Patents
Literature
99results about How to "Minimal level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
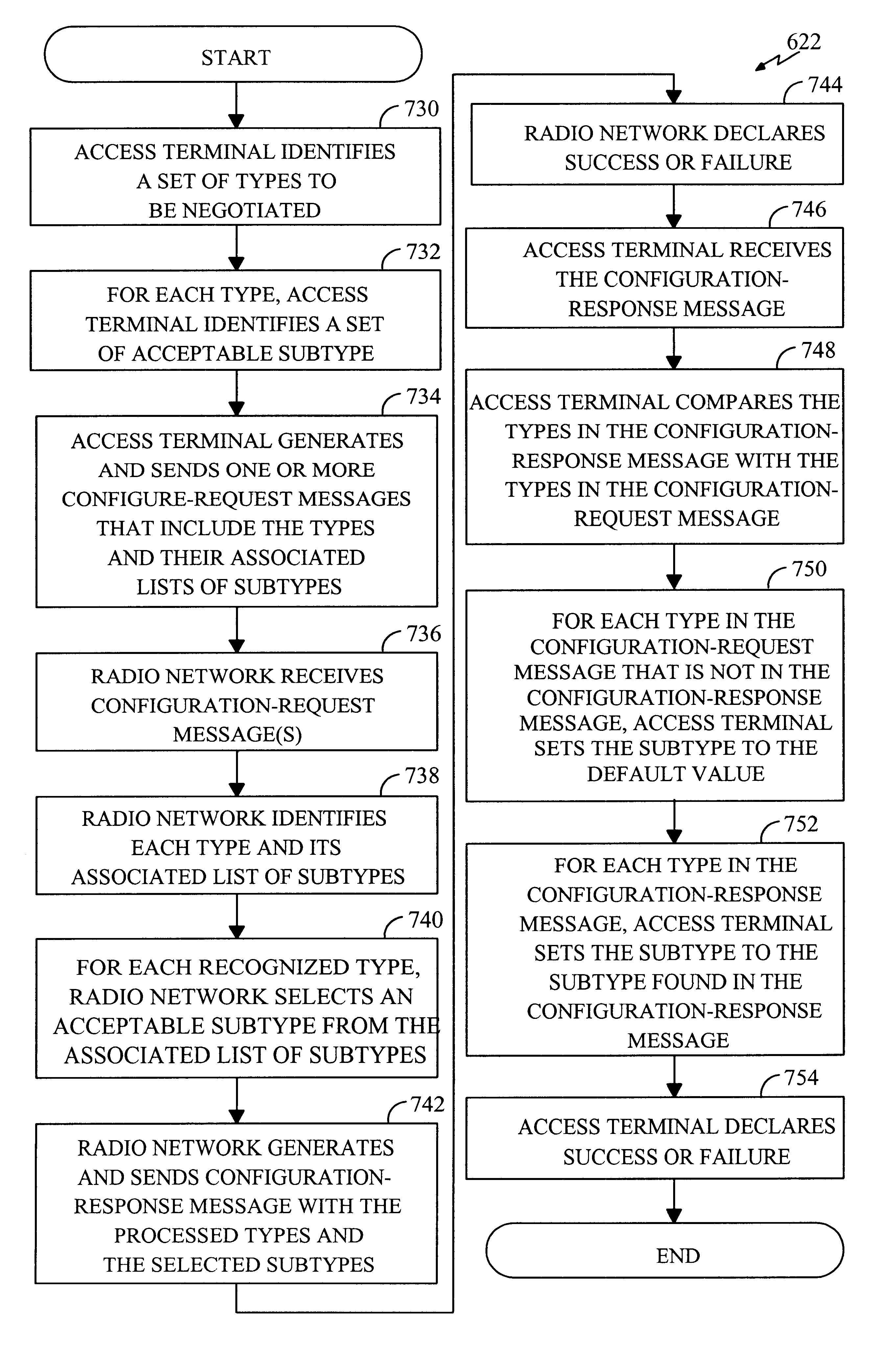
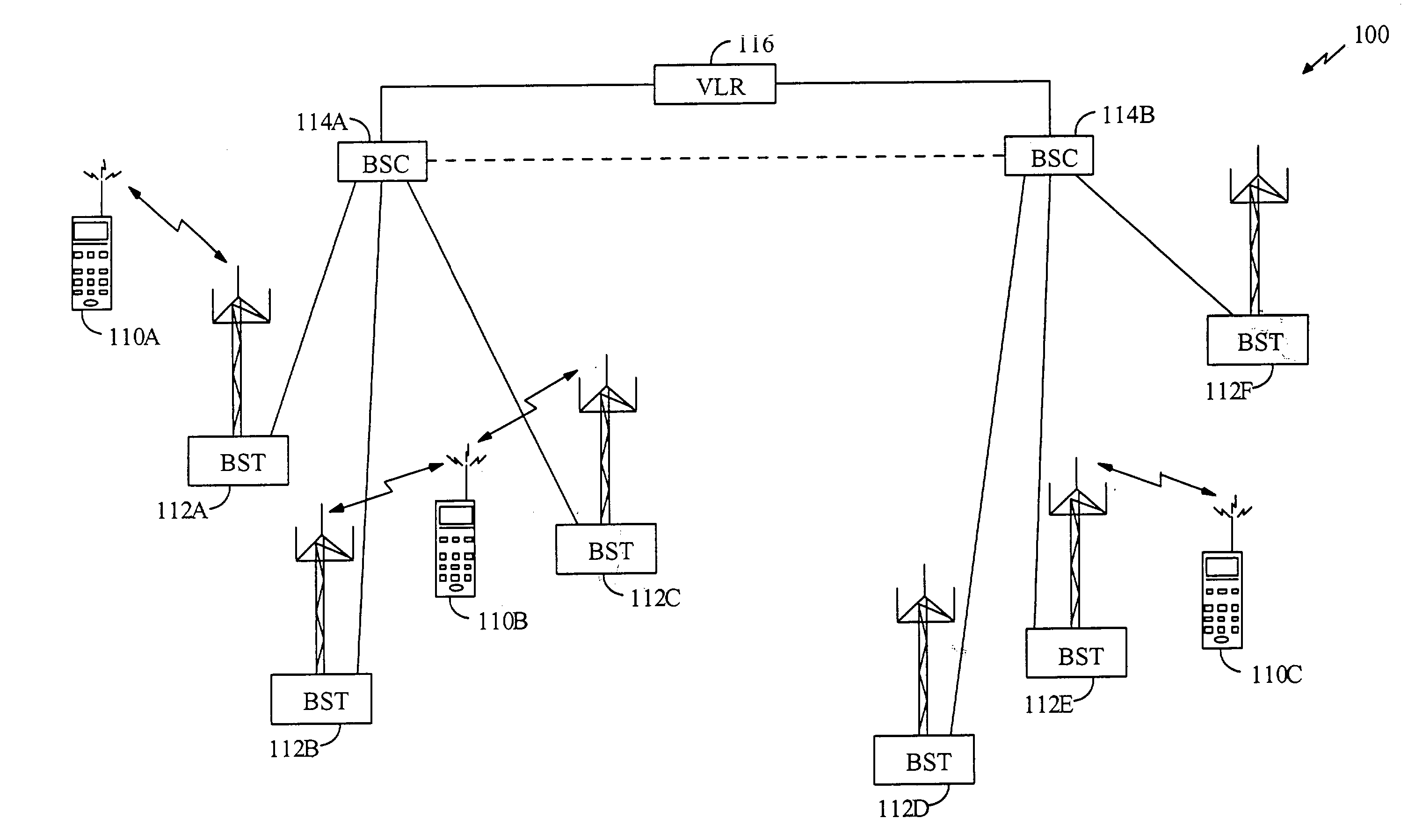
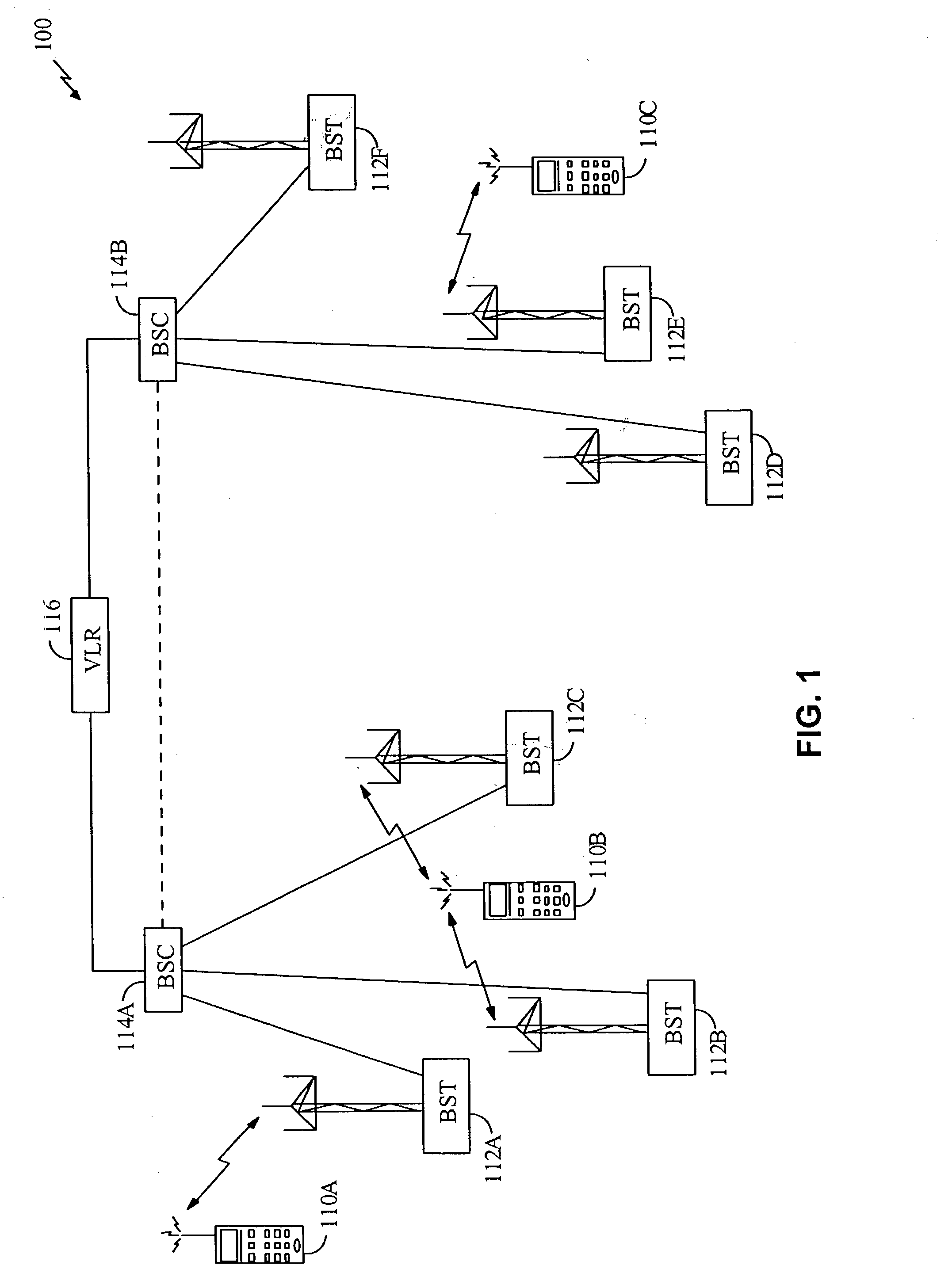
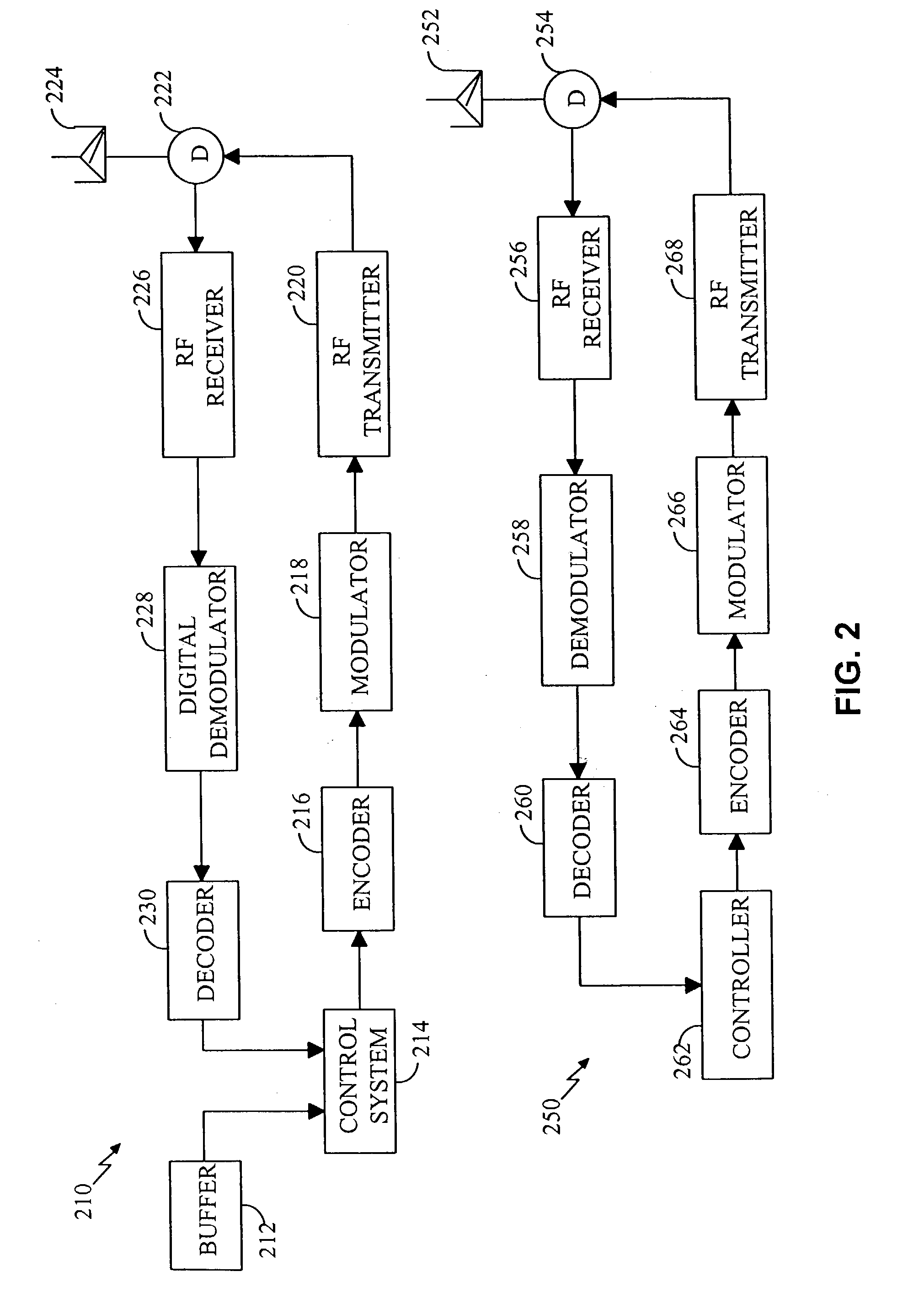
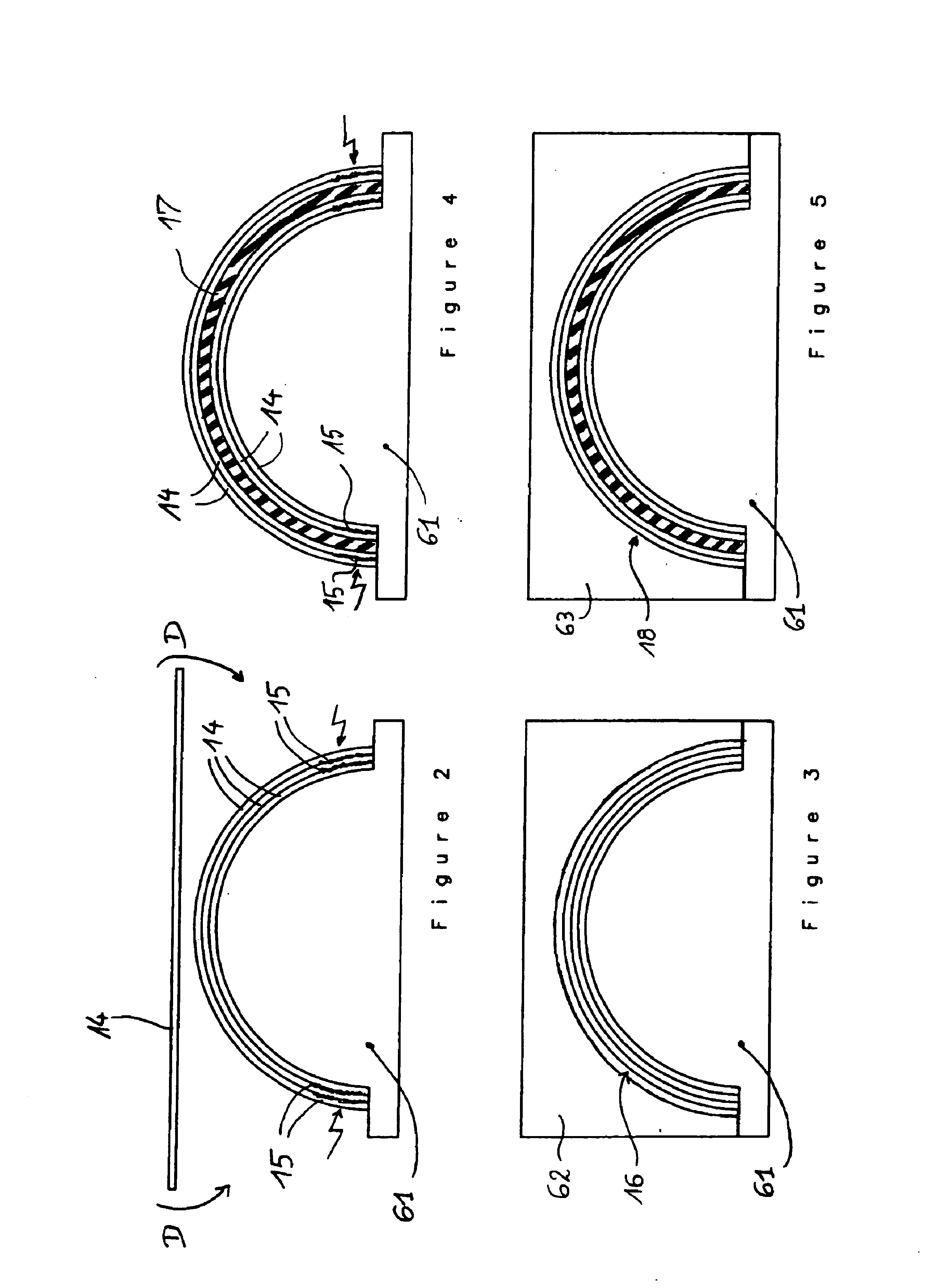
Method and apparatus for providing configurable layers and protocols in a communications system
InactiveUS6539030B1Easy to implementMinimal levelNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexModularityRadio networks
The layers and protocols of an air interface layering architecture are designed to be modular and can be modified and upgraded to support new features, perform complex tasks, and implement additional functionality. Prior to commencement of data communication between a first entity (e.g., an access terminal) and a second entity (e.g., a radio network), a set of layers and / or protocols is selected for negotiation. For each selected layer and protocol (i.e., each attribute), a list of attribute values considered acceptable to the first entity is determined. The selected attributes and their associated attribute values are sent from the first entity and, in response, a list of processed attributes and their associated lists of processed attribute values are received. Each list of processed attribute values includes attribute values considered acceptable to the second entity. The layers and protocols in the first entity are then configured in accordance with the received list of processed attributes and their associated processed attribute values. Other features related to configurable layers and protocols are also provided.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
