Patents
Literature
500results about "Inorganic fibres/flakes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
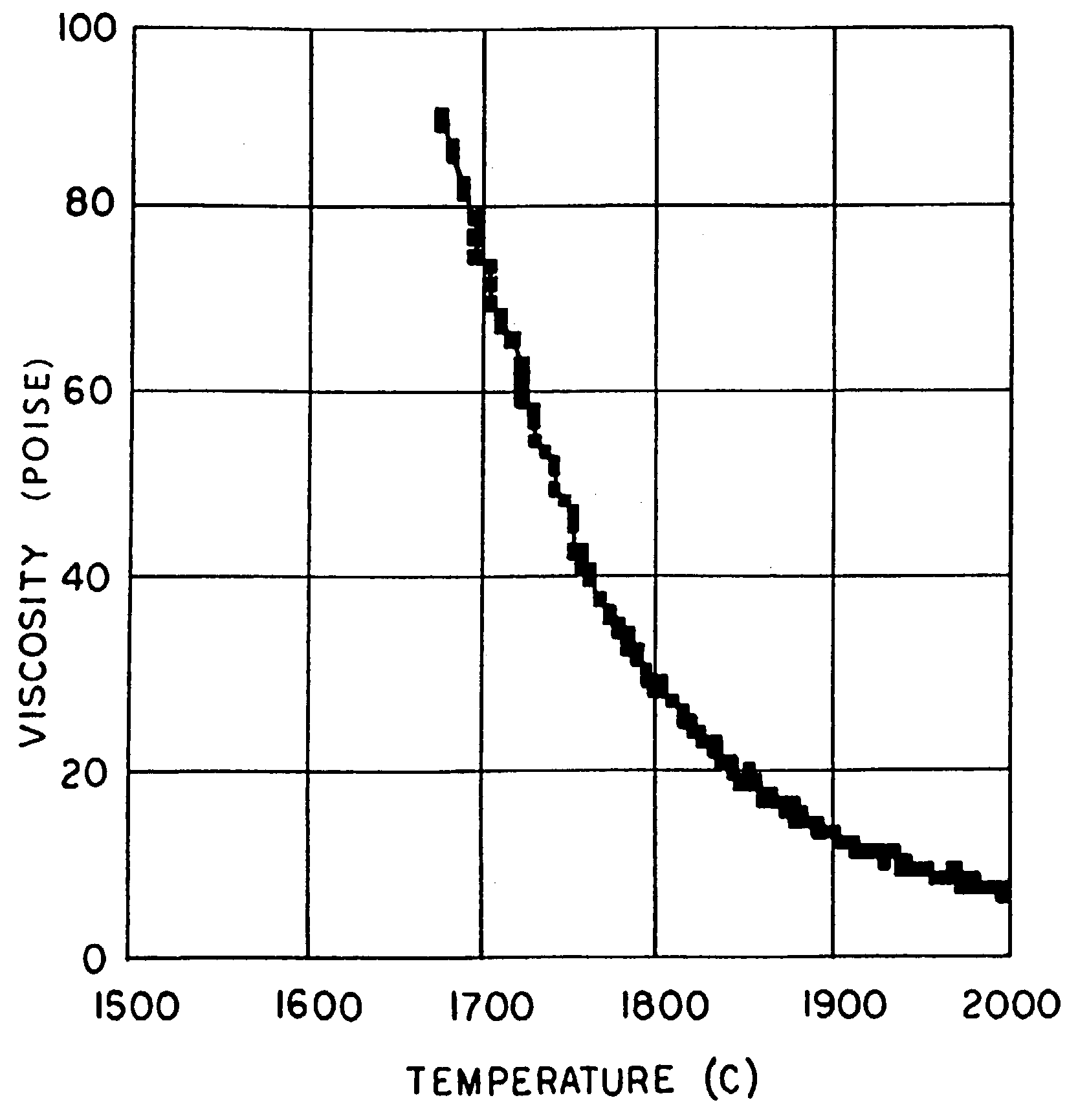
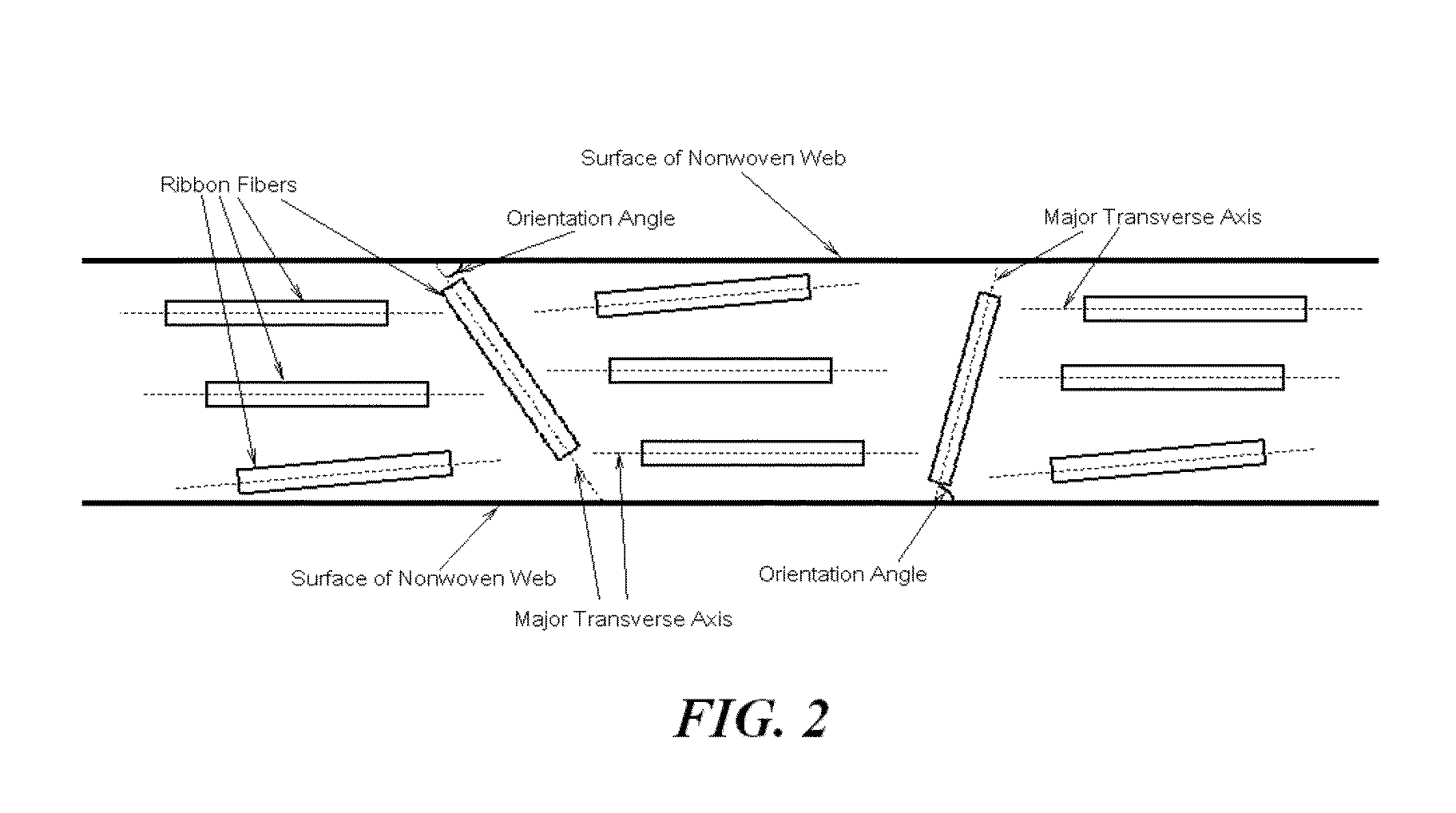
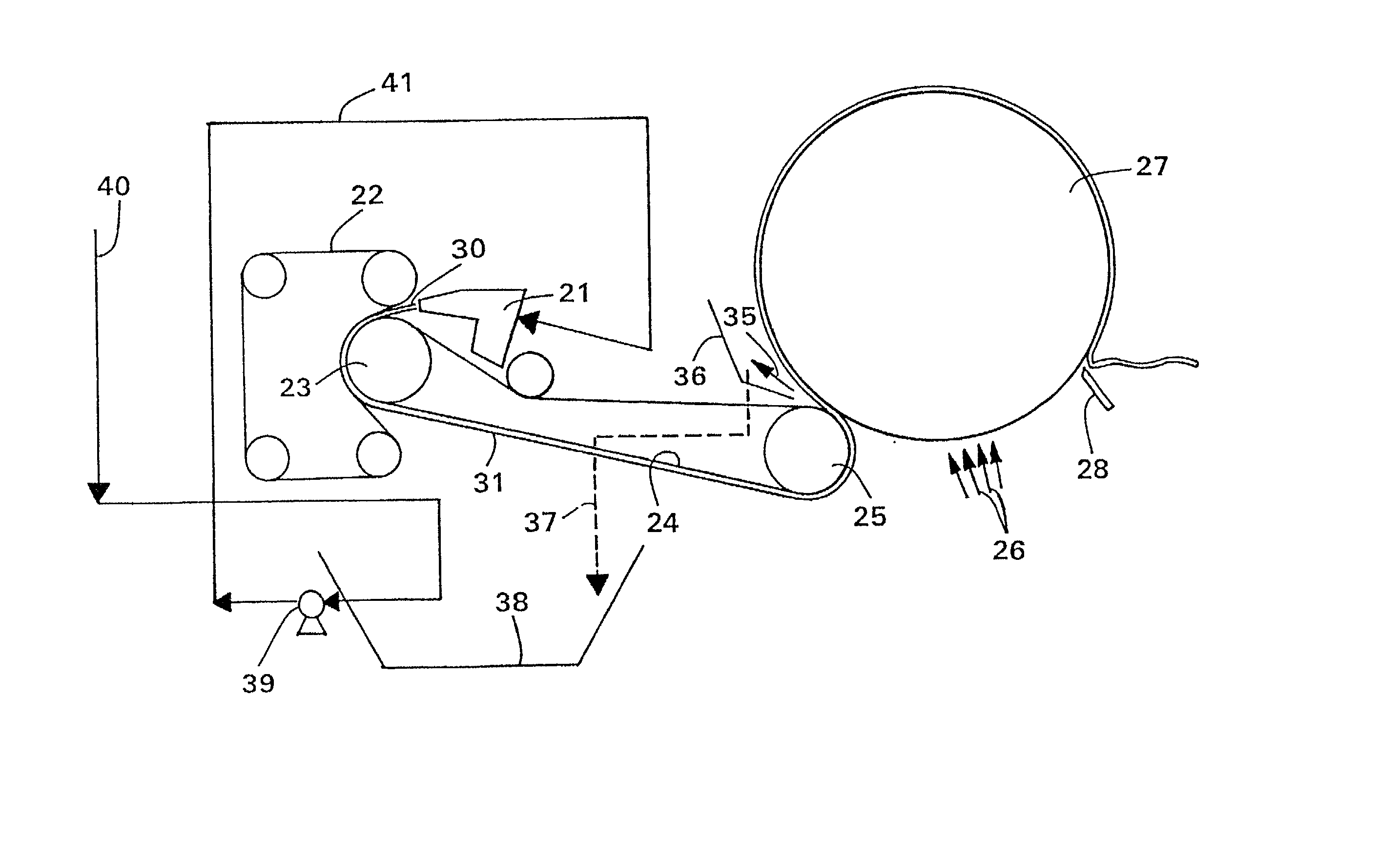
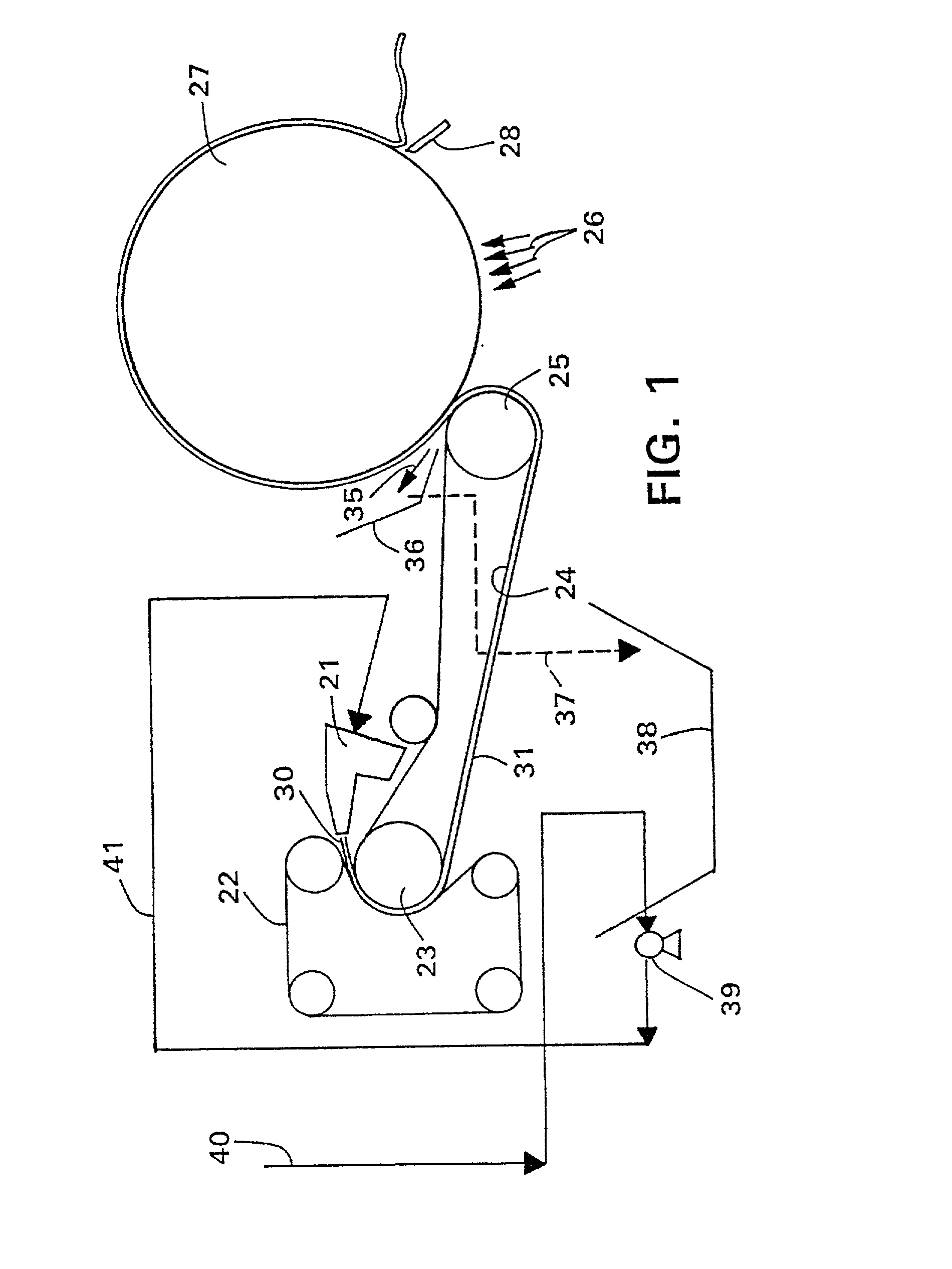
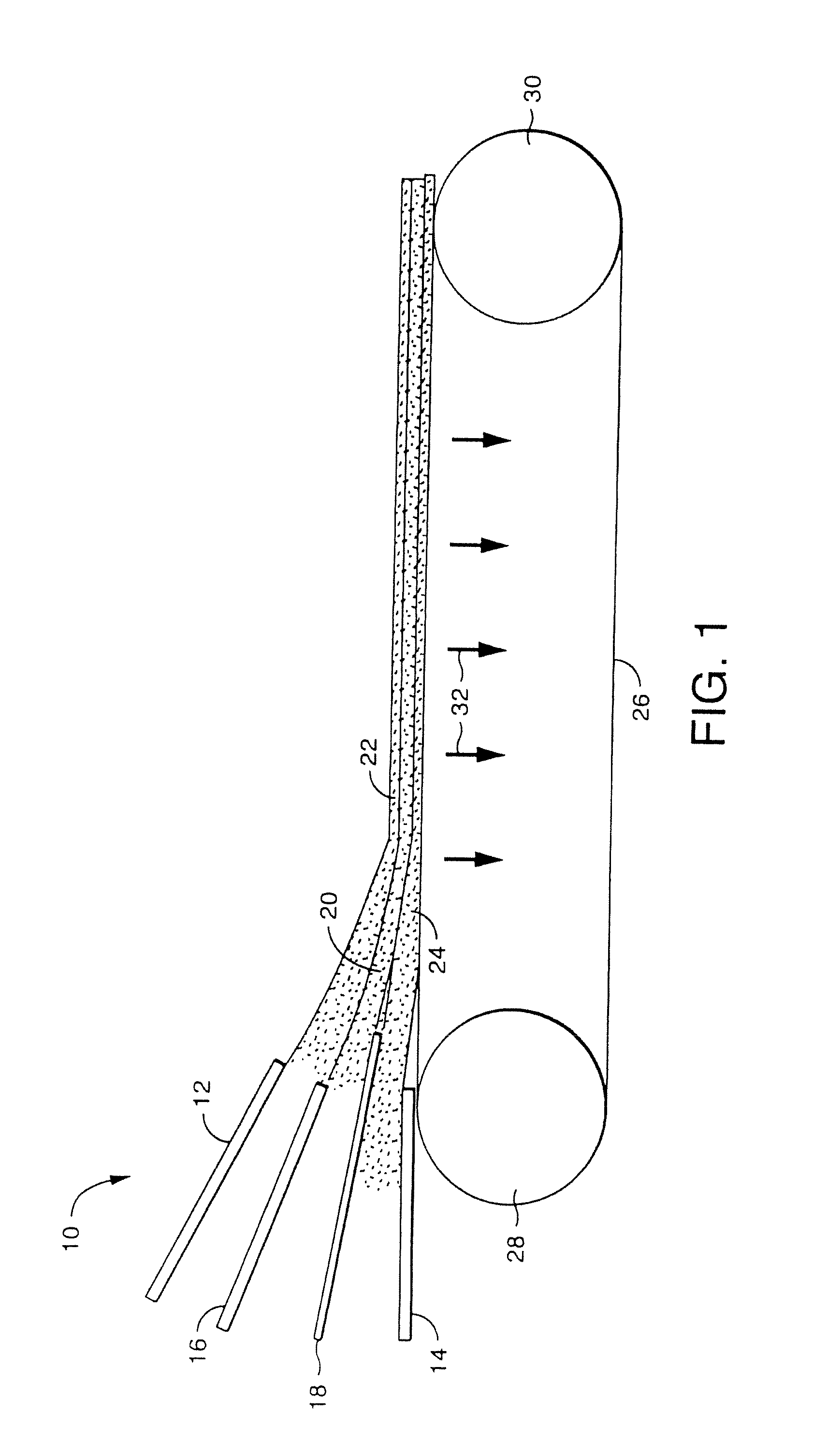
High temperature a resistant vitreous inorganic fiber
InactiveUS6953757B2Easy to manufactureLow shrinkageInorganic fibres/flakesInorganic material artificial filamentsFiberPhysiological fluid
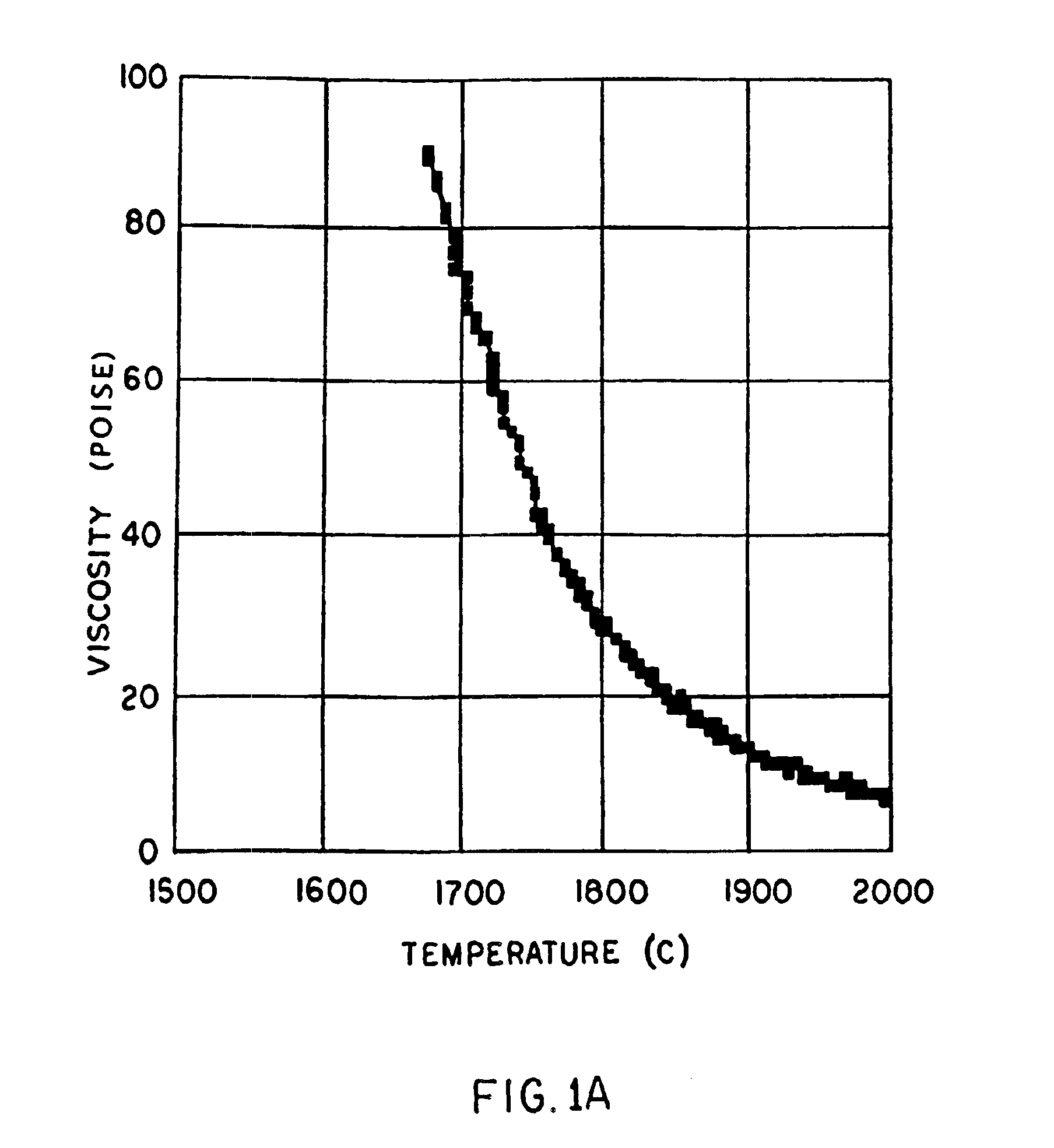
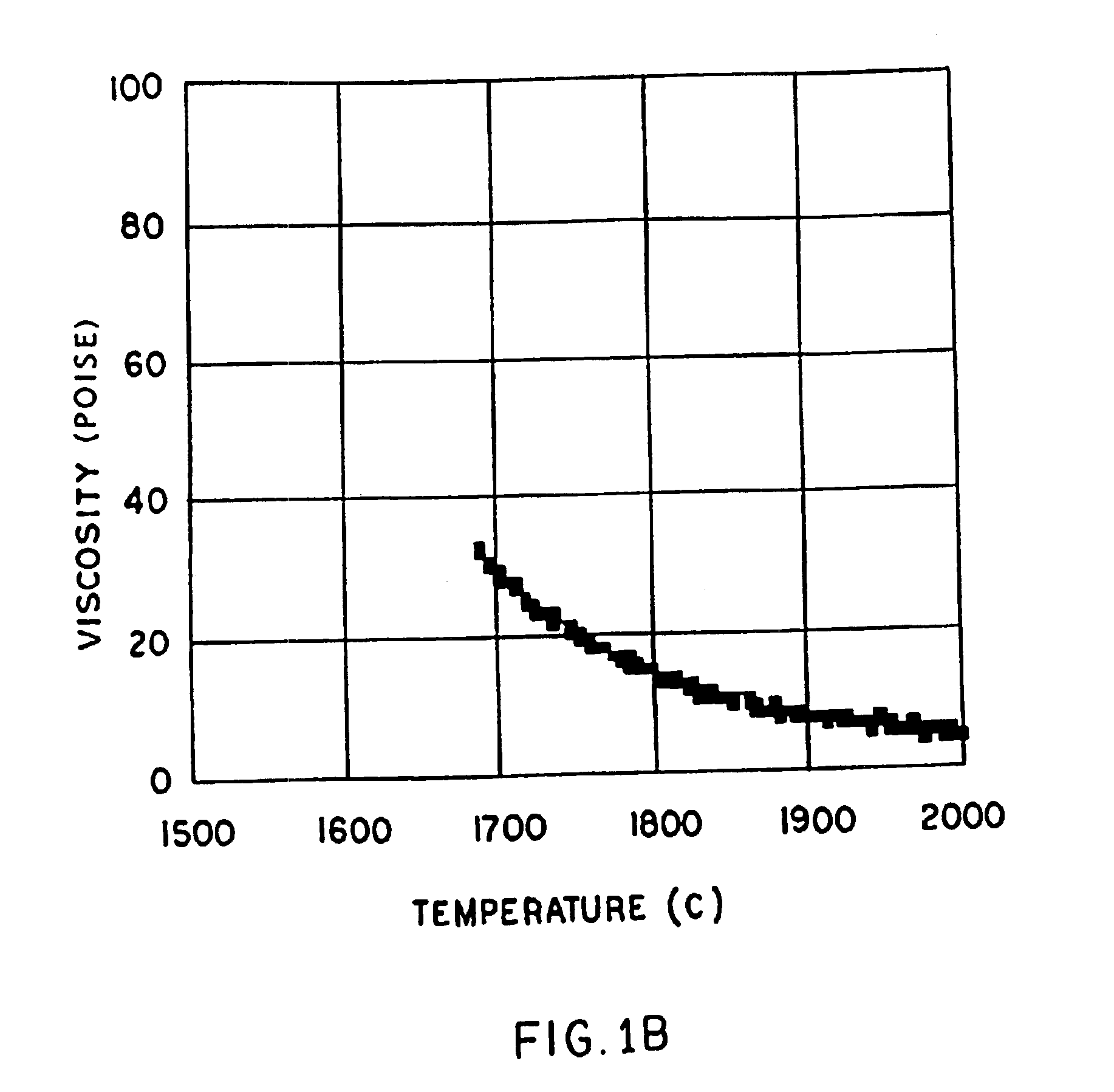
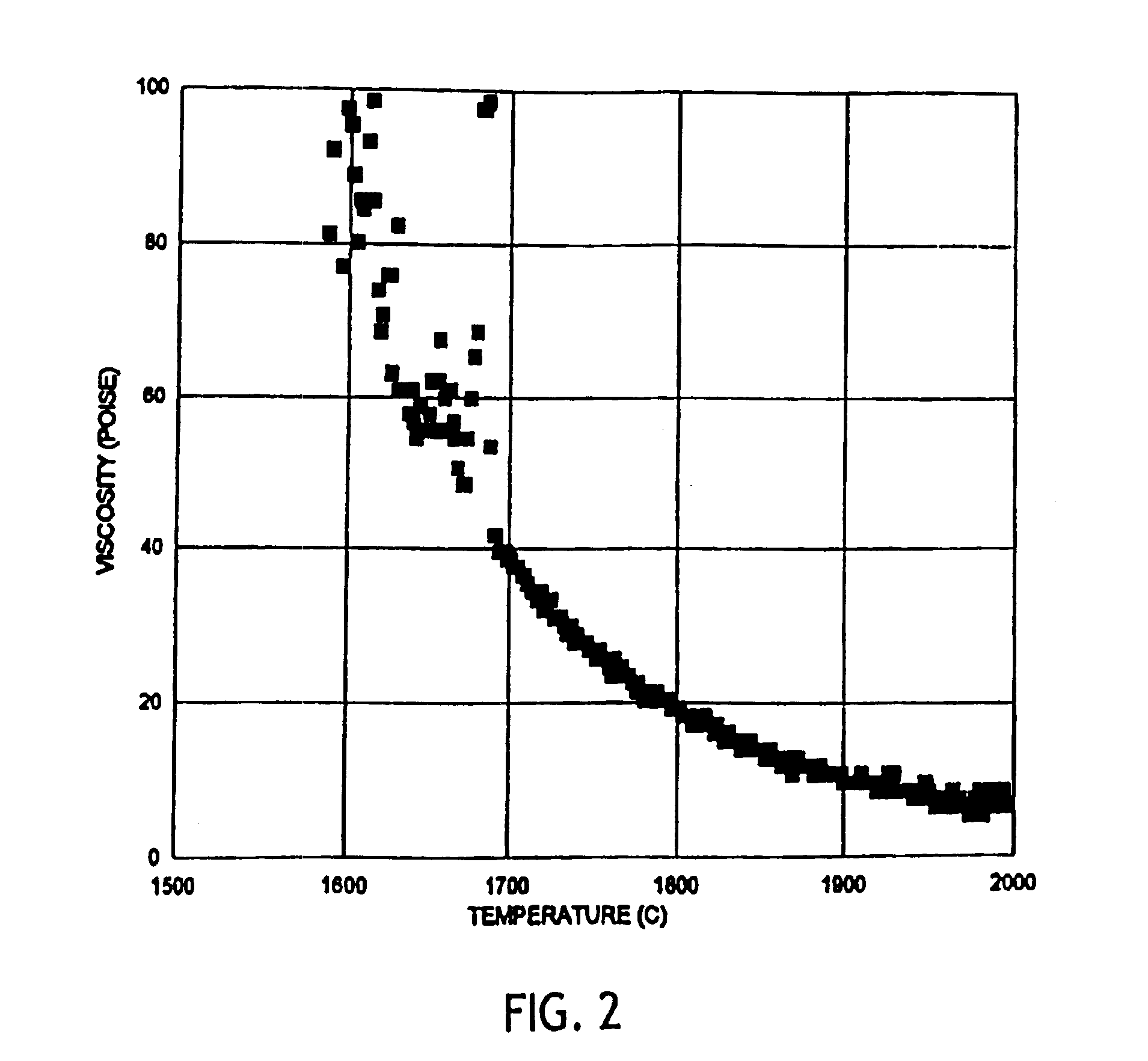
A low shrinkage, high temperature resistant vitreous inorganic fiber having a use temperature up to at least 1330° C., which maintains mechanical integrity after exposure to the use temperature and which is non-durable in physiological fluids, is prepared by the method of forming a melt with ingredients including greater than 71.25 weight percent silica, 0 to about 20 weight percent magnesia, and about 5 to about 28.55 weight percent of calcia, 0 to about 5 weight percent zirconia, and optionally a viscosity modifier in an amount effective to render the product fiberizable; and producing fibers from the melt.
Owner:UNIFRAX I LLC
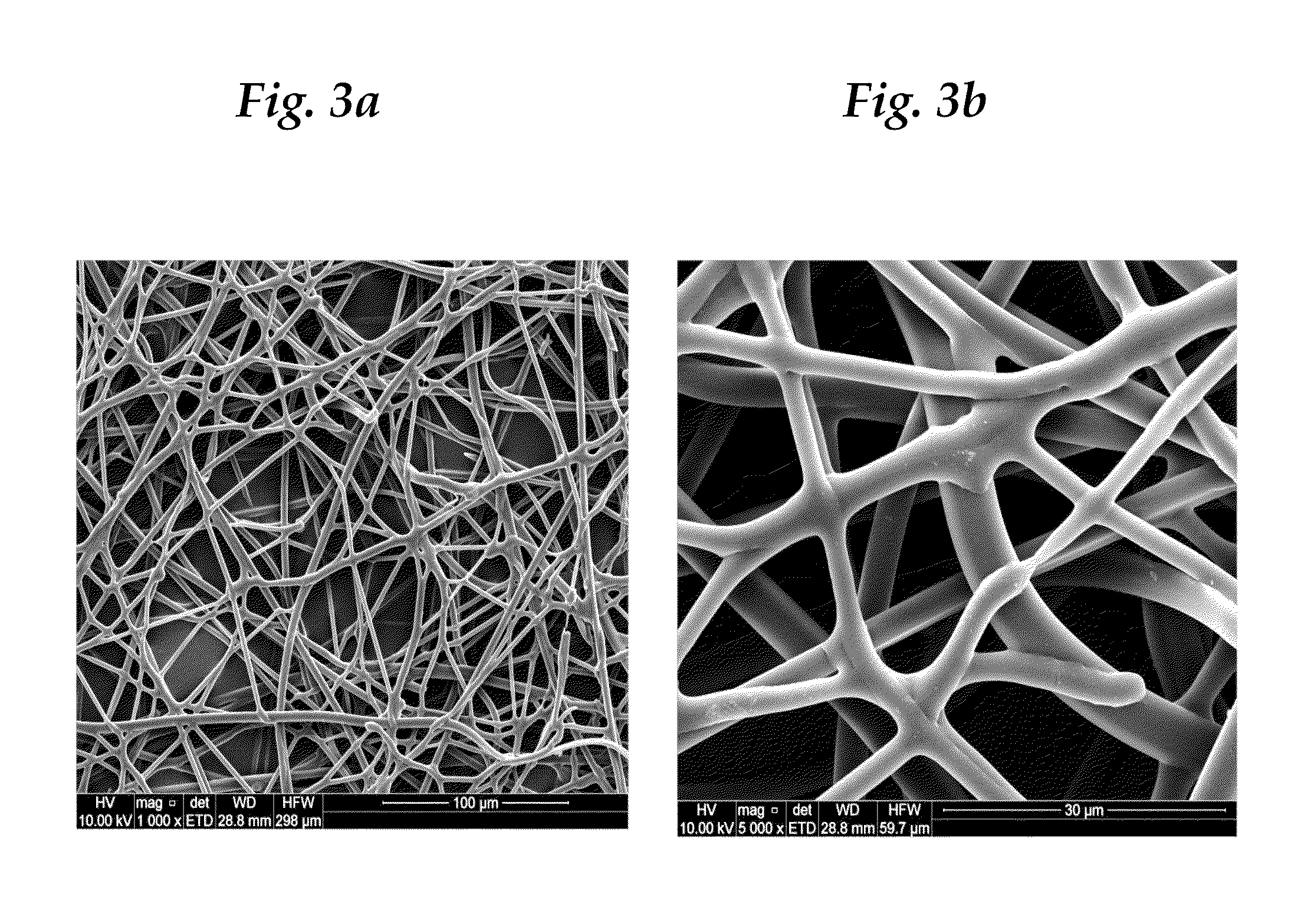
Paper and nonwoven articles comprising synthetic microfiber binders
InactiveUS20140311695A1Inorganic fibres/flakesNon-fibrous pulp additionPolymer scienceMelting temperature
A process of making a paper or nonwoven article is provide. The process comprising:a) providing a fiber furnish comprising a plurality of fibers and a plurality of binder microfibers, wherein the binder microfibers comprise a water non-dispersible, synthetic polymer; wherein the binder microfibers have a length of less than 25 millimeters and a fineness of less than 0.5 d / f; and wherein the binder microfibers have a melting temperature that is less than the melting temperature of the fibers;b) routing the fiber furnish to a wet-laid nonwoven process to produce at least one wet-laid nonwoven web layer;c) removing water from the wet-laid nonwoven web layer; andd) thermally bonding the wet-laid nonwoven web layer after step (c); wherein the thermal bonding is conducted at a temperature such that the surfaces of the binder microfibers at least partially melt without causing the fibers to melt thereby bonding the binder microfibers to the fibers to produce the paper or nonwoven article.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Composite material with improved structural, acoustic and thermal properties
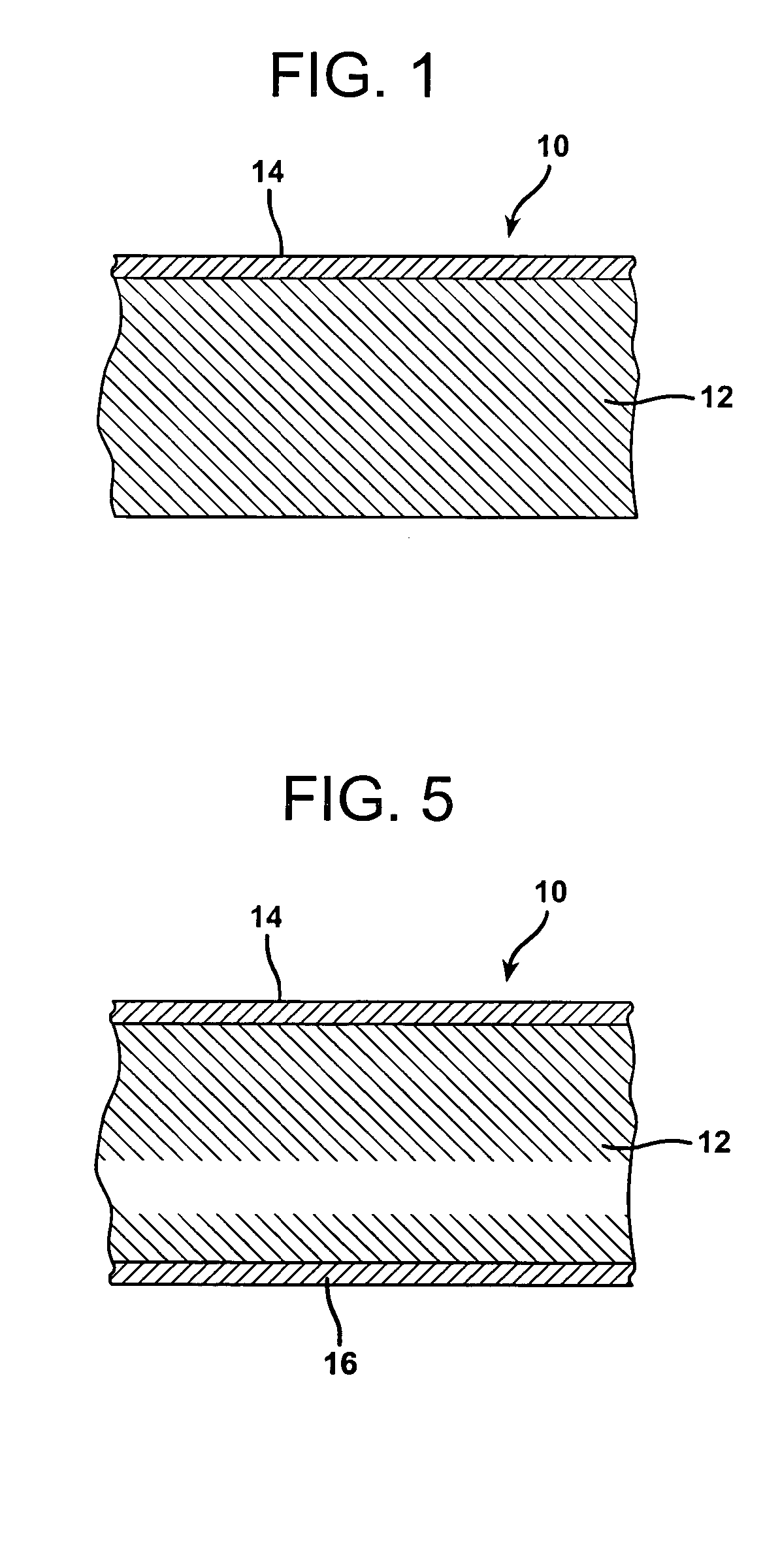
InactiveUS20050115662A1Simple structureImprove thermal propertiesWood working apparatusHeat proofingGlass fiberFiber
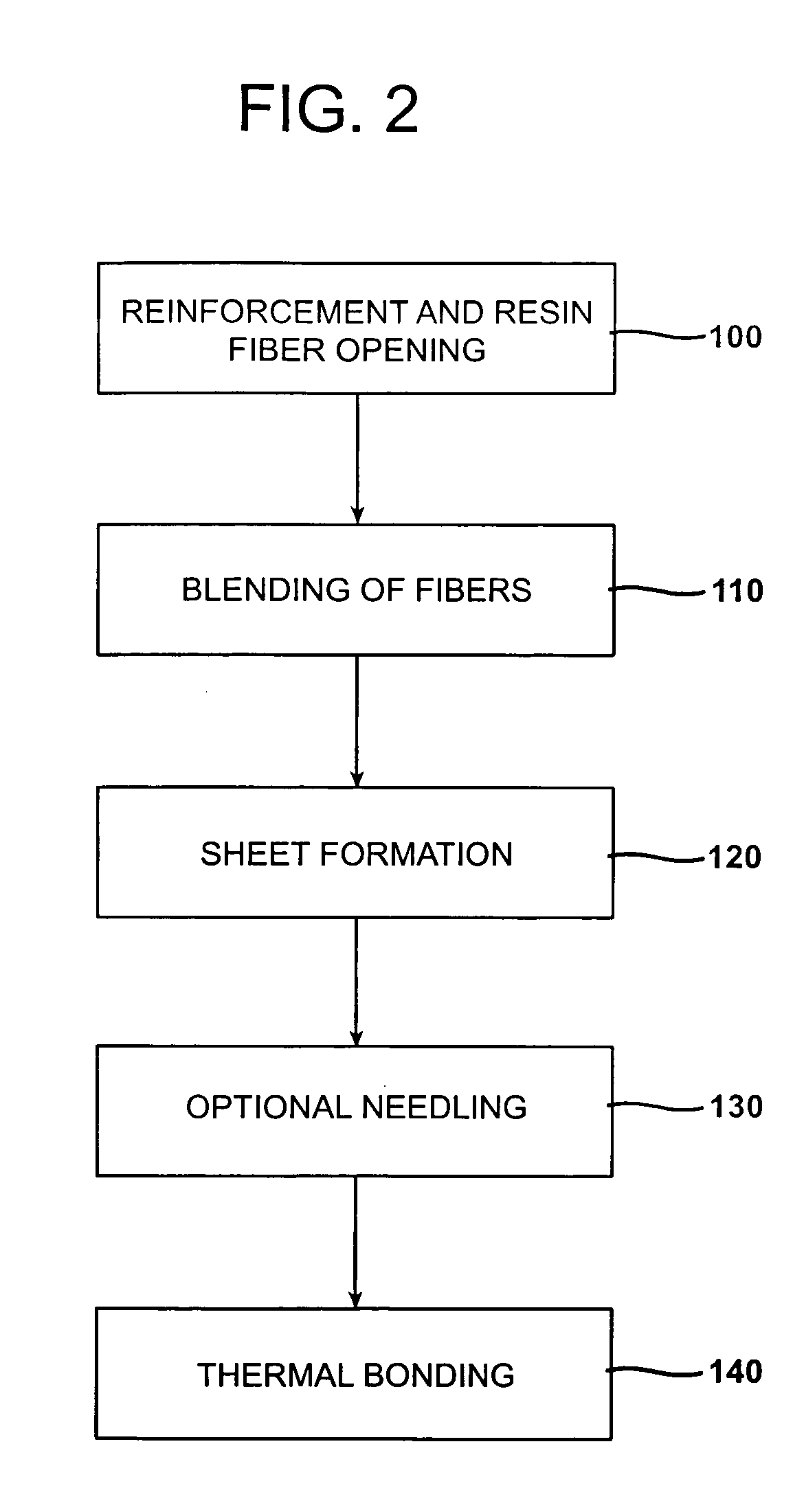
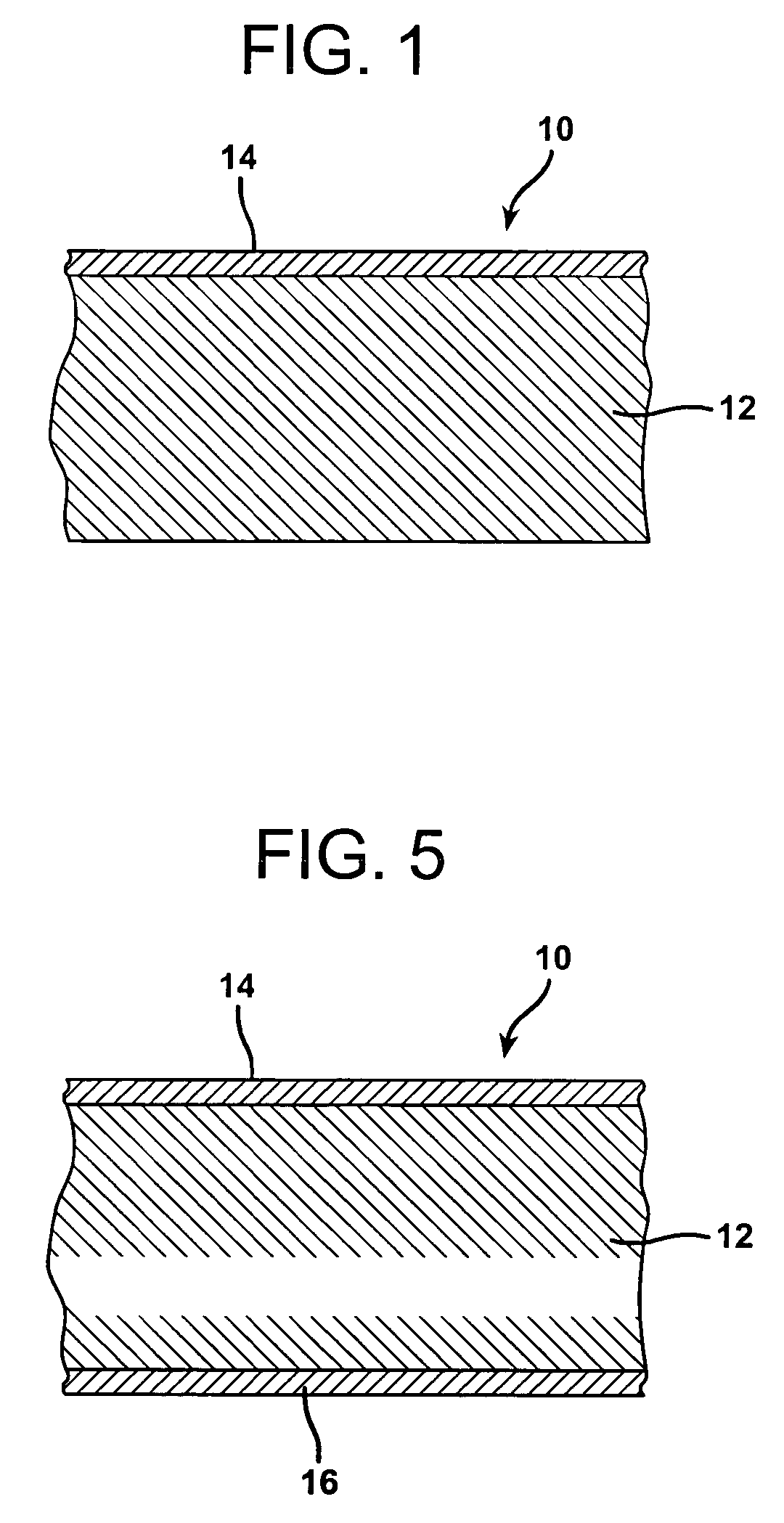
