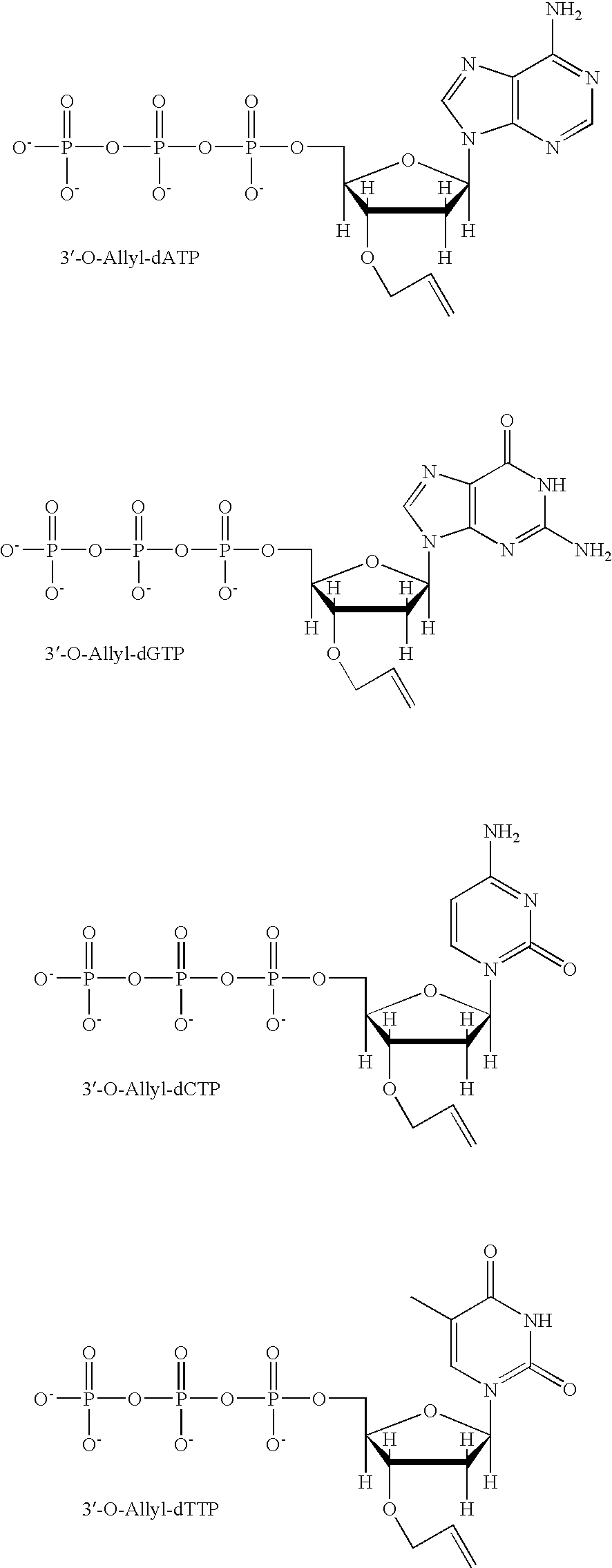
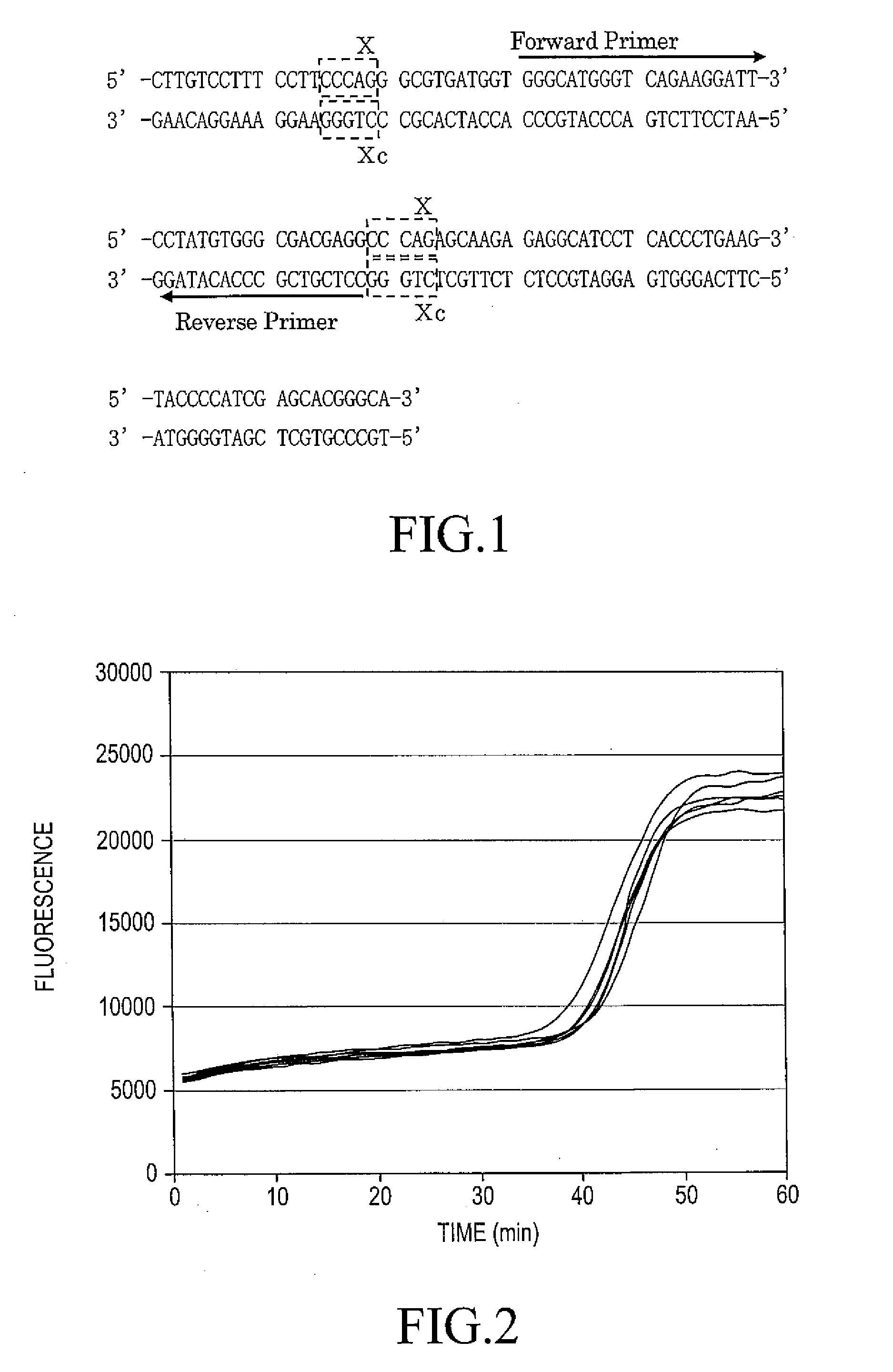
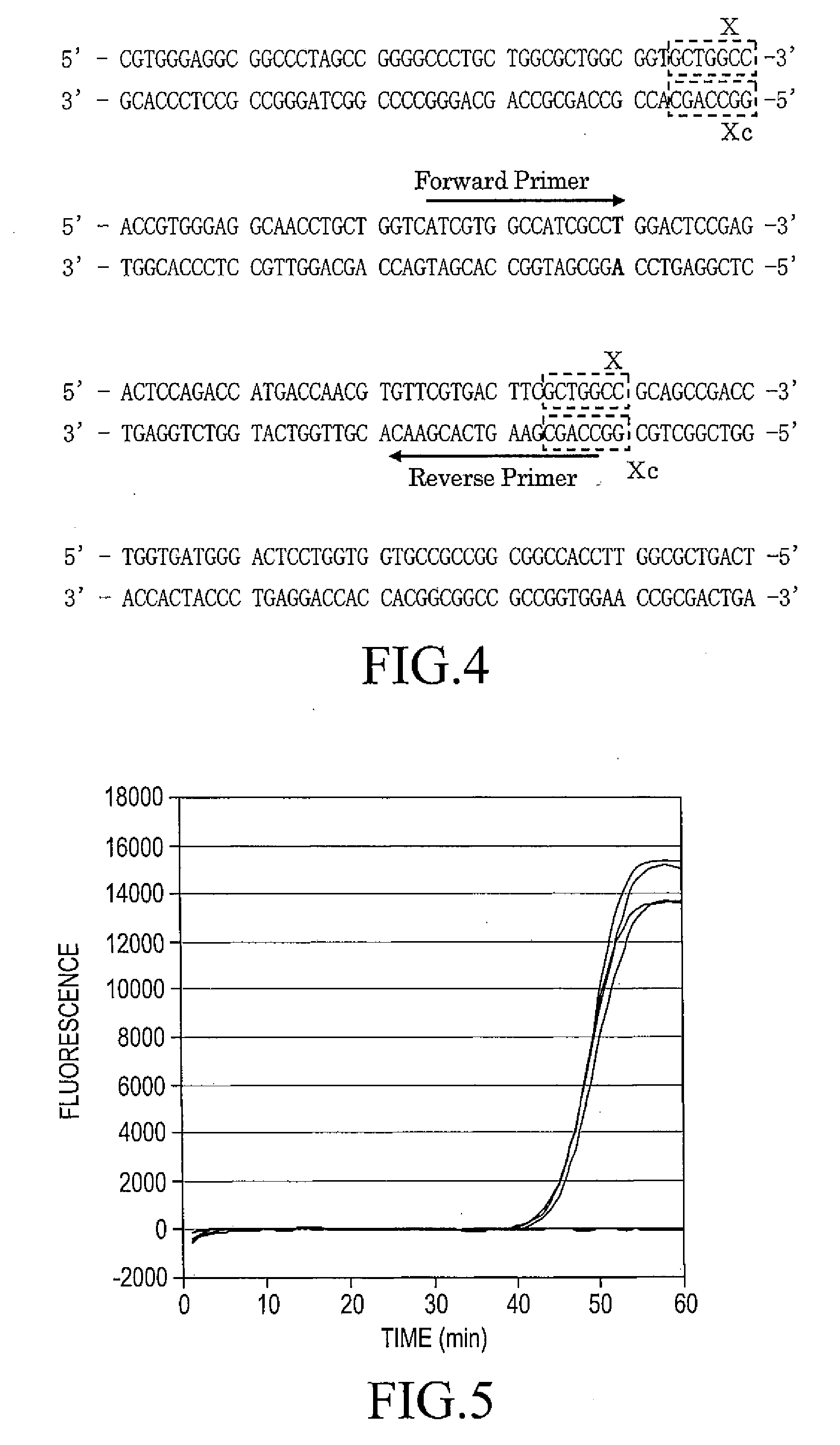
Patents
Literature
69 results about "Deoxynucleoside triphosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
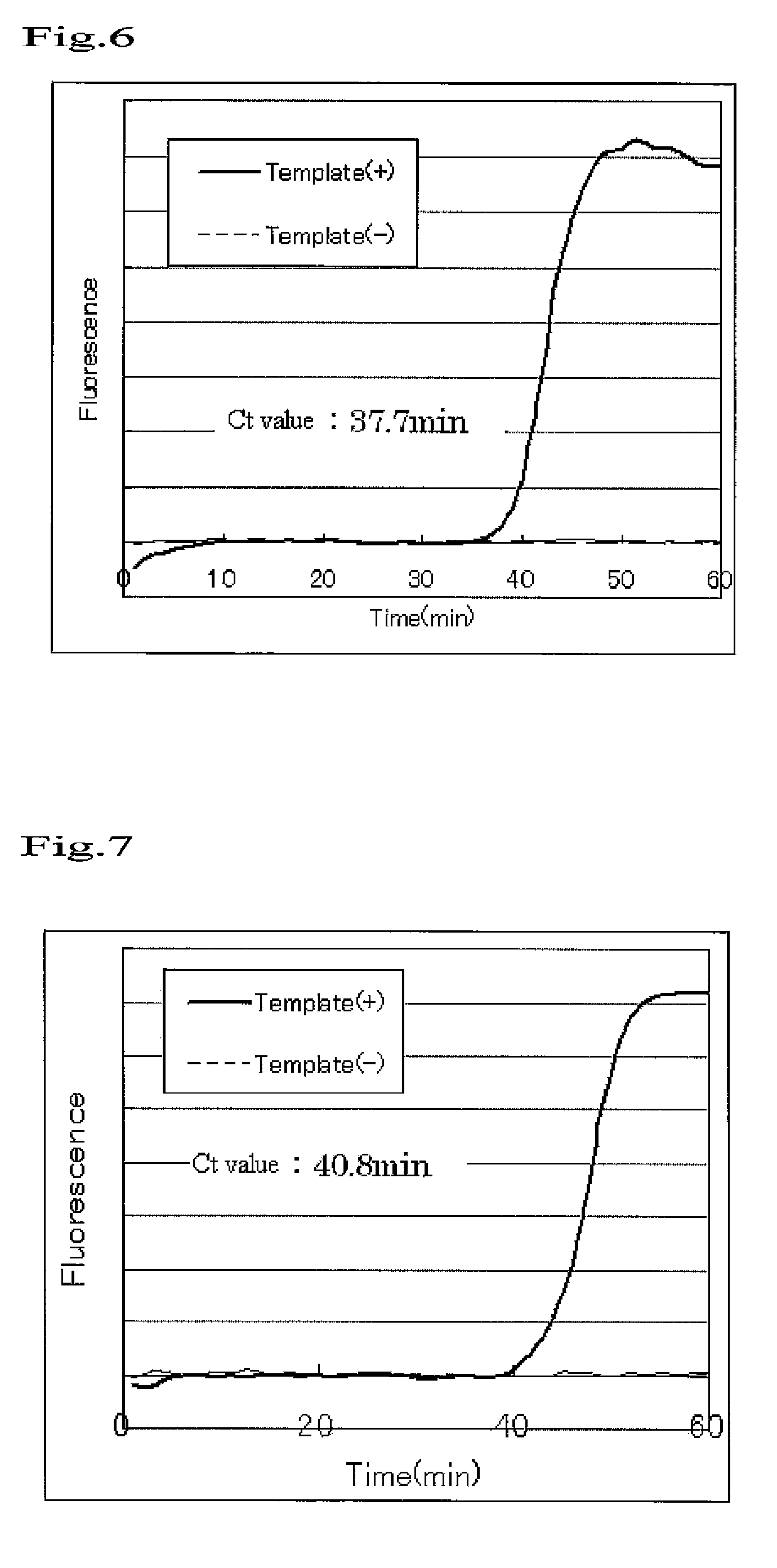
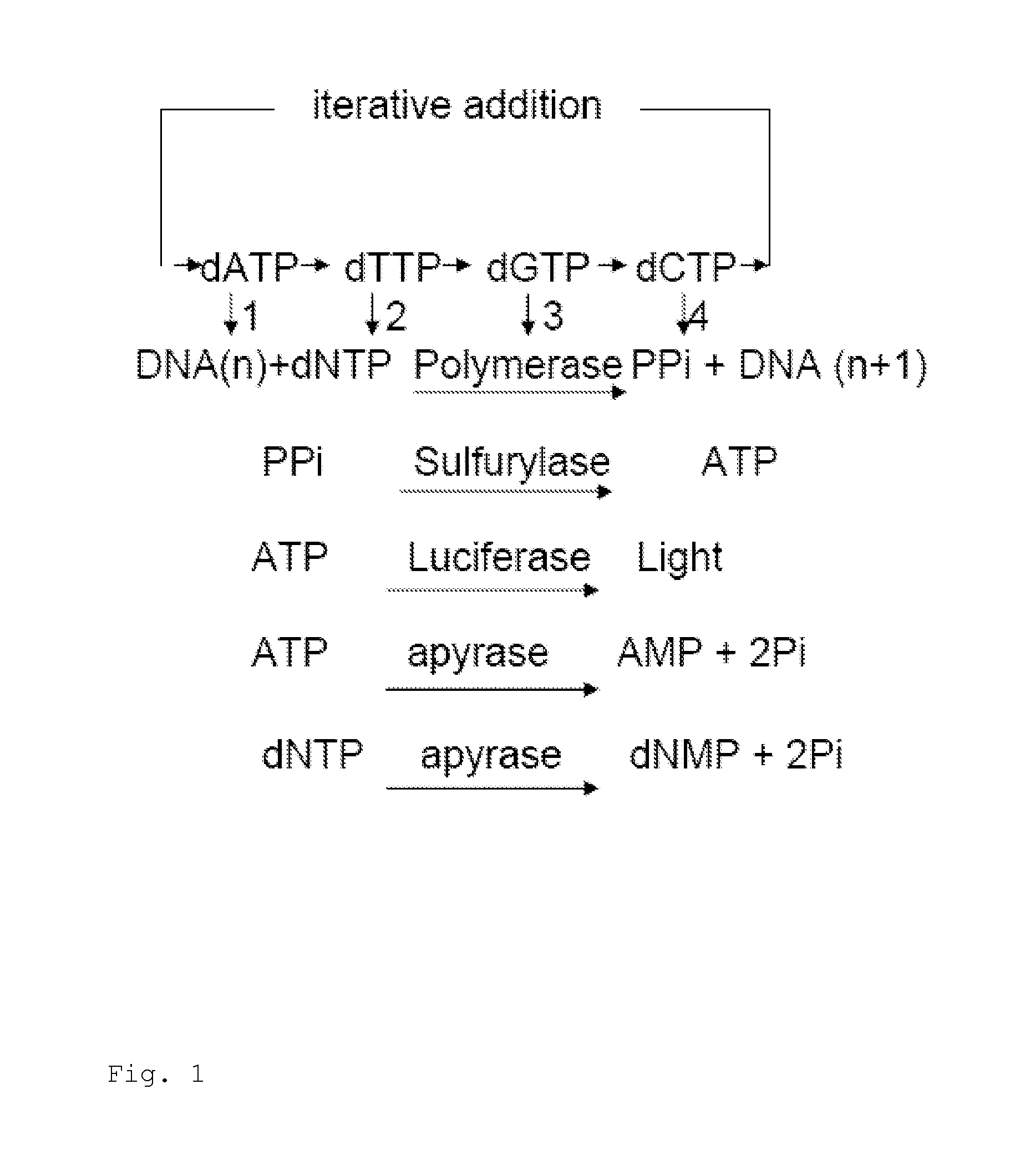
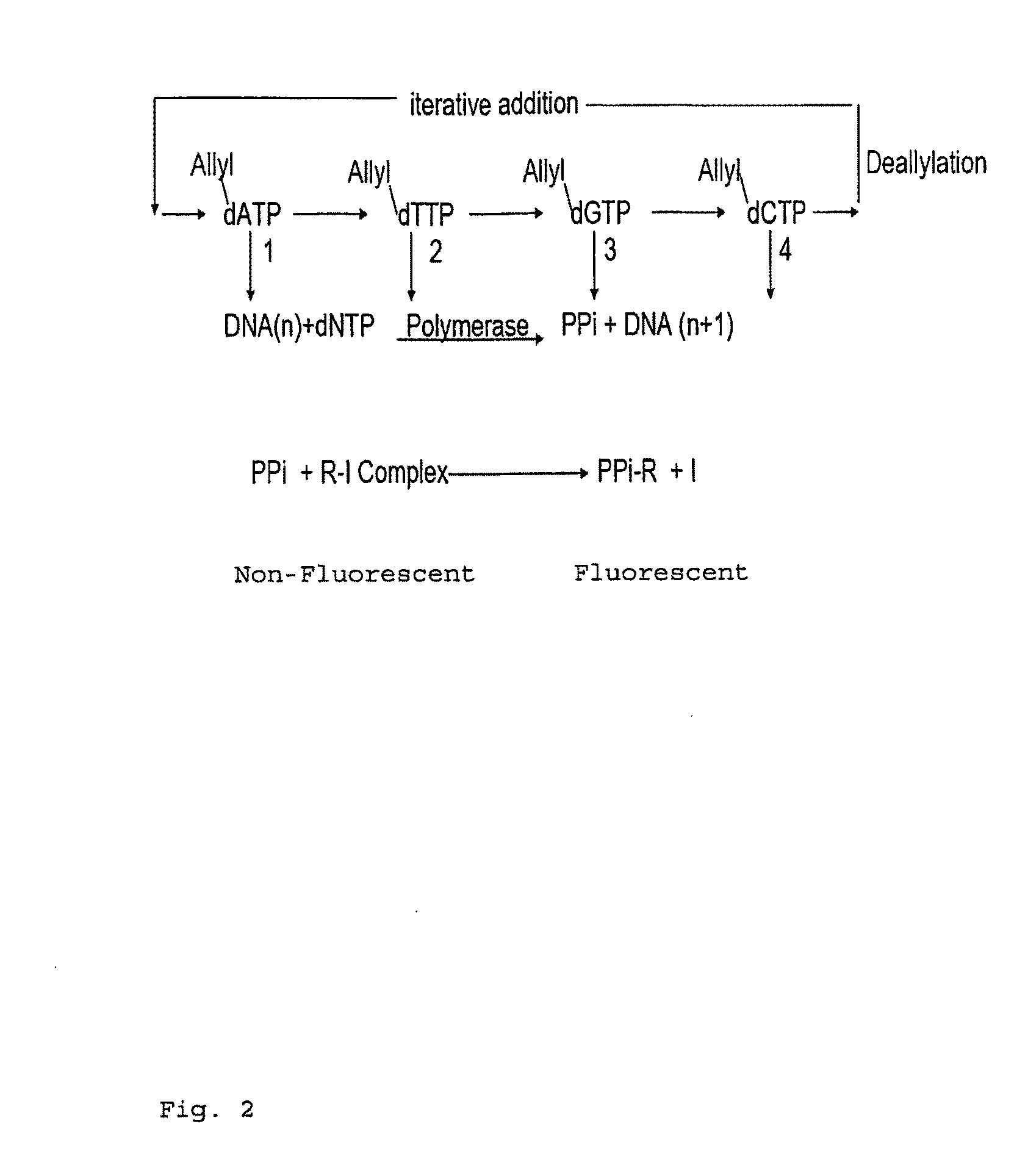
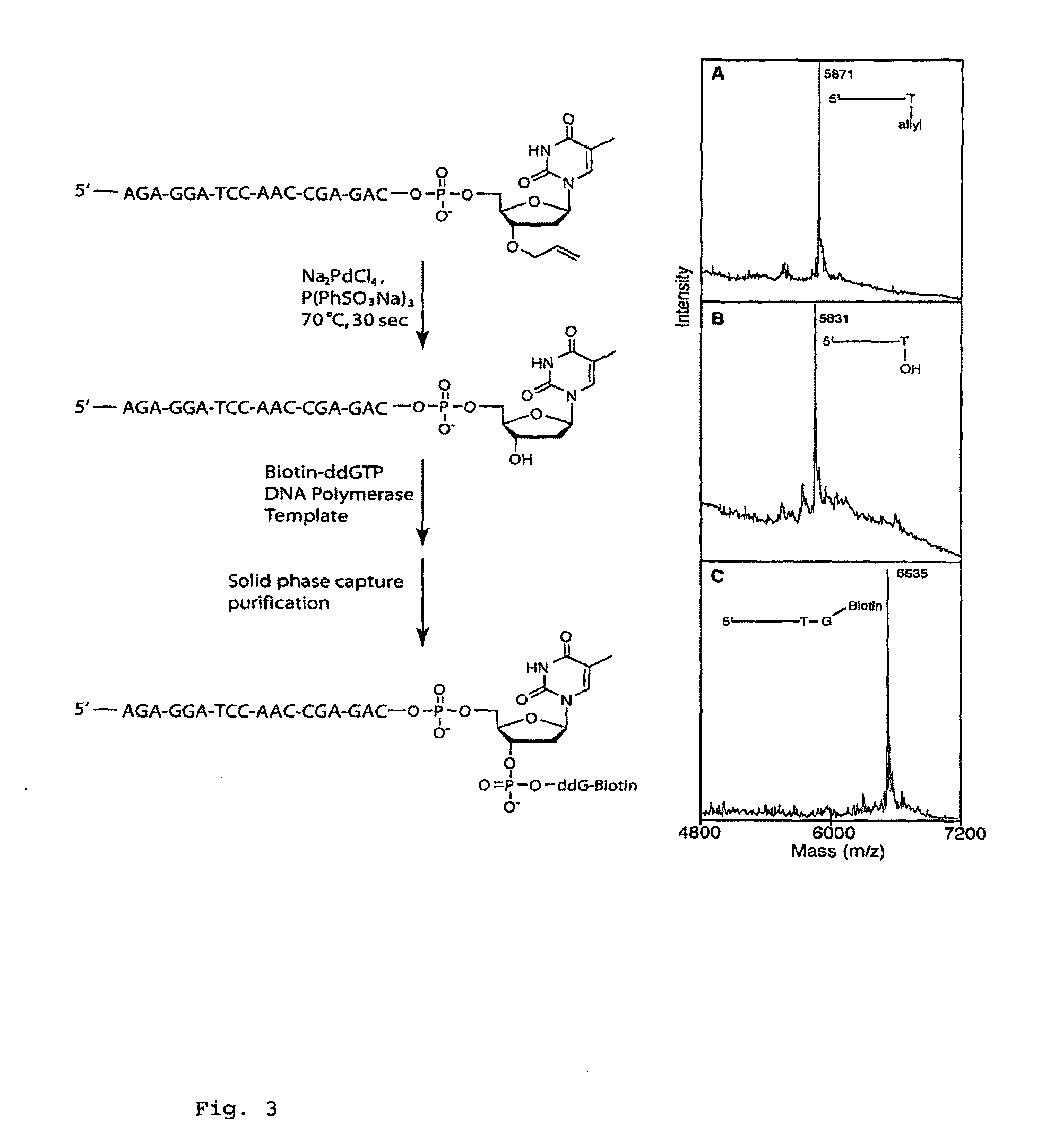
Deoxynucleoside triphosphate is the molecule added to the DNA strand, but it loses 2 phosphates to become a nucleotide, which releases energy.
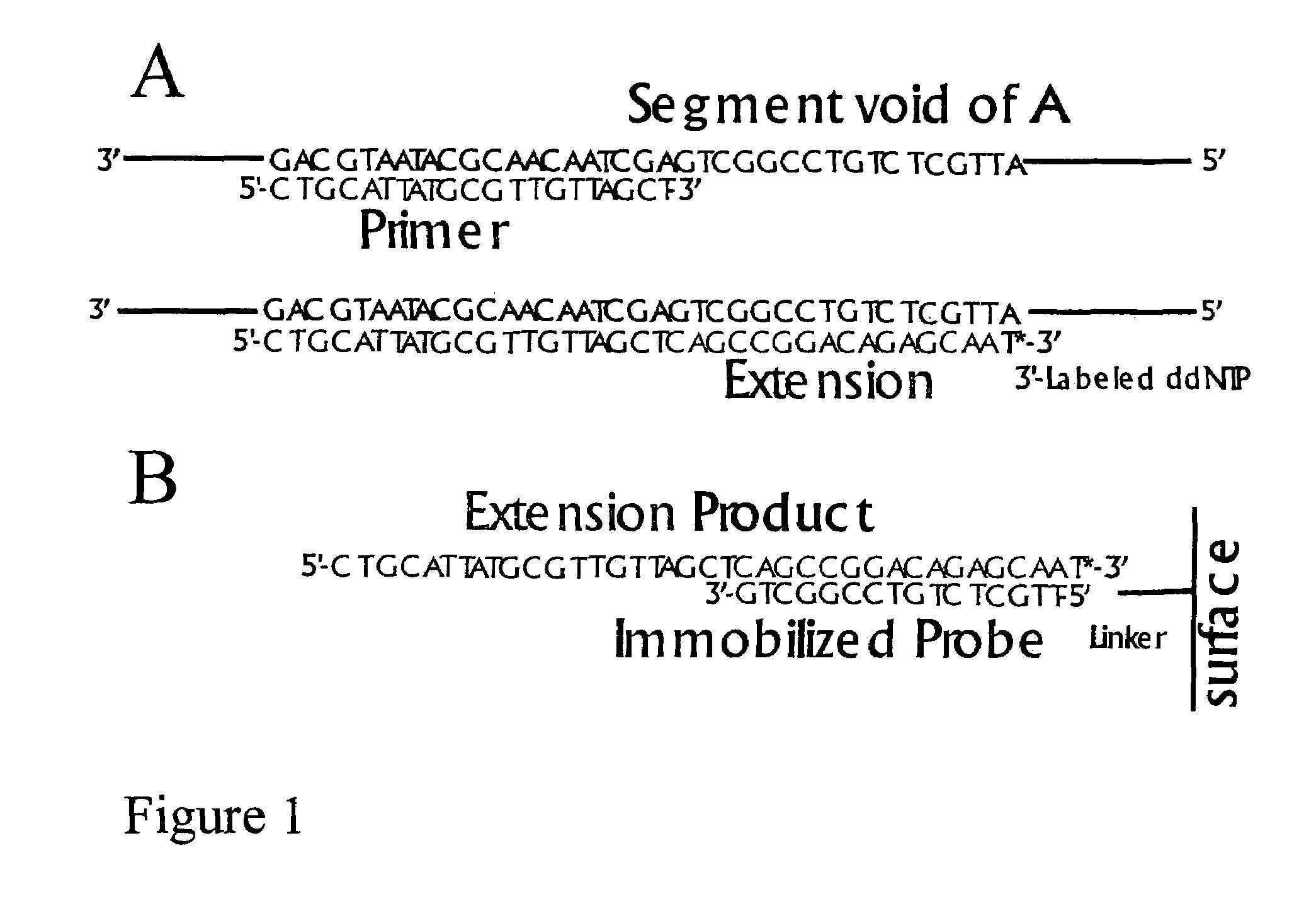
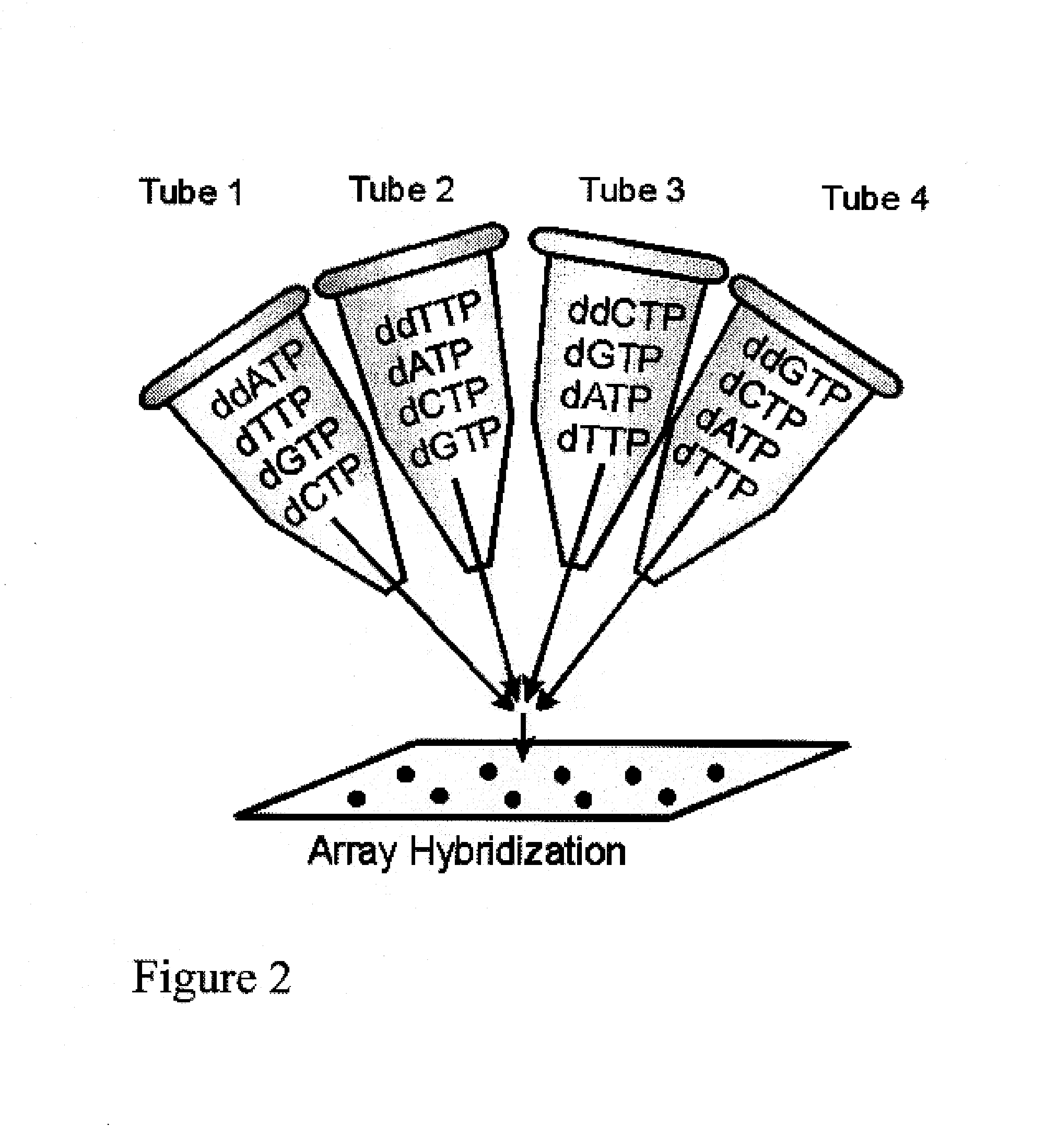
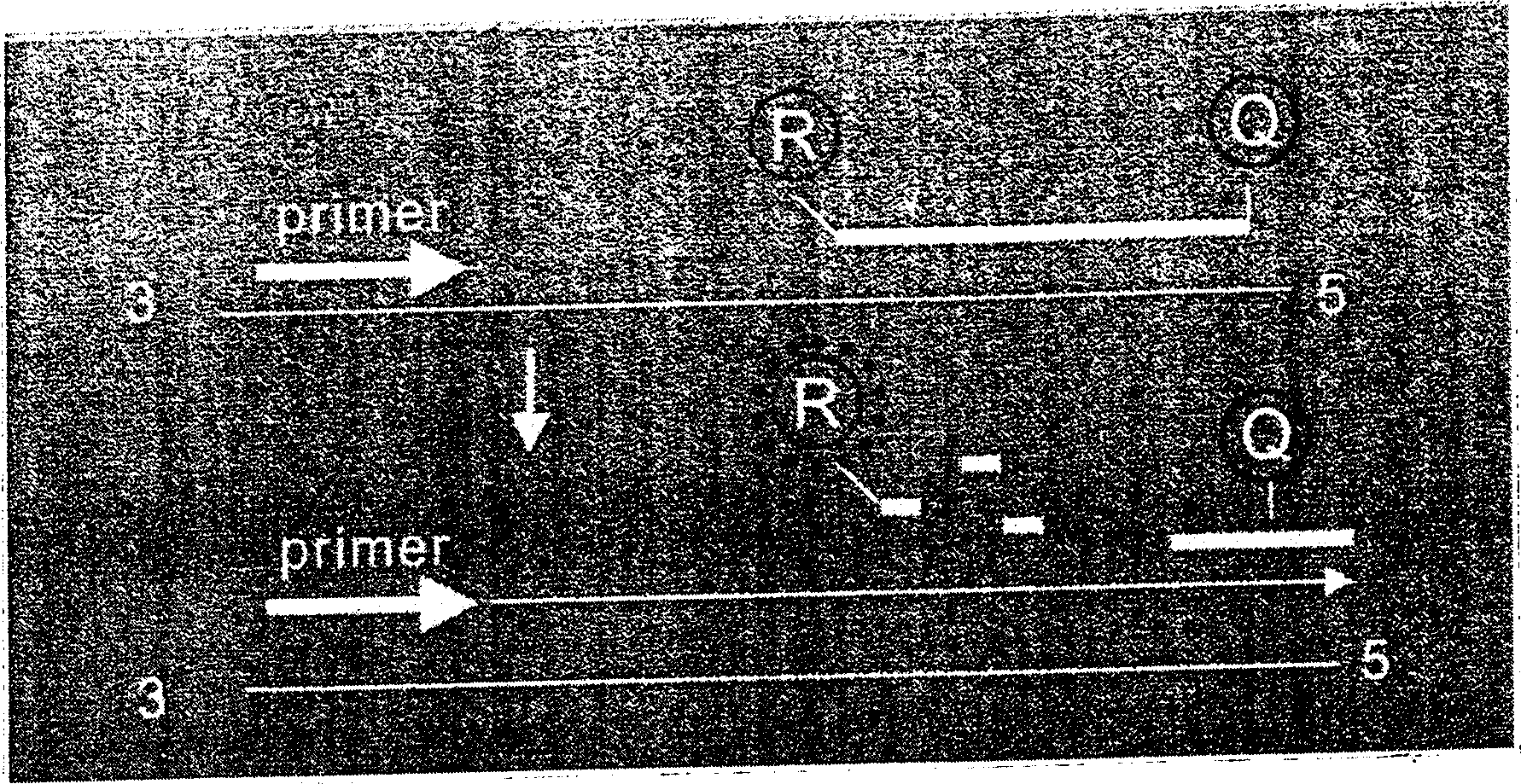
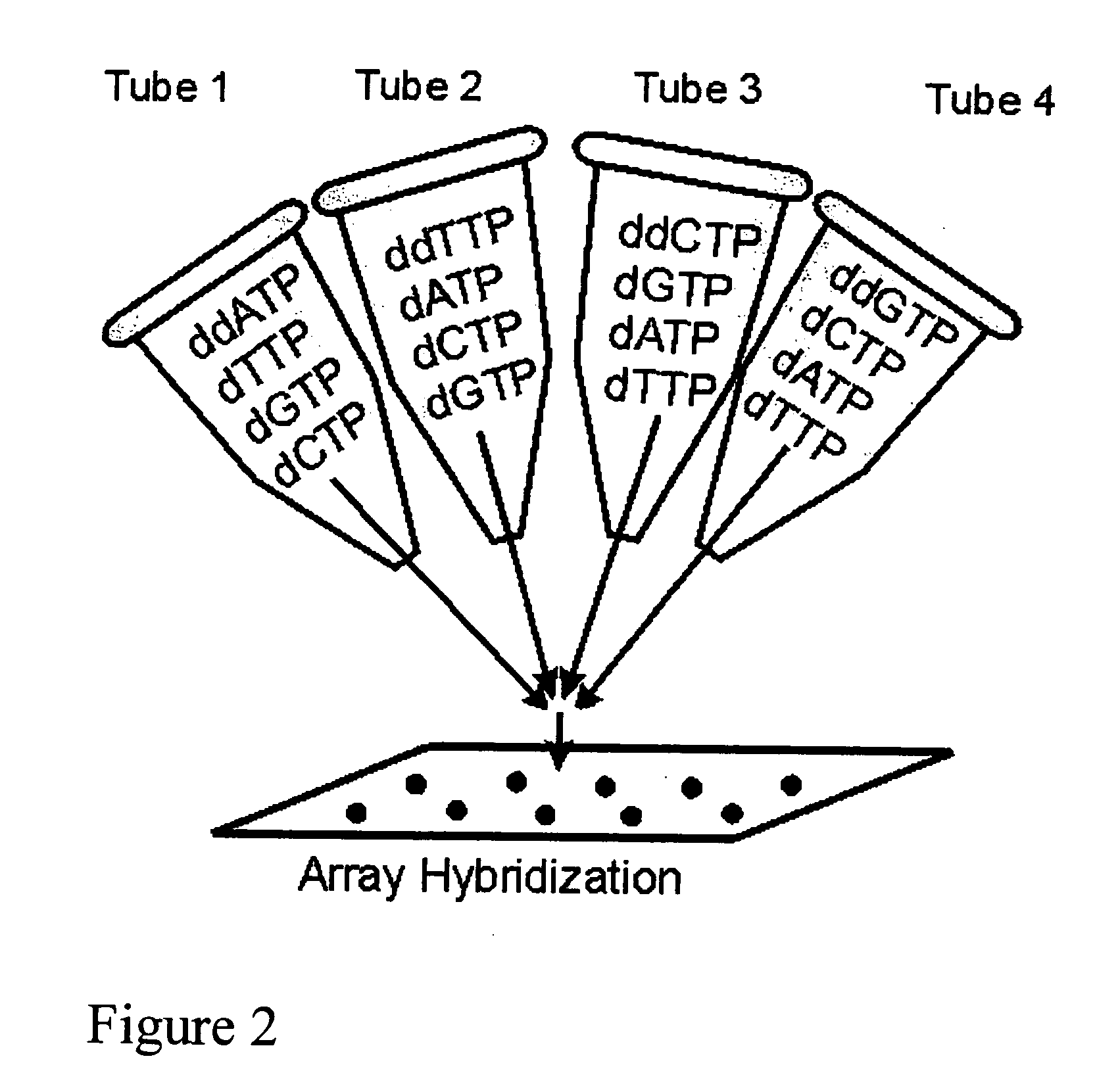
DNA sequence detection by limited primer extension
