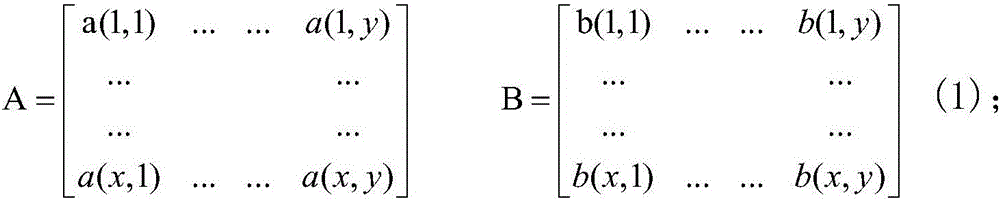Patents
Literature
258 results about "Low Confidence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A response indicating a low level of confidence.
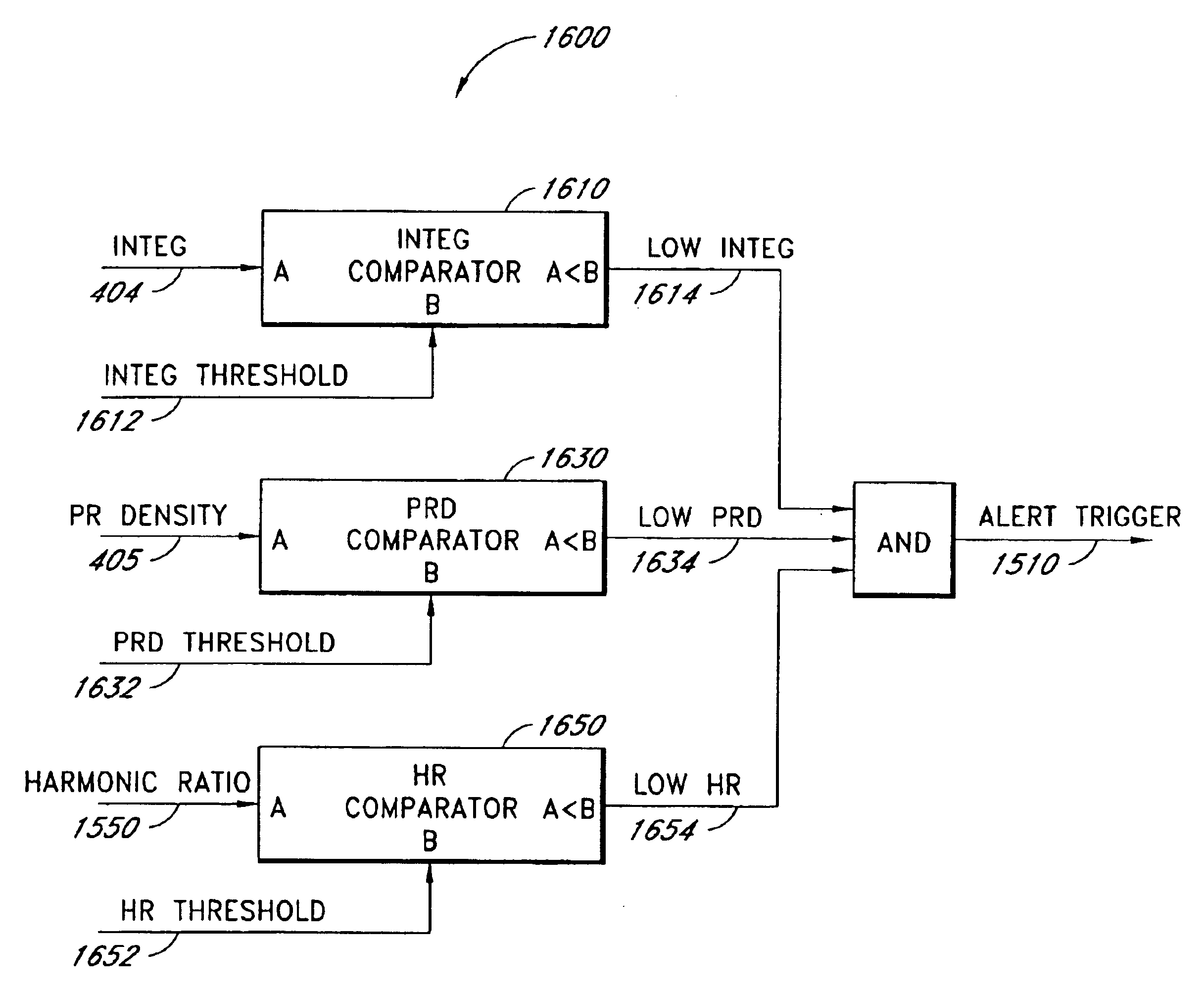
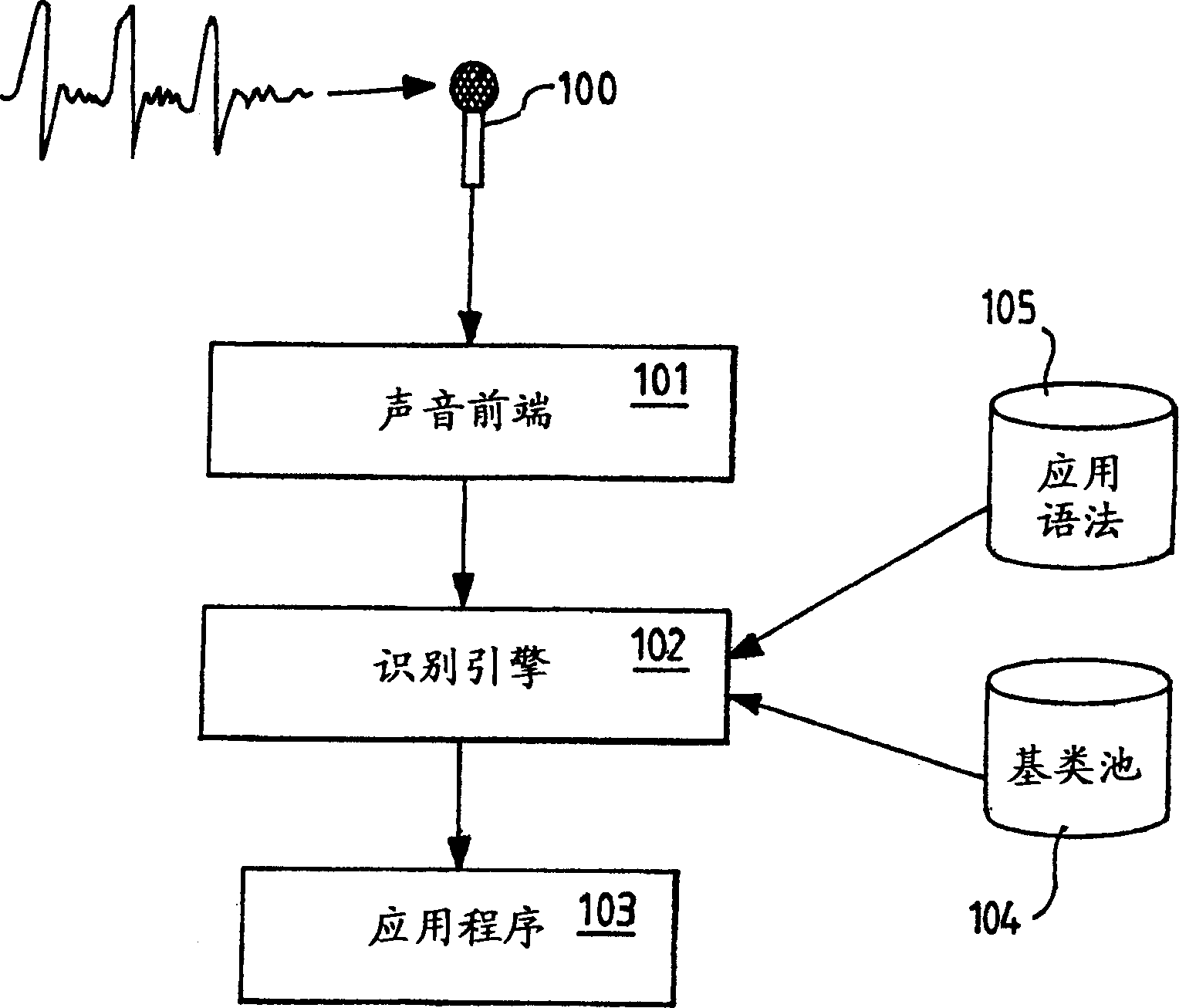
Pulse oximetry data confidence indicator
InactiveUS6996427B2Reduce probabilitySensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateSignal qualityPulse rate
A data confidence indicator includes a plurality of physiological data and a plurality of signal quality measures derived from a physiological sensor output, and a plurality of comparator outputs each responsive to one of the measures and a corresponding one of a plurality of thresholds. An alert trigger output combines the comparator outputs. A low signal quality warning is generated in response to the alert trigger output, wherein the thresholds are set so that the warning occurs during a time period when there is low confidence in the data. The alert may be in the form of a message generated on the pulse oximeter display to warn that the accuracy of saturation and pulse rate measurements may be compromised. A confidence-based alarm utilizes signal quality measures to reduce the probability of false alarms when data confidence is low and to reduce the probability of missed events when data confidence is high.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
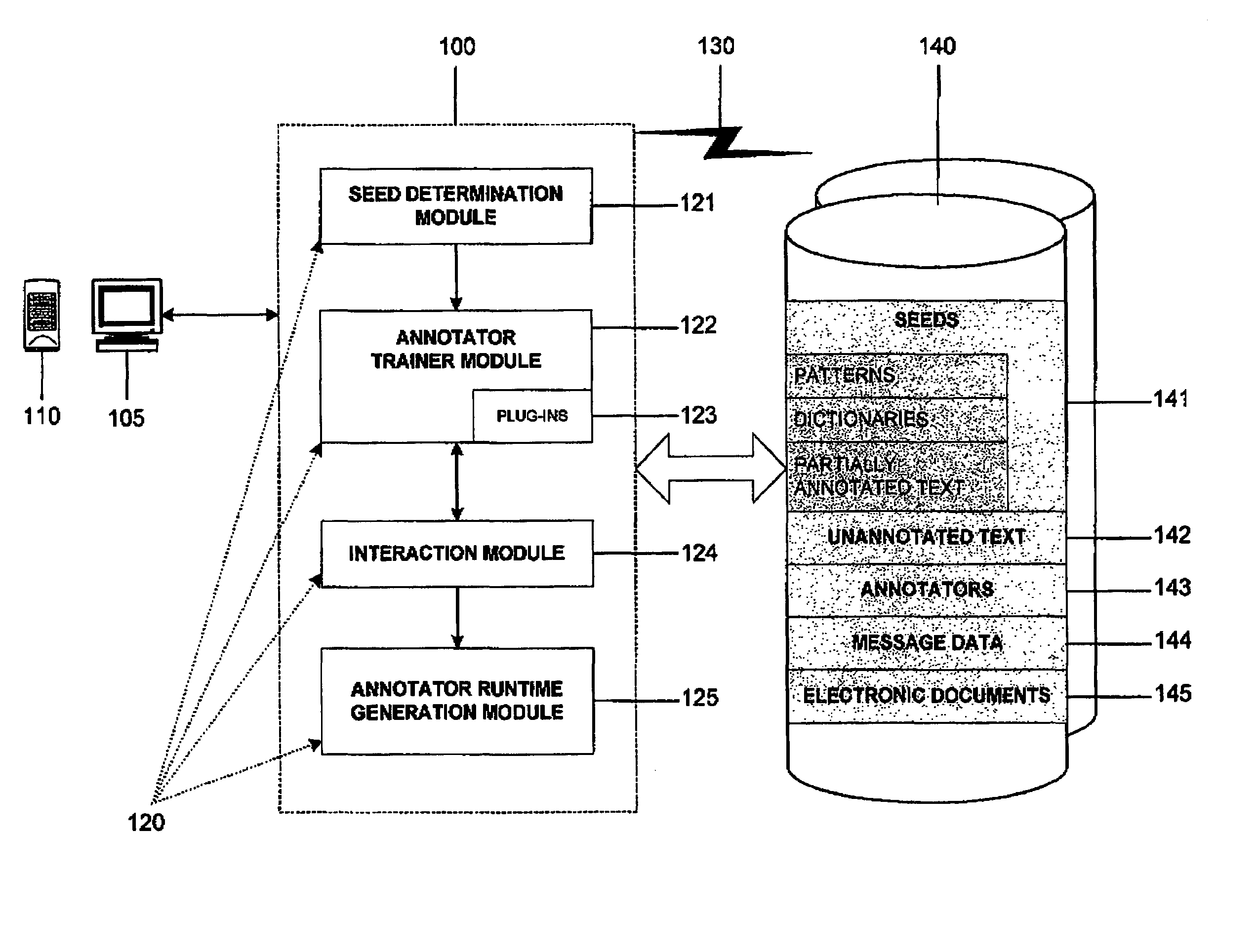
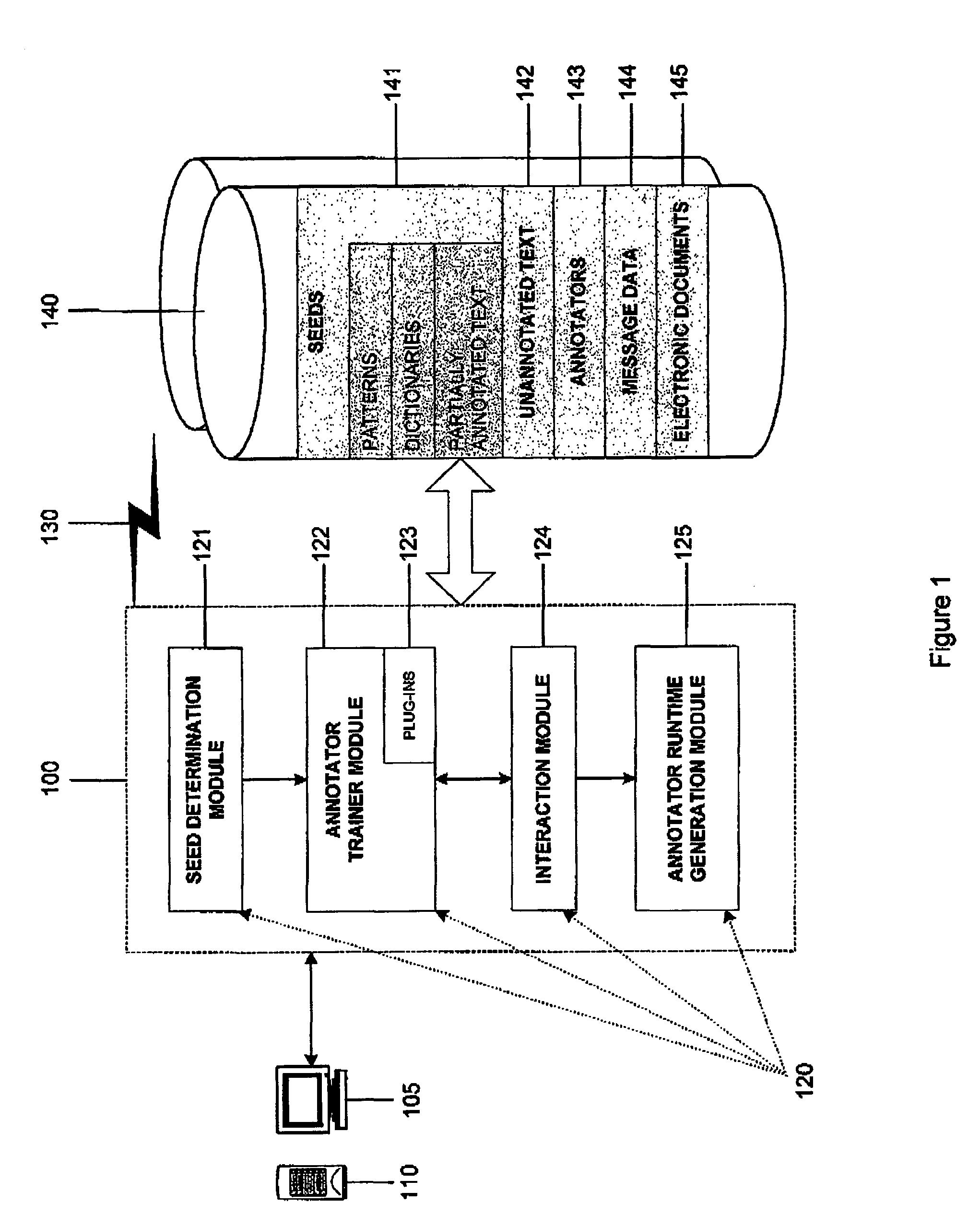
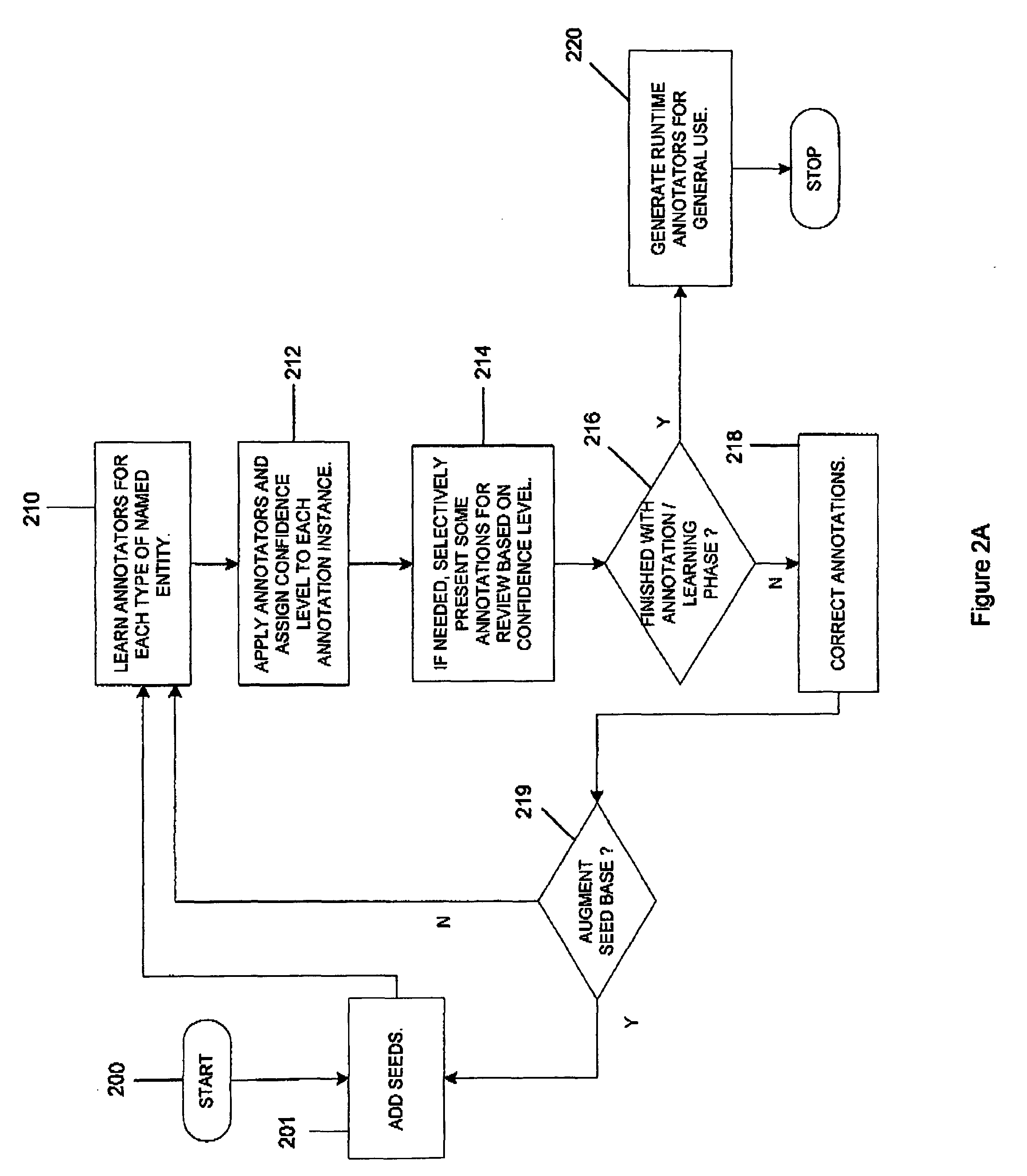
Interactive machine learning system for automated annotation of information in text
InactiveUS20050027664A1Natural language translationDigital computer detailsLearning basedConfidence metric
An interactive machine learning based system that incrementally learns, on the basis of text data, how to annotate new text data. The system and method starts with partially annotated training data or alternatively unannotated training data and a set of examples of what is to be learned. Through iterative interactive training sessions with a user the system trains annotators, and these are in turn used to discover more annotations in the text data. Once all of the text data or a sufficient amount of the text data is annotated, at the user's discretion, the system learns a final annotator or annotators, which are exported and available to annotate new textual data. As the iterative training process occurs the user is selectively presented for review and appropriate action, system-determined representations of the annotation instances and provided a convenient and efficient interface so that context of use can be verified if necessary in order to evaluate the annotations and correct them, where required. At the user's discretion, annotations that receive a high confidence level can be automatically accepted and those with low confidence levels can be automatically rejected.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods and system to quantify depth data accuracy in three-dimensional sensors using single frame capture
InactiveUS7408627B2Improve reliabilityHighly unreliableOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhotodetectorConfidence map
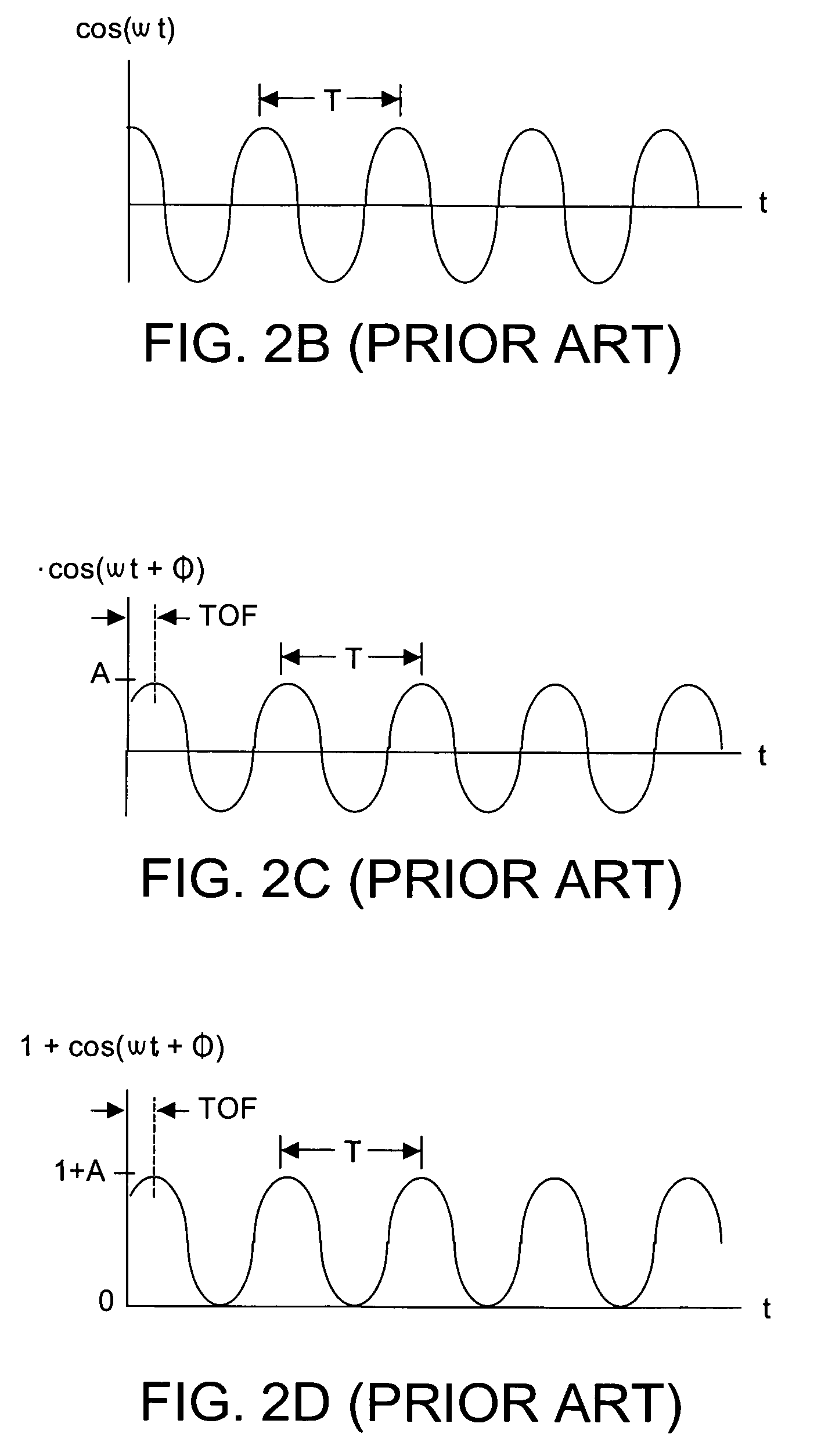
A method and system dynamically calculates confidence levels associated with accuracy of Z depth information obtained by a phase-shift time-of-flight (TOF) system that acquires consecutive images during an image frame. Knowledge of photodetector response to maximum and minimum detectable signals in active brightness and total brightness conditions is known a priori and stored. During system operation brightness threshold filtering and comparing with the a priori data permits identifying those photodetectors whose current output signals are of questionable confidence. A confidence map is dynamically generated and used to advise a user of the system that low confidence data is currently being generated. Parameter(s) other than brightness may also or instead be used.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Detection of security incidents with low confidence security events
Techniques are disclosed for detecting security incidents based on low confidence security events. A security management server aggregates a collection of security events received from logs from one or more devices. The security management server evaluates the collection of security events based on a confidence score assigned to each distinct type of security event. Each confidence score indicates a likelihood that a security incident has occurred. The security management server determines, based on the confidence scores, at least one threshold for determining when to report an occurrence of a security incident from the collection of security events. Upon determining that at least one security event of the collection has crossed the at least one threshold, the security management server reports the occurrence of the security incident to an analyst.