A method of forming a multilayer insulation material formed of an acoustical composite layer and a first thermal layer is provided. The acoustical and insulting layer is formed of a polymer based thermoplastic material and reinforcing fibers. Preferably the reinforcing fibers are wet use chopped strand glass fibers (WUCS). The acoustical composite layer may be formed by opening the WUCS fibers, blending the reinforcement and polymer fibers, forming the reinforcement and polymer fibers into a sheet, and then bonding the sheet. A first thermal layer formed of one or more polymer based thermoplastic organic materials is then positioned on a first major surface of the acoustical composite layer. A second thermal layer of polymeric fibers may be optionally positioned on a second major surface of the acoustical composite layer. The multilayer acoustic material may be utilized in semi-structural and acoustical applications.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Paper and nonwoven articles comprising synthetic microfiber binders
ActiveUS20140311694A1Inorganic fibres/flakesNon-fibrous pulp additionPolymer scienceMelt temperature
A paper or nonwoven article is provided comprising a nonwoven web layer, wherein the nonwoven web layer comprises a plurality of fibers and a plurality of binder microfibers, wherein the binder microfibers comprise a water non-dispersible, synthetic polymer; wherein the binder microfibers have a length of less than 25 millimeters and a fineness of less than 0.5 d / f; and wherein the binder microfibers have a melting temperature that is less than the melting temperature of the fibers.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Paper-imitating biodegradable resin and preparation method
ActiveCN101914294AAvoid pollutionAvoid degradationInorganic fibres/flakesPaper/cardboardBiopolymerVegetable fibers
The invention discloses a paper-imitating biodegradable resin and a preparation method. For improving the degradability and natural recoverability of paper-imitating materials and making the paper-imitating materials have similar lightness, foldability and printing and writing performance as the conventional paper. The paper-imitating biodegradable resin uses mineral fibers, vegetable fibers and starch fibers as main components, and concretely comprises the following components in part by weight: 40 to 70 parts of mineral fibers, 10 to 30 parts of vegetable fibers, 5 to 20 parts of starch fibers, 5 to 15 parts of biopolymer, 3 to 5 parts of modifier, 3 to 5 parts of compatibilizer and 3 to 8 parts of processing assistant. The mineral fibers, vegetable fibers and starch fibers are interweaved through thermoplastic processing, and the preparation process is clear and pollution-free. The paper-imitating biodegradable resin can be processed into various paper-imitating products by hot plasticizing equipment, and the products, when discarded, can be swallowed and decomposed by microbes without polluting the environment.
