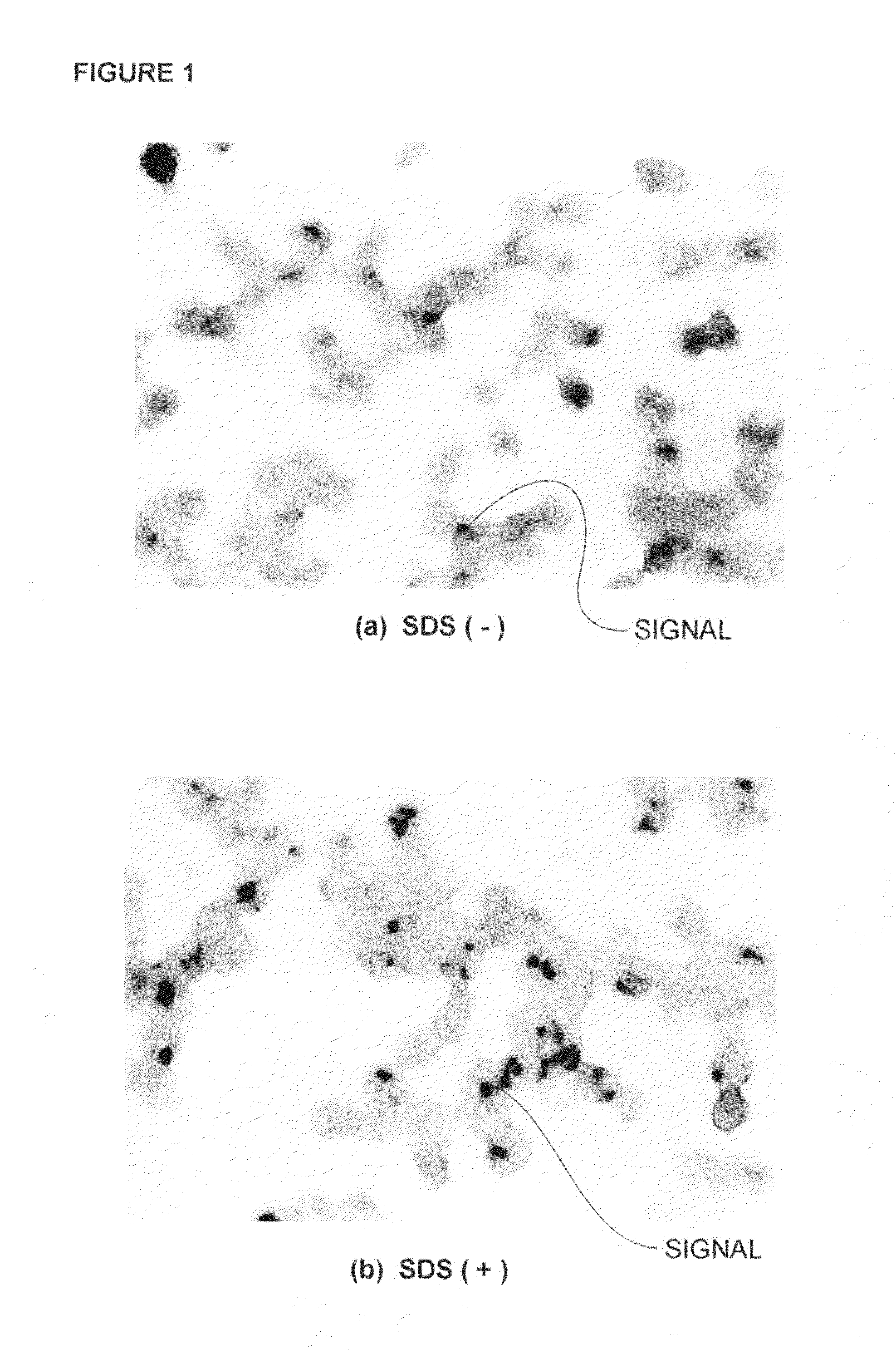
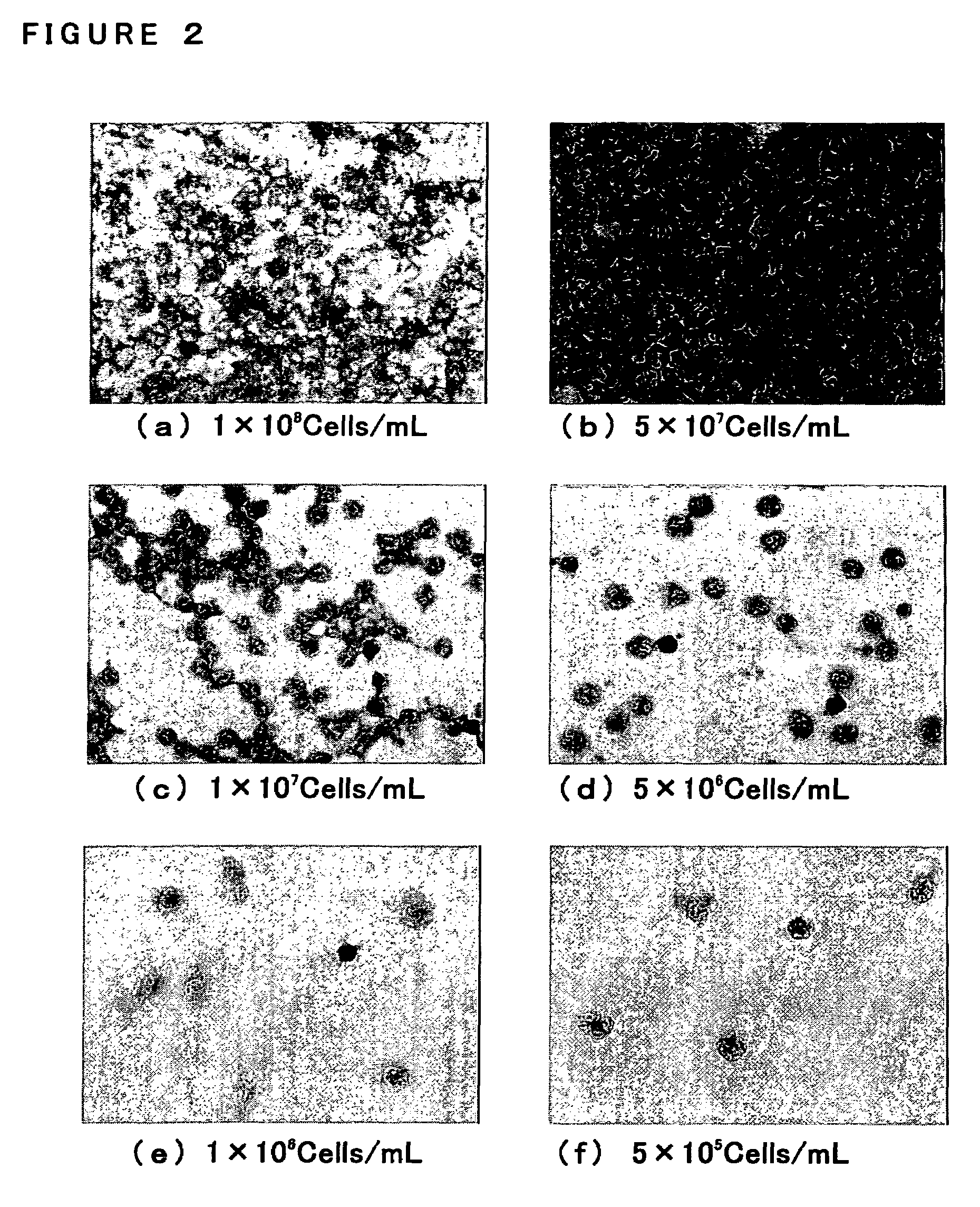
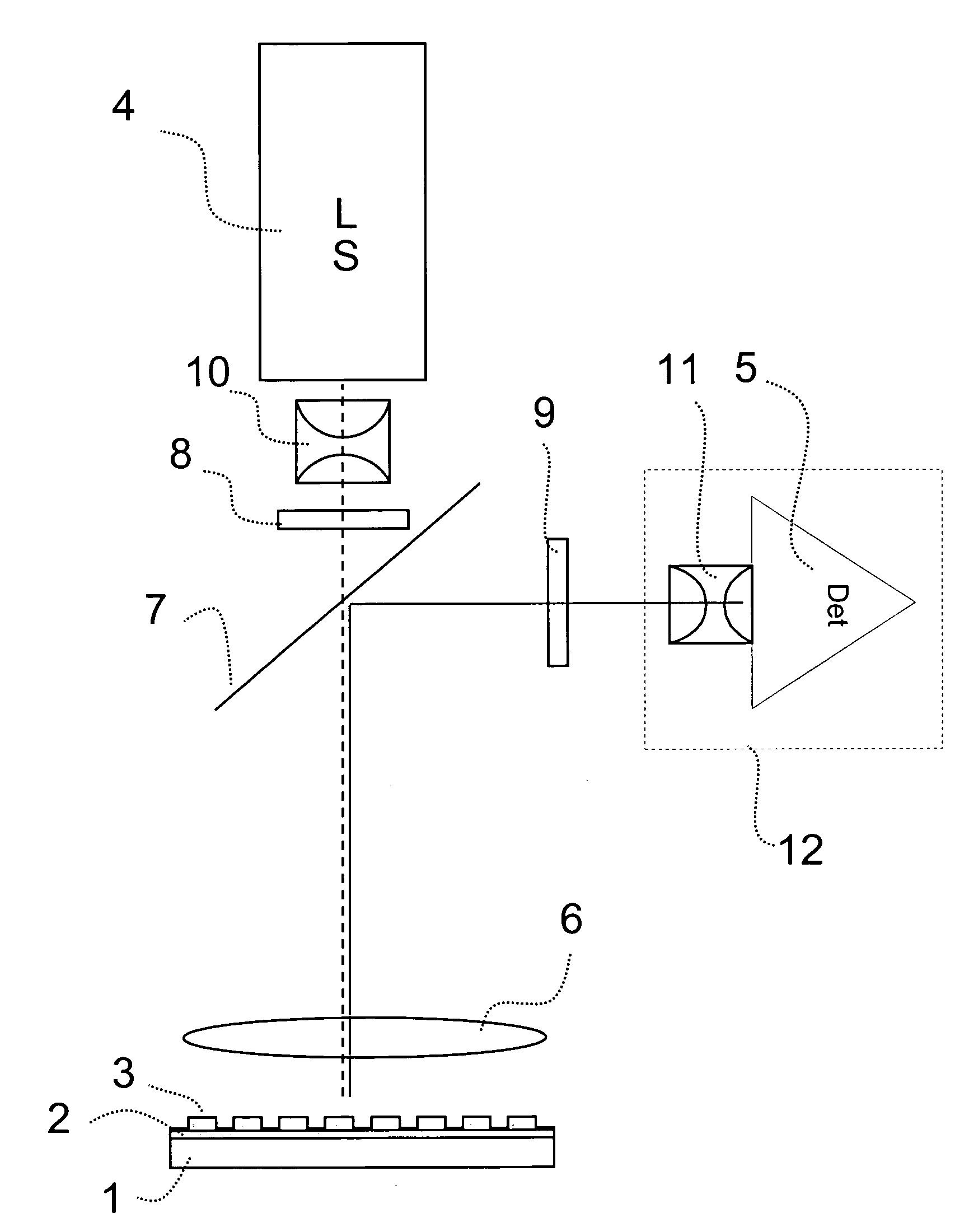
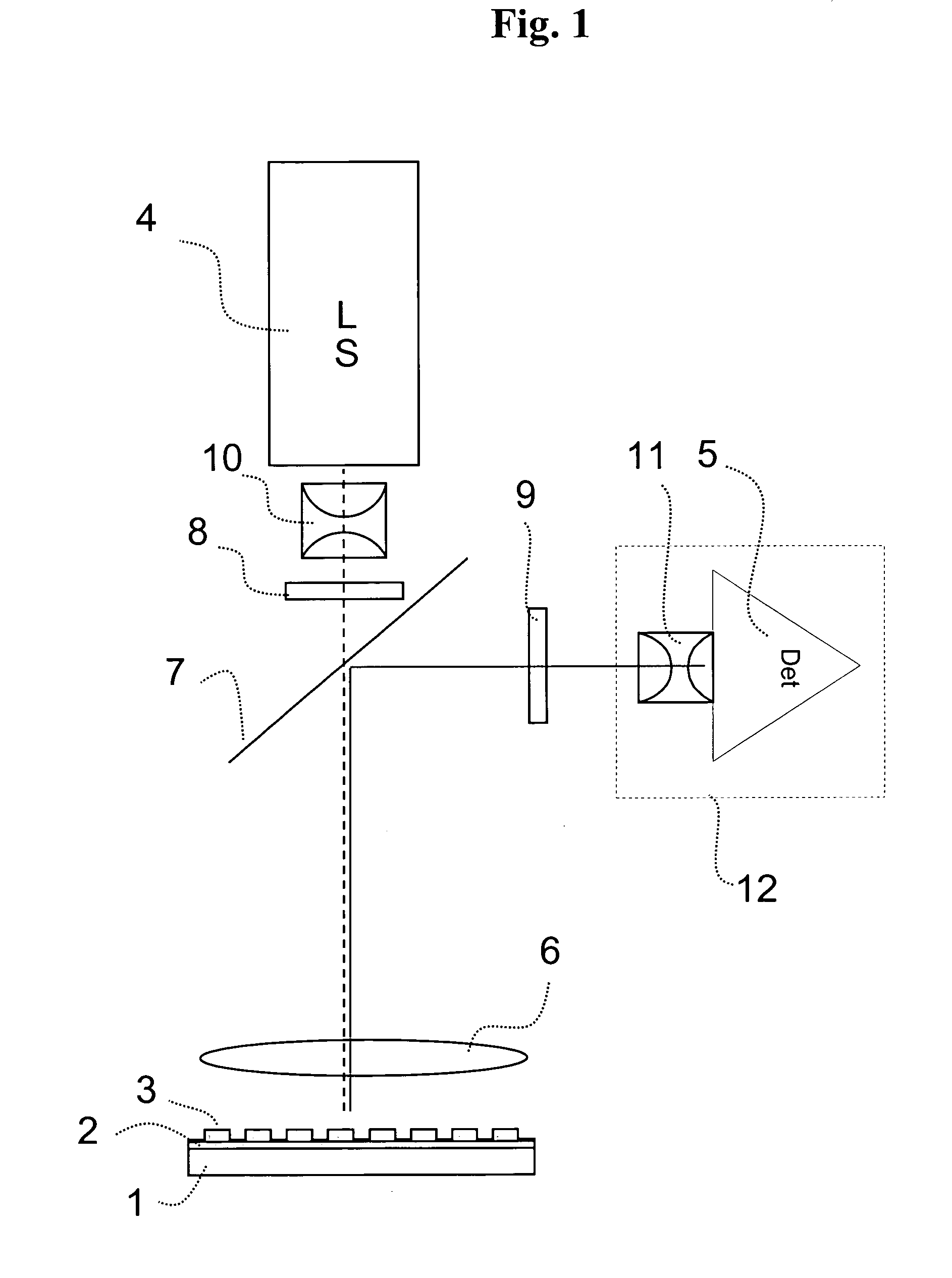
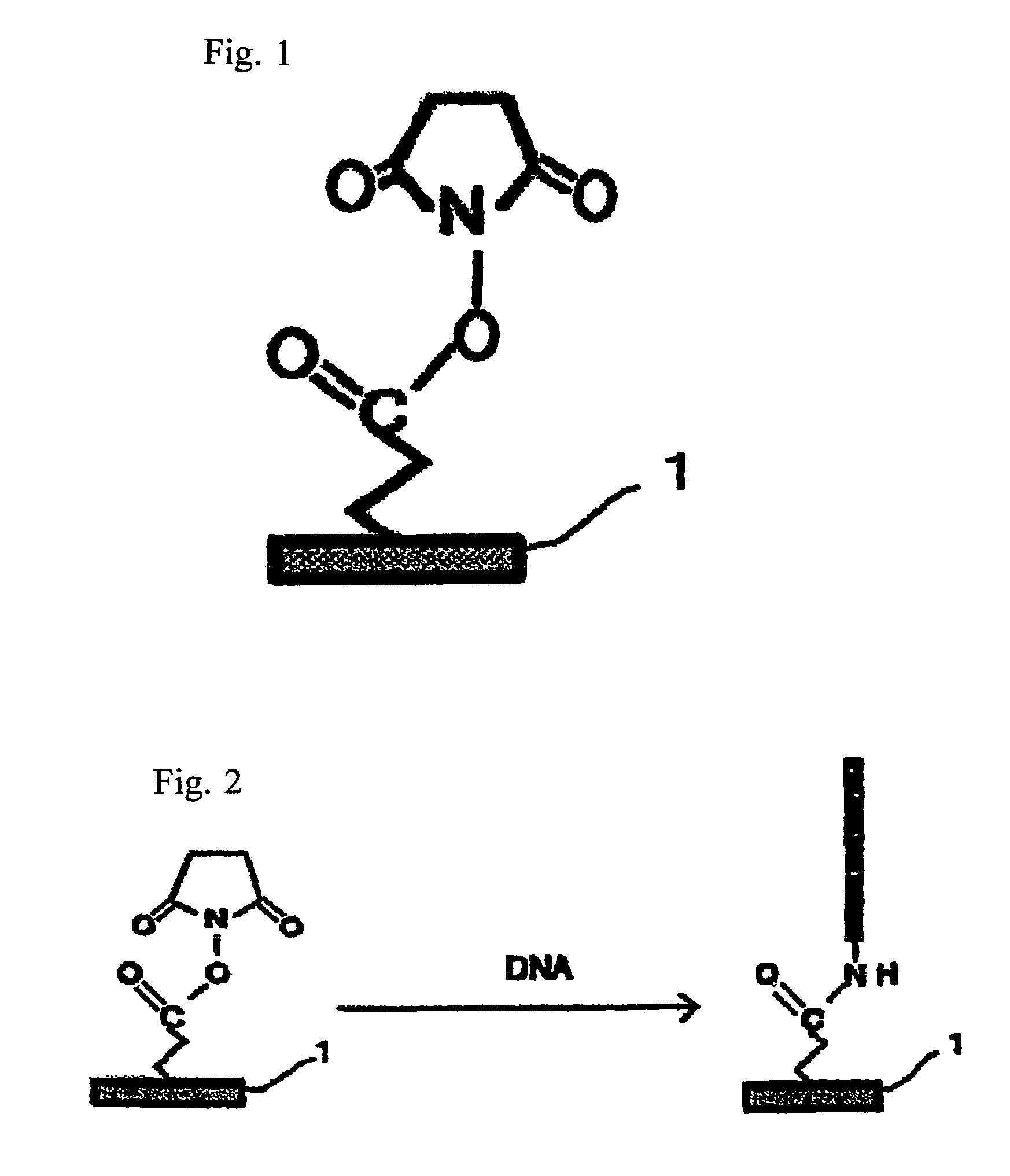
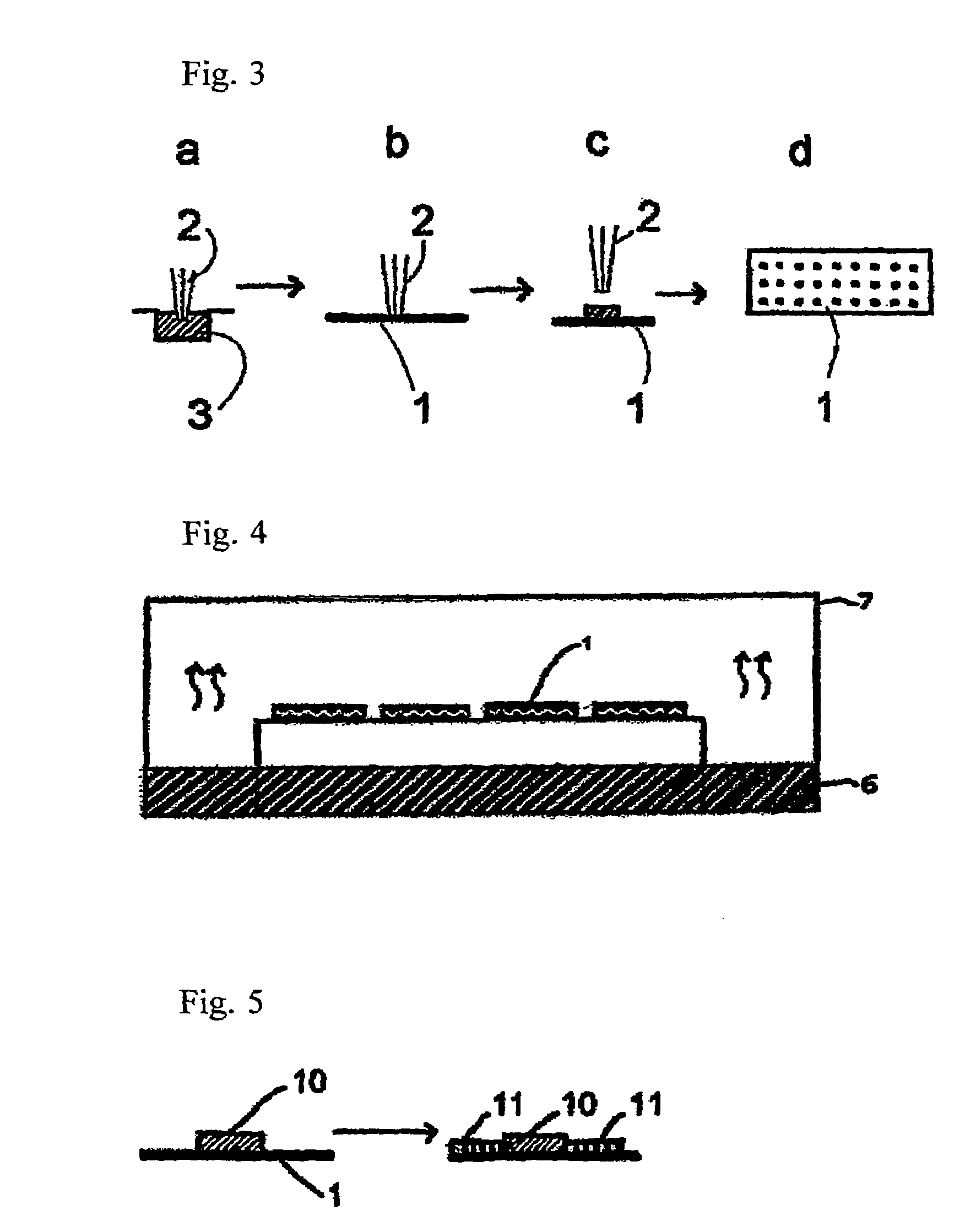
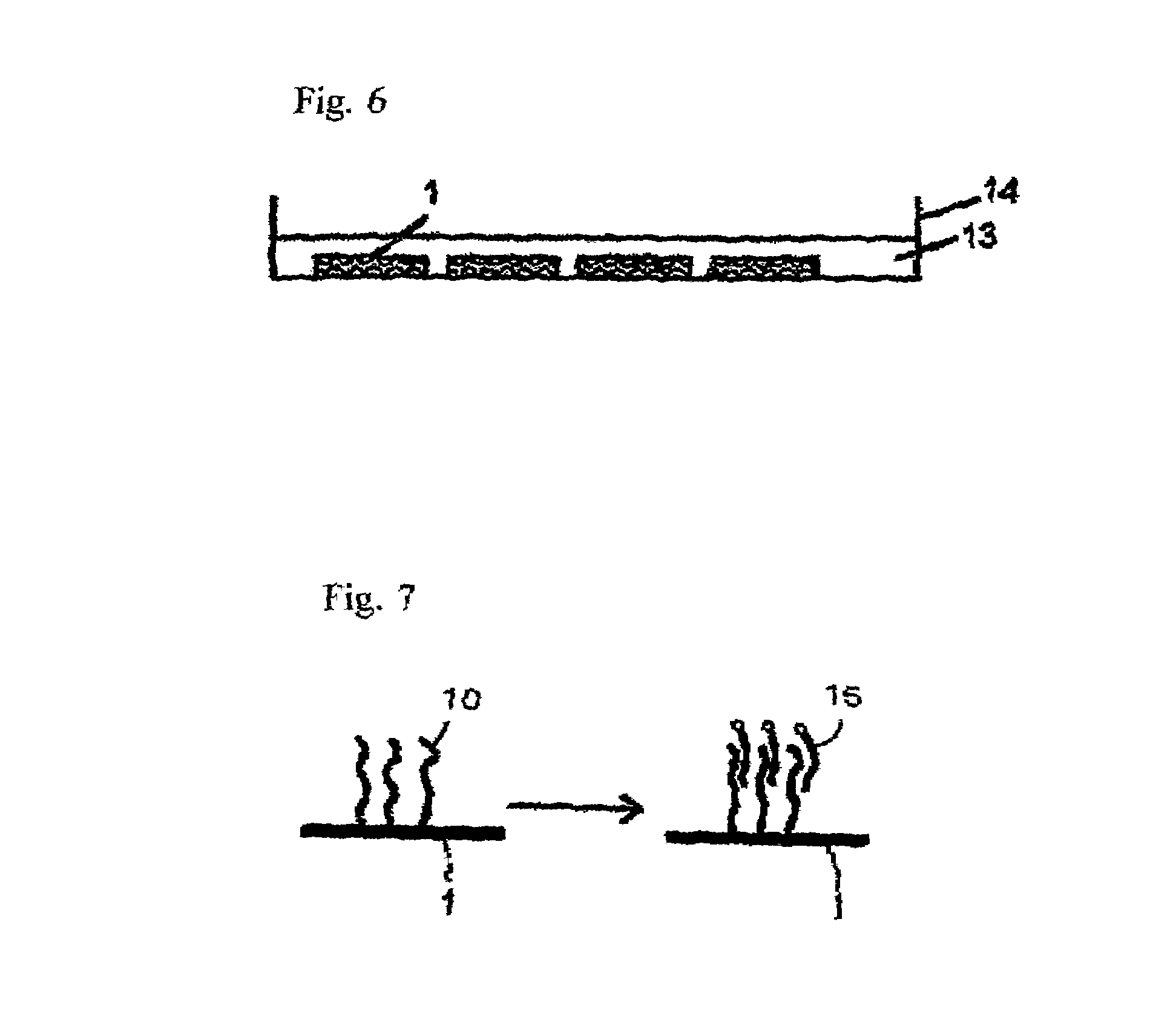
Patents
Literature
276 results about "DNA hybridisation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hybridization probe. topic. In molecular biology , a hybridization probe is a fragment of DNA or RNA of variable length (usually 100–1000 bases long) which can be radioactively labeled . It can then be used in DNA or RNA samples to detect the presence of nucleotide sequences (the DNA target) that are complementary to the sequence in the probe.