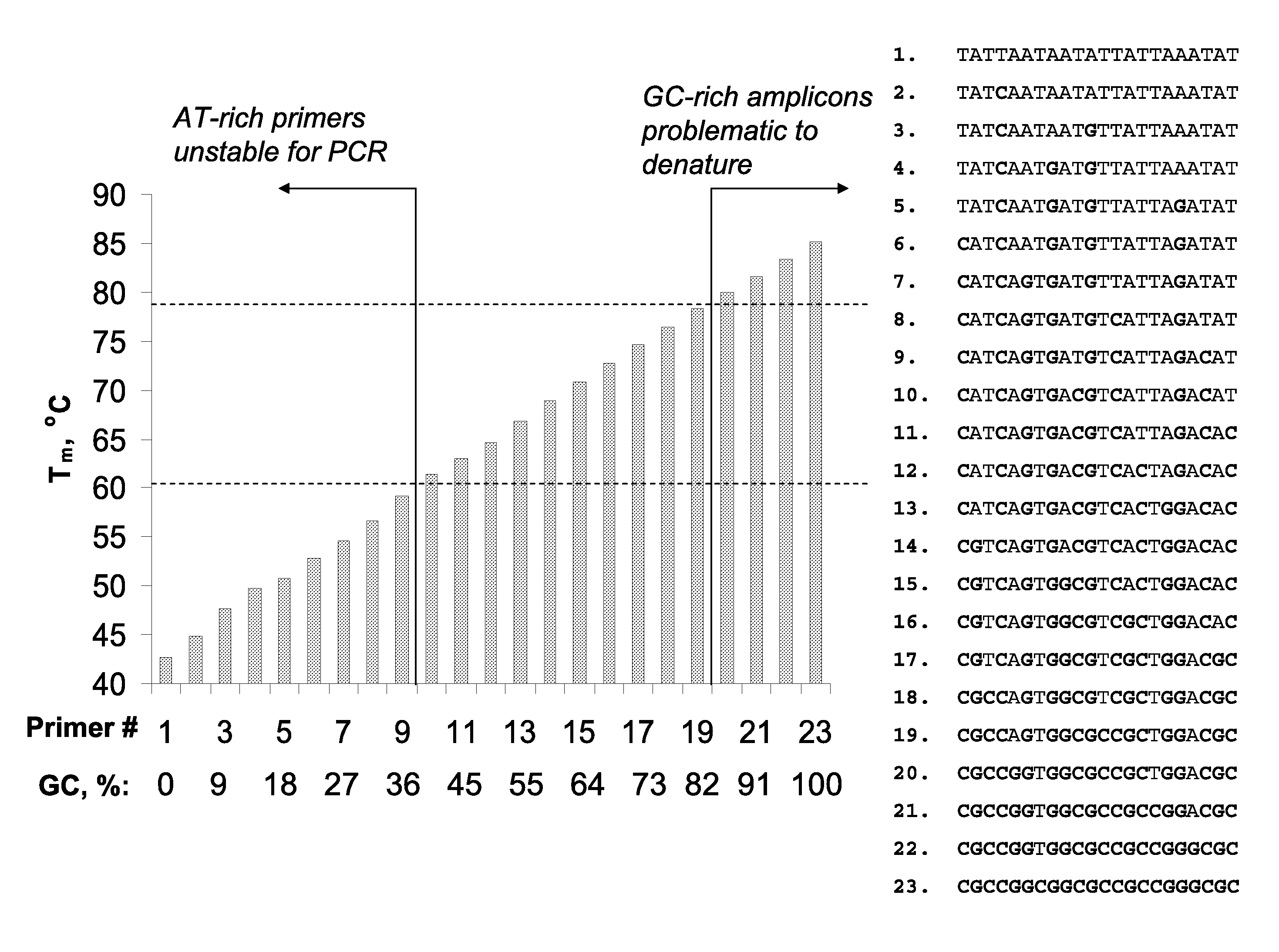
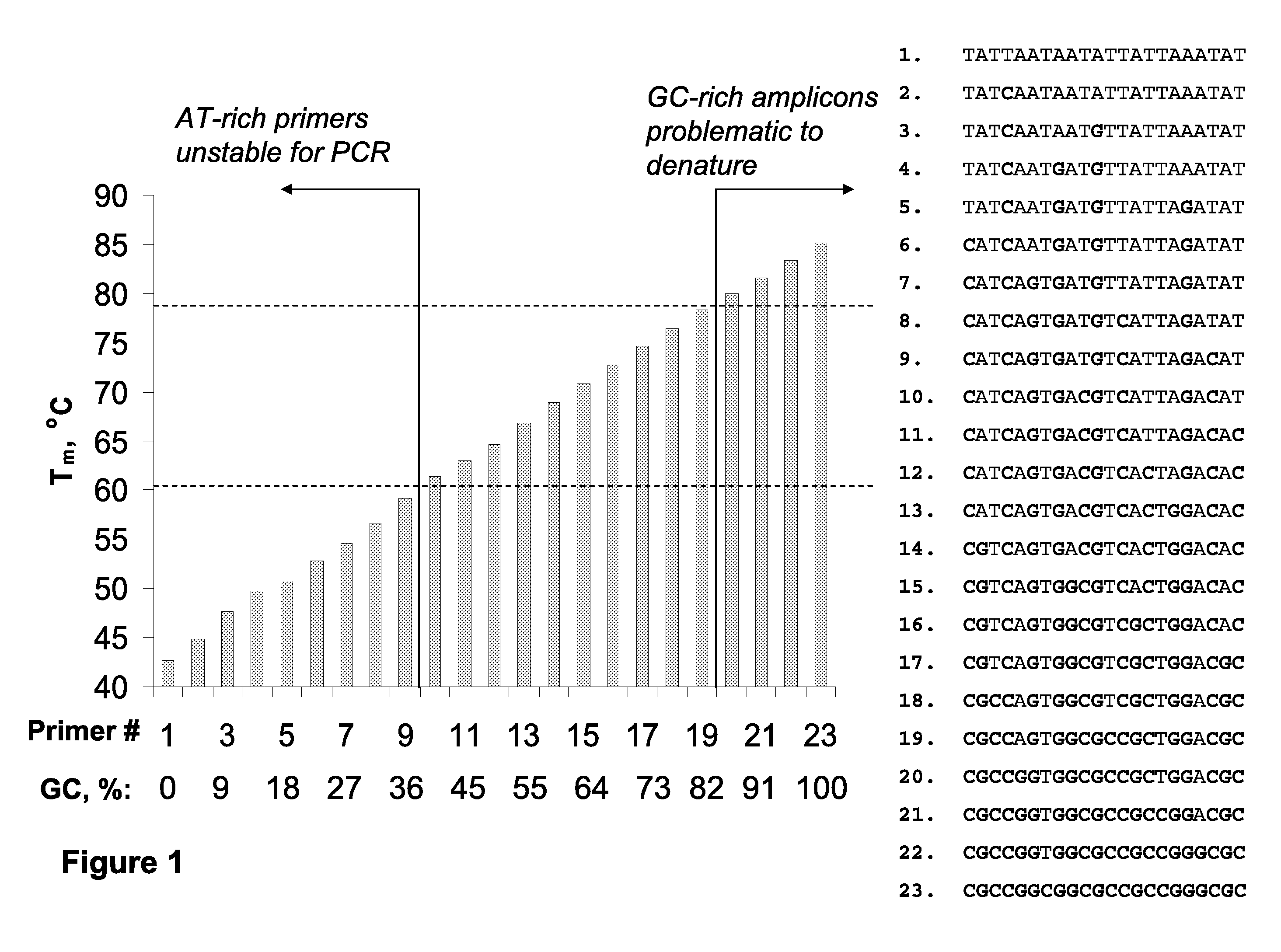
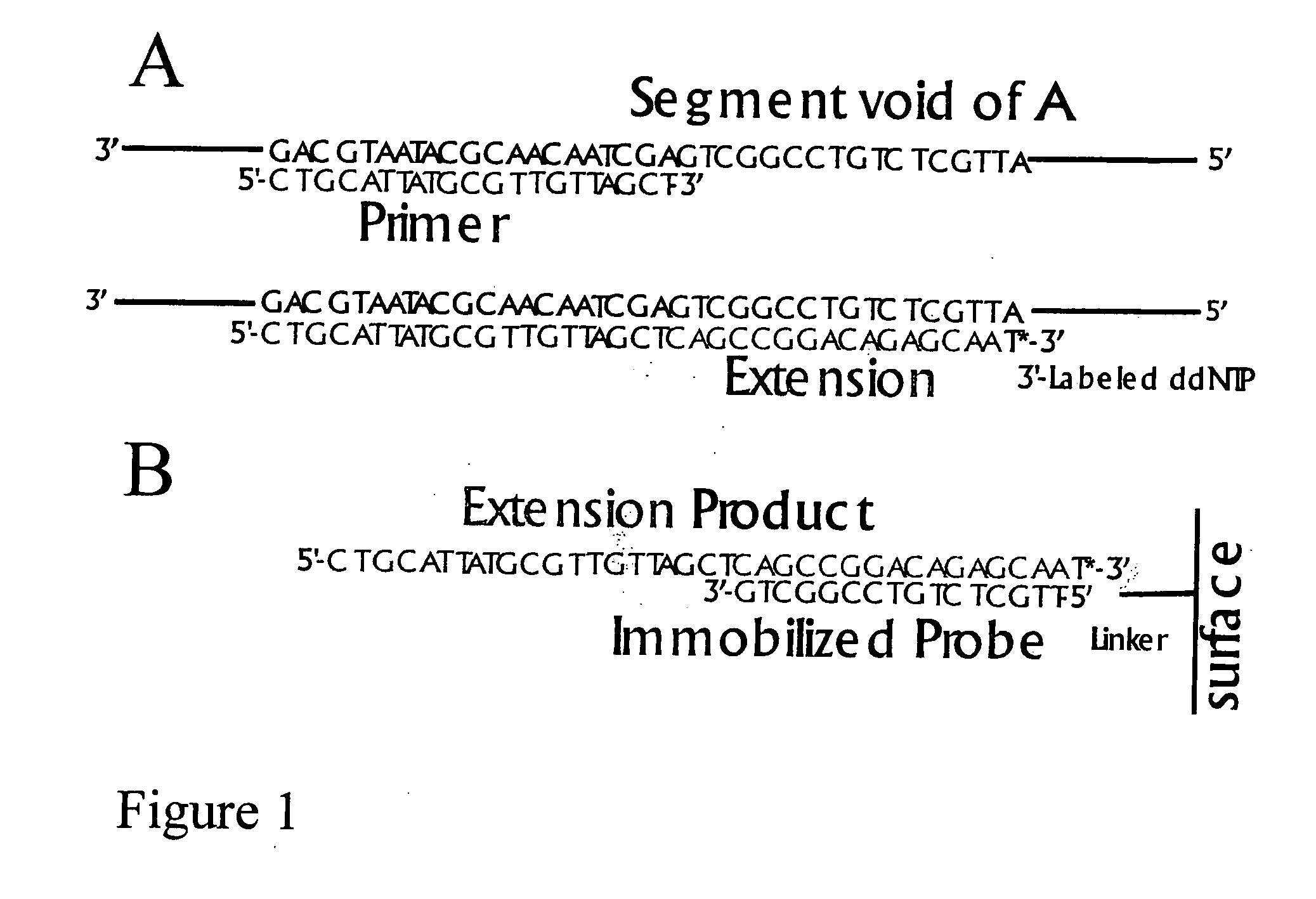
A novel limited primer extension reaction improves detection sensitivity and specificity in a variety of hybridization platforms. In the invention, a sequence of target DNA that lacks one of the four types of nucleic acid bases for a span of eight or more adjacent nucleotide positions is selected for use. This sequence is referred to as the extension complement sequence, or ECS. A primer with a sequence that is complementary to the target sequence that is immediately downstream (to the 3′ side) of this ECS is used to initiate an extension reaction. Extension occurs using a DNA polymerase and standard deoxynucleoside triphosphates for three of the four types of nucleic acid bases. The fourth base, which is complementary to the base missing in the ECS, is either absent or present only in the form of a dideoxynucleoside triphosphate, which does not support further extension. In either case, the extension reaction does not proceed past the first occurrence in the template of the base that is missing in the ECS. This results in a primer extension product with fixed length determined by the length of the ECS. The process can be repeated using a thermal-stable polymerase in a thermal-cycled reaction that results in a linear amplification of the targeted sequence. The resulting limited primer extension products serve as ideal hybridization analytes for determination of sample sequence content using microarrays.
