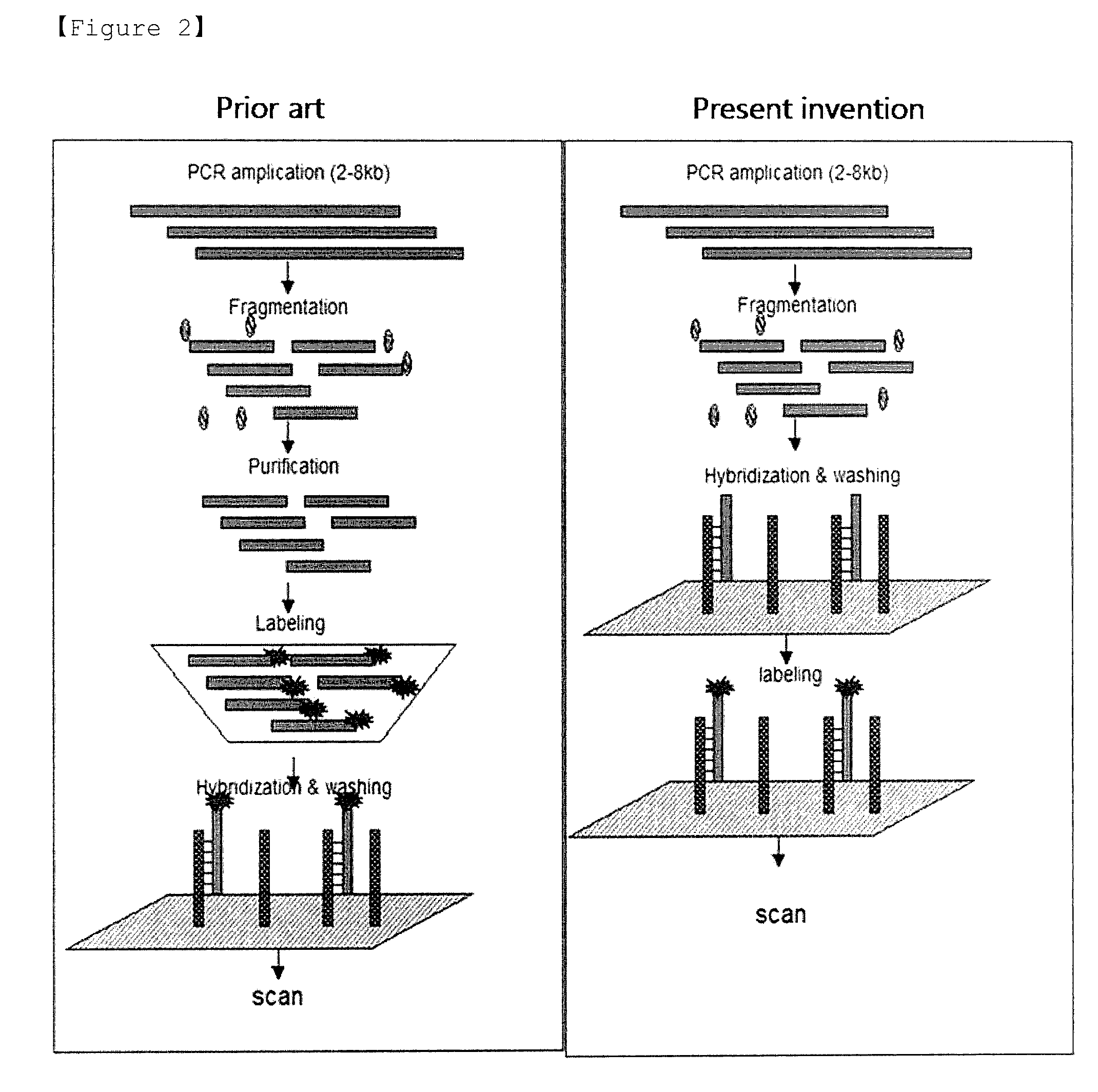
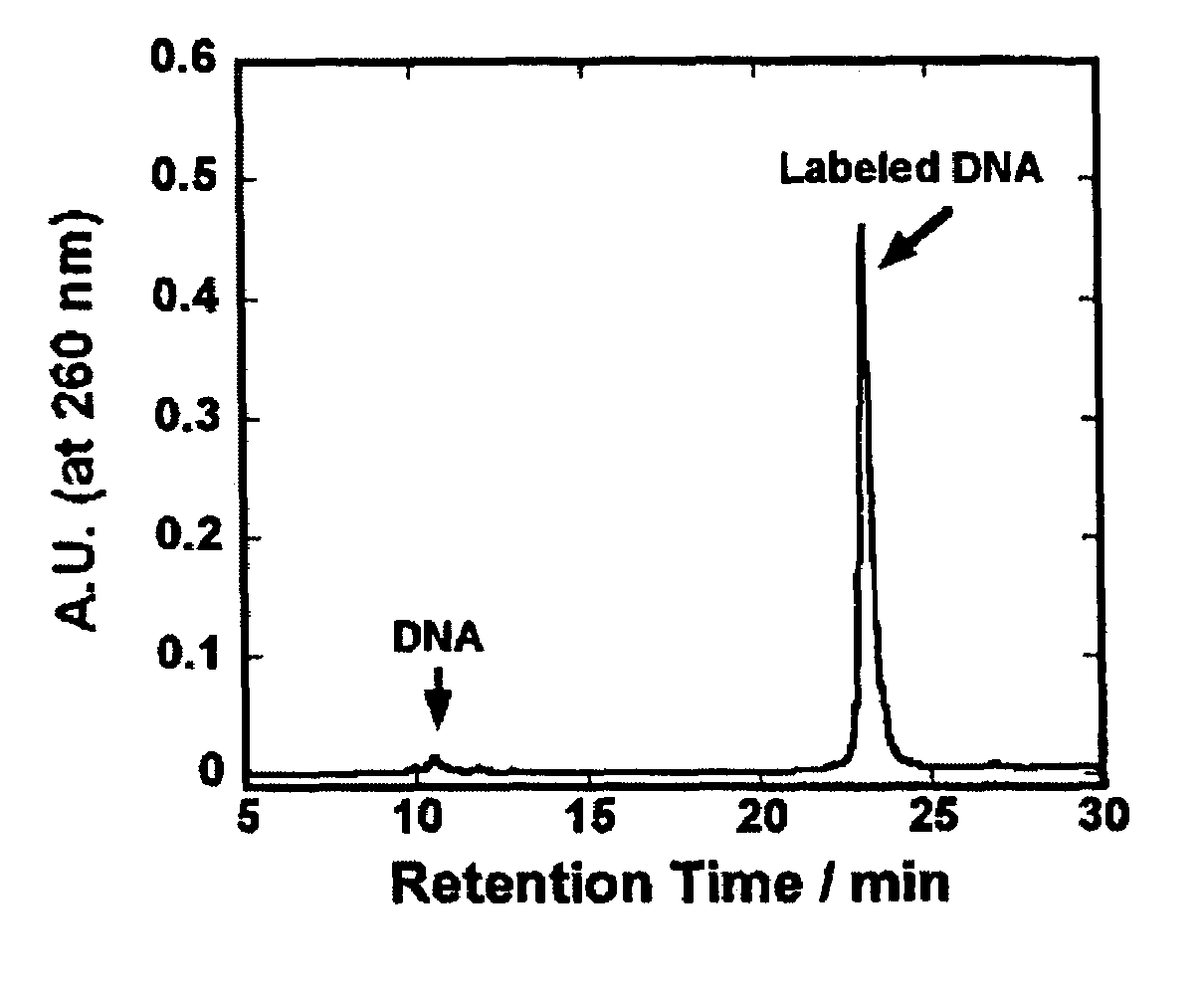
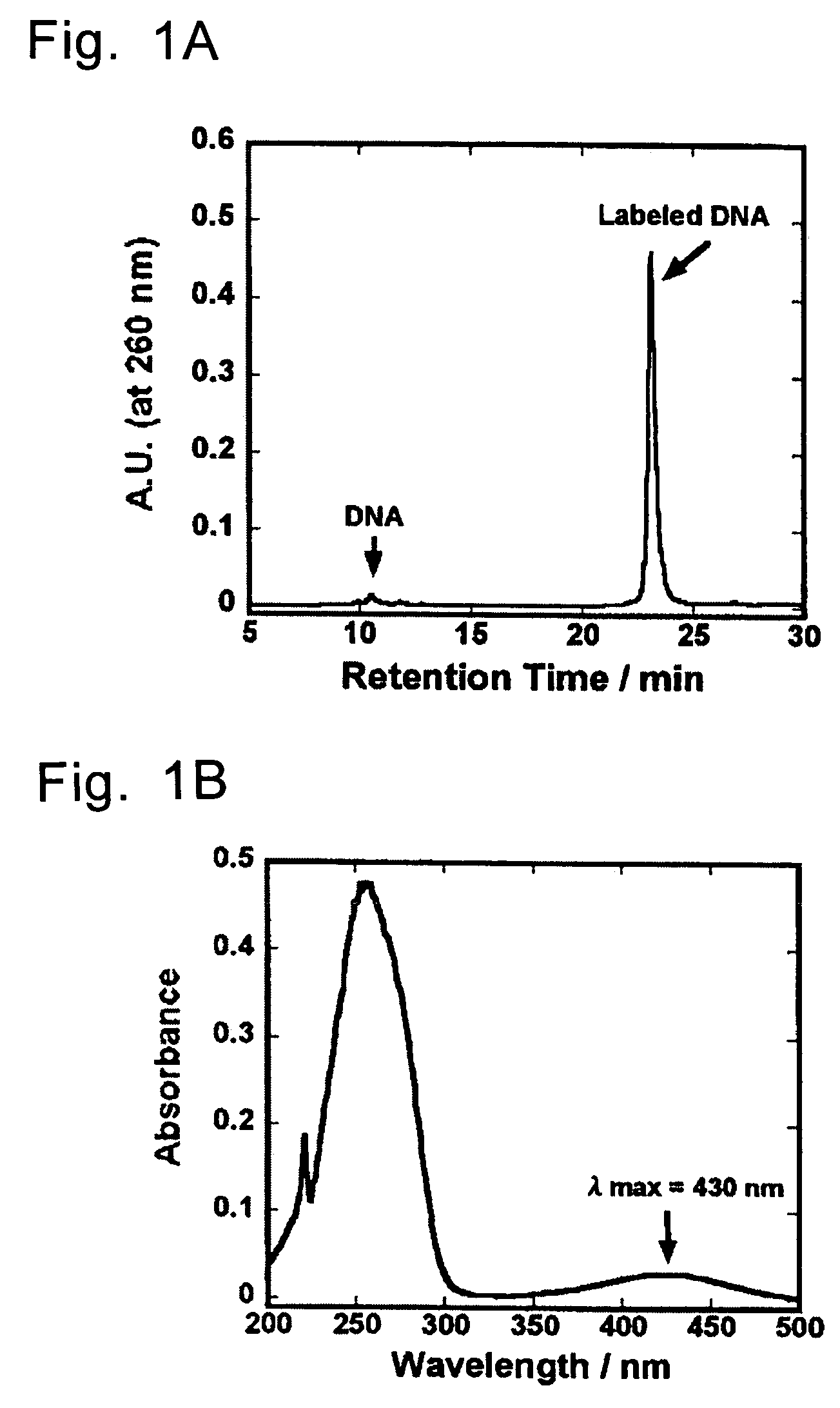
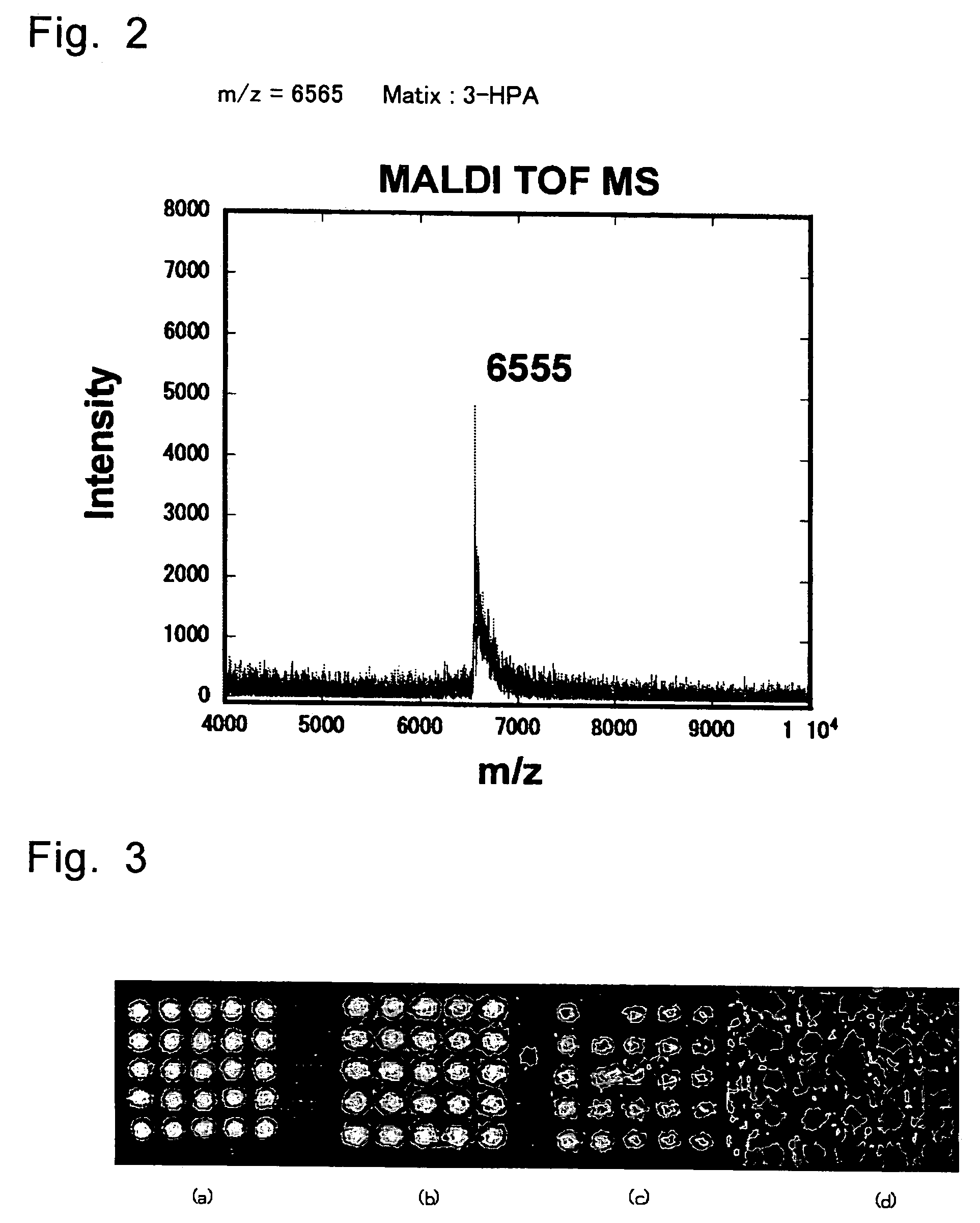
Patents
Literature
38results about How to "Efficiently labeled" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
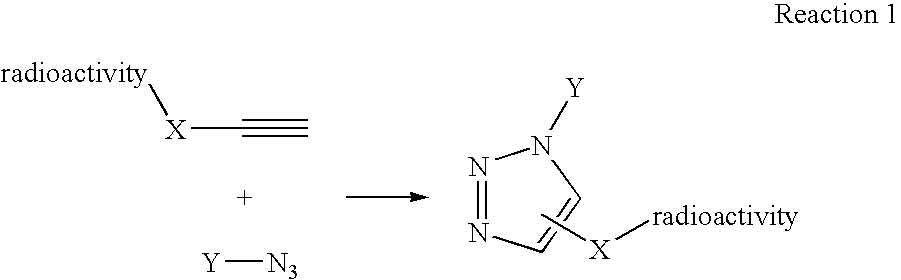
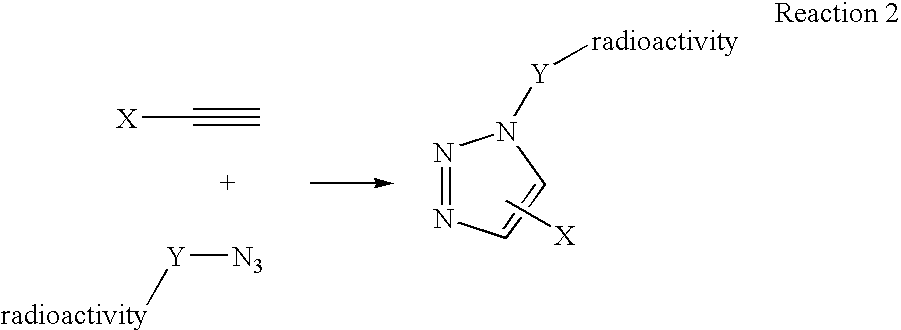
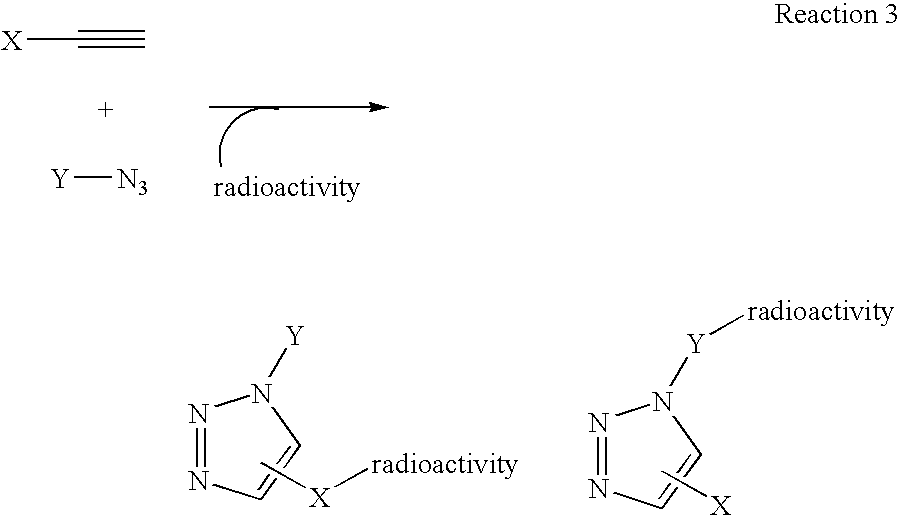
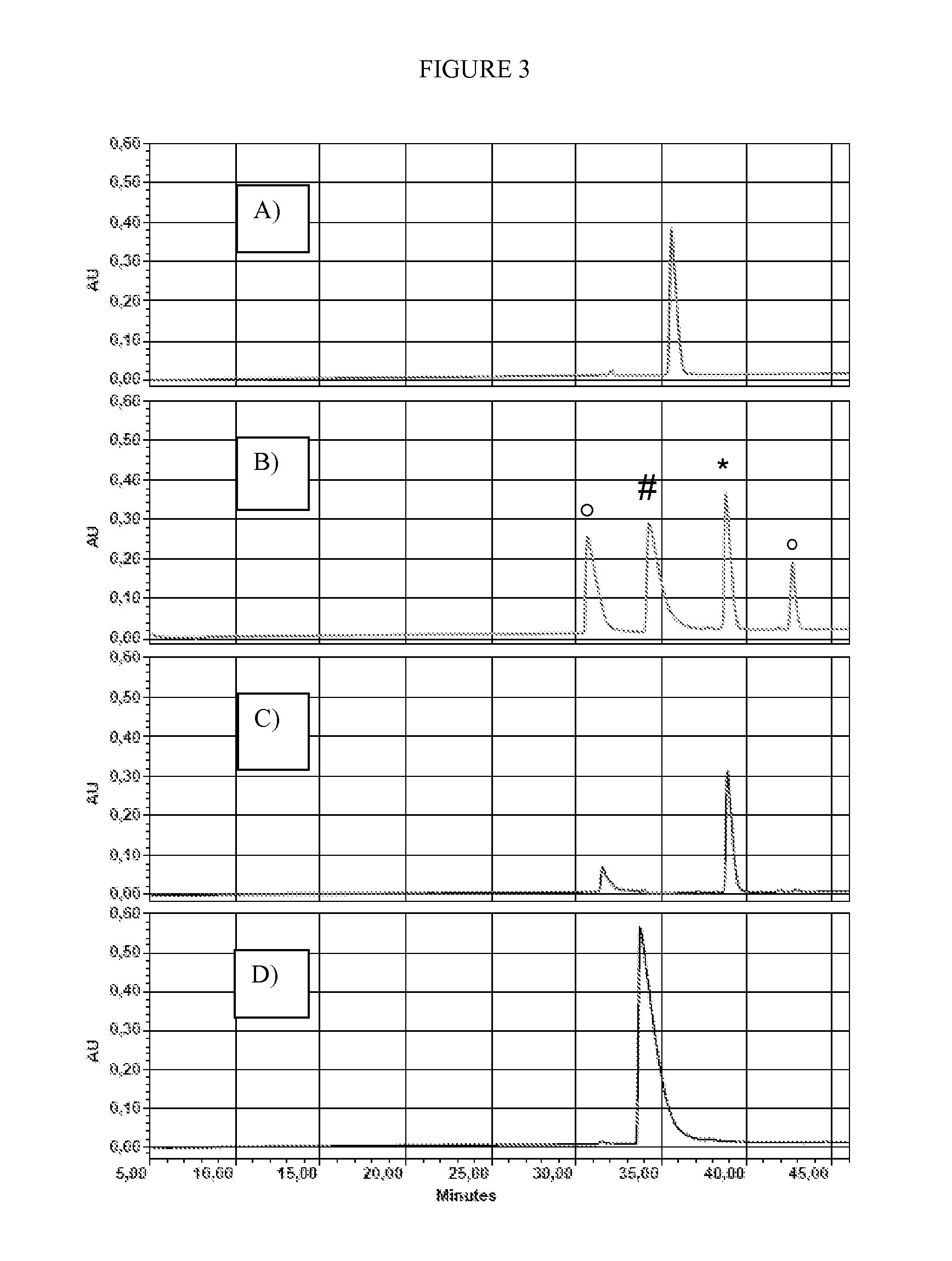
Click chemistry method for synthesizing molecular imaging probes
InactiveUS20060263293A1High reaction specificityEfficiently labeledSaccharide with heterocyclic radicalsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsLeaving groupChemical reaction
The present disclosure provides a method for preparing a radioactive ligand or radioactive substrate having affinity for a target biomacromolecule, the method comprising: (a) reacting a first compound comprising a first functional group capable of participating in a click chemistry reaction, with a radioactive reagent under conditions sufficient to displace the leaving group with a radioactive component of the radioactive reagent to form a first radioactive compound; (b) providing a second compound comprising a second complementary functional group capable of participating in a click chemistry reaction with the first functional group; (c) reacting the first functional group of the first radioactive compound with the complementary functional group of the second compound via a click chemistry reaction to form the radioactive ligand or substrate; and (d) isolating the radioactive ligand or substrate.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
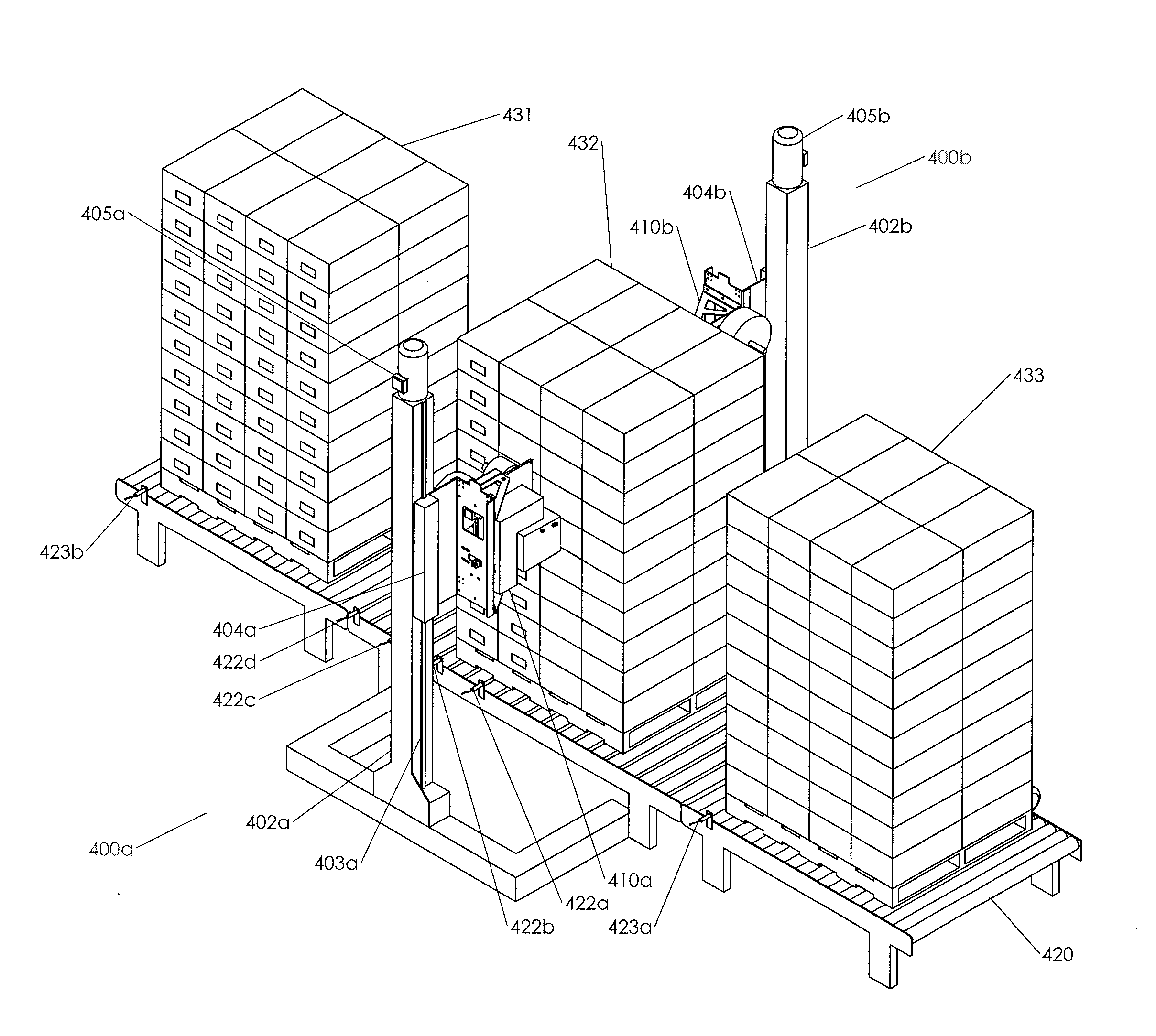
Container Labeling Systems and Methods of Use
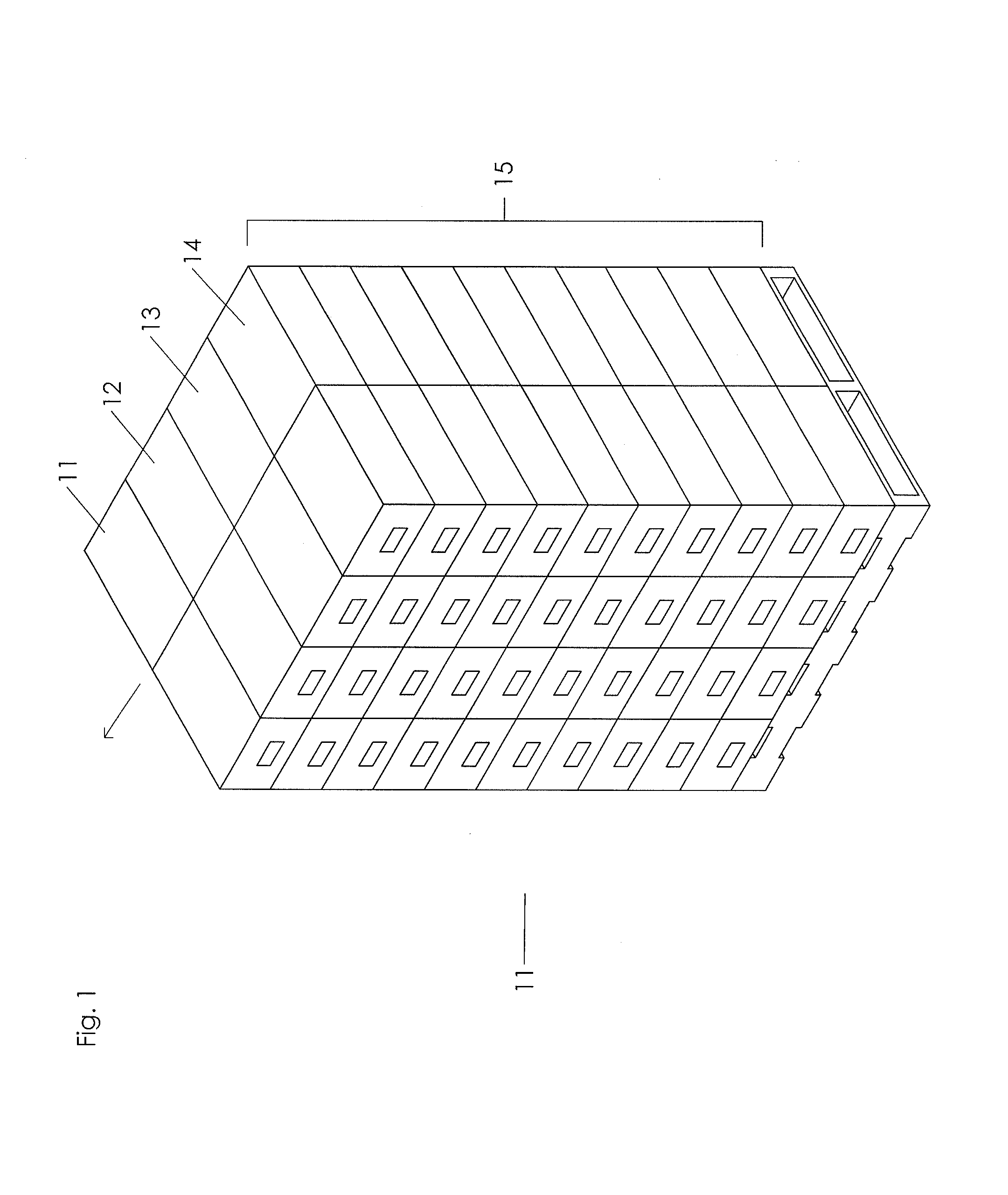
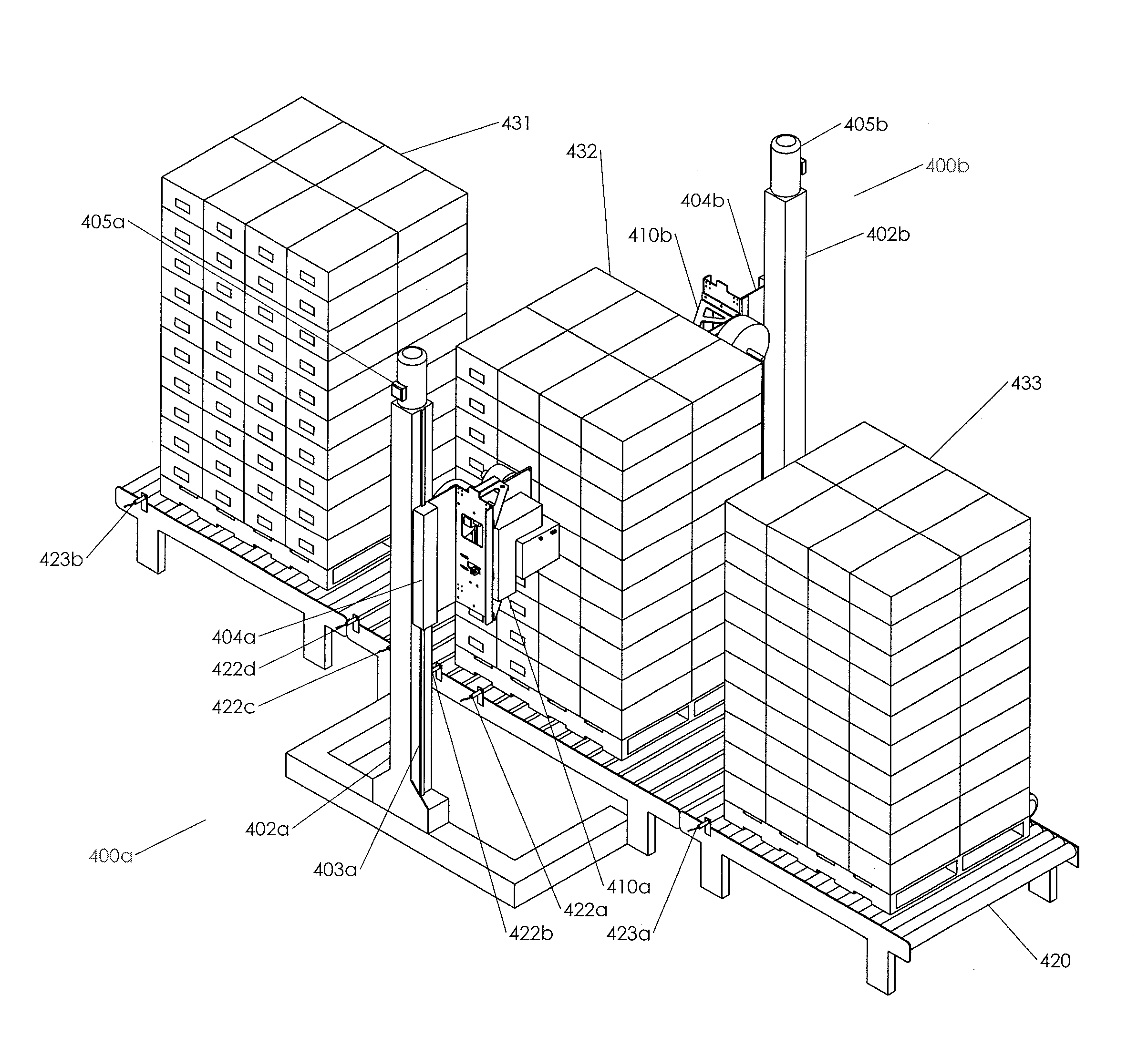
ActiveUS20150225104A1Quickly and efficiently labeledLaborious and time-consumingMechanical working/deformationTypewritersEngineeringPallet
The invention relates to labeling and / or printing devices, methods and systems for applying coding and / or labeling to containers that are stacked or otherwise organized in a group (e.g., containers stacked on a pallet). In embodiments of the invention, labeling and / or printing devices are mounted on carriages that are capable of moving in a vertical direction to apply labels as they move. Horizontal movement is imparted either by moving such carriages in a horizontal direction adjacent to the containers, or by moving the containers themselves (or the pallet holding them) in a horizontal direction adjacent to such carriages. Multiple carriages with labeling devices may be provided to provide simultaneous labeling to more than one side of a group of stacked containers. Embodiments of the invention are capable of providing labeling of containers that are uniformly or non-uniformly grouped or stacked.