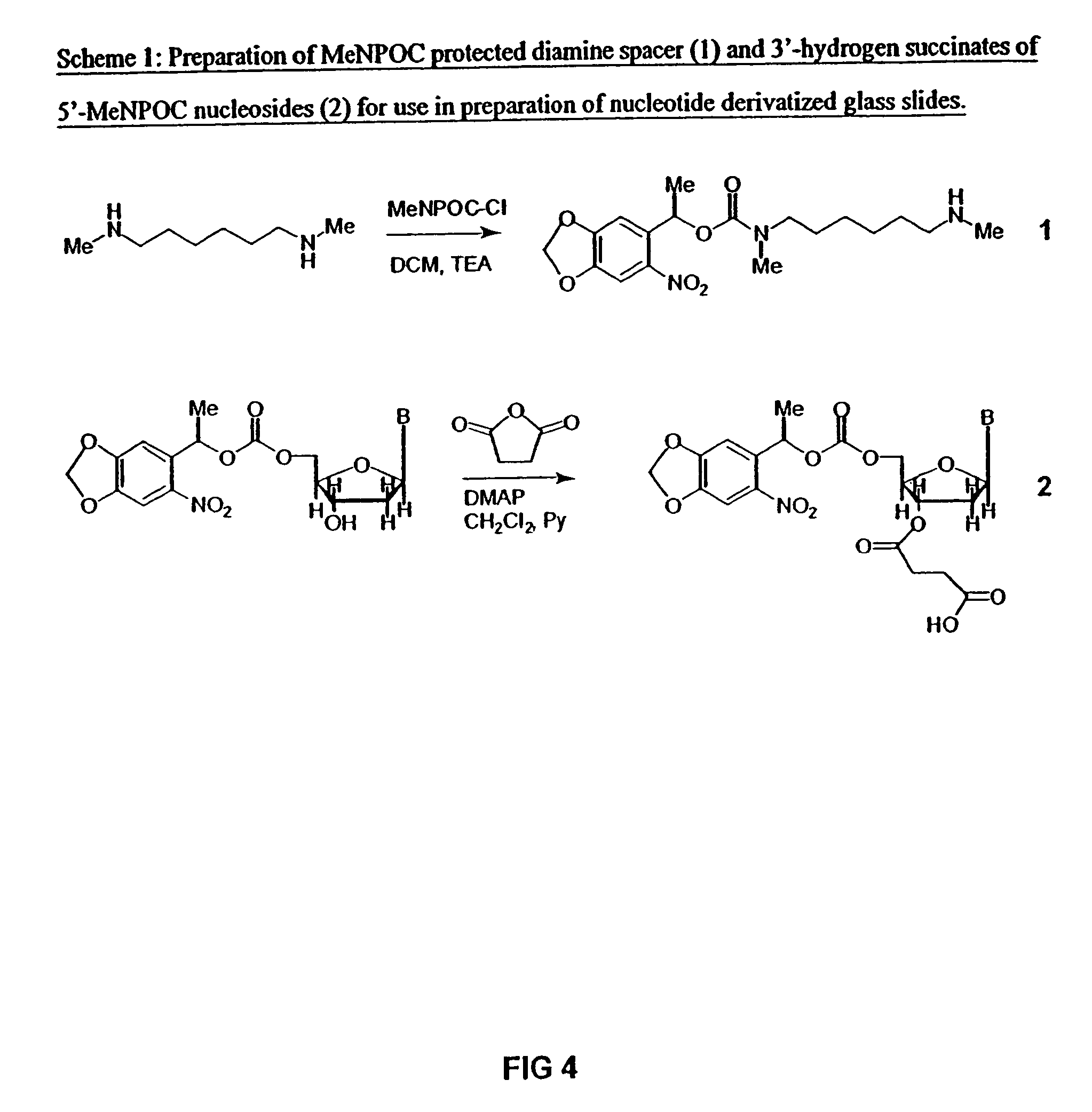
Method for the synthesis of DNA sequences
InactiveUS7183406B2Material nanotechnologyGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsDNA microarrayDNA construct
A method is disclosed for the direct synthesis of double stranded DNA molecules of a variety of sizes and with any desired sequence. The DNA molecule to be synthesis is logically broken up into smaller overlapping DNA segments. A maskless microarray synthesizer is used to make a DNA microarray on a substrate in which each element or feature of the array is populated by DNA of a one of the overlapping DNA segments. The DNA segments are released from the substrate and held under conditions favoring hybridization of DNA, under which conditions the segments will spontaneously hybridize together to form the desired DNA construct. This method makes possible the remote assembly of DNA sequence, through a process analogous to facsimile transmission of documents, since the information on DNA to be made can be transmitted remotely to an instrument which can then synthesize any needed DNA sequence from the information.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
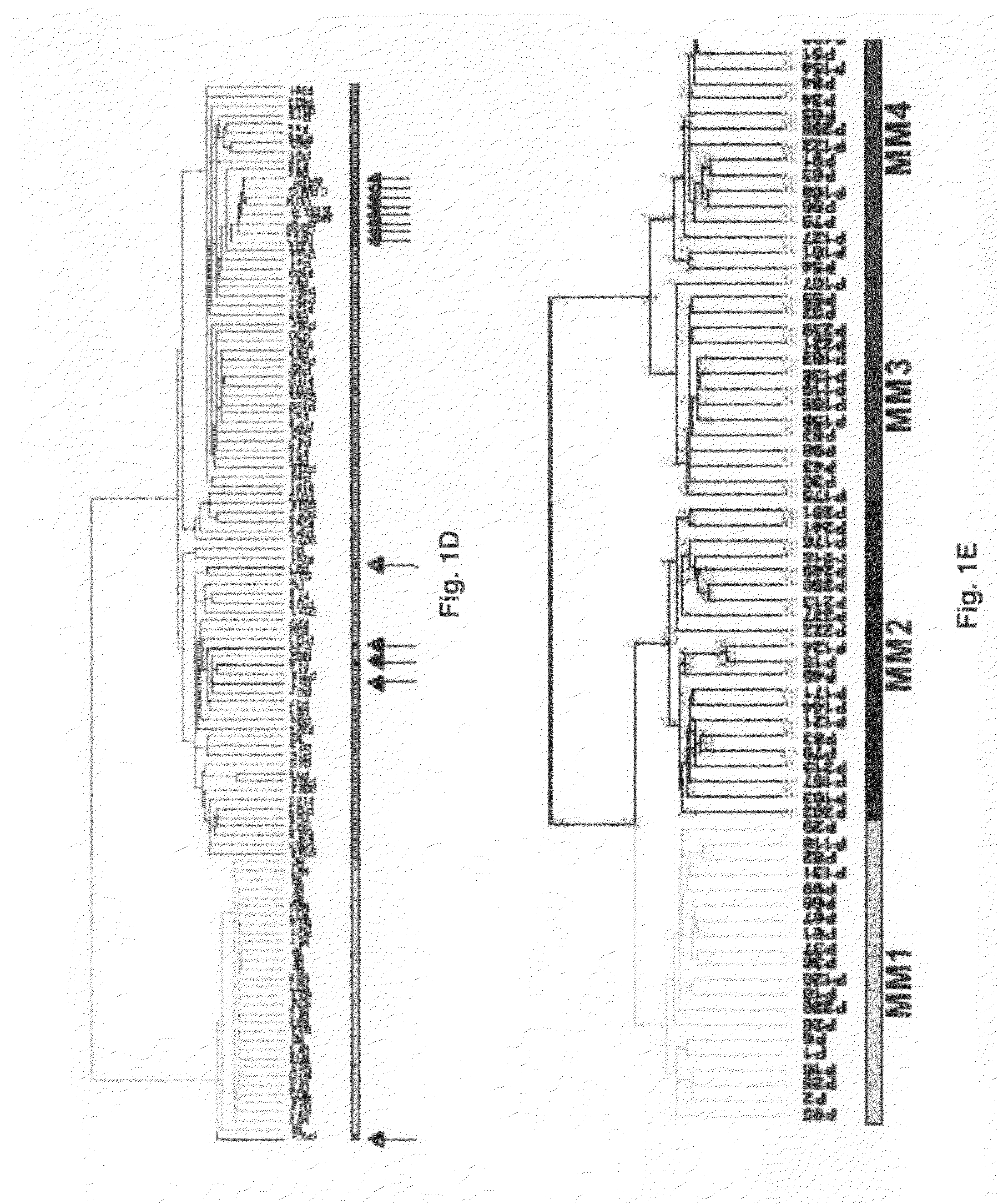
Diagnosis, prognosis and identification of potential therapeutic targets of multiple myeloma based on gene expression profiling
InactiveUS20080293578A1Microbiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesGene targetsGene model
Provided herein is a method for gene expression profiling multiple myeloma patients into distinct subgroups via DNA hybridization and hierarchical clustering analysis of the hybridization data where the results may further be used to identify therapeutic gene targets. Also provided is a method for controlling bone loss in an individual via pharmacological inhibitors of DKK1 protein. In addition provided herein is a method for diagnosing multiple myeloma using a 15-gene model that classifies myeloma into groups 1-7.
Owner:BIOVENTURES LLC
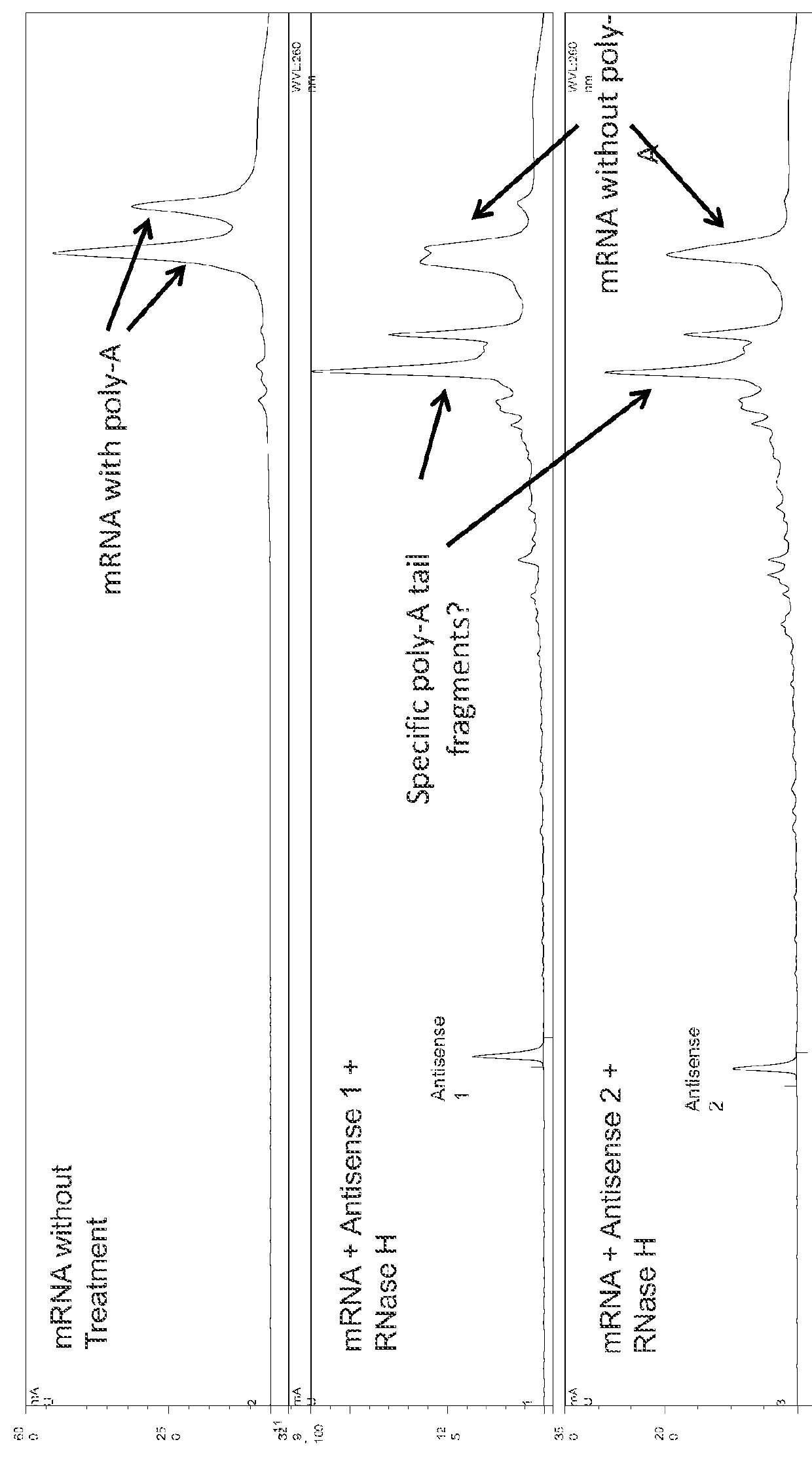
Characterization of mRNA molecules
InactiveUS20160032273A1Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisReverse transcriptase
The present invention describes methods for the characterization of mRNA molecules during mRNA production. Characterizing mRNA includes processes such as oligonucleotide mapping, reverse transcriptase sequencing, charge distribution analysis, and detection of RNA impurities. Oligonucleotide mapping includes using an RNase to digest antisense duplexes from an RNA transcript, and then subjecting the digested RNA to reverse phase HPLC, anion exchange HPLC, and / or mass spectrometry analysis. Reverse transcriptase sequencing involves reverse transcription of an RNA transcript followed by DNA sequencing. Charge distribution analysis can comprise procedures such as anion exchange HPLC, or capillary electrophoresis. Detection of impurities includes detecting short mRNA transcripts, RNA-RNA hybrids, and RNA-DNA hybrids.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
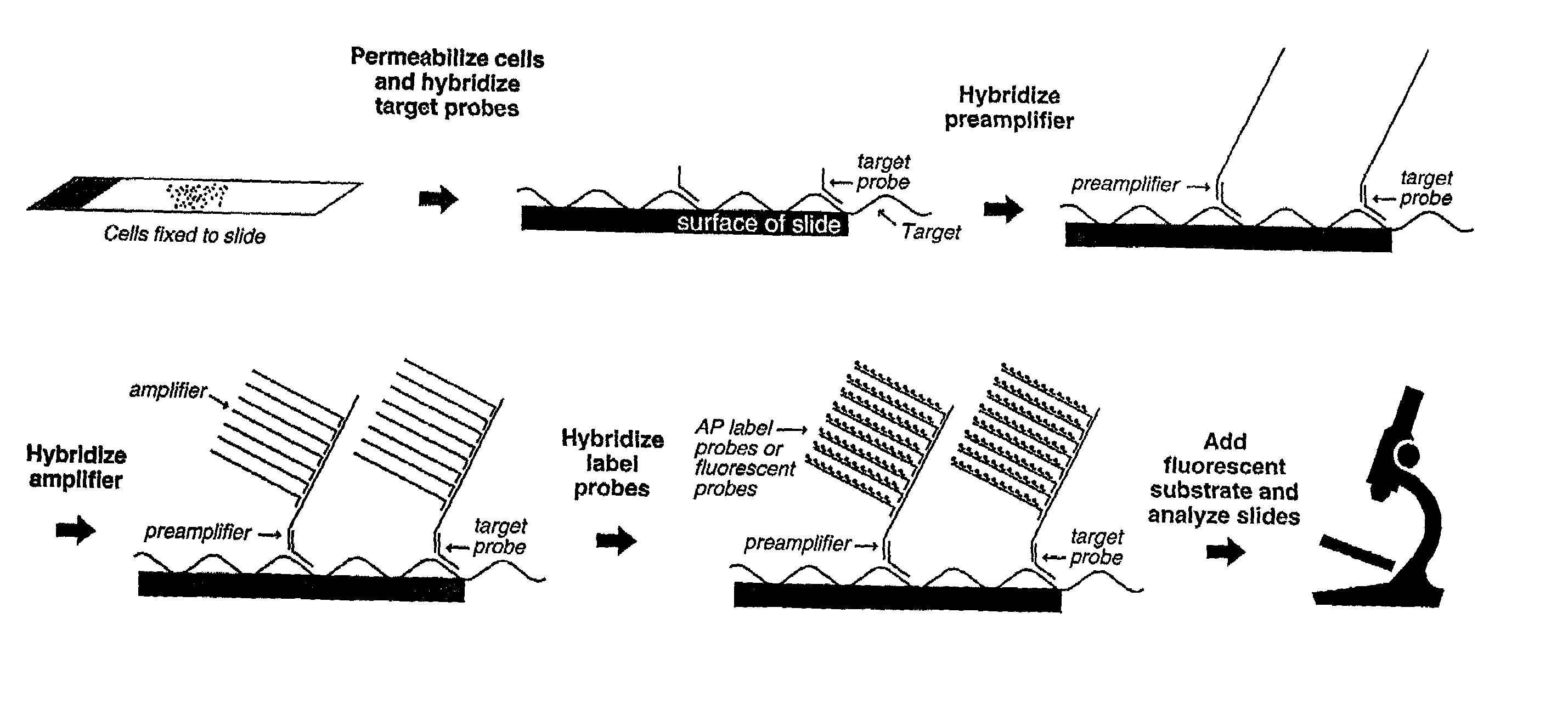
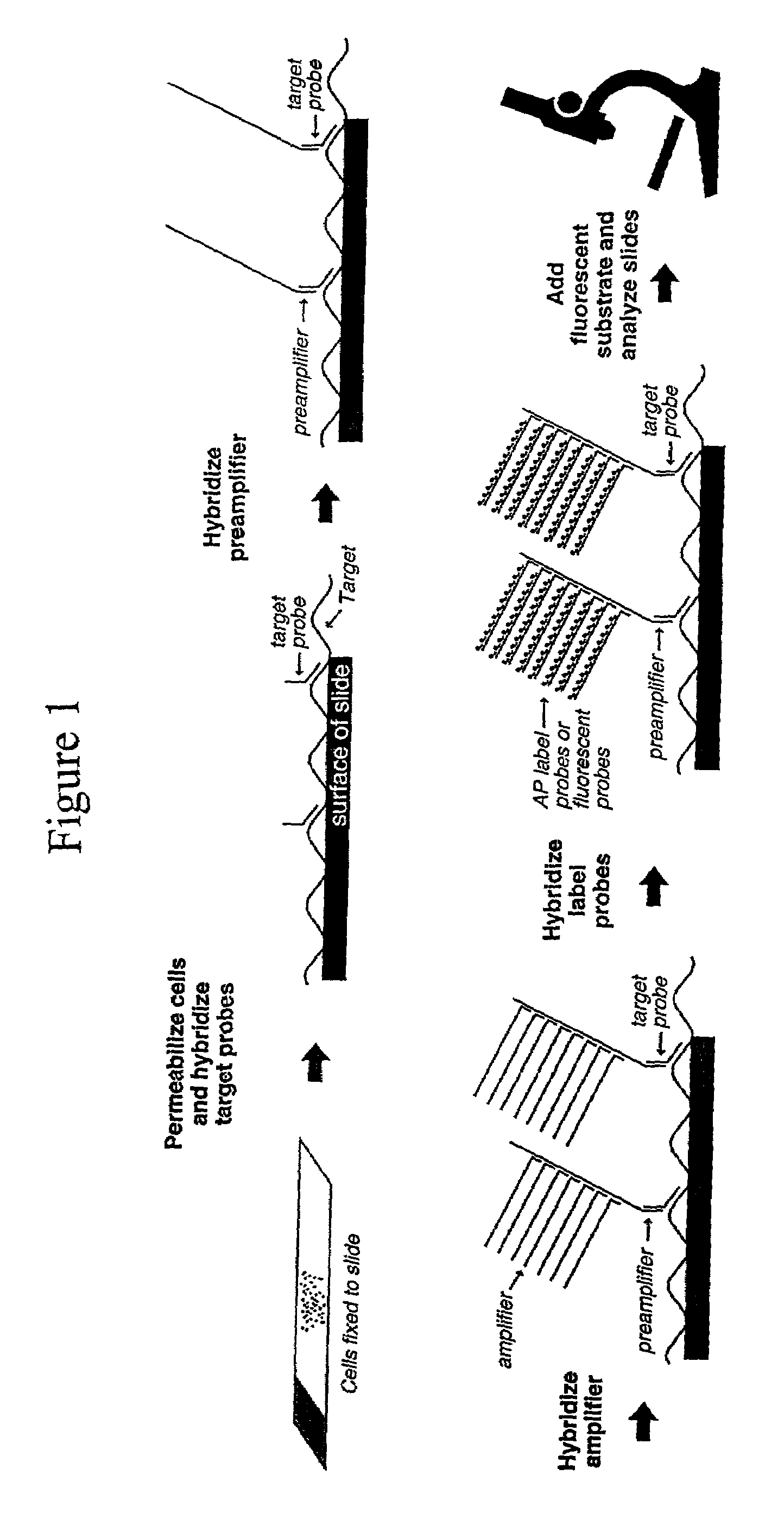
Highly sensitive gene detection and localization using in situ branched-DNA hybridization
InactiveUS7033758B2High sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteBiological materials
Methods are provided for highly sensitive and rapid in situ detection of a nucleic acid analyte of a known sequence. The method employs oligonucleotide probes in a series of optimized steps to amplify a signal and decrease background. Sensitivity is enhanced such that the method can detect as few as 1–2 copies of nucleic acid analyte per sample, the sample containing a cell, tissue or similar biological material. Methods of detecting and identifying the position of the nucleic acid analyte in a cell are also provided.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
DNA measuring system and method
InactiveUS20080318243A1Suppress deterioration in reproducibility of measurementHigh-precision detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDNA sequencerA-DNA
The present invention provides a DNA sequencer using a FET sensor, capable of long-base decoding. Target DNAs are immobilized on the surfaces of spherical fine particles, the fine particles are disposed in the vicinity of metal electrodes each of which is connected electrically to a corresponding one of conductive wirings of the FET sensor and partly has a spherical surface capable of contacting with the fine particles, and the FET sensor detects a change in interfacial potential incident to an extension reaction of DNA molecules containing a hybridization of the target DNA and probe DNA.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
