Patents
Literature
163 results about "Physiological fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
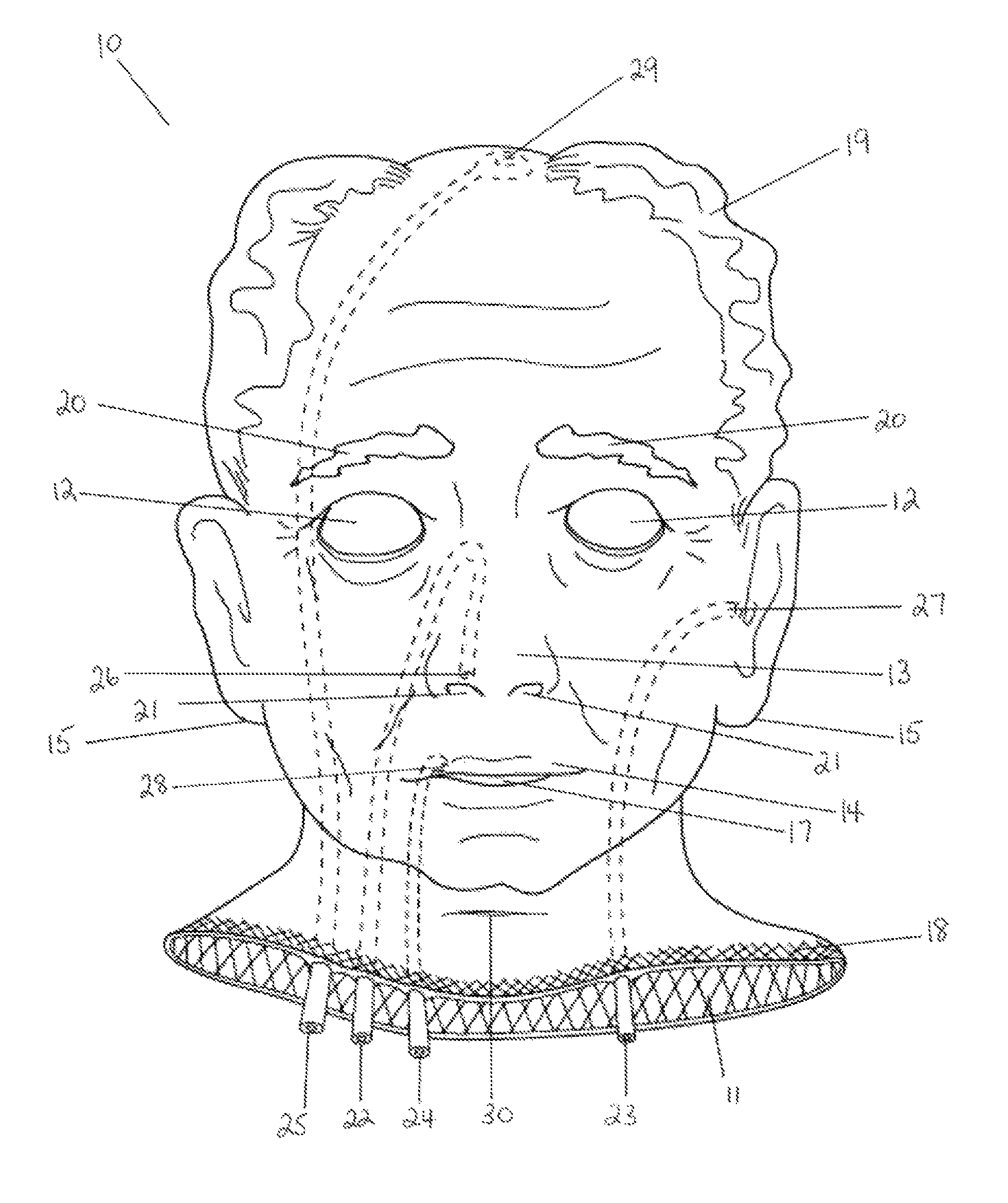
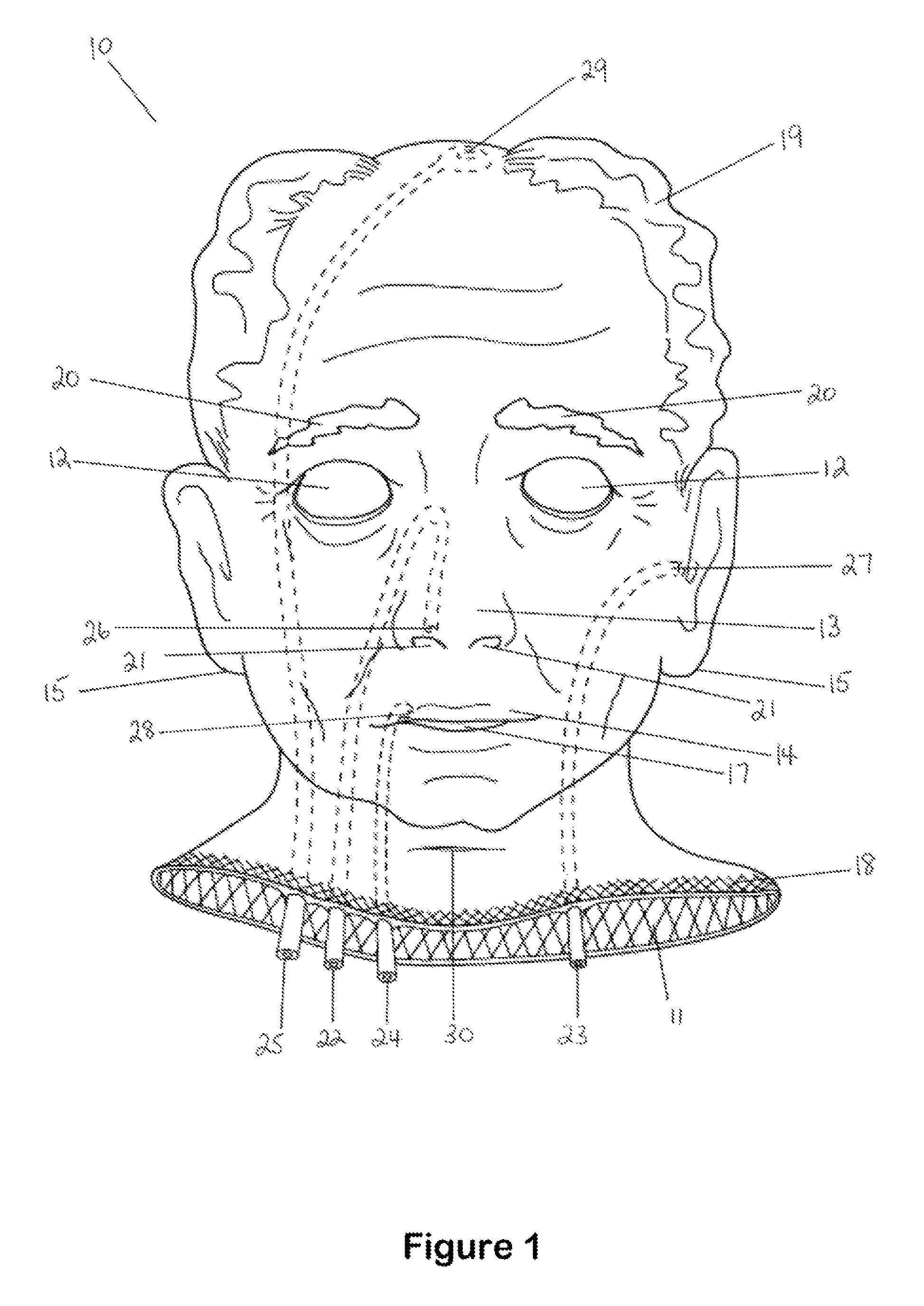
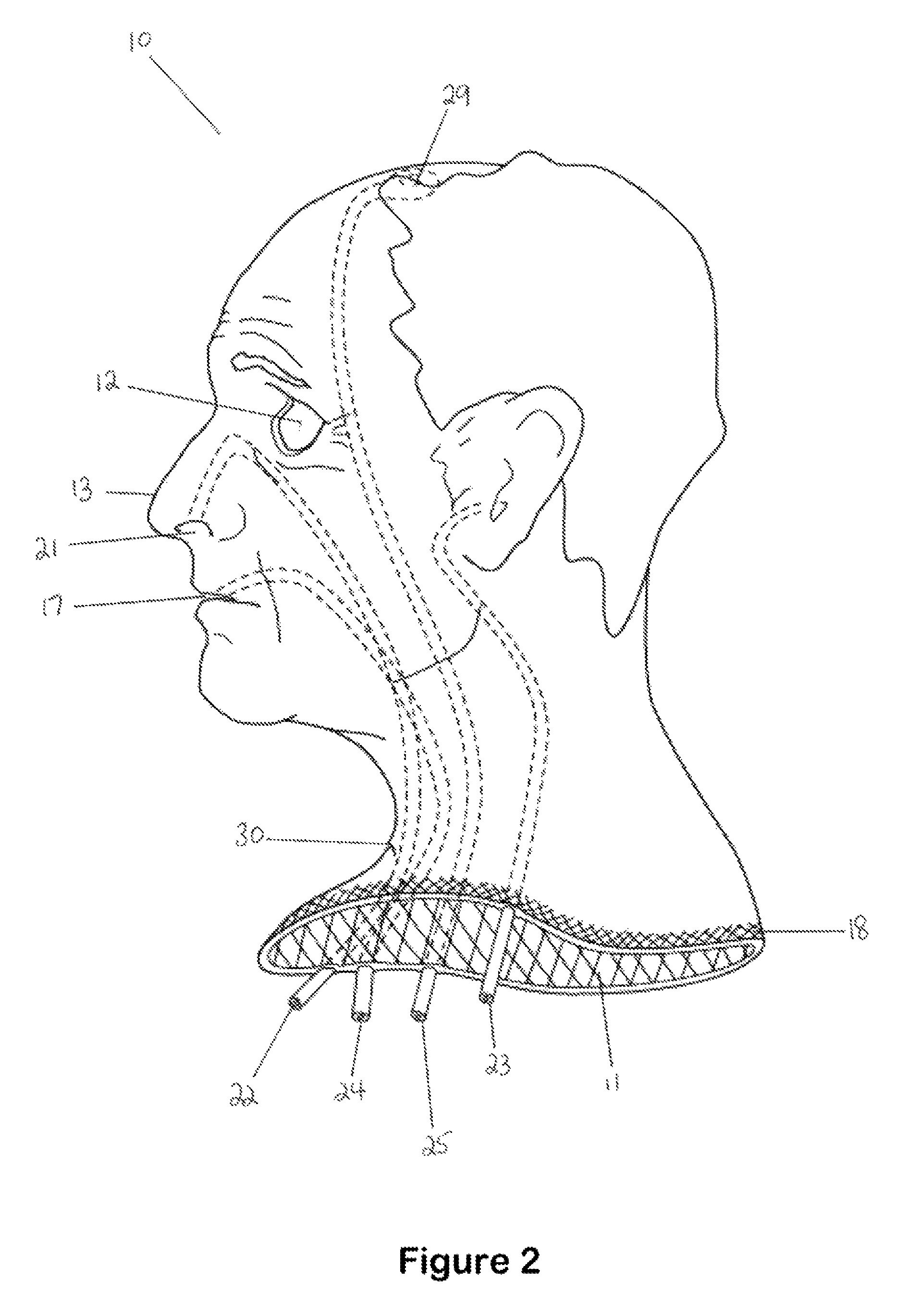
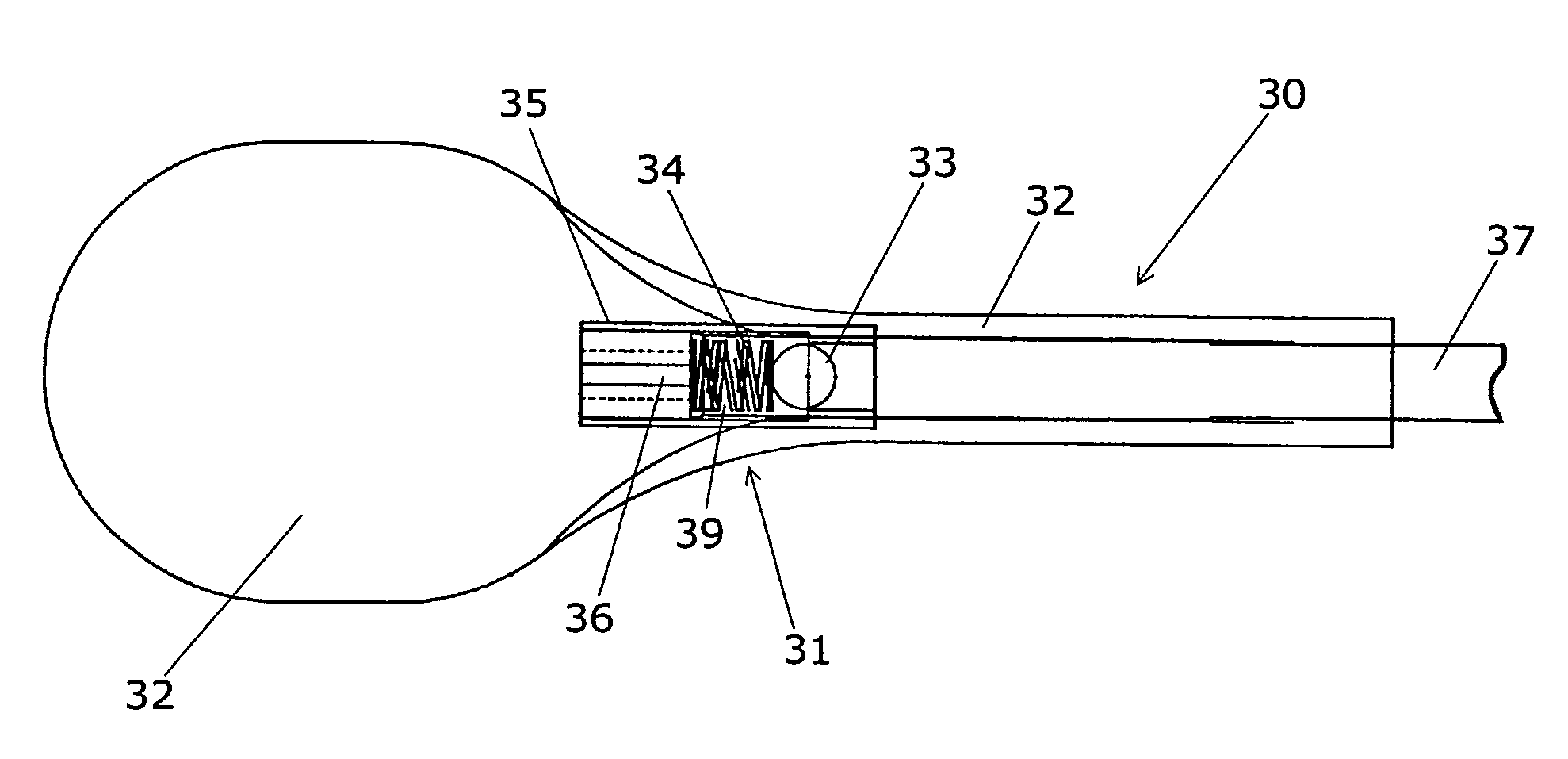
Hemostatic implant
The present disclosure relates to hemostatic implants including a porous substrate having a first hydrogel precursor and a second hydrogel precursor applied thereto in a manner such that the first hydrogel precursor and second hydrogel precursor do not react with each other until the implant is placed at the site of implantation and exposed to the physiological fluids of a patient.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Wearable Sensor Device and System
InactiveUS20070270672A1Reduce power consumptionLocal control/monitoringTelemedicinePhysiological fluidAnalyte
A system for determining the level of an analyte in a physiological fluid of a live individual is described. A wearable sensor periodically obtains data representative of the level of the analyte and has a passive RFID tag that stores the data. A receiver wirelessly interrogates the sensor with an RF interrogation signal. The RFID tag modulates or otherwise modifies the wireless interrogation signal using the data and the receiver receives back the modulated or otherwise modified interrogation signal and extracts the data from it. The receiver then determines, from the data, the level of the analyte in the fluid. The sensor may be a photometric or colorimetric sensor or an electrochemical sensor. The receiver may be, or be incorporated into, a hand-held device, a portable device, a PDA, a mobile telephone, or a laptop computer. The resulting system is more versatile and consumes less power than conventional systems.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Devices and methods for accessing and analyzing physiological fluid
InactiveUS7343188B2Convenient angleReduce painSensorsBiological testingLiquid glucosePhysiological fluid
Systems, devices and methods for determining the concentration of physiological fluid analytes are provided. The subject systems have a plurality of biosensor devices present on a disposable cartridge. Each biosensor device includes a biosensor and a skin penetration means. In practicing the subject methods, a movement means of the device is used to move each biosensor device in a first direction that provides for penetration of the skin-piercing means into a skin layer followed by movement of the biosensor in a second direction that provides for removal of the skin-piercing means from the skin layer, where this movement profile provides for physiological fluid access and analyte concentration determination by the analyte sensor means. The subject systems, devices and methods for using the same find use in determining the concentration of a variety of different physiological fluid analytes, and are particularly suited for use in detection of physiological fluid glucose concentration.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
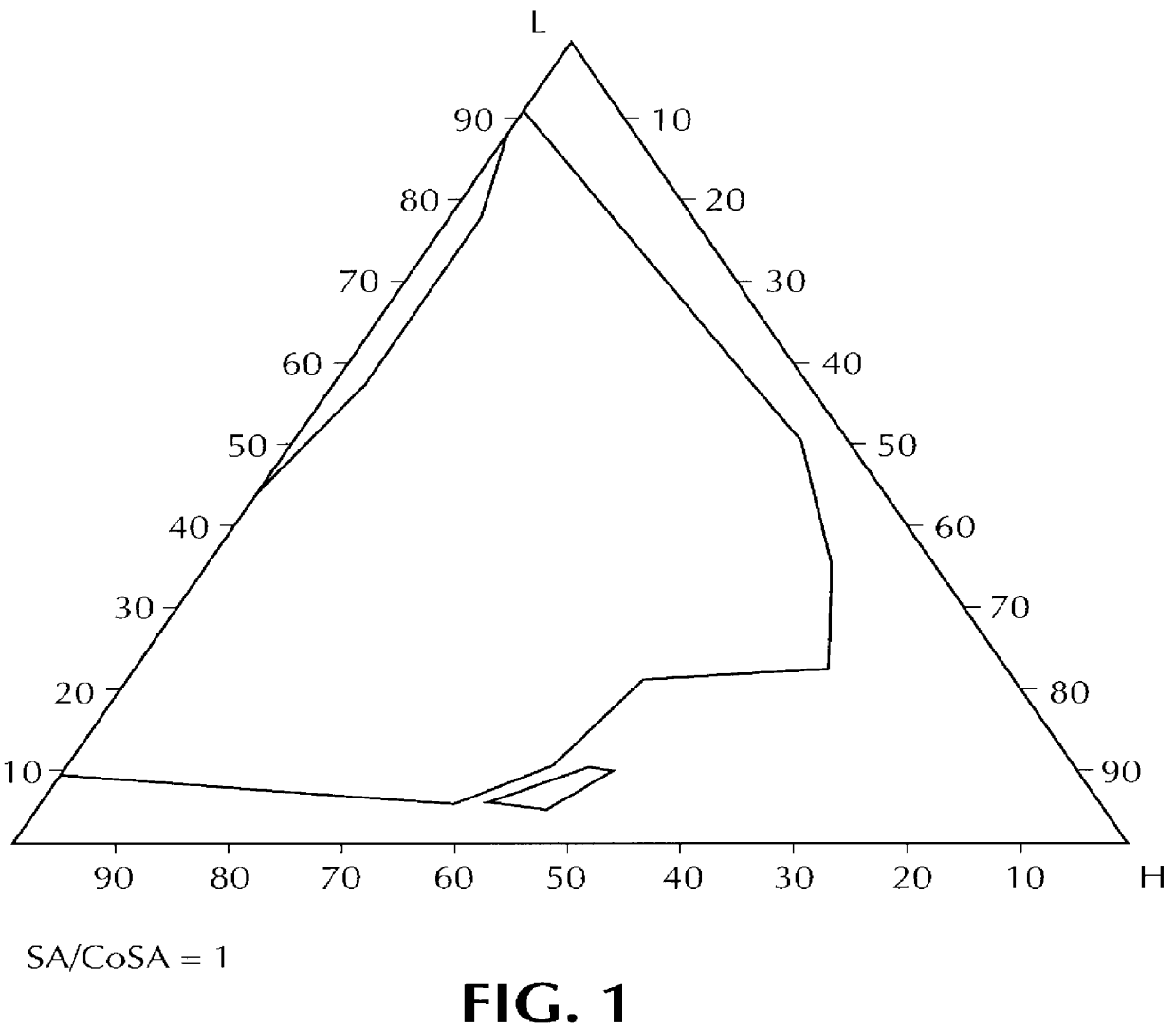
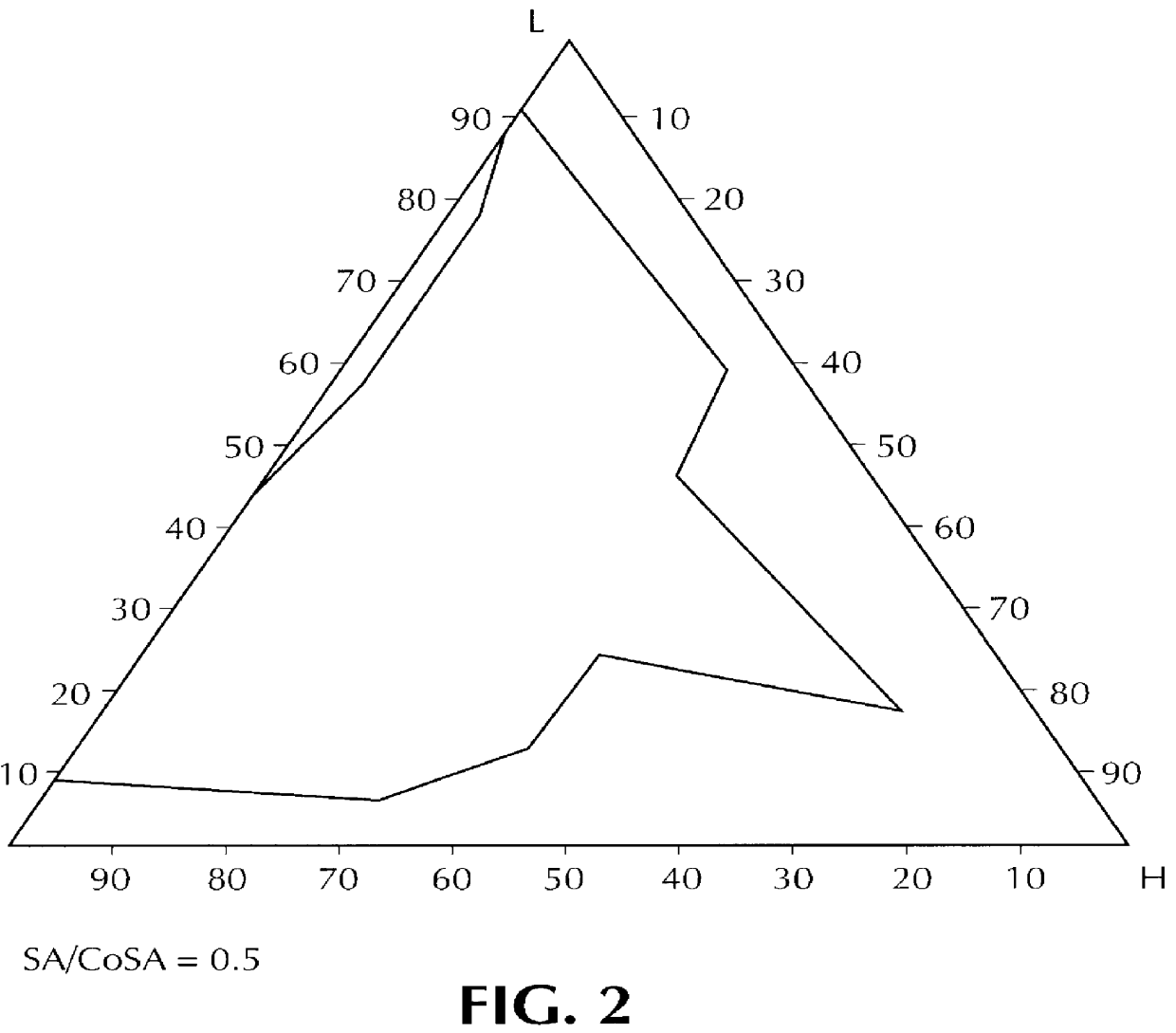
Orally administrable composition capable of providing enhanced bioavailability when ingested
InactiveUS6054136AImprove solubilityImprove bioavailabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsFatty acid esterIngestion
Composition for pharmaceutical or cosmetic use, capable of forming a microemulsion, comprising at least: an active principle, a lipophilic phase consisting of a mixture of fatty acid esters and glycerides, a surfactant (SA), a cosurfactant (CoSA), a hydrophilic phase, characterized: in that the lipophilic phase consists of a mixture of C8 to C18 polyglycolized glycerides having a hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) of less than 16, this lipophilic phase representing from 30 to 75% of the total weight of the composition; in that the surfactant (SA) is chosen from the group comprising saturated C8-C10 olyglycolized glycerides and oleic esters of polyglycerol, this surfactant having an HLB of less than 16; in that the cosurfactant (CoSA) is chosen from the group comprising lauric esters of propylene glycol, oleic esters of polyglycerol and ethyl diglycol; in that the SA / CoSA ratio is between 0.5 and 6; and in that the hydrophilic phase of the final microemulsion is supplied after ingestion by the physiological fluid of the digestive milieu.