Owner:CHENDU NEW KELI CHEM SCI CO LTD
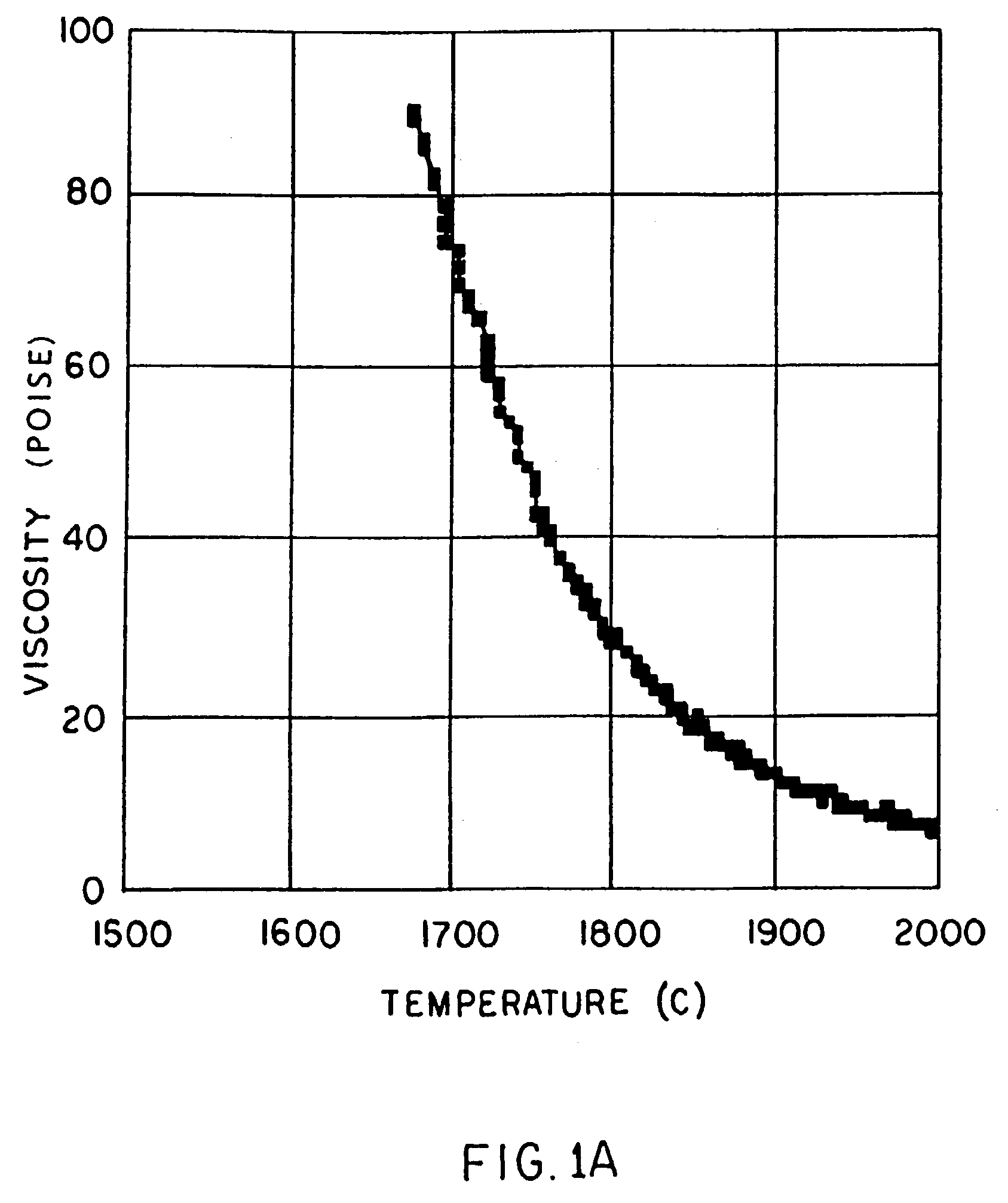
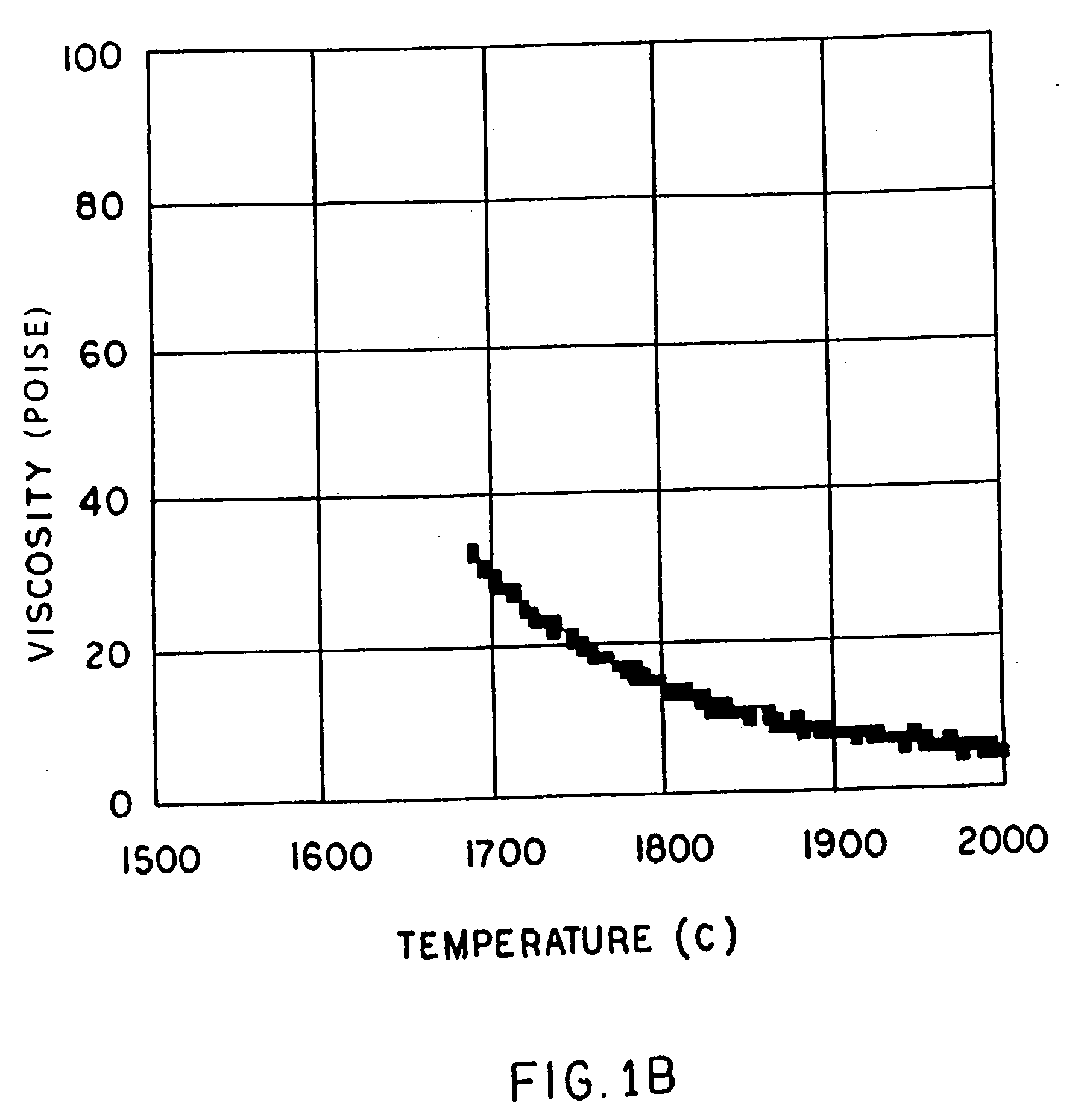
High temperature resistant vitreous inorganic fiber
InactiveUS20030162019A1Non-durableImprove shrinkage resistanceInorganic fibres/flakesInorganic material artificial filamentsFiberPhysiological fluid
A low shrinkage, high temperature resistant vitreous inorganic fiber having a use temperature up to at least 1330° C., which maintains mechanical integrity after exposure to the use temperature and which is non-durable in physiological fluids, is prepared by the method of forming a melt with ingredients including greater than 71.25 weight percent silica, 0 to about 20 weight percent magnesia, and about 5 to about 28.55 weight percent of calcia, 0 to about 5 weight percent zirconia, and optionally a viscosity modifier in an amount effective to render the product fiberizable; and producing fibers from the melt.
Owner:UNIFRAX I LLC
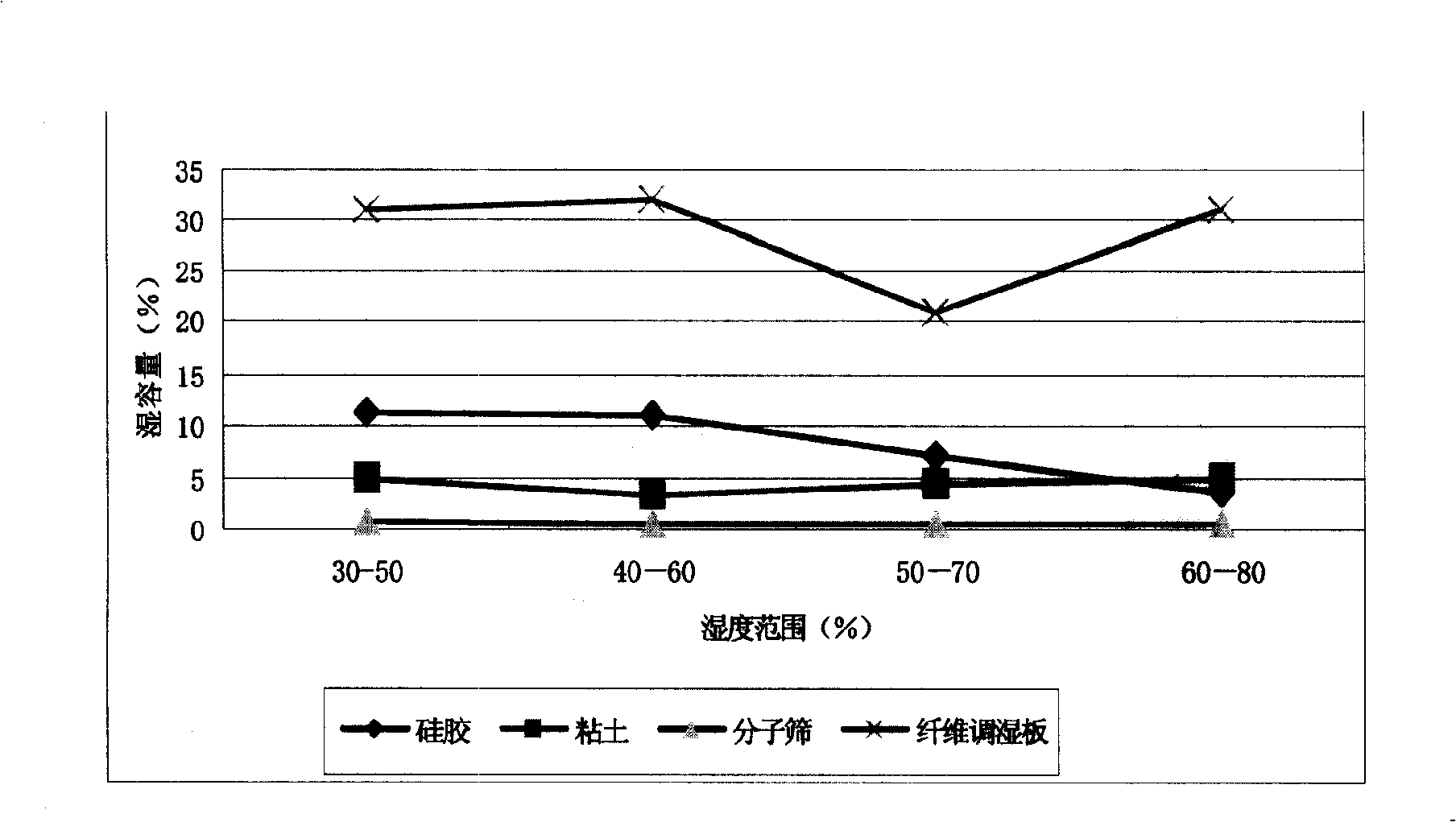
Fibre conditioning plate
InactiveCN101343850AFully adsorbedConstant humidityFibreboardInorganic fibres/flakesSilica gelMoisture
The invention provides a fiber humidity adjusting board. The fiber humidity adjusting board is obtained by soaking a composite board in a humidity adjusting liquid, and the composite board is composed of a fiber material treated by carboxylation and porous inorganic particles dispersed in the fiber material, wherein the mass of the inorganic particles accounts for 5 to 30 percent of the solid content of the fiber, and the inorganic particles adopt one or the combination of silica gel, clay, concavo-convex rods, diatomaceous earth, activated carbon, wood charcoal and bamboo charcoal. The invention has the advantages that the fiber humidity adjusting board is a precise humidity adjusting product, when the ambient humidity changes, response can be rapidly made, and through moisture absorbing and releasing, the ambient humidity can be balanced, so as to maintain the humidity in the environment to be constant and ensure that the phenomena of wetting, mould damage or drying and cracking of the stored articles can not occur within the adjusting environment. A strap-shaped fiber humidity adjusting board is adopted, which can be cut arbitrarily; the humidity adjustment can be performed in function, and the moisture holding amount can reach and surpass the equivalent international humidity adjusting products. The fiber humidity adjusting board adopts non-toxic, harmless and recoverable raw material, and the fiber humidity adjusting board is a new-generation green and environment-friendly product.
Owner:SHANGHAI HENGYUAN MACROMOLECULAR MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Method for preparing coated paper
ActiveCN101418532AImprove resource utilization efficiencyReduce manufacturing costInorganic fibres/flakesPaper coatingFiberCellulase
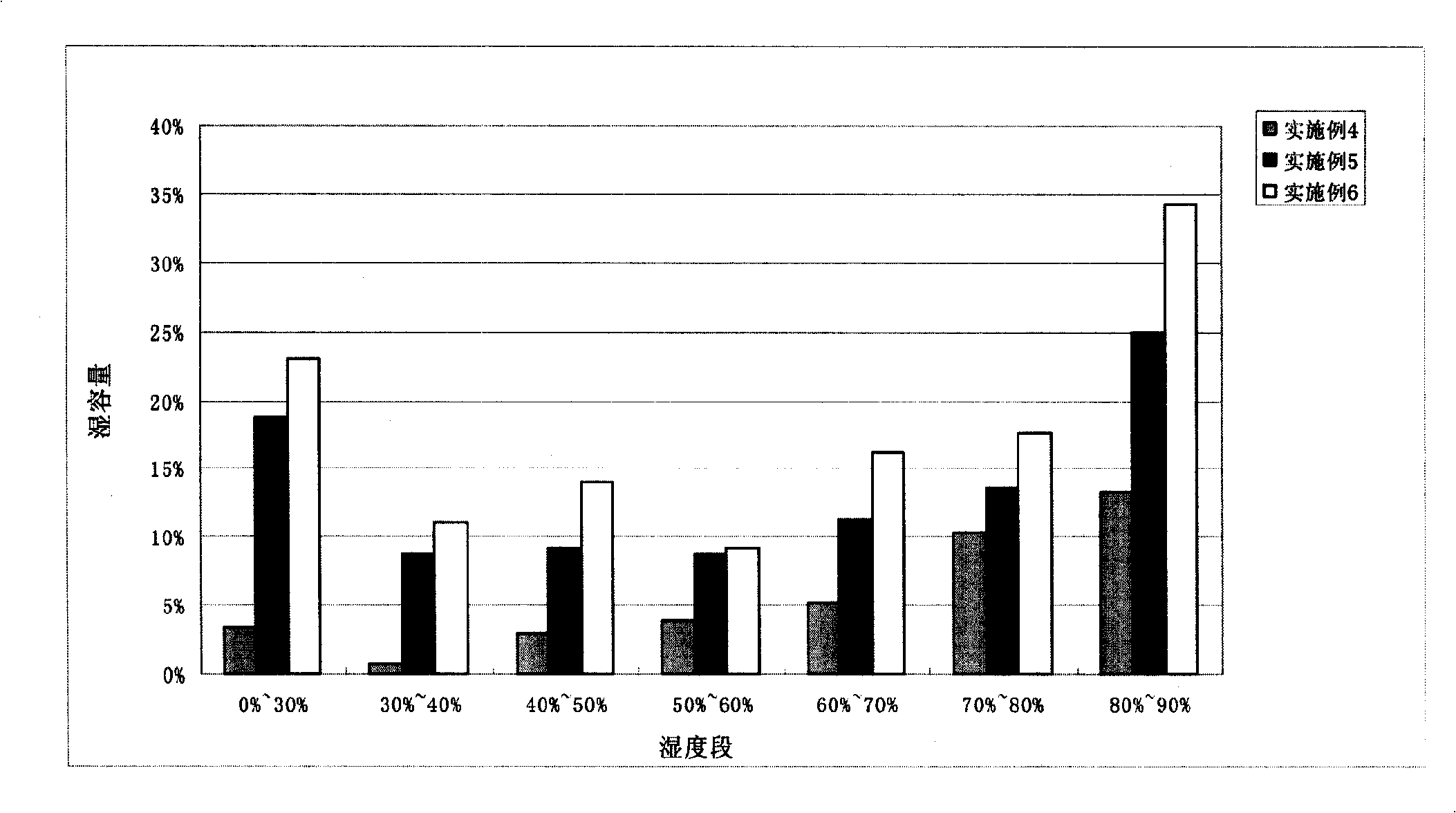
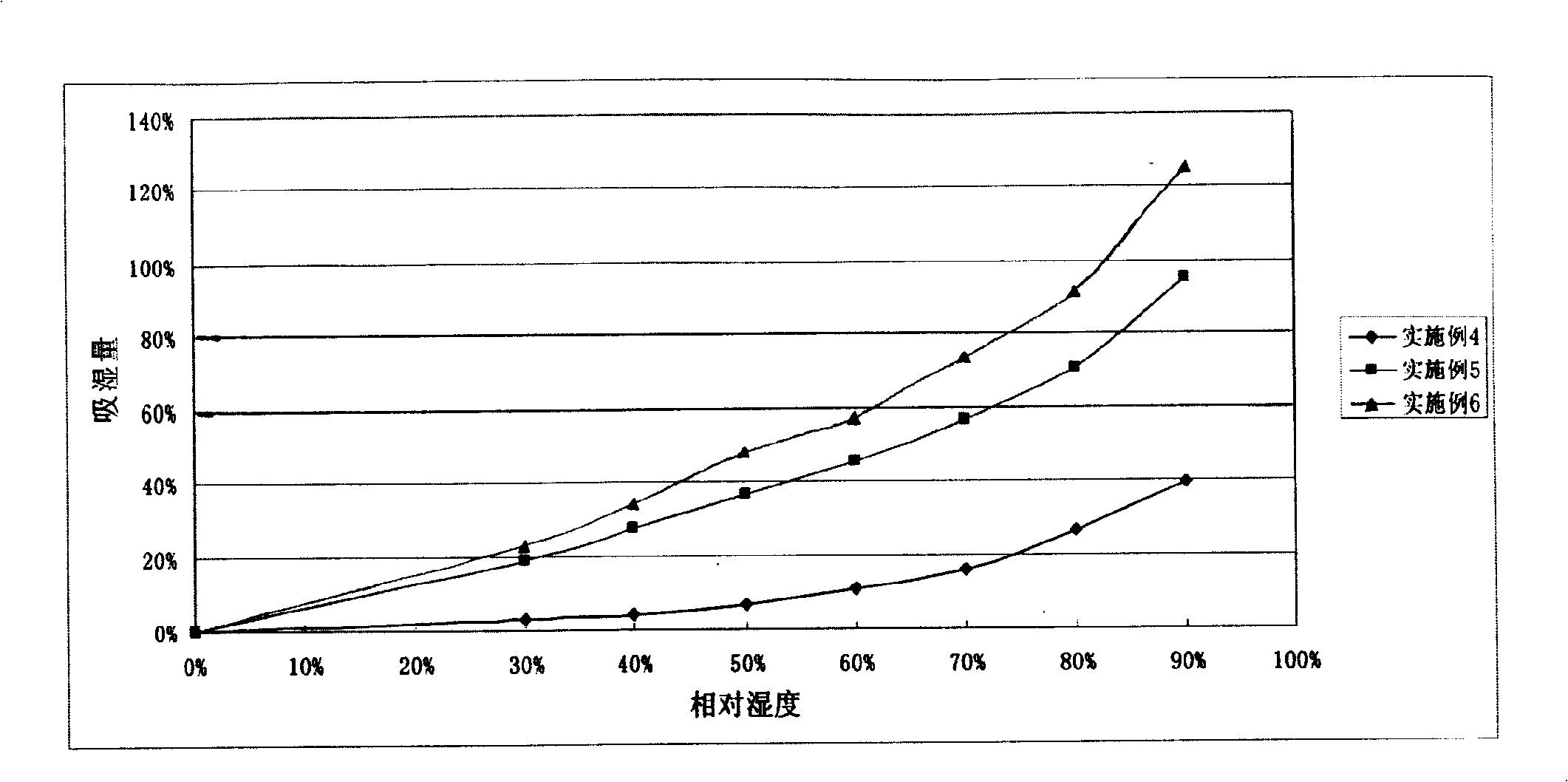
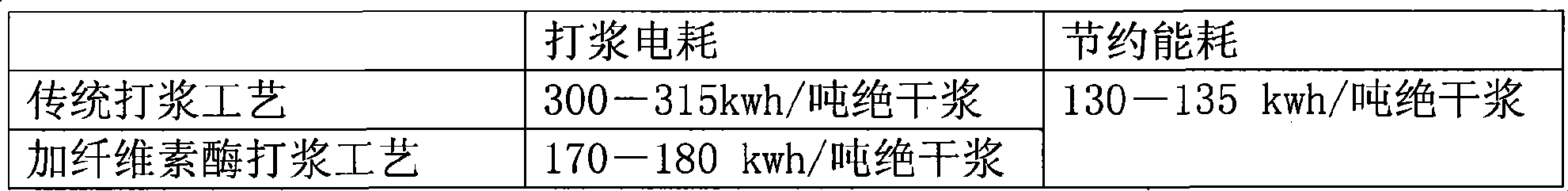
The invention relates to a method for preparing enamel paper. Through the addition of cellulase, the preparation method effectively reduces energy consumption of pulping and improves pulp quality; a mineral fiber ingredient is used to replace wood fiber so as to save wood resource and simultaneously reduce production cost; and the prepared enamel paper has anti-counterfeit function.