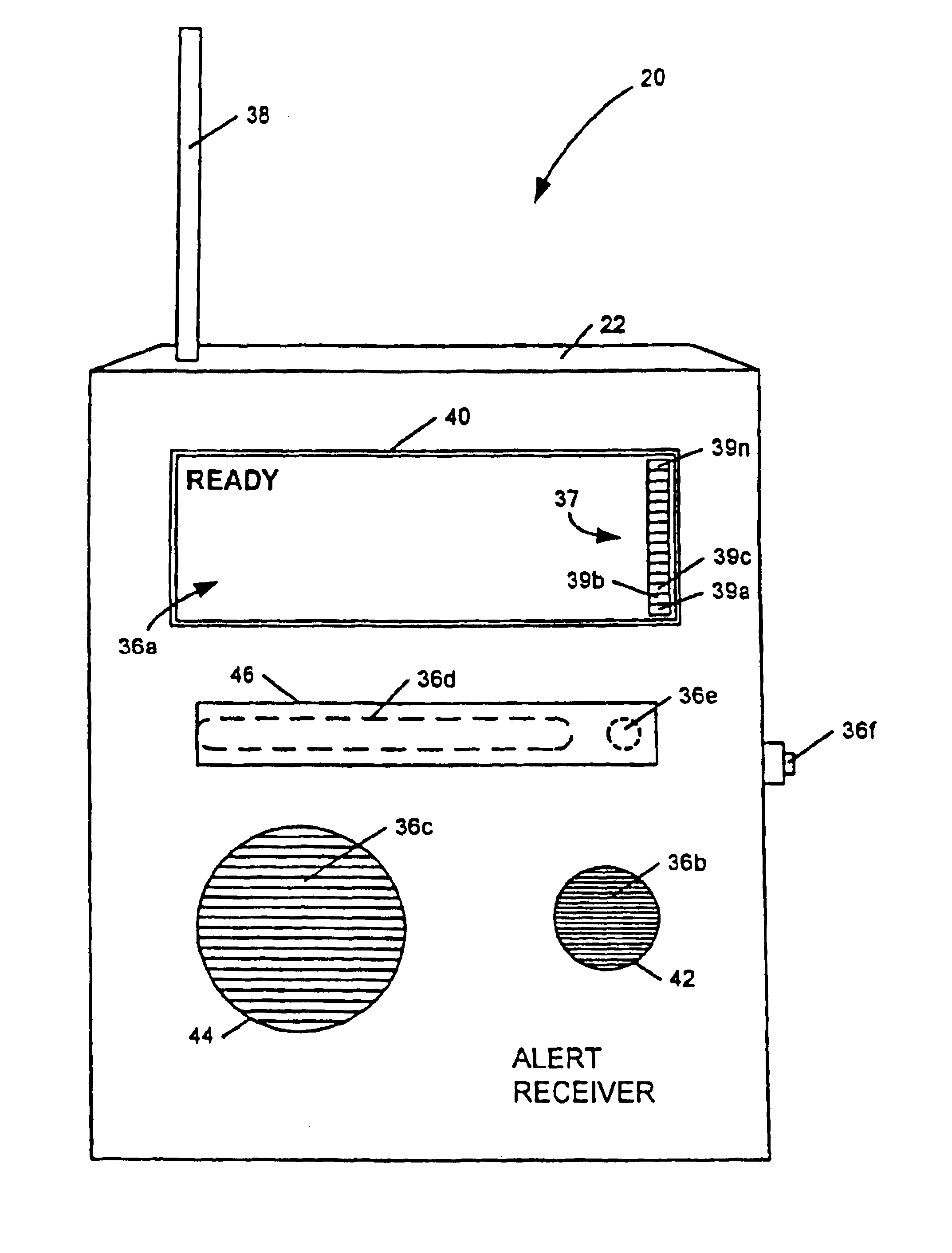
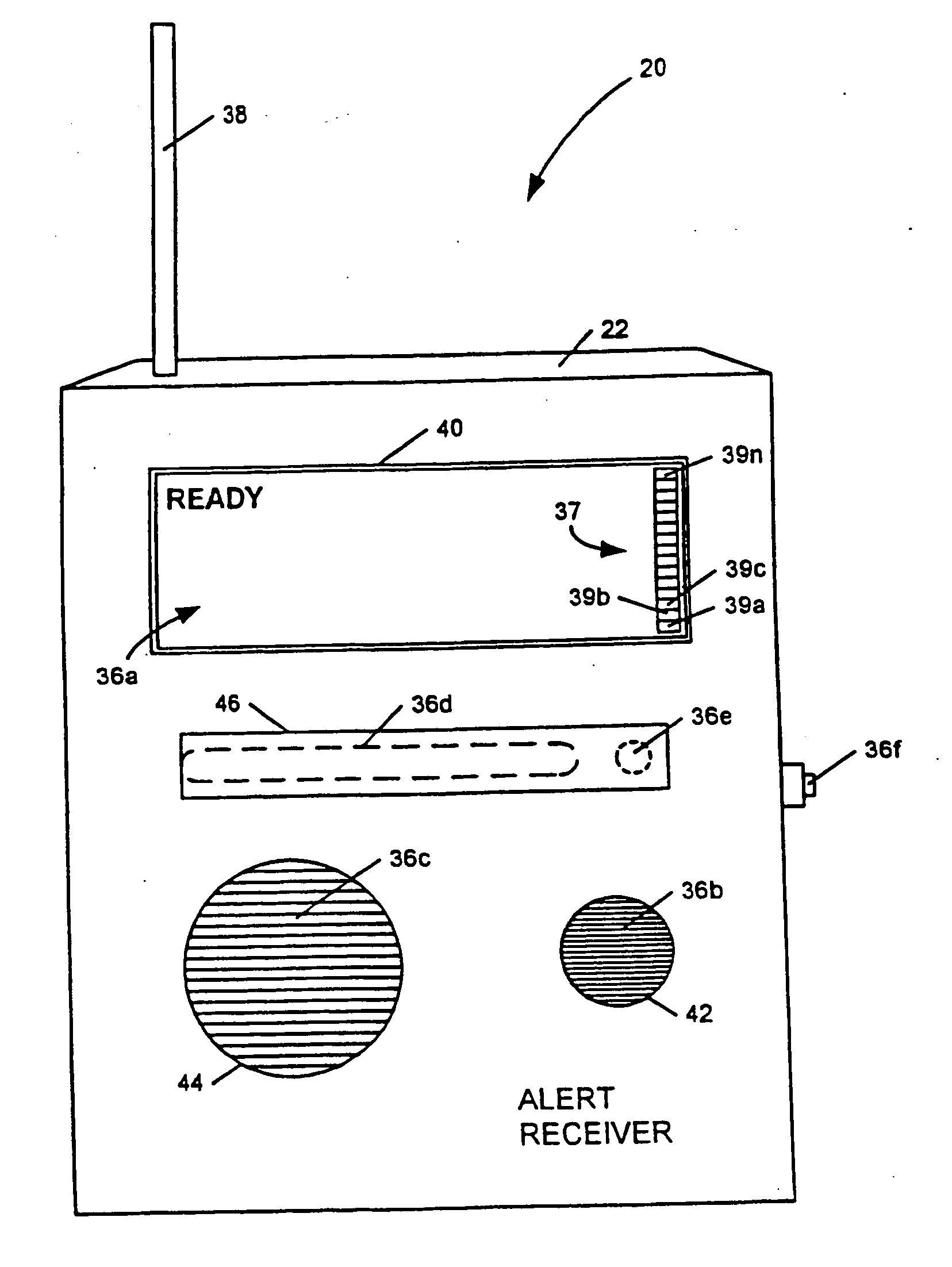
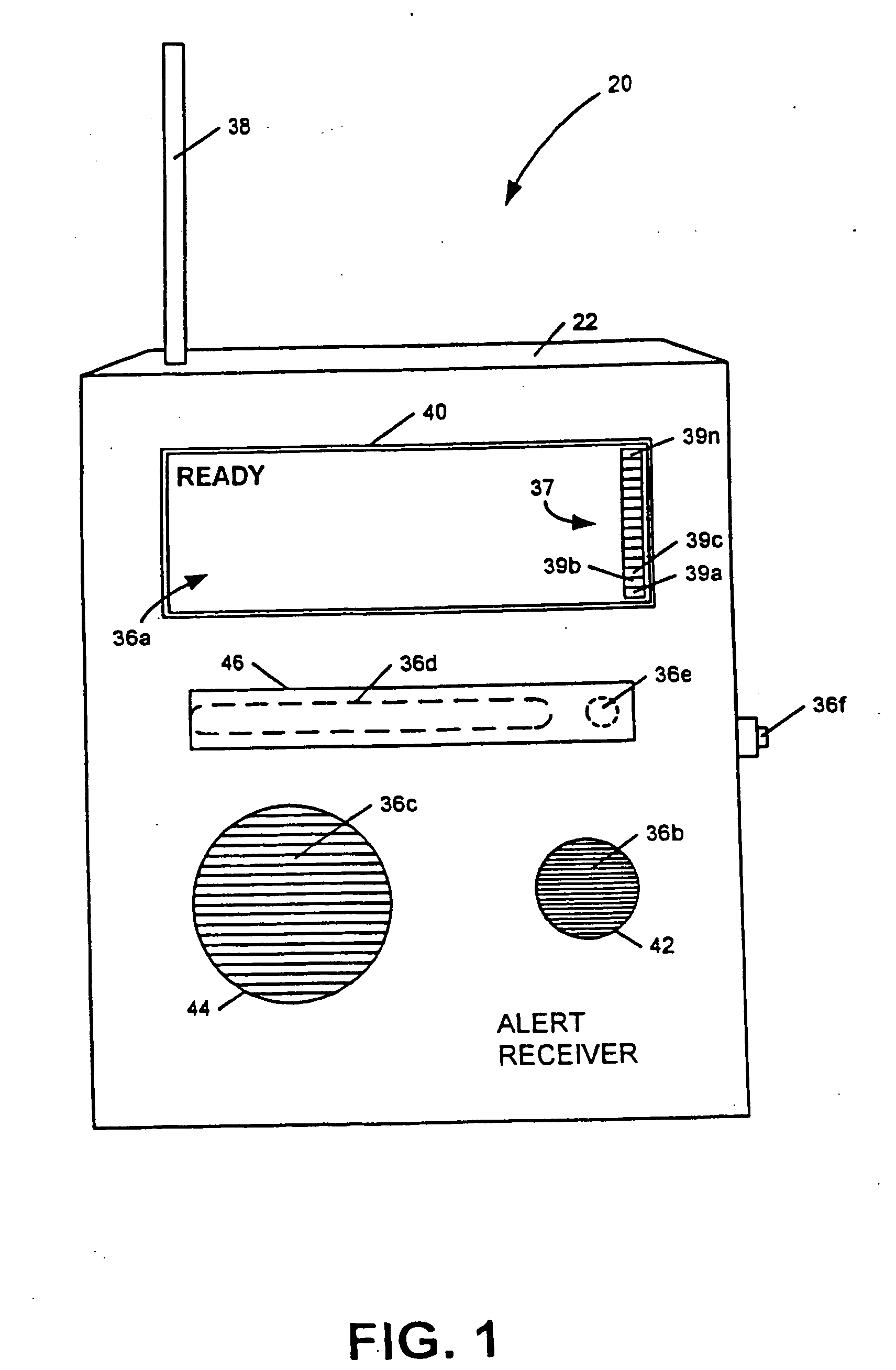
Apparatus and method for providing weather and other alerts
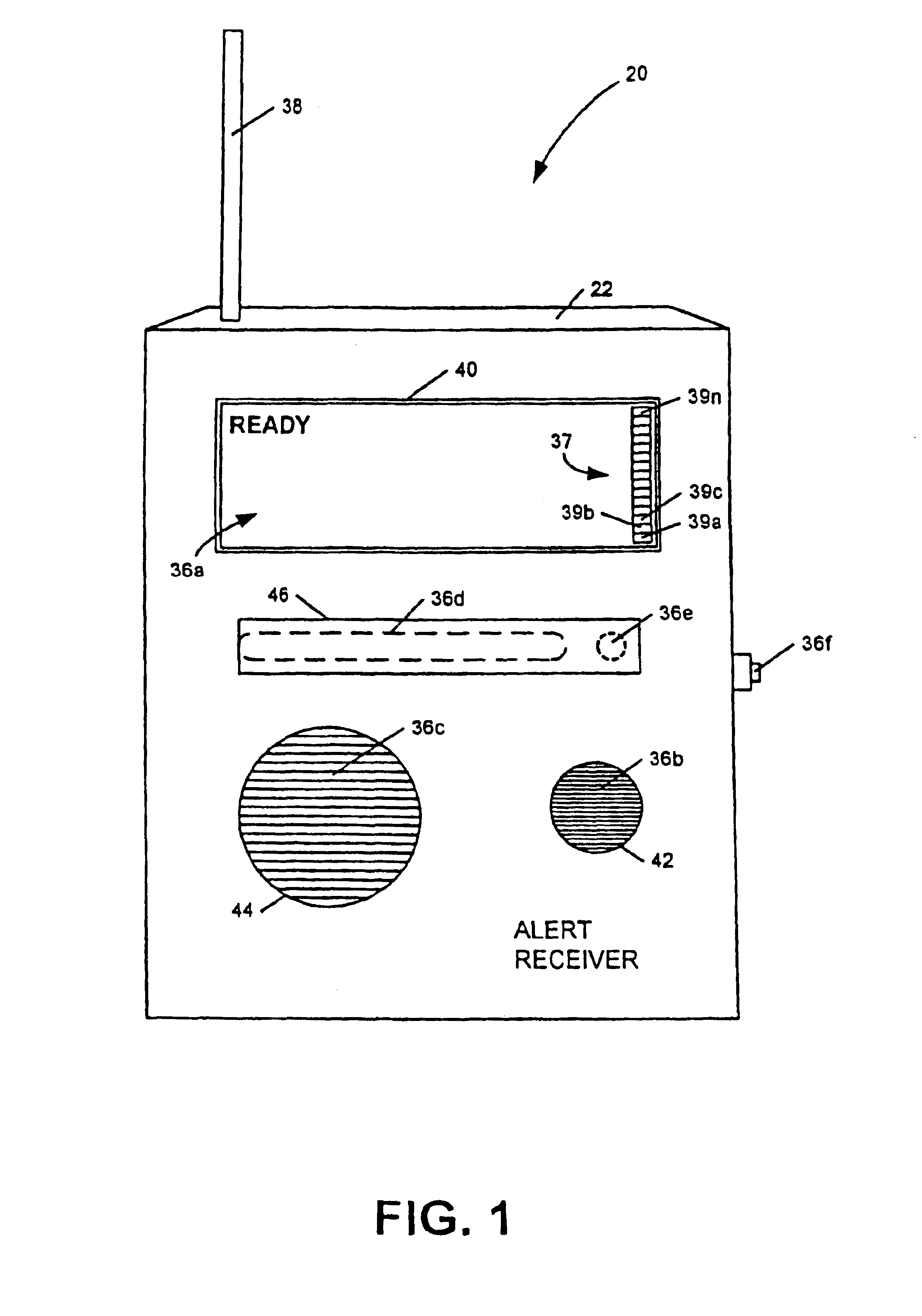
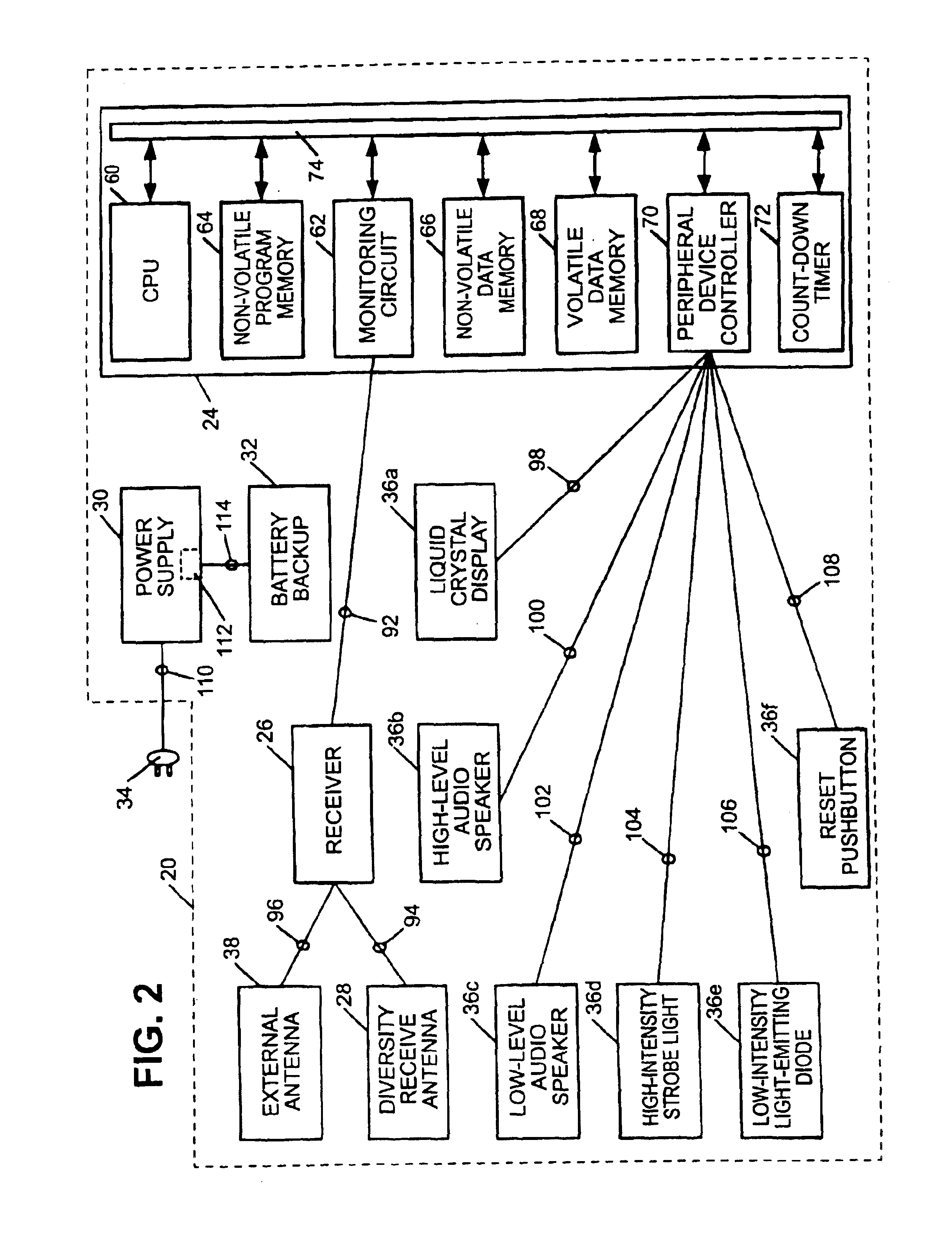
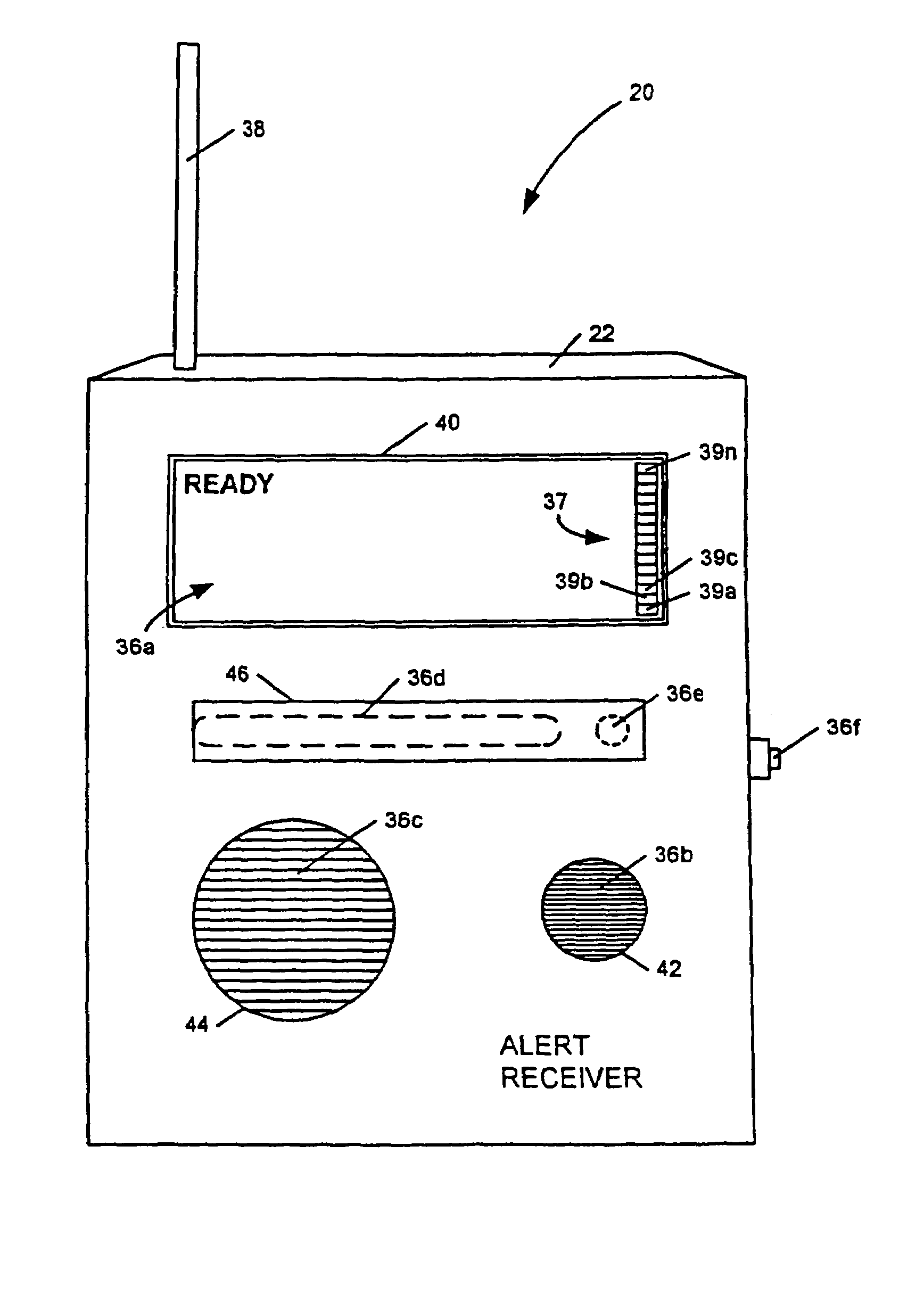
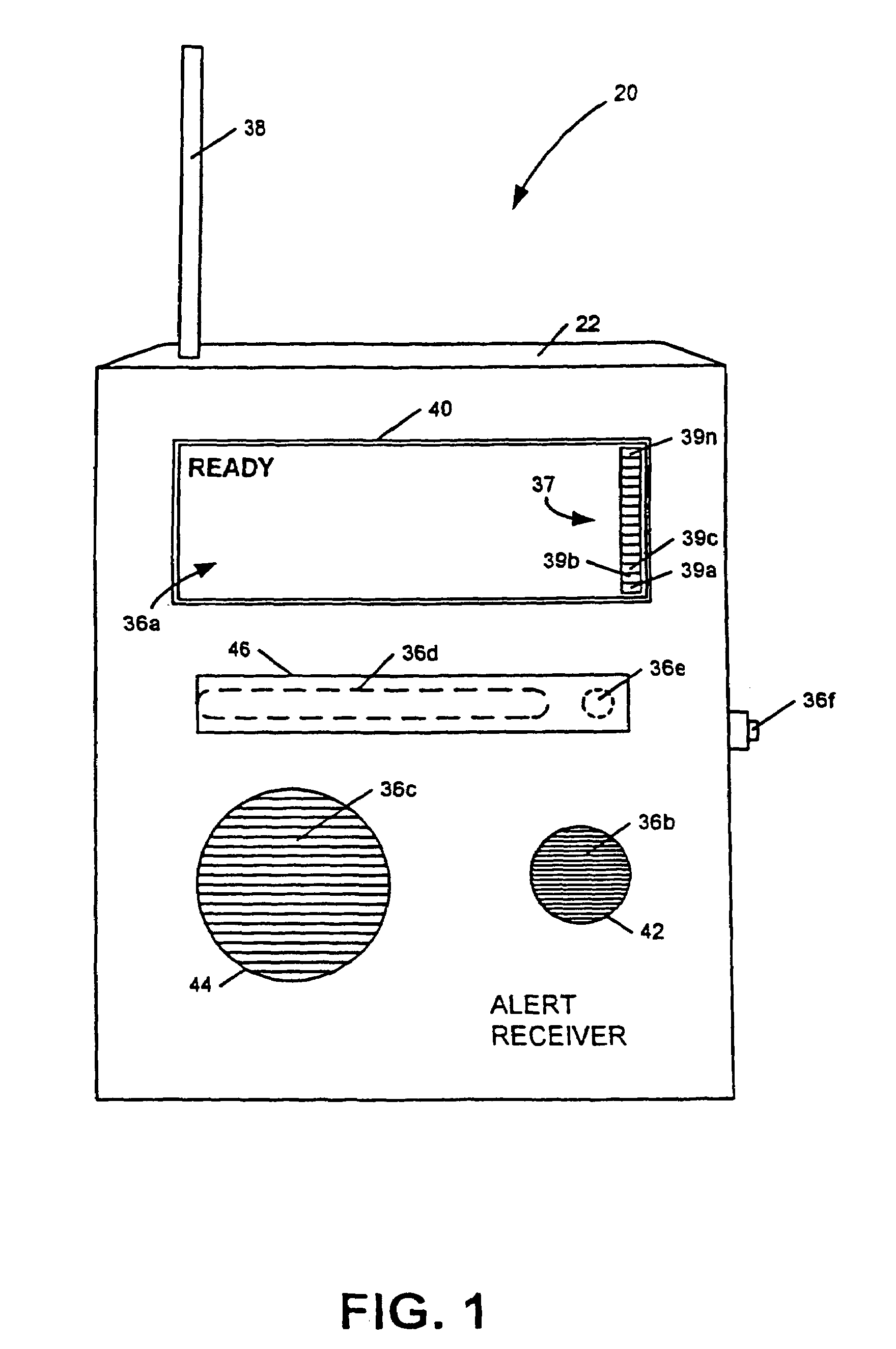
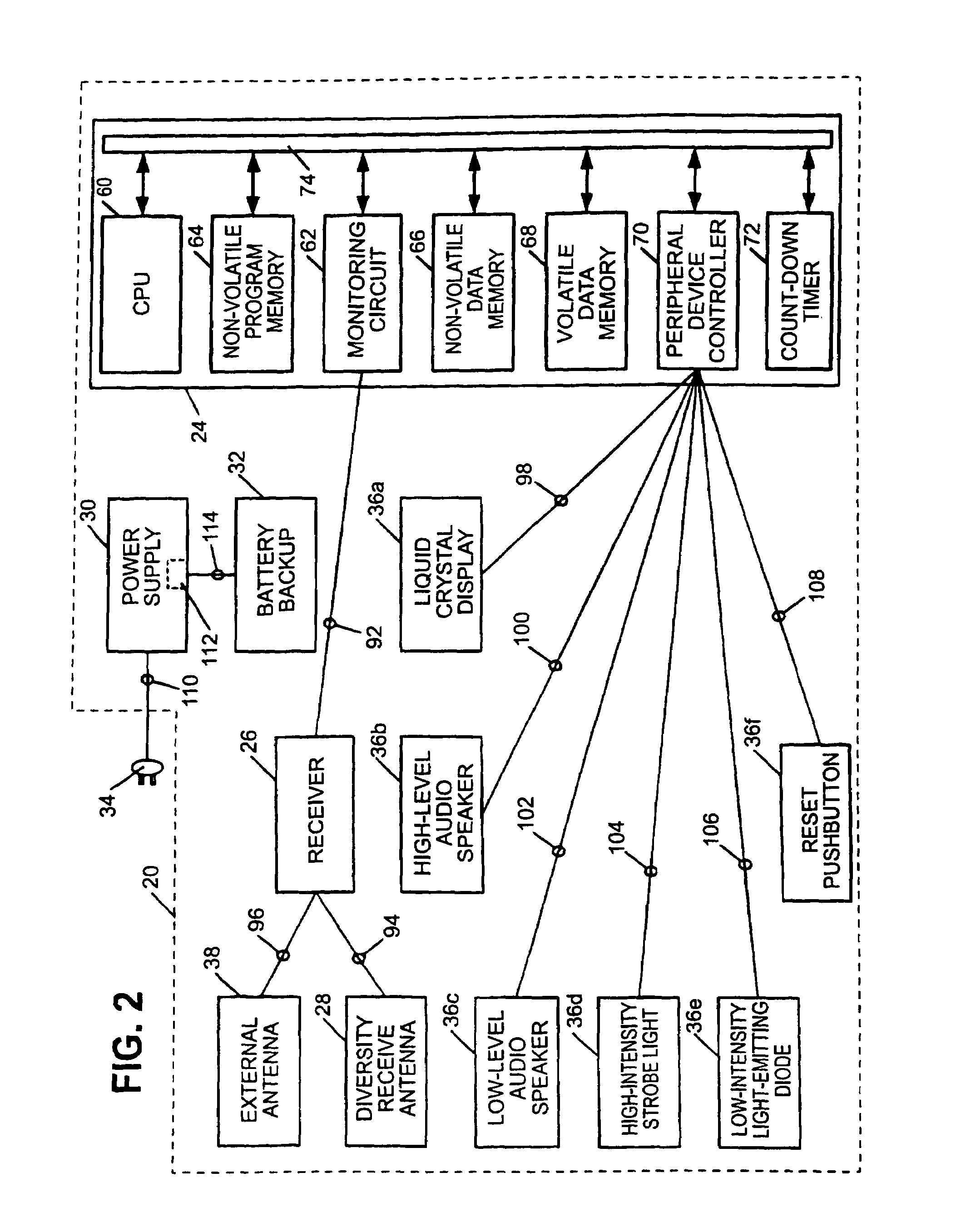
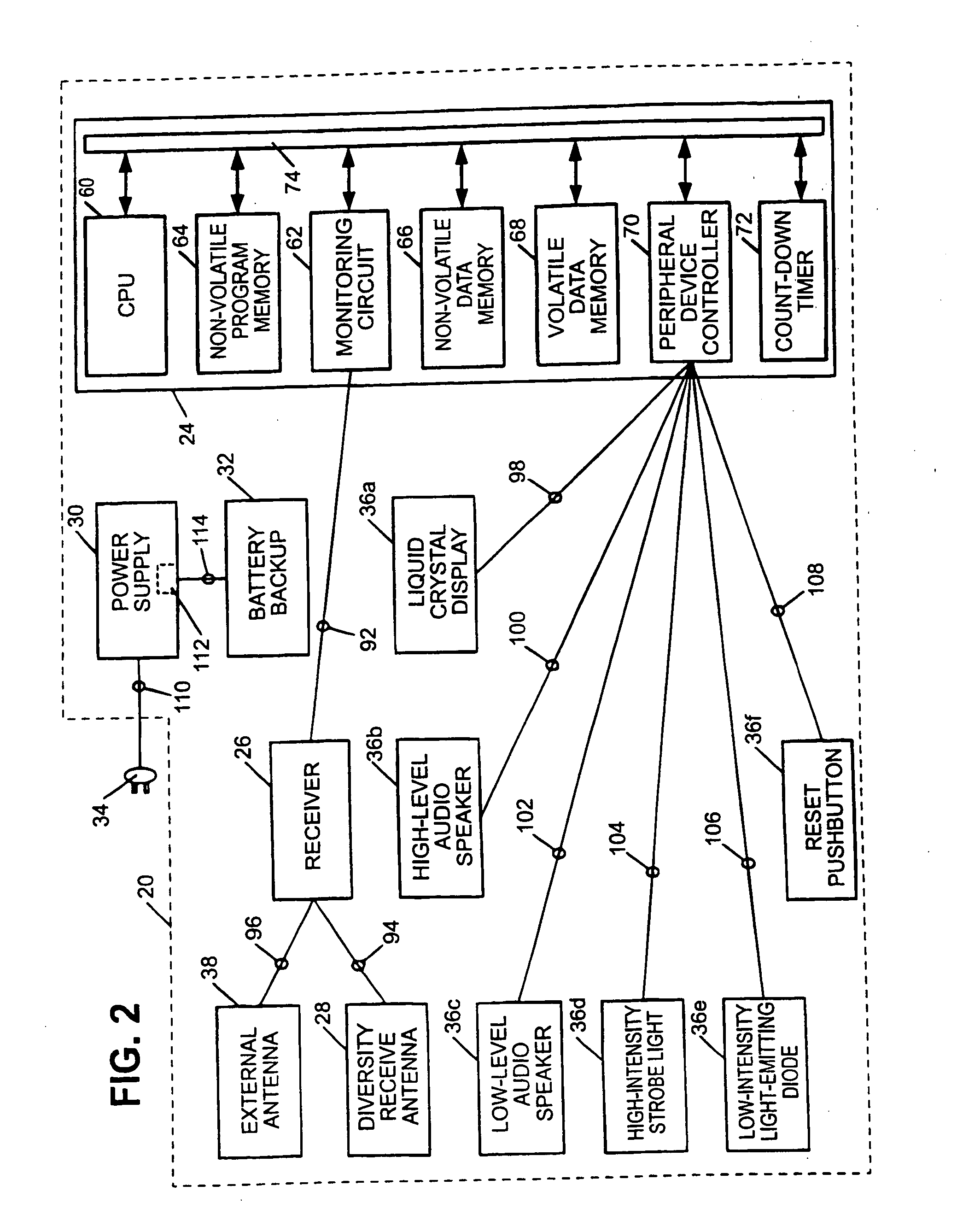
InactiveUS6867688B2Increase signal strengthPrecise functionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexMicrocomputerTelecommunications network
An apparatus, including an alert device having a receiver, and method are provided for receiving alert information broadcast via particular telecommunication transmitters operating within a cellular, PCS, or other wireless telecommunications network, thereby allowing delivery of a message. The alert device includes a receiver for receiving digital messages in the form of broadcast messages on a digital control channel, a microcomputer having a monitoring circuit that monitors received digital messages for the presence of an alert code associated with alert messages regarding an alert condition, and a plurality of peripheral devices which produce various tones and flashing lights in response to the alert device's reception of an appropriate alert message. The alert device can be provisioned over the air to respond to particular preferred system providers and controlled user groups. The alert device can also control and external device to provide a warning to the user.
