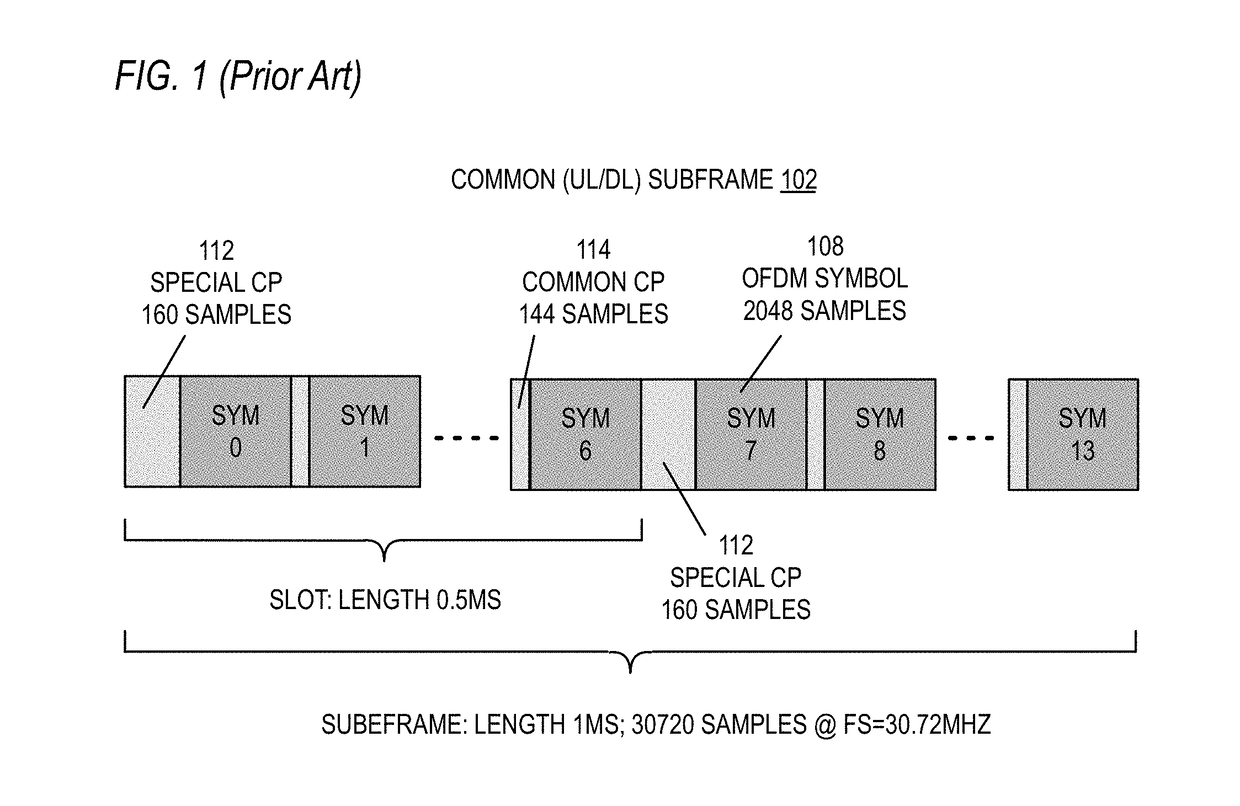
Patents
Literature
118 results about "Region specific" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Region Specific. Reference the region specific forms that are customized for region processes and procedures when administering a construction contract.
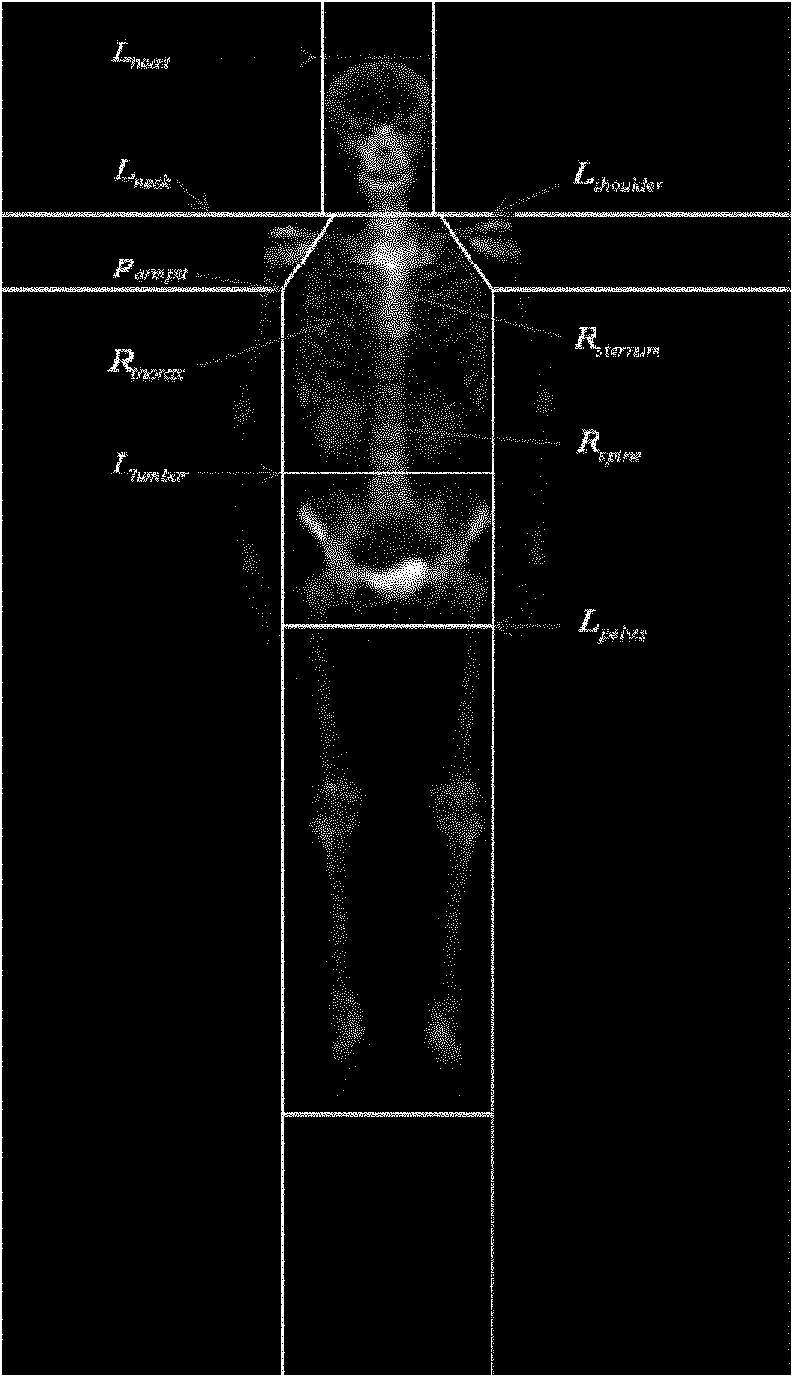
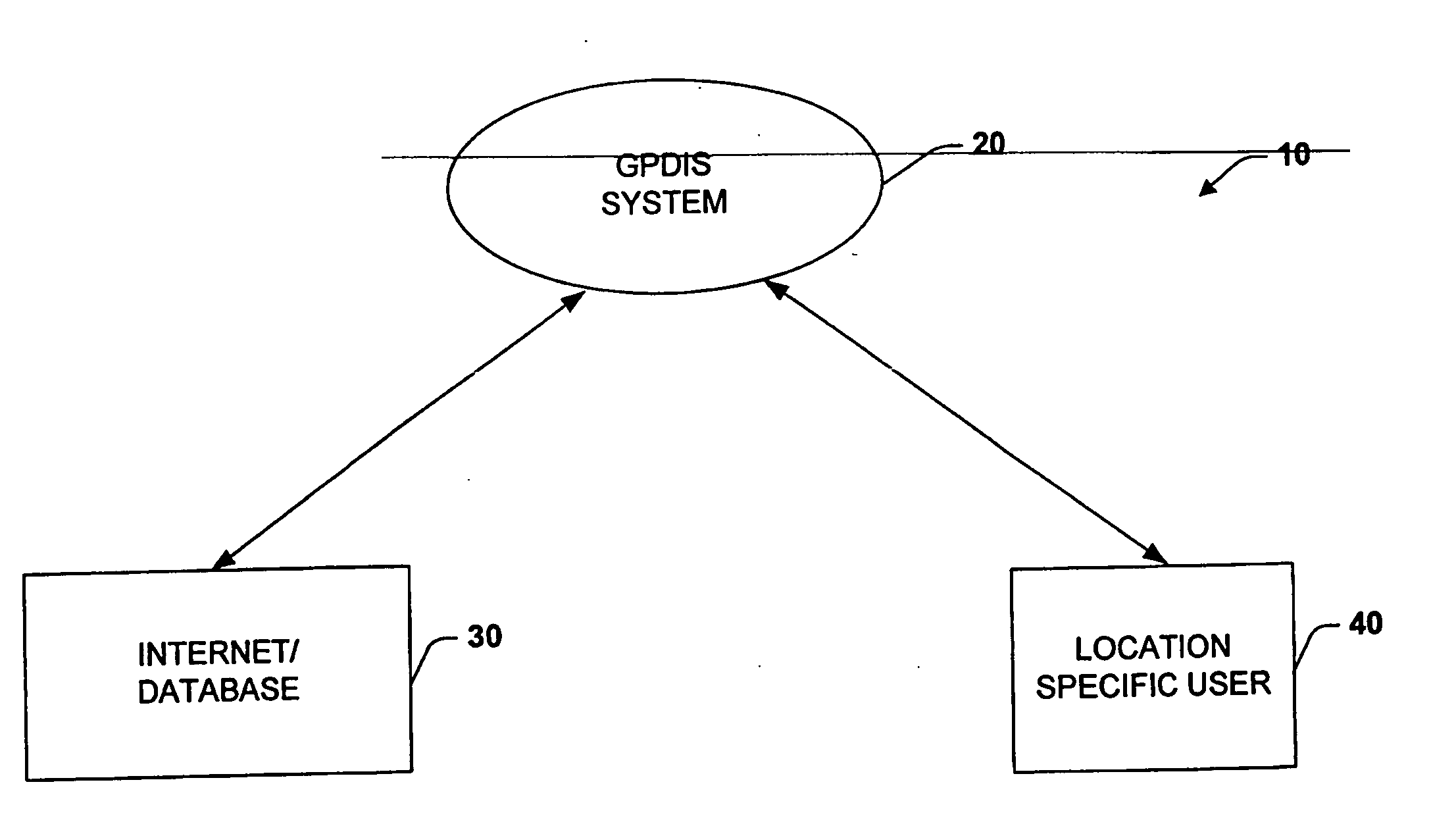