Owner:山东晨鸣纸业集团股份有限公司 +1
Paper and nonwoven articles comprising synthetic microfiber binders
A paper or nonwoven article is provided comprising a nonwoven web layer, wherein the nonwoven web layer comprises a plurality of fibers and a plurality of binder microfibers, wherein the binder microfibers comprise a water non-dispersible, synthetic polymer; wherein the binder microfibers have a length of less than 25 millimeters and a fineness of less than 0.5 d / f; and wherein the binder microfibers have a melting temperature that is less than the melting temperature of the fibers.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Filter paper of energy-saving and environment-friendly filter and making method thereof
ActiveCN102199903AHigh filtration precisionHigh burst resistanceInorganic fibres/flakesFiltration separationAir filterFuel filter
The invention relates to filter paper of an energy-saving and environment-friendly filter and a making method thereof. The filter paper is made from an energy-saving and environment-friendly ceramic powder material, a silane coupling agent, a dilute, a sizing agent and wood pulp. The filter paper can be made into an air filter and a fuel filter so as to improve the power performance by 6-12%, save the fuel by 2-5% and reduce pollutants in discharged tail gas by 16-47%.
Owner:北京联飞翔科技股份有限公司
Composite material with improved structural, acoustic and thermal properties
InactiveUS7294218B2Improved structural and thermal propertyReduce the amount requiredWood working apparatusHeat proofingFiberGlass fiber
A method of forming a multilayer insulation material formed of an acoustical composite layer and a first thermal layer is provided. The acoustical and insulting layer is formed of a polymer based thermoplastic material and reinforcing fibers. Preferably the reinforcing fibers are wet use chopped strand glass fibers (WUCS). The acoustical composite layer may be formed by opening the WUCS fibers, blending the reinforcement and polymer fibers, forming the reinforcement and polymer fibers into a sheet, and then bonding the sheet. A first thermal layer formed of one or more polymer based thermoplastic organic materials is then positioned on a first major surface of the acoustical composite layer. A second thermal layer of polymeric fibers may be optionally positioned on a second major surface of the acoustical composite layer. The multilayer acoustic material may be utilized in semi-structural and acoustical applications.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Mold-resistant gypsum panel paper
InactiveUS20120088114A1Improves biocide retentionReduce the amount requiredFibreboardNatural cellulose pulp/paperSlurryGypsum
A mold resistant gypsum panel having improved mold- and fungal-resistance to the gypsum panel facing paper is provided. Mold-resistant gypsum panels include a gypsum core formed from a gypsum slurry that has voids as a result of foaming of the gypsum slurry. A first paper is located on one side of the gypsum core and a second paper opposes the first paper. A first paper comprises at least one liner ply and at least one filler ply. A second paper also comprises at least one liner play and at least one filler ply. The first and second papers may be substantially the same. At least one of the first paper and the second paper also includes a biocide having 75% retention of the biocide. Also included in at least one of the first and second paper are a retention aid and a sizing agent.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