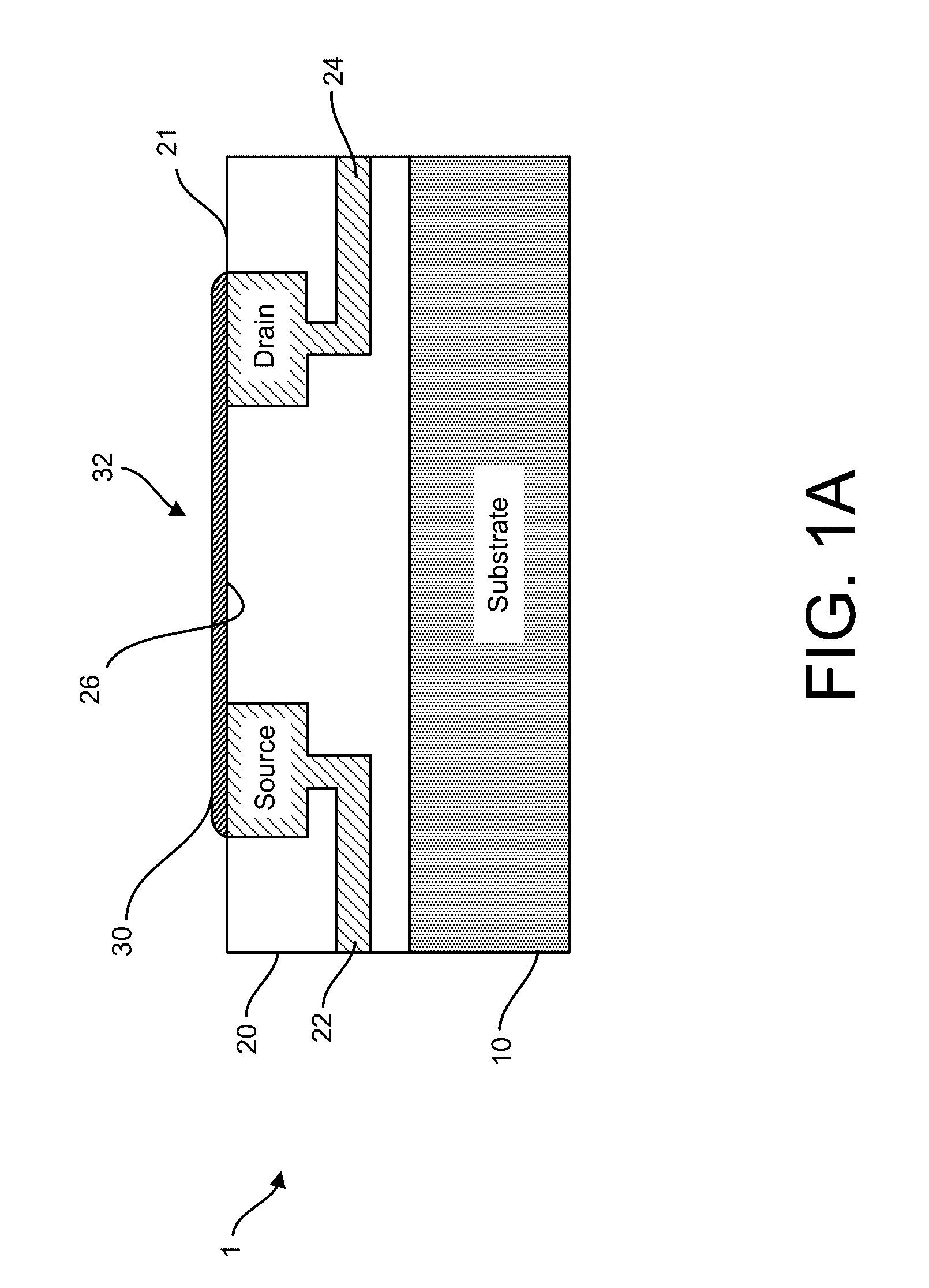
Graphene fet devices, systems, and methods of using the same for sequencing nucleic acids
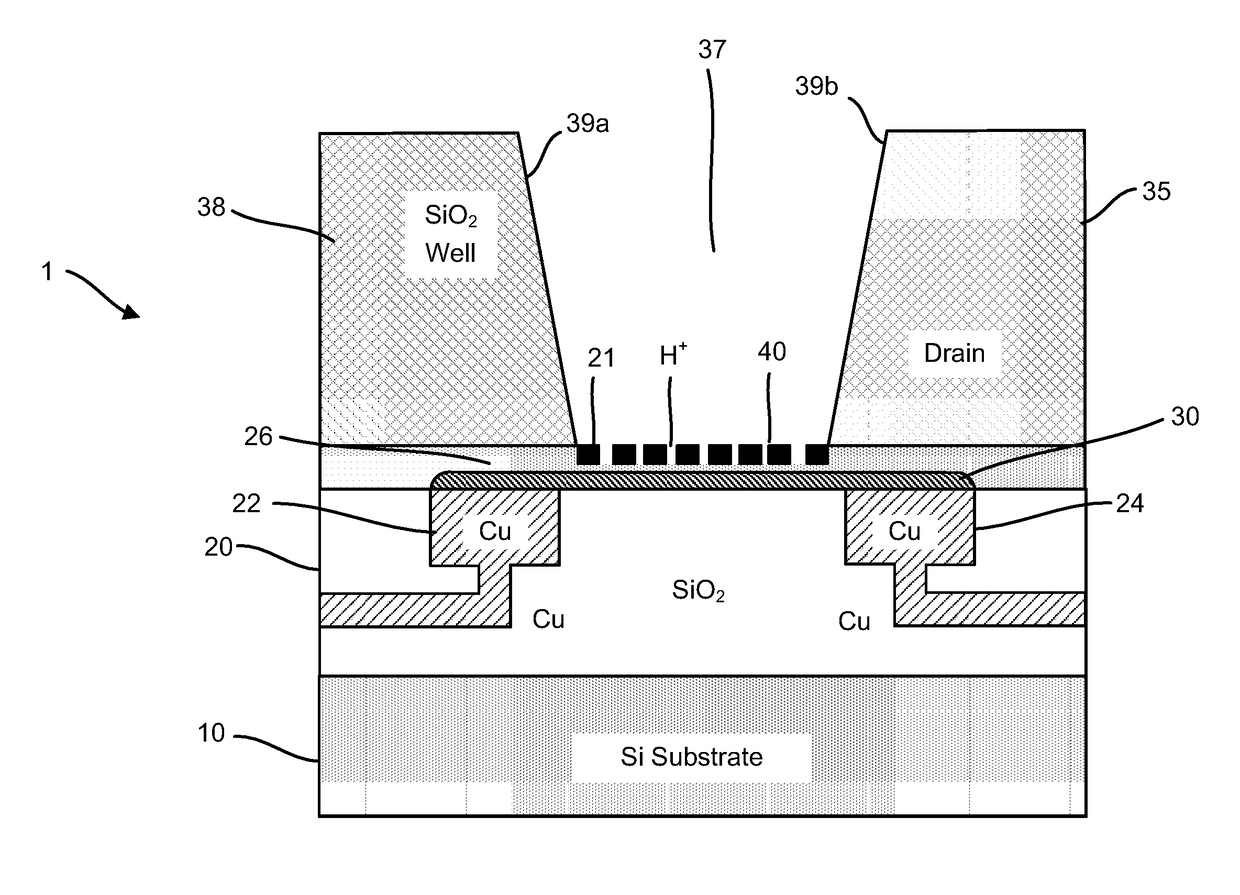
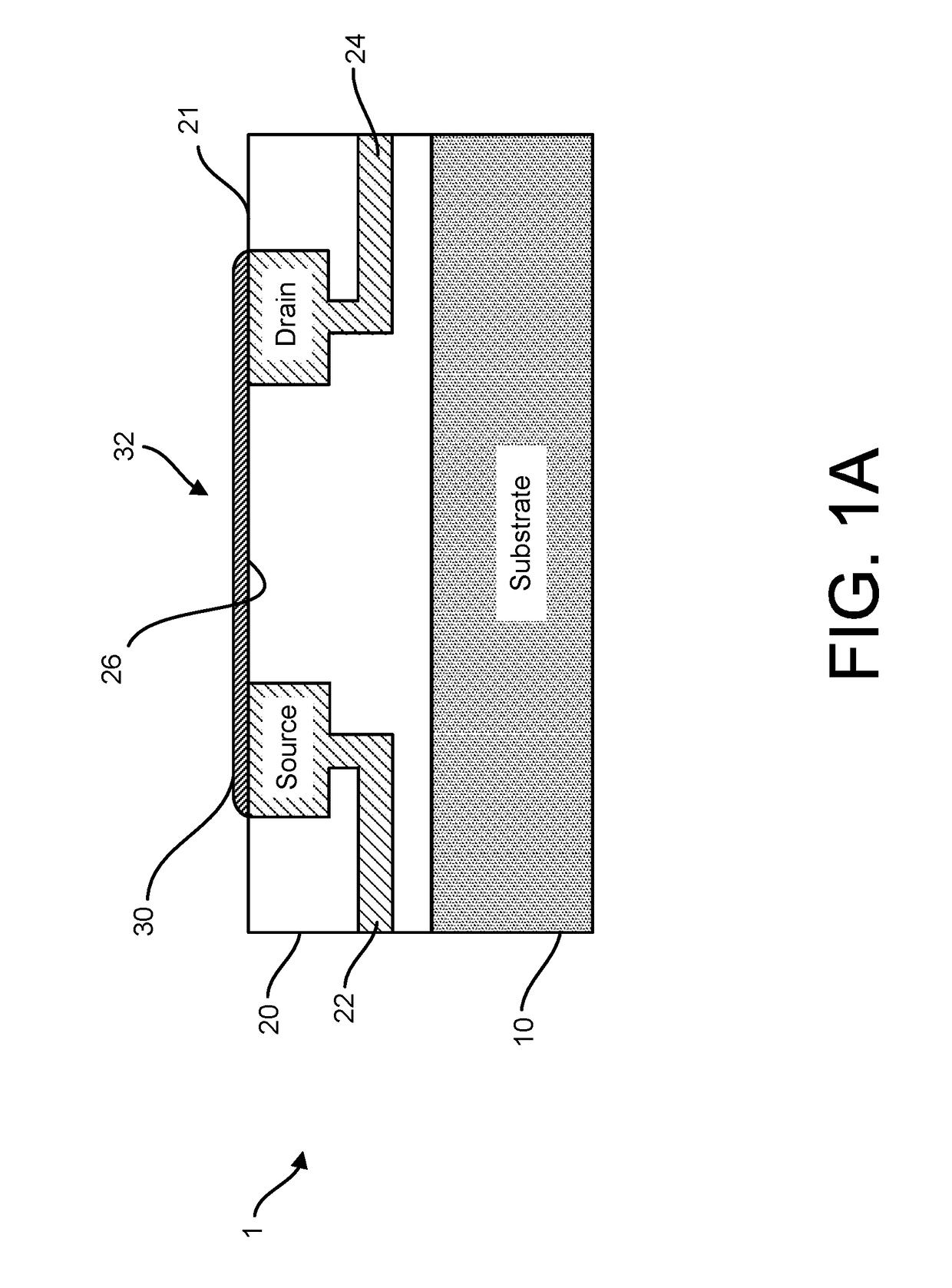
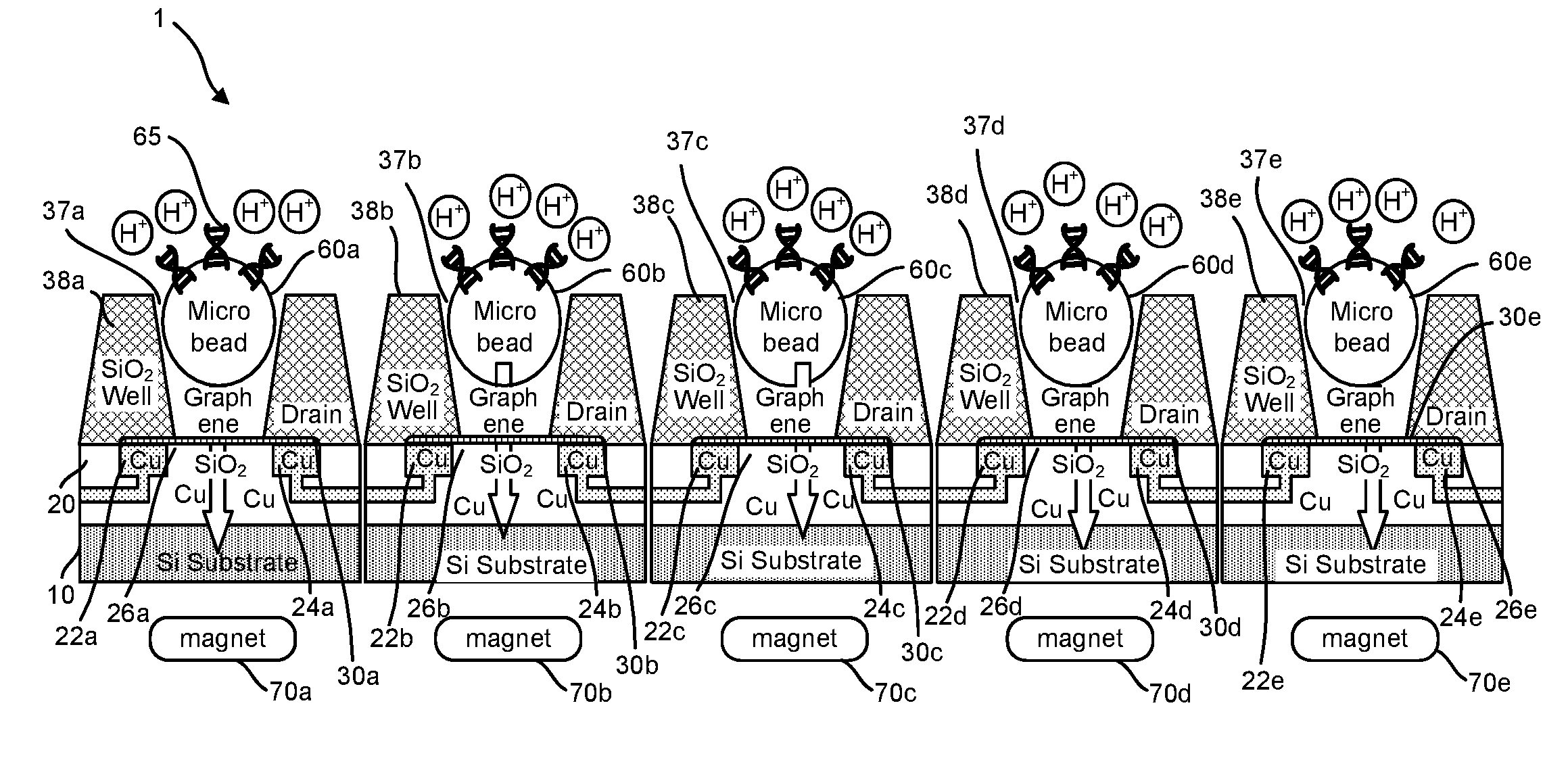
ActiveUS20160265047A1Number of EliminationsFaster data acquisitionTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementSensor arrayReaction layer
Provided herein are devices, systems, and methods of employing the same for the performance of bioinformatics analysis. The apparatuses and methods of the disclosure are directed in part to large scale graphene FET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits employing the same for analyte measurements. The present GFET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved GFET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense GFET sensor based arrays. Improved fabrication techniques employing graphene as a reaction layer provide for rapid data acquisition from small sensors to large and dense arrays of sensors. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes, including DNA hybridization and / or sequencing reactions. Accordingly, GFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis within a gated reaction chamber of the GFET based sensor.
Owner:CARDEA BIO INC
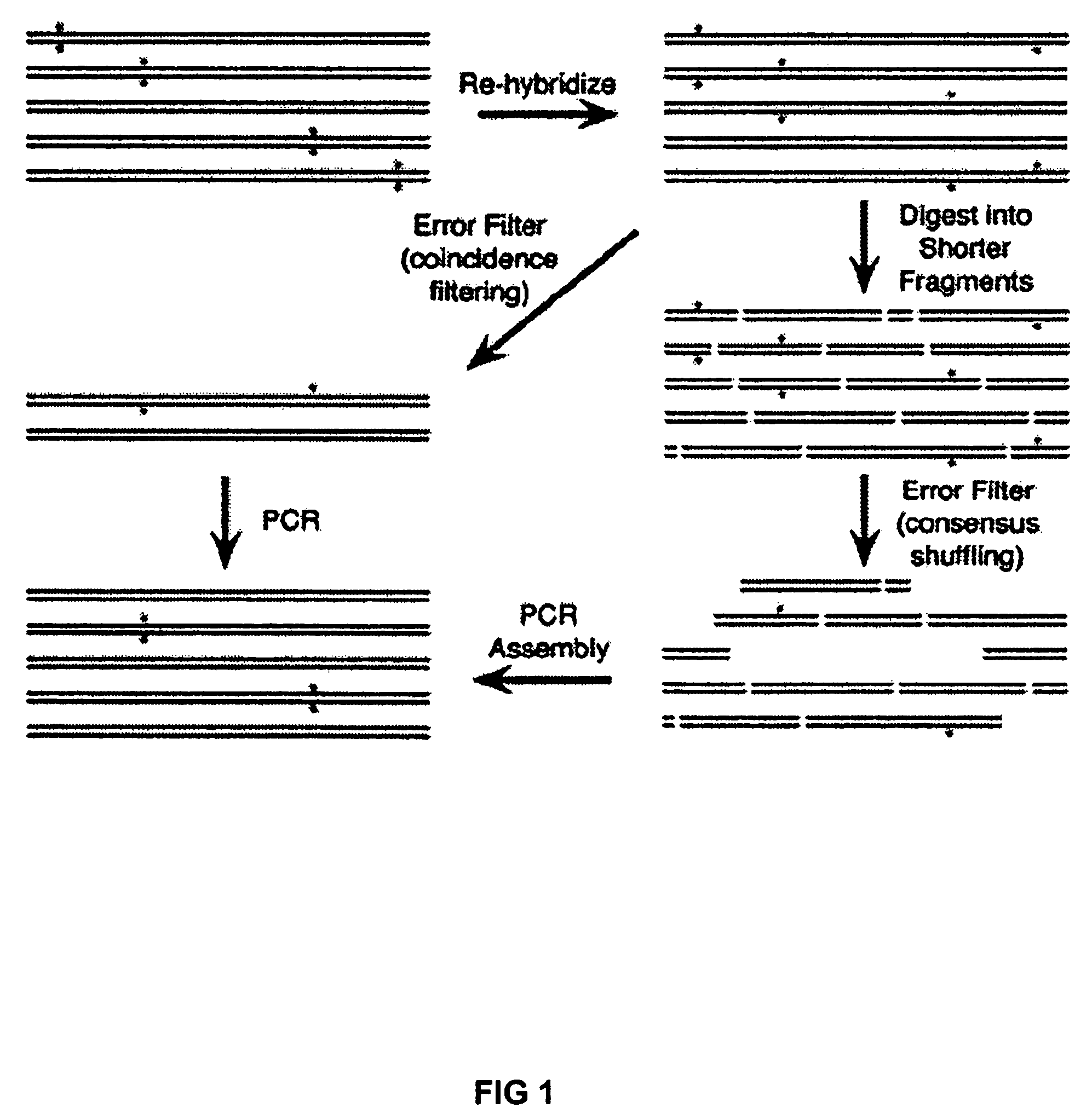
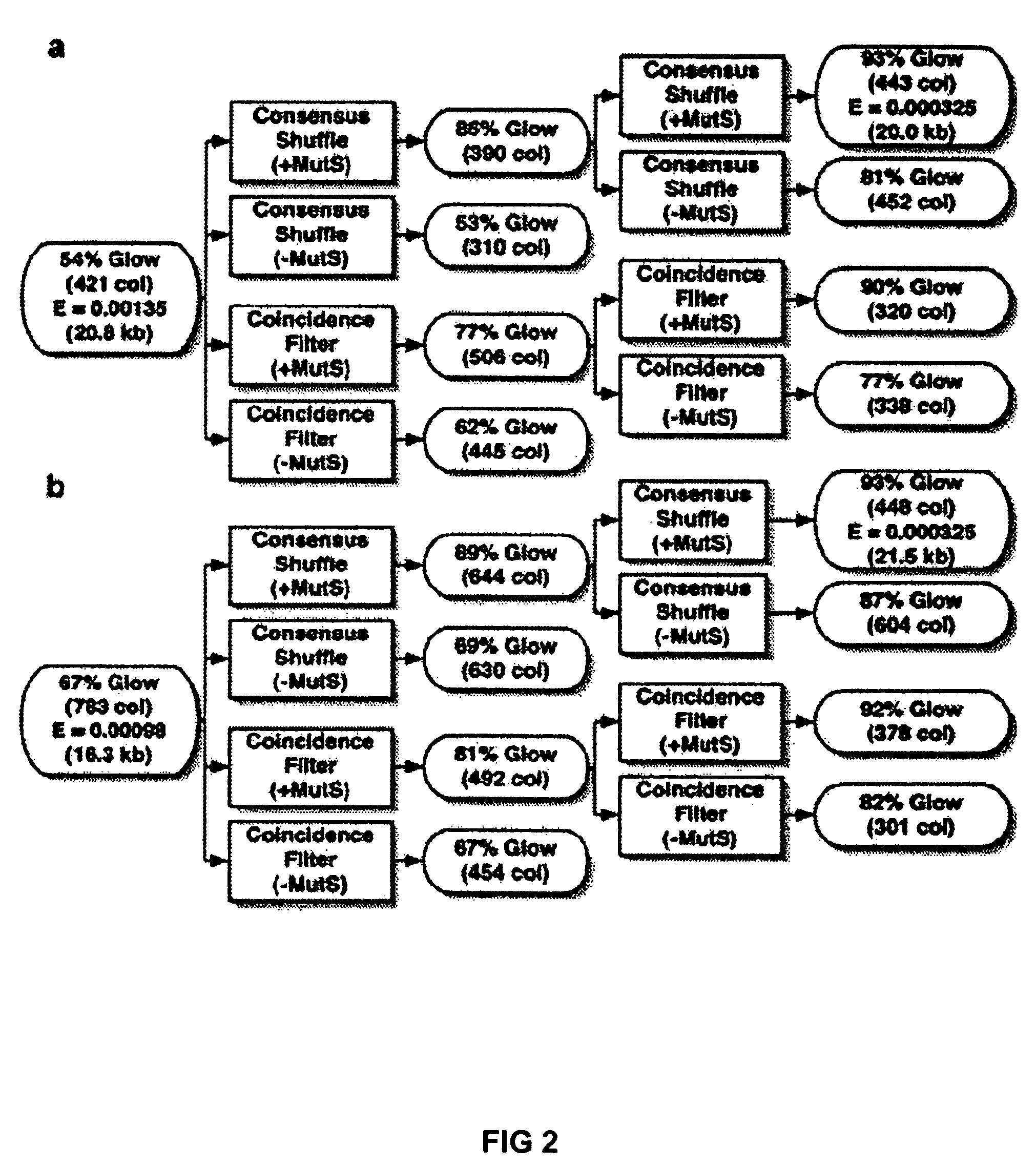
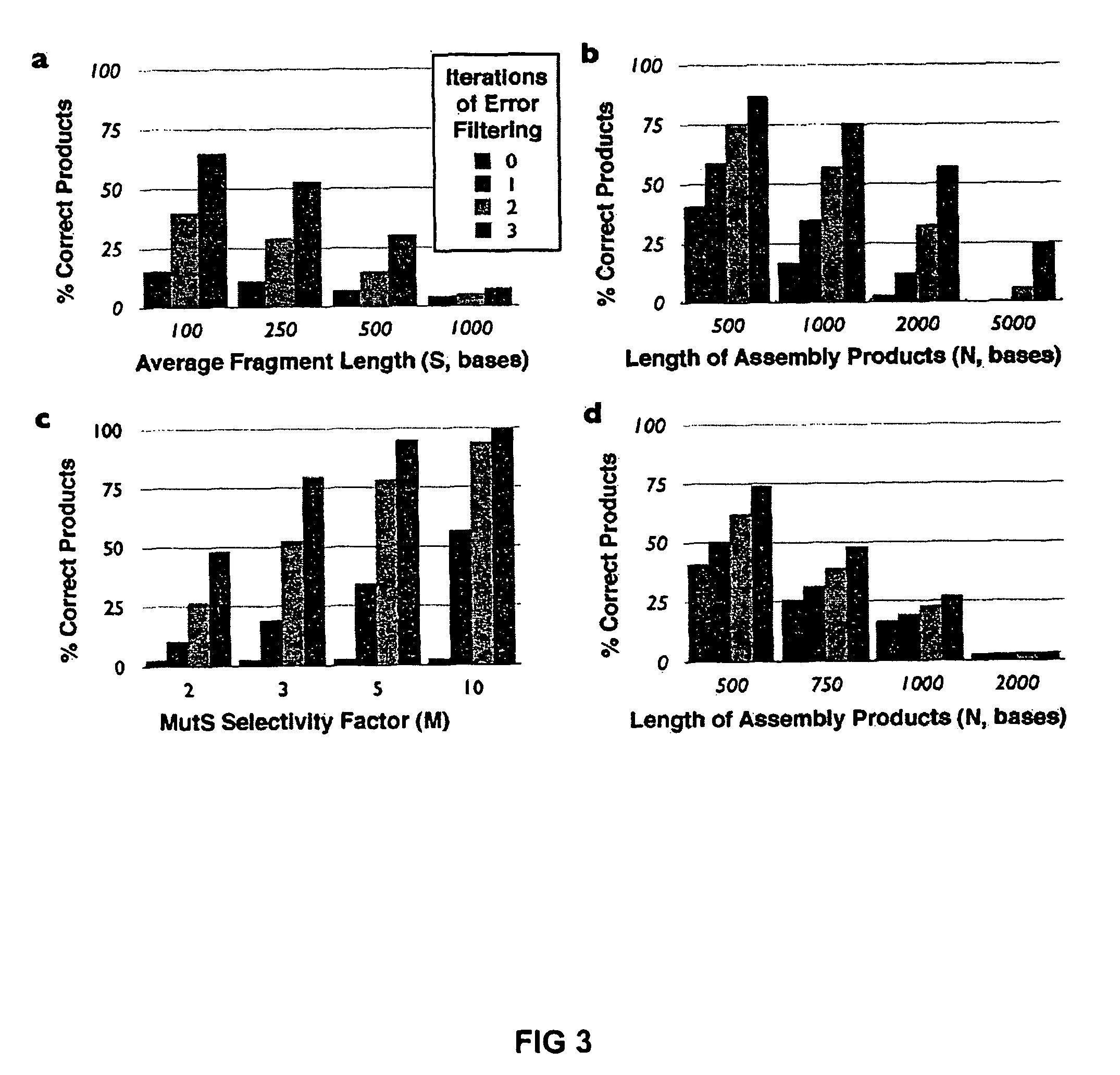
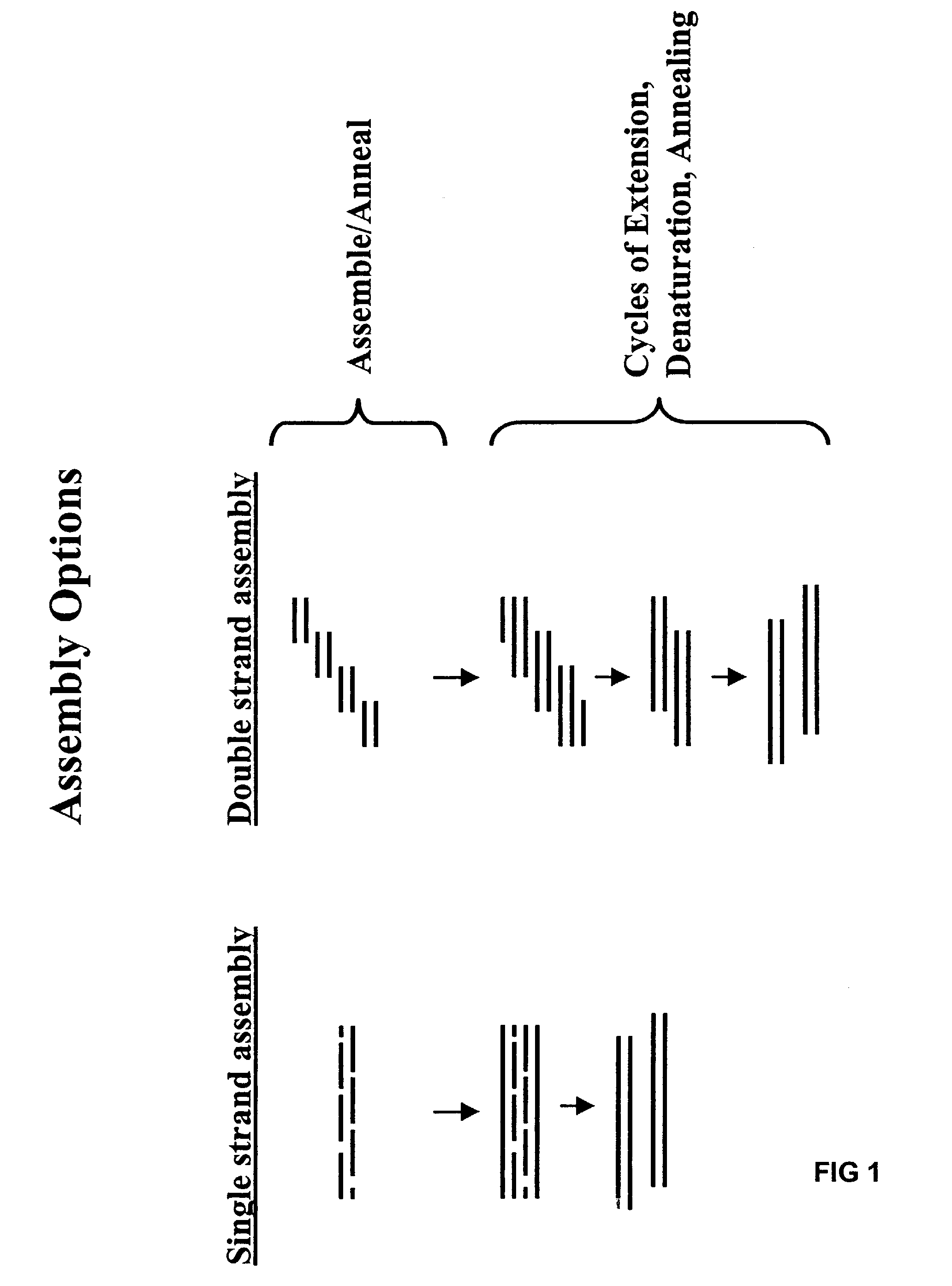
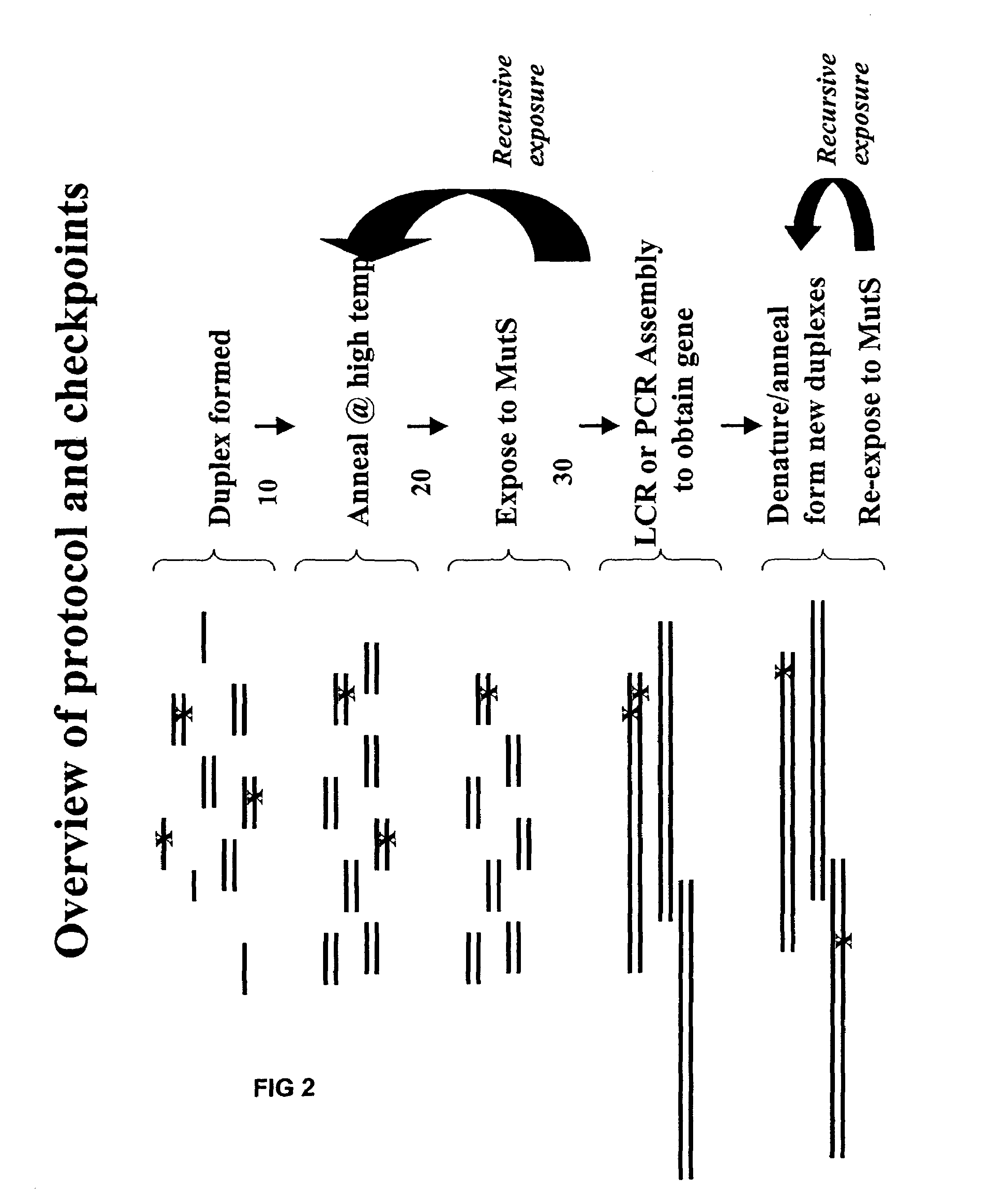
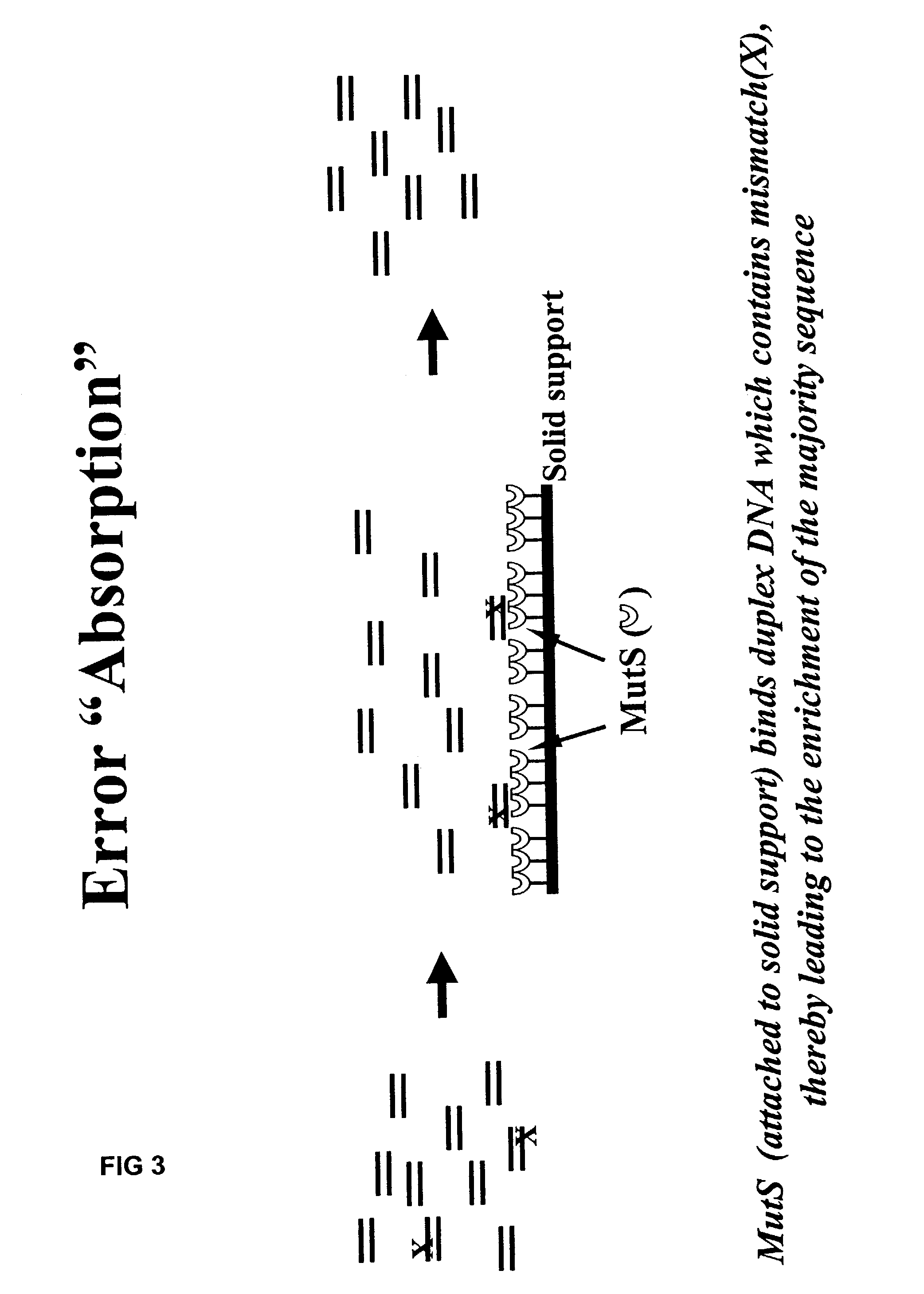
Method of error reduction in nucleic acid populations
A method is disclosed for the direct synthesis of double stranded DNA molecules of a variety of sizes and with any desired sequence. The DNA molecule to be synthesis is logically broken up into smaller overlapping DNA segments. A maskless microarray synthesizer is used to make a DNA microarray on a substrate in which each element or feature of the array is populated by DNA of a one of the overlapping DNA segments. The complement of each segment is also made in the microarray. The DNA segments are released from the substrate and held under conditions favoring hybridization of DNA, under which conditions the segments will hybridize to form duplexes. The duplexes are then separated using a DNA binding agent which binds to improperly formed DNA helixes to remove errors from the set of DNA molecules. The segments can then be hybridized to each other to assemble the larger target DNA sequence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Graphene FET devices, systems, and methods of using the same for sequencing nucleic acids
ActiveUS9618474B2Faster data acquisitionImprove accuracyTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementReaction layerSensor array
Provided herein are devices, systems, and methods of employing the same for the performance of bioinformatics analysis. The apparatuses and methods of the disclosure are directed in part to large scale graphene FET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits employing the same for analyte measurements. The present GFET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved GFET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense GFET sensor based arrays. Improved fabrication techniques employing graphene as a reaction layer provide for rapid data acquisition from small sensors to large and dense arrays of sensors. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes, including DNA hybridization and / or sequencing reactions. Accordingly, GFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis within a gated reaction chamber of the GFET based sensor.
Owner:CARDEA BIO INC
Graphene fet devices, systems, and methods of using the same for sequencing nucleic acids
ActiveUS20170018626A1Number of EliminationsFaster data acquisitionTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementReaction layerSensor array
Provided herein are devices, systems, and methods of employing the same for the performance of bioinformatics analysis. The apparatuses and methods of the disclosure are directed in part to large scale graphene FET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits employing the same for analyte measurements. The present GFET sensors, arrays, and integrated circuits may be fabricated using conventional CMOS processing techniques based on improved GFET pixel and array designs that increase measurement sensitivity and accuracy, and at the same time facilitate significantly small pixel sizes and dense GFET sensor based arrays. Improved fabrication techniques employing graphene as a reaction layer provide for rapid data acquisition from small sensors to large and dense arrays of sensors. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in a wide variety of chemical and / or biological processes, including DNA hybridization and / or sequencing reactions. Accordingly, GFET arrays facilitate DNA sequencing techniques based on monitoring changes in hydrogen ion concentration (pH), changes in other analyte concentration, and / or binding events associated with chemical processes relating to DNA synthesis within a gated reaction chamber of the GFET based sensor.