Owner:REED LORIN
Method for forming full-length cDNA libraries
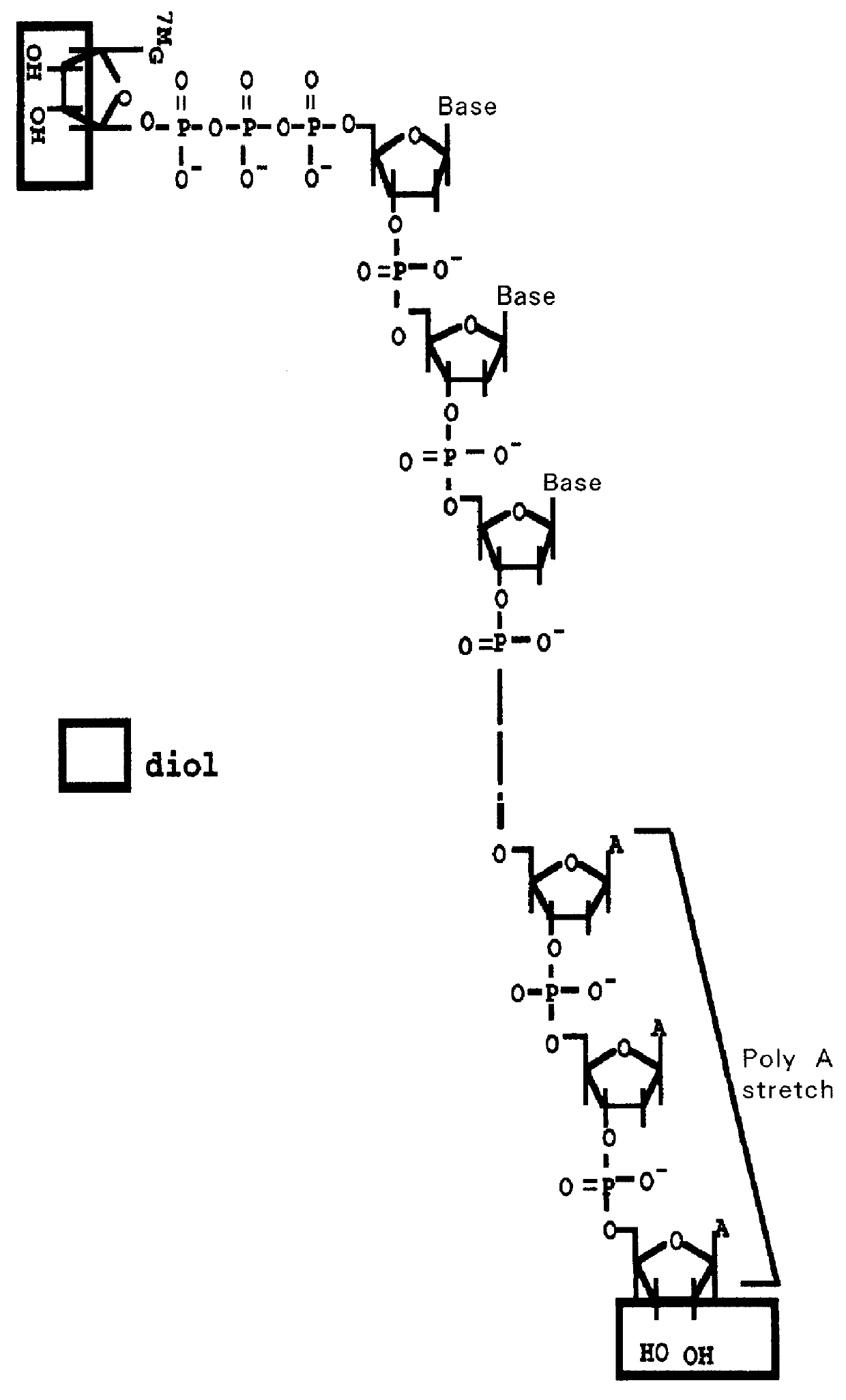
InactiveUS6143528AEasy to prepareEfficiently labeledSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPresent methodFull length cdna
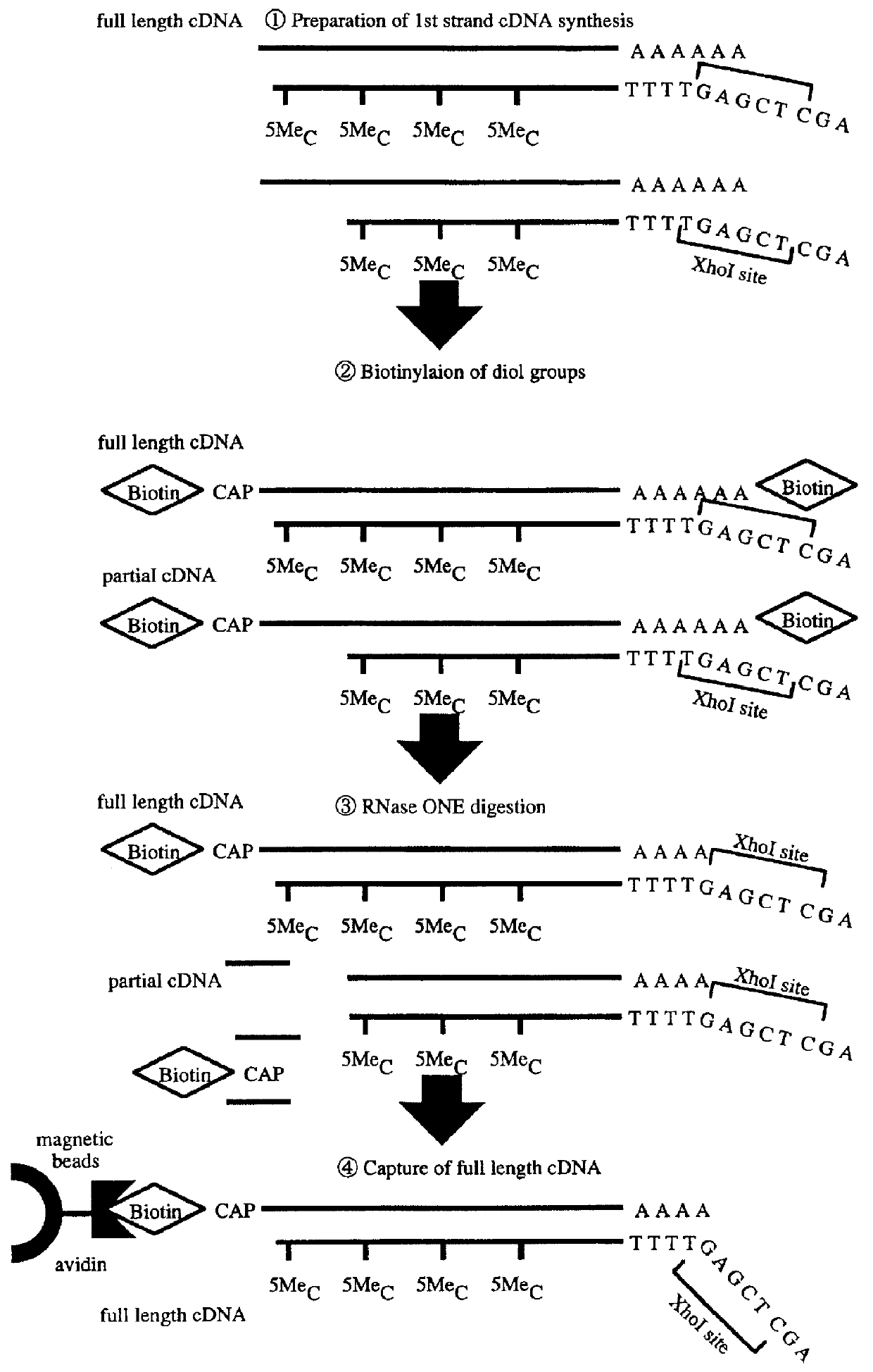
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 03992 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 16, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 16, 1999 PCT Filed Oct. 31, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 20122 PCT Pub. Date May 14, 1998Disclose is a method for making full-length cDNA libraries, which is for making libraries of cDNAs having lengths corresponding to full lengths of mRNAs and comprises the following steps of; forming RNA-DNA hybrids by reverse transcription starting from primers using mRNAs as templates, chemically binding a tag molecule to a diol structure present in the 5' Cap (7MeGpppN) site of a mRNA which is forming a RNA-DNA hybrid, and separating RNA-DNA hybrids carrying a DNA corresponding to a full-length mRNA from the RNA-DNA hybrids formed above by using a function of the tag molecule. The present method is a method for preparing full-length cDNA libraries utilizing a method for labeling the 5' Cap site more efficiently than protein enzyme reactions, which is avoidable a decrease of a full-length cDNA synthesis efficiency caused by cleavage of mRNA, and can synthesize a full-length cDNA more efficiently.
Owner:RIKEN
Mutant Pfu DNA polymerase
ActiveUS8435775B2Reduced discriminationEasy to detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideWild type
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
Cell assay kit and method
ActiveUS20090148869A1Increase density and magnetic susceptibilityHigh densityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell concentrationMagnetic susceptibility
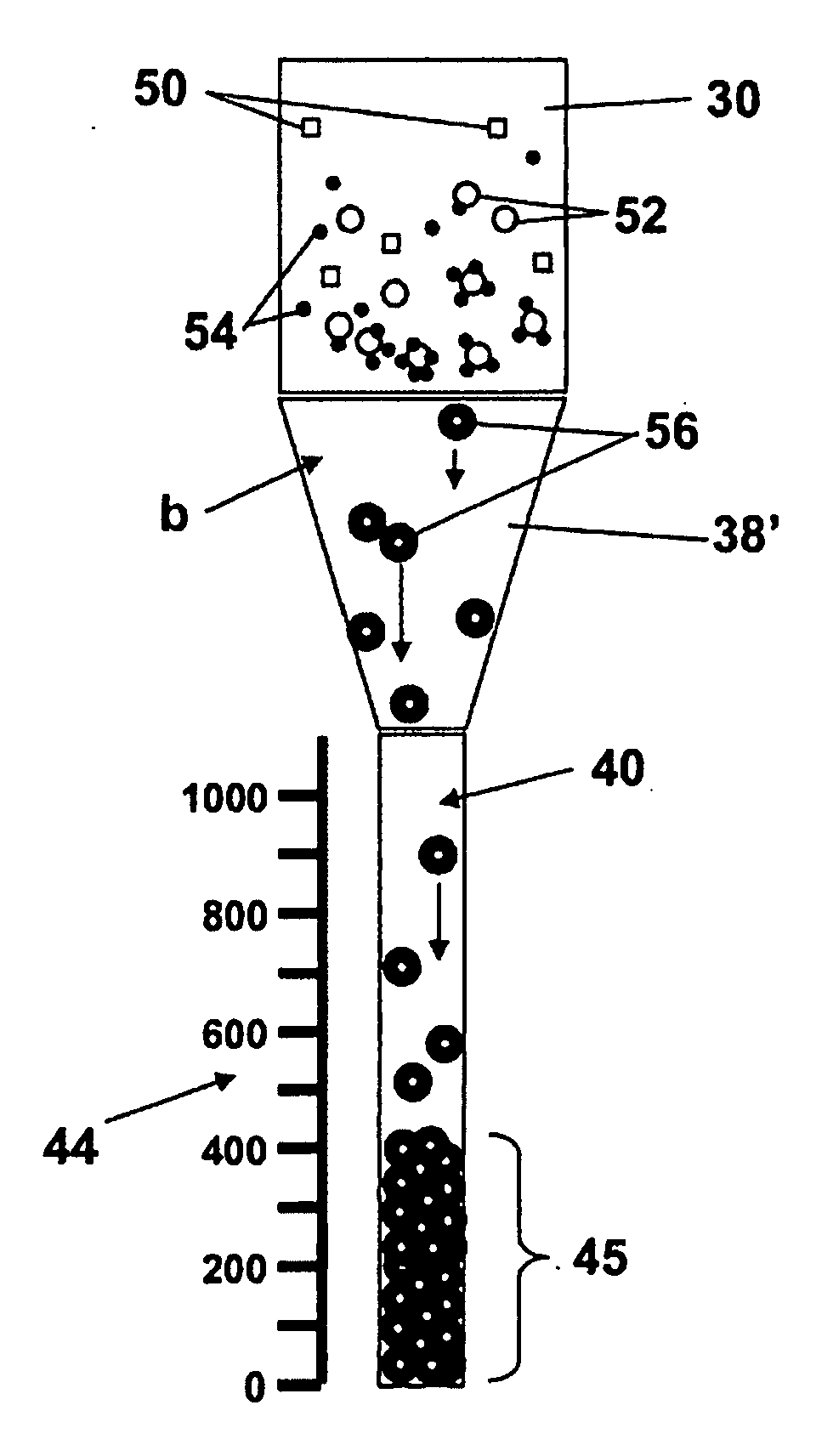
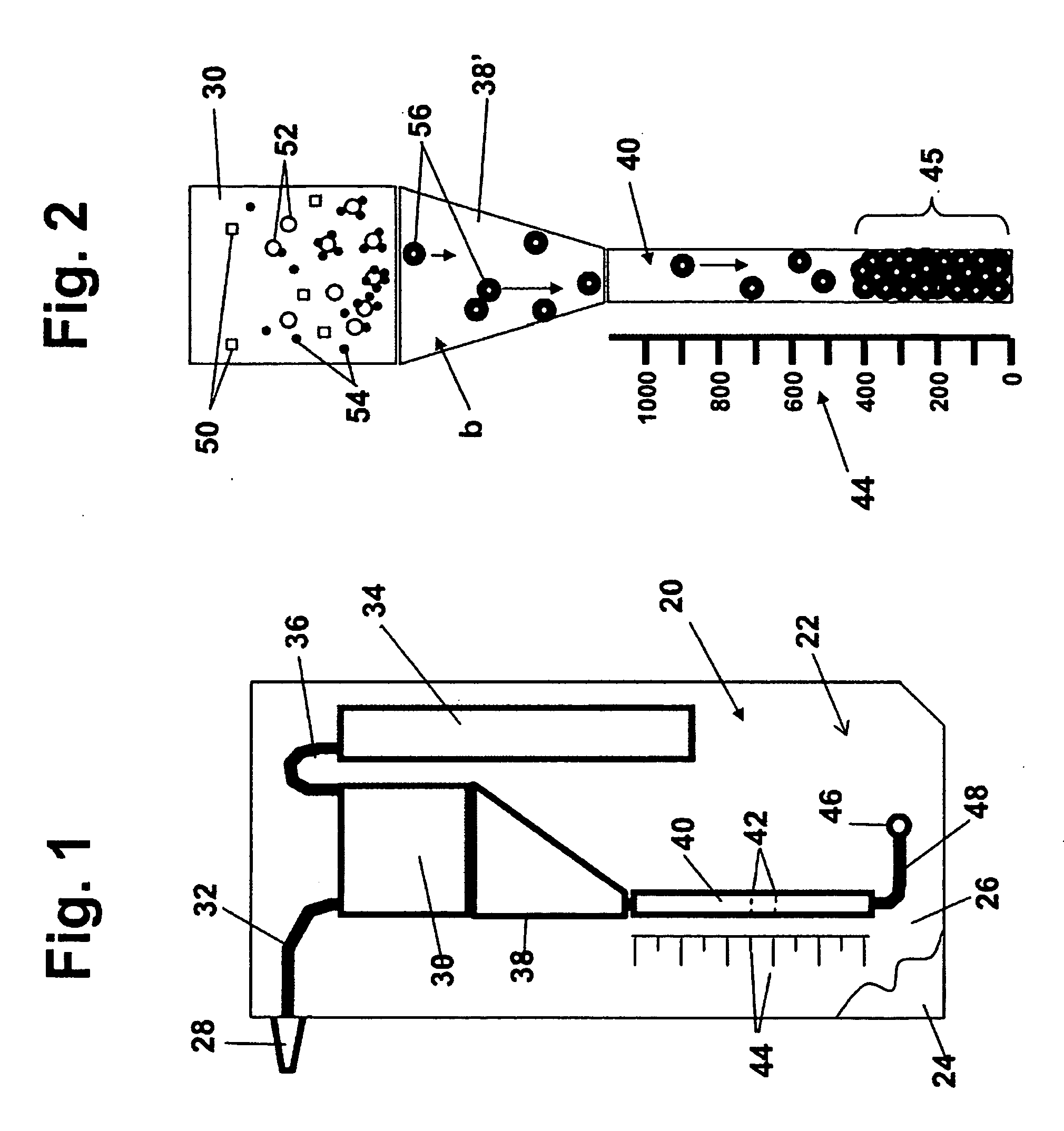
A method and kit for assaying a cell sample for the presence of at least a threshold number of cells of a given type are disclosed. The kit includes an assay device having a sample chamber for receiving the cell sample and an elongate collection chamber containing a selected-density and / or viscosity medium and having along its length, a plurality of cell-collection regions, and particles which are capable of specific attachment to cells of the selected cell type, and which are effective, when attached to the cells, to increase the density or magnetic susceptibility of the cells. In operation, particle-bound cells and particles in the cell sample are drawn through the elongate collection chamber under the influence of a gravitational or selected centrifugal or magnetic-field force until the particle-bound cells and particles completely fill successive cell-collection regions in the collection chamber. Indicia associated with at least one collection regions indicates a concentration of cells of the selected type effective to at least partially fill that collection region.
Owner:STEMCELL TECH CANADA INC
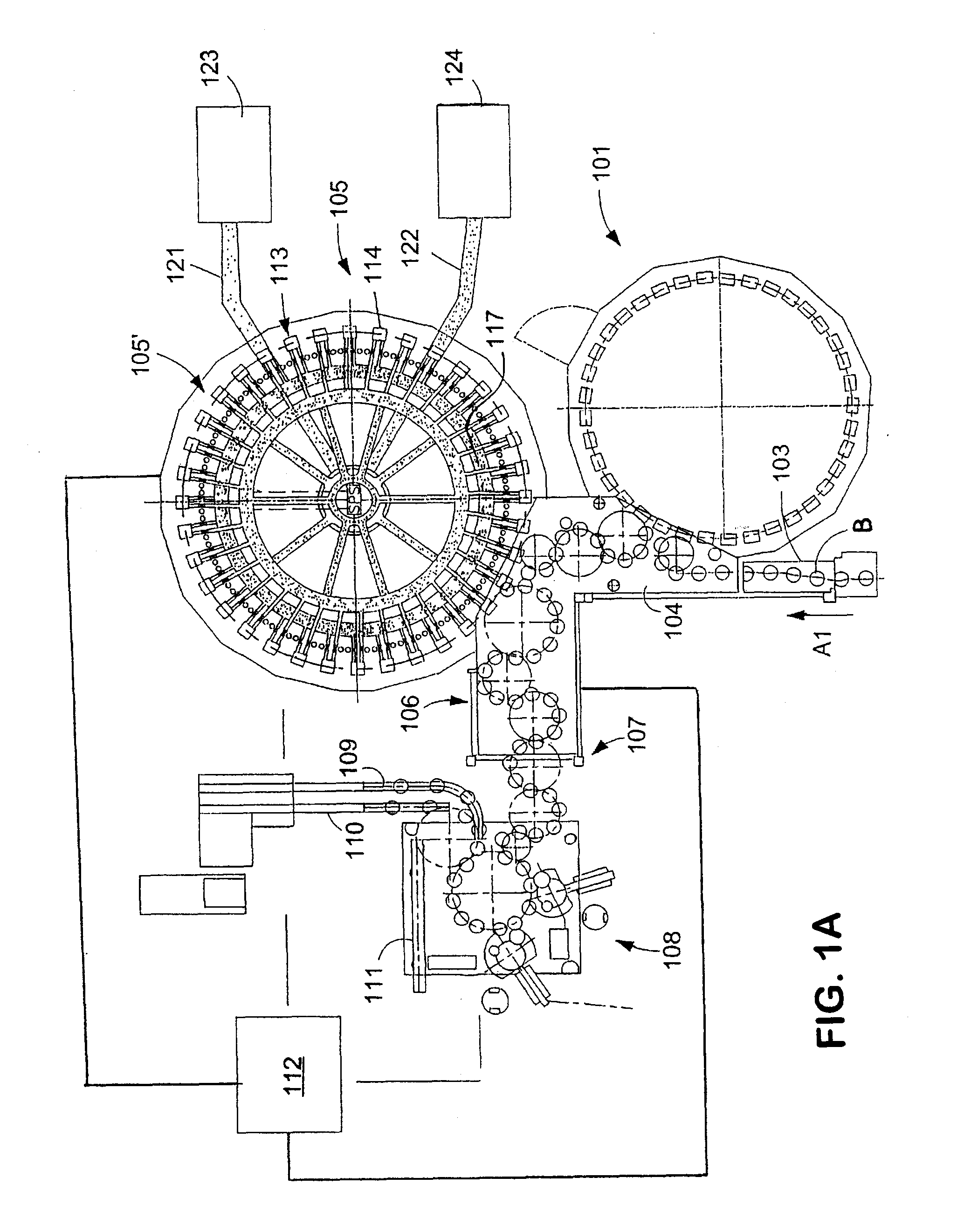
Beverage bottling plant for filling beverage bottles with a liquid beverage, with an information adding arrangement for adding information relating to the beverage bottles, and a method of operating the beverage bottling plant
A beverage bottling plant for filling beverage bottles with a liquid beverage, with an information adding arrangement for adding information relating to the beverage bottles, and a method of operating the beverage bottling plant. The abstract of the disclosure is submitted herewith as required by 37 C.F.R. §1.72(b). As stated in 37 C.F.R. §1.72(b): A brief abstract of the technical disclosure in the specification must commence on a separate sheet, preferably following the claims, under the heading “Abstract of the Disclosure.” The purpose of the abstract is to enable the Patent and Trademark Office and the public generally to determine quickly from a cursory inspection the nature and gist of the technical disclosure. The abstract shall not be used for interpreting the scope of the claims. Therefore, any statements made relating to the abstract are not intended to limit the claims in any manner and should not be interpreted as limiting the claims in any manner.
Owner:KHS MASCHEN UND ANALAGENBAU AKTIENGES
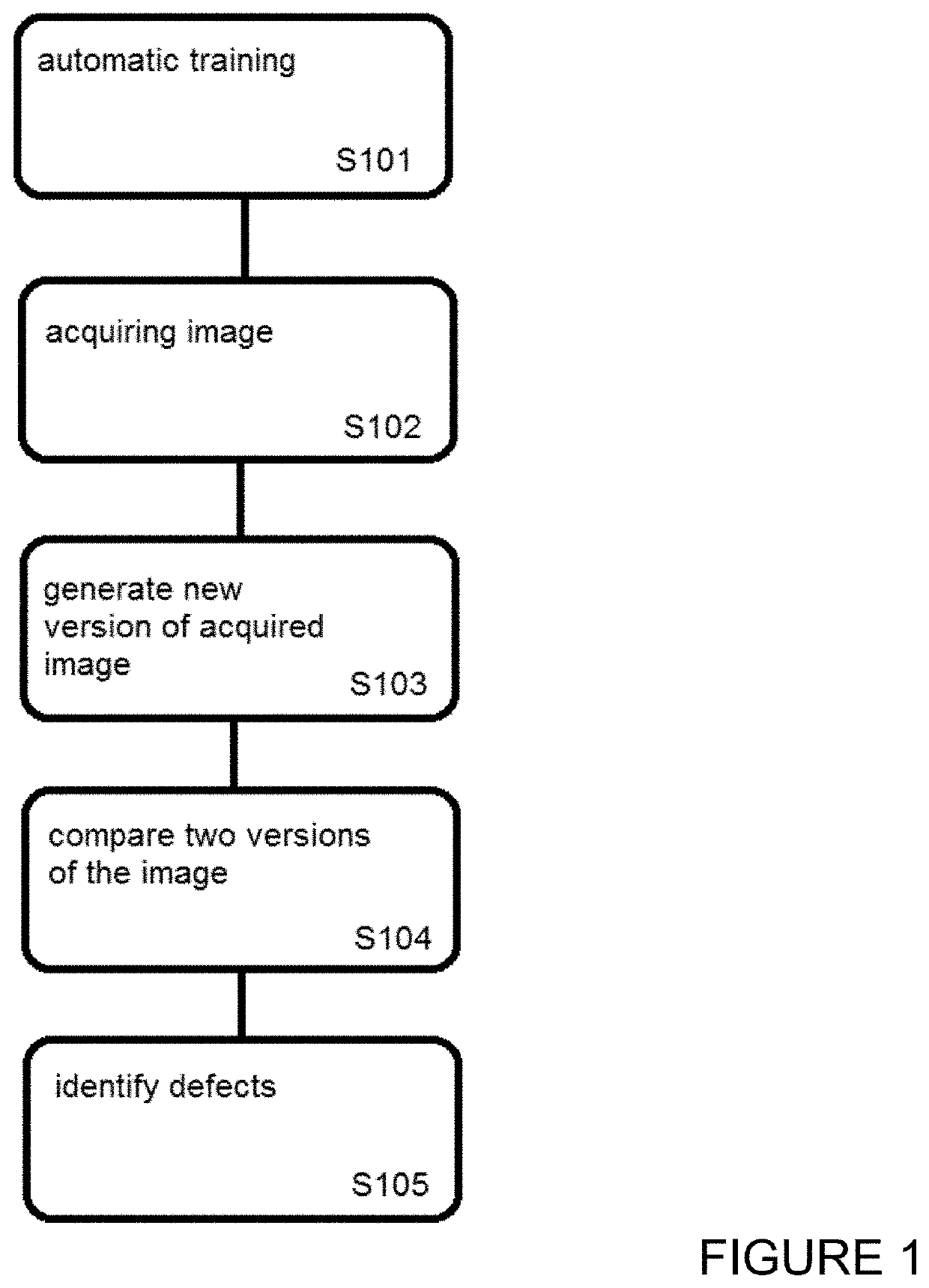
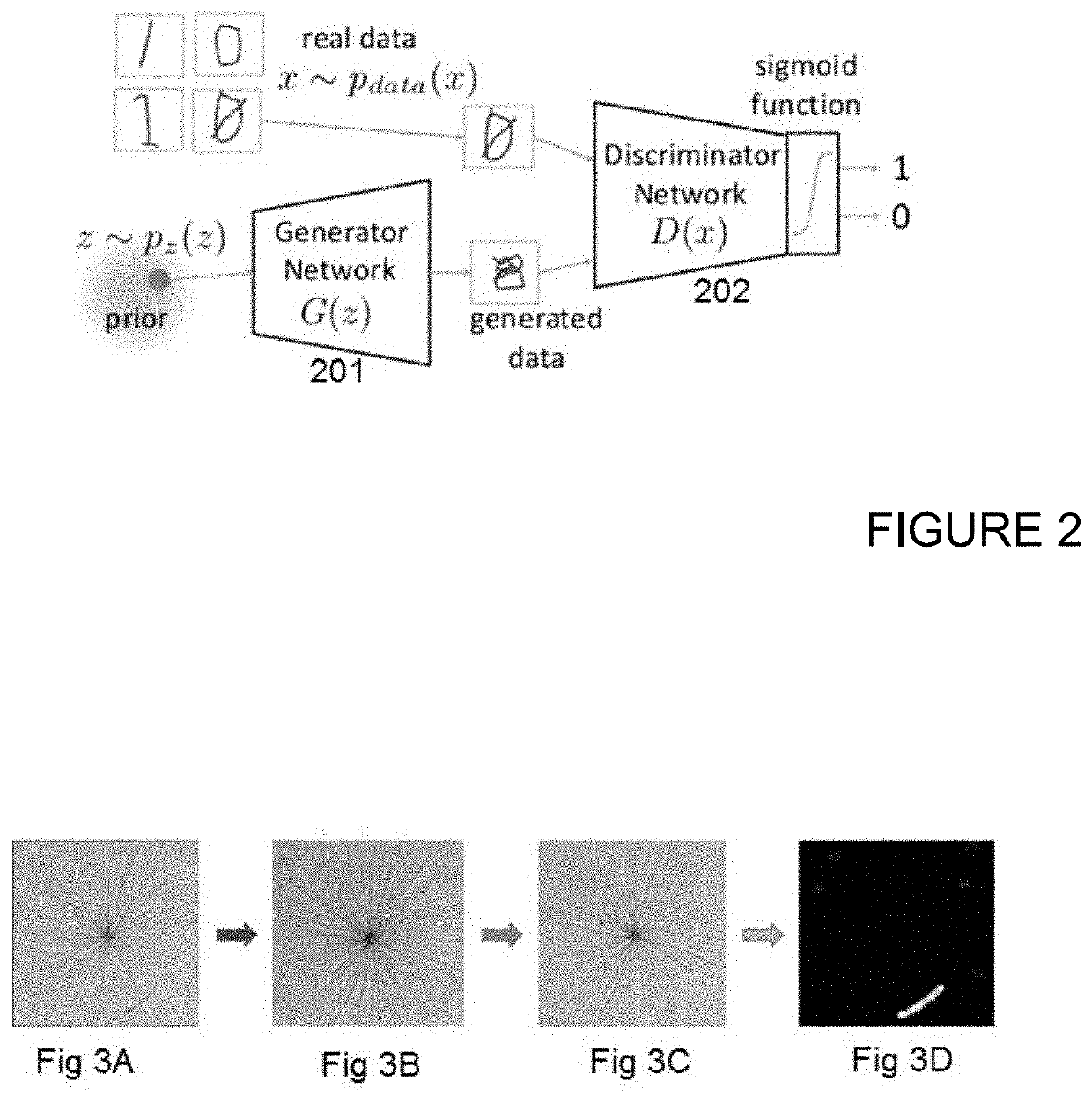
Surface defect identification method and apparatus
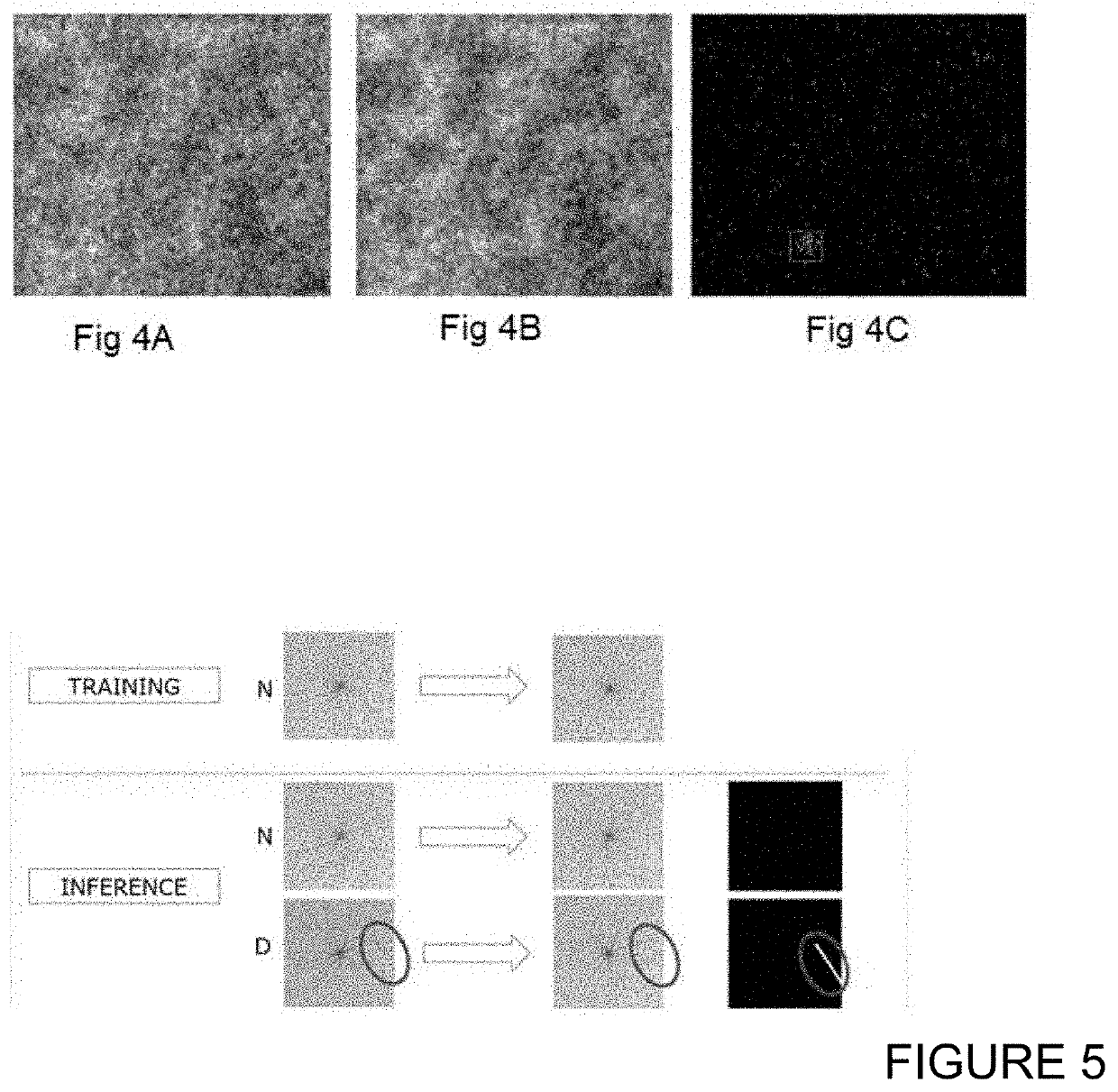
ActiveUS20200364842A1Reduce the cost of trainingLow costImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionPattern recognition
Embodiments include a computer implemented method of processing images of material surfaces to identify defects on the imaged material surface, the method including training a neural network to generate reduced-defect versions of training images of material surfaces; acquiring an image of a subject material surface; inputting the acquired image to the neural network to generate a reduced-defect version of the acquired image; and comparing the reduced-defect version of the acquired image with the acquired image to identify differences. Defects on the subject material surface at locations of the identified differences are identifiable.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Cell assay kit and method
ActiveUS20100311085A1High densityIncreased susceptibilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayCell type
A method and kit for assaying a cell sample for the presence of at least a threshold number of cells of a given type are disclosed. The kit includes an assay device having a sample chamber for receiving the cell sample and an elongate collection chamber containing a selected-density and / or viscosity medium and having along its length, a plurality of cell-collection regions, and particles which are capable of specific attachment to cells of the selected cell type, and which are effective, when attached to the cells, to increase the density or magnetic susceptibility of the cells. In operation, particle-bound cells and particles in the cell sample are drawn through the elongate collection chamber under the influence of a gravitational or selected centrifugal or magnetic-field force until the particle-bound cells and particles completely fill successive cell-collection regions in the collection chamber. Indicia associated with at least one collection regions indicates a concentration of cells of the selected type effective to at least partially fill that collection region.