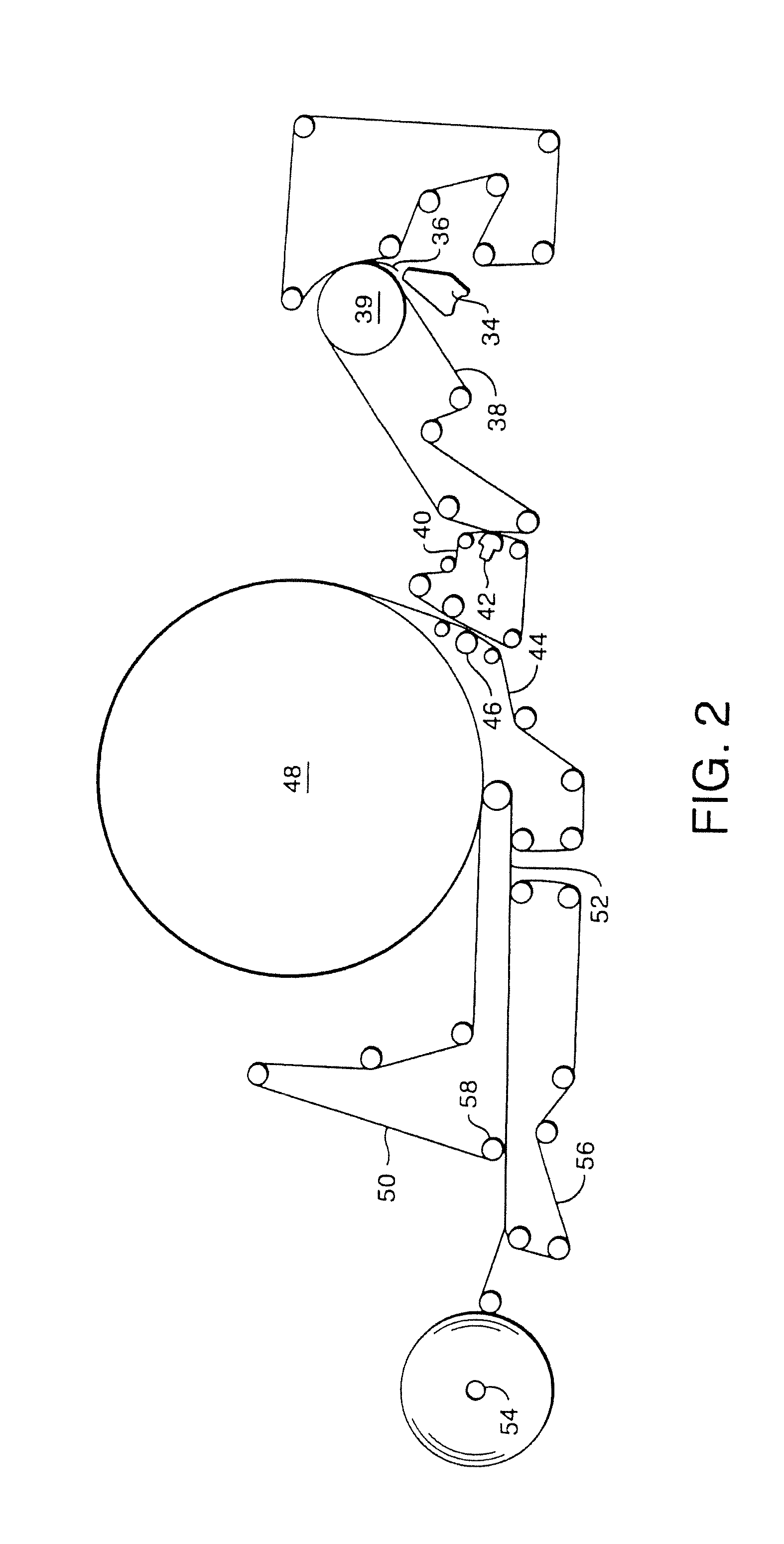
Development of thermoplastic composites using wet use chopped strand (Wucs)
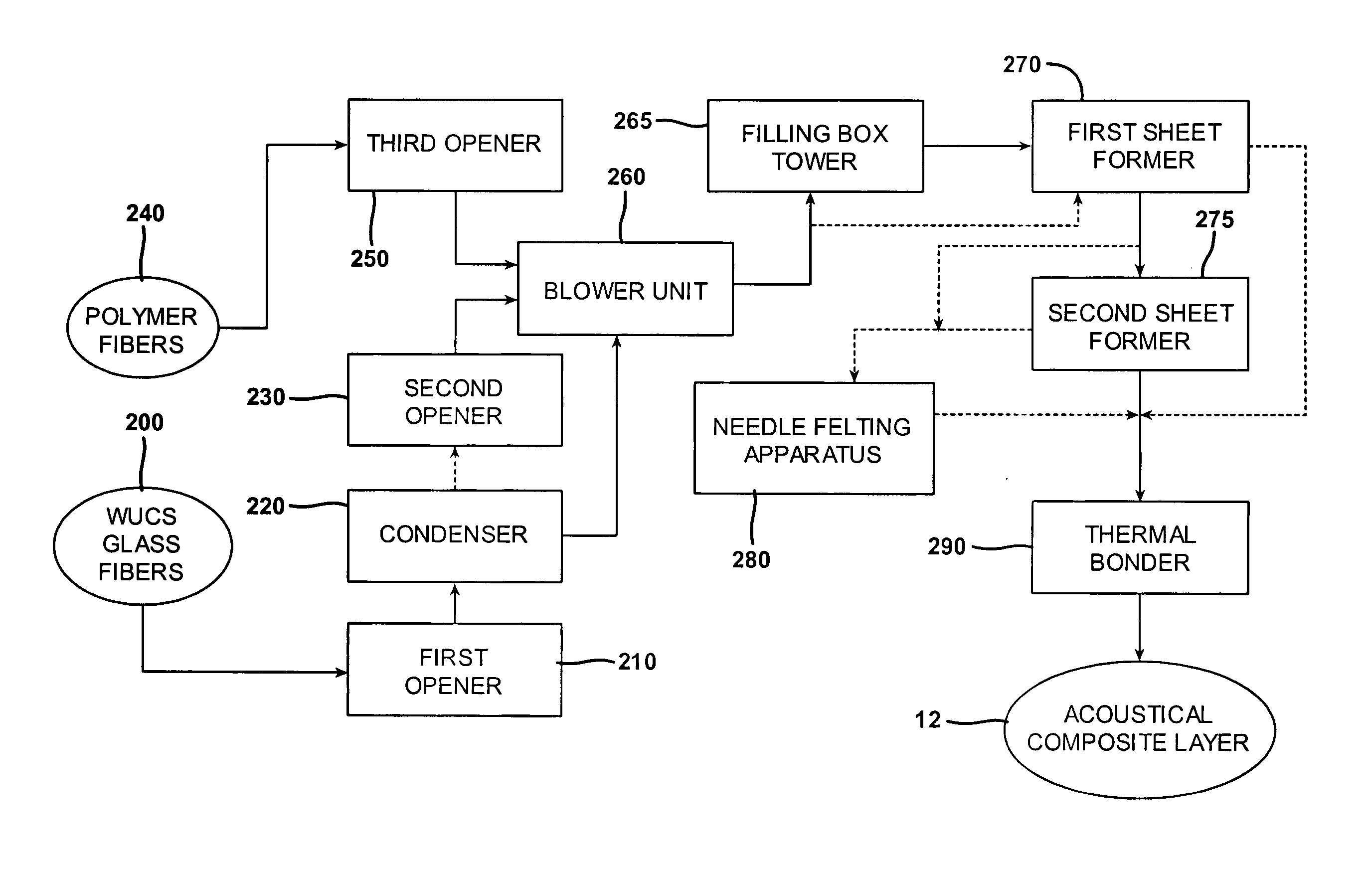
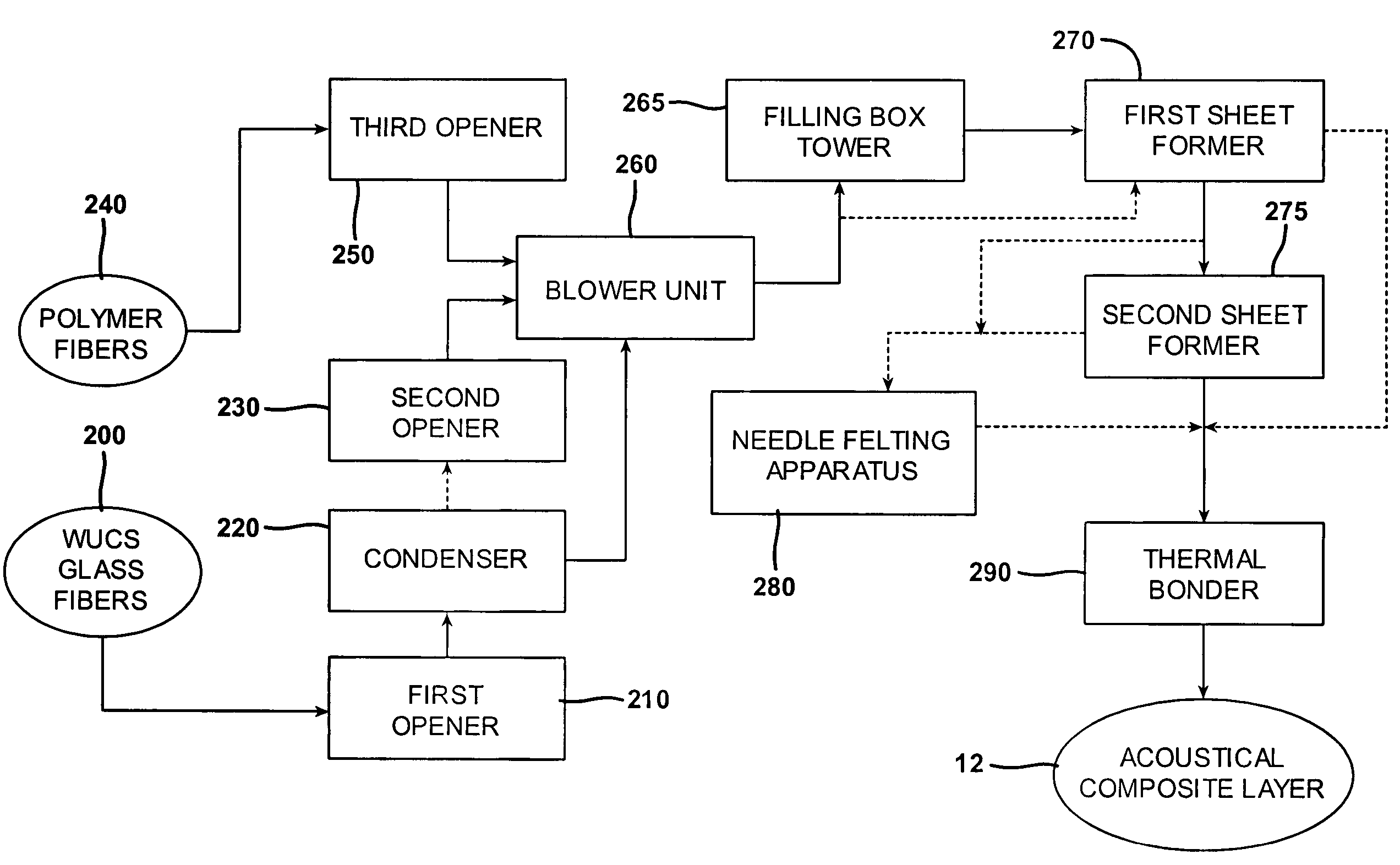
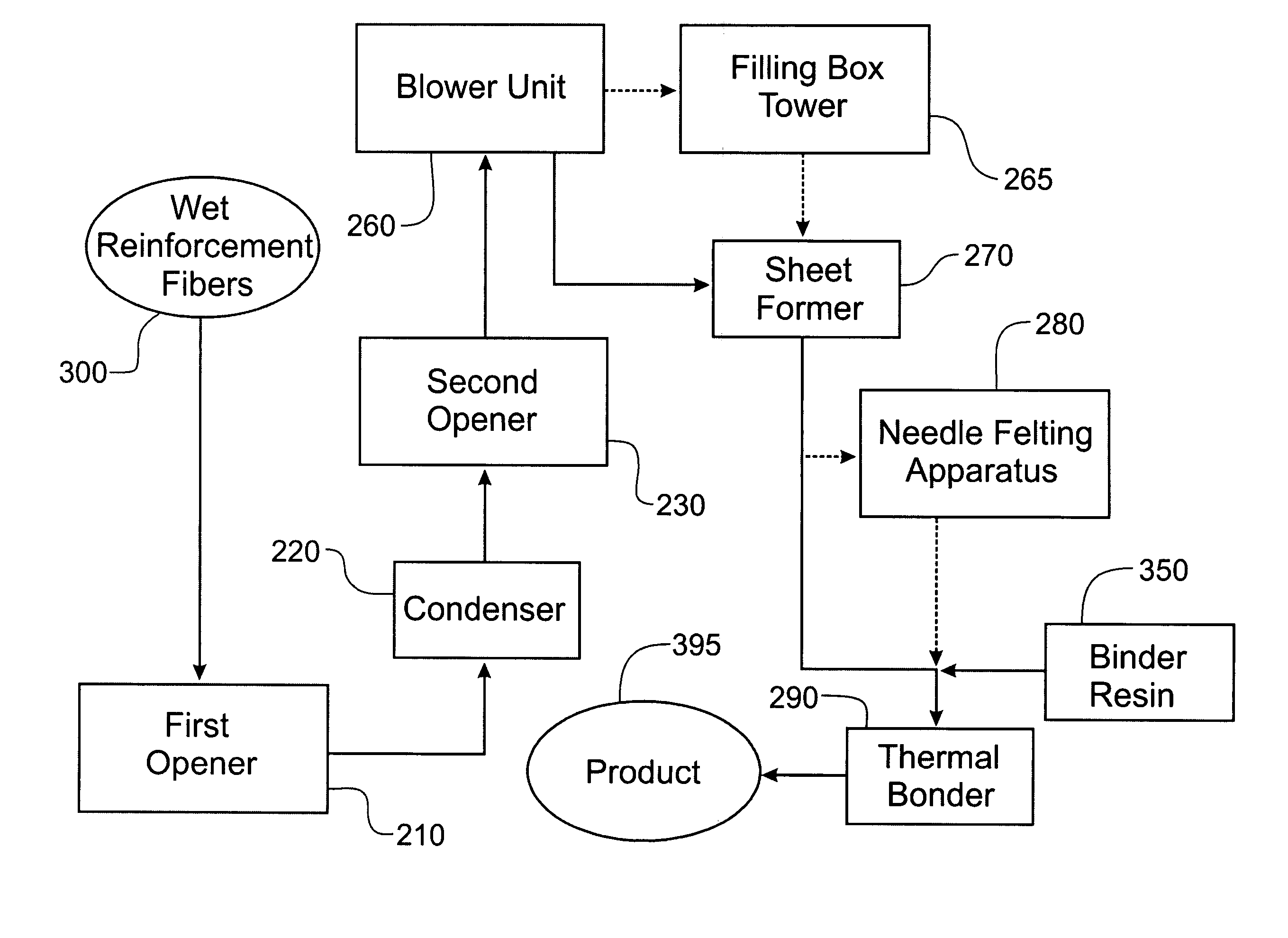
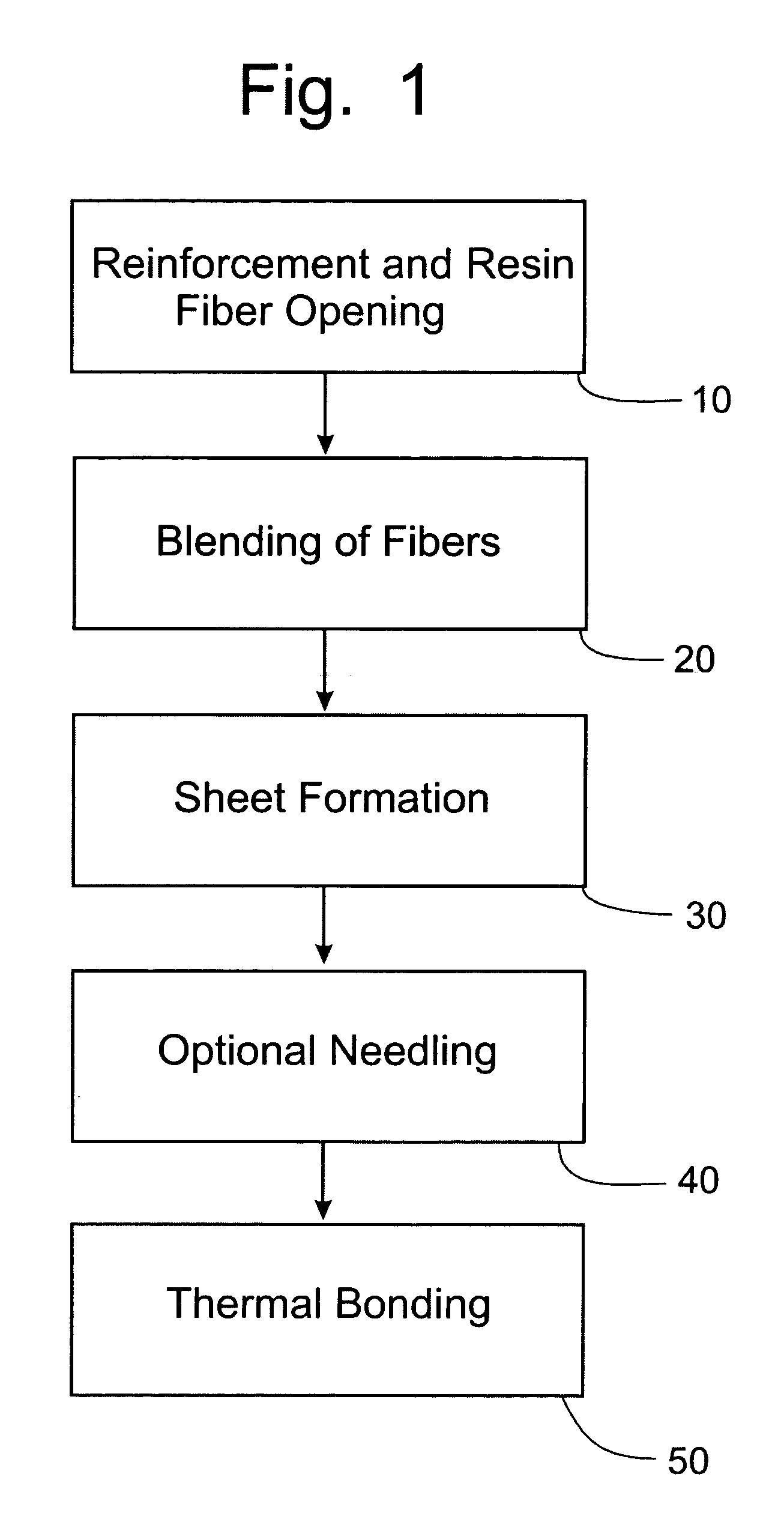
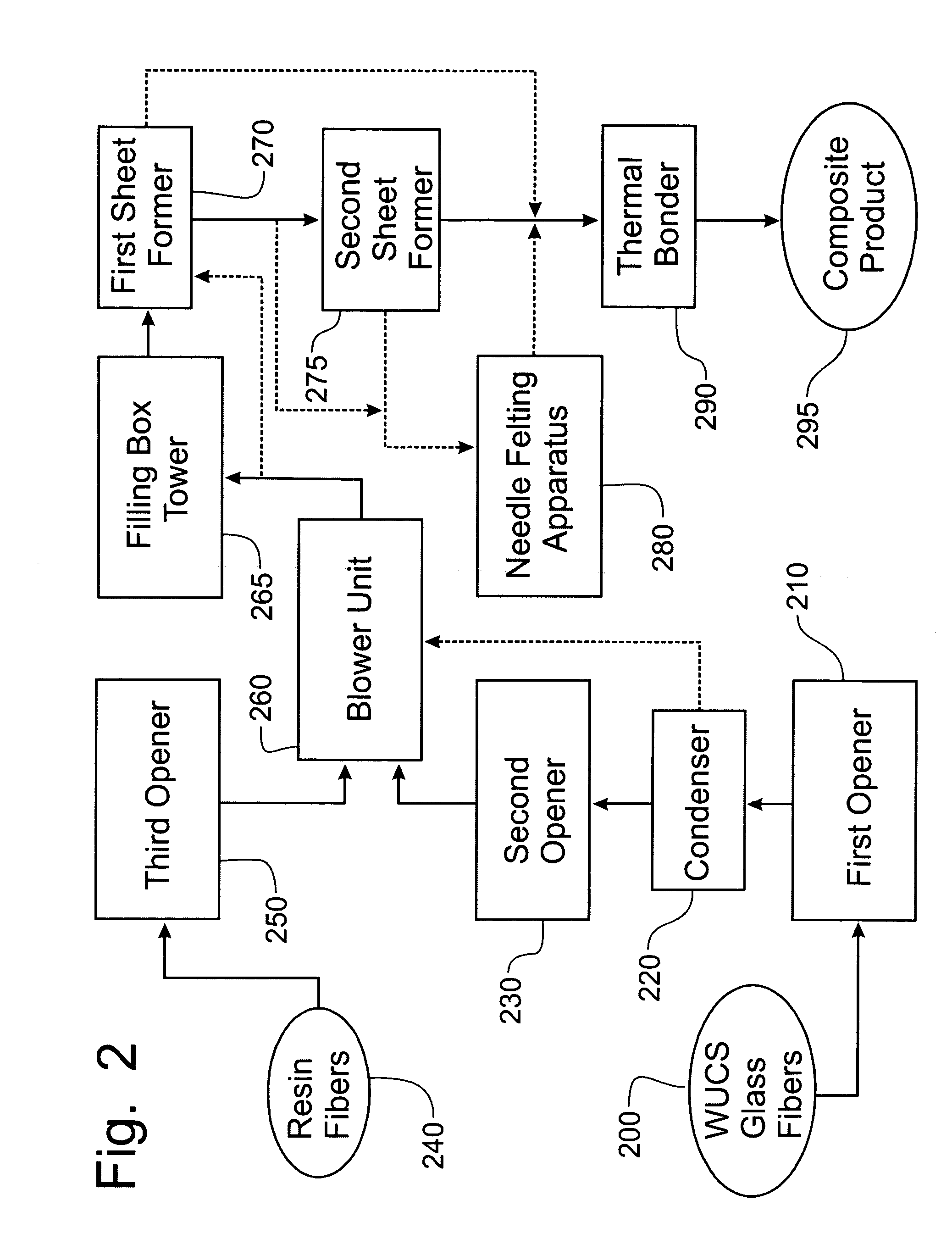
InactiveUS20050082721A1Little structural integrityReduce weightConfectioneryPress rollersGlass fiberPolymer science
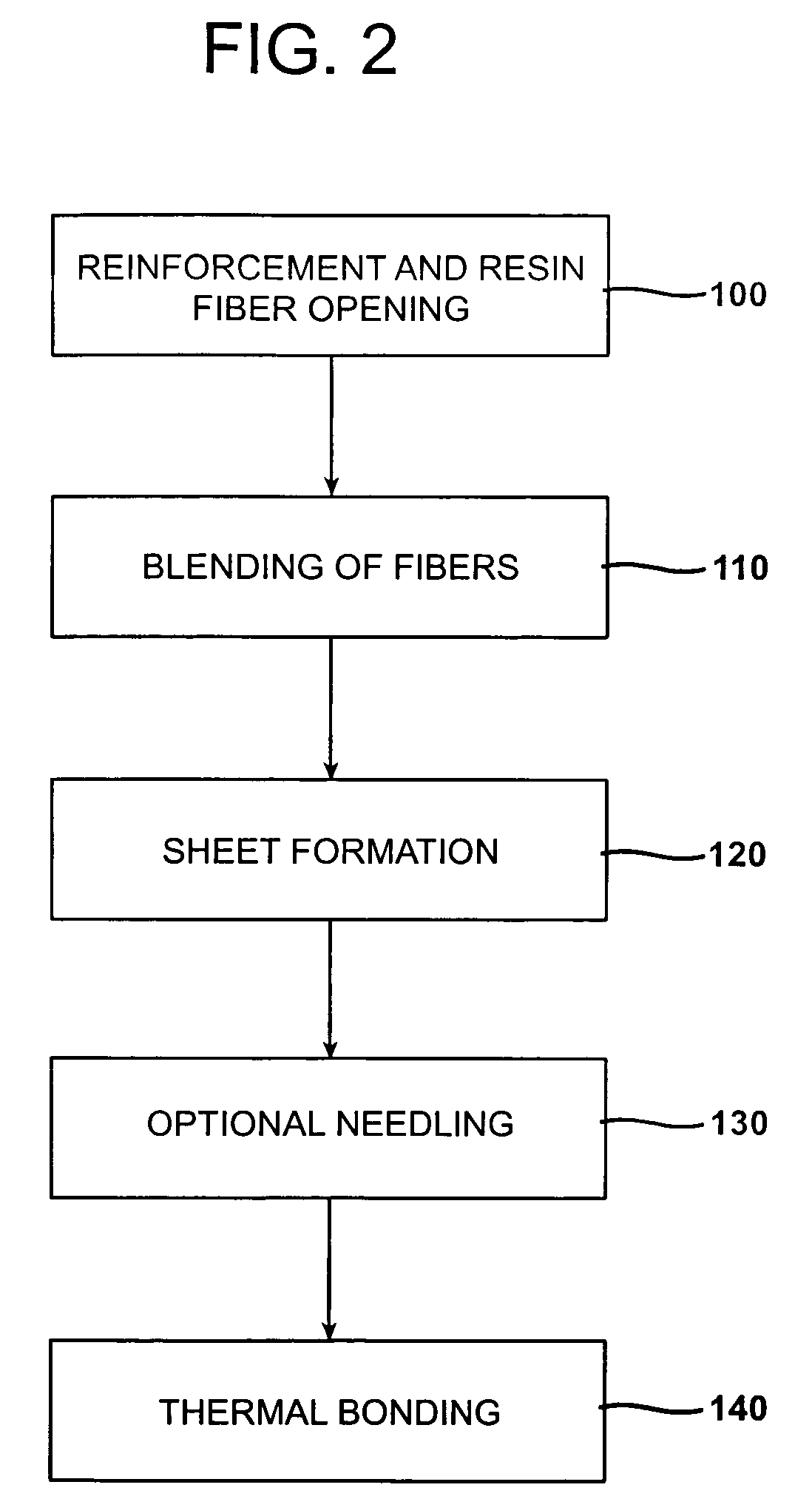
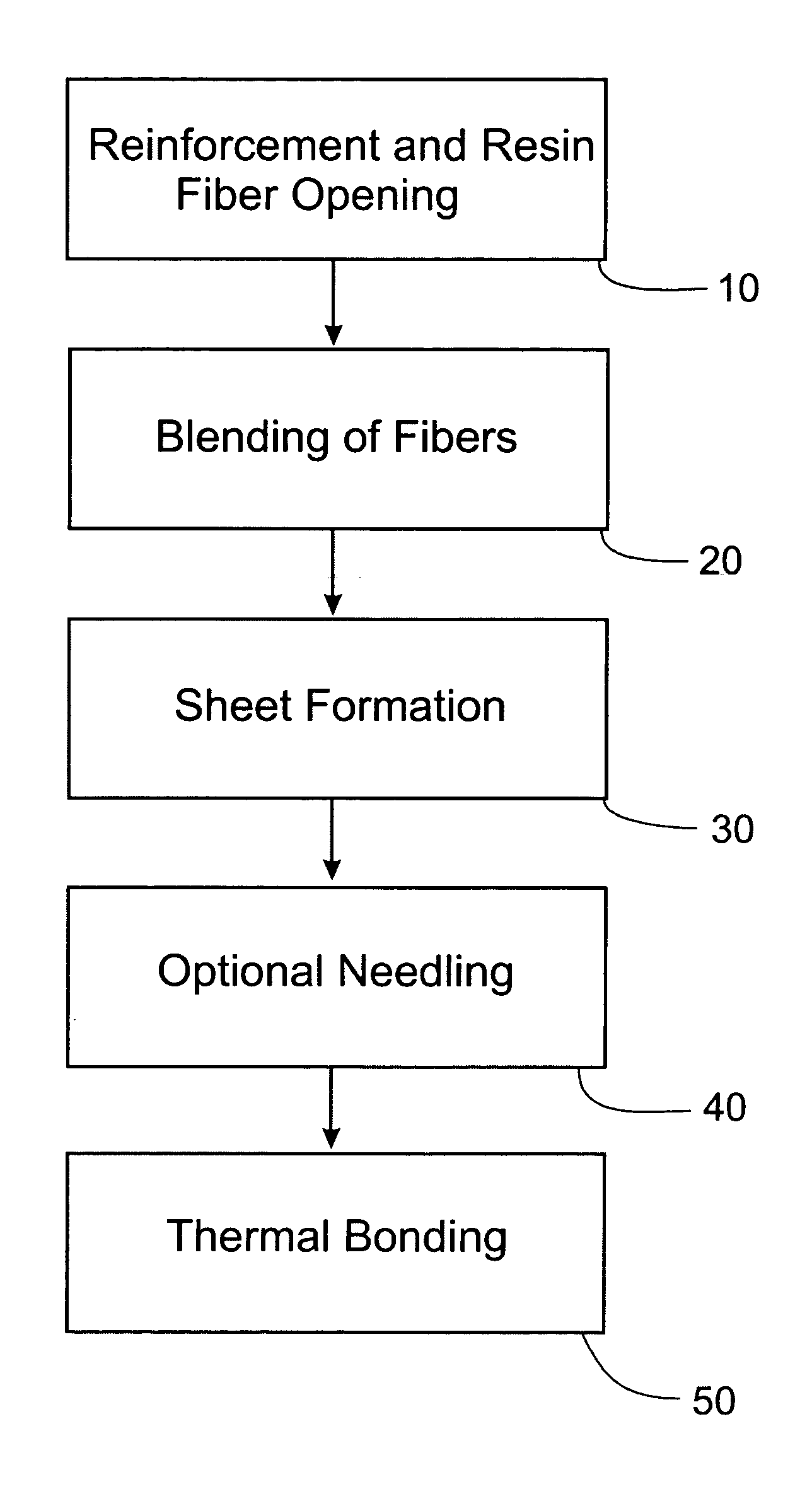
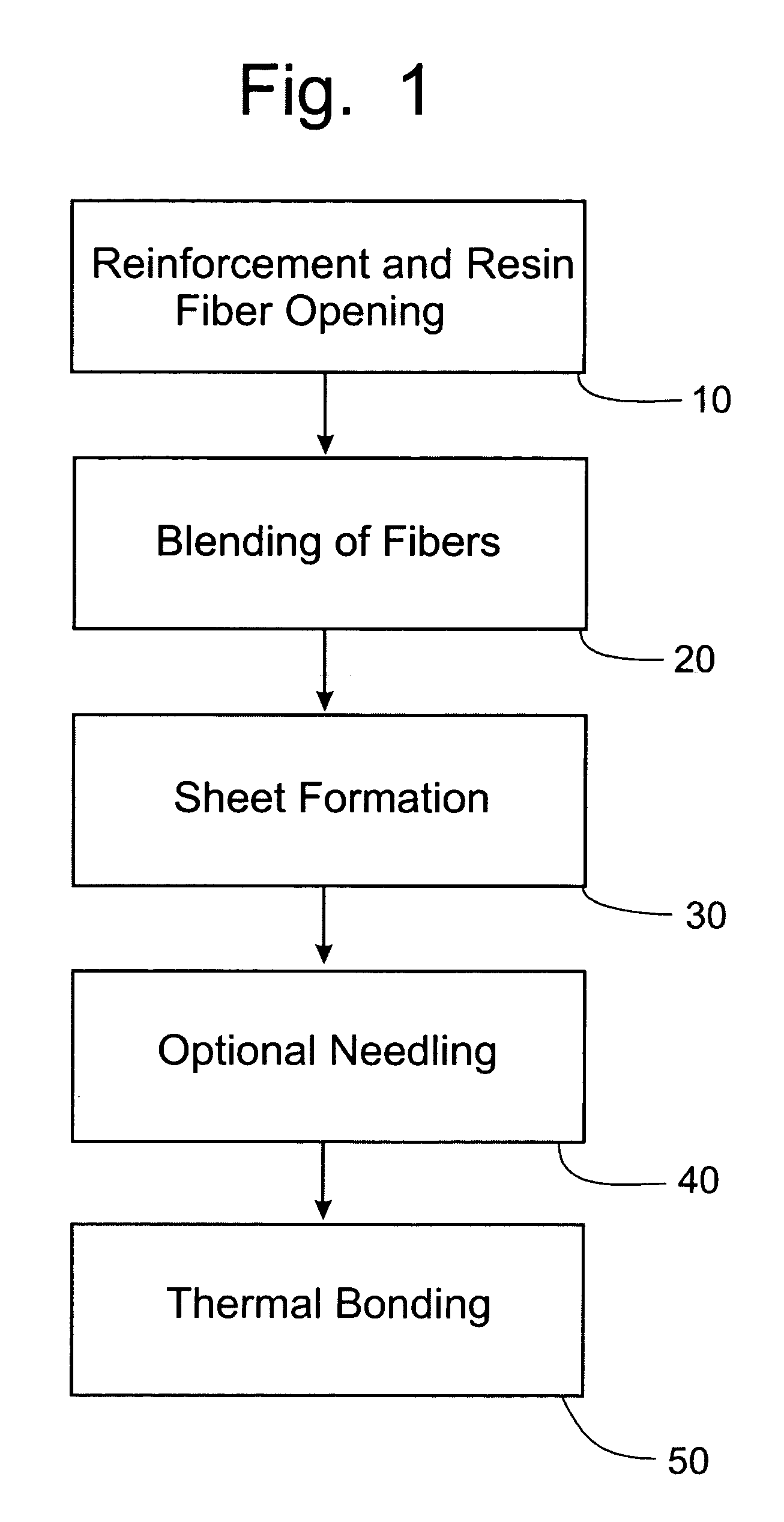
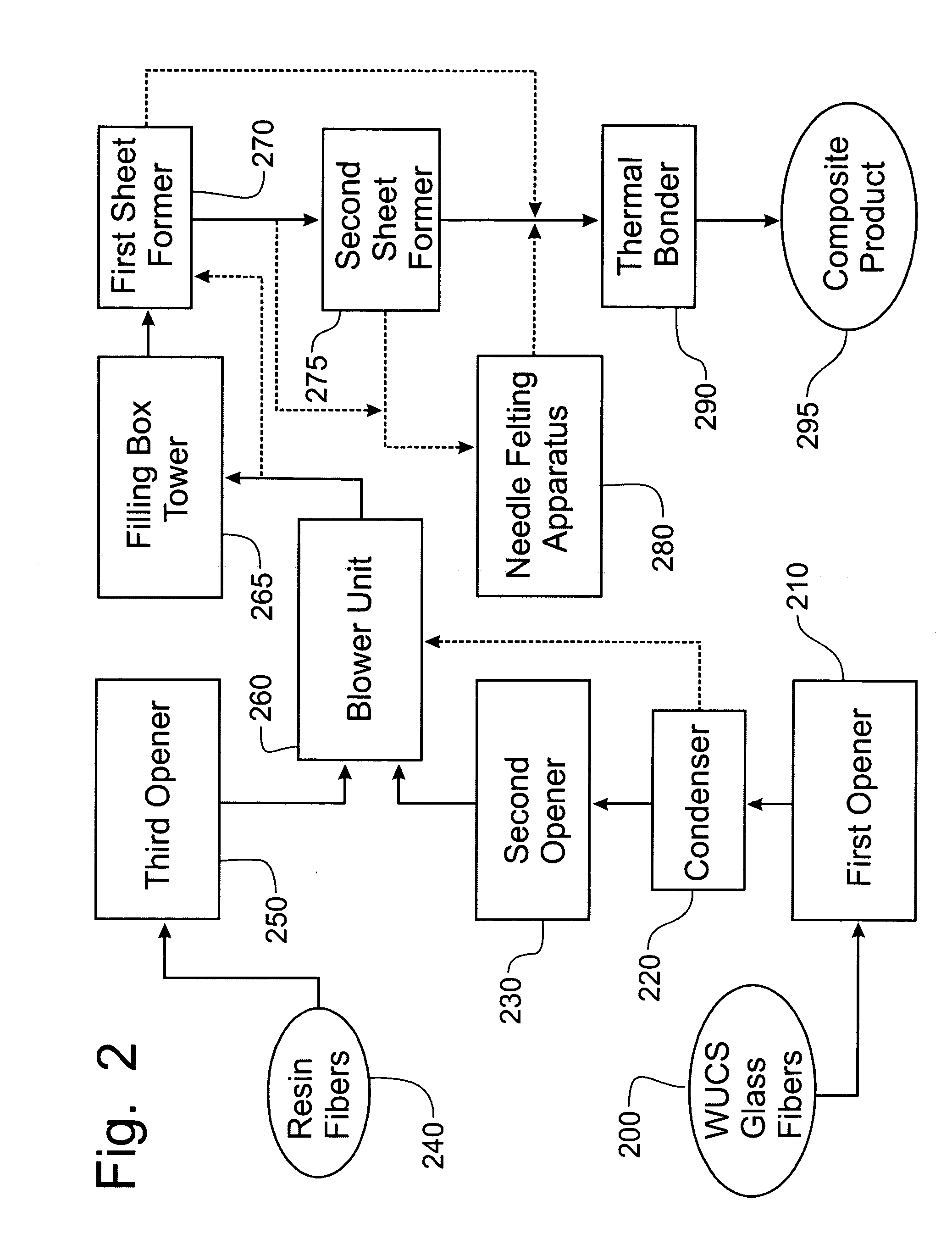
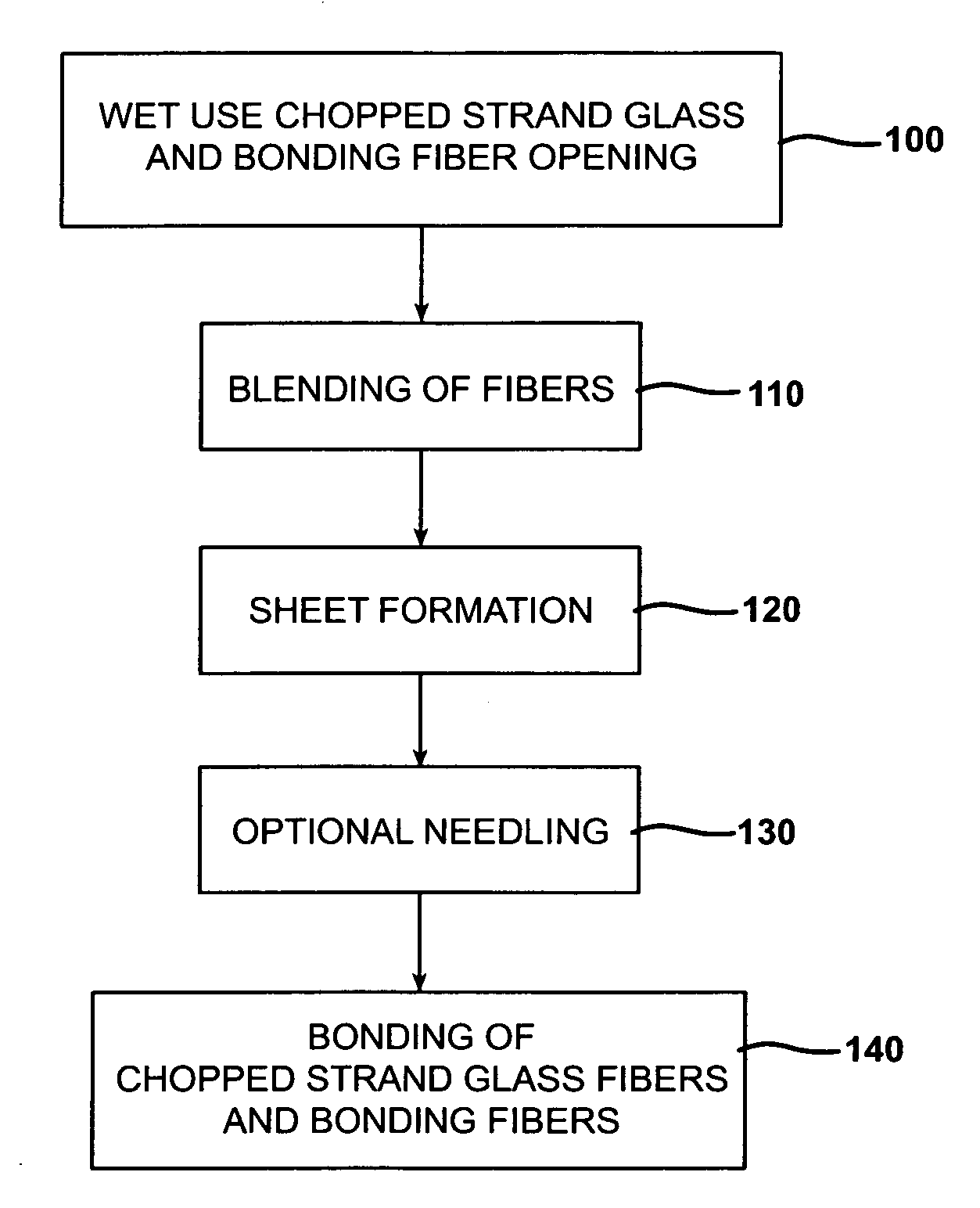
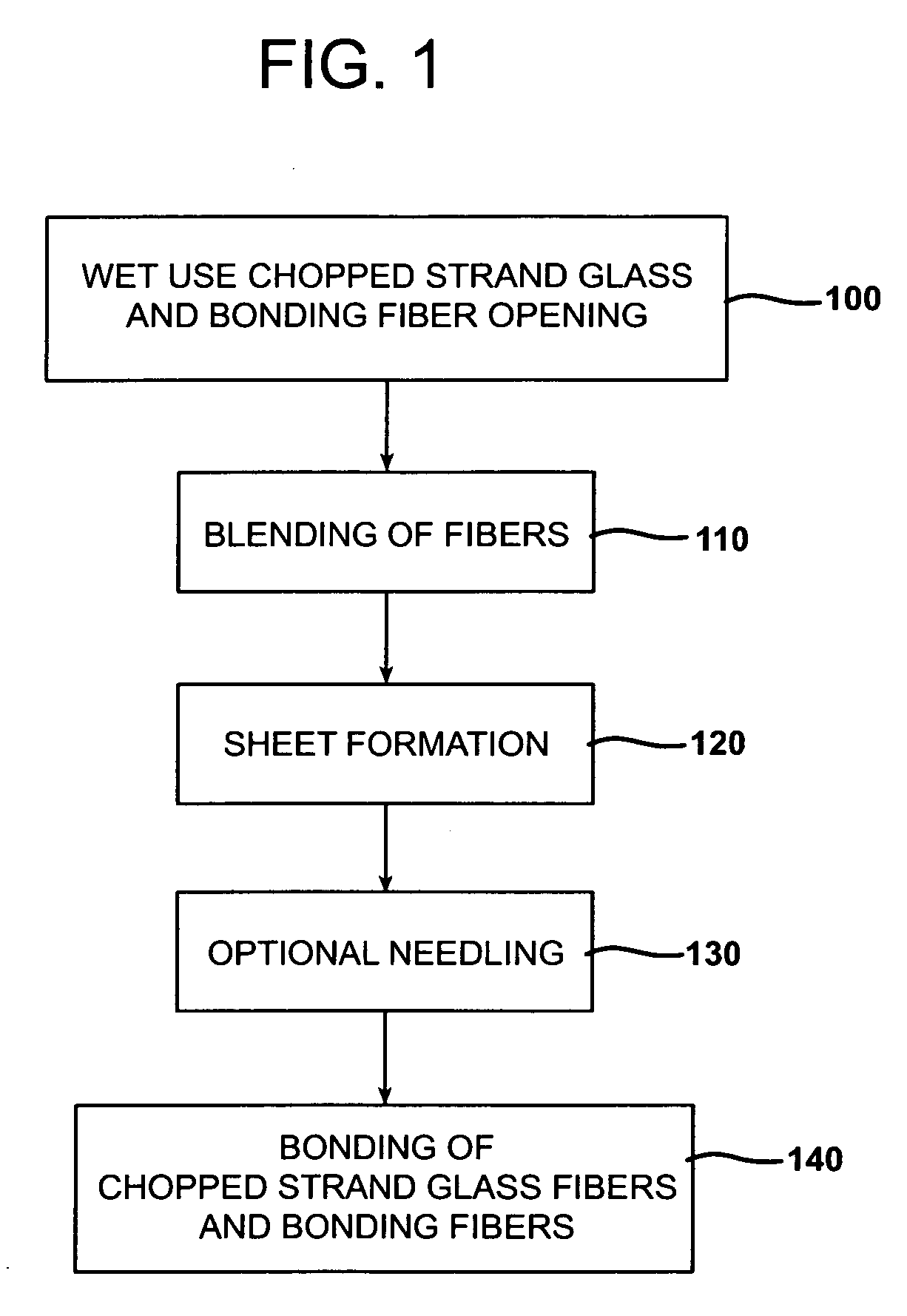
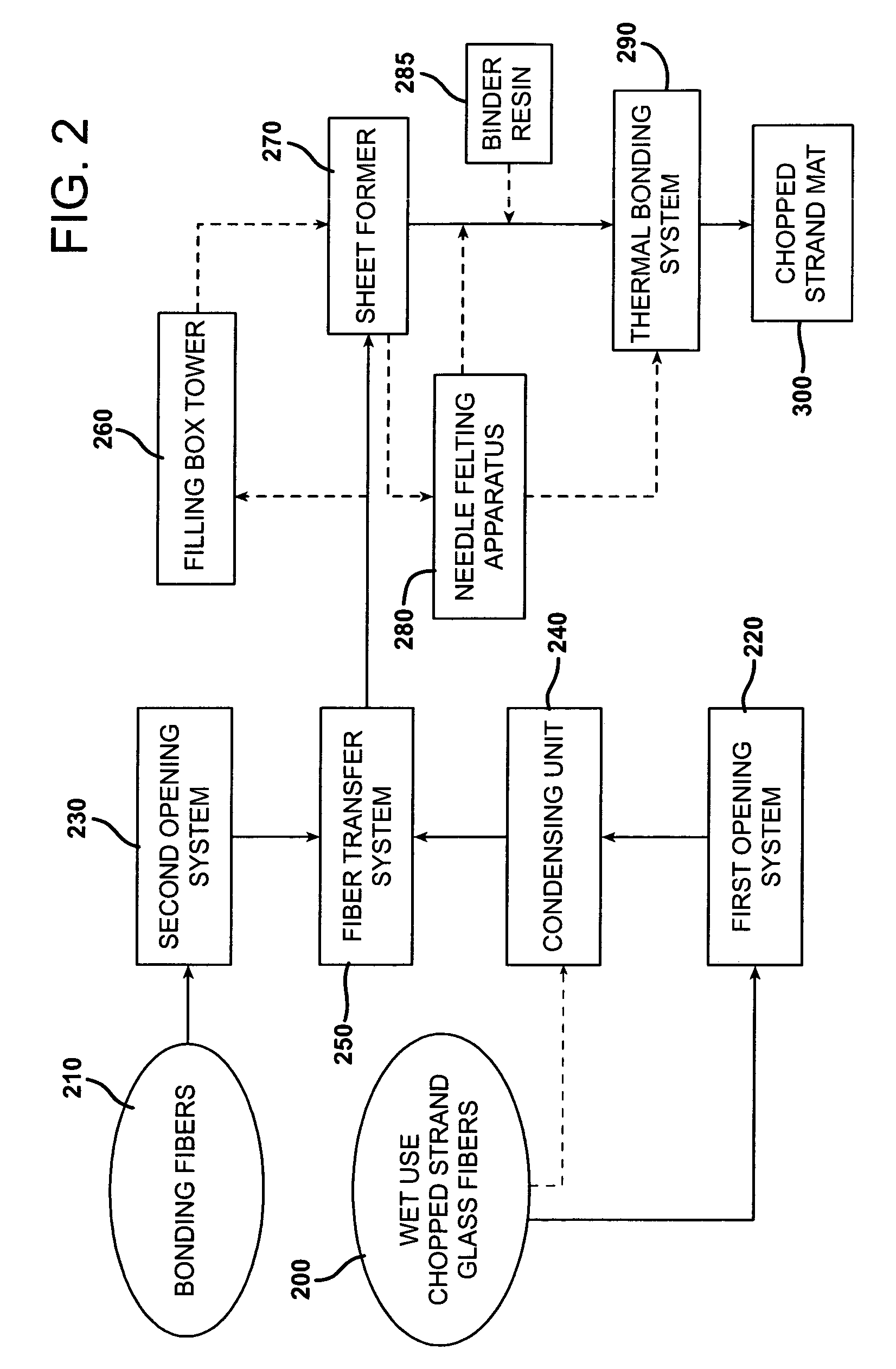
A process for forming thermoplastic composites that uses wet use chopped strand glass is provided. Wet reinforcement fibers such as wet chopped strand glass fibers are opened by passing the fibers consecutively through a first opener, a condenser, and, optionally, a second opener. The opened reinforcement fibers are mixed with a resin and transferred to a first sheet former. The resin is preferably polypropylene fibers. An optional second sheet former may be used to form a final composite having high structural integrity. The resulting sheet may be optionally passed through a needle felting machine for mechanical strengthening. The sheet is then passed through a thermal bonder to thermally bond the reinforcement glass fibers and resin. The composite product that exits the thermal bonder can be subsequently used as a reinforcement in a molding process to produce composite articles.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Process for making paper and nonwoven articles comprising synthetic microfiber binders
A process of making a paper or nonwoven article is provide. The process comprising:a) providing a fiber furnish comprising a plurality of fibers and a plurality of binder microfibers, wherein the binder microfibers comprise a water non-dispersible, synthetic polymer; wherein the binder microfibers have a length of less than 25 millimeters and a fineness of less than 0.5 d / f; and wherein the binder microfibers have a melting temperature that is less than the melting temperature of the fibers;b) routing the fiber furnish to a wet-laid nonwoven process to produce at least one wet-laid nonwoven web layer;c) removing water from the wet-laid nonwoven web layer; andd) thermally bonding the wet-laid nonwoven web layer after step (c); wherein the thermal bonding is conducted at a temperature such that the surfaces of the binder microfibers at least partially melt without causing the fibers to melt thereby bonding the binder microfibers to the fibers to produce the paper or nonwoven article.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
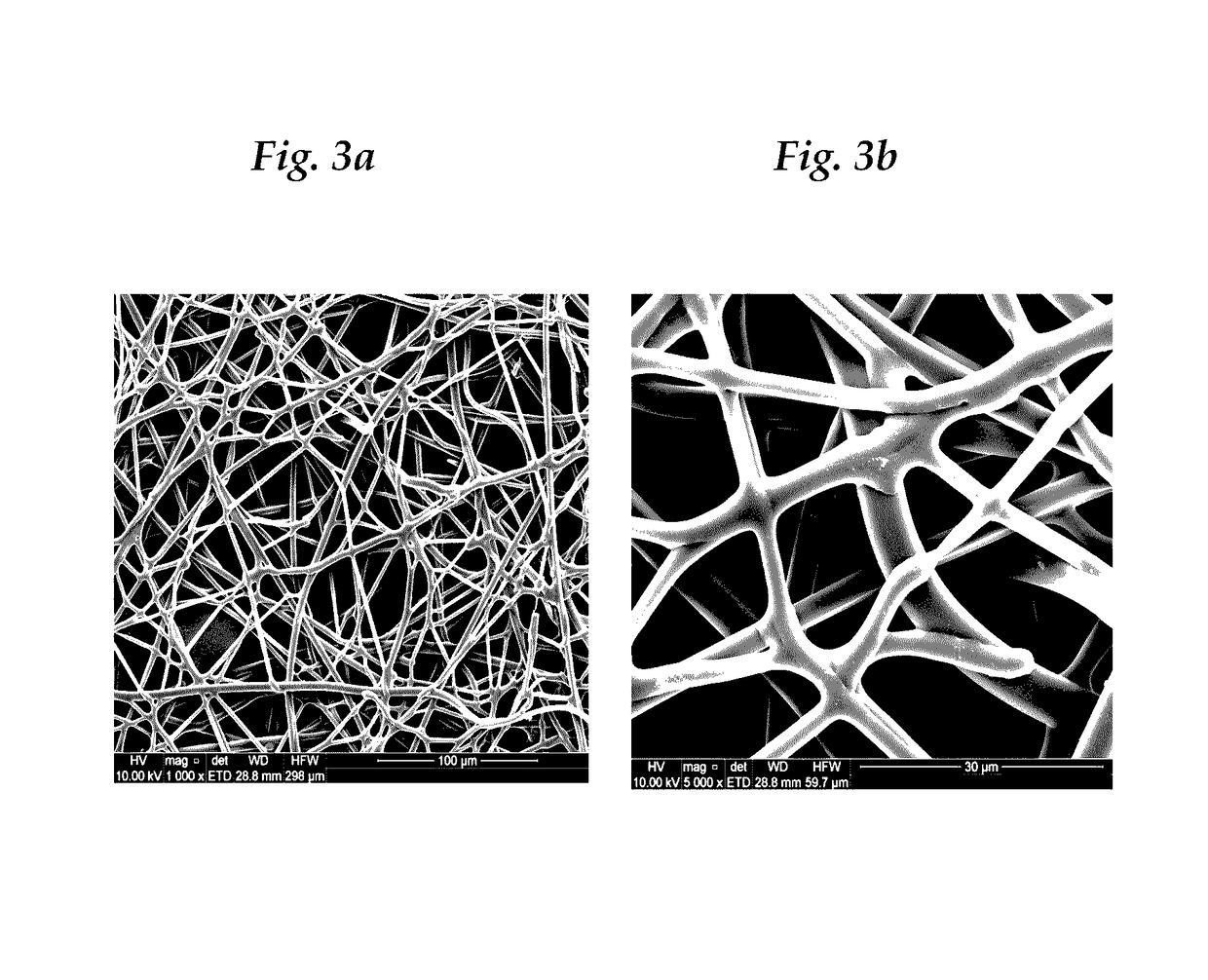
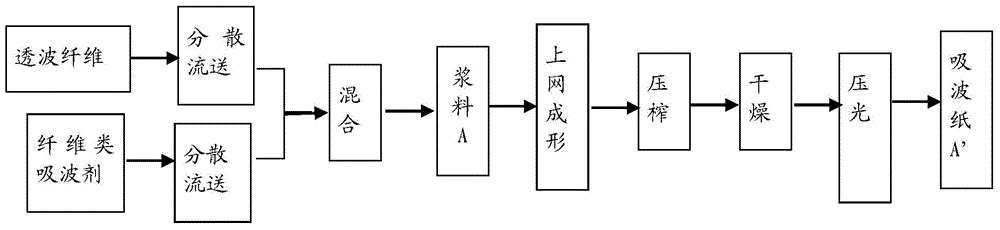
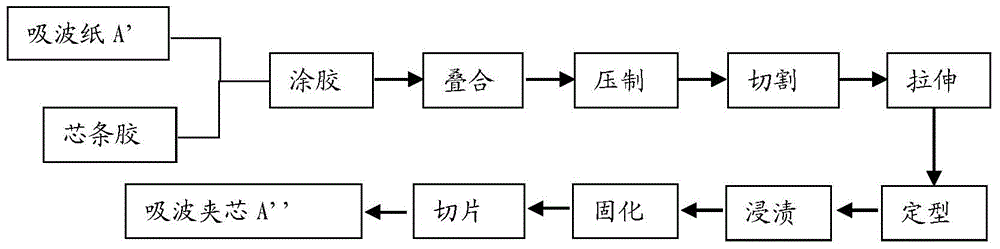
