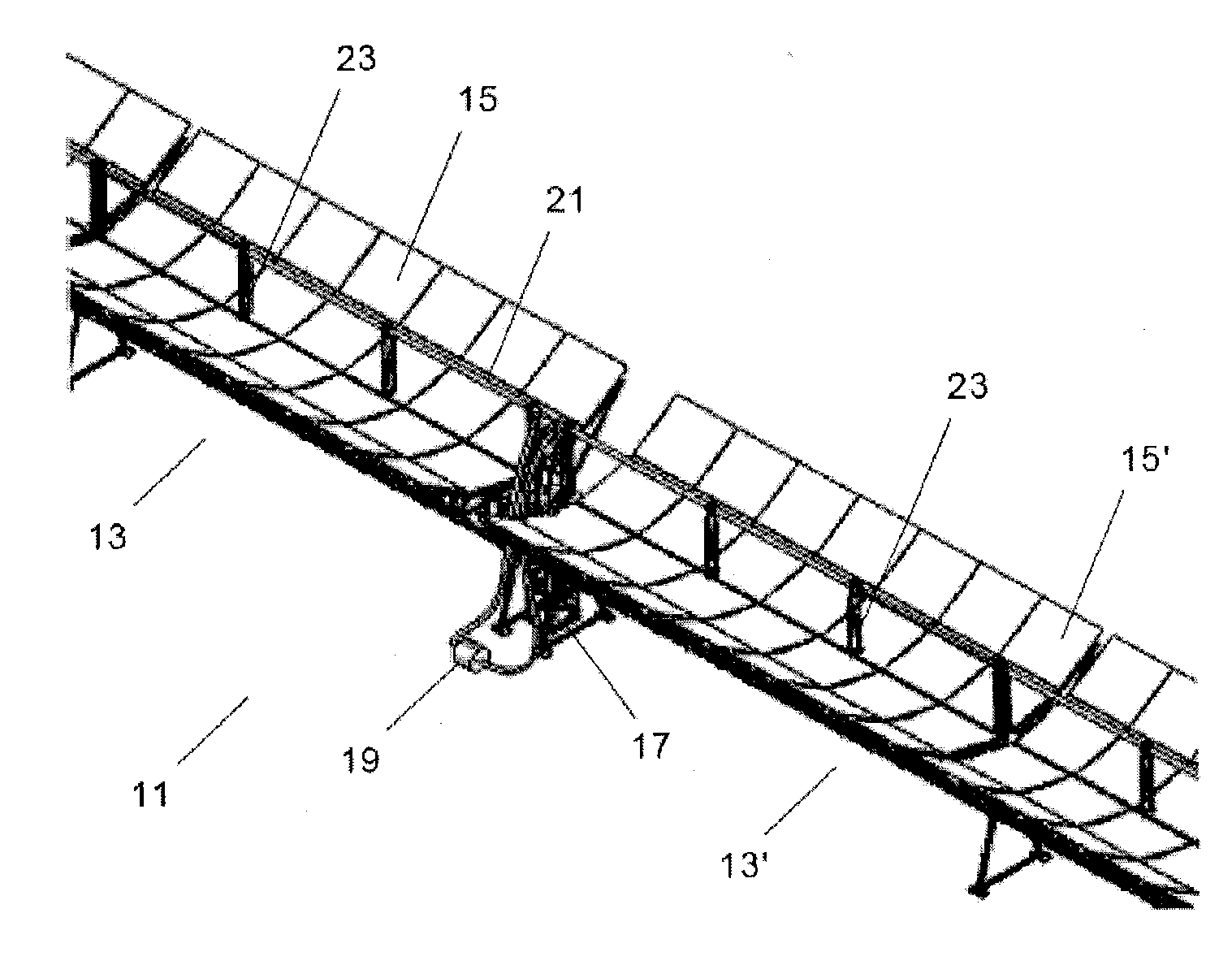
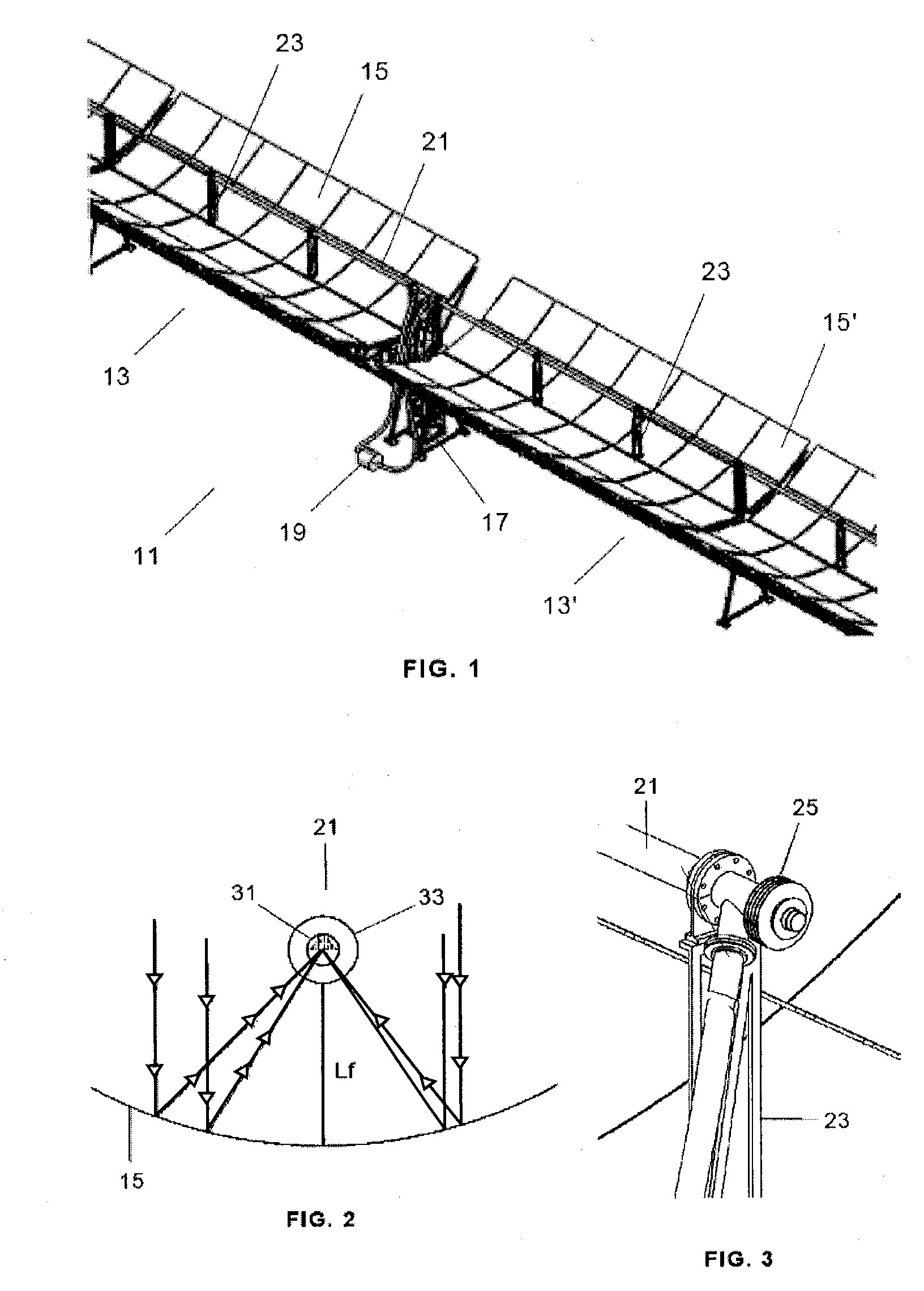
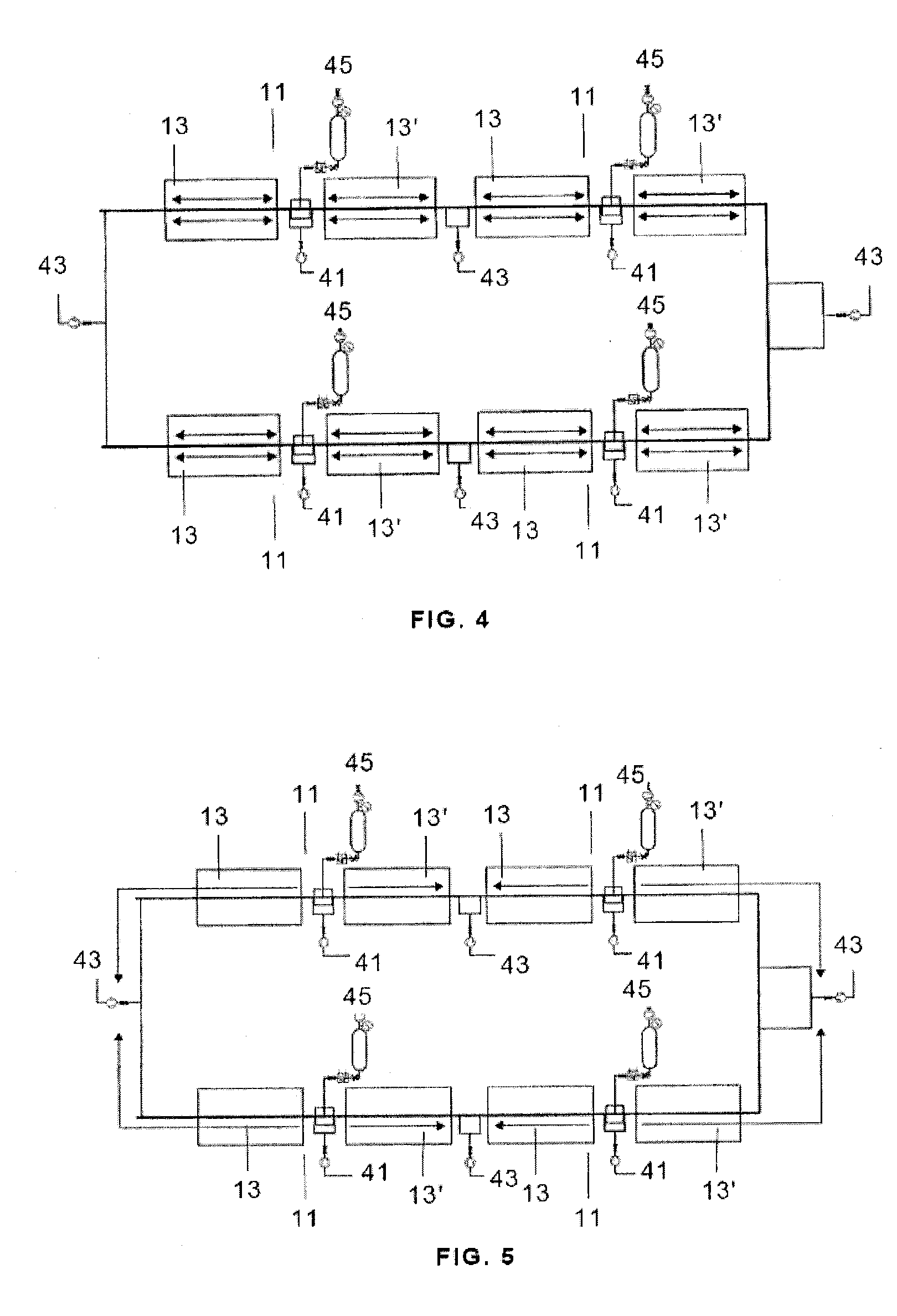
Radiation heat collection device
a technology of radiation heat collection and heat collection tube, which is applied in the direction of solar heat collectors with working fluids, solar radiation concentration, solar heat collectors safety, etc., can solve the problems of high cost of absorber tubes, significant yield loss, and loss of vacuum, and achieve the effect of reducing the level of inoperativity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0072]As regards the segment joints of outer envelope tube 33, below we will describe this invention, in accordance with FIGS. 8-10.
[0073]Each joint 51 comprises:[0074]Two flanges 53, 53′ with axial tightening means (FIGS. 8 and 9 do not show the typical bolts used in this type of flanges, but they do show the flange openings), the configuration whereof includes sloping surfaces 55, 55′, which co-operate with enlarged edges 57, 57′ of the ends of segments 35, 35′ of envelope tube 33 through contact elements 59, 59′; these have a high elasticity and a low hardness in order to prevent the generation of local stresses in the glass.