Nucleic acid amplification method
A technology for amplifying nucleic acids and oligonucleotides, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbiological measurement/inspection, fermentation, etc. It can solve problems such as long reaction time, increased time consumption, troublesome temperature control, etc., and achieve high The effect of amplification efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
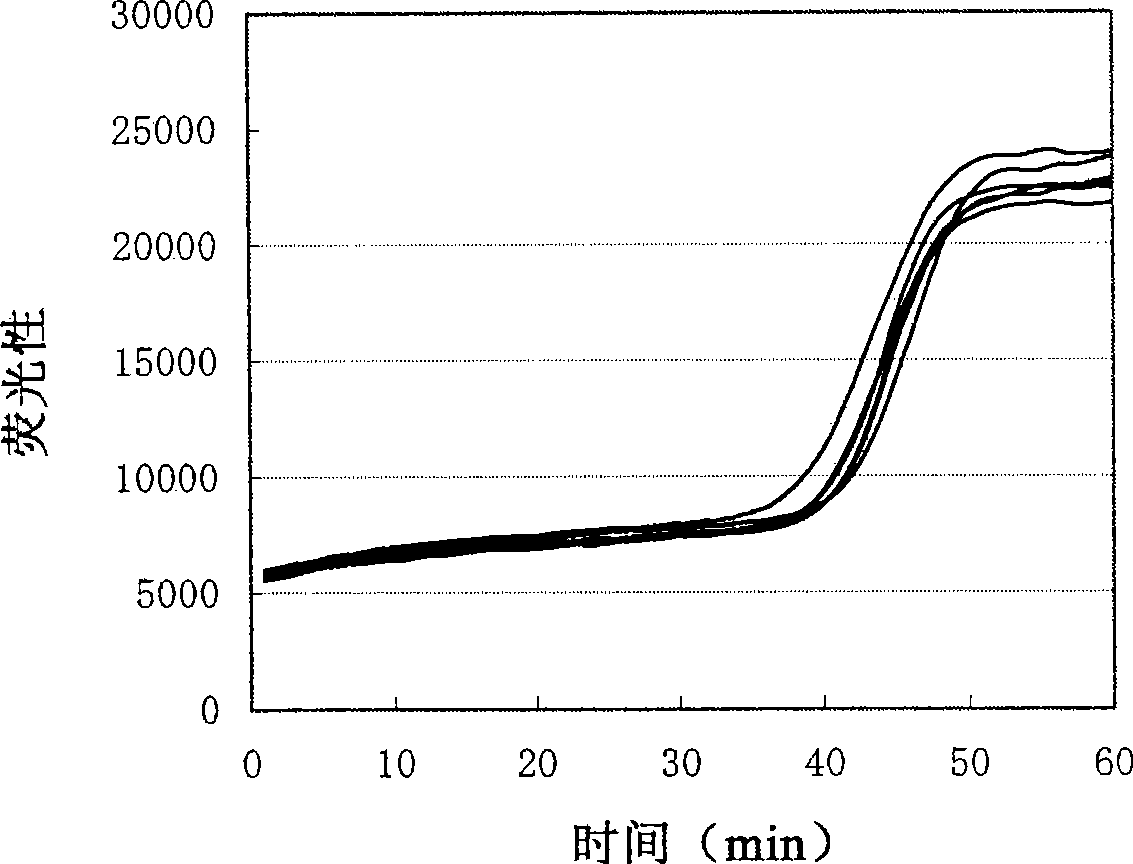
[0158] Amplification reaction of nucleic acid
[0159] (1) Preparation of nucleic acid sample solution containing target nucleic acid fragments
[0160] After heating 3.0 ng of Human Genomic DNA (manufactured by Clontech) at 98° C. for 3 minutes to make it single-stranded, the sequence in the β-actin gene was amplified under the following conditions.
[0161]
[0162] Primer design was performed using the β-actin gene as a target. The sequences of the respective primers are shown below.
[0163] Primer (1) (forward primer):
[0164] 5'-GGGCATGGGTCAGAAGGATT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 1)
[0165] Primer (2) (reverse primer):
[0166] 5'-CCTCGTCGCCCACATAG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 2)
[0167] The positional relationship of the above primers relative to the β-actin gene is specifically as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0168] Here, the sequence X is 5'-CCCAG-3', and the distance between the two sequences X is 54 bases. Primer (1) is designed for the region between the 5' terminal base of the sequ...