Owner:STEMCELL TECH CANADA INC
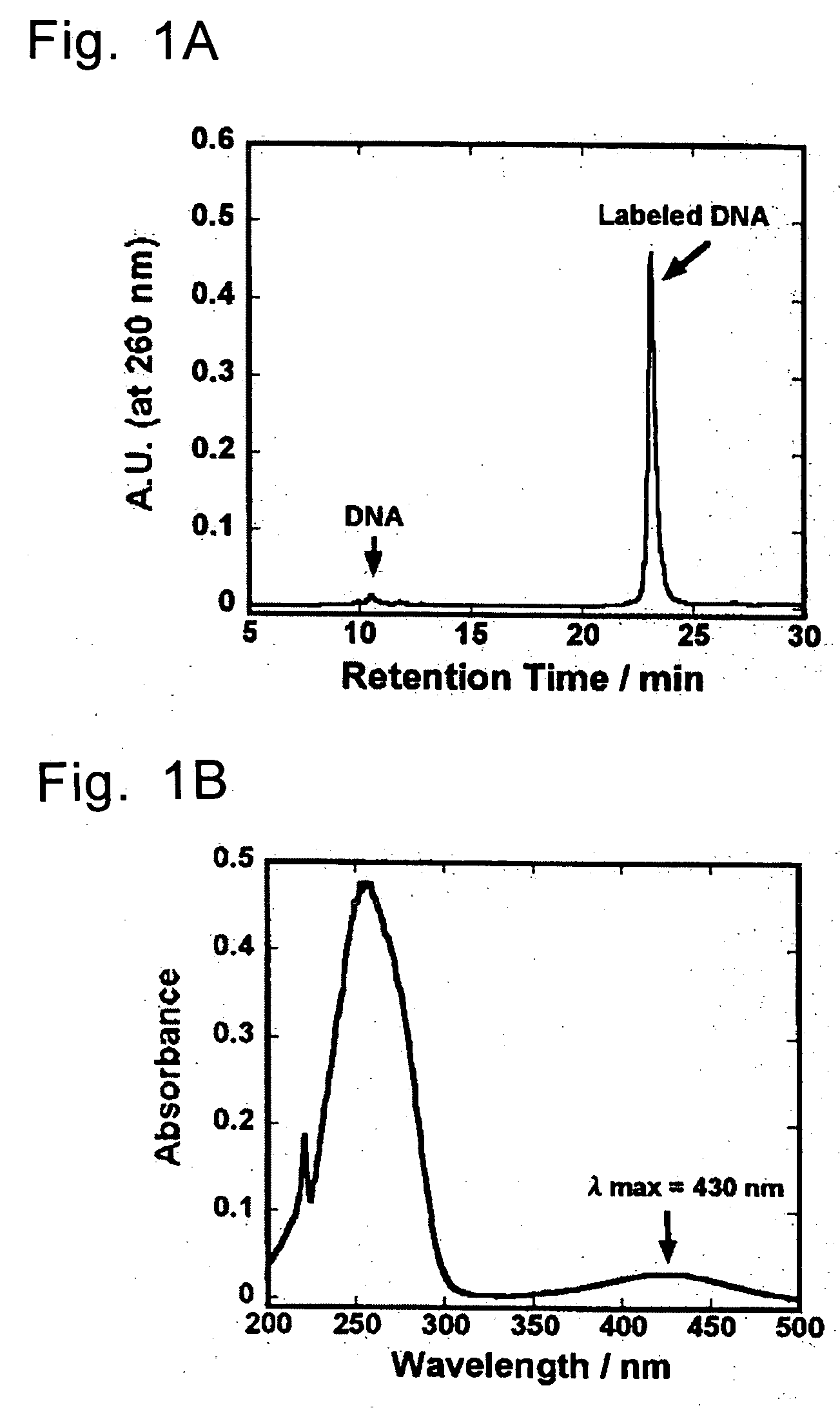
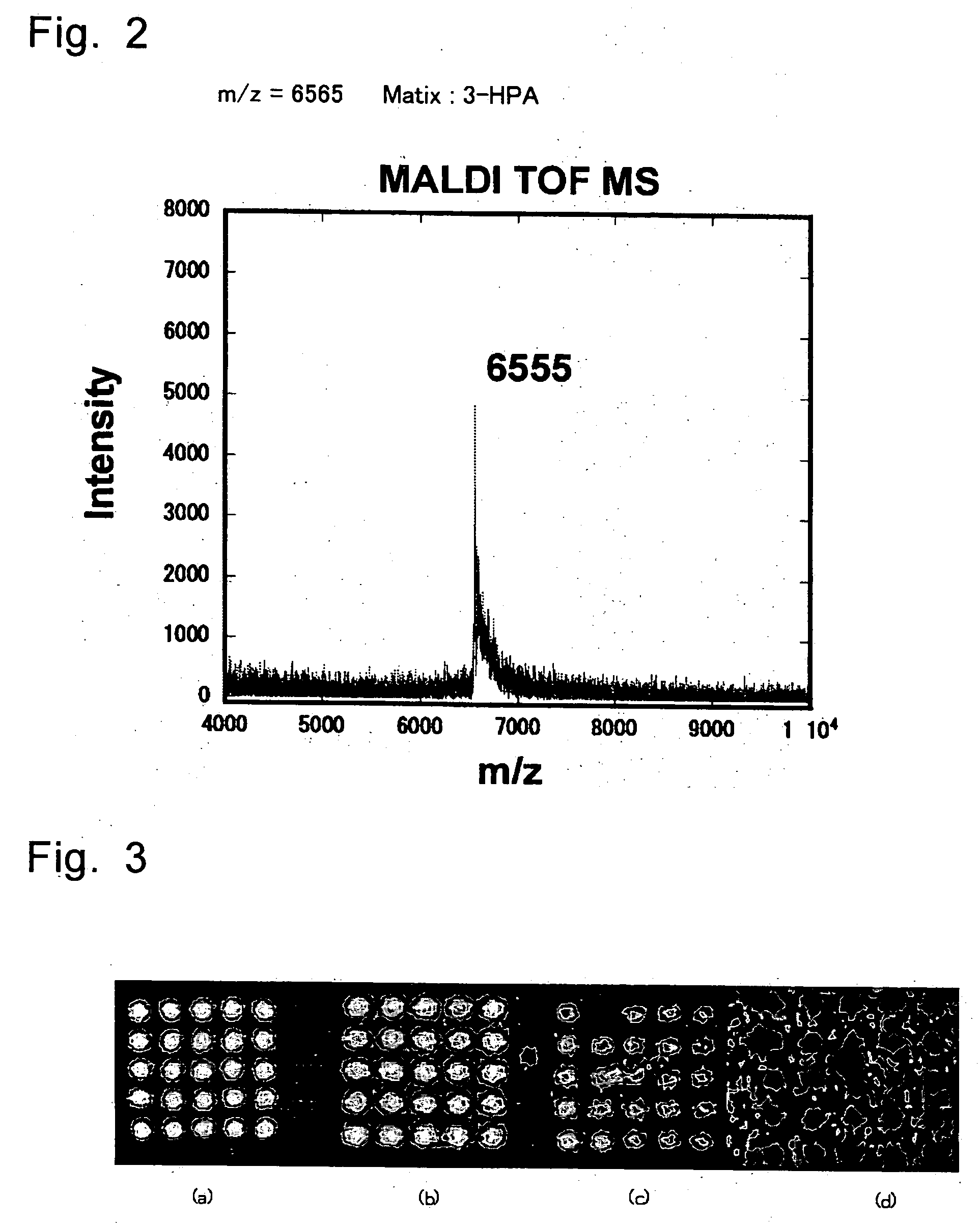
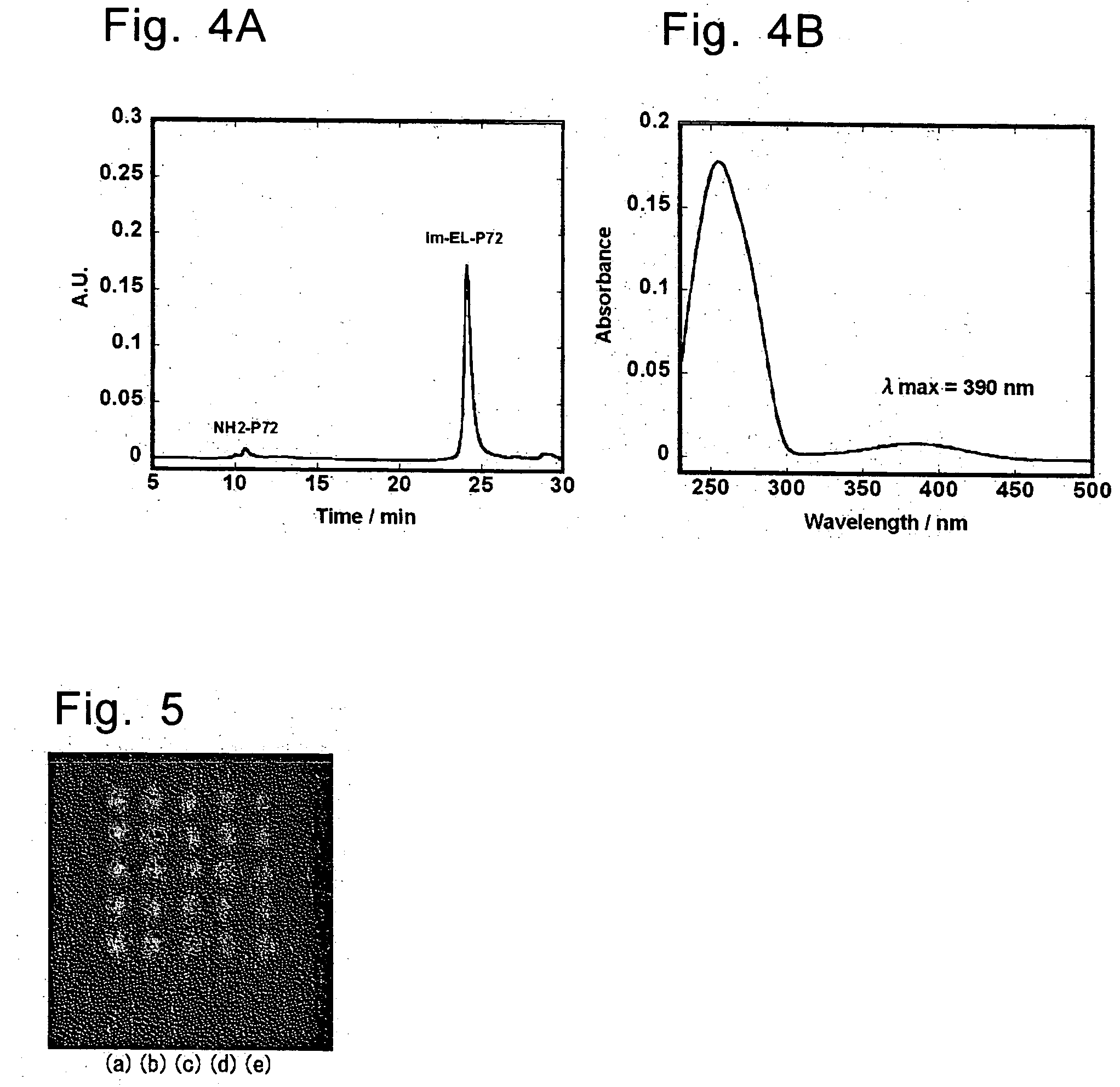
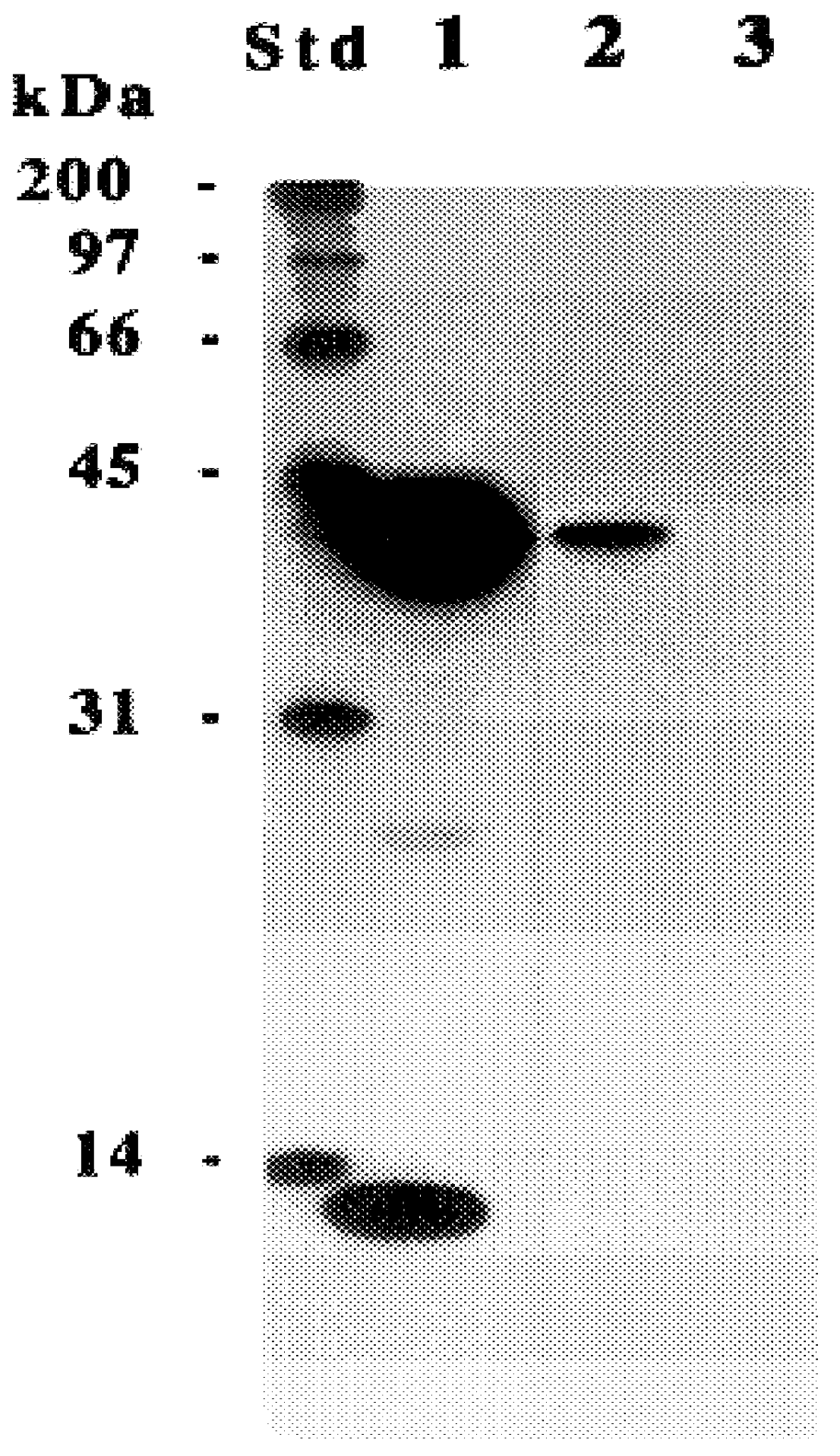
Method of detecting biological molecules, and labeling dye and labeling kit used for the same
InactiveUS20050181380A1High fluorescence intensityLow costSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceOrganic dye
The present invention provides a method of detecting a biological molecule. The method includes reacting a biological molecule sample with an organic EL-dye and measuring the fluorescence of the biological molecule sample labeled with the organic EL-dye. The method provides a highly sensitive method of detecting a biological molecule at lower cost.
Owner:SHINCHIRO ISOBE
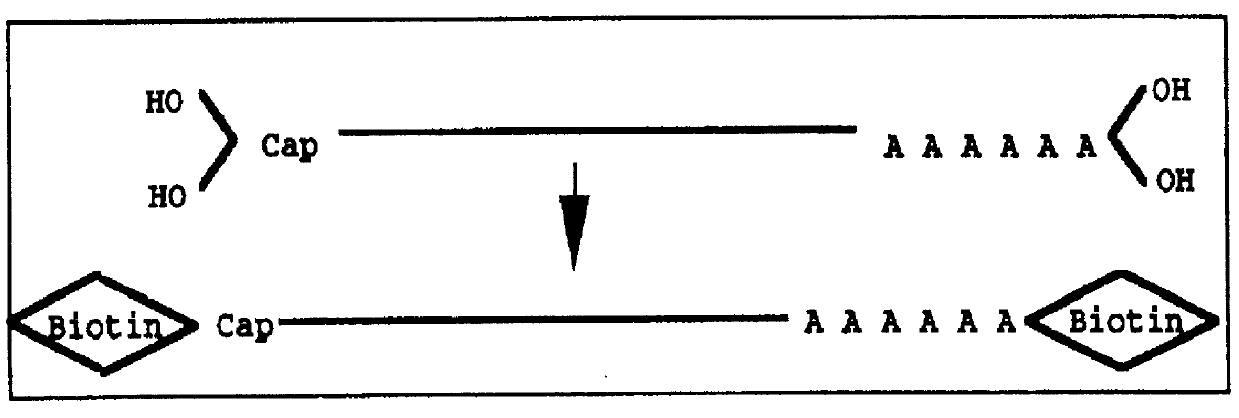
Affinity biotinylation
InactiveUS6150123AEfficiently labeledDrawback can be obviatedEnzymologyDepsipeptidesProtonCombinatorial chemistry
The present invention relates to a method for biotinylating a desired subset of a larger population of proteins, wherein the subset of proteins is first selectively bound to a solid phase, thereby separating it from undesired proteins of the population, and then, still bound to solid phase, it is biotinylated. Unreacted biotin may then be washed from the solid phase, and the biotinylated protein may be uncoupled from the solid phase.
Owner:FOND MONDIALE RES & DEV & PREVENTION SIDA
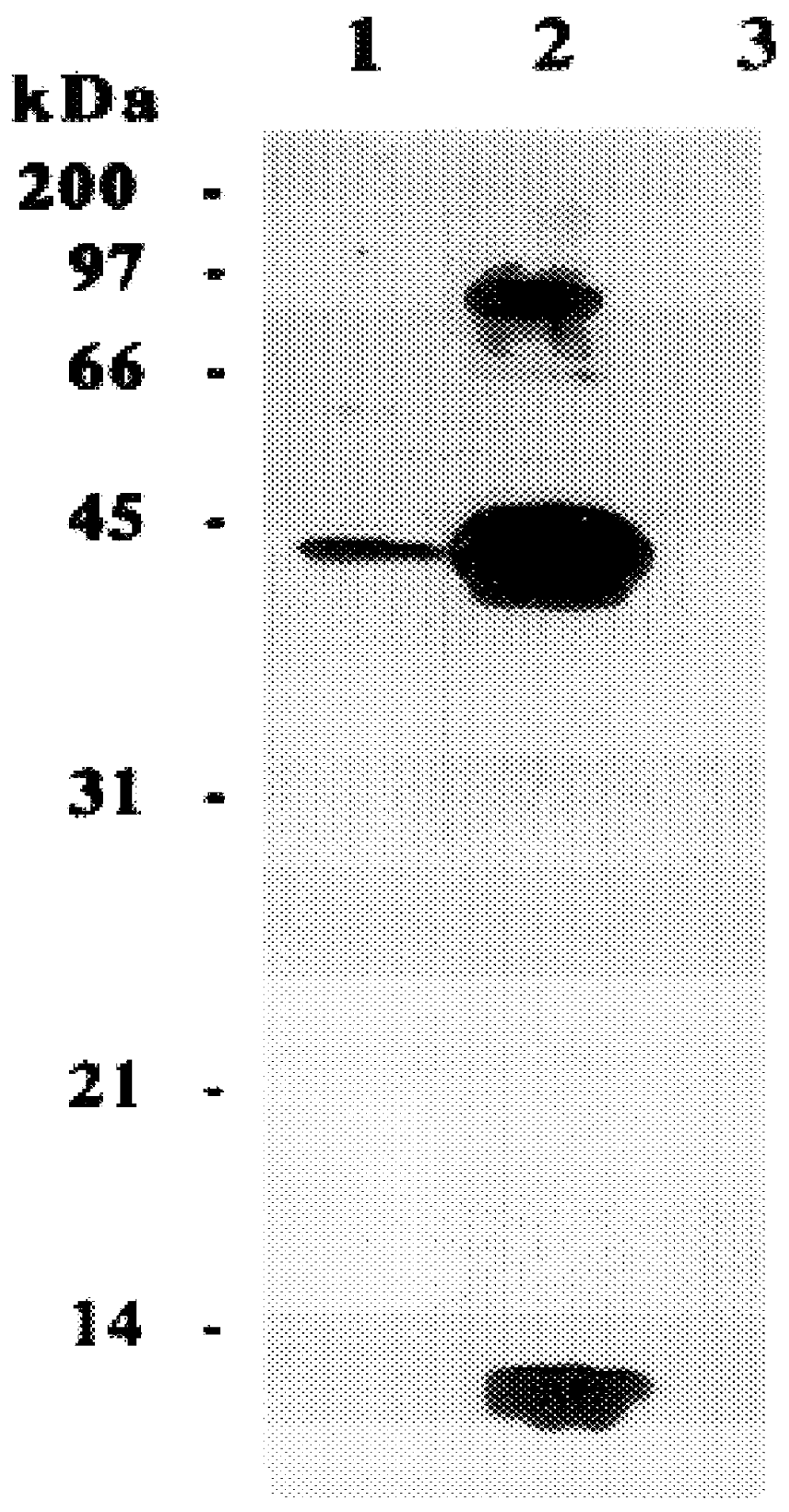
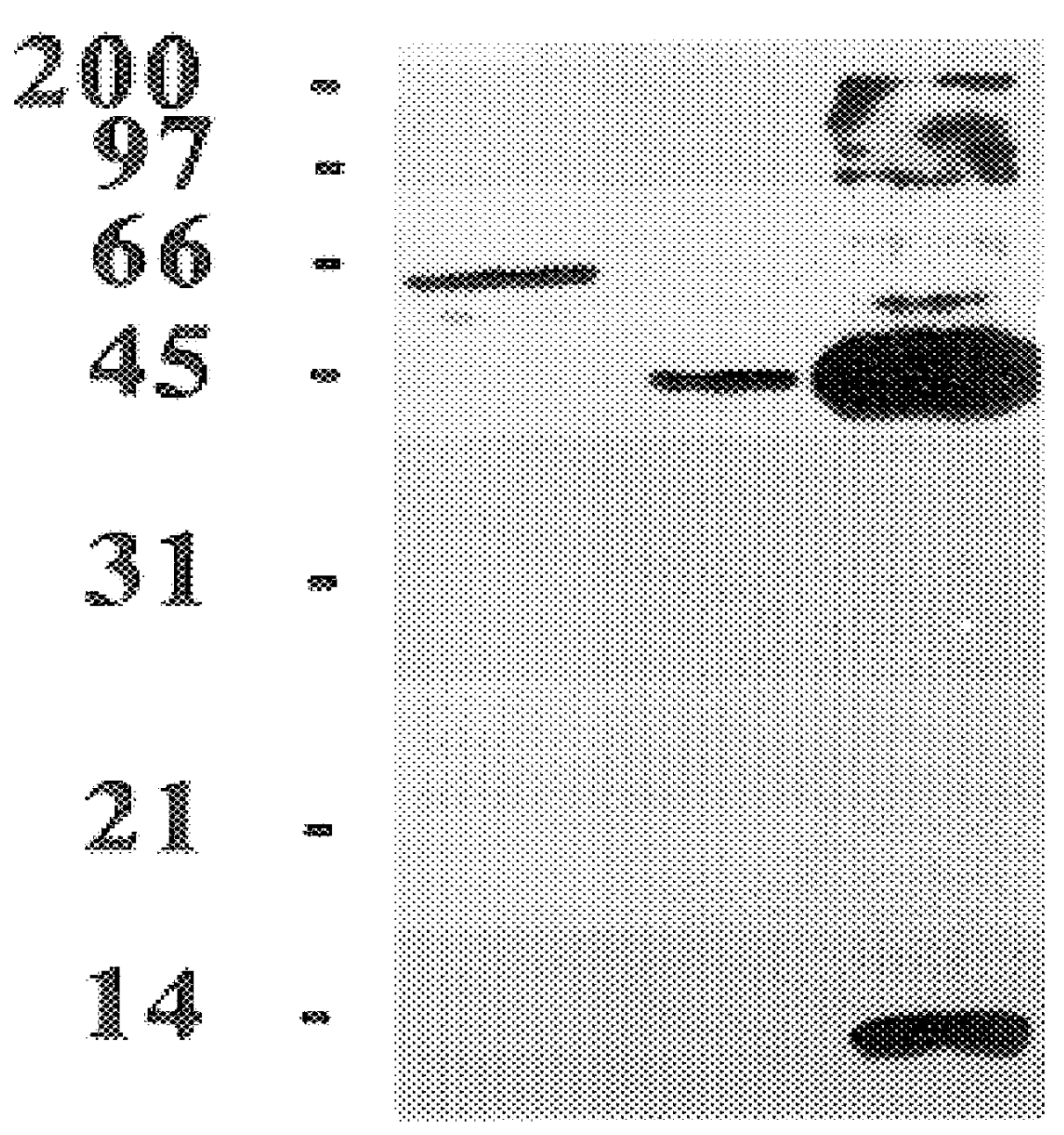
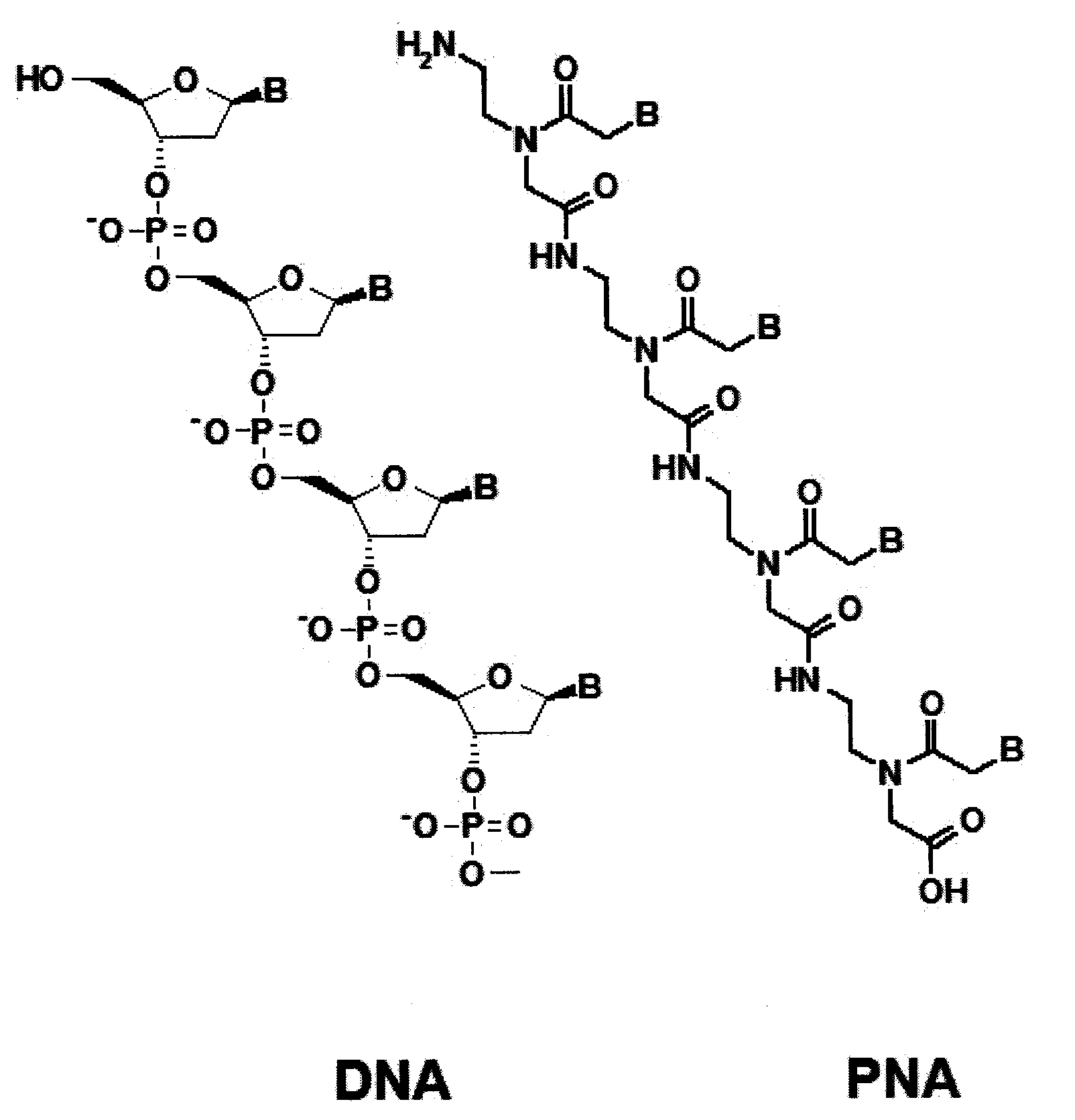
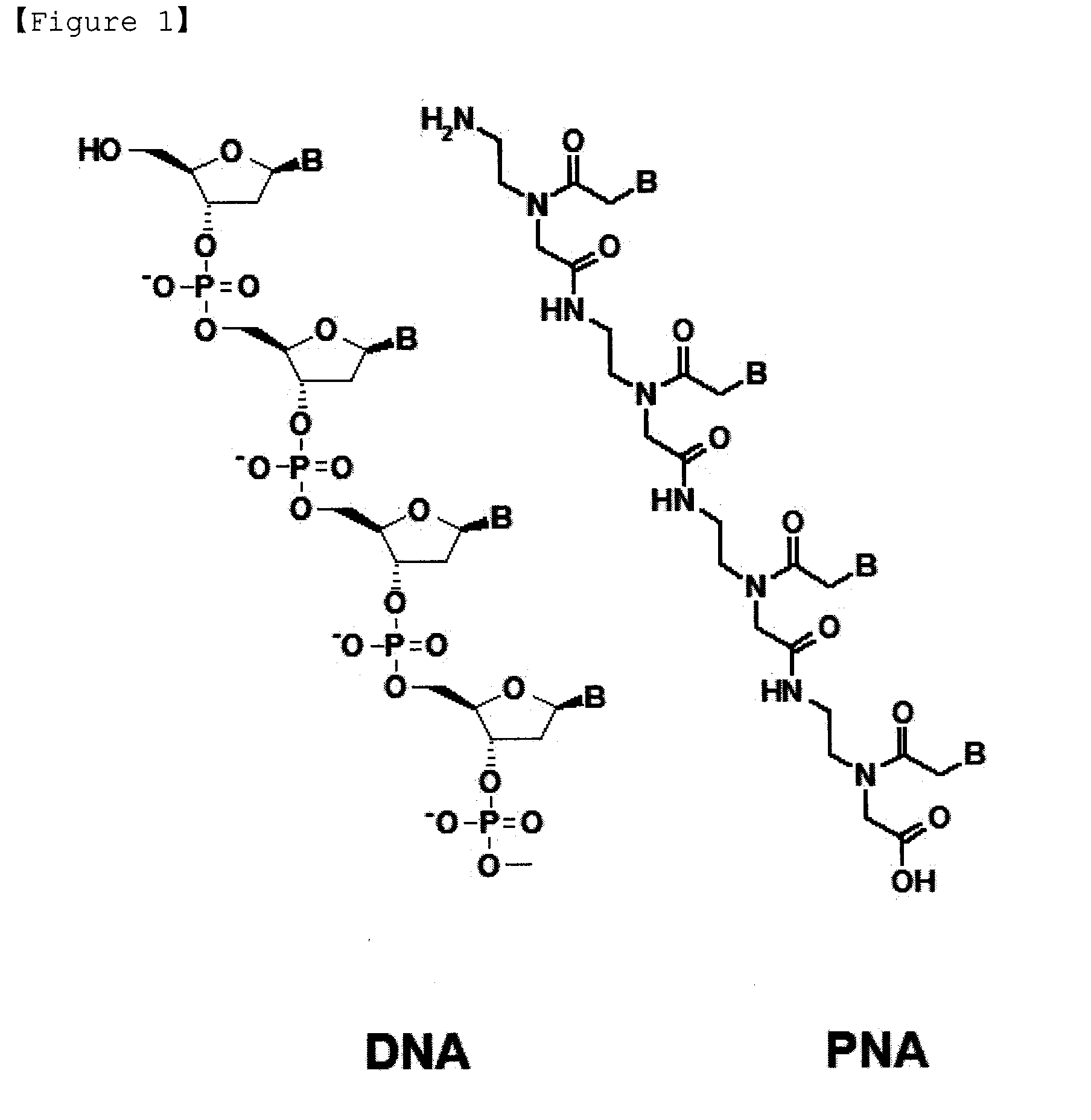
Method for Selective Labeling and Detection of Target Nucleic Acids Using Immobilized Peptide Nucleic Acid Probes
InactiveUS20100248980A1Raise the ratioStrong specificityLibrary tagsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesNucleic acid analogue
Disclosed are a method for selective labeling of target nucleic acids on an array having nucleic acid analogue, e.g. PNA (peptide nucleic acid), probes immobilized on a support or supports, comprising adding to the array a detectable label and an agent for introducing the label into the target nucleic acids, after hybridization between the target nucleic acids and the nucleic acid analogue probes, and a method for detection of target nucleic acids using the same.