Owner:CARDEA BIO INC
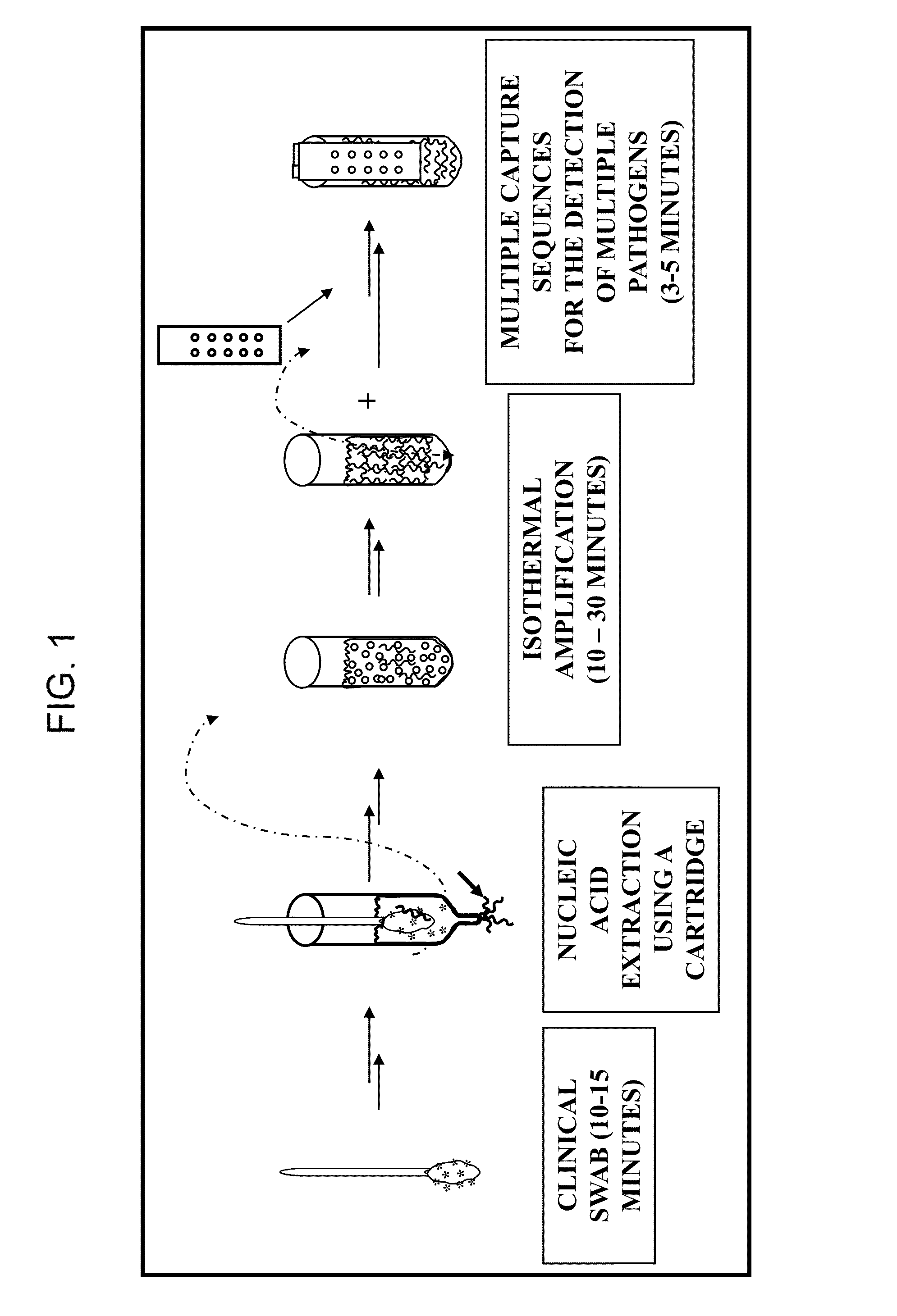
Nucleic acid testing method for point-of-care diagnostics and genetic self-monitoring
InactiveUS20080050735A1The testing process is simpleSpecial trainingMicrobiological testing/measurementPoint of careGenomic DNA
This invention describes a nucleic acid testing procedure in a form of portable device or a test kit for the purposes of clinical genetic testing, infectious disease diagnostics, biodefense, forensic analysis, paternity testing, pet and cattle breeding, food testing, etc. This testing does not include toxic chemicals and is simple enough to be used by an average individual without any special laboratory training. The procedure includes collecting the sample, potential isothermal amplification of the whole genomic DNA or a fragment of genomic DNA, denaturing double-stranded DNA into single-stranded form, hybridizing the denatured sample DNA to single-stranded allele-specific tester oligonucleotides complementary to the analyzed DNA sequence of interest, selective removal of single-stranded DNA from DNA hybrids, and finally detecting the label in double-stranded hybrids to determine the presence or absence of a particular sequence in the initial sample.
Owner:PUSHNOVA ELENA
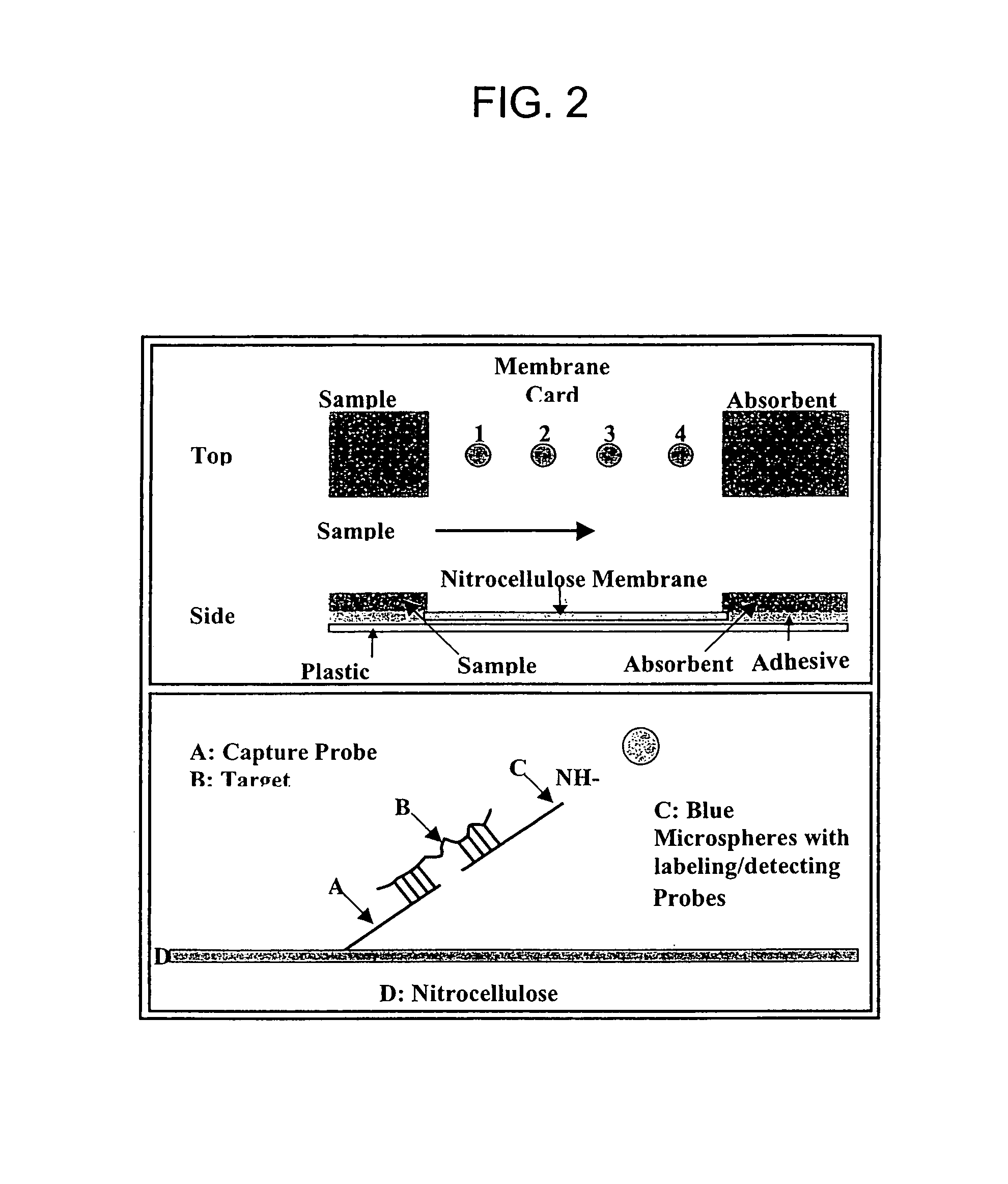
Nucleic acid detection system and method for detecting influenza
ActiveUS8980561B1Minimize extentUnprecedented assay speedMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDna amplificationSingle strand dna
The invention provides a rapid, sensitive and specific nucleic acid detection system which utilizes isothermal nucleic acid amplification in combination with a lateral flow chromatographic device, or DNA dipstick, for DNA-hybridization detection. The system of the invention requires no complex instrumentation or electronic hardware, and provides a low cost nucleic acid detection system suitable for highly sensitive pathogen detection. Hybridization to single-stranded DNA amplification products using the system of the invention provides a sensitive and specific means by which assays can be multiplexed for the detection of multiple target sequences.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
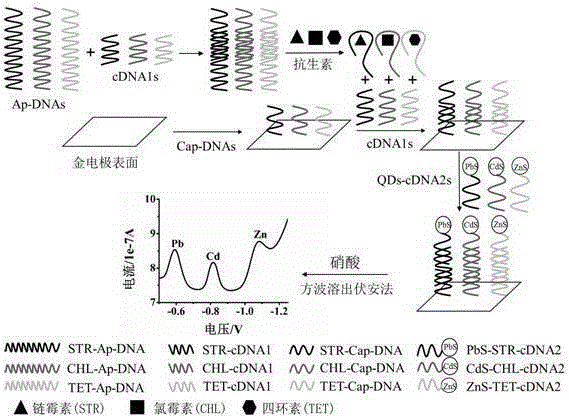
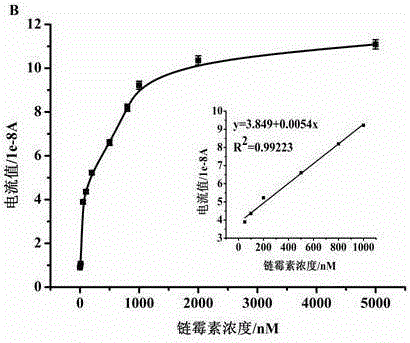
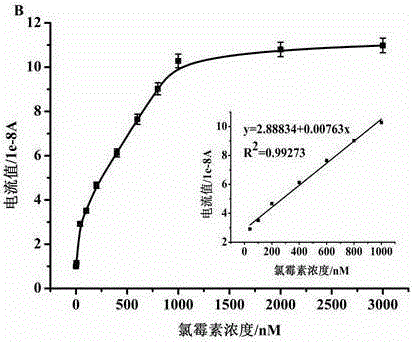
Method for simultaneously detecting three antibiotic residues including streptomycin, chlorampenicol and tetracycline based on nucleic acid aptamer and quantum dots
ActiveCN105301085AEasy to manufactureEasy to retouchMaterial electrochemical variablesDissolutionAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously detecting three antibiotic residues including streptomycin, chlorampenicol and tetracycline based on nucleic acid aptamers and quantum dots and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry. Three-section complementary cDNA 1 sequences are designed and synthesized and are complemented with three antibiotic aptamers DNA sequences and are further complemented with respective capturing probe DNA sequences of three antibiotics and complementary cDNA 2 sequence part. The three cDNAs 1 are first hybridized with aptamer DNAs supplemented with each other to form double-stranded DNAs. When target antibiotics exist in a sample, the aptamer DNAs are combined with corresponding antibiotics as a priority to cause the double-stranded DNAs to be de-hybridized and release cDNAs 1. The free cDNAs 1 are combined with capturing probe DNAs modified on the surface of a gold electrode, and cDNAs 2 modified with three quantum dots are hybridized with the other end of each cDNA 1. The three quantum dots on the surface of the gold electrode generate dissolution volt-ampere peaks corresponding to the target antibiotics. The three antibiotics are detected by utilizing the relations of changes of peak current values and antibiotic concentration. The method is good in repeatability and stability and high in sensitivity and can be used for directly measuring the three antibiotic residues in samples such as milk.