Owner:GEN DIGITAL INC
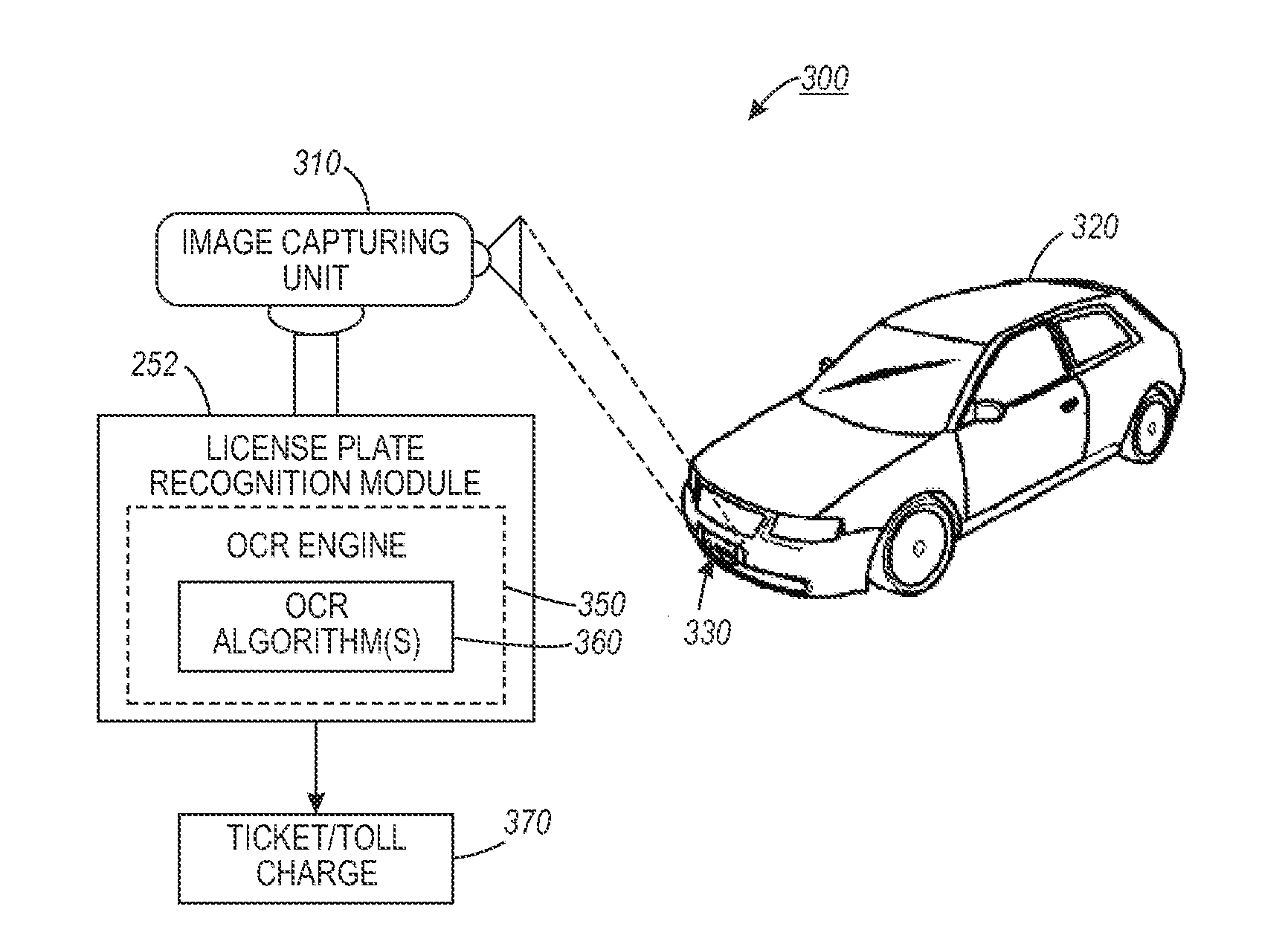
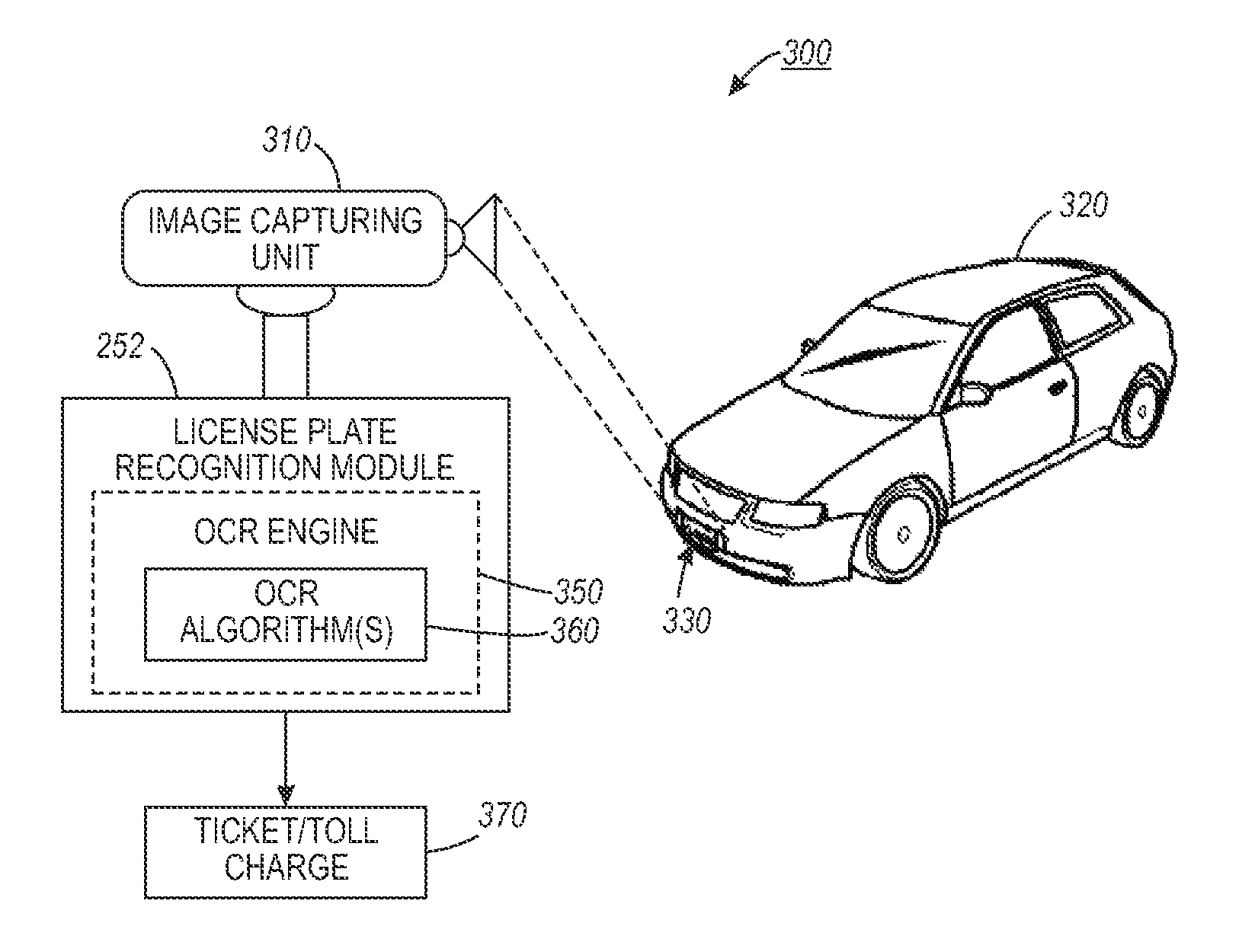
Automated license plate recognition system and method using human-in-the-loop based adaptive learning
ActiveUS20120148105A1Reduce labor costsRoad vehicles traffic controlCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive learningData set
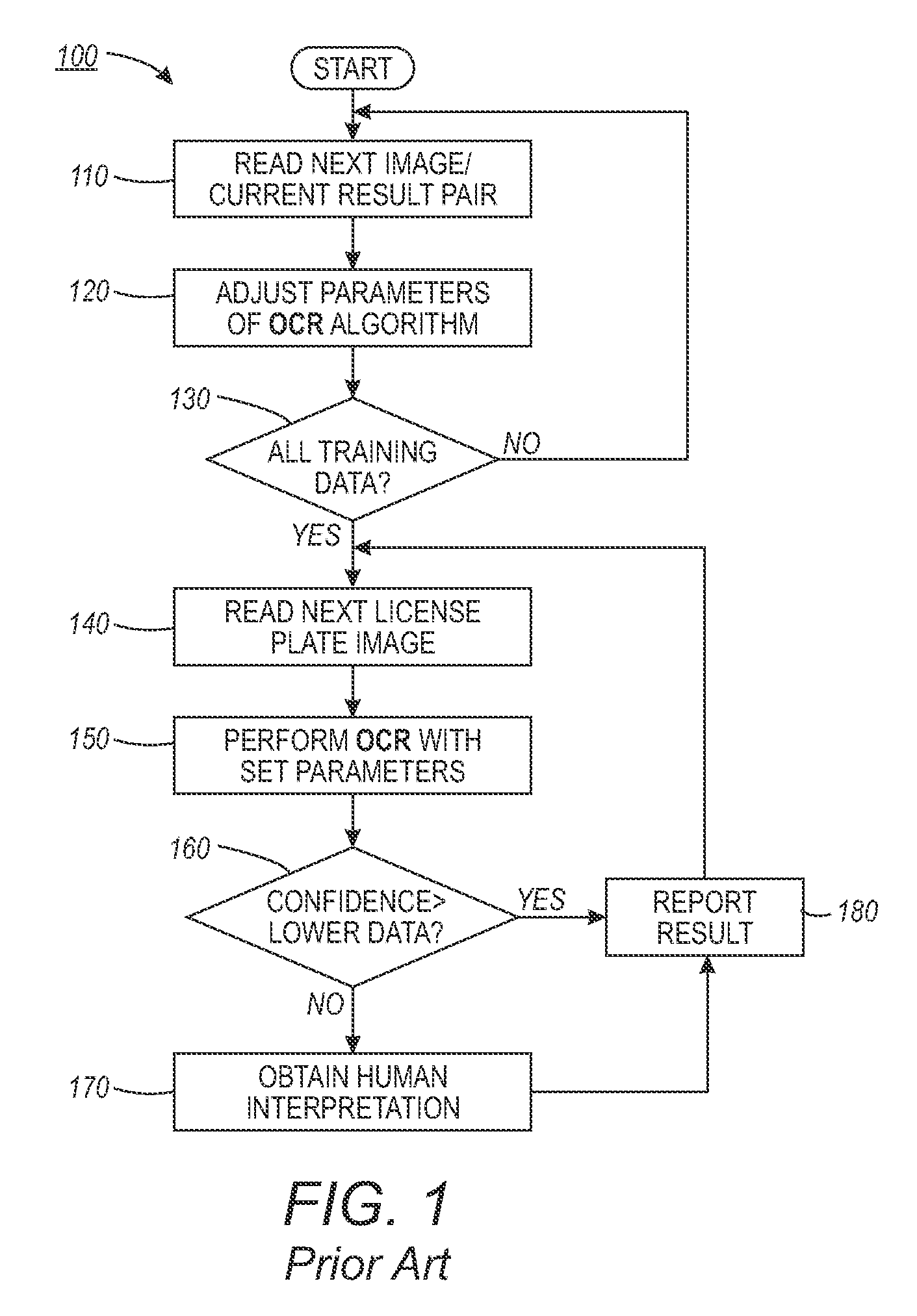
An automated license plate recognition (ALPR) system and method using a human-in-the-loop based adaptive learning approach. One or more images with respect to an automotive vehicle can be segmented in order to determine a license plate of the automotive vehicle within a scene. An optical character recognition (OCR) engine loaded with an OCR algorithm can be further adapted to determine a character sequence of the license plate based on a training data set. A confidence level with respect to the images can be generated in order to route a low confidence image to an operator for obtaining a human interpreted image. The parameters with respect to the OCR algorithm can be adjusted based on the human interpreted image and the actual image of the license plate. A license plate design can be then incorporated into the OCR engine in order to automate the process of recognizing the license plate with respect to the automotive vehicle in a wide range of transportation related applications.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
Identification and automatic propagation of geo-location associations to un-located documents
InactiveUS20070112777A1High location confidenceLocation confidenceDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsConfidence metricDocument preparation
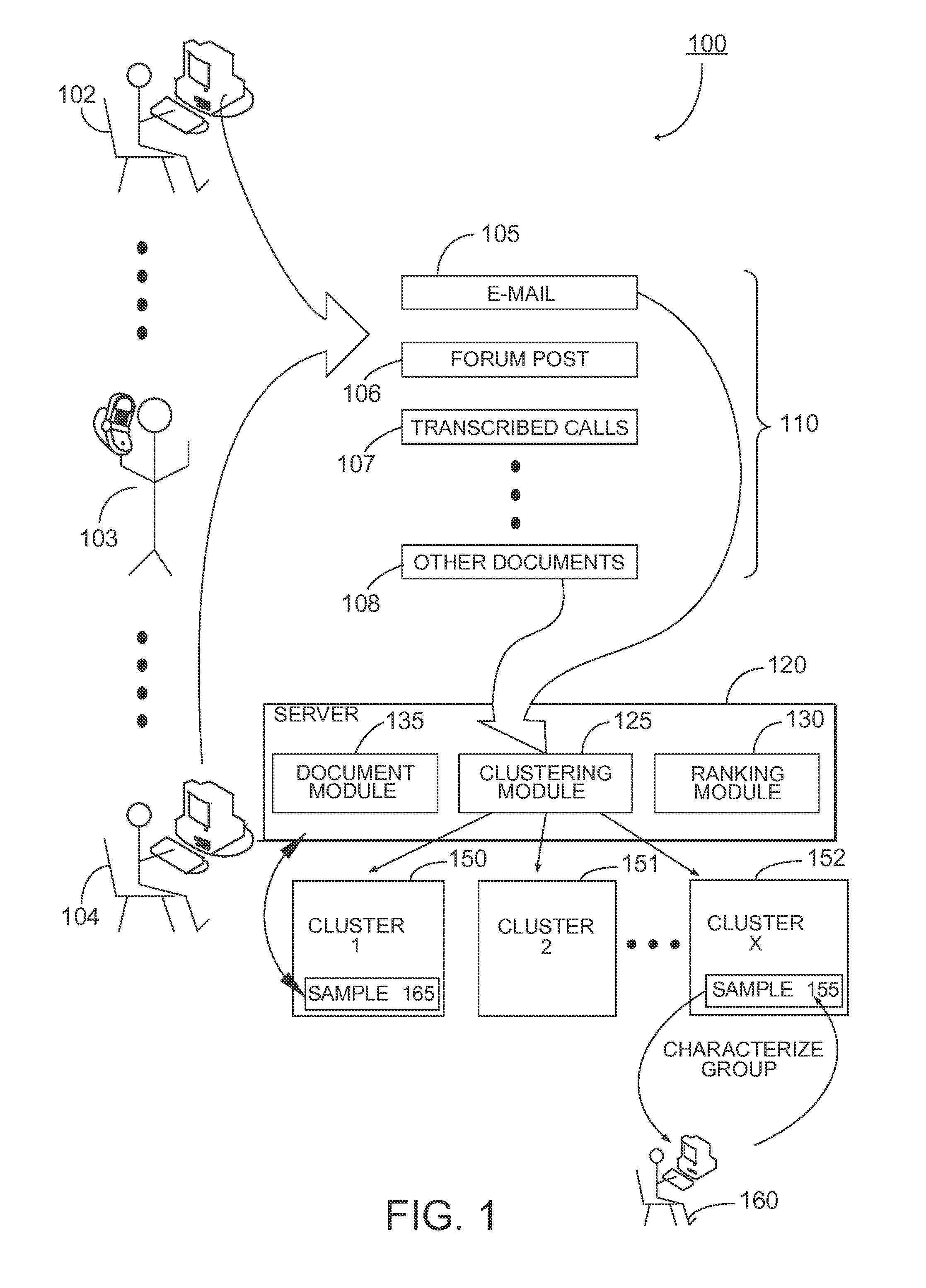
Systems and methods are provided for identifying pages that can be authoritatively, to some confidence level or another, associated with a geographic location, and systems and methods for grouping documents such that authoritative location associations can be propagated from pages with higher location confidence to pages with lower location confidence. Pages might be identified with authoritative indicators, groups of pages identified including at least one addressed page and at least one unaddressed page, wherein an addressed page is a page having a higher confidence level than an unaddressed page, and at least one processing step performed that is location specific. The confidence level assigned to a page as part of the process represents the confidence that the page is associated with an identifiable geographic location, with documents having a high confidence level being determined to be strongly associated with a particular geographic location while documents having a low confidence level being determined to be weakly associated with a particular geographic location or not associated at all with a geographic location.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
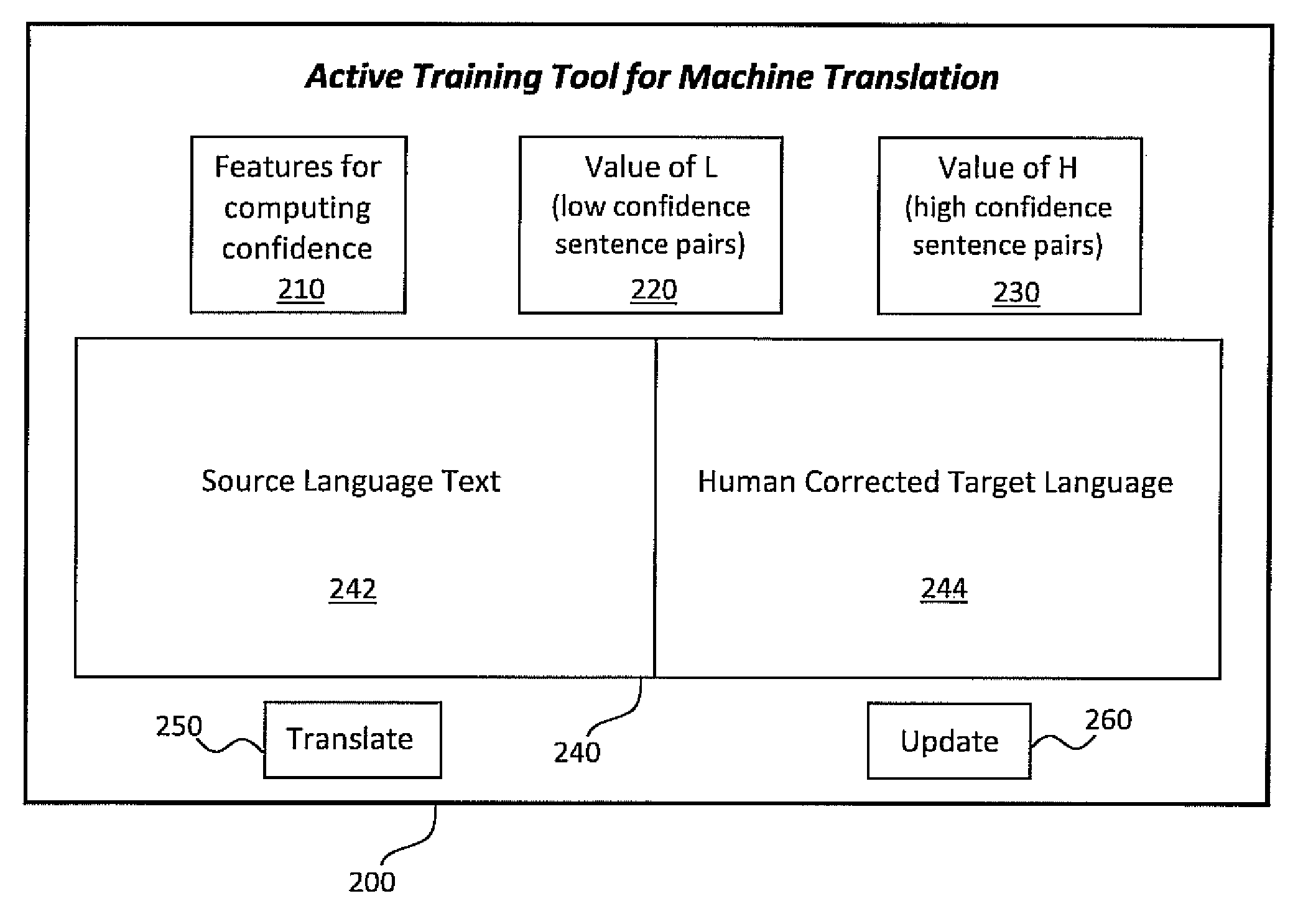
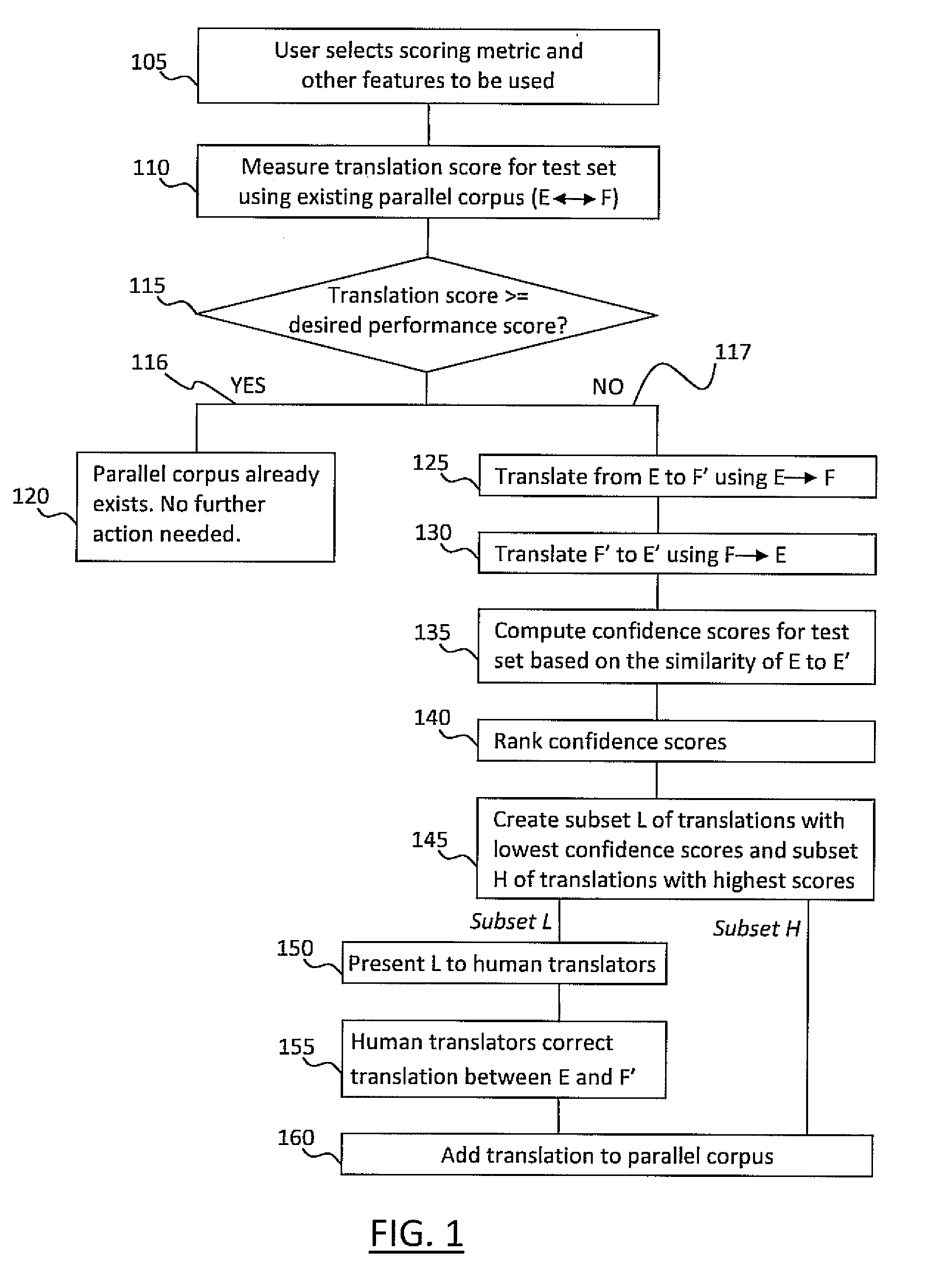
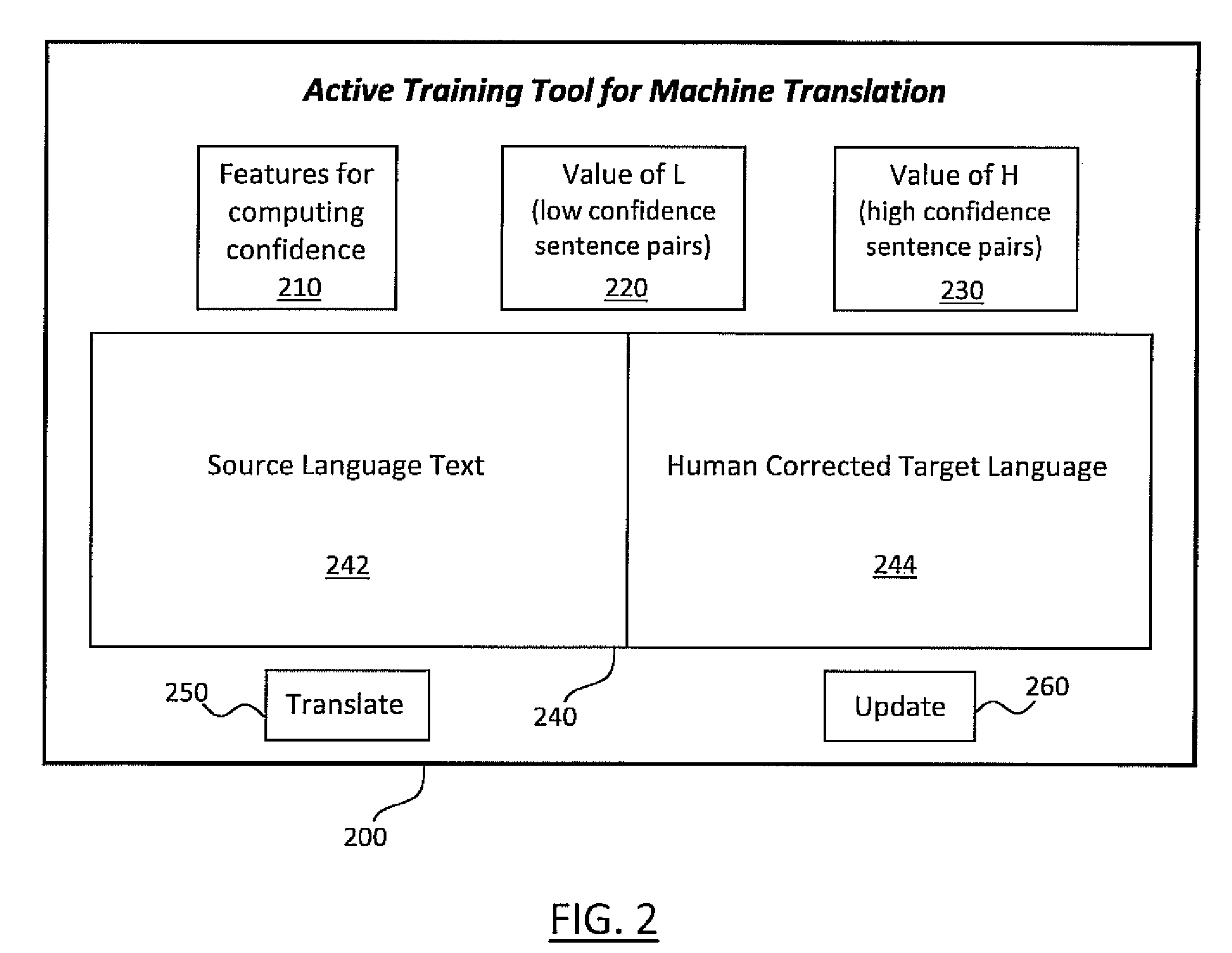
Active learning systems and methods for rapid porting of machine translation systems to new language pairs or new domains
InactiveUS20110022381A1Increase speedLow costNatural language translationDigital data processing detailsMachine translation systemProactive learning
Systems and methods for active learning of statistical machine translation systems through dynamic creation and updating of parallel corpus. The systems and methods provided create accurate parallel corpus entries from a test set of sentences, words, phrases, etc. by calculating confidence scores for particular translations. Translations with high confidence scores are added directly to the corpus and the translations with low confidence scores are presented to human translations for corrections.