Owner:GATTEFOSSE HLDG
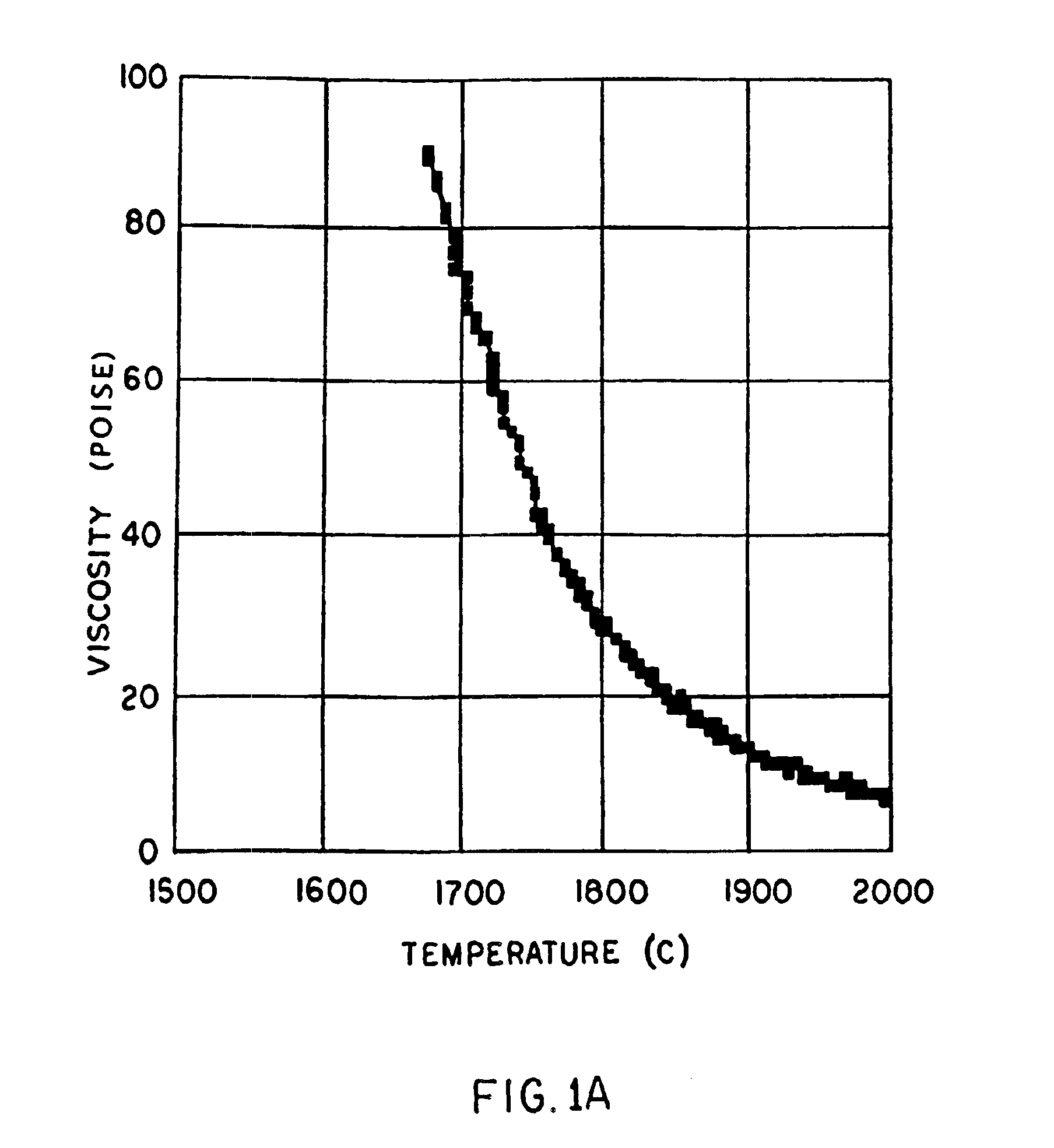
High temperature a resistant vitreous inorganic fiber
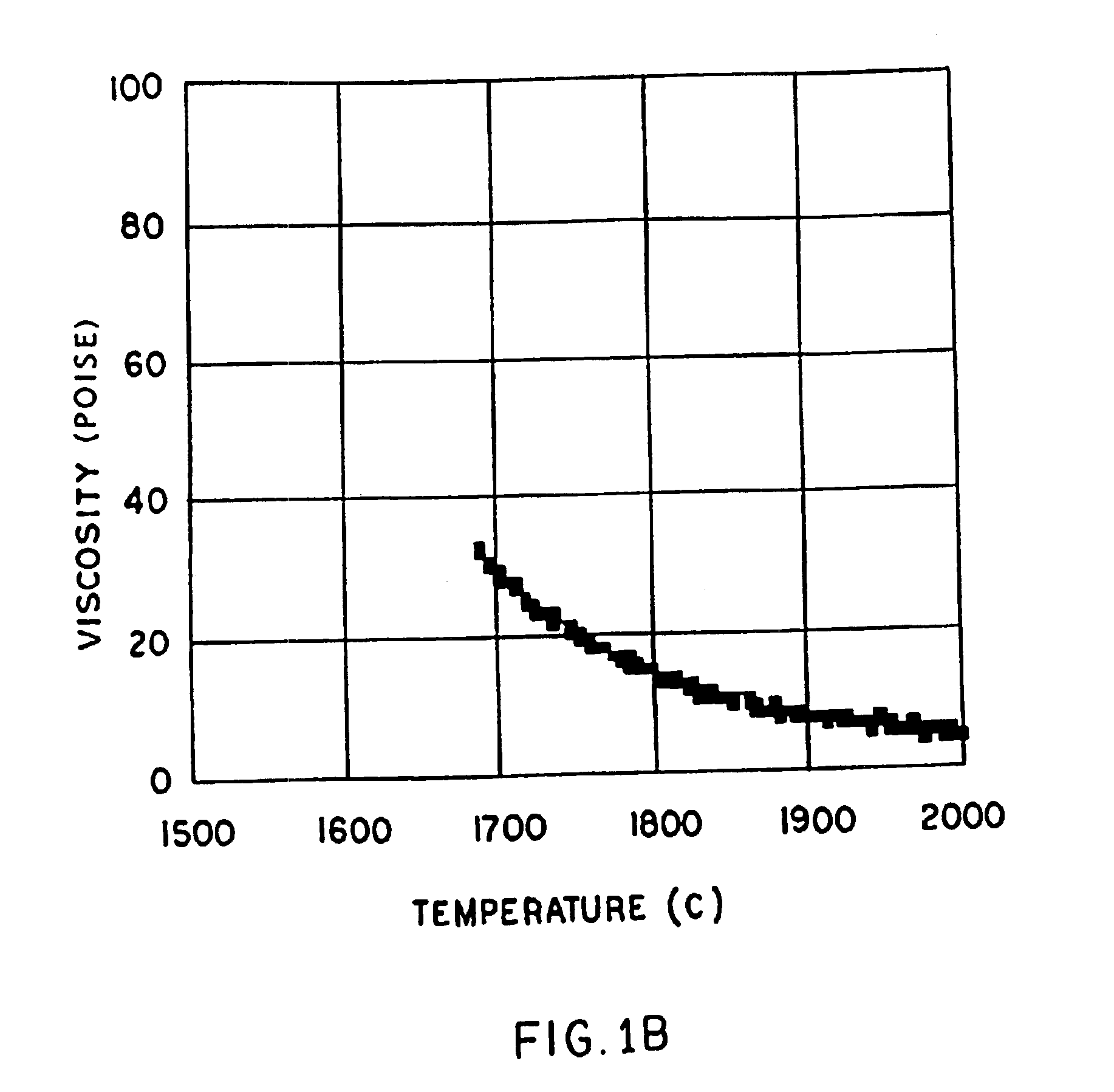
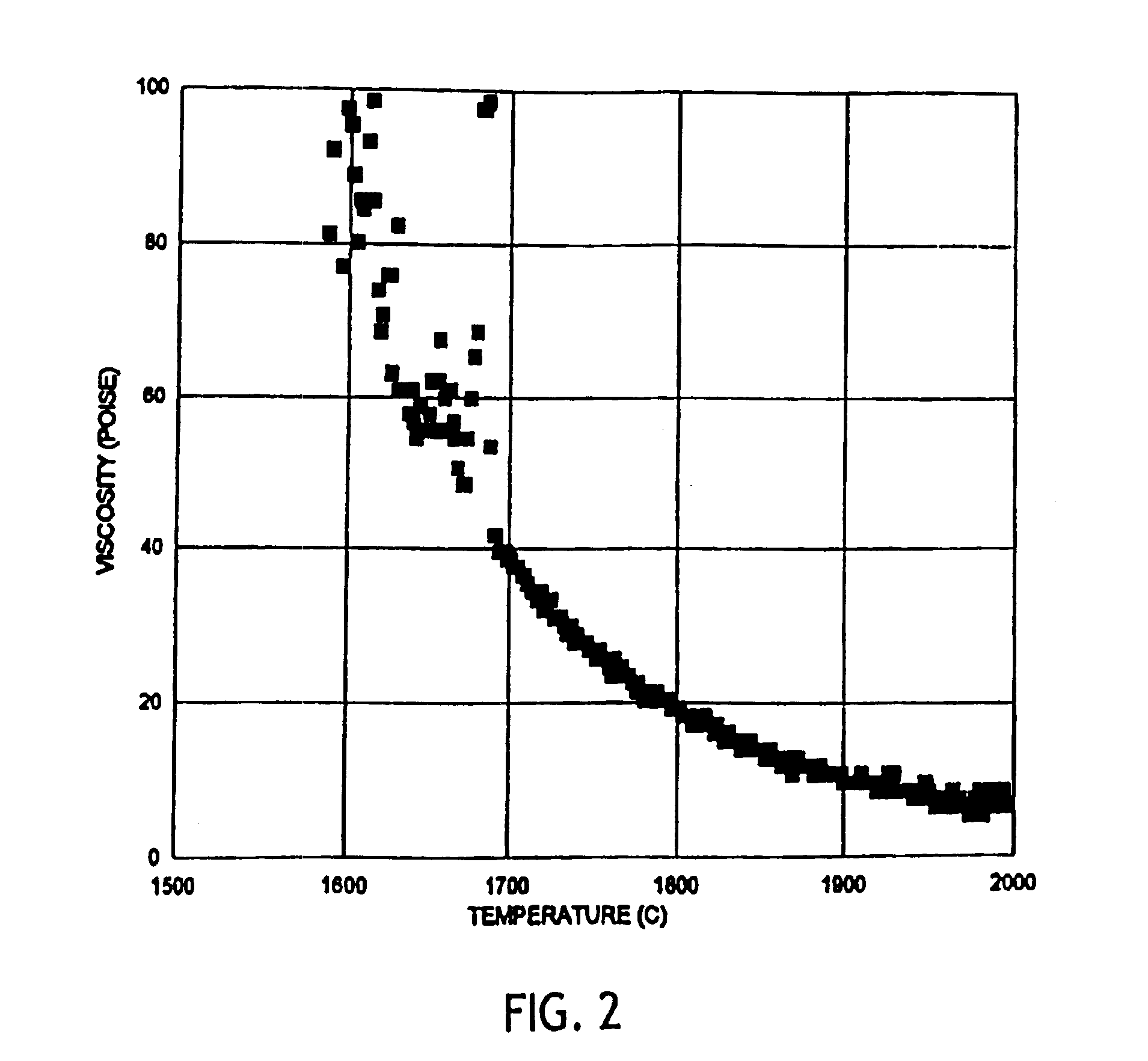
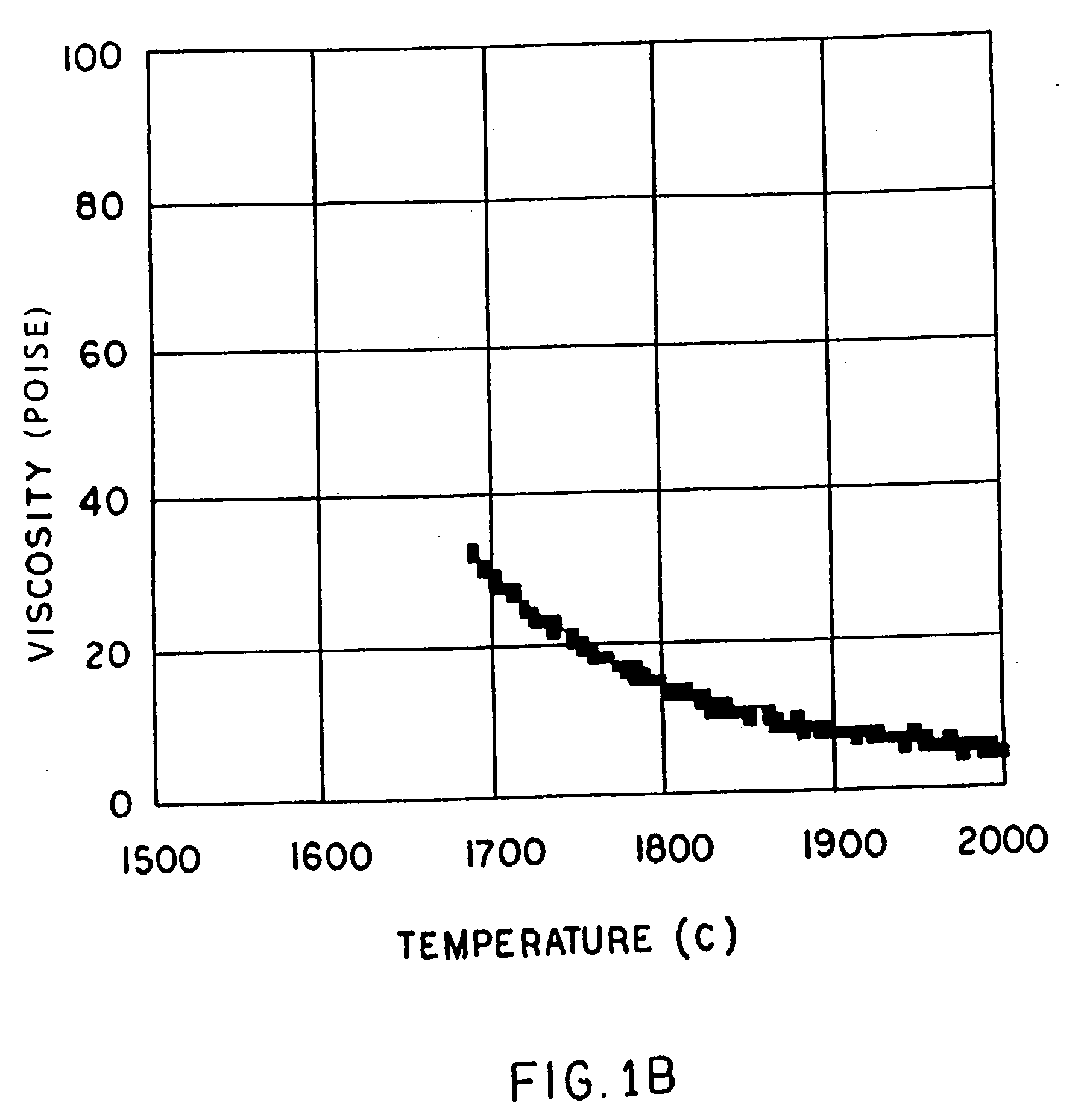
InactiveUS6953757B2Easy to manufactureLow shrinkageInorganic fibres/flakesInorganic material artificial filamentsFiberPhysiological fluid
A low shrinkage, high temperature resistant vitreous inorganic fiber having a use temperature up to at least 1330° C., which maintains mechanical integrity after exposure to the use temperature and which is non-durable in physiological fluids, is prepared by the method of forming a melt with ingredients including greater than 71.25 weight percent silica, 0 to about 20 weight percent magnesia, and about 5 to about 28.55 weight percent of calcia, 0 to about 5 weight percent zirconia, and optionally a viscosity modifier in an amount effective to render the product fiberizable; and producing fibers from the melt.
Owner:UNIFRAX I LLC
Surface-modified wick for diagnostic test strip
InactiveUS6967105B2Improve accuracyGood precisionAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAlkaneBlood sugar
A wicking material is disclosed that exhibits a horizontal wicking velocity of at least about 1.0 millimeter per second when contacted with a physiological fluid such as blood, lymph or cellular interstitial fluid. This high wicking rate is achieved by means of treatment of a fibrous wicking material candidate with a low temperature gas plasma, particularly a glow discharge gas plasma formed in a gaseous blend made up predominantly of a mixture of oxygen with a saturated alkane chosen from the group consisting of methane, ethane and propane. Diagnostic test strips made with the surface-modified wicking material, and containing an immobilized reagent means for analysis of an analyte in a physiological fluid, show improved performance in terms of increased accuracy, finer precision of analyses, reduced time of analysis, a smaller fluid sample size requirement, and improved compliance with manufacturing standards resulting in lower manufacturing costs blood sugar determinations.
Owner:QUESTSTAR MEDICAL
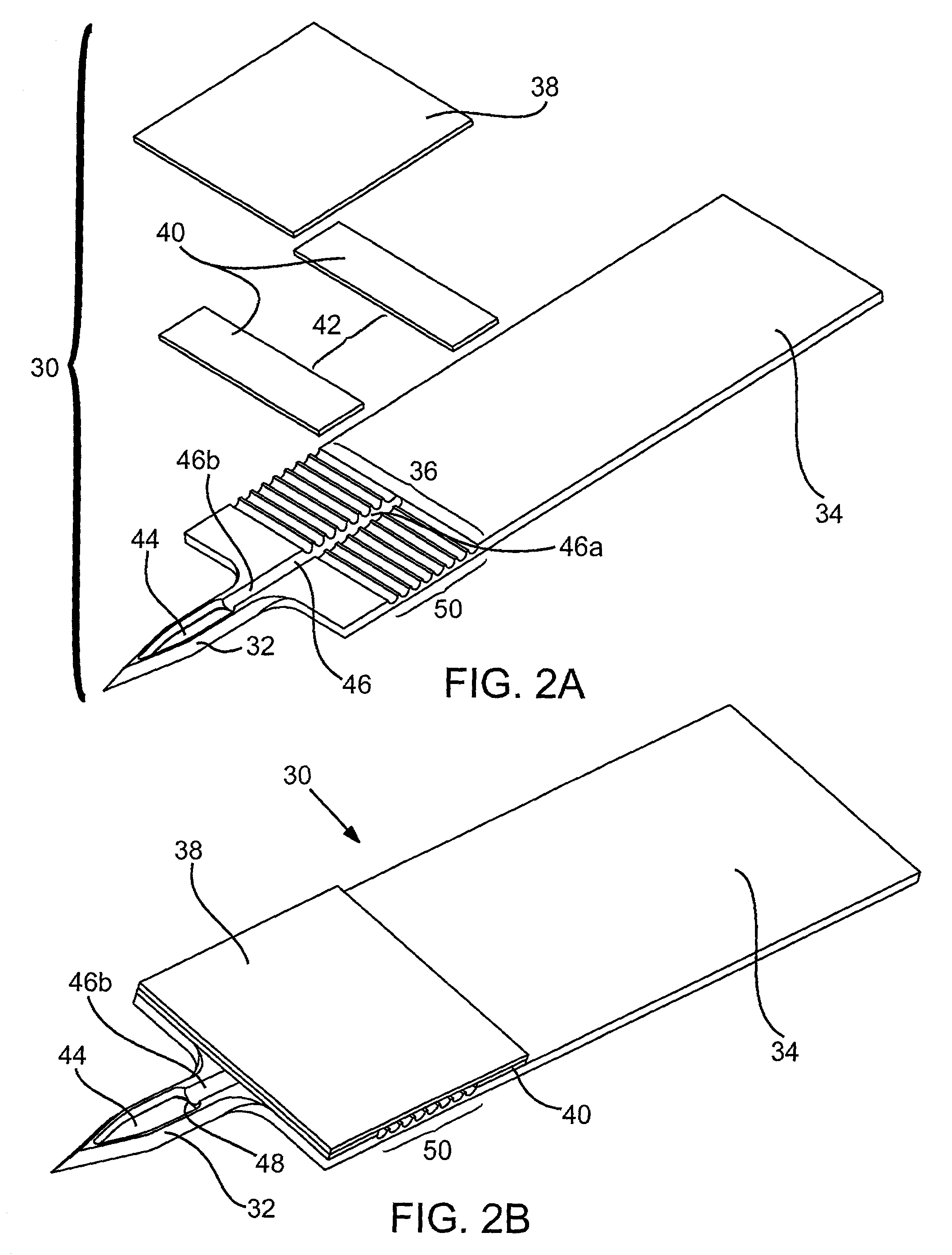
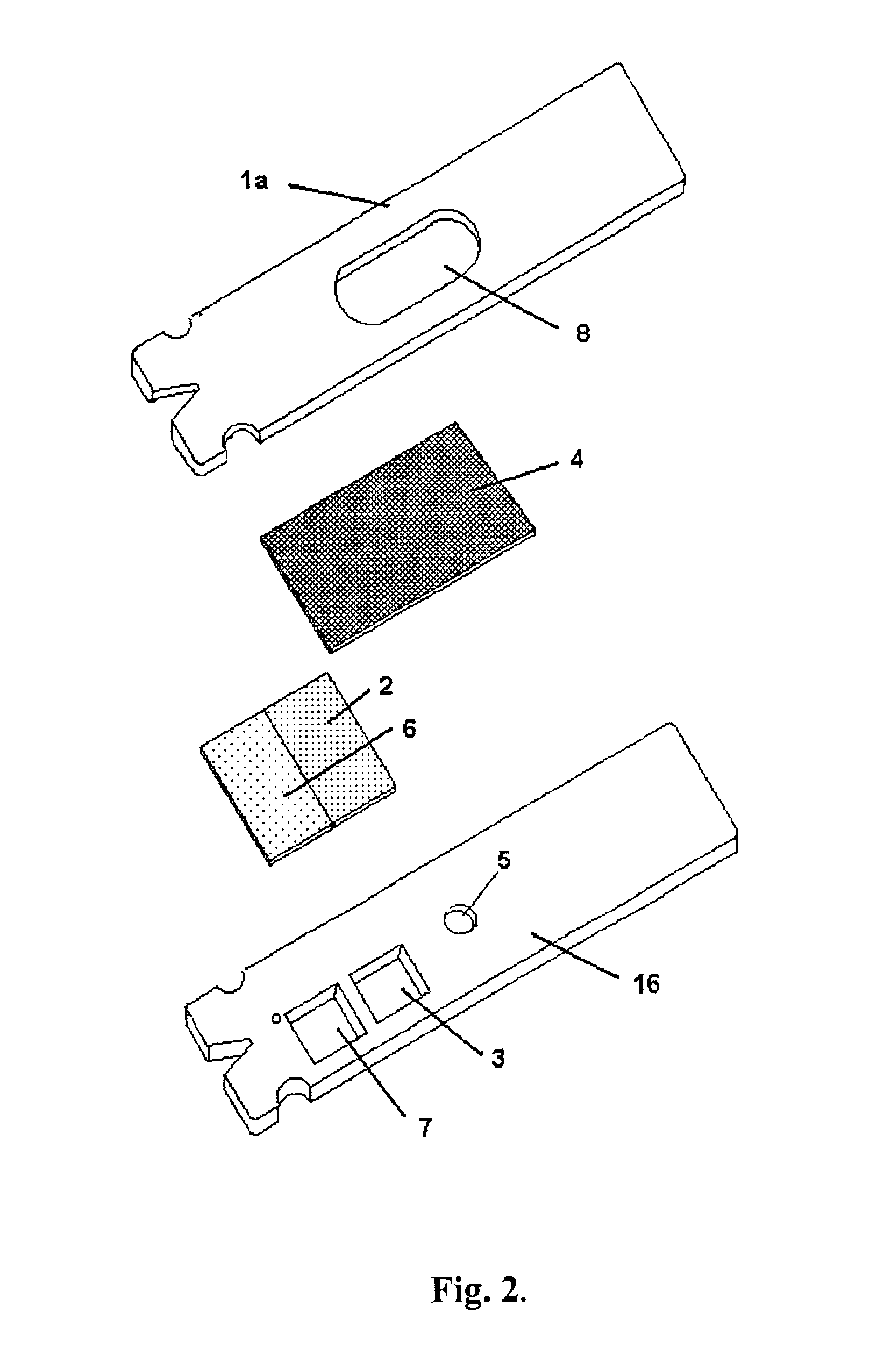
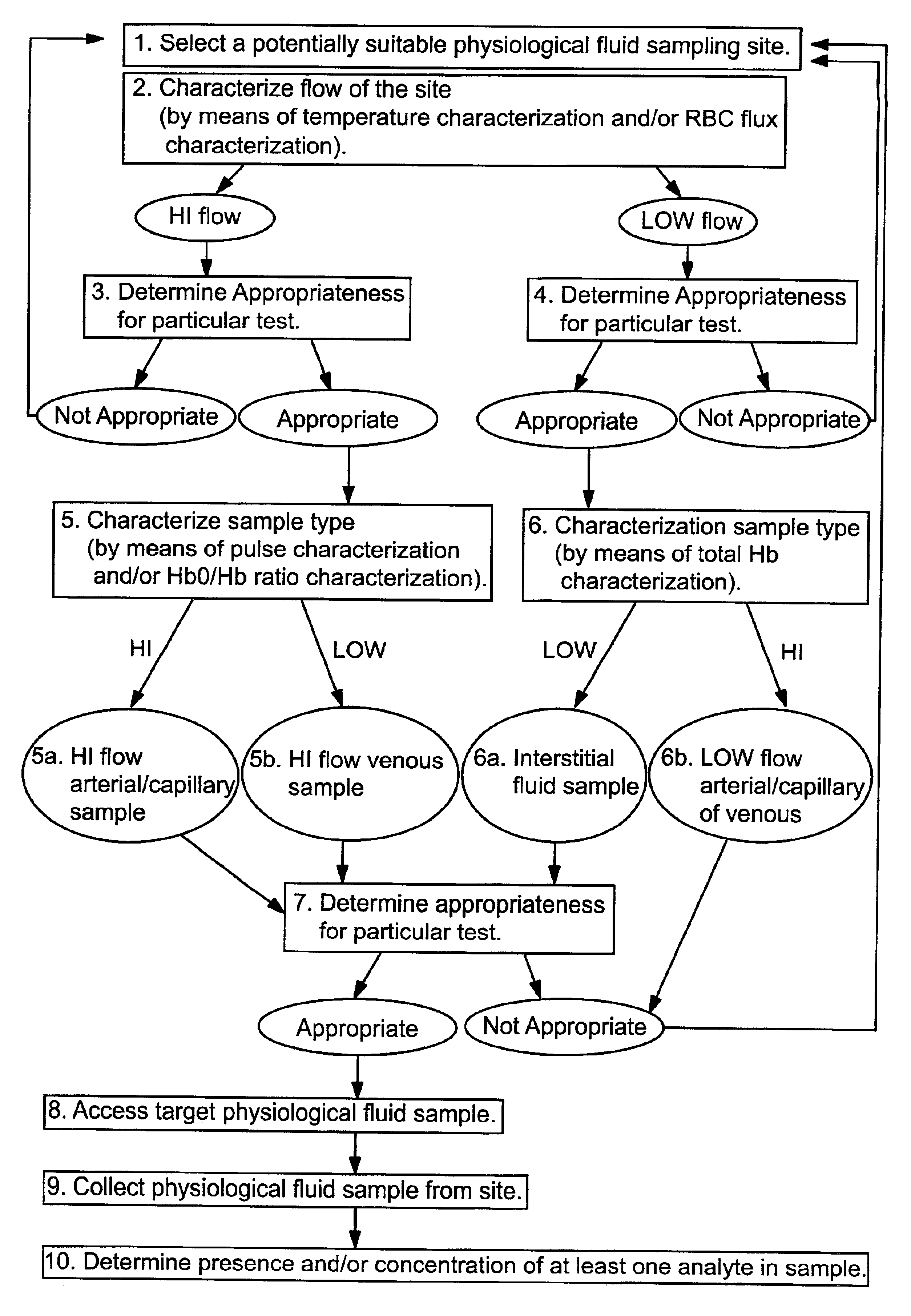
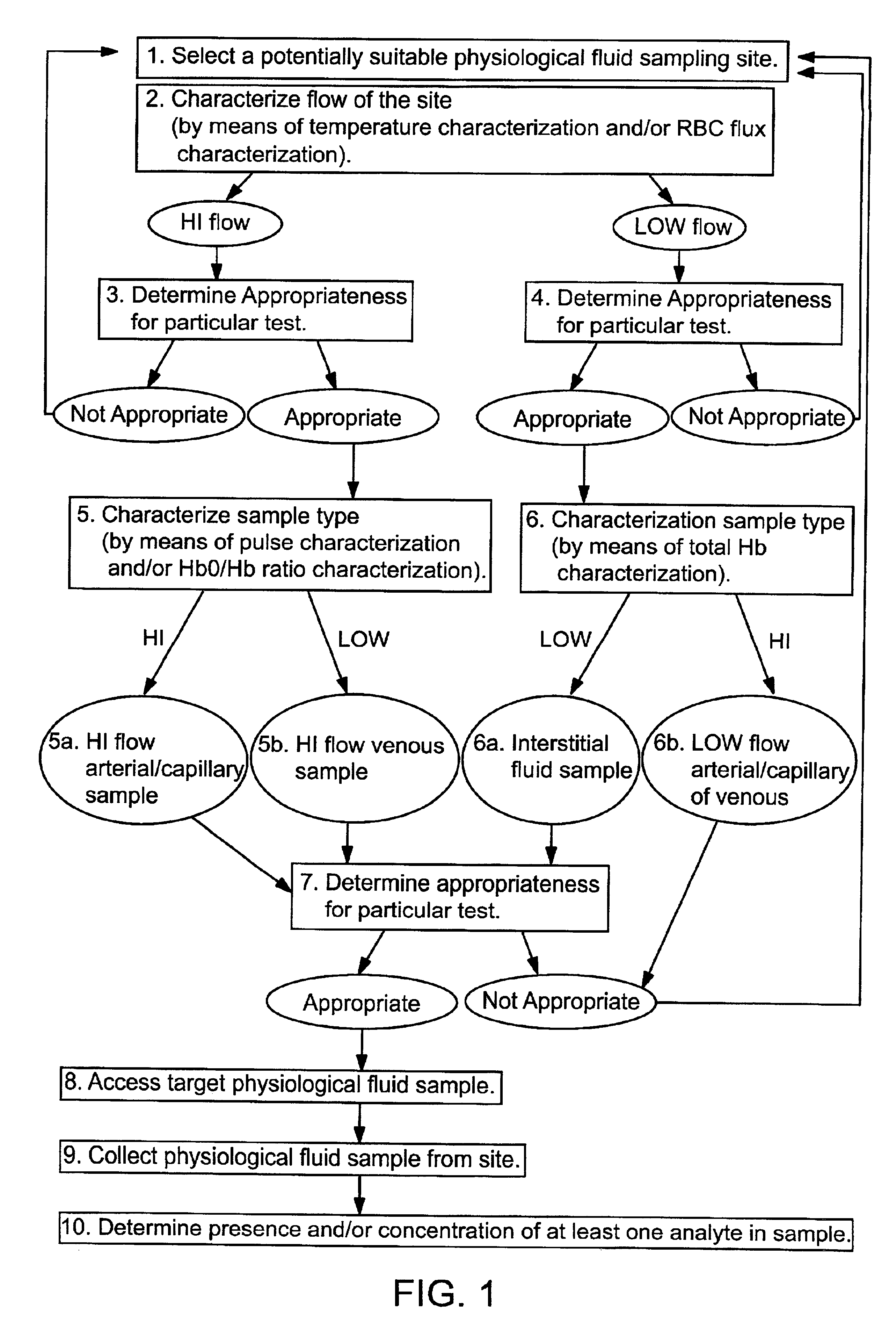
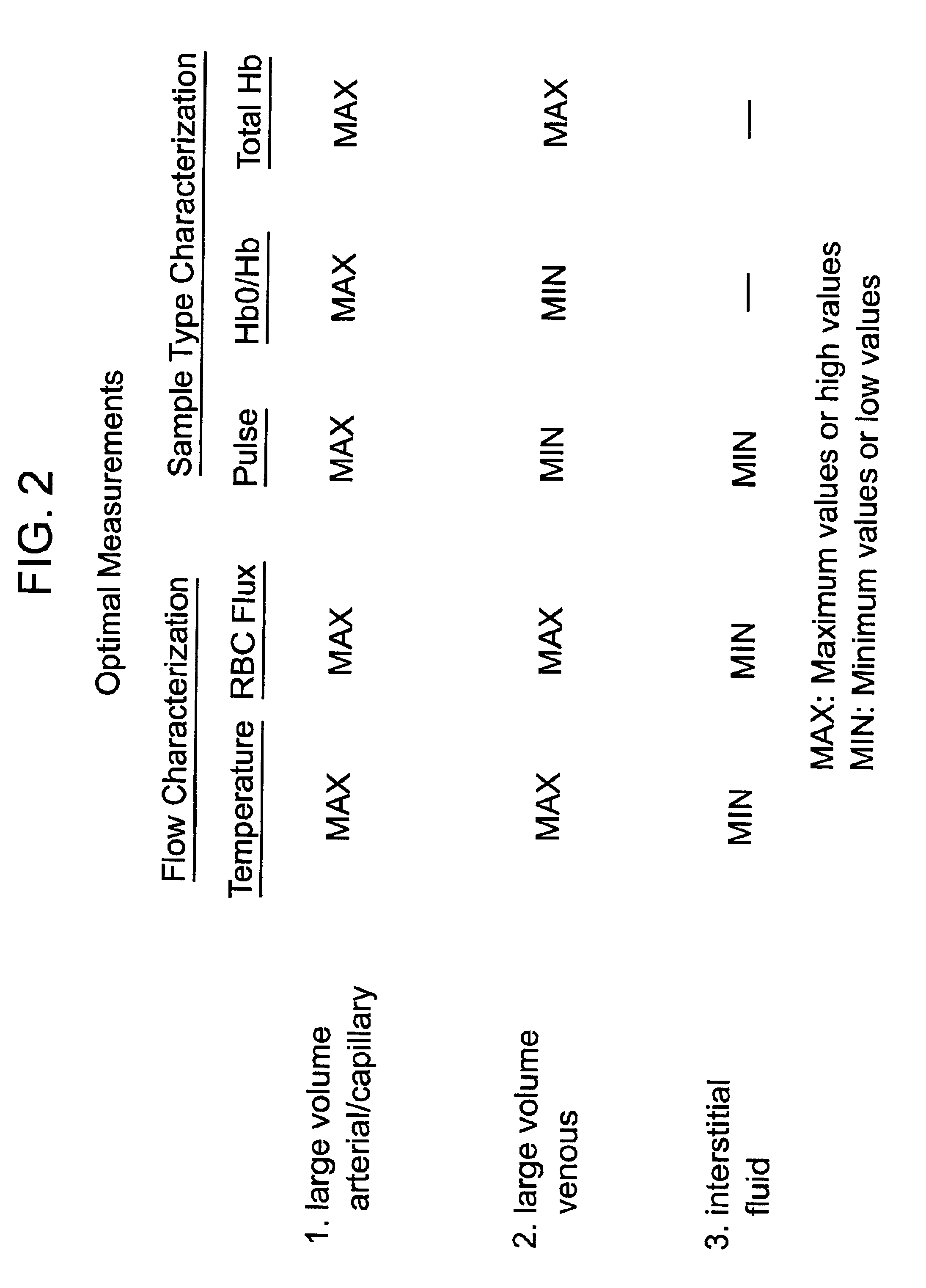
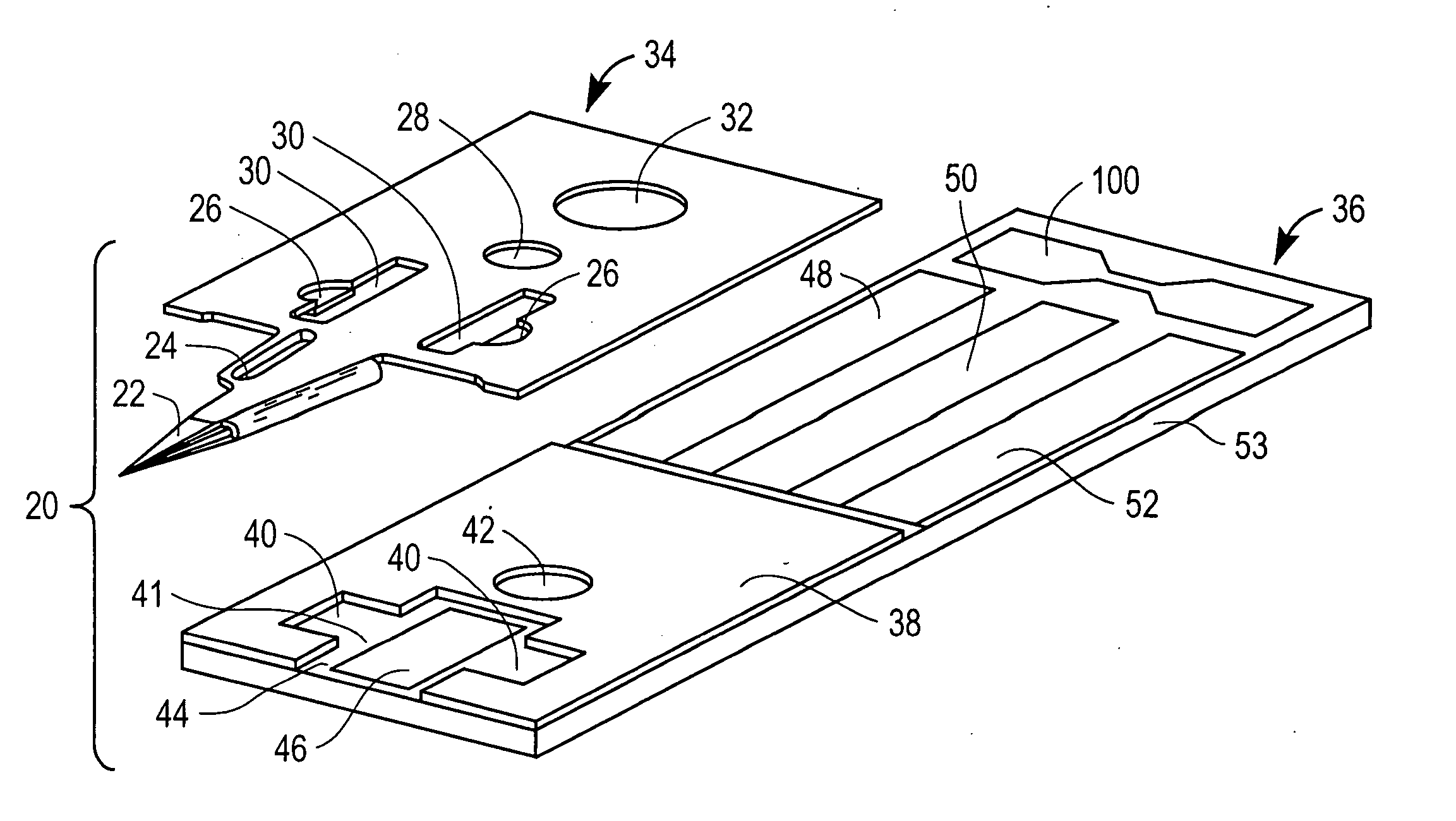
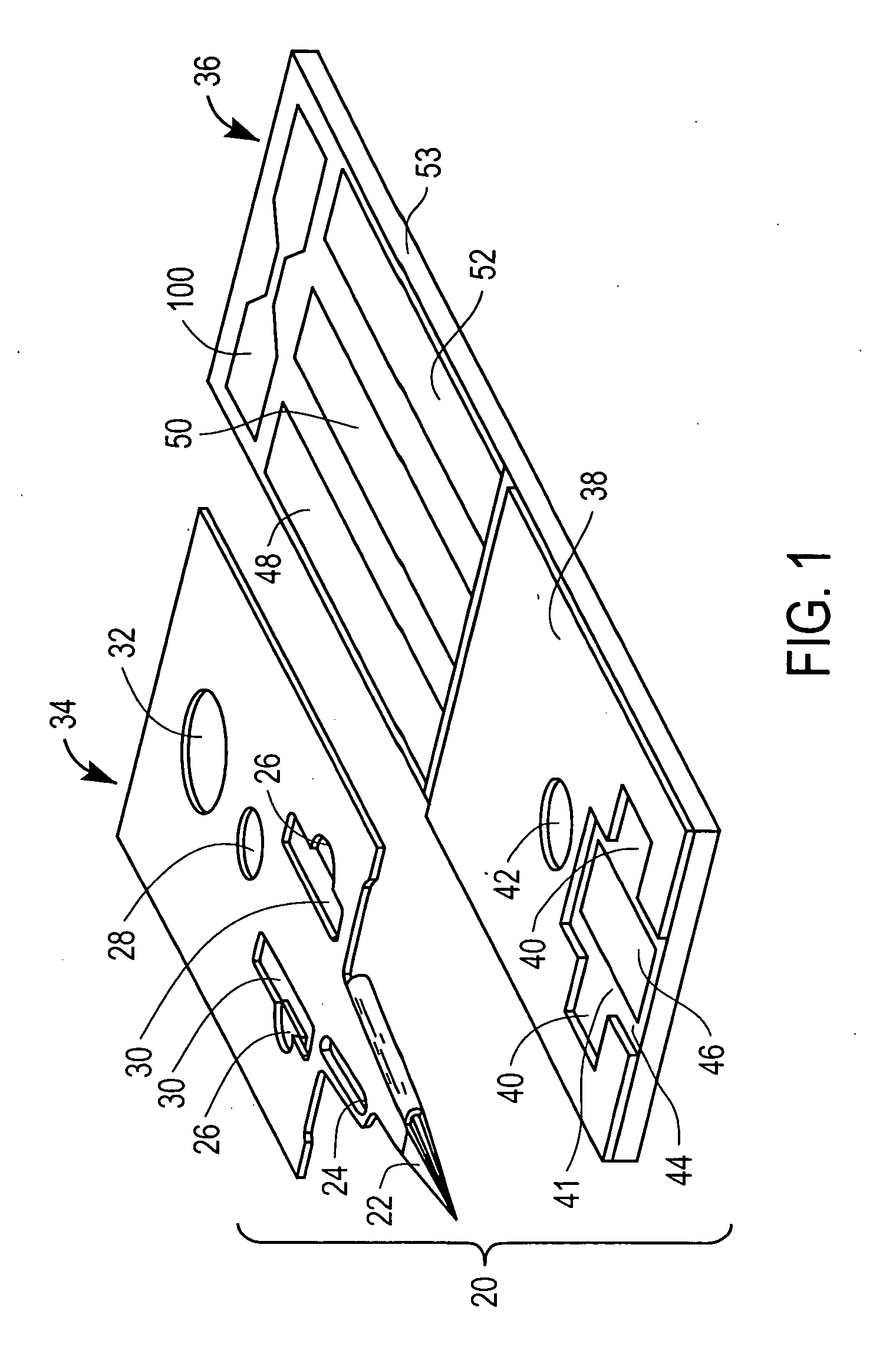
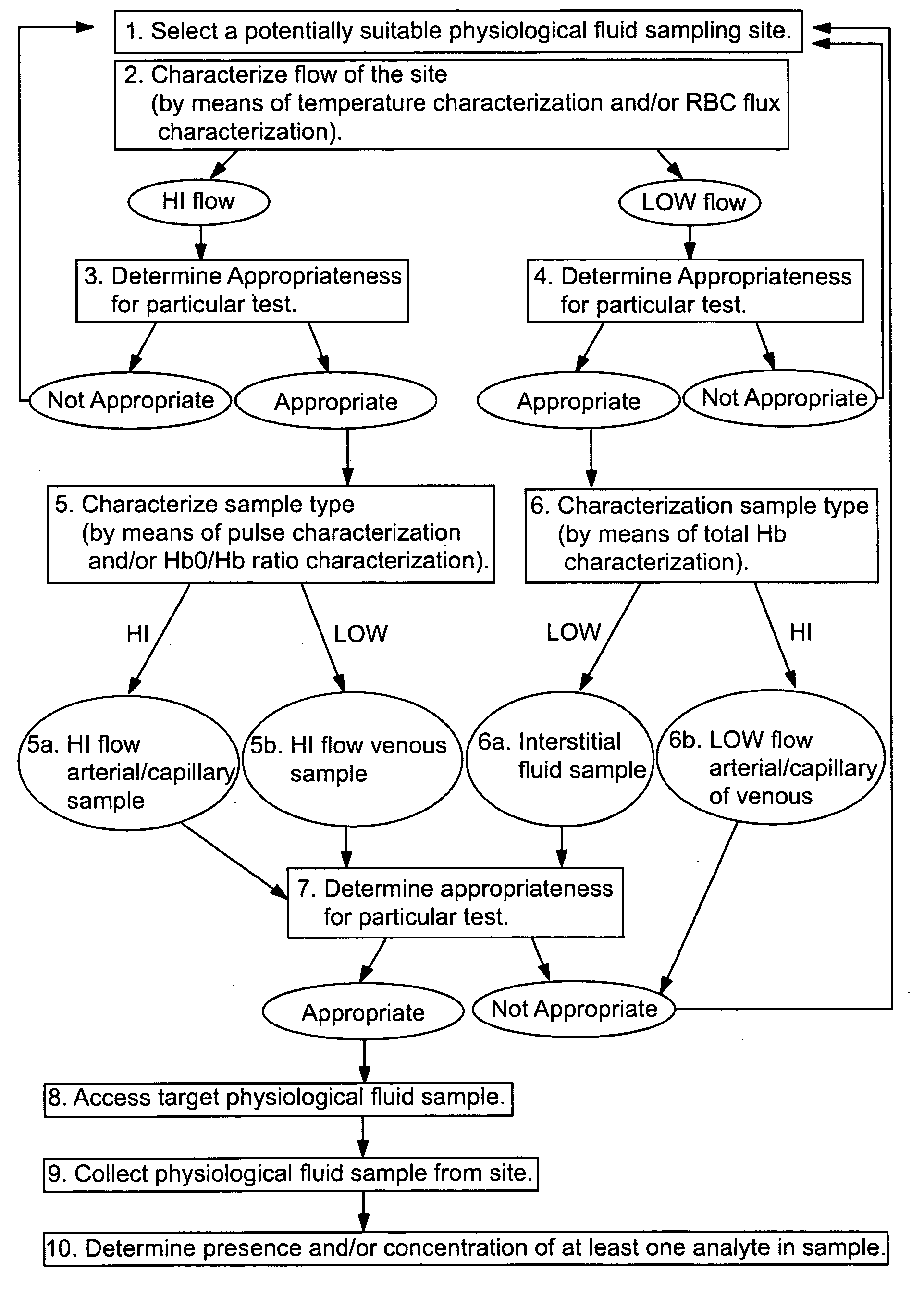
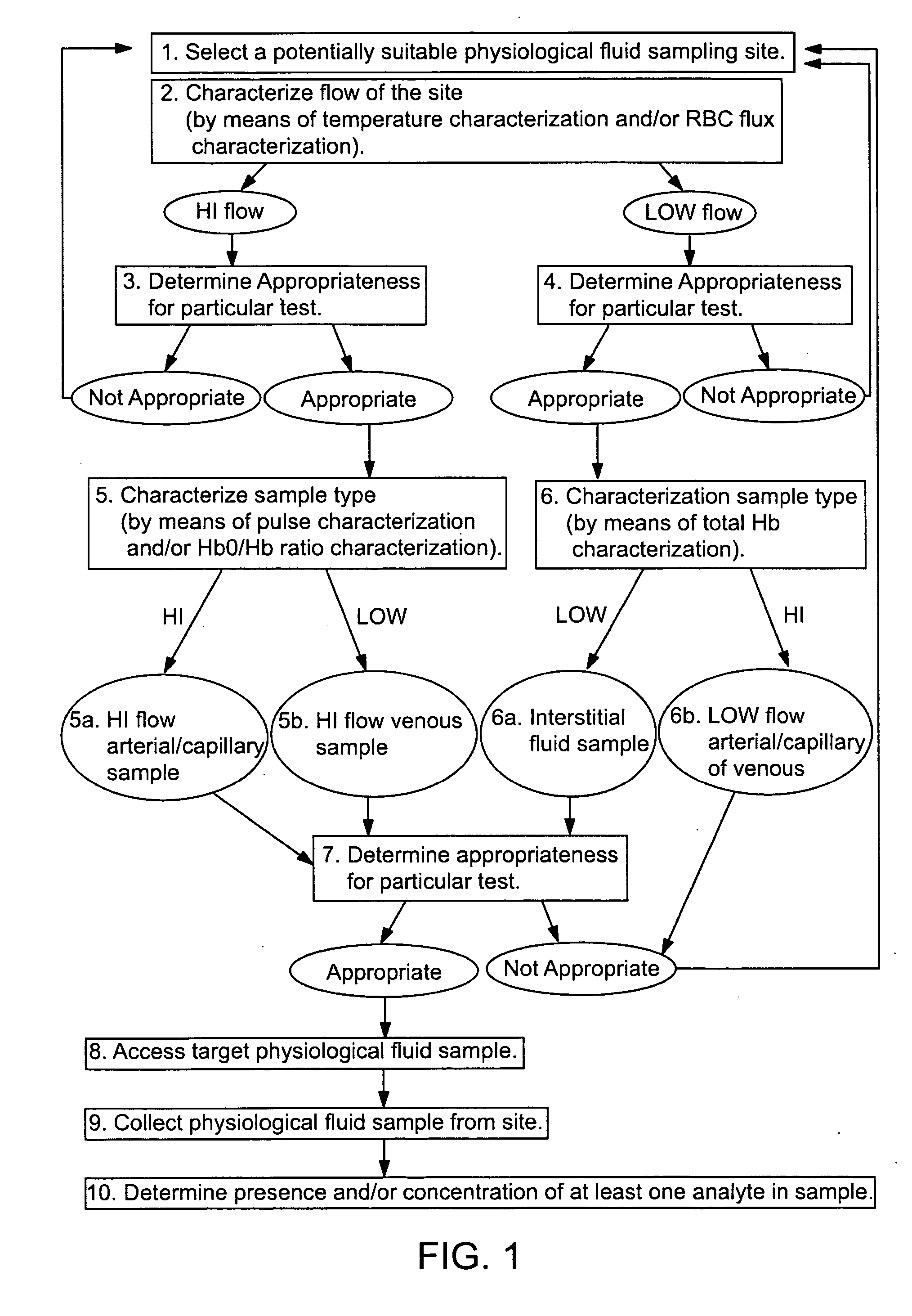
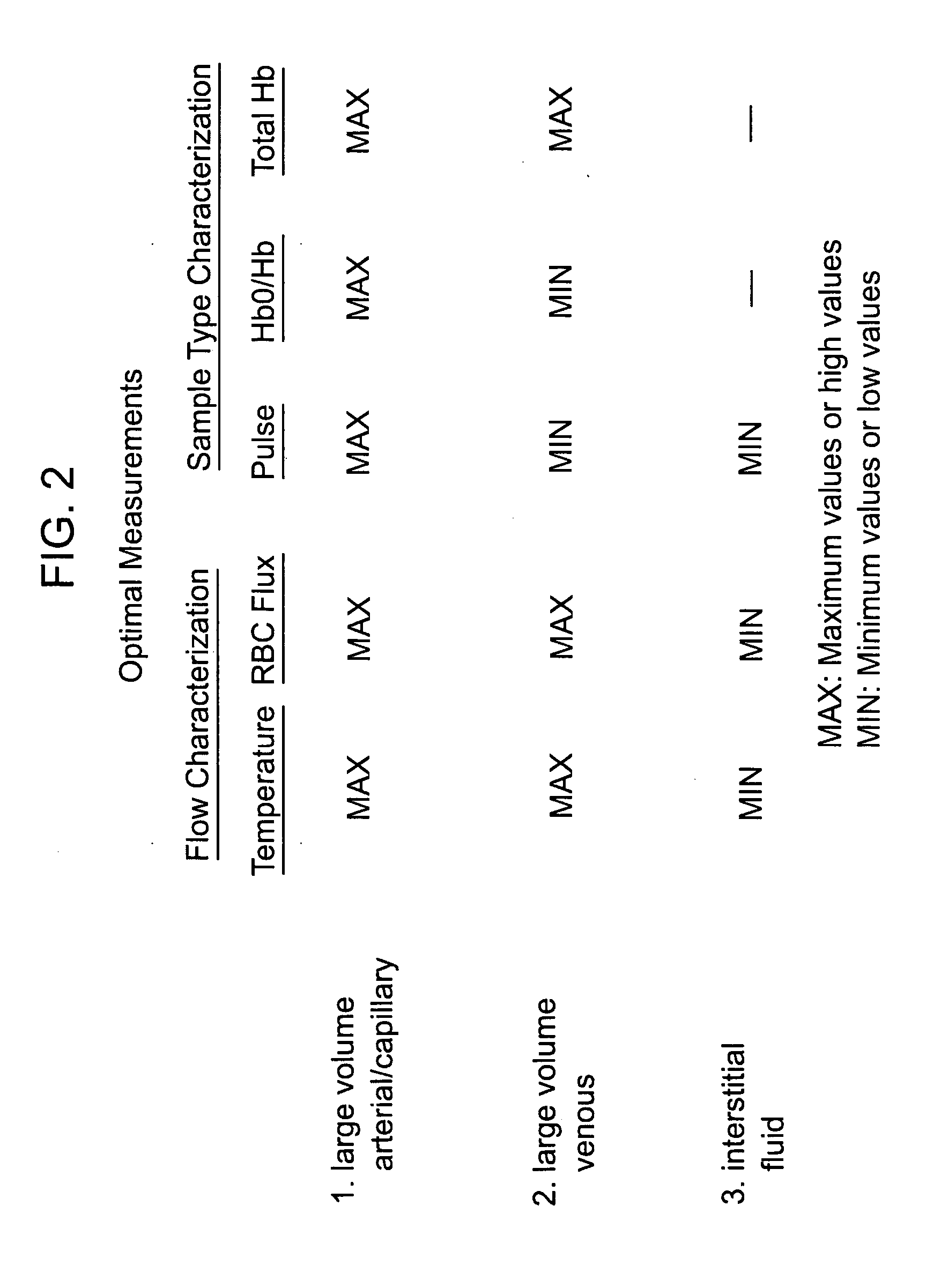
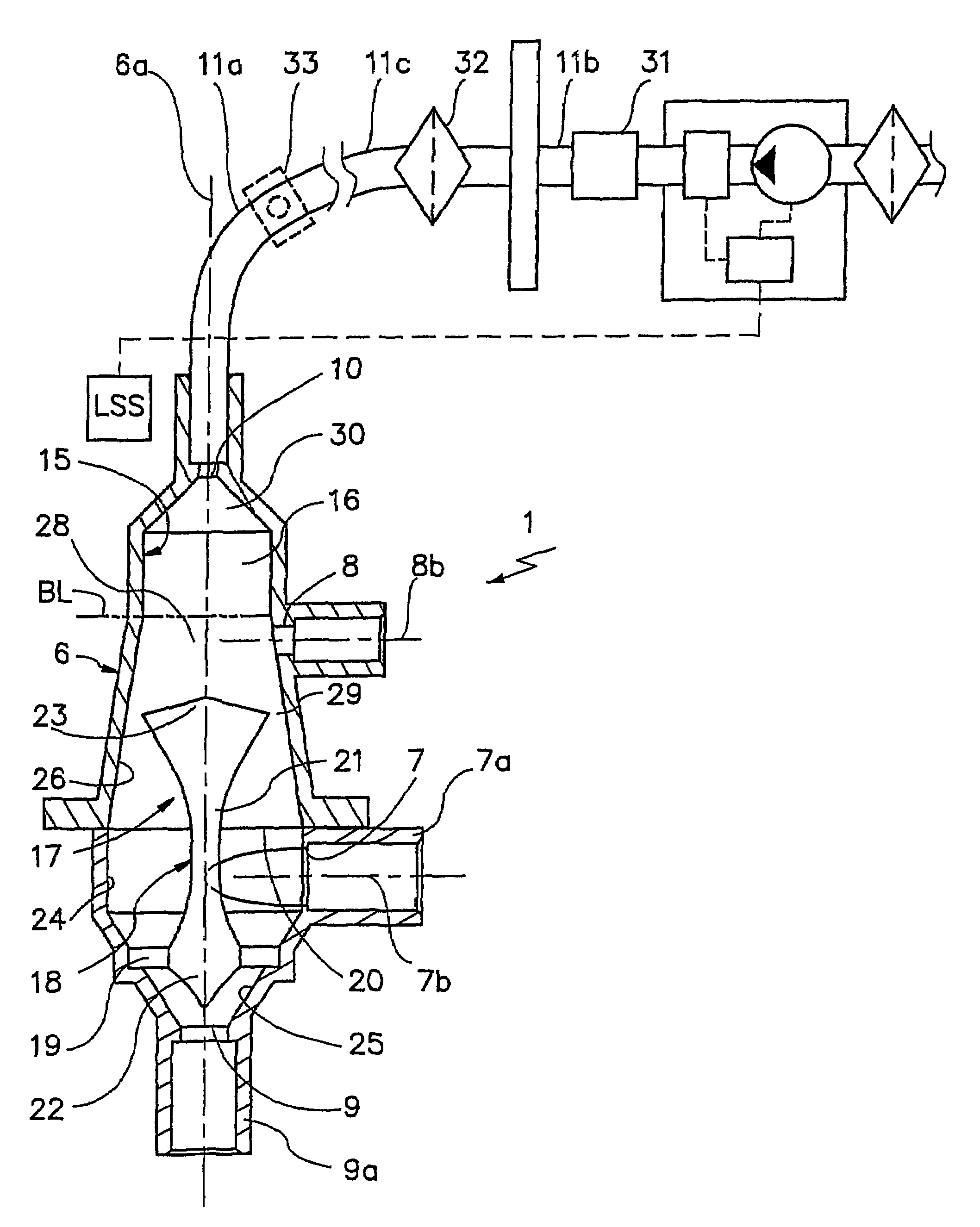
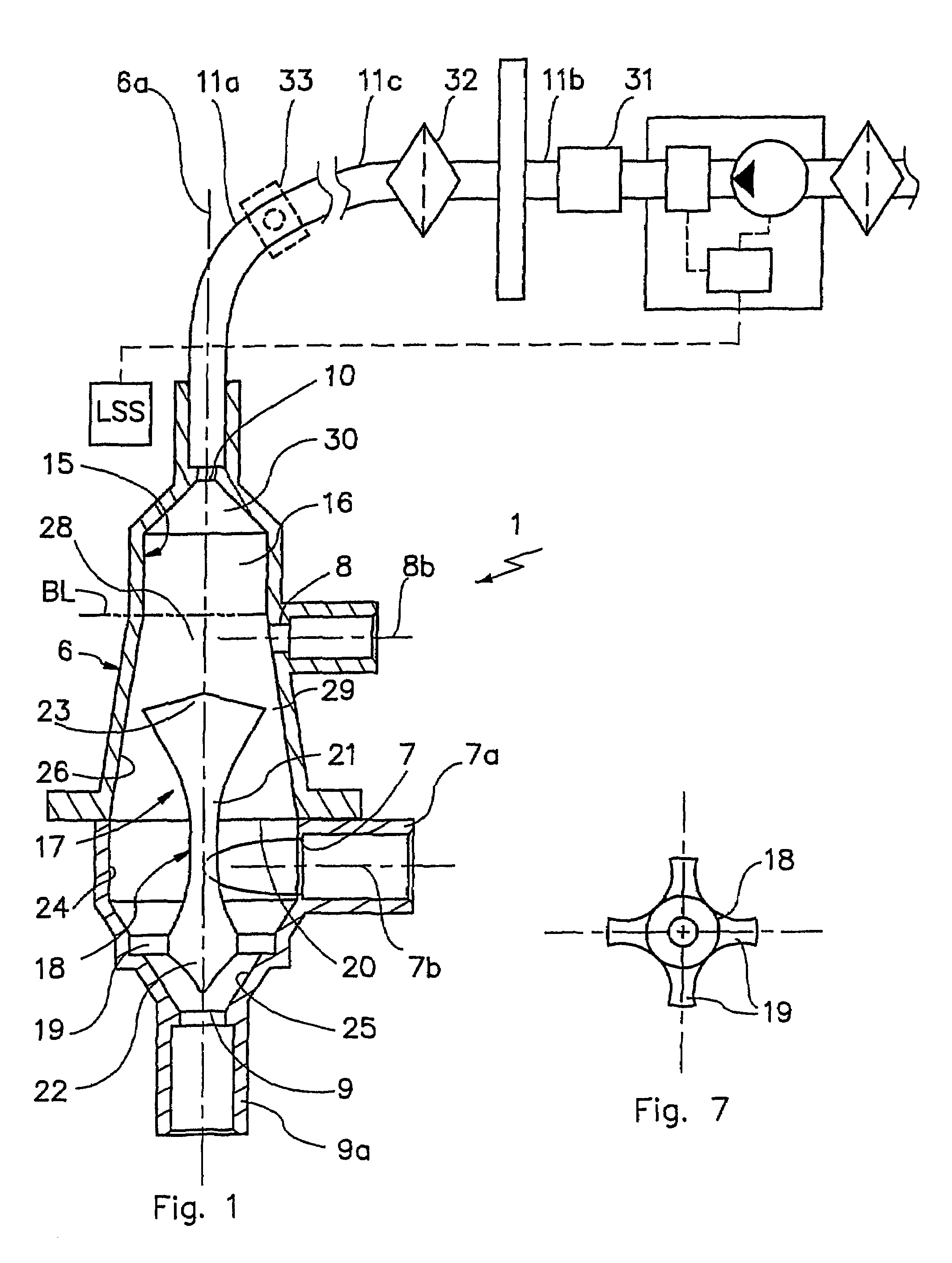
Devices for physiological fluid sampling and methods of using the same
Methods and devices are provided for determining a suitable site for sampling physiological fluid. In the subject methods, a potentially suitable physiological sampling site is selected, the fluid flow of the site is characterized and the site is then determined to be suitable based on the whether the site has high or low flow. Suitability may also be determined based on the type of sample obtainable from the site, where the order of the above-described steps may be altered. The subject devices include at least one site flow characterization element for determining the flow characteristics of a potential physiological sampling site and / or at least one sample type characterization element for determining whether the vasculature is arterial, venous or neither, i.e., an interstitial fluid sampling site. The subject methods and devices are particularly suited for use in the detection of physiological sampling sites in the fingers, arms, legs, earlobes, heels, feet, nose and toes. Also provided are kits that include the subject devices for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Analyte measuring system which prevents the reuse of a test strip