Owner:SAFETY THROUGH CELLULAR +1
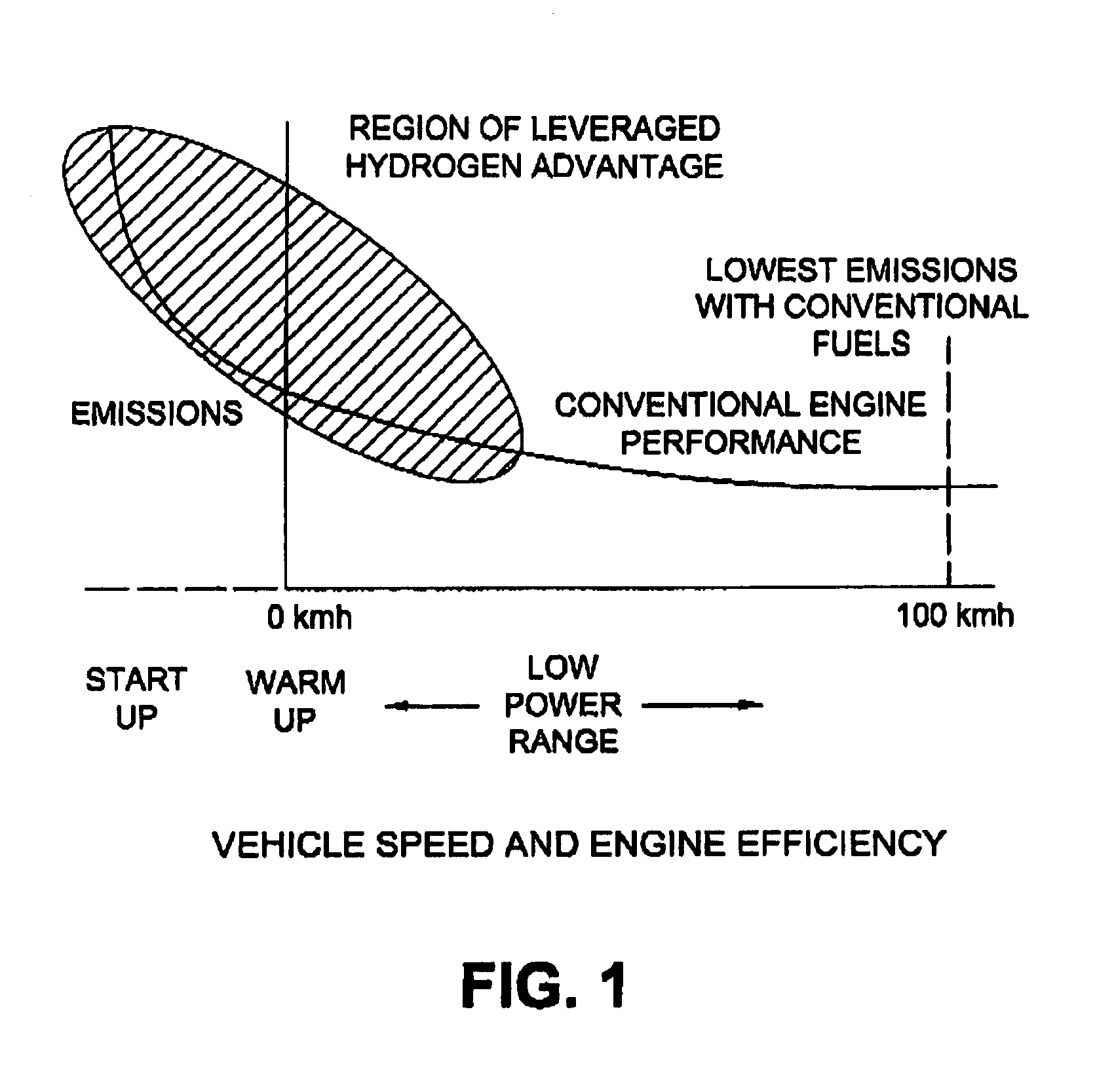
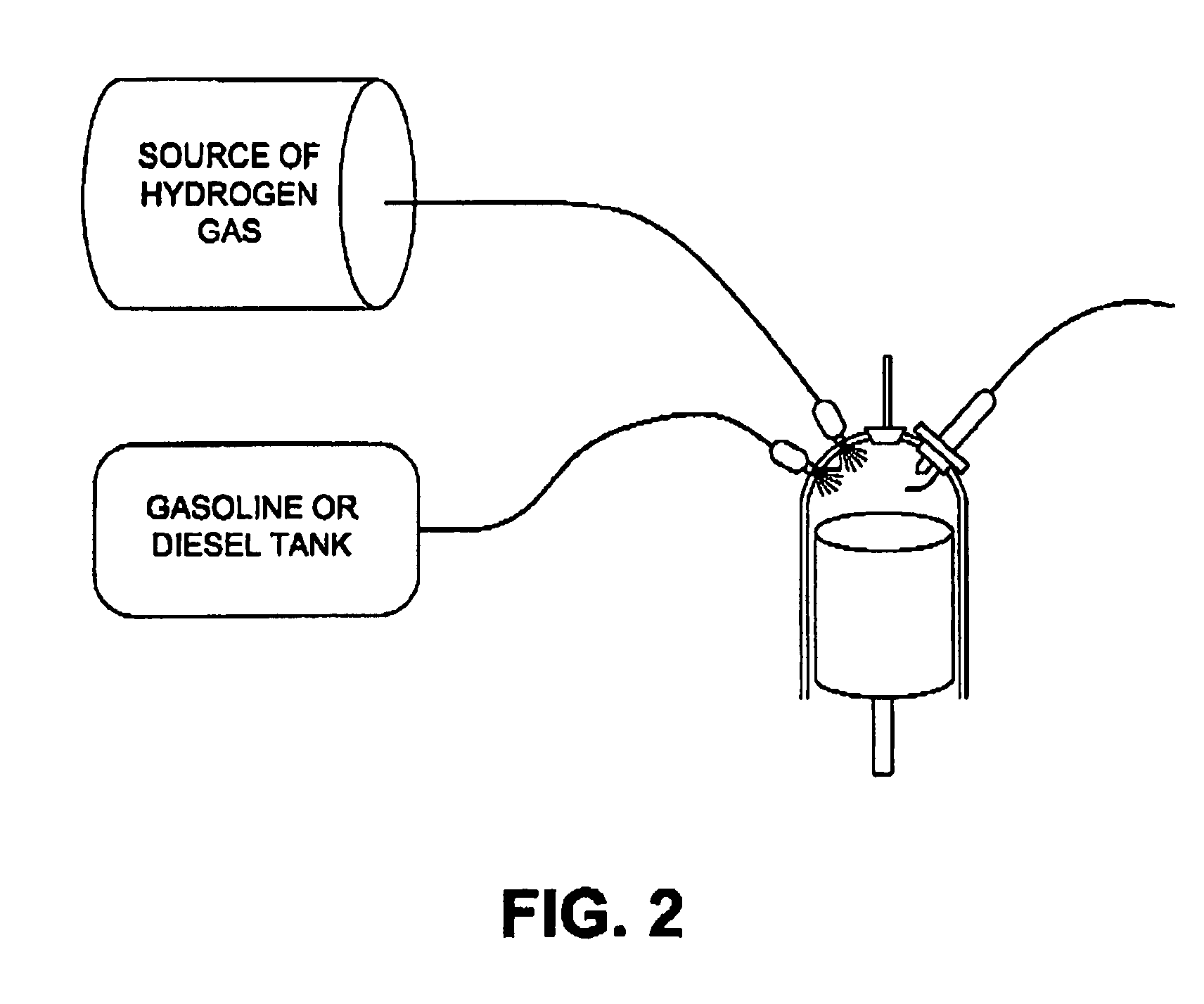
System and method for operating an internal combustion engine with hydrogen blended with conventional fossil fuels
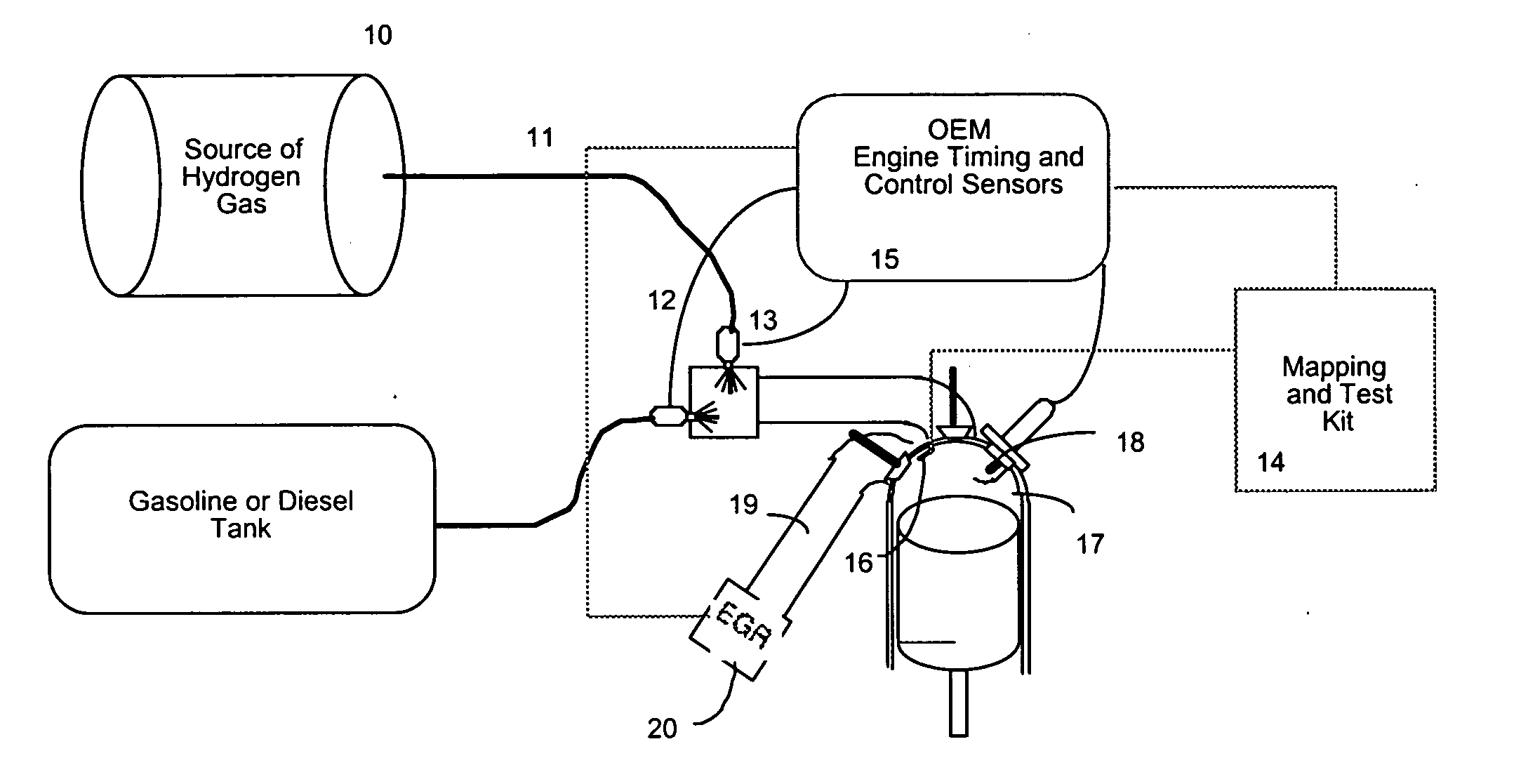
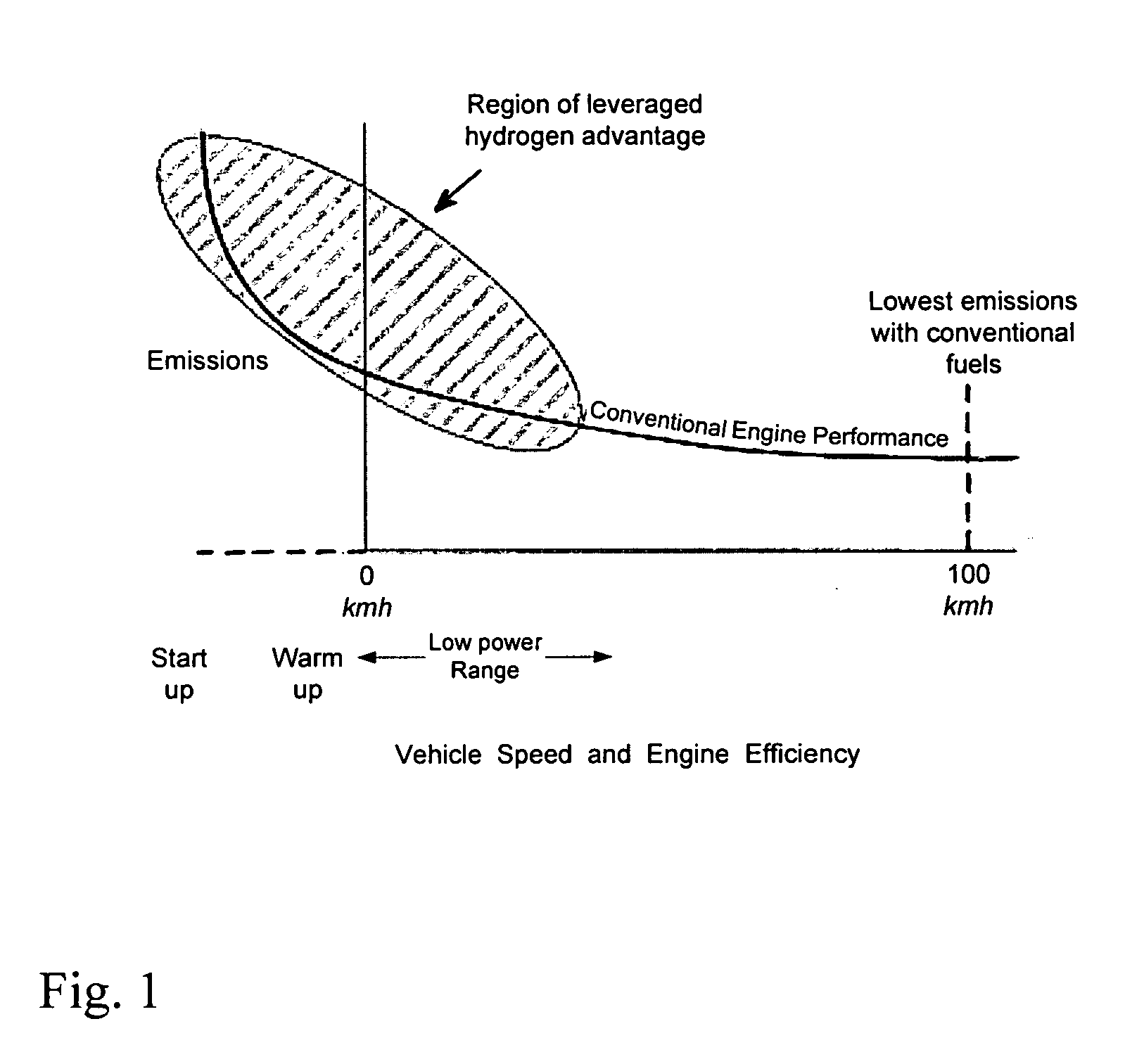
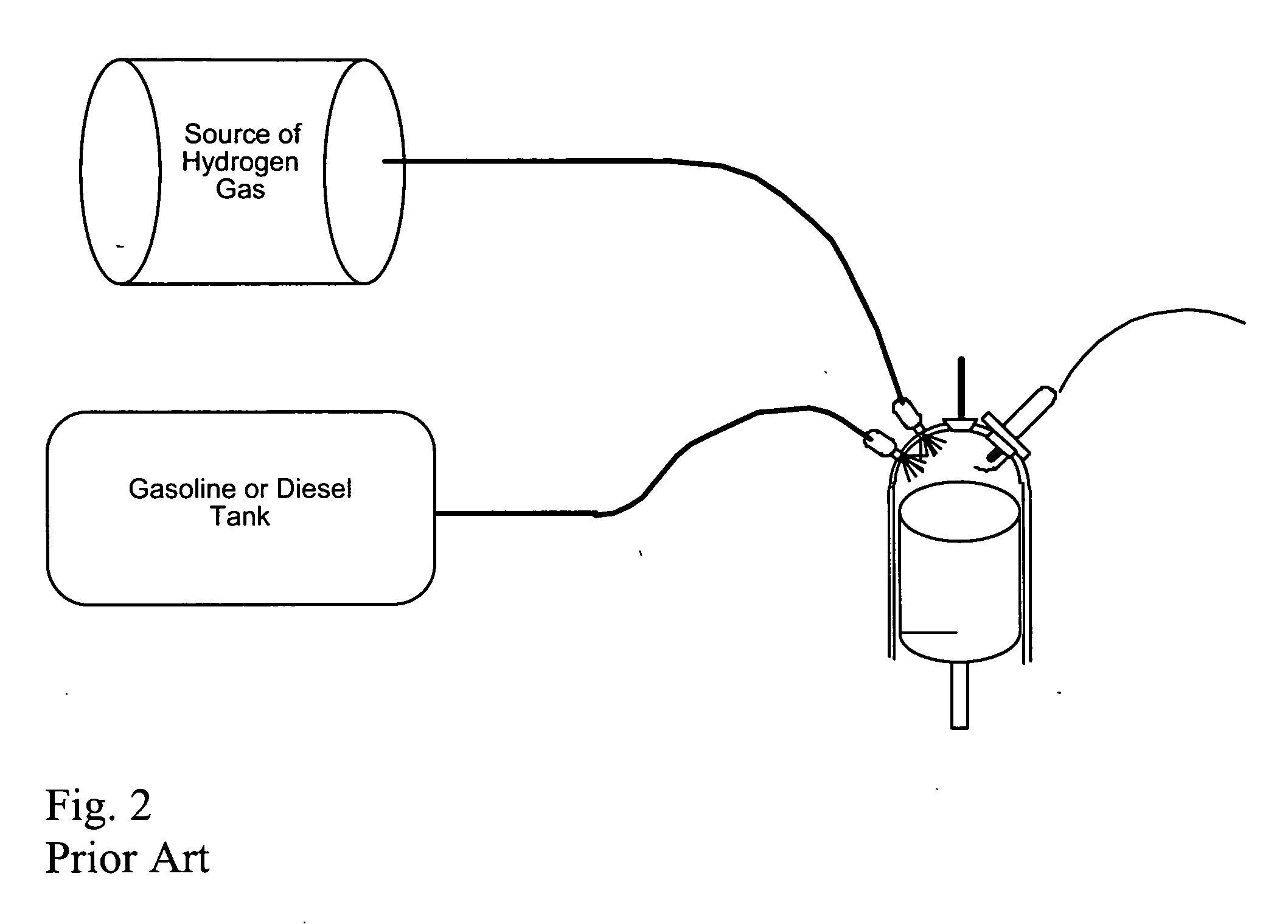
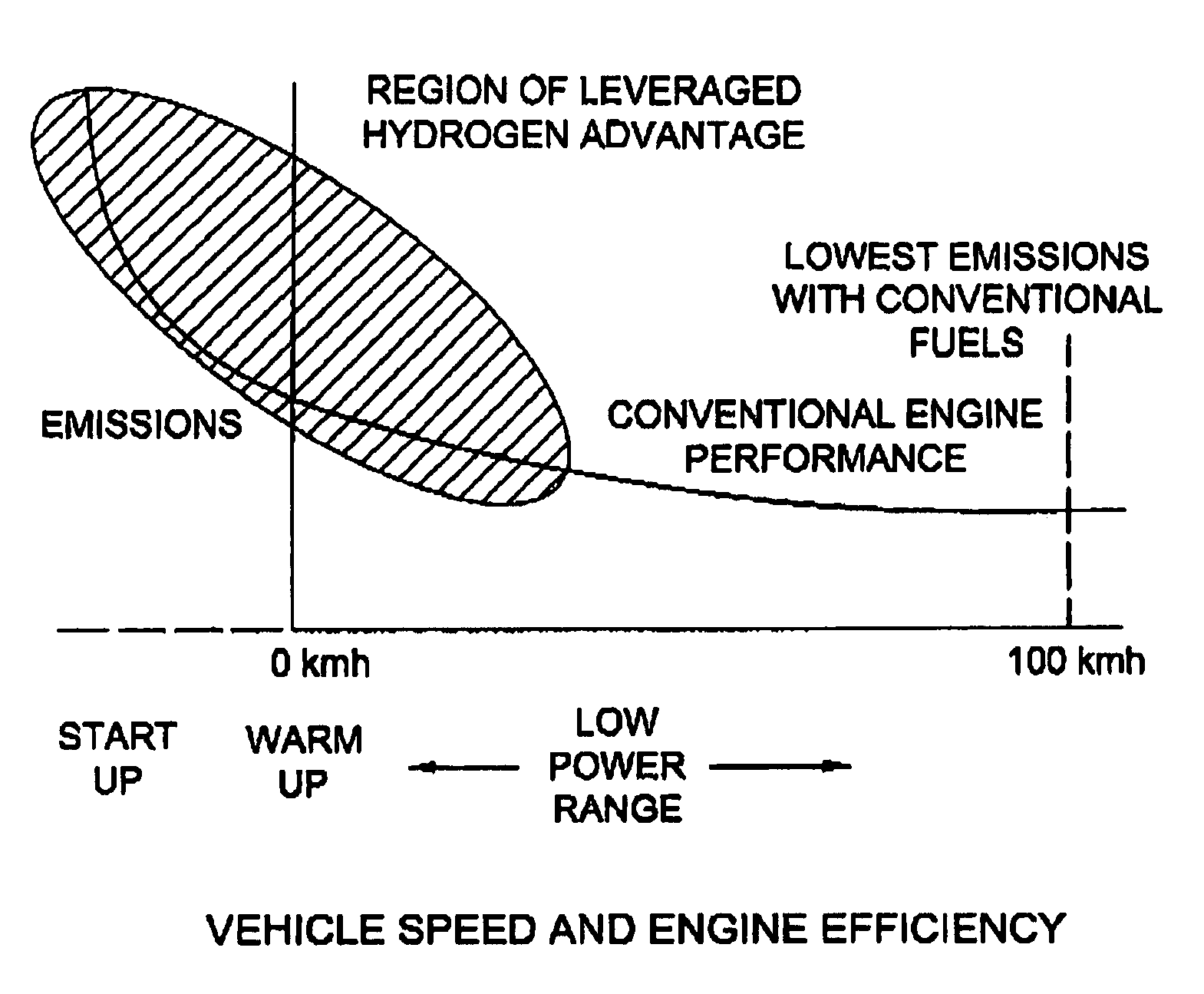
ActiveUS20050229872A1Inexpensively repAccelerate emissionsHydrogenElectrical controlHydrogenExternal combustion engine
A system for retrofitting an internal combustion engine to use a proportion of hydrogen gas and existing fossil fuel is disclosed. The system is comprised of a source of hydrogen gas and means for delivering hydrogen gas to the combustion chamber of the engine. The engine operating parameters are adjusted and the delivery of hydrogen is controlled to provide selective introduction of hydrogen gas throughout the engine's operating cycle. The source of hydrogen gas can comprise an onboard hydrogen reformer, or hydrogen and carbon monoxide can be reformed inside the cylinder from an on board carrier of hydrogen. A single point injector placed at the intake manifold in close proximity to the engine intake valve can be used to mix the hydrogen gas to the air / fossil fuel mixture or sequential injectors can deliver hydrogen in close proximity to each engine intake valve, or directly into each cylinder.
Owner:OREILLY HUGH
Apparatus and method for providing weather and other alerts
InactiveUS7339467B2Increase signal strengthPrecise functionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexComputer networkRemote sensing
An apparatus for providing location-specific alert information associated with an alert condition relevant to a geographical area may include a receiver adapted to receive transmissions comprising formatted text on a communication channel of a wireless bi-directional communication network; a peripheral device operable to indicate an alert condition, including displaying the formatted text; and a controller communicatively coupled to the receiver and the peripheral device. The controller is operable to monitor a communication channel of the network for the receipt of a transmission of location-specific alert information from a transmitter servicing a geographical area and to operate the peripheral device in response to the reception of the transmission of the location-specific alert information to display the formatted text. The location-specific alert information is broadcast within the geographical area by at least one transmitter of the wireless bi-directional communication network having communication channels and transmitters which are each positioned to provide communication services to specific geographical areas serviced by the communication network.
Owner:AT&T DELAWARE INTPROP INC +1
Method and Apparatus For Limiting Peer-to-Peer Communication Interference
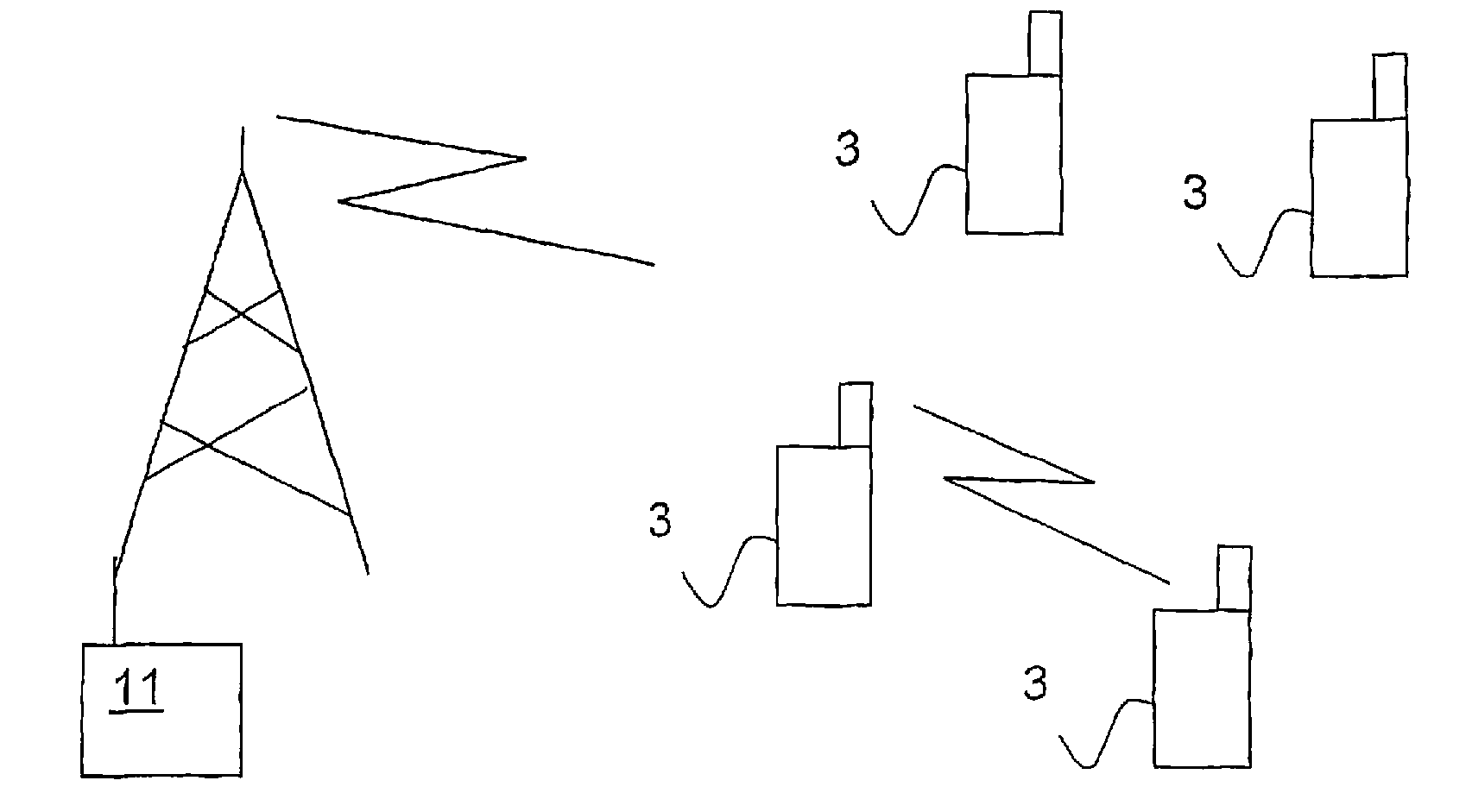
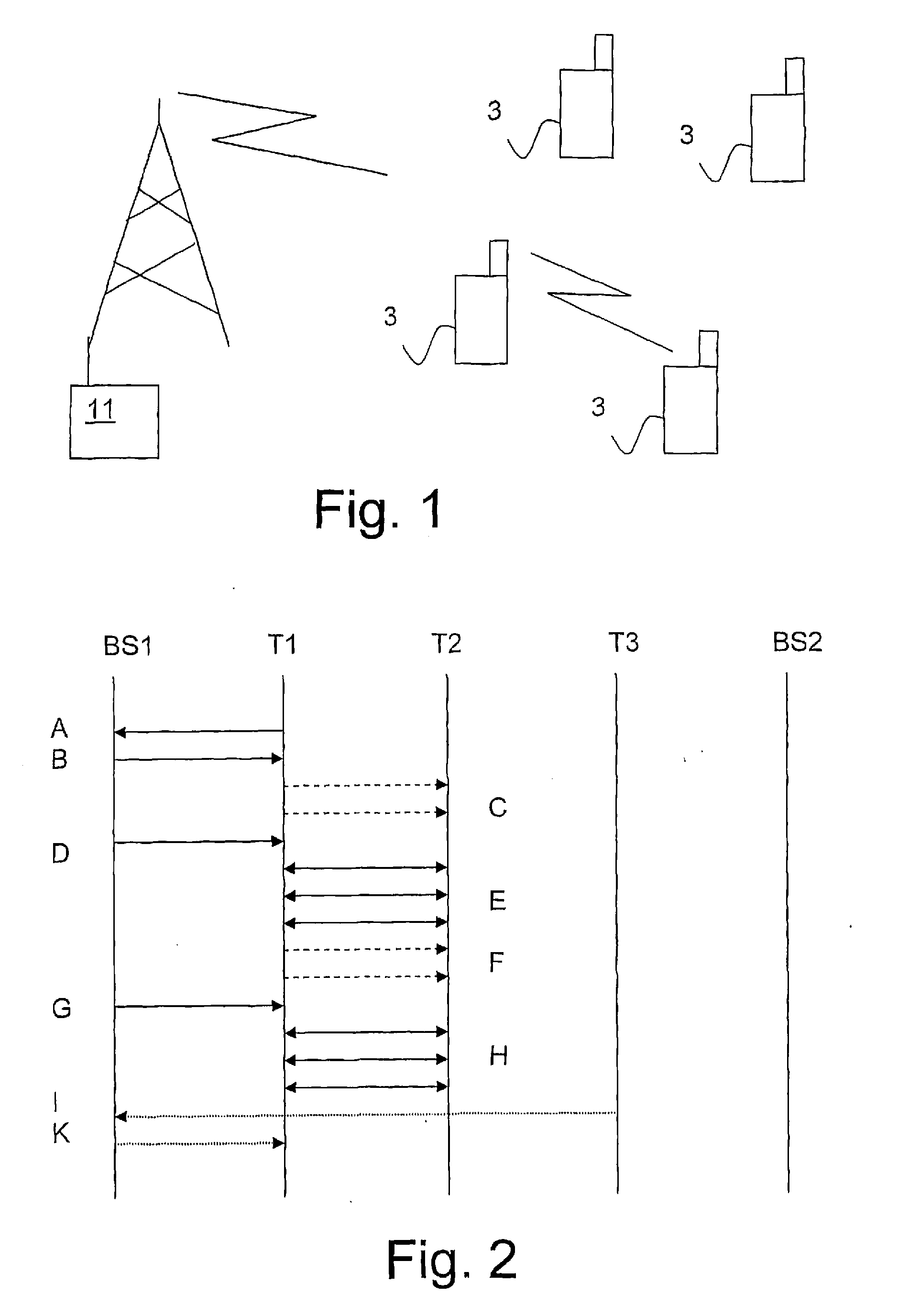
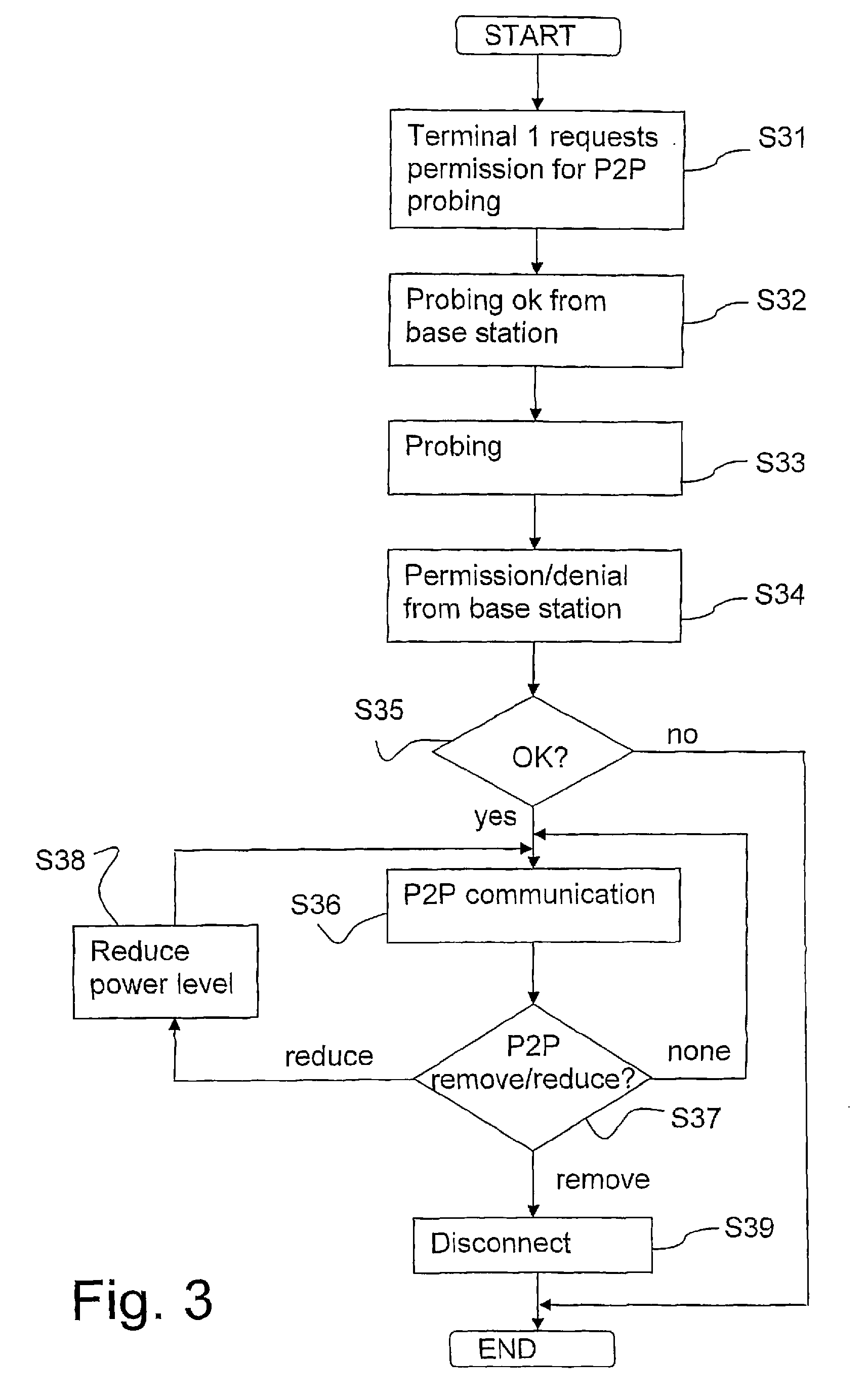
ActiveUS20080318612A1Increase power levelMinimal levelConnection managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsFrequency spectrumControl signal