Owner:ATOM SCI
Pyrosequencing Methods and Related Compositions
This invention provides methods for pyrosequencing and compositions comprising 3′-O— modified deoxynucleoside triphosphates.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Nucleic acid amplification method
InactiveUS20090155856A1Improve efficiencyImprove efficacyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideOligonucleotide primers
An object to be achieved by the present invention is to provide a nucleic acid amplification method by which a nucleic acid can be amplified using oligonucleotide primers and DNA polymerase. The present invention provides a nucleic acid amplification method which comprises performing incubation of a reaction solution containing at least one type of deoxynucleotide triphosphate, at least one type of DNA polymerase having strand displacement activity, at least two types of oligonucleotide primer, and the nucleic acid fragment as a template so as to perform a polymerase reaction that initiates from the 3′ end of the primer and thus amplifying the nucleic acid fragment, wherein a first oligonucleotide primer and a second oligonucleotide primer are designed in such a way that a region which contains two identical sequences X of serial 4 or more nucleotides within, the region of 200 or less nucleotides, or apart thereof can be amplified.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
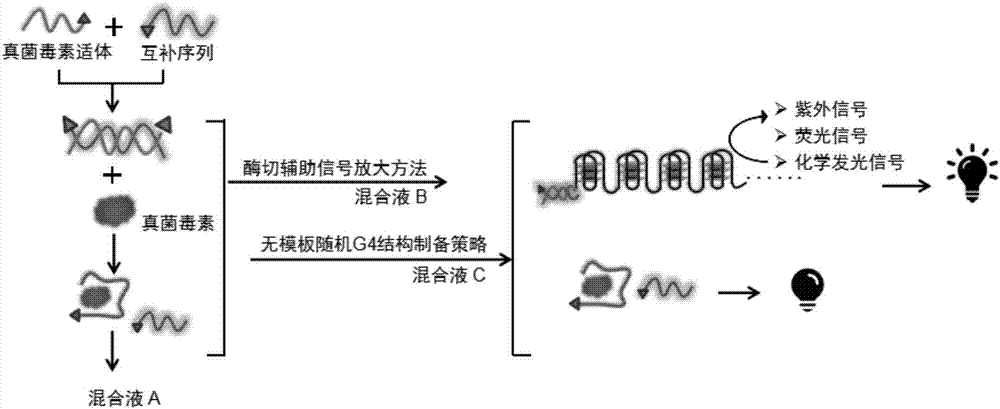
Method for detecting fungaltoxin through multiple signals and kit
ActiveCN107271668ARich identification methodsRich Signal TransformationBiological material analysisBiological testingFluorescenceUltraviolet
The invention discloses a method for detecting fungaltoxin through multiple signals. The method comprises the following steps: 1) combining fungaltoxin with aptamer: adding a to-be-detected sample after the reaction of the fungaltoxin aptamer and complementary sequence thereof, thereby acquiring a mixed solution A; 2) amplifying a digestion auxiliary signal: reacting the mixed solution A with restriction enzyme, thereby acquiring a mixed solution B; 3) preparing a guanine tetramer structure: reacting the mixed solution B with tail-end deoxynucleotide transferase and deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate and reacting with ligand molecules, thereby acquiring a mixed solution C; and 4) detecting and analyzing: performing catalytic oxidation reaction on the mixed solution C and different substrates, generating ultraviolet, fluorescent and chemiluminescent signals and calculating the content of fungaltoxin in the to-be-detected sample according to the relation of the response strength of all the signals and the fungaltoxin concentration. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of quick and simple operation and treatment, short detection time, marker-free effect, low cost, high precision, high sensitivity, and the like.
Owner:ACAD OF NAT FOOD & STRATEGIC RESERVES ADMINISTRATION
Gene detection reagent kit for SARS virus and its detection method
InactiveCN1468965AFacilitate early diagnosis"The shortened windowMicrobiological testing/measurementVenous blood specimenRNA extraction
The detection process of SARS virus of the gene detection reagent kit with rationing standard specific SARS virus nucleic acid as reference includes RNA extraction, PCR amplification and fluorescent detection. The venous blood sample, gargled liquid or respiratory tract secretion of the patient is used as the analysis sample directly, RNA of the sample is extracted as the nucleic acid template, and the template is used in fluorescent PCR amplification. The used fluorescent amplification detecting reagents includes one-step process RT-PCR buffering liquid, deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) mixture, specific amplification primer and specific probe. The method of the present invention is fast and convenient in detecting SARS virus.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL ZHEJIANG UNIV COLLEGE OF MEDICINE +1
Nucleic acid amplification method
ActiveUS8420323B2Simple and rapid methodShort timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotidePolymerase L
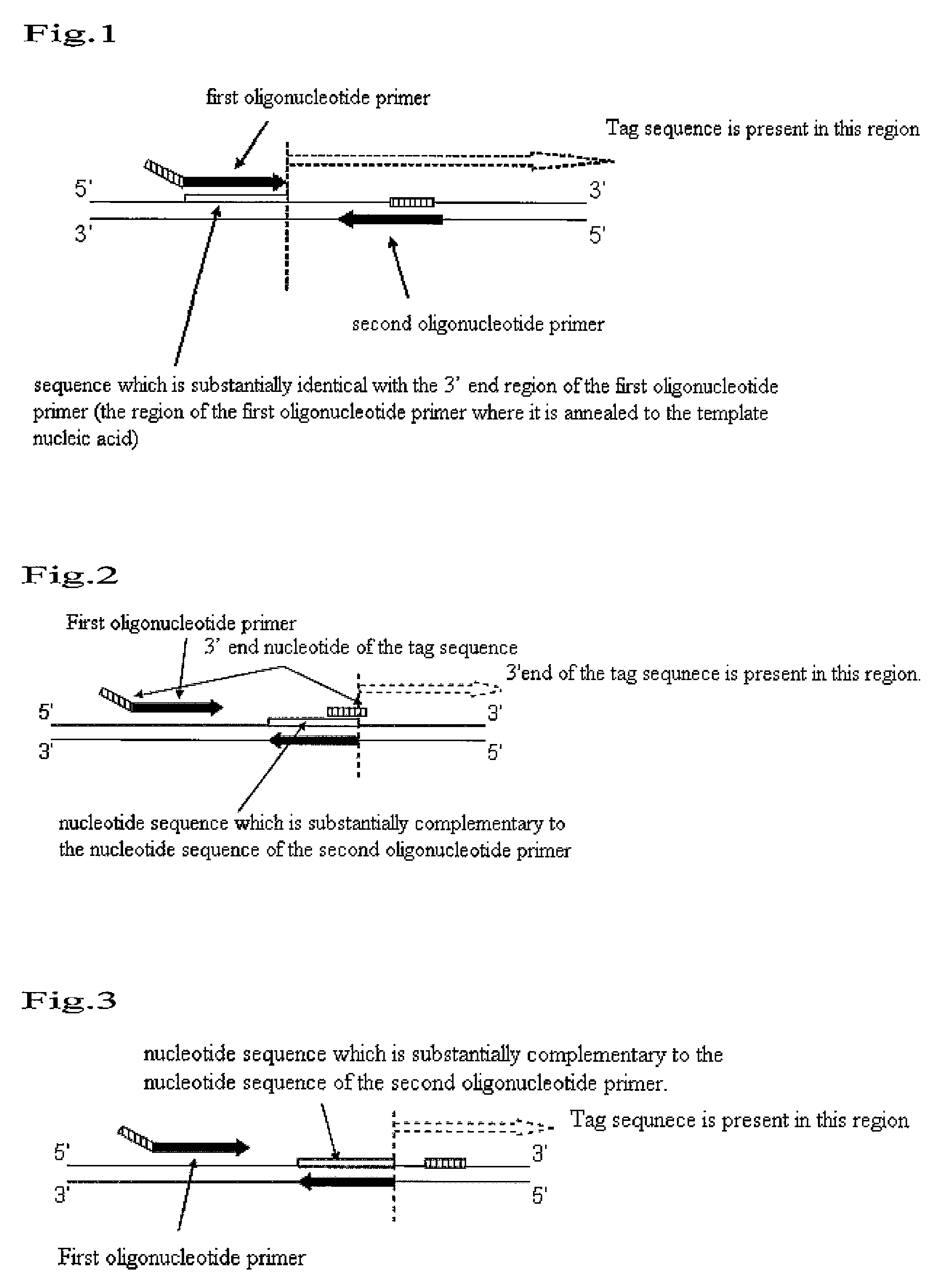
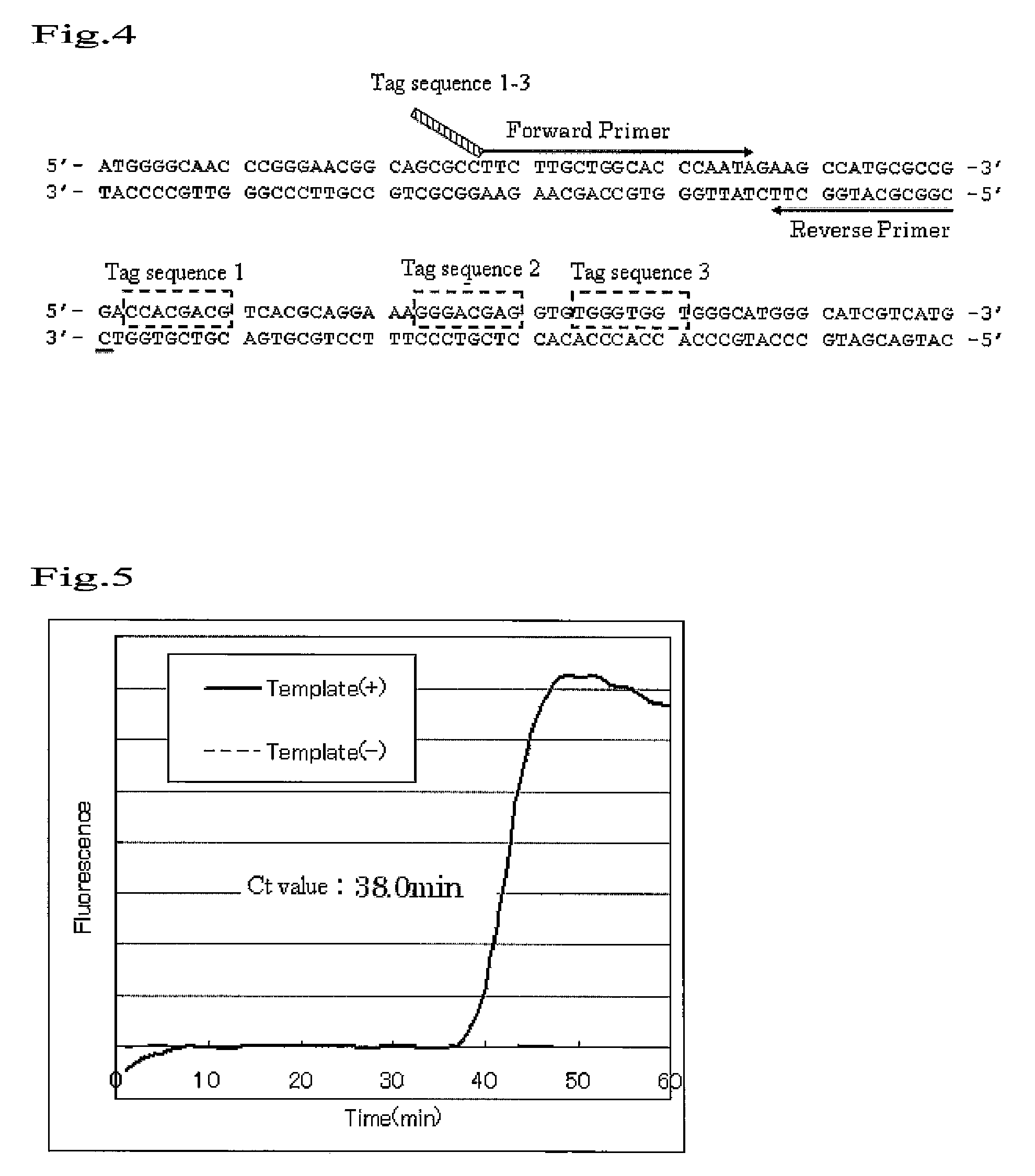
An object to be achieved by the present invention is to provide a nucleic acid amplification method by which a nucleic acid can be amplified using oligonucleotide primers and DNA polymerase. The present invention provides a nucleic acid amplification method which comprises performing incubation of a reaction solution containing at least one type of deoxynucleotide triphosphate, at least one type of DNA polymerase, at least two types of oligonucleotide primer, and the nucleic acid fragment as a template so as to perform a polymerase reaction that initiates from the 3′ end of the primer and thus amplifying the nucleic acid fragment, wherein a tag sequence is added at the 5′ end of the first oligonucleotide primer, and the tag sequence is a nucleotide sequence on the template nucleic acid fragment which is present downstream of the sequence which is substantially complementary with the 3′ end region of the first oligonucleotide primer (a region where the first oligonucleotide is annealed to the template nucleic acid).
