A method for predicting pregnancy-related diseases based on high-throughput sequencing of peripheral blood cell-free DNA
A prediction method and high-throughput technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, genomics, sequence analysis, etc., can solve problems such as low positive rate, high extraction cost, and easy degradation of samples
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] 1. Experimental method
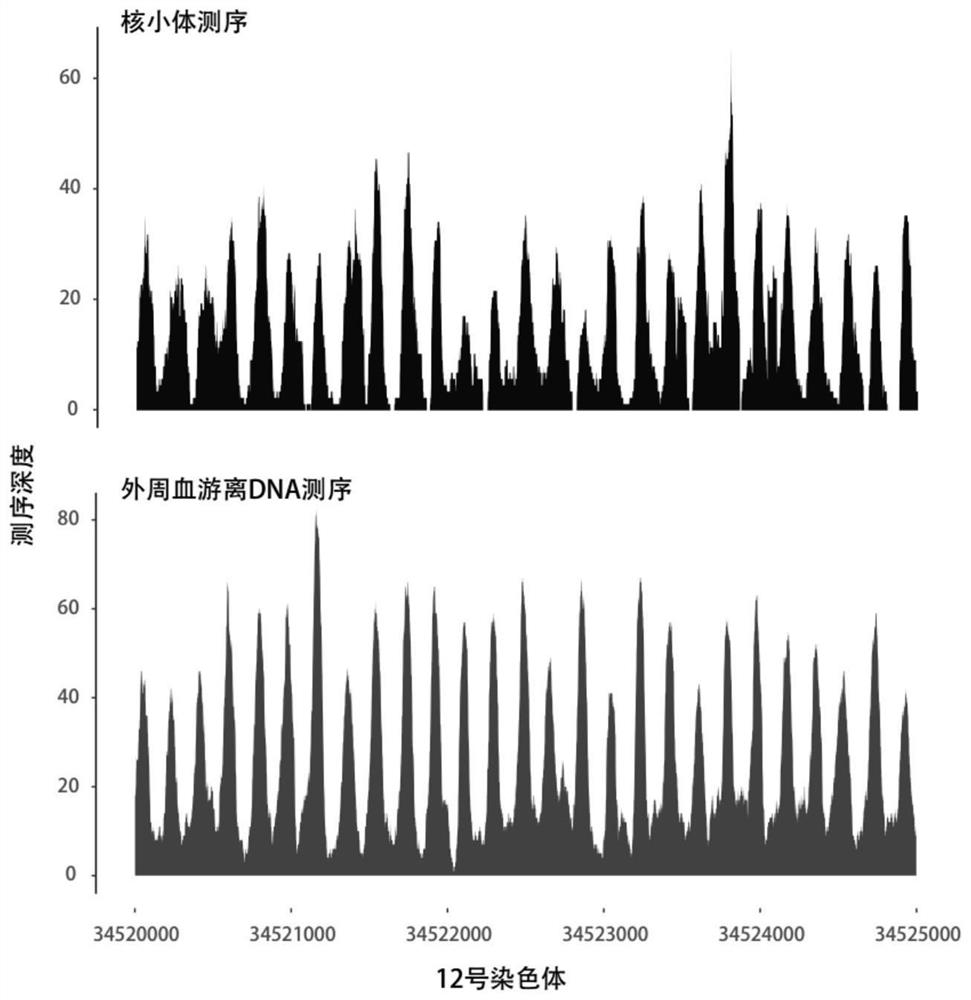
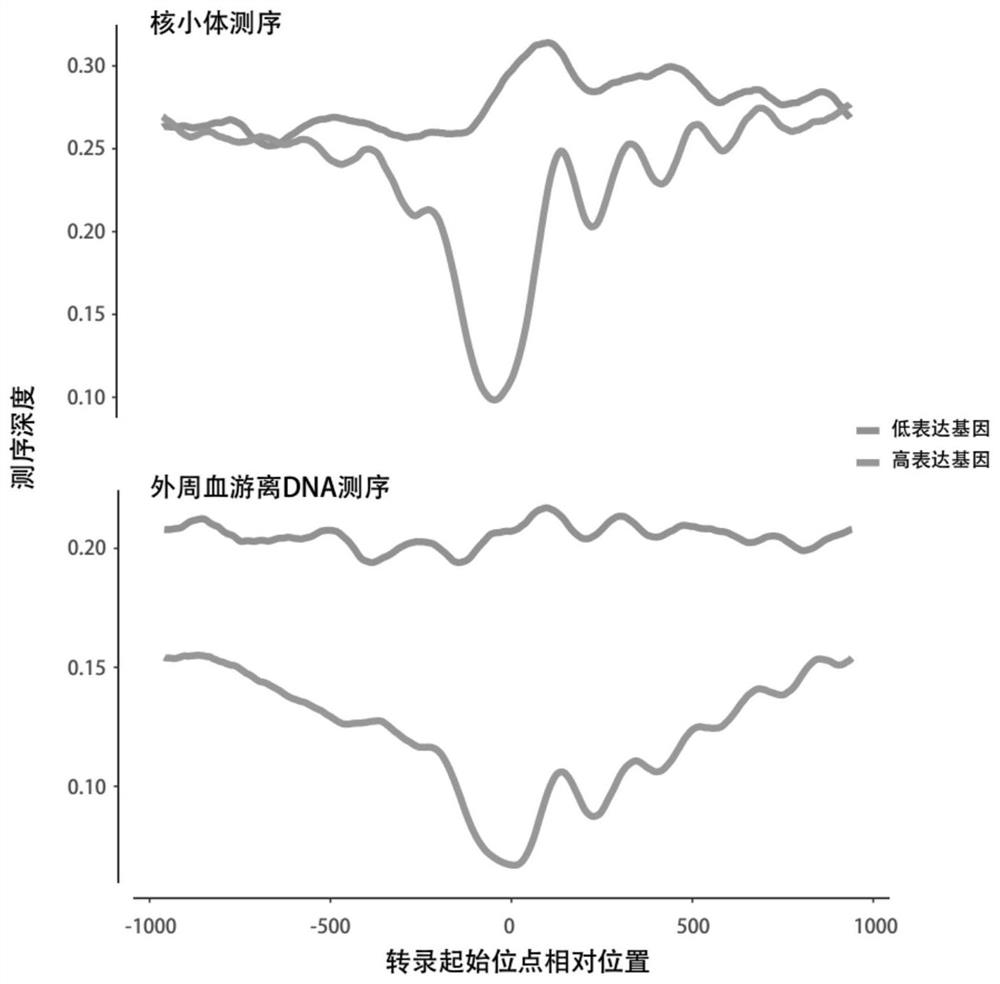
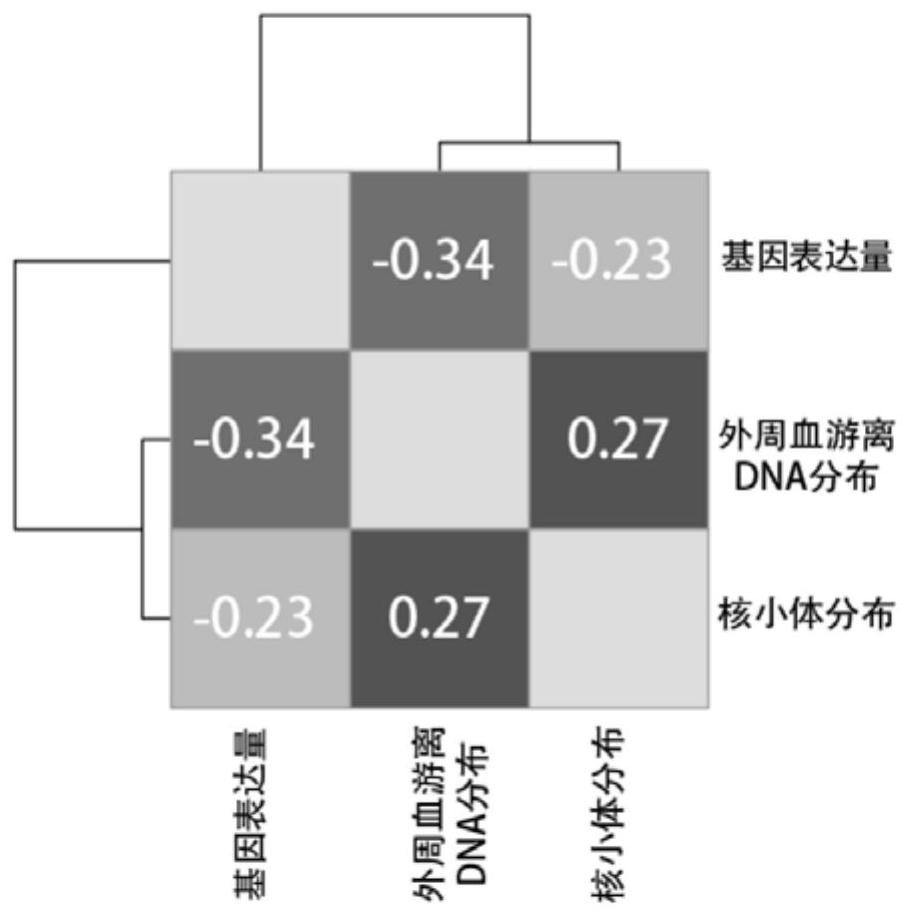
[0059] (1) Collect free peripheral blood DNA, peripheral blood leukocyte DNA and RNA from the same sample. Micrococcal Nuclease (MNase) was used to treat peripheral blood leukocyte DNA to obtain the DNA sequence bound to nucleosomes. Perform high-throughput sequencing of free peripheral blood DNA, peripheral blood leukocyte RNA, and peripheral blood leukocyte nucleosome-bound DNA, compare the sequencing results with the genome sequence map, and calculate the transcription start sites from all genes in the same sample The number of regional DNA fragments, the number of nucleosome-bound DNA fragments, and the number of RNA fragments of the gene to be tested.