Peer-to-peer communication between user terminals in a licensed spectrum is enabled by a method comprising the following steps: —communicating directly, peer-to-peer, between the first and the second mobile terminal, and —disconnecting the peer-to-peer communication in dependence of control signals received or not received from the base station. Thus, according to the invention, the network is enabled to control the peer-to-peer communication between two user terminals.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System and method for operating an internal combustion engine with hydrogen blended with conventional fossil fuels
ActiveUS7290504B2Accelerate emissionsCheap replacementHydrogenElectrical controlOn boardExternal combustion engine
Owner:OREILLY HUGH
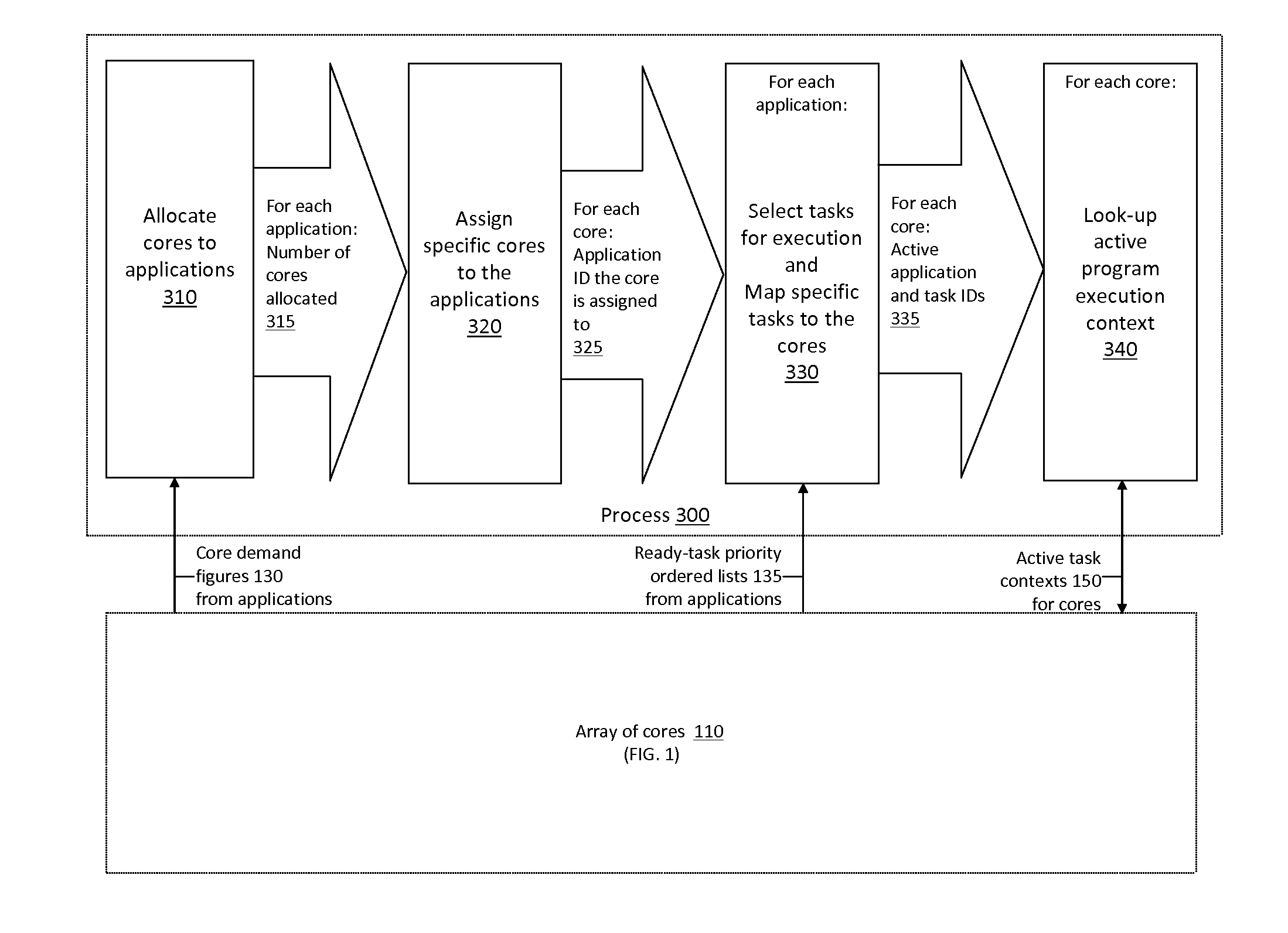
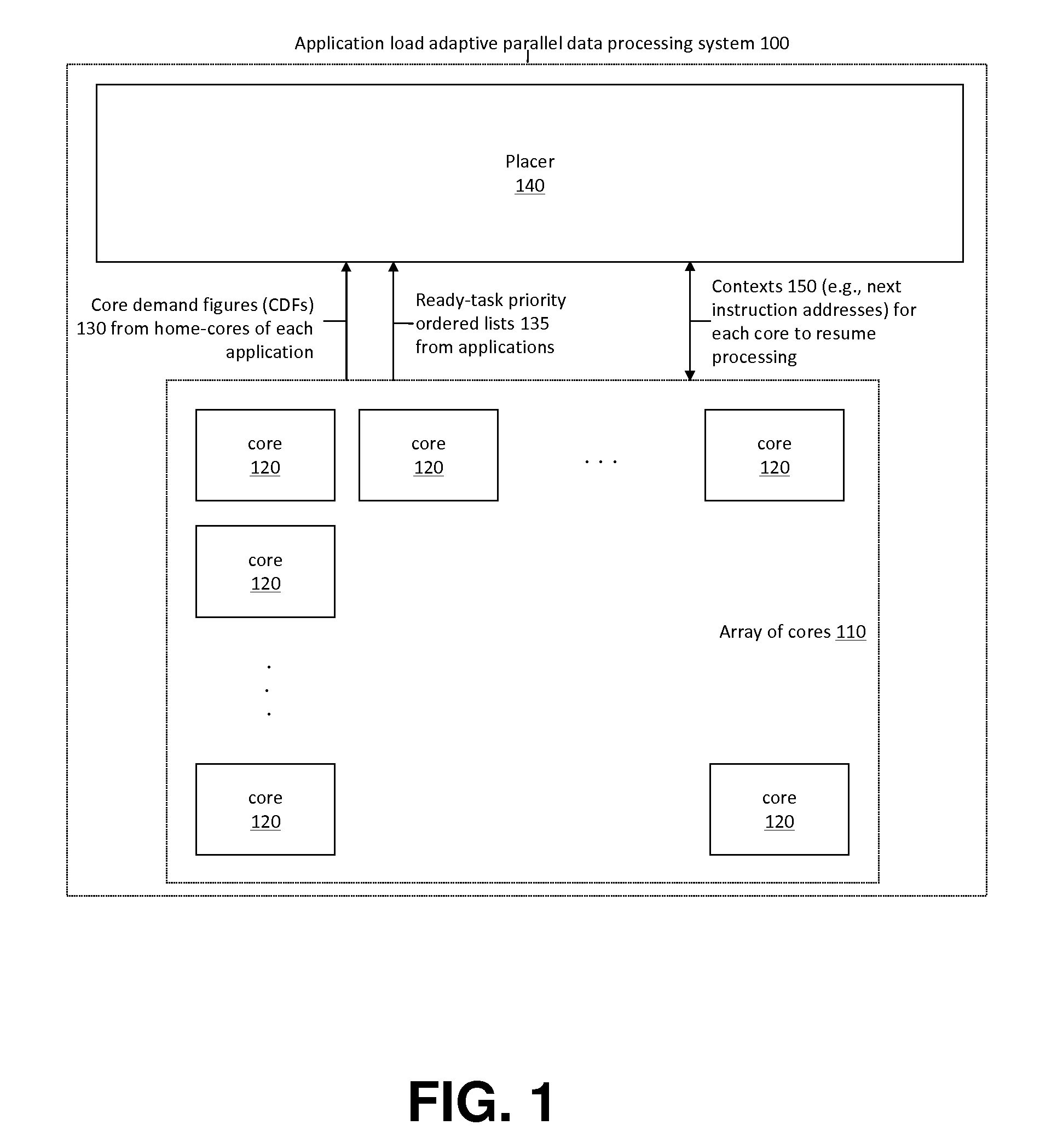
Application Load Adaptive Processing Resource Allocation
InactiveUS20120079501A1Maximized number of processing coreMaximizing whole system data processing throughputMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsData processing systemMulti core computing
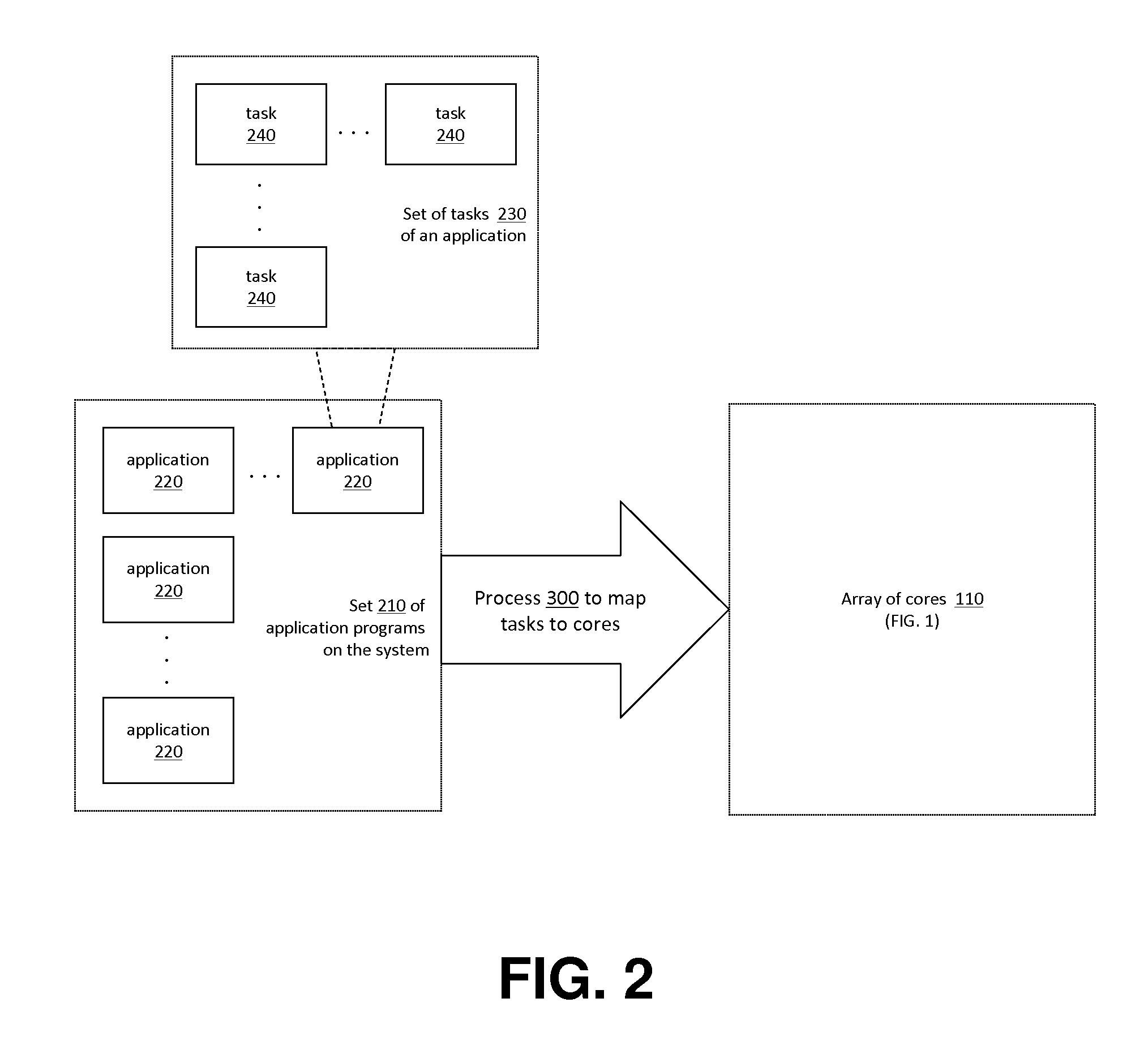
The invention provides hardware-automated systems and methods for efficiently sharing a multi-core data processing system among a number of application software programs, by dynamically reallocating processing cores of the system among the application programs in an application processing load adaptive manner. The invention enables maximizing the whole system data processing throughput, while providing deterministic minimum system access levels for each of the applications. With invented techniques, each application on a shared multi-core computing system dynamically gets a maximized number of cores that it can utilize in parallel, so long as all applications on the system still get at least up to their entitled number of cores whenever their actual processing load so demands. The invention provides inherent security and isolation between applications, as each application resides in its dedicated system memory segments, and can safely use the shared processing system as if it was the sole application running on it.
Owner:THROUGHPUTER
Group-iii nitride compound semiconductor device and production method thereof, group-iii nitride compound semiconductor light-emitting device and production method thereof, and lamp
InactiveUS20090194784A1Improve in-plane uniformityLower Level RequirementsSolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingRocking curveInter layer
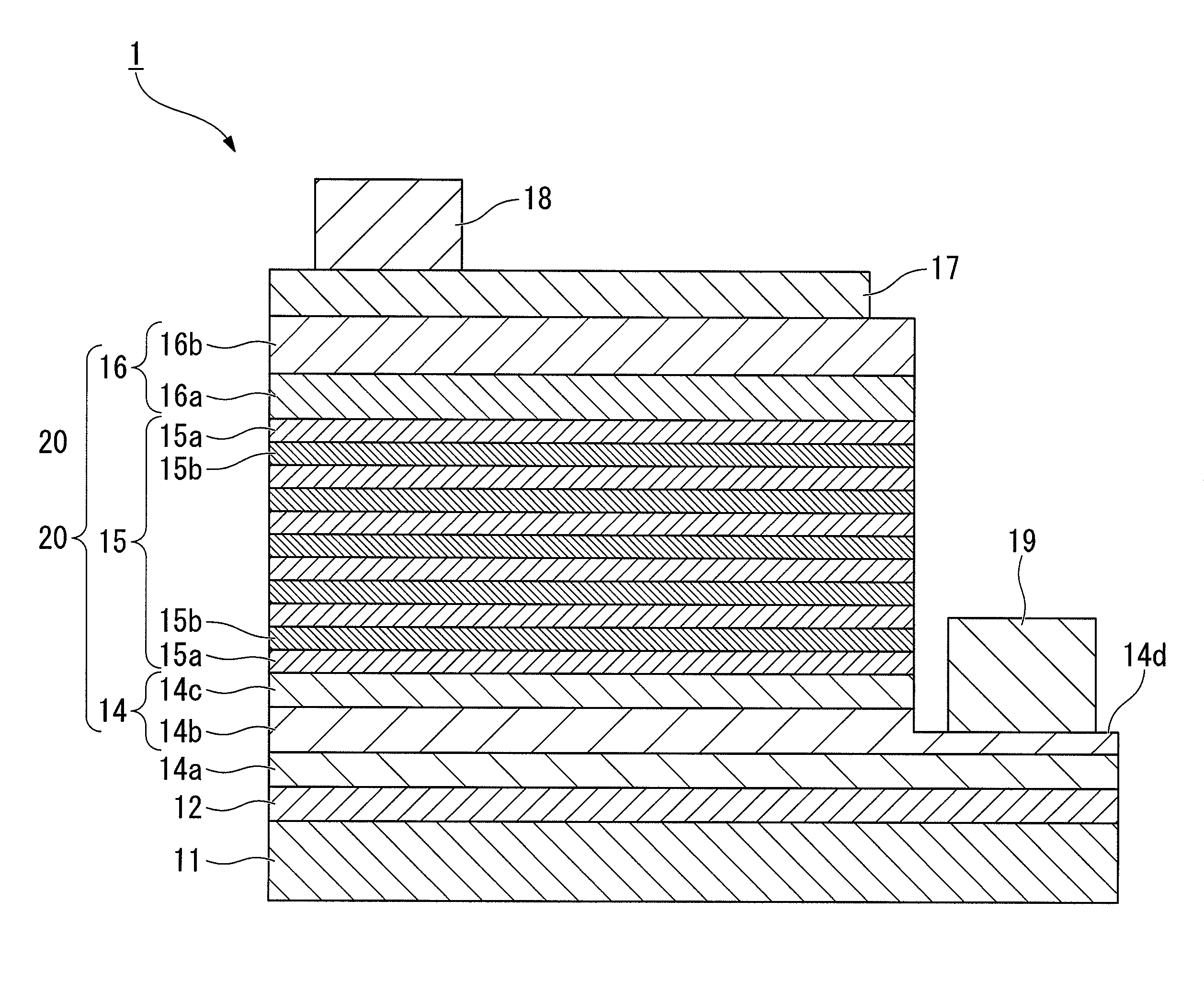
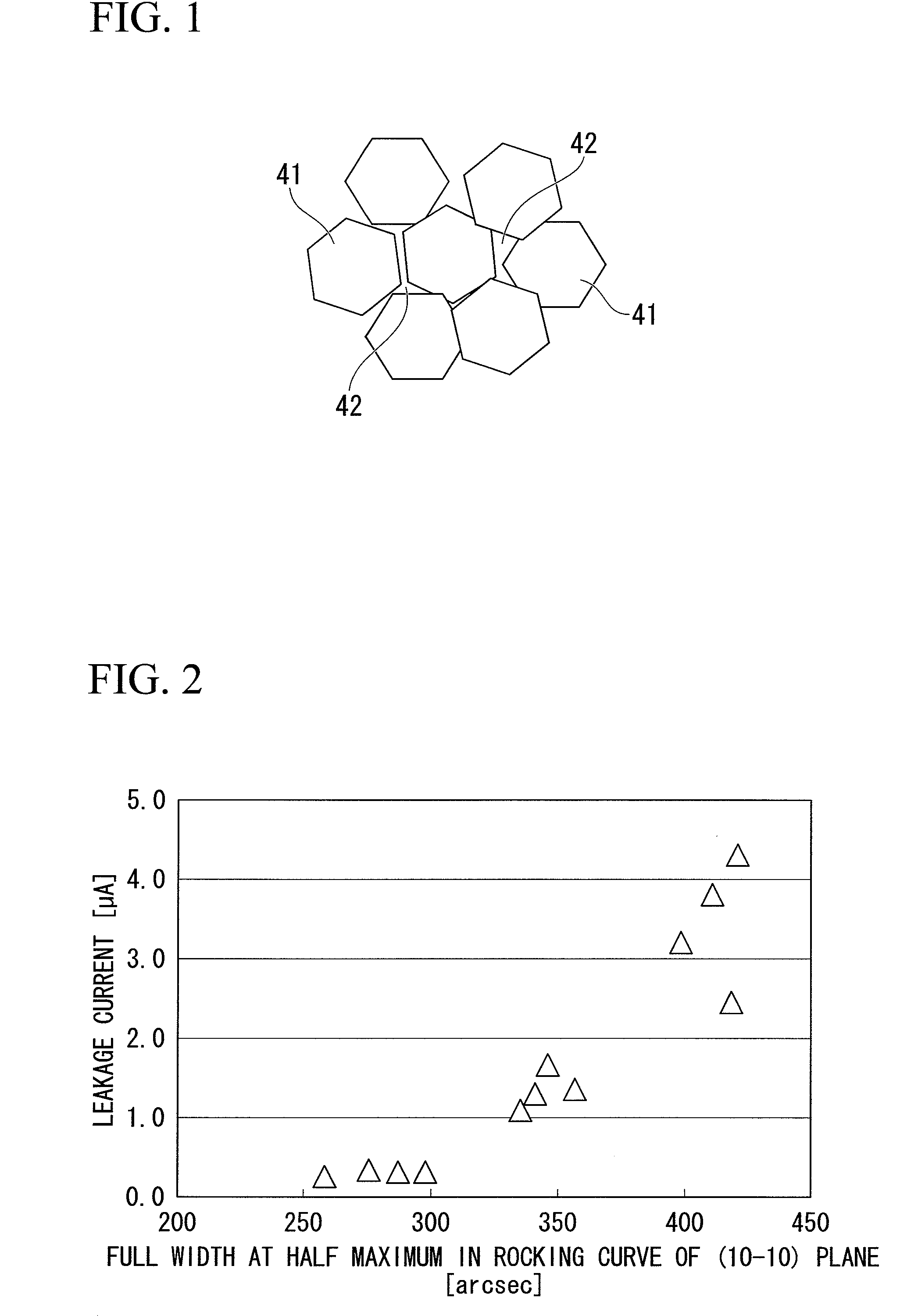
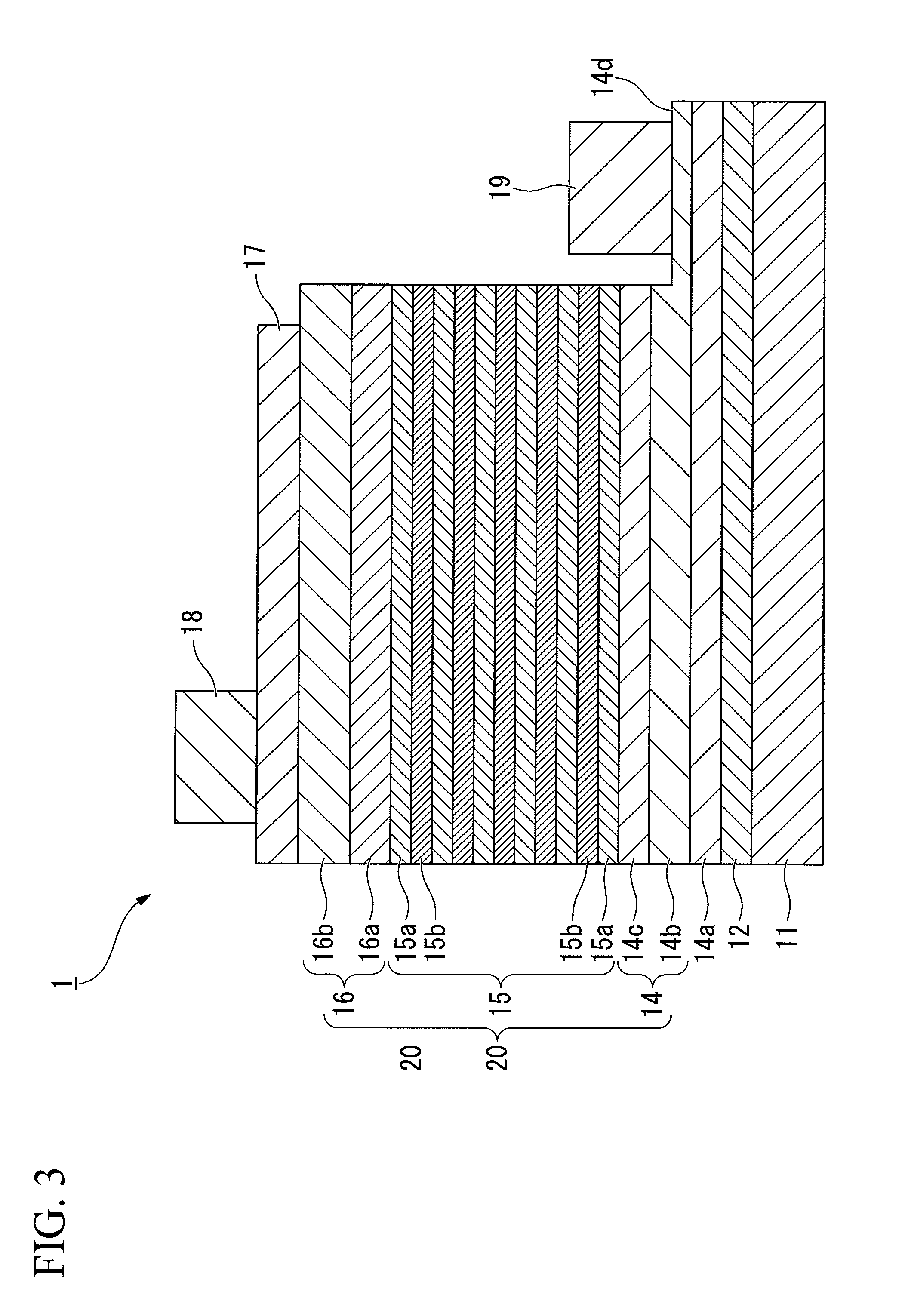
A group-III nitride compound semiconductor device of the present invention comprises a substrate, an intermediate layer provided on the substrate, and a base layer provided on the intermediate layer in which a full width at half maximum in rocking curve of a (0002) plane is 100 arcsec or lower and a full width at half maximum in rocking curve of a (10-10) plane is 300 arcsec or lower. Also, a production method of a group-III nitride compound semiconductor device of the present invention comprises forming the intermediate layer by using a sputtering method.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
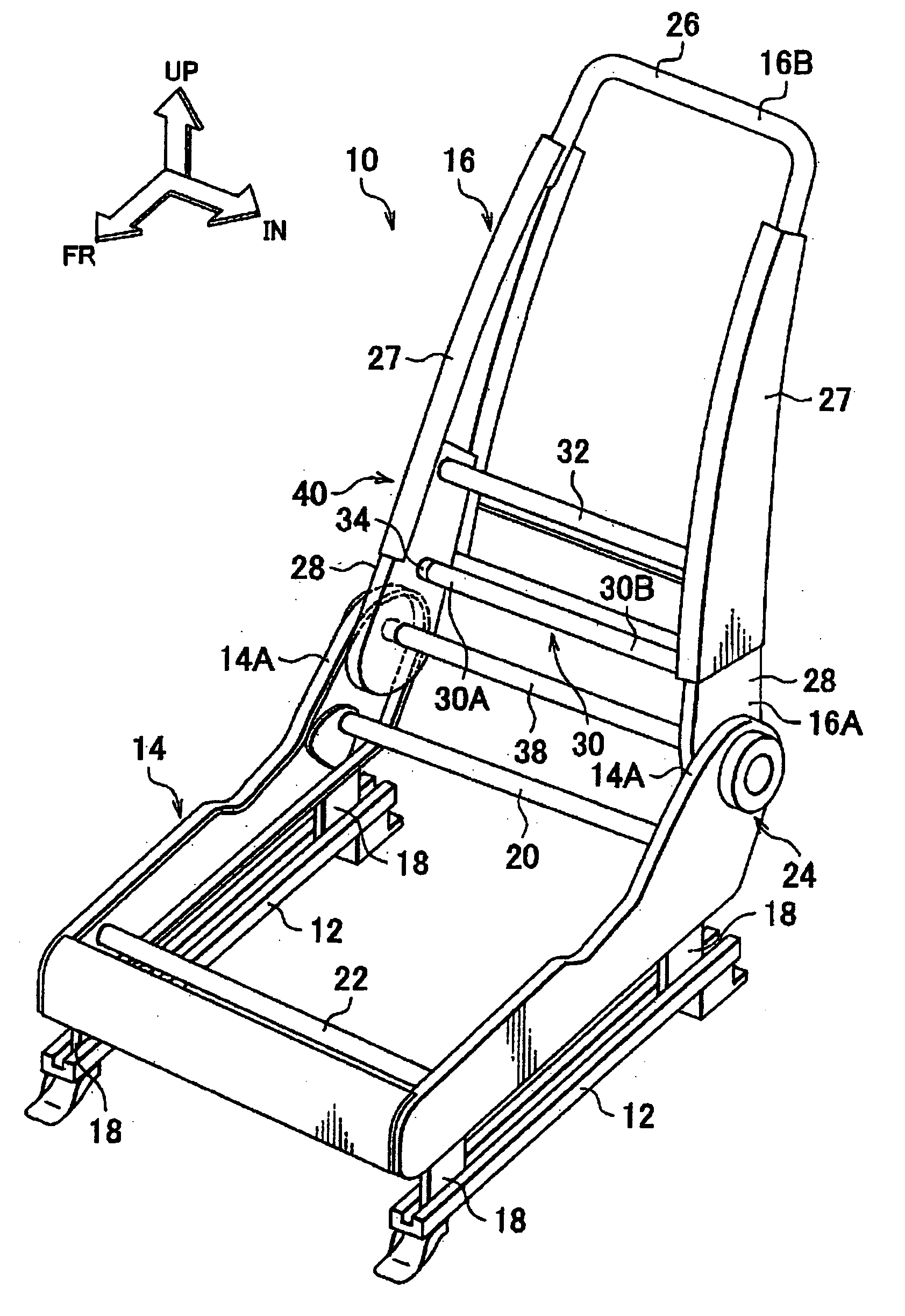
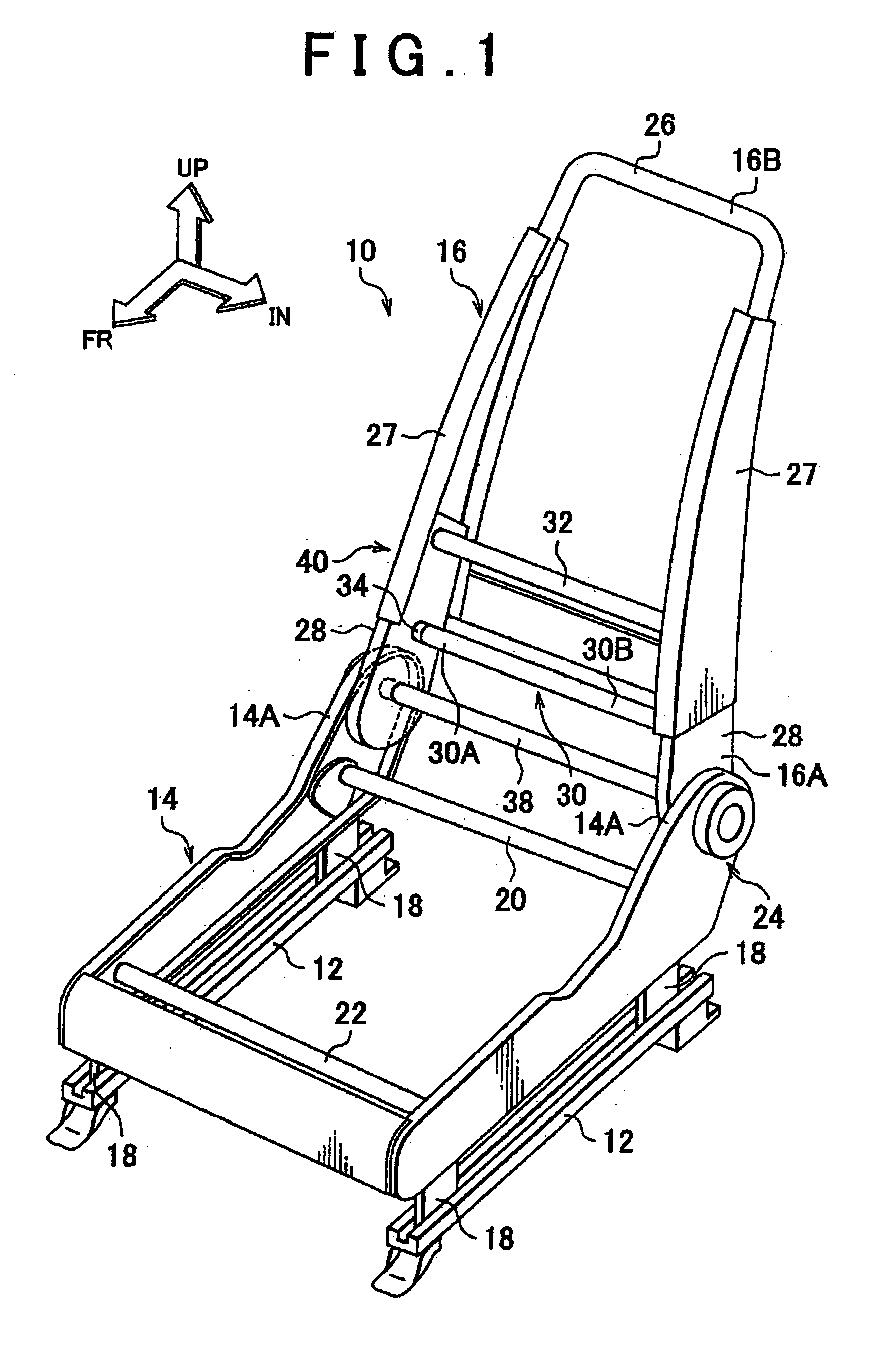
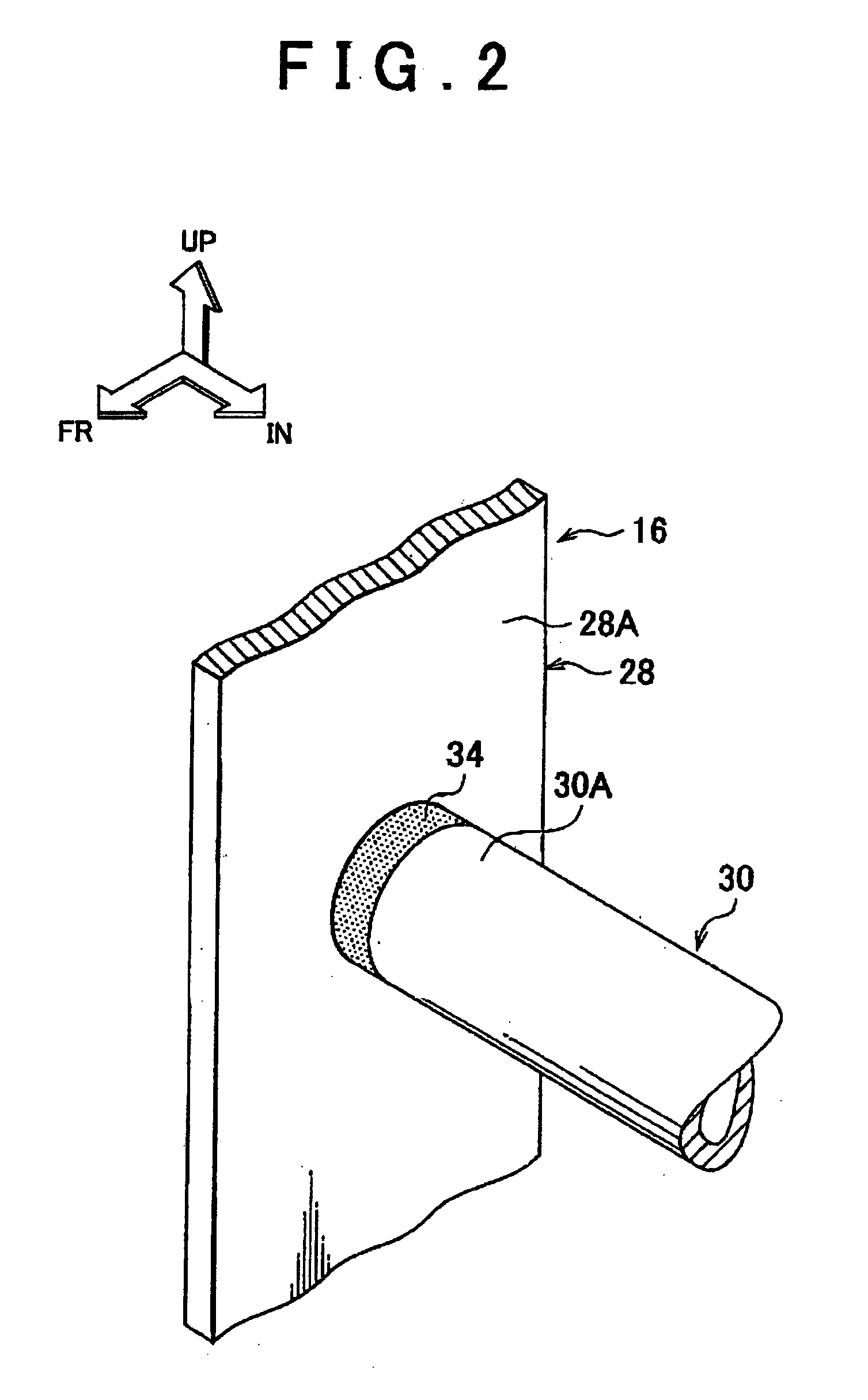
Vehicle seat
InactiveUS20110006580A1Sufficient rigidityReduce level of minor vibrationSeat framesStoolsMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
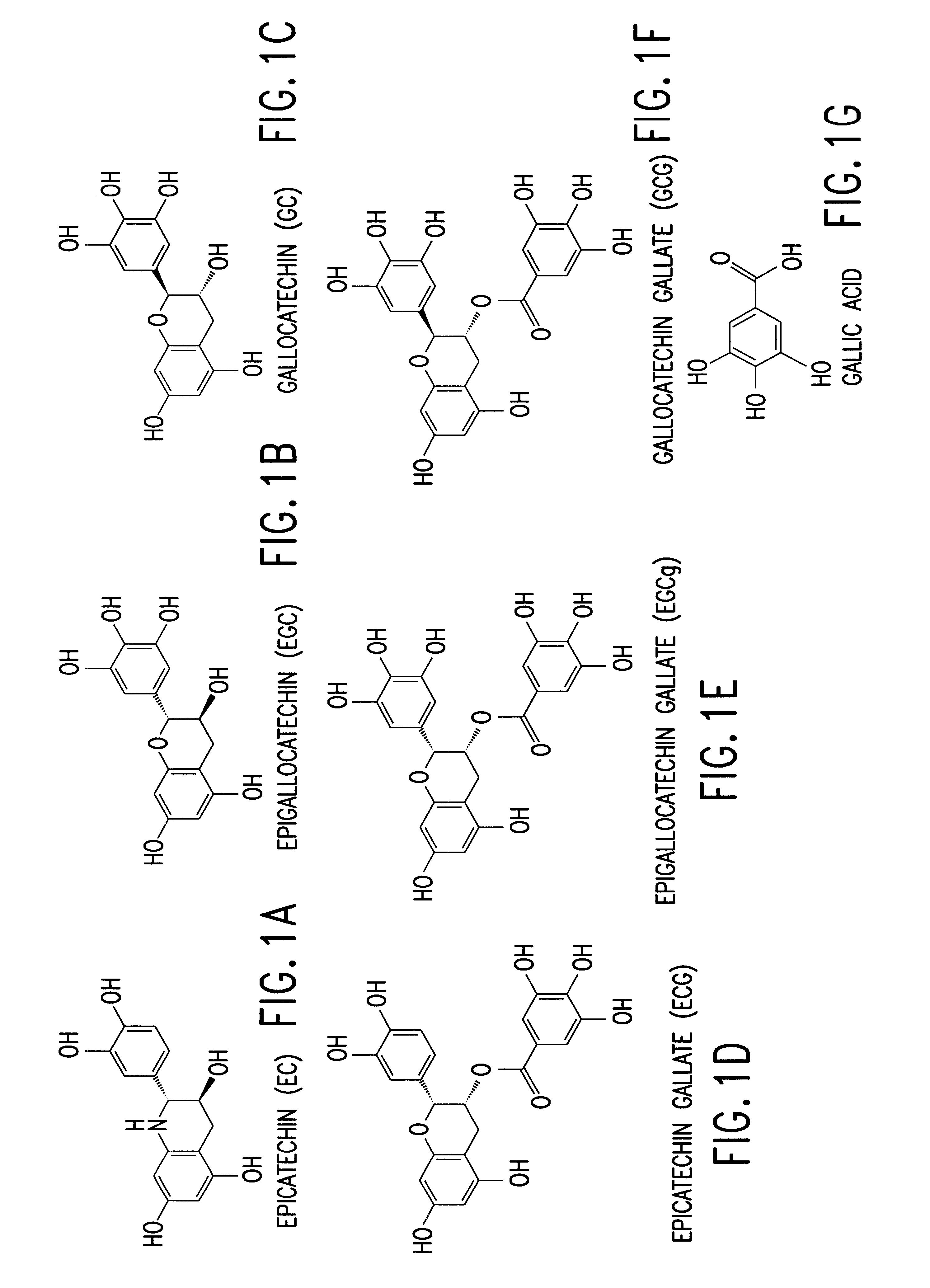
Tea catechin formulations and processes for making same
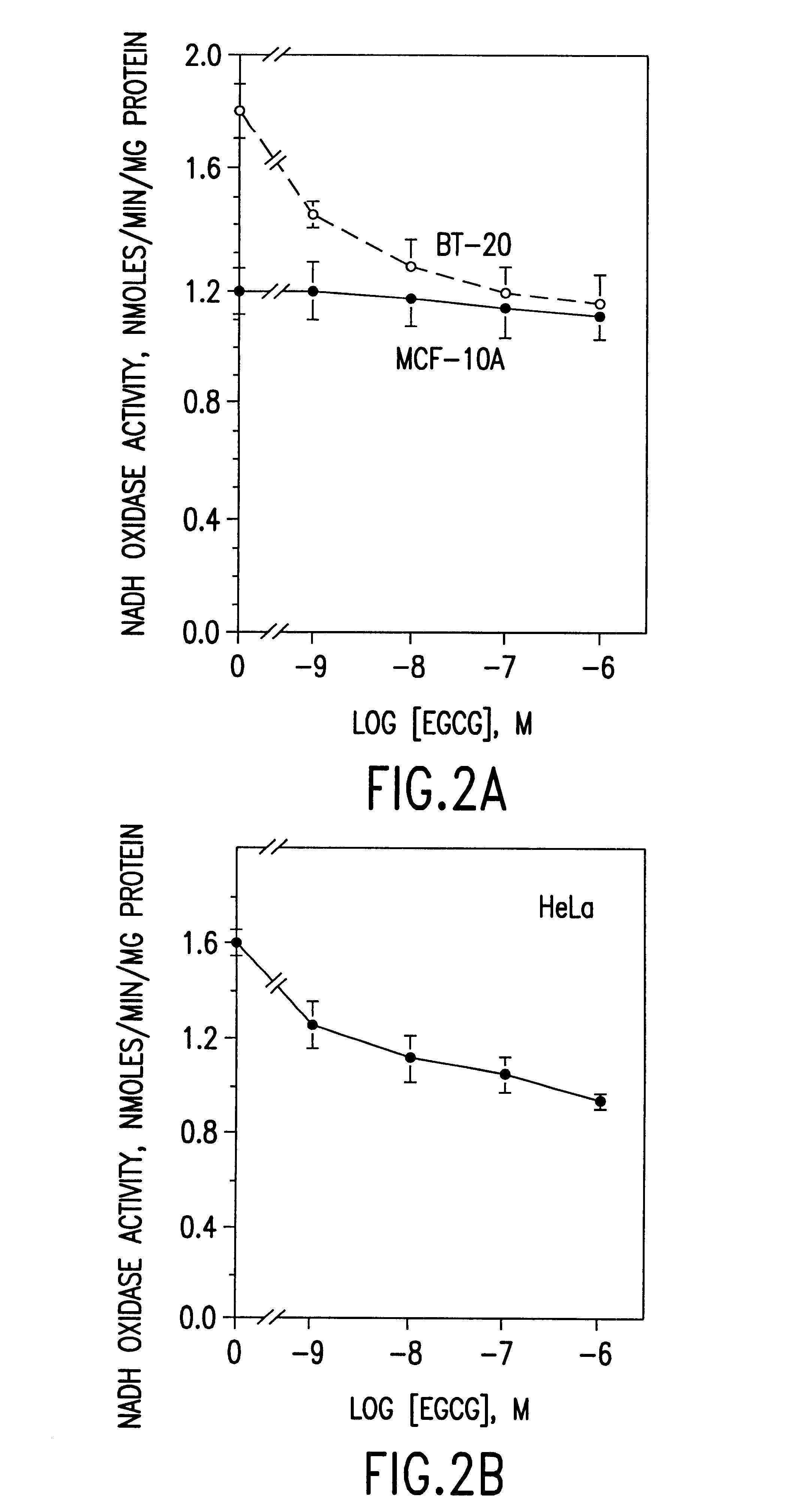
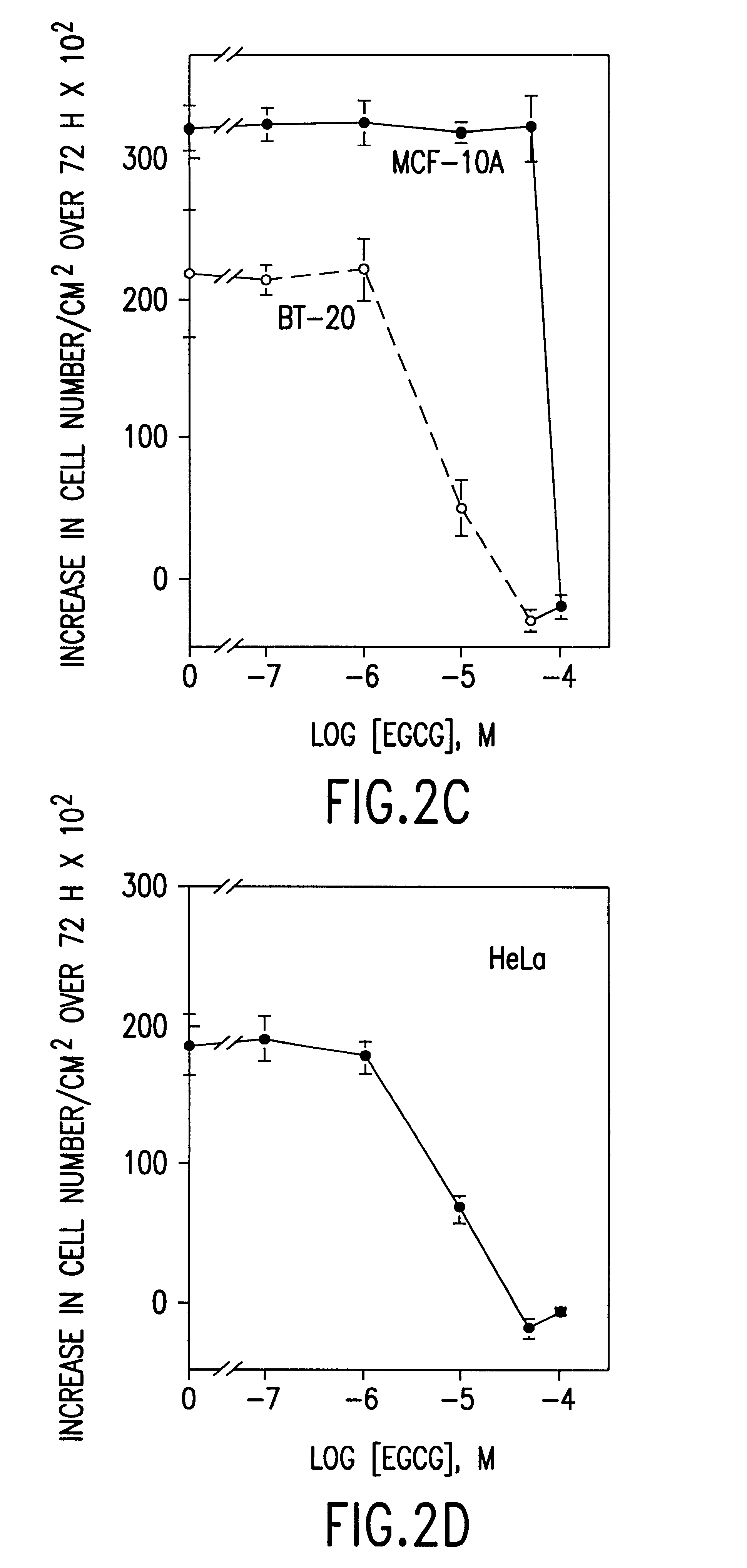
InactiveUS6428818B1Inhibit activity of specificMinimal levelBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsSolid tumorGreen tea