InactiveUS20050284757A1Microbiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresAnalytePhysiological fluid
The present invention may be used in test strips for measuring an analyte or indicator such as glucose in a physiological fluid such as blood, interstitial fluid, or urine. The present invention also relates to test strips incorporating an integrated lance such as a needle, blade, or other sharp or skin puncturing device. In particular, in one embodiment of the present invention, a fused link is incorporated into the test strip. The fused link may be destroyed once the test is completed, preventing reuse of the strip.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Devices for physiological fluid sampling and methds of using the same
Methods and devices are provided for determining a suitable site for sampling physiological fluid. In the subject methods, a potentially suitable physiological sampling site is selected, the fluid flow of the site is characterized and the site is then determined to be suitable based on the whether the site has high or low flow. Suitability may also be determined based on the type of sample obtainable from the site, where the order of the above-described steps may be altered. The subject devices include at least one site flow characterization element for determining the flow characteristics of a potential physiological sampling site and / or at least one sample type characterization element for determining whether the vasculature is arterial, venous or neither, i.e., an interstitial fluid sampling site. The subject methods and devices are particularly suited for use in the detection of physiological sampling sites in the fingers, arms, legs, earlobes, heels, feet, nose and toes. Also provided are kits that include the subject devices for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
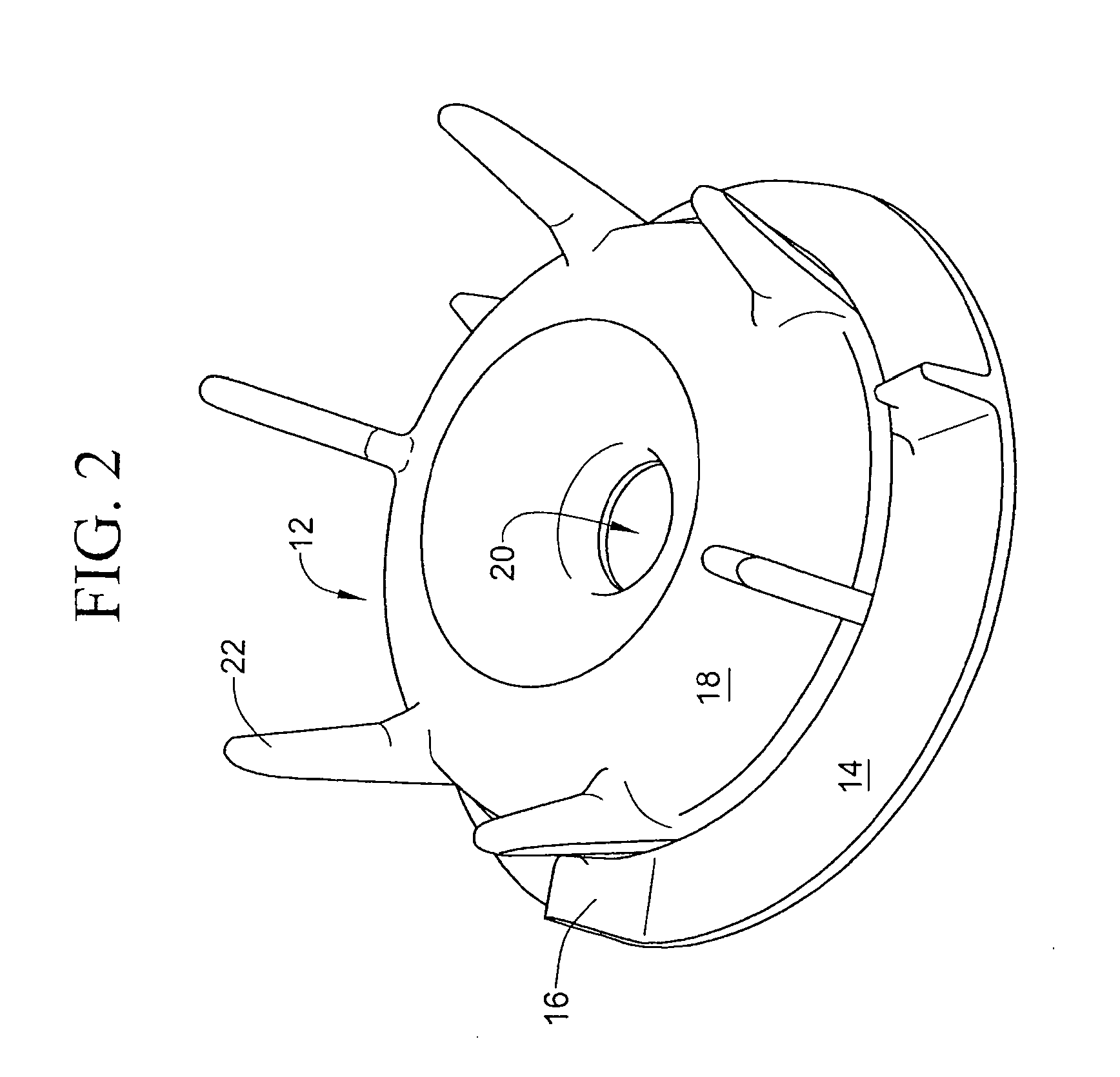
Gas separation devices
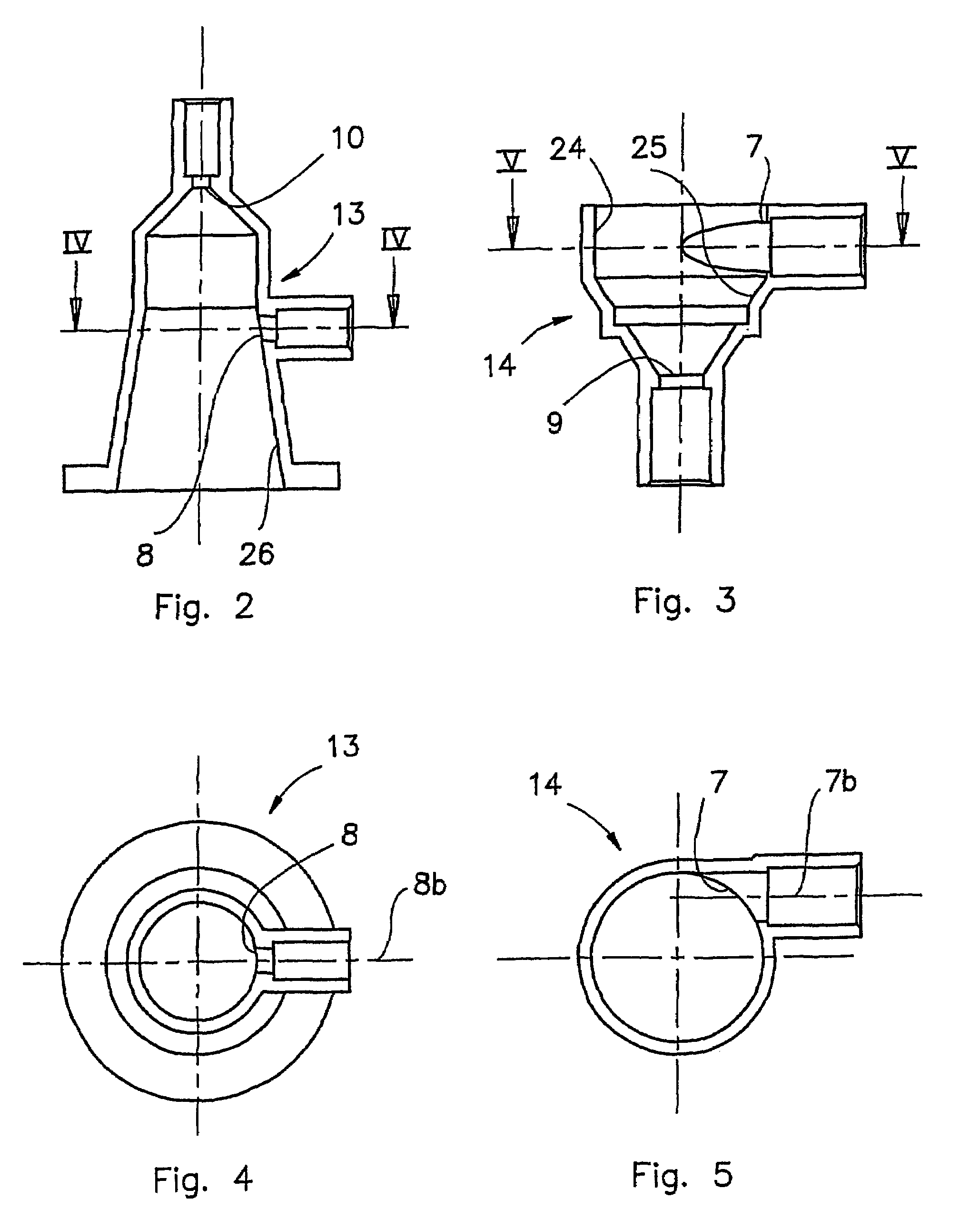
ActiveUS7517387B2Minimized volumeEasy to operateLiquid degasificationReversed direction vortexPhysiological fluidEffective surface
A description is given of a gas separation device for a physiological fluid, comprising a containing body (6) having at least a first inlet aperture (7) for a physiological fluid, positioned with a tangential direction of access, at least one outlet aperture (9) for the said fluid, spaced apart from the said inlet aperture, and a guide element (17) housed within the said body. The guide element (17) has a continuous active surface (15) designed to contact and guide the said fluid and delimits, together with the containing body (6), a first annular chamber (20) into which the first inlet aperture (7) opens directly.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Disposable cartridge for producing gas-enriched fluids
InactiveUS20020136662A1Other blood circulation devicesTransportation and packagingPhysiological fluidMedicine
A device generates a gas-enriched physiologic fluid and combines it with a bodily fluid to create a gas-enriched bodily fluid. The device may take the form of a disposable cartridge. The cartridge may include a fluid supply chamber for delivering physiologic fluid under pressure to an atomizer. The atomizer delivers fluid droplets into a gas-pressurized atomization chamber to enrich the physiologic fluid with the gas. The gas-enriched physiologic fluid is delivered to a mixing chamber in the cartridge where the gas-enriched physiologic fluid is mixed with a bodily fluid, such as blood, to create a gas-enriched bodily fluid.