Owner:PANAGENE INC
Method of detecting biological molecules, and labeling dye and labeling kit used for the same
InactiveUS7015002B2Low costSensitive highSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceOrganic chemistry
The present invention provides a method of detecting a biological molecule. The method includes reacting a biological molecule sample with an organic EL-dye and measuring the fluorescence of the biological molecule sample labeled with the organic EL-dye. The method provides a highly sensitive method of detecting a biological molecule at lower cost.
Owner:SHINCHIRO ISOBE
Labeling system and method
InactiveUS20070244934A1Avoid troubleManagement of developmentBootstrappingSpecial data processing applicationsElectronic systemsComputer science
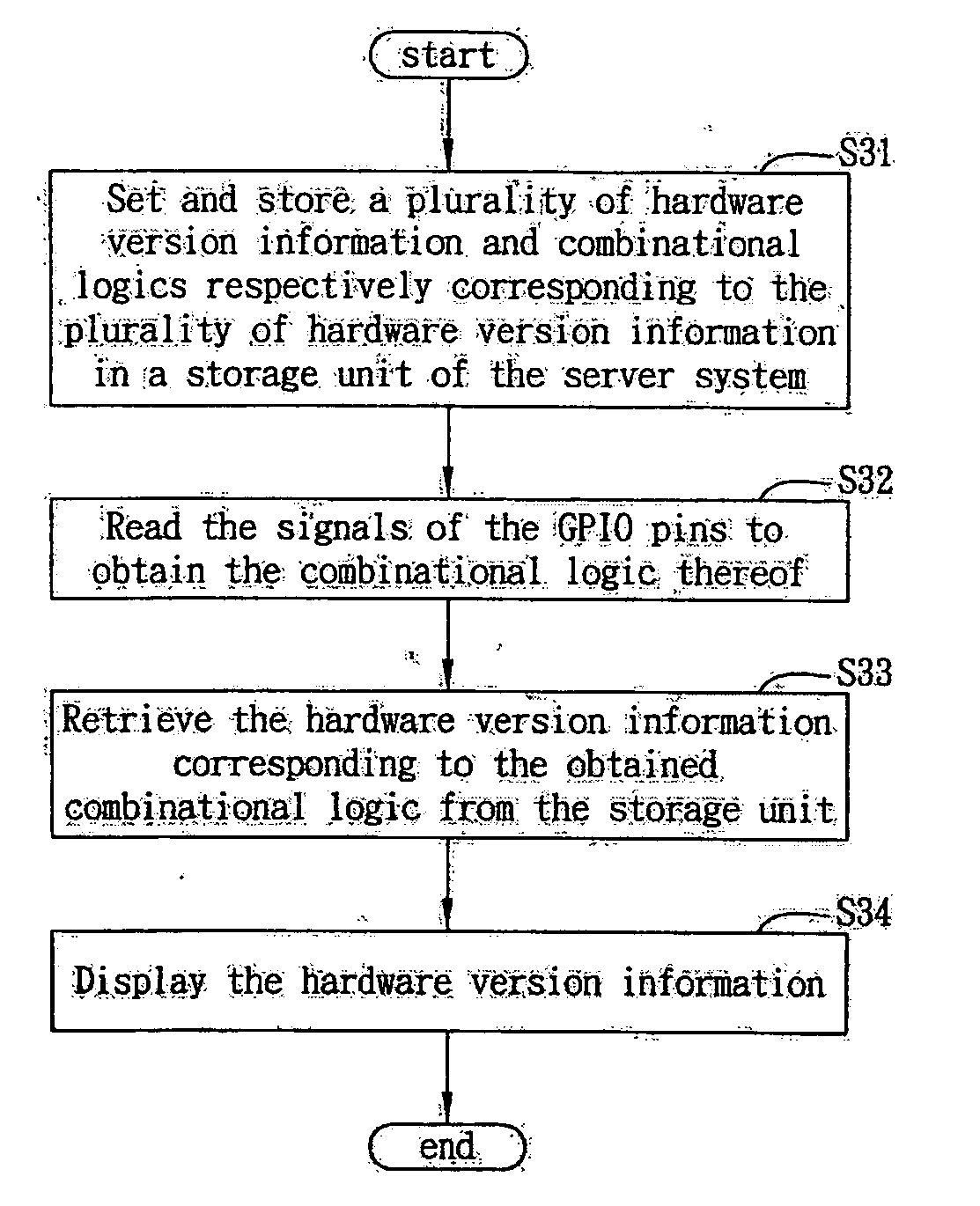
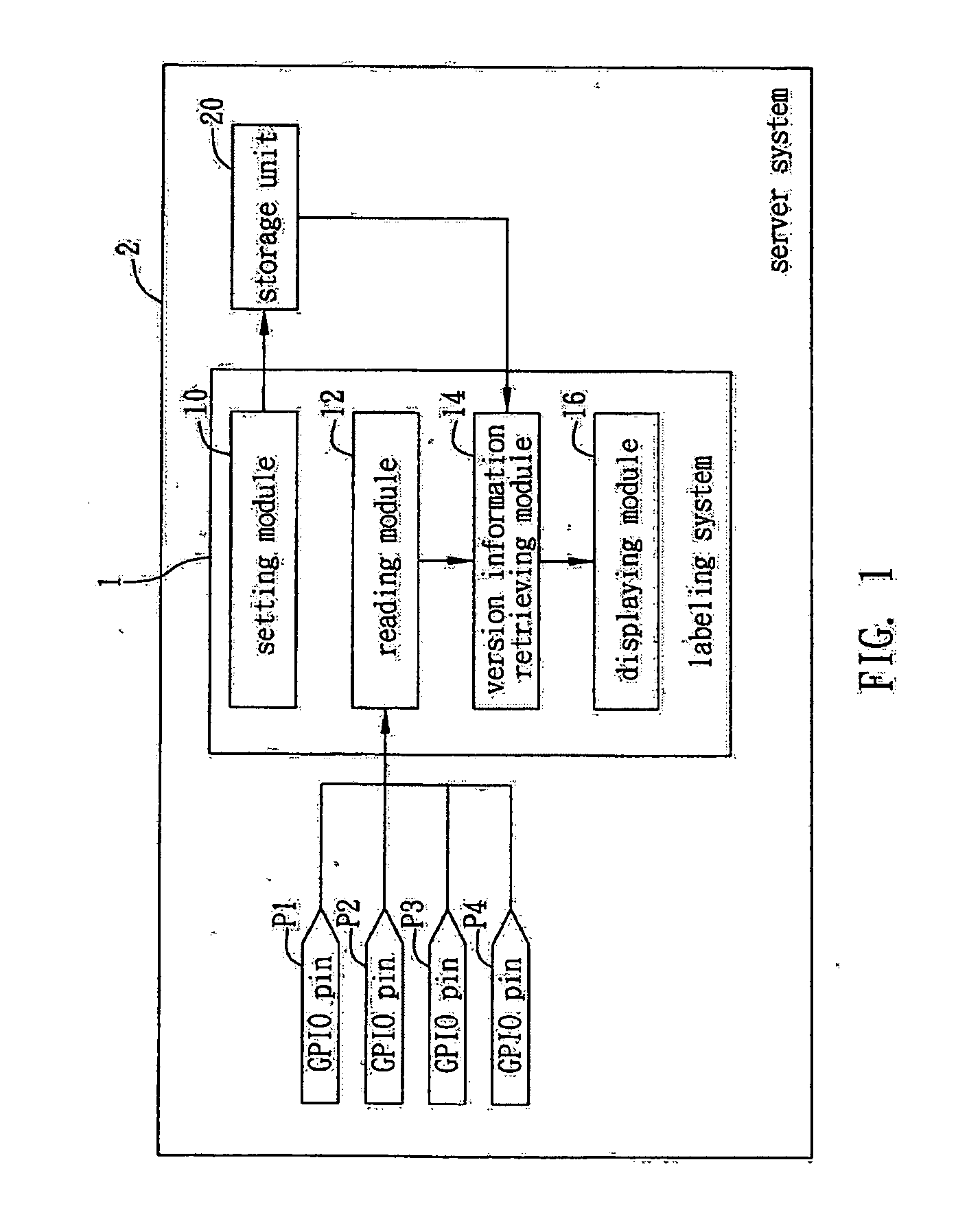
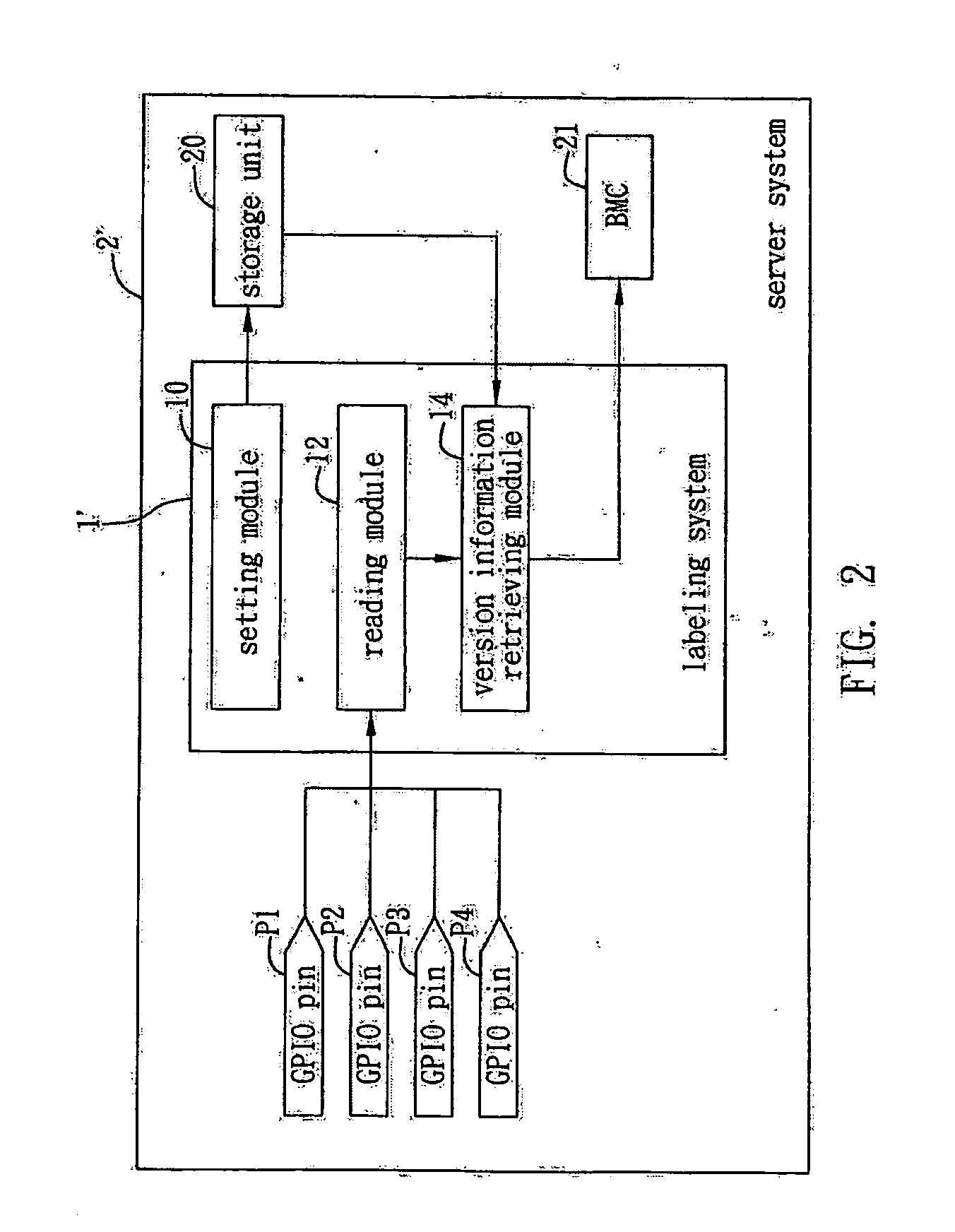
A labeling system and method applicable to an electronic system with a storage unit and General Purpose Input / Output (GPIO) pins is proposed. First, a setting module sets a plurality of hardware version information and combinational logics of the GPIO pins each corresponding to a different hardware version information, and stores the contents being set in the storage unit of the server system, so that the combinational logics of signals of the GPIO pins can then be read by a reading module and the corresponding hardware version information can be retrieved by a version information retrieving module, thereby allowing fast and easy determination of the current hardware version of the electronic system.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
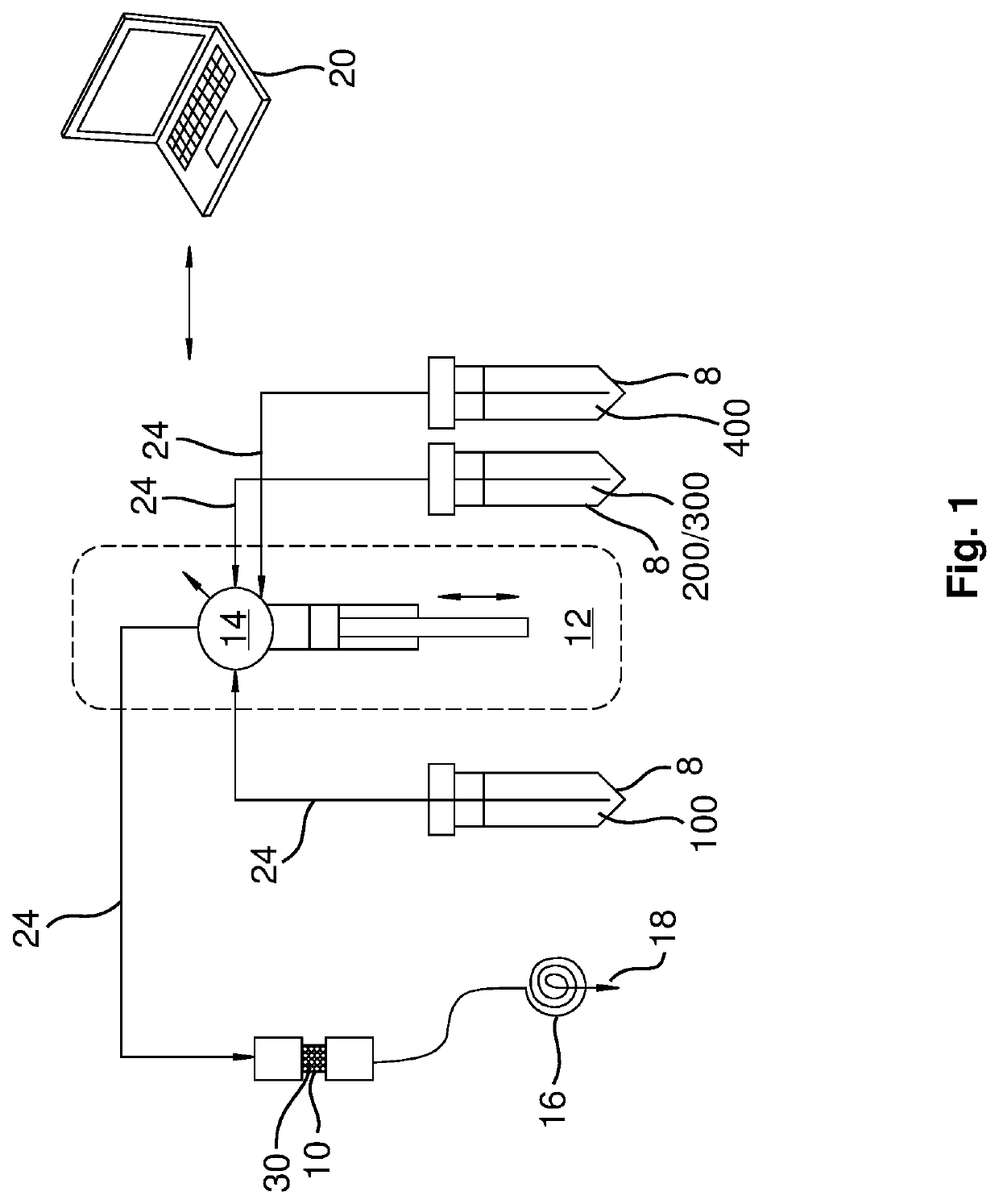
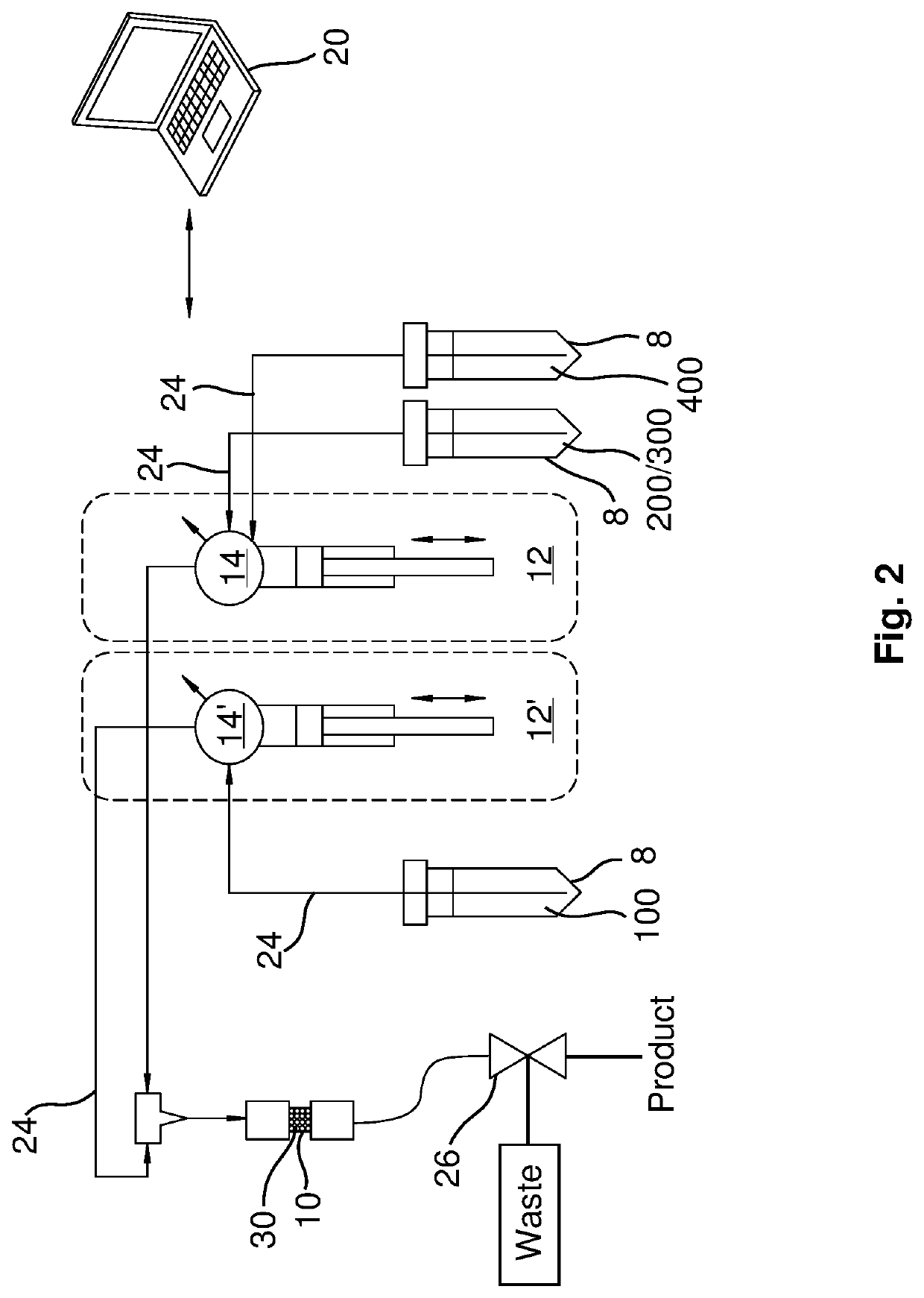
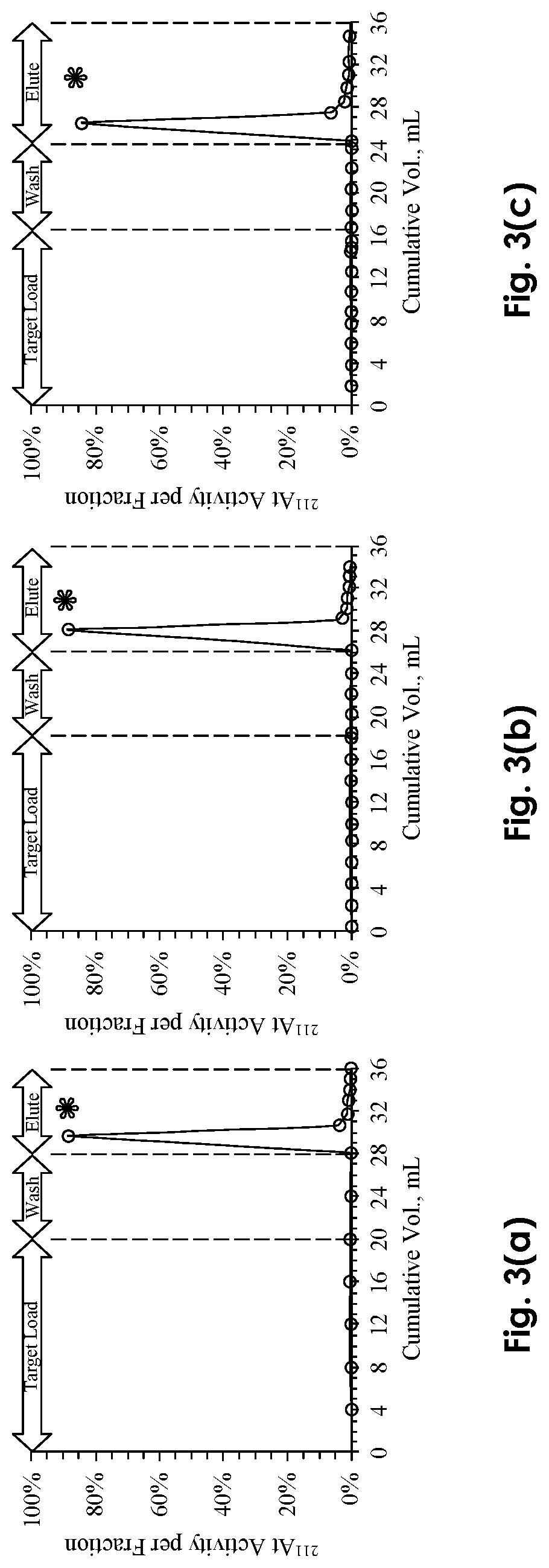
System and process for purification of astatine-211 from target materials
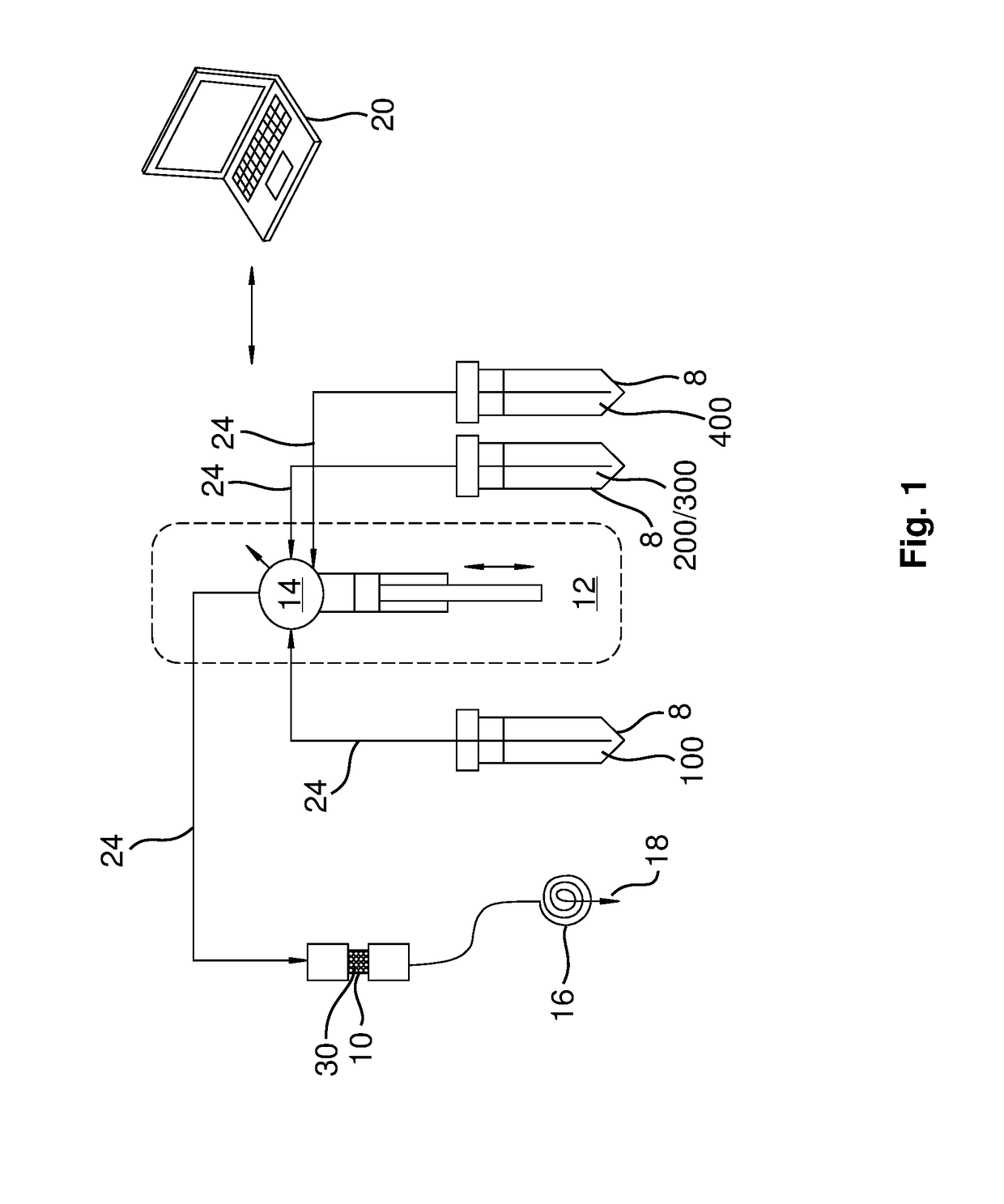
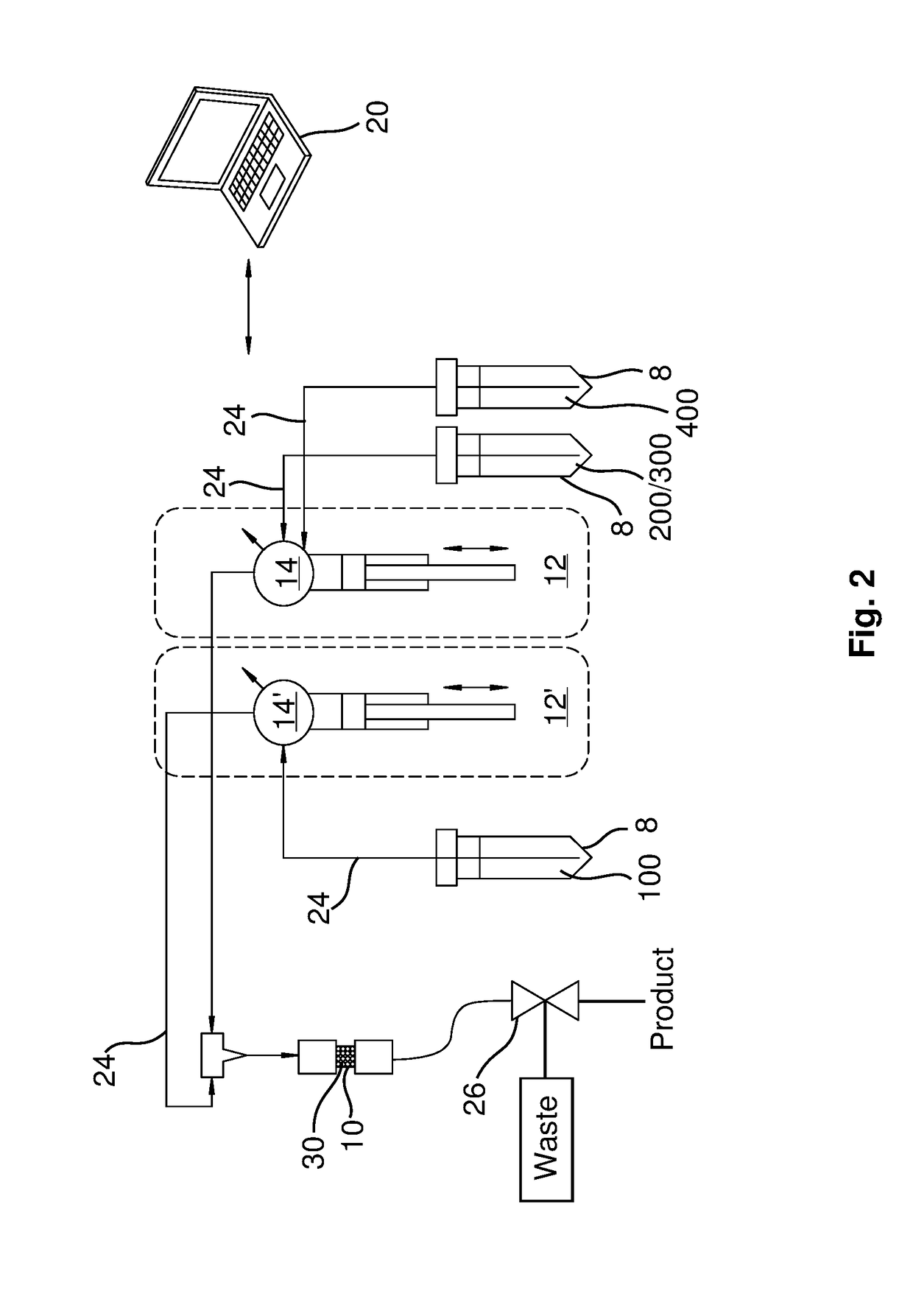
ActiveUS20180308599A1Processing be lowerReduce preparation timeSpecific isotope recoveryIn-vivo radioactive preparationsAntibody labelingAstatine
A new column-based purification system and approach are described for rapid separation and purification of the alpha-emitting therapeutic radioisotope 211At from dissolved cyclotron targets that provide highly reproducible product results with excellent 211At species distributions and high antibody labeling yields compared with prior art manual extraction results of the prior art that can be expected to enable enhanced production of purified 211At isotope products suitable for therapeutic medical applications such as treatment of cancer in human patients.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Container labeling systems and methods of use
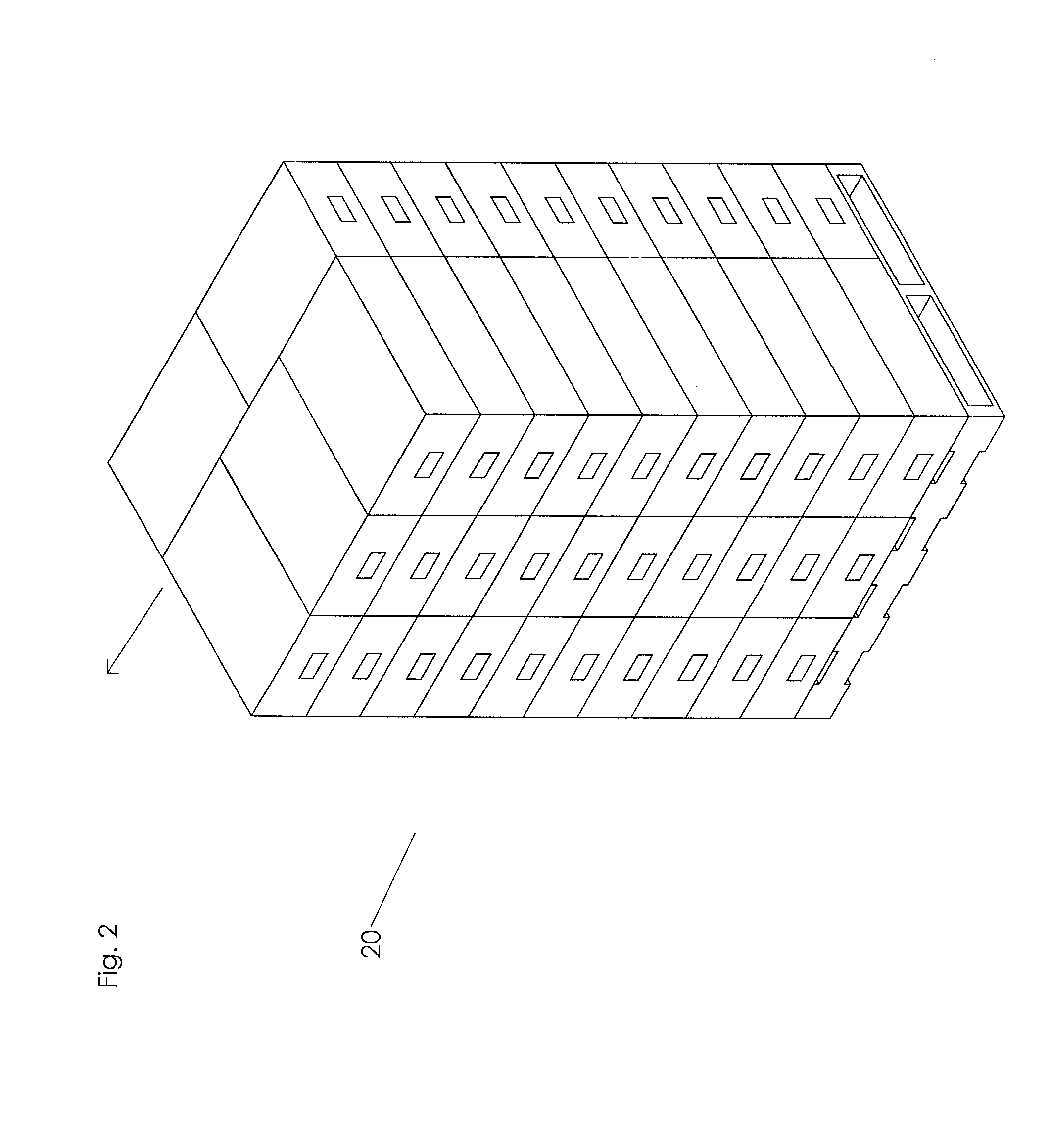
ActiveUS9440759B2Laborious and time-consumingEfficient importTypewritersPackaging automatic controlEngineeringPallet