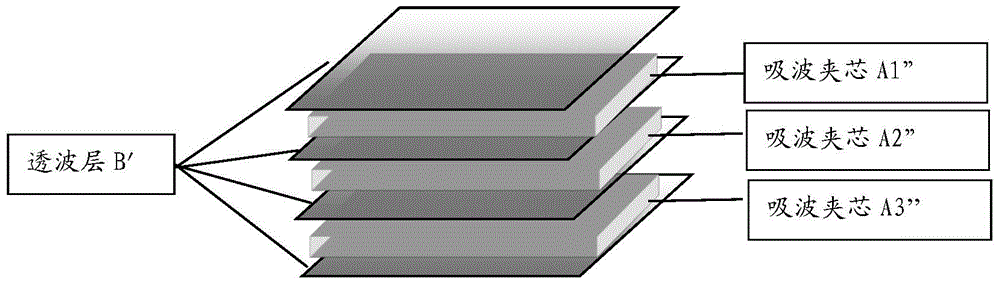
Wave-absorbing paper and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104404814AExcellent electromagnetic attenuation effectImprove mechanical propertiesInorganic fibres/flakesSpecial paperFiberPapermaking
The invention provides wave-absorbing paper and a preparation method and application thereof. The wave absorbing paper contains 0.1-95 wt% of a fiber wave-absorbing agent and 5-99.9 wt% of wave-transparent fiber. The fiber wave-absorbing agent and wave-transparent fiber are mixed and prepared into the wave-absorbing paper by a papermaking process; and then the wave-absorbing paper as a lattice wall material is prepared into a wave-absorbing core sandwich; and then the wave-absorbing core sandwiches prepared from wave-absorbing paper with different fiber wave-absorbing agent content are separated by wave-permeable layers; and finally the entire structure is impregnated and cured to obtain the wave-absorbing material. The wave-absorbing material of the invention has the advantages of high wave-absorbing efficiency, stable wave-absorbing property, wide absorption band, and light weight and high strength.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Opacity enhancement of tissue products with thermally expandable microspheres
InactiveUS20020104632A1Lose weightInorganic fibres/flakesNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberMicrosphere
The present invention is generally directed to an opaque tissue product and a process for making the same. The tissue products of the present invention comprise thermally expandable microspheres which impart increased opacity to the tissues. The thermally expandable microspheres are added to a fiber furnish during the wet end of a manufacturing process for bath tissue, facial tissue, towels, or the like.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
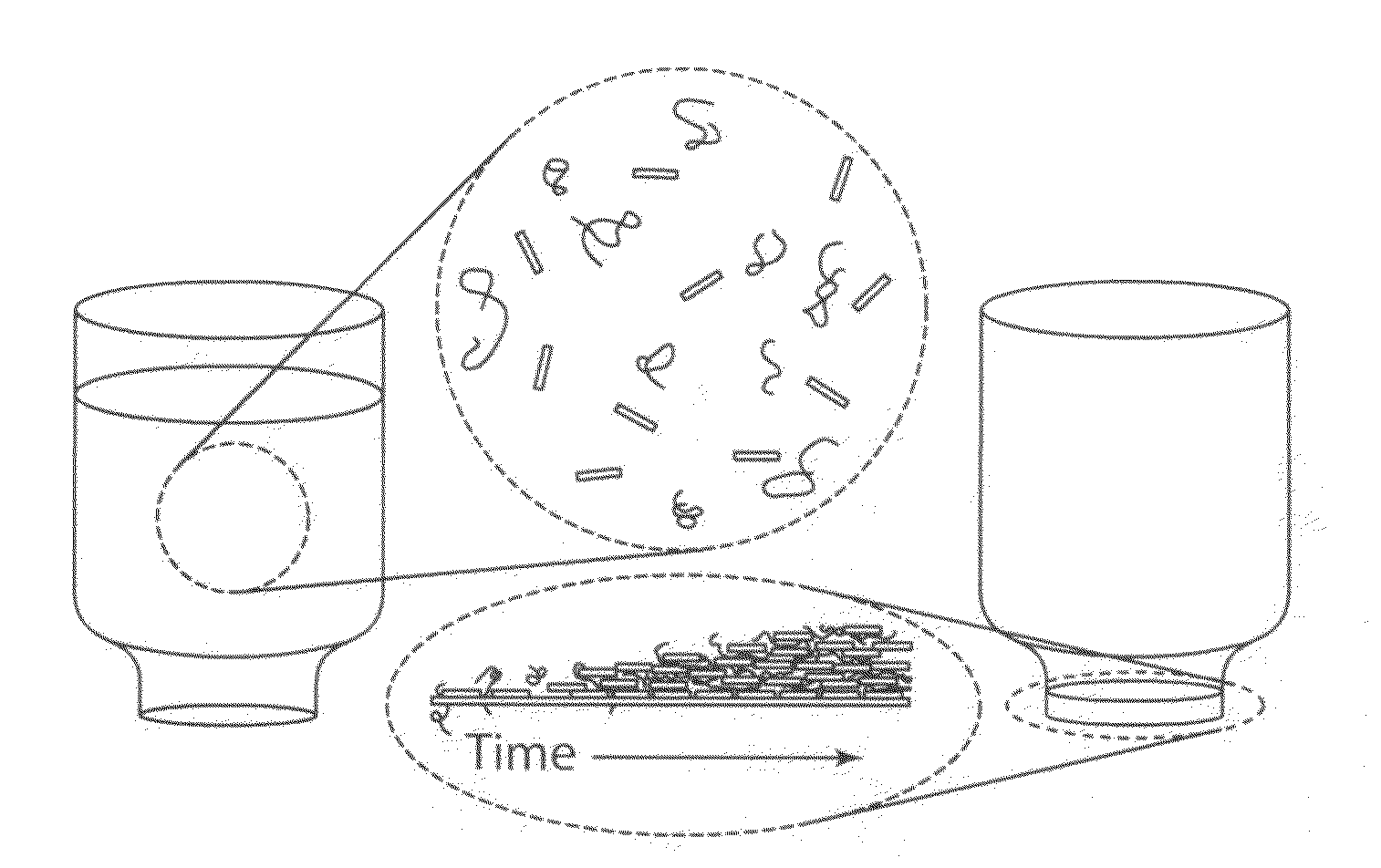
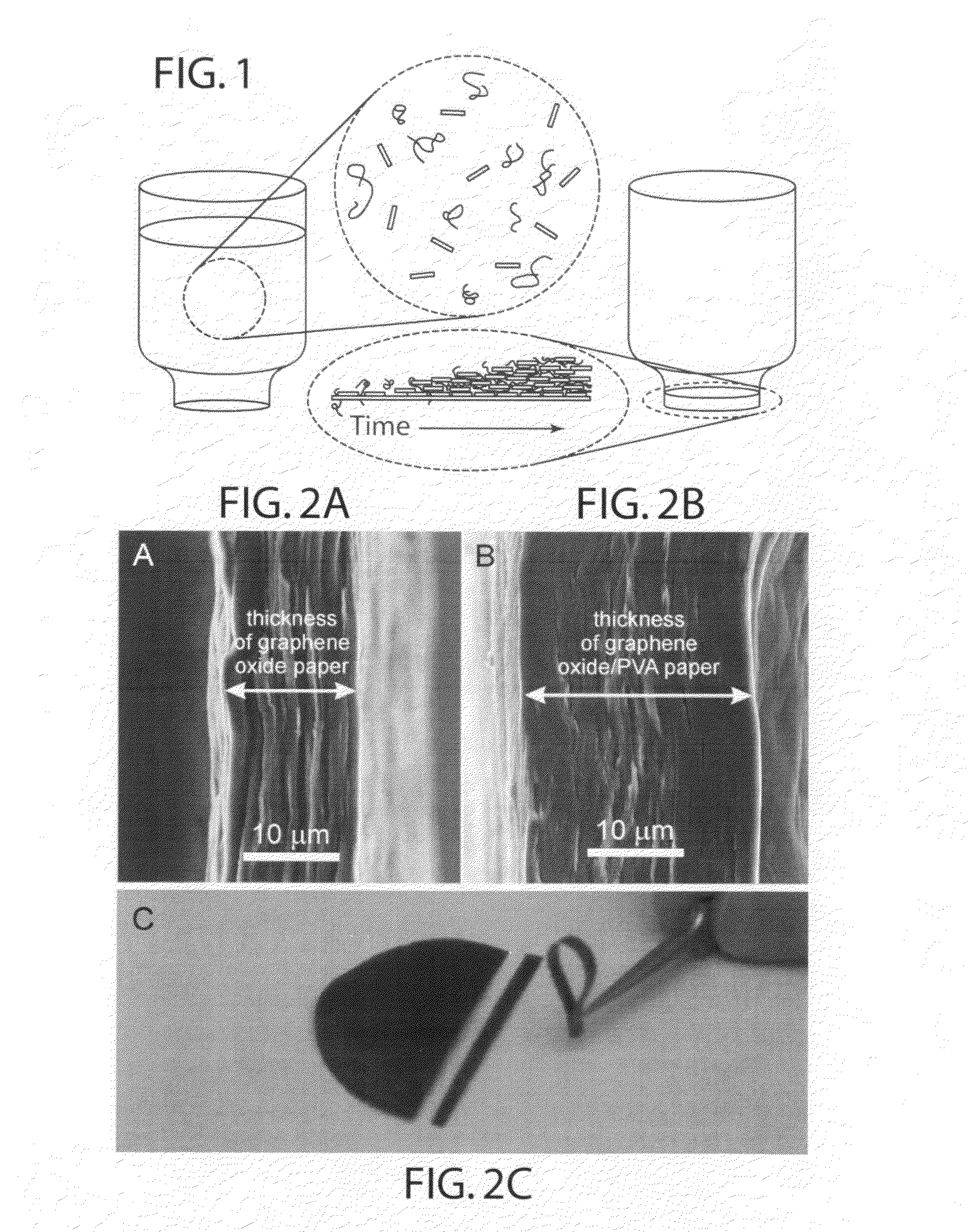
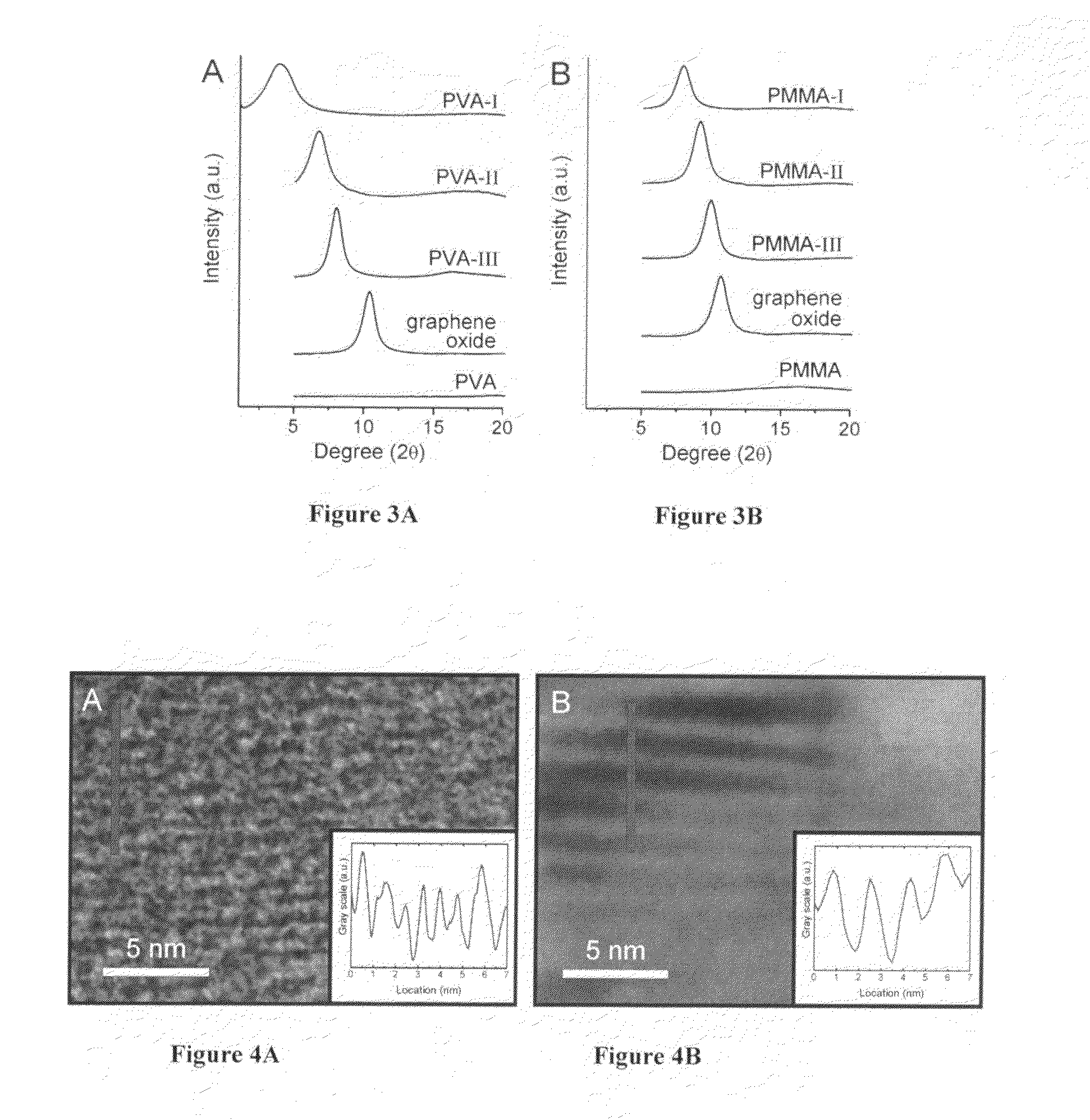
Composite graphene oxide-polymer laminate and method
ActiveUS20110256376A1Excellent macroscopic flexibilityImprove mechanical propertiesInorganic fibres/flakesSemi-permeable membranesComposite laminatesPolymer solution
A macroscale, self-supporting, composite laminate sheet includes individual, layered graphene oxide sheets and a polymer in spaces between the sheets. This composite product can be fabricated by combining a suspension of individual graphene oxide sheets and a solution of polymer, passing the resulting fluid through a fluid-permeable support, and assembling the graphene oxide sheets and polymer as a laminate sheet by flow-directed assembly. The laminate is dried and released from the membrane filter as a self-supporting thin films.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
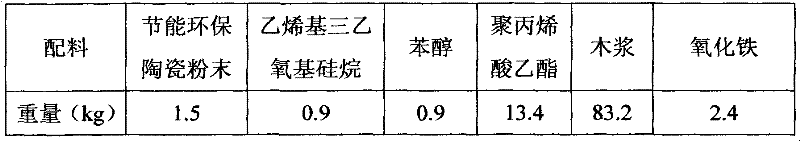
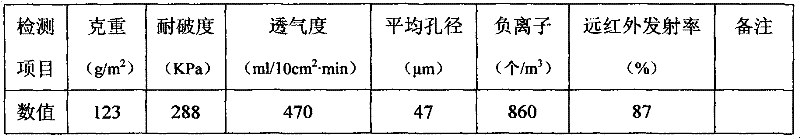
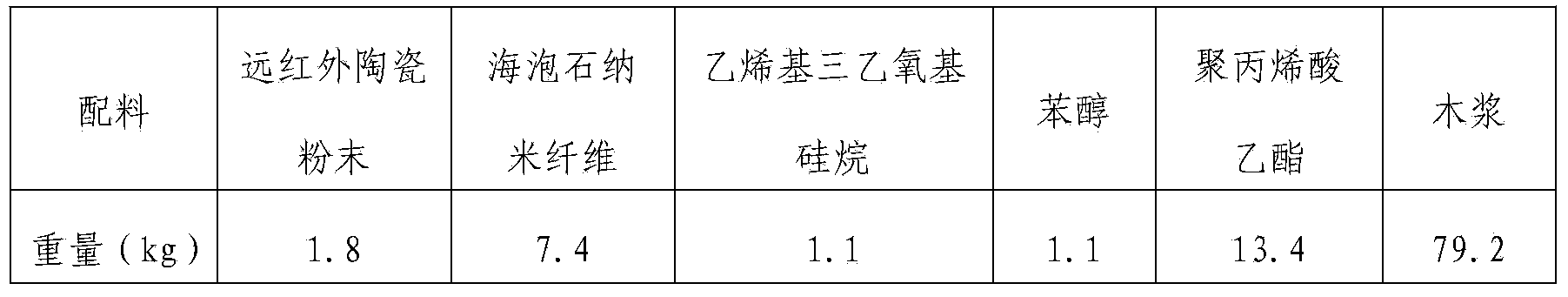
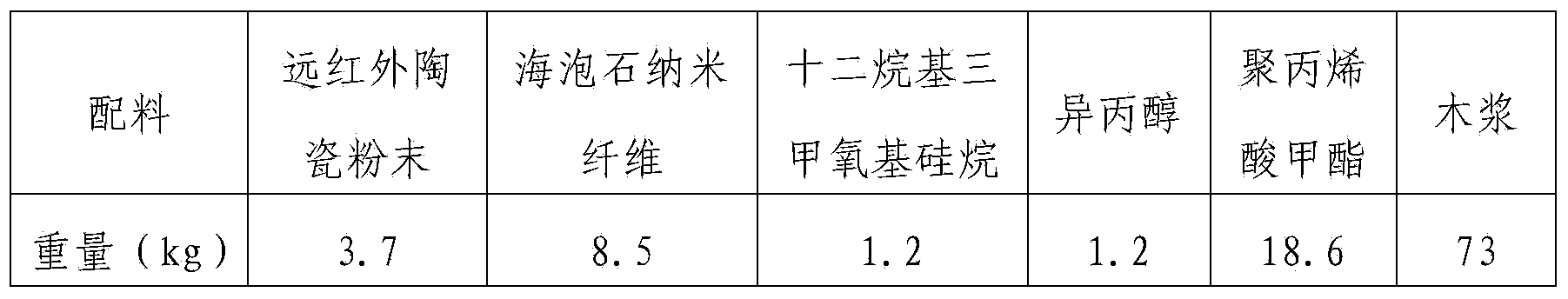
Filter paper for environmental-friendly automobile filter and preparation method of filter paper
InactiveCN103774503ASimple processHigh filtration precisionInorganic fibres/flakesWater-repelling agents additionExhaust gas emissionsEmission standard