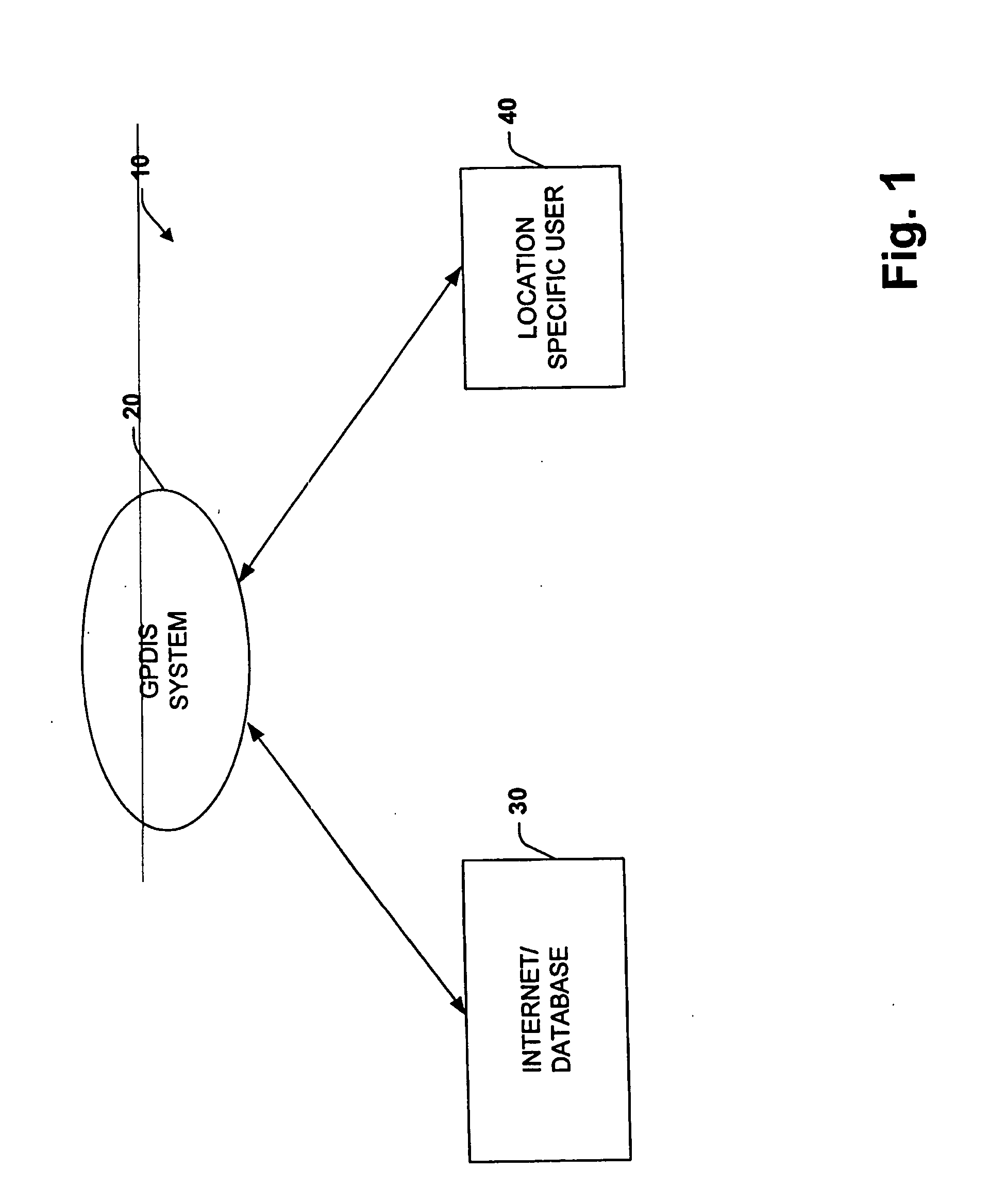
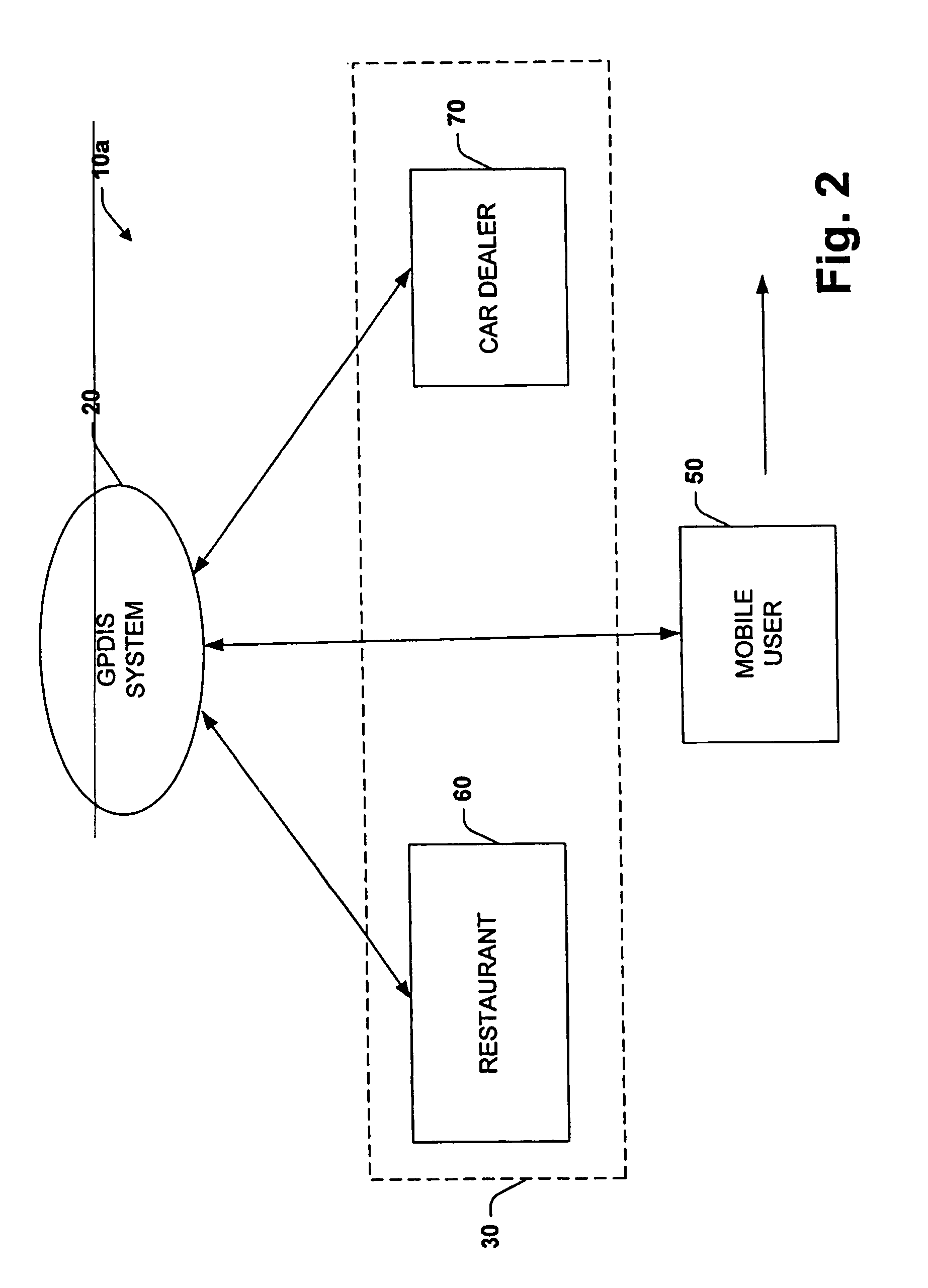
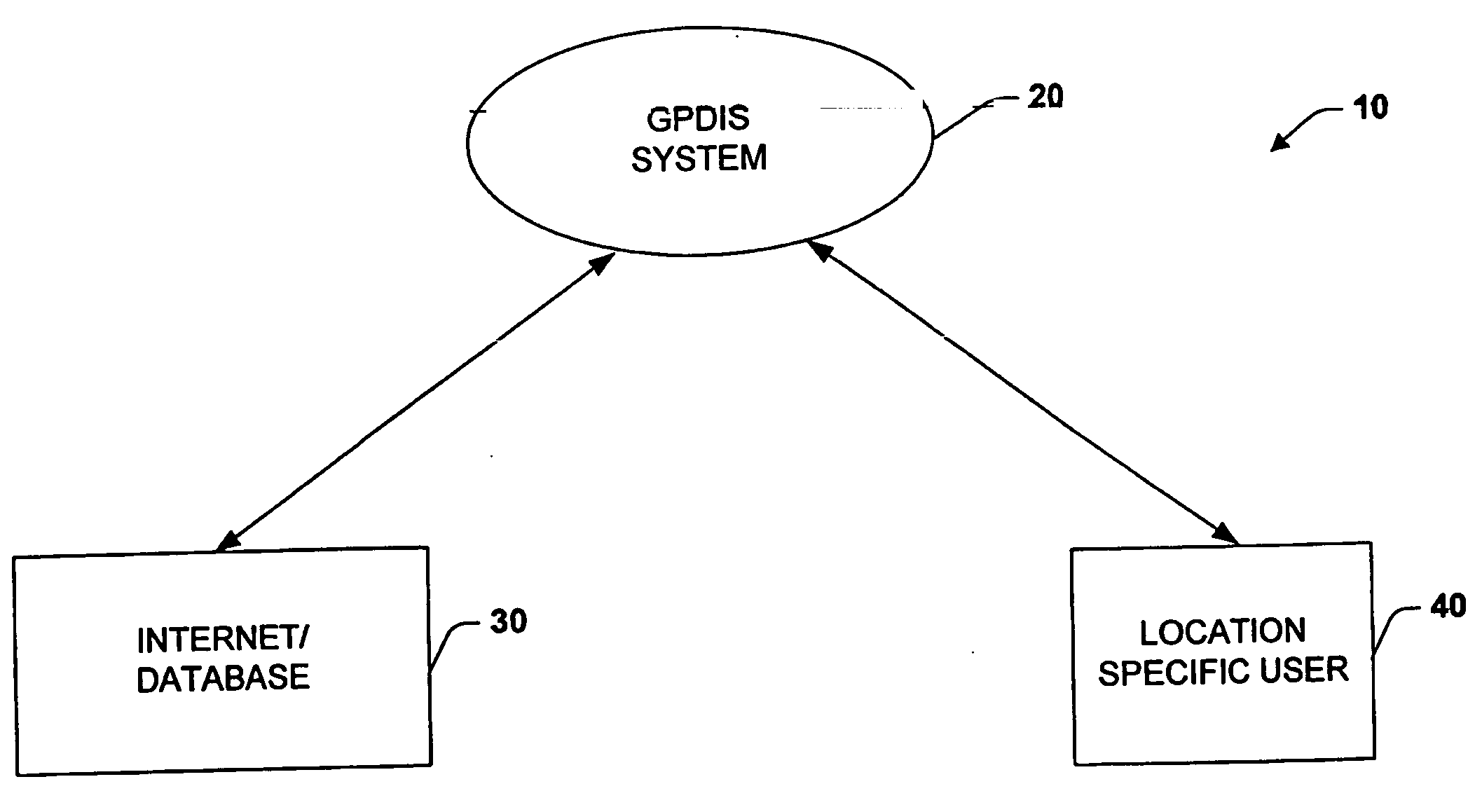
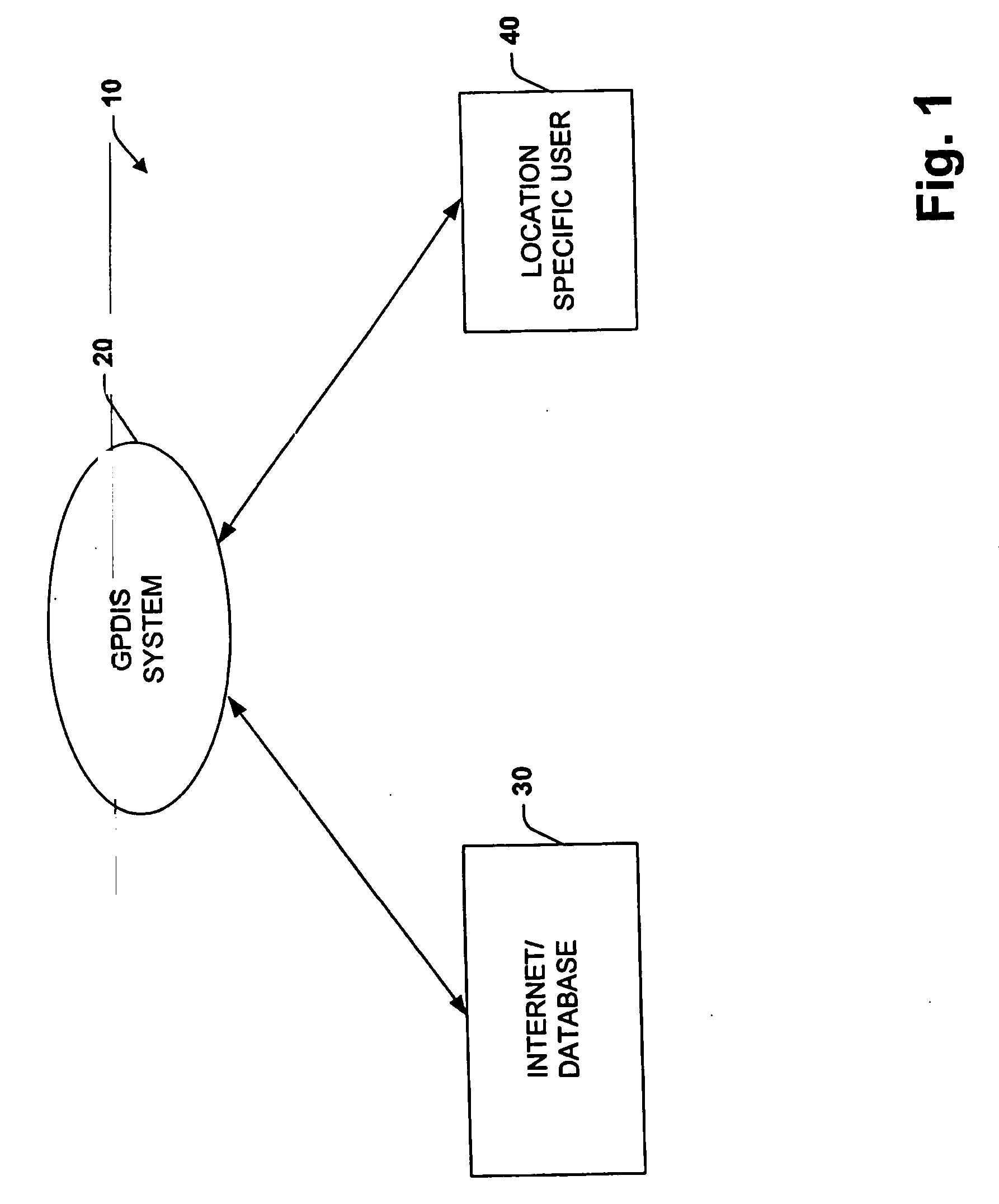
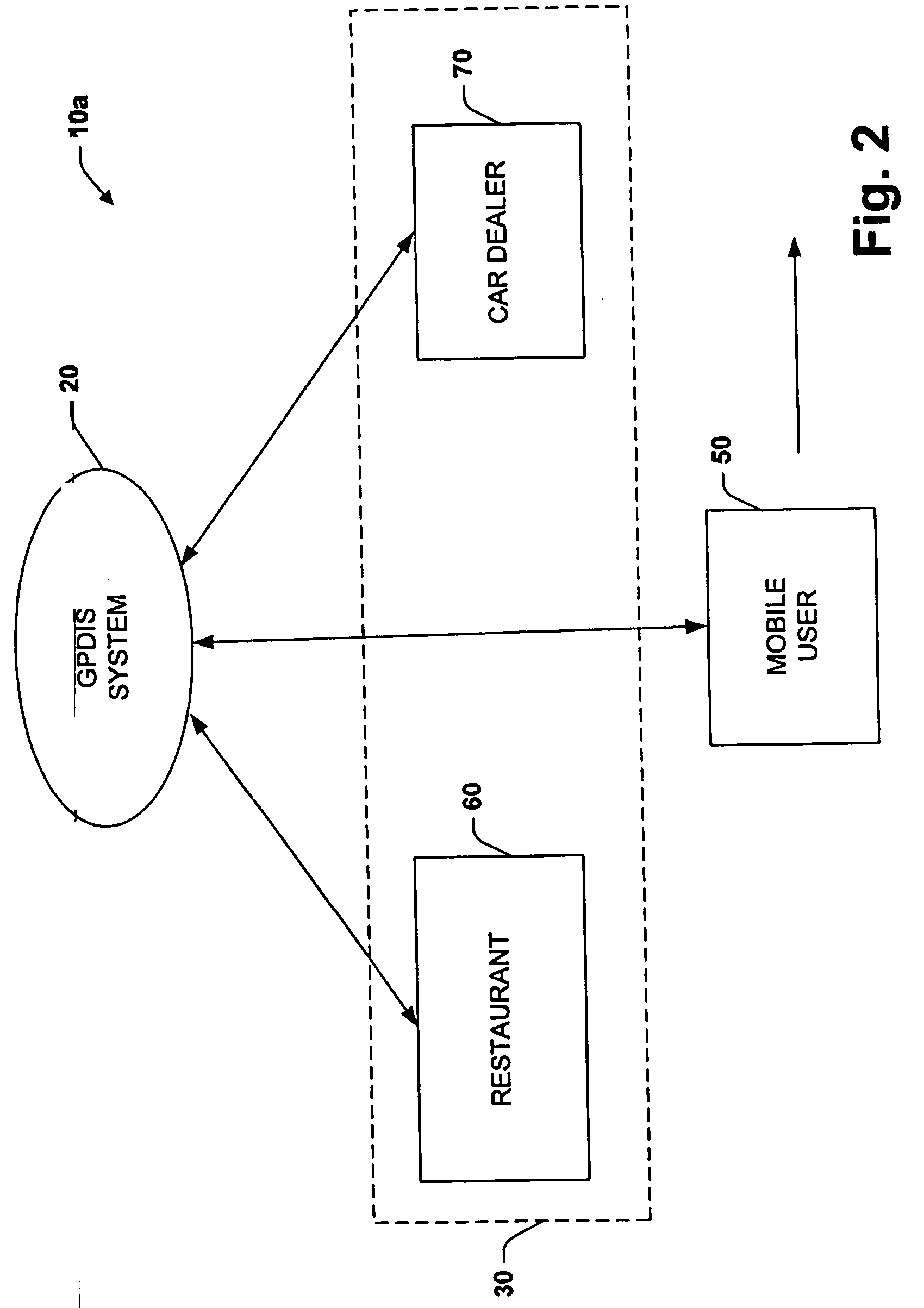
System for dynamically pushing information to a user utilizing global positioning system
InactiveUS20050272442A1Precious timeConsiderable convenienceInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGlobal Positioning SystemRegion specific
Owner:CORRINO HLDG LLC
System for dynamically pushing information to a user utilizing global positioning system
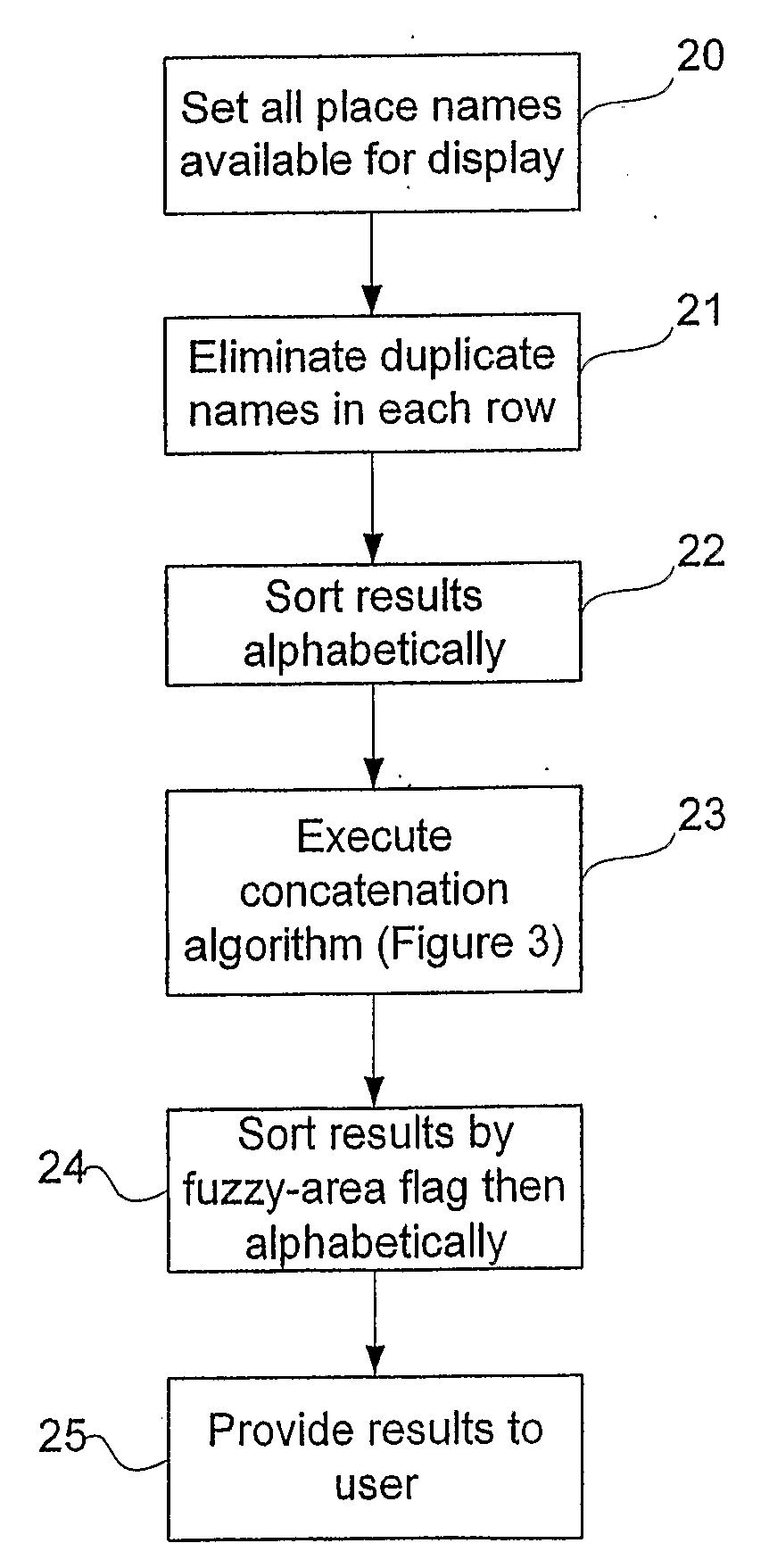
InactiveUS20050266858A1Considerable conveniencePrecious timeRoad vehicles traffic controlTelephonic communicationGlobal Positioning SystemRegion specific
Owner:CORRINO HLDG LLC
Method and system for listing items globally and regionally, and customized listing according to currency or shipping area
InactiveUS7660740B2Easy to optimizeBuying/selling/leasing transactionsRegion specificInformation retrieval
A method to facilitate network-based commerce includes determining a site that a user accesses, the site being one of multiple sites operated by a network-based commerce facility. A category list available for the site is retrieved, the category list identifying categories of offerings available via the site. The category list is communicated to the user. The site is a regional site, and the category list is a region-specific category list.
