays an image by transmission or reflection of the illuminating light. A viewing optical system leads the image to an observer's eyeball (10). The apparatus has two image display devices (9a and 9b). An optical coupling / separating element having a light-coupling or light-separating action is provided between the image display devices (9a and 9b) and the observer's eyeball (10) to superimpose images of the two image display devices on one another. The optical coupling / separating element has an optical coupling / separating surface (40) tilted at an angle of approximately 45 degrees with respect to each of the image display devices (9a and 9b). The viewing optical system projects the superimposed images into one eyeball (10) of the observer as an enlarged virtual image.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Compact mid-IR laser
ActiveUS20070291804A1Enhanced cooling techniqueLight weightLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor laser optical deviceThermoelectric coolingAspheric lens
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes a quantum cascade laser to provide mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser is thermally coupled.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
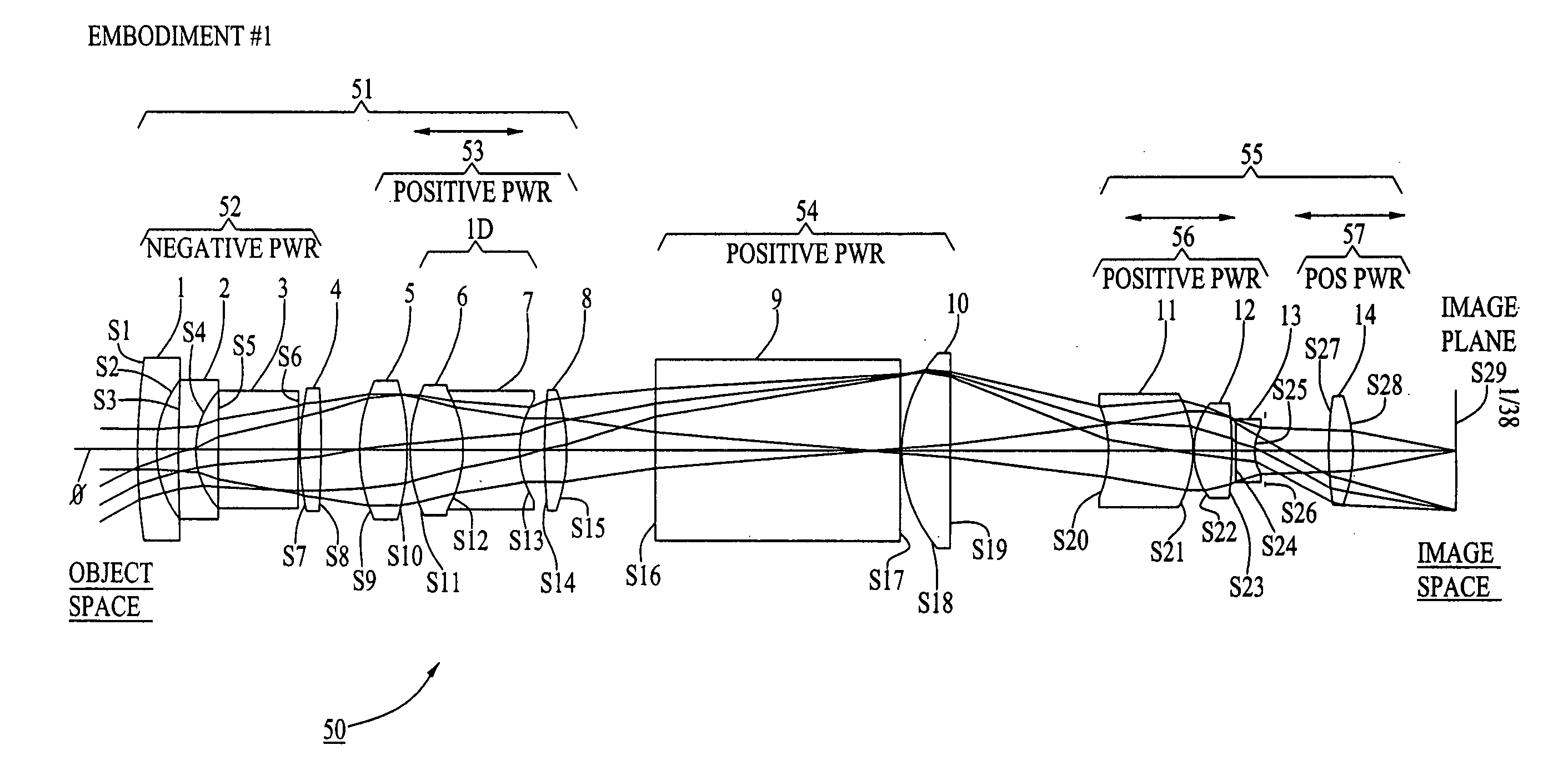
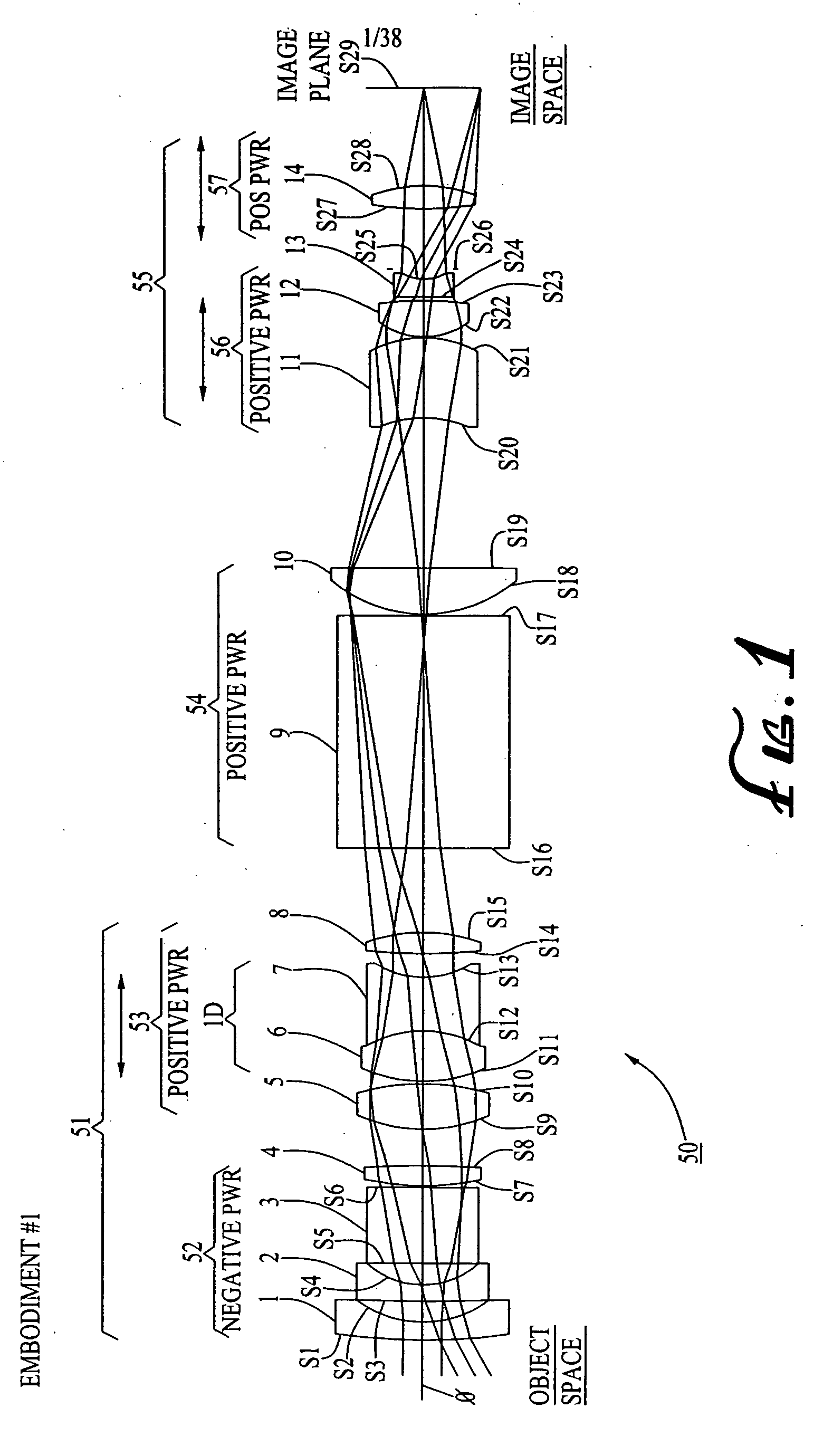
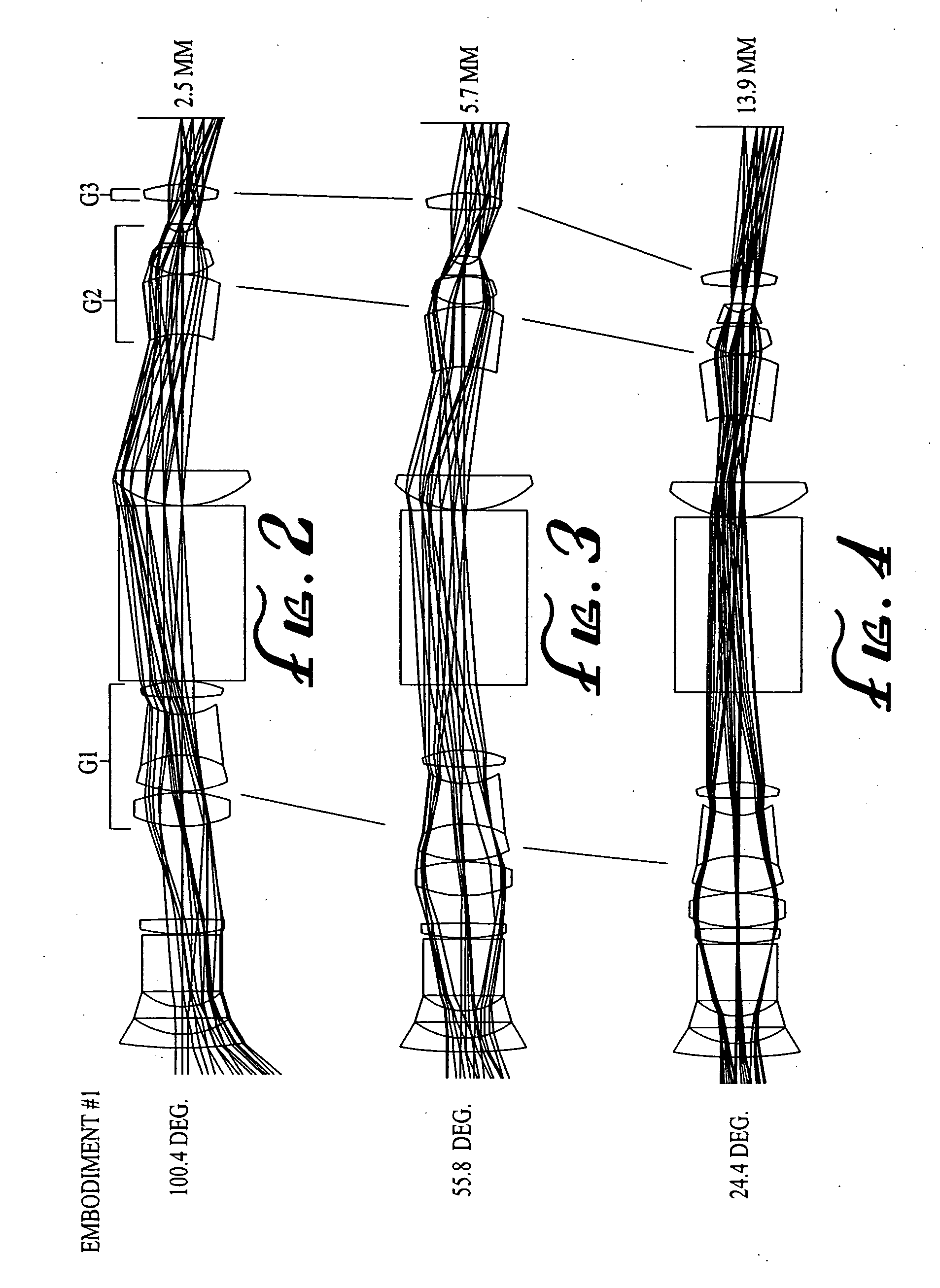
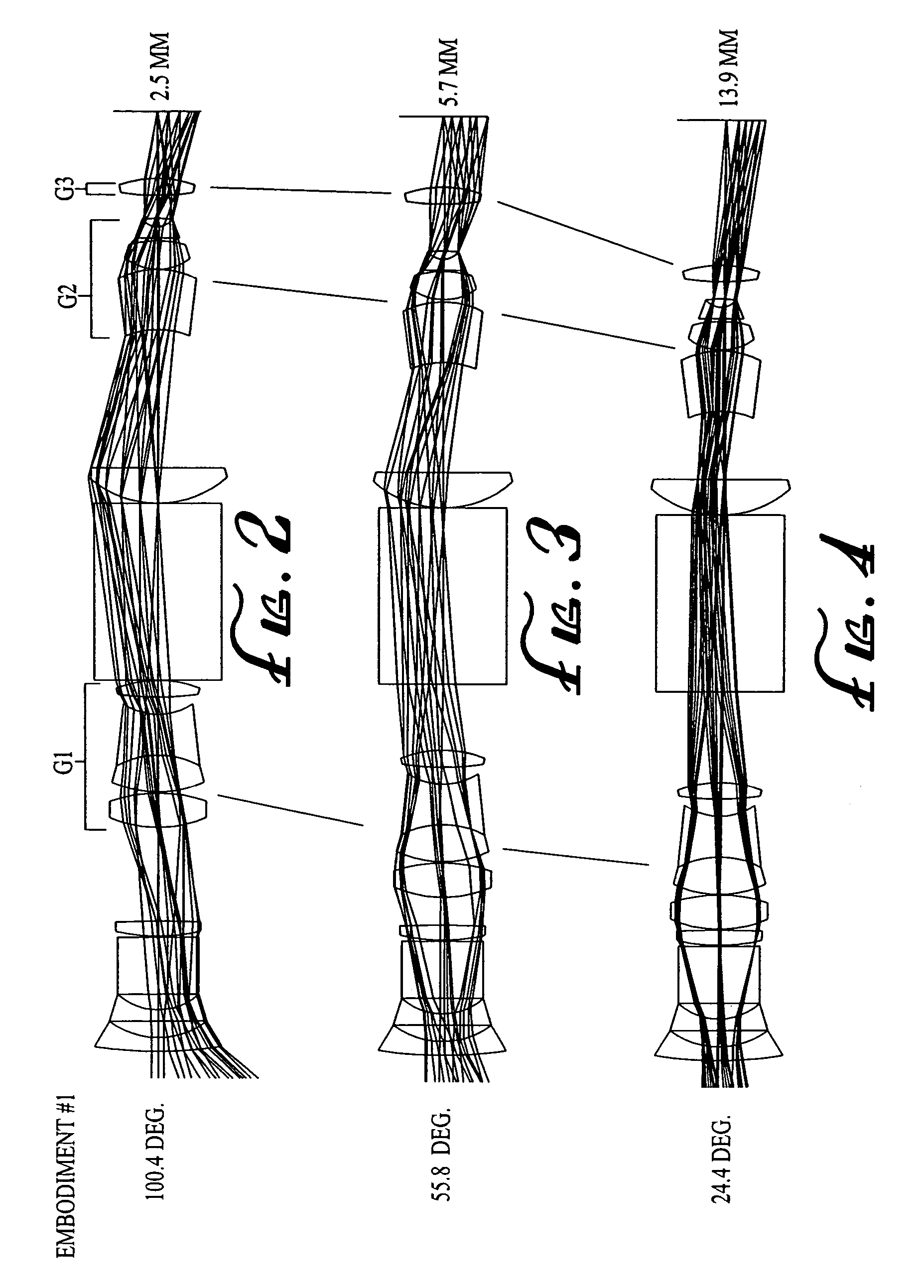
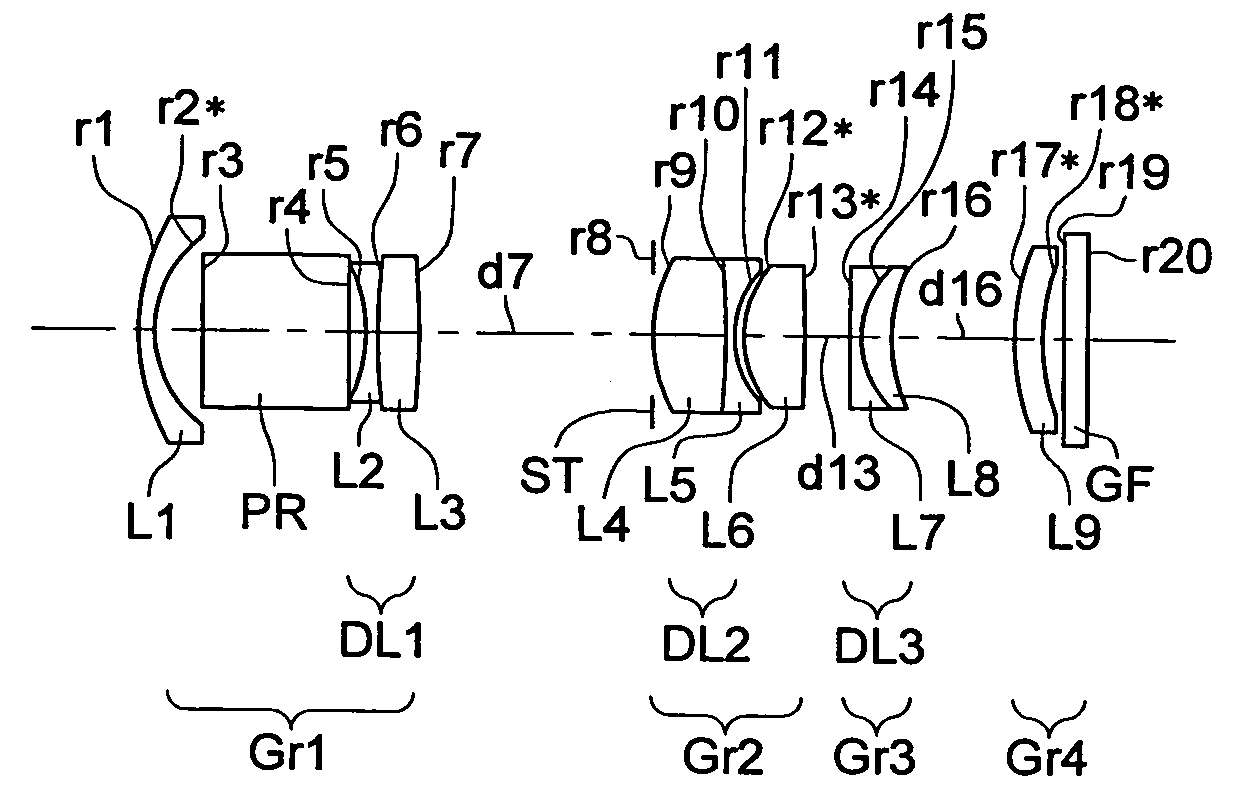
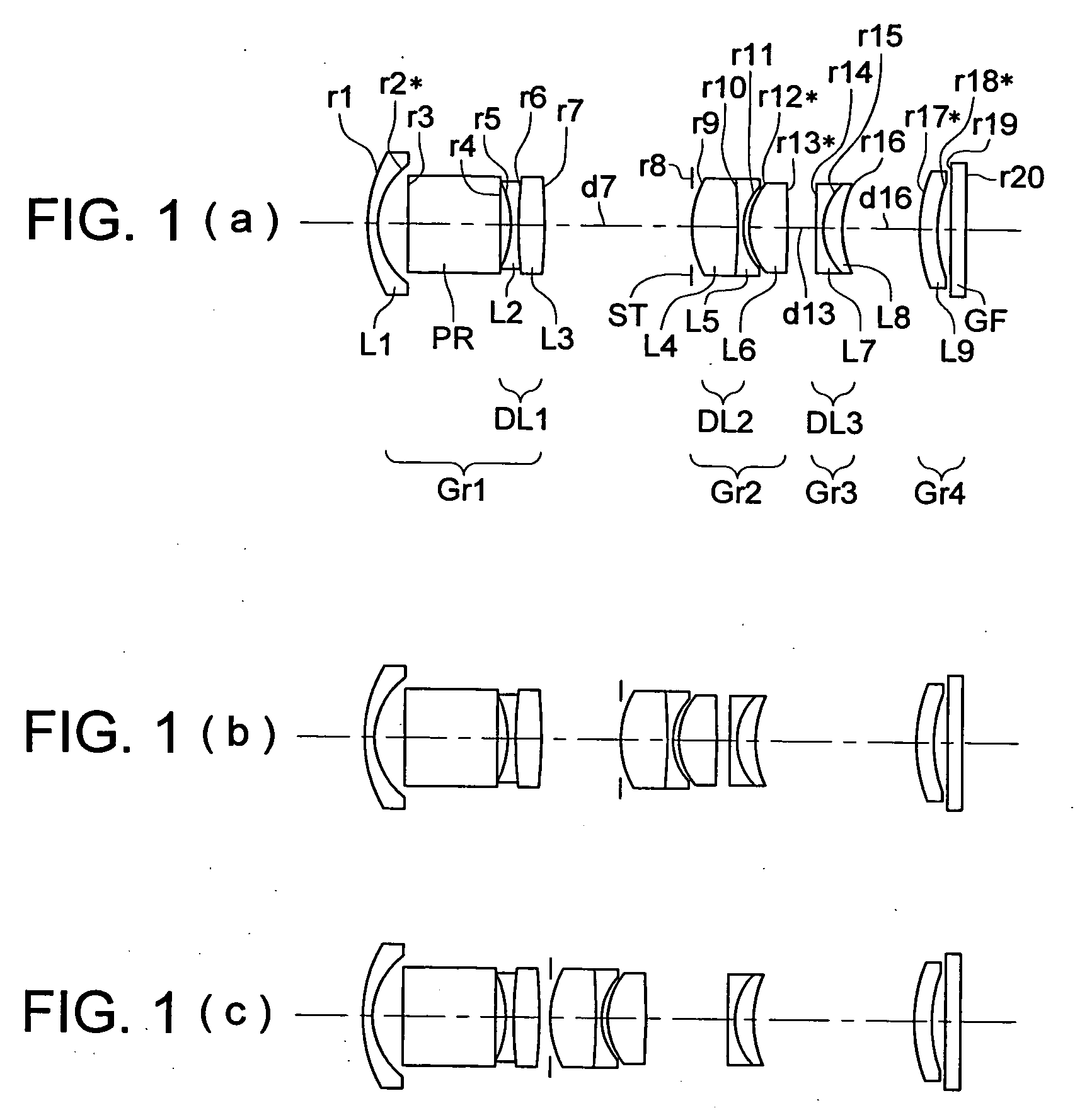
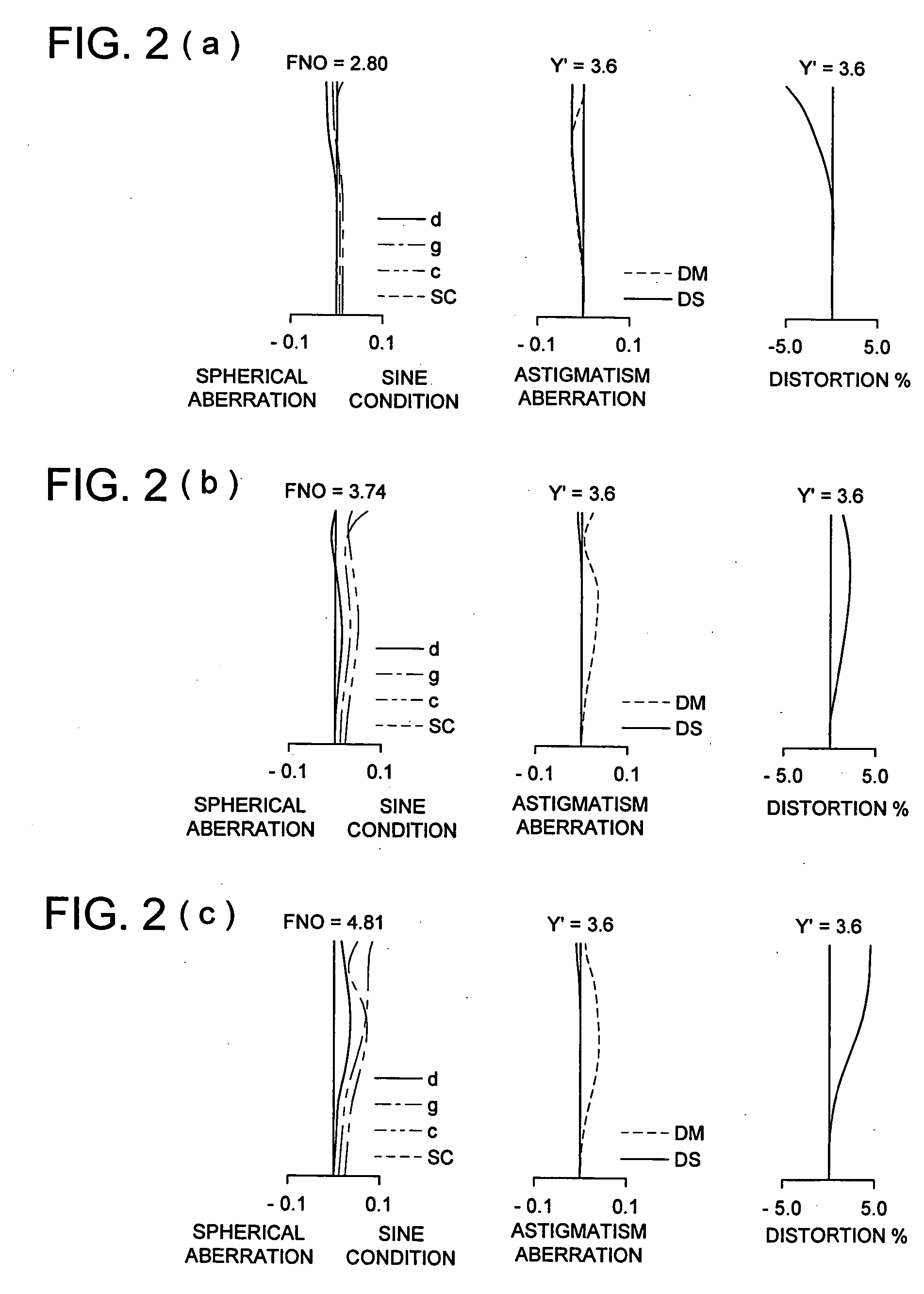
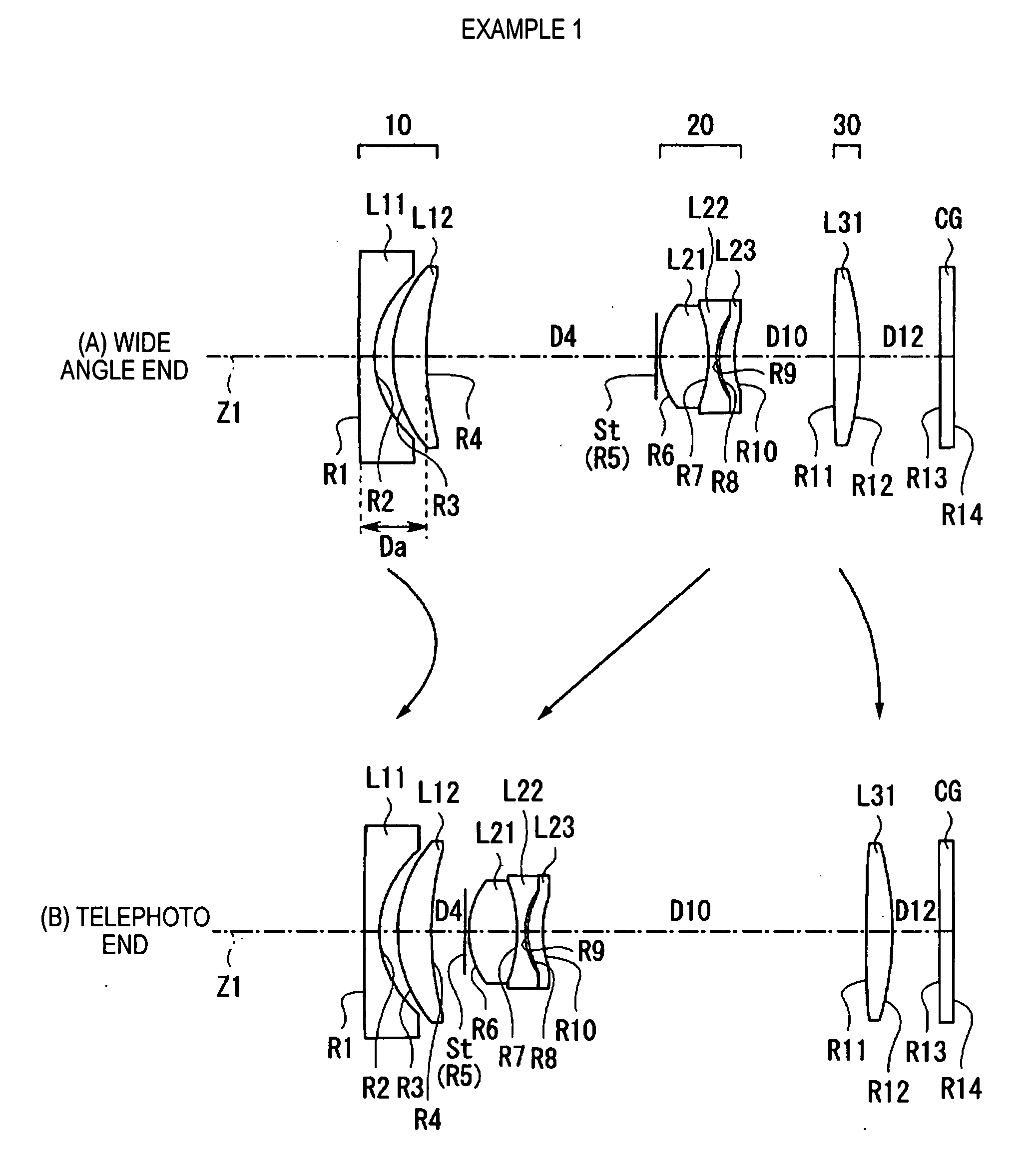
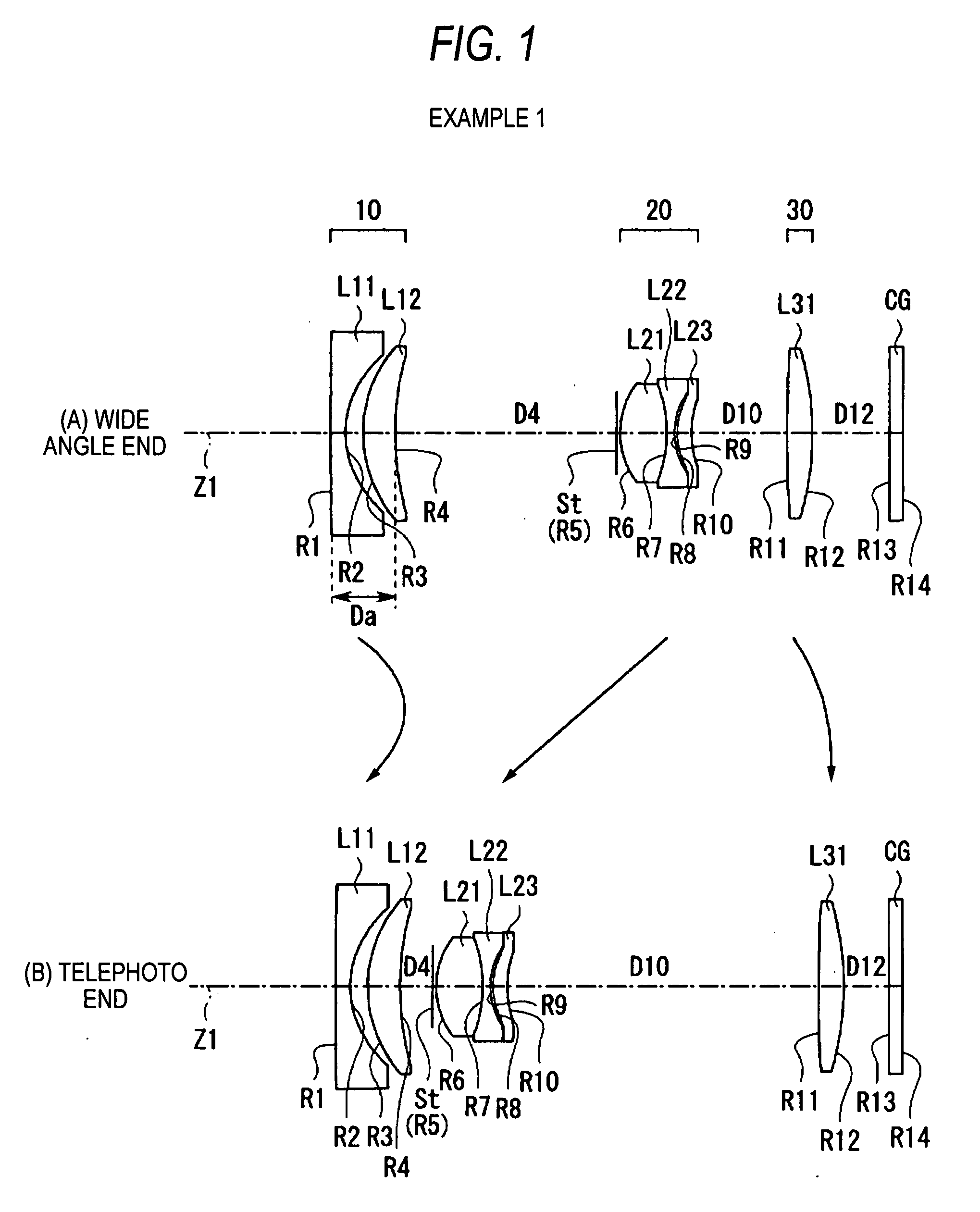
Wide-range, wide-angle compound zoom with simplified zooming structure
A zoom lens is disclosed having a zoom ratio larger than four with a field of view at the short focal length position larger than 85 degrees and with a minimal number of moving groups. The zoom lens utilizes a compound zoom structure comprising an NP or NPP zoom kernel followed by a P or PP zoom relay, with only two or three moving groups that can be used for both zooming, focusing and athermalization. An overall compact package size is achieved by the use of prisms to fold the optical path in strategic locations. An optional variable power liquid cell can provide close focusing with little or no focus breathing.