Owner:IBM CORP
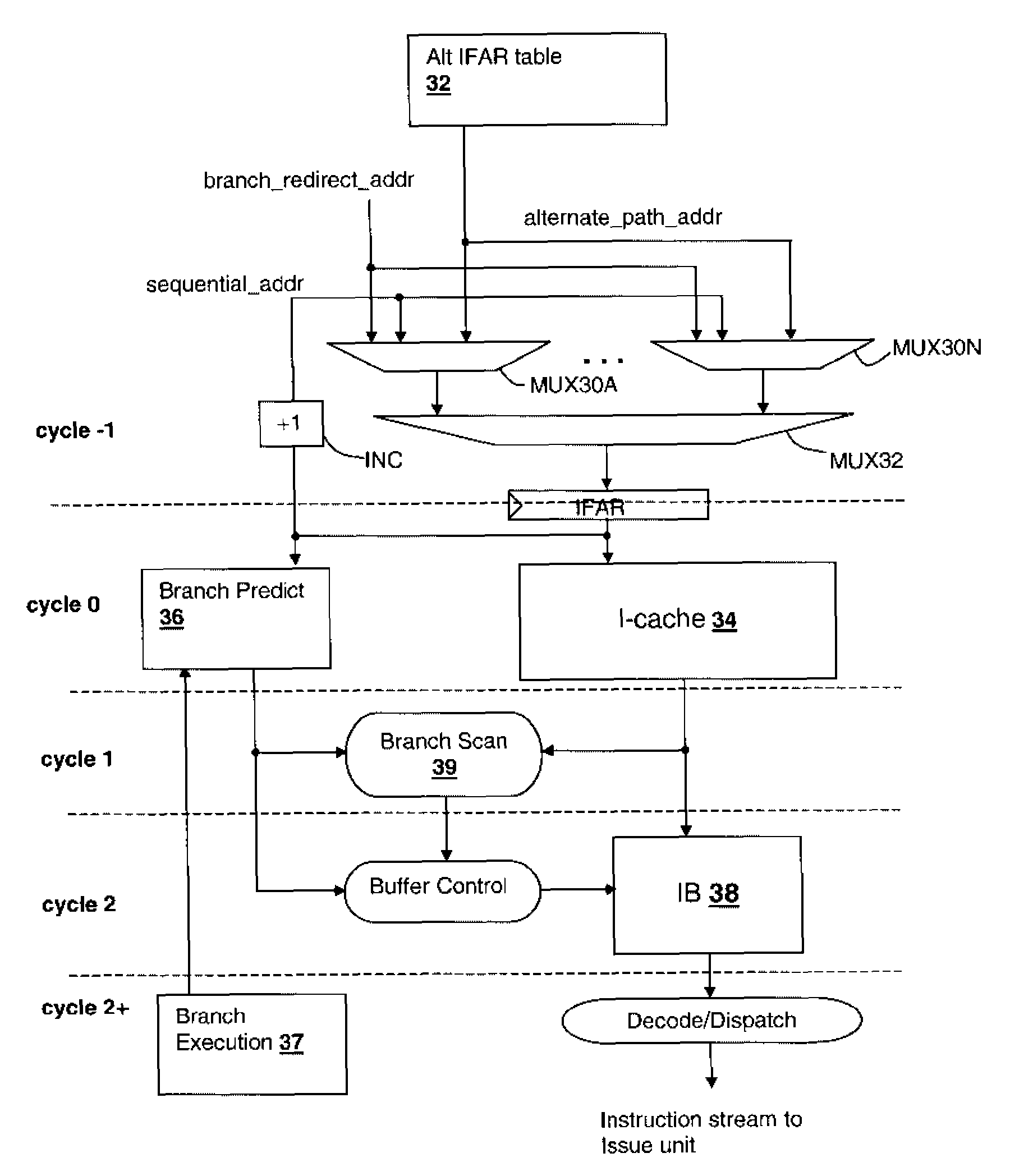
Method and apparatus for dynamically managing instruction buffer depths for non-predicted branches
InactiveUS7779232B2Reduces resource and energy wastedDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsProcessor registerDynamic management
A method and apparatus for dynamically managing instruction buffer depths for non-predicted branches reduces wasted energy and resources associated with low confidence branch prediction conditions. A portion of the instruction buffer for a instruction thread is allocated for storing predicted branch instruction streams and another portion, which may be zero-sized during high prediction confidence conditions, is allocated to the non-predicted branch instruction stream. The size of the buffers is adjusted dynamically in conformity with an on-going prediction confidence that provides a measure of how well branch prediction mechanisms are working for a given instruction thread. An alternate instruction fetch address table can be maintained and multiplexed with the main fetch address register for addressing the instruction cache, so that the instruction stream can be quickly shifted to the non-predicted path when a branch instruction is resolved to the non-predicted path.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Methods and apparatus for automatic speech recognition
InactiveCN1783213AImproved selection of hintsGood choiceSpeech recognitionSpoken languageGoal recognition
An automatic speech recognition (ASR) system that includes a speech-response application and a speech recognition engine. The ASR system generates user prompts to elicit certain spoken input, and when the spoken input is recognized, the voice-response application performs an action. The recognition engine compares sounds in the input audio signal to phonemes in the acoustic model to identify candidate matching phonemes. A recognition confidence score is calculated for each candidate matching phoneme, and the confidence score is used to aid in the recognition of one or more possible matching phoneme sequences that appear to match the word in the speech-response application's grammar. A confidence score for each phoneme is evaluated against predefined confidence score criteria (eg, a discrimination score below a "low confidence" threshold), and the results of the evaluation are used to influence the selection of subsequent user prompts. One such system uses confidence scores to select cues for object recognition training - encouraging input to be recognized as phonemes with low confidence recognition scores. Another system selects prompts to block input of sounds that are not easily recognizable.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
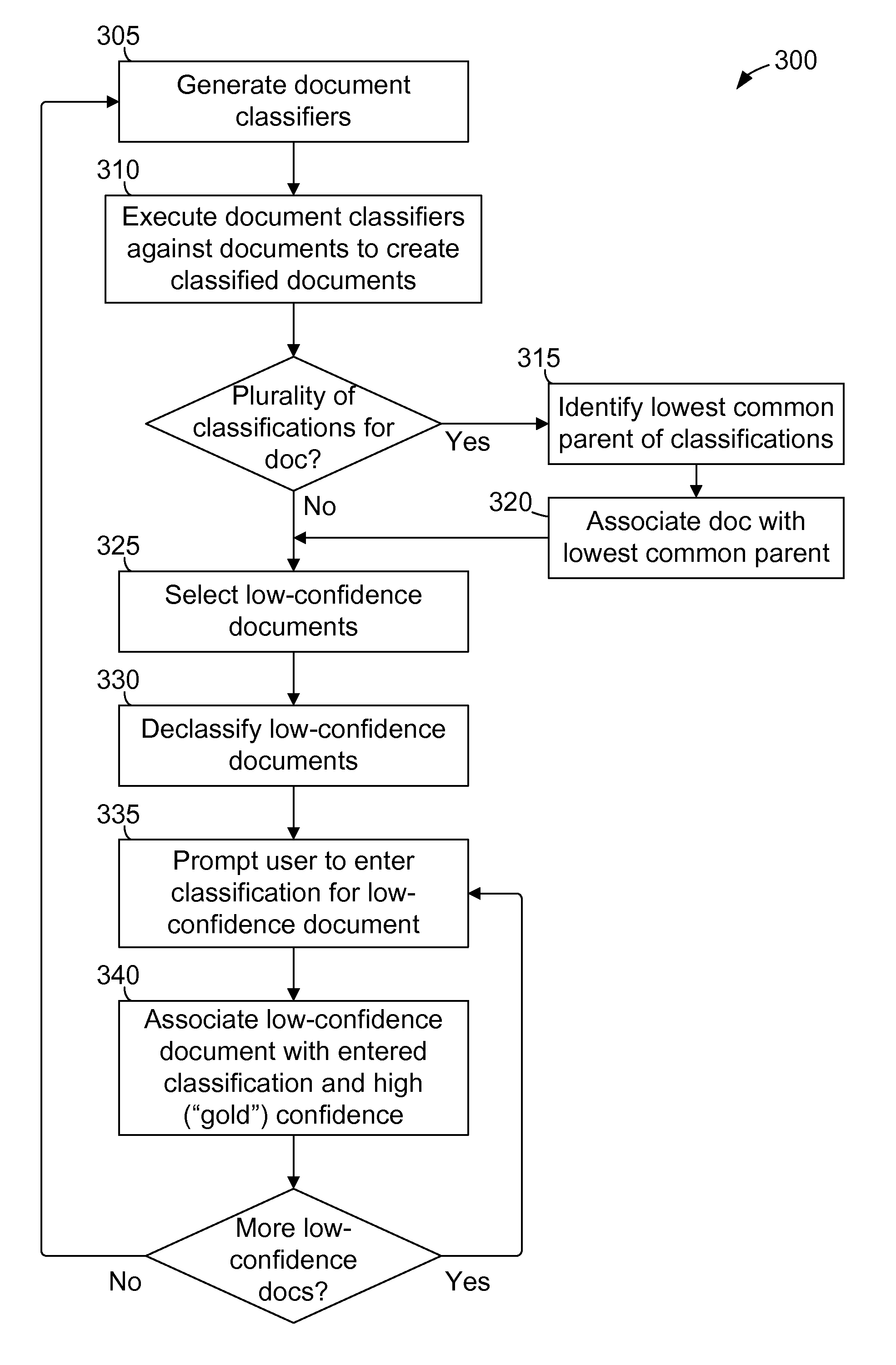
Methods and systems for classifying data using a hierarchical taxonomy
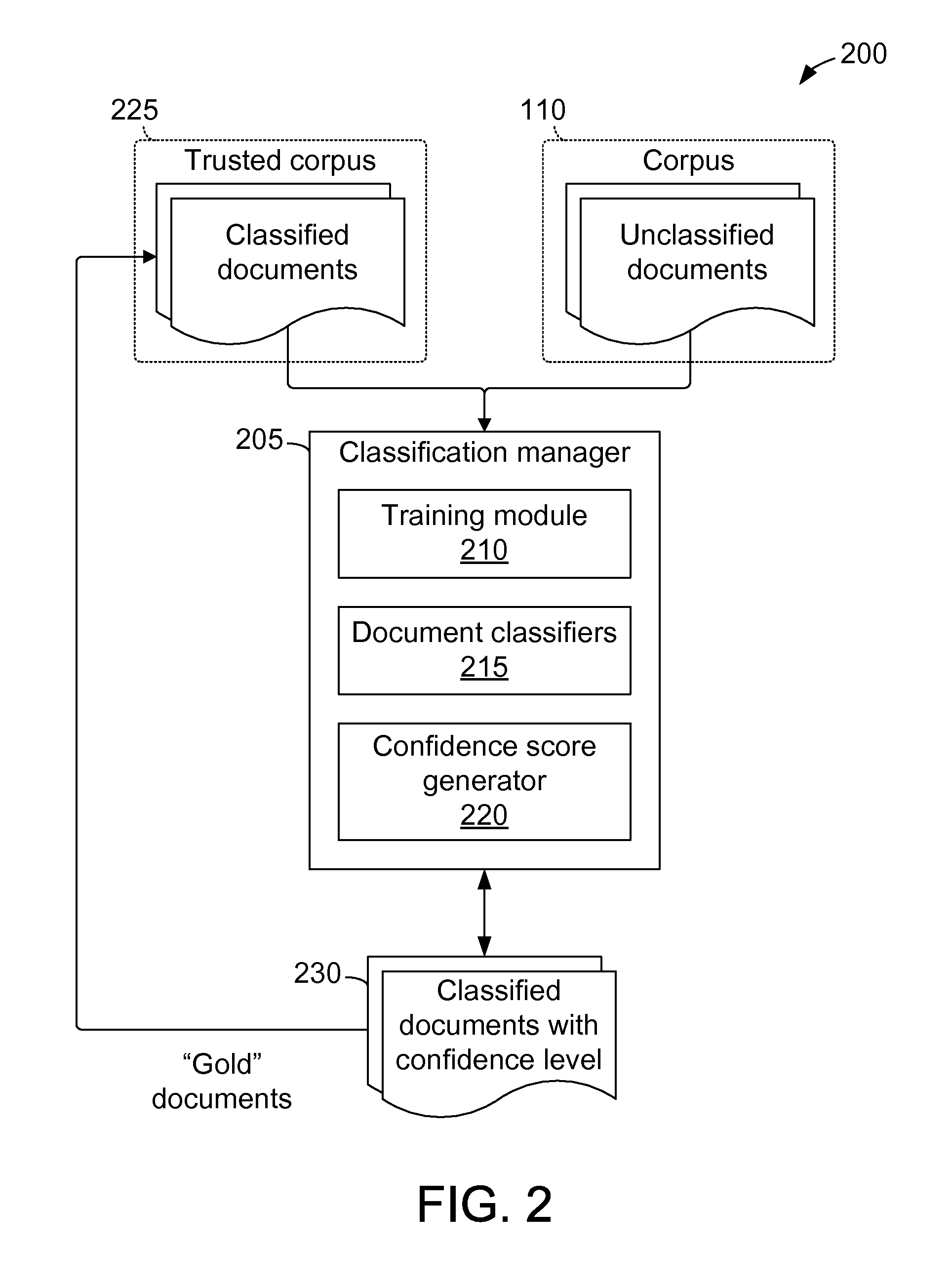
A method and system for classifying documents is provided. A set of document classifiers is generated by applying a classification algorithm to a trusted corpus that includes a set of training documents representing a taxonomy. One or more of the generated document classifiers are executed against a plurality of input documents to create a plurality of classified documents. Each classified document is associated with a classification within the taxonomy and a classification confidence level. One or more classified documents that are associated with a classification confidence level below a predetermined threshold value are selected to create a set of low-confidence documents. The low-confidence documents are disassociated from each of the associated classifications. A user is prompted to enter a classification within the taxonomy for at least one low-confidence document. The low-confidence document is associated with the entered classification and with a predetermined confidence level to create a newly classified document.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and system for voice recognition menu navigation with error prevention and recovery
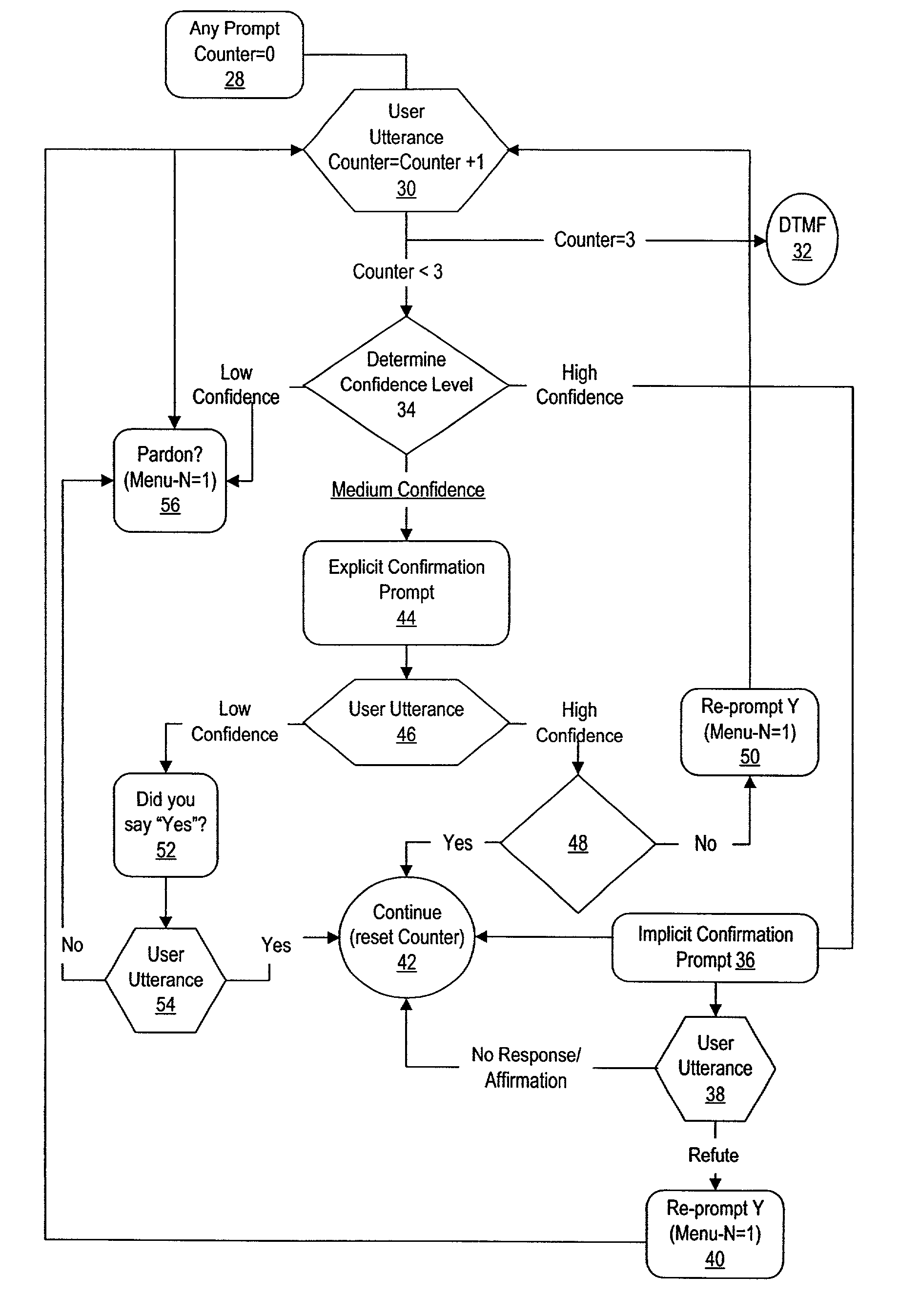
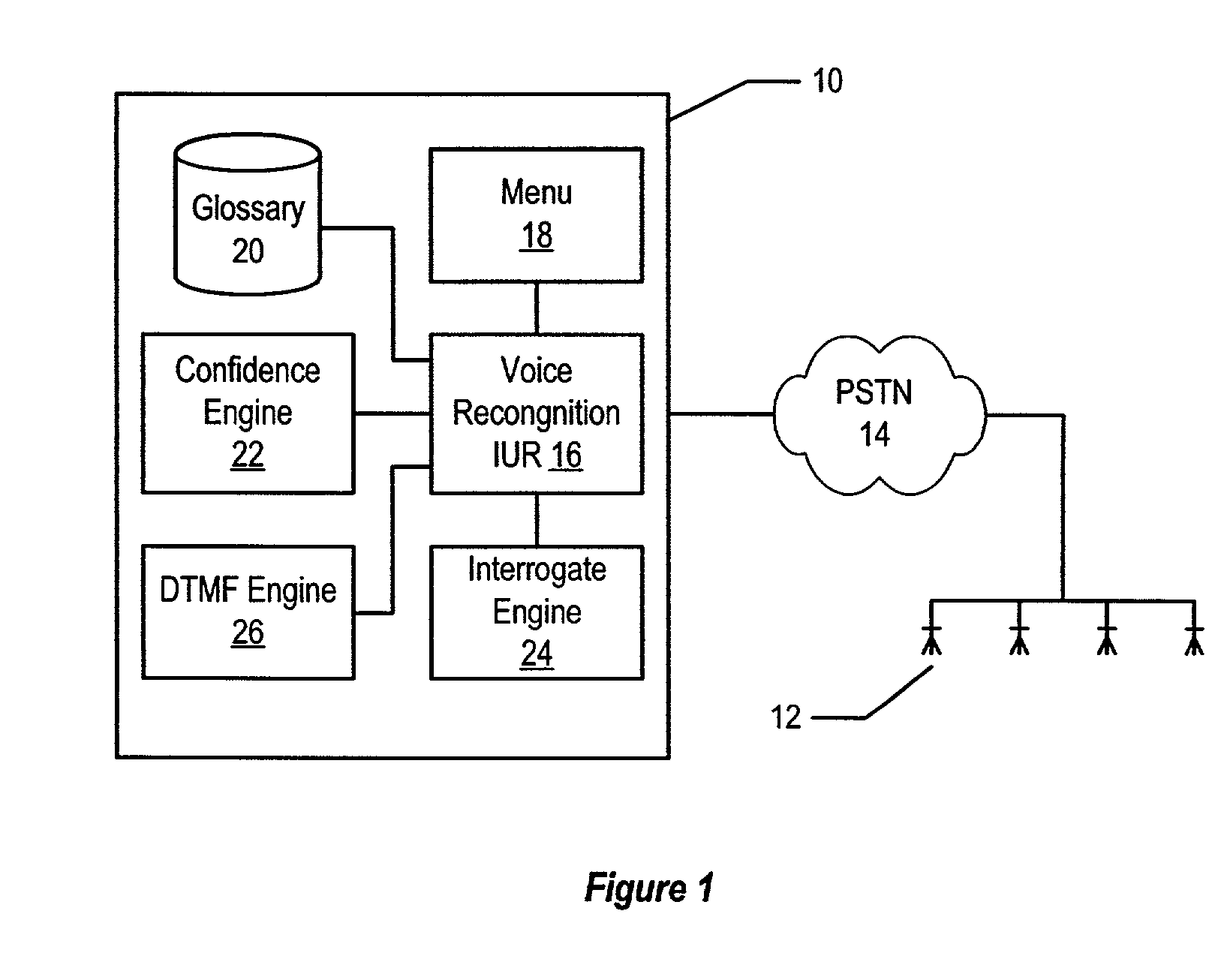
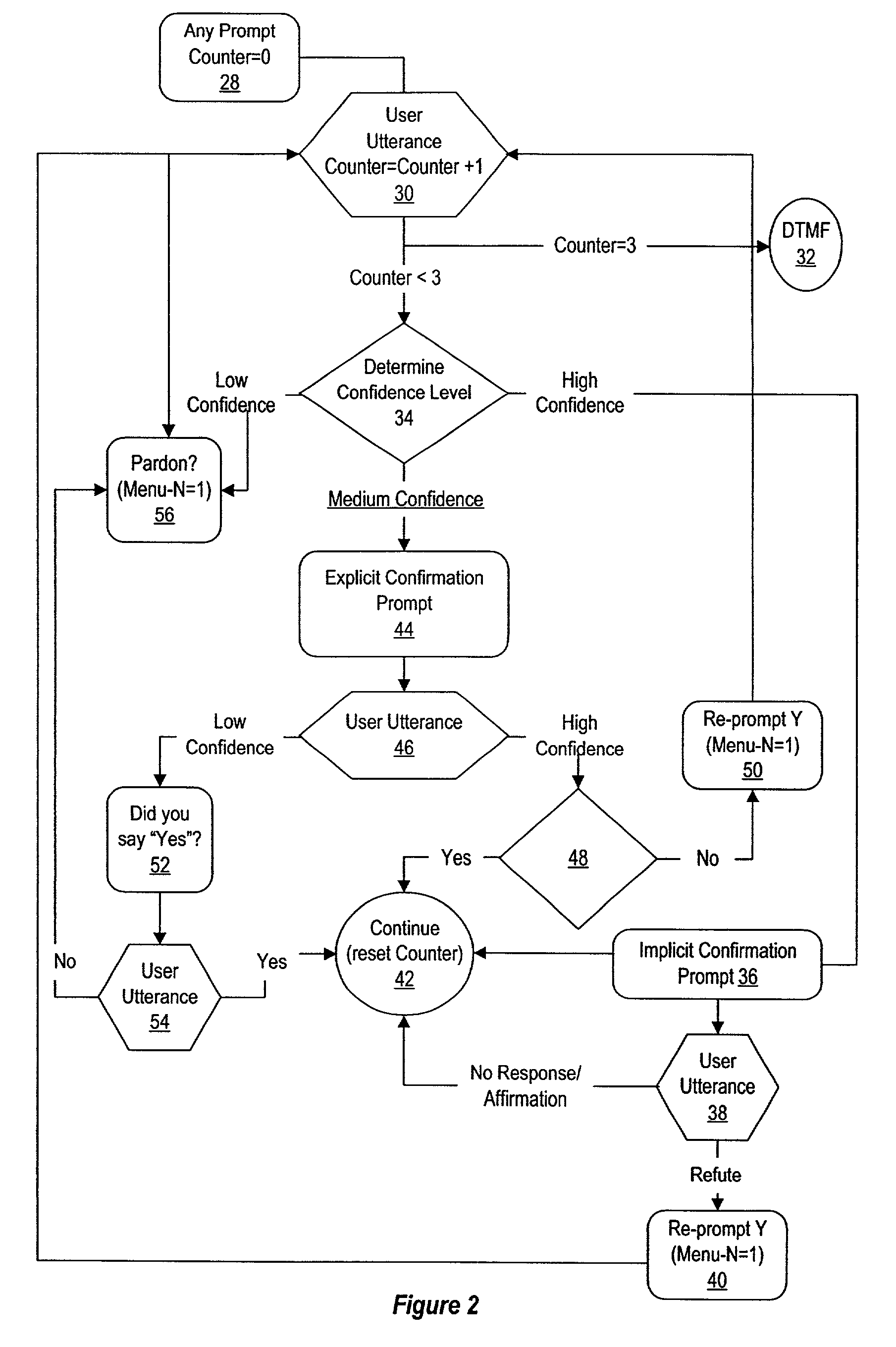
A method and system for error prevention and recovery of voice activated navigation through a menu having plural nodes provides situation dependent utterance verification by relating confirmation to utterance determination confidence levels. In one embodiment, a high confidence level results in implicit confirmation, a medium confidence level results in explicit confirmation and a low confidence level results in a concise interrogative prompt of a single word that requests the user to repeat the utterance. In situations where voice recognition is difficult, dual modality with DTMF navigation is provided as an option for menu selections.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Adaptive Automatic Defect Classification
ActiveUS20170082555A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementEnsemble learningClassification methodsTraining set
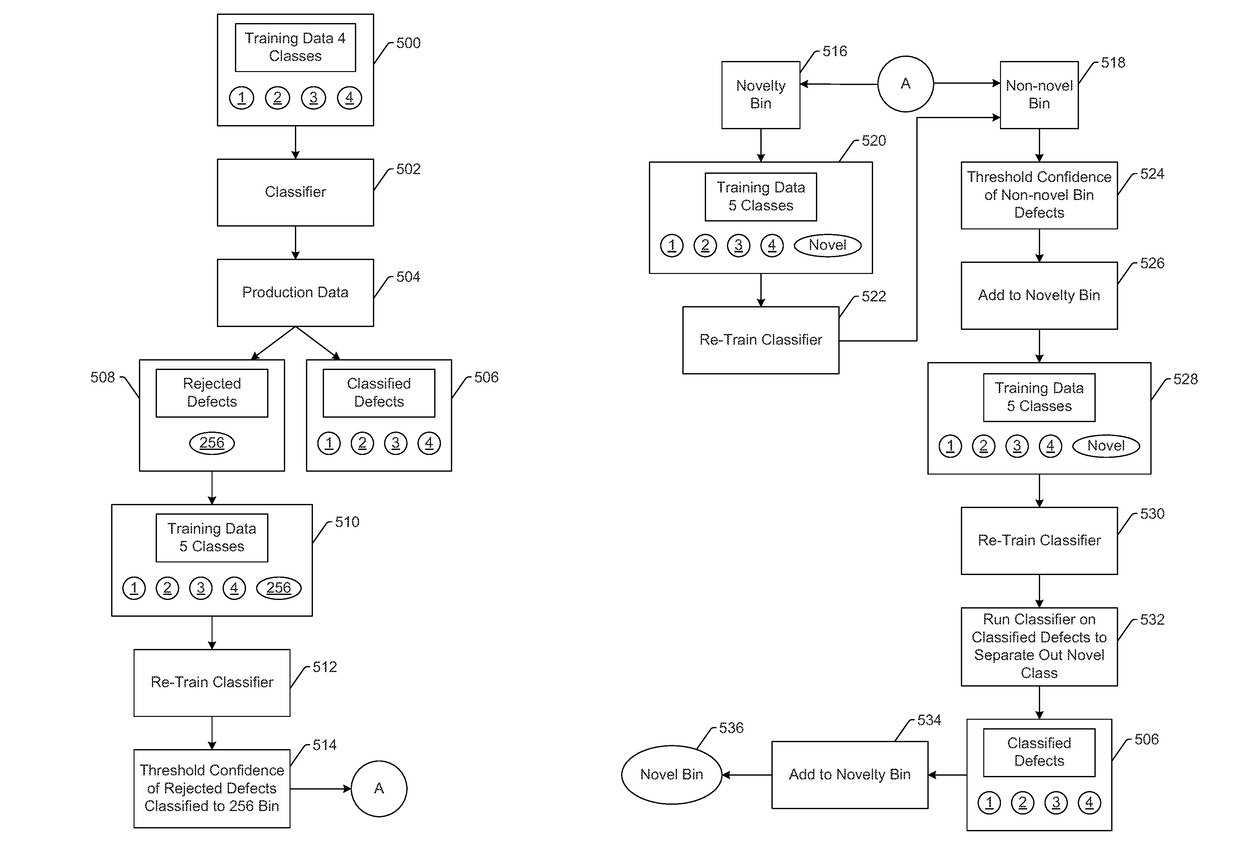
Methods and systems for classifying defects detected on a specimen with an adaptive automatic defect classifier are provided. One method includes creating a defect classifier based on classifications received from a user for different groups of defects in first lot results and a training set of defects that includes all the defects in the first lot results. The first and additional lot results are combined to create cumulative lot results. Defects in the cumulative lot results are classified with the created defect classifier. If any of the defects are classified with a confidence below a threshold, the defect classifier is modified based on a modified training set that includes the low confidence classified defects and classifications for these defects received from a user. The modified defect classifier is then used to classify defects in additional cumulative lot results.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Character confidence degree-based secondary license plate identification method and apparatus
ActiveCN106845478AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed recognition speedCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesTemplate matchingTime domain
The invention relates to the field of double dynamic license plate identification, and provides a character confidence degree-based secondary license plate identification method and apparatus for the problems existent in the prior art. The method comprises the steps of performing character identification through template matching; giving out confidence degrees of identification results; for the results with relatively low confidence degrees, performing video super-resolution processing to obtain a frame of high-quality image; and based on the image, performing secondary license plate identification through a neural network classifier. According to the method and the apparatus, a license plate confidence degree threshold Th is preset; a picture is captured from a front end and license plate locating and segmenting are performed; characters of a license plate are identified; character identification confidence degrees and license plate identification confidence degree are calculated; when the character confidence degrees are all higher than the threshold Th, a license plate identification result is directly given, otherwise, the video super-resolution processing is performed; a frame of high-quality image is obtained by utilizing time domain information; and based on the image, the to-be-identified characters are input to classifiers for performing identification according to a position relationship of the to-be-identified characters, so that a final license plate identification result is obtained.