Owner:THEROX
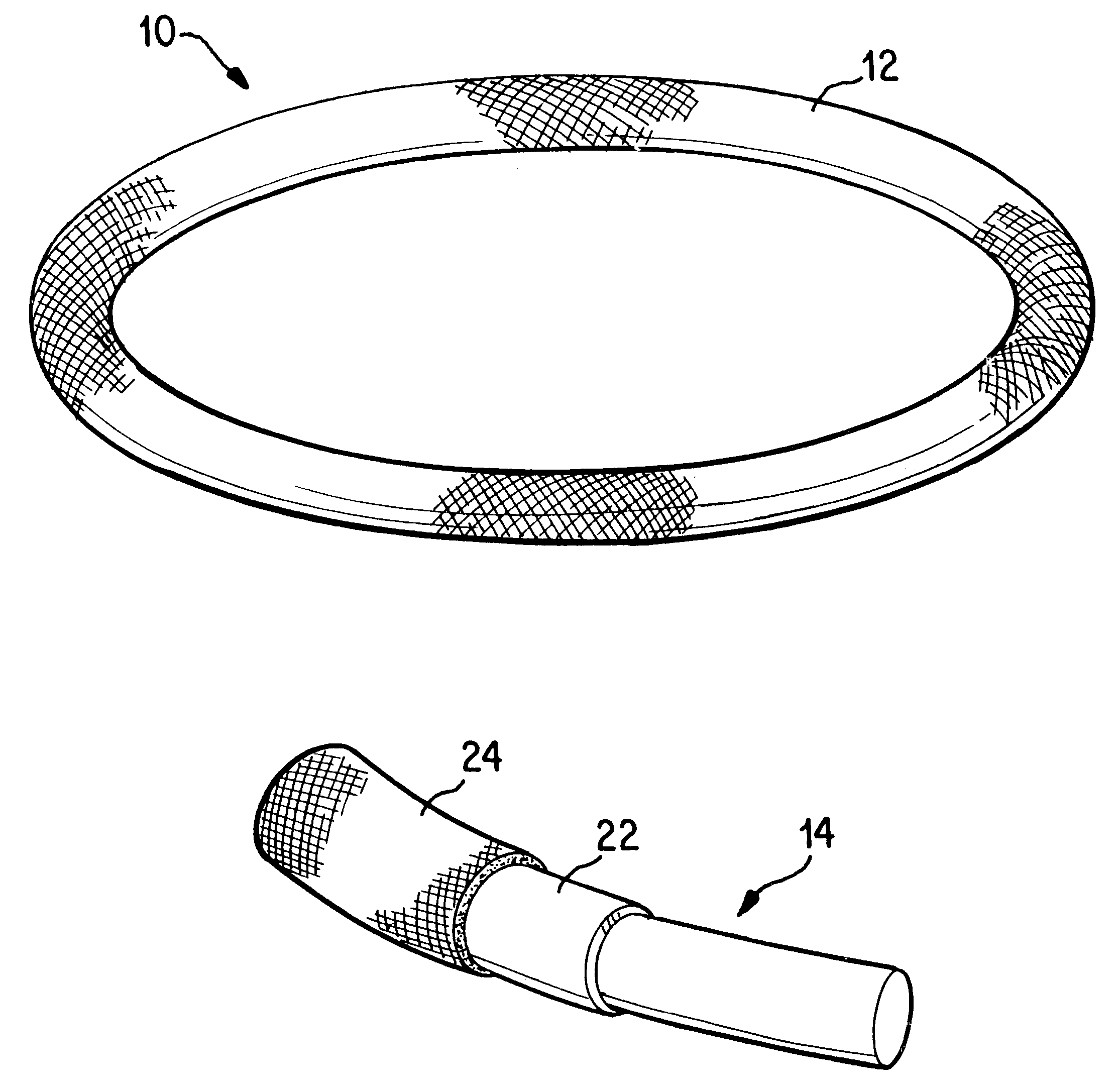
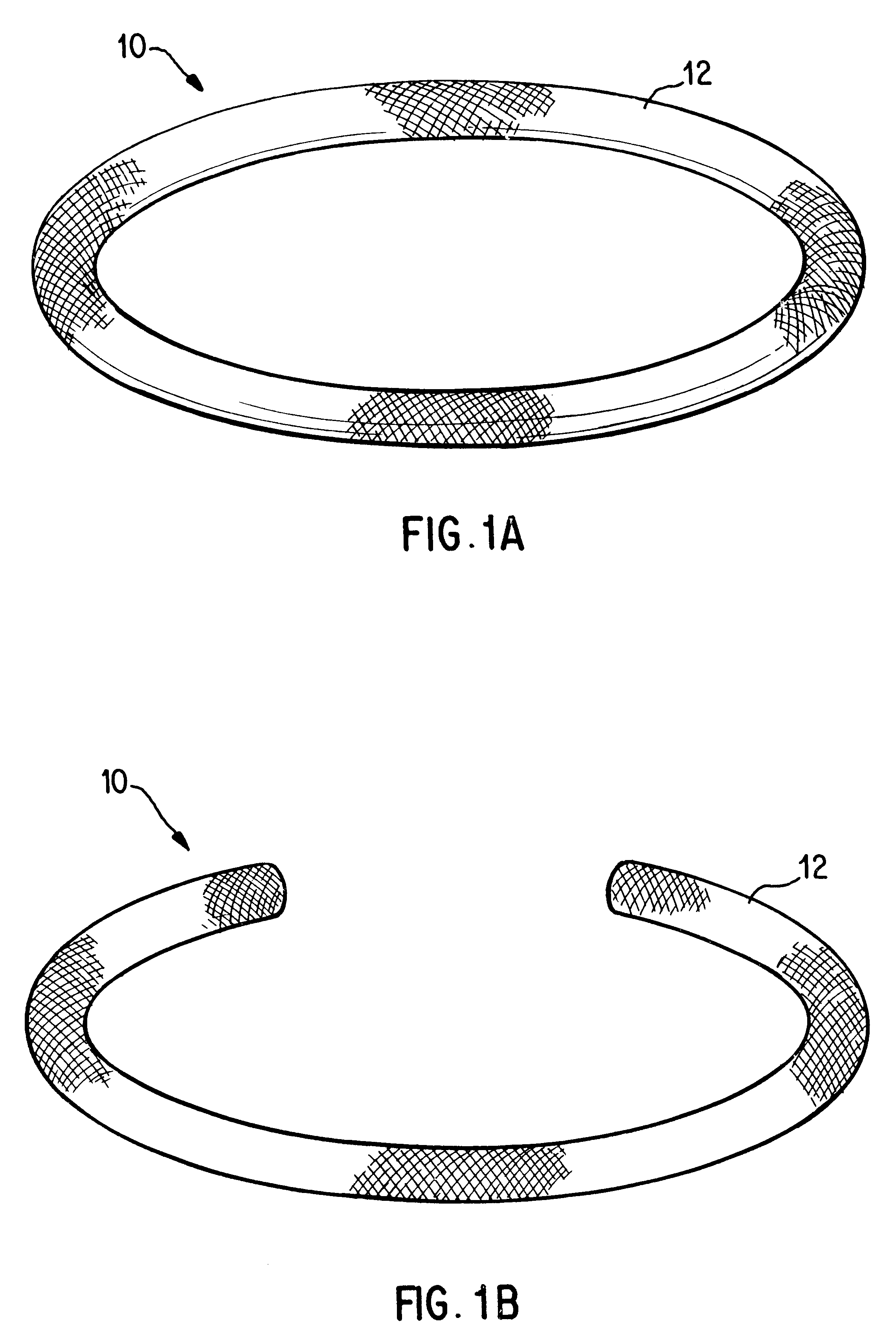
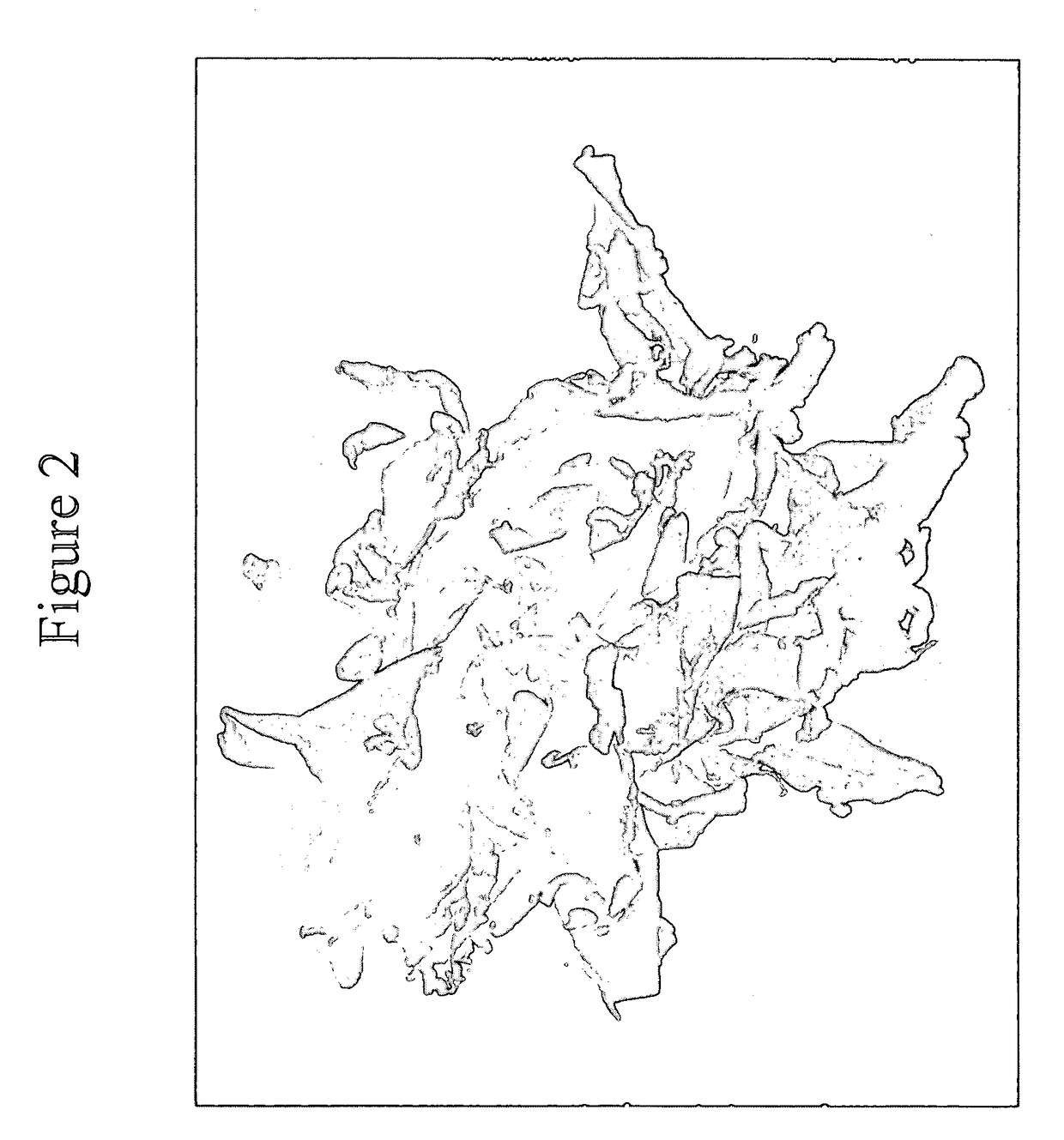
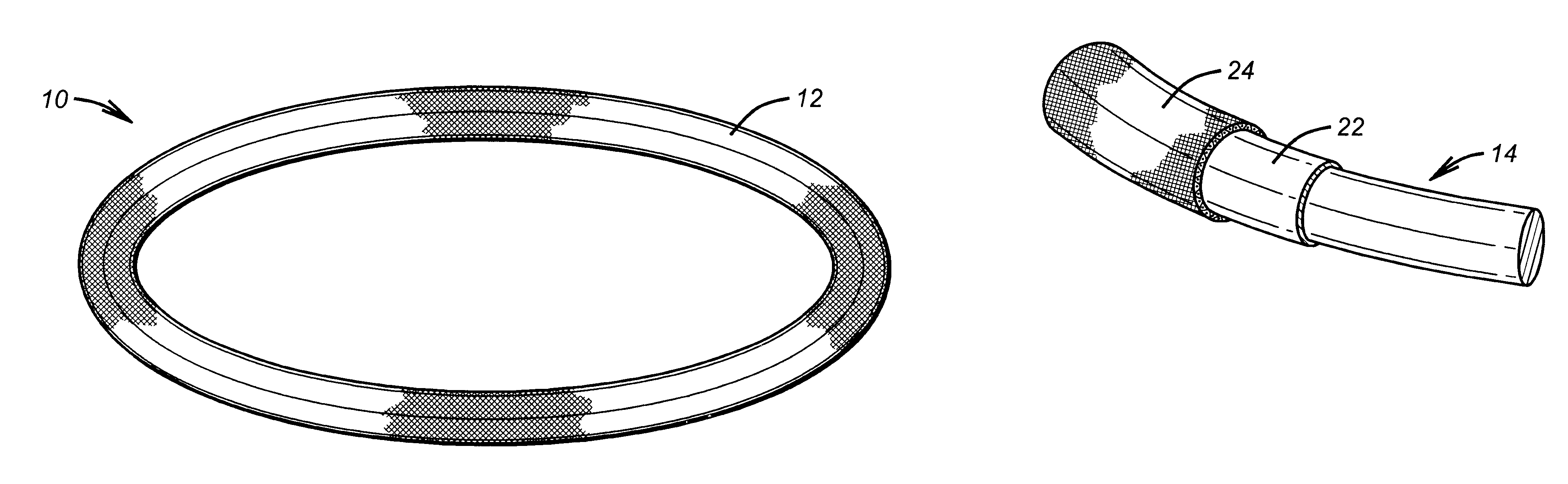
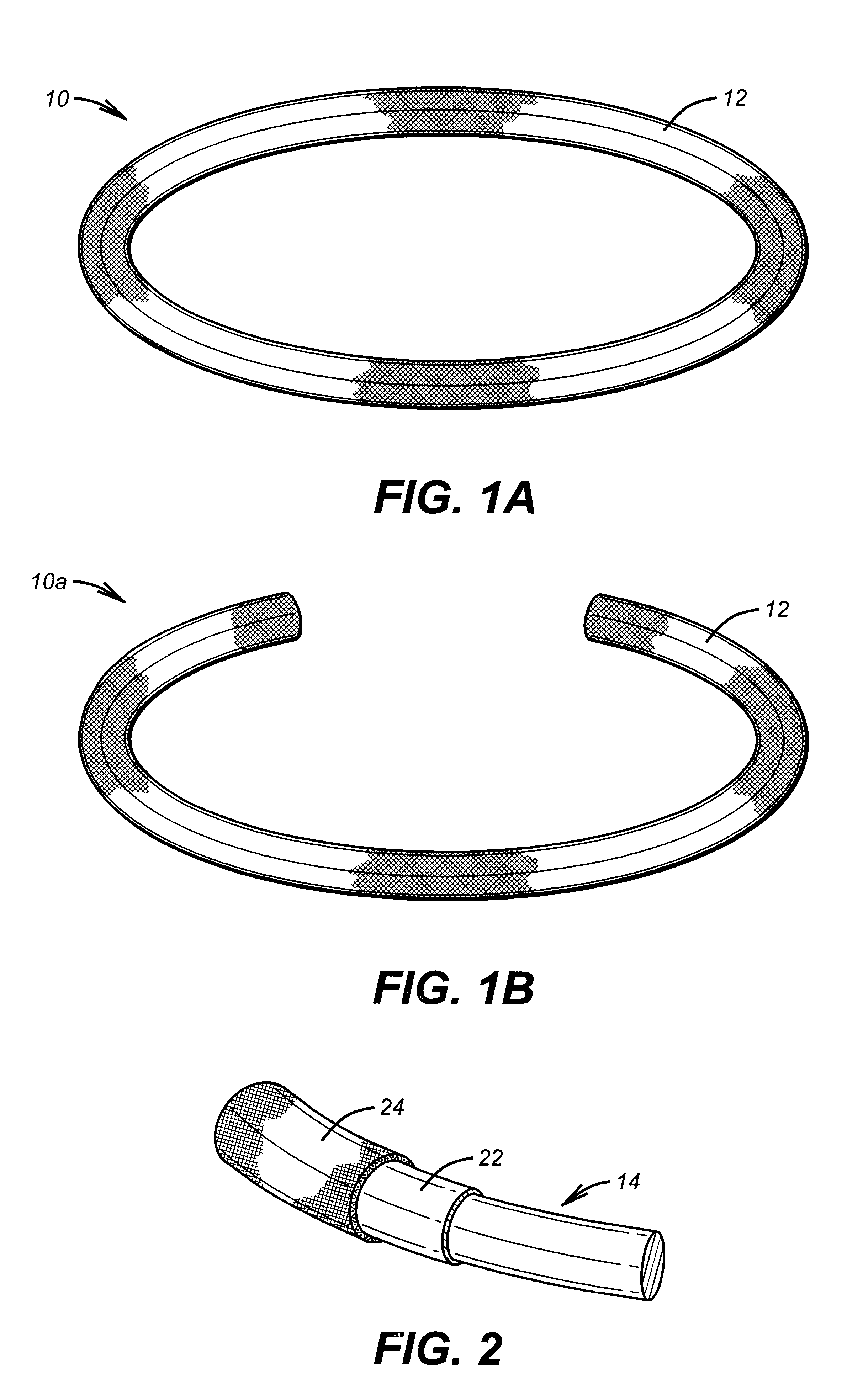
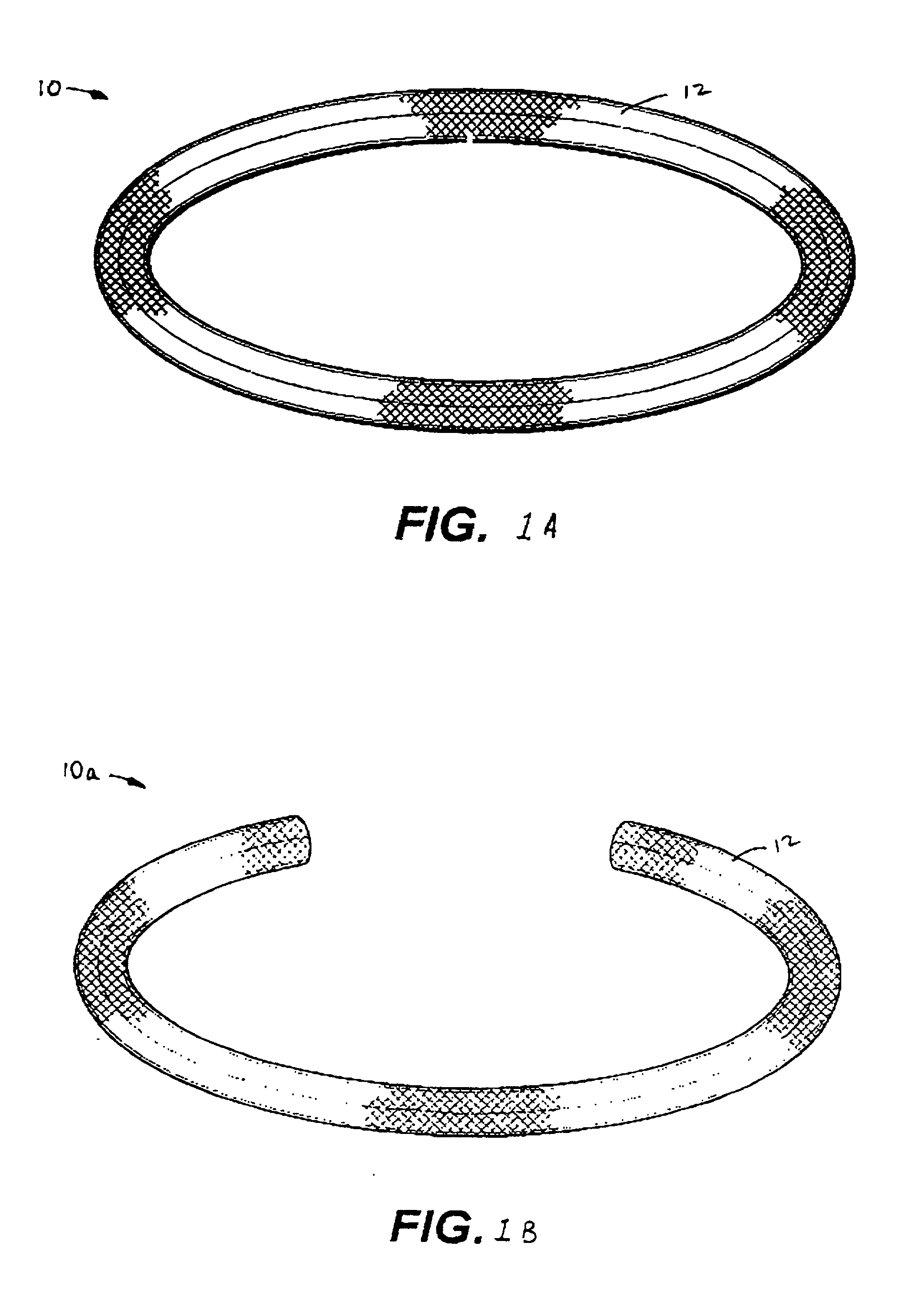
Antimicrobial annuloplasty ring having a biodegradable insert
Owner:CORCYM SRL +1
Hemostatic compositions and devices
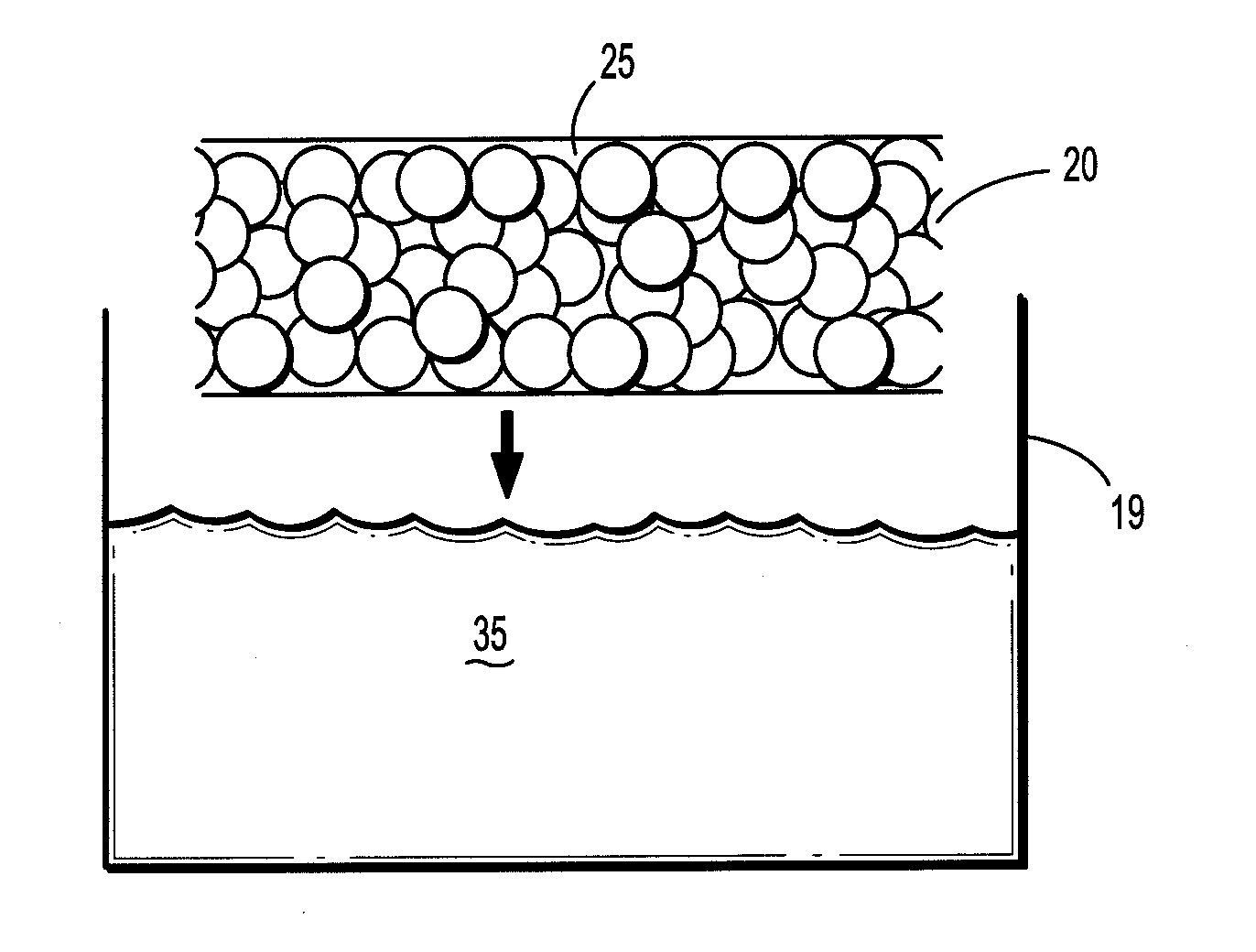
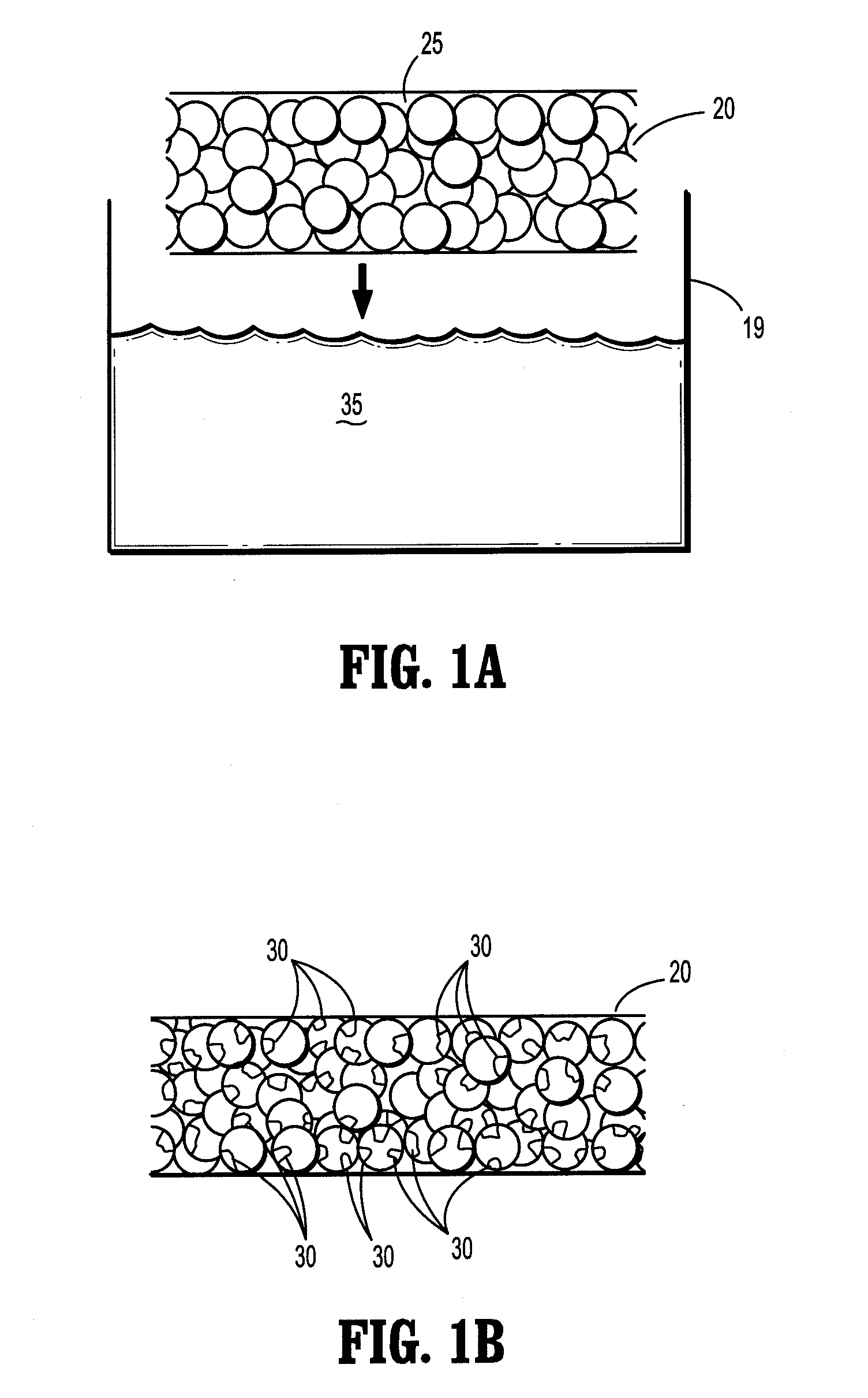
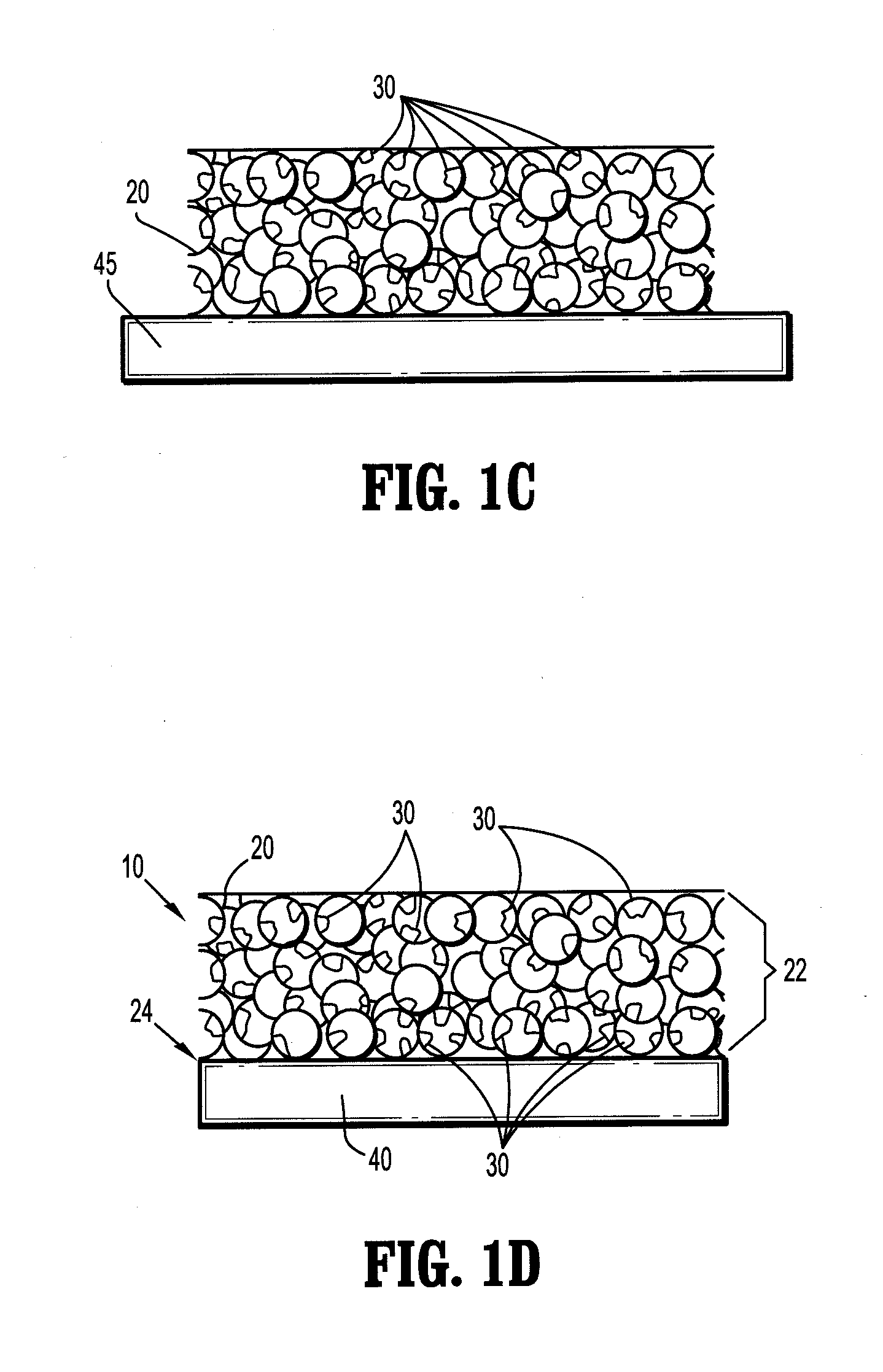
The present inventions includes a plurality of packed particles that contain interstitial pores, where the interstitial pores have a pore volume and a median pore diameter effective to provide improved absorption of physiological fluids or an aqueous media when placed in contact therewith, compared to a plurality of unpacked particles of the same material, where the particles are made of a biocompatible material and hemostatic agents and have an average diameter suitable for use in providing hemostasis to a site of a body of a mammal requiring hemostasis, hemostatic compositions containing such plurality of packed particles, methods of making such particles and compositions and medical devices suitable for delivering and containing the hemostatic plurality of particles and / or composition to a site of a body.