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Pyrosequencing methods and related compositions
ActiveUS9169510B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsPyrophosphoric acidBiology
This invention provides methods for pyrosequencing and compositions comprising 3′-O— modified deoxynucleoside triphosphates.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
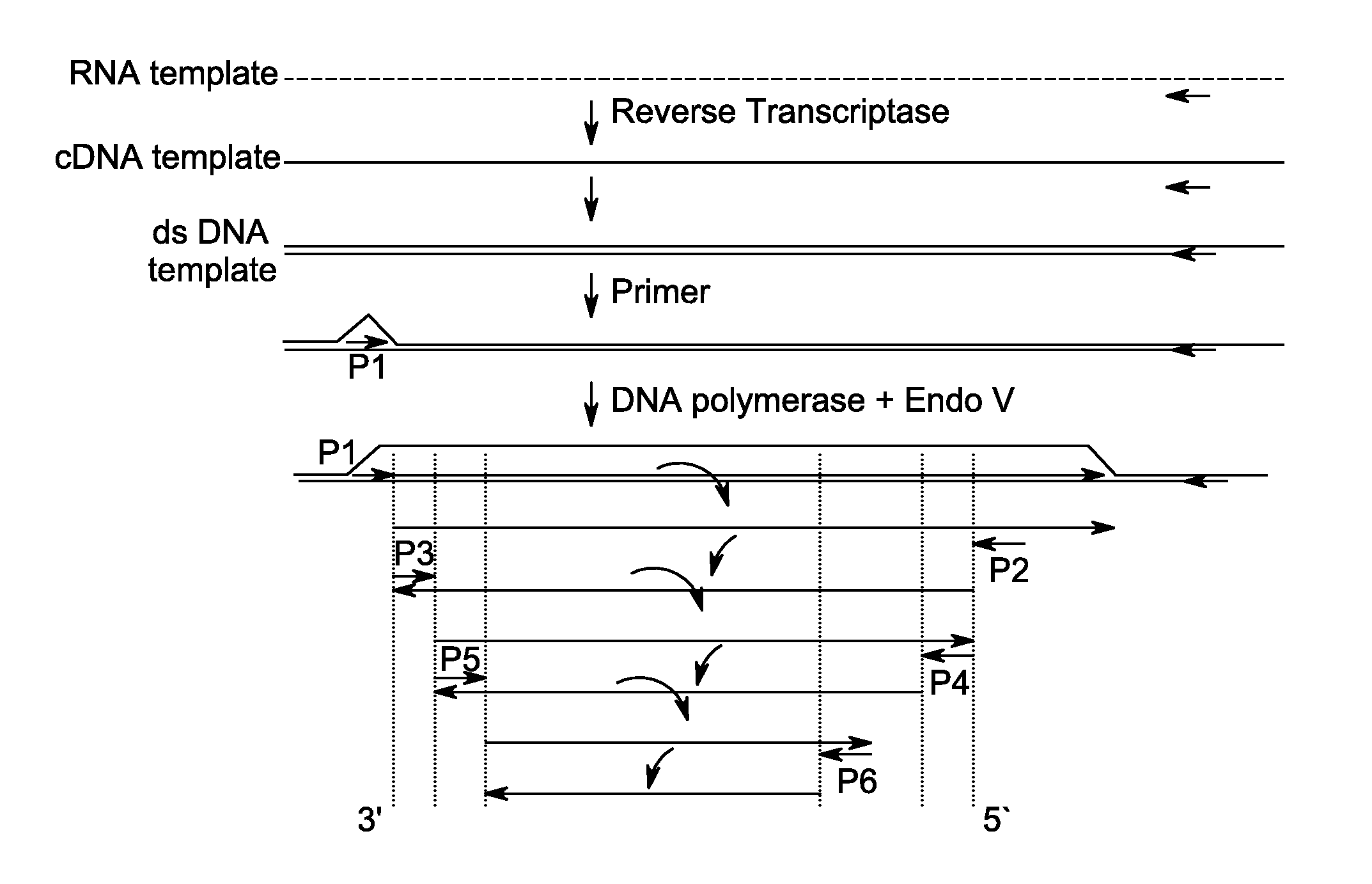
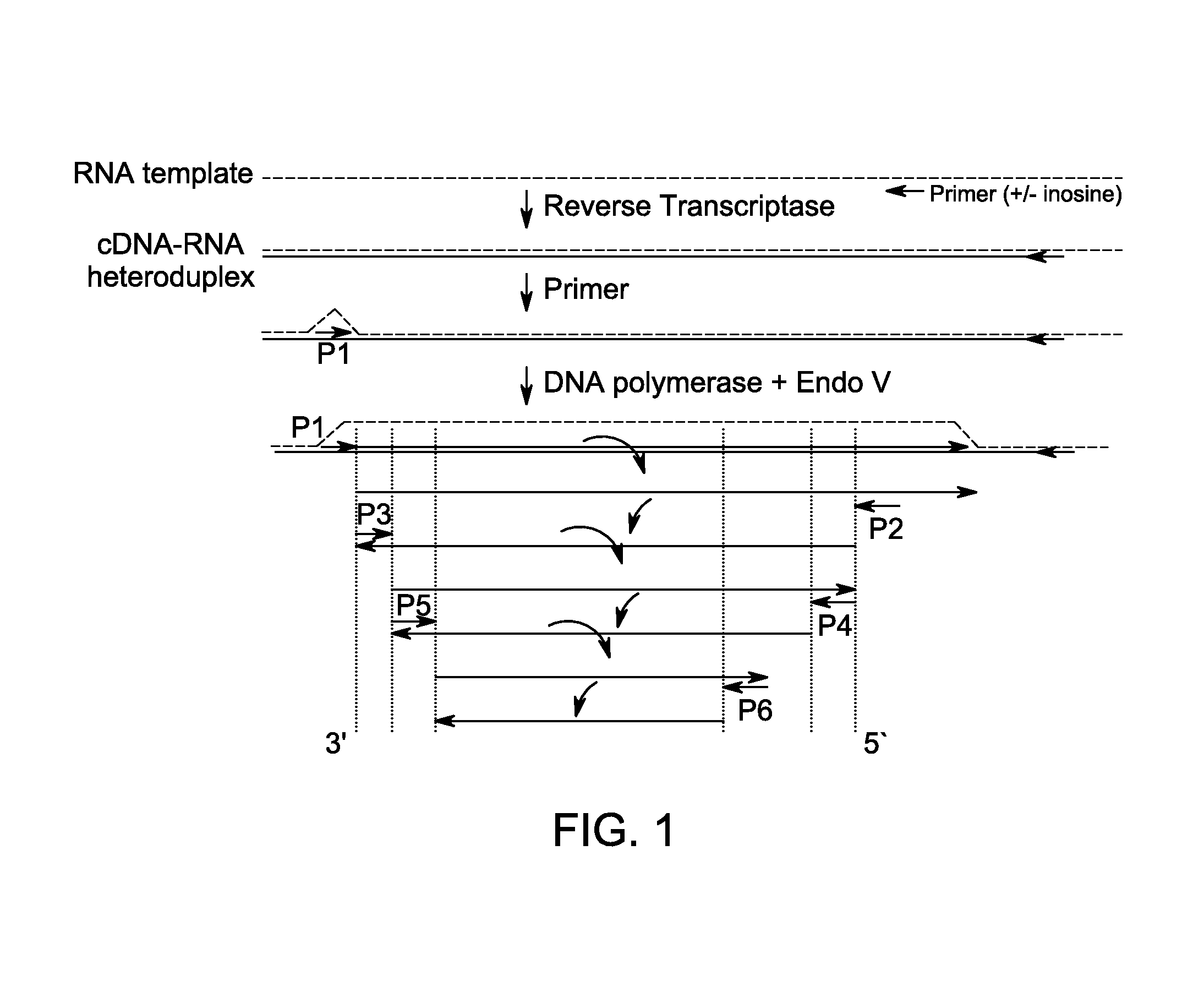
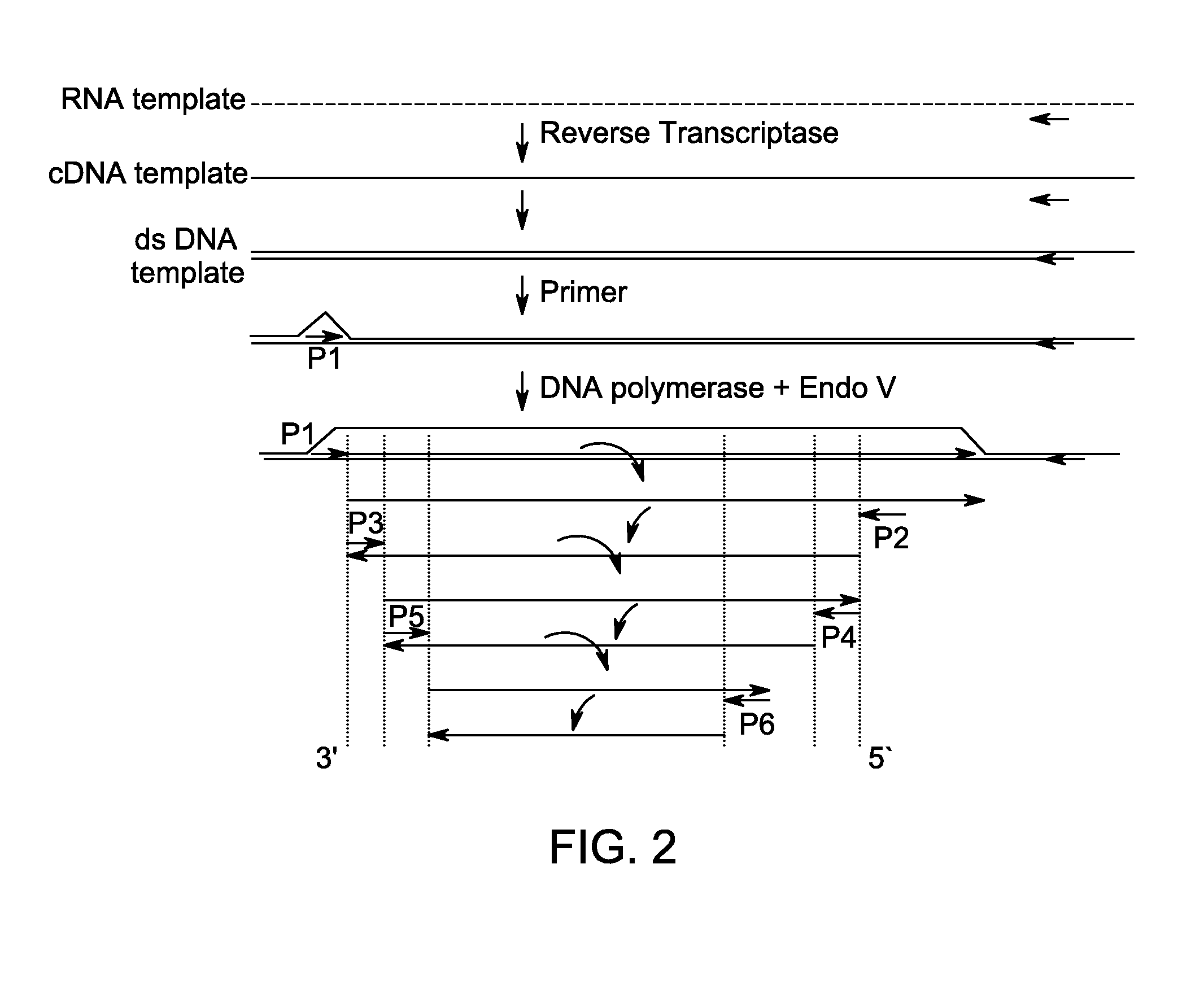
Kit for isothermal DNA amplification starting from an RNA template
A method of amplifying RNA template is provided. The method comprises reverse-transcribing a ribonucleic acid (RNA) template to form a cDNA using a first reaction mixture comprising RNA template, at least one primer capable of hybridizing to the RNA template, a reverse transcriptase and deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs); and amplifying the cDNA to form an amplified product using a second reaction mixture comprising at least one strand displacement DNA polymerase, at least one inosine-containing primer and a nuclease that is capable of nicking DNA 3' to an inosine residue of the primer. The method is accomplished under an isothermal condition without denaturing the cDNA template. A method of quantifying RNA template in a sample and a method of detecting RNA template in a sample are also provided. Kits for amplifying deoxynucleic acid (DNA) from ribonucleic acid (RNA) template are also provided.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
Porcine Delta coronavirus detection kit based on constant temperature isolation type fluorescent polymerase chain reaction (PCR) platform, and application of porcine Delta coronavirus detection kit
InactiveCN107022650AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFreeze-dryingReverse transcriptase
The invention discloses a porcine Delta coronavirus detection kit based on a constant temperature isolation type fluorescent polymerase chain reaction (PCR) platform, and application of the porcine Delta coronavirus detection kit. The porcine Delta coronavirus detection kit consists of reaction buffer, a fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction liquid freeze-drying tube, a positive reference substance freeze-drying tube and a negative reference substance freeze-drying tube, wherein the fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction liquid freeze-drying tube is formed by mixing and freeze-drying Taq enzyme, reverse transcriptase, a detection primer, a probe and deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP). The kit provided by the invention is short in detection time (the reaction time is only 42min), high in specificity and sensitivity and convenient to store (at 4 DEG C); when being matched with a constant temperature isolation type PCR instrument for use, the kit is very suitable for the rapid field detection of the porcine Delta coronavirus and can be widely popularized at the grassroots level.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Use of base-modified deoxynucleoside triphosphates to improve nucleic acid detection
ActiveUS8349556B2Stable amplificationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSugar derivativesNucleic acid detectionPcr assay
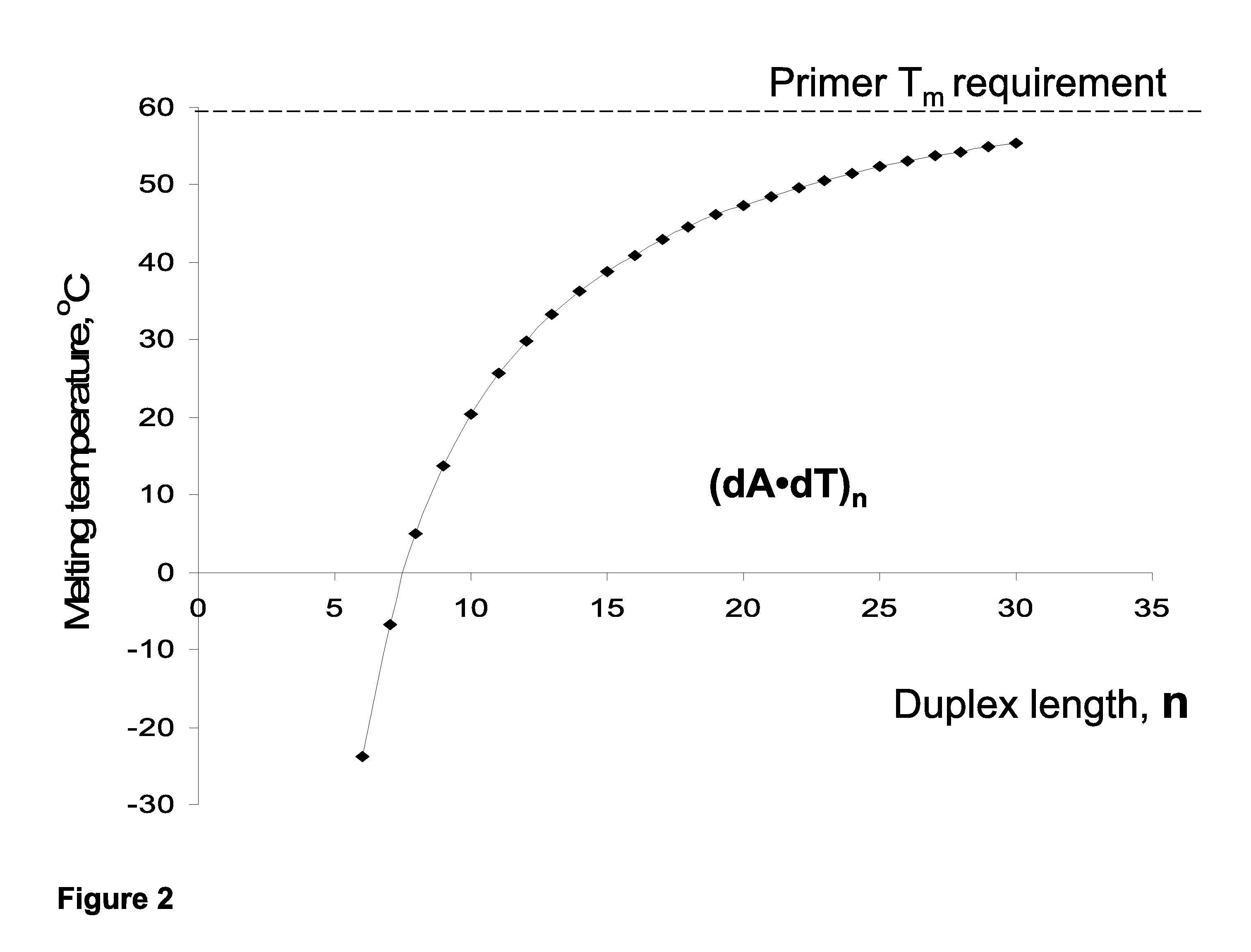
Aspects of the invention provide novel and surprisingly effective methods for the detection of nucleic acids, comprising nucleic acid amplification using base-modified deoxynucleoside 5′-triphosphates (dNTPs). Particular aspects relate to methods for enhancing hybridization properties of oligonucleotide primers and probes in assays detecting nucleic acids, comprise amplifying target DNAs in presence of base-modified duplex-stabilizing deoxyribonucleoside 5′-triphosphates to provide for modified target DNAs, and thereby considerably improving performance of the detection assays. The disclosed methods allow for increasing of the reaction temperature in PCR-based detection systems or, alternatively, reducing the length of the oligonucleotide primers and probes. Certain aspects relates to improvement of real time PCR assays, wherein nucleic acids of interest are detected as the reaction proceeds using fluorescent agents or oligonucleotide FRET probes.
Owner:KUTYAVIN IGOR
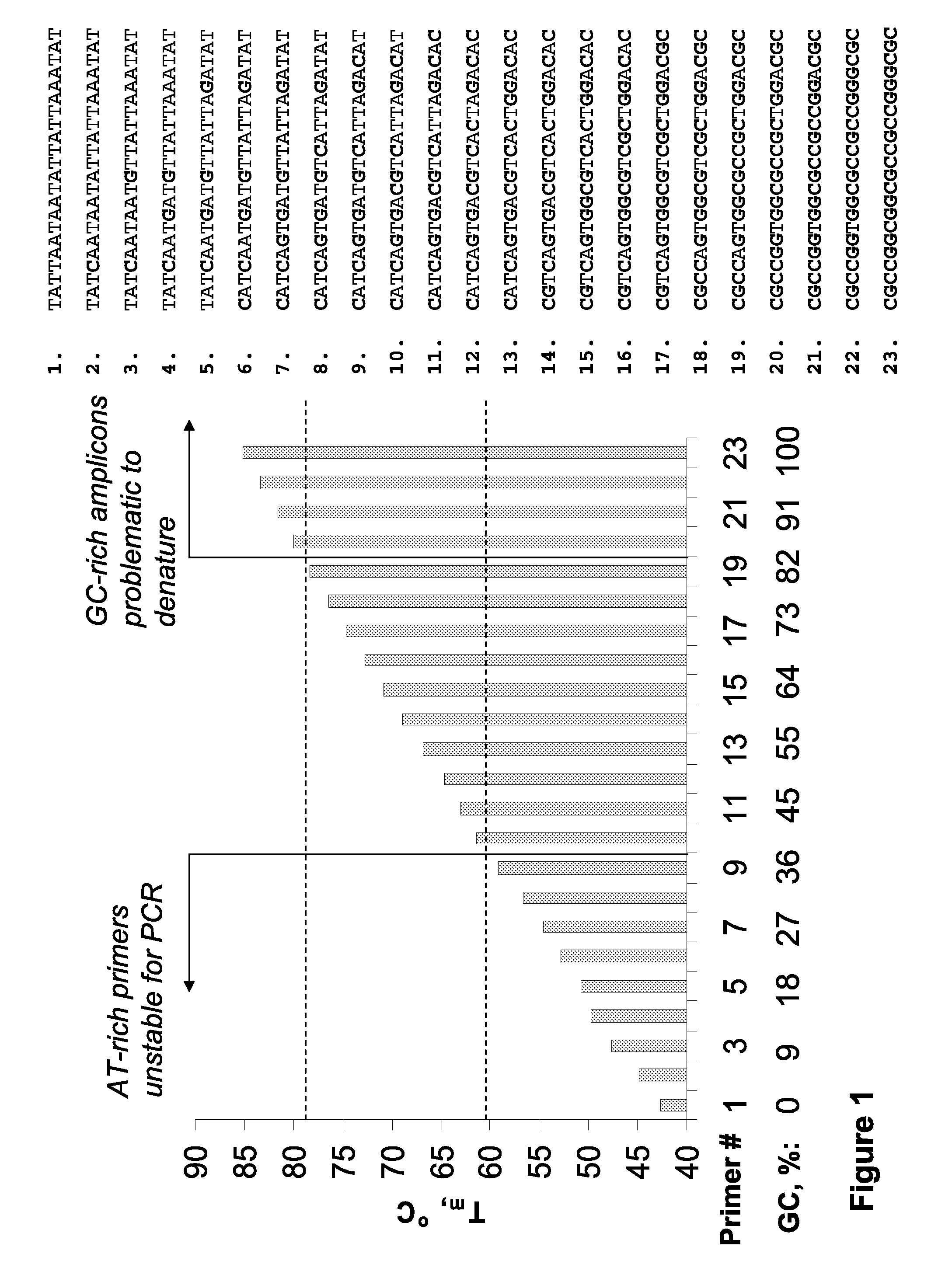
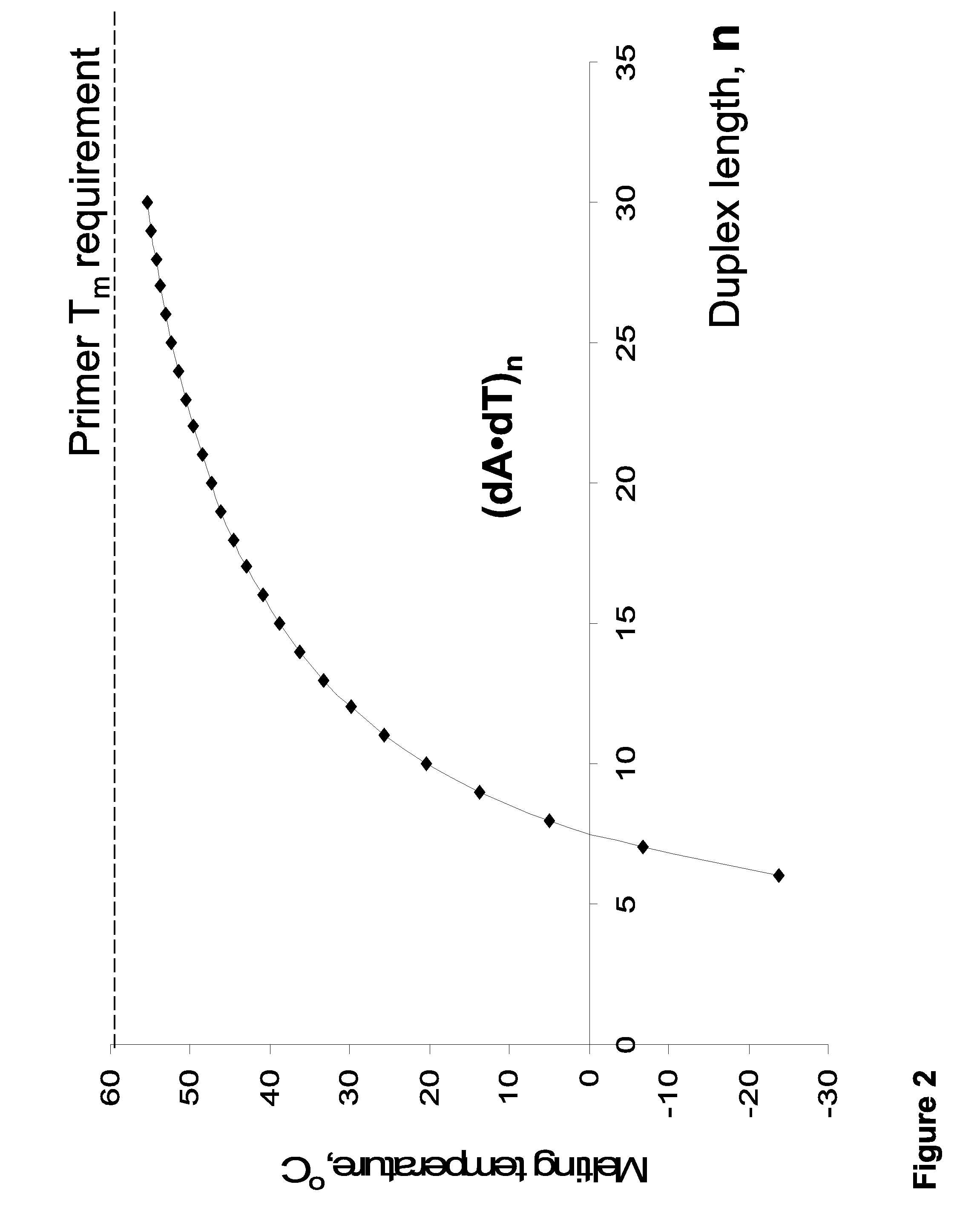
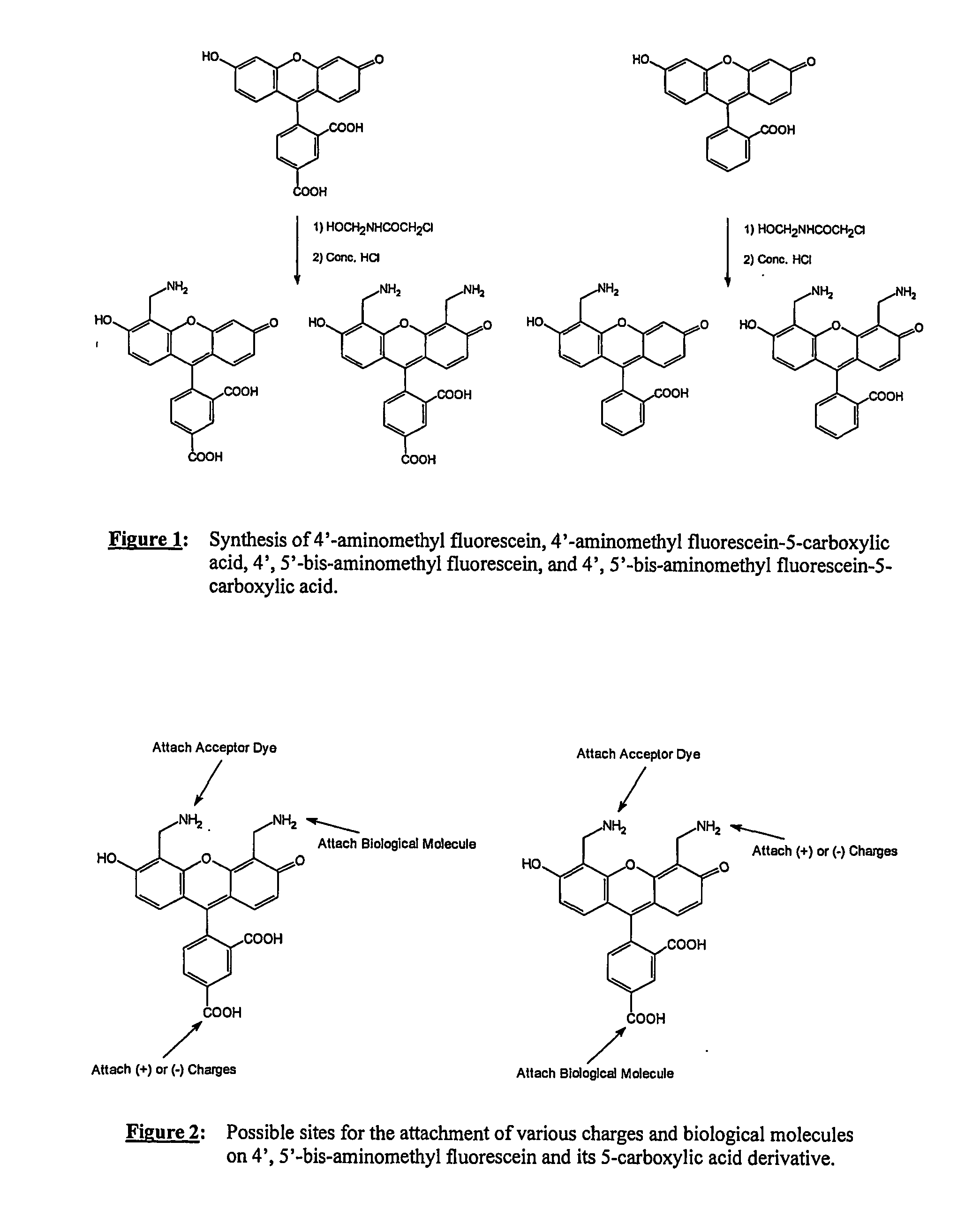
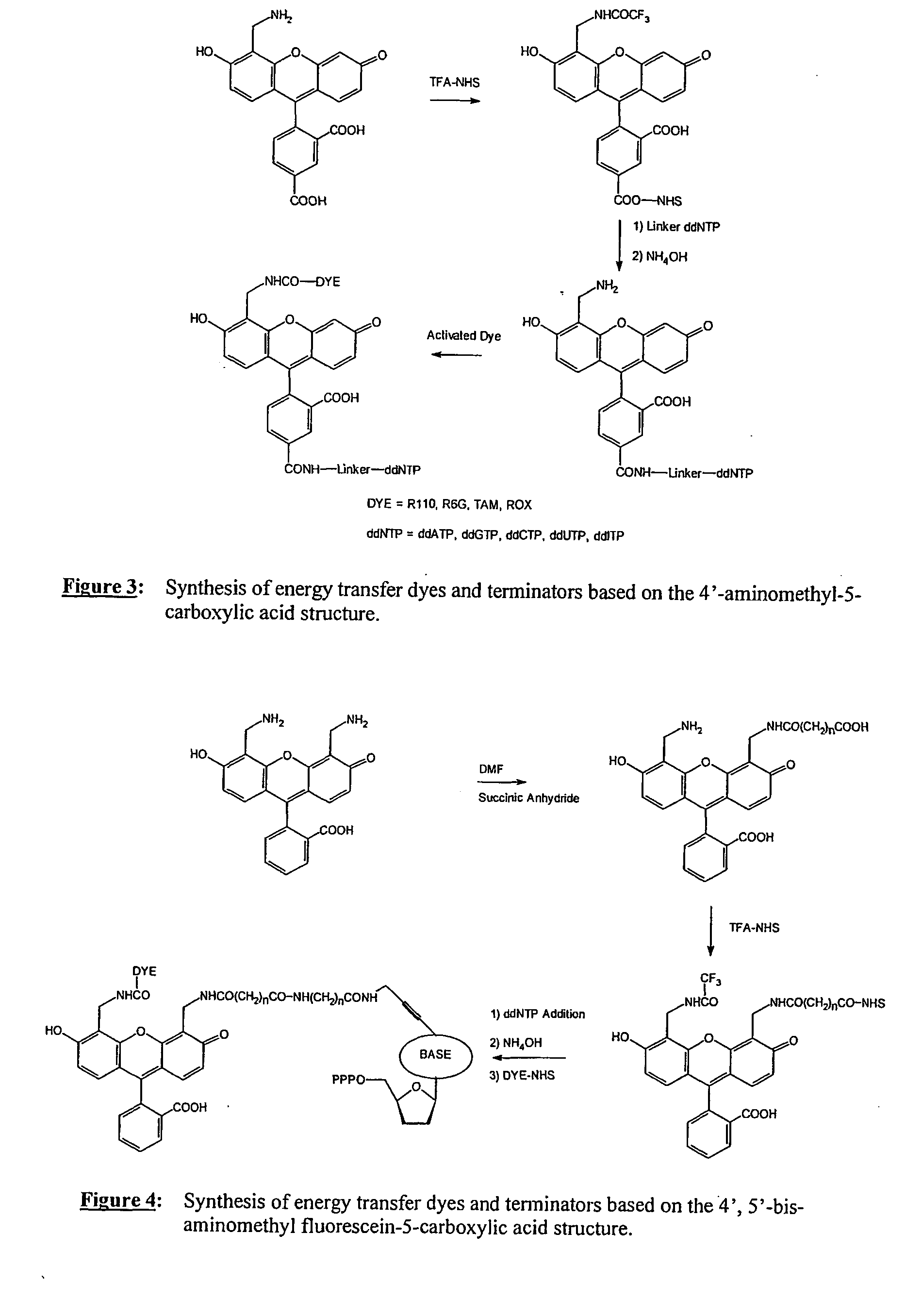
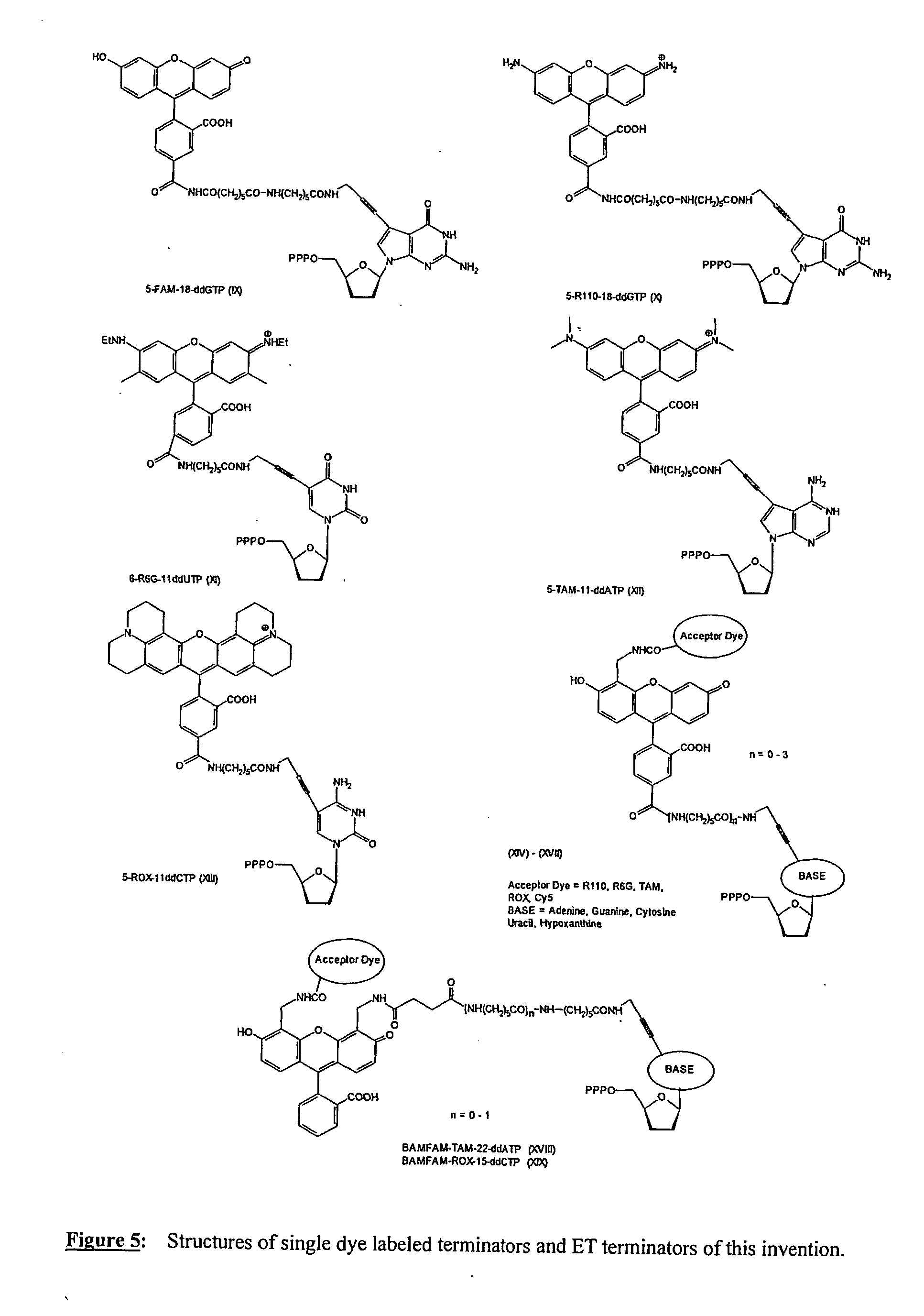
Energy transfer dyes, terminators and use thereof
InactiveUS20050255475A1Increase brightnessExtend possible rangeMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphorus organic compoundsEnergy transferResonance