[0075]A ring 61, placed between flanges 53, 53′, with two hermetic sealing bands 63, 63′ designed to maintain the vacuum, with a fixation base 69 on a support 23.[0076]An insulation crown 62 bound to ring 61, and support and slide means for inner absorber tube 31, consisting of inner radial teeth 64 which provide point contacts with inner absorber tube 31 and...
second embodiment
[0081]In a second embodiment, as may be observed in FIGS. 11-14, joints 81 comprise:[0082]Two clamp-flanges 83, 83′ with radial tightening means (not shown) that join to frames 84, 84′, which are fixed on supports 23.[0083]An insulation crown 85 with, on the one hand, slots 87, 87′ designed to receive the pair of segments 35, 35′ of outer envelope tube 33, with sufficient clearance to this end, and, on the other hand, support and slide means for inner absorber tube 31 consisting of inner radial teeth 86 which provide point contacts for inner absorber tube 31 and allow it to slide with a suitable tribologic behaviour that minimizes friction and wear. Insulation crown 85 also fulfils a thermal insulation function in order to minimize losses by conduction. Preferably, it is made of a ceramic material.[0084]Two pairs of sealing bands 89, 89′ placed on lateral openings of insulation crown 85, on the edges of said slots 87, 87′, such that said segments 35, 35′ remain between them and, con...
third embodiment
[0087]In the invention, illustrated in FIGS. 15-18, a group of two segments 36, 37 of outer envelope tube 33 is united by means of a joint 95 fixed onto a support 23 and the ends of that group are united to other adjacent groups by means of pairs of joints 95′ supported in a displaceable manner on a support 23 with an intermediate bellows device 97 which, in turn, facilitates welding of the components of inner absorber tube 31 between two joints 95′ by the contraction of bellows 97 and the subsequent assembly thereof.
[0088]As observed in FIG. 15, the group formed by segments 36 and 37, which has a length L of, for example, 12 m, is centrally united by a joint 95 fixed onto a support 23 and, on the ends, by joints 95′ supported in a displaceable manner on supports 23. In turn, end joints 95′ of each group are connected by means of a bellows 97. The arrows, f, indicate the displacements of the end joints as a consequence of the dilations of segments 36, 37 of outer envelope tube 33.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com