Owner:ETHICON INC
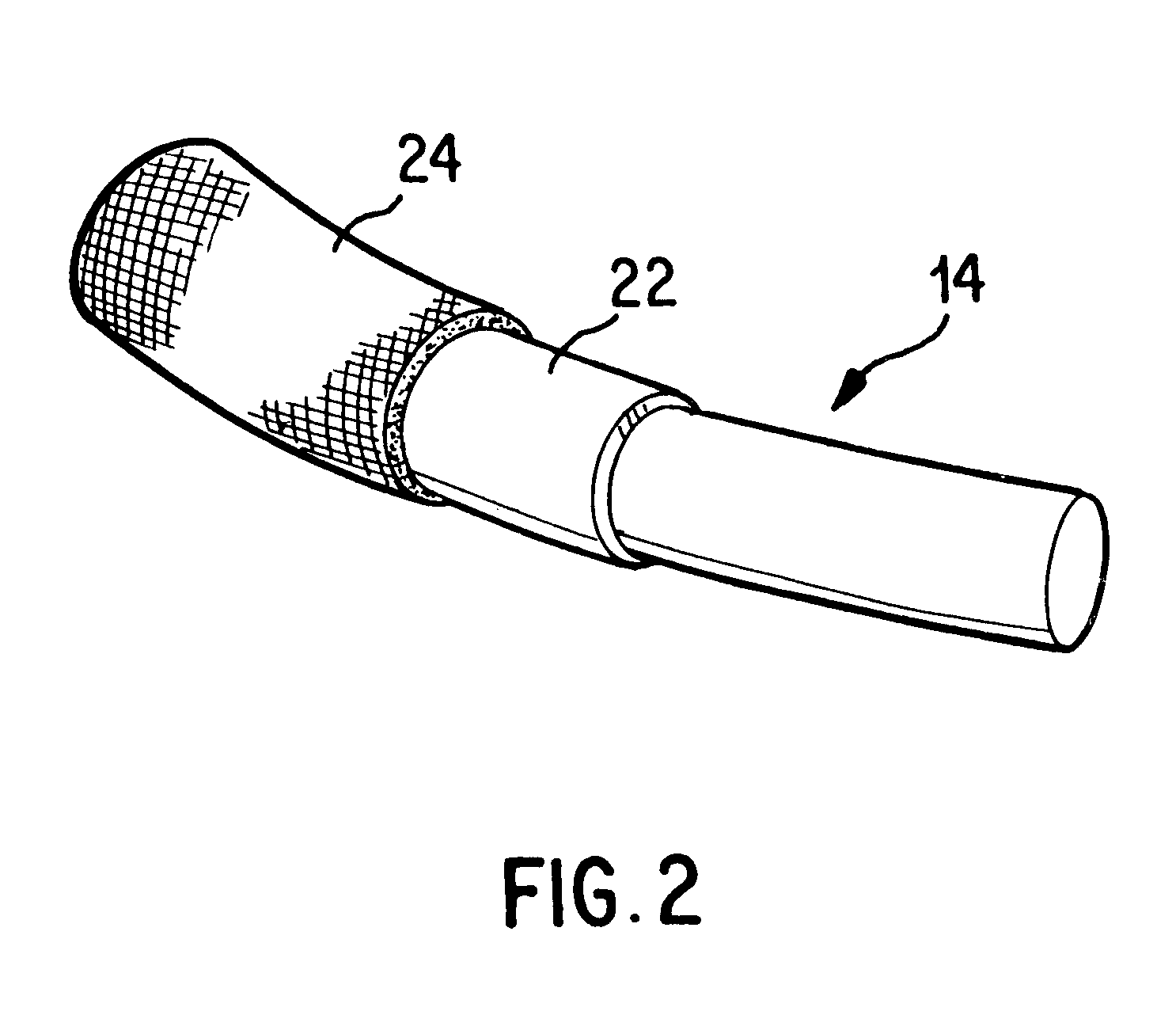
Antithrombogenic annuloplasty ring having a biodegradable insert
This invention provides an antithrombogenic annuloplasty rings, and methods for making the same, wherein the annuloplasty rings have a desired degree of initial rigidity to facilitate ease of handling during implantation but which becomes flexible some time after implantation. The annuloplasty ring contains a relatively rigid insert enclosed by a fabric sheath, the insert being at least partly comprised of a biodegradable material. Following surgical implantation of the annuloplasty ring, the rigid insert component of the ring, upon exposure to blood and / or other physiological fluids, undergoes a controlled biodegradation which decreases its rigidity, thereby increasing the flexibility of the implanted annuloplasty ring. Furthermore, at least some portion of the annuloplasty ring has incorporated into or onto its structure one or more antithrombogenic agents or materials in a manner which reduces the likelihood of thrombosis following implantation.
Owner:SULZER CARBOMEDICS +1
Floating disk for separating blood components
ActiveUS20110036786A1Minimize the differenceQuantity minimizationWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationCentrifugal force sediment separationBlood componentPhysiological fluid
A floating separating element for use in centrifugal separation of components of a physiological fluid comprises a positioning part and a separating part, where the positioning part is designed to automatically assume a position in a supernatant and a separating part is positioned at a desired location with respect to the interface between the supernatant and heavier components. In preferred embodiments the physiological fluids are blood or bone marrow aspirate, and the heavier components comprise red blood cells. The positioning part comprises the majority of the mass of the separating element and is thin so that differences in the position of the separating element with respect to the interface are small compared to differences in the densities of the separated compoments, particularly the component comprising red blood cells. A method allows red blood cells to move the separating element during decanting to ensure complete decant of the supernatant.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
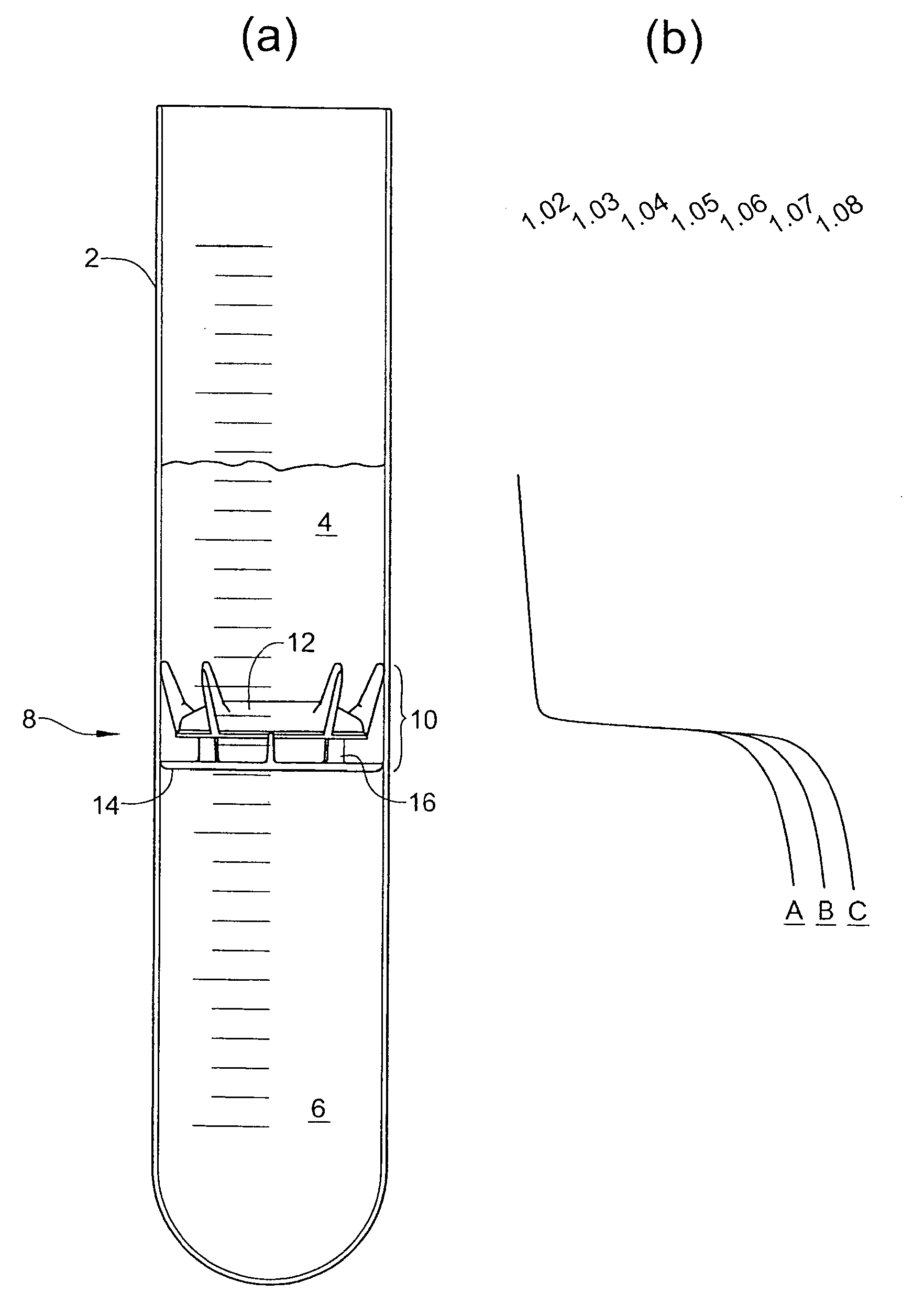
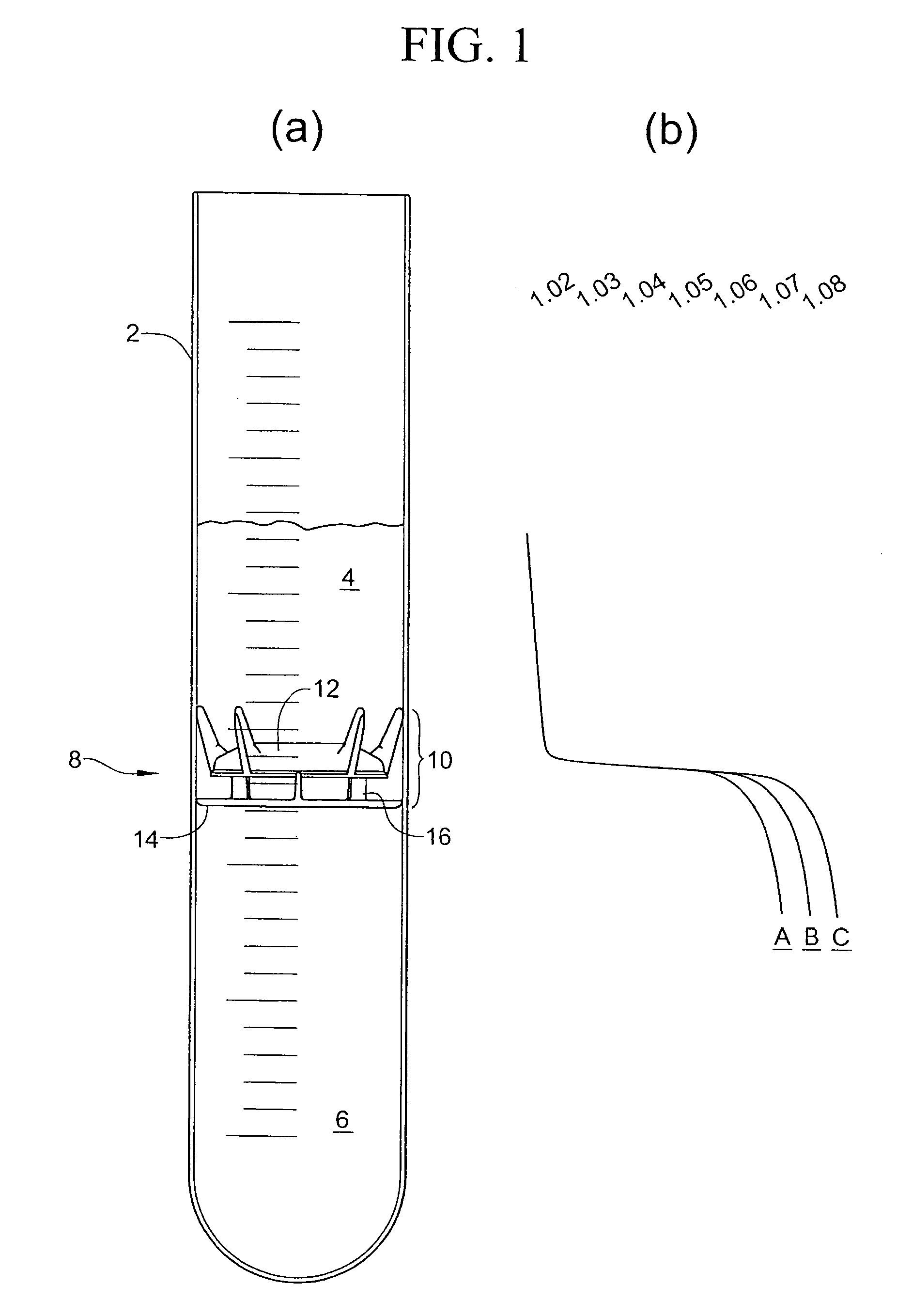
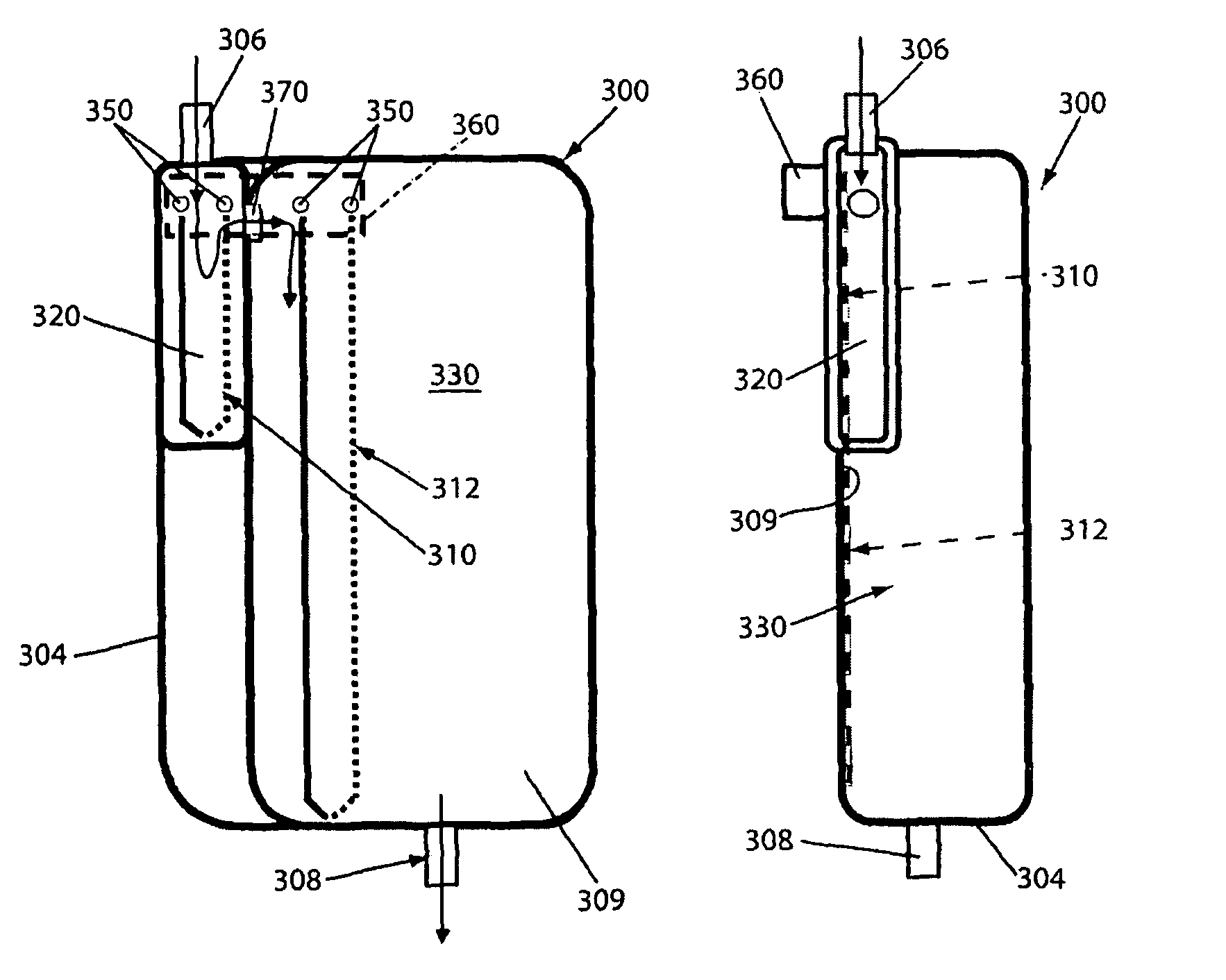
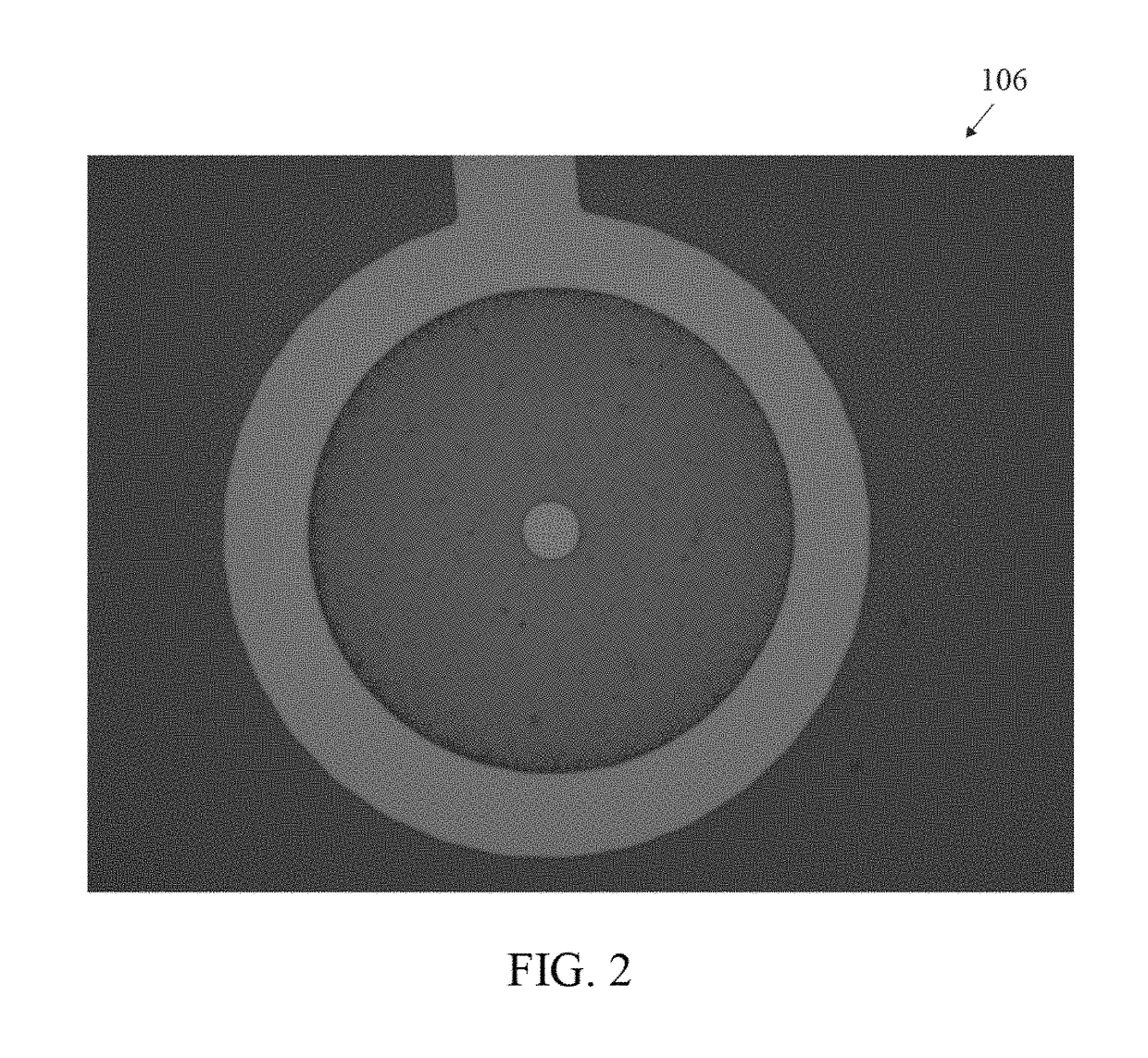
Container for physiological fluids
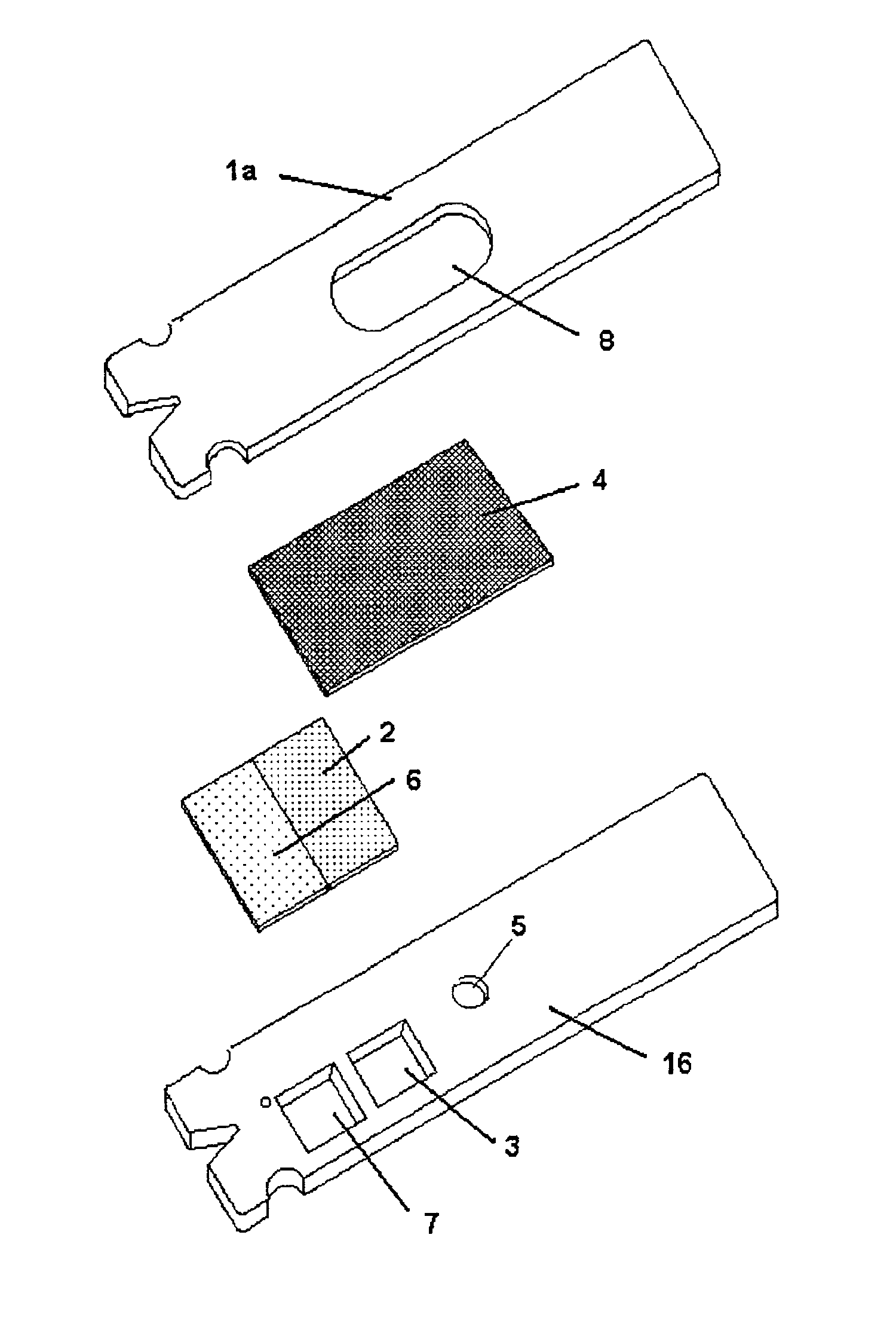
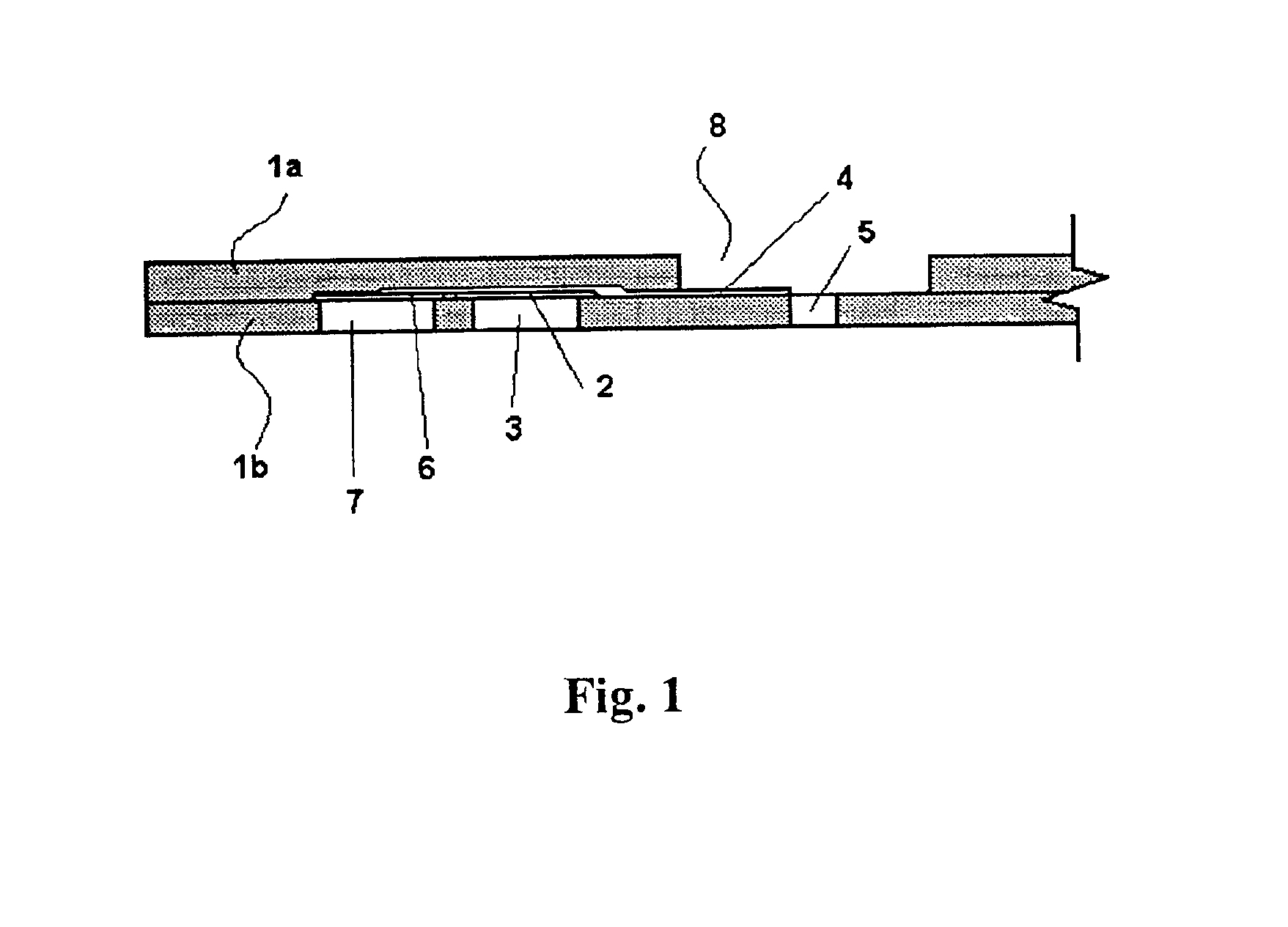
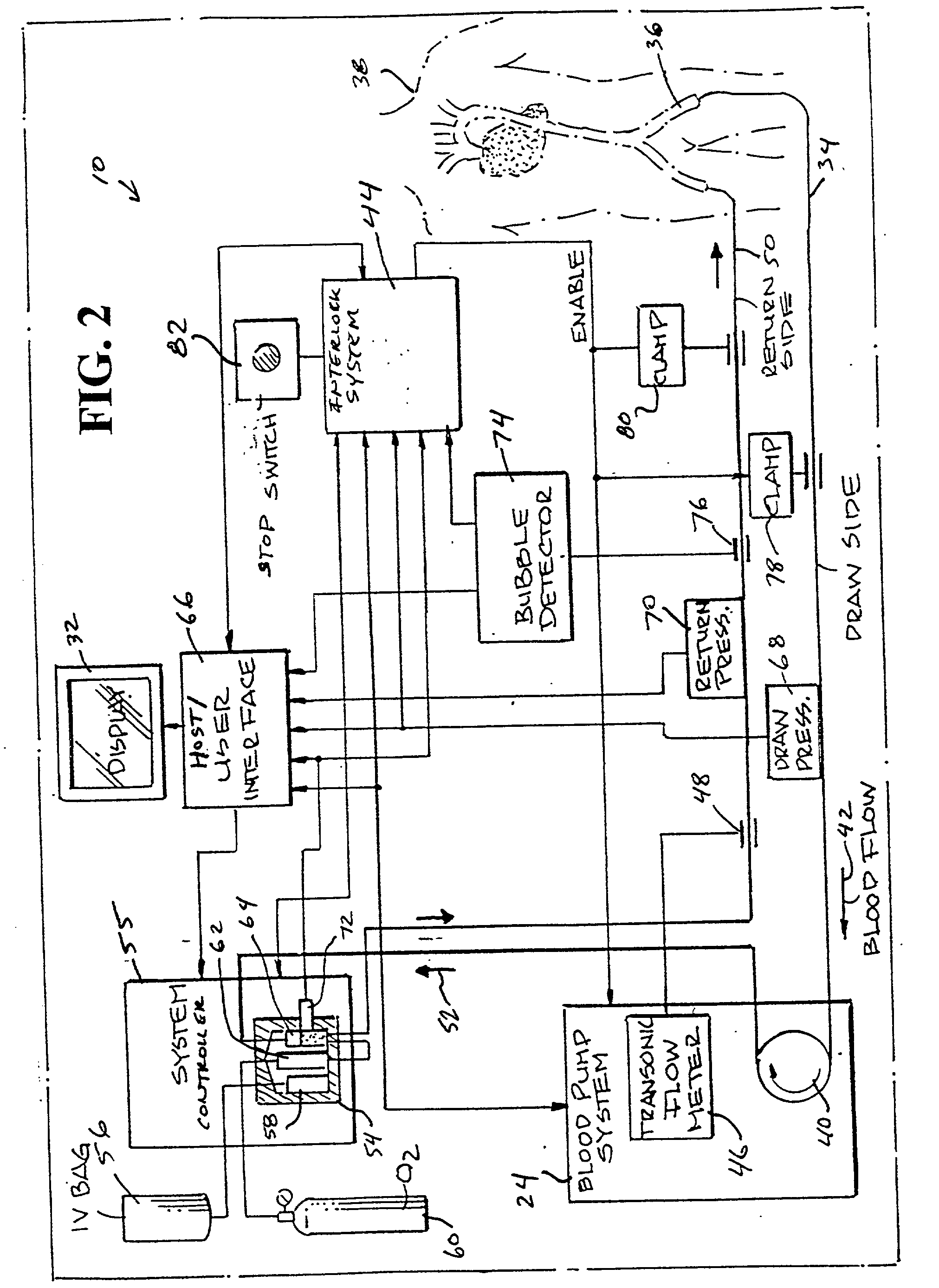
ActiveUS7739907B2Avoid flowInternal framesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsPhysiological fluidEngineering
A container includes a chamber for containing fluid. At least one sensor is disposed within the chamber for sensing a property of fluid in the container. A unit that receives a signal from the sensor communicates with a device that displays the property of the fluid in the container. The container may include first and second chambers. A first sensor is disposed within the first chamber. The first sensor is in contact with fluid in the first chamber. The first sensor senses a volume of fluid in the first chamber. A second sensor is disposed within the second chamber. The second sensor is in contact with fluid in the second chamber. The second sensor senses a volume of fluid in the second chamber. A diverter may direct fluid from an inlet to a bottom portion of the chamber and prevents the fluid from contacting the sensor. A releasable device may prevent fluid from flowing from the first chamber to the second chamber. The releasable device permits fluid to flow from the first chamber into the second chamber upon release of the releasable device. An element of the sensor may have a first portion with an electrical resistance per unit length greater than an electrical resistance per unit length of a second portion of the element. A shunt resistor extending between lower portions of first and second elements of the sensor may have a resistance equal to approximately 0.08 times a resistance of the sensor when the chamber is empty.