The invention relates to labeling and / or printing devices, methods and systems for applying coding and / or labeling to containers that are stacked or otherwise organized in a group (e.g., containers stacked on a pallet). In embodiments of the invention, labeling and / or printing devices are mounted on carriages that are capable of moving in a vertical direction to apply labels as they move. Horizontal movement is imparted either by moving such carriages in a horizontal direction adjacent to the containers, or by moving the containers themselves (or the pallet holding them) in a horizontal direction adjacent to such carriages. Multiple carriages with labeling devices may be provided to provide simultaneous labeling to more than one side of a group of stacked containers. Embodiments of the invention are capable of providing labeling of containers that are uniformly or non-uniformly grouped or stacked.
Owner:REED LORIN
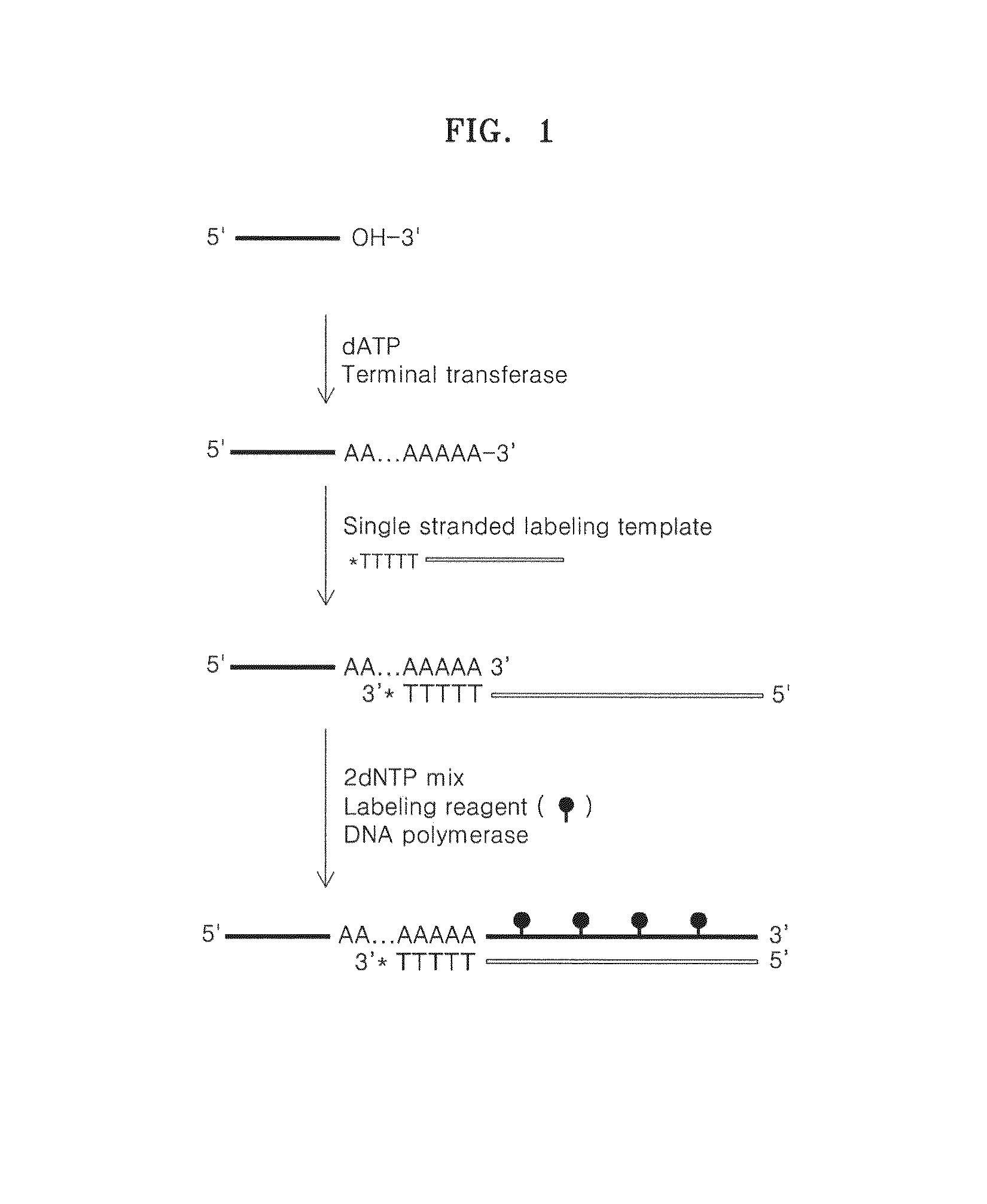
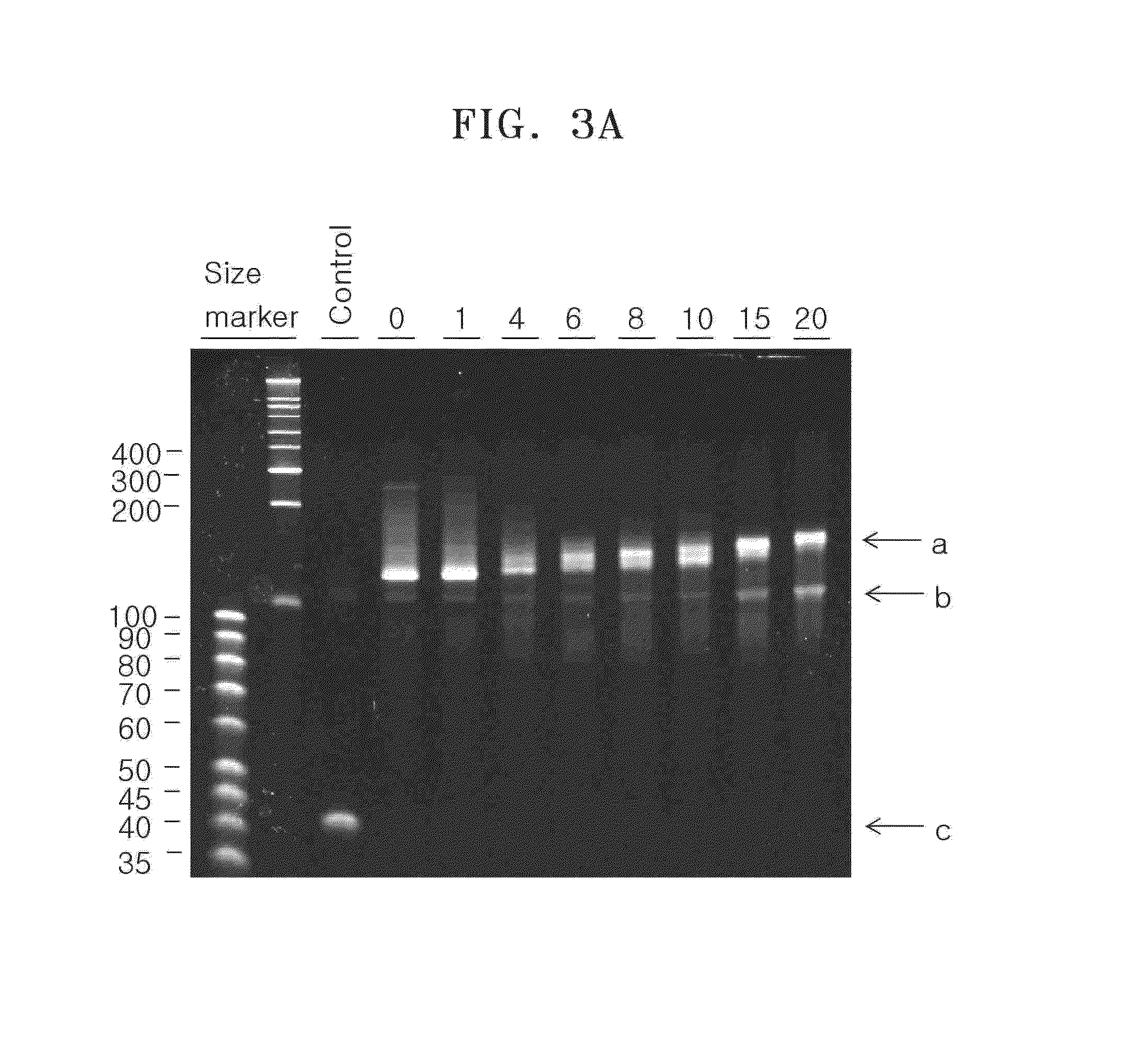
Method of labeling a target nucleic acid
ActiveUS20140147840A1Efficiently labeledEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescencePolymerase LNucleotide sequencing
Methods of labeling and detecting a target nucleic acid by incubating a target nucleic acid with a terminal transferase to extend a terminus of the target nucleic acid and provide an extended region; hybridizing the extended region of the target nucleic acid with a template polynucleotide having a nucleotide sequence complementary to the extended region to obtain a hybridization product; and incubating the hybridization product with a nucleic acid polymerase and either a deoxynucleotide triphosphate (dNTP) having a detectable label or nucleotide triphosphate (NTP) having a detectable label to further extend the extended target nucleic acid.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
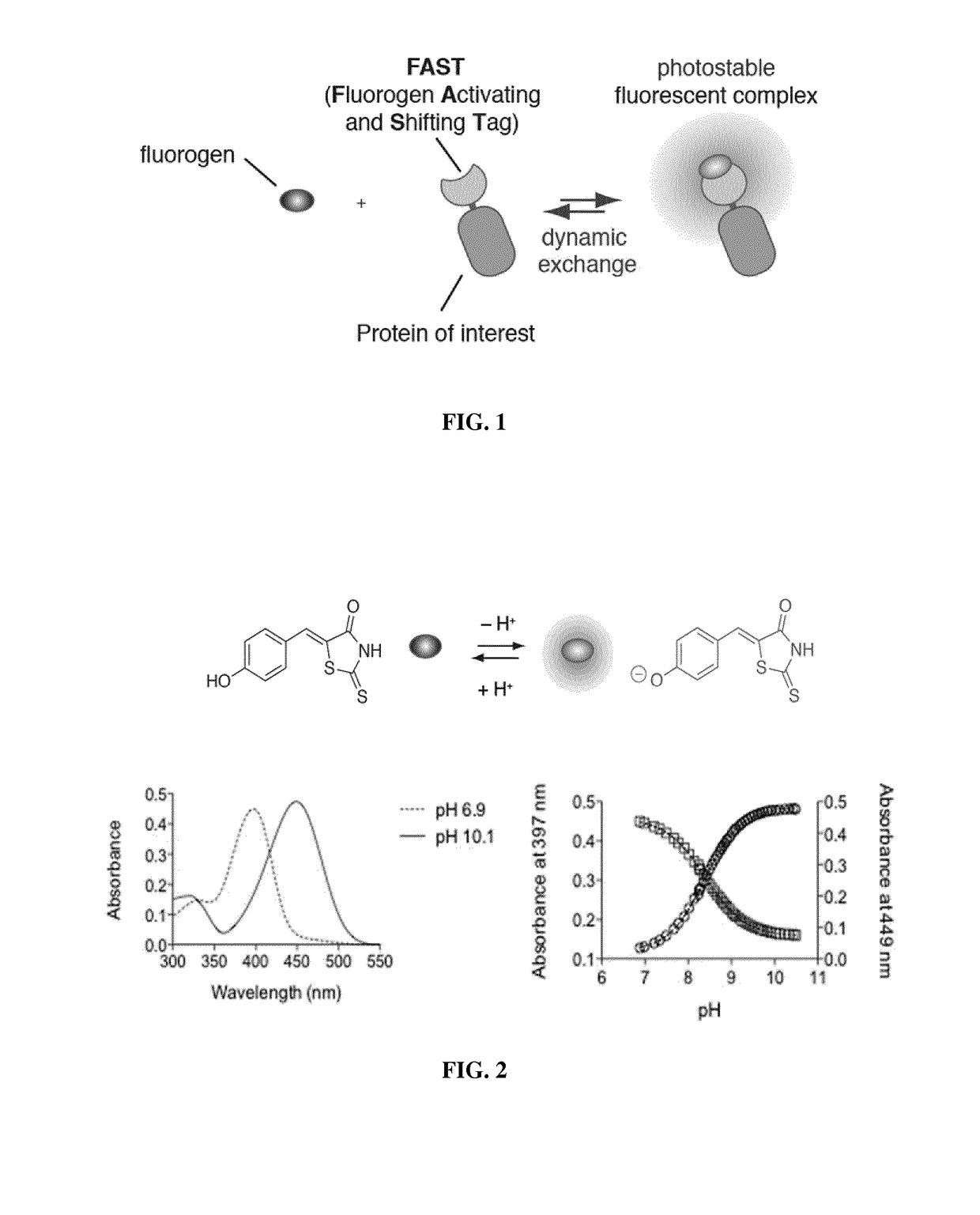
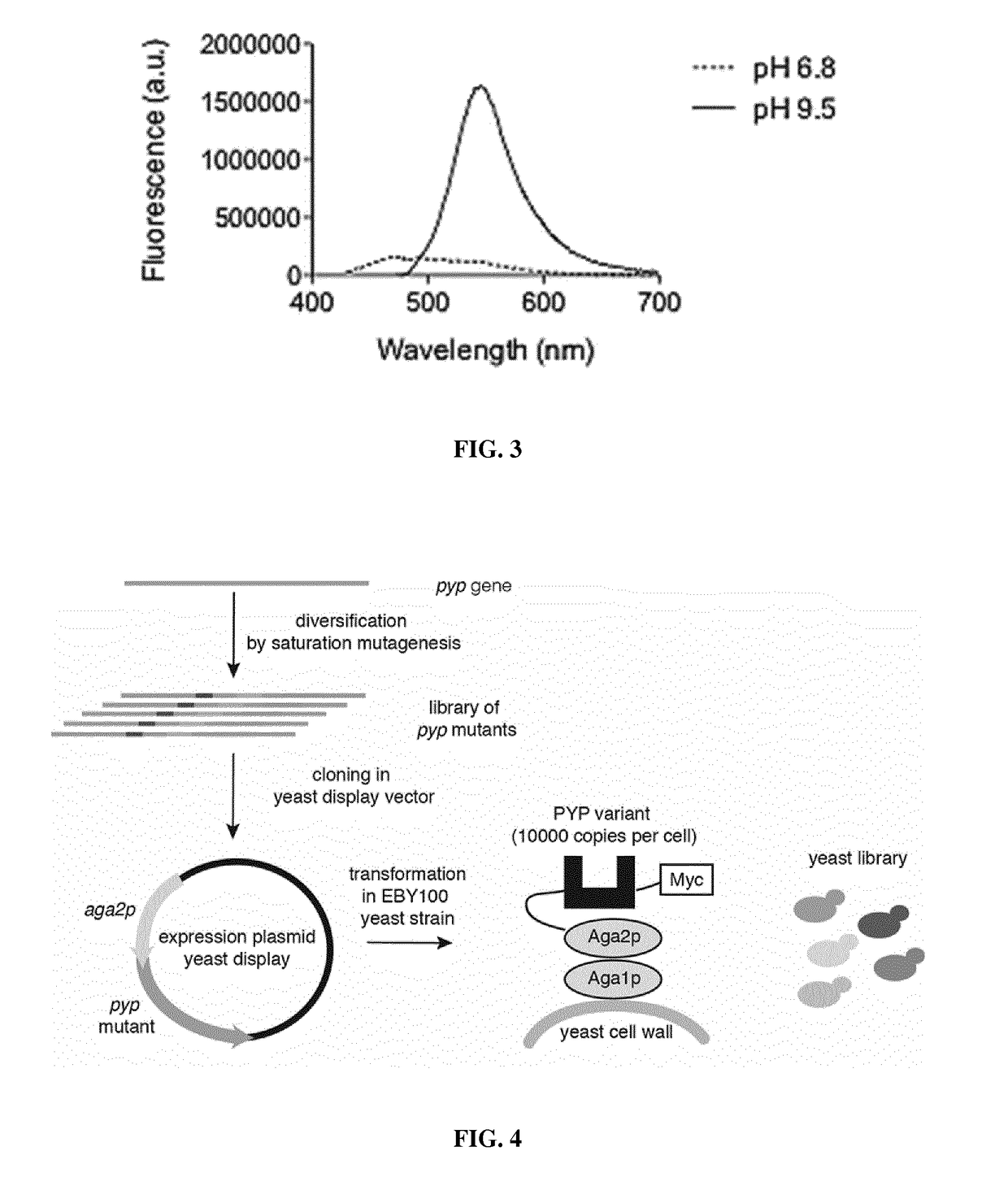
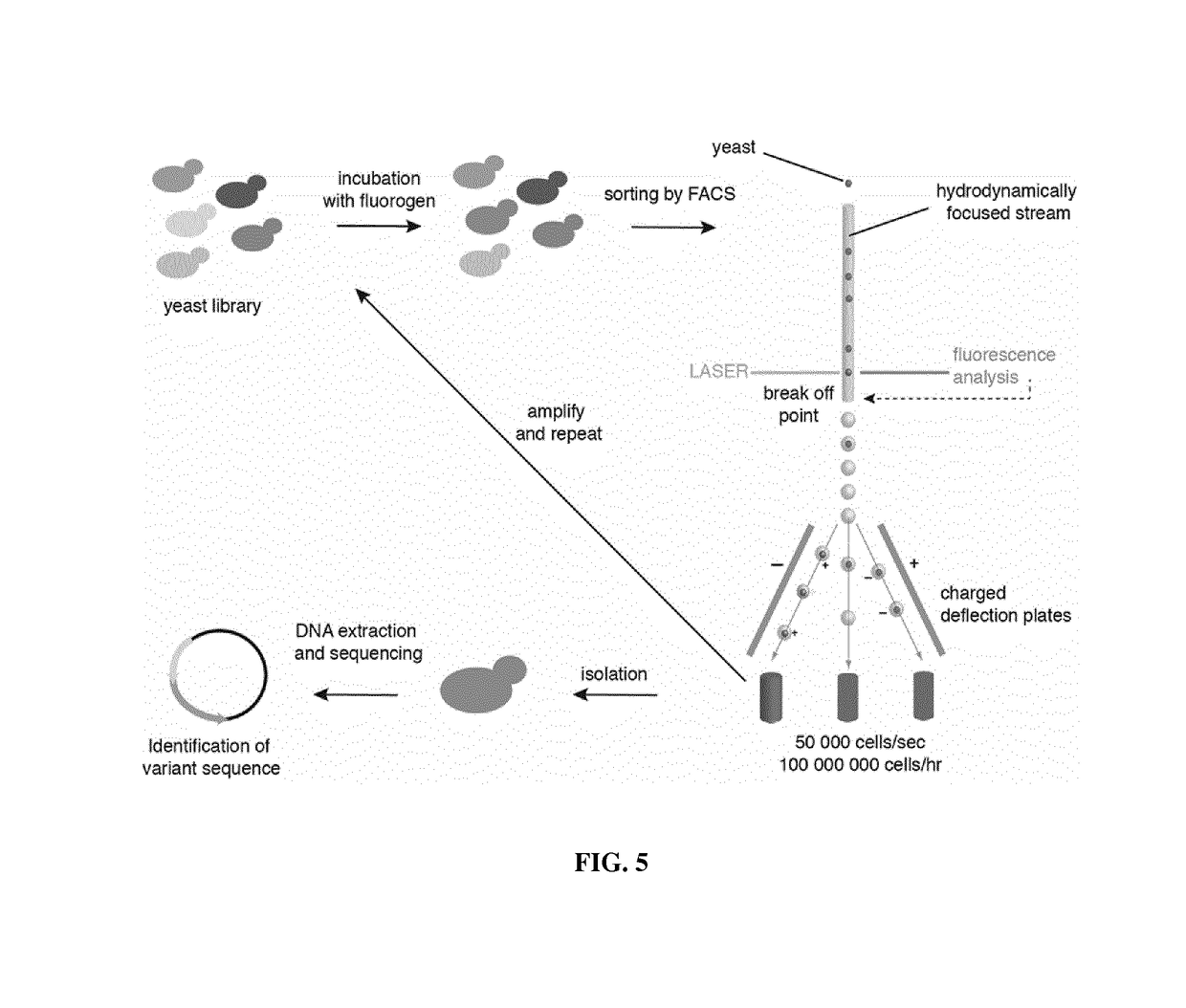
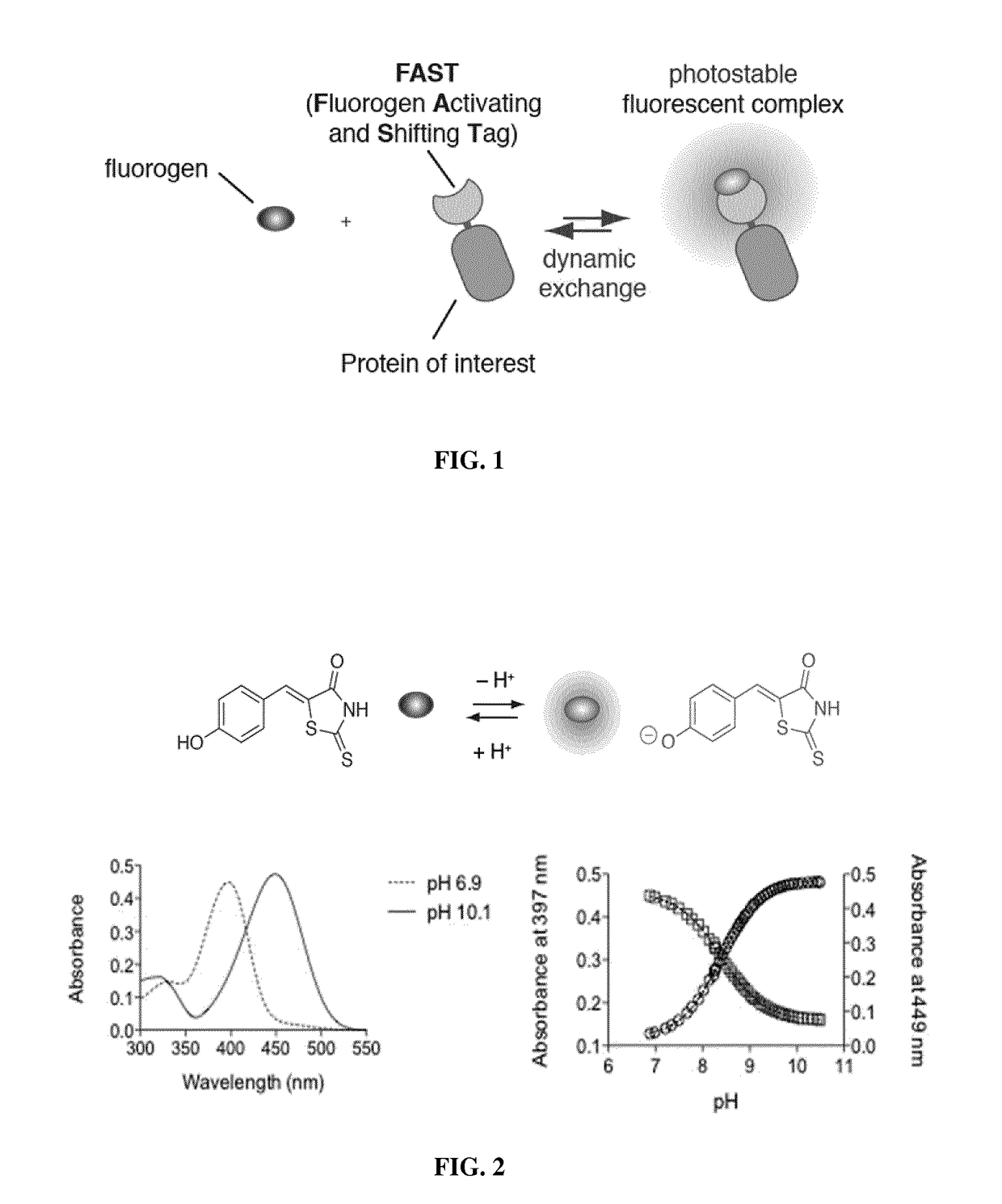
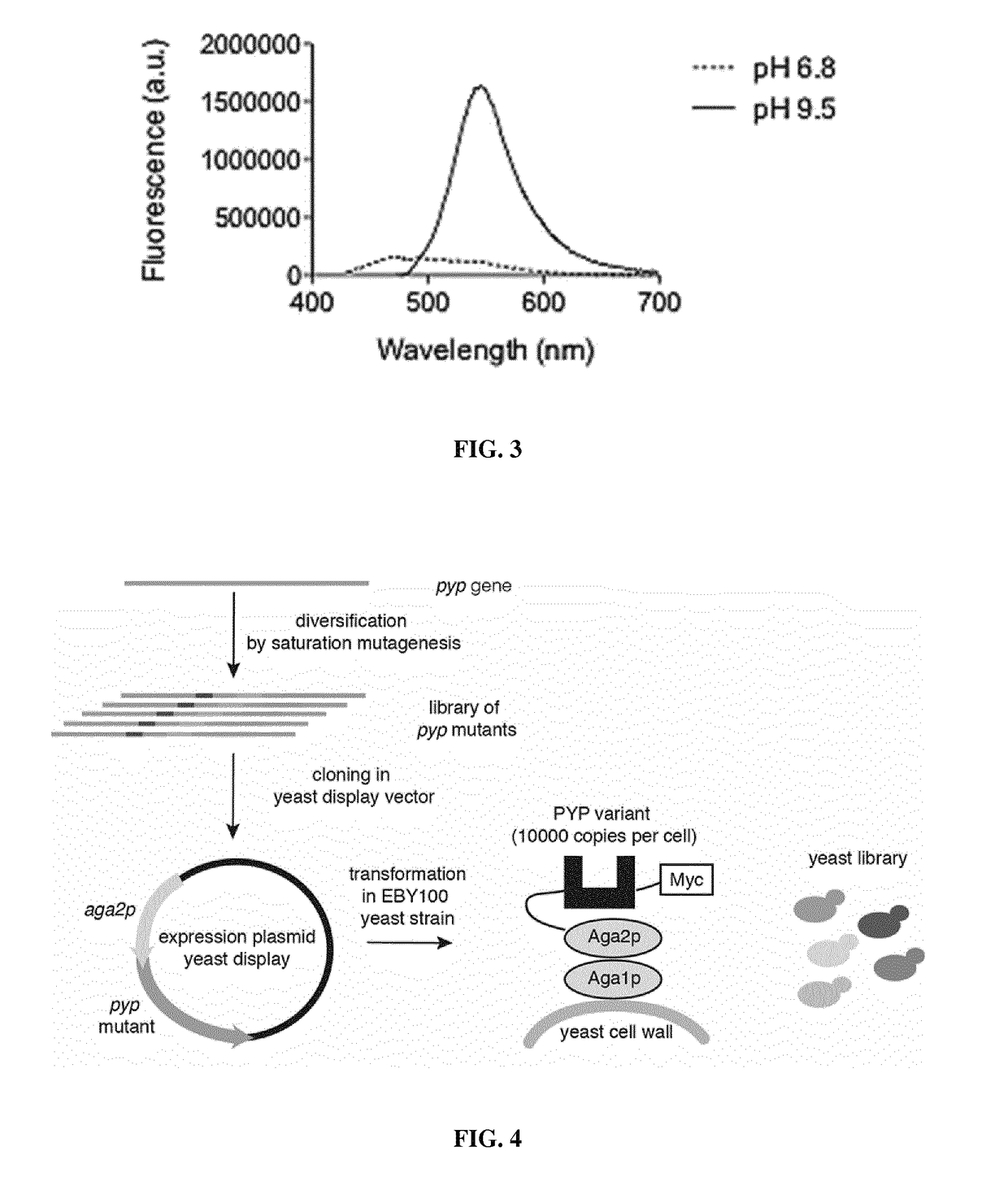
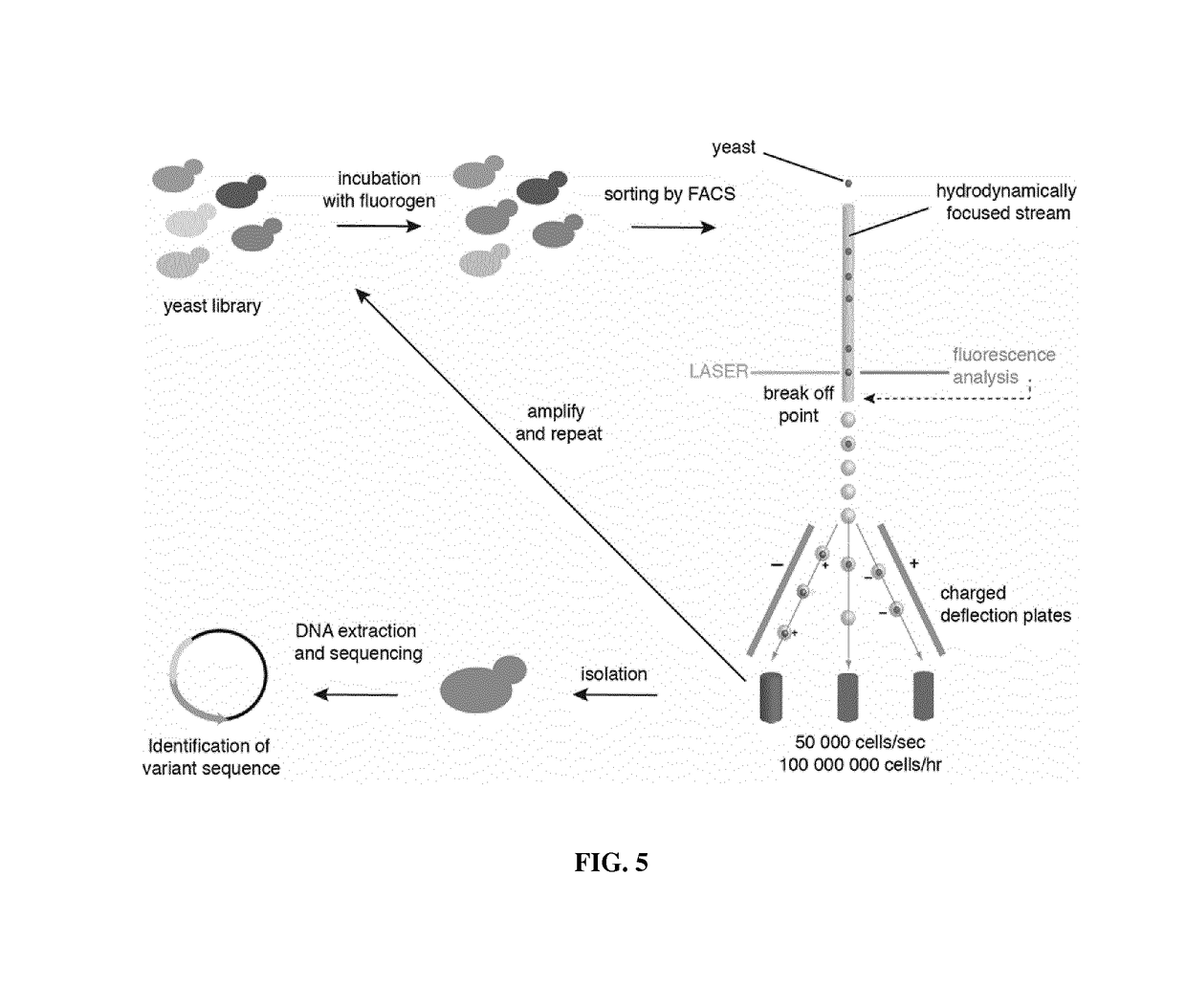
Fluorogen activating and shifting tag (FAST)
ActiveUS20170137473A1Increase brightnessEfficiently labeledBacteria peptidesBiological testingPhotoactive yellow proteinIonization
Disclosed is a functional derivative of a Photoactive Yellow Protein (PYP), or a functional fragment thereof, for fluorescently labelling particles, e.g. proteins, or surfaces, which is capable of binding reversibly a fluorogenic chromophore of formula (I), and which is capable of enhancing the brightness of the fluorogenic chromophore upon complexation thereto; and of inducing the spectral shift of the fluorogenic chromophore through the ionization of an auxochromic group thereof.