Owner:长信智控网络科技有限公司
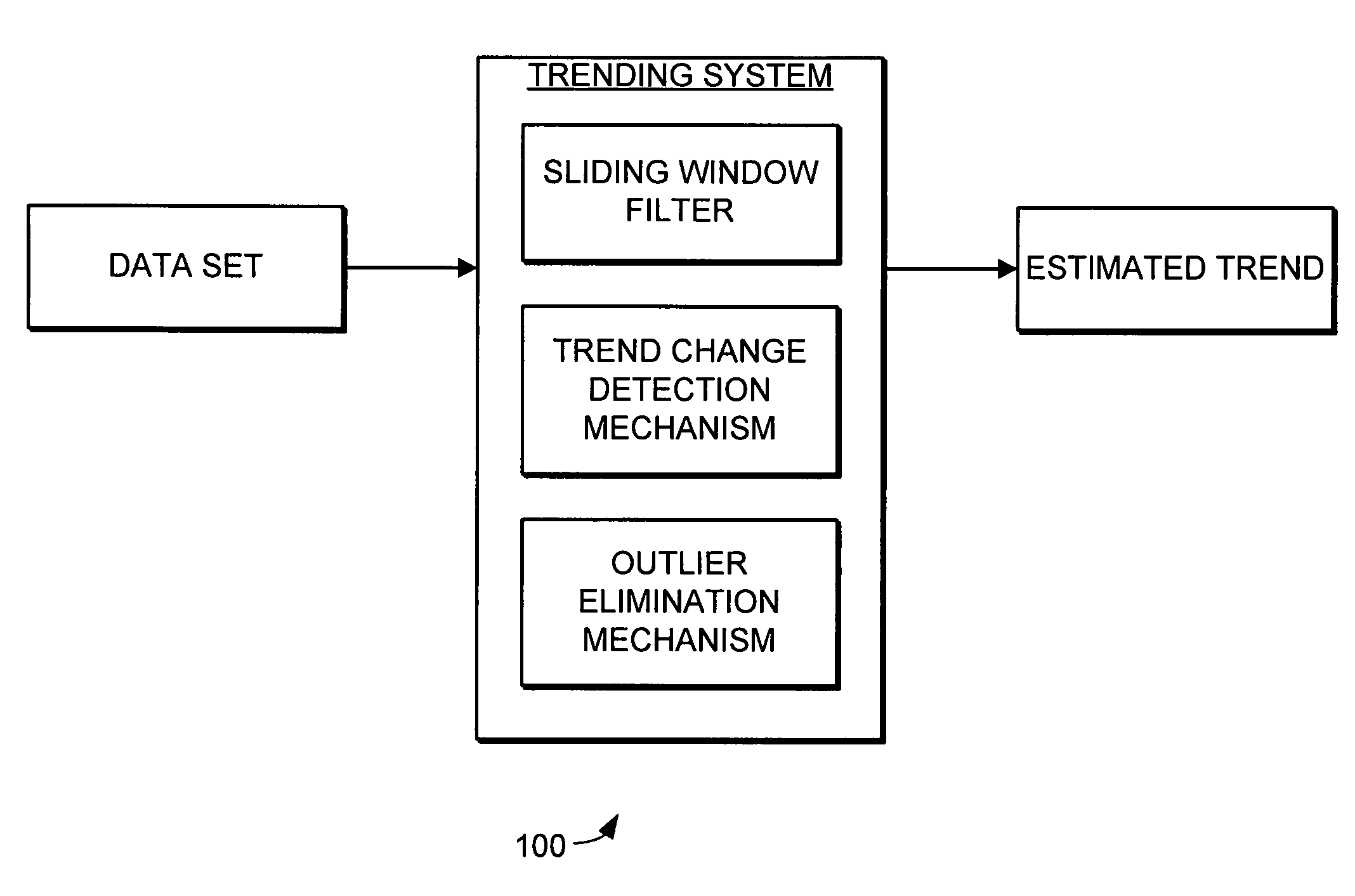
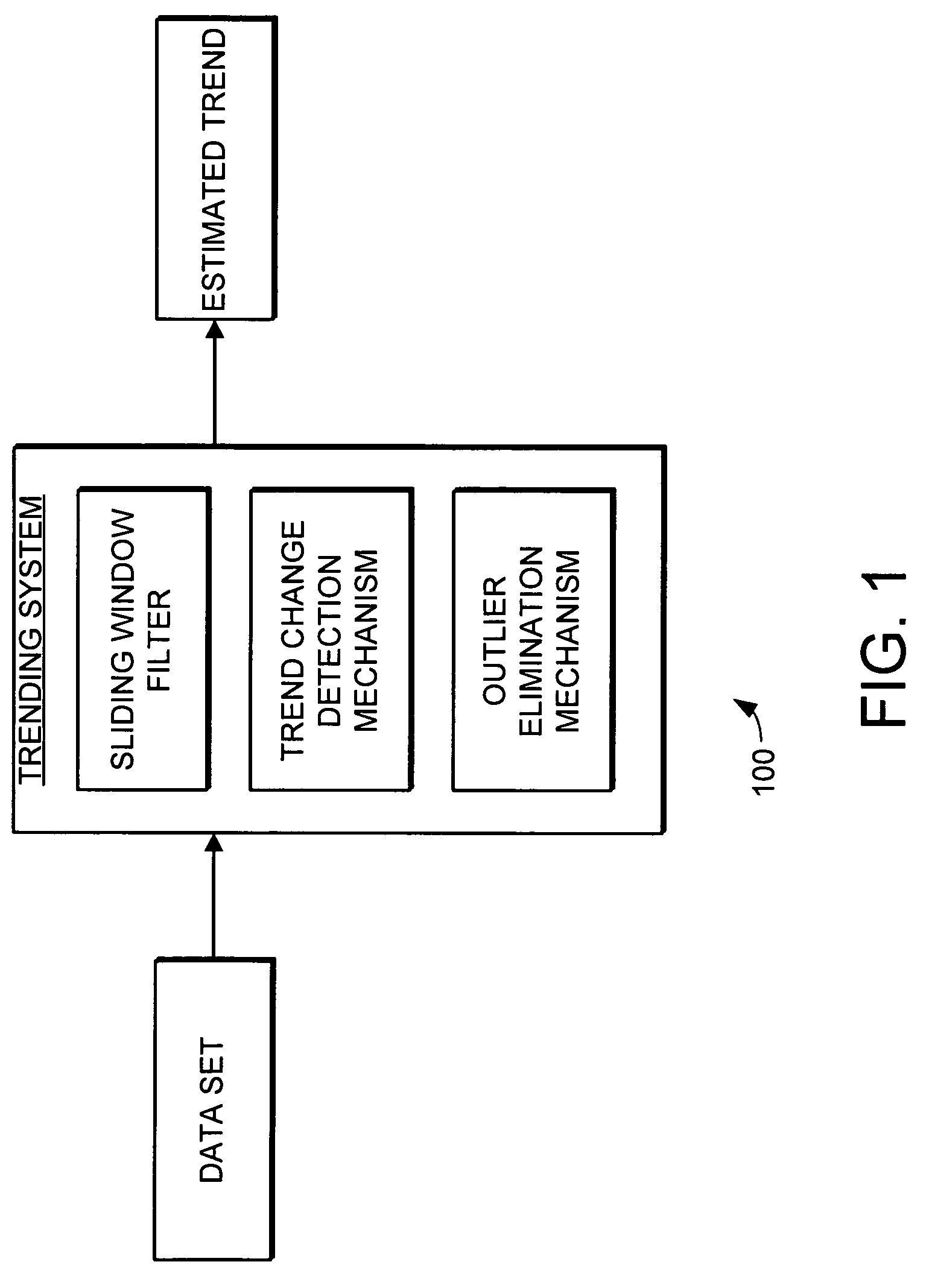
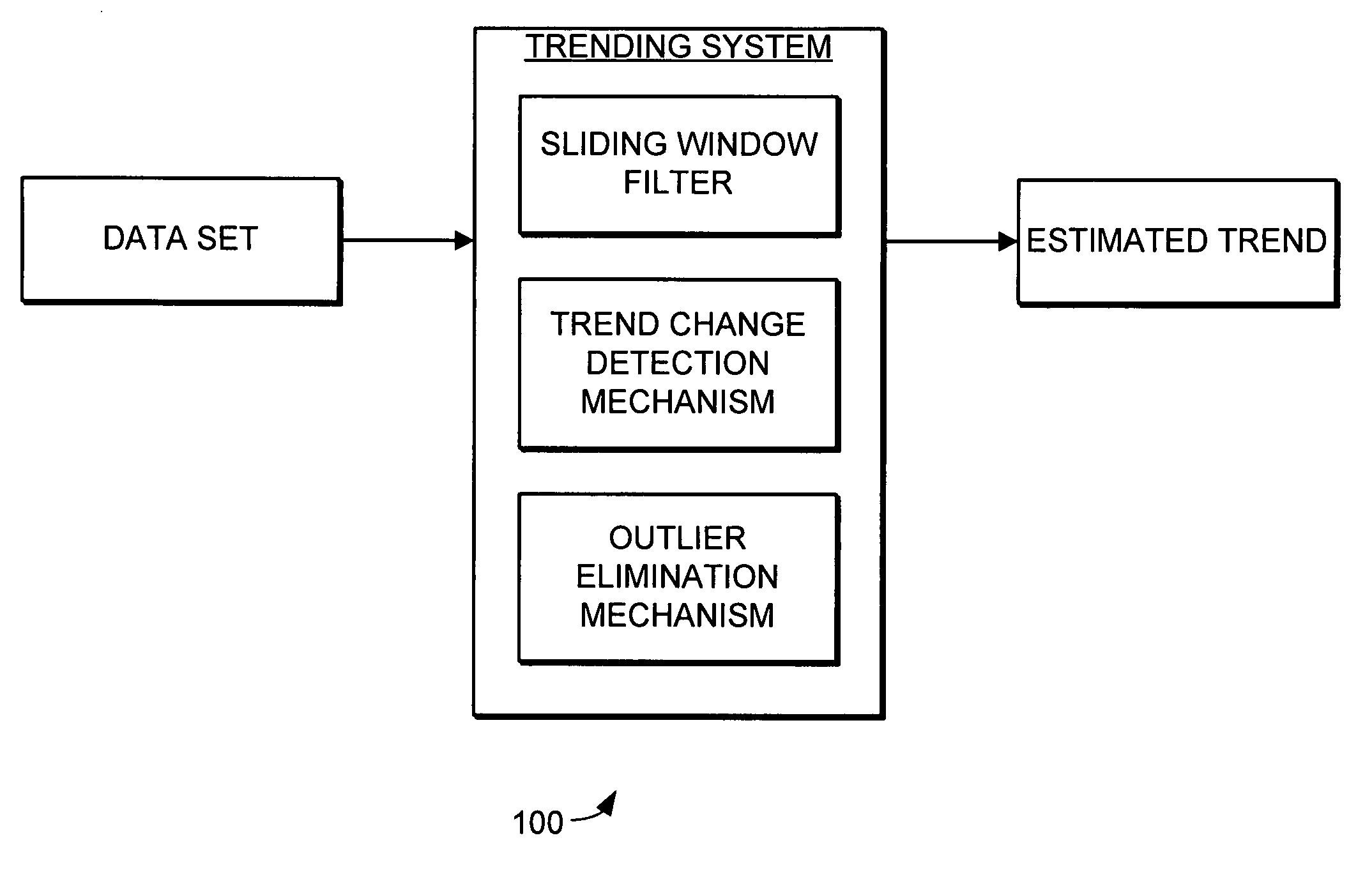
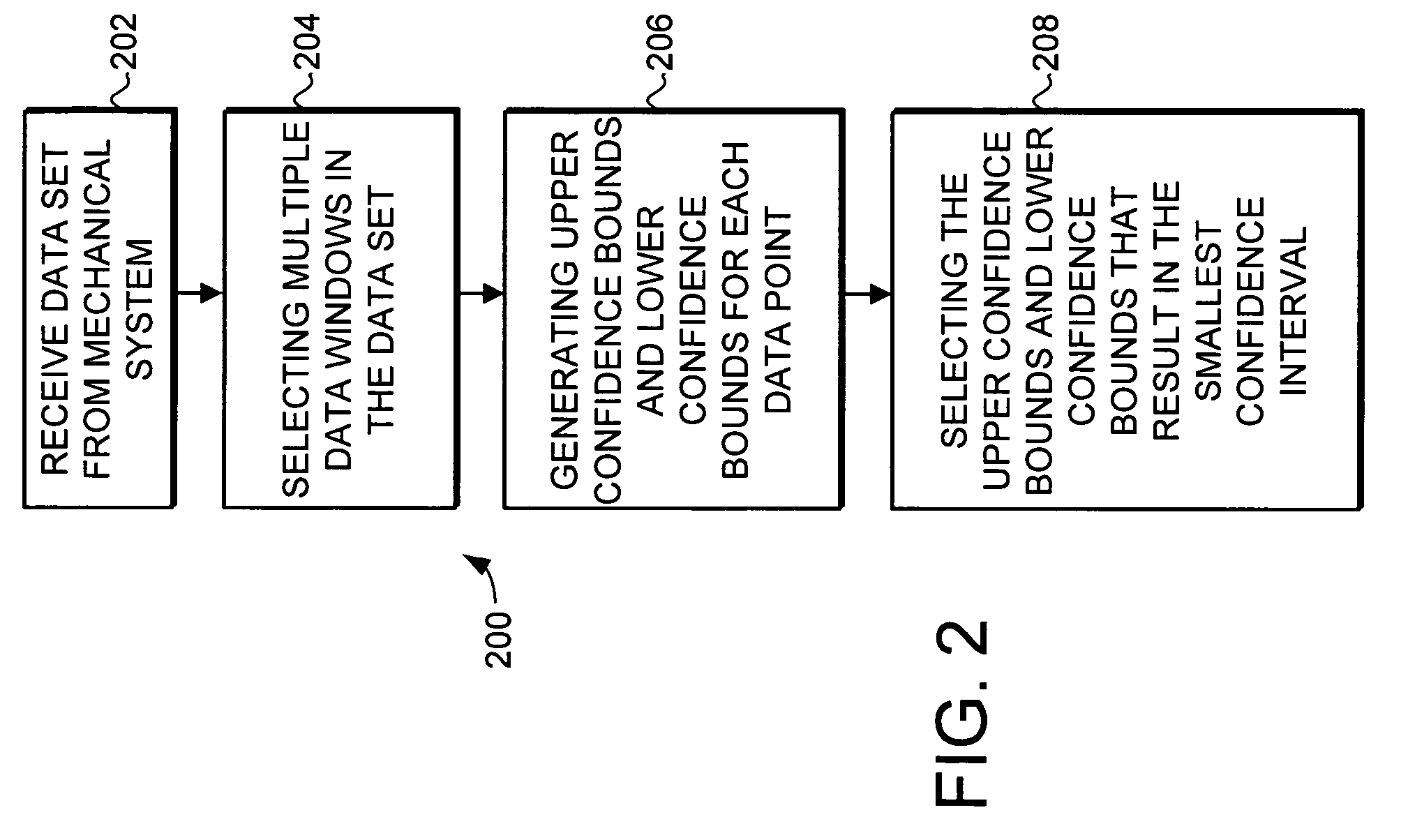
Trending system and method using window filtering
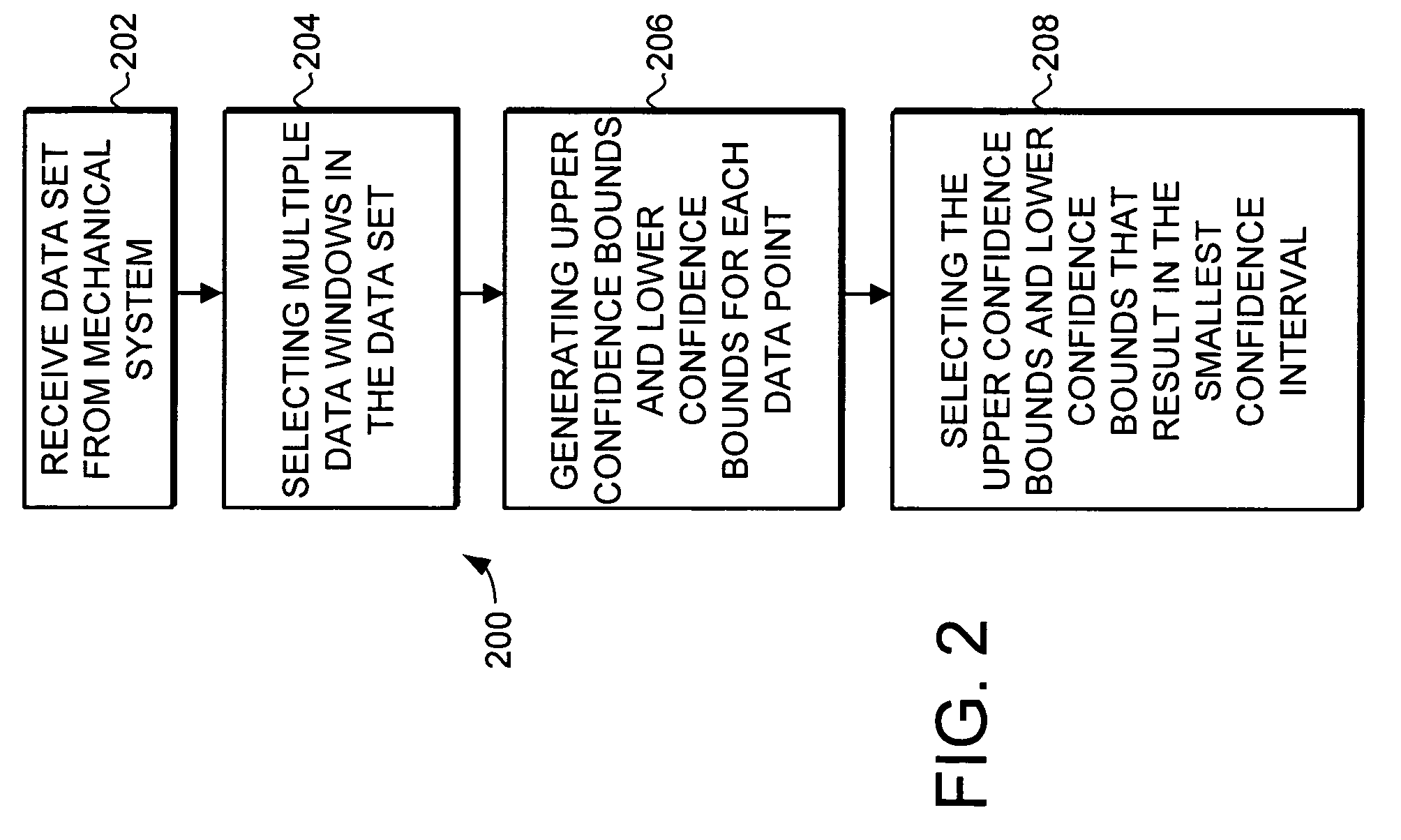
ActiveUS7580812B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital data processing detailsData setConfidence interval
A trending system and method for trending data in a mechanical system is provided. The trending system includes a sliding window filter. The sliding window filter receives a data set of data points generated by the mechanical system. The sliding window filter partitions the data set into a plurality of data windows, and uses the data windows to calculate upper and lower confidence bounds for the data set. Specifically, the sliding window filter calculates an upper confidence bounds and lower confidence bounds for each data point using each of the multiple data windows that includes the data point. The sliding window filter then selects the upper confidence bounds and the lower confidence bounds that results in the smallest mean prediction confidence interval for that data point. This results in a smoothed estimated trend for the data set that can be used for prognostication and fault detection.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
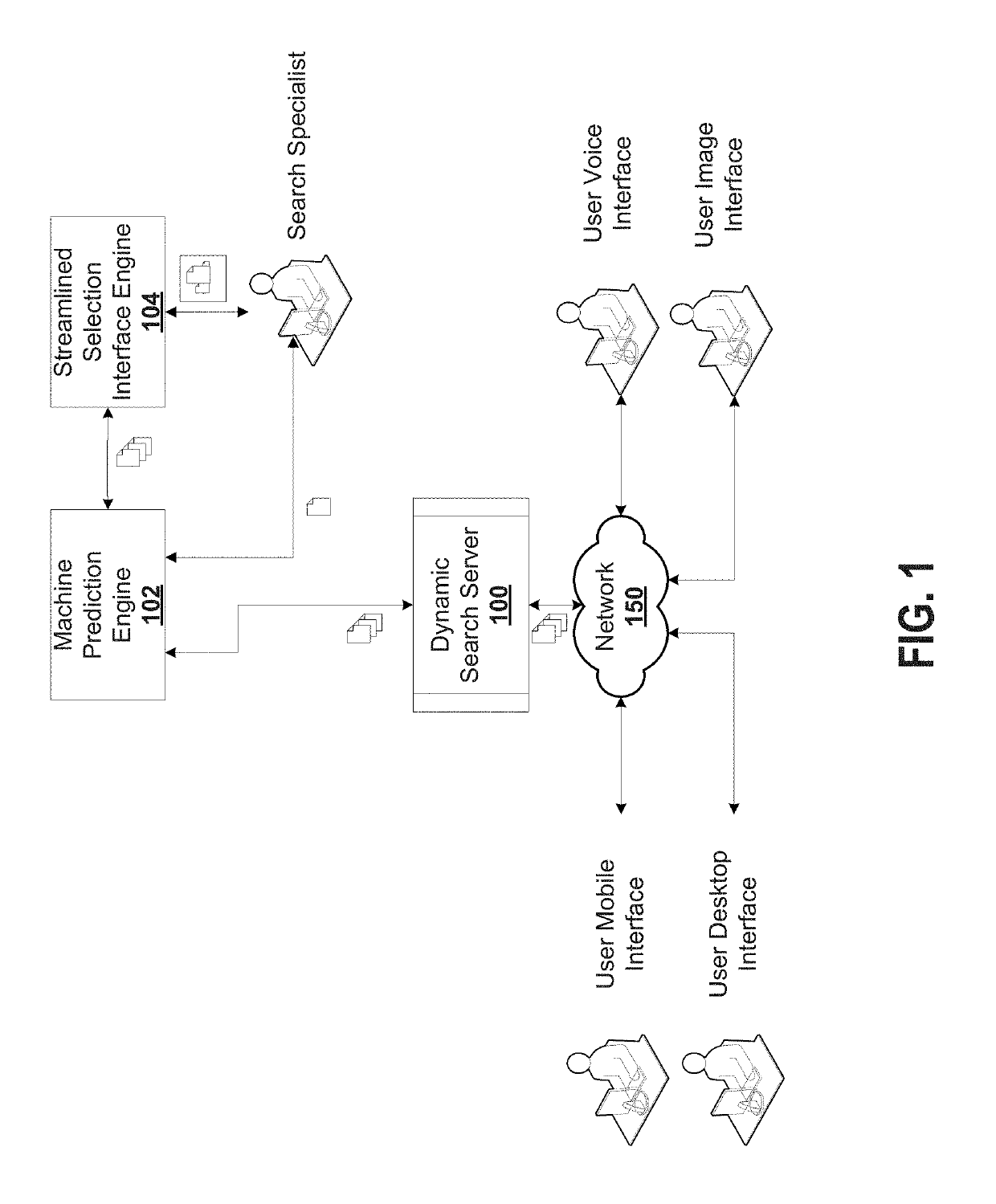
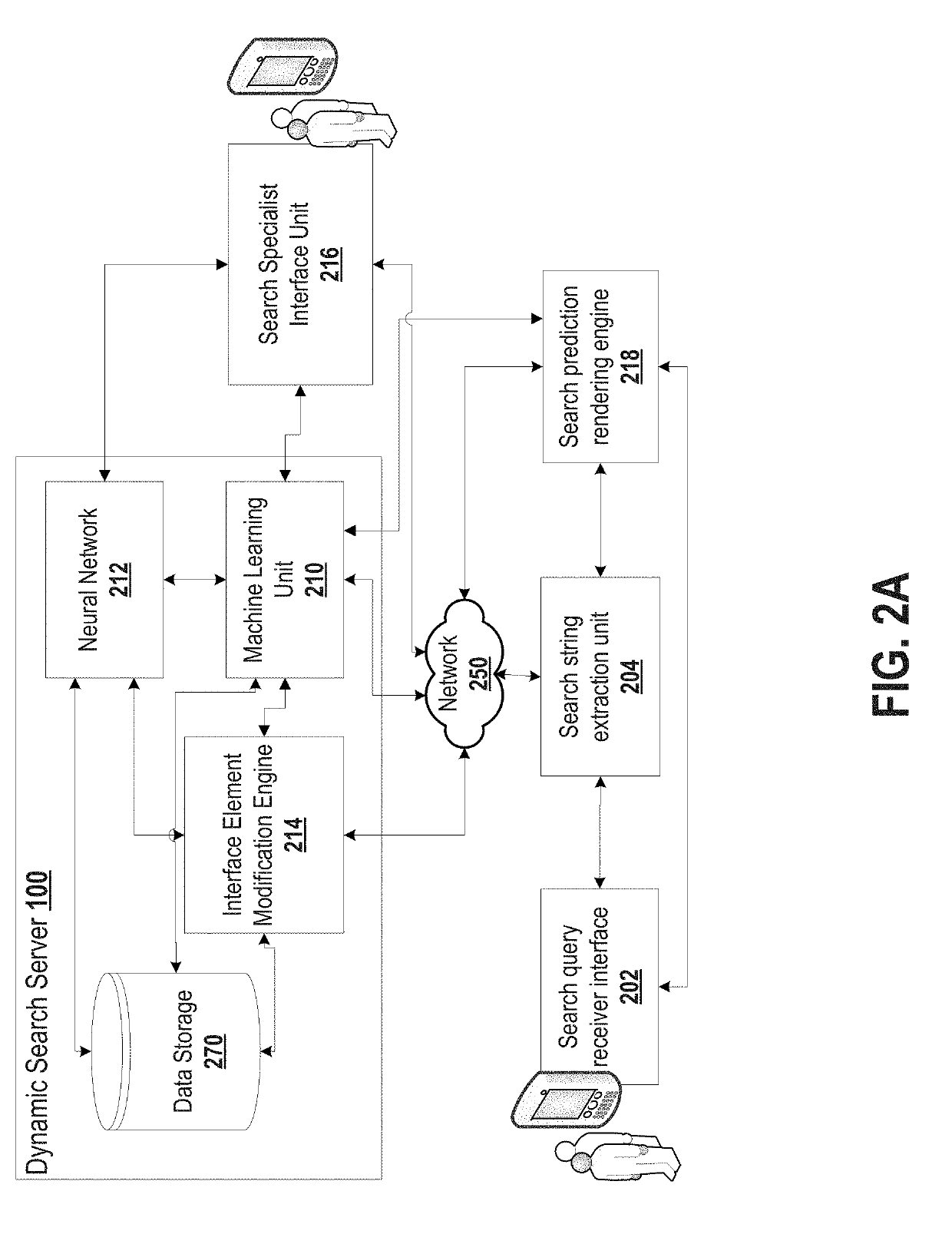
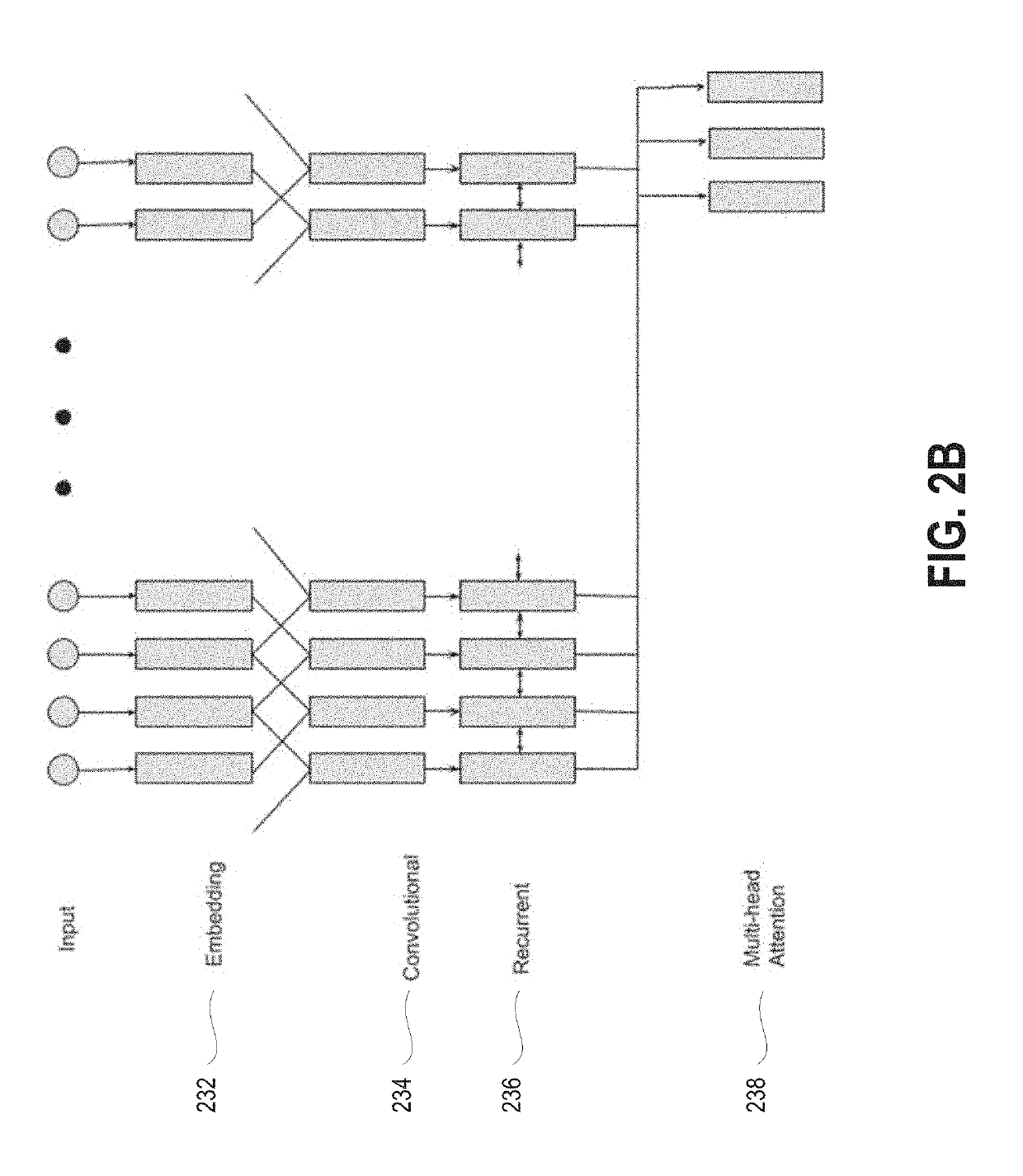
System and method for dynamic online search result generation
InactiveUS20190205761A1Increase sampling rateEasy to trainNeural architecturesText database queryingNerve networkConfidence metric
Owner:ADEPTMIND INC
Automated license plate recognition system and method using human-in-the-loop based adaptive learning
ActiveUS9092979B2Reduce labor costsRoad vehicles traffic controlCharacter and pattern recognitionAdaptive learningData set
An automated license plate recognition (ALPR) system and method using a human-in-the-loop based adaptive learning approach. One or more images with respect to an automotive vehicle can be segmented in order to determine a license plate of the automotive vehicle within a scene. An optical character recognition (OCR) engine loaded with an OCR algorithm can be further adapted to determine a character sequence of the license plate based on a training data set. A confidence level with respect to the images can be generated in order to route a low confidence image to an operator for obtaining a human interpreted image. The parameters with respect to the OCR algorithm can be adjusted based on the human interpreted image and the actual image of the license plate. A license plate design can be then incorporated into the OCR engine in order to automate the process of recognizing the license plate with respect to the automotive vehicle in a wide range of transportation related applications.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
System and Method for Correcting Low Confidence Characters From an OCR Engine With an HTML Web Form
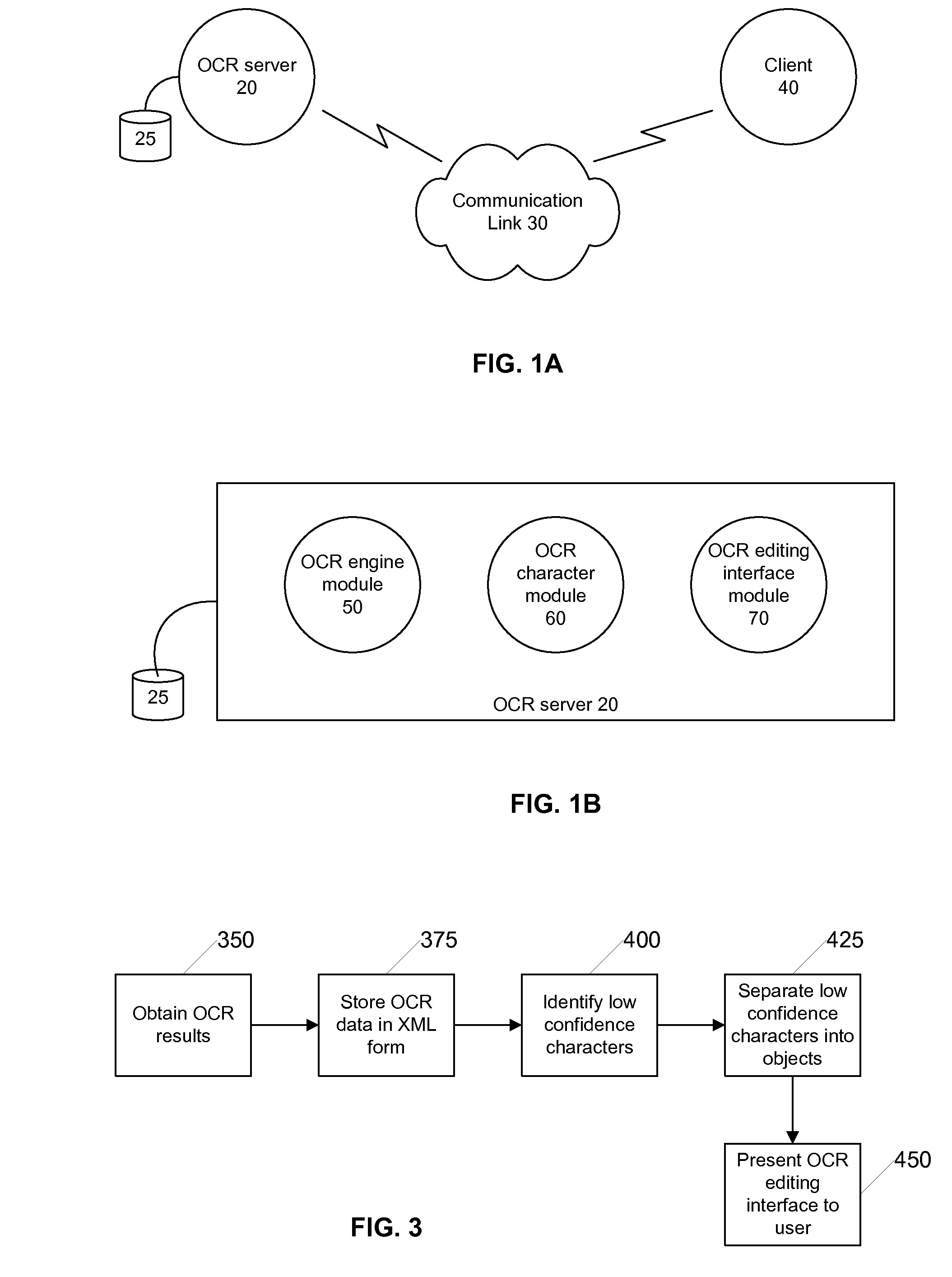
InactiveUS20080212901A1Lower confidenceMinimize timeCharacter and pattern recognitionConfidence metricApplication software
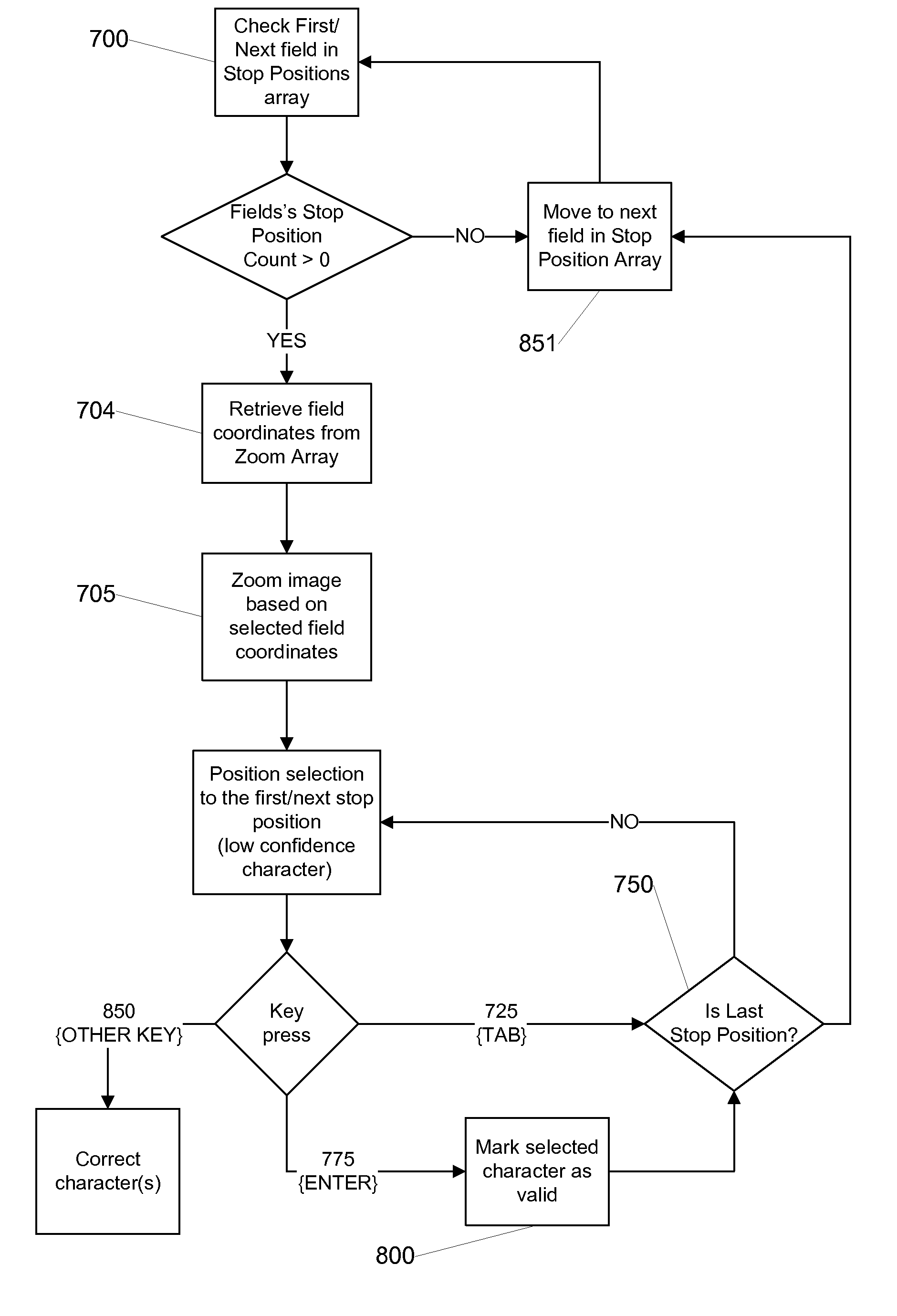
A character based system and method for correcting low confidence characters from an OCR system facilitates operator review, editing and correction of character and field level data generated by an OCR system without the need for an application that is installed at the operator workstation. The system creates a data structure of OCR information and provides that information to an operator through an HTML interface that is rendered using HTML and JavaScript. The data structure includes an OCR confidence level for each character and / or field and the operator is prompted to review only those characters / fields that meet a predetermined threshold for the confidence level. The operator can use an input key (e.g., TAB or ENTER) to navigate to each character / field with a low confidence level and thereby correct or validate each low confidence character / field as appropriate.