Owner:EBAY INC
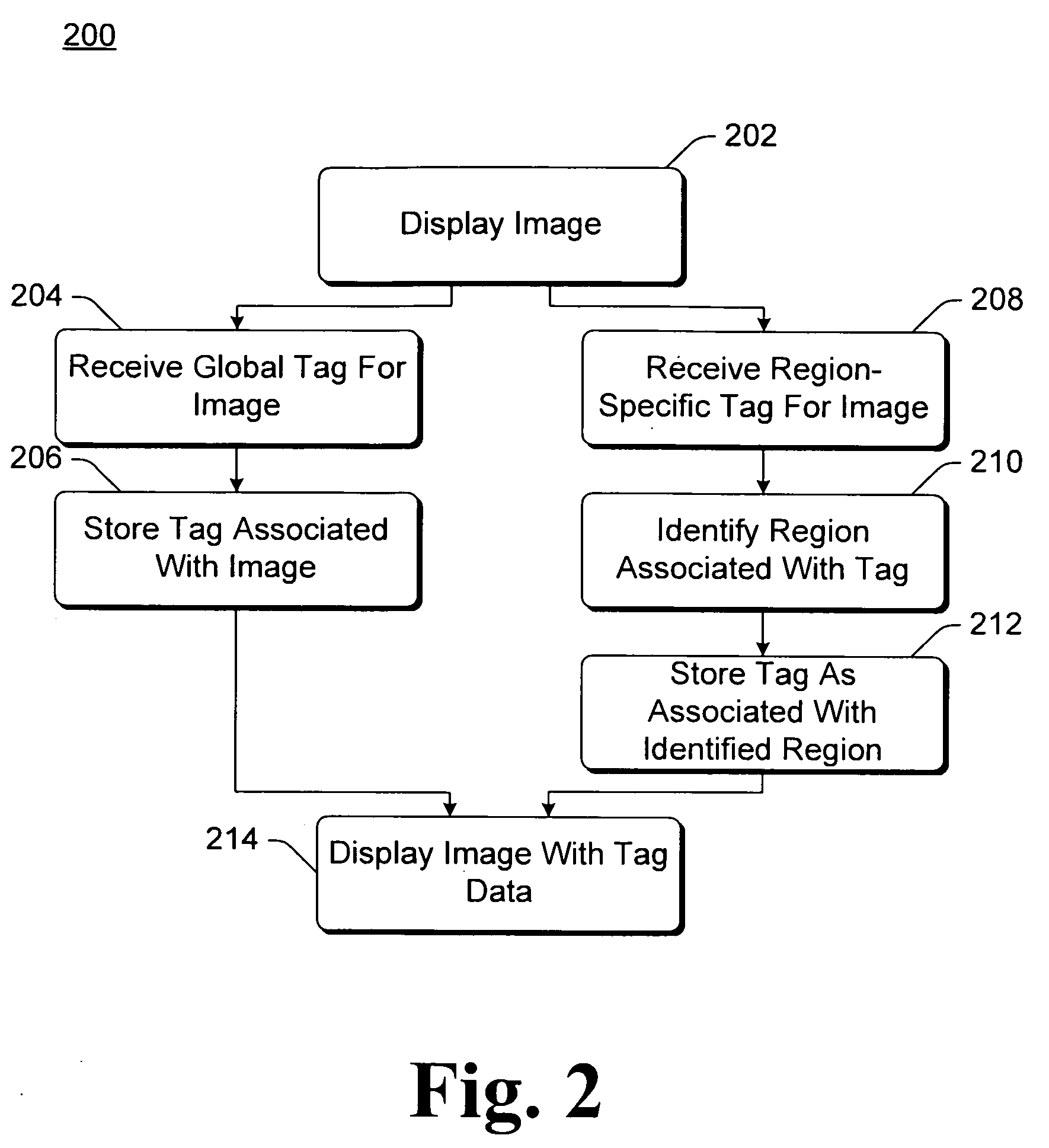
Image Tagging User Interface
ActiveUS20100054601A1Well formedImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Region specific
A global tag for an image is received identifies one or more objects in the image, and a region-specific tag for the image identifies one or more objects in a region of the image. The global tag and the region-specific