Owner:PARIS SCI & LETTRES +2
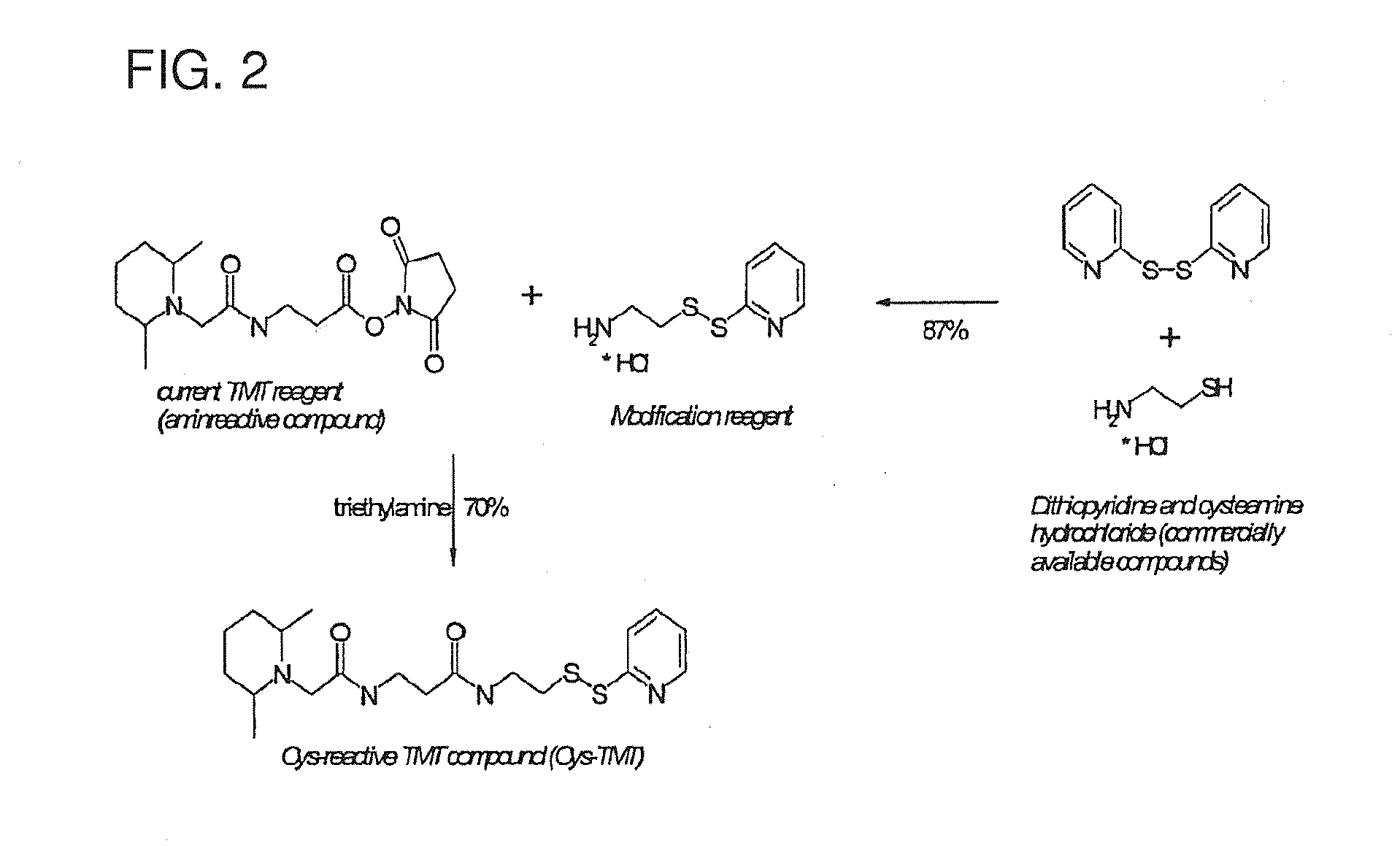
Mass labels
ActiveUS20120283137A1High selectivityRaise the pHIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsMicrobiological testing/measurementChemistryCarbonyl group
A reactive mass label for labelling a biological molecule for detection by mass spectrometry, which label comprises a reactive functionality for labelling thiol groups or carbonyl groups. Also provided is a reactive mass label for labelling a biological molecule for detection by mass spectrometry, wherein the mass label comprises the following structure:X-L-M-S-Rewherein X is a mass marker moiety, L is a cleavable linker, M is a mass normalization moiety, S is a mass series modifying group comprising the following group:wherein J is C═O, K is NH, and n is 2 or J and K are both CH2 and n is 1, and wherein m is at least 1; and Re is a reactive functionality for attaching the mass label to a biological molecule.
Owner:ELECTROPHORETICS LTD
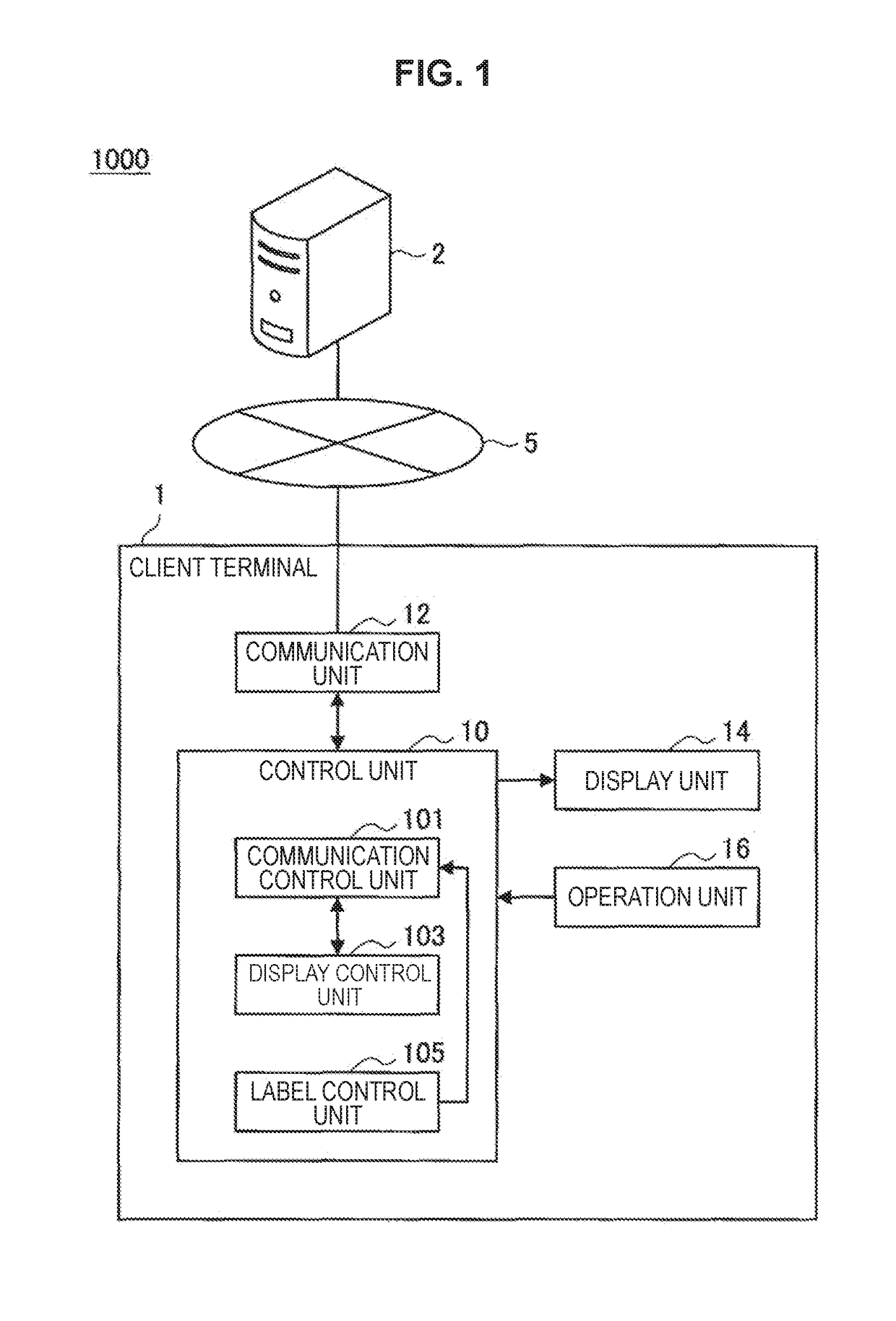
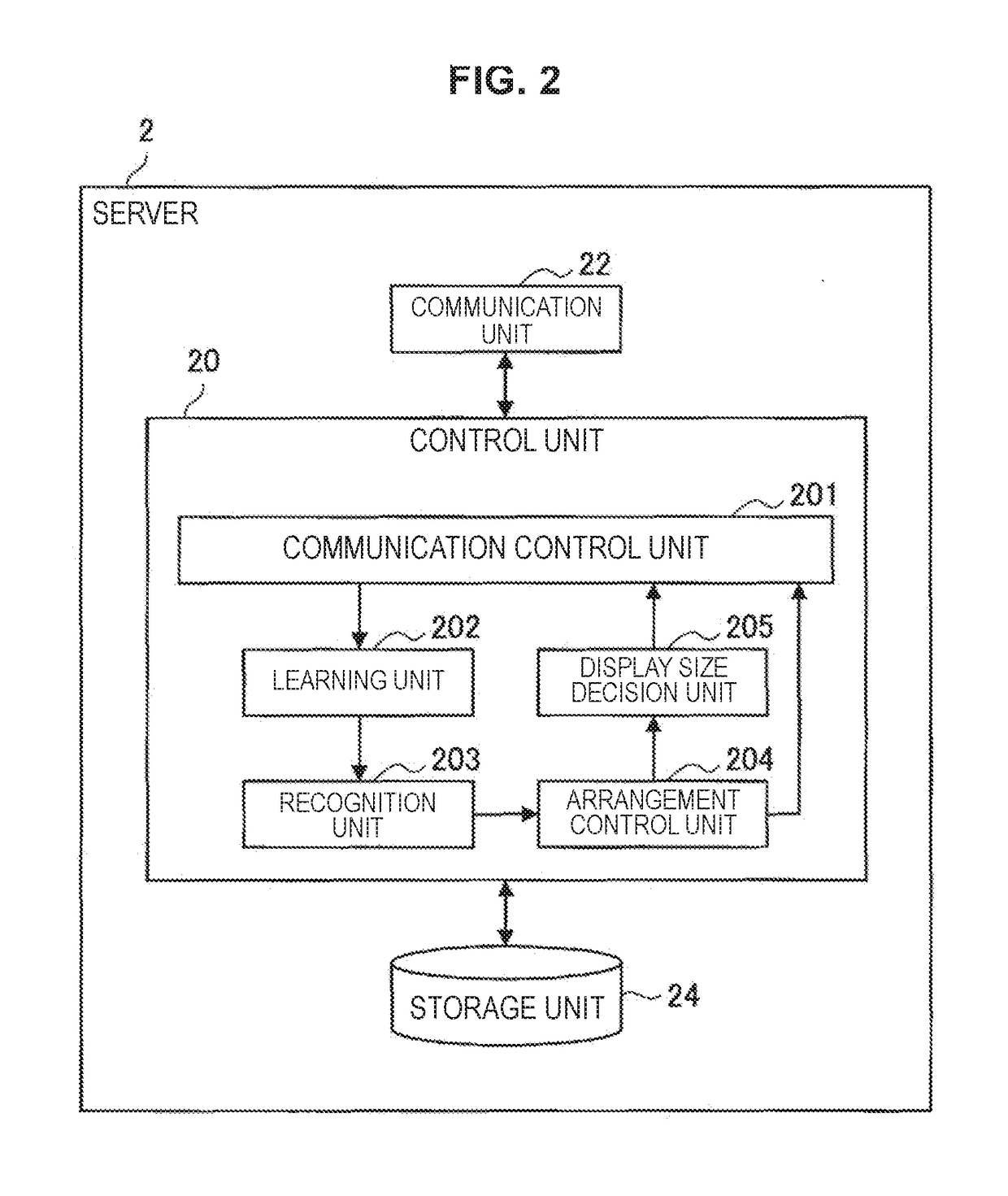
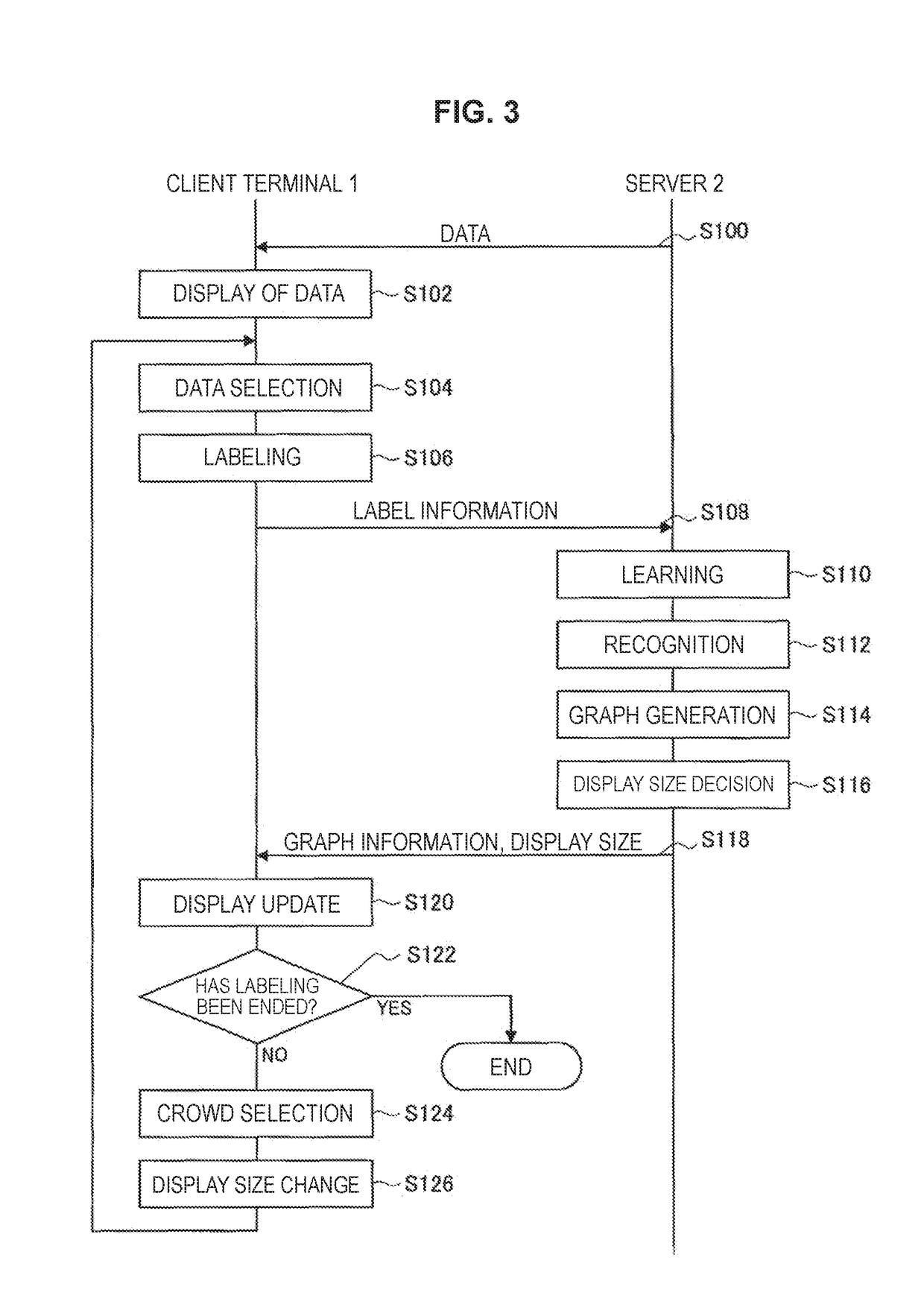
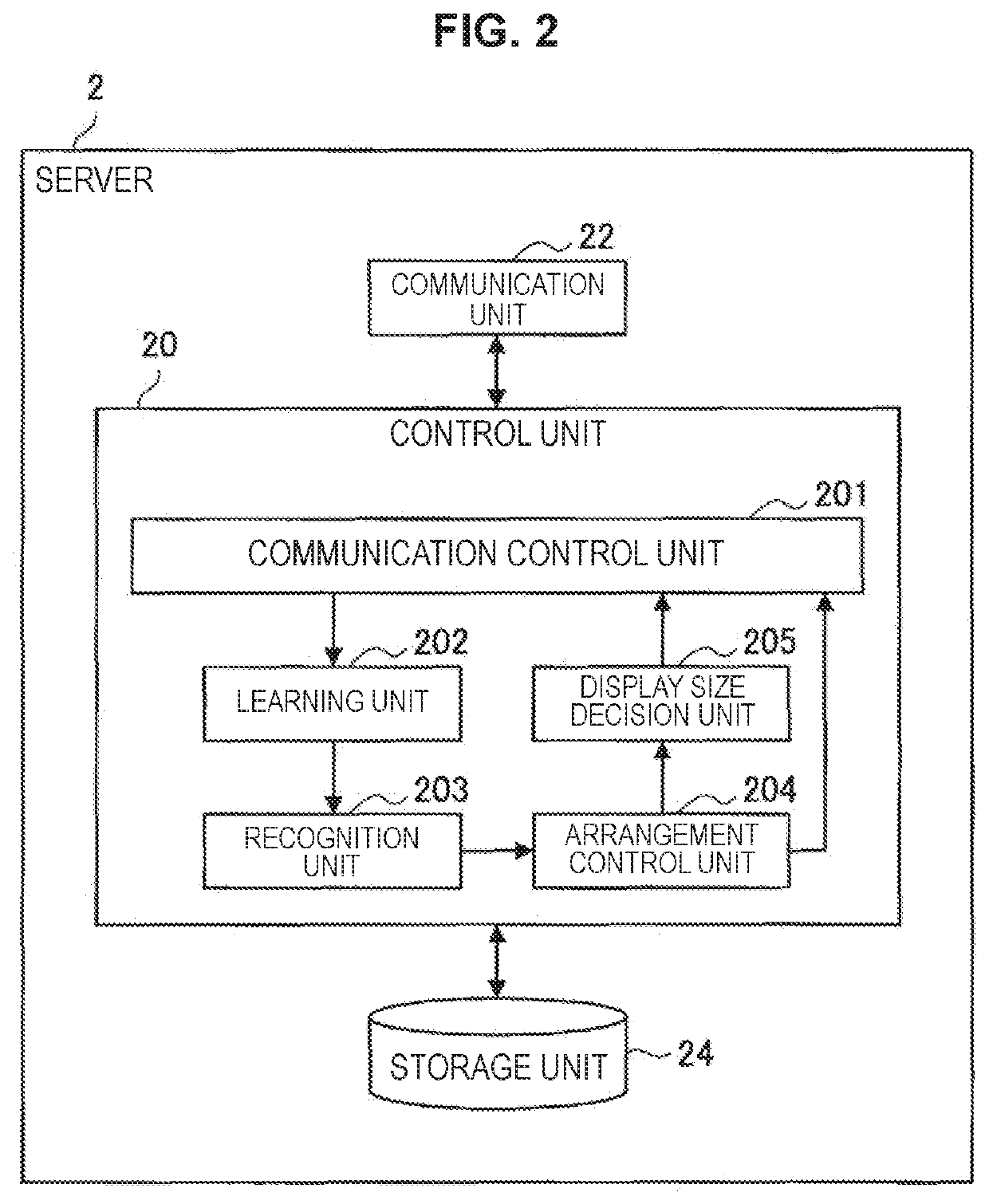
Information processing apparatus and information processing method
ActiveUS20190035122A1Data efficientEfficiently labeledDrawing from basic elementsComputing modelsInformation processingPattern recognition
[Object] To provide an information processing apparatus and an information processing method.[Solution] The information processing apparatus including: a display size decision unit configured to decide a display size of data that is based on learning of a label corresponding to a class, on the basis of a distance between a position of the data arranged on the basis of a likelihood vector obtained by recognition of the data, and a position of a class to which the data belongs; and a communication control unit configured to cause the display size to be transmitted.
Owner:SONY CORP
Fluorogen activating and shifting tag (FAST)
ActiveUS10138278B2Increase brightnessEfficiently labeledSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPhotoactive yellow proteinIonization
Disclosed is a functional derivative of a Photoactive Yellow Protein (PYP), or a functional fragment thereof, for fluorescently labelling particles, e.g. proteins, or surfaces, which is capable of binding reversibly a fluorogenic chromophore of formula (I), and which is capable of enhancing the brightness of the fluorogenic chromophore upon complexation thereto; and of inducing the spectral shift of the fluorogenic chromophore through the ionization of an auxochromic group thereof.
Owner:PARIS SCI & LETTRES +2
Information processing apparatus and information processing method
ActiveUS10891765B2Data efficientEfficiently labeledDrawing from basic elementsComputing modelsInformation processingEngineering
There is provided an information processing apparatus and an information processing method, the information processing apparatus including: a display size decision unit configured to decide a display size of data that is based on learning of a label corresponding to a class, on the basis of a distance between a position of the data arranged on the basis of a likelihood vector obtained by recognition of the data, and a position of a class to which the data belongs; and a communication control unit configured to cause the display size to be transmitted.
Owner:SONY CORP
Polymerase
InactiveUS20130295559A1Reduced discriminationEasy to detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideWild type
The present invention relates to an engineered polymerase with an expanded substrate range characterised in that the polymerase is capable of incorporating an enhanced occurrence of detection agent-labelled nucleotide analogue into nucleic acid synthesised by that engineered polymerase as compared with the wild type polymerase from which it is derived.