Owner:H B P OF SAN DIEGO
Automatic supervised classifier setup tool for semiconductor defects
ActiveUS7359544B2Effective maintenanceEfficient settingsImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionData mining
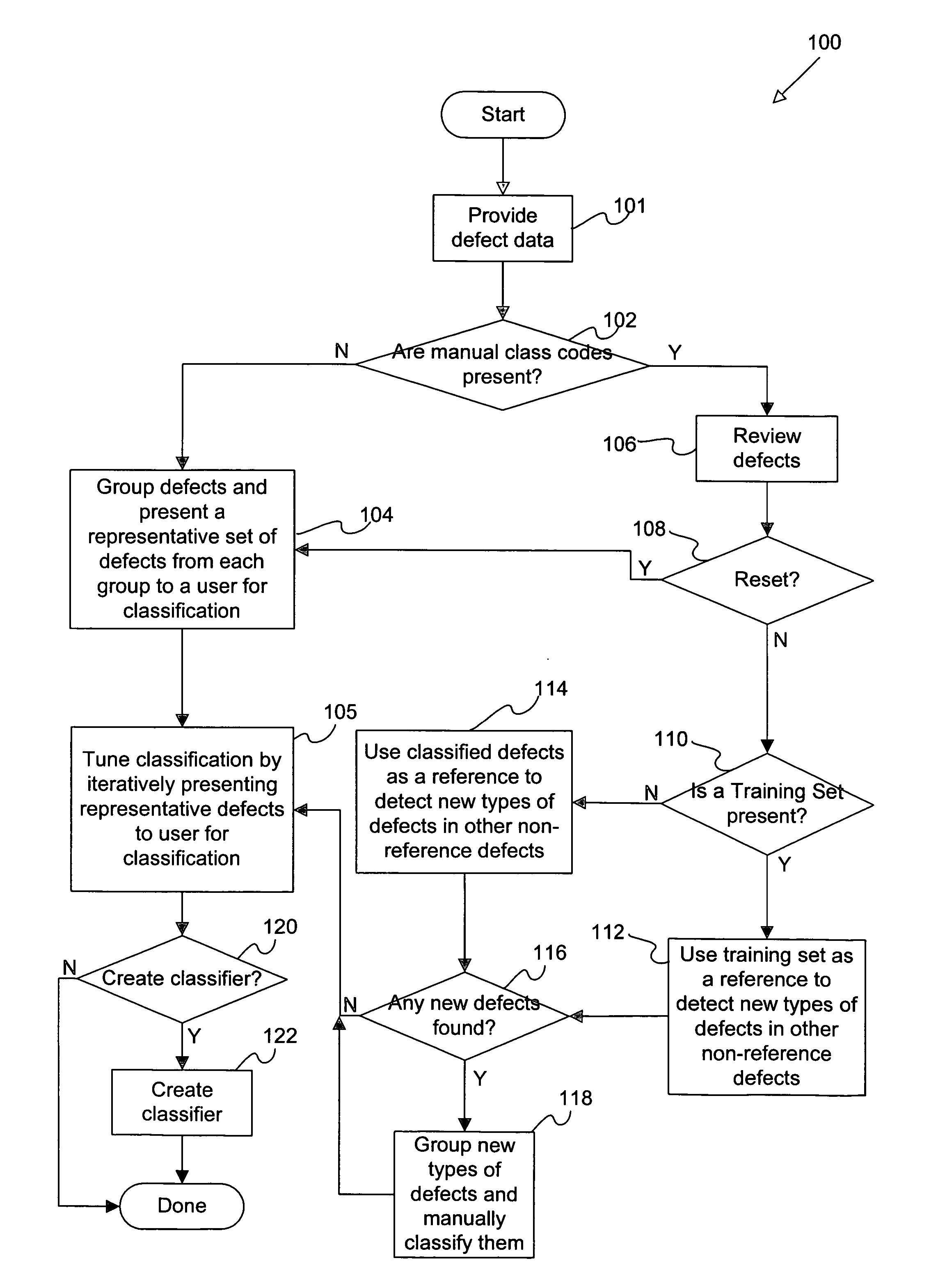
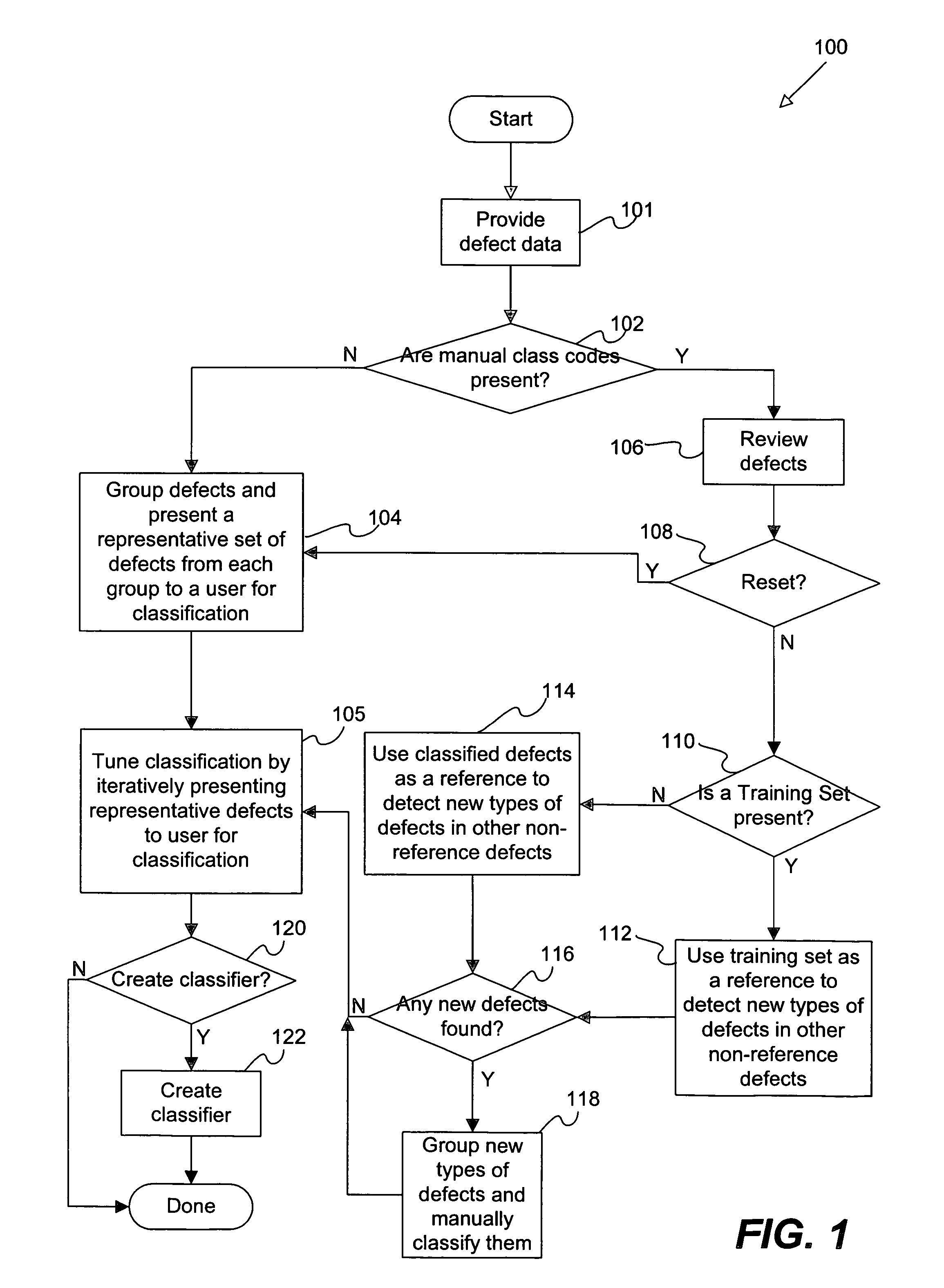
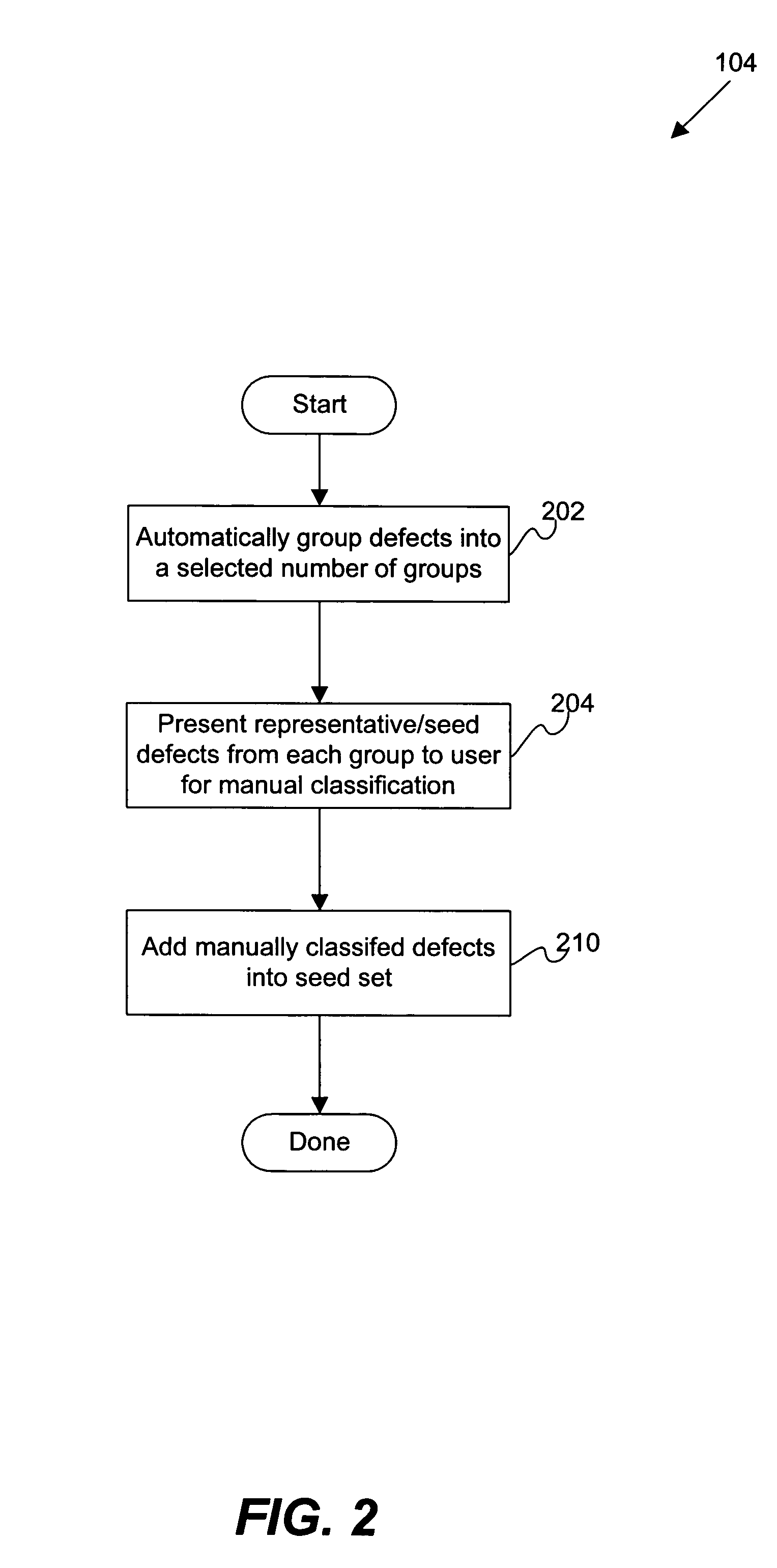
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for efficiently setting up and maintaining a defect classification system. In general terms, the setup procedure optionally includes automatically grouping a set of provided defects and presenting a representative set from each defect group to the user for classification. After the initial manual classification of the representative defects, the setup procedure includes an automatic procedure for classifying the non-reviewed or unclassified defects based on the manual class codes from the user-reviewed defects. After the automatic classification operation, the user may also be presented with defects from each class which may require re-classification. In particular embodiments, the user is iteratively presented with defects which have classifications that are suspect, which are near classification boundaries, or have classifications that have a low confidence level until each class is pure or contains a same type of defect classes as assigned by the user.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
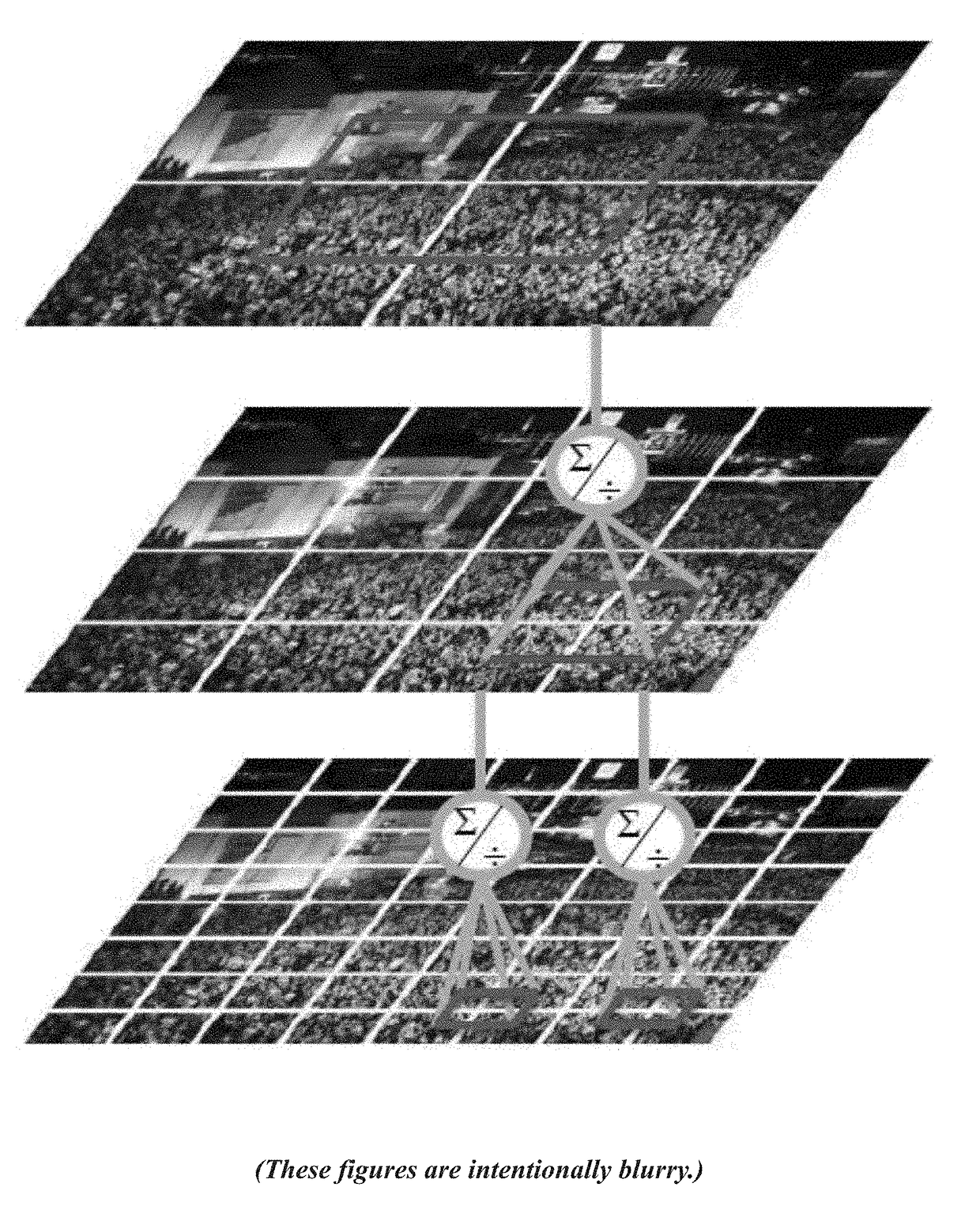
Multi-Source, Multi-Scale Counting in Dense Crowd Images
A method for counting individuals in an image containing a dense, uniform or non-uniform crowd. The current invention leverages multiple sources of information to compute an estimate of the number of individuals present in a dense crowd visible in a single image. This approach relies on multiple sources, such as low confidence head detections, repetition of texture elements (using SIFT), and frequency-domain analysis to estimate counts, along with confidence associated with observing individuals in an image region. Additionally, a global consistency constraint can be employed on counts using Markov Random Field. This caters for disparity in counts in local neighborhoods and across scales. The methodology was tested on a new dataset of fifty (50) crowd images containing over 64,000 annotated humans, with the head counts ranging from 94 to 4,543. Efficient and accurate results were attained.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Trending system and method using window filtering
ActiveUS20050165519A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital data processing detailsLower limitData set
A trending system and method for trending data in a mechanical system is provided. The trending system includes a sliding window filter. The sliding window filter receives a data set of data points generated by the mechanical system. The sliding window filter partitions the data set into a plurality of data windows, and uses the data windows to calculate upper and lower confidence bounds for the data set. Specifically, the sliding window filter calculates an upper confidence bounds and lower confidence bounds for each data point using each of the multiple data windows that includes the data point. The sliding window filter then selects the upper confidence bounds and the lower confidence bounds that results in the smallest mean prediction confidence interval for that data point. This results in a smoothed estimated trend for the data set that can be used for prognostication and fault detection.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Methods and apparatus for audio data analysis and data mining using speech recognition
InactiveUS20070083370A1Simplify the search processAutomatic exchangesSpeech recognitionSQLConfidence metric
A system and method provide an audio analysis intelligence tool with ad-hoc search capabilities using spoken words as an organized data form. An SQL-like interface is used to process and search audio data and combine it with other traditional data forms to enhance searching of audio segments to identify those audio segments satisfying minimum confidence levels for a match.