Owner:ANHUI HUATENG AGRI TECH CO LTD
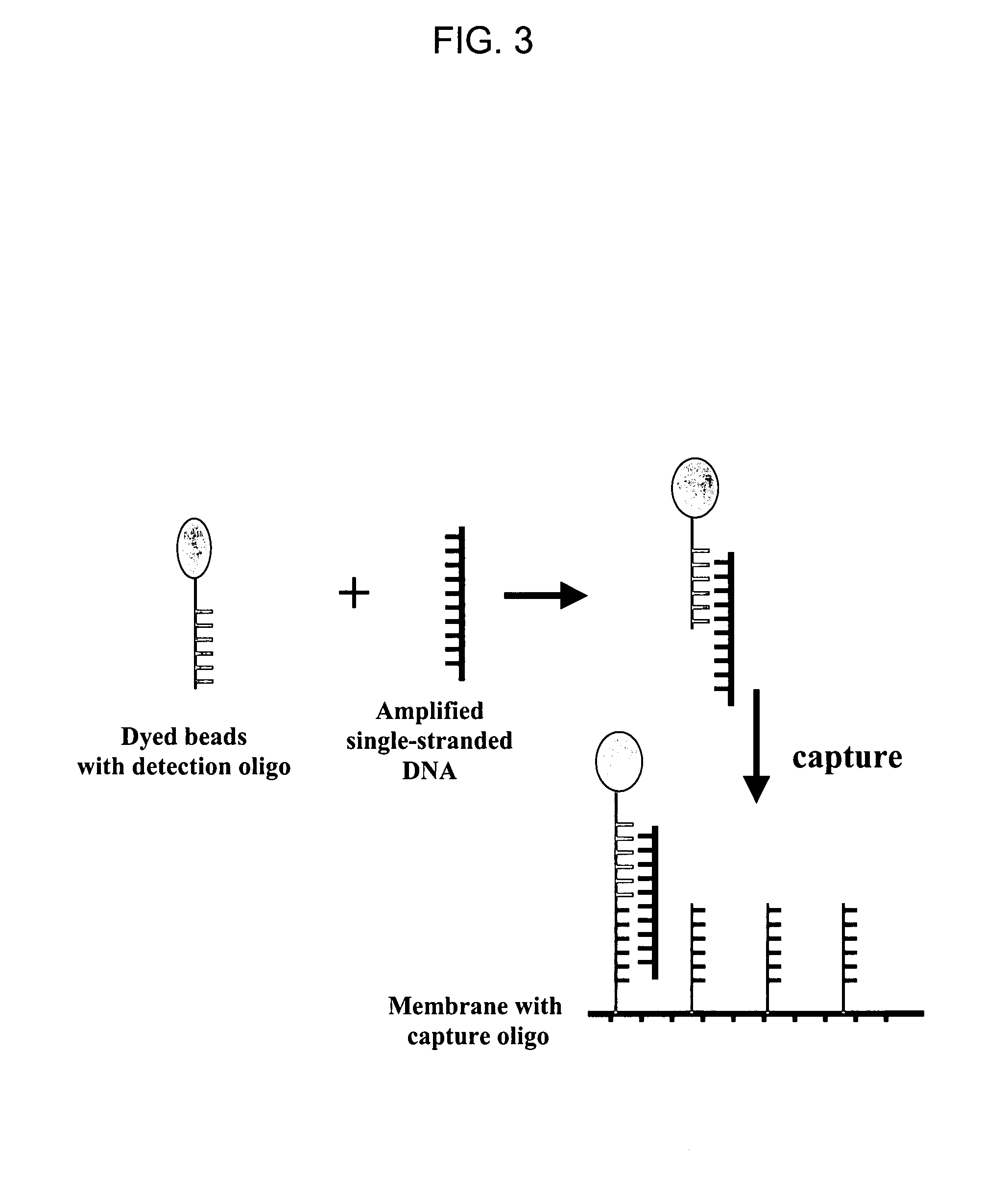
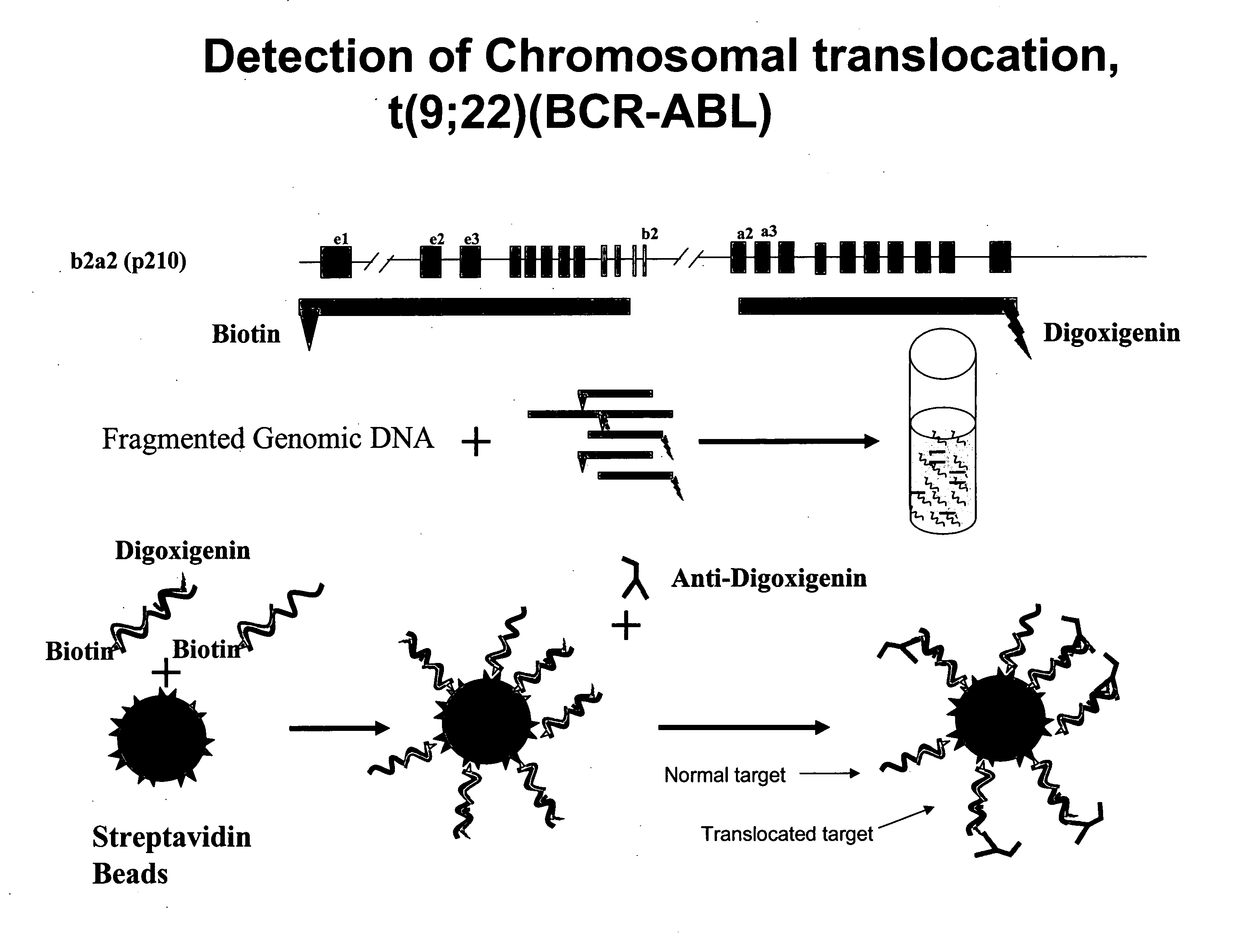
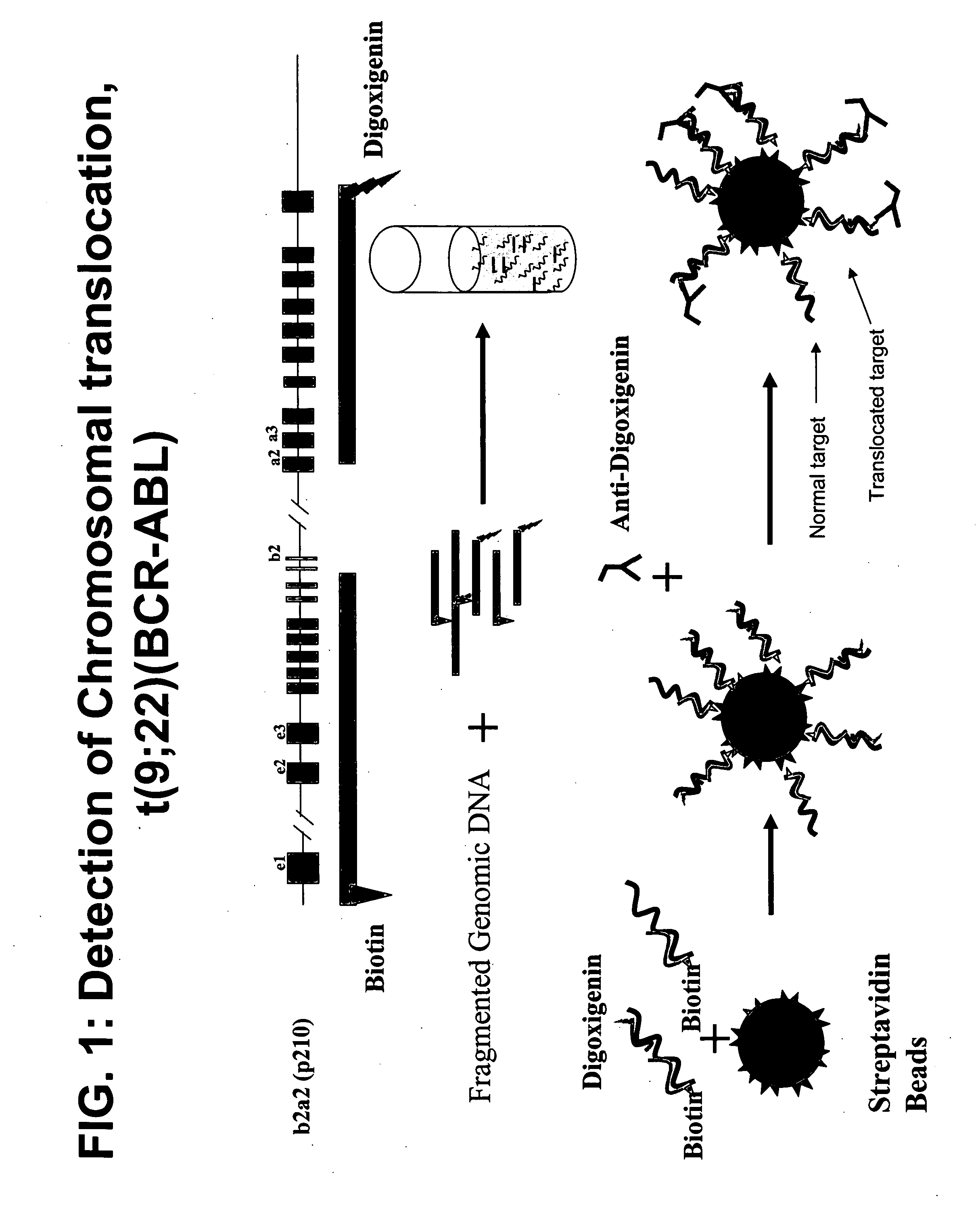
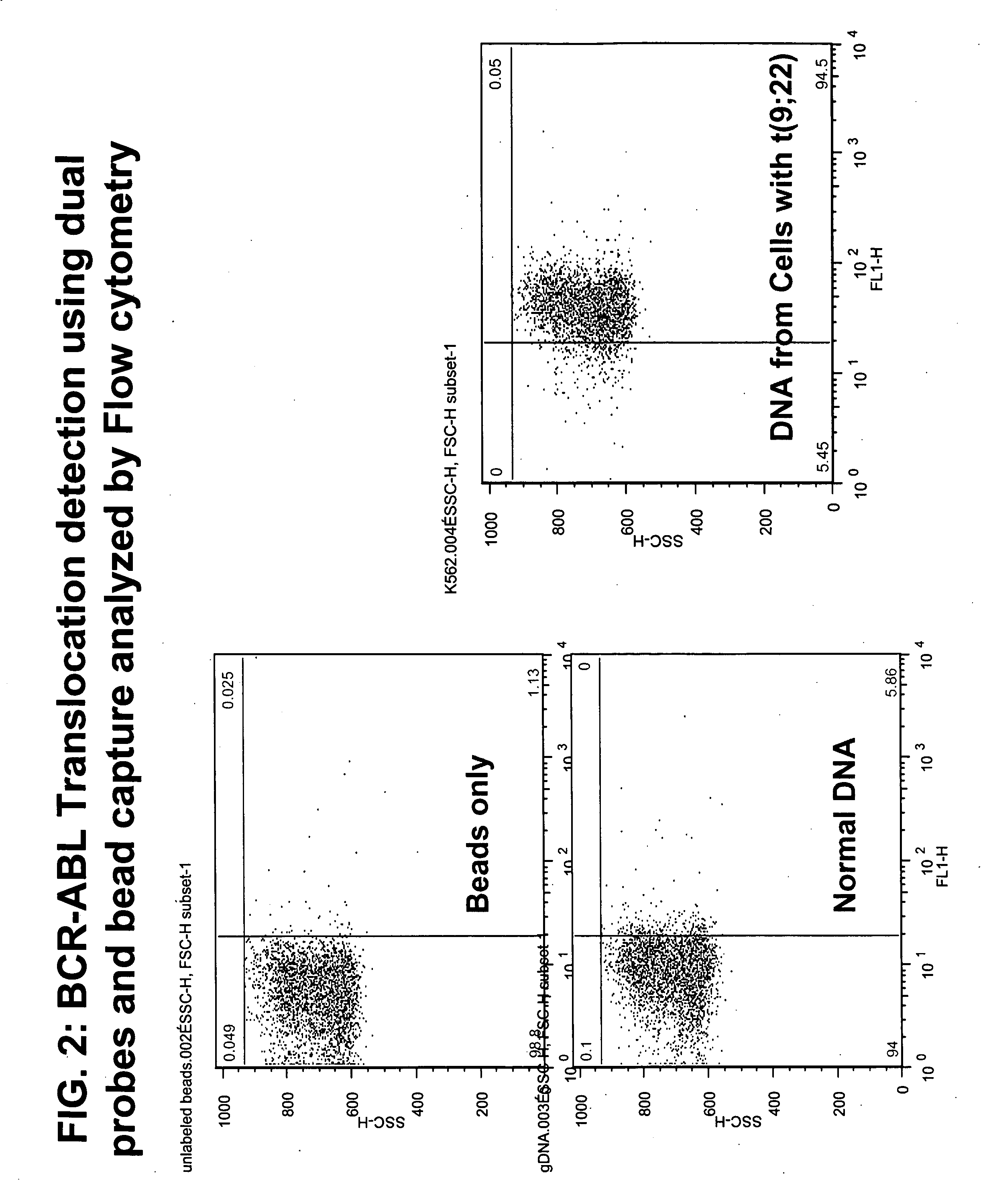
Non-in situ hybridization method for detecting chromosomal abnormalities
The present invention provides methods of detecting chromosomal or genetic abnormalities associated with various diseases or with predisposition to various diseases. In particular, the present invention provides advanced methods of performing DNA hybridization, capture, and detection on solid support. Invention methods are useful for the detection, diagnosis, predicting response to therapy, detecting minimal residual disease, prognosis, or monitoring of disease treatment or progression of particular disease conditions such as cell proliferative disorders
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Method for detecting and identifying microorganism causative of infection
InactiveUS7651837B2Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationPhagocytePathogenic microorganism
Causative microorganisms of infectious diseases are detected and / or identified rapidly and with high sensitivity by taking phagocytes from clinical specimens containing active phagocytes, immobilizing the phagocytes so taken, treating the phagocytes to improve cell membrane permeabilities thereof, further treating the phagocytes to bare DNA in the causative microorganisms which might exist in the phagocytes, and detecting the causative microorganisms with DNA probes which can hybridize with such DNA under stringent conditions.
