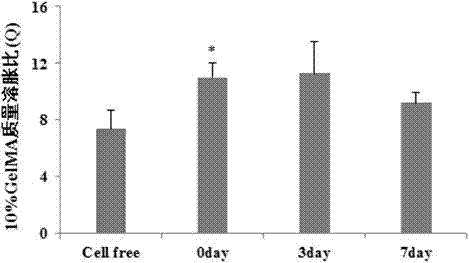
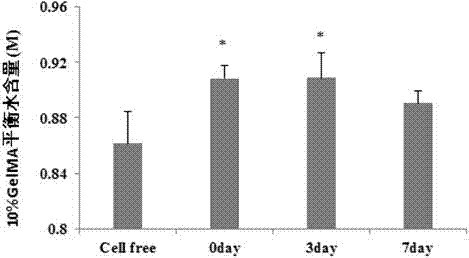
3D hepatoma tissue construction method based on biological 3D printing hydrogel
A 3D printing, liver cancer tissue technology, applied in the fields of biology and tissue engineering, can solve the problems of inability to objectively evaluate indicators, lack of cell morphology and function in 2D culture system, and achieve strong repeatability, easy operation, and promotion of liver cancer tissue. The effect of function formation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The implementation of the present invention will be illustrated by specific specific examples below, and those skilled in the art can easily understand other advantages and effects of the present invention from the contents disclosed in this specification.
[0021] A method for constructing three-dimensional liver cancer tissue based on biological 3D printing hydrogel, comprising the following steps:
[0022] (1) Synthesize the GelMA scaffold material, and detect the acylation rate and photopolymerization time, then configure the photoinitiator and save it for later use. The photoinitiator is prepared with PBS to obtain the photoinitiator I2959, and save it for later use. Dissolve the GelMA scaffold material in a water bath until The final concentration was 10%.
[0023] (2) After uniformly mixing and dissolving GelMA and photoinitiator, the GelMA solution was obtained, and the human liver cancer cell HepG2 and GelMA solutions were mixed, and the cell concentration was ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com