Owner:RINGCENTRAL INC
Improved kernel-related filtering tracking method based on ultra-pixel optical flow and self-adaptive learning factor
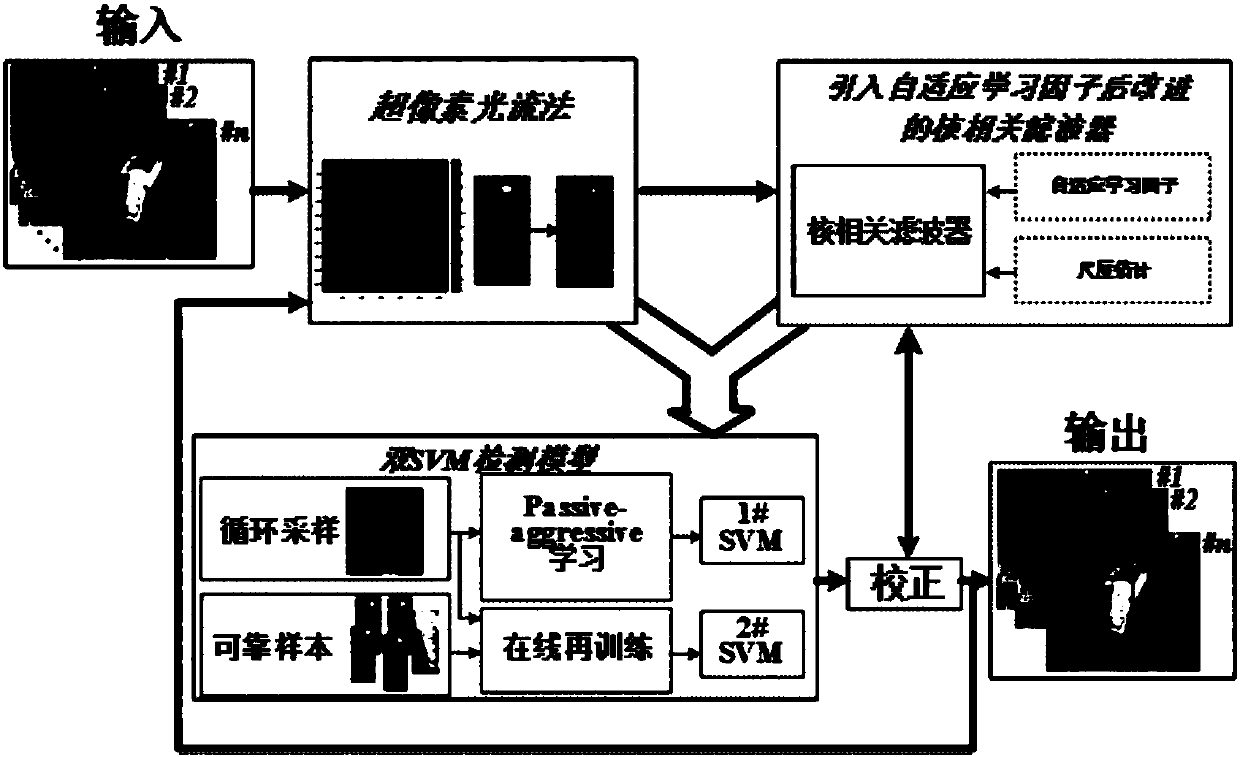
ActiveCN108090919AAccurate tracking is easy to achievePrecise positioningImage enhancementImage analysisLearning factorAdaptive learning
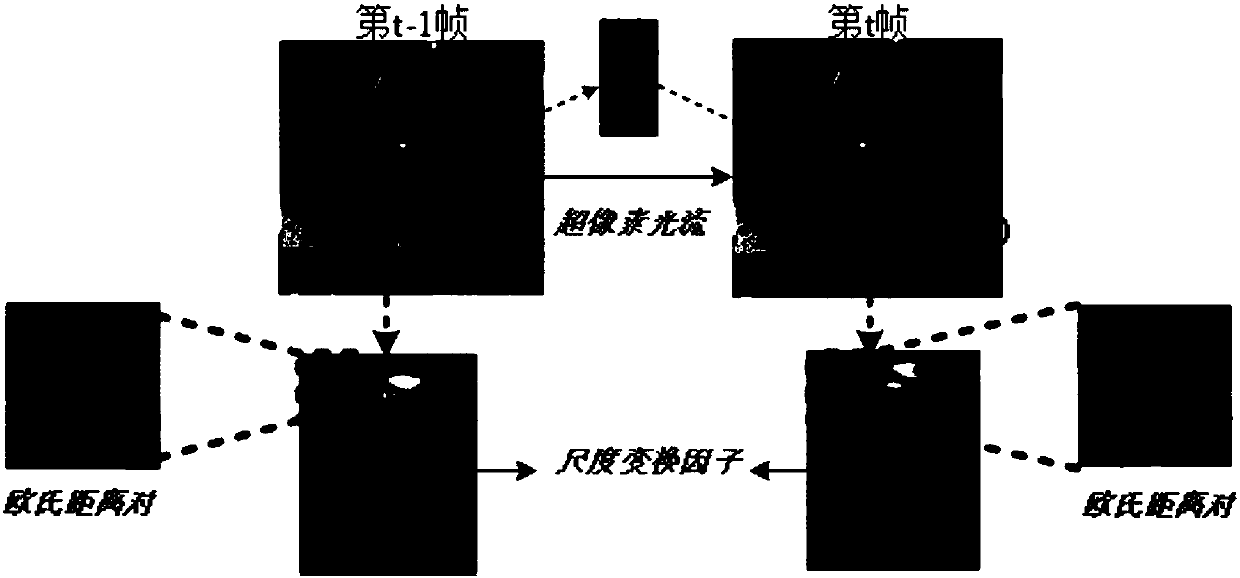
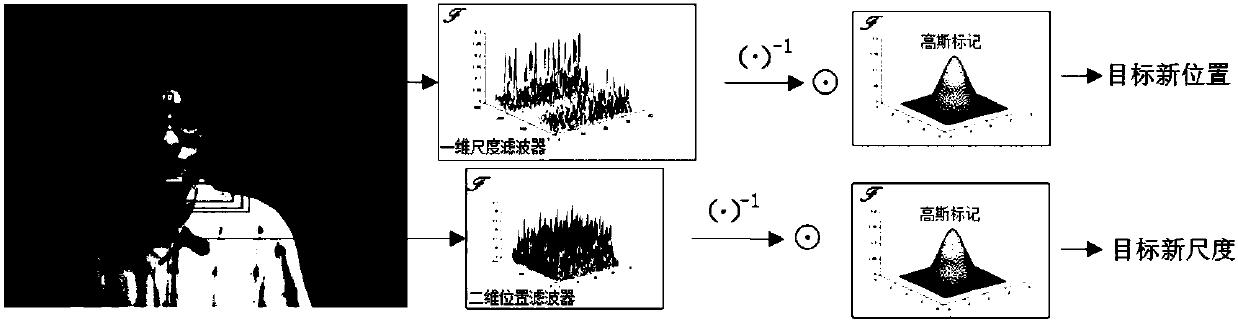
The invention discloses an improved kernel-related filtering tracking method based on ultra-pixel optical flow and self-adaptive learning factor. The appearance reconstruction of target can be realized through ultra-pixel analysis, and the target is divided into ultra-pixel blocks which are clustered into an ultra-pixel center. The displacement change of the optical flow analysis pixel point of each ultra-pixel center is calculated, and the movement offset and scale change of the target can be detected. Based on the predicted parameter, cycled sampling is conducted on each new-frame image, andan improved and gauss kernel-based filtering target tracking method which introduces the self-adaptive learning factor is adopted by each sample, and the accurate position and scale of the target canbe detected. The detection result is detected and corrected through an on-line SVM detection model, and the position with low confidence is corrected, and finally the target position can be accurately positioned and the target accurate scale can be obtained. The invention is advantageous in that the tracking problems like scale change, shielding, deforming, and motion blur, which exit in the target tracking process can be overcome, and real-time and highly-precise target tracking can be realized.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GUANGDA INNOVATION TECH CO LTD
Conditional multipass automatic speech recognition
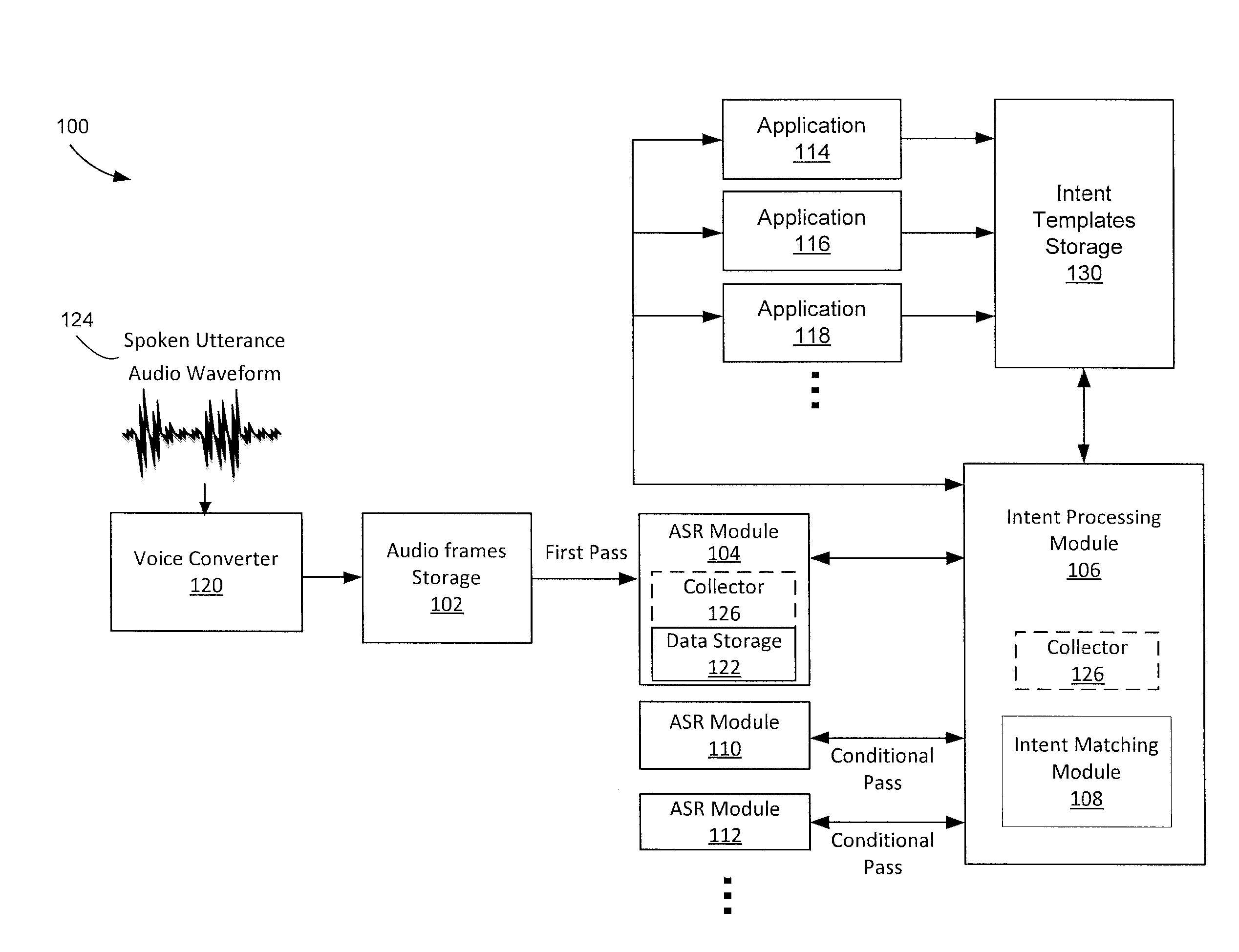
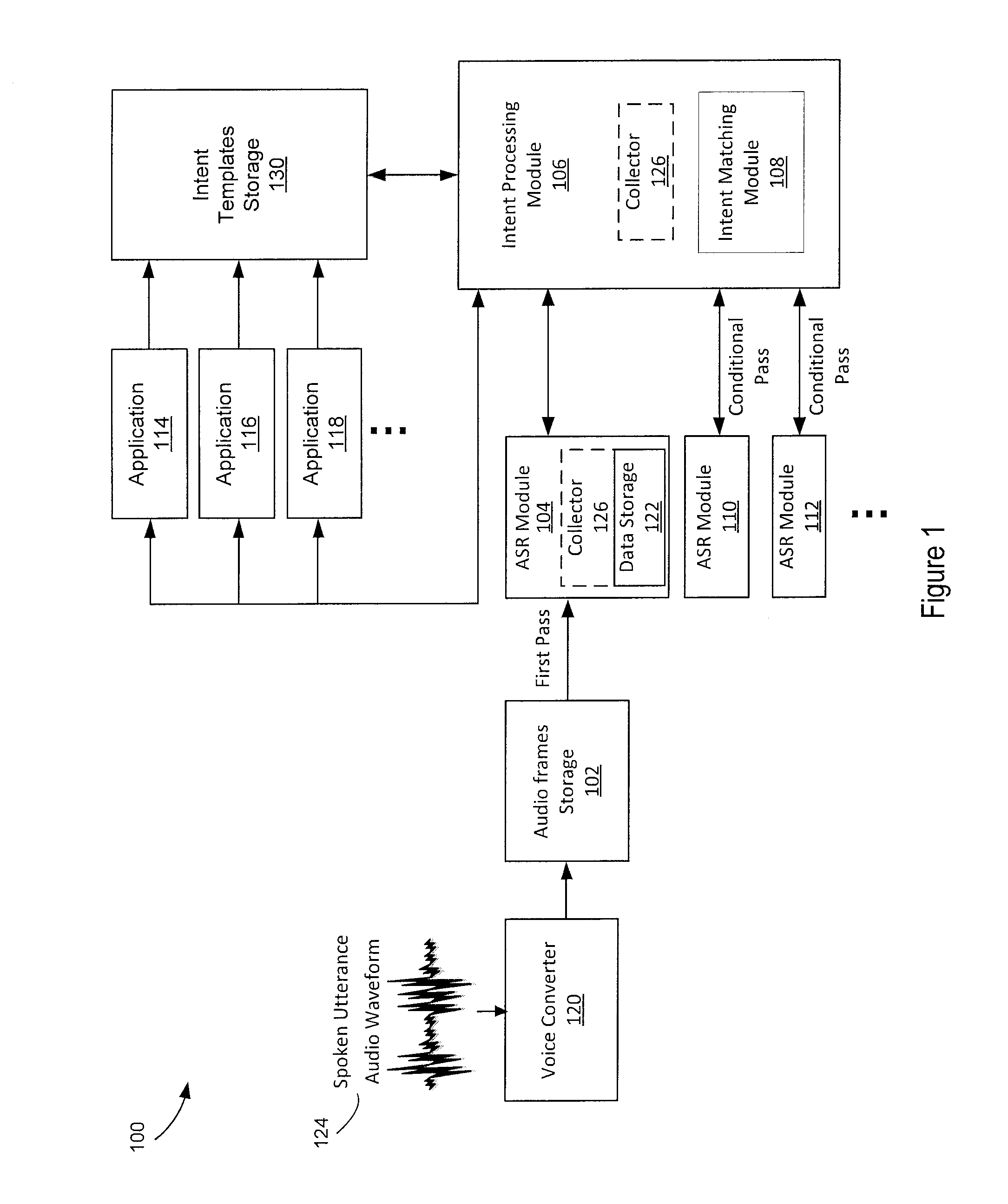
In a conditional multipass automatic speech recognition system, one or more intent templates may be received from an application. A spoken utterance is received and audio frames are generated from the utterance. The audio frames are compared to a first grammar. Recognized speech results are generated and unrecognized audio frames or low confidence frames are collected. One of one or more intent templates and one or more corresponding intent parameters may be determined based on the recognized speech results. The unrecognized audio frames may be conditionally compared to a second grammar in instances when additional information is requested, relative to the determined intent template or the corresponding intent parameters.