Owner:PANAVISION INT LP +1
Compact mid-IR laser
ActiveUS7492806B2Guaranteed uptimeSmall portabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionThermoelectric coolingAspheric lens
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
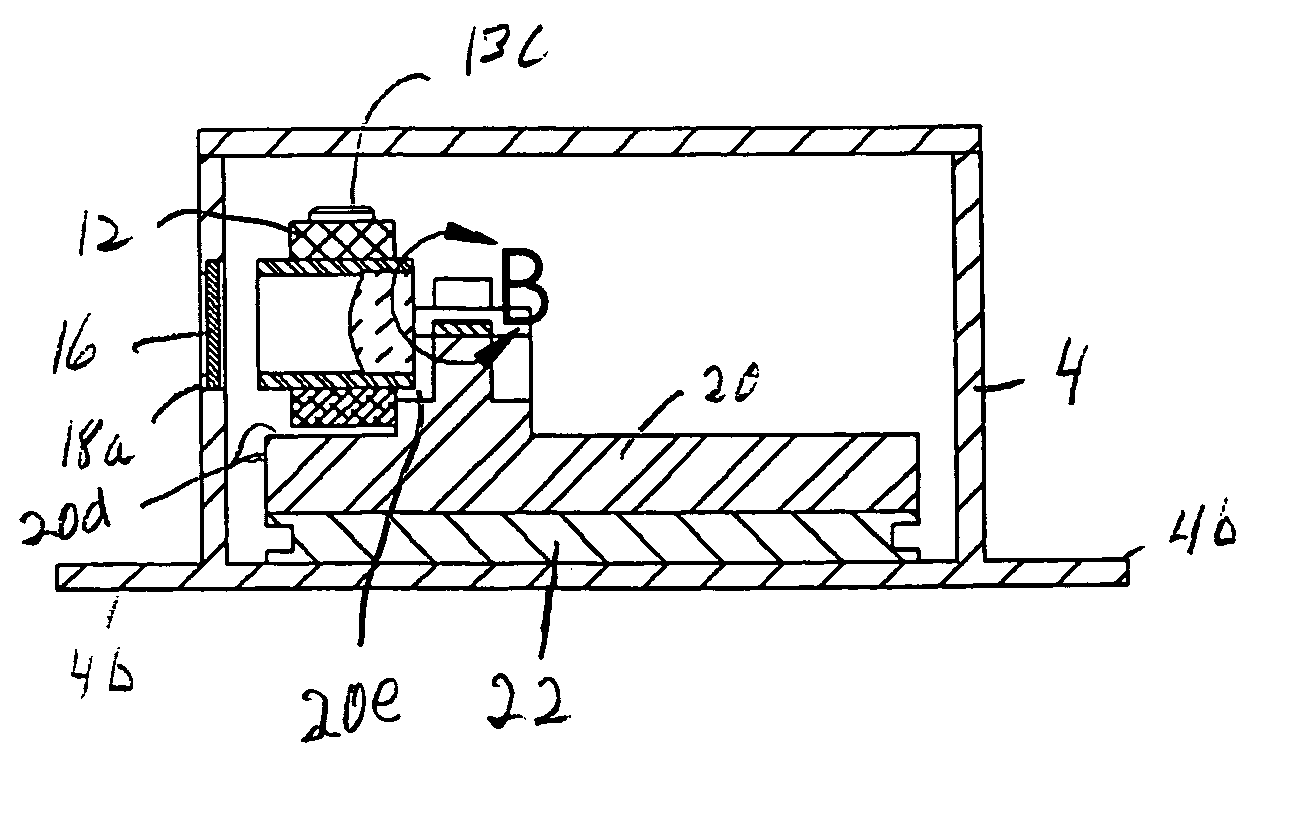
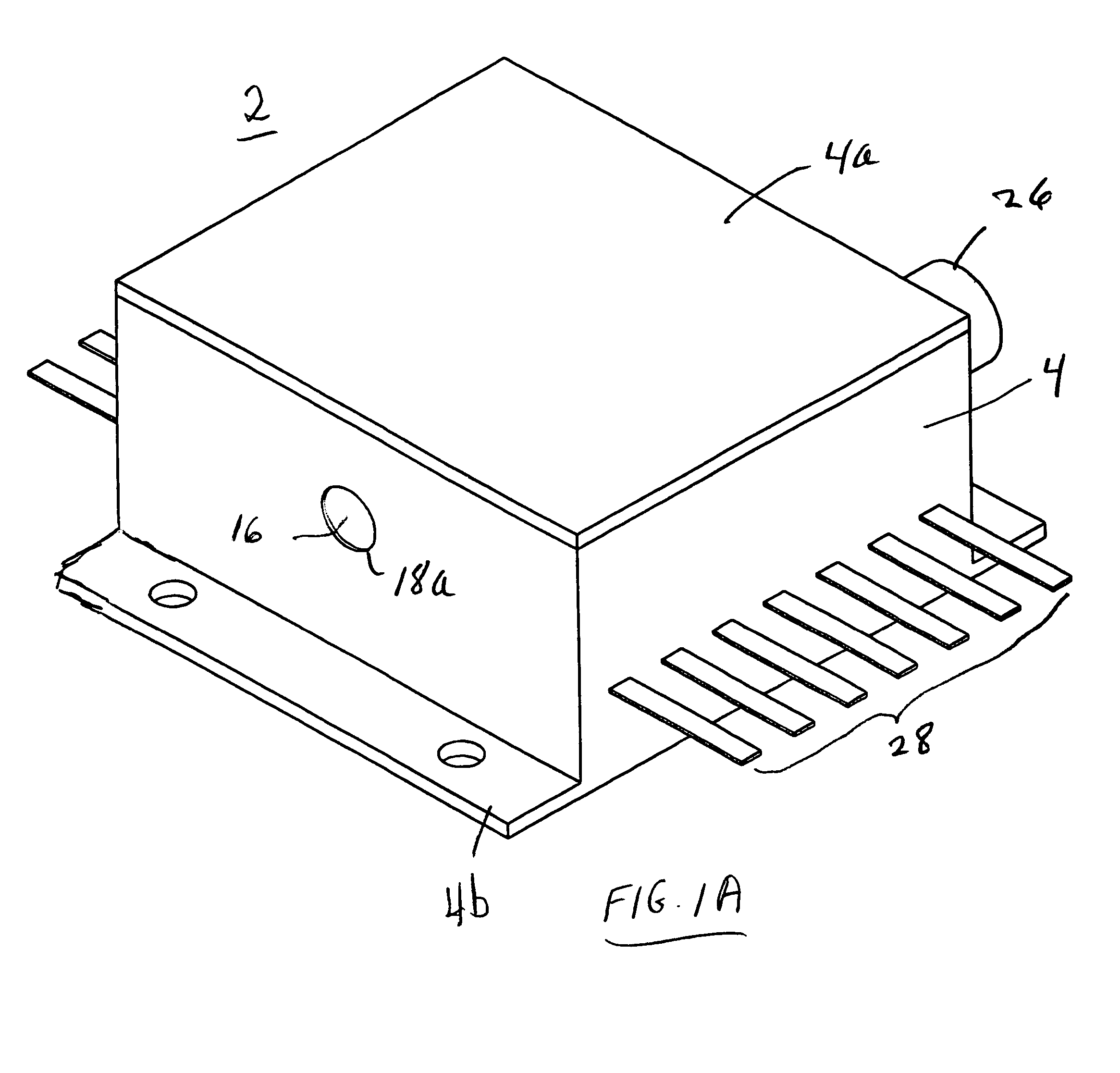
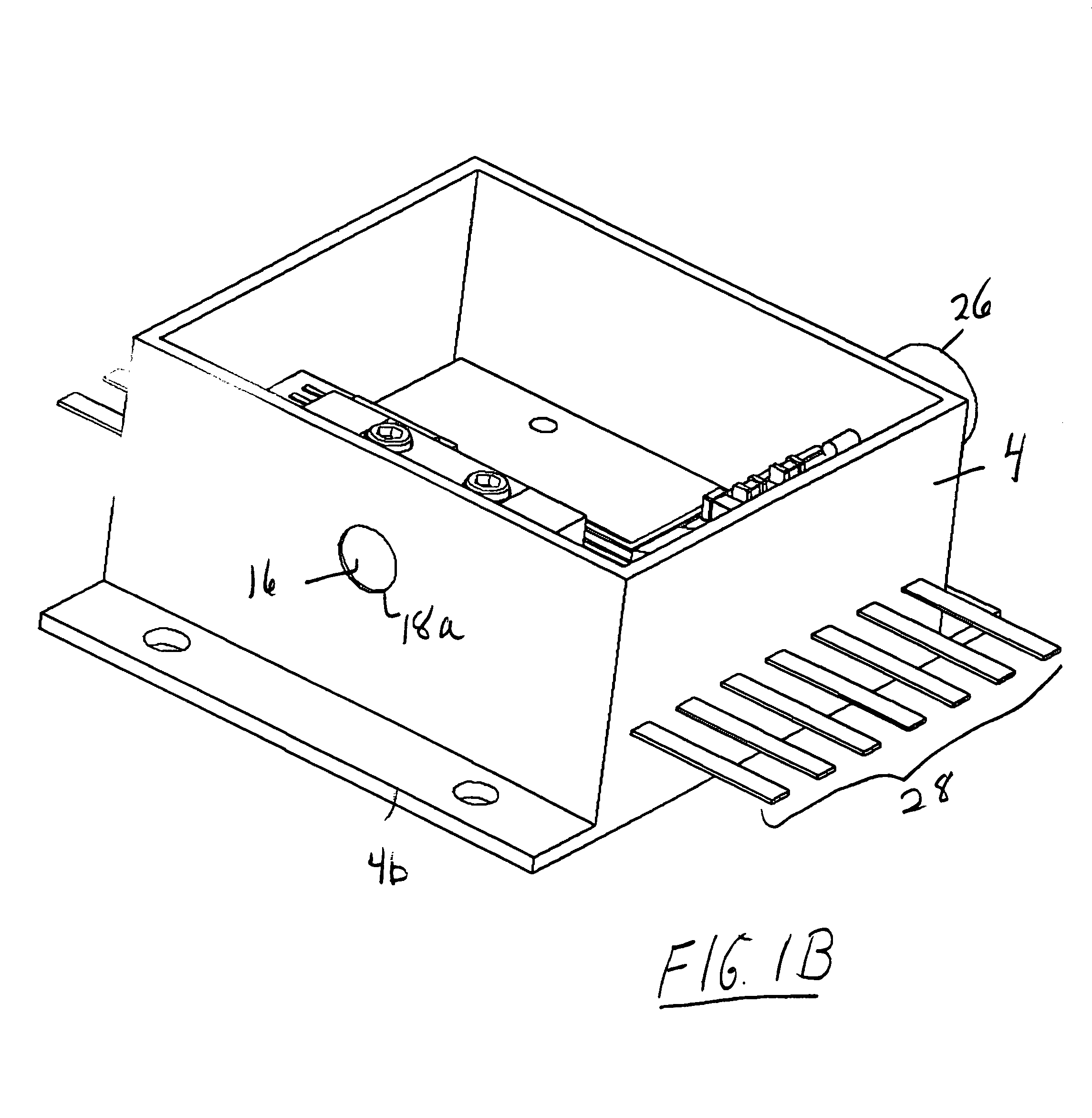
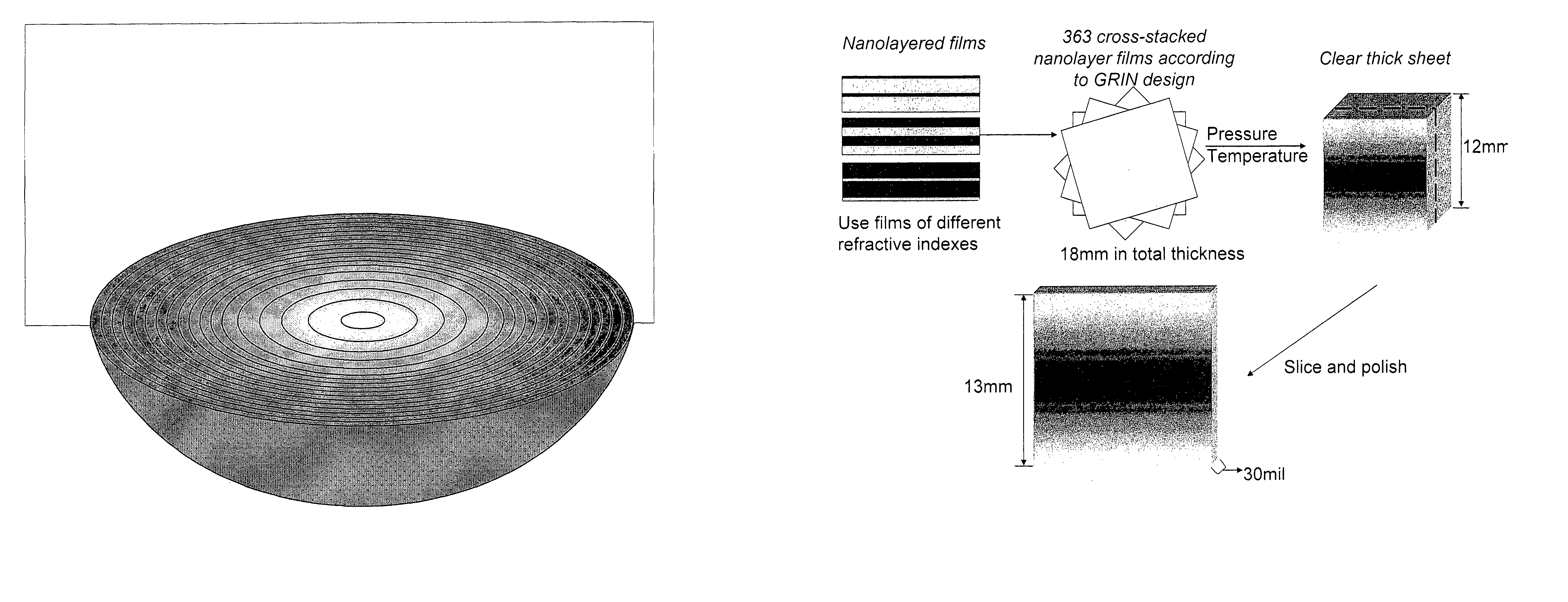
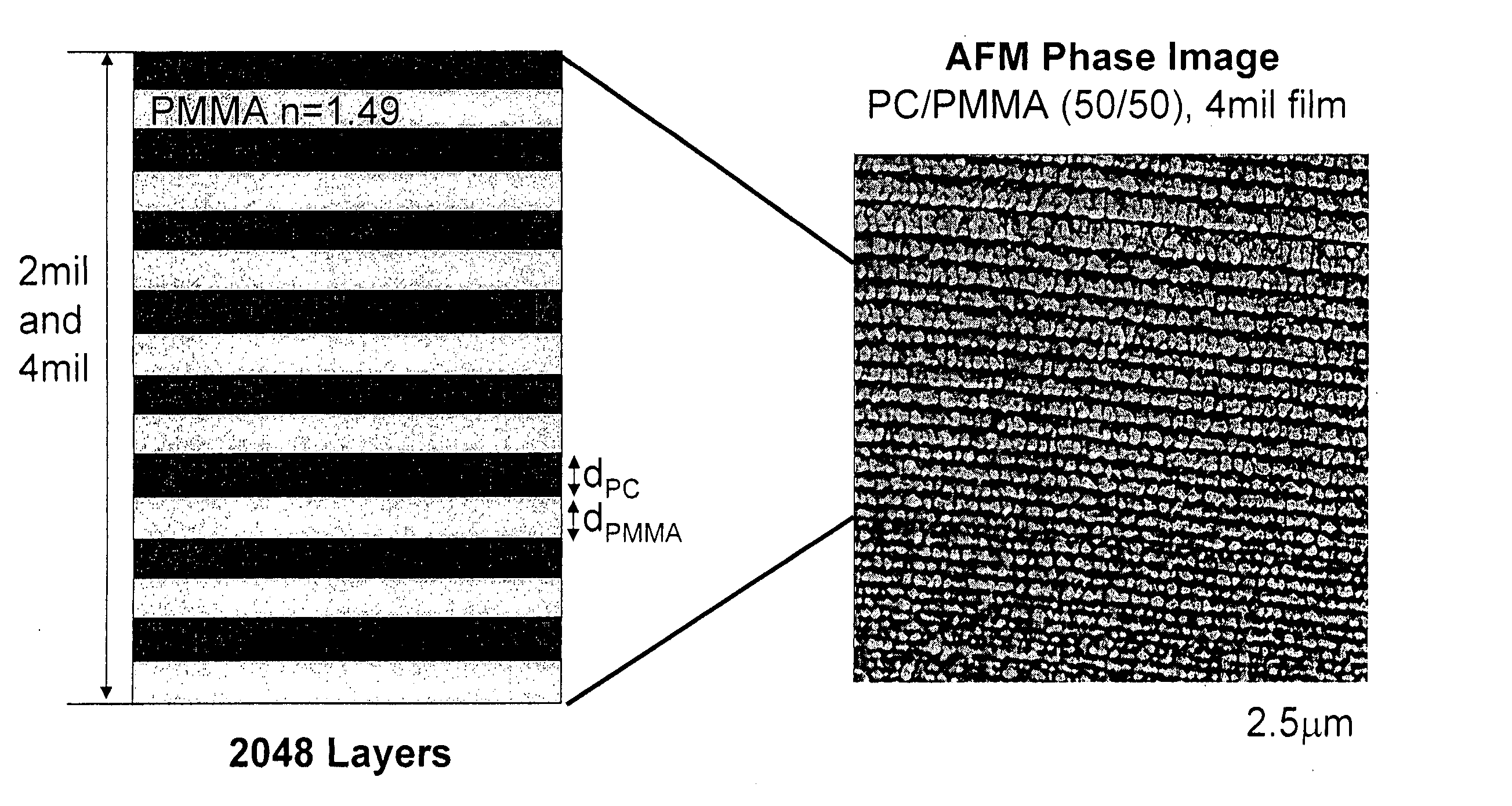
Multilayer polymer gradient index (GRIN) lenses
Disclosed are axial, radial or spherical gradient index (GRIN) lenses fabricated by layering composite polymer films into an hierarchical structure.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +1
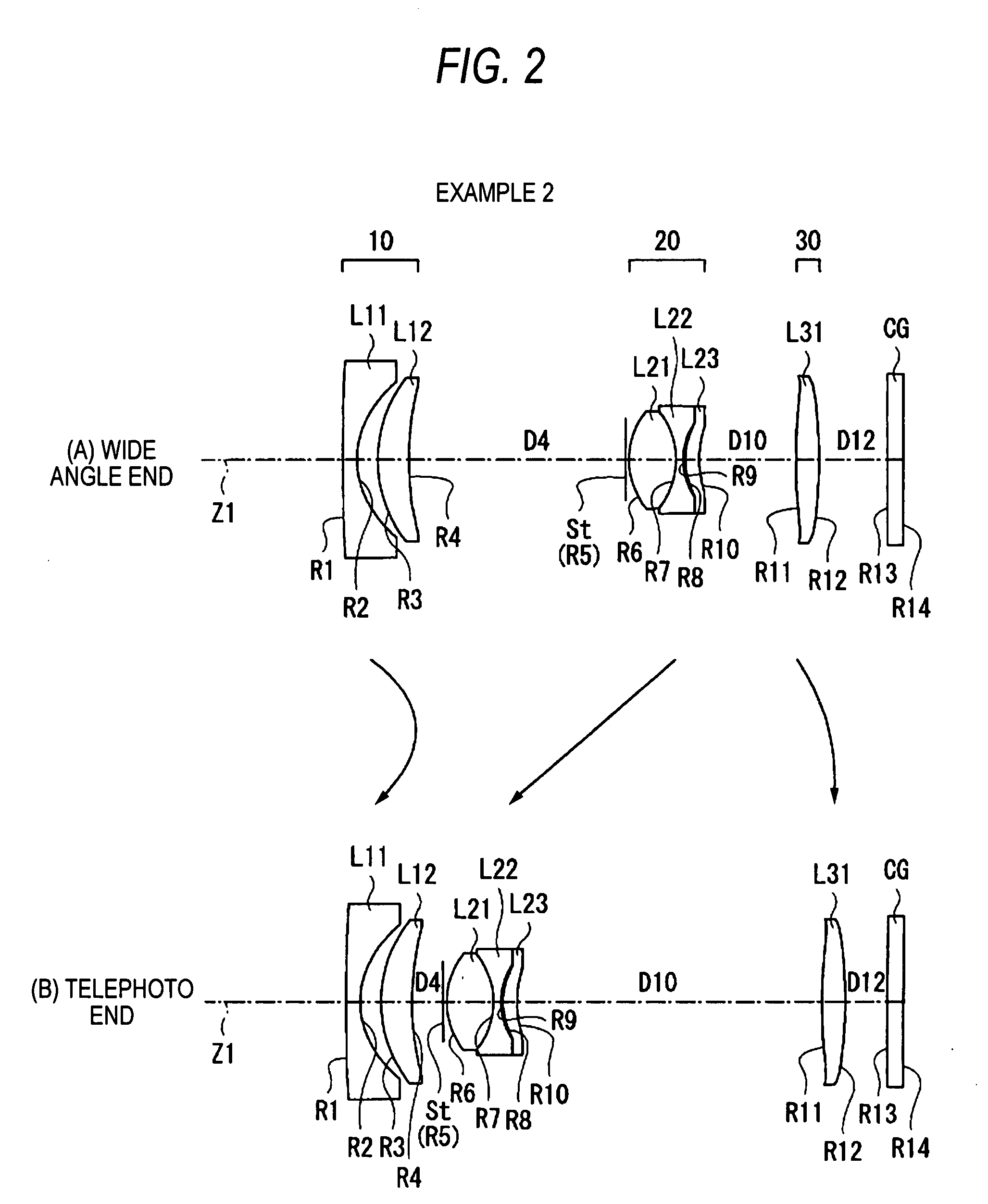
Wide-range, wide-angle compound zoom with simplified zooming structure
A zoom lens is disclosed having a zoom ratio larger than four with a field of view at the short focal length position larger than 85 degrees and with a minimal number of moving groups. The zoom lens utilizes a compound zoom structure comprising an NP or NPP zoom kernel followed by a P or PP zoom relay, with only two or three moving groups that can be used for both zooming, focusing and athermalization. An overall compact package size is achieved by the use of prisms to fold the optical path in strategic locations. An optional variable power liquid cell can provide close focusing with little or no focus breathing.
Owner:PANAVISION INT LP +1
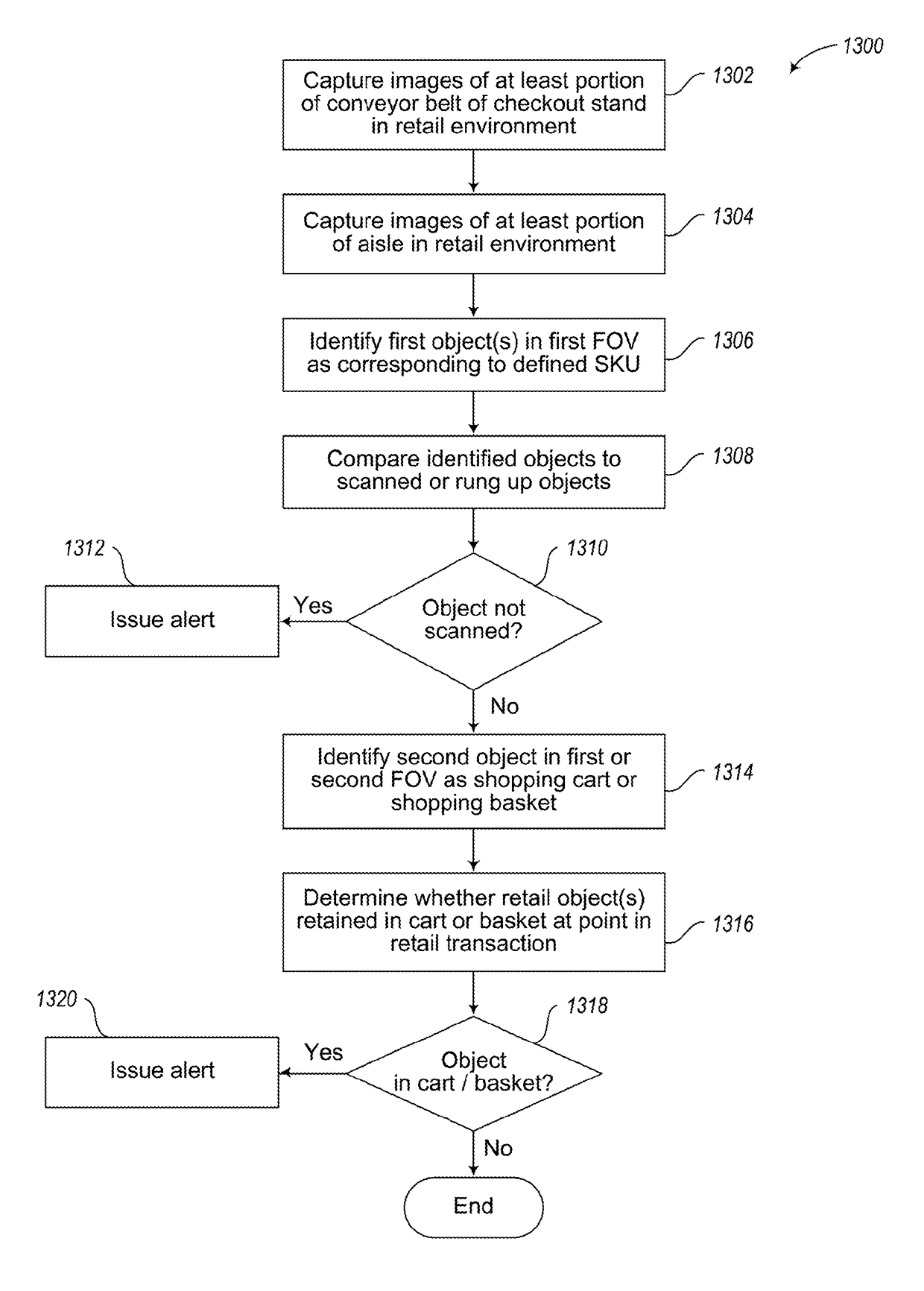
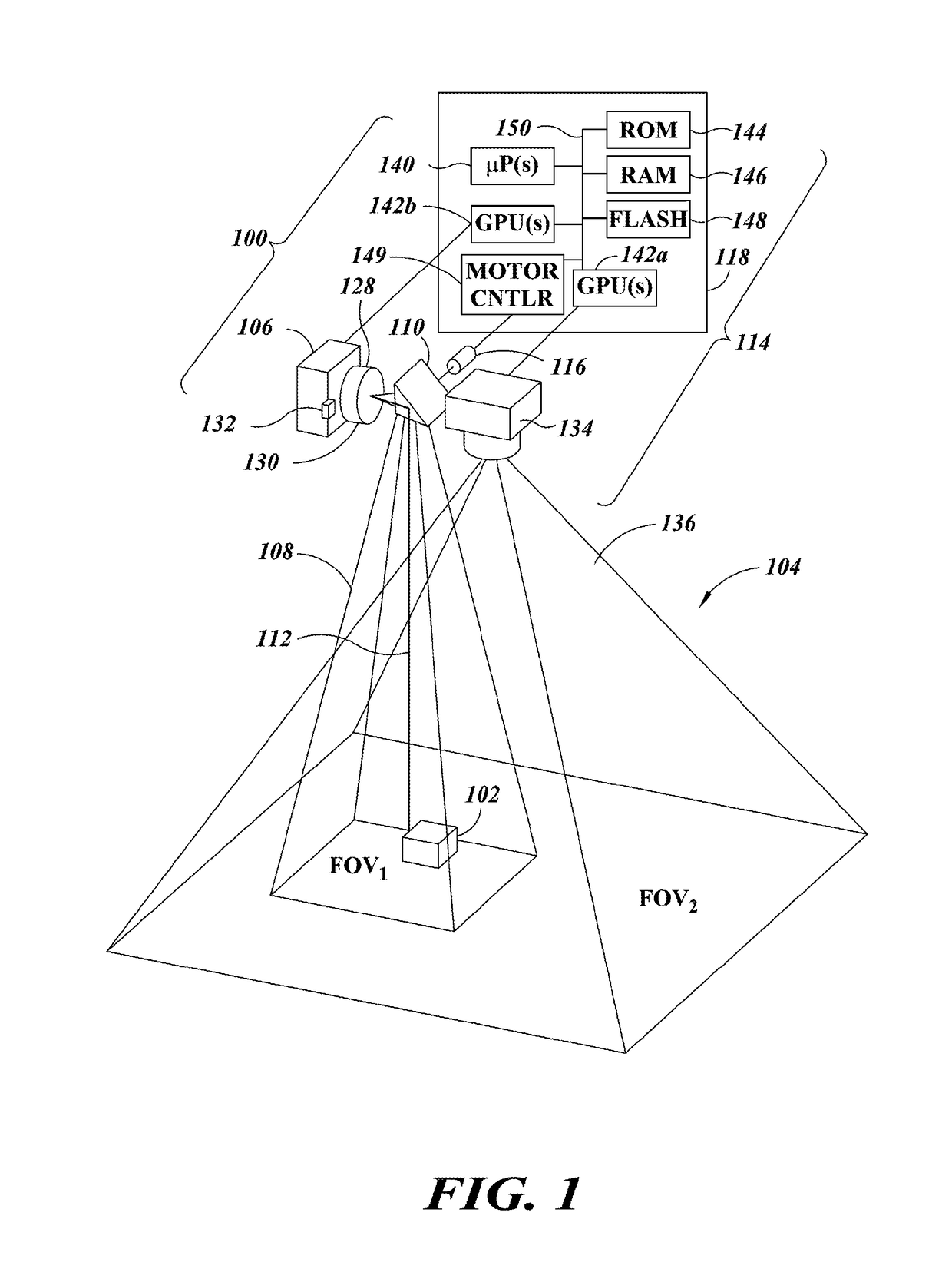
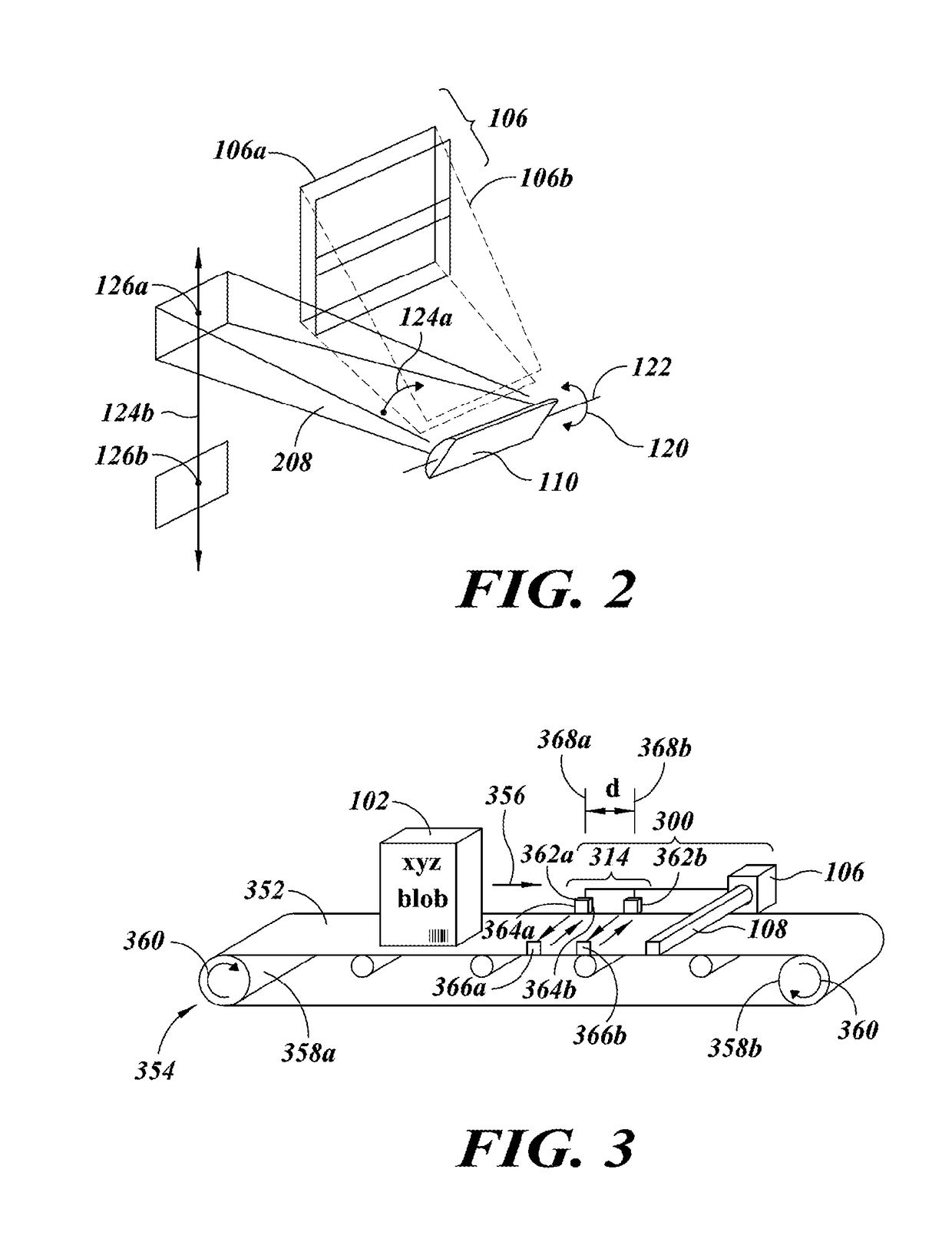
Imaging systems and methods for tracking objects
ActiveUS20180218224A1Low costFast trackCharacter and pattern recognitionCash registersImage resolutionComputer graphics (images)