The invention described herein encompasses methods and compositions of treating cancer or solid tumors comprising the administration of a therapeutically effective amount of catechins, a group of polyphenols found in green tea, to a mammal in need of such therapy. Compositions of catechins include but not limited to, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCg), epicatechin (EC), epicatechin gallate (ECG), epigallocatechin (EGC). The unique compositions of the invention contain various combinations of the catechins with reduced levels of EGCg, alone or in combination with each other or other therapeutic agents and are used to treat primary and metastatic cancers in humans. The invention also encompasses the varying modes of administration of the therapeutic compounds.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC +1
Apparatus and method for providing weather and other alerts
InactiveUS20050237183A1Increase signal strengthPrecise functionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexNetwork serviceComputer science
An apparatus for providing location-specific alert information associated with an alert condition relevant to a geographical area may include a receiver adapted to receive transmissions comprising formatted text on a communication channel of a wireless bi-directional communication network; a peripheral device operable to indicate an alert condition, including displaying the formatted text; and a controller communicatively coupled to the receiver and the peripheral device. The controller is operable to monitor a communication channel of the network for the receipt of a transmission of location-specific alert information from a transmitter servicing a geographical area and to operate the peripheral device in response to the reception of the transmission of the location-specific alert information to display the formatted text. The location-specific alert information is broadcast within the geographical area by at least one transmitter of the wireless bi-directional communication network having communication channels and transmitters which are each positioned to provide communication services to specific geographical areas serviced by the communication network.
Owner:AT&T DELAWARE INTPROP INC +1
Optical vend sensing system for product delivery detection
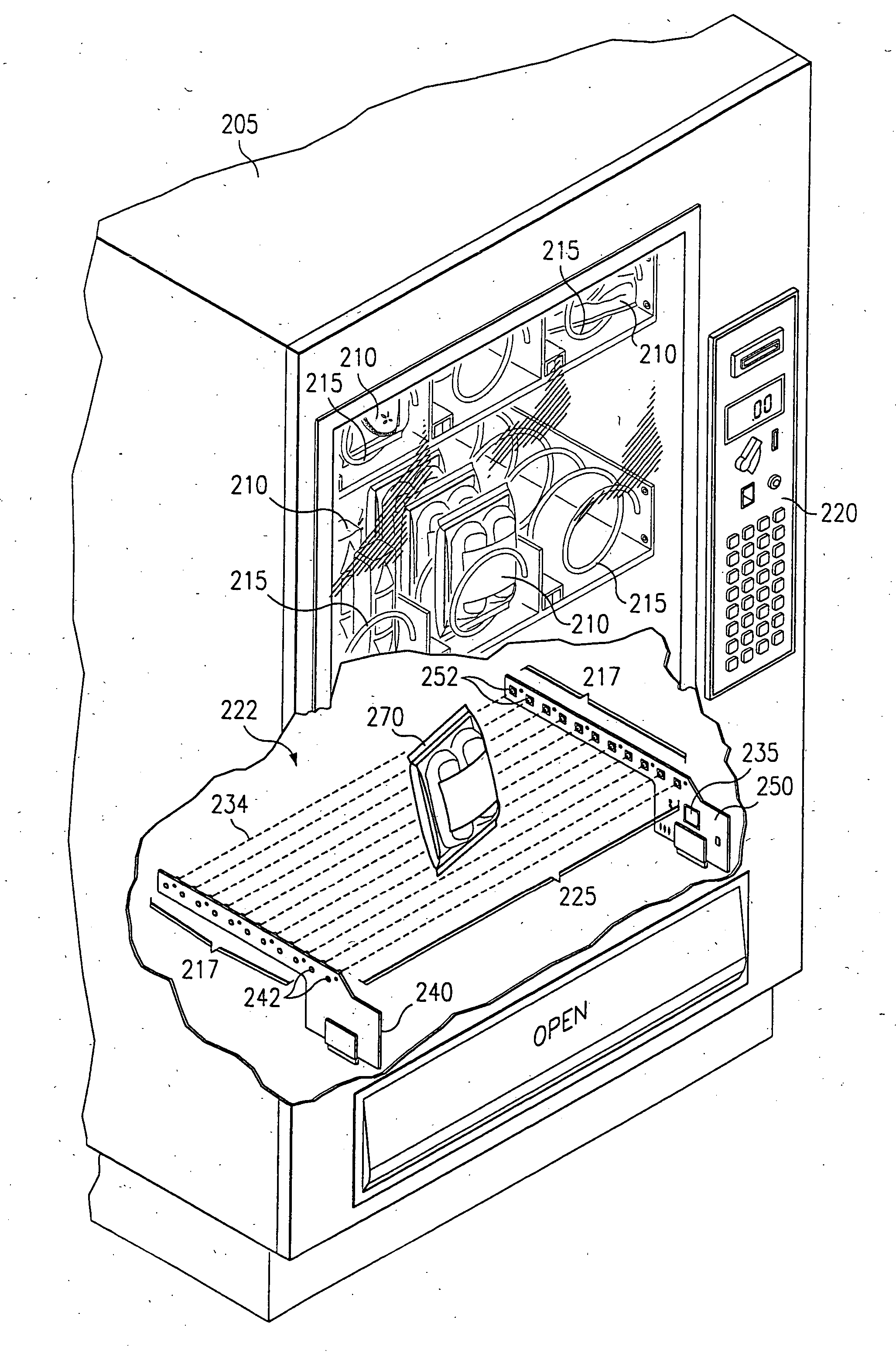
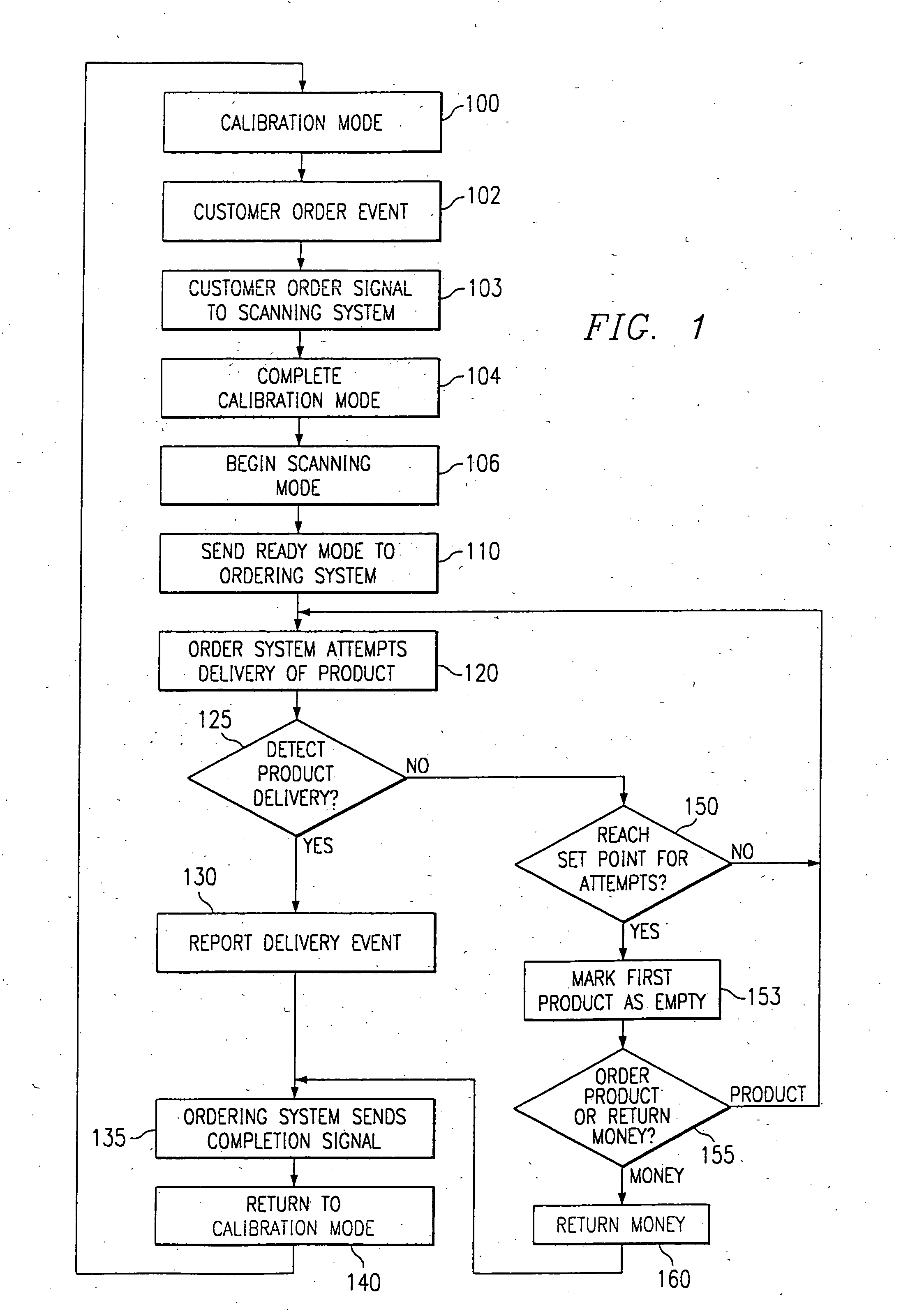
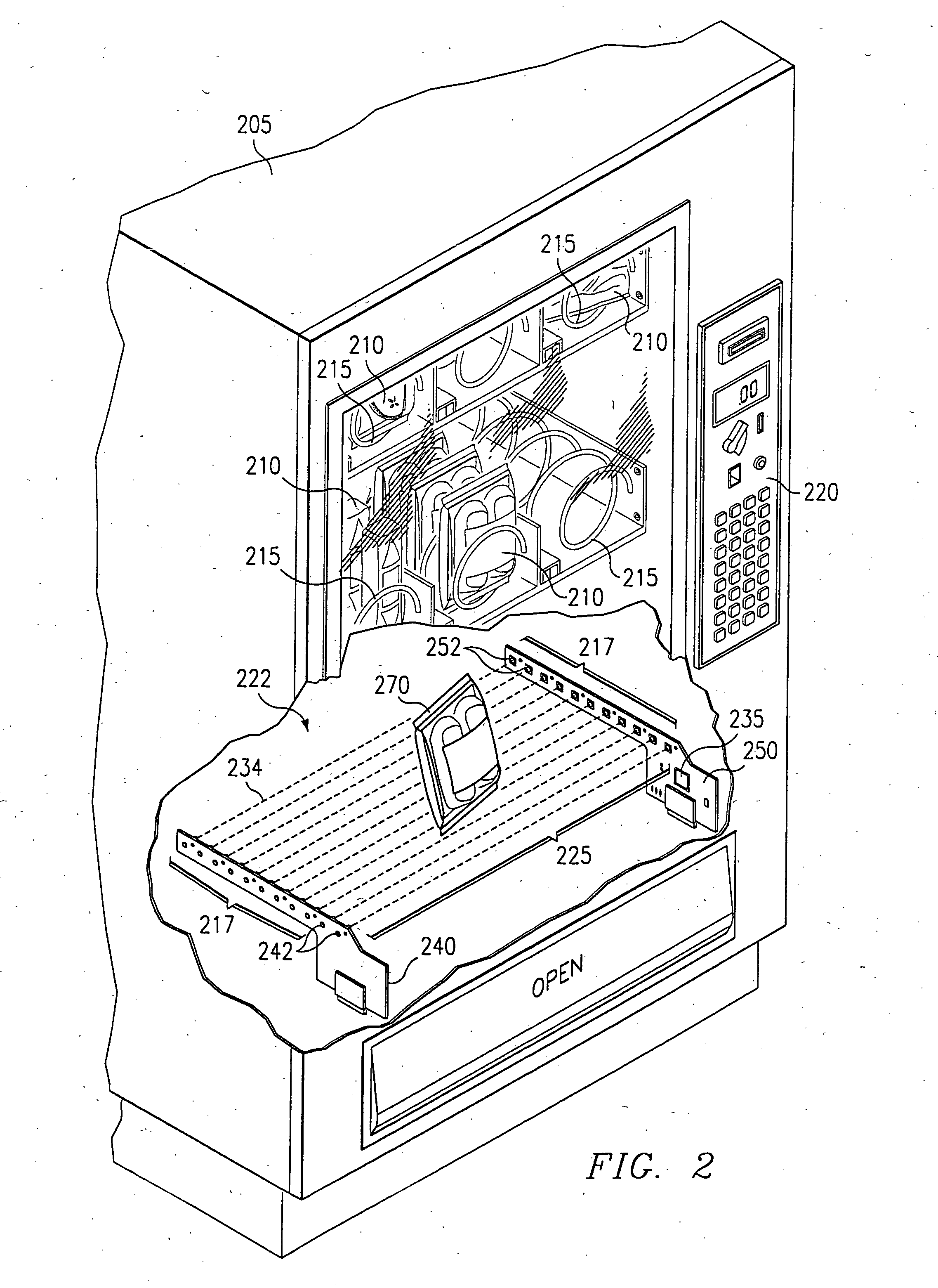
InactiveUS20070213871A1Minimal levelCoin-freed apparatus detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamEngineering
An optical vend sensing system for use in vending machines employs a row of light emitters on one side of a region through which a vend product passes during delivery and a row of light detectors on the opposite side. Each detector is substantially aligned with a corresponding one of the emitters, and is capable of receiving light from any of more than one of the emitters when that emitter is activated. The emitters are individually activated in sequential, round-robin fashion and multiple detectors are monitored for each emitter when activated. Interruption of detectible beams between an activated emitter and one of the multiple emitters monitored for the activated emitter. Power applied to an activated emitter is calibrated in steps to a minimum level sufficient to ensure detection by all monitored detectors of light emitted by an activated emitter, plus a safety margin.