tag are stored with the image. Displayed, along with the image, is an identifier for each of the one or more objects identified in the global tag, and an identifier for each of the one or more objects identified in the region-specific tag. Different users are able to maintain different names for the same person, allowing the same tag of the image to be used as the basis for displaying the image with different names for the different users. Additionally, the tags can be used as a basis for generating a credits list of people that are included in a compilation of images.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
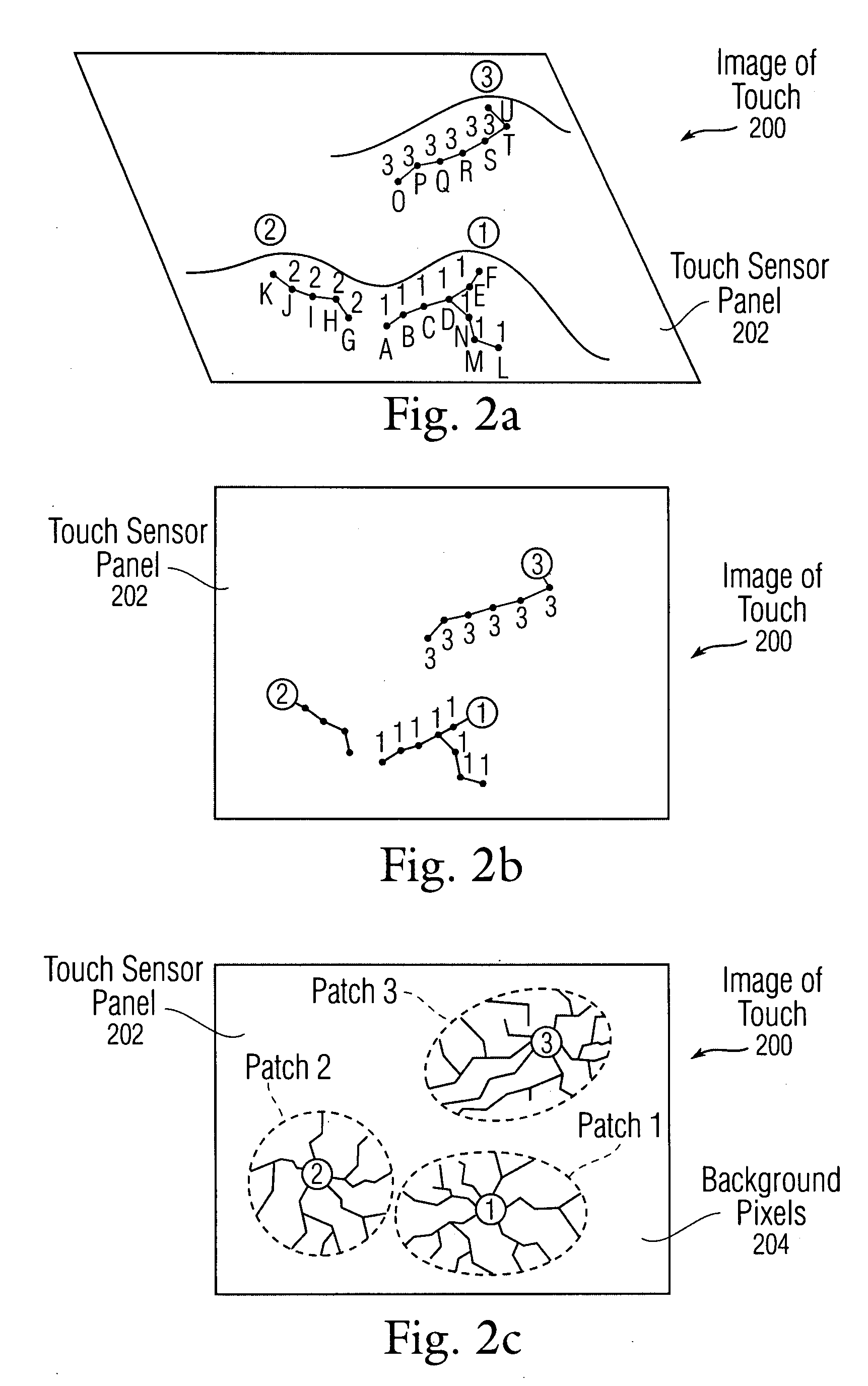
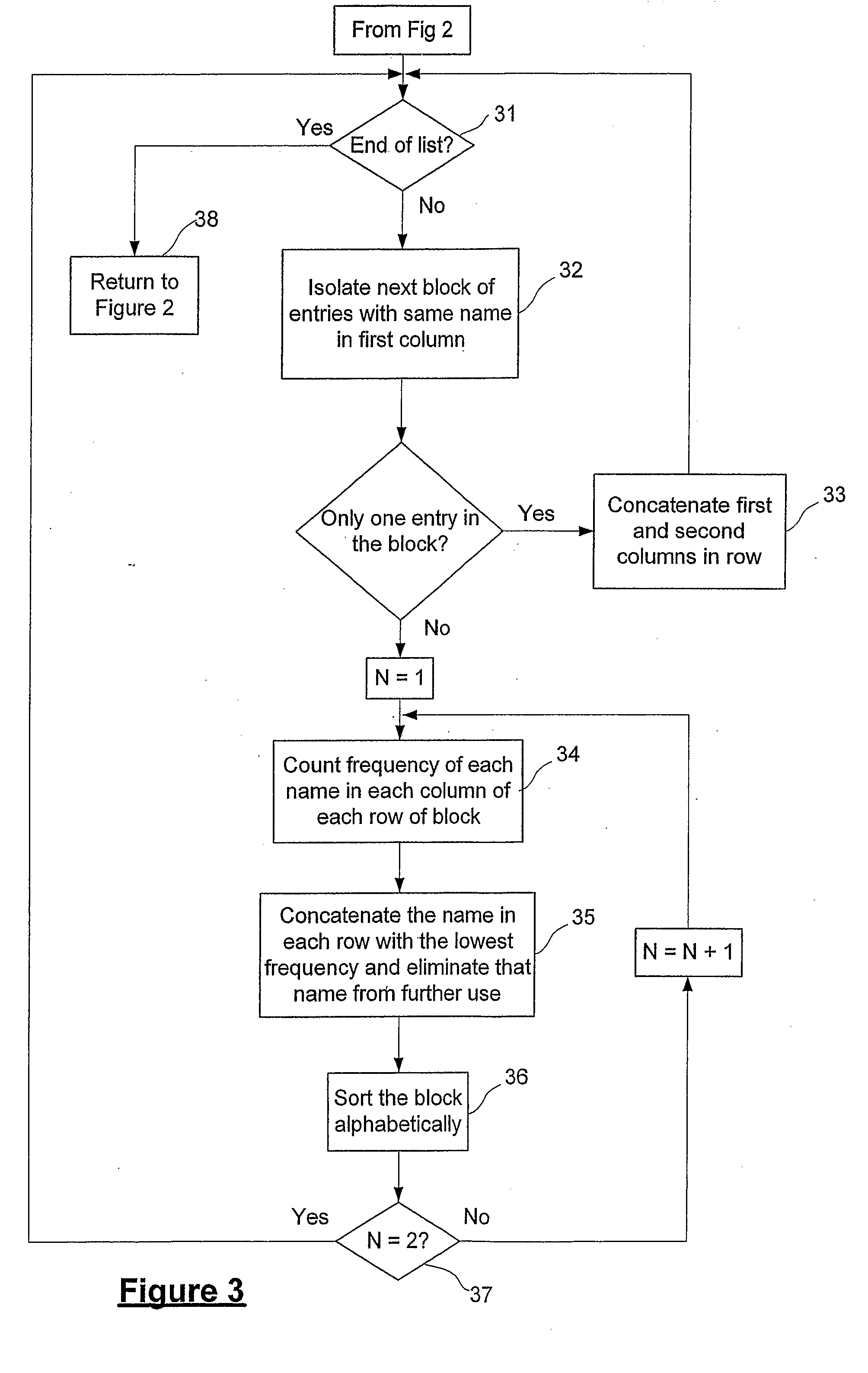
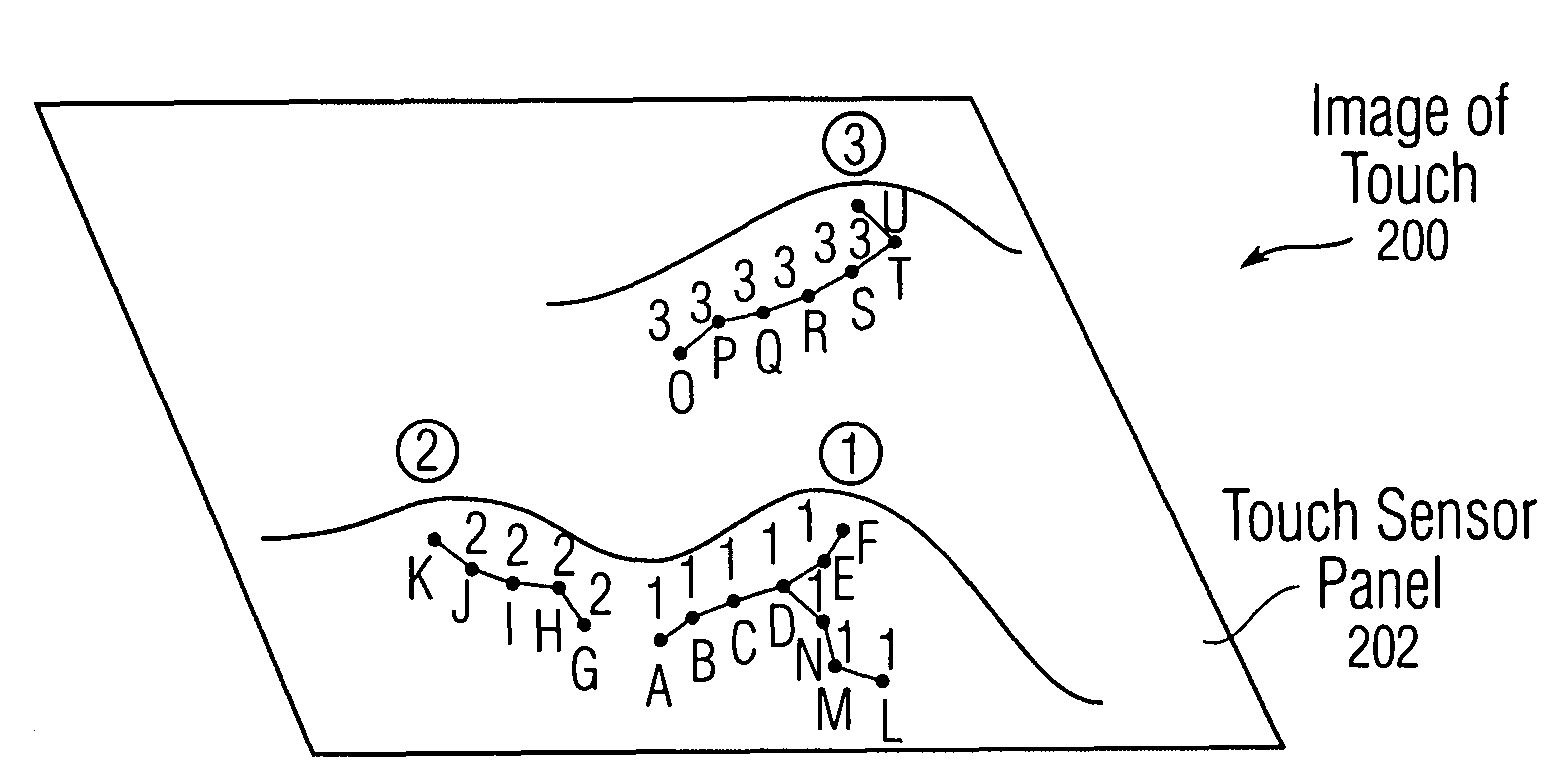
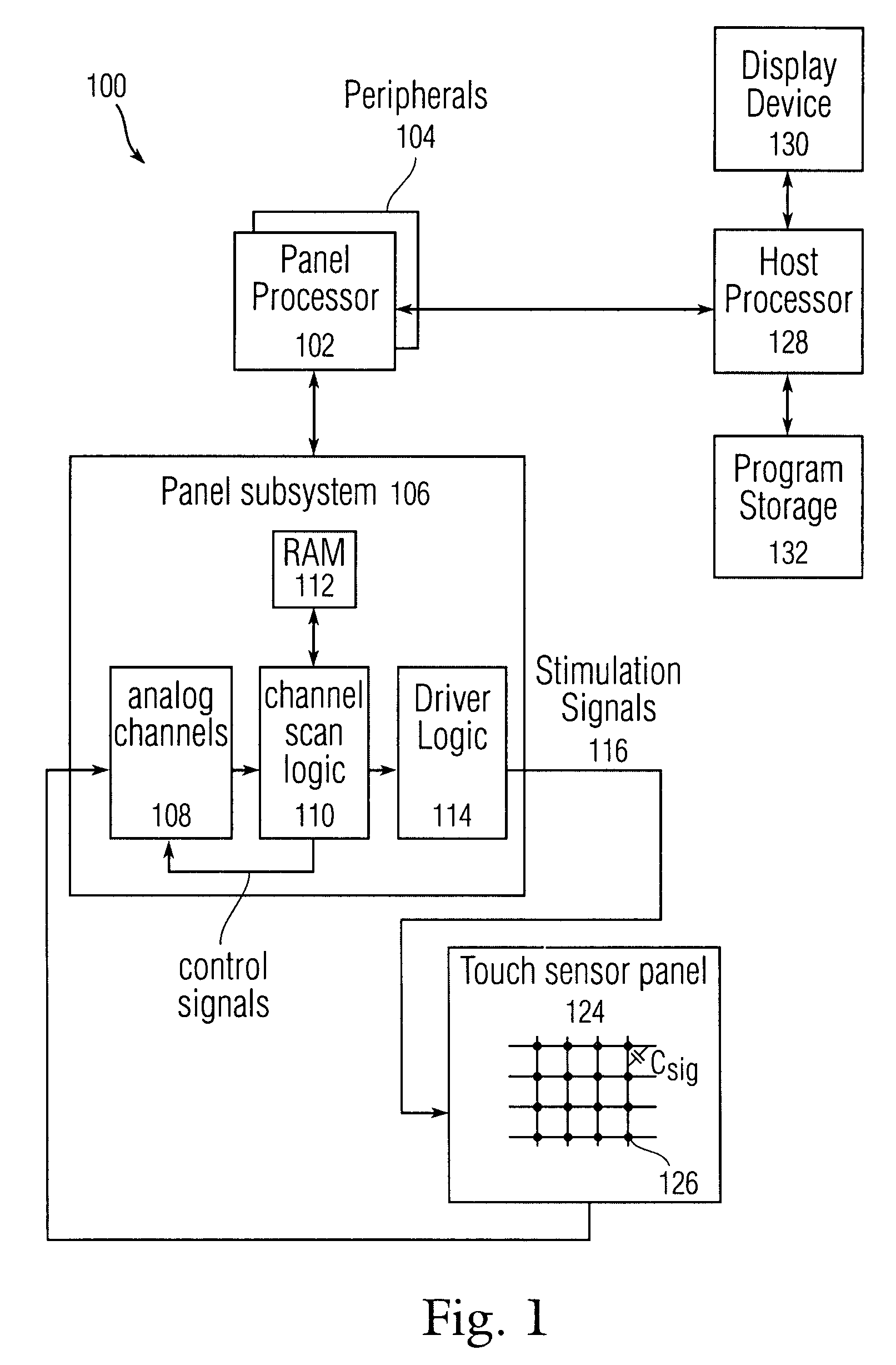