A first imager has a relatively high resolution and a relatively narrow first field-of-view. Information about objects in an environment is detected or captured, and used to steer the first field-of-view of the first imager. The sensor(s) may take the form of a second imager with a relatively lower resolution and relatively wider second field-of-view. Alternatively, other types of sensors, for instance presence / absence sensors may be employed. The first field-of-view may be directed toward an object that satisfies one or more conditions, for instance matching a particular SKU. The first field-of-view may track a moving object, for instance via a tracking mirror and actuator. This approach may be employed in retail locations, for example in grocery or convenience stores, for instance to reduce various forms of theft or in industrial environments.
Owner:DATALOGIC USA INC
Multilayer polymer gradient index (GRIN) lenses
Disclosed are axial, radial or spherical gradient index (GRIN) lenses fabricated by layering composite polymer films into an hierarchical structure.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Imaging apparatus and image sensor including the same
ActiveUS20160316180A1Long focal lengthShort focal lengthTelevision system detailsColor television detailsThin lensNanostructure
An imaging apparatus and an image sensor including the same are provided. The imaging apparatus includes first, second, and third optical devices. At least one of the first, second, and third optical devices is a thin-lens including nanostructures.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Compact mid-ir laser
InactiveUS20100243891A1Enhanced cooling techniqueLight weightLaser active region structureMaterial analysis by optical meansThermoelectric coolingAspheric lens
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes a quantum cascade laser to provide mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser is thermally coupled. The heat spreader not only serves to dissipate heat and conduct same to the TEC, but also serves as an optical platform to secure the optical elements within the housing in a fixed relationship relative on one another. A small diameter aspheric lens may have a diameter of 10 mm or less and is positioned to provided a collimated beam output from the quantum cascade laser. The housing is hermetically sealed to provide a rugged, light weight portable MIR laser source.