Owner:CRANE MERCHANDISING SYSTEMS
Method and apparatus for providing configurable layers and protocols in a communications system
InactiveUS20030118049A1Easy to implementMinimal levelNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexProtocol designCommunications system
The layers and protocols of an air interface layering architecture are designed to be modular and can be modified and upgraded to support new features, perform complex tasks, and implement additional functionality. Prior to commencement of data communication between a first entity (e.g., an access terminal) and a second entity (e.g., a radio network), a set of layers and / or protocols is selected for negotiation. For each selected layer and protocol (i.e., each attribute), a list of attribute values considered acceptable to the first entity is determined. The selected attributes and their associated attribute values are sent from the first entity and, in response, a list of processed attributes and their associated lists of processed attribute values are received. Each list of processed attribute values includes attribute values considered acceptable to the second entity. The layers and protocols in the first entity are then configured in accordance with the received list of processed attributes and their associated processed attribute values. Other features related to configurable layers and protocols are also provided.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
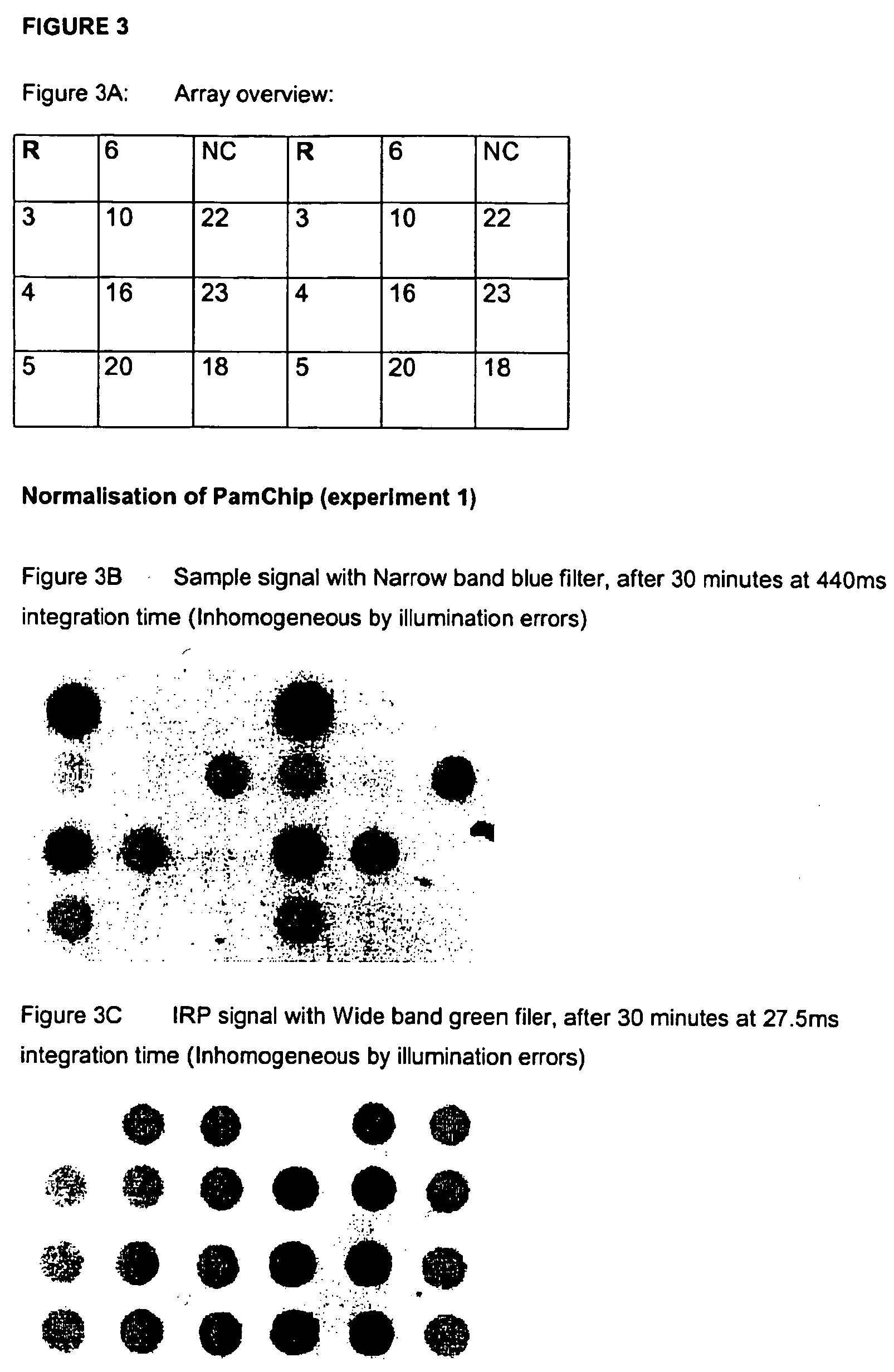
Normalisation of microarray data based on hybridisation with an internal reference
InactiveUS20050153290A1Large intensityMinimal levelBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteQuantitative determination
The invention relates to methods and corresponding arrays especially suited to correct for signal errors due to variations in sample preparation. Methods and compositions for performing quantitative array-based assays are provided. In the subject methods, both a reporter and an analyte is employed, where the reporter is characterized by binding selectively to an internal reference present on the array, i.e. at least a subset of, if not all of, the spots present on the array employed in the method contain an internal reference which can be bound by reporter.
Owner:PAMGENE
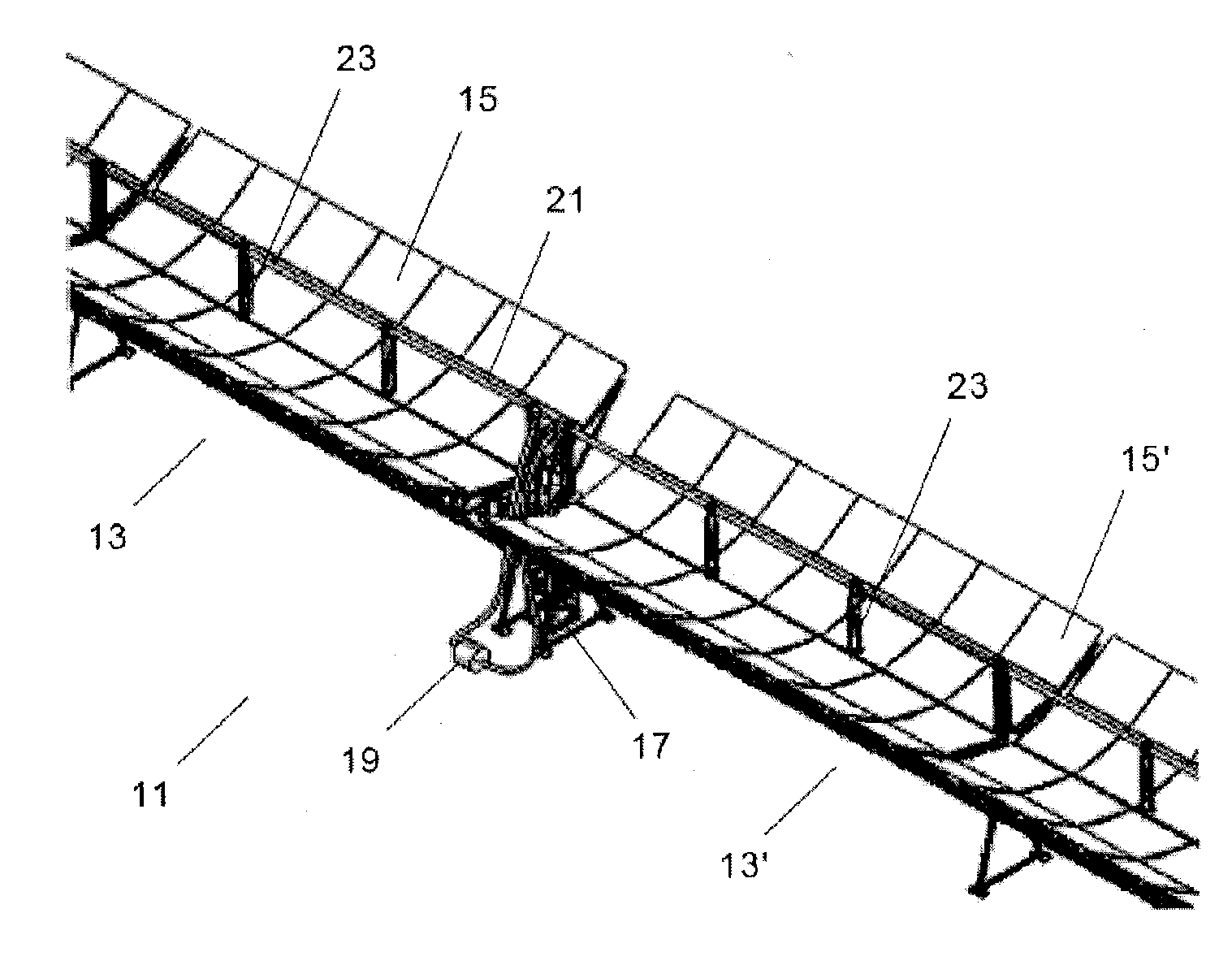
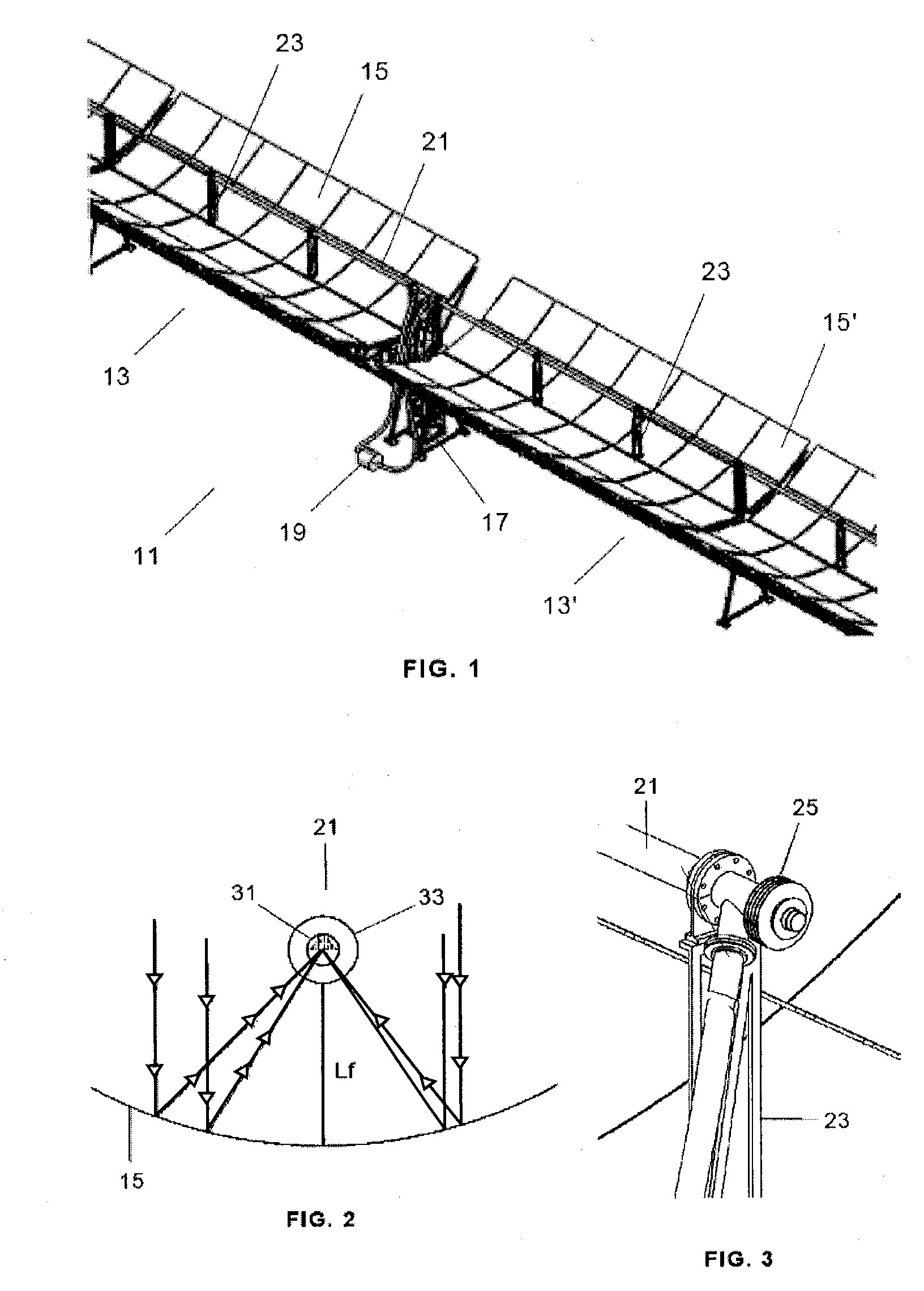
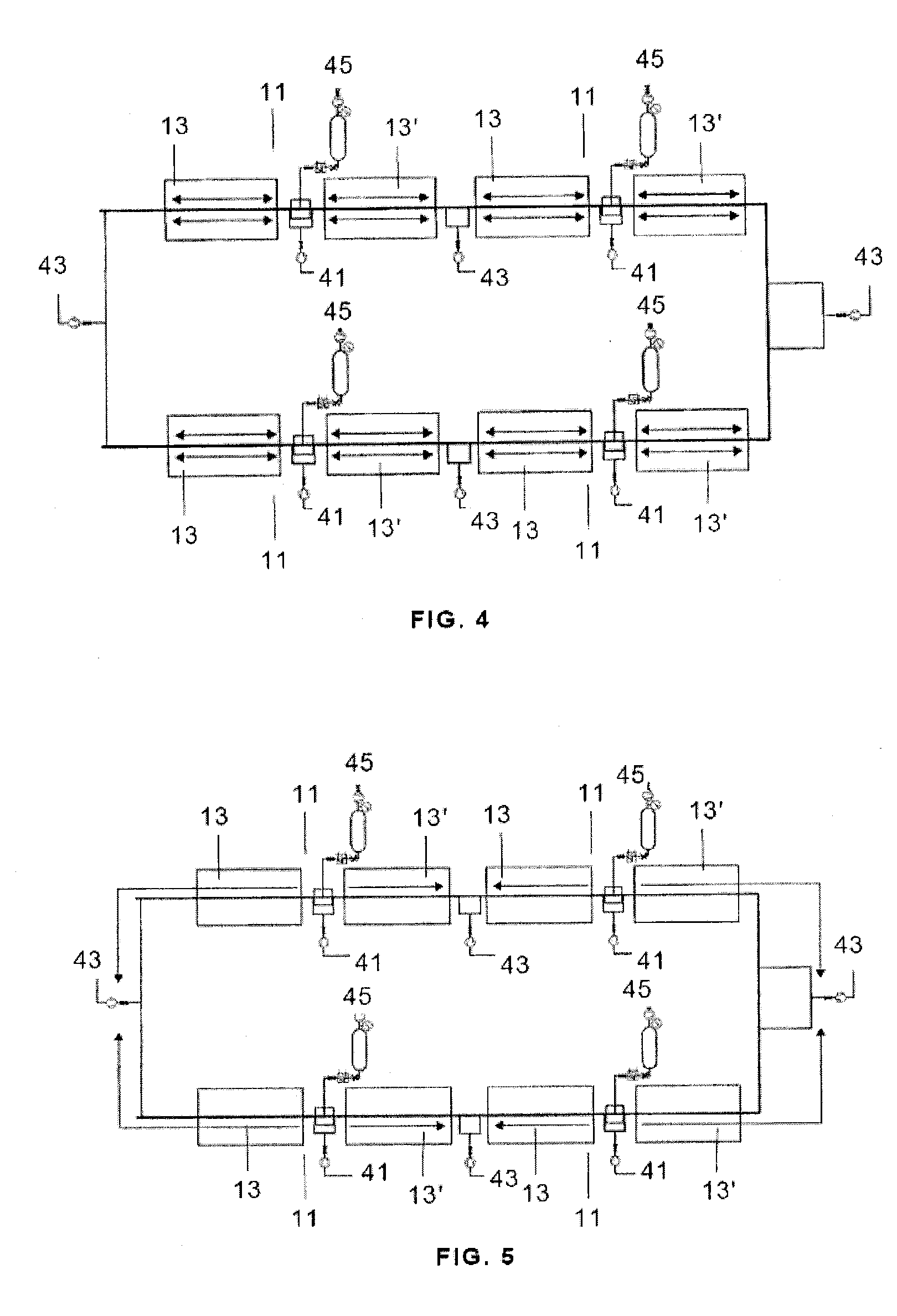
Radiation heat collection device
InactiveUS20100300431A1Minimal levelFlexible and cost-optimized and exploitationSolar heating energySolar heat devicesTube placementMechanical engineering
This invention relates to a device that comprises at least one collection unit (11), equipped with a collection tube (21) placed on supports (23), which is formed by an inner absorber tube (31) shaped as a continuous tube and an outer envelope tube (33). The collection unit (11) also comprises reflectors (15) that direct the radiation toward the collection tube (21). Moreover, the device comprises means (41, 43) designed to maintain the collection tube (21) space between the absorber tube (31) and the envelope tube (33) at a pressure of between 5·10−1-5·10−2 mbar. The main advantages of the invention include the reduction in the breaking of glass due to the lower stresses to fatigue, an increase in the effective collection surface (97%-98%) and active management of the vacuum, which makes it possible to monitor the evolution thereof at all times.
Owner:ARIES ING Y SISTEMAS
Data encoding method
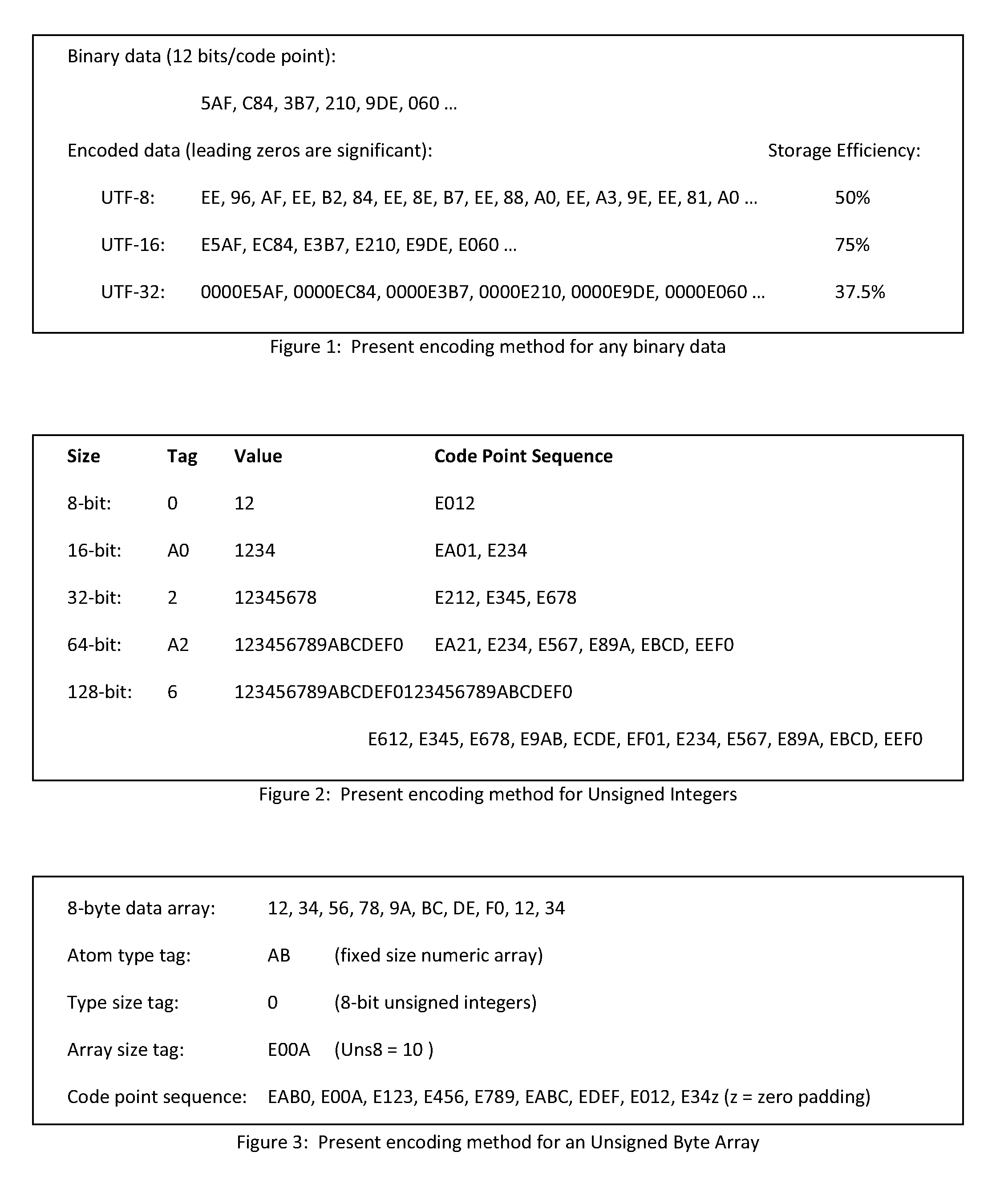
ActiveUS20110037625A1Efficient methodMaximize process efficiencyIndividual digits conversionNatural language data processingStorage efficiencyUTF-8
The present encoding method encodes binary data as sequences of code points occupying the Private Use Area of the Unicode Basic Multilingual Plane. The encoded data can be contained within a stream of UTF-8, UTF-16 or UTF-32 code units and subsequently decoded to yield the original binary data. This method requires minimal processing for both encoding and decoding operations, and yields a 75% storage efficiency limit. Each datum encoding sequence includes type and encoding length information, enhancing parse and search operation performance. The type system includes elements for creating complex structured data-text sequences, and a mechanism for application defined extensions.
Owner:JOYCE STEPHEN ALLYN
Process for preparing a noncrystallizable polyol syrup
The invention relates to a process for preparing a noncrystallizable polyol syrup stable to heat and to alkaline medium, using a step of hydrogenation of a sugar syrup and a step of caramelization of the hydrogenated sugar syrup, wherein the hydrogenated and caramelized sugar syrup is subjected to purification on ion-exchange resins, the said purification comprising at least one passage over a strong cationic resin at a temperature of less than 50° C., the said temperature being chosen according to the level of reducing sugars desired in the noncrystallizable polyol syrup. It also relates to the use of the polyol syrup obtained for the preparation of toothpastes.