Owner:FUTURE PATH MEDICAL
High temperature resistant vitreous inorganic fiber
InactiveUS20030162019A1Non-durableImprove shrinkage resistanceInorganic fibres/flakesInorganic material artificial filamentsFiberPhysiological fluid
A low shrinkage, high temperature resistant vitreous inorganic fiber having a use temperature up to at least 1330° C., which maintains mechanical integrity after exposure to the use temperature and which is non-durable in physiological fluids, is prepared by the method of forming a melt with ingredients including greater than 71.25 weight percent silica, 0 to about 20 weight percent magnesia, and about 5 to about 28.55 weight percent of calcia, 0 to about 5 weight percent zirconia, and optionally a viscosity modifier in an amount effective to render the product fiberizable; and producing fibers from the melt.
Owner:UNIFRAX I LLC
Apparatus And Methods For Aspirating And Separating Components Of Different Densities From A Physiological Fluid Containing Cells
ActiveUS20120129676A1Increase stiffnessLow stiffnessDispersed particle separationRotary centrifugesPhysiological fluidCentrifugation
A system for separating components defining a cavity for receiving the fluid. The system further includes a rigid insert slidably disposed in the cavity, the insert including a funnel-shaped upper portion and a hole therethrough. The insert has a density such that upon centrifugation a selected component of the fluid resides within the upper portion of the insert. A bone marrow aspiration device includes an introducer needle assembly and an aspiration needle assembly. The introducer needle assembly includes an introducer cannula and a removable trocar. The aspiration needle assembly includes a flexible aspiration cannula and a flexible stylet. The length of the aspiration cannula is substantially greater than the length of the introducer cannula. The aspiration needle assembly is receivable in the introducer cannula when the trocar is removed from the introducer needle assembly. The aspiration cannula forms a channel for aspirating bone marrow when the stylet is removed.
Owner:CERVOS MEDICAL LLC
Antimicrobial annuloplasty ring having a biodegradable insert
This invention provides an antimicrobial annuloplasty rings, and methods for making the same, wherein the annuloplasty rings have a desired degree of initial rigidity to facilitate ease of handling during implantation but which becomes flexible some time after implantation. The annuloplasty ring contains a relatively rigid insert enclosed by a fabric sheath, the insert being at least partly comprised of a biodegradable material. Following surgical implantation of the annuloplasty ring, the rigid insert component of the ring, upon exposure to blood and / or other physiological fluids, undergoes a controlled biodegradation which decreases its rigidity, thereby increasing the flexibility of the implanted annuloplasty ring. Furthermore, at least some portion of the annuloplasty ring of the invention has incorporated therein one or more antimicrobial agents in a manner which reduces the likelihood of device infection following implantation.
Owner:CORCYM SRL +1
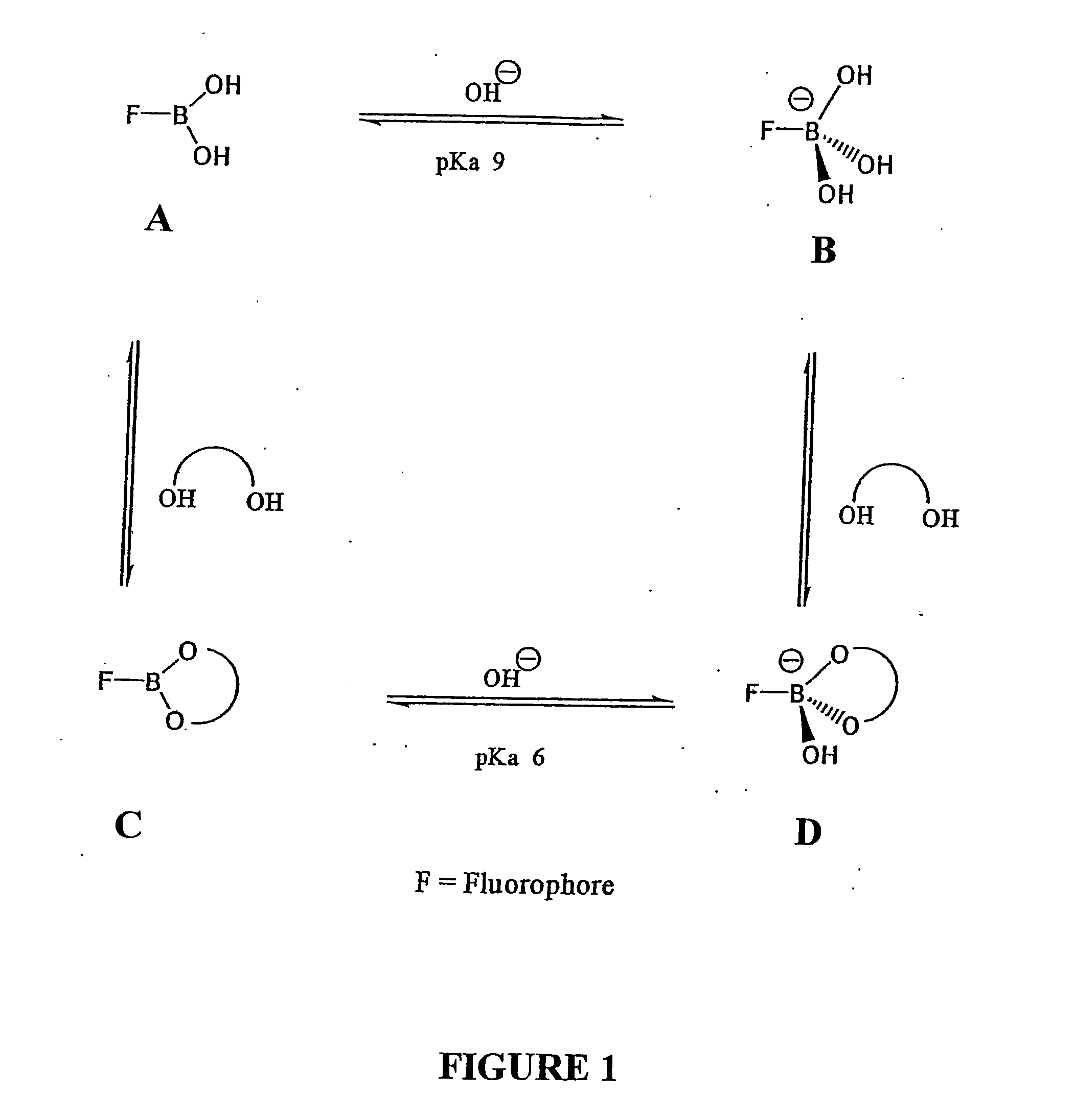
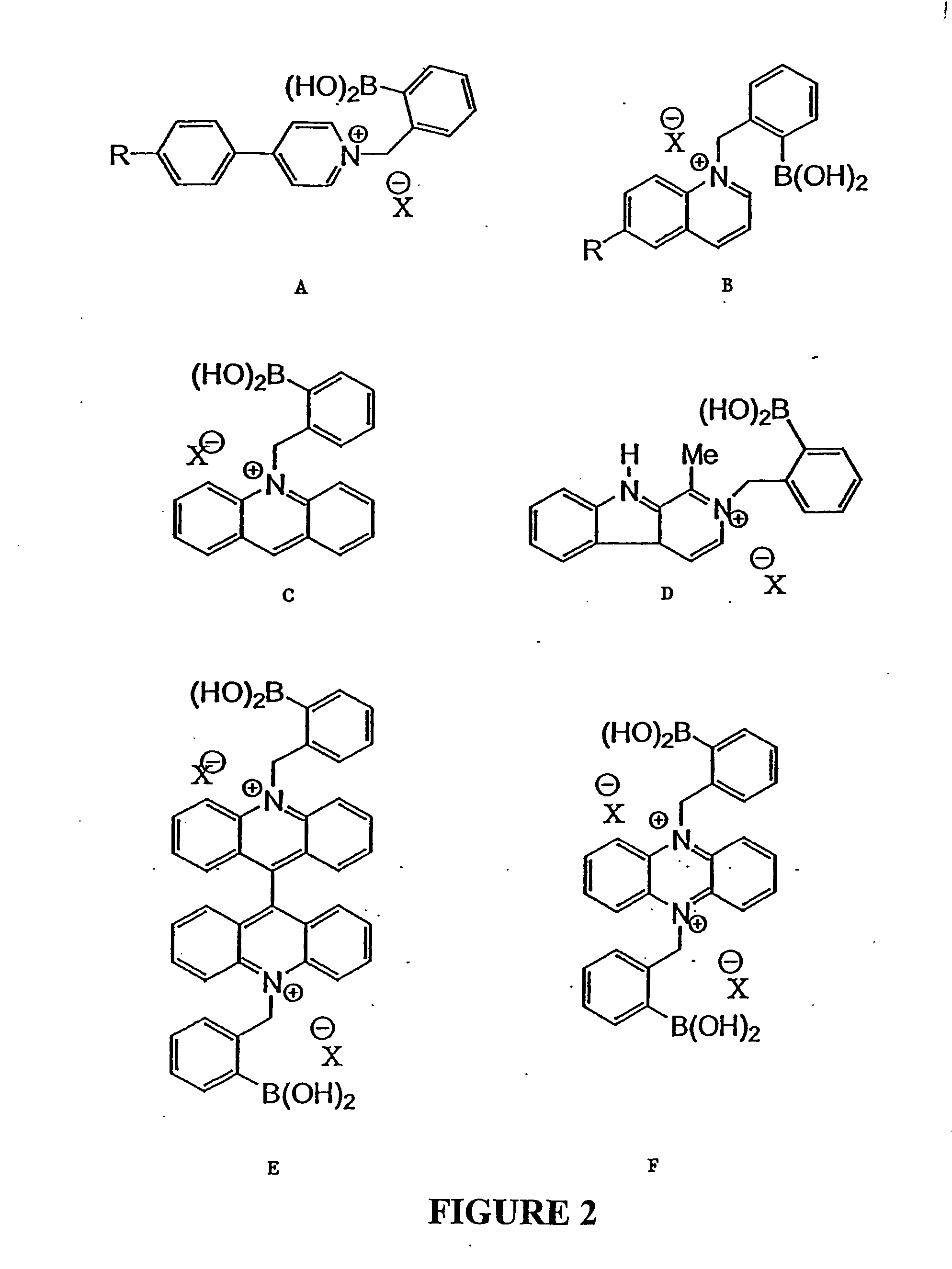
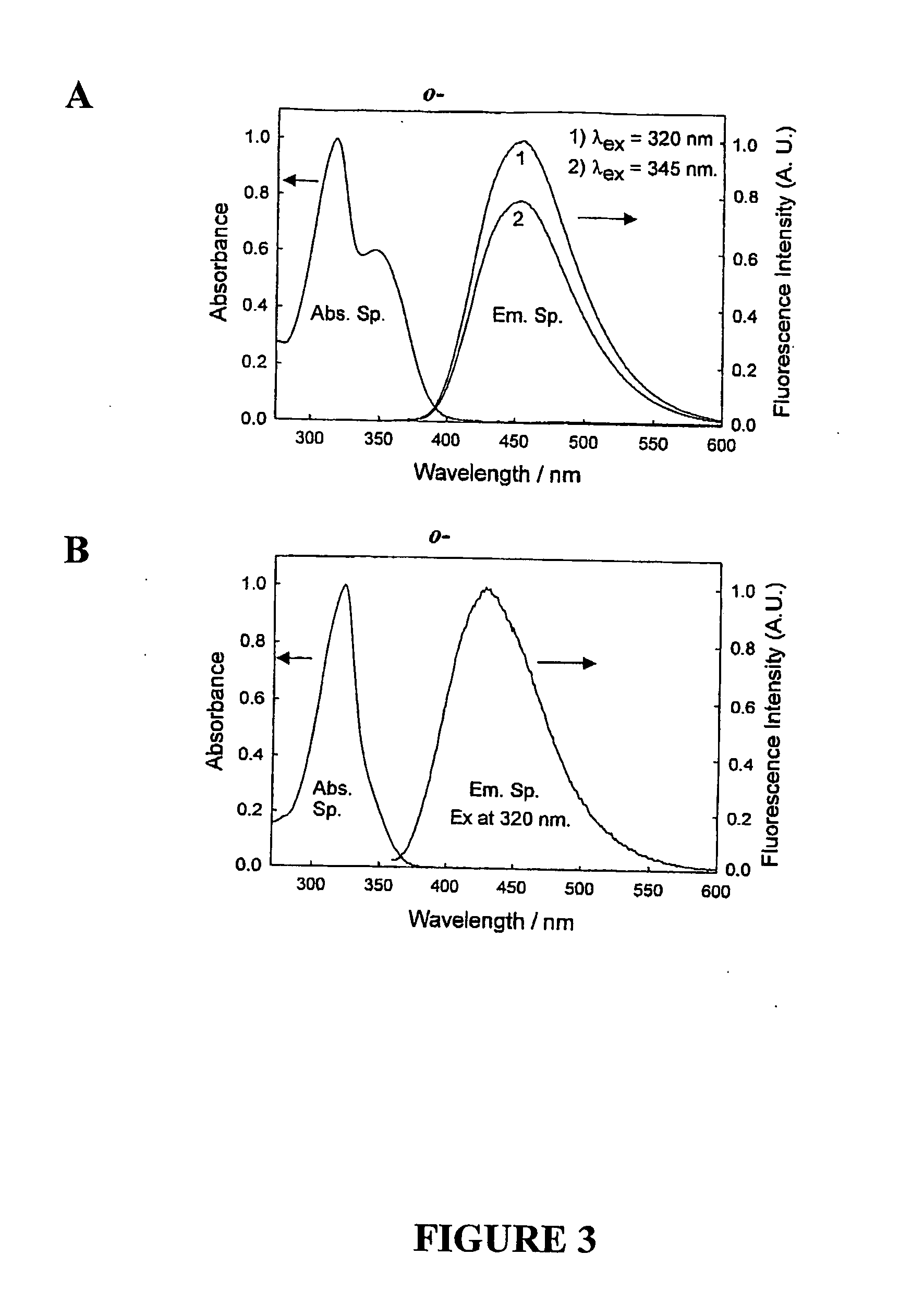
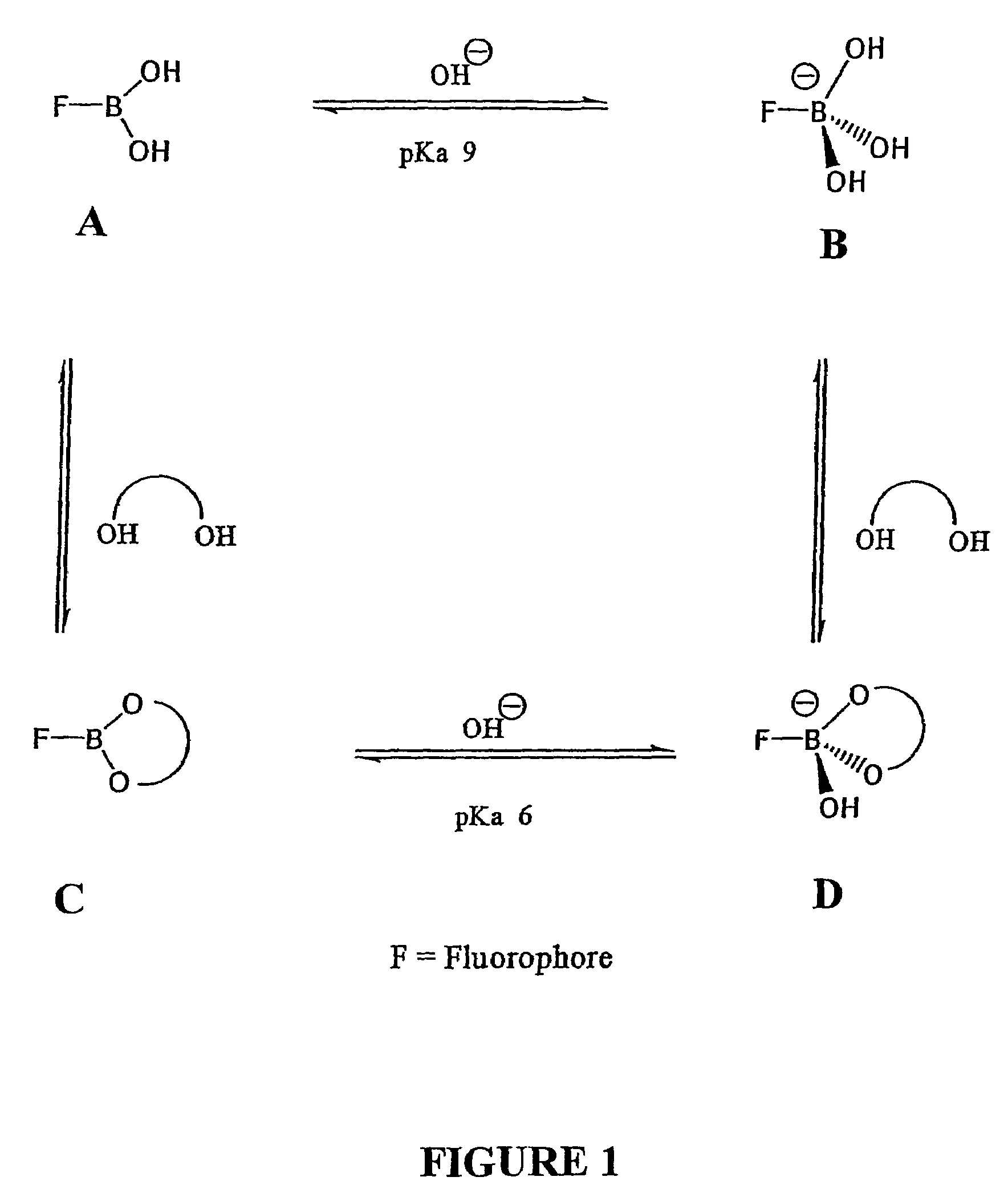
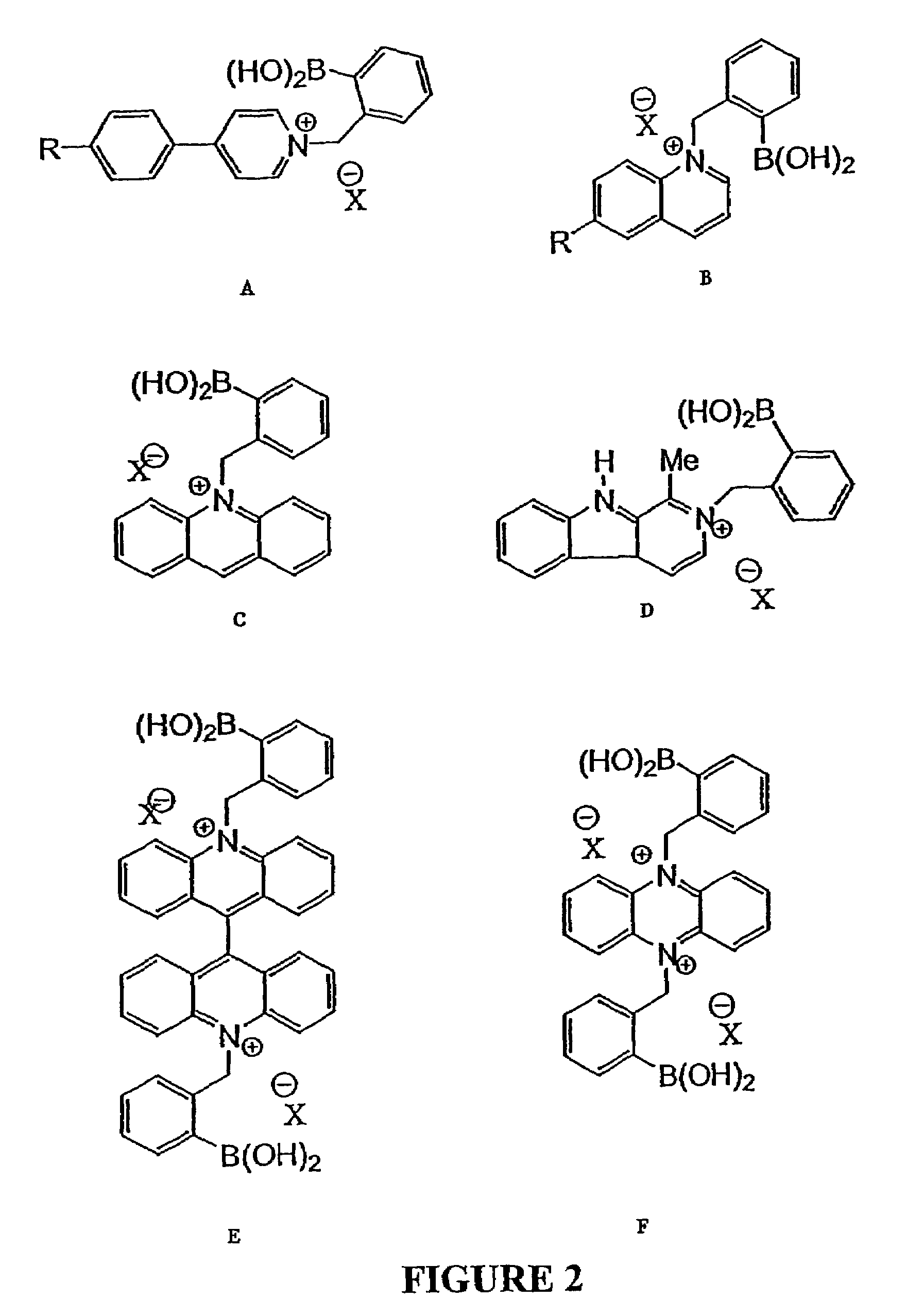
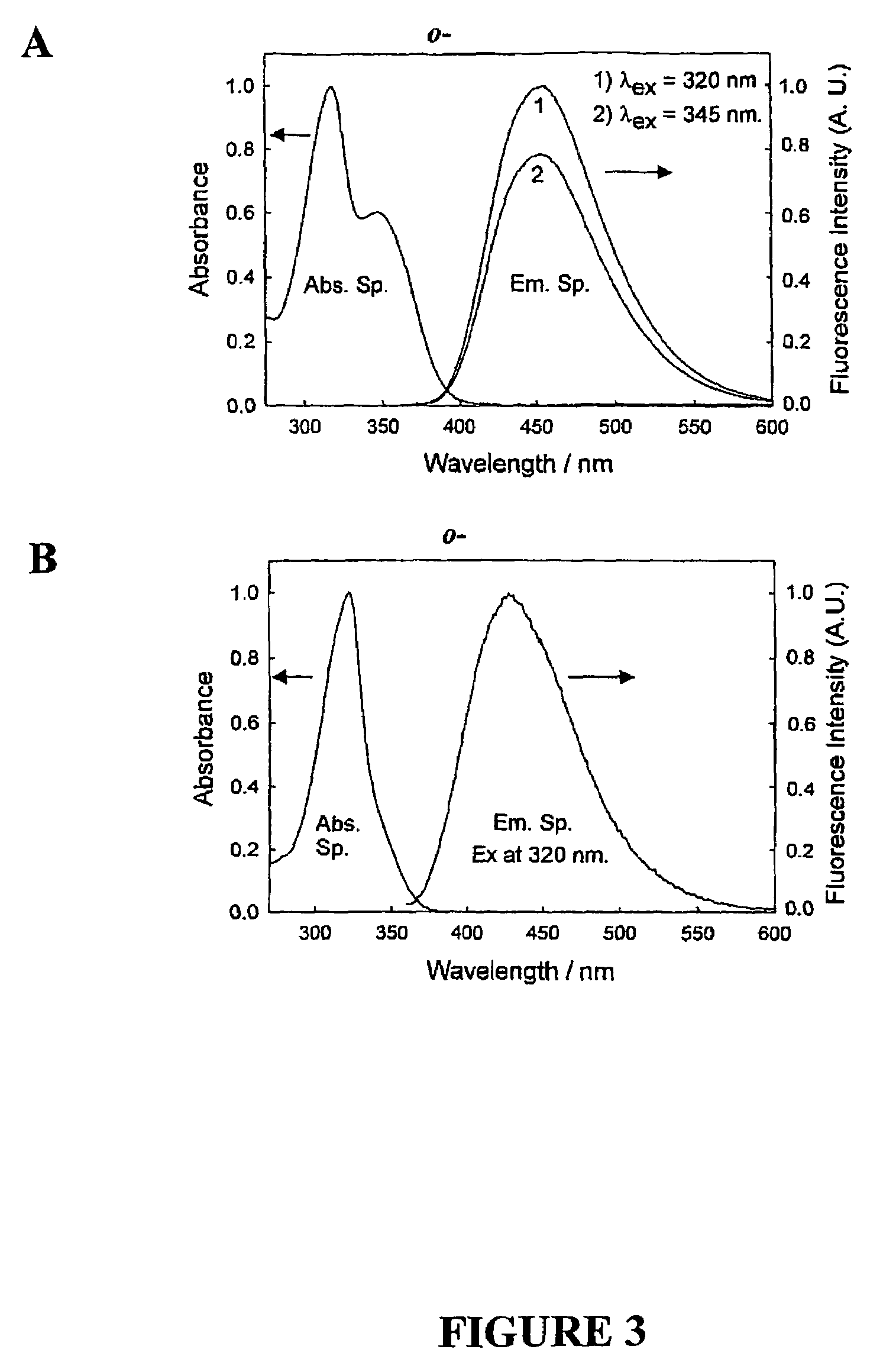
Quaternary nitrogen heterocyclic compounds for detecting aqueous monosaccharides in physiological fluids
Quaternary nitrogen heterocyclic boronic acid-containing compounds are described, which are sensitive to glucose and fructose, as well as a variety of other physiologically important analytes, such as aqueous chloride and iodide, and a method of using the compounds. Also disclosed is a contact lens doped with the quaternary nitrogen heterocyclic boronic acid-containing compound, and a method of using the doped contact lens to measure the concentration of analyte in tears under physiological conditions.
Owner:GEDDES CHRIS DR
Quaternary nitrogen heterocyclic compounds for detecting aqueous monosaccharides in physiological fluids
Quaternary nitrogen heterocyclic boronic acid-containing compounds are described, which are sensitive to glucose and fructose, as well as a variety of other physiologically important analytes, such as aqueous chloride and iodide, and a method of using the compounds. Also disclosed is a contact lens doped with the quaternary nitrogen heterocyclic boronic acid-containing compound, and a method of using the doped contact lens to measure the concentration of analyte in tears under physiological conditions.