Owner:FUSO PHARMA INDS
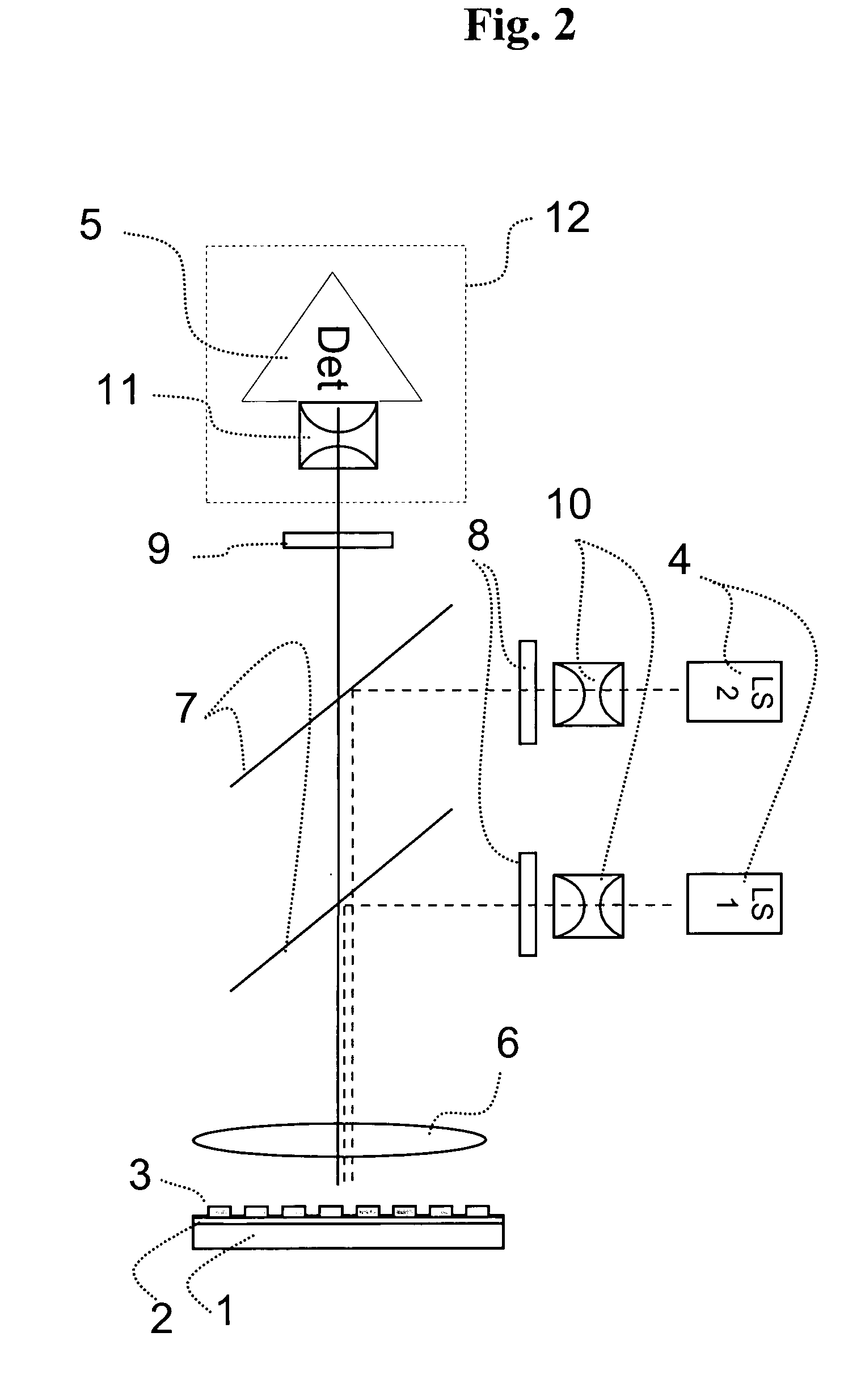
Imaging fluorescence signals using telecentric optics
ActiveUS7687260B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDNA microarrayParallel imaging
The present invention relates to the field of DNA analysis. In particular, the present invention is directed to a device for the parallel imaging of fluorescence intensities at a plurality of sites as a measure for DNA hybridization. More particular, the present invention is directed to a device to image multiplex real time PCR or to read out DNA microarrays.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Method of error reduction in nucleic acid populations
InactiveUS7303872B2Minimum errorSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA microarrayError reduction
A method is disclosed for the direct synthesis of double stranded DNA molecules of a variety of sizes and with any desired sequence. The DNA molecule to be synthesis is logically broken up into smaller overlapping DNA segments. A maskless microarray synthesizer is used to make a DNA microarray on a substrate in which each element or feature of the array is populated by DNA of a one of the overlapping DNA segments. The complement of each segment is also made in the microarray. The DNA segments are released from the substrate and held under conditions favoring hybridization of DNA, under which conditions the segments will hybridize to form duplexes. The duplexes are then separated using a DNA binding agent which binds to improperly formed DNA helixes to remove errors from the set of DNA molecules. The segments can then be hybridized to each other to assemble the larger target DNA sequence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
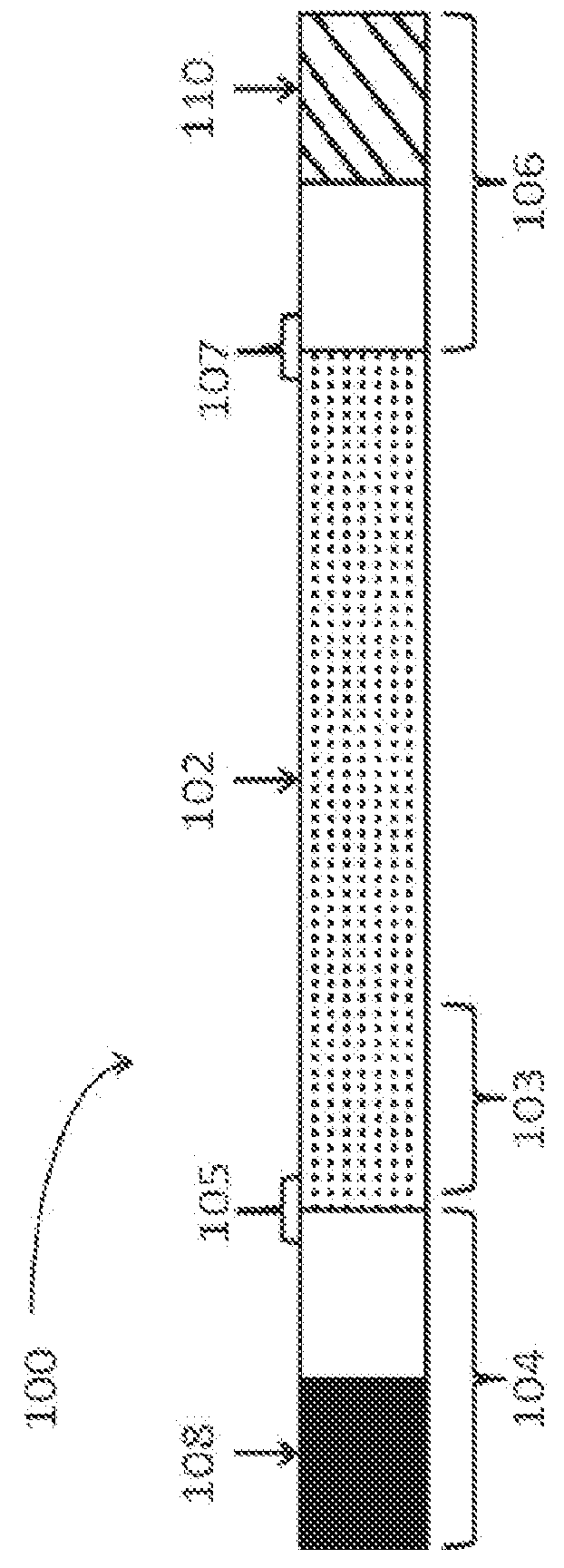
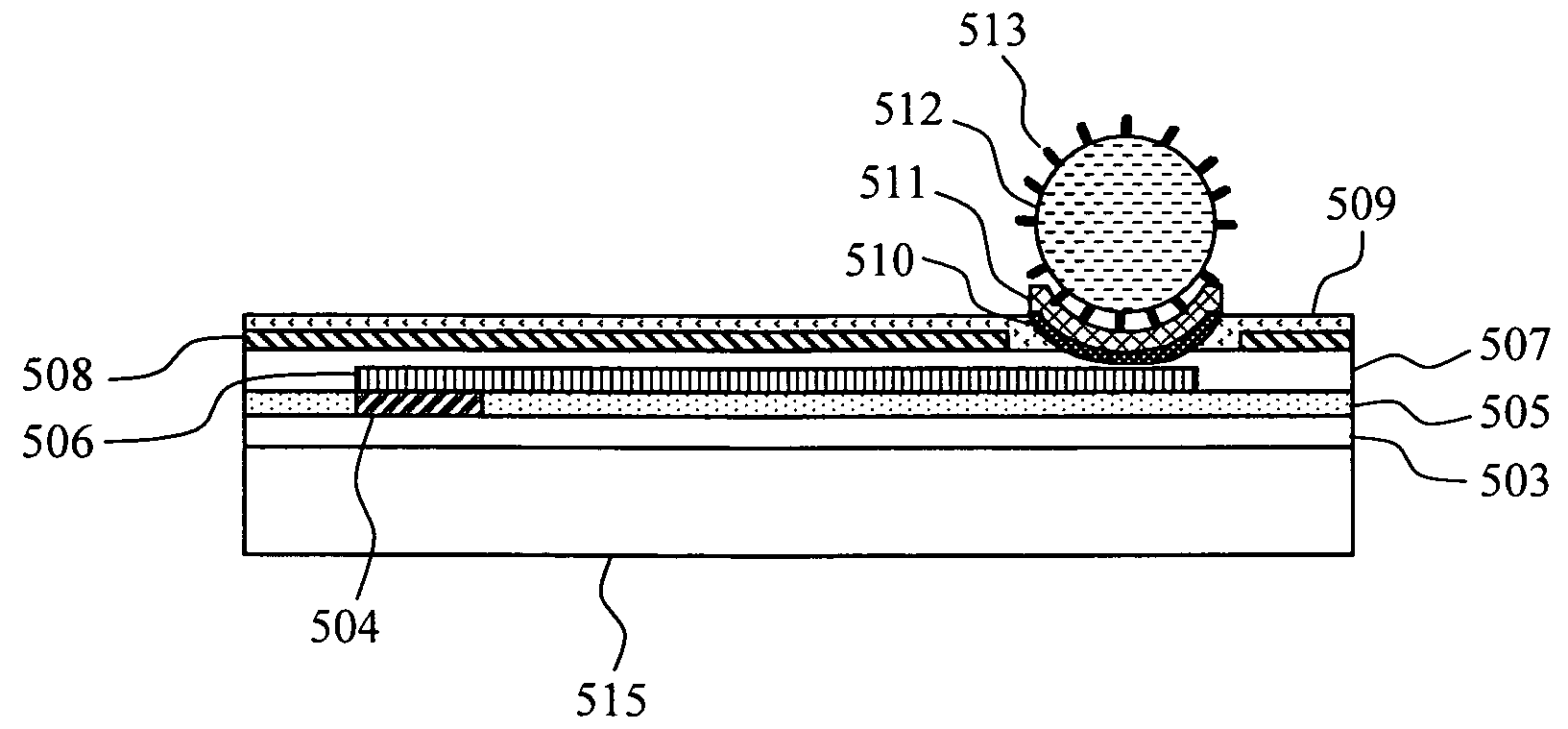
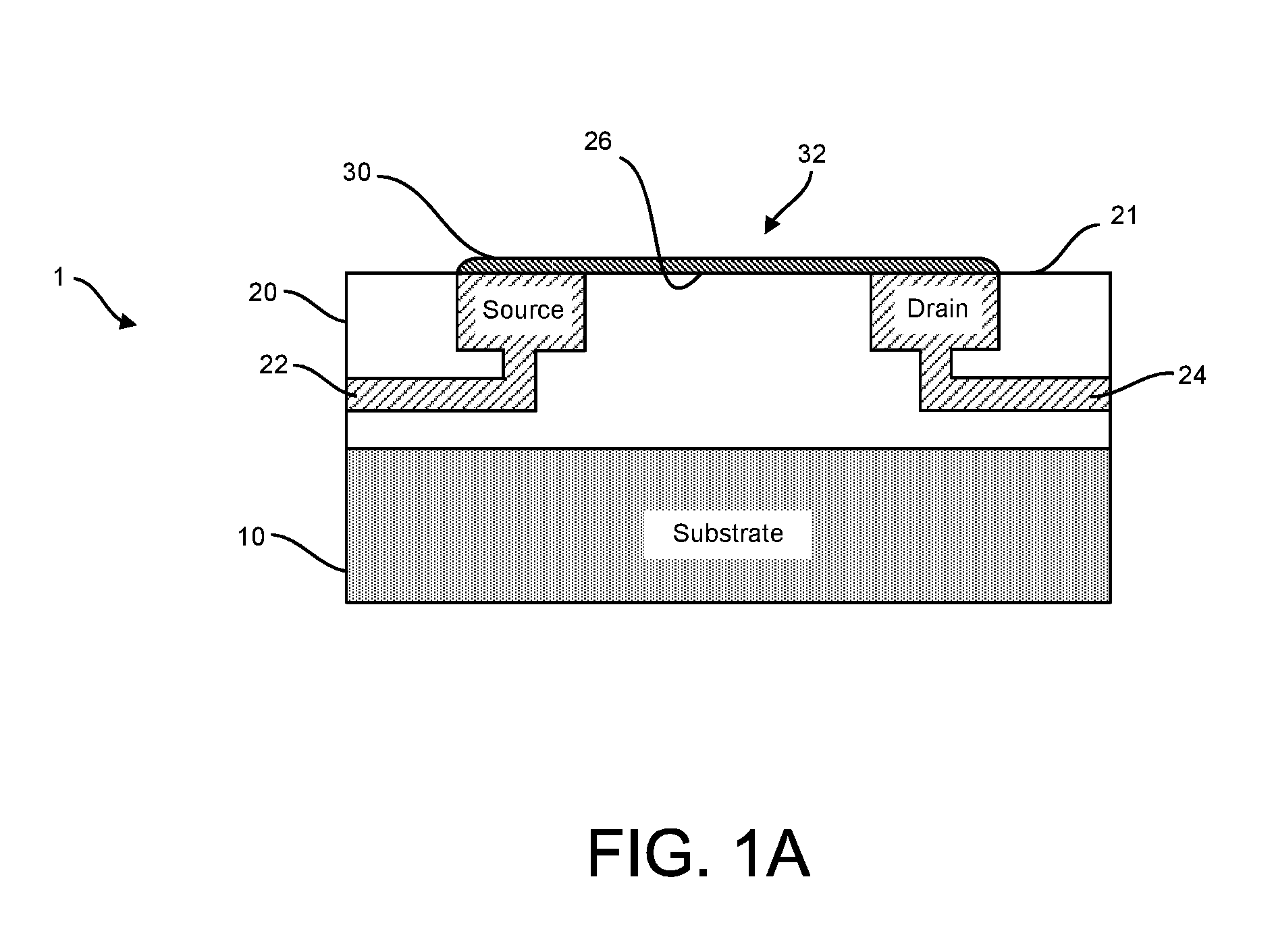
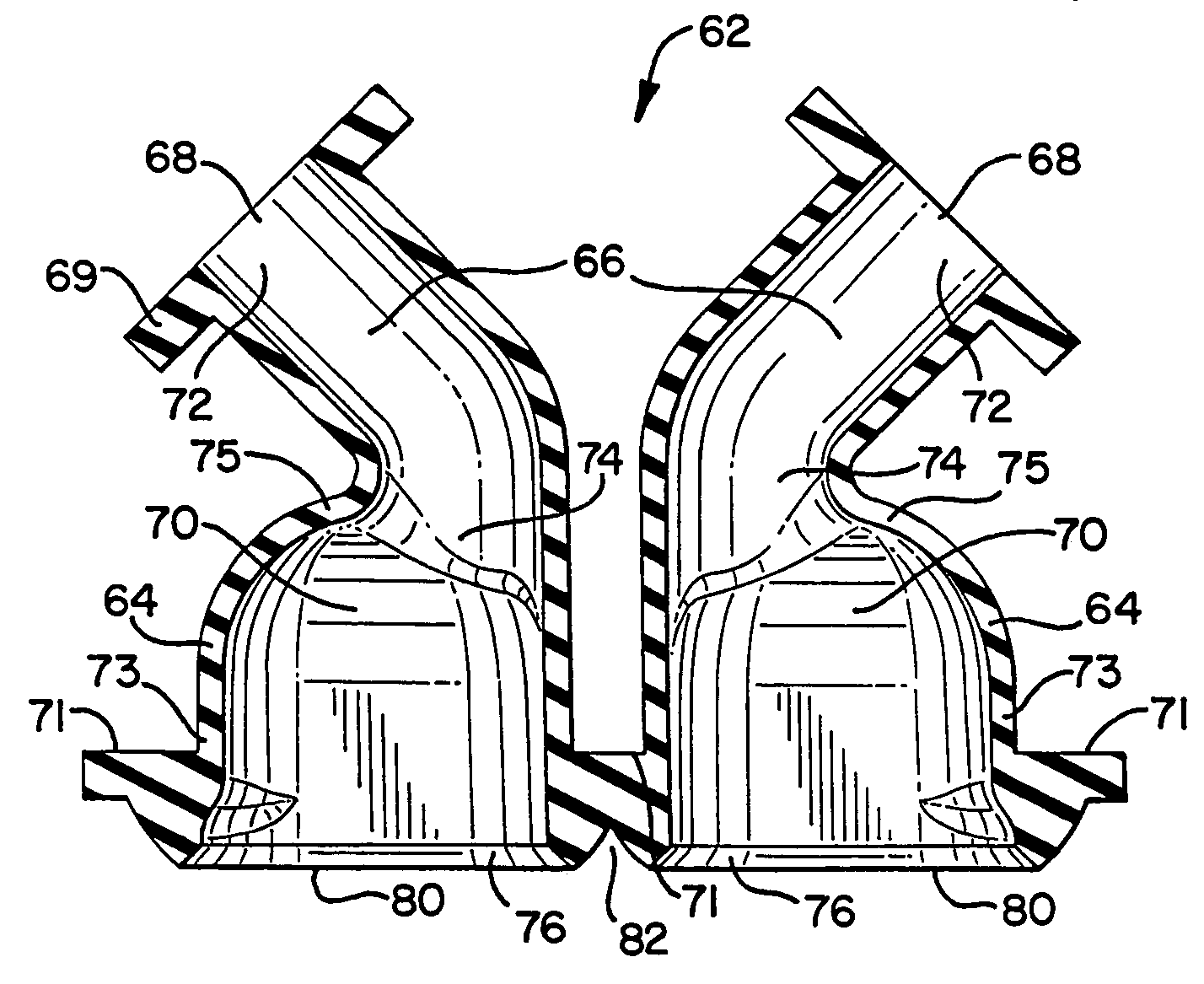
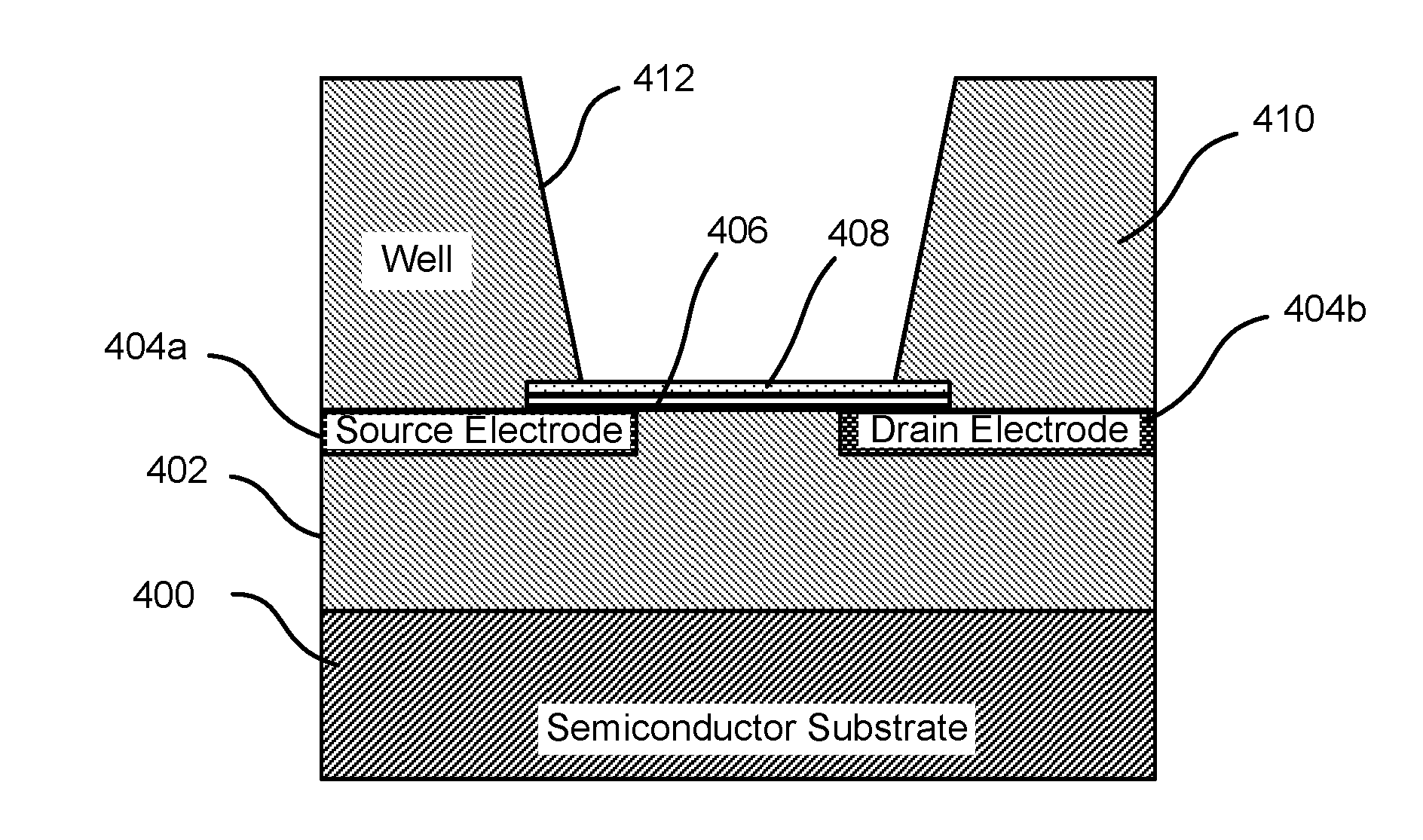
DNA hybridization device and method
ActiveUS7163823B2Reduce pressureProvide structureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringDNA hybridisation
An apparatus and method for DNA hybridization is provided. The apparatus and method work in conjunction with a substrate comprising an upper surface having probes. The apparatus may comprise a material which abuts the substrate, with at least a portion of the material being pliable. The material and the substrate form a plurality of chambers, each chamber having a bottom including at least a portion of the upper surface, at least one sidewall, and an opening. The apparatus further comprises a mechanism for closing the openings of the chambers, thereby sealing the chambers.
Owner:NANOSPHERE INC
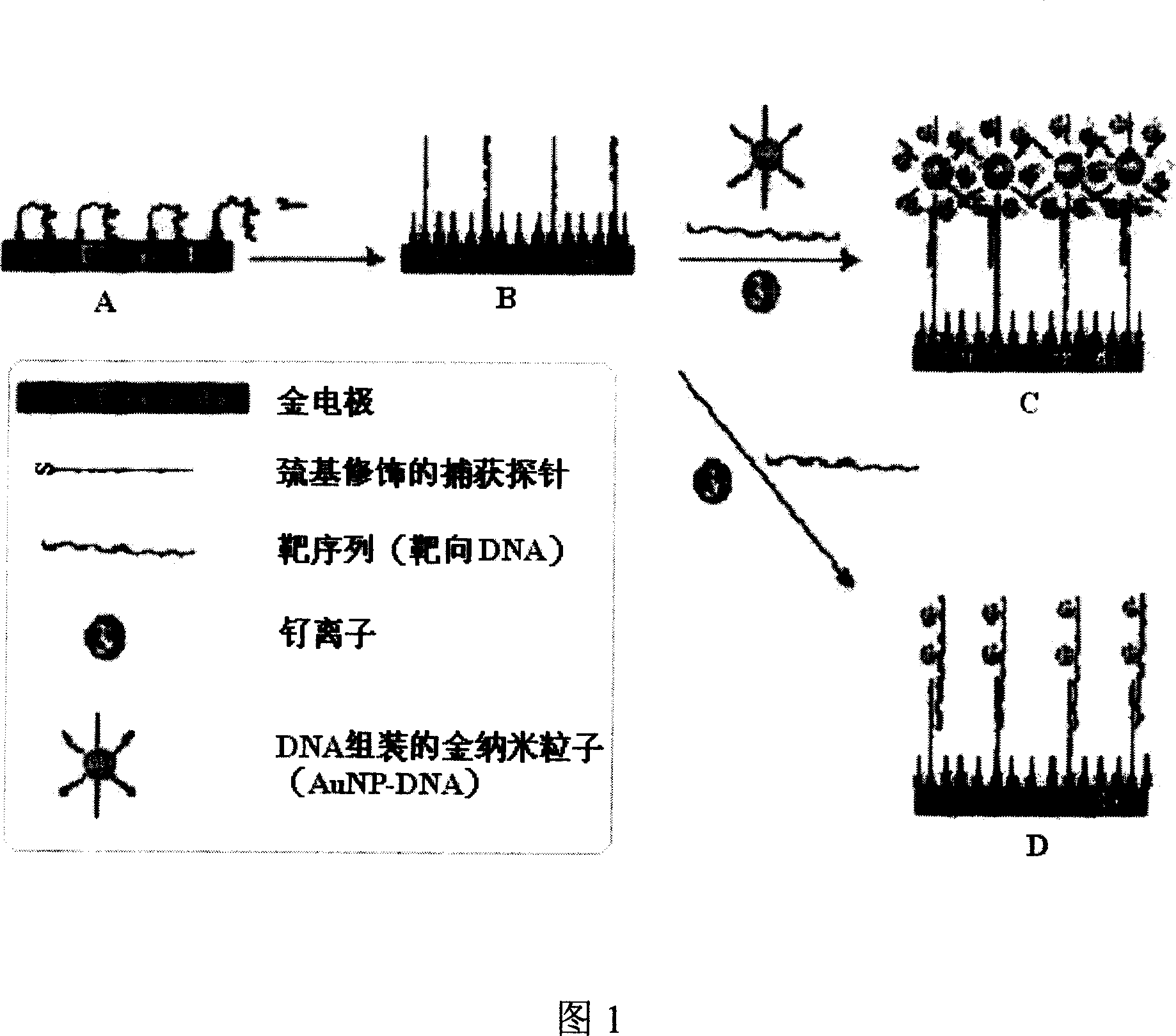
DNA electrochemical sensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101078026AHigh densityStrong Mismatch CapabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization reactionElectrochemistry
The invention describes a kind of DNA electrochemistry sensor, which comprises gold pole, complementary DNA, gold nano-particles and electrochemistry indicator. It is characterized in that one segment of complementary DNA is assembled onto the gold pole as capture probe, and the other segment as detection probe is integrated with the gold nano-particles to be the carrier of electrochemistry indicator. The preparation method is disclosed. By means of 'sandwich' hybridization method, the surface of the pole has high DNA chains with negative charge and The VIII family transition metal ions with positive charge was introduced to combine with DNA as electrochemistry indicator. The DNA hybridization reaction is indicated by detecting the electrochemistry numerical change (electric current or quantity) of the pole surface. Because of the amplification effect of the gold nano-particles, the sensor can detect trace DNA with high selectivity and the gold pole modified with DNA can be used repeatedly.
Owner:JIANGSU WUZHONG HIGH & NEW TECH IND
Method for the synthesis of DNA sequences
A method is disclosed for the direct synthesis of double stranded DNA molecules of a variety of sizes and with any desired sequence. The DNA molecule to be synthesis is logically broken up into smaller overlapping DNA segments. A maskless microarray synthesizer is used to make a DNA microarray on a substrate in which each element or feature of the array is populated by DNA of a one of the overlapping DNA segments. The DNA segments are released from the substrate and held under conditions favoring hybridization of DNA, under which conditions the segments will spontaneously hybridize together to form the desired DNA construct. This method makes possible the remote assembly of DNA sequence, through a process analogous to facsimile transmission of documents, since the information on DNA to be made can be transmitted remotely to an instrument which can then synthesize any needed DNA sequence from the information.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Graphene fet devices, systems, and methods of using the same for sequencing nucleic acids
ActiveUS20170053908A1Number of EliminationsFaster data acquisitionTransistorMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteConductive materials
Provided herein are integrated circuits for use in performing analyte measurements and methods of fabricating the same. Such arrays may be employed to detect a presence and / or concentration changes of various analyte types in chemical and / or biological processes, including DNA hybridization and / or sequencing reactions. The methods for fabricating the integrated circuits include steps of depositing an insulating layer on a semiconducting substrate, and forming trenches in the insulating dielectric layer. Conductive material may be deposited in the trenches to form electrodes, and the insulating layer may be conditioned so that the electrodes protrude above the insulating layer. A 2D material, such as graphene, may be deposited on the electrodes to form a channel between the electrodes.