Owner:ROQUETTE FRERES SA
Ionic additives for extreme low dielectric constant chemical formulations
InactiveUS6896955B2Minimal levelSufficient mechanical propertySilicaLayered productsAlkali ionsPhosphate
A process for depositing porous silicon oxide-based films using a sol-gel approach utilizing a precursor solution formulation which includes a purified nonionic surfactant and an additive among other components, where the additive is either an ionic additive or an amine additive which forms an ionic ammonium type salt in the acidic precursor solution. Using this precursor solution formulation enables formation of a film having a dielectric constant less than 2.5, appropriate mechanical properties, and minimal levels of alkali metal impurities. In one embodiment, this is achieved by purifying the surfactant and adding ionic or amine additives such as tetraalkylammonium salts and amines to the stock precursor solution. In some embodiments, the ionic additive is a compound chosen from a group of cationic additives of the general composition [NR(CH3)3]+A−, where R is a hydrophobic ligand of chain length 1 to 24, including tetramethylammonium and cetyltrimethylammonium, and A− is an anion, which may be chosen from the group consisting essentially of formate, nitrate, oxalate, acetate, phosphate, carbonate, and hydroxide and combinations thereof. Tetramethylammonium salts, or more generally tetraalkylammonium salts, or tetraorganoammonium salts or organoamines in acidic media are added to surfactant templated porous oxide precursor formulations to increase the ionic content, replacing alkali ion impurities (sodium and potassium) removed during surfactant purification, but which are found to exhibit beneficial effects in promoting the formation of the resulting dielectric.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
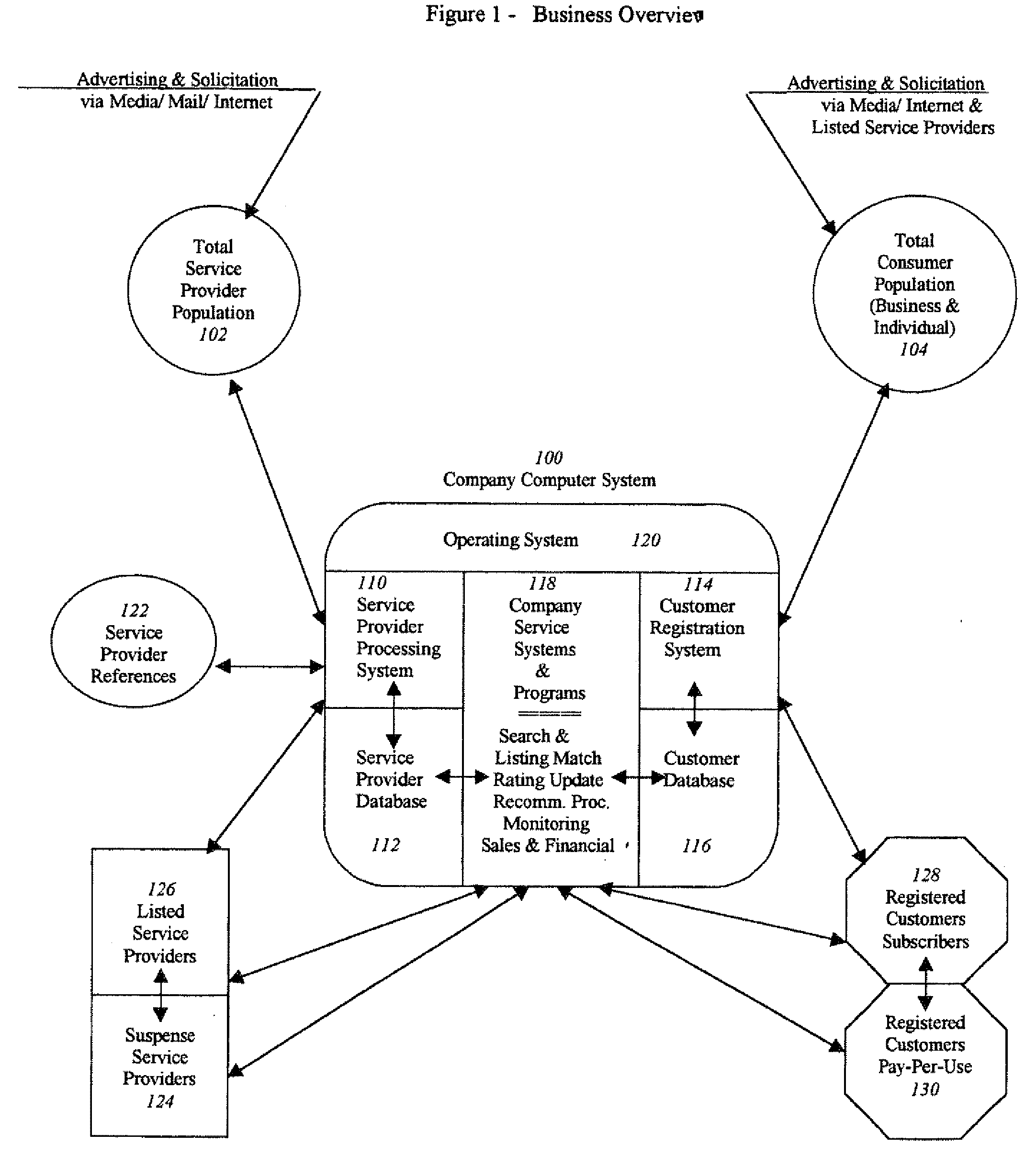
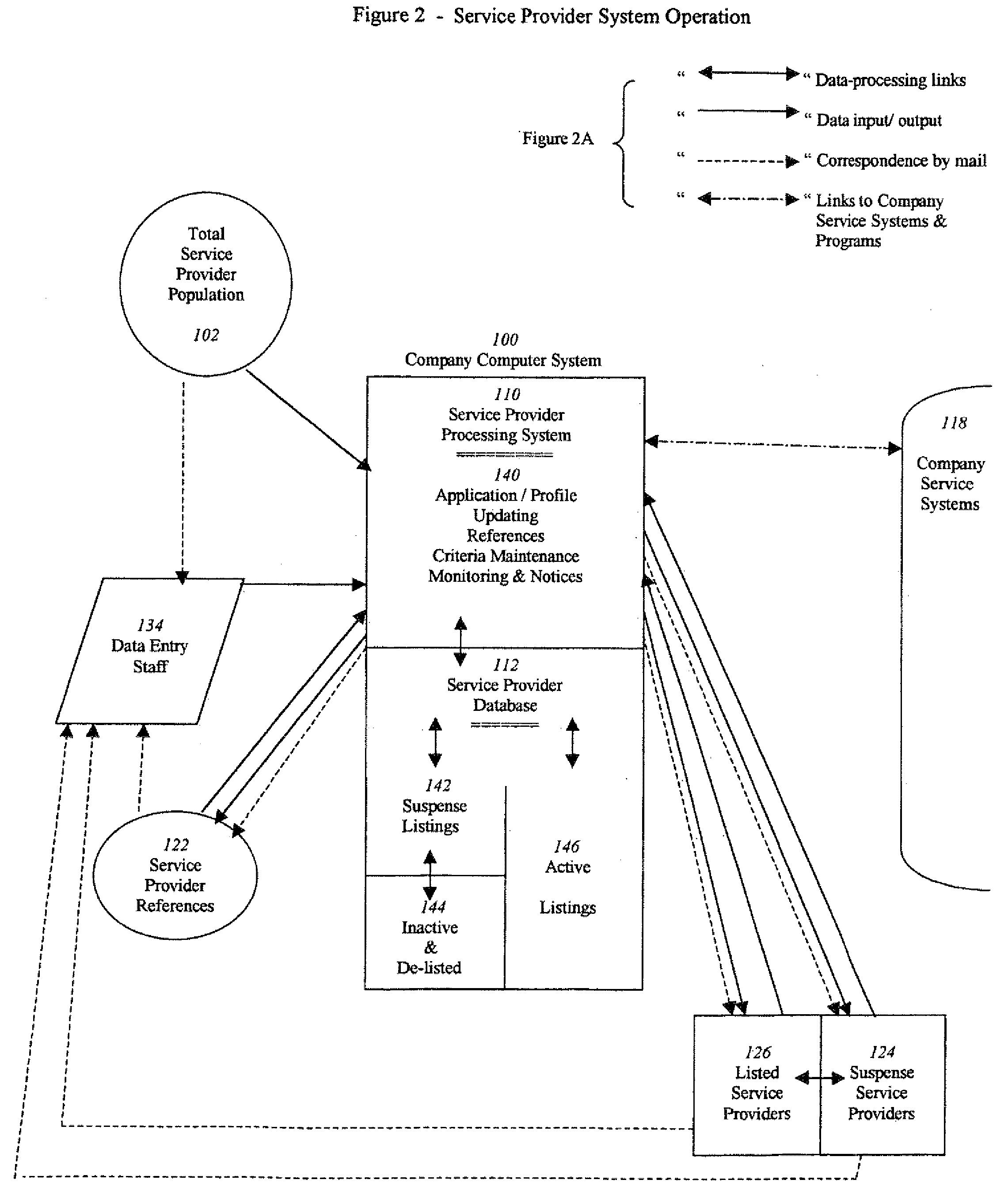
Accessible service provider clearinghouse
InactiveUS20080263016A1Minimal levelEasy accessDigital data processing detailsCustomer communicationsRating systemService provision
A service that maintains a minimum criteria level for service providers to be listed and available for public access. It can list not only the service provider's credentials and insurance support (with monitored expiration dates), but may also provide a current up-to-date rating system by the users themselves, as to the satisfaction level of the quality and reliability of the work performed. It can also offer a double-check of the credentials by customer verification input. Furthermore, the example service can be easily accessible by the general public (for individual or business use) on the Internet, or by printed text directories sold direct or in bookstores.
Owner:LOKITZ SHEILA
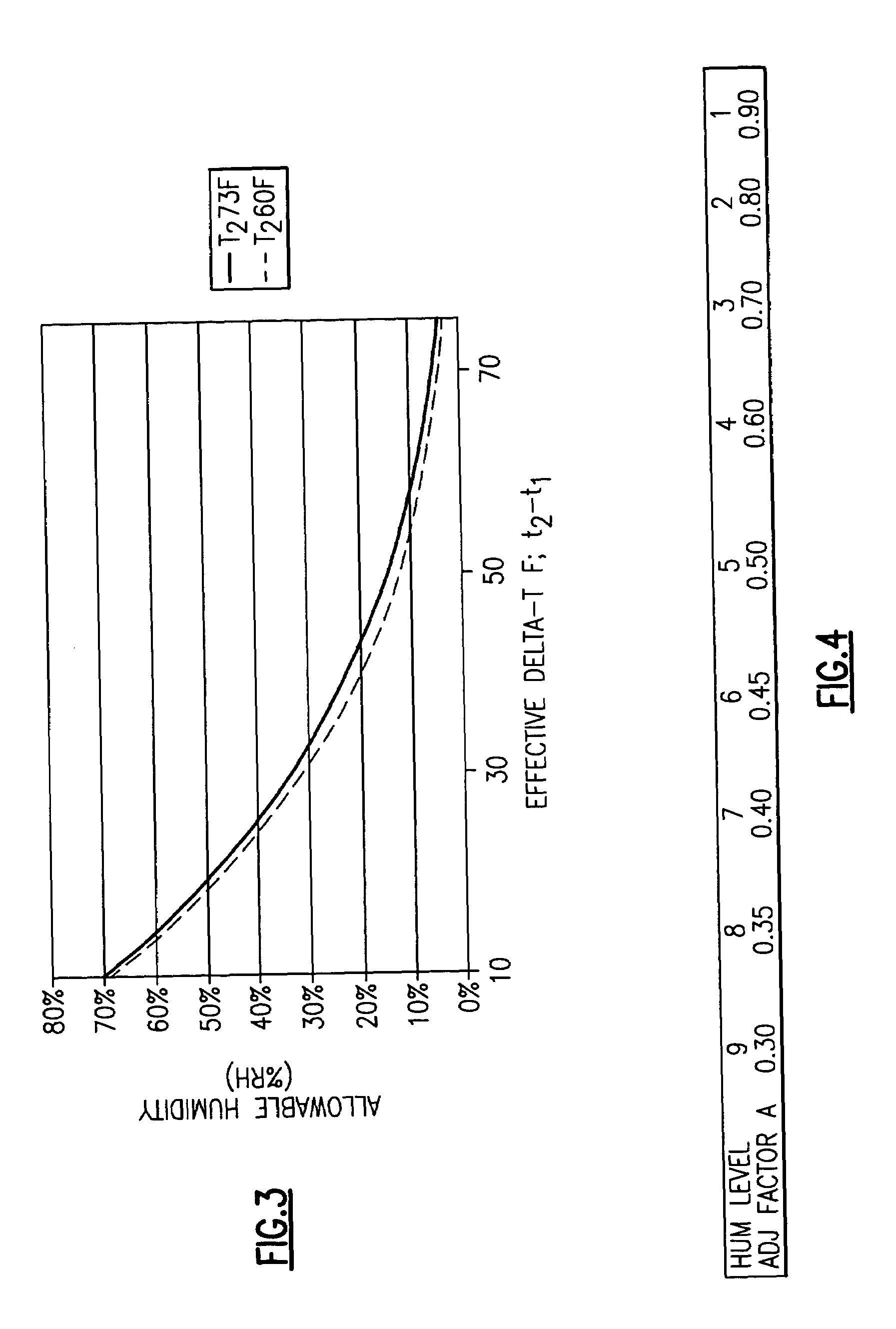
Determination of maximum allowable humidity in indoor space to avoid condensation inside building envelope
ActiveUS7178350B2Reduce moisture contentReduce heat lossMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsEngineeringBuilding envelope
Owner:CARRIER CORP
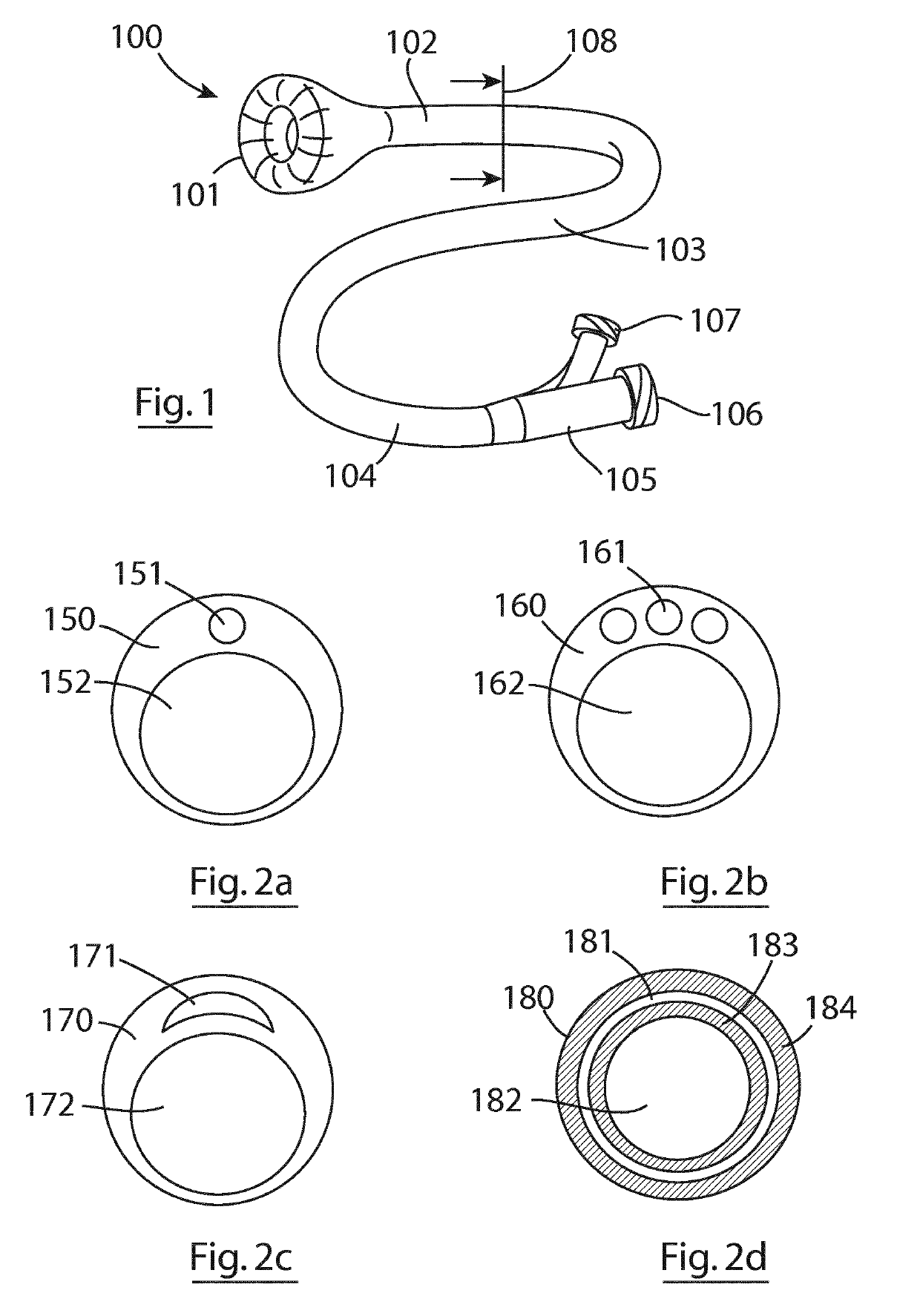
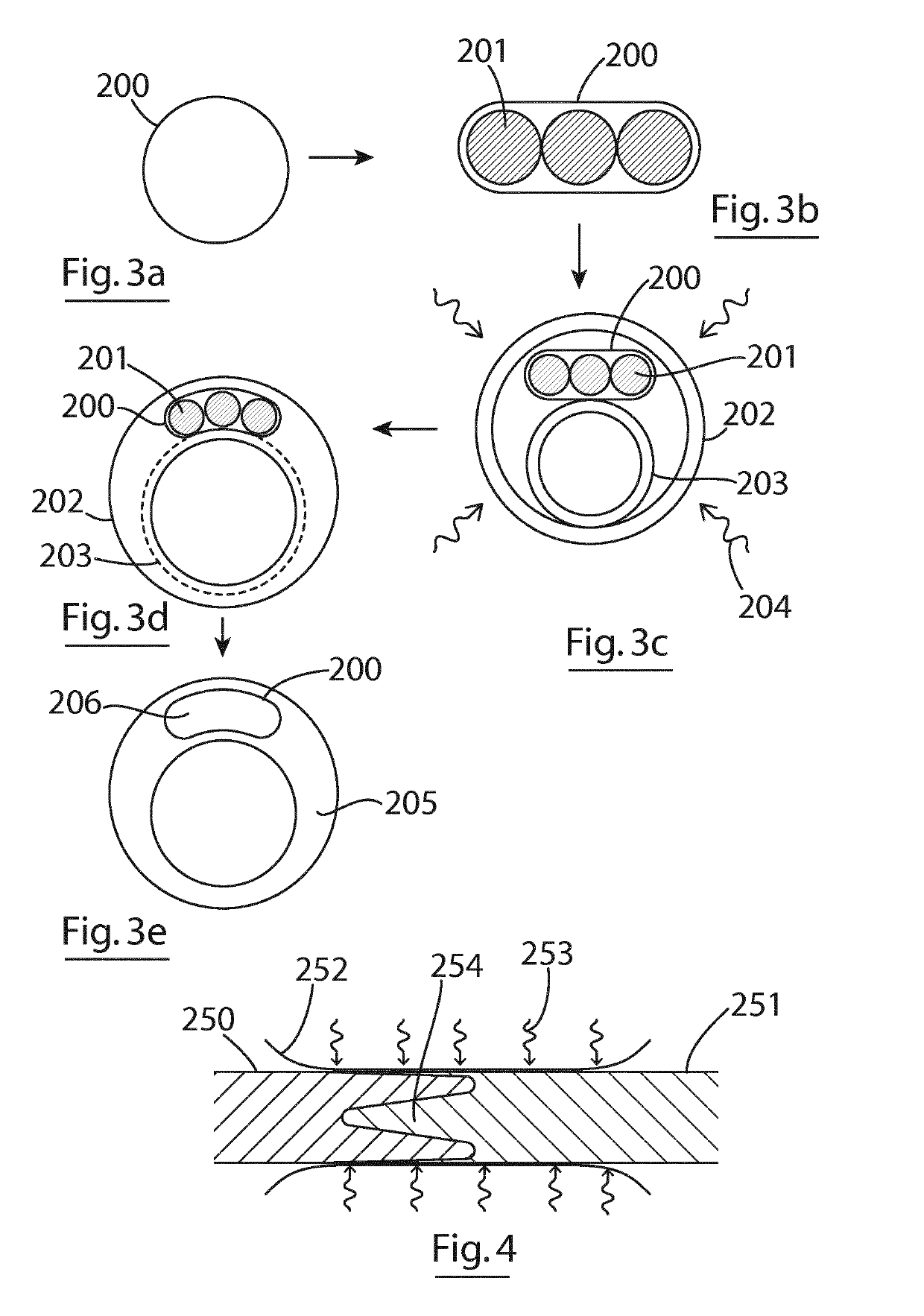
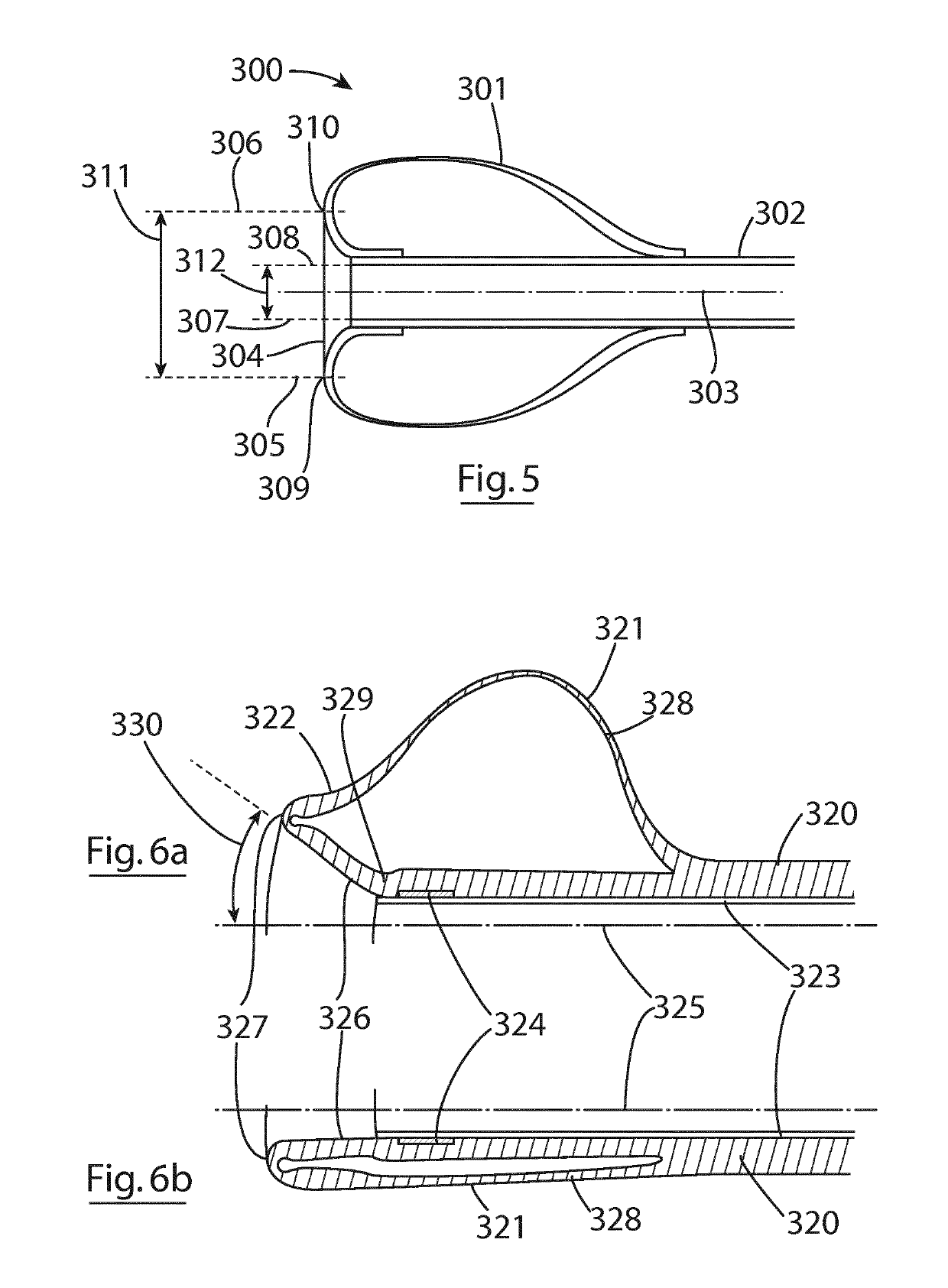
Neonatal airway adaptor
InactiveUS6926005B1Without distortionAvoid distractionTracheal tubesSurgeryAirway adaptorEndotracheal tube
This invention is a neonatal airway adapter (10) with a sliding internal passage (54), which virtually eliminates void volumes (112) within the bore (76) of the airways, such that mixing of the exhaled gases with void gases is reduced, and the waveform of the breath is maintained without undue distortion. Furthermore, the virtual elimination of void volumes reduces the level of re-breathing. The neonatal airway adapter connects to endotracheal tube adapters in such a way as to nullify the effect of the differing internal diameters (20) and internal lengths which are used in ET adapters currently available. The cross section of the internal bore of the airway through which the breath flows from the ET adapter to the connector of the ventilator is maintained almost constant, especially in the region of the gas sampling point (66), to ensure that reasonable conditions of laminar flow, and accurate sampling are maintained.
Owner:ORIDION MEDICAL
System, method and apparatus for electrosurgical instrument with movable suction sheath
ActiveUS20110077643A1Minimal levelLarge levelSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesLeading edgeEngineering
An electrosurgical instrument having active and return electrodes with a movable suction sheath for variable fluid and debris removal during surgical procedures is disclosed. The suction apparatus has an outer sheath that is external to a shaft to provide a lumen. The sheath assembly is axially movable relative to the fluid aspiration element between first and second positions for treating the target site and fluid and debris removal, respectively. The first position positions the distal end of the shaft axially distal to a leading edge of the sheath assembly. The second position positions the distal leading edge of the sheath assembly axially adjacent to the end of the shaft. The fluid aspiration element comprises an inner lumen extending through the shaft, and at least one port extending radially through the shaft. The port is in communication with the inner lumen. A vacuum provides suction through the port and inner lumen.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Method of regulating tension/compression in a multi-frame hot rolling mill, and a corresponding control system
InactiveUS6205829B1Minimal levelRoll force/gap control deviceRolling mill drivesMultiple frameControl system
The value of the rolling torque is measured at each frame through which a metal product passes, and the measurement is performed at the moment when said product reaches the following frame, at which point the frame at which the measurement is performed is switched over to torque regulation. The last frame reached by the product remains in speed regulation and it acts as a controlling frame for all other frames situated upstream therefrom so as to enable them to conserve torque equal to their respective reference torques by adapting their speeds. Once the reference torque measurements have been stored in the control system, regulation is obtained by making use of a distribution key for the stresses between the frames.
Owner:ALSTOM SA
Process for manufacturing highly stressed composite parts
InactiveUS6875297B1Easy maintenanceFacilitate deformationEngine sealsLamination ancillary operationsPhotoinitiatorFiber
A process for making a composite product in which reinforcement fibers are subjected to a composition based on a thermohardening resin and a photoinitiator appropriate to the irradiation by which the composition is to be treated. The resulting pre-impregnated material is introduced into a prepolymerization device, in which the pre-impregnated material is prepolymerized by appropriate irradiation. Lengths of the precomposite are applied to a support, the shape of which is dictated by the shape of one face of the composite part which is to be made, and are stacked one on another in a suitable number and placed snugly against the shape of the support, and the stack is subjected to final molding at a suitable pressure and temperature in order to polymerize the resin and to join the different lengths of precomposite.