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
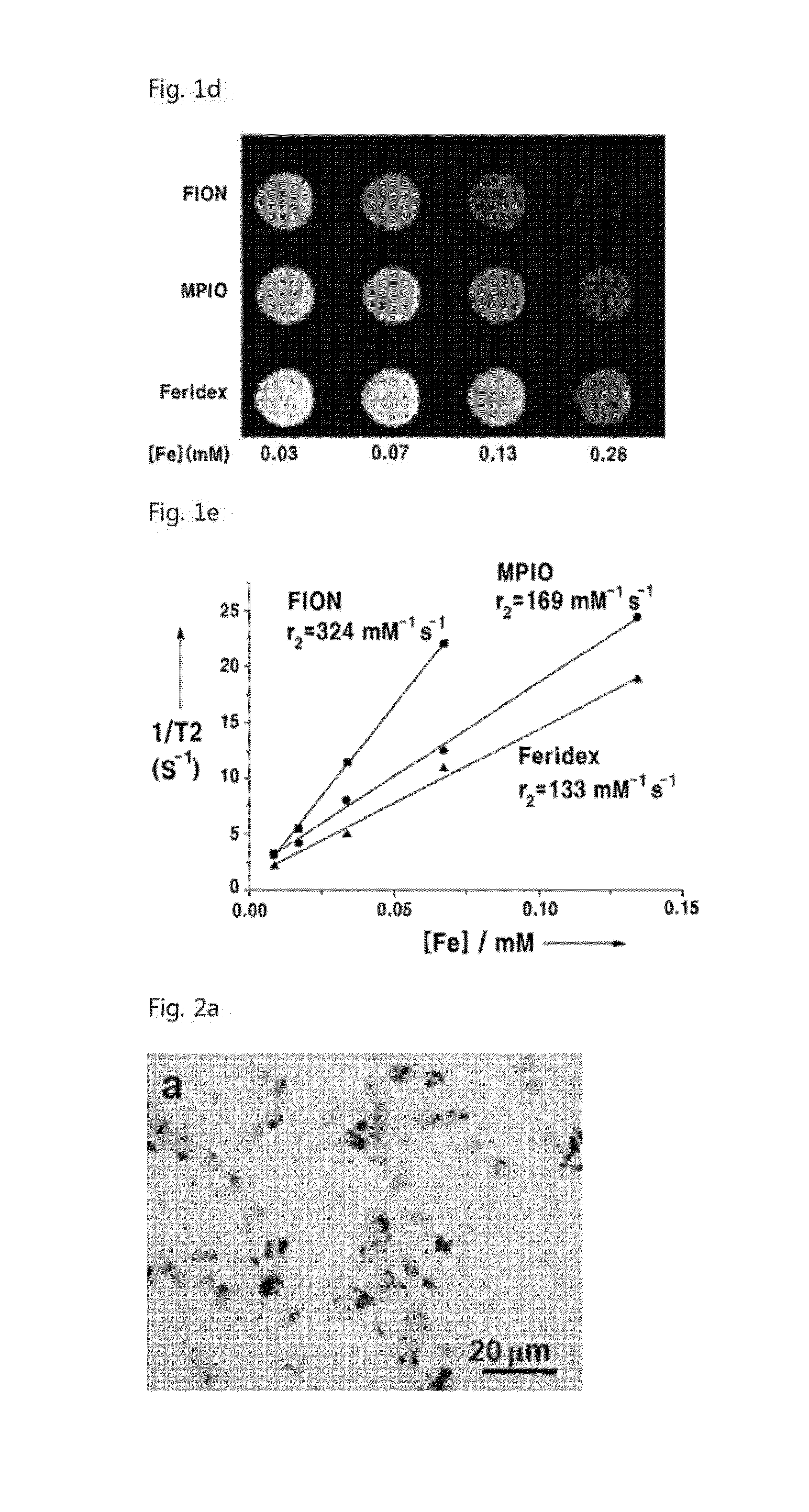
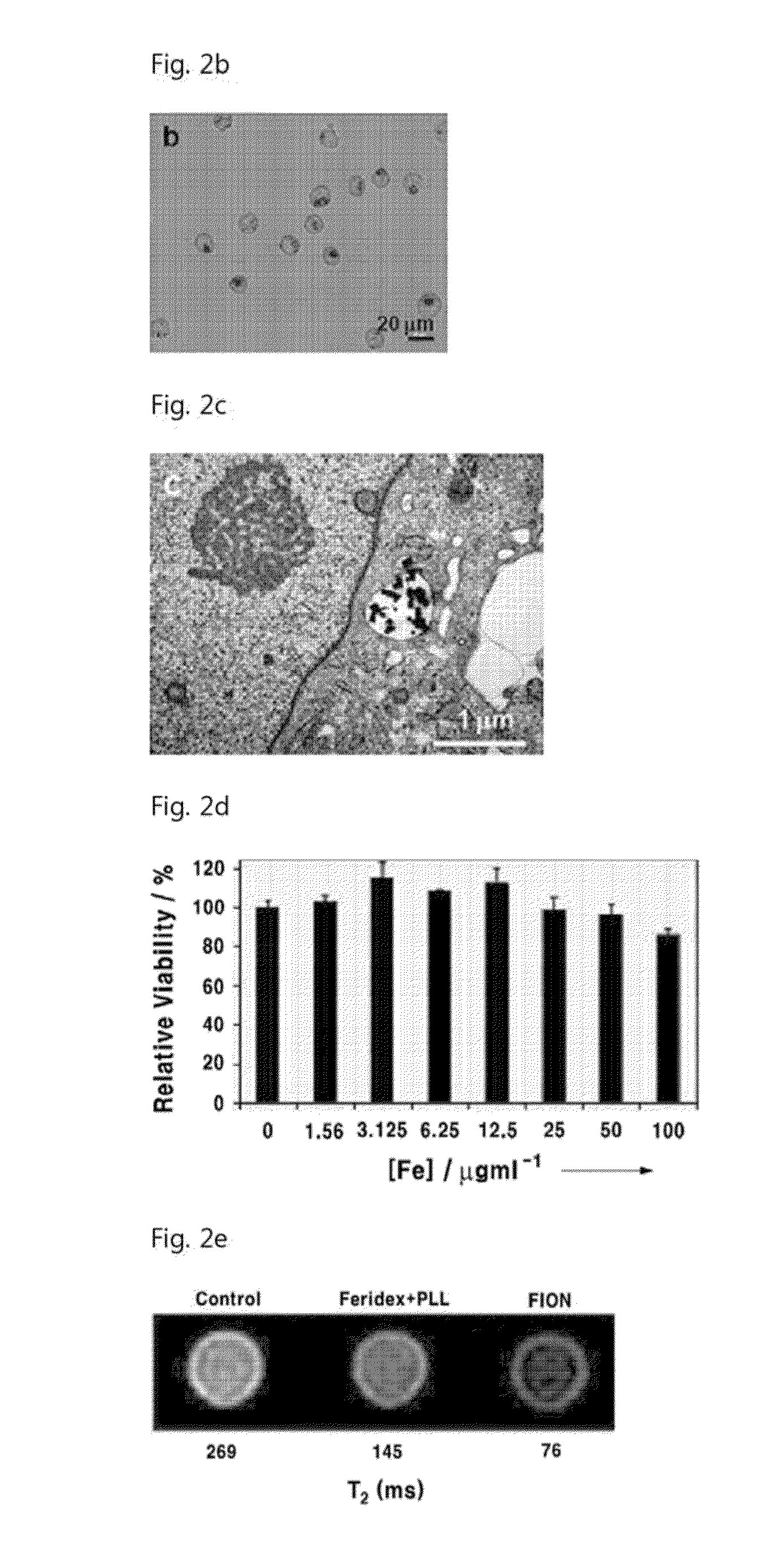
Magnetic resonance imaging t2 contrast medium for cell contrasting, and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20140170078A1High relaxation rateEfficiently labeledBiocideGenetic material ingredientsT2 contrastResonance
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance imaging T2 contrast medium (agent) for cell contrasting, and to a method for manufacturing the same. The magnetic resonance imaging T2 contrast agent for imaging at cellular level comprises magnetic nanoparticles exhibiting ferrimagnetism at room temperature, has a very high relaxivity, and has an effective uptake into cells. Thus, the T2 contrast agent may effectively mark various types of cells, and in vitro and in vivo magnetic resonance imaging at the single cell level may he realized.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
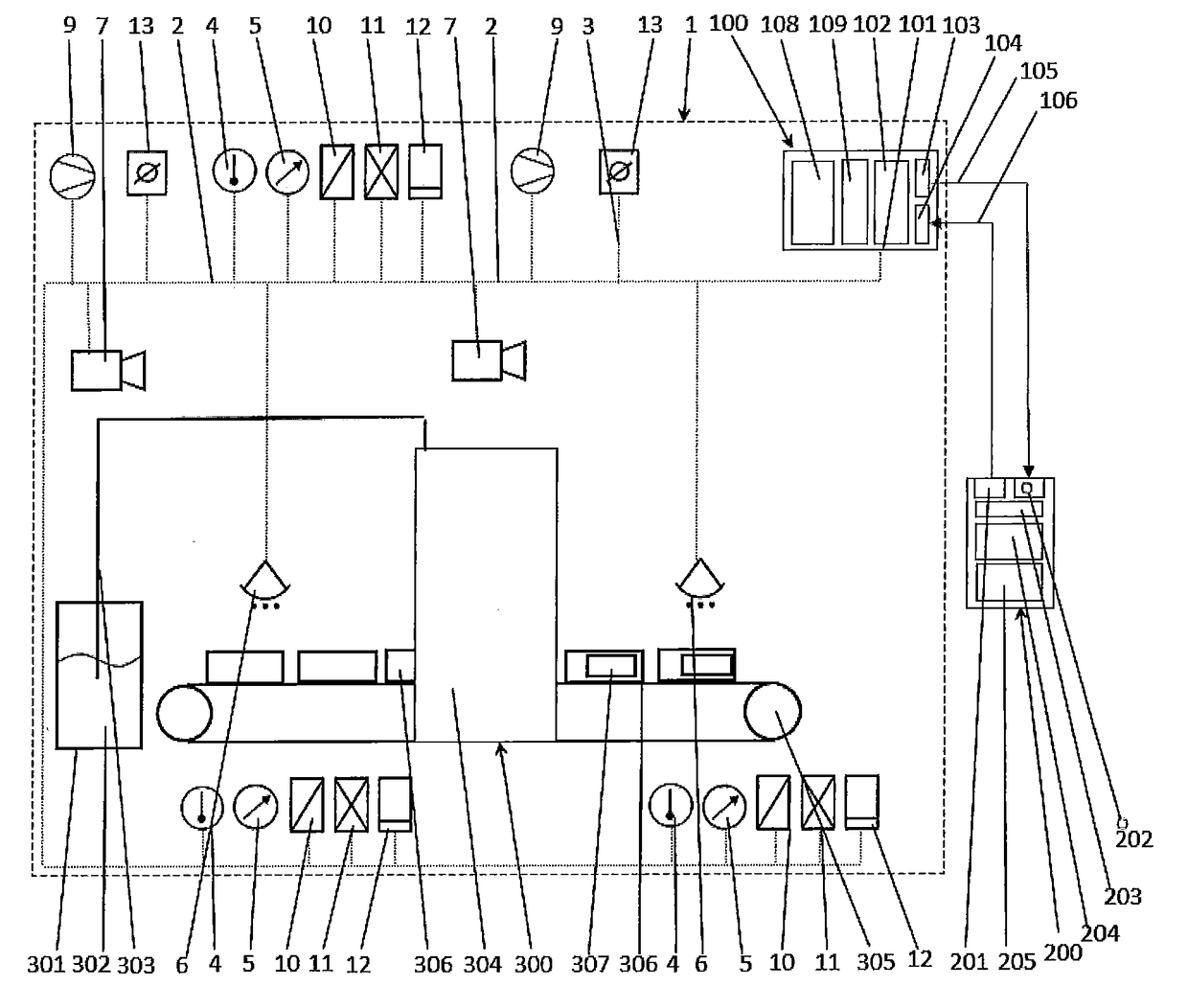
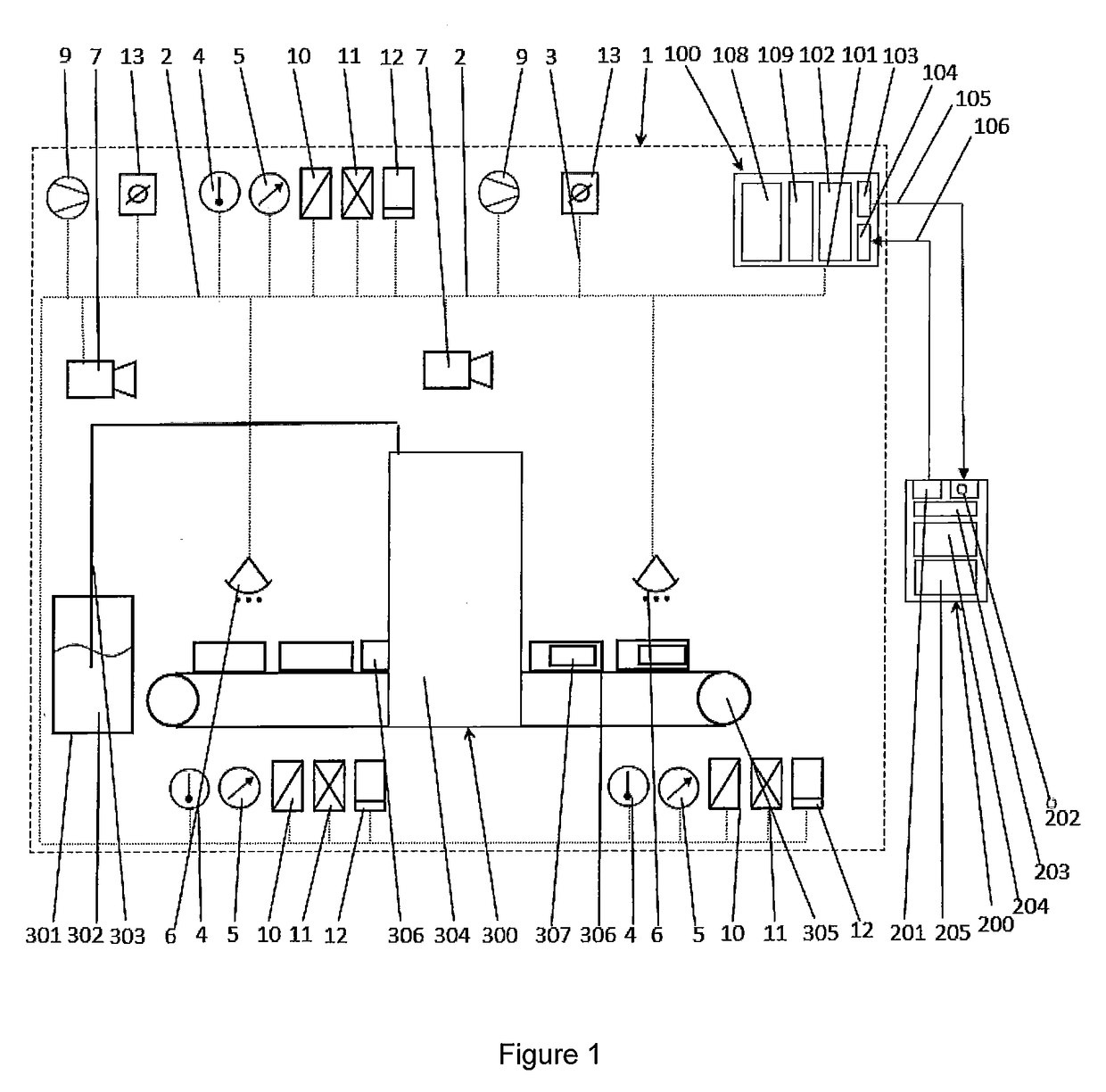
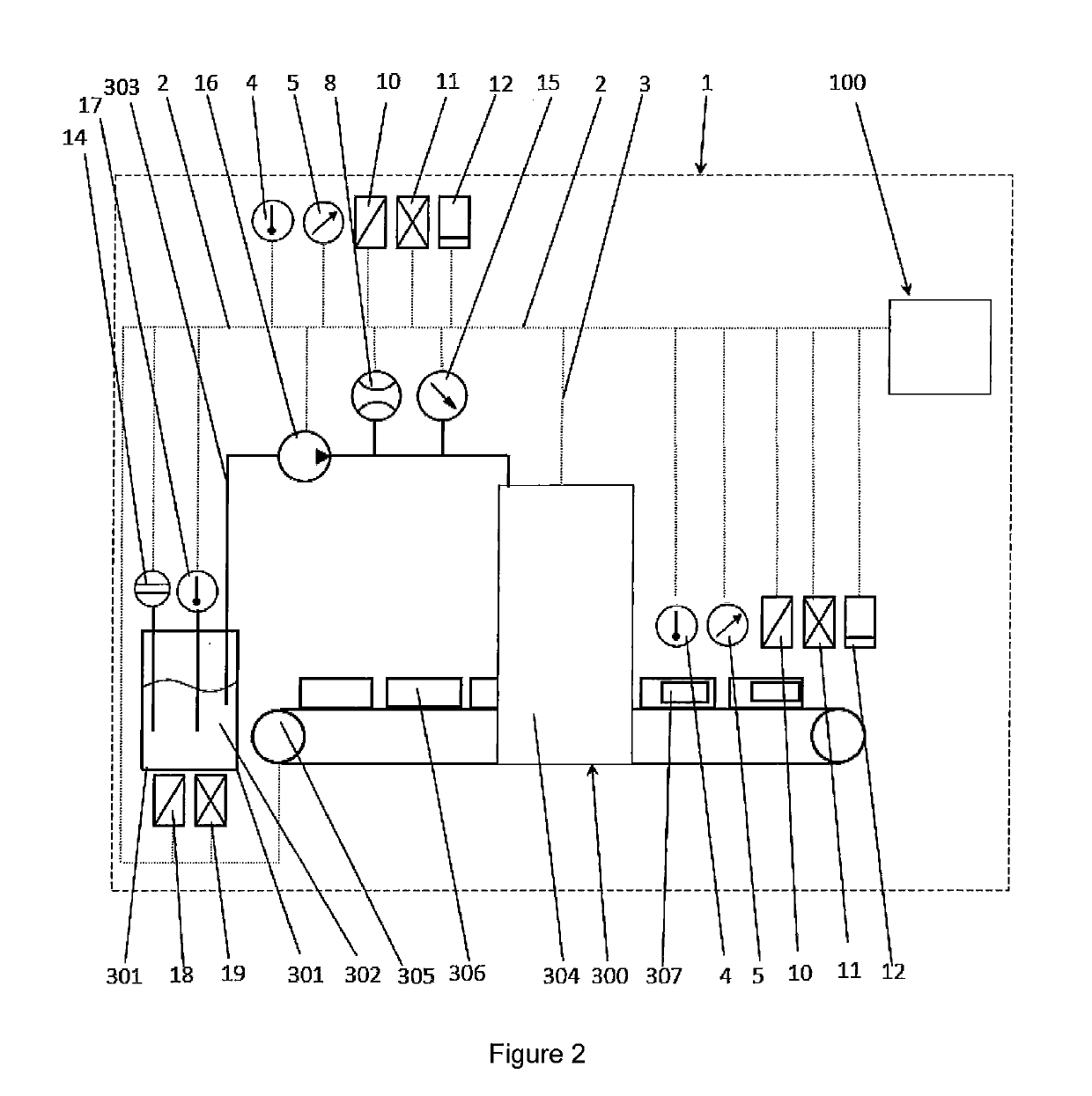
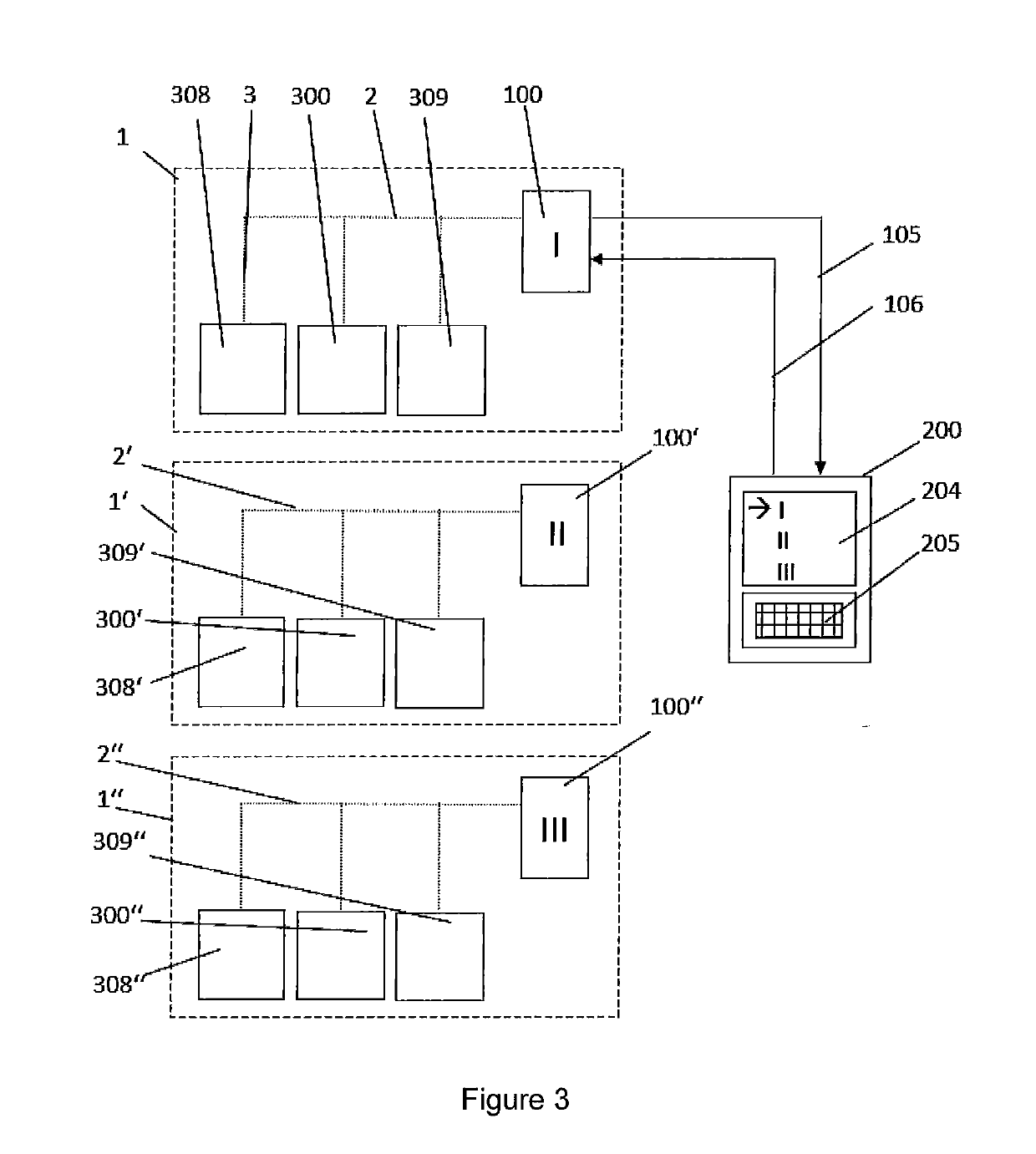
Method and device for monitoring a labeling process
ActiveUS20170183117A1Easy to monitorEfficiently labeledComputer controlLabelling machinesData processing systemAdhesive
A method for monitoring a labeling process, characterized in that parameters of the adhesive used for labeling and / or of the objects (306) to be labeled and / or of the environmental conditions of the environment of the labeling process are recorded, wherein the recorded parameters are processed by a control device (100) comprising a data processing system (101) in a given time interval or continuously and are matched with corresponding desired values, wherein said corresponding desired values can be changed via an input interface (104, 109) and wherein deviations between the recorded parameters and the desired values detected by the data processing system are output via an output interface (103) to an external device (200).