Owner:CARDEA BIO INC
Probe and method for DNA detection
InactiveUS20110212540A1Enhanced fluorescence emissionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeFluorescence
A hybridization probe containing two linear strands of DNA lights up upon hybridization to a target DNA using silver nanoclusters that have been templated onto one of the DNA strands. Hybridization induces proximity between the nanoclusters on one strand and an overhang on the other strand, which results in enhanced fluorescence emission from the nanoclusters.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Method for forming full-length cDNA libraries
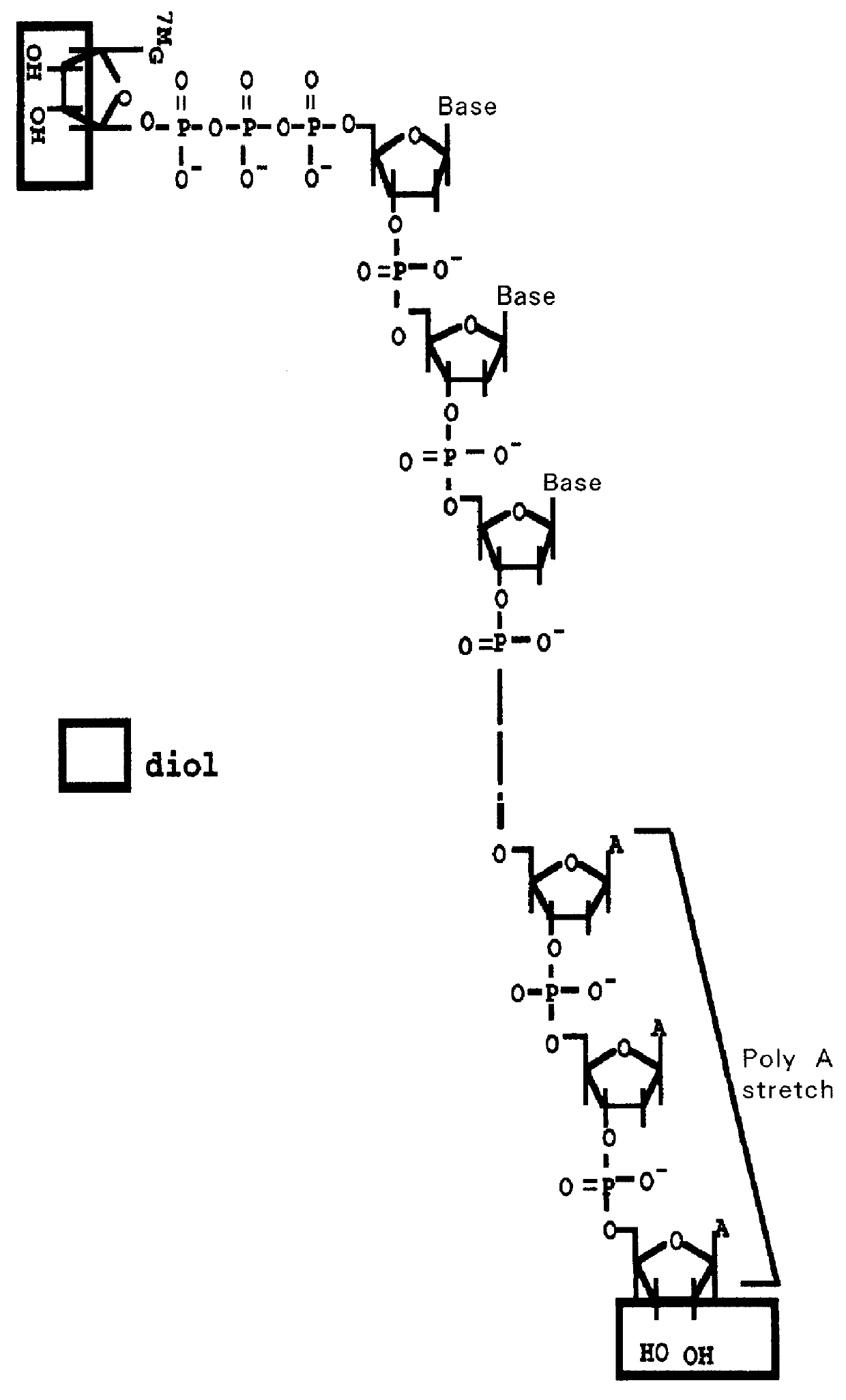
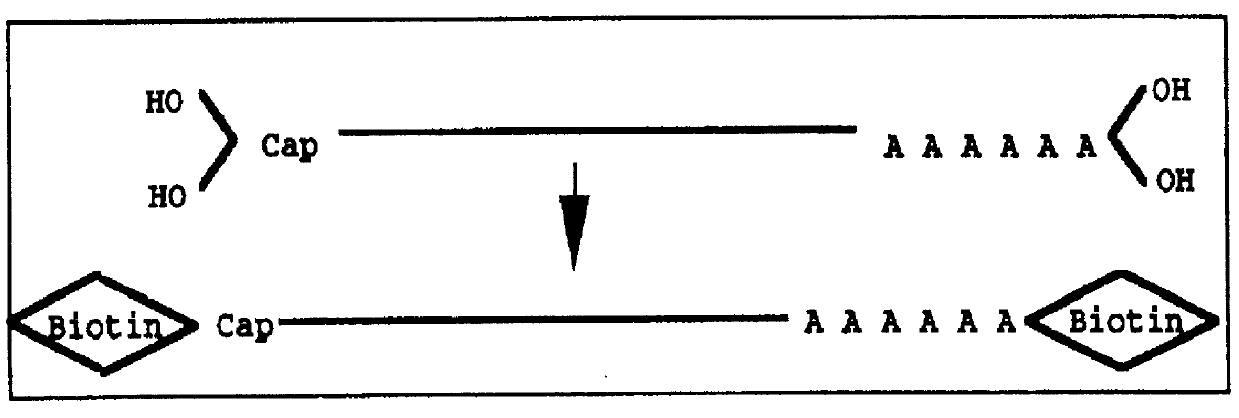
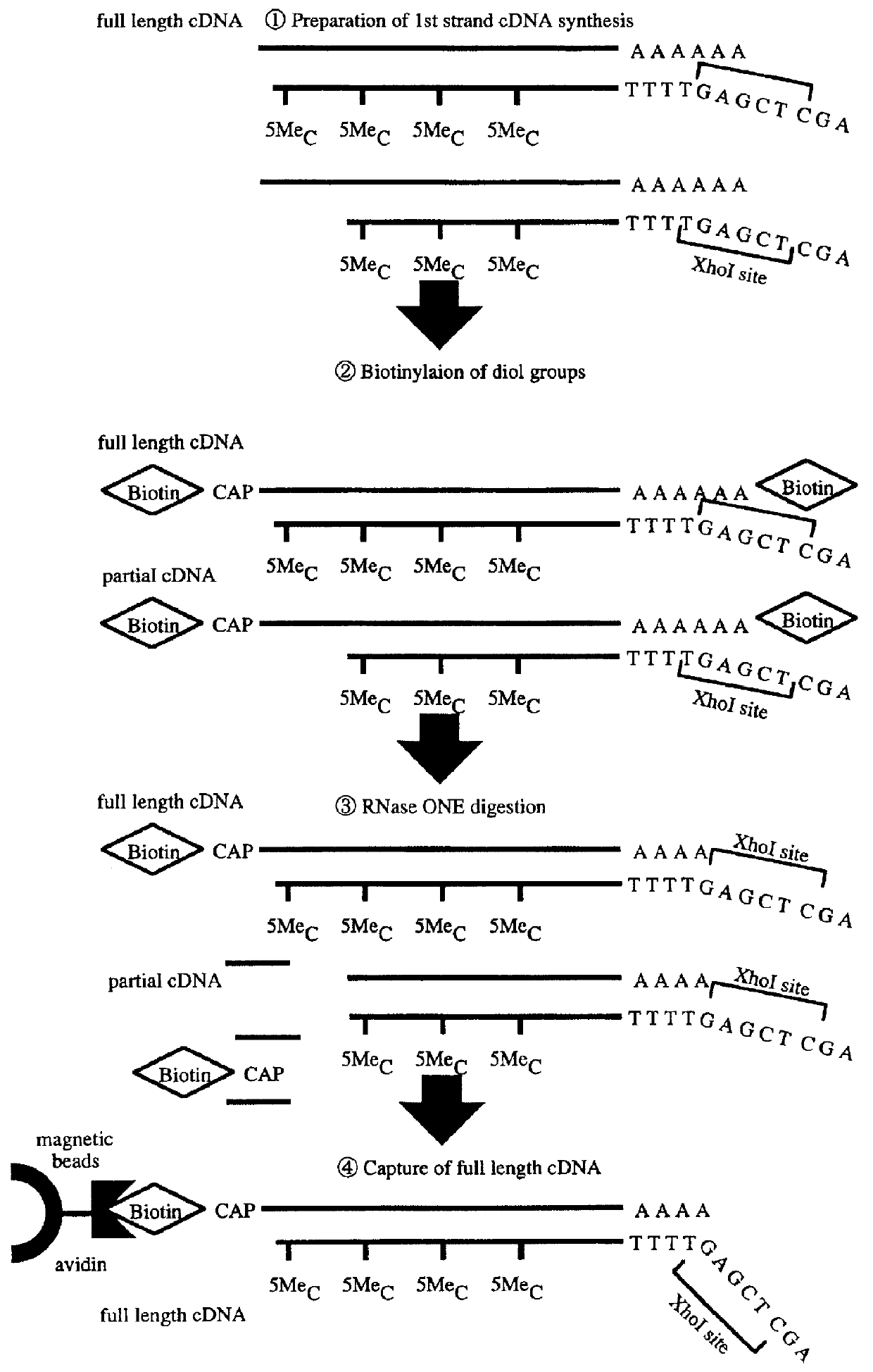
InactiveUS6143528AEasy to prepareEfficiently labeledSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPresent methodFull length cdna
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 03992 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 16, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 16, 1999 PCT Filed Oct. 31, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 20122 PCT Pub. Date May 14, 1998Disclose is a method for making full-length cDNA libraries, which is for making libraries of cDNAs having lengths corresponding to full lengths of mRNAs and comprises the following steps of; forming RNA-DNA hybrids by reverse transcription starting from primers using mRNAs as templates, chemically binding a tag molecule to a diol structure present in the 5' Cap (7MeGpppN) site of a mRNA which is forming a RNA-DNA hybrid, and separating RNA-DNA hybrids carrying a DNA corresponding to a full-length mRNA from the RNA-DNA hybrids formed above by using a function of the tag molecule. The present method is a method for preparing full-length cDNA libraries utilizing a method for labeling the 5' Cap site more efficiently than protein enzyme reactions, which is avoidable a decrease of a full-length cDNA synthesis efficiency caused by cleavage of mRNA, and can synthesize a full-length cDNA more efficiently.
Owner:RIKEN
Substrate activation kit and method for detecting DNA and the like using the same
InactiveUS7078172B1Accurate detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh densityFluorescence
It is intended to provide a method whereby DNA can be conveniently and rigidly immobilized on a substrate at such a high density as achieved by the conventional methods and a method of accurately detecting DNA. A substrate activation kit comprising a phosphate buffer (pH6), a solution A (an aqueous solution) of N-hydroxysuccinimide and a solution B (a dioxide solution) of 1-[3-(dimethylamino) propyl]3-ethylcarbodiimide; and a method of detecting DNA characterized by comprising spotting DNA on a substrate having been activated by using the above activation kit and then hybridizing the spotted DNA with fluorescence labeled DNA.
Owner:TOYO KOHAN CO LTD
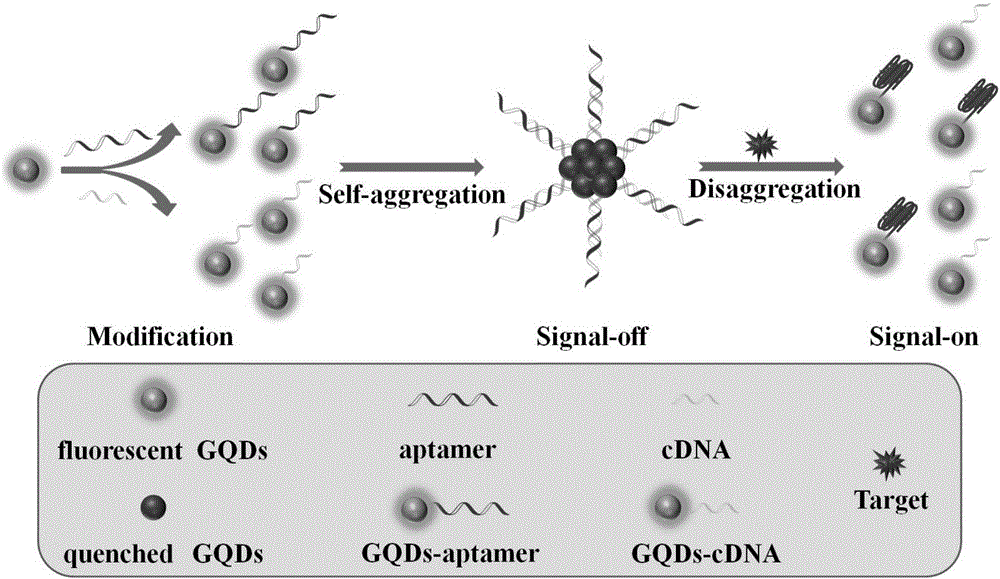
Fluorescent sensor for detecting mycotoxins and application method thereof
A fluorescent sensor for detecting mycotoxins and an application method thereof belong to the field of analytical chemistry. The surfaces of two groups of graphene quantum dots are modified respectively with aptamer DNA corresponding to mycotoxins or probe DNA complementary to the aptamer DNA, the graphene quantum dots are aggregated by DNA hybridization, exciton energy is transferred, and graphene quantum dot fluorescent signals are cancelled at last; mycotoxins are added then and engage in specific binding with the aptamer DNA, structural changes occur, the graphene quantum dot aggregation is disassembled and re-dispersed, and the system fluorescent strength is restored. The preparation method of the fluorescent sensor for detecting mycotoxins has a simple and feasible process, and the fluorescent sensor is green, low in cost, high in sensitivity and good in specificity and is successfully applied to standard added recovery of mycotoxins in actual wine samples.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Methods and Compositions for Identifying Sulfur and Iron Modifying Bacteria
ActiveUS20110104684A1Easy to controlSave moneySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification dnaSulfur
The invention relates to methods and compositions for identifying specific bacterial species, which are sulfur and iron oxidizers and / or reducers, from wall board (e.g., dry wall) and / or a patient tissue or body fluid. The method comprises the steps of extracting and recovering DNA of the bacterial species from the wall board and / or the patient tissue or body fluid, amplifying the DNA, hybridizing a probe to the DNA to specifically identify the bacterial species, and specifically identifying the bacterial species. Kits and nucleic acids for use in the methods are also provided. Methods for eliminating the sulfur and iron oxidizing and / or reducing bacteria from wall board using a zeolite are also provided.
Owner:ADVATECT DIAGNOSTICS LLC
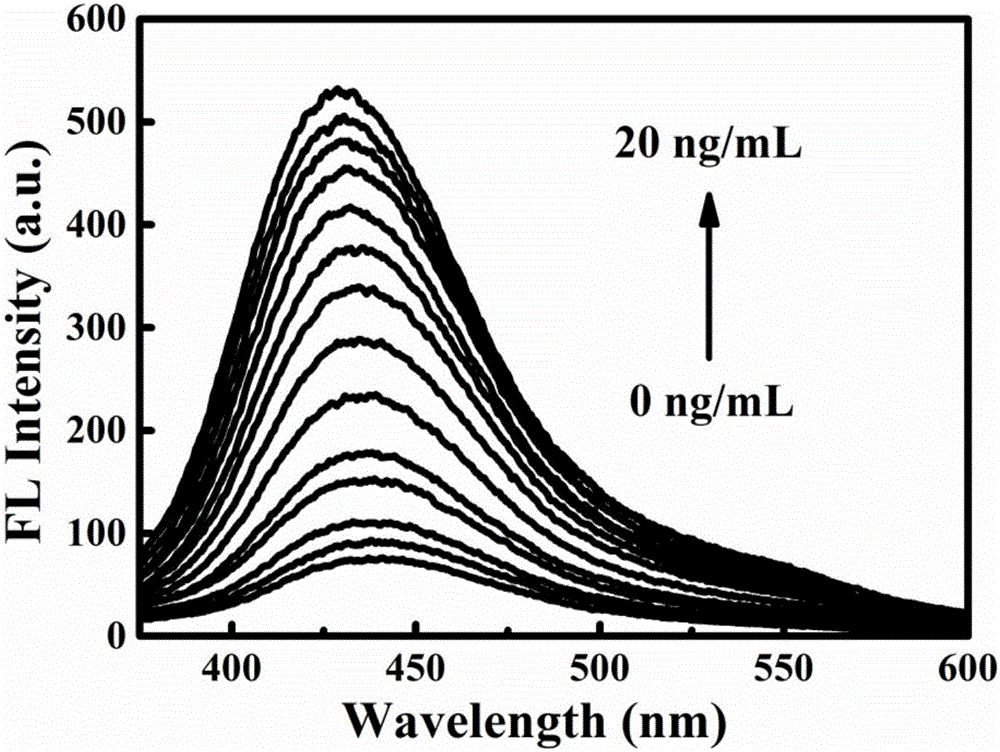
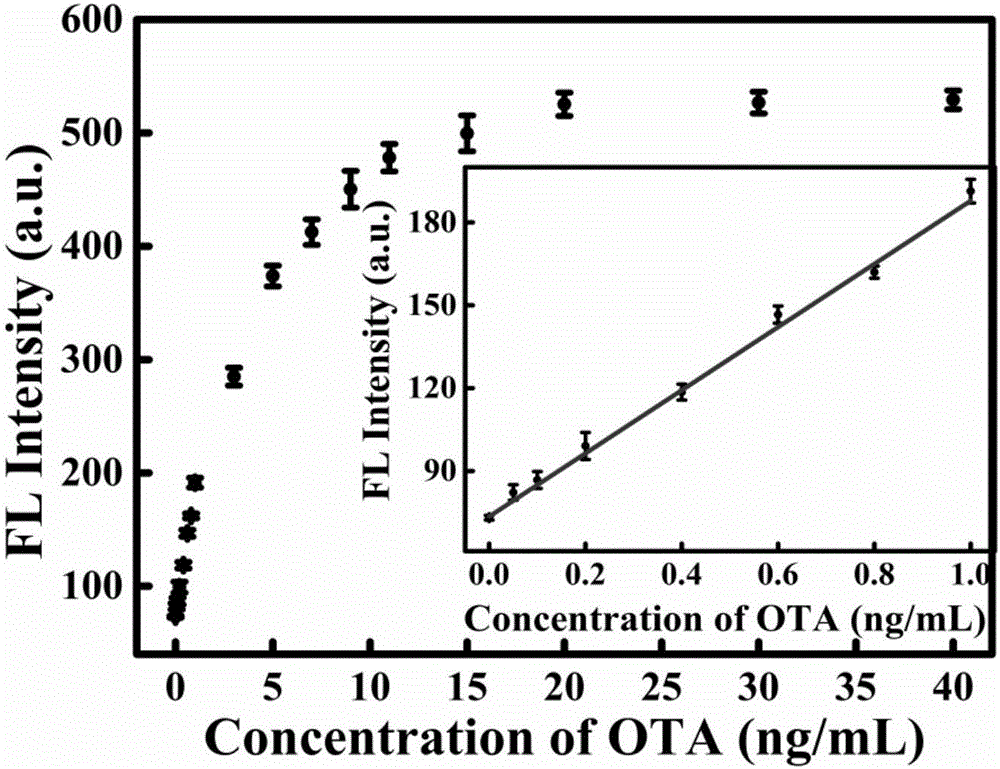
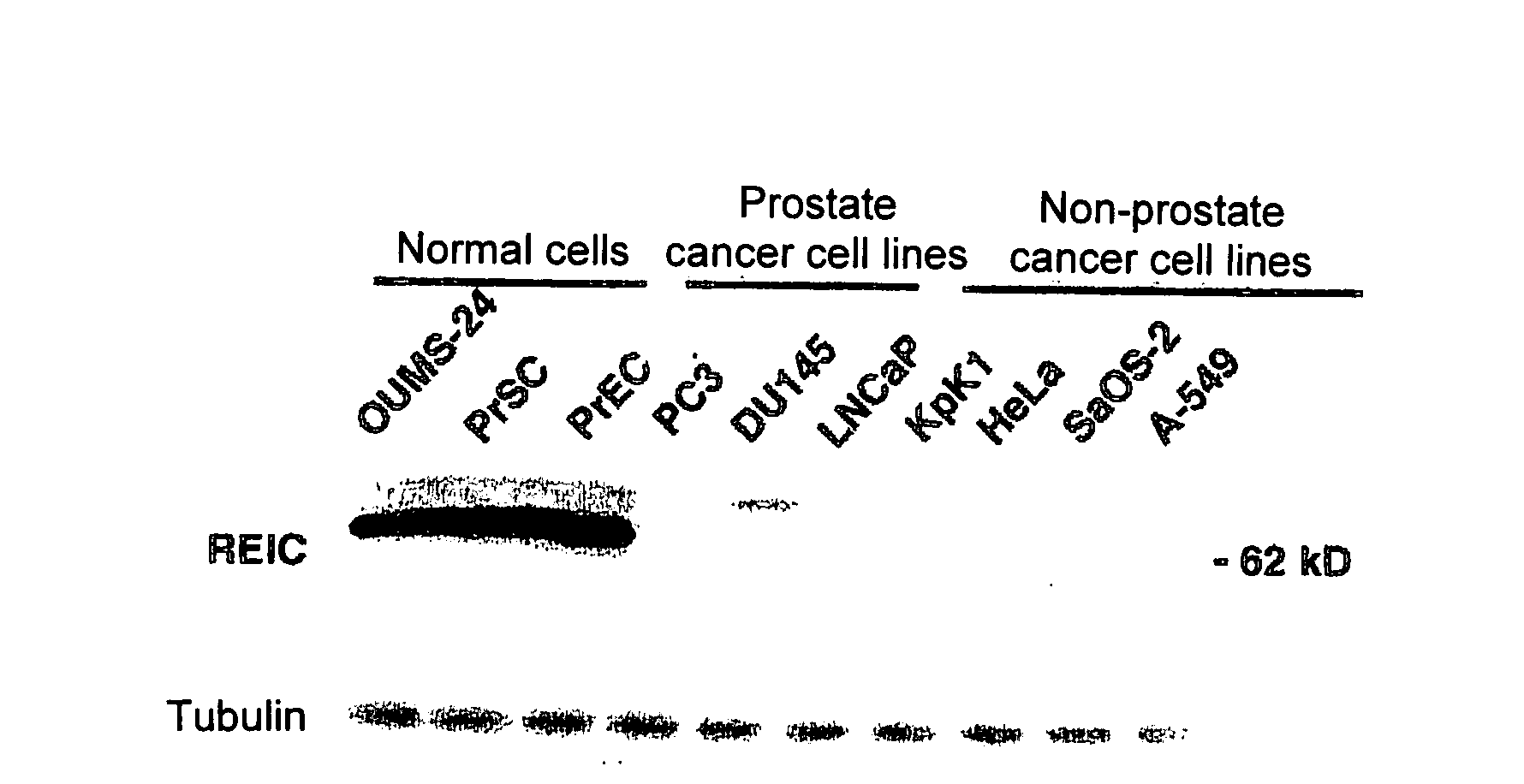
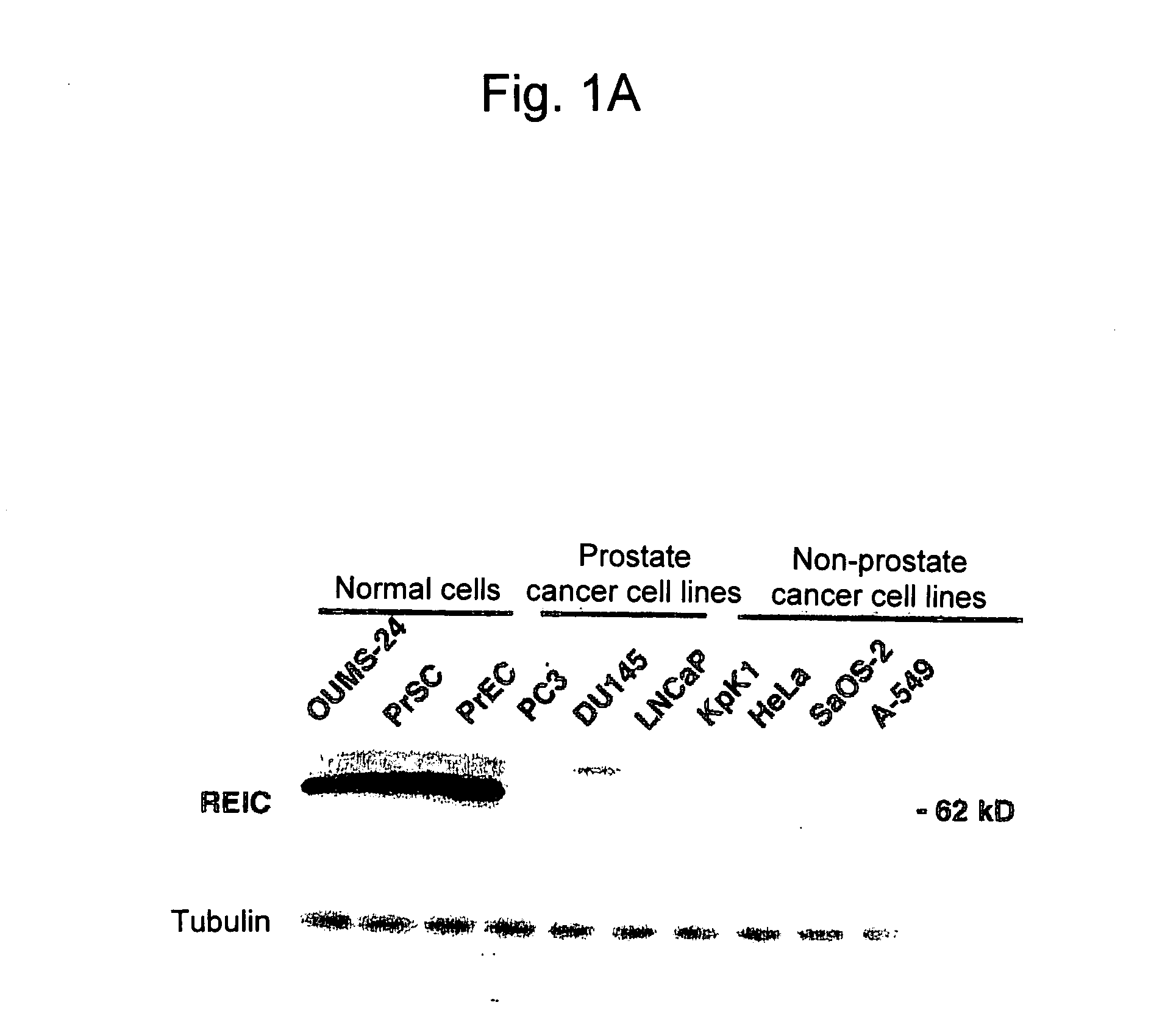
Apoptosis-Inducing Agent for Prostate Cancer Cells
InactiveUS20090005538A1Reduced expression levelInhibit prostate cancerPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesProstate cancer cellLymphatic Spread