Owner:CONCEPTION & DEV MICHELIN SA
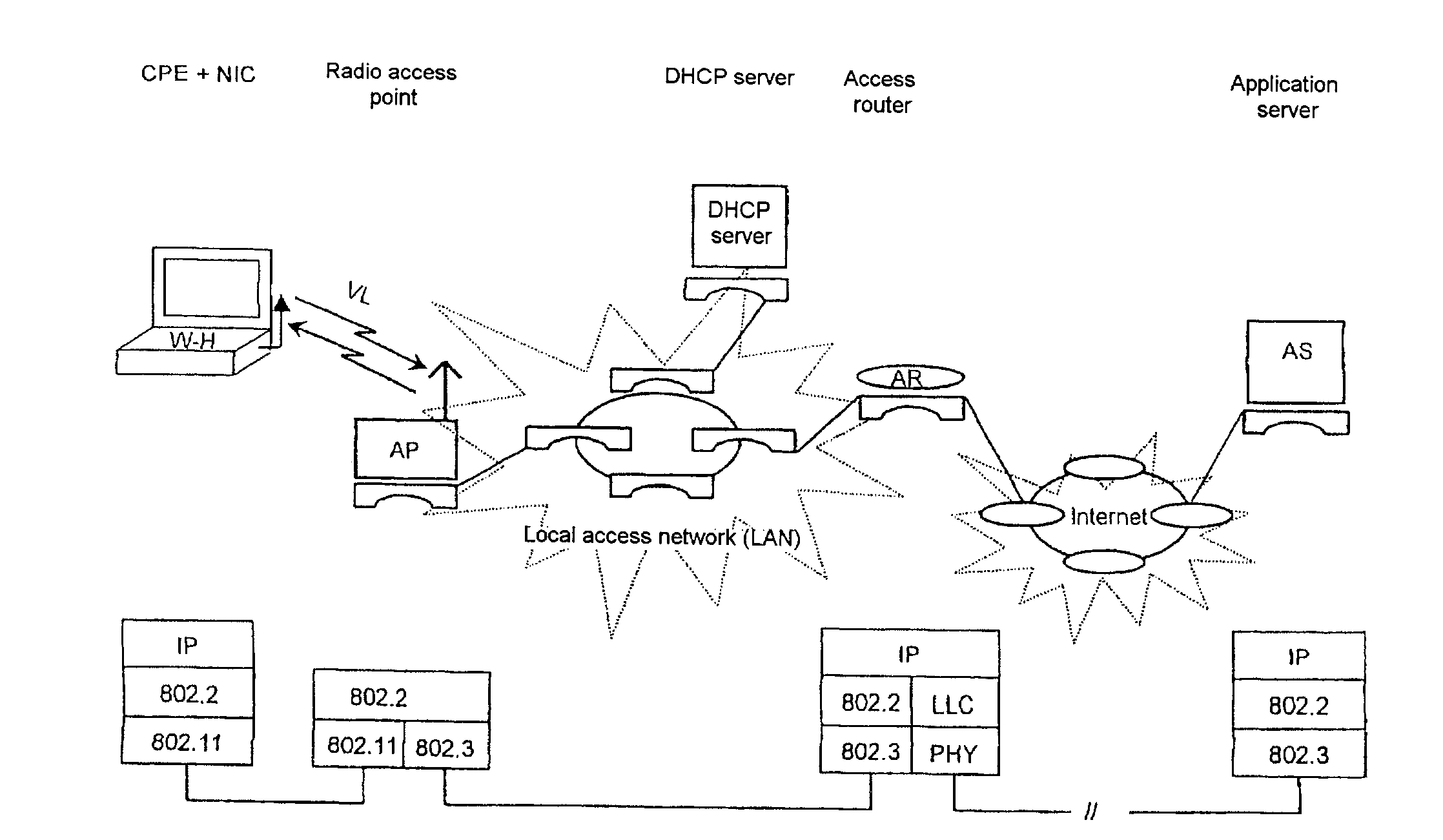
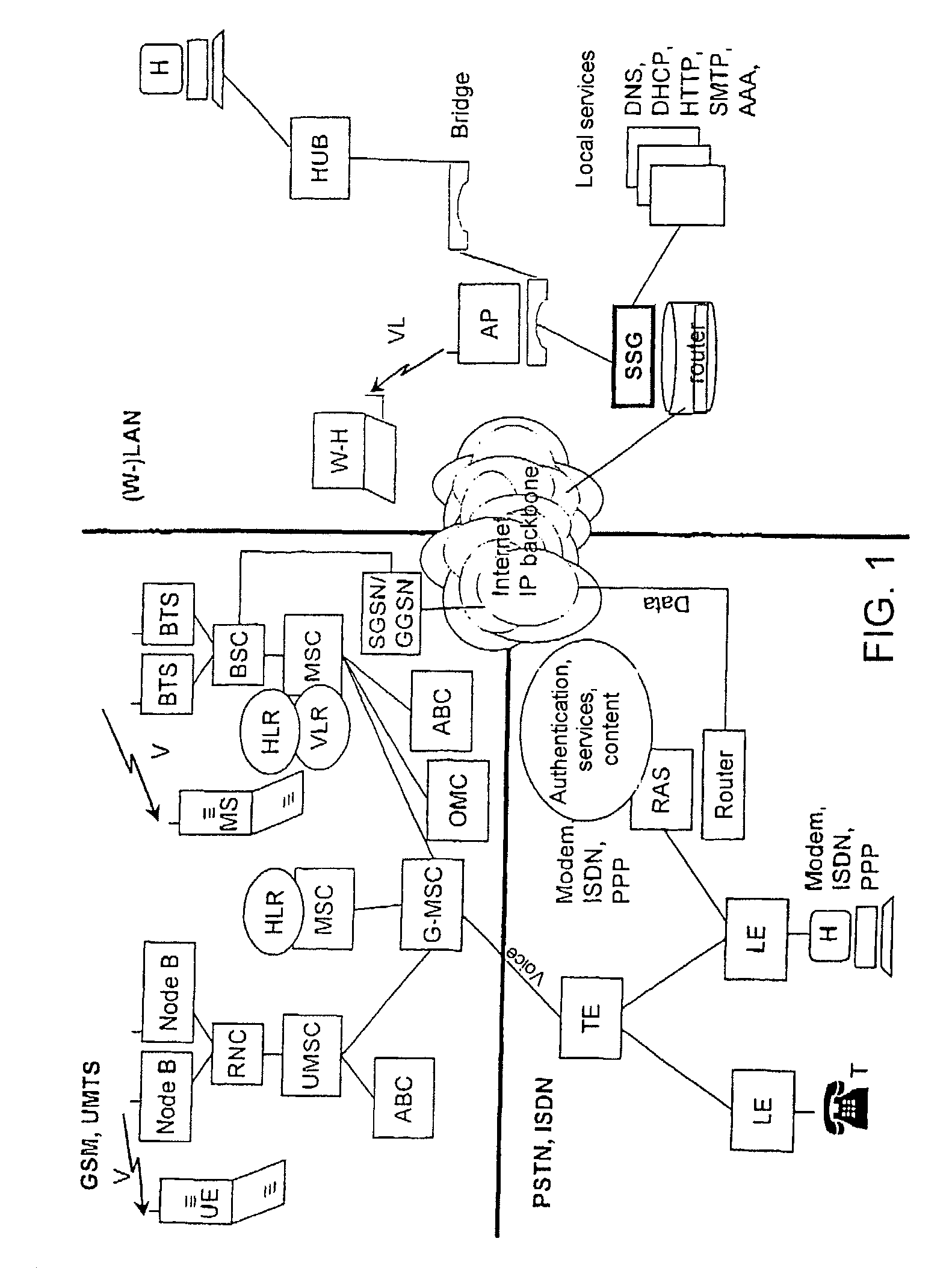
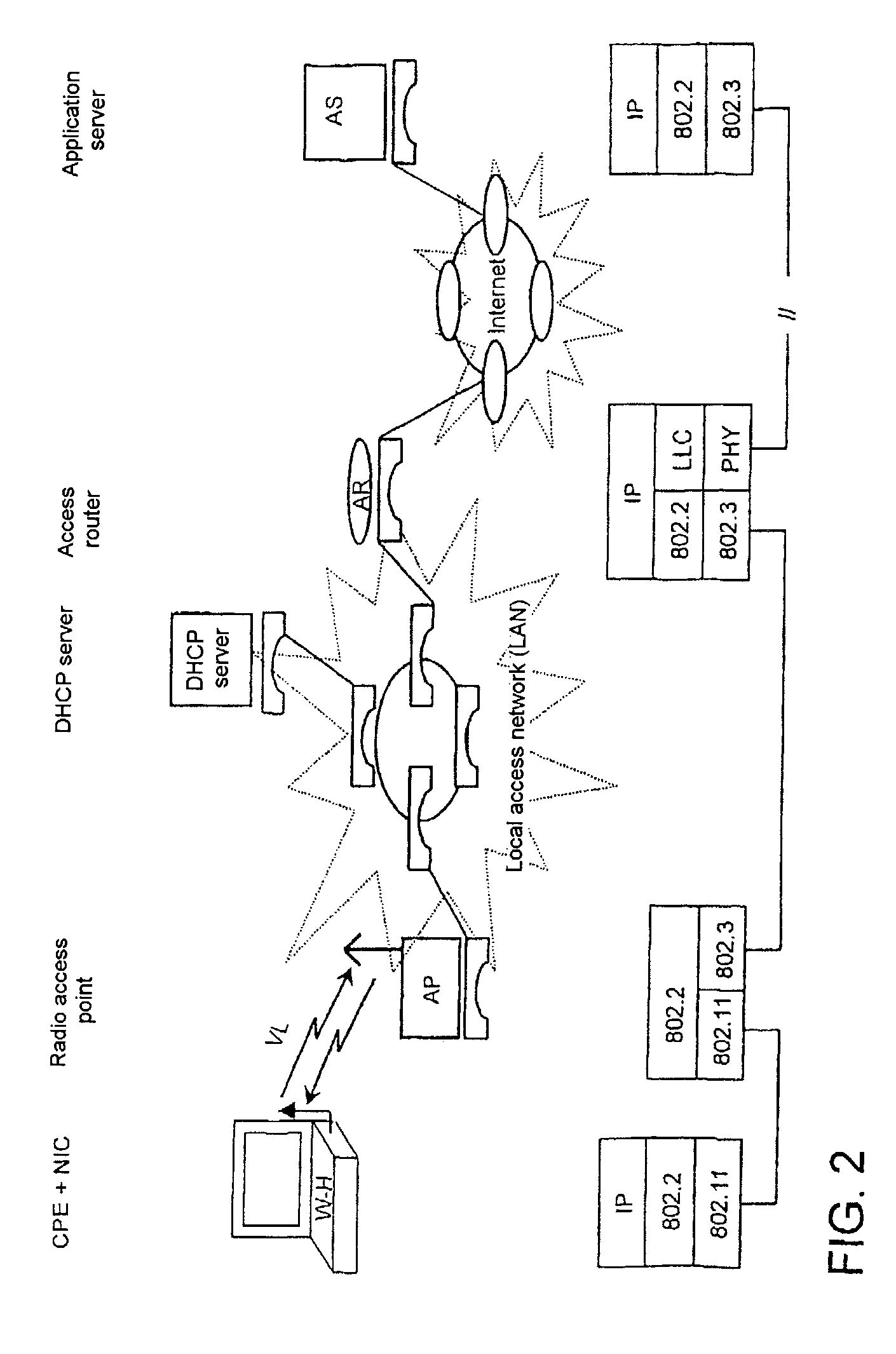
Generic wlan architecture
InactiveUS7522907B2Minimal amount of structuralMinimal amount of programming complexityMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccounting/billing servicesComputer networkNetwork structure
A first network is structured according to a first technology, especially a data network, comprising one or several network devices and / or interfaces, which are configured to establish communication with at least one station using the first technology and have basic functions for autonomous operation of the first network. In order to be able to collect subscriber-related data from a data source outside the network, especially a second network structured according to a second technology, more particularly a cellular mobile telephone network, when a subscriber who is not registered in the first network is connected, one of the two networks generically enables logical functions of components of the other network. A network facility enables the implementation of the above-mentioned method.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Water treatment compositions
InactiveUS7201856B2Minimising manganese-associated post-flocculation discolorationMinimising or preventing the post-flocculation discoloration effectWater softeningSedimentation separationFood additiveWater insoluble
Compositions, methods and kits for purifying and clarifying and / or nutrifying contaminated drinking water and which comprise a primary coagulant material, a microbiocidal disinfectant and an oxidant system. Highly preferred compositions also contain one or more of a bridging flocculent material, the levels and ratios of coagulant to flocculent preferably falling within certain ranges, a cationic coagulant aid, especially chitosan, a water-soluble alkali, a water-insoluble silicate, and a food additive or nutrient source. The purified water remains free of discoloration for extended periods of storage.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
A clot retrieval system for removing occlusive clot from a blood vessel
ActiveUS20190167287A1Minimizes shear forceFacilitate easy entryStentsBalloon catheterBlood vessel spasmBlood vessel
A clot capture catheter comprises an elongate tubular shaft having a proximal end, a distal end and an inflatable expansile member at the distal end. The expansile member is inflatable from a collapsed delivery configuration to an expanded configuration. In the expanded configuration, the expansile member extends to define a funnel shape having an enlarged distal clot entry mouth at the distal-most end of the catheter. In the expanded configuration, the expansile member may extend distally beyond the distalmost tip of the shaft. The expansile member may be integral with the distal tip of the catheter shaft.
Owner:NEURAVI
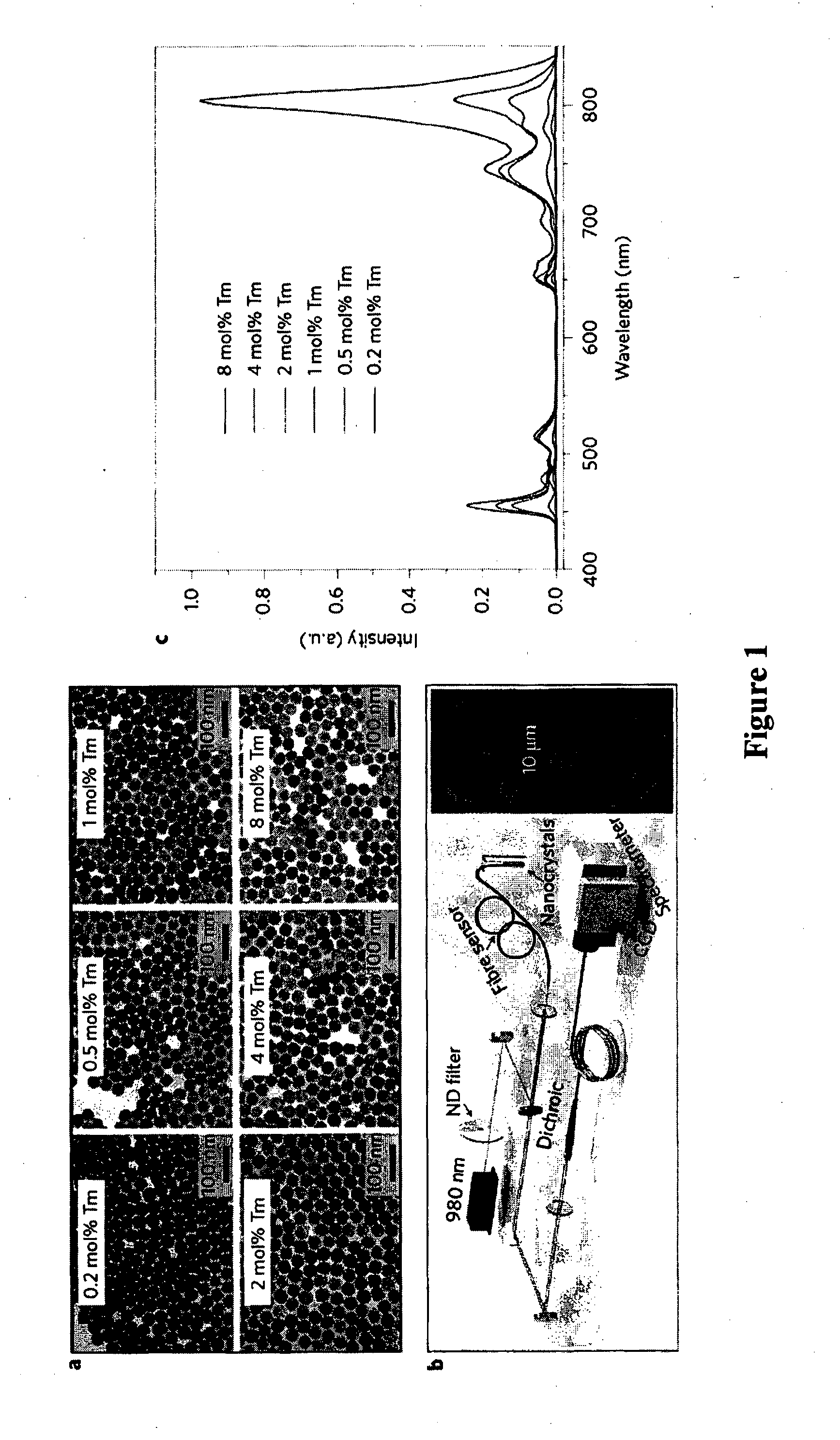
Enhancing upconversion luminescence in rare-earth doped particles
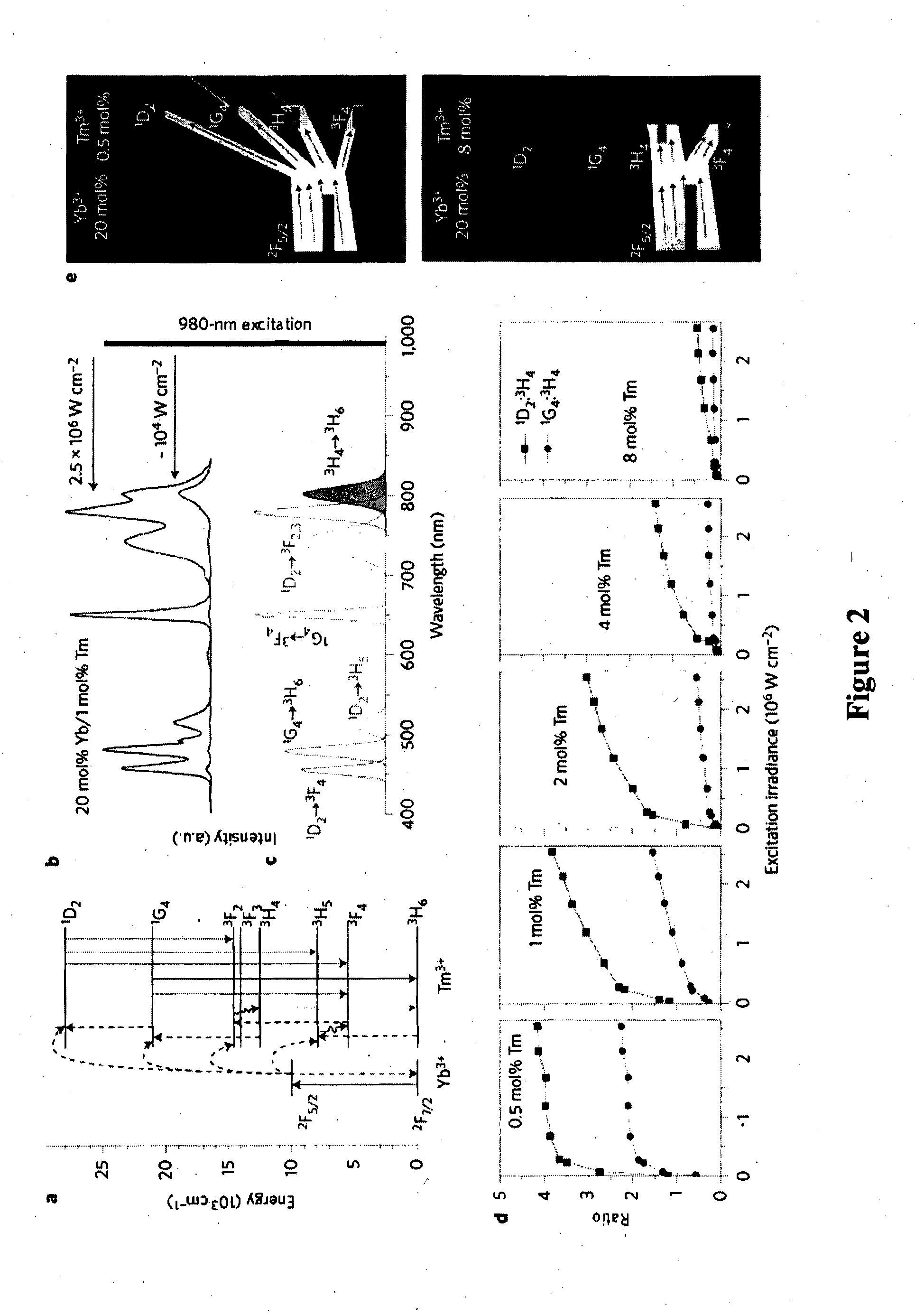
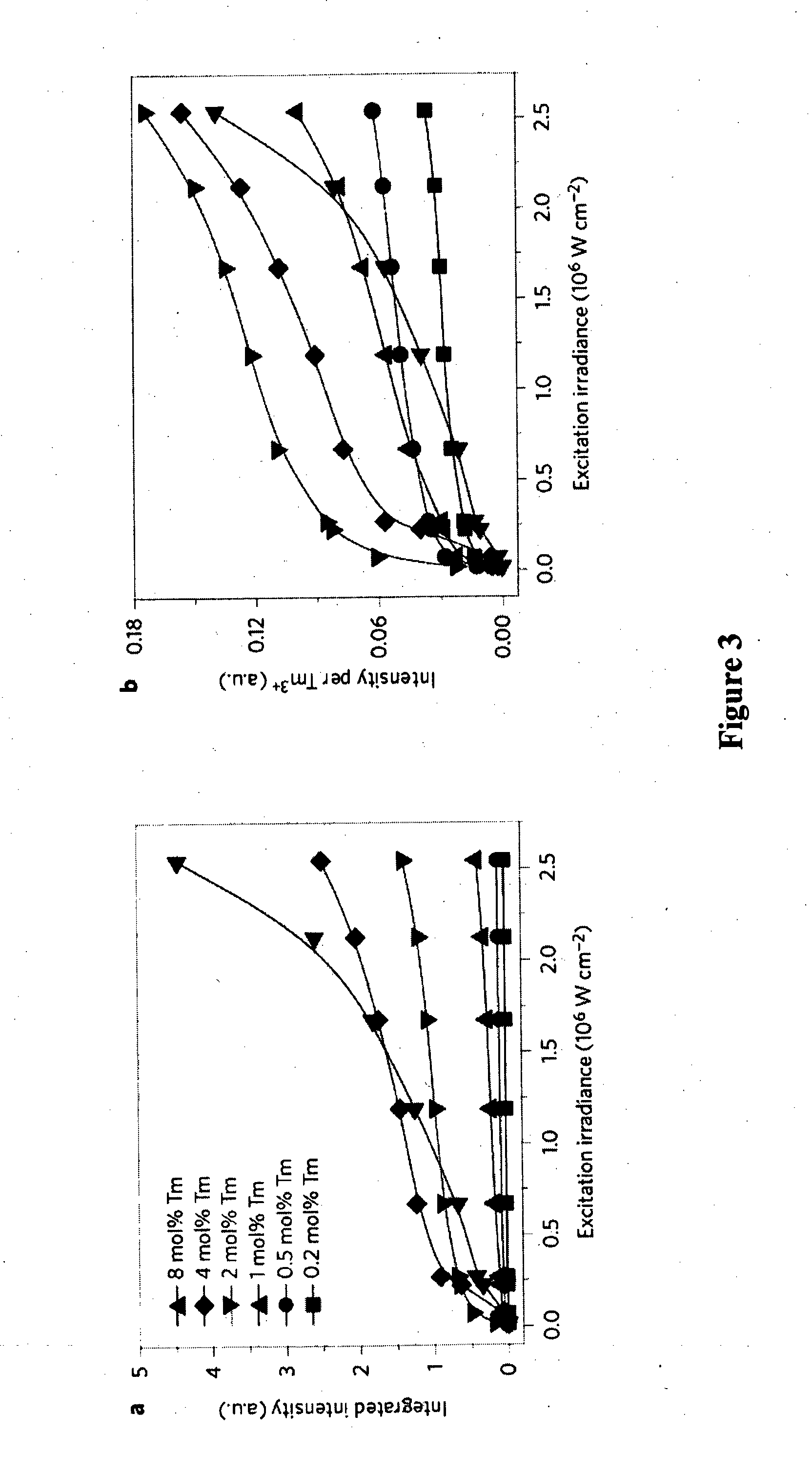
InactiveUS20150252259A1Enhancing upconversion luminescenceIncrease irradiancePowder deliveryPattern printingRare earthConcentration quenching
Disclosed is a method for enhancing upconversion luminescence of rare-earth doped particles comprising a host material, an enriched concentration of activator (emitter) and a sufficient concentration level of sensitiser, the method comprising subjecting the particles to increased irradiance. The increased irradiance is higher than presently used relatively low irradiance levels. Enhancing upconversion luminescence involves enhancing luminescence intensity, brightness and / or upconversion efficiency. Particles are preferably subjected to an irradiance power density sufficient to overcome or reverse concentration quenching. The activator preferably has an intermediate meta stable energy level which accepts resonance energy from the sensitiser excited state level. In another form, particles are designed to minimize or exclude quenchers from the upconversion system between sensitizer and activator, such as the core-shell particles wherein the core comprises the host material, sensitiser and the activator, and the shell comprises a material which prevents, retards or inhibits surface quenching.
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
Multiple simultaneous bin sizes
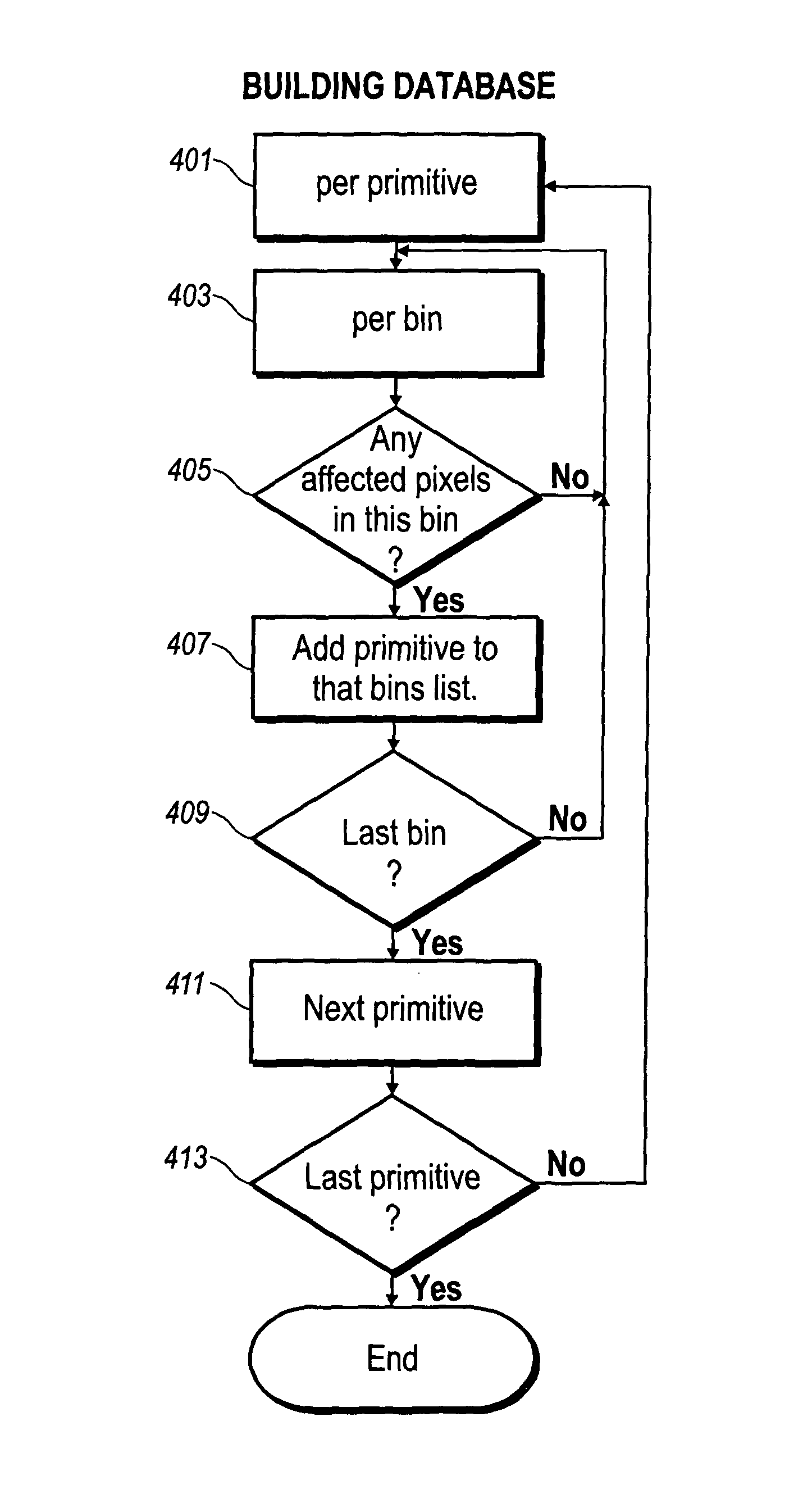
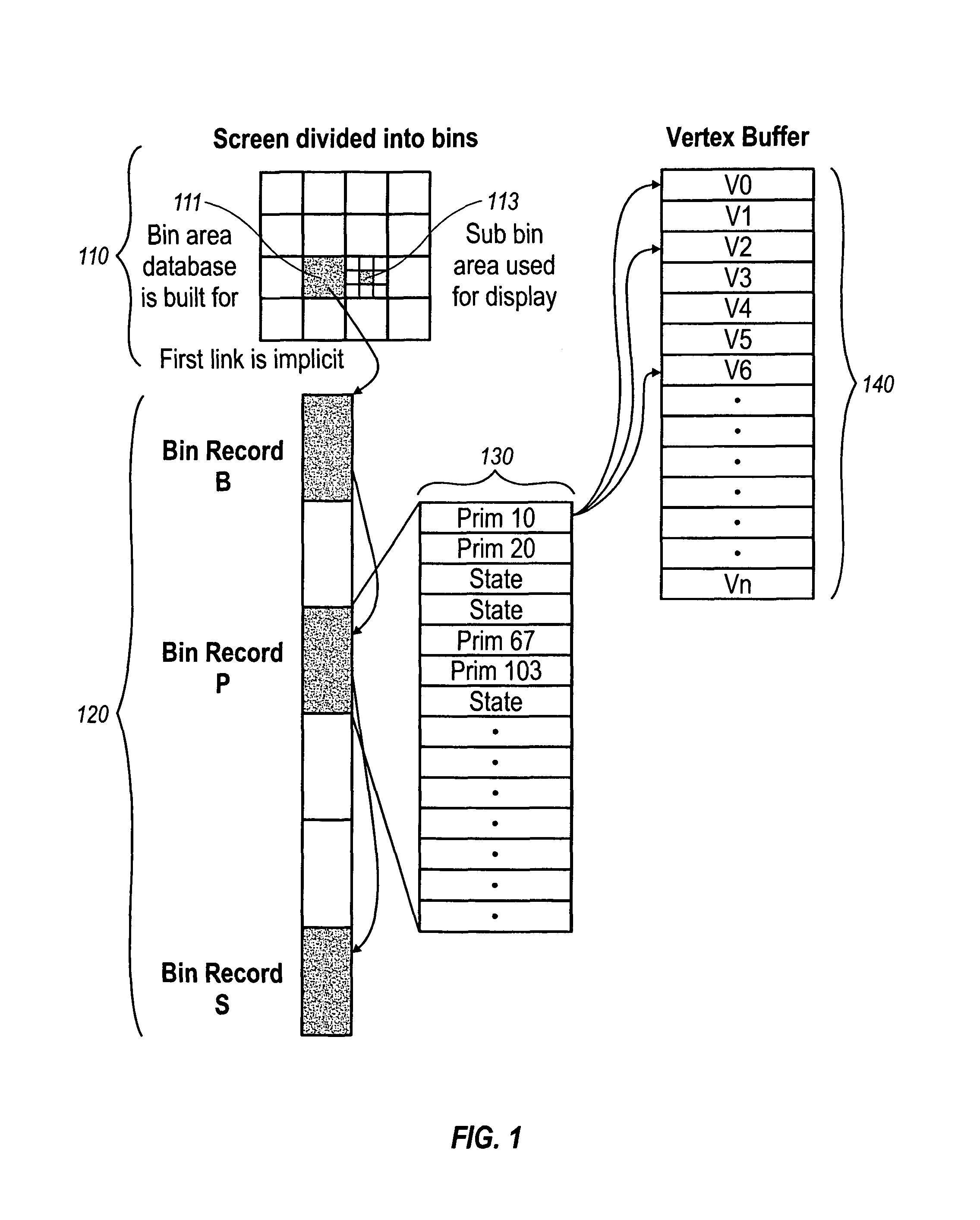
ActiveUS9098943B1Increased complexityIncrease frame rateImage memory managementCathode-ray tube indicatorsTrade offsMemory bandwidth
Conflicts between the database-building and traversal phases are resolved by allowing the database bin size to be different from the display bin size. The database bin size is some multiple of the bin display bin size, and when there are multiple display bins in a database bin, each database bin is traversed multiple times for display, and the rasterizer discards primitives outside of the current display bin. This allows a trade off between memory bandwidth consumed for database building and bandwidth consumed for display, particularly when the display traversal is done multiple of times.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Pressure-sensitive adhesive tape
The present invention relates to a pressure-sensitive adhesive tape including a substrate and at least one pressure-sensitive adhesive layer disposed on at least one surface of the substrate, in which the substrate is formed of an olefinic resin composition containing a polyolefin resin and a metal hydroxide, and in which the pressure-sensitive adhesive layer is formed of an emulsion-type acrylic adhesive composition containing an acrylic emulsion in which emulsion particles have a mean particle size of 0.2 μm or less. The pressure-sensitive adhesive tape of the invention has excellent edge-peeling resistance and is capable of exhibiting a suitable rewinding power.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com