Owner:GEDDES CHRIS DR
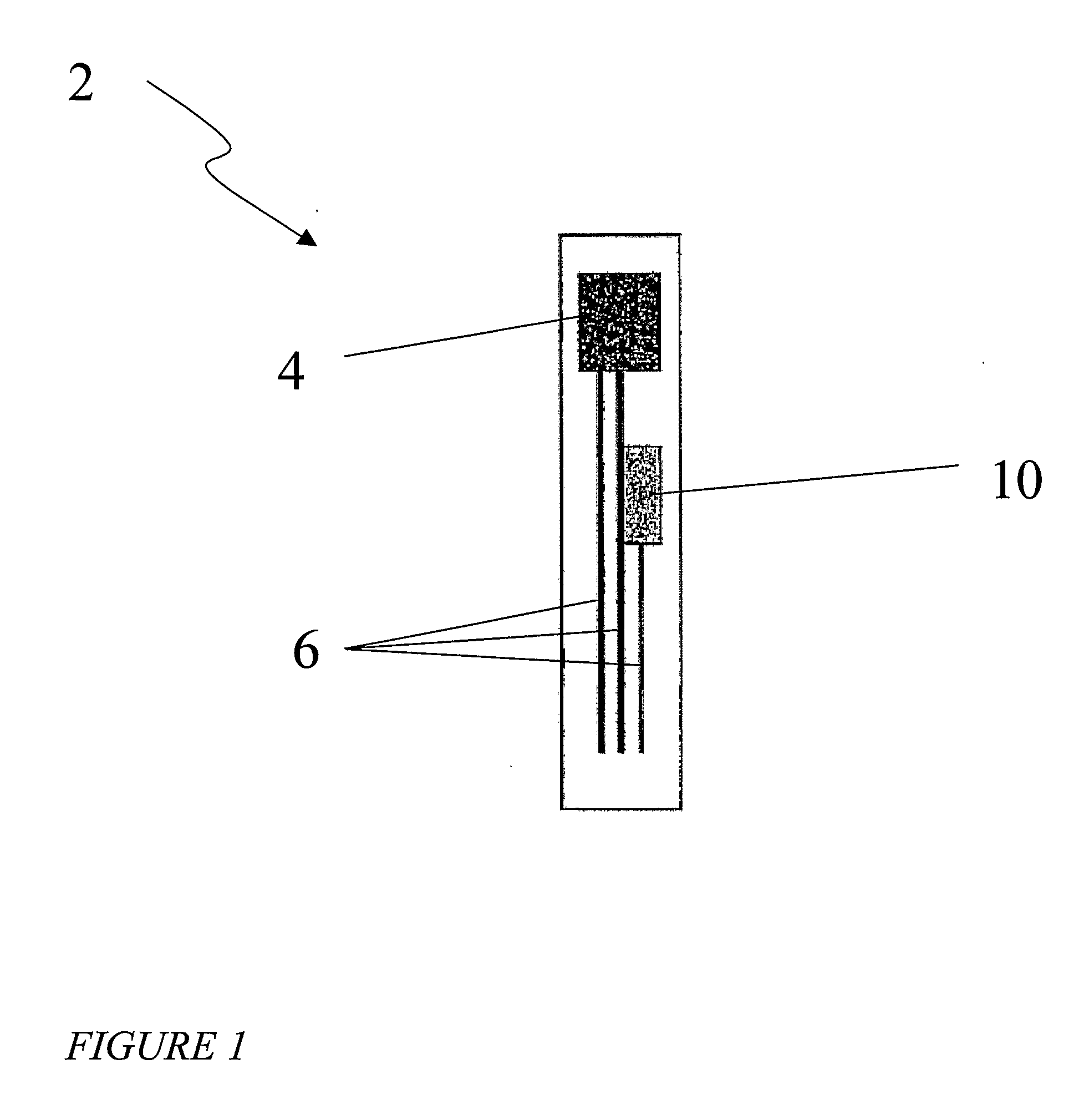
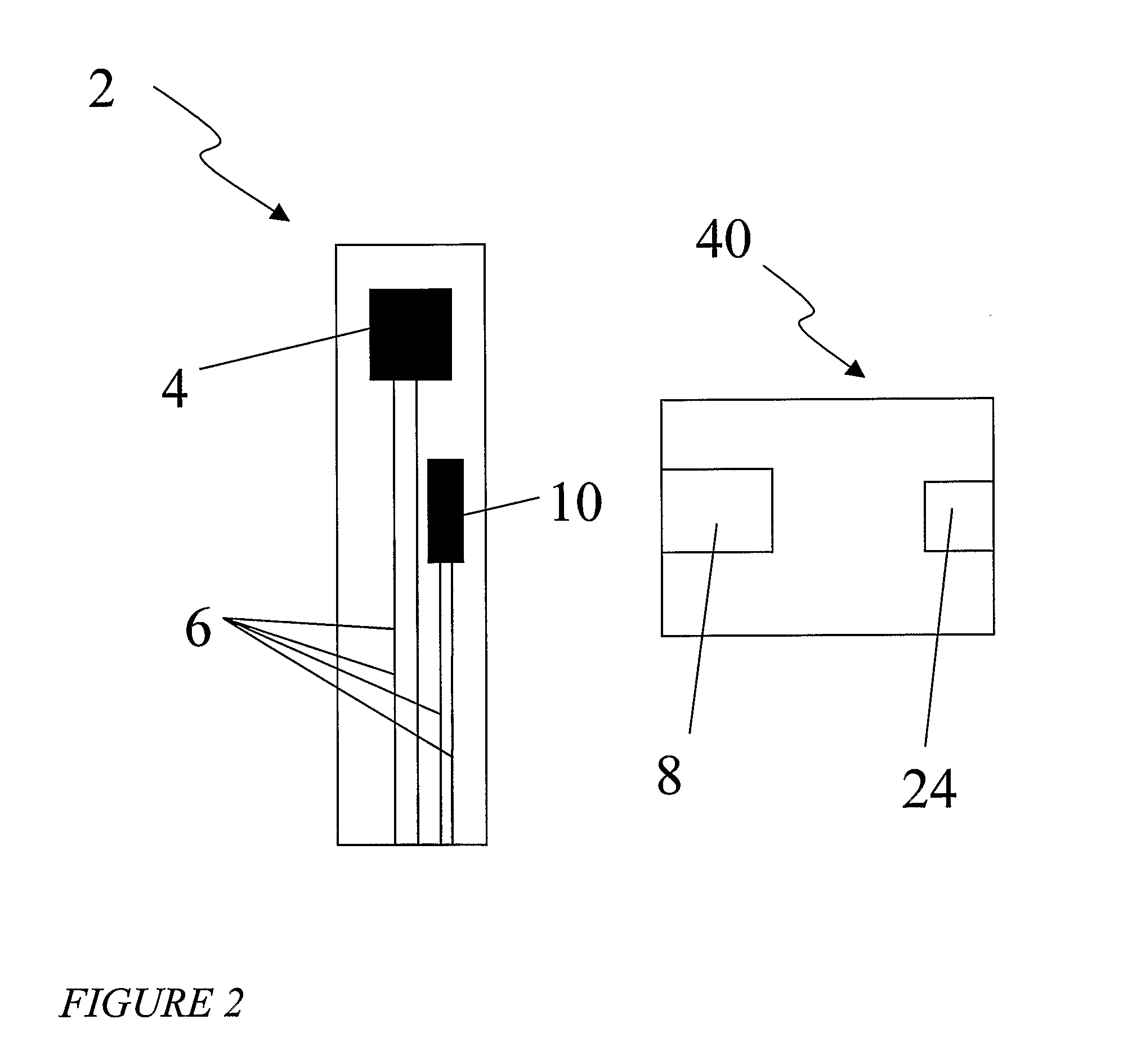
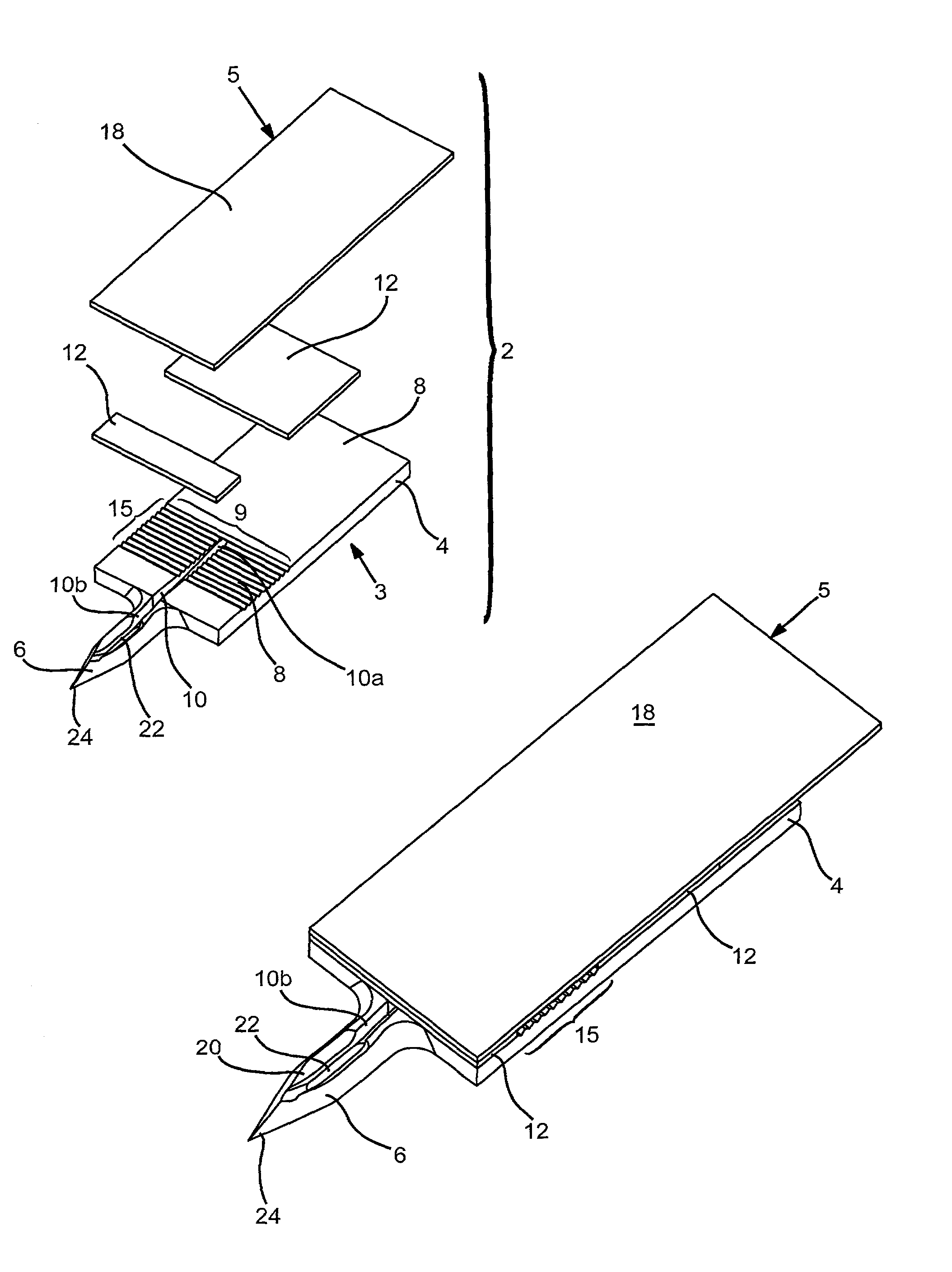
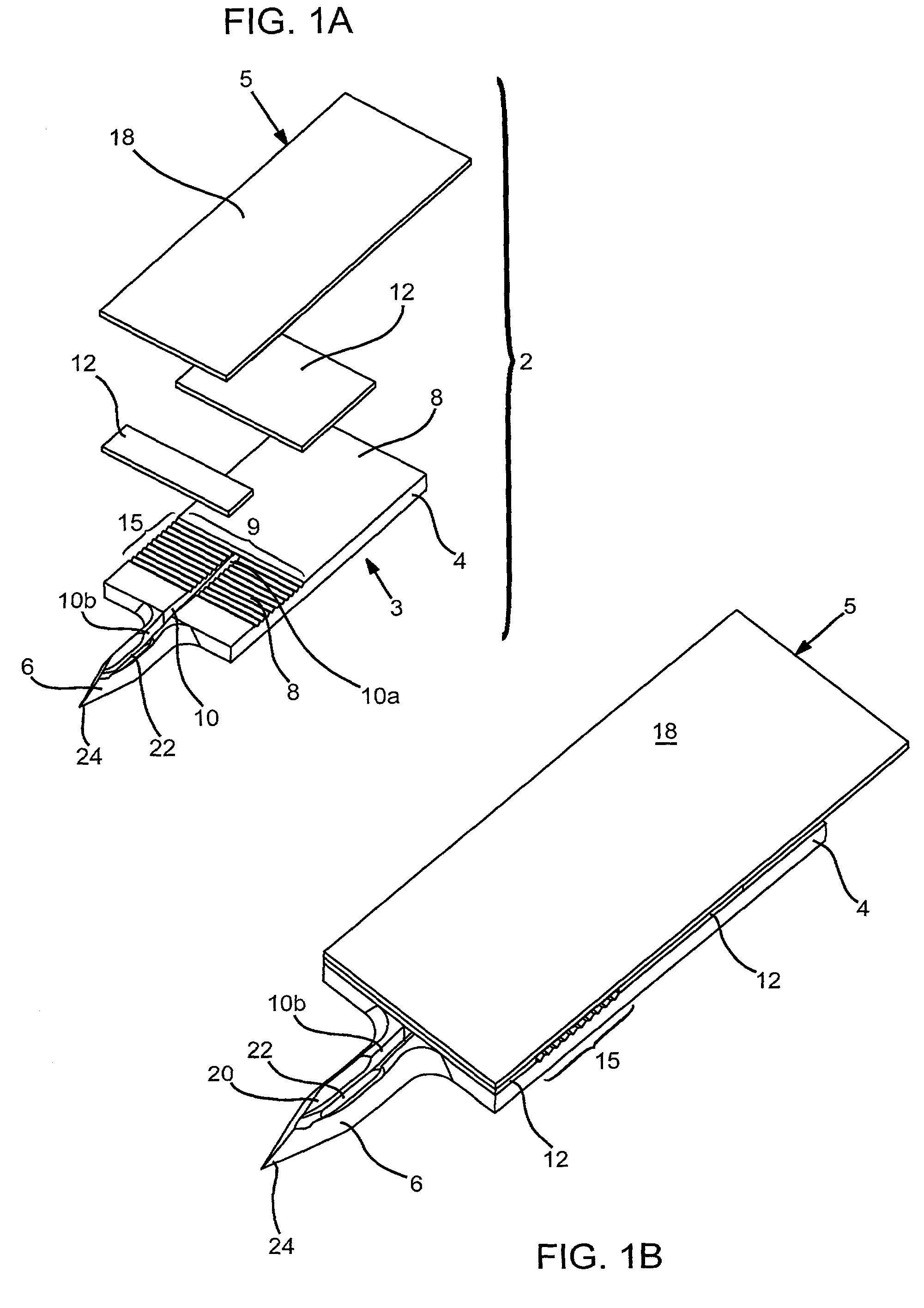
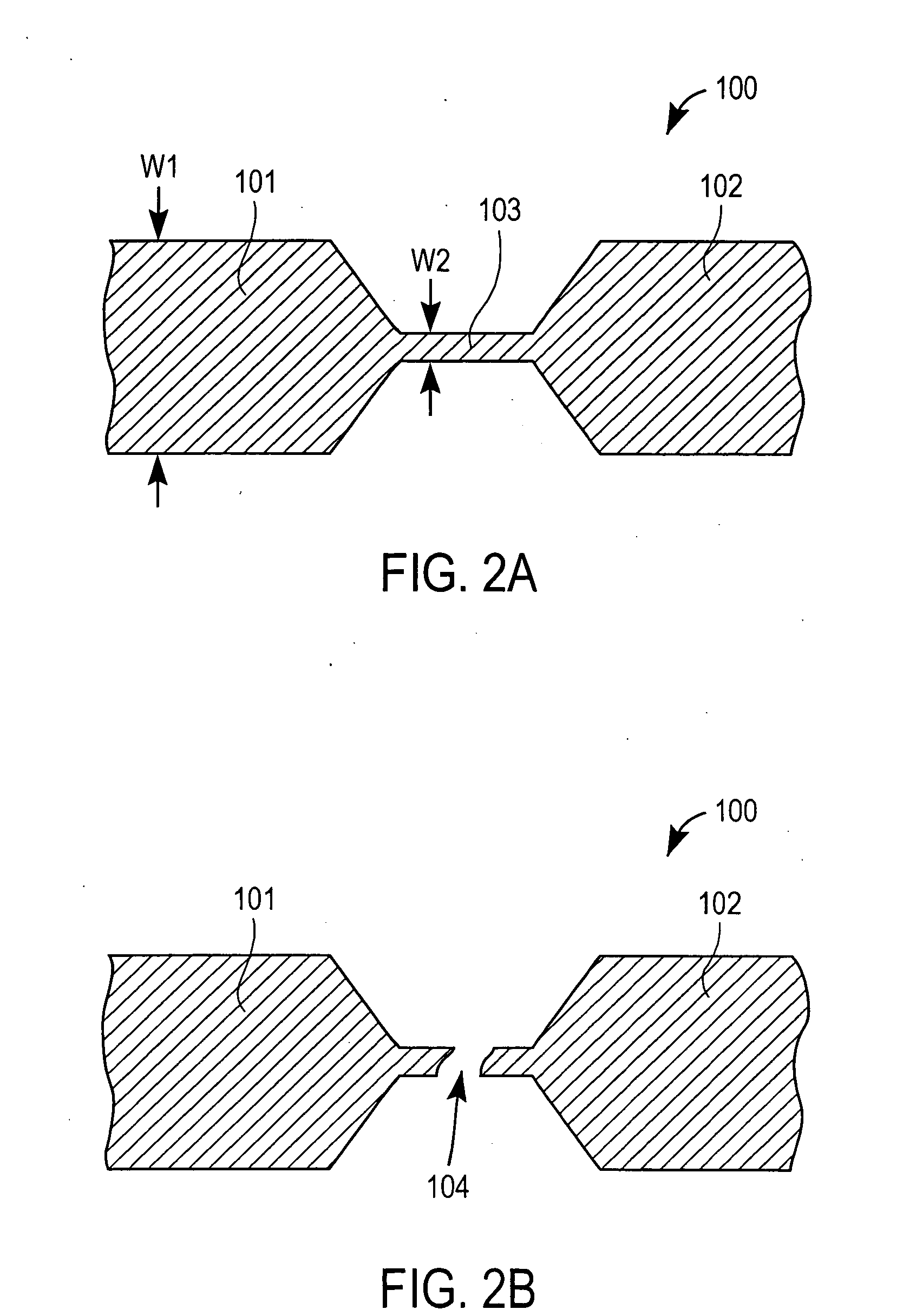
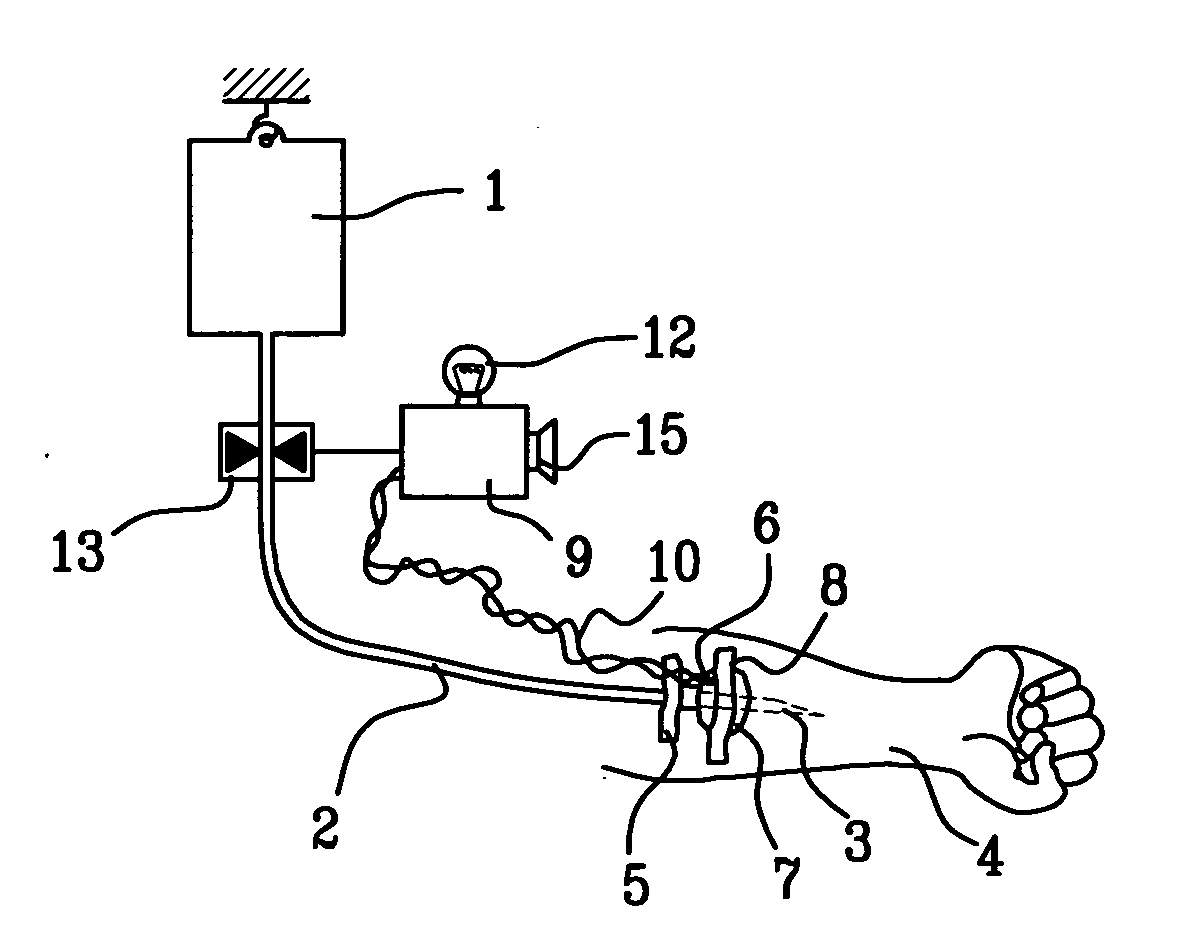
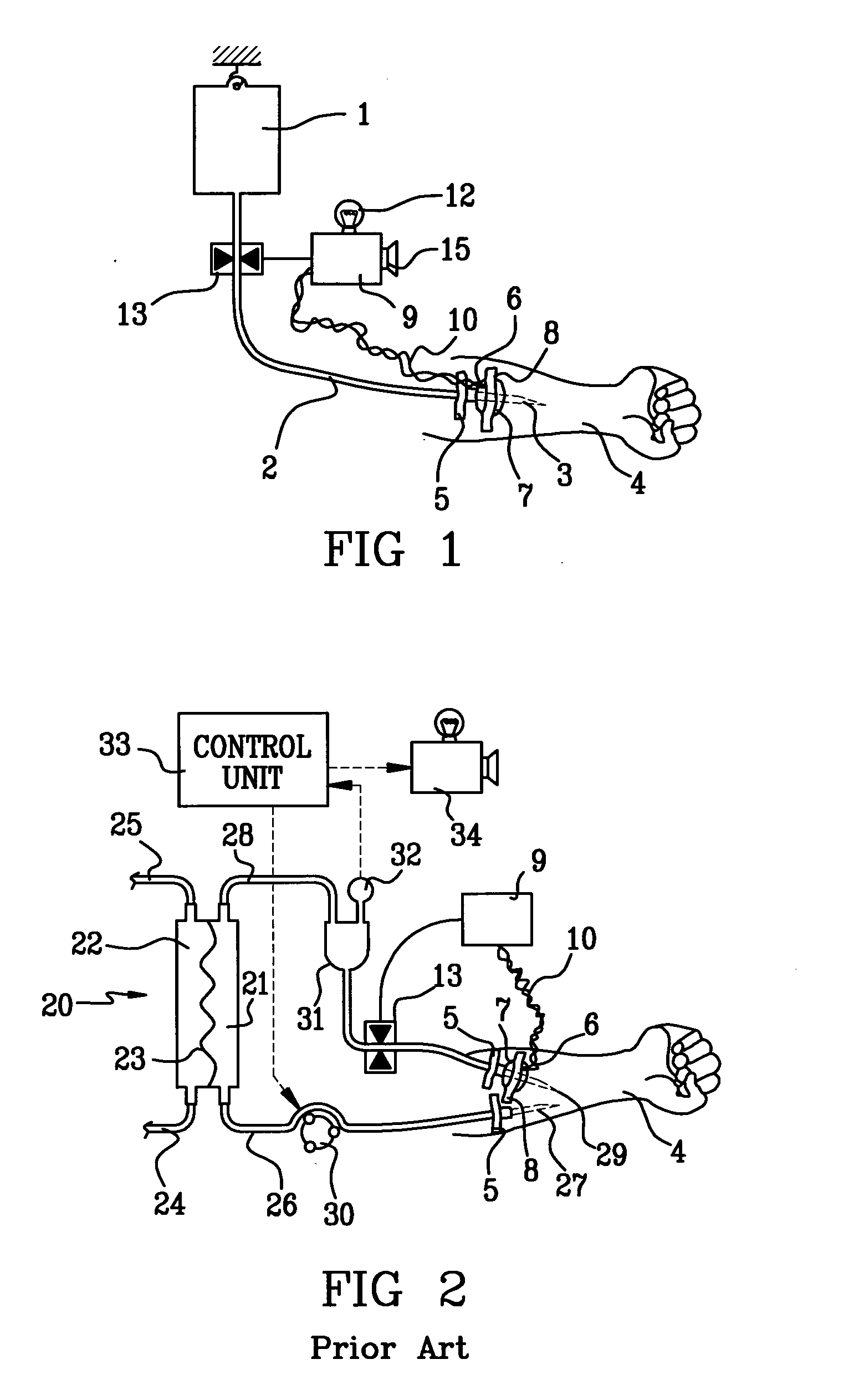
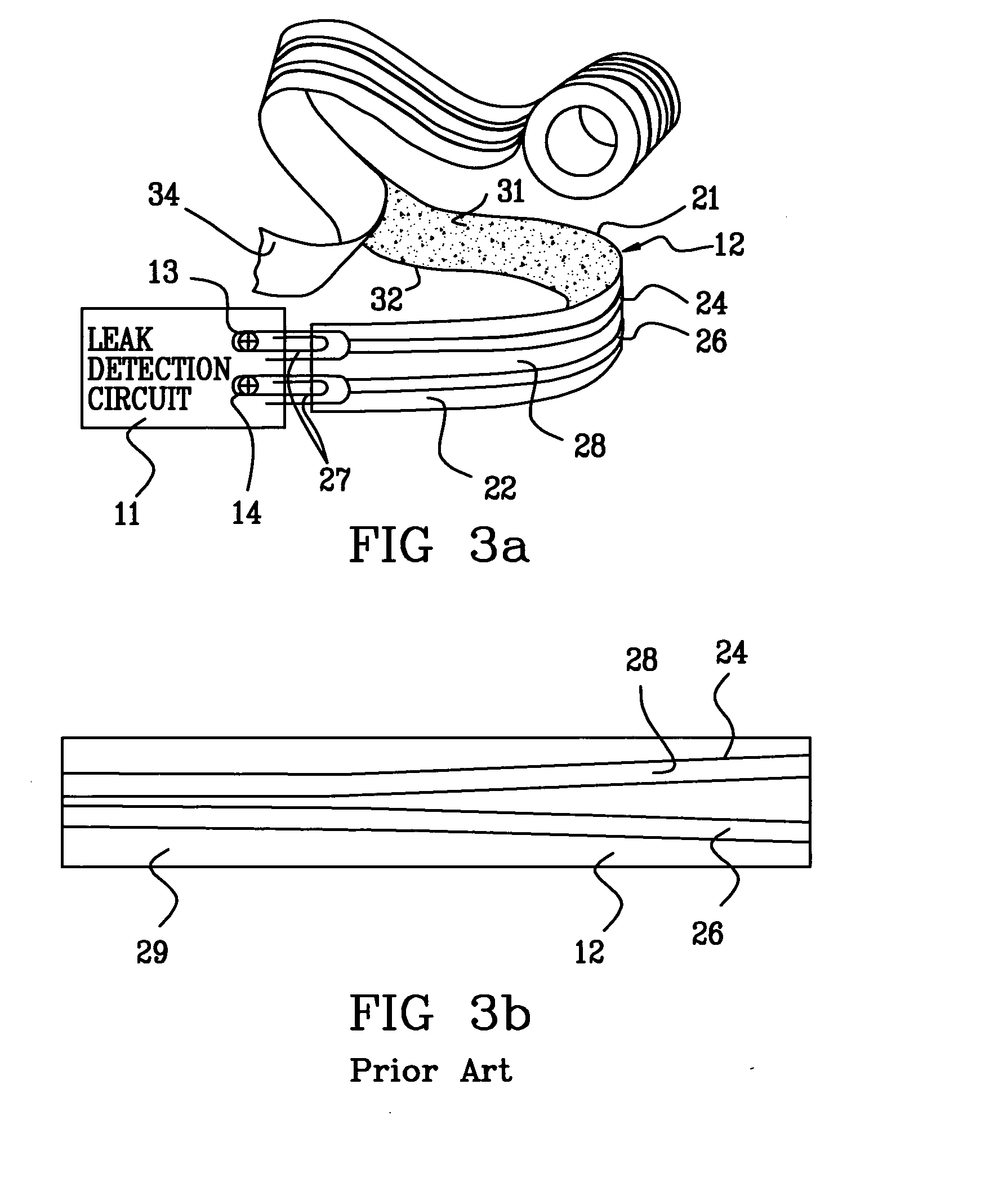
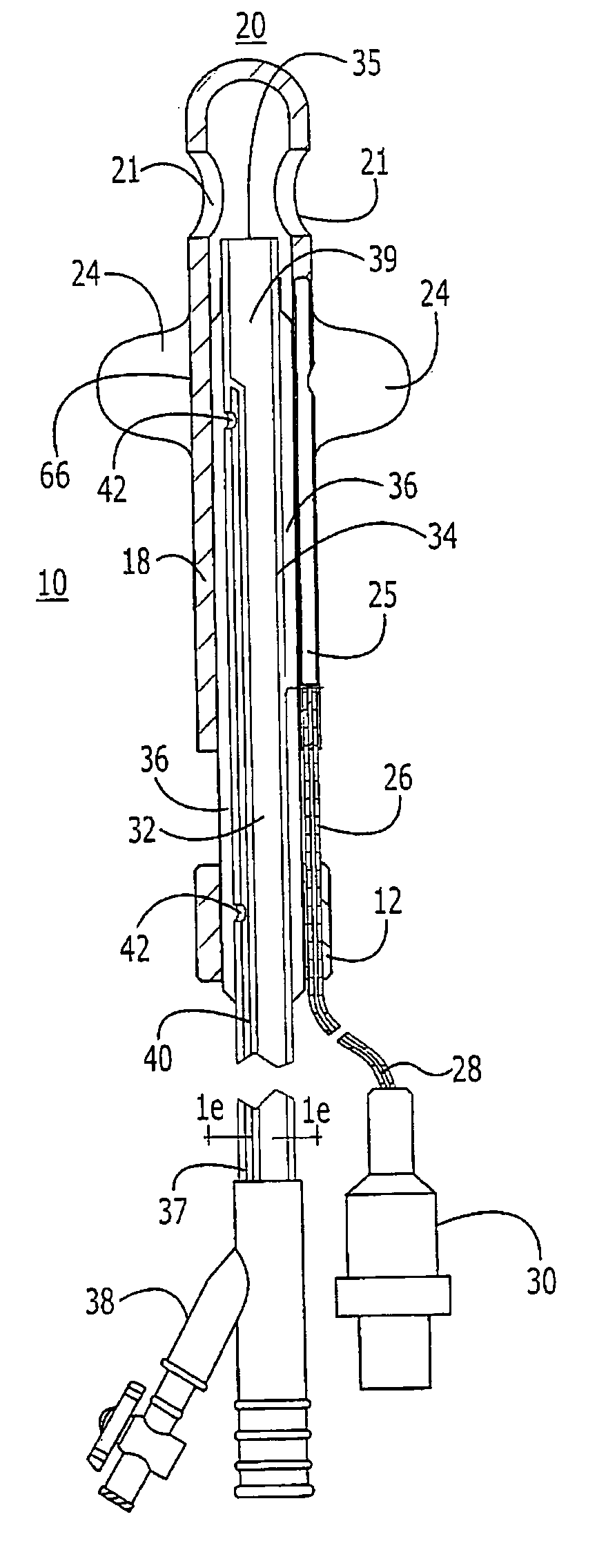
Probe for fluid leak detection with specific distal part
A disposable medical probe for detecting a leak of physiological fluid comprising a support layer, a conductive layer on top of the support layer, the conductive layer comprising two conducting electrodes both placed exclusively on each side of a longitudinal axis, the conductive layer defining two zones: a proximal zone with two proximal electrode parts being placed parallel to each other and being spaced apart by a constant distance d, and a distal zone with two distal electrode parts being spaced apart from each other by a gap e greater than said distance d, where the distal zone of the electrodes defines an increase in the gap between the distal parts of the electrodes, followed by a decrease in the gap between the distal parts of the electrodes.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Urethral catheter and guide
An indwelling catheter for insertion into a patient's urinary tract is provided that includes first and second tubular members that enable drainage of physiological fluids. An inflatable balloon is attached to the second tubular member. The first and second tubular members are interconnected by a connecting tube forming a gap between the first and second tubular members. The connecting tube is in fluid communication with the balloon to enable the balloon to be inflated via the connecting tube. When the balloon is anchored within the urinary bladder the second tubular member is located within the prostatic urethra with one end in close proximity to the sphincter and the other end protruding into the urinary bladder. The first tubular member is located within the penile urethra with one end in close proximity to the sphincter so that the connecting tube traverses the sphincter permitting voluntary control of the sphincter.