According to the present invention, an apoptosis-inducing agent for prostate cancer comprising REIC / Dkk-3 DNA or an REIC / Dkk-3 protein, and a therapeutic agent for prostate cancer and an agent for inhibiting prostate cancer metastasis that comprise such apoptosis-inducing agent are provided.An apoptosis-inducing agent for prostate cancer, comprising, as an active ingredient, an REIC / Dkk-3 protein (a) or (b) or REIC / Dkk-3 DNA (c) or (d):(a) a protein consisting of the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 2;(b) a protein consisting of an amino acid sequence derived from the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 2 by substitution or deletion of 1 or more amino acids;(c) DNA consisting of the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1; or(d) DNA that hybridizes under stringent conditions to DNA consisting of a nucleotide sequence complementary to the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 and encodes a protein having apoptosis activity; anda therapeutic agent for prostate cancer comprising such apoptosis-inducing agent are provided
Owner:KUMON HIROMI +3
Aptamer electrochemical biosensor, as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104391019AEasy to synthesizeReduce energy consumptionMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorDNA hybridisation
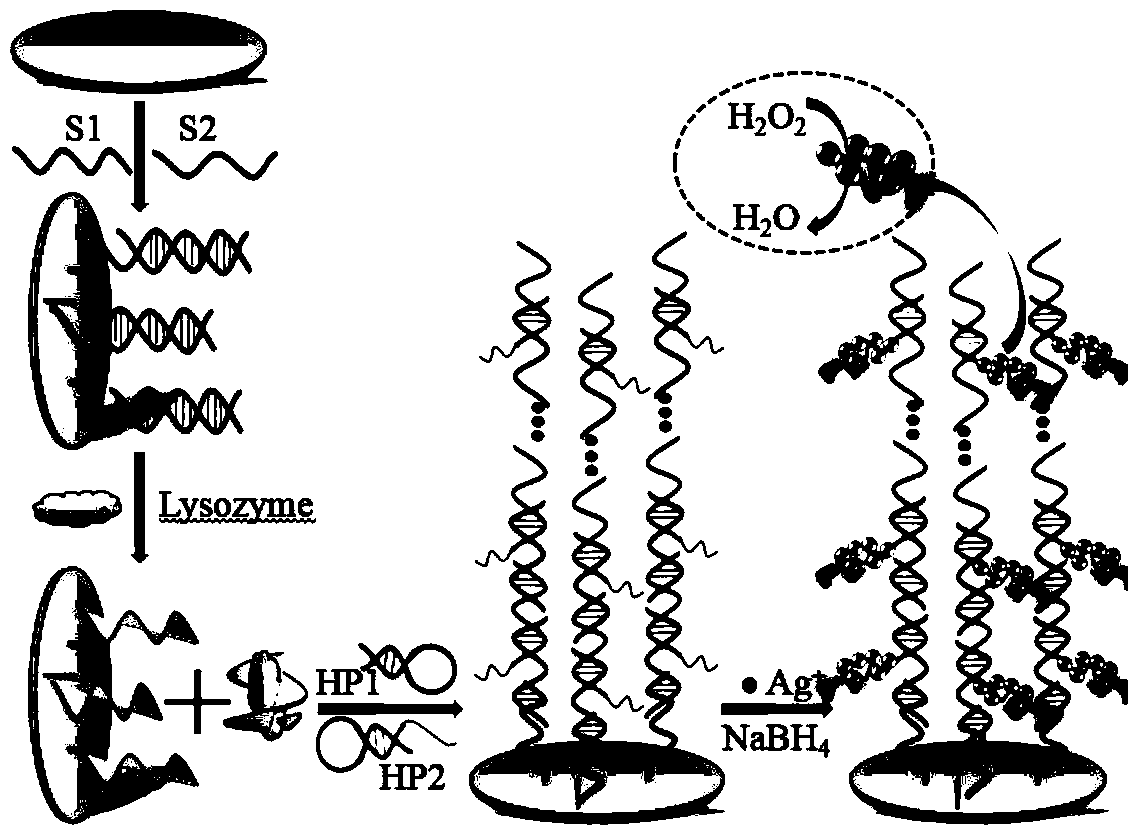
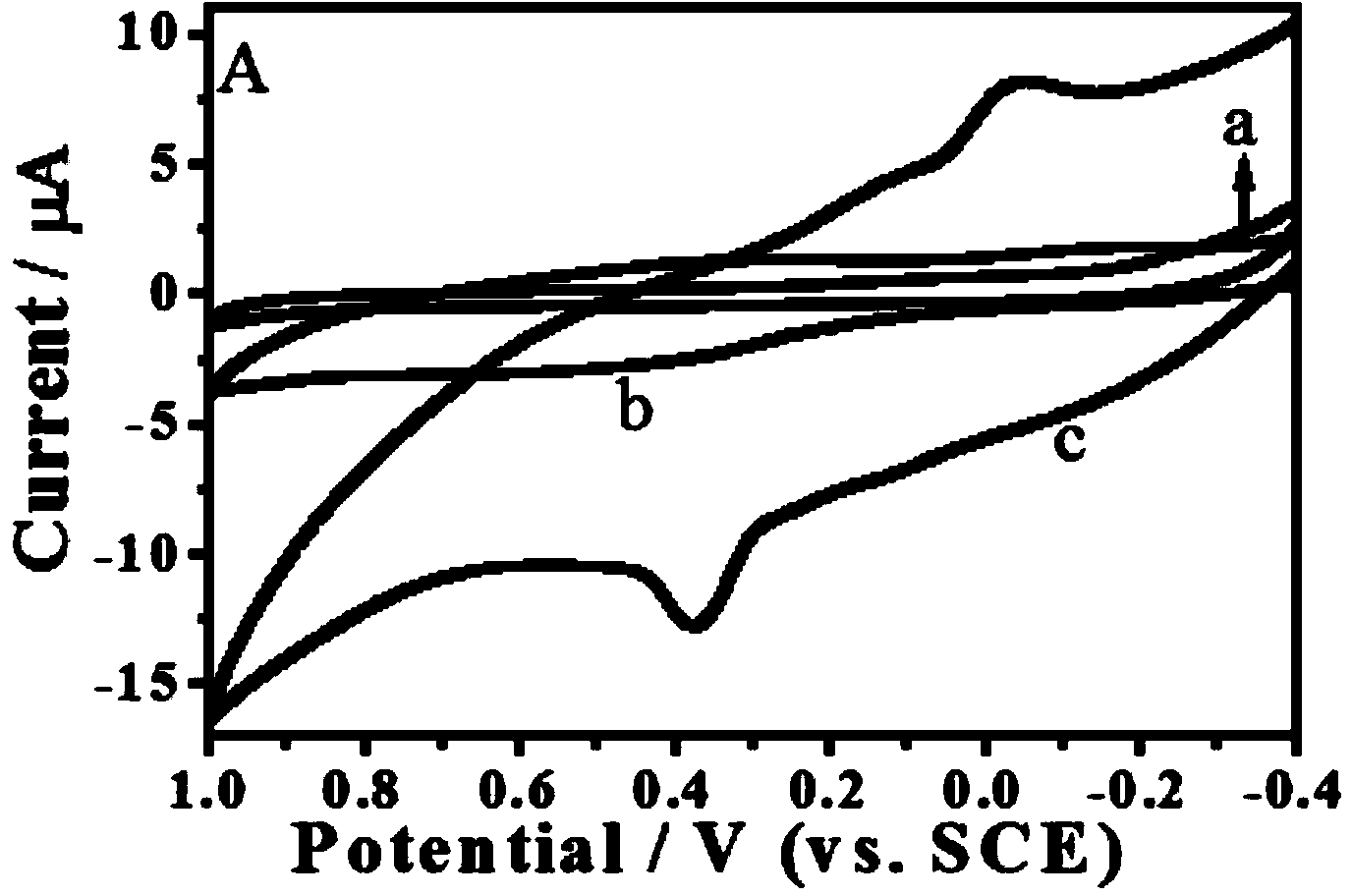
The invention relates to an aptamer electrochemical biosensor, as well as a preparation method and application therof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) respectively dissolving DNA sequences into a PBS buffer solution; (2) firstly polishing and washing a gold electrode; (3) dispensing the buffer solution containing a probe S1 and a probe S2 onto the gold electrode for culturing; (4) dispensing the PBS buffer solution onto an S2-S1 / GE electrode for culturing; (5) placing S2-S2 / GE into the PBS buffer solution to be cultured; washing the electrode to obtain a Aptasensor; (6) culturing the acquired Aptasensor in the buffer solution, and thus obtaining a decorative electrode HP2-HP1-Aptasensor of a super-sandwiched structure by virtue of DNA hybrid chain reaction; and (7) culturing the HP2-HP1-Aptasensor in the buffer solution to obtain a silver nano-cluster decorated electrode AgNCs / HP2-HP1-Aptasensor. According to the preparation method of the biosensor, the used nano material is simple to synthesize, the energy consumption is low, the cost is low, the biological compatibility is good, the mimic enzyme catalytic activity of the nano material is studied and used as an electrochemical detection signal; moreover, a signal detected by the prepared biosensor is amplified by utilizing the DNA hybrid chain reaction.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
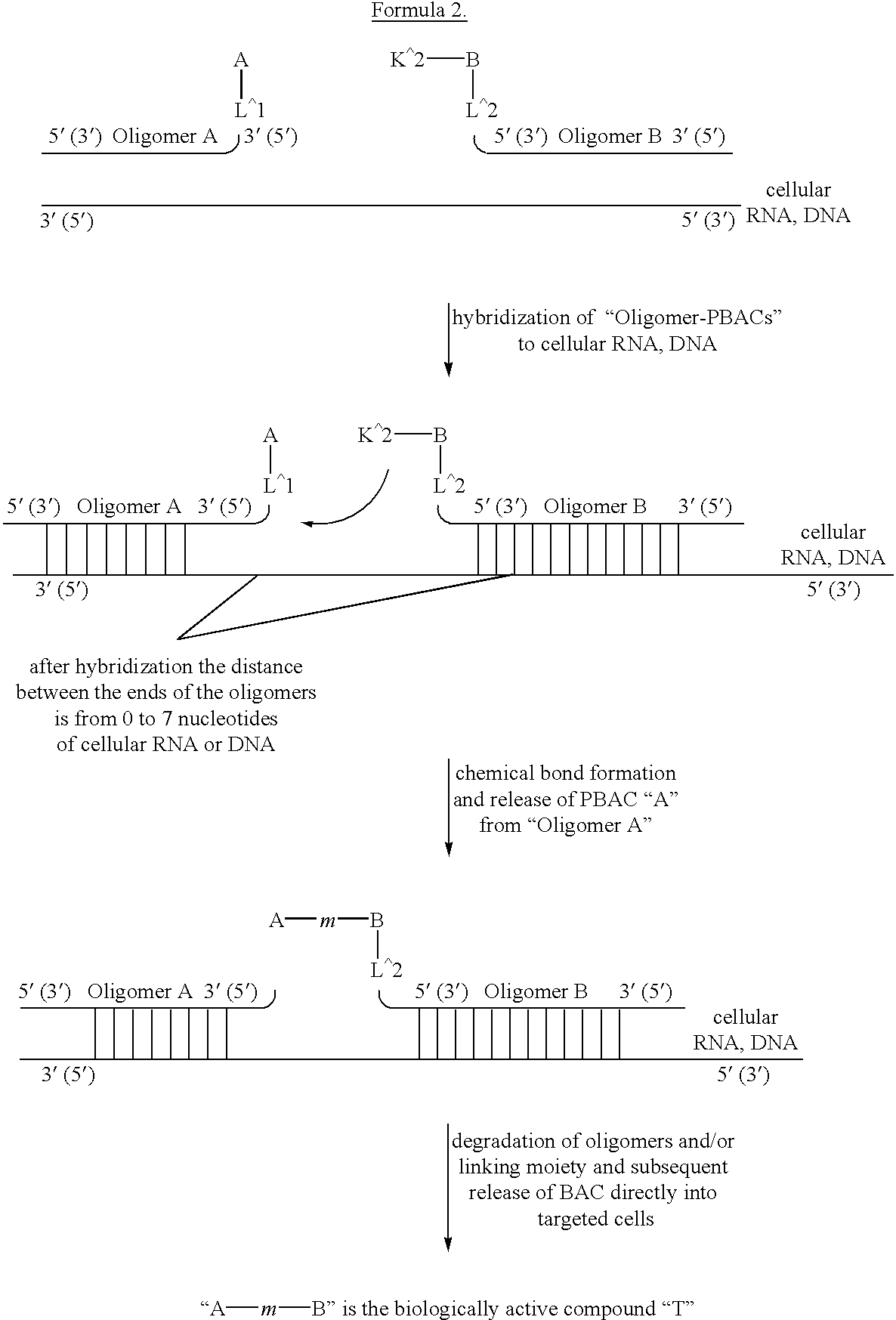
Synthesis of biologically active compounds in cells
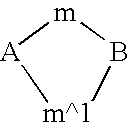
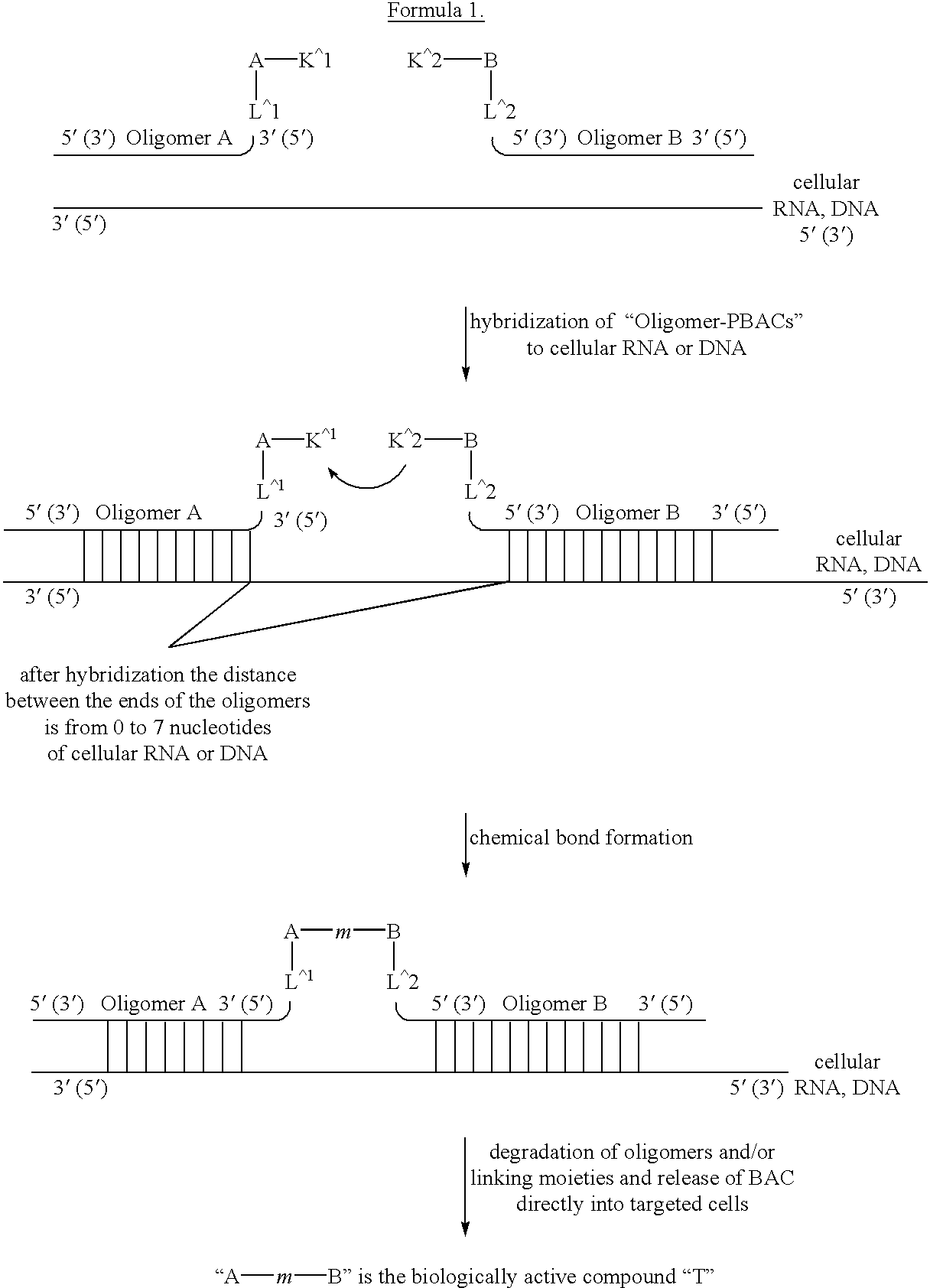
This invention relates to a new method of synthesis of biologically active substances of determined structure directly in the cells of living organisms containing specific RNA or DNA molecules of determined sequence. The method is based on the hybridization of two or more oligomers bound with biologically inactive precursors of biologically active substances to specific RNA or DNA in vivo in the cells of living organisms. After hybridization of the oligomers to RNA or DNA the biologically inactive precursors bound to the 5' and / or 3' ends of the oligomers can interact with each other to make biologically active form of the substances. This changing of properties is due to chemical reactions which bind the biologically inactive precursors through a chemical bond into a biologically active form of the whole compound.
Owner:SERGEEV PAVEL
Method for catalyzing and enhancing chemical luminescence by nano particles
InactiveCN101148584AEasy to prepareHigh luminous intensityLuminescent compositionsLuminous intensityAlloy
The present invention belongs to the field of nanometer technology, and is especially method of catalyzing and enhancing the luminous intensity of chemical light-emitting material with nanometer particle. Catalyst of nanometer noble metal particle and oxidant H2O2 are adopted in enhancing the luminous intensity of chemical light-emitting material. The nanometer noble metal particle may be nanometer particle of Au, Ag, Pt, Cu or their mixture or their core-shell structure with core of nanometer oxidant or polymer particle and shell of nanometer noble metal particle. The chemical light-emitting material with greatly enhanced luminous intensity may be applied in inorganic analysis, organic analysis, immunological analysis, DNA hybridization analysis and nucleic acid analysis in high detecting sensitivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
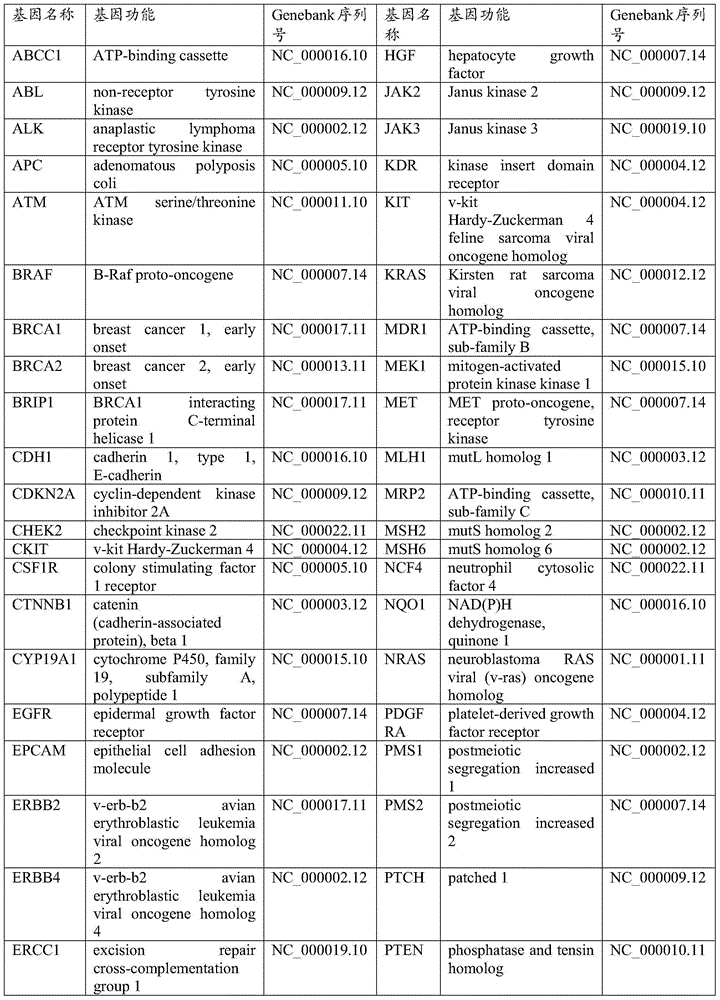
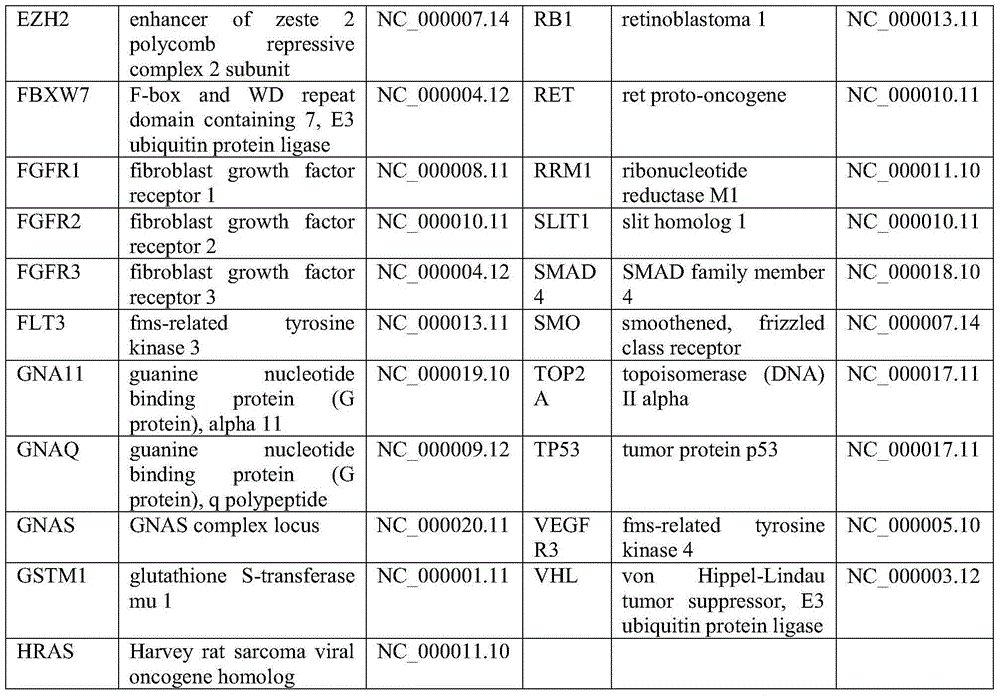
Capture kit and method of target gene
ActiveCN105524981AWide coverageDeep sequencingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyBiotin-streptavidin complex
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and discloses a capture probe of a target gene, a capture kit comprising the capture probe of the target gene, and a method for capturing the target gene. The capture probe of the target gene includes a biotin-labeled 63-probe specific probe set for the target gene, the probe set is hybridized with genome-wide DNA, capturing DNA fragments combined with probes by using magnetic beads coated with streptavidin, and a specific target genome area is enriched before secondary high-throughput sequencing. The capture probe of the target gene has a wide coverage and great sequencing depth, giving a great increase in the study efficiency of the target area in the genome and a significant reduction in the sequencing cost. The target gene capture kit is simple in composition, widely applicable, low in cost and applicable to vast laboratories and scientific and search work.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com