Owner:ONTARIO INC
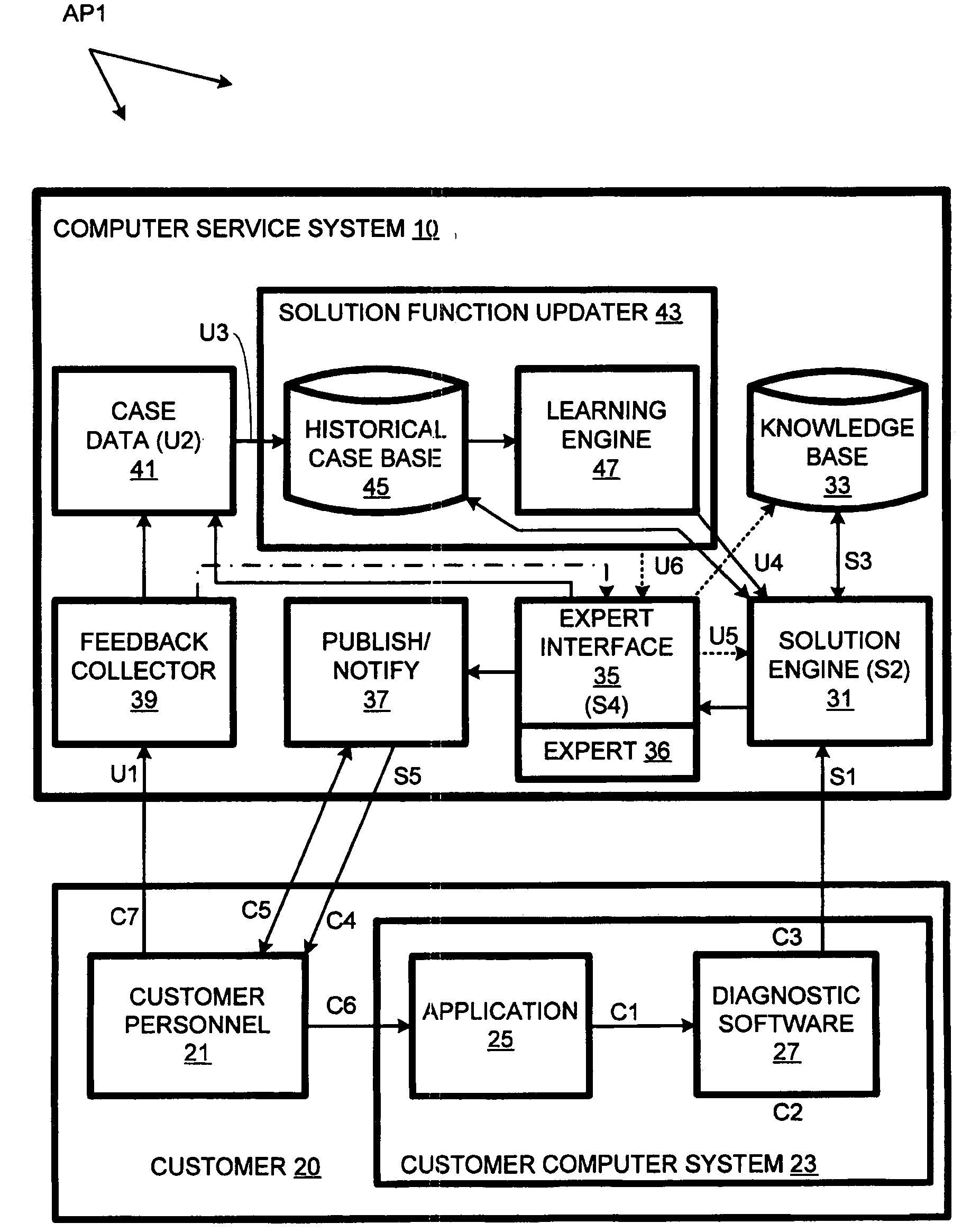
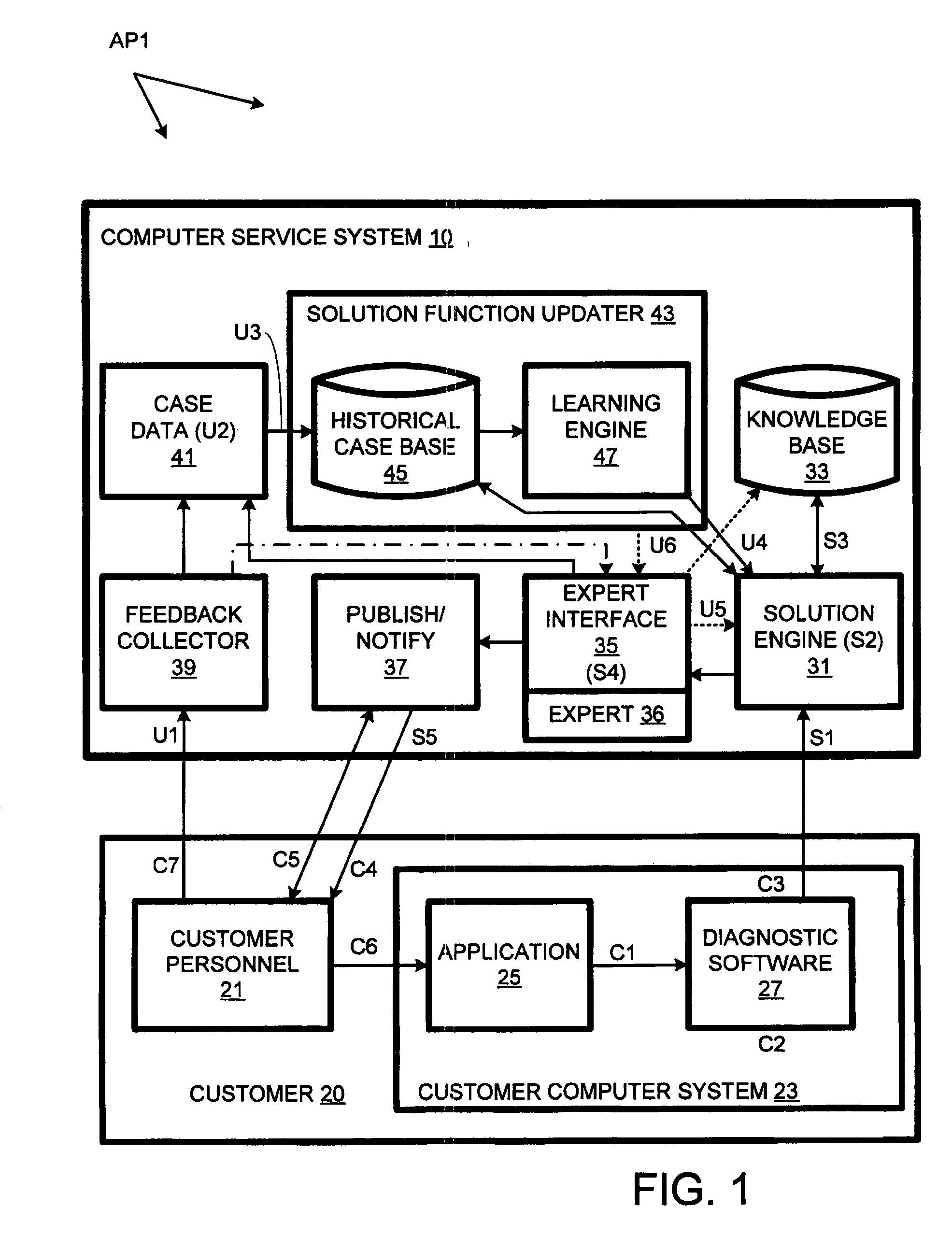
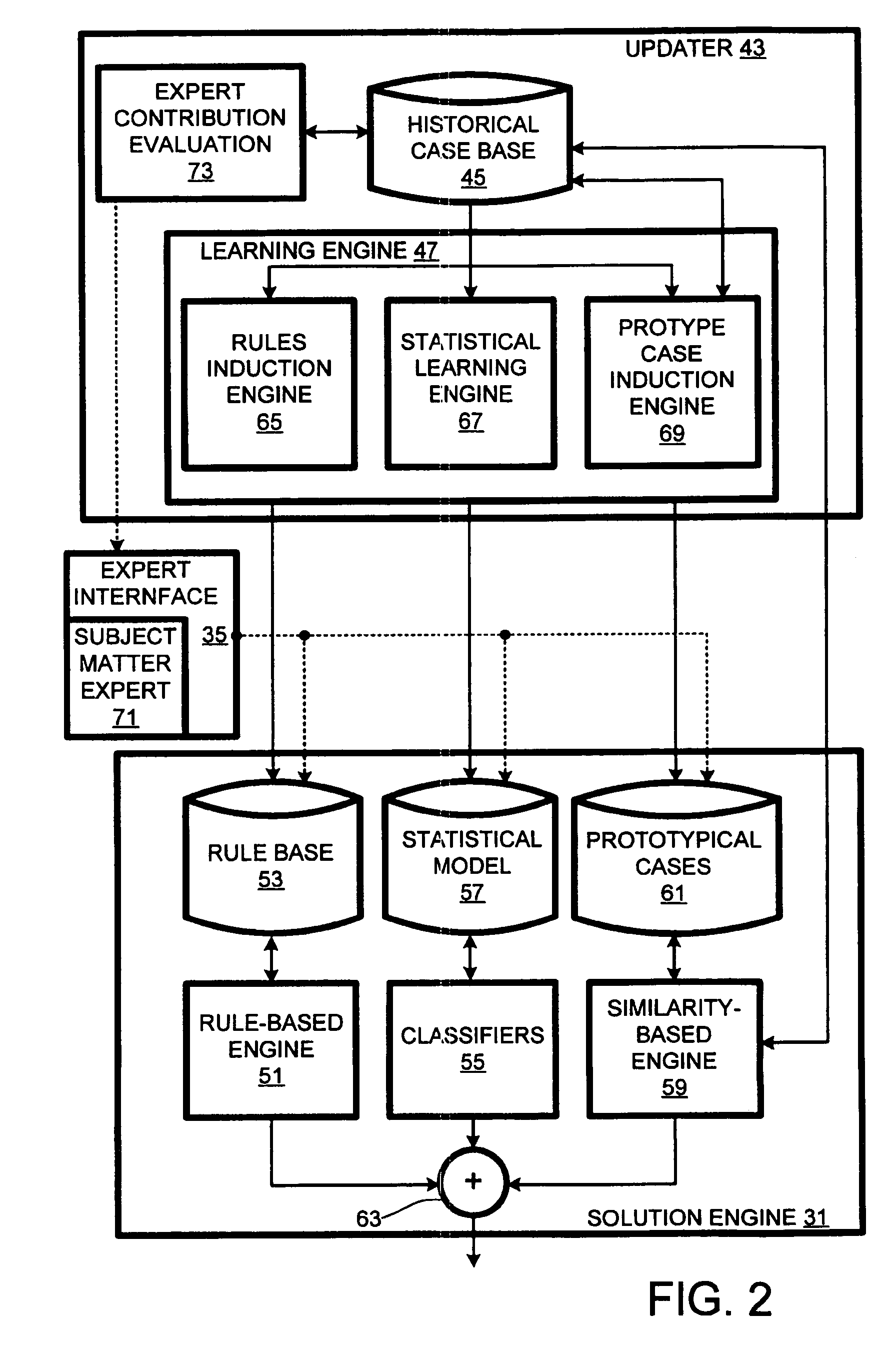
Computer support service with solution function updates as a function of pre-delivery expert changes to automatically generated solutions
A solution engine (31) of a vendor's highly-automated adaptive computer support system (10) for a remote customer (20) automatically generates proposed solutions, e.g., sets of support documents, as a function of diagnostic data received from a customer's computer system (23). The automatically generated solution can be subject to expert review (35) prior to publication (37) to the customer, e.g., when the automated system assigns a low confidence level to the solution. In addition, expert review can be triggered by feedback (39) from the customer once a proposed solution is communicated. The diagnostic data, solutions and feedback for an incident are packaged (at 41) as a “case” and entered into an historical case database (45). A solution function updater (43) updates the solution function as a function, at least in part, of the expert review and customer feedback.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
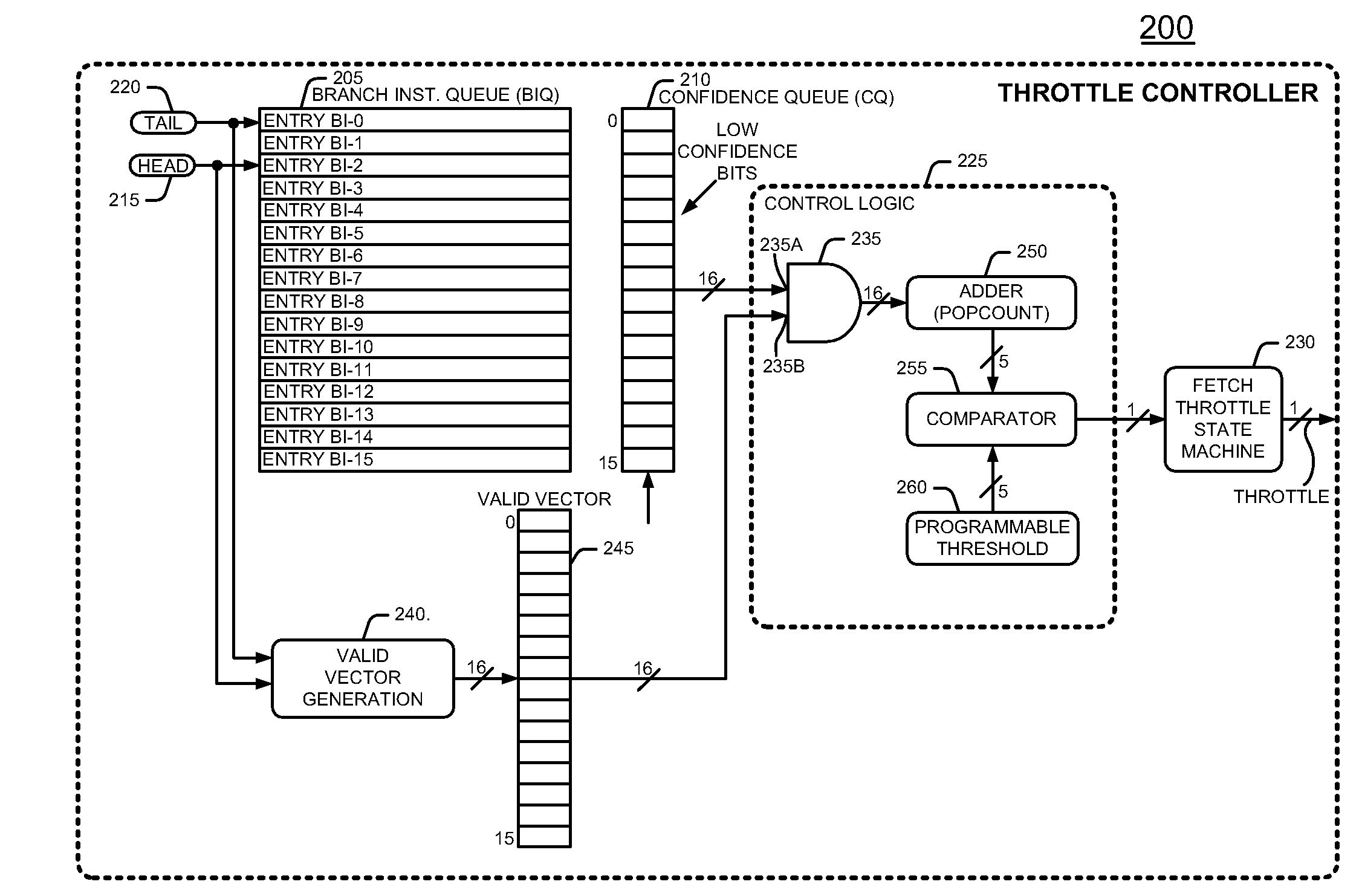
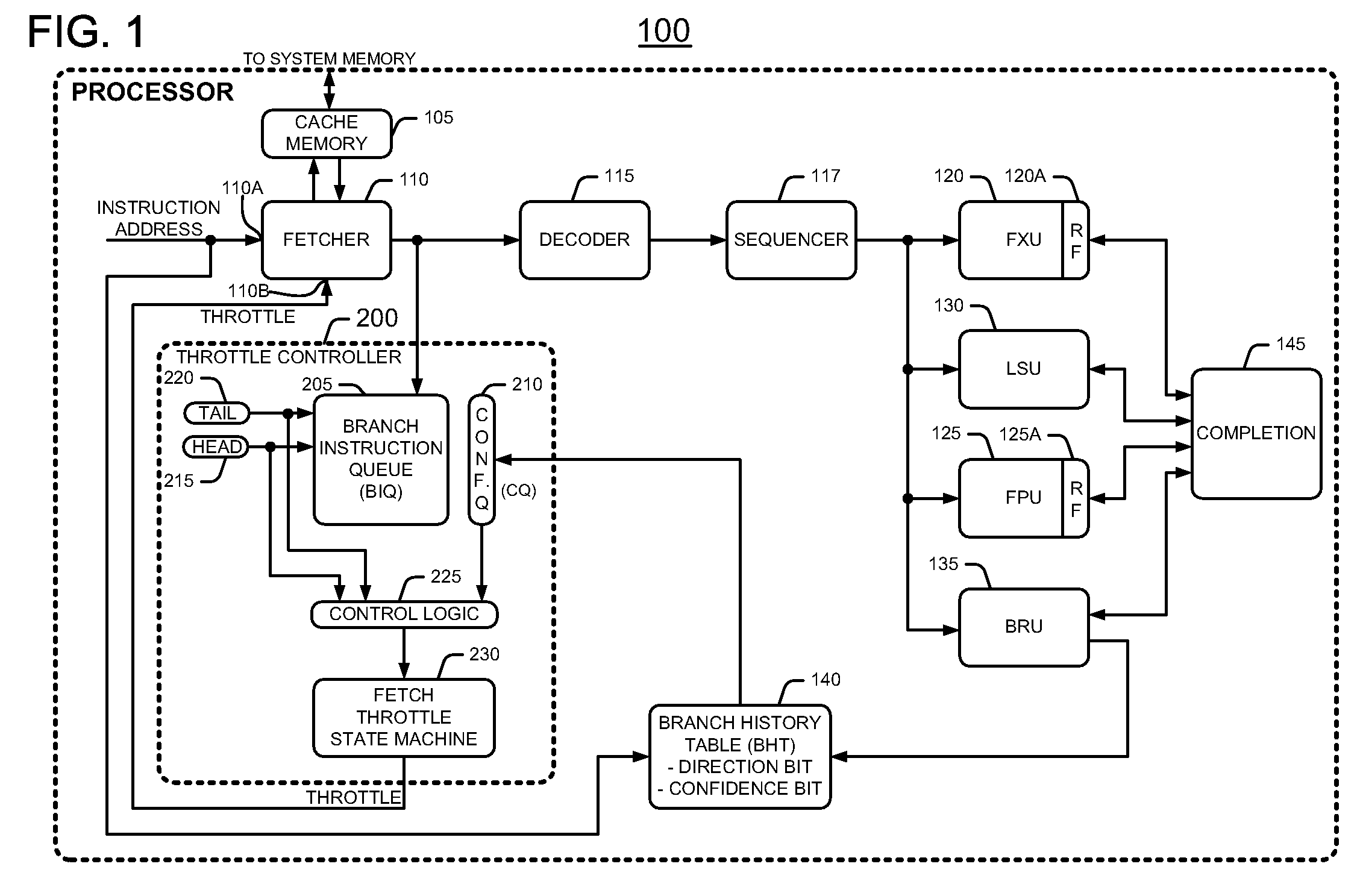
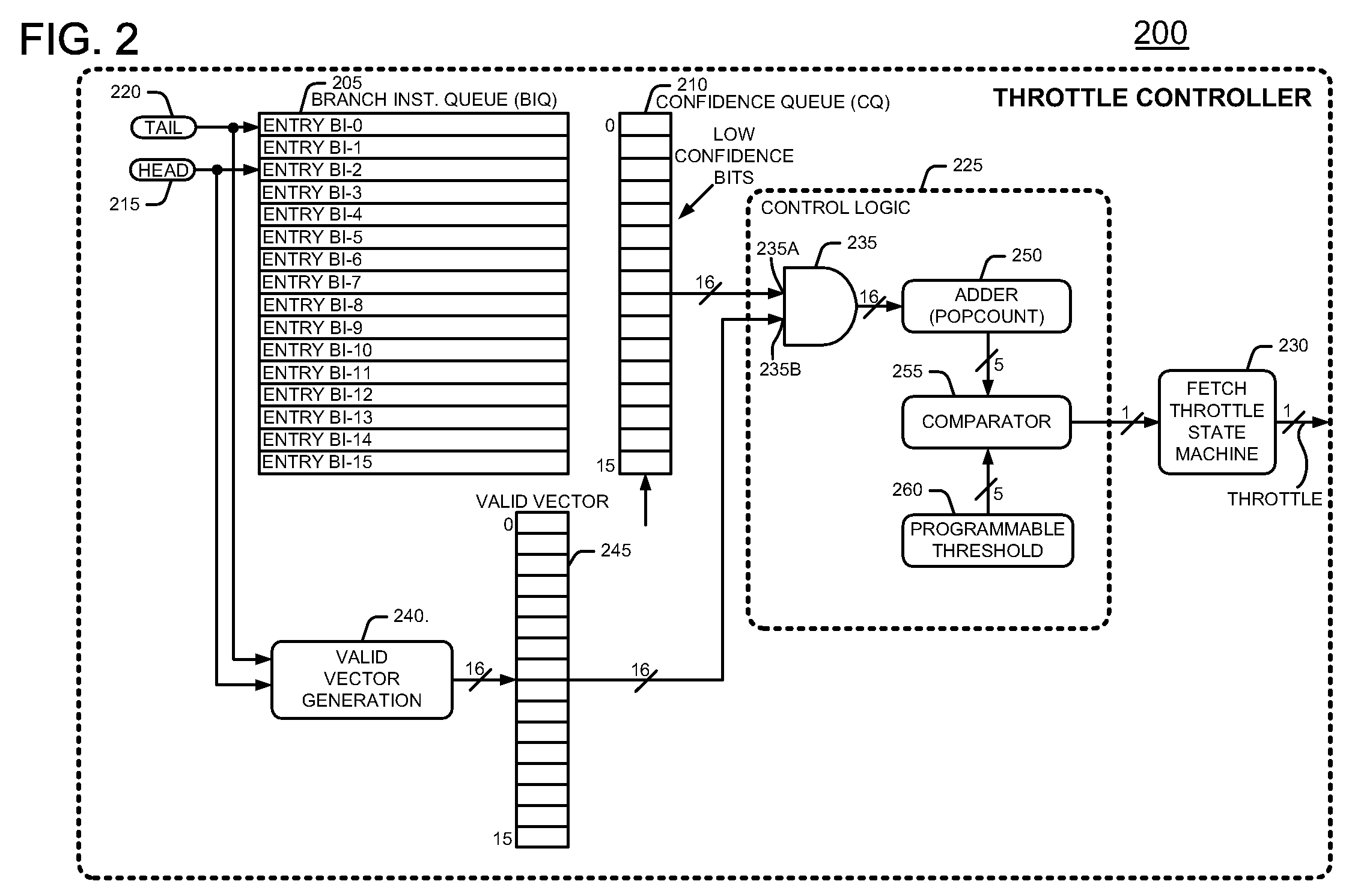
Method and apparatus for conserving power by throttling instruction fetching when a processor encounters low confidence branches in an information handling system
InactiveUS7627742B2Reduce power consumptionDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionParallel computingHandling system
An information handling system includes a processor that throttles the instruction fetcher whenever the inaccuracy, or lack of confidence, in branch predictions for branch instructions stored in a branch instruction queue exceeds a predetermined threshold confidence level of inaccuracy or error. In this manner, fetch operations slow down to conserve processor power when it is likely that the processor will mispredict the outcome of branch instructions. Fetch operations return to full speed when it is likely that the processor will correctly predict the outcome of branch instructions.
Owner:IBM CORP
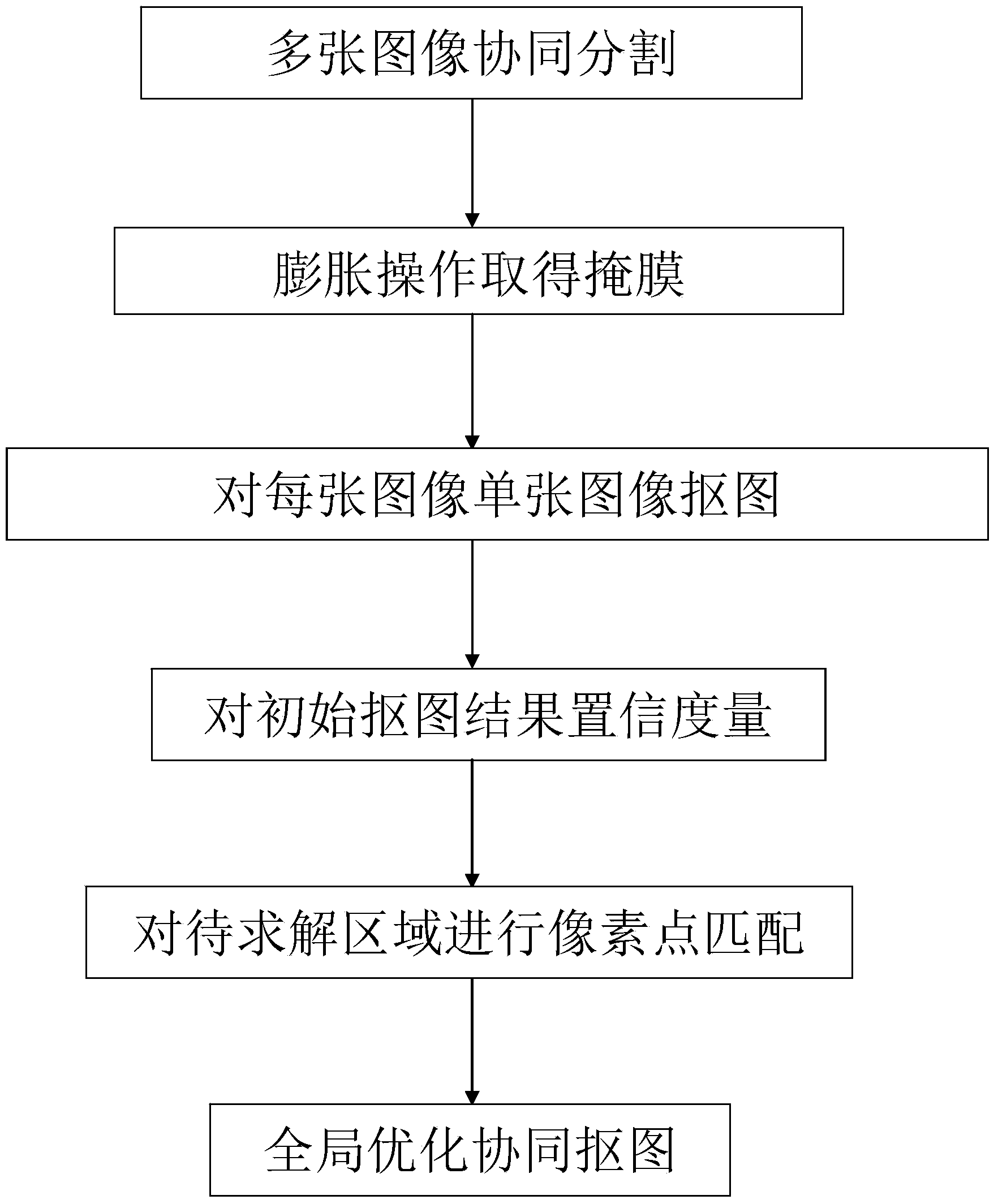
Image collaborative cutout method based on confidence level
The invention discloses an image collaborative cutout method based on confidence level. The method aims to conduct collaborative cutout on images with a foreground of slight deformation and a background of large difference. According to the method, front background segmentation is conducted on multiple images by the adoption of a collaborative segmentation algorithm, each image is marked as a mask of a foreground, a background and a region to be solved through morphological operation, cutout is conducted on each source image by the utilization of the source image and the mask by the adoption of an existing single common cutout method, confidence measurement is conducted on the cutout result, pixel points in the region to be solved in all the images are matched, a global optimization function is defined based on the matching so that the cutout effect on all the images is improved in coordination, the method aims to conduct cutout result spread from a high confidence region to a low confidence region matched with the high confidence region, and thus more accurate cutout result is obtained in the corresponding low confidence region. By means of the method, multiple images are input, and the cutout result of the images is output.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
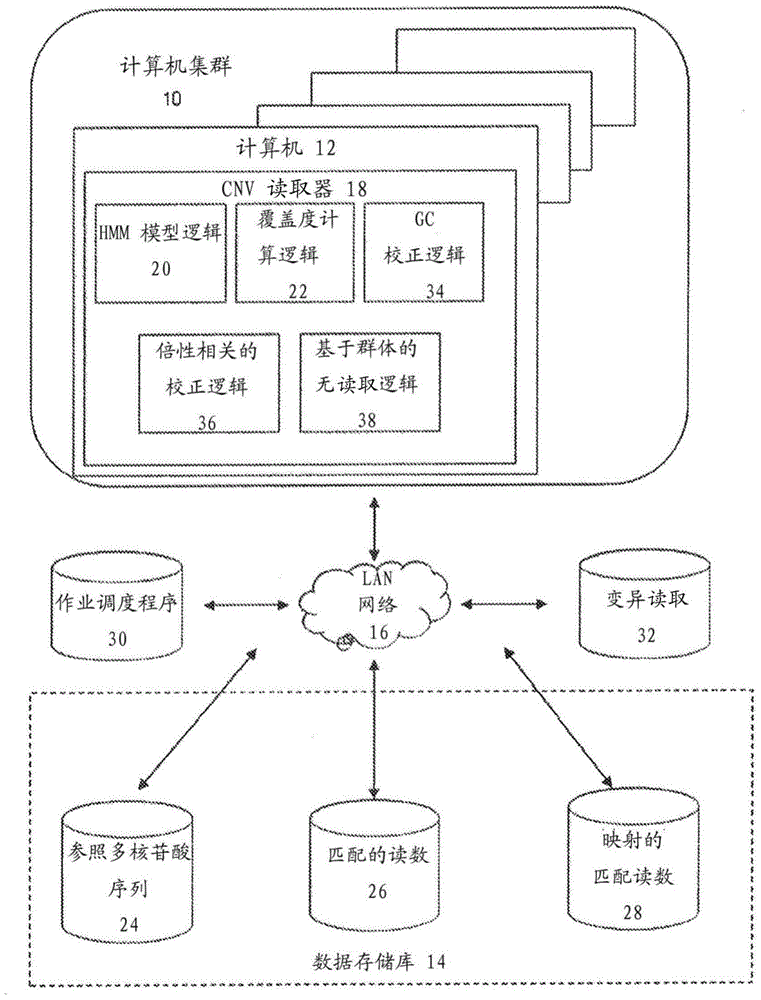
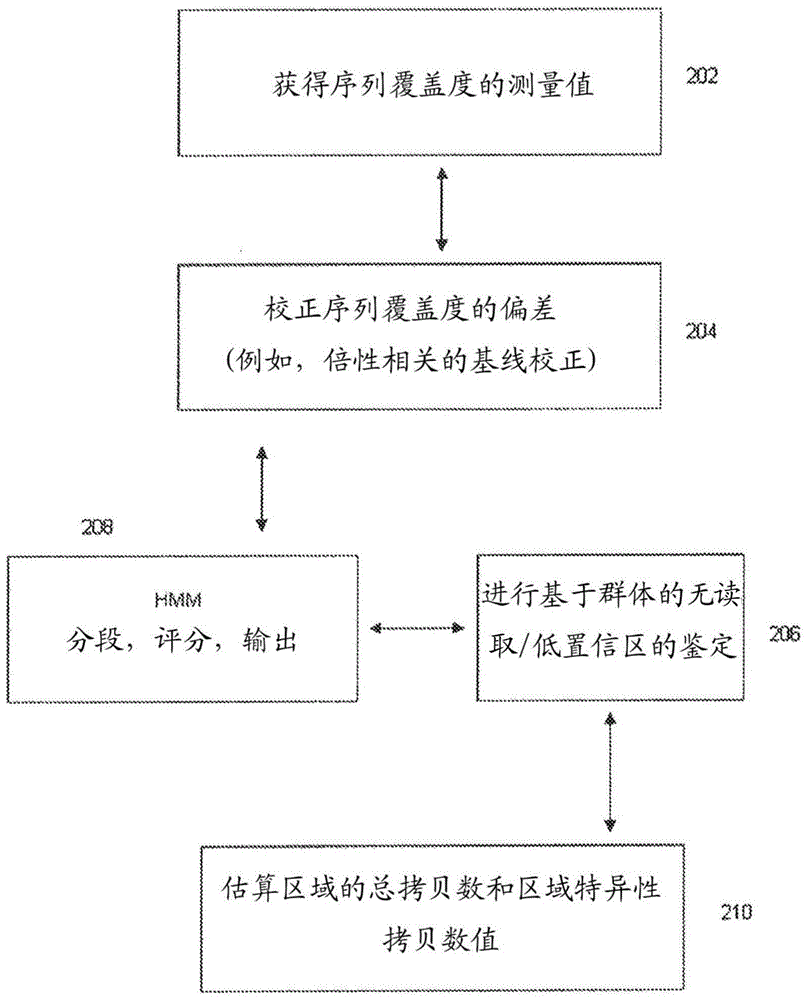
Methods for determining absolute genome-wide copy number variations of complex tumors
Methods for interpreting absolute copy number of complex tumors and for determining the copy number of a genomic region at a detection position of a target sequence in a sample are disclosed. In certain aspects, genomic regions of a target sequence in a sample are sequenced and measurement data for sequence coverage is obtained. Sequence coverage bias is corrected and may be normalized against a baseline sample. Hidden Markov Model (HMM) segmentation, scoring, and output are performed, and in some embodiments population-based no-calling and identification of low-confidence regions may also be performed. A total copy number value and region-specific copy number value for a plurality of regions are then estimated.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Model training method, customer service system, data labeling system and readable storage medium
ActiveCN109582793AImprove classification accuracyQuality improvementSpecial data processing applicationsText database clustering/classificationData setData needs
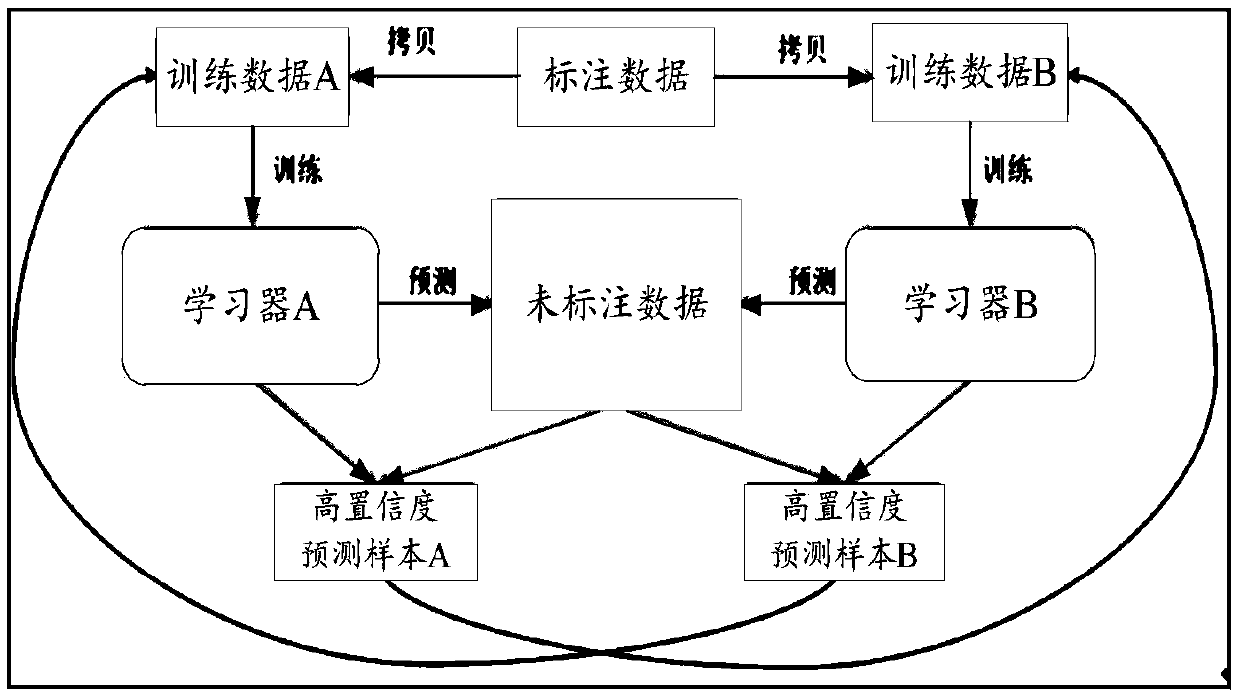
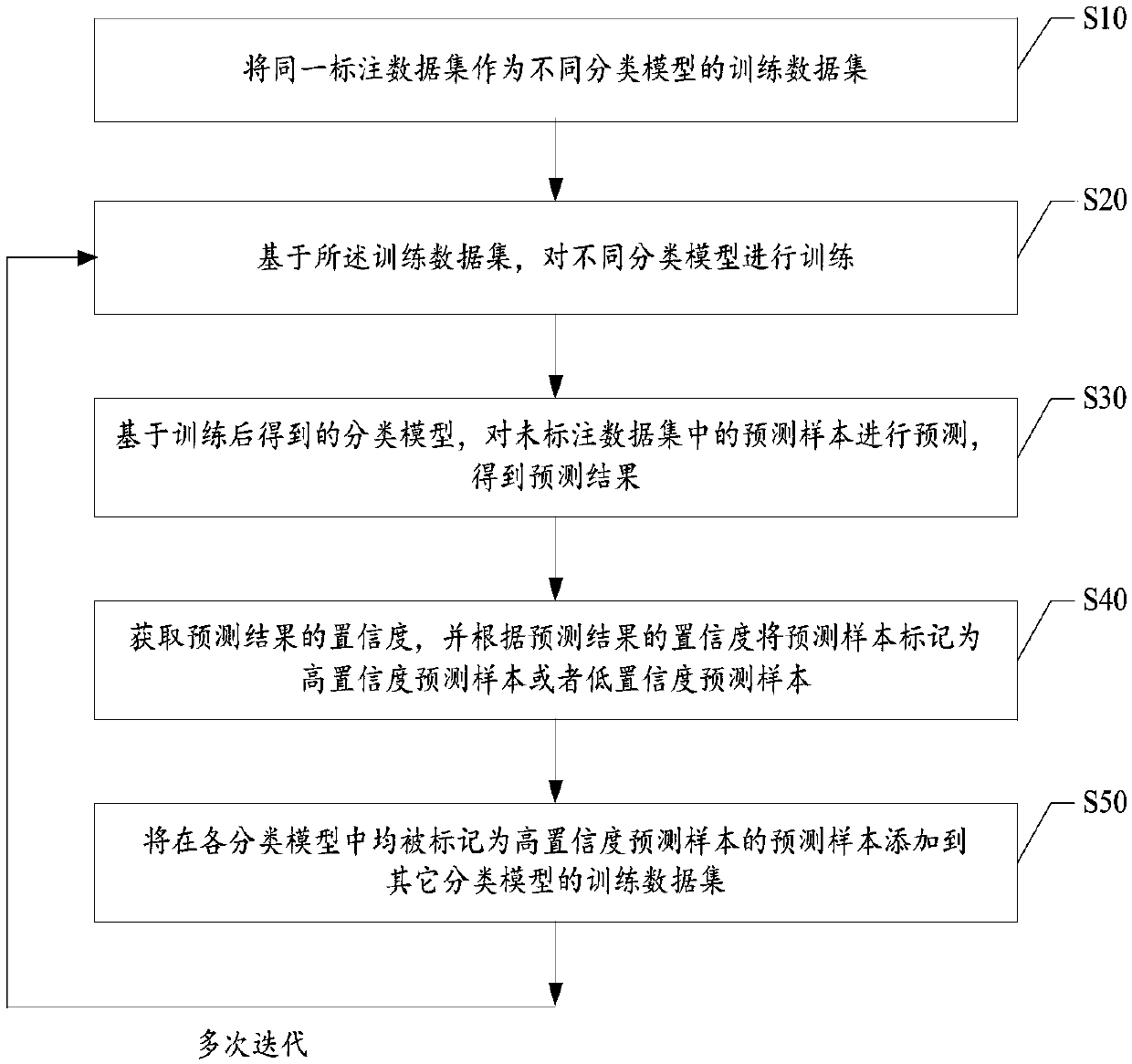
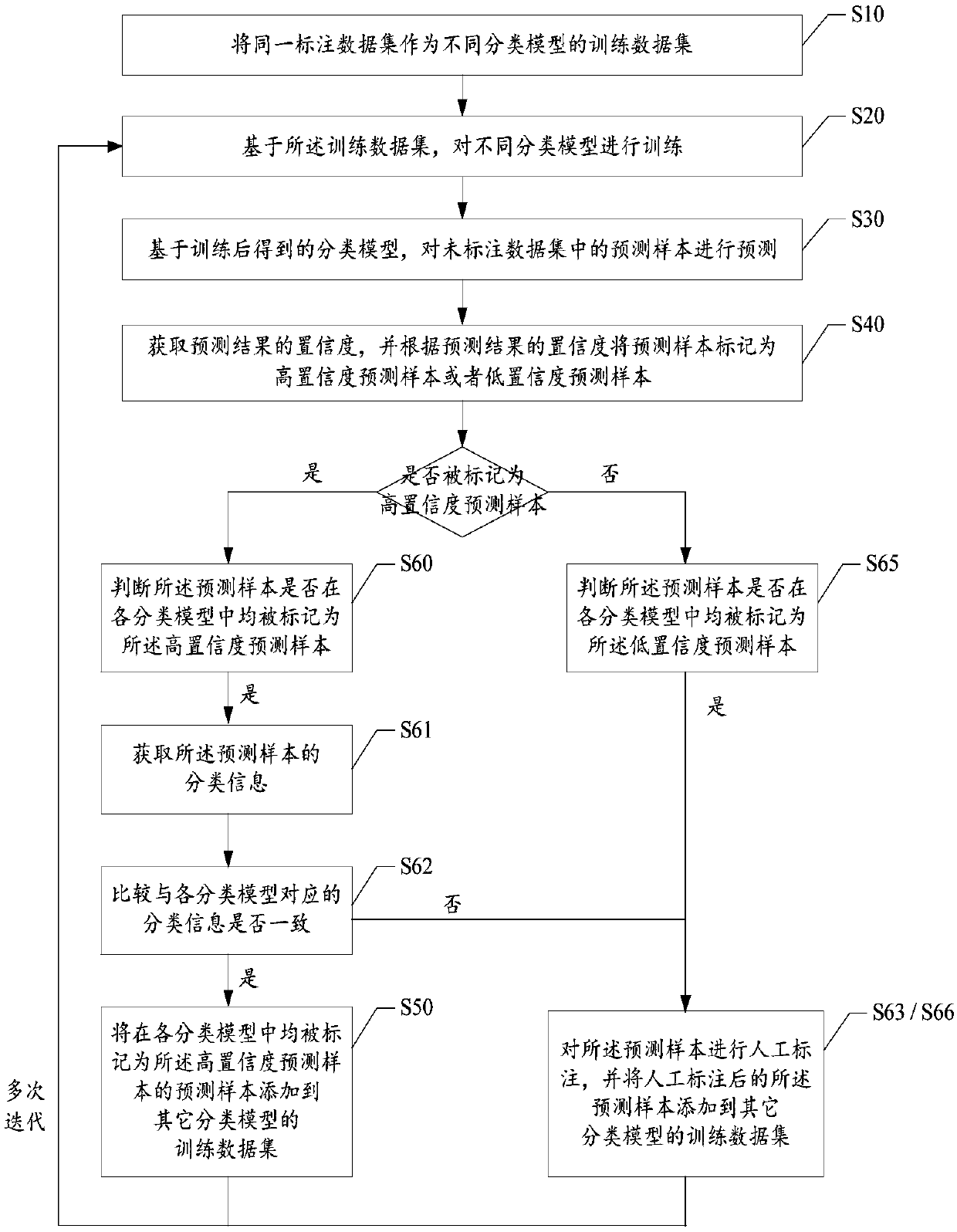