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Symmetrical double-telecentric projection optical system
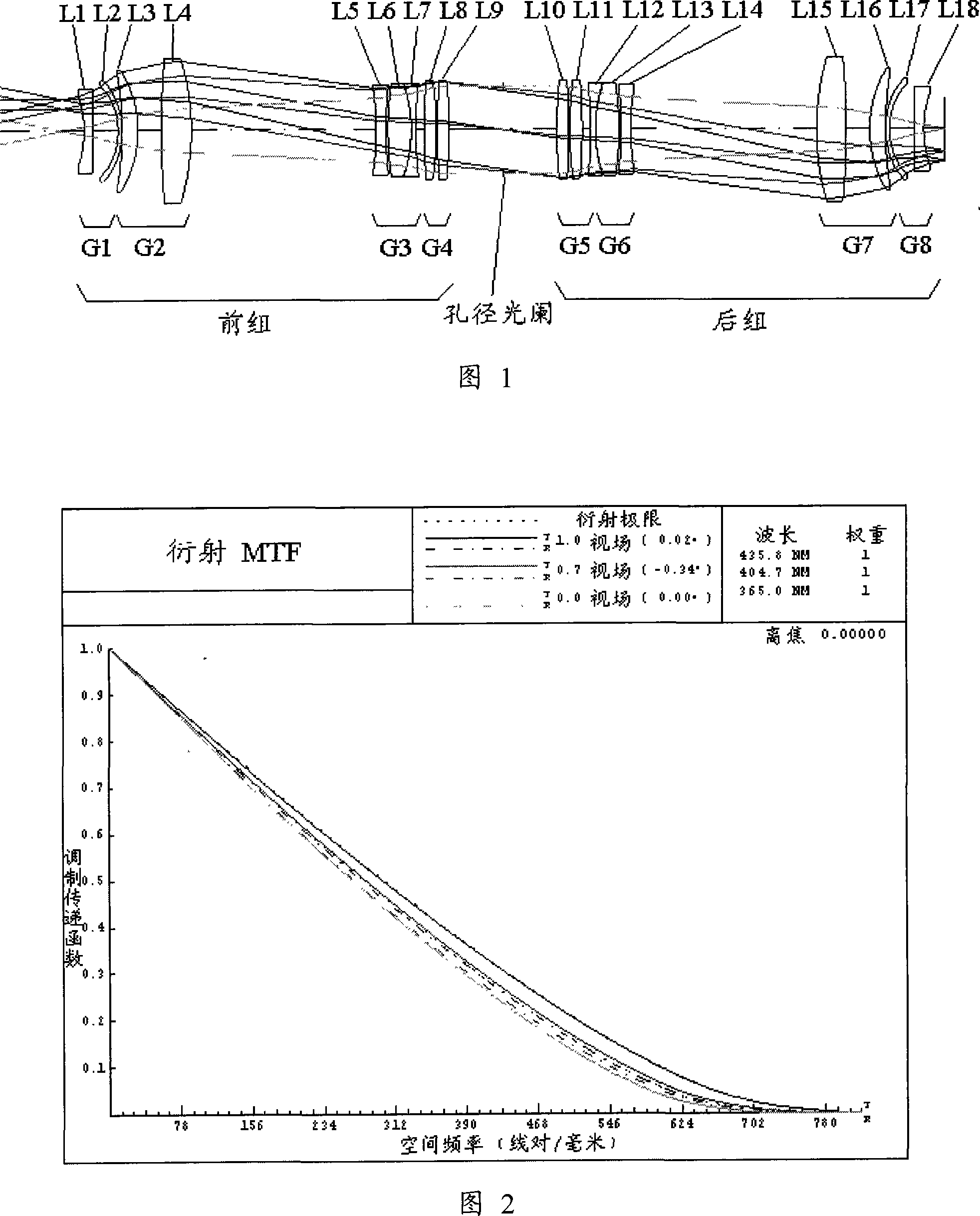
ActiveCN101021607AEffective correctionImprove image qualityOptical elementsProjection opticsManufacturing cost reduction
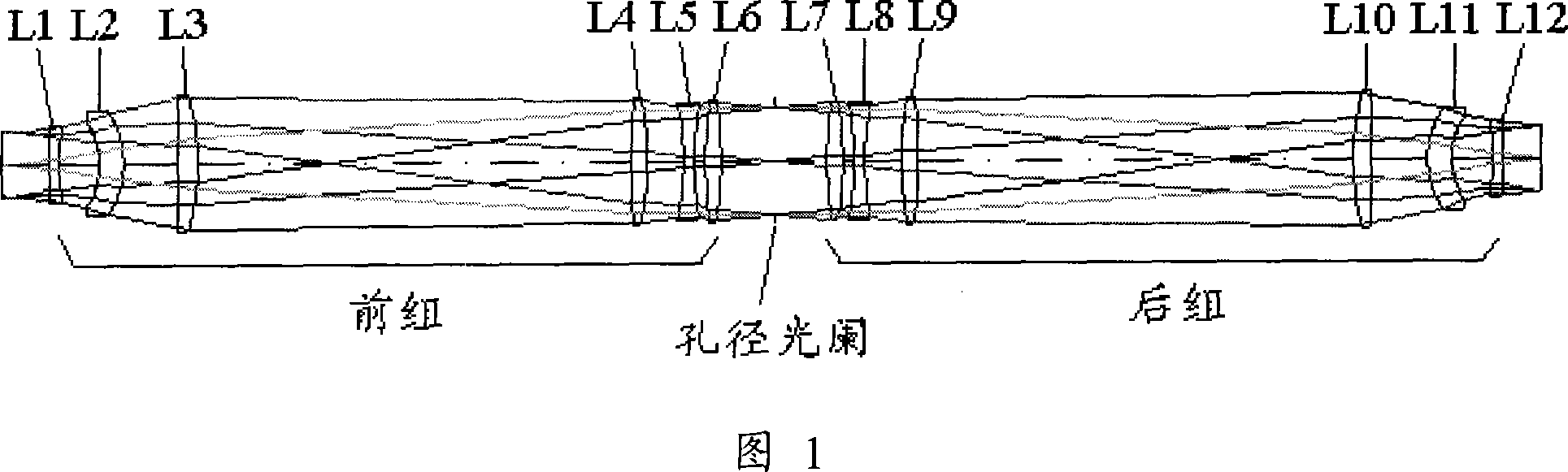
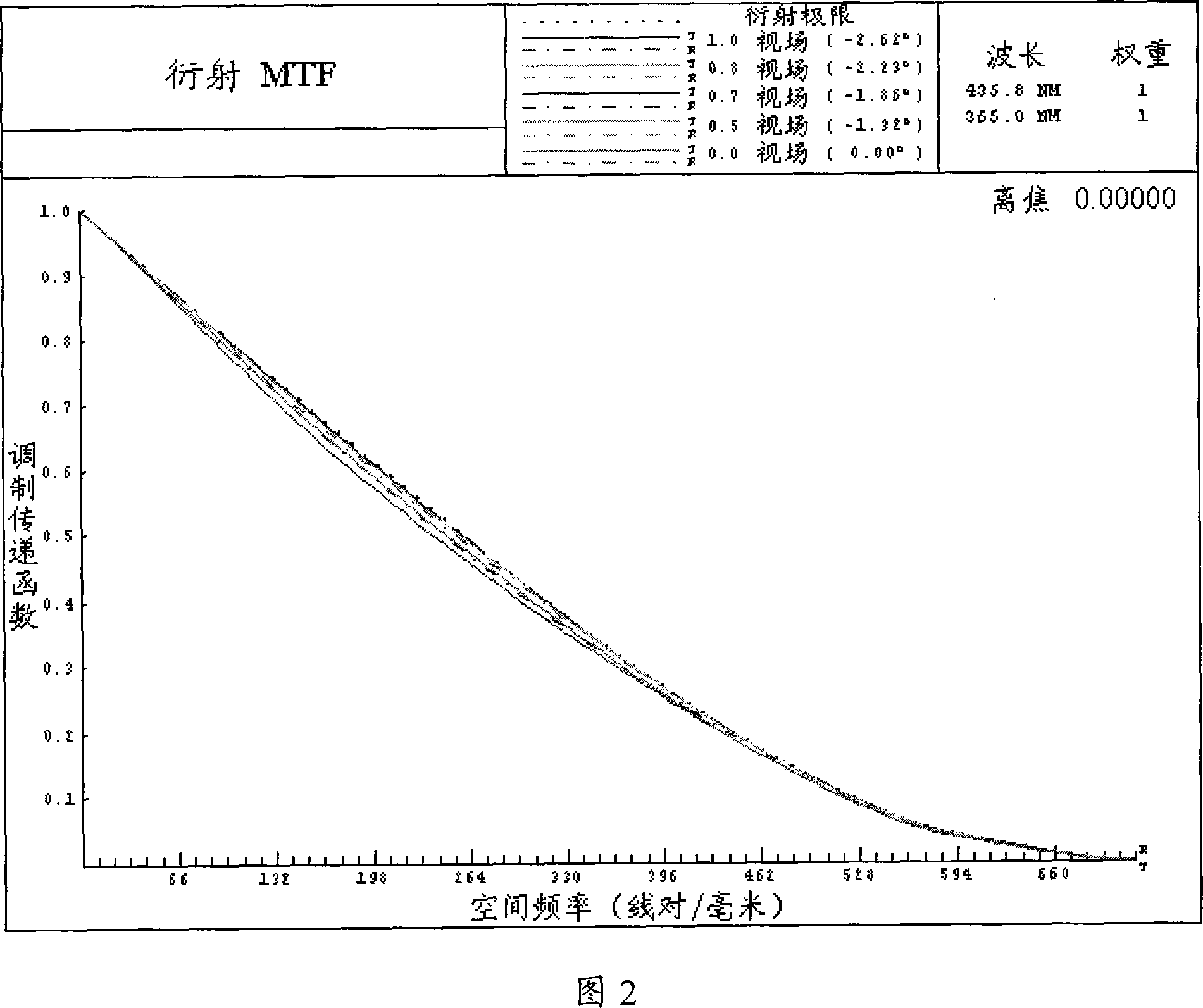
The invention provides a symmetrical double telecentric projection optical system, for imaging a graph in object plane into image plane. And it is a total refraction projection optical system, comprising front set and rear set, using aperture diaphragm as symmetrical surface, where the front set comprises first-fourth lens sets, the first lens set and the third lens set have negative focal power, and the second lens set and the fourth lens set have positive focal power, and the first and second lens sets and the third and fourth lens sets respectively compose retrofocus structure; the rear set comprises in turn fifth-eighth lens sets along the optical axis, respectively symmetrical with the fourth-first lens sets with respect to the aperture diaphragm; and it does not comprise nonspherical lens. And it can effectively correct aberration, enlarge operating focus length and improve imaging quality; and it is relatively simple to machine and detect, able to largely reduce the manufacturing cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
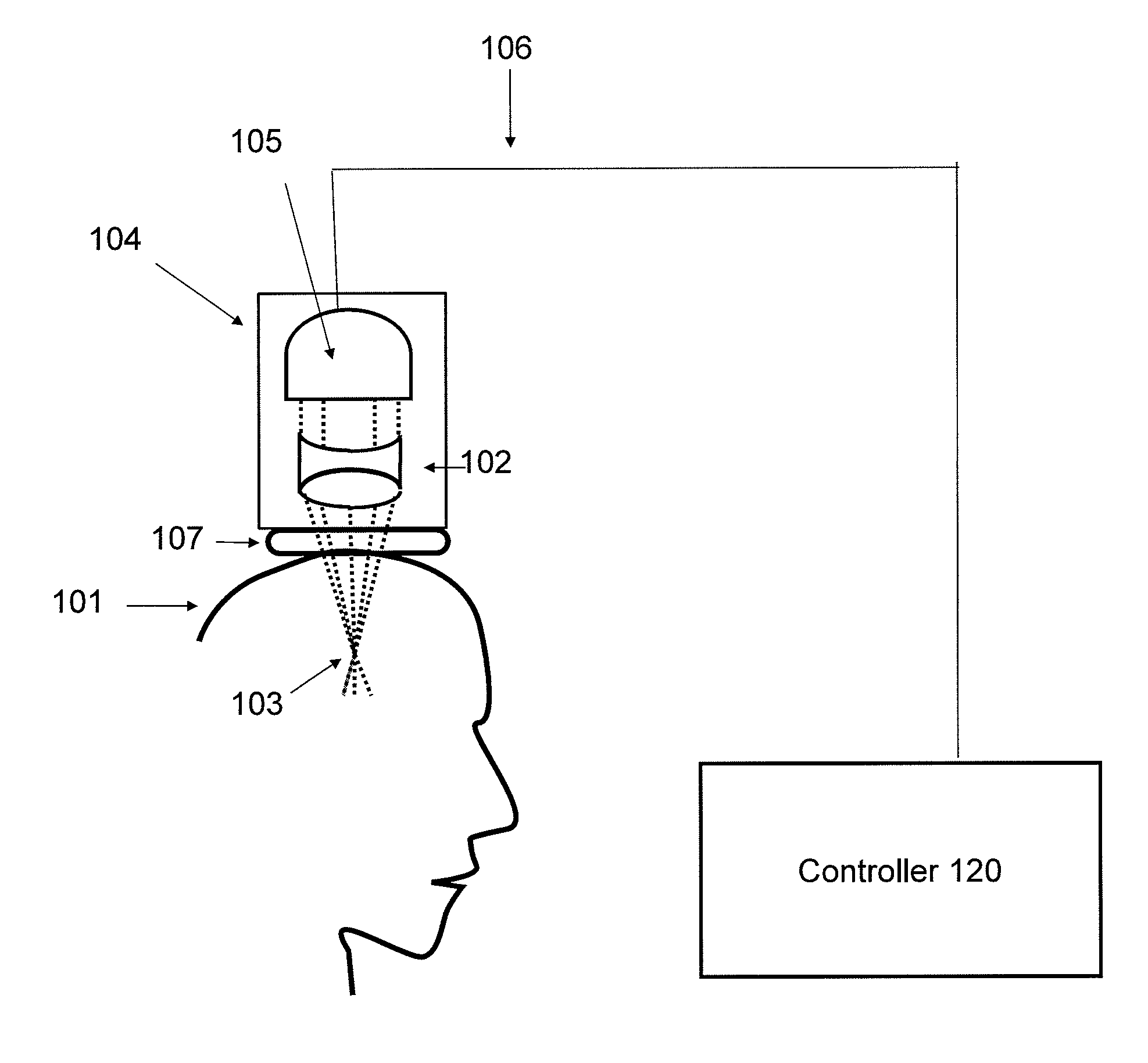
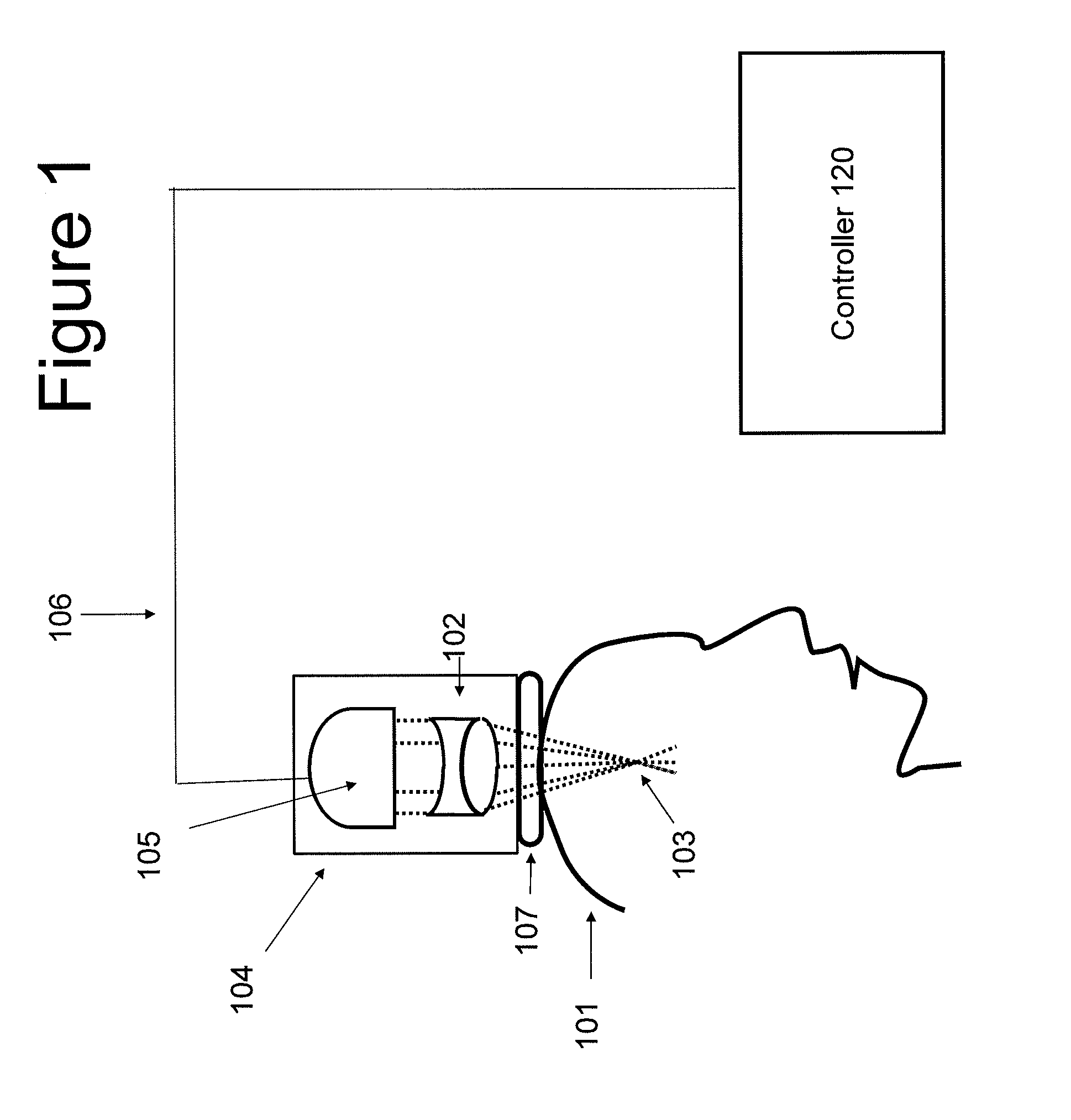
Focused transcranial ultrasound systems and methods for using them
InactiveUS20160038770A1Highly focused ultrasoundMinimizing standing waveUltrasound therapyChiropractic devicesAcoustic energyMedicine