The invention relates to filter paper for an environmental-friendly automobile filter. The filter paper for the environmental-friendly automobile filter is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 1-5 parts of far infrared ceramic powder, 2-20 parts of sepiolite nanofibers, 0.8-1.6 parts of a silane coupling agent, 0.8-1.6 parts of a diluent, 9-20 parts of a sizing agent and 60-96 parts of wood pulp. Air, fuel oil and engine oil filters made of the filter paper are obvious in comprehensive effect; pollutants generated by exhaust gas emission of an automobile are reduced by 16-47%; the dynamic performance is improved by 6-12%; fuel oil can be saved by 2-5%; the emission standard reaches the European IV standard.
Owner:北京联飞翔科技股份有限公司
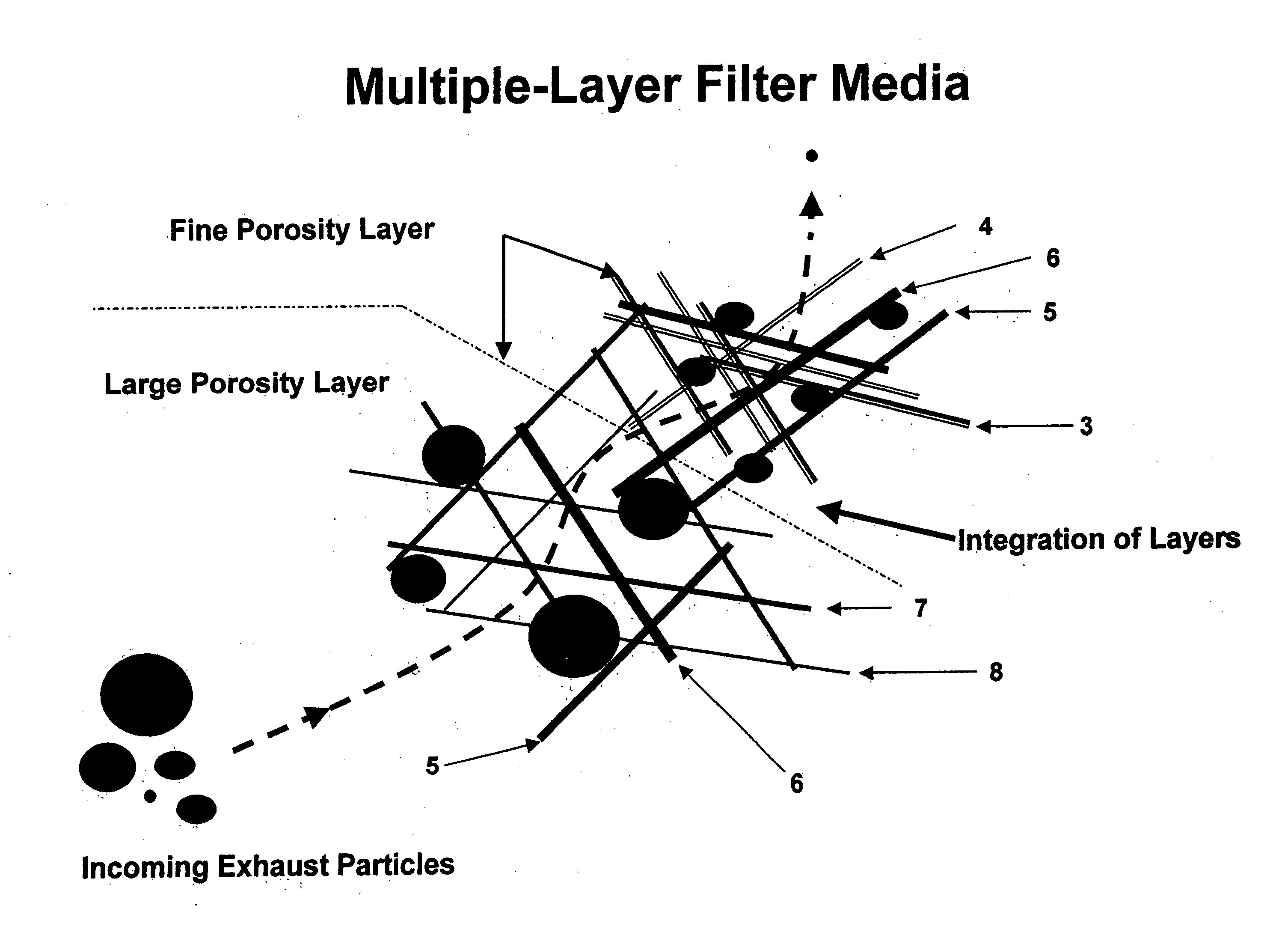
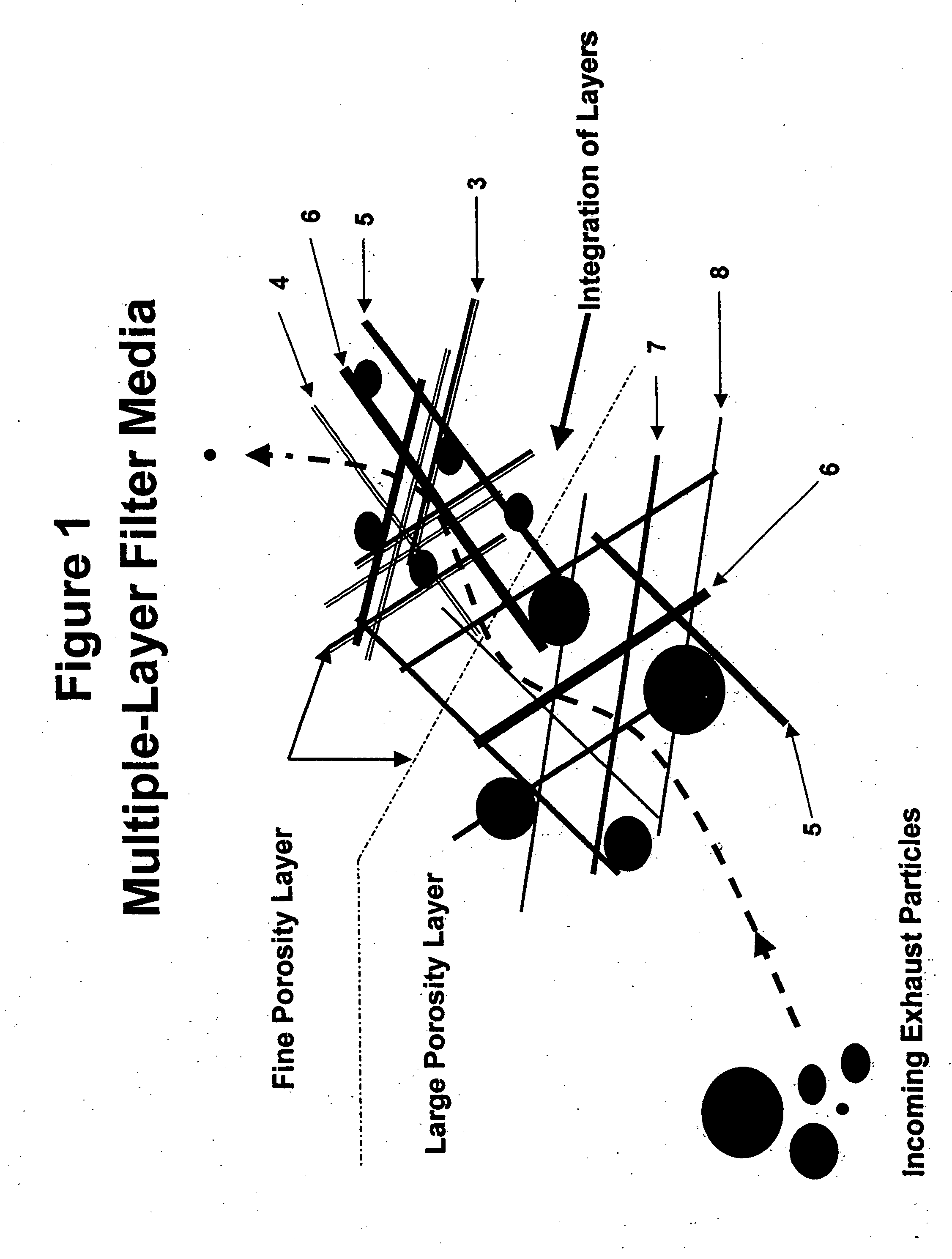
Multiple integrated-layer ceramic fiber filter paper and method
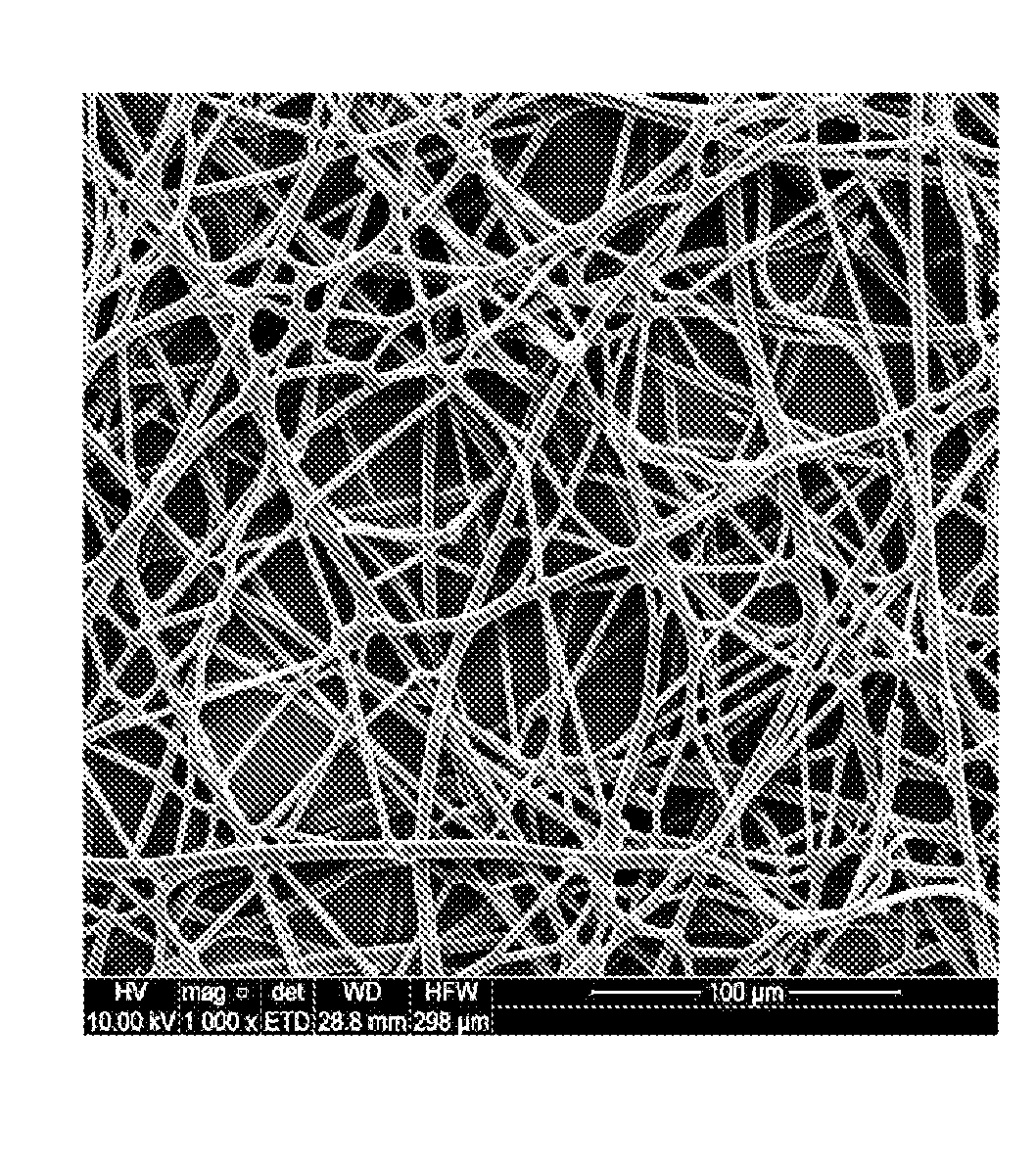
A composition of a multiple-layered ceramic fiber filter paper and method for manufacturing for use in a filter apparatus removes particulate from high temperature gas streams. In this application, ceramic fibers of varying diameters and lengths are combined in such a manner to yield different specific average pore sizes in segregated locations in the filter paper. The fiber combinations are formed into a paper sheet using a method that produces two or three porosity zones with different average pore sizes in each layer or porosity zone. The porosity gradient from large at gas stream entry to fine at gas stream exit increases particle-holding capacity while reducing the filtered gas backpressure experienced in single sized porosity layer media.
Owner:INDAL CERAMIC SOLUTIONS
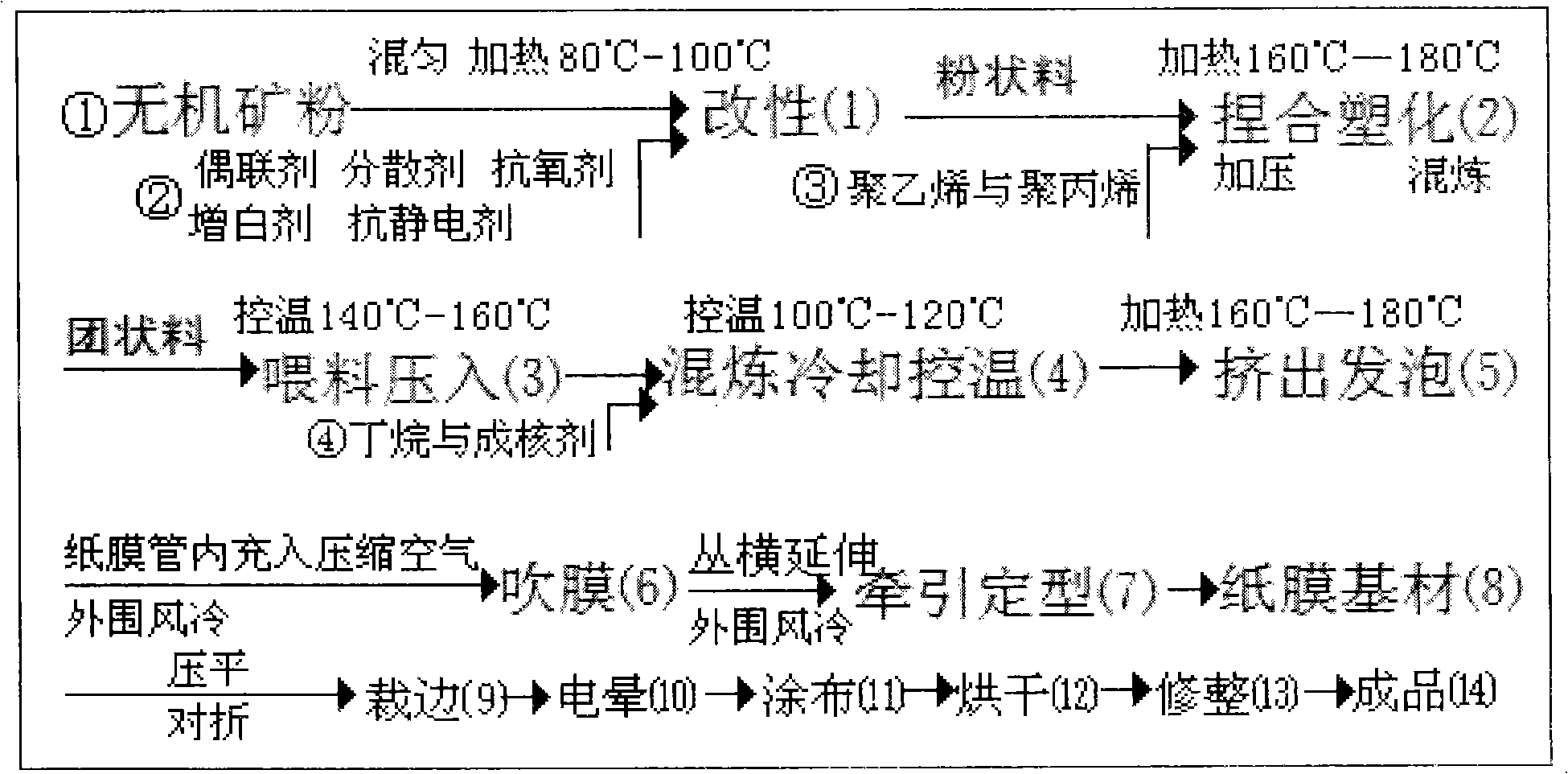
Stone papermaking method
InactiveCN101831835AControl the amount of inflationLight weightInorganic fibres/flakesSpecial paperFilm baseWhite powder
The invention discloses a stone papermaking method, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: adding 2 to 2.5 weight percent of auxiliary agent such as stearic acid and the like into 70 to 80 percent of natural inorganic ore powder such as heavy calcium, light calcium, talcpowder, titanium white powder and the like serving as main raw materials to modify the raw materials, adding 18 to 11.5 weight percent of polyethylene and 9 to 5 weight percent of polypropylene into the raw materials, and mixing, plasticizing and kneading the mixture to form a bulk material; and performing double-fold feed on the bulk material, pressing the bulk material into a paper film extruder, injecting 0.5 weight percent of butane and 0.5 weight percent of nucleating agent into the extruder, mixing and heating the mixture, extruding a paper film, then foaming, blowing, drawing, cooling and shaping the paper film to form a paper film base material, and forming a stone paper finished product through corona, coating, drying and finishing. The gram weight of stone paper is reduced by physical micro-foaming technology. The method has the advantages of simple manufacturing process, low cost, dry production, use of few water circulating cooling machines, no three-waste discharge and pollution avoidance.