The invention provides a model training method which comprises the following steps: taking the same annotated data set as a training data set of different classification models, and training the different classification models; Based on the trained classification model, predicting prediction samples in the unlabeled data set to obtain a prediction result; obtaining Confidence of a prediction result, and marking the prediction sample as a high-confidence prediction sample or a low-confidence prediction sample; Adding prediction samples marked as high-confidence prediction samples in each classification model to training data sets of other classification models; And based on the new training data set, performing preset rounds of iterative training, and obtaining a classification model aftermultiple times of iterative training. The invention further provides a customer service system, a data labeling system and a readable storage medium. The technical problem that the response quality ofa customer service system is poor due to the fact that the obtaining cost of the mark data needed by an existing classification model is high and the quality of the classification model is low is solved.
Owner:WEBANK (CHINA)
Method for sequencing polynucleotides
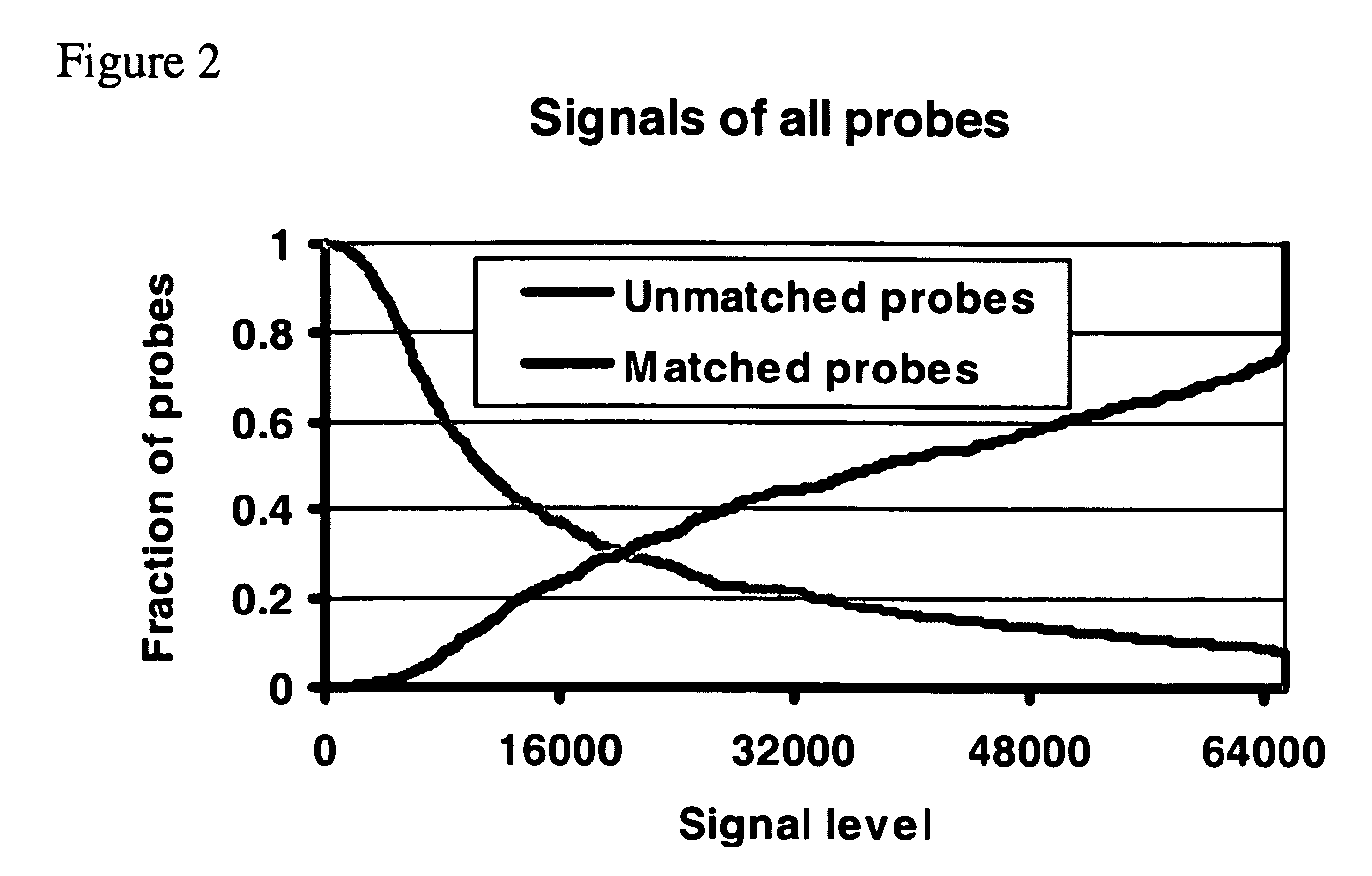
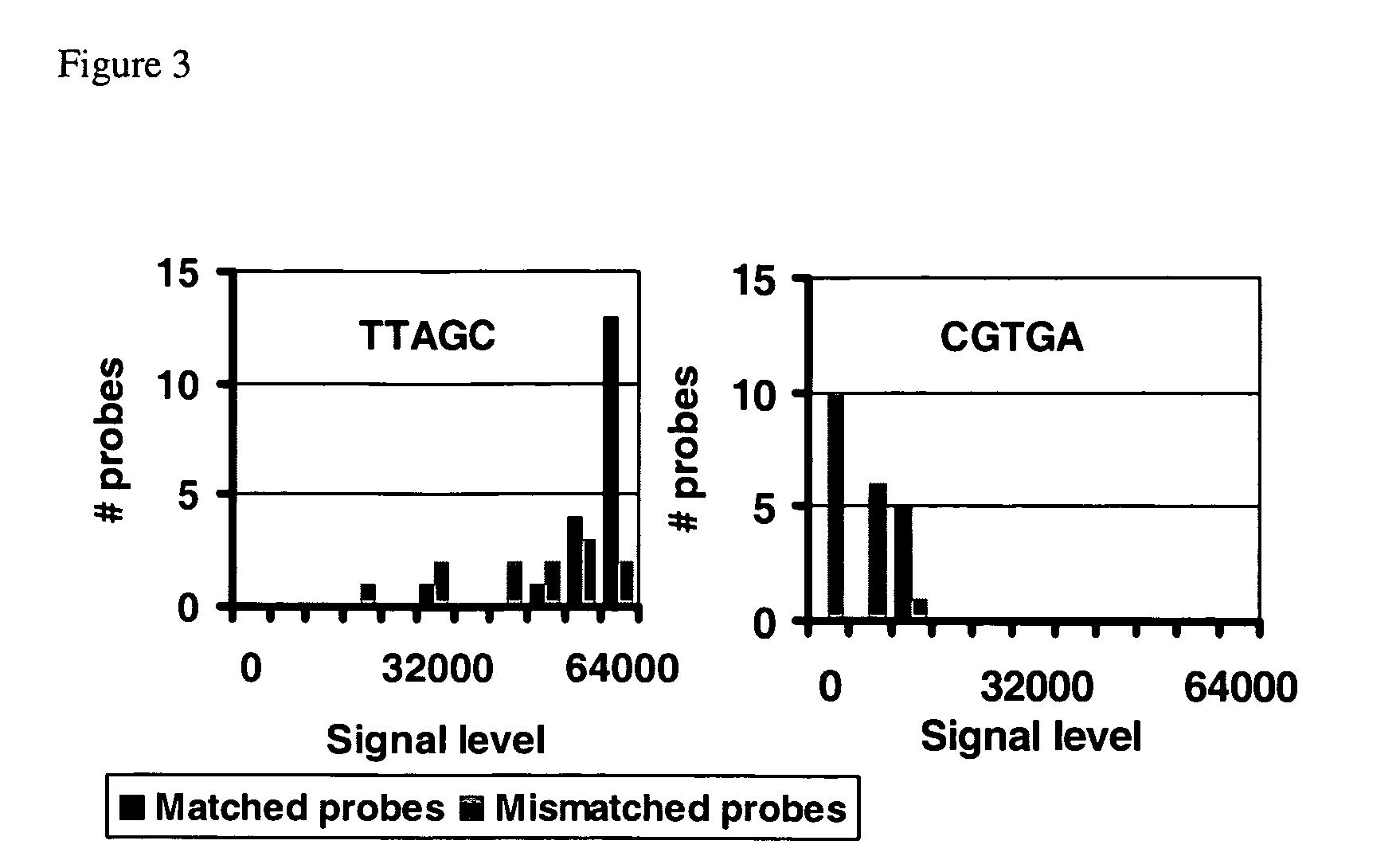
InactiveUS20050149272A1Reduce spurious biochemical outcomeEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotide sequencLow Confidence
A method for obtaining a candidate nucleotide sequence S indicative of a sequence of a target polynucleotide molecule that produces a hybridization signal I({right arrow over (x)}) upon incubation with a polynucleotide {right arrow over (x)} for each polynucleotide {right arrow over (x)} in a set E of polynucleotides. For each polynucleotide {right arrow over (x)} in the set E of polynucleotides, a probability P0({right arrow over (x)}) of the hybridization signal I({right arrow over (x)}) when the sequence {right arrow over (x)} is not complementary to a subsequence of T and a probability P1({right arrow over (x)}) of the hybridization signal when the sequence {right arrow over (x)} is complementary to a subsequence of T are obtained; so as to obtain a probabilistic spectrum (PS) of T. A score is then assigned to each of a plurality of candidate nucleotide sequences that is being based upon the probabilistic spectrum and upon a reference nucleotide sequence H. A candidate nucleotide sequence having an essentially maximal score is selected and one or more low confidence intervals and one or more reliable intervals in the selected candidate nucleotide sequence are identified. For each low confidence interval detected in the selected candidate nucleotide sequence, a score is assigned to each of a plurality of candidate nucleotide sequences of the low confidence region, where the score is based upon a probabilistic spectrum obtained by filtering from the PS signals the signals present in the reliable regions; and upon an interval of the reference nucleotide sequence H homologous with the low confidence interval. A candidate nucleotide sequence having an essentially maximal score is then selected. A revised candidate sequence S′ is then obtained indicative of the sequence of the target polynucleotide molecule T by substituting the sequence of the low confidence region in the candidate sequence S with the selected candidate sequence.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
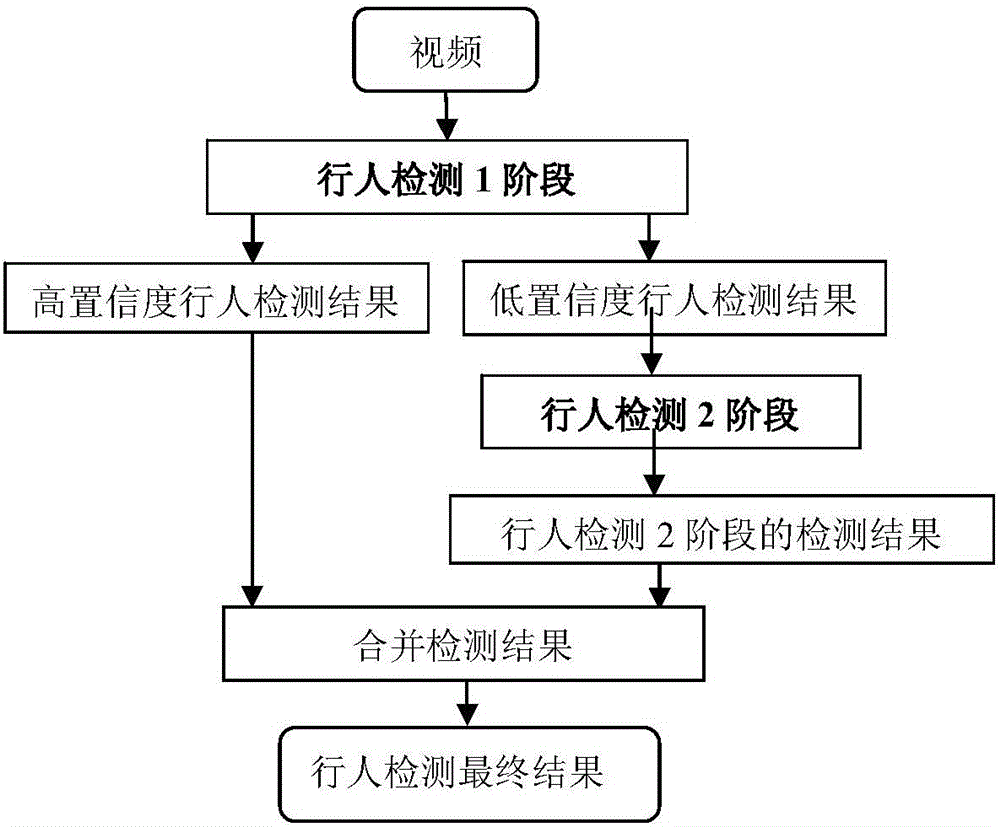
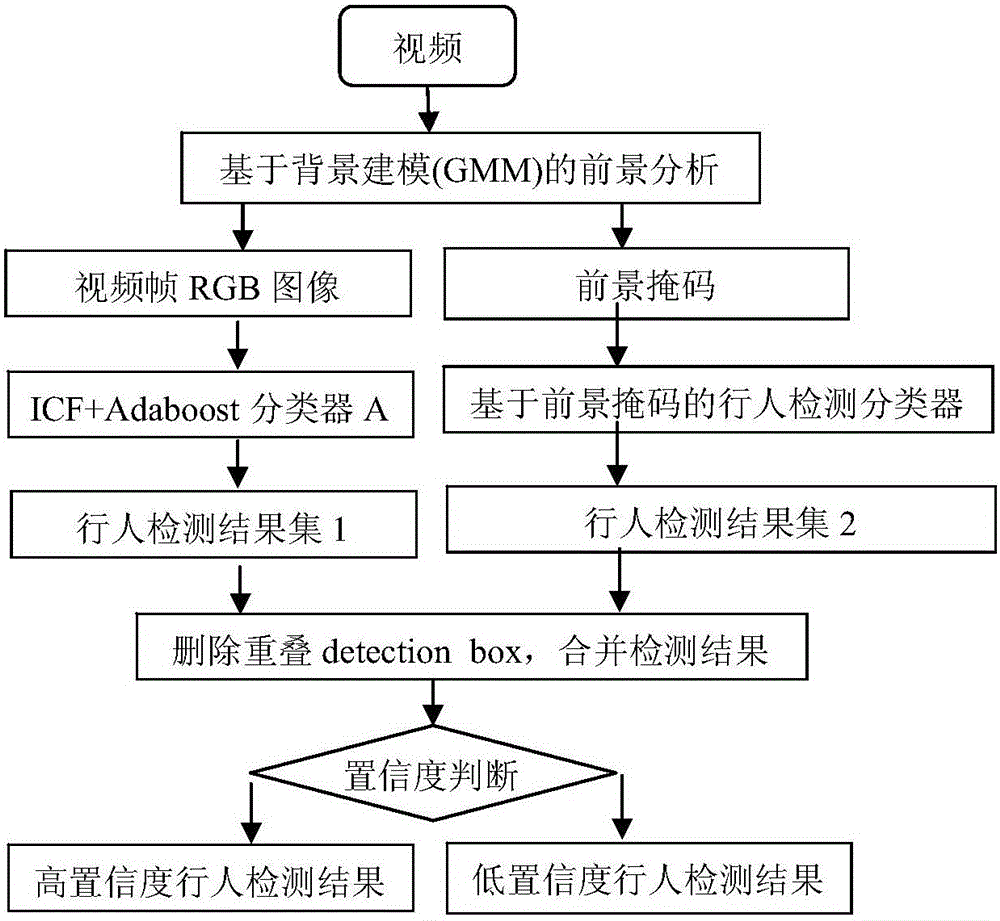
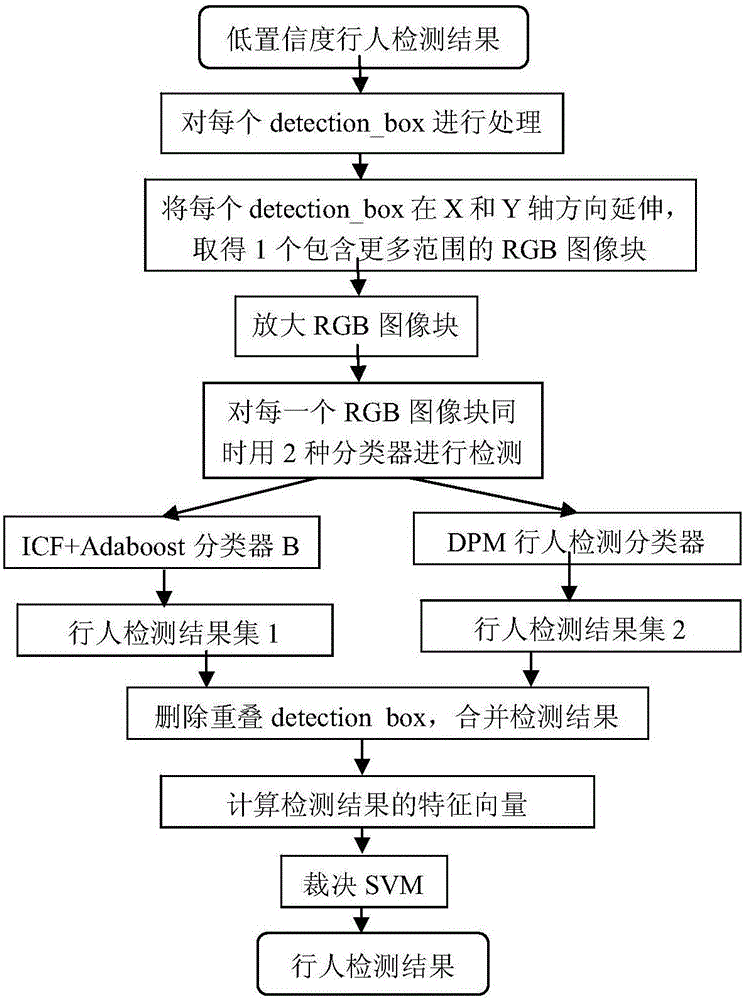
Multi-characteristic multi-model pedestrian detection method
ActiveCN105913003ASolve the high rate of misjudgmentImprove detection rateBiometric pattern recognitionRgb imageOverlap ratio
The invention discloses a multi-characteristic multi-model pedestrian detection method, comprising steps of using an ICF+Adaboost classifier A to process a video frame RGB image, using a foreground-mask-based pedestrian detection classifier to process the foreground mask, combining results of the two classifiers, dividing the results into a high confidence level pedestrian detection result and a low confidence level pedestrian detection result according to a threshold value, using an ICF+Adaboost classifier B and a DPM pedestrian detection classifier to perform respective detection on the low confidence level pedestrian detection result, combining detection results of the two classifiers, using a detection score, an overlapping ratio, a width-height ratio, a classifier sequence number and a foreground ratio of each detected pedestrian as characteristic vectors, inputting the characteristic vectors into a ruling SVM to determine whether the detected pedestrian is correct pedestrian detection, outputting a new pedestrian detection result and combining the new pedestrian detection result and the high confidence level pedestrian detection result into a set as a final detection result. The multi-characteristic multi-model pedestrian detection method effectively solves the problem in the prior art that the misjudgment rate is high, and improves the detection rate.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com