Apparatus and methods for focusing transcranial ultrasound. The systems described herein are advantageous for noninvasive neuromodulation and other transcranial ultrasound applications such as high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU). In particular, described herein are compound acoustic lens apparatus having a short focal length for use with a transcranial ultrasound system, systems including methods of using them. These compound lens assemblies allow transcranial stimulation of even superficial cortical regions of the brain for ultrasound neuromodulation with a compact, single transducer element system at low (e.g., 0.2 to 1 MHz) frequencies with relatively large diameter (e.g., >15 mm) transducers applying 1 to 10 watts / cm2 of acoustic energy (spatial-peak, temporal-average intensity at the target brain region), and short focal length (e.g., between 15 and 35 mm).
Owner:CEREVAST MEDICAL
Two zone automatic lens focusing system for digital still cameras
InactiveUS6961090B2Reduce processing timeLess expensiveTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementFar distanceCamera lens
A two zone lens auto-focusing system to be used in a digital still camera includes a picture taking lens, a solenoid to switch the lens focus point between near distance point and far distance point. The CPU or the electronically controlled distance measuring system of the camera having detected the position of the object, it excites the solenoid, and the head of the solenoid is pulled into the solenoid body with a very short stroke, and the arm that is provided on the lens barrel and coupled with the solenoid head is also pulled toward the solenoid body to transfer the movement of solenoid head to the lens barrel, so that the lens focus may be set at either of far position or near position automatically. These members are assembled and form a simple two zone auto-focusing system of digital still cameras.