Embodiment 2
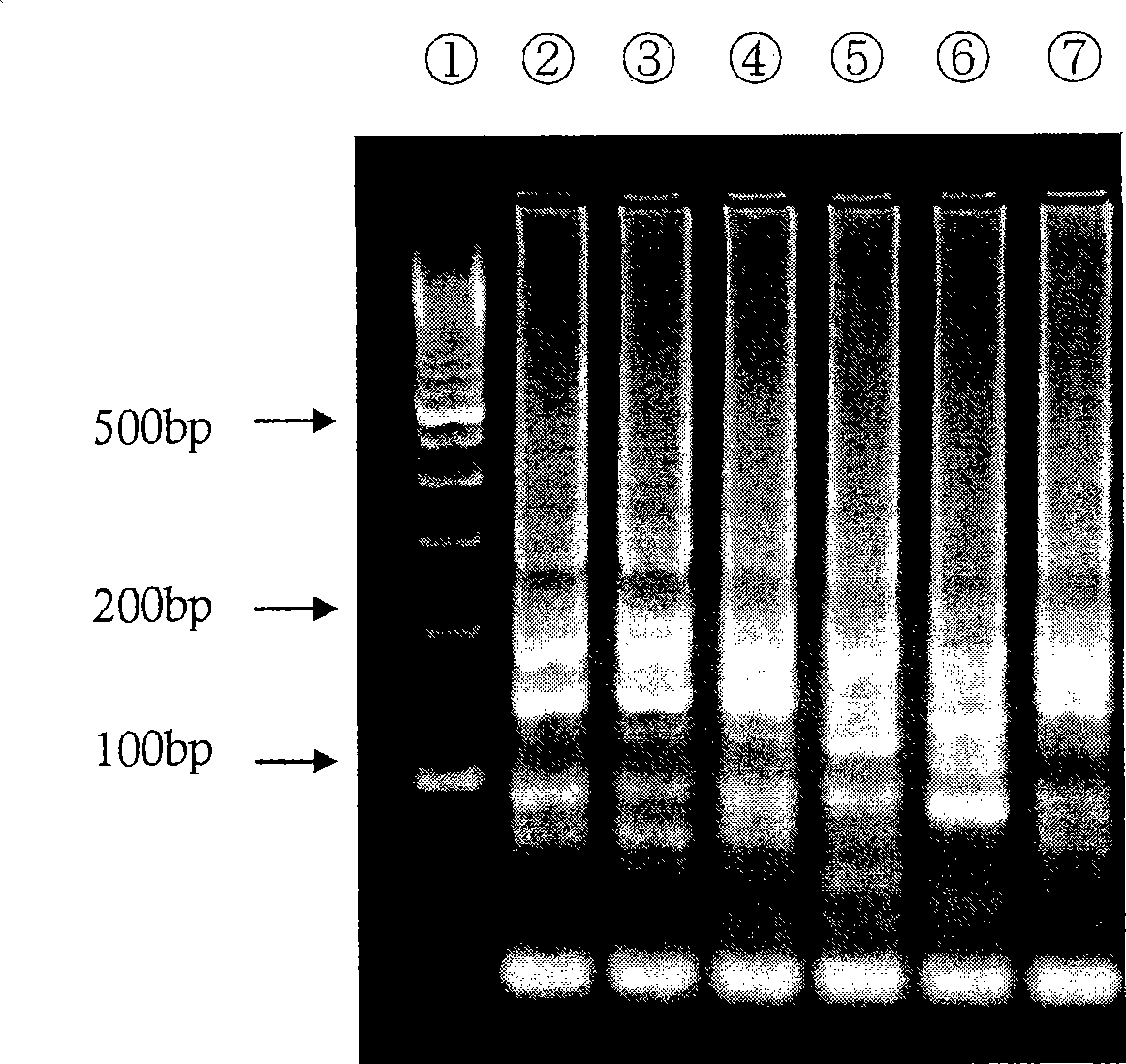
[0189] Electrophoresis of amplified products
[0190] Electrophoresis was performed at 100 V for 60 minutes using 3% by weight agarose gel, 0.5 x TBE buffer (50 mM Tris, 45 mM boric acid, 0.5 mM EDTA, pH 8.4). The result is as image 3 shown. The electrophoretic patterns of the 6 samples are substantially the same, thus it can be seen that the amplified products are obtained according to the same reaction mechanism.
Embodiment 3
[0191] Cloning of amplified product
[0192] After electrophoresis, the gel in the region below 200 bp was cut out, and the DNA in the gel was recovered using QIAEX II (manufactured by Qiagen).
[0193] The recovered DNA was recombined into a vector using TOPO TA Cloning Kit (manufactured by Invitrogen), and Escherichia coli was transformed with the vector. The transformed Escherichia coli were cultured in LB medium supplemented with ampicillin.
[0194] Plasmid DNA was recovered from the cultured Escherichia coli using QIAprep Miniprep (manufactured by Qiagen).
[0195]The recovered plasmid DNA was sequenced to determine the base sequence. M13 reverse primer (M13 Reverse Primer) was used as a primer.
[0196] M13 reverse primer
[0197] 5'-CAGGAAACAGCTATGAC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 3)
[0198] From the results of sequencing, it was found that the following three types of amplification products existed.
[0199] (1)
[0200] 5'-GGGCATGGGT CAGAAGGATT CCTATGTGGG CGACGAGG-3'
[02...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com