[0060] This step is specifically to determine where the DNA or RNA fragment comes from on the chromosome: after DNA double-end sequencing (alternatively, single-end sequencing can also be used), the sequences at both ends can be compared with the human genome standard sequence 37.1( http: / ...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Based on the above research results of genes, the present invention uses machine learning algorithms to provide a relatively non-invasive and economical and convenient early prediction method for pregnancy-related diseases through the optimal combination of different differential genes, which can be used for pre-eclampsia, gestational diabetes, fetal growth disorders Early detection and screening of pregnancy-related diseases such as limited and macrosomia.
[0076] Specifically, a pregnancy-related disease prediction model based on high-throughput sequencing of peripheral blood cell-free DNA includes three modules:
[0077] (1) High-throughput sequencing and analysis module for free peripheral blood DNA of samples to be tested:
[0078] Perform high-throughput sequencing of free peripheral blood DNA of the sample to be tested, compare the sequencing results with the genome sequence map, and calculate the number of DNA fragments from the transcription start site region of...
Embodiment 3
[0101] Embodiment 3 detection example
[0102] 1. Example of gestational diabetes detection
[0103] Operate according to the method of Example 2. In step 2, the total number of aligned sequences of the sample is counted. In this example, sample 1 and sample 2 are 69479 and 57037, respectively. Calculate the number of DNA fragments in the region of the transcription start site of the gene to be tested in the same sample, and use Formula 1 to correct the abundance of DNA fragments. Table 1 is an example of the calculation of the abundance of DNA fragments in the region of the transcription start site of the gene to be tested in two samples:
[0104] Table 1
[0105]
[0106] Use Equation 2 to calculate the risk of developing gestational diabetes mellitus. An example calculation is as follows:
[0107] Sample 1 (pre-onset sample with confirmed gestational diabetes):
[0108] logit(Y)=0.957+0.565×CC2D2B–1.060×NAT10–1.070×SIPA1–0.620×ZNF565–0.805×ZNF552–0.367×WDR35+0.559×M...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com