Owner:ARC DESIGN
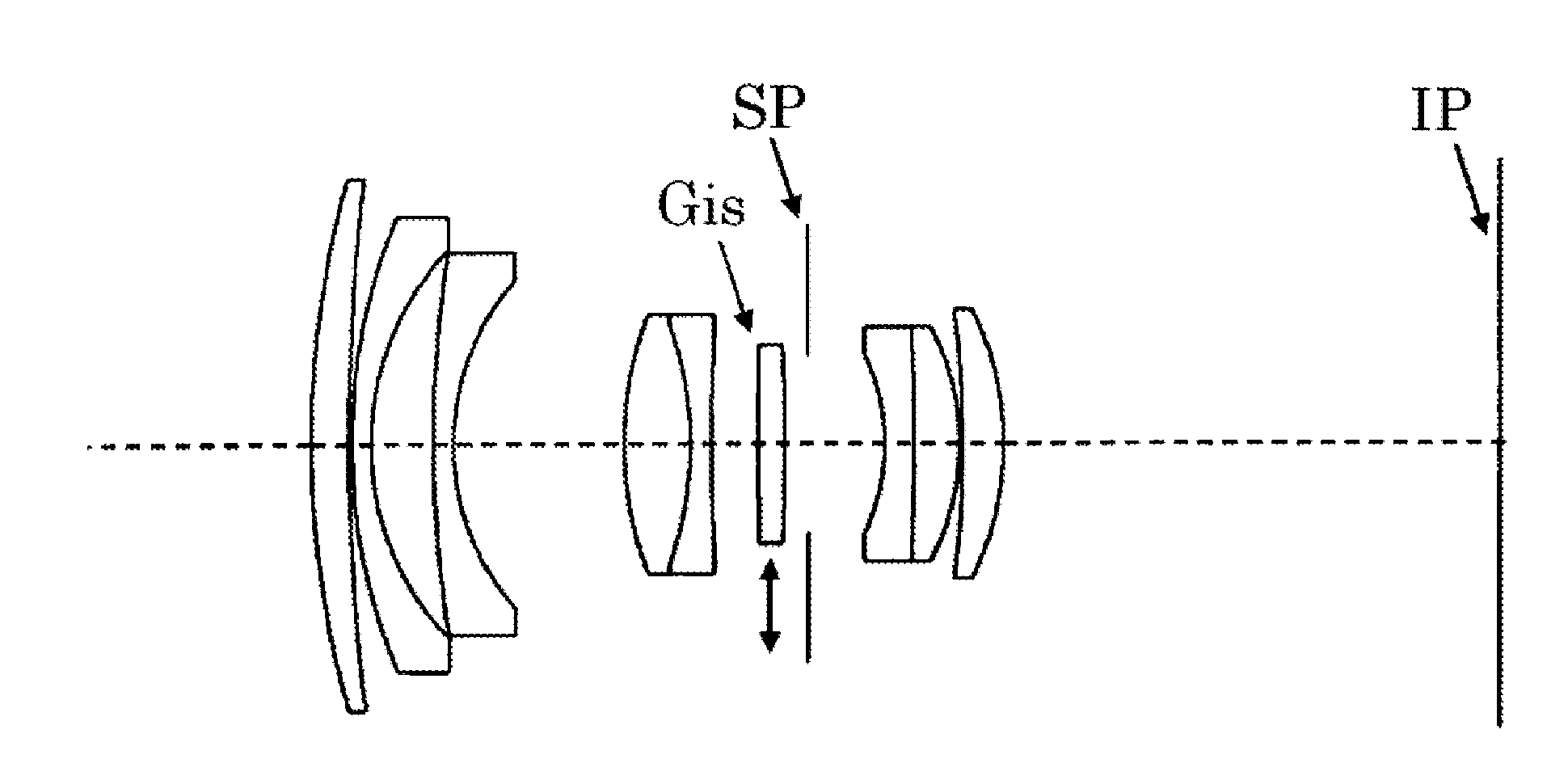
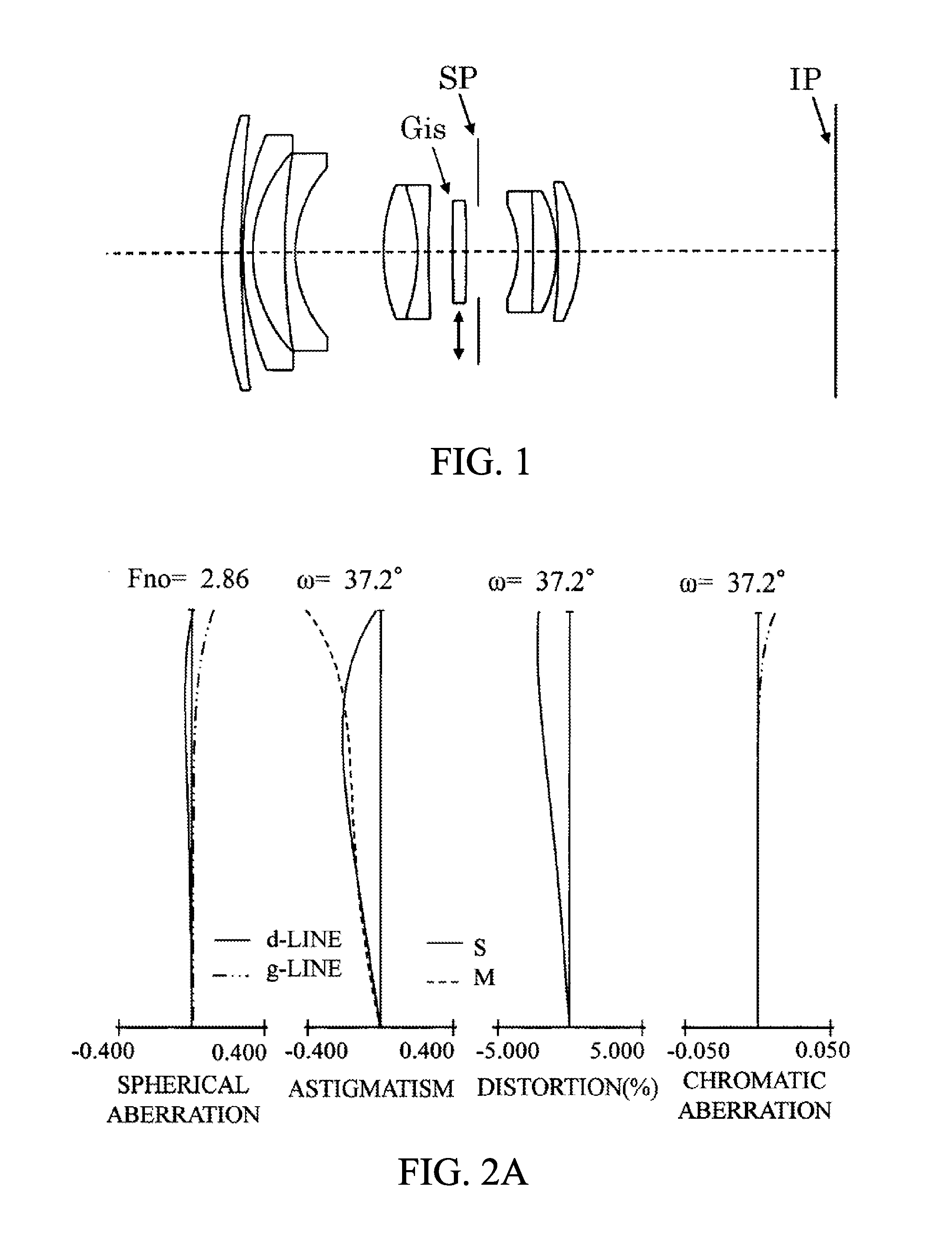
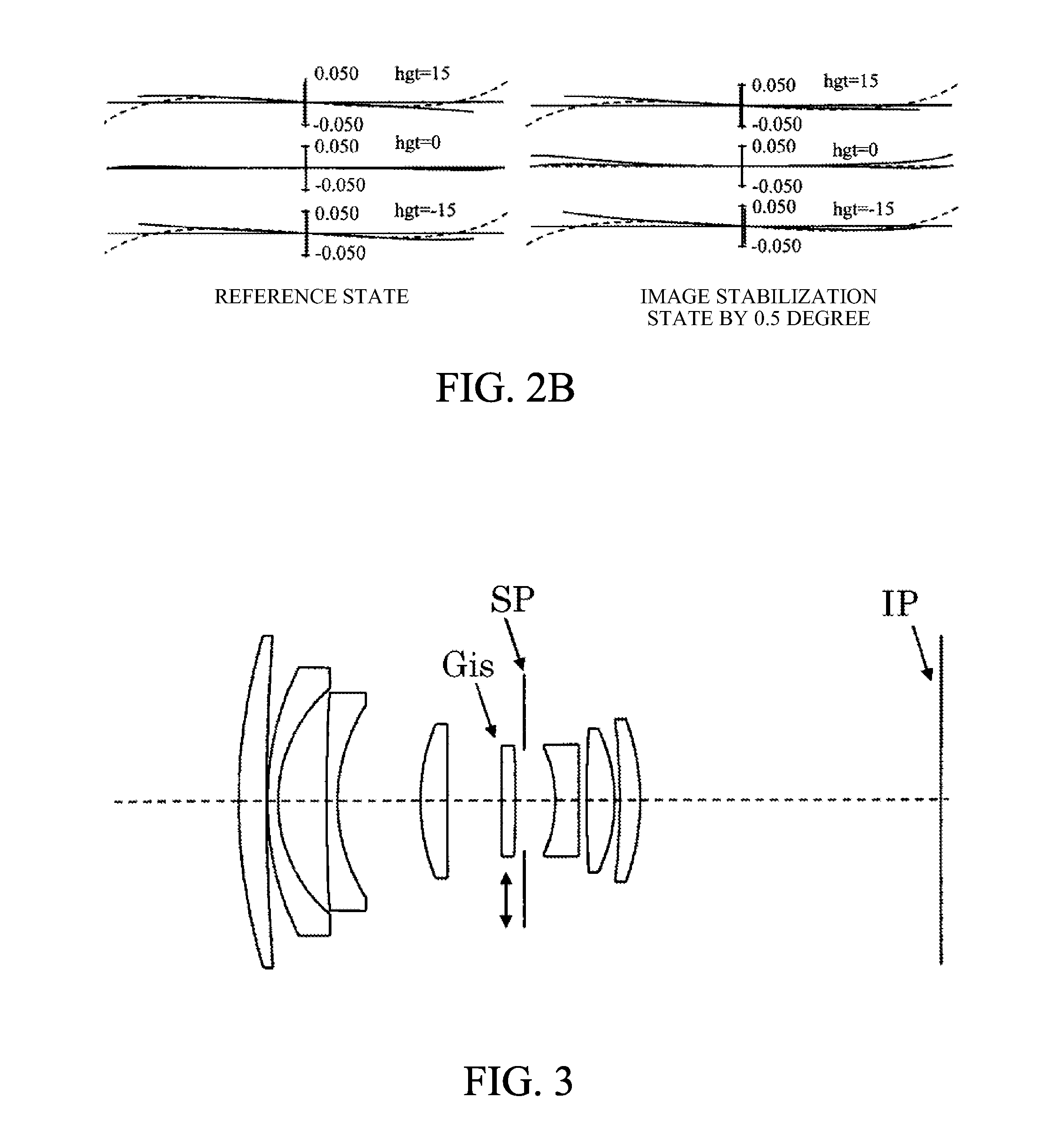
Fixed focal length lens having image stabilization function
A fixed focal length lens has a focal length of a whole system shorter than a back focus. The fixed focal length lens includes an aperture stop, and an image-stabilizing lens unit that moves in a direction including a component of a direction orthogonal to an optical axis to reduce an image blur. The conditions of 0.1<f / |fis|<0.5 and −0.35<Dis / DL<0.25 are met, where f is the focal length of the whole system, fis is a focal length of the image-stabilizing lens unit, Dis is a distance from the aperture stop to a surface farthest from the aperture stop of the image-stabilizing lens unit, and DL is a distance from a first surface closest to an object side to a final surface closest to an image side of the fixed focal length lens. A sign of the distance is positive in a direction from the object side to the image side.
Owner:CANON KK
Effective method to improve sub-micron color filter sensitivity
ActiveUS7372497B2High sensitivityLong focal lengthTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPhotodiodeMicro lens array
An image sensor device and method for forming said device are described. The image sensor structure comprises a substrate with photodiodes, an interconnect structure formed on the substrate, a color filter layer above the interconnect structure, a first microlens array, an overcoat layer, and a second microlens array. A key feature is that a second microlens has a larger radius of curvature than a first microlens. Additionally, each first microlens and second microlens is a flat convex lens. Thus, a thicker second microlens with a short focal length is aligned above a thinner first microlens having a long focal length. A light column that includes a first microlens, a second microlens and a color filter region is formed above each photodiode. A second embodiment involves replacing a second microlens in each light column with a plurality of smaller second microlenses that focus light onto a first microlens.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Full refraction projection optical system
ActiveCN101063743AEffective correctionImprove image qualityOptical elementsImaging qualityOptical axis
This invention provides one total reflection projection optical system for object plane to form imaging plane, wherein the said system is divided into front and back sets to form hole diaphragm as symmetric surfaces; the front set comprises first to sixth lens with one to three lens form reverse distant structure; the back set orderly comprises seven to twelve lens symmetric to six to one lens about hole radium; the said whole reflection projection optical system all surface types are of sphere or plane without non-sphere surface.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Optical link module, optical interconnection method, information processor including the optical link module, signal transfer method, prism and method of manufacturing the prism
An optical link module of the present invention for connecting light beams by deflection and including light-emitting devices arranged in a planar manner; an optical fiber bundle that is an optical waveguide for receiving the light beams from the light-emitting devices, and an optical turn which includes a plurality of aspherical lenses which are disposed between the light-emitting devices and the optical fiber bundle and are formed while corresponding to the number of the light-emitting devices and the number of optical fibers.
Owner:IBM CORP
Three-dimensional imaging optical thin film
The invention discloses a three-dimensional imaging optical thin film, which comprises a transparent spacing layer, a micro-reflective focusing unit array layer, and a micro-graphic unit array layer. The transparent spacing layer has two opposite surfaces. The micro-reflective focusing unit array layer is arranged on one surface of the transparent spacing layer and comprises a plurality of asymmetrically arranged micro-reflective focusing units. The micro-graphic unit array layer, opposite to the micro-reflective focusing unit array layer, is arranged on the other surface of the transparent spacing layer and comprises a plurality of micro-graphic units. The micro-reflective focusing unit array layer and the micro-graphic unit array layer are matched with each other, so that the three-dimensional imaging optical thin film can form one and only one suspended image suspended in the transparent spacing layer only when being viewed form the side of the micro-graphic units. The suspended image of the three-dimensional imaging optical thin film is a single-channel or multi-channel pattern. When the imaging thin film is inclined from side to side or inclined back and forth, no other amplified micro-graphic unit enters the viewing area. The thin film is unique in visual experience and can be clearly observed in the front perpendicular condition.
Owner:SHINE OPTOELECTRONICS KUNSHAN CO LTD
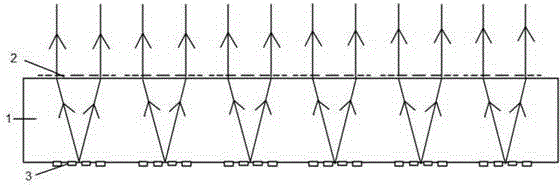
Optical position measuring device
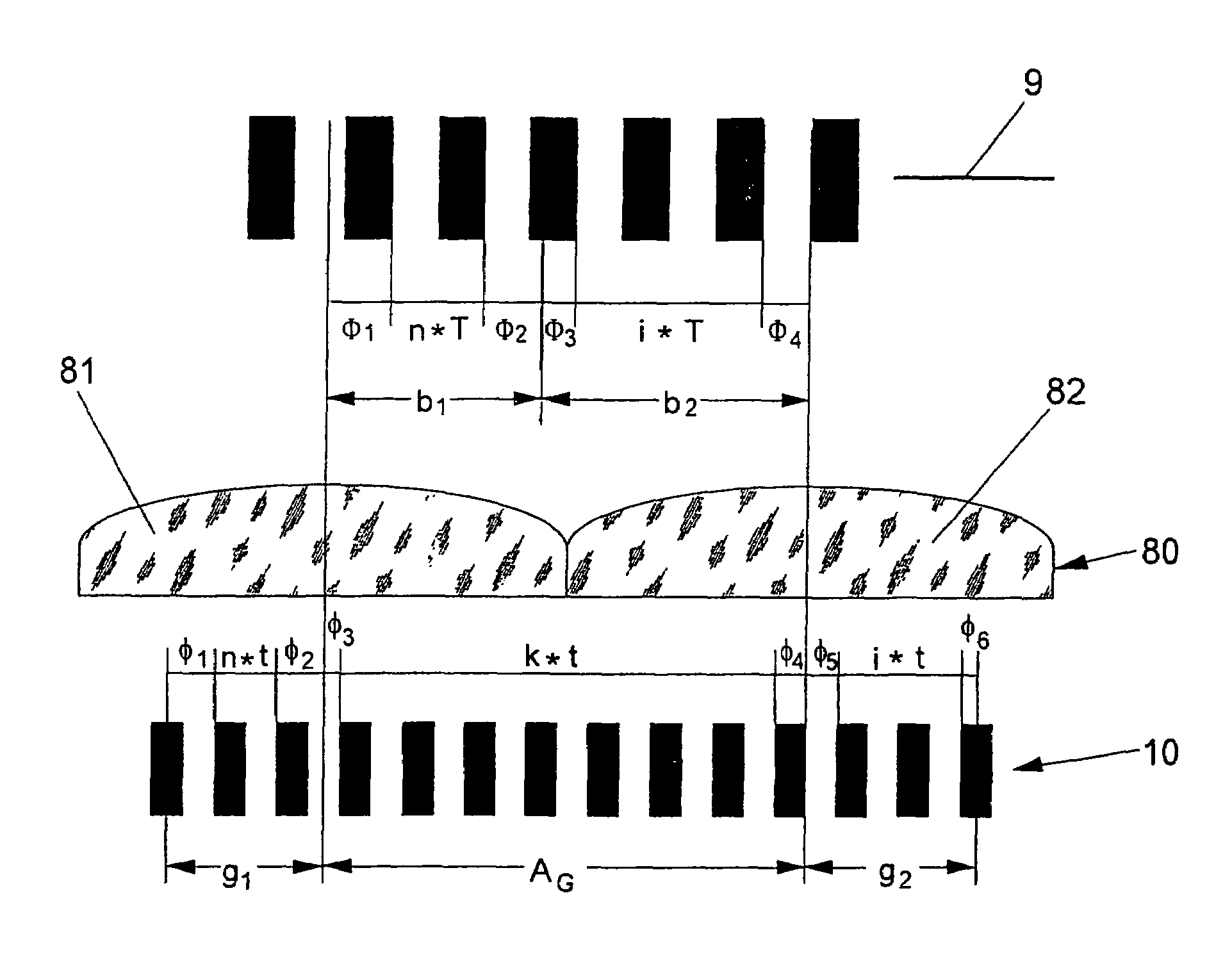
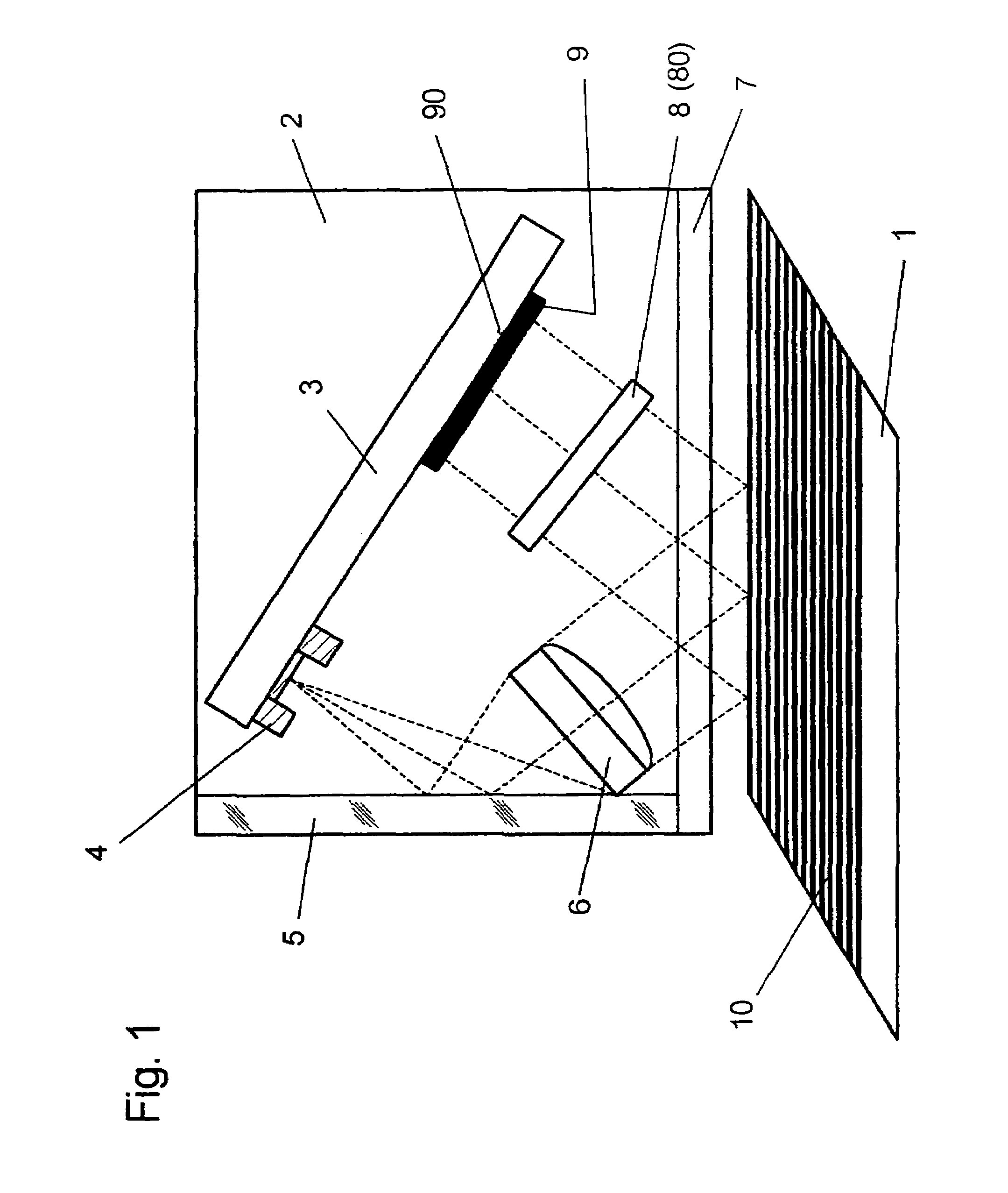
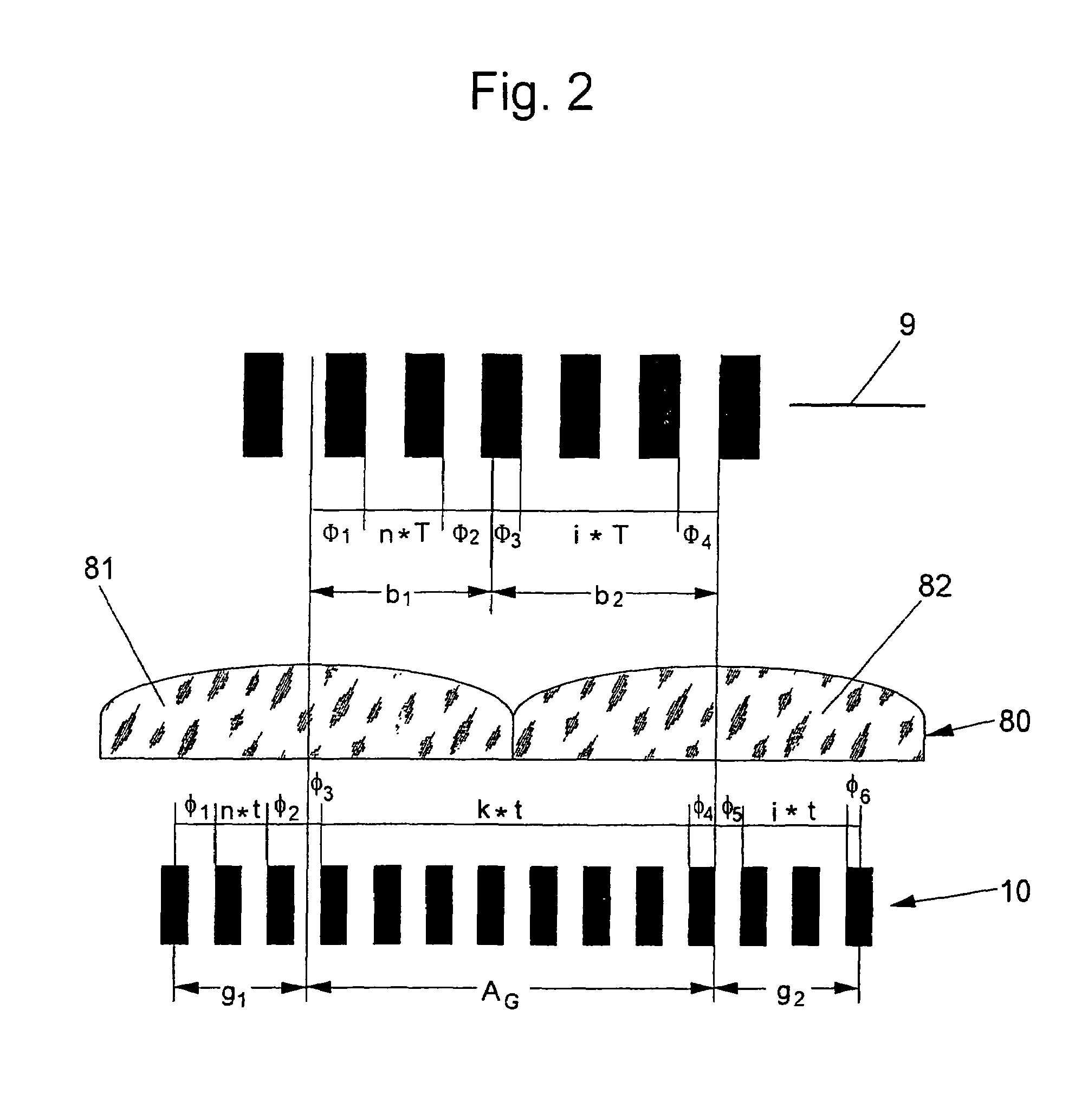
InactiveUS6963409B2Short focal lengthSmall structure sizeInvestigating moving sheetsUsing optical meansPhase shiftedMagnification
An optical position measuring system including a periodic grating structure and a scanning unit. The scanning unit includes a light source that directs light towards the periodic grating structure and an optical lens device that receives light from the periodic grating structure and creates an image of the periodic grating structure in an image plane, the optical lens device having a periodic lens array with a grating period, AG(r) or the mutual distance between adjoining lenses of said lens array defined by the equation: AG(r)=β(r)*[t(r)*[k+i+n]+ψ](β(r)+1)whereinAG(r) is the grating pert(r) the period of the periodic grating structure,|β(r)| the absolute amount of the image magnification factor β of the lens arrayΨ a presettable defined phase shiftr the radius of the grating arrangement, wherein inthe case of a linear grating r=∞ and AG,t and |β| are constants,i, k, n ε N, i.e. are natural numbers, including zero.