Owner:ESHEL UZI +2
Liquid pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of a posterior eye disease
The invention provides pharmaceutical compositions based on liquid vehicles whose density is substantially higher than that of aqueous physiological fluids. The compositions are useful as medicines in ophthalmology, in particular for the treatment of conditions affecting the posterior segment of an eye. They may be administered topically into the eye or in a minimally invasive manner by periocular injection. Preferred liquid carriers are selected from semifluorinated alkanes.
Owner:NOVALIQ GMBH
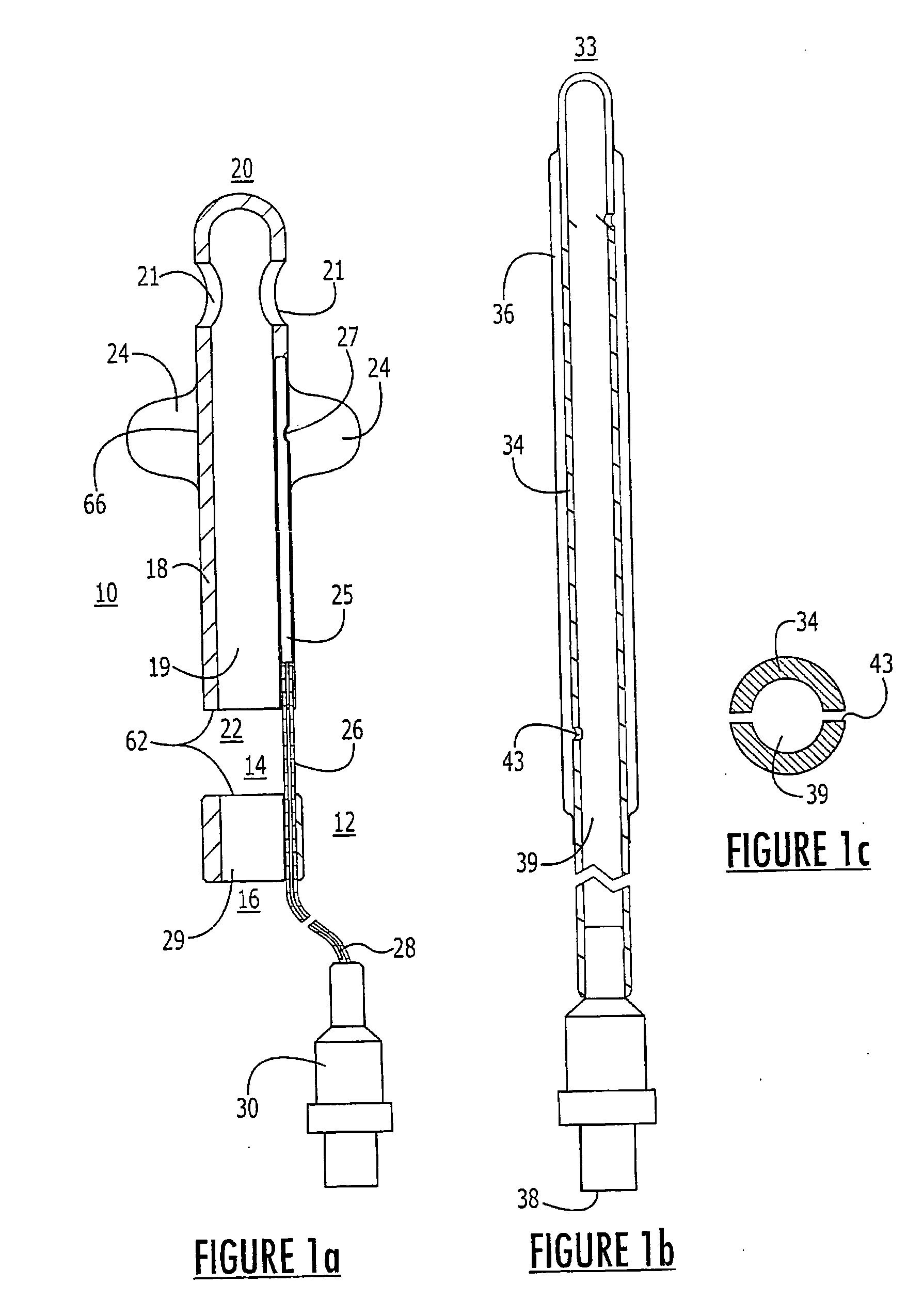
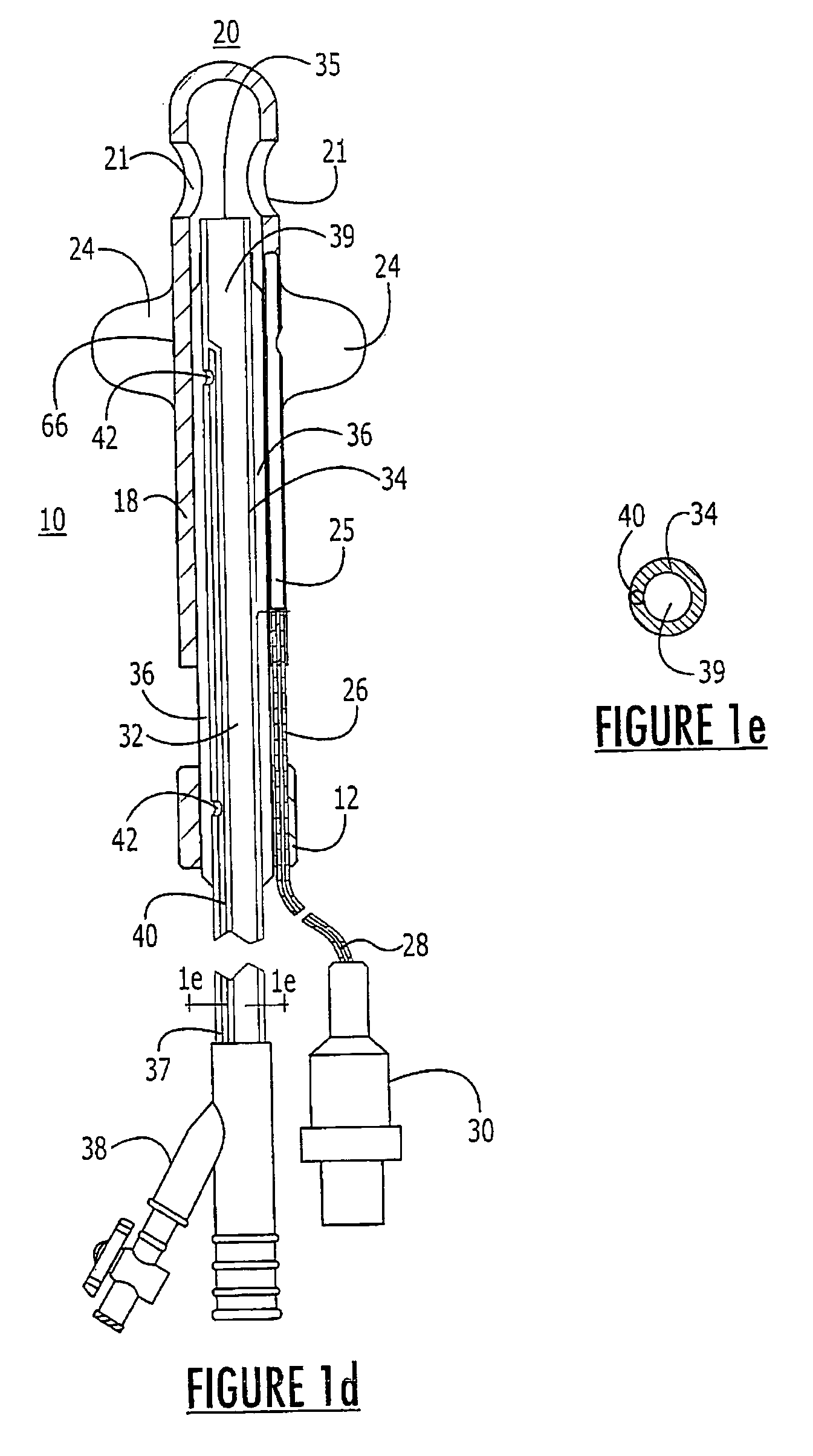
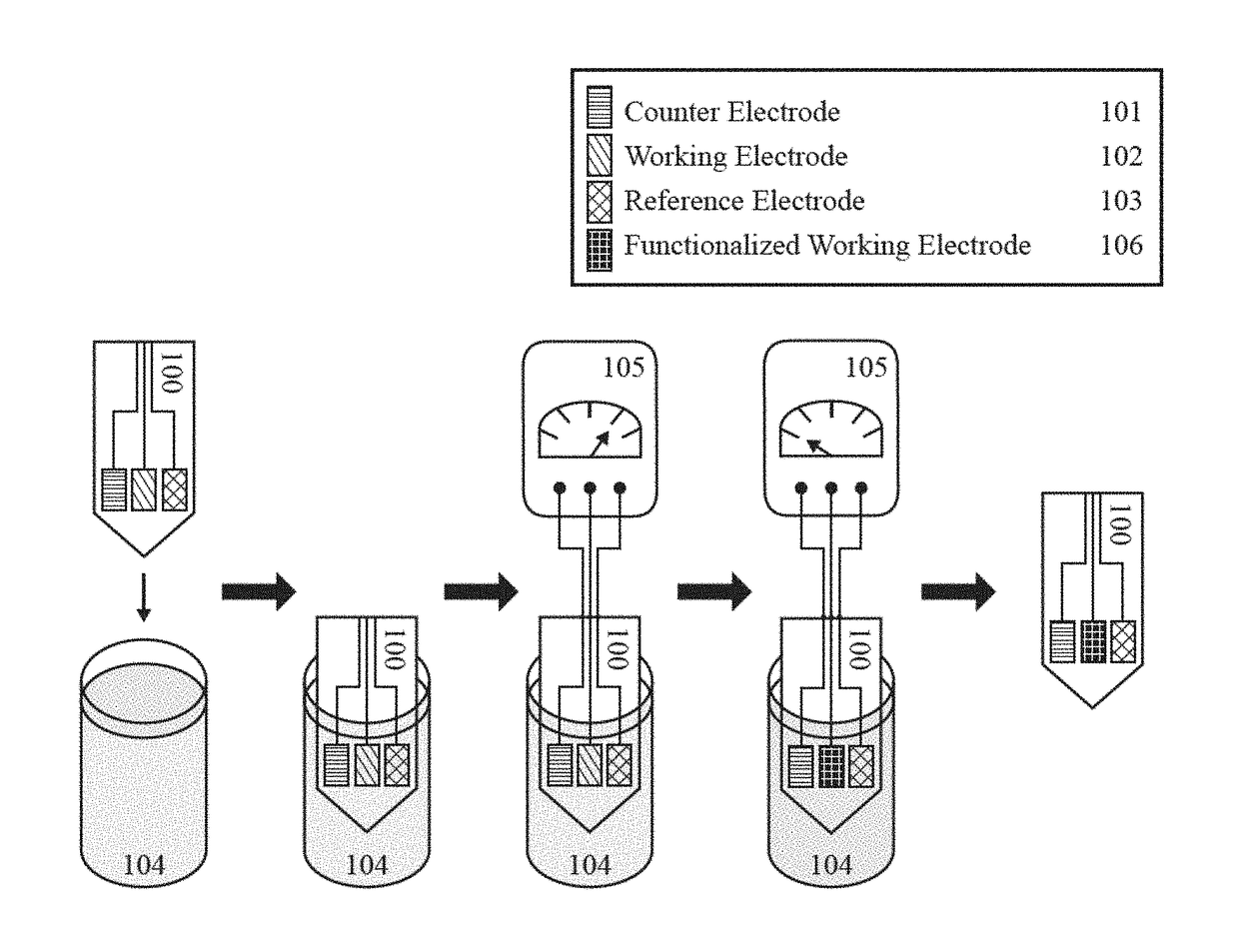
Tissue-penetrating electrochemical sensor featuring a co-electrodeposited thin film comprised of polymer and bio-recognition element
A method and device to impart the ability to selectively quantify chemical / biochemical analytes occupying physiological fluids via an automated process that allow the precise and spatially-defined simultaneous deposition of a thin-film of polymer containing an immobilized biorecognition element dispersed therein. A tissue penetrating electrochemical sensor comprises at least one working electrode and at least one of a reference electrode and a counter electrode.
Owner:BIOLINQ INC
Device that accurately measures physiological fluid flow
Owner:FUTURE PATH MEDICAL
Teaching prop
The present invention relates to teaching props for use in clinical education.The teaching props are in the form of synthetic body parts adapted to be worn by the instructor to facilitate demonstration of physiological functions and clinical procedures to the students. The synthetic body parts include simulated skin or tissue and one or more internal conduits adapted to contain at least one simulated physiological fluid and is adapted to facilitate simulation of physiological functions or clinical procedures. The props allow the students to practice clinical procedures and techniques in a realistic situation without any risk of harm or discomfort to a real patient.
Owner:REID SEARL KERRY +1
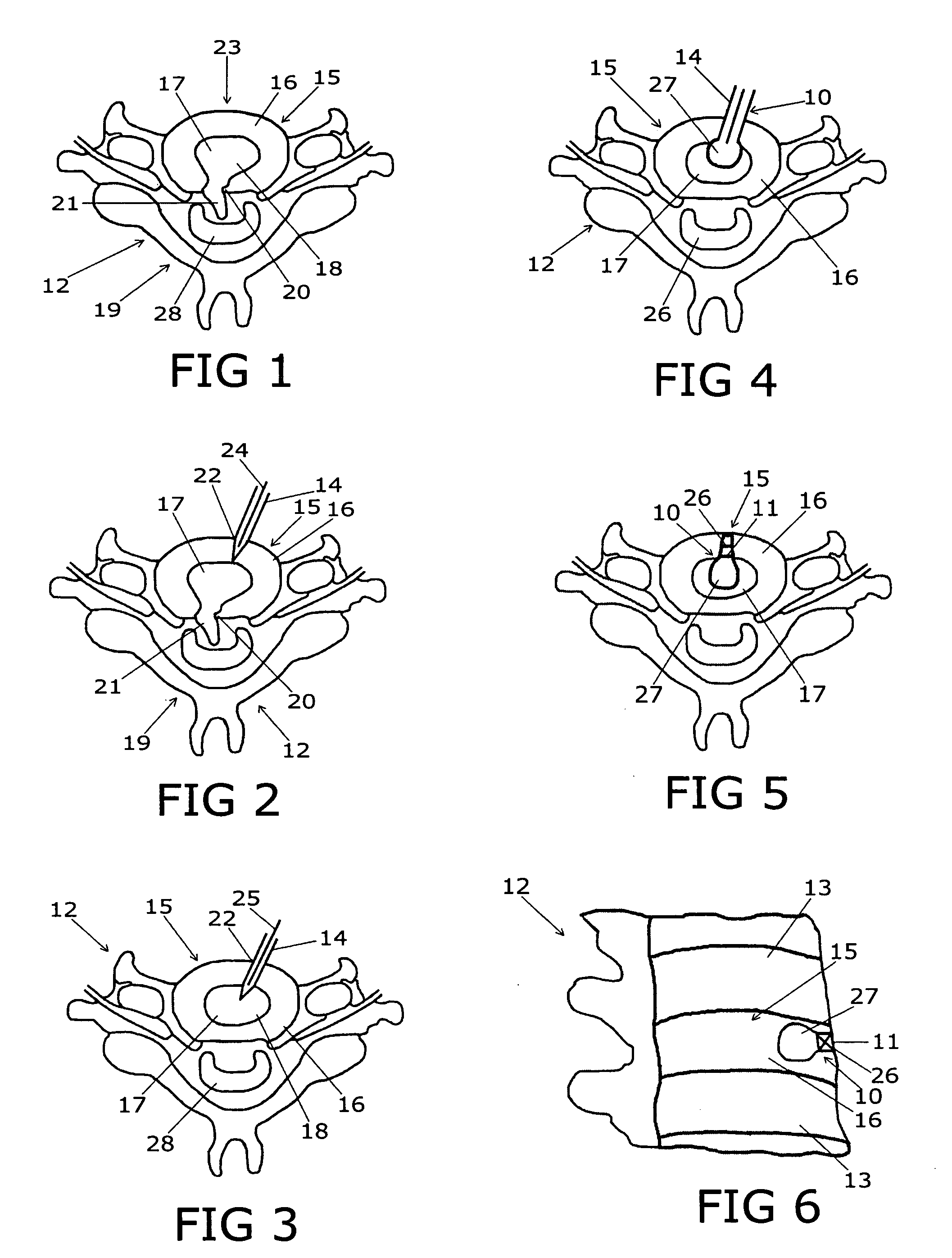
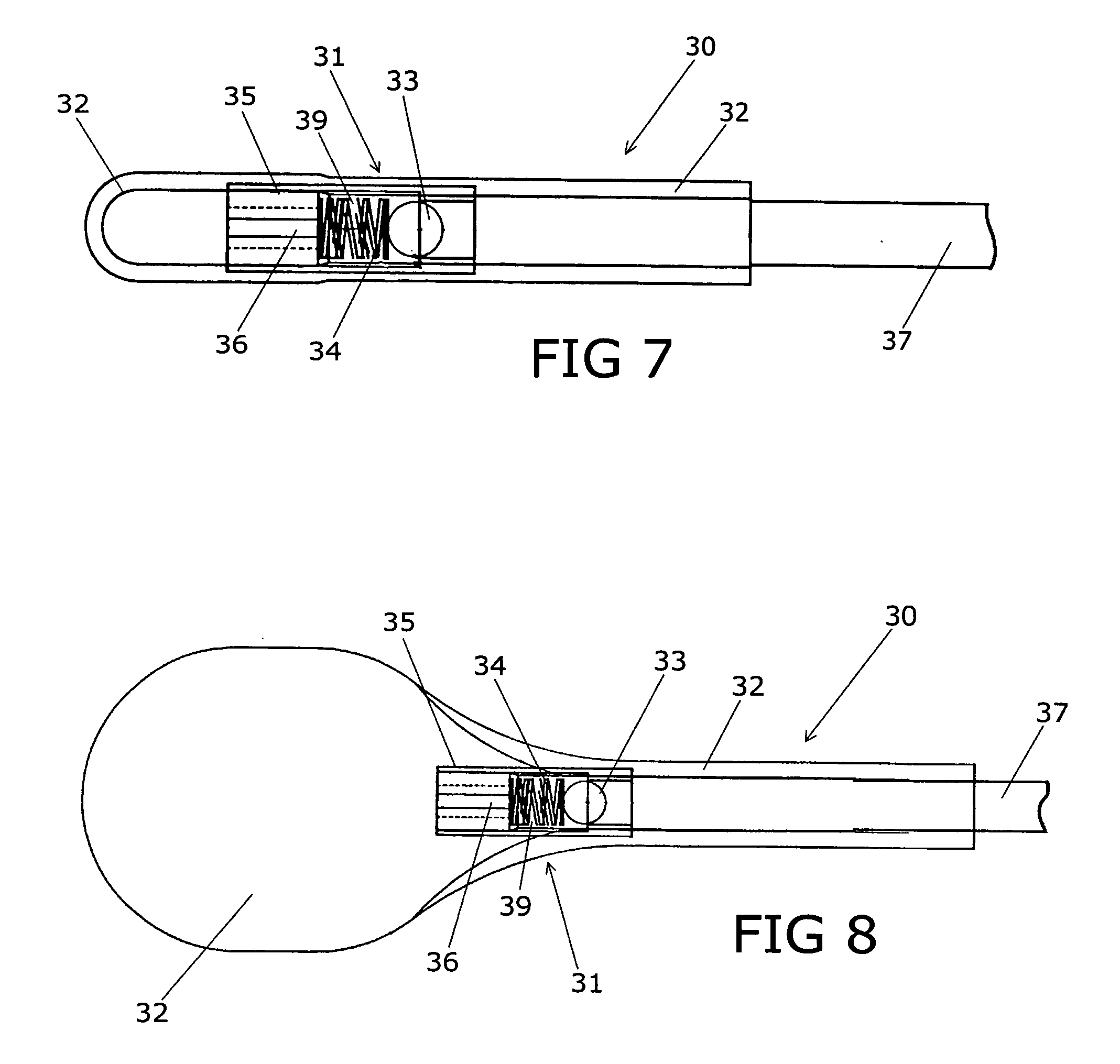
Device for treating intervertebral disc herniations
InactiveUS20050049604A1Minimize compressionMore processedJoint implantsSpinal implantsDistractionEndoscopic Procedure
A method and device for treating human intervertebral disc herniations using an endoscopic procedure. An access port is opened into and through the annulus of a disc to remove nucleus pulposus. Subsequent treatment, a balloon device having a valve structure is positioned via an endoscopic procedure into the disc space. The balloon device is filled with a physiological fluid to occupy the disc interspace or to maintain some degree of distraction of the created disc space. Post surgery, after fibrocollagenous tissue has grown into the disc space, a second endoscopic procedure is performed to remove the balloon device. Fluid is removed to collapse the balloon structure and then removed via the guide tube. The ingrowth of fibrocollagenous tissue will continue to fill the void formerly occupied by the balloon device. The balloon device has a rigid valve body and a flexible balloon member. The valve body has an end plug, a valve chamber holding a valve member and a cooperating biasing structure. The balloon member of the device is inserted into a vacated nucleus space of a herniated disc and then inflated with a physiological fluid using a fill tube. The balloon member, valve body, and fill tube or portions thereof may be constructed of a radiolucent material to provide visibility during implantation, surveillance and removal. The balloon device may be used in the cervical, lumbar or thoracic region of the spine.
Owner:PMT
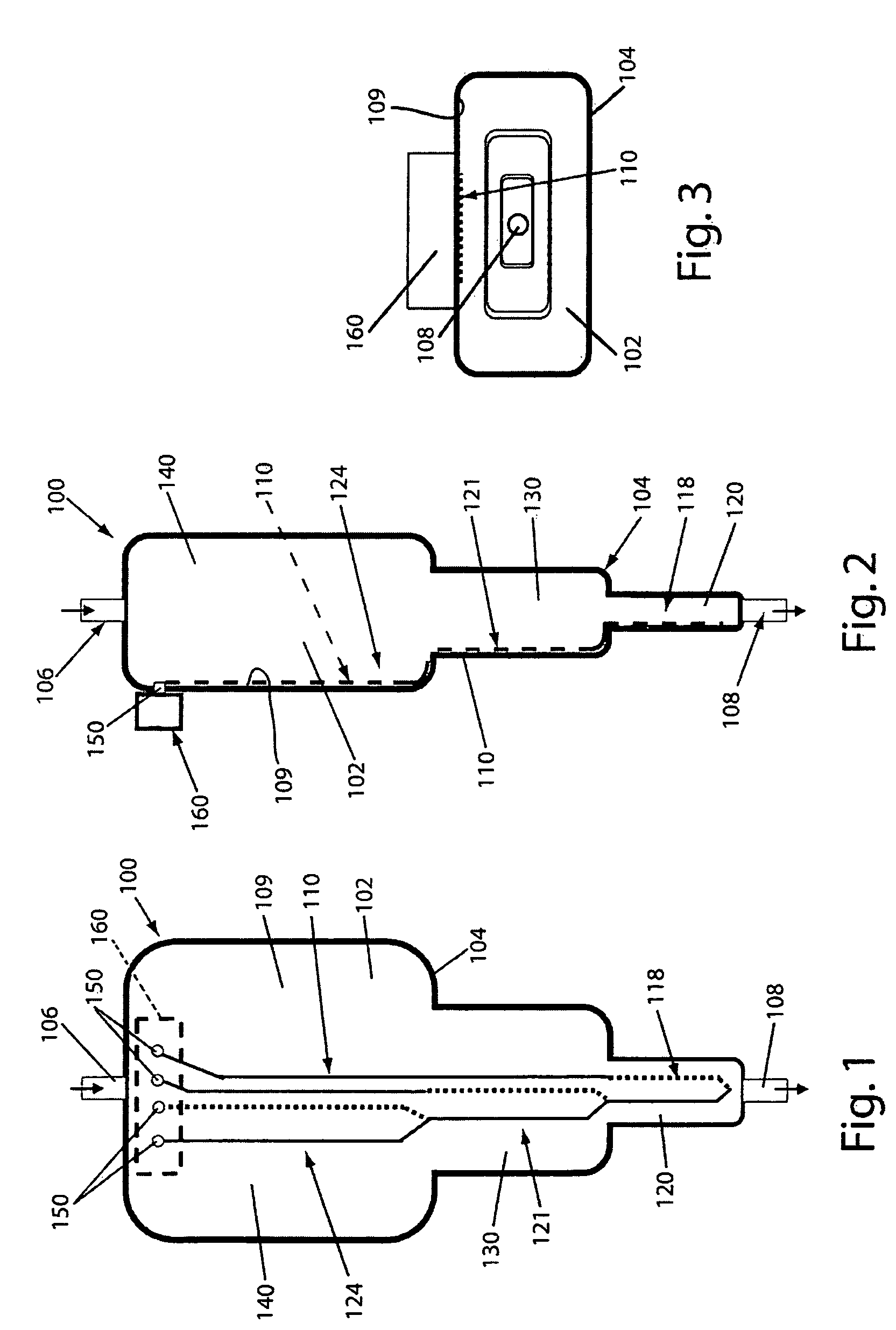
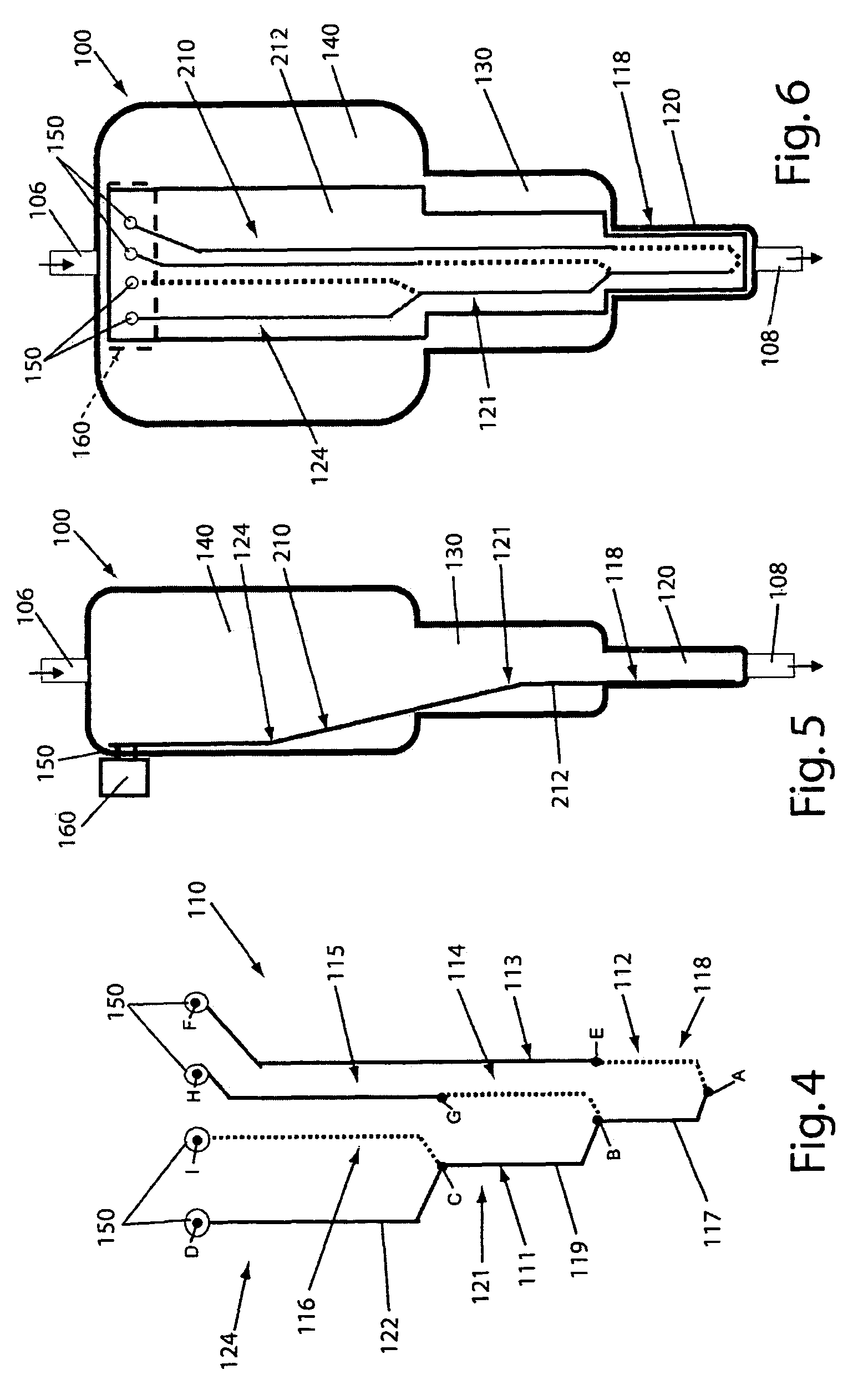
Disposable device for the continuous centrifugal separation of a physiological fluid
ActiveUS8070664B2Reduced Tolerance RequirementsReduce amount of shrinkageCentrifugesPhysiological fluidSingle-Use Device
The invention relates to disposable device for the continuous centrifugal separation of a physiological fluid. The inventive device comprises: a fixed axial element; a centrifugation chamber which is mounted such that it can rotate around the axis of said element; an inlet channel for the blood to be centrifuged, the dispensing port of which is located close to the base of the chamber; and an outlet passage for a separated constituent, the inlet port of which is located close to the other end of the chamber in a concentrated area of one of the separated constituents having the lowest mass density in order for same to be removed continuously. The above-mentioned chamber takes the form of a long tube. The fixed axial element comprises a second outlet passage for a second of the separated constituents, the inlet port of which is located close to the end of the chamber opposite the above-mentioned base in a concentrated area of said second separated constituent having the highest mass density in order for same to be removed continuously.
Owner:SORIN GRP ITAL SRL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com