Owner:山西典石晨晶科技有限公司
Development of thermoplastic composites using wet use chopped strand (WUCS)
A process for forming thermoplastic composites that uses wet use chopped strand glass is provided. Wet reinforcement fibers such as wet chopped strand glass fibers are opened by passing the fibers consecutively through a first opener, a condenser, and, optionally, a second opener. The opened reinforcement fibers are mixed with a resin and transferred to a first sheet former. The resin is preferably polypropylene fibers. An optional second sheet former may be used to form a final composite having high structural integrity. The resulting sheet may be optionally passed through a needle felting machine for mechanical strengthening. The sheet is then passed through a thermal bonder to thermally bond the reinforcement glass fibers and resin. The composite product that exits the thermal bonder can be subsequently used as a reinforcement in a molding process to produce composite articles.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Modification method for inorganic fibers
InactiveCN103215844AGood flexibilityHigh strengthInorganic fibres/flakesNon-fibrous pulp additionFiberPVA - Polyvinyl alcohol
The invention provides a modification method for inorganic fibers. The method comprises the following steps of: stirring polyvinyl alcohol and water at 80 to 90 DEG C until the polyvinyl alcohol is completely dissolved, then adding sodium hydroxide and hydrogen peroxide, and performing reaction for 4 hours at 80 to 90 DEG C to obtain treated polyvinyl alcohol; mixing the treated polyvinyl alcohol with gamma-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane, performing reaction at 90 to 110 DEG C under an alkaline condition to graft the gamma-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane onto the treated polyvinyl alcohol, and adjusting a pH value to be 7 to 9 to obtain an inorganic fiber softening reinforcing agent; and adding the inorganic fibers into water for stirring and dispersion, then adding the inorganic fiber softening reinforcing agent for uniform stirring, and after the system is reacted, performing suction filtering to obtain modified inorganic fibers. According to the modification method, the flexibility and the strength of the inorganic fibers can be improved; and when the inorganic fibers treated by the method are used for papermaking, the performance of paper can be improved.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Inorfil softening intensifier and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101503280AGood flexibilityHigh strengthInorganic fibres/flakesGlass fiberPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention relates to an inorganic fiber softening reinforcing agent and a preparation method thereof. The method is to lead H2O2, polyvinyl alcohol and potassium hydroxide to react for 2 to 4 hours at a temperature between 50 and 60 DEG C, adds an etherifying agent after the reaction to react for 4 to 8 hours at a temperature between 50 and 70 DEG C, and regulates the pH value of the solution to 7 to 8 so as to obtain the inorganic fiber softening reinforcing agent. The softening reinforcing agent is applicable to various inorganic fiber materials produced by physical or hot melt method, including basalt fibers, aedelforsite fibers, meerschaum fibers, gypsum fibers, flyash fibers and glass fibers. The softening reinforcing agent can improve the softness and strength of inorganic fibers, improve the defect of easy fracture of the inorganic fibers in processes of pulping, dispersing and transporting, change the charge property of the inorganic fiber surface, reinforce the bonding force of the inorganic fibers and plant fibers, and greatly improve application performance of the inorganic fibers in making paper, insulating wool boards and the like by wet method.
Owner:鹤壁洁联新材料科技有限公司
Conductive webs
InactiveUS8058194B2Easy to mergeAmenable to thermal bonding to other componentsNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberEngineering
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Heating non-combustible cigarette paper and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106368069ANo tar spotsDoes not start carbonationInorganic fibres/flakesSpecial paperFiberBurn cigarette
The invention discloses heating non-combustible cigarette paper and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the heating non-burning cigarette paper comprises the following steps: 1) pulping the plant fiber with the length of 0.5 to 4mm, or adding the appropriate proportion of inorganic fiber; 2) adding the inorganic filler in the process of dilution of the pulp, wherein the addition ratio of the inorganic filler is 5 to 50% of the mass of the pulp; 3) sizing the paper to improve water and oil resistance, and cigarette paper is quantified at 50 to 120 g / m<2>. Compared with the existing heated non-combustible cigarette paper that is heated at 350 DEG C, the non-combustible cigarette paper of the present invention has very few yellow stitches, and no tar spots and carbonization, while the entire surface of the existing non-combustible cigarette paper turns yellow, with large tar penetrating and carbonized. In addition, the non-combustible cigarette paper of the present invention is rarely present broken in actual production, and there is almost no deformation and wrinkling after being sucked as the heated cigarette paper.
Owner:中烟摩迪(江门)纸业有限公司
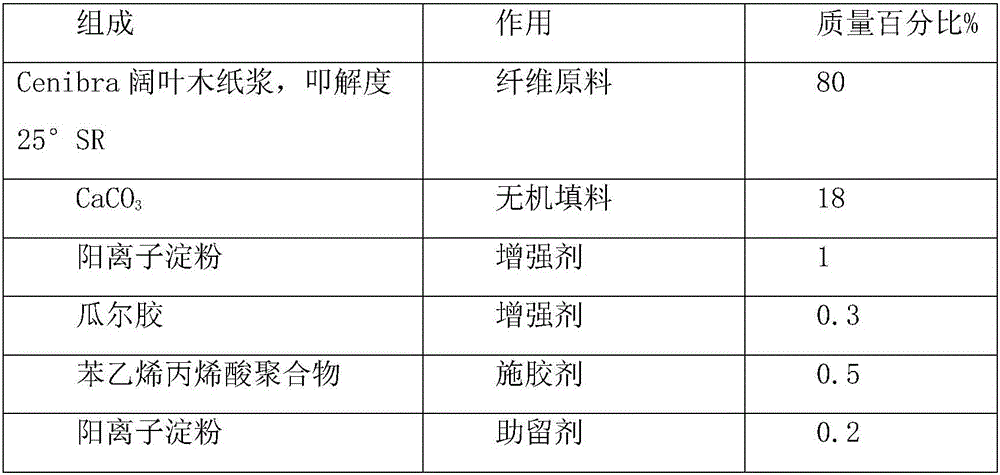
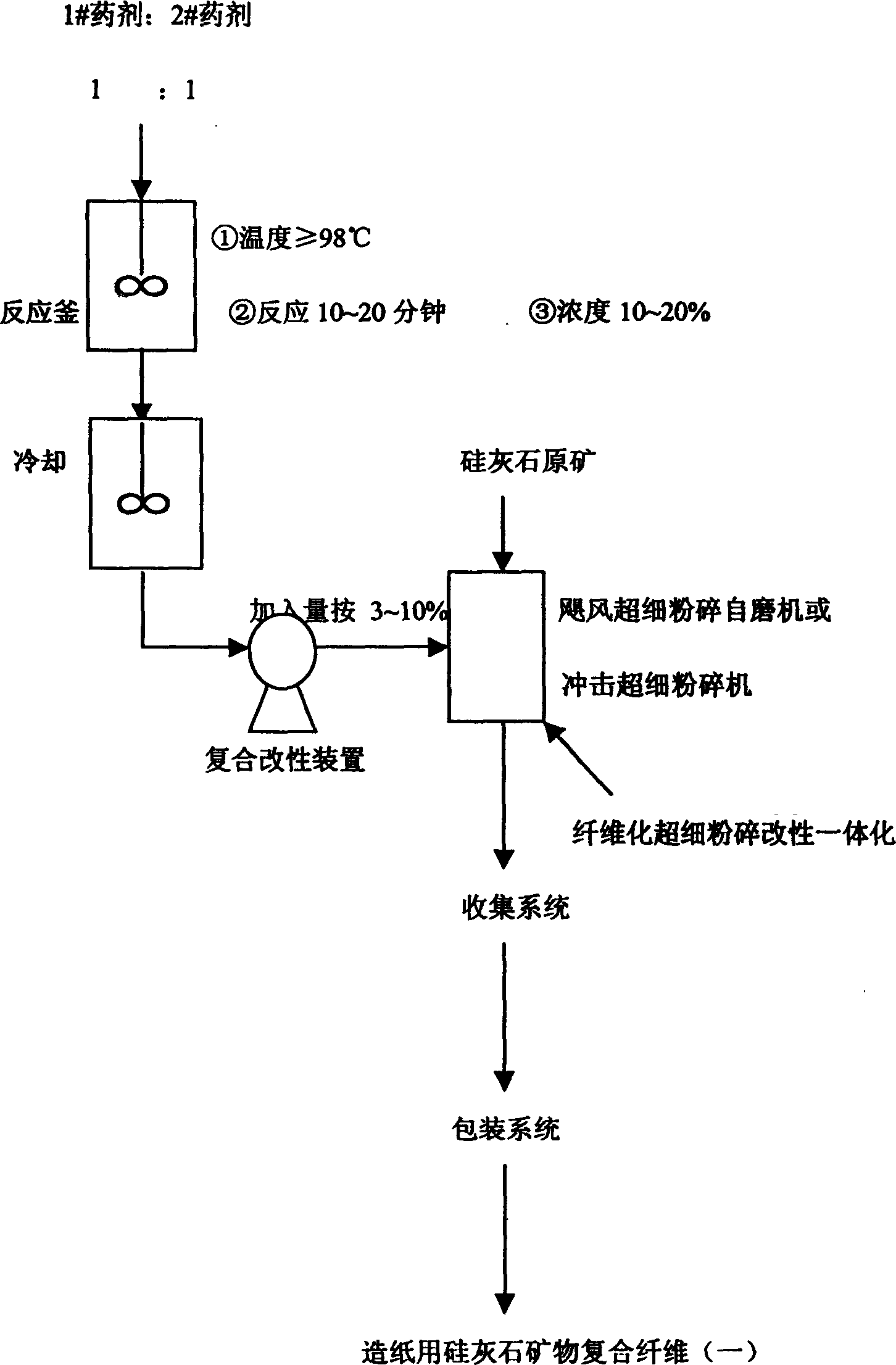
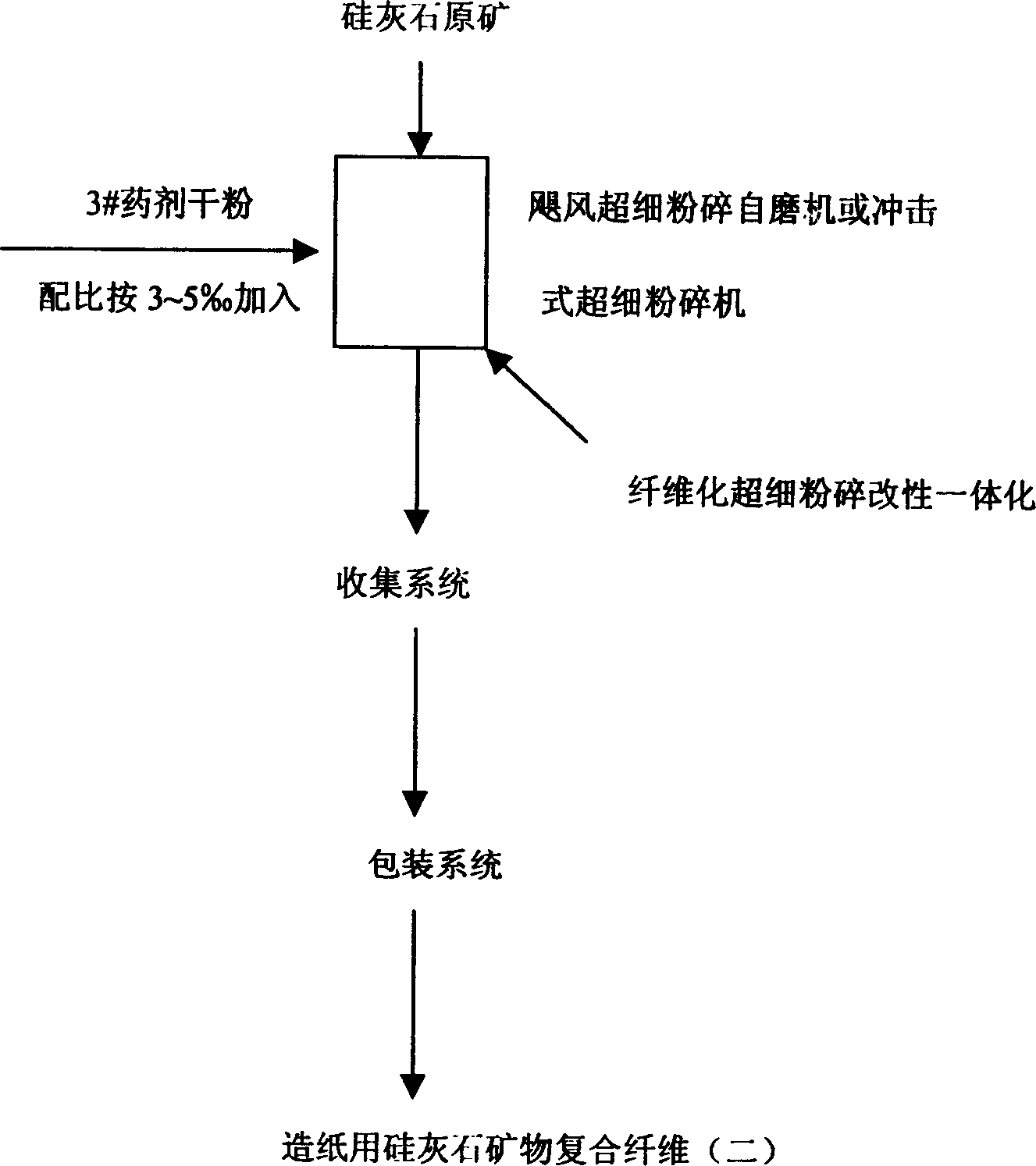
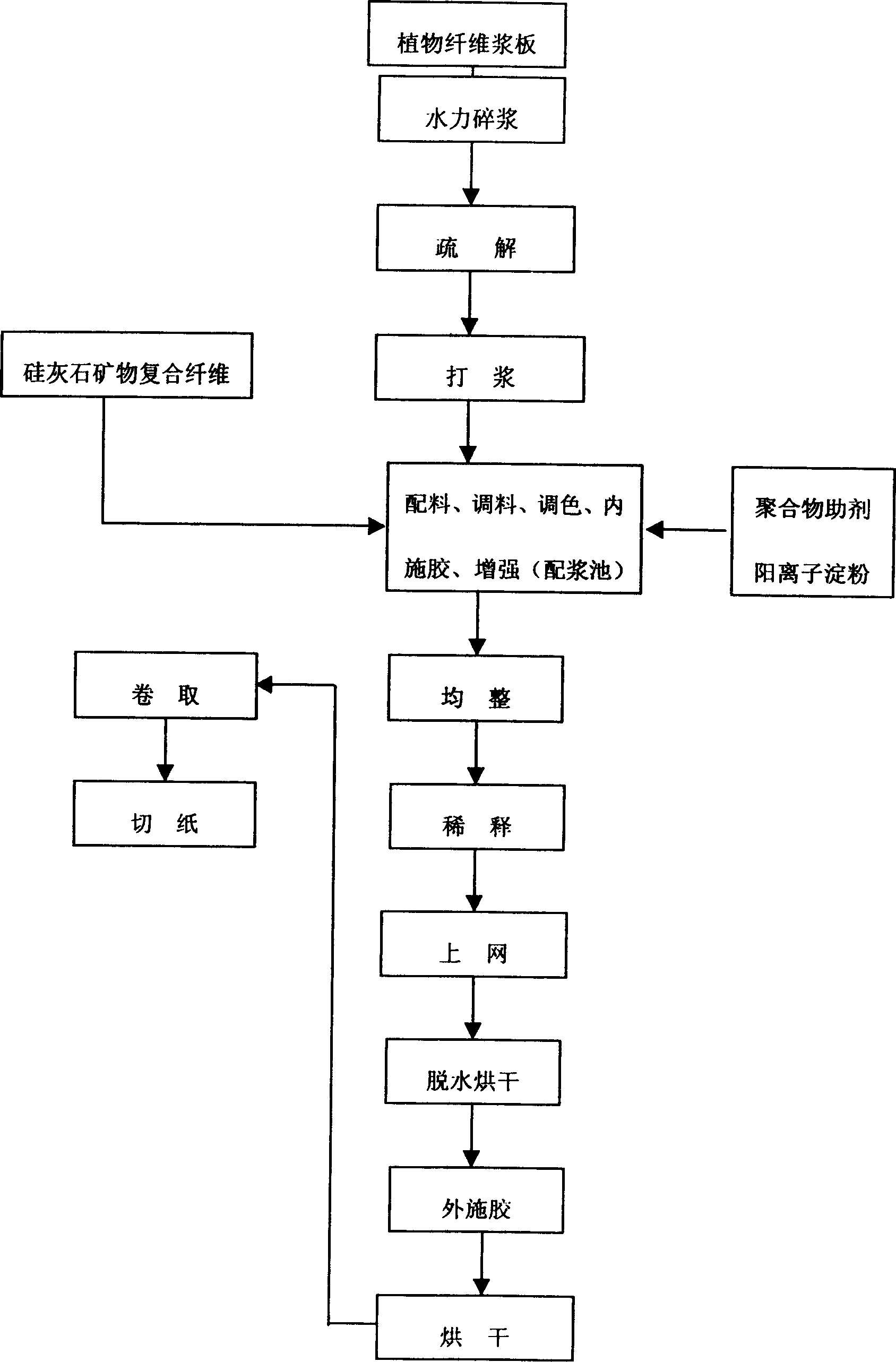
Modified wollastonite mineral composite fibre for making paper and its paper-making process
The present invention provides a modified wollastonite mineral composite fibre for making paper and its paper-making method. It includes the following steps: breaking wollastonite raw ore to obtain the thin-long fibre whose grain size is 5-20 micrometer and the ratio of mid-diameter:length=1:6-30, and according to the ratio of alkali or salt of aluminium: alkali or salt of sodium=1:1 adding modification agent whose added quantity is 3-10% of wollastonite mineral composite fibre weight so as to obtain the wollastonite mineral composite fibre covered with modification agent. In the course of preparing pulp in paper-making process 5-50% of modified wollastonite mineral composite fibre and 50-95% of plant fibre and paper-making auxiliary material are added, it can reduce production cost.
Owner:云南省非金属矿产应用研究所
Flyash fiber pulp and papermaking method using same as raw material
InactiveCN1580391AImprove the added value of the applicationReduce consumptionInorganic fibres/flakesNon-fibrous pulp additionSlurryFire prevention
This invention discloses fly ash fiber pulp and its use in paper making including the following components and weight percentage: emulsifier 1-10%, dispersant 1-8%, surface modifier 1-10%, powder-coal fiber 20-80%, organic fiber 20-80% and reset for water said pulp is conveyed onto a paper-making machine by conventional method to turn them into paper, which physical performance reaches to the same level as plant fiber paper and water resistance, corrosion prevention and fire prevention are tested better than plant fiber paper by related national standards.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Electroconductive aramid paper
InactiveUS20060266486A1Inorganic fibres/flakesNon-fibrous pulp additionApparent densityPolymer science
This invention relates to aramid papers, and a process for making such papers, the papers comprising 5 to 65 parts by weight aramid fiber, 30-90 parts by weight aramid fibrids, and 1-20 parts by weight of conductive filler, based on the total weight of the aramid fiber, fibrids, and filler; the papers having an apparent density of not more than 0.43 g / cm3 and a tensile index not less than 60 Nm / g.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Preparation method and application of composite paper based material with organic matter adsorption and degradation function
InactiveCN101319478AIncrease the burdenSolve problems such as light radiation is blockedInorganic fibres/flakesSpecial paperFiberCardboard
The invention relates to a method for preparing a composite paper base material with functions of adsorbing and degrading organic matters, and an application of the composite paper base material. The material consists of 30 to 50 percent of metal oxide powder, 15 to 35 percent of absorbent powder, 0 to 25 percent of inorganic fiber, 10 to 30 percent of paper pulp and 0.5 to 5 percent of dual retention aid. When the material is prepared, the metal oxide powder, the absorbent powder, the inorganic fiber and the paper pulp are mixed into a suspension liquid with the concentration of between 2 to 8 percent, the suspension liquid is subjected to mediation for 5 to 30min, and added with the dual retention aid to dilute until the concentration is reduced down to 0.5 percent so as to prepare wet paper sheets; the paper sheets are subjected to pressing and drying to prepare the composite paper base material. The composite paper base material prepared is further processed into a paper component, and the paper component is placed in a low concentration volatile organic compound environment to realize continuous photocatalysis degradation. By utilizing the paper base material of the invention, the problems that the cost is high and the pulverization occurs due to the friction between granular materials when the zeolite is used as a carrier to prepare compound catalytic materials are resolved, and the paper base material can also adsorb low concentration volatile organic gases.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Static free wet use chopped strands (WUCS) for use in a dry laid process
InactiveUS20050266757A1Improve controlReduce staticInorganic fibres/flakesSynthetic resin layered productsGlass fiberAntistatic agent
A method of forming a chopped strand mat formed of bonding materials and wet use chopped strand glass fibers (WUCS) which demonstrate a reduced occurrence of static electricity is provided. In one exemplary embodiment, the occurrence of static electricity on the glass fibers is reduced or eliminated by increasing the total solids content on the glass fibers, such as by applying an increased or excess amount of size composition to the glass fibers. Alternatively, an anti-static agent may be added directly to the sizing composition and applied to the glass filaments by any suitable application device. The antistatic agent may be applied to the wet chopped strand glass prior to chopping the strands or as the wet chopped strands are packaged. The static free wet use chopped strand glass fibers may be used in dry-laid processes to form chopped strand mats having a reduced tendency to accumulate static electricity.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com