The present invention relates to a novel set of four fluorescently labeled dye terminators. Two of them are single dye labeled terminators and the other two dye terminators are based on fluorescent resonance energy transfer (FRET). The FRET dye terminators are generated from the 4′,5′-bis-aminomethylfluorescein. Of the two amino groups of the donor dye, 4′,5′-bis-aminomethylfluorescein, one amino group is used to attach the acceptor dye, and the other amino group is used to attach the dideoxynucleoside-5′-triphosphate. Their preparation, energy transfer efficiency, and use as labels, specifically, in DNA sequencing reactions is disclosed.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
PCR-RFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism) method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism of Pax3 gene of yellow cattle and application of method
InactiveCN103789406ASolve the cumbersomeFix instabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionTranscription start
The invention discloses a PCR-RFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism) method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of a Pax3 gene of yellow cattle. The method comprises the following steps: detecting gene polymorphisms according to DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) pool sequencing results, wherein the gene polymorphisms comprise SNP of a sequence transcription start site -580 T or G of the Pax3 gene of the yellow cattle; in the presence of a Taq DNA polymerase, a Buffer (a buffer environment), Mg<++> and dNTPs (deoxynucleoside triphosphate), performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the Pax3 gene of the yellow cattle, digesting a PCR amplification product by HinfI and HaeIII restriction enzymes respectively, and performing agarose gel electrophoresis on enzyme digestion segments. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a foundation is laid for creating a relationship between the SNP and the growth trait of the Pax3 gene, so that the marker assisted selection of the growth trait of the yellow cattle in China can be conveniently carried out and a new strain of high-quality special beef in China can be quickly, efficiently and accurately bred.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Dual fluorescence quantification RT-PCR detection kit and application thereof
ActiveCN102230023AIncreased biosecurity riskPerfecting flu testingMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceSequence analysisReverse transcriptase
The invention provides a dual fluorescence quantification RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) detection kit, comprising a deoxynucleoside triphosphate mixture, MgCl2, an RNA enzyme inhibitor, a Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase, a DNA polymerase, a influenza virus standard and a reference substance. Based on sequence analysis of present pervasive A H1N1 influenza virus, the invention provides a multiple fluorescence quantification PCR molecular biology gene diagnosis method and a diagnostic kit which are rapid, specific, accurate and sensitive. In addition, one reaction tube can simultaneously detect and differentiate an influenza A virus or an influenza B virus in 2h, so as to improve influenza detection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
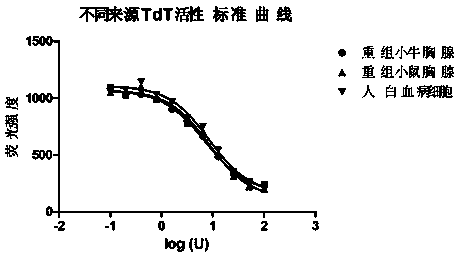
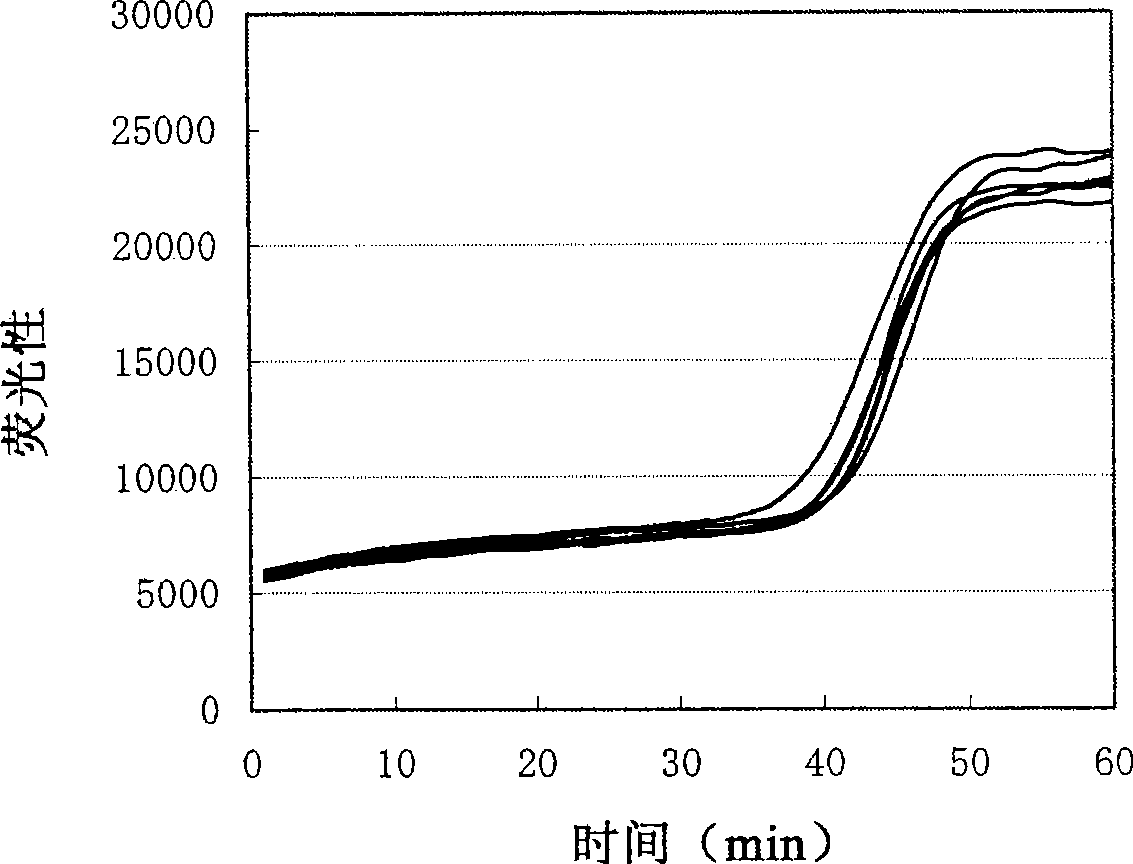
Method for measuring activity of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
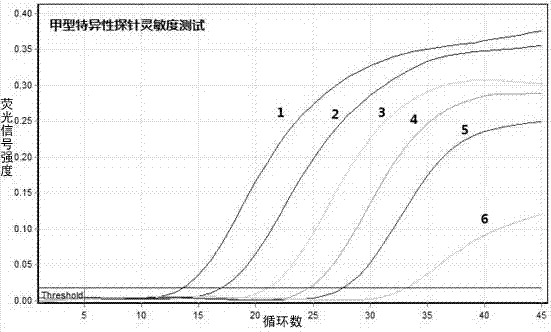
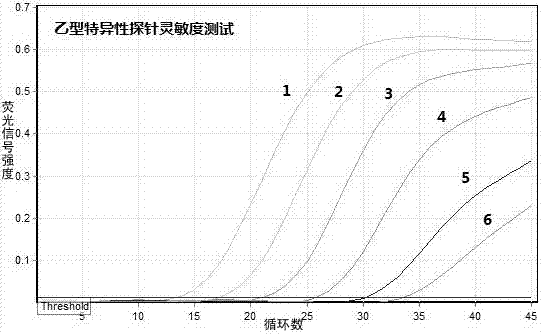
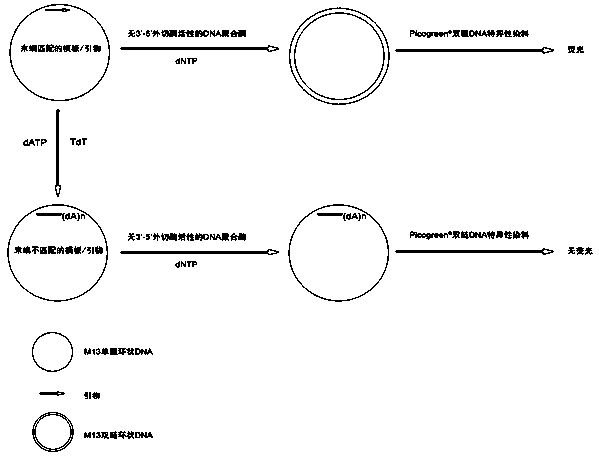
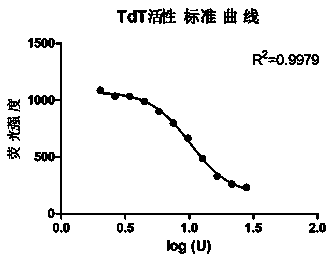
InactiveCN104293883ALow costEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LSingle strand
The invention discloses a method for measuring activity of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, synthesizing a primer according to a single stranded template, annealing the single stranded template, then performing a 3' end tailing reaction catalyzed by TdT enzyme in the presence of one of four deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, after the 3' end tailing reaction is completed, performing a polymerization reaction in the presence of enough DNA polymerase without 3'-5 'excision enzyme activity to generate double stranded DNA, finally measuring the relative quantity of the double stranded DNA or single stranded DNA in the reaction system after the polymerization reaction is finished, and deducing the activity degree of the Poly (A) polymerase according to the detection result, wherein the basic group at the first site on the used single stranded template in the 3' direction and the deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate used in the tailing reaction are not complementary. Compared with the existing method, the method disclosed by the invention is free of radioactive pollution, simple and quick to operate, low in reagent preparation cost and high in sensitivity.