Owner:DR JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GMBH
Zoom optical system and image pickup apparatus
A zoom optical system according to the present invention is provided with, in order from an object side thereof: a first lens group having a negative refractive power; a second lens group having a positive refractive power; a third lens group having a negative refractive power; and a fourth lens group having a positive refractive power. The zoom optical system moves at least the second lens group and the third lens group for zooming operation from a wide-angle end to a telephoto end. The zoom optical system moves the third lens group for a focusing operation. The first lens group is provided with, in order from the object side of the zoom optical system, a meniscus lens having a negative refractive power whose concave surface faces an image side of the zoom optical system, a reflective optical element, and at least one lens.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA PHOTO IMAGING
Dynamic amplifying optical film of flat Fresnel lens array
ActiveCN104614790AShort focal lengthUnaffected by printingLensInformation cardsFresnel lensMicro pattern
The invention discloses a dynamic amplifying optical film of a flat Fresnel lens array. The optical film comprises a substrate layer, a plurality of Fresnel lens array layers positioned above the substrate layer, and a plurality of micro-pattern layers positioned below the substrate, wherein each Fresnel lens array layer consists of a plurality of Fresnel lenses which are arranged in an array; the distance between the Fresnel lens array layers and the micro-pattern layers is the focus distance of each Fresnel lens. According to the dynamic amplifying optical film disclosed by the invention, patterns in the micro-pattern layers are amplified and reproduced because of the imaging effect of the Fresnel lenses; the reproduced and amplified image has a dynamic three-dimensional effect.
Owner:SVG TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Zoom lens and imaging device
A zoom lens comprises: a stationary group that is stationary at the time of variable power; and a variable power group, disposed on an image side of the stationary group, that makes a variable power operation by moving in an optical axis direction at the time of variable power, wherein the stationary group comprises: a first lens group including a negative meniscus lens and a positive lens and having a positive refractive power as a whole; and a second lens group, disposed on the image side of the first lens group, including: a negative lens group including a negative meniscus lens and a positive lens; and a positive lens group including at least one positive lens, in order from an object side, the second lens group having a positive refractive power as a whole.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Head-mounted display device and optical lens system thereof
ActiveCN105068253AGuaranteed viewing fieldImprove image qualityOptical elementsCamera lensOptical axis
The invention relates to a head-mounted display device and an optical lens system thereof. The optical lens system comprises a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens and a sixth lens which are arranged in sequence from a light inlet side to a light outlet side along an optical axis, wherein each lens is a spherical lens with an refractive index, the first lens is a negative focal power lens, the second lens is a positive focal power lens, the third lens is a positive focal power lens, the fourth lens is a positive focal power lens, the fifth lens is a positive focal power lens, and the sixth lens is a negative focal power lens. The head-mounted display device provided by the invention comprises a machine shell and a display module which is installed in the machine shell, wherein the display module comprises at least one optical lens system disclosed in the invention and at least one display screen which is arranged on an optical axis, facing the light inlet side, of a second surface of the sixth lens. The head-mounted display device and the optical lens system thereof ensure angle of field of view, ensure good imaging quality, and have the advantages of short focal length and long working distance.
Owner:宿州飞目光电科技有限公司
Zoom lens and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20080043341A1Quality improvementAberration correctionOptical elementsCamera lensConditional expression
A zoom lens is provided and includes: in order from an object side thereof, a first lens group having a negative refractive power, a stop; a second lens group having a positive refractive power; and a third lens group having a positive refractive power. The magnification of the zoom lens is varied from a wide angle end to a telephoto end by changing a space between the first lens group and the second lens group and a space between the second lens group and the third lens group. The first lens group includes: in order from an object side thereof, a negative lens having at least one aspherical surface and having a concave surface on an image side thereof; and a positive meniscus lens having a convex surface on the object side thereof. The zoom lens satisfies conditional expressions specified in the specification.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
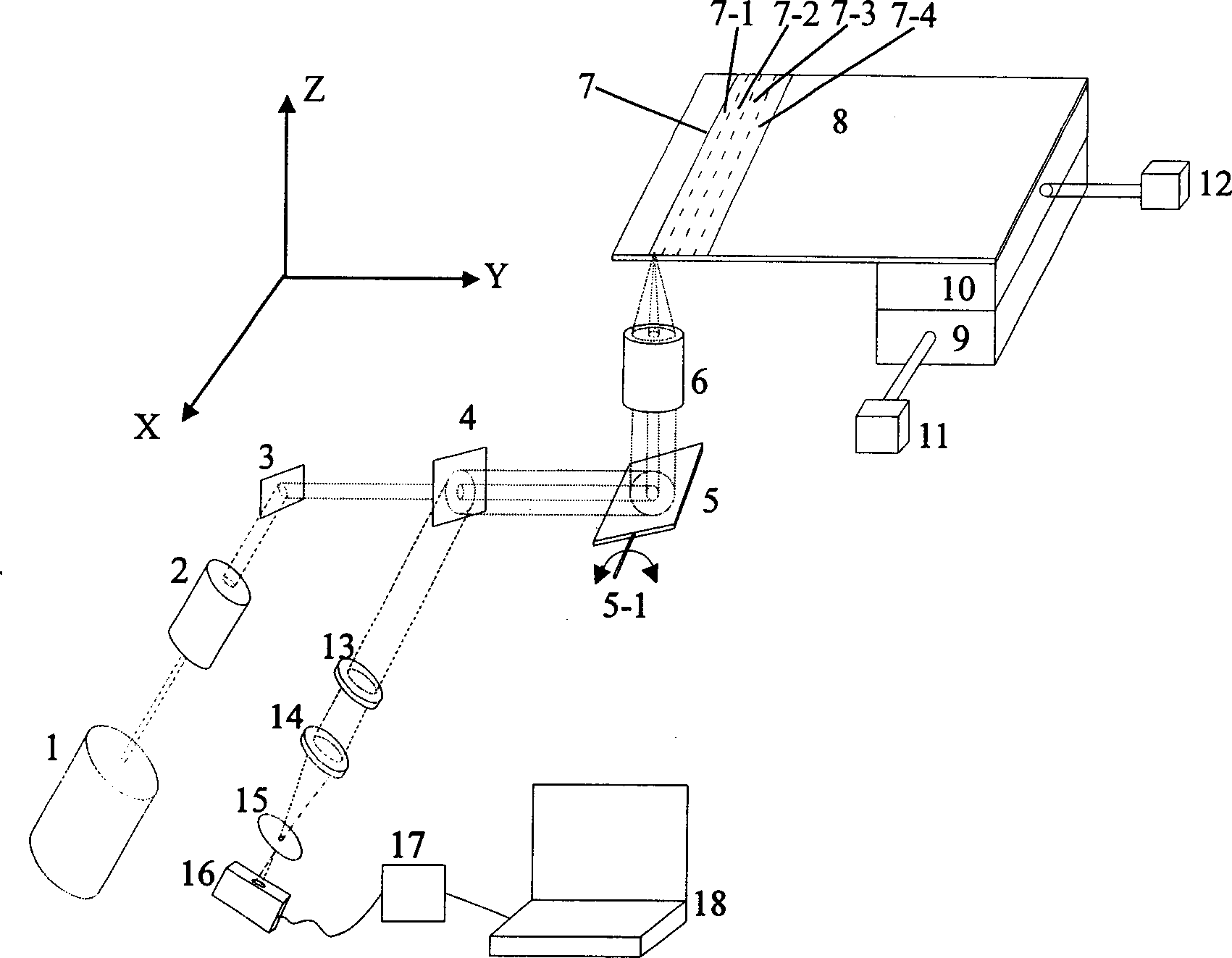
Biochip imaging method splitted with laser cofocus scanning combined image and its device
InactiveCN1793860AHigh resolutionImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroscopesFluorescenceOptoelectronics
A biological chip imaging device with laser confocal scan integrated on image splicing is prepared as dividing biological chip to be multiple sub regions as each sub regional one ¿C dimensional scan being finalized by optical scanning formed with vibration mirror and planar field objective lens, and another dimensional being finalized by mechanical scanning formed with motor and guide track; converting fluorescent signal to be electric signal by photoelectric detector; using computer to collect and rebuild fluorescent image of current sub region; doing the same operation as above for each sub region then using computer to splice each fluorescent image for obtaining complete fluorescent image of biological chip.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com