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
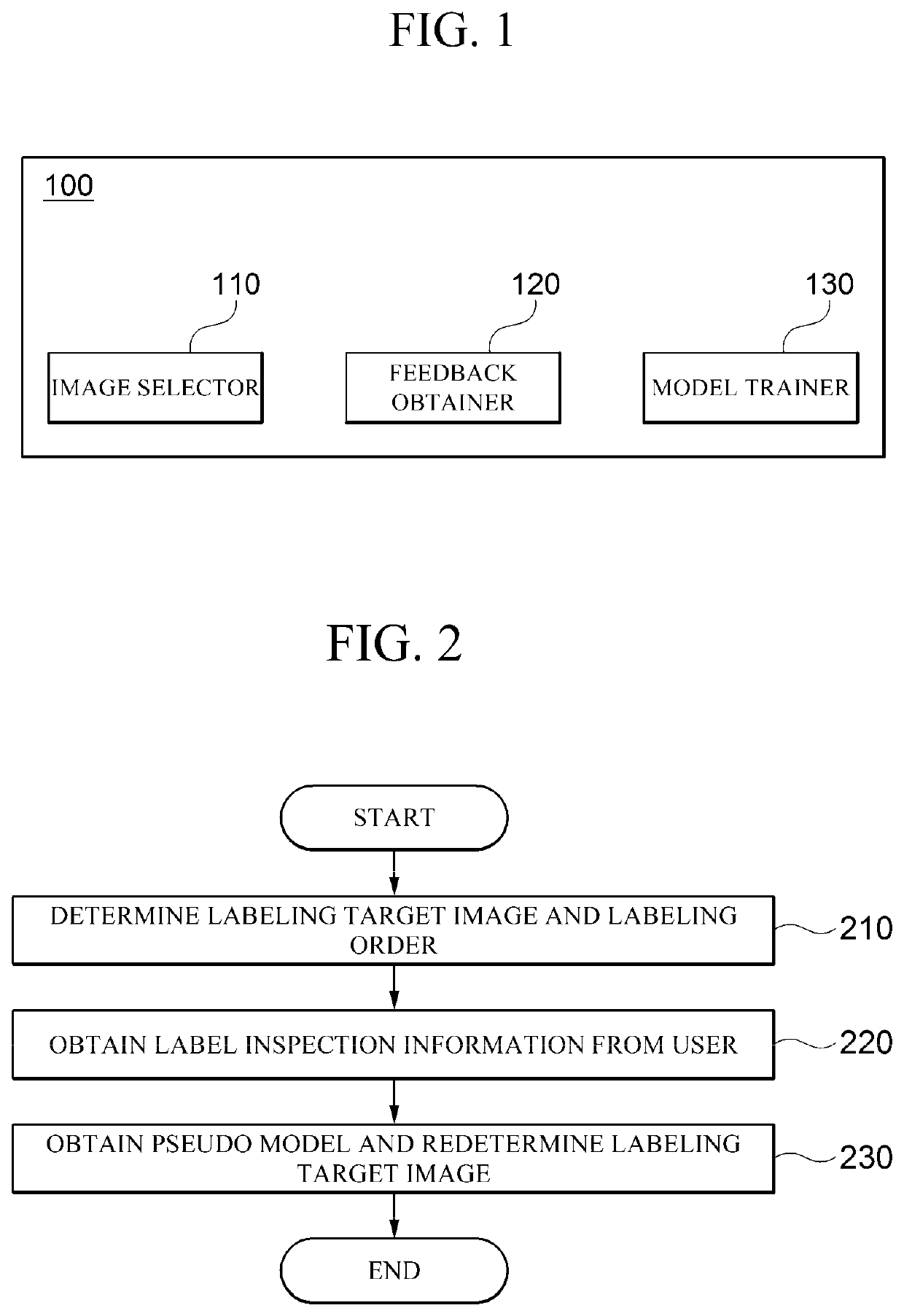
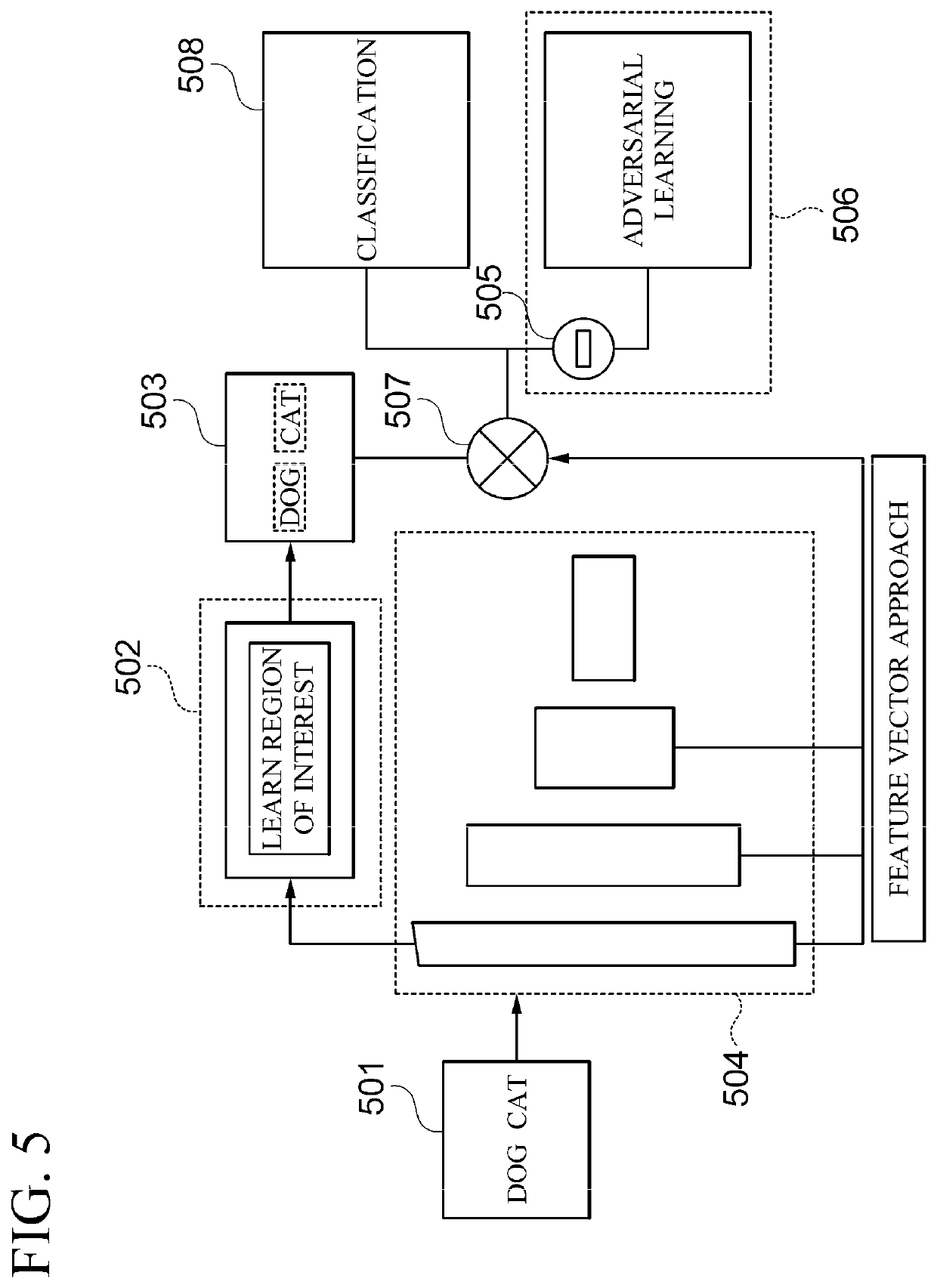
Apparatus and method of labeling for object detection
ActiveUS20220121872A1Efficiently labeledHigh labeling accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesMedicineRadiology
An apparatus of labeling for object detection according to an embodiment of the present disclosure includes an image selector that determines a plurality of labeling target images from among a plurality of unlabeled images, and determines a labeling order of the plurality of labeling target images, a feedback obtainer that obtains label inspection information on the plurality of labeling target images from a user, and a model trainer that learns the label inspection information input from the user by using the labeling target images, obtains a pseudo label for supervised learning based on a learning result using the label inspection information, and re-determines the labeling order of the labeling target images based on the pseudo label.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDS CO LTD
Mass labels
InactiveUS20150065392A1High selectivityRaise the pHIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsOrganic compound librariesMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryChemistry
Owner:ELECTROPHORETICS LTD
68Ge/68Ga generator
ActiveUS10943709B2High affinityImprove performanceIsotope delivery systemsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsNiobiumEngineering
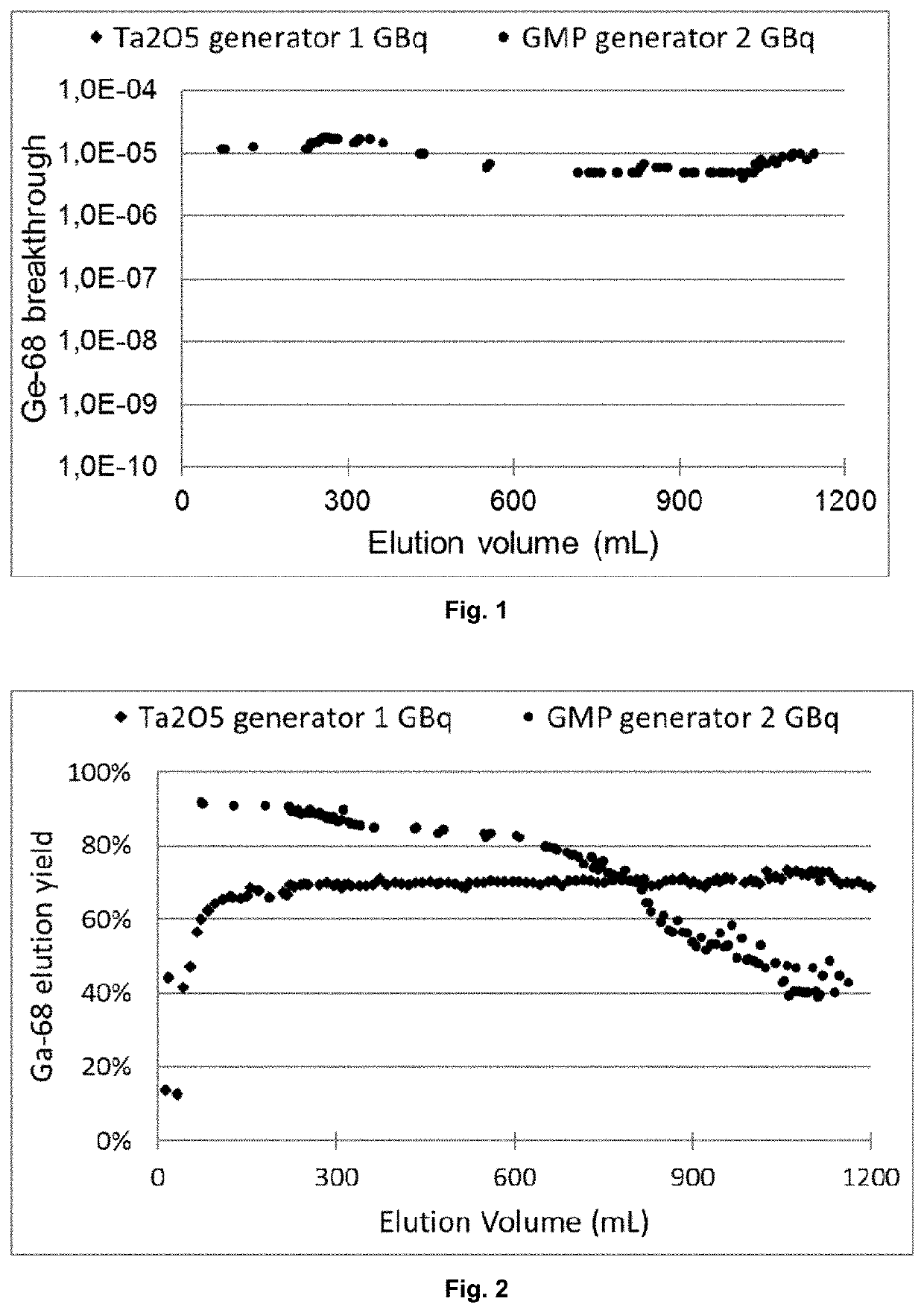
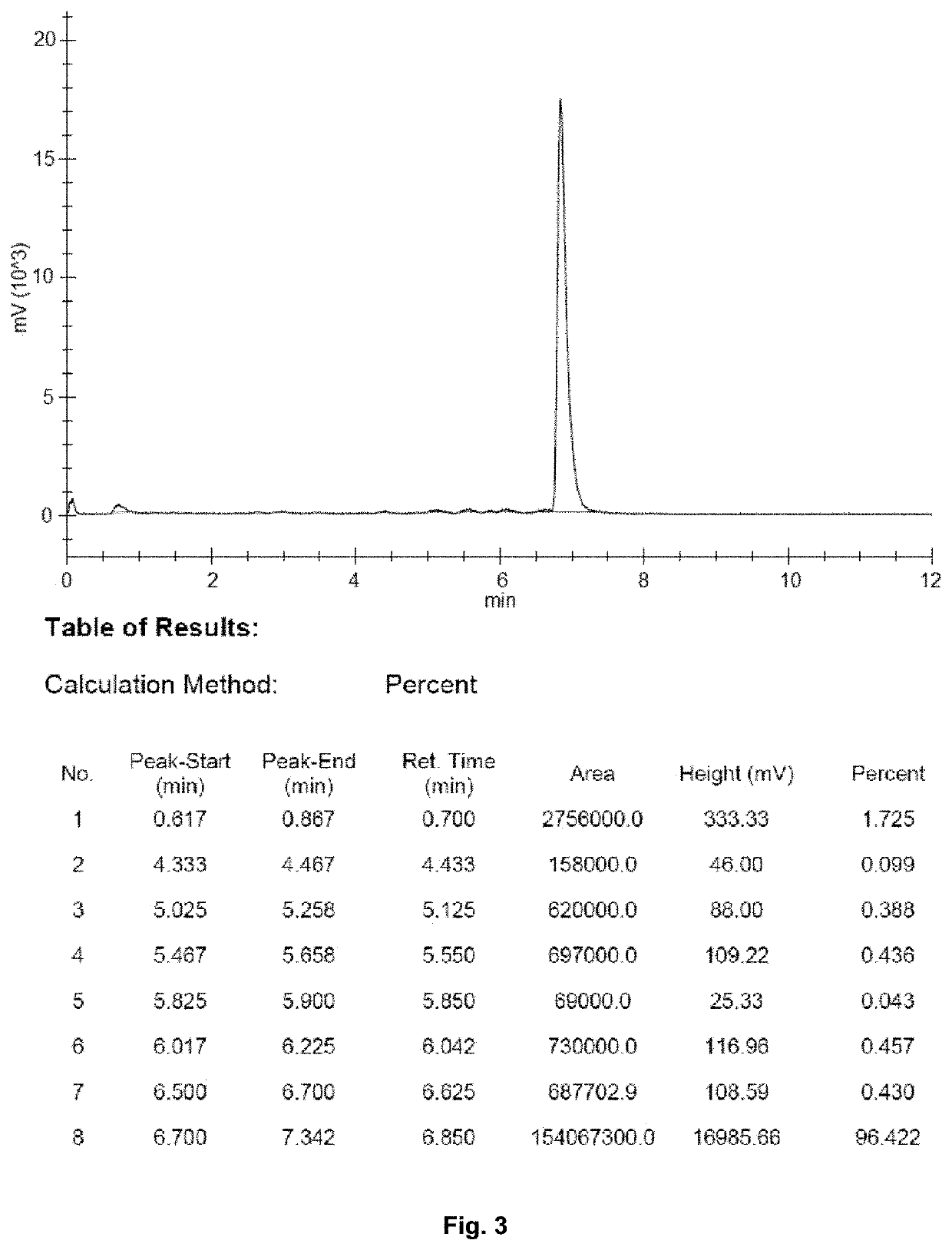
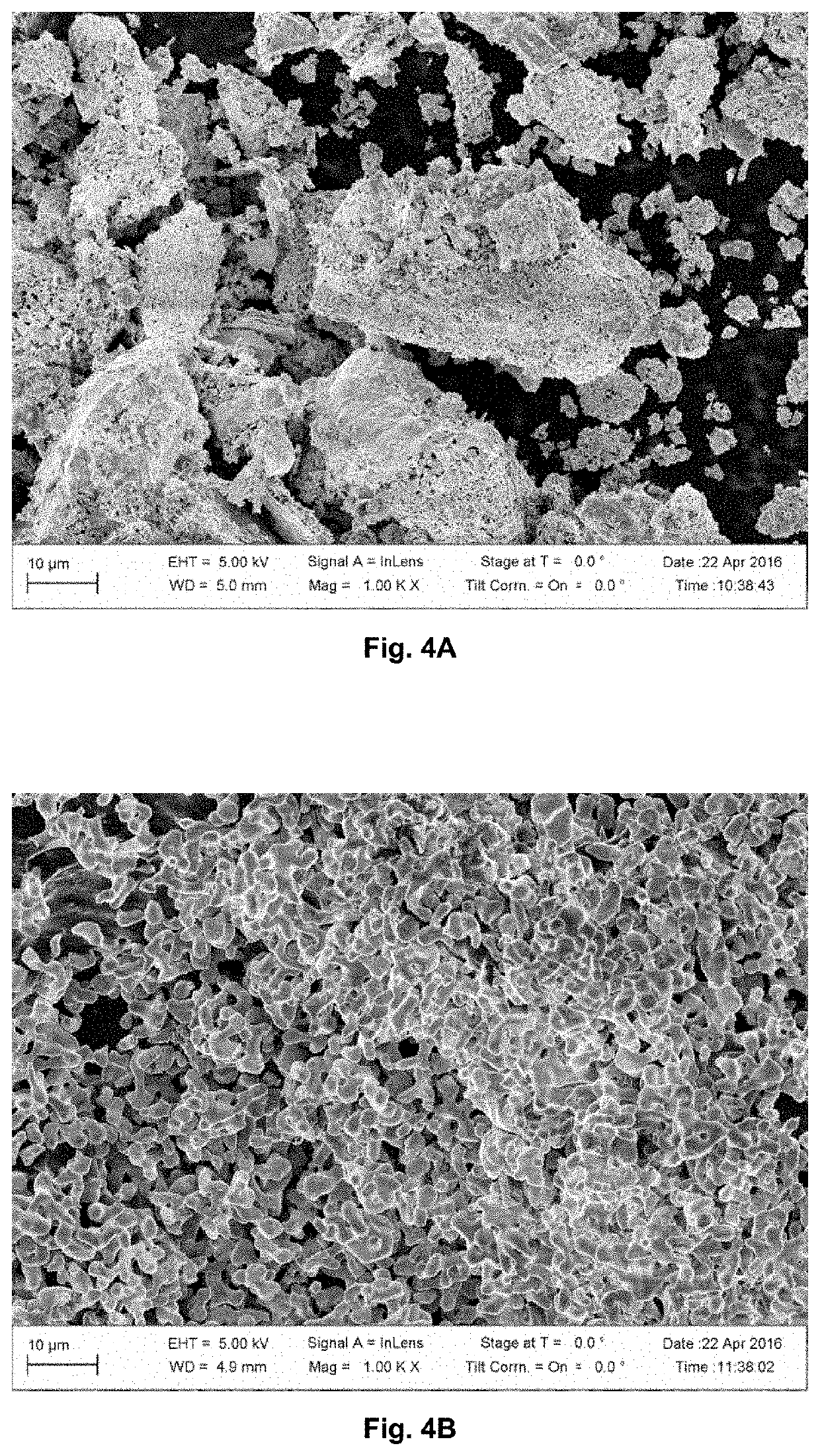
A 68Ge / 68Ga generator for a continuous production of a 68Ga daughter nuclide, wherein the 68Ge parent nuclide thereof is specifically adsorbed to an inorganic support material and wherein said 68Ge parent nuclide continuously decays to 68Ga by electron capture at a half-life of 270.82 d, wherein the inorganic support material is at least one oxide of a metal being selected from the group consisting of: Vanadium, Niobium and Tantalum. The use of at least one oxide of a metal being selected from the group consisting of: Vanadium, Niobium and Tantalum as an inorganic support material for the manufacture of a 68Ge / 68Ga generator for pharmaceutical purposes. With the inorganic support material of the present invention, it is possible to load 68Ge / 68Ga generators with up to 8000 MBq of 68Ge (corresponding to 80 μg Germanium).
Owner:ITM ISOTOPE TECH MUNICH SE
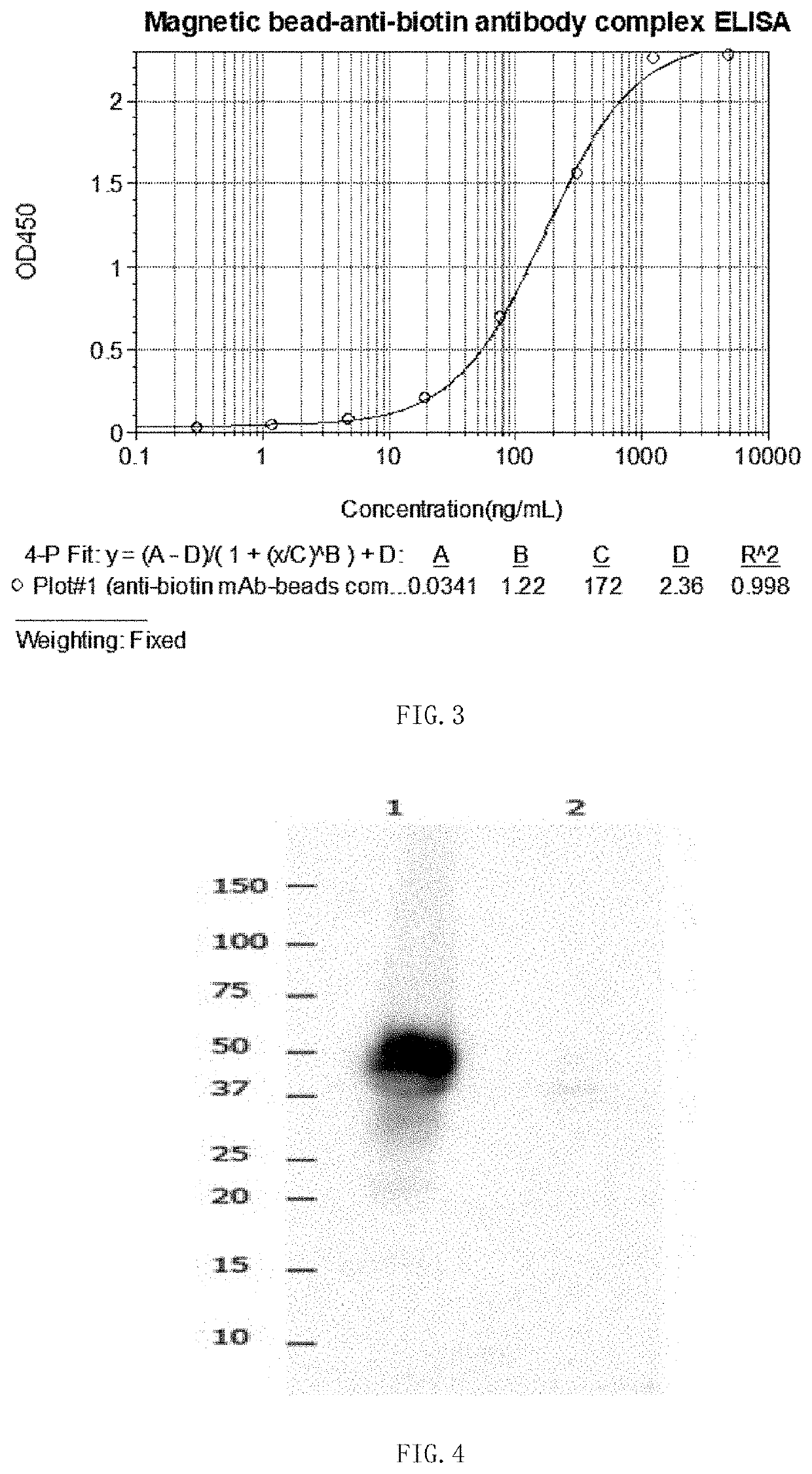
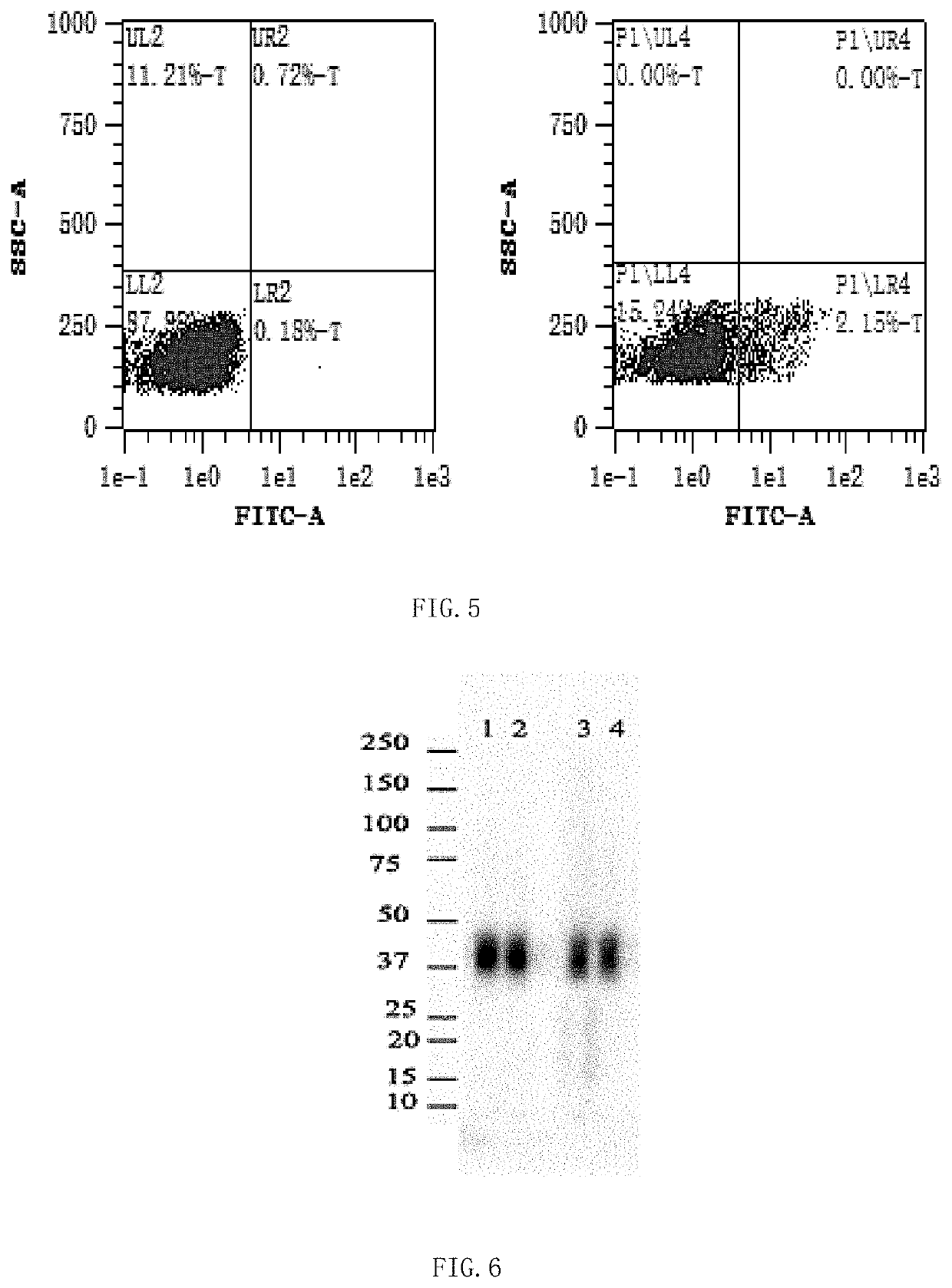
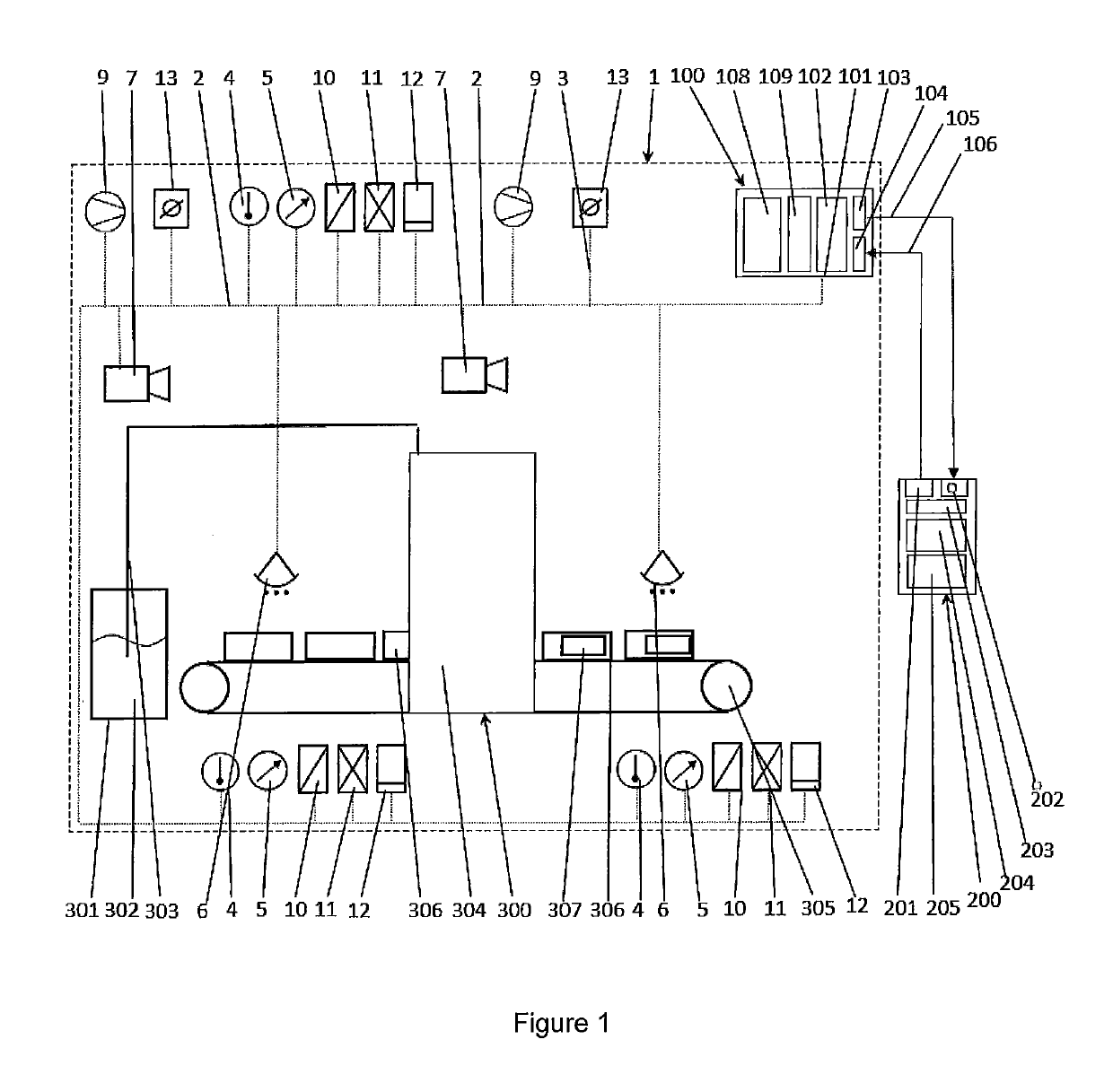
Anti-biotin antibody and application thereof
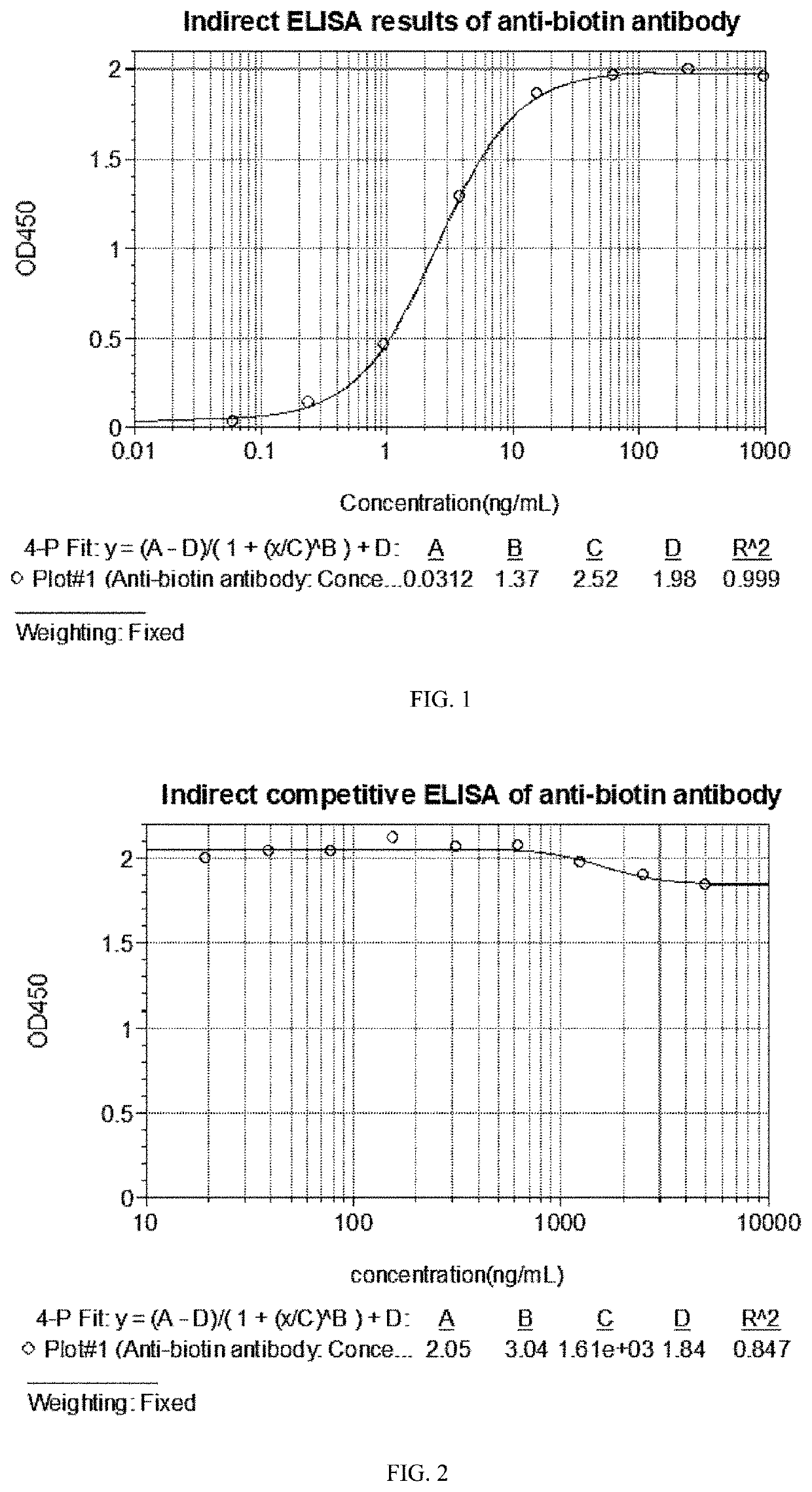
ActiveUS20220041755A1Efficiently labeledImprove controllabilityImmunoglobulinsBiological testingStainingAntibody conjugate
The present disclosure provides an anti-biotin antibody, and provides an amino acid sequence encoding the CDRs of the antibody. Studies have shown that the antibody only reacts with a biotin conjugate or derivative, and does not react with free biotin. The present disclosure further provides applications of the antibody in, including but not limited to, ELISA, cell capture, sorting and enrichment, western blotting, flow cytometry, immunocytofluorescent staining, and immunohistochemistry. The anti-biotin antibody conjugated immunomagnetic beads can specifically and directly recognize a biotin labeled antigen, and do not bind to free biotin which is often presented in clinical samples and culture media. In addition, the anti-biotin antibody-conjugated magnetic beads or anti-biotin antibody-fluorescein provide an ideal solution for the isolation of specific cells, and can even enrich and separate target cells from samples rich in debris or other rare biological materials.
Owner:HANGZHOU BIOLYNX TECH CO LTD
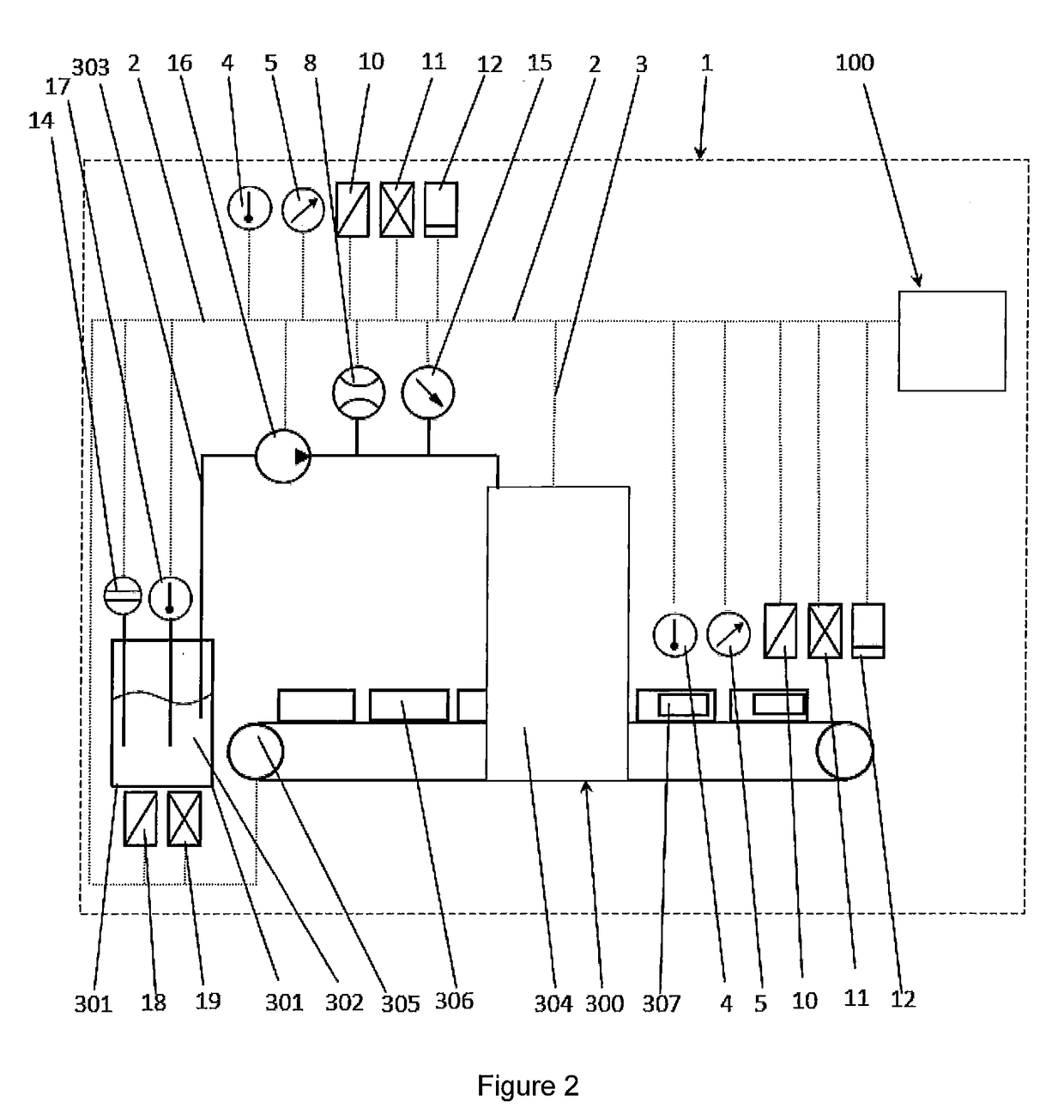
Method and device for monitoring a labeling process
ActiveUS10370137B2Efficiently labeledComputer controlLabelling machinesData processing systemAdhesive
A method for monitoring a labeling process, characterized in that parameters of the adhesive used for labeling and / or of the objects (306) to be labeled and / or of the environmental conditions of the environment of the labeling process are recorded, wherein the recorded parameters are processed by a control device (100) comprising a data processing system (101) in a given time interval or continuously and are matched with corresponding desired values, wherein said corresponding desired values can be changed via an input interface (104, 109) and wherein deviations between the recorded parameters and the desired values detected by the data processing system are output via an output interface (103) to an external device (200).
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com