Owner:VAZYME BIOTECH NANJING
Nucleic acid amplification method
ActiveCN101368197AHigh amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOligonucleotide primersNucleotide
The present invention provides a nucleic acid amplification method by using a oligonucleotide primer and a DNA polyase. The nucleic acid amplification method provided by the invention comprises performing incubation of a reaction solution containing at least one type of deoxynucleotide triphosphate, at least one type of DNA polymerase having strand displacement activity, at least two types of oligonucleotide primer, and the nucleic acid fragment as a template so as to perform a polymerase reaction that initiates from the 3' end of the primer and thus amplifying the nucleic acid fragment, wherein the characteristic is that a first oligonucleotide primer and a second oligonucleotide primer are designed in such a way that a region which contains two identical sequences X of serial 4 or more nucleotides within the region of 200 or less nucleotides, or a part thereof can be amplified.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
RT-LAMP (reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification) detection kit and RT-LAMP detection method for SVCV (spring viremia of carp virus)
InactiveCN102876811AEfficient detectionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementWater bathsBetaine
The invention discloses a RT-LAMP (reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification) detection kit and a RT-LAMP detection method for SVCV (spring viremia of carp virus). The RT-LAMP detection kit of SVCV comprises 10*ThermoPol Reaction buffer, Bst DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase, dNTPs (deoxynucleoside triphosphates), AMV reverse transcriptase, outer primer F3 and B3, inner primer FIP, BIP and Betaine, MgC 12, DTT, and 1000*SYBR Green I. The RT-LAMP detection kit is simple, fast, and high in specificity and sensitivity, only needs a water bath kettle or a metal bath to accurately detect SVCV in samples in 2 hours, can detect SVCV of infected tissues of sick fish, can detect cells infected by SVCV, and is suitable for fast field detection of SVCV.
Owner:YANGTZE RIVER FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
H5N1 type poultry grippal virus fluorescent augmentation detection kit and detection method
InactiveCN1904068AEarly isolationImprove isolationMicrobiological testing/measurementHemagglutininFluorescence
The present invention provides a kind of H5N1-type avian influenza virus fluorescence amplification detection kit and detection method for detecting avian influenza virus byusing said kit. Said kit includes the following several portions: H5N1-type avian influenza virus hemagglutinin gene standard product, fluorescence amplification detection reagent and DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase. The fluorescence amplification detection reagent mainly includes one-step method RT-PCR buffer fluid, specific amplification primer and specific probe and deoxynucleoside triphosphate mixture. Said method can directly detect pathogen nucleic acid, and can detect specific gene containing H5N1-type avian influenza virus.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Chikungunya virus isothermal amplification detection kit and primer thereof
InactiveCN102399903ASimple designOptimizing Primer SpacingMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesFluorescenceChikungunya fever
The invention provides a chikungunya virus isothermal amplification detection kit and a primer thereof. The kit comprises the primer, Bst DNA polymerase, a reaction liquid and SYBR Green I fluorescent dye, wherein the reaction liquid is 10mM deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate, 10*reaction buffer liquid and 150mM MaSO4; the sequences of the primer are sequences represented by SEQ ID NO:1-4 or sequences represented by SEQ ID NO:5-8 or sequences represented by SEQ ID NO:9-12 or sequences represented by SEQ ID NO:13-16. The kit provided by the invention has the advantages of short detection time, strong specificity, high sensitivity, high detection accuracy and programmed reaction, is easy and convenient to qualify and is widely applied to conventional detection and epidemiological survey in clinic and ports.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF GUANGDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU +1
Detection format for hot start real time polymerase chain reaction
InactiveUS20090181401A1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyLength waveDouble strand
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
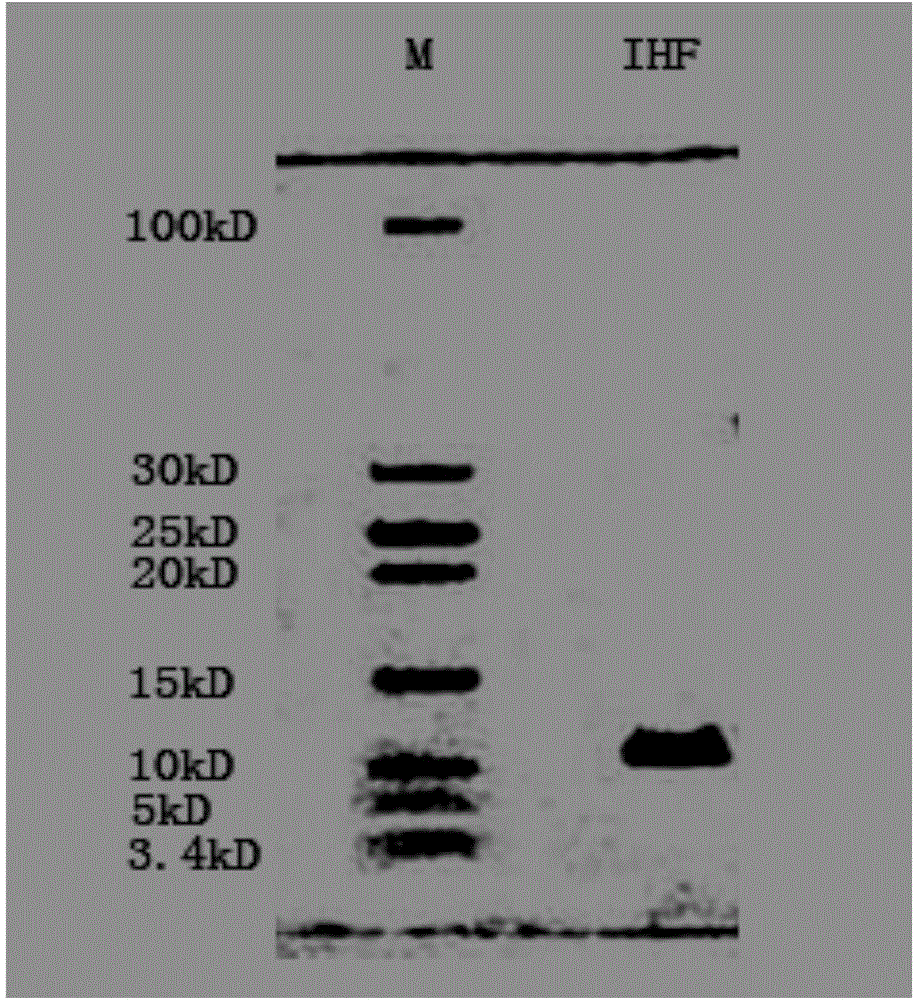
Method for improving PCR amplification sensitivity by using integrated host factor
ActiveCN104593491AHigh sensitivityImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementHost factorsOligonucleotide primers
The invention provides a method for improving PCR amplification sensitivity by using an integrated host factor. The method comprises the following steps: adding the integrated host factor IHF into a reaction solution containing deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate, DNA polymerase, an oligonucleotide primer and a nucleic acid fragment which serves as a template, carrying out repeated heat circulation according to three steps of unwinding, annealing and extending of the normal PCR, thereby amplifying a target nucleic acid fragment, wherein the mole ratio of a primer to the integrated host factor IHF is 0.005-1. The method is capable of specifically and efficiently amplifying a target nucleic acid sequence.
Owner:华桥生物工程科技有限公司
Vancomycin-resistant enterococcus multiplex fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit and detection method thereof
ActiveCN103993089AAccurate detectionQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescencePolymerase L
The invention relates to a vancomycin-resistant enterococcus multiplex fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit. The kit comprises a VanA specific primer, a VanB specific primer, a VanA fluorescent probe, a VanB fluorescent probe, a PCR buffer solution, a deoxynucleoside triphosphate mixture, a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase, a VanA gene standard product sequence and a VanB gene standard product sequence. The kit disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that due to the adoption of the PCR detection method, accurate, fast and quantitative detection can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING T&OINTL TECH
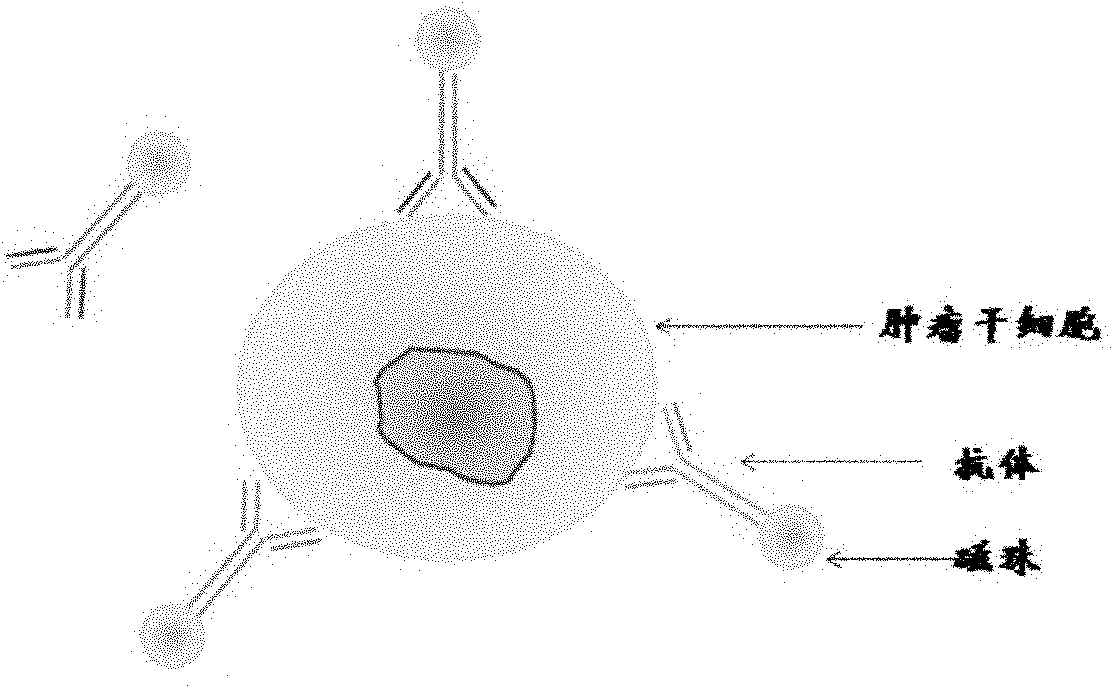
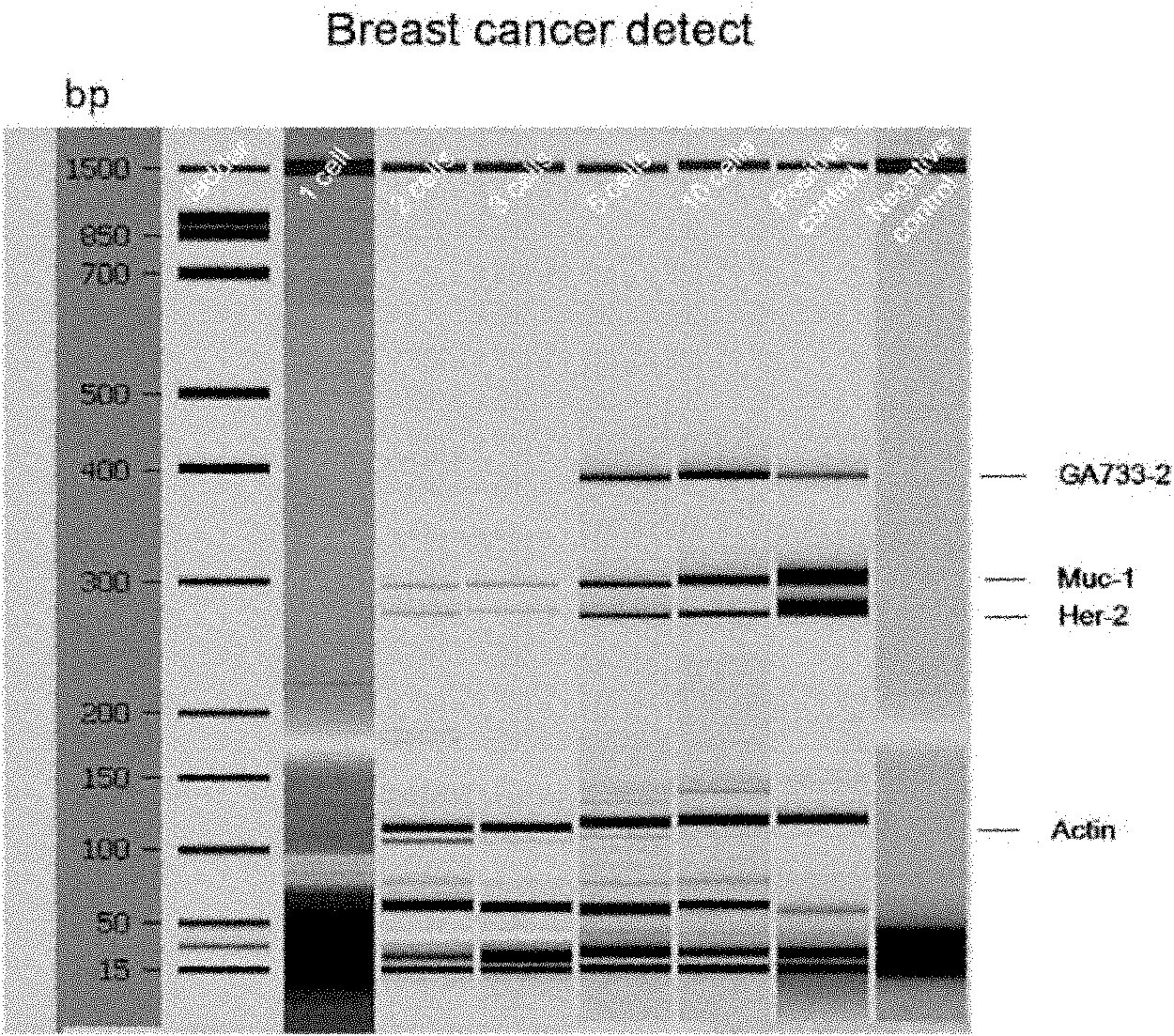
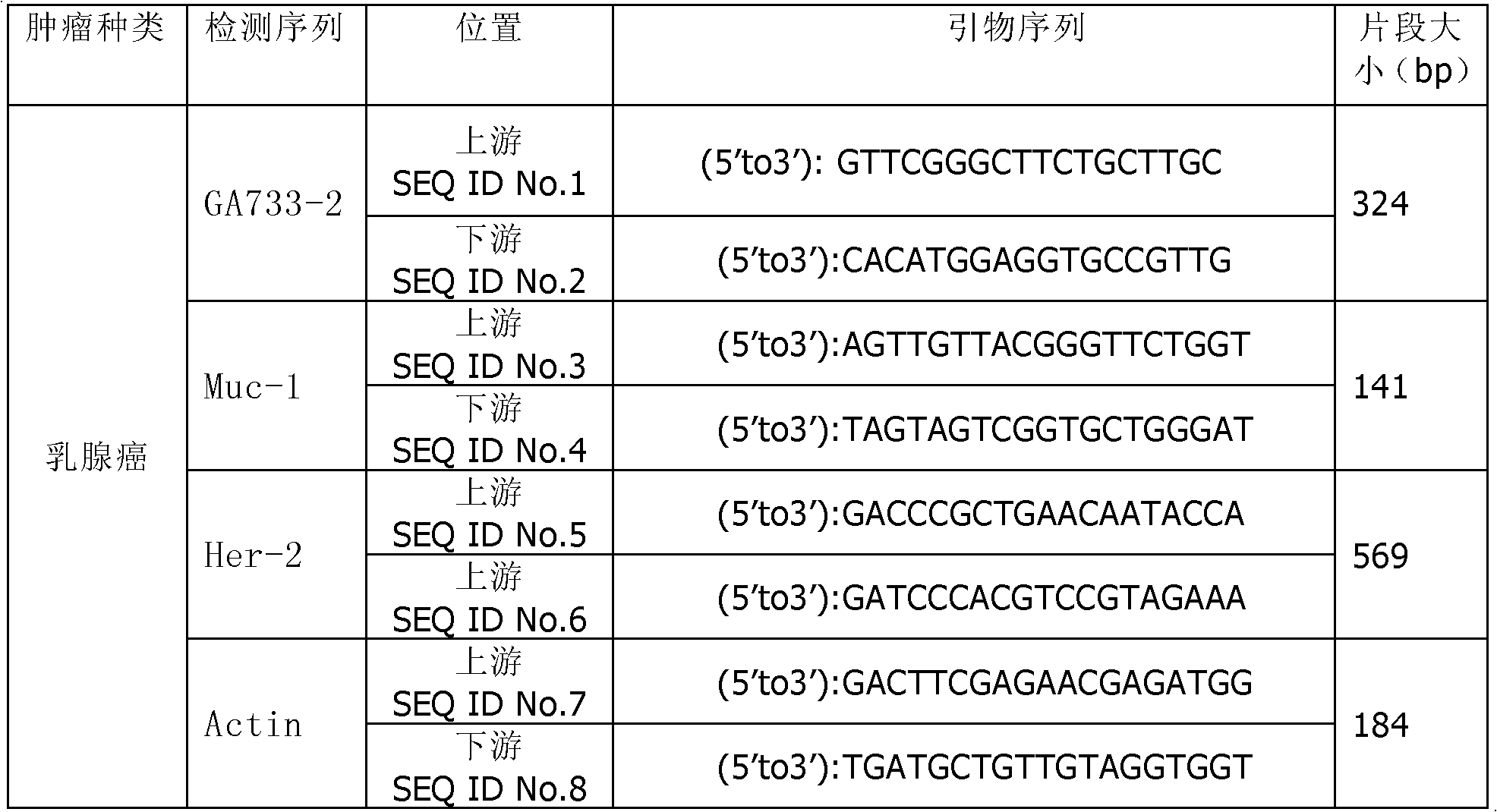
Kit for detecting free breast cancer cell marker in blood
ActiveCN102109525AReliable observation dataStrong data supportMaterial analysisReverse transcriptaseMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a kit for detecting a breast cancer marker. The kit comprises the following components: magnetic bead processing solution, a magnetic bead with a breast cancer antibody, 4.0 to 5.0mu l of 10X buffer solution, 4.0 to 5.0mu l of deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs), 2.0 to 3.0mu l of reverse transcriptase, 0.4 to 0.6mu l of 40u / mu l ribonucleic acid (RNA) enzyme inhibitor, 20.0 to 30.0mu l of 10X hot start polymerase chain reaction (PCR) mixed solution, 10.0 to 15.0mu l of ddH2O and 3.0 to 5.0mu l of breast cancer marker primer. Compared with the prior art, the kit can more accurately detect the breast cancer marker in peripheral blood, and has great guiding significance for selecting breast cancer prognosis schemes and treatment schemes.
Owner:牛刚 +2
Use of base-modified deoxynucleoside triphosphates to improve nucleic acid detection
ActiveUS20100151455A1Stable amplificationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSugar derivativesPcr assayFluorescence
Aspects of the invention provide novel and surprisingly effective methods for the detection of nucleic acids, comprising nucleic acid amplification using base-modified deoxynucleoside 5′-triphosphates (dNTPs). Particular aspects relate to methods for enhancing hybridization properties of oligonucleotide primers and probes in assays detecting nucleic acids, comprise amplifying target DNAs in presence of base-modified duplex-stabilizing deoxyribonucleoside 5′-triphosphates to provide for modified target DNAs, and thereby considerably improving performance of the detection assays. The disclosed methods allow for increasing of the reaction temperature in PCR-based detection systems or, alternatively, reducing the length of the oligonucleotide primers and probes. Certain aspects relates to improvement of real time PCR assays, wherein nucleic acids of interest are detected as the reaction proceeds using fluorescent agents or oligonucleotide FRET probes.
Owner:KUTYAVIN IGOR
DNA sequence detection by limited primer extension
A novel limited primer extension reaction improves detection sensitivity and specificity in a variety of hybridization platforms. In the invention, a sequence of target DNA that lacks one of the four types of nucleic acid bases for a span of eight or more adjacent nucleotide positions is selected for use. This sequence is referred to as the extension complement sequence, or ECS. A primer with a sequence that is complementary to the target sequence that is immediately downstream (to the 3′ side) of this ECS is used to initiate an extension reaction. Extension occurs using a DNA polymerase and standard deoxynucleoside triphosphates for three of the four types of nucleic acid bases. The fourth base, which is complementary to the base missing in the ECS, is either absent or present only in the form of a dideoxynucleoside triphosphate, which does not support further extension. In either case, the extension reaction does not proceed past the first occurrence in the template of the base that is missing in the ECS. This results in a primer extension product with fixed length determined by the length of the ECS. The process can be repeated using a thermal-stable polymerase in a thermal-cycled reaction that results in a linear amplification of the targeted sequence. The resulting limited primer extension products serve as ideal hybridization analytes for determination of sample sequence content using microarrays.
Owner:ATOM SCI
Method for isothermal DNA amplification starting from an RNA template
ActiveUS20140004508A1Microbiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceInosineReverse transcriptase
A method of amplifying RNA template is provided. The method comprises reverse-transcribing a ribonucleic acid (RNA) template to form a cDNA using a first reaction mixture comprising RNA template, at least one primer capable of hybridizing to the RNA template, a reverse transcriptase and deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs); and amplifying the cDNA to form an amplified product using a second reaction mixture comprising at least one strand displacement DNA polymerase, at least one inosine-containing primer and a nuclease that is capable of nicking DNA 3′ to an inosine residue of the primer. The method is accomplished under an isothermal condition without denaturing the cDNA template. A method of quantifying RNA template in a sample and a method of detecting RNA template in a sample are also provided.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
Nucleotide analogues
ActiveCN109476694AGood removal effectGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsMethine/polymethine dyesBase JPhosphoric acid
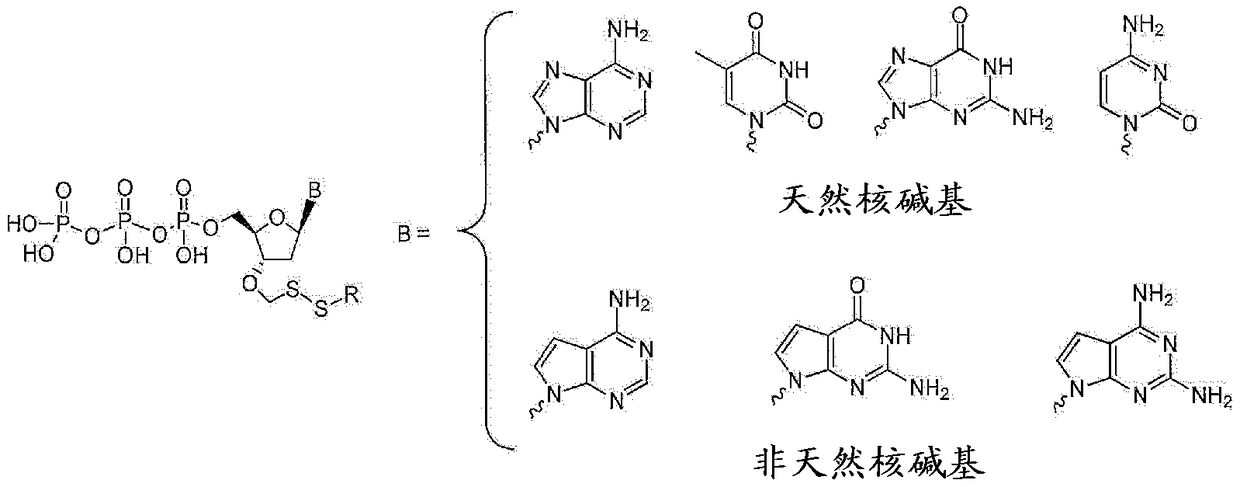
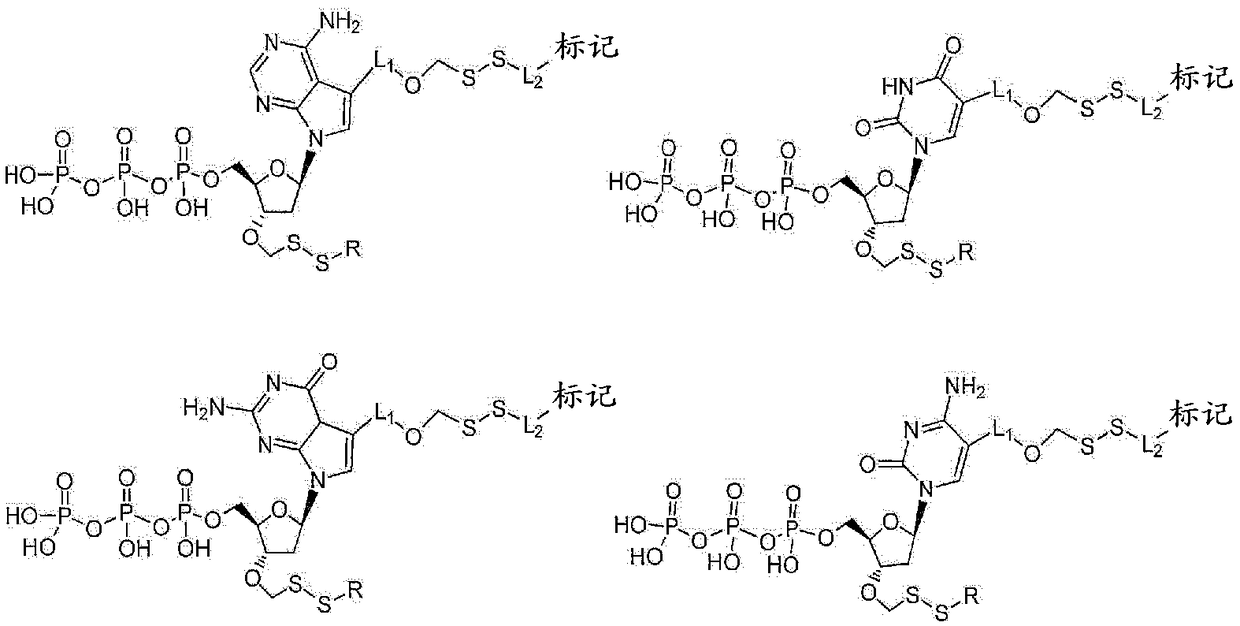
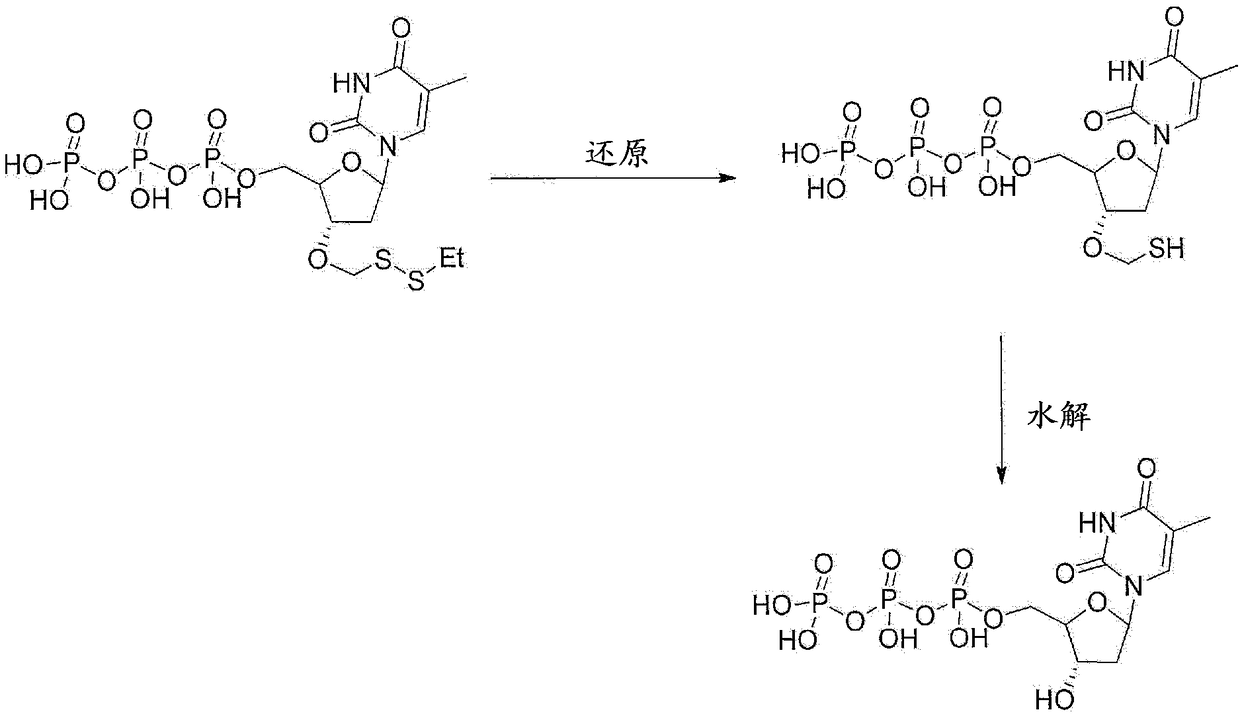
The present invention provides methods, compositions, mixtures and kits utilizing deoxynucleoside triphosphates comprising a 3'-O position capped by a group comprising methylenedisulfide as a cleavable protecting group and a detectable label reversibly connected to the nucleobase of said deoxynucleoside. Such compounds provide new possibilities for future sequencing technologies, including but notlimited to Sequencing by Synthesis.
Owner:奇根科学有限责任公司
Methods, compositions, and kits for amplifying and sequencing polynucleotides
In one aspect, there are provided methods of amplifying and sequencing a polynucleotide. In some embodiments, the method includes (a) amplifying the polynucleotide with at least one amplification primer, a processive amplification polymerase, a sequencing primer, a sequencing polymerase, deoxynucleoside triphosphates suitable for template-dependent primer extension, and one or more terminating nucleotides, the incubation being carried out at a first temperature suitable for amplifying the polynucleotide with the processive amplification polymerase; (b) incubating the product of step (a) at a second temperature suitable for forming a plurality of differently-sized extended sequencing primers with the sequencing polymerase; (c) evaluating the extended sequencing primers in order to determine the sequence of the polynucleotide. The reactions at the first and second temperatures can be carried out in a single reaction vessel. In other aspects, compositions and kits for carrying out the methods are also provided.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Methods, compositions, and kits for amplifying and sequencing polynucleotides
InactiveUS20060141487A1Eliminate needMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPolymerase LPolynucleotide
In one aspect, there are provided methods of amplifying and sequencing a polynucleotide. In some embodiments, the method includes (a) amplifying the polynucleotide with at least one amplification primer, a processive amplification polymerase, a sequencing primer, a sequencing polymerase, deoxynucleoside triphosphates suitable for template-dependent primer extension, and one or more terminating nucleotides, the incubation being carried out at a first temperature suitable for amplifying the polynucleotide with the processive amplification polymerase; (b) incubating the product of step (a) at a second temperature suitable for forming a plurality of differently-sized extended sequencing primers with the sequencing polymerase; (c) evaluating the extended sequencing primers in order to determine the sequence of the polynucleotide. The reactions at the first and second temperatures can be carried out in a single reaction vessel. In other aspects, compositions and kits for carrying out the methods are also provided.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Nucleic acid amplification method
ActiveCN101353683AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOligonucleotide primersPolymerase L
The invention provides a DNA polymerase using oligonucleotide primer and having strand displacement ability, which is capable of amplifying nucleic acid under substantially constant temperature condition. The invention provides a method of amplifying nucleic acid, comprising: under the substantially constant temperature condition, incubating reaction solution comprising at least a deoxy nucleoside triphosphate, at least a DNA polymerase having strand displacement ability, bivalent catio, at least over 0.01% surfactant, at least two oligonucleotide primers and as nucleic acid segment of templet; the polymerase reaction is carried out by taking 3'-back end of the primer as the start, thereby amplifying the nucleic acid segment.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for separating and purifying deoxynucleoside triphosphate
InactiveCN101633681AAvoid the pitfalls of high energy consumptionAvoid separation and purificationSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationFreeze-dryingNucleoside triphosphate
The invention discloses a method for separating and purifying deoxynucleoside triphosphate, which comprises the following steps: when the temperature is below 4 DEG C, depositing deoxynucleoside triphosphate biosynthesized reaction solution directly with an organic solvent to obtain a solid mixture of the deoxynucleoside triphosphate, wherein the volume ratio of the deoxynucleoside triphosphate biosynthesized reaction solution to the organic solvent is between 1:1 and 1:25; when the temperature is below the 4 DEG C, dissolving the solid mixture in ultrapure water, adjusting the pH value to between 0.1 and 2 by using acidic aqueous solution, and using the organic solvent to perform deposition again to obtain a solid matter of the deoxynucleoside triphosphate; and dissolving the solid matter in the ultrapure water, adjusting the pH value to between 5 and 11 by using sodium hydroxide alkaline aqueous solution, and performing liquid nitrogen frozen and freeze-drying to obtain a sodium salt product of the deoxynucleoside triphosphate. The method has the advantages of quick separation, good purification effect, production cost reduction, water resource pollution reduction, process energy consumption reduction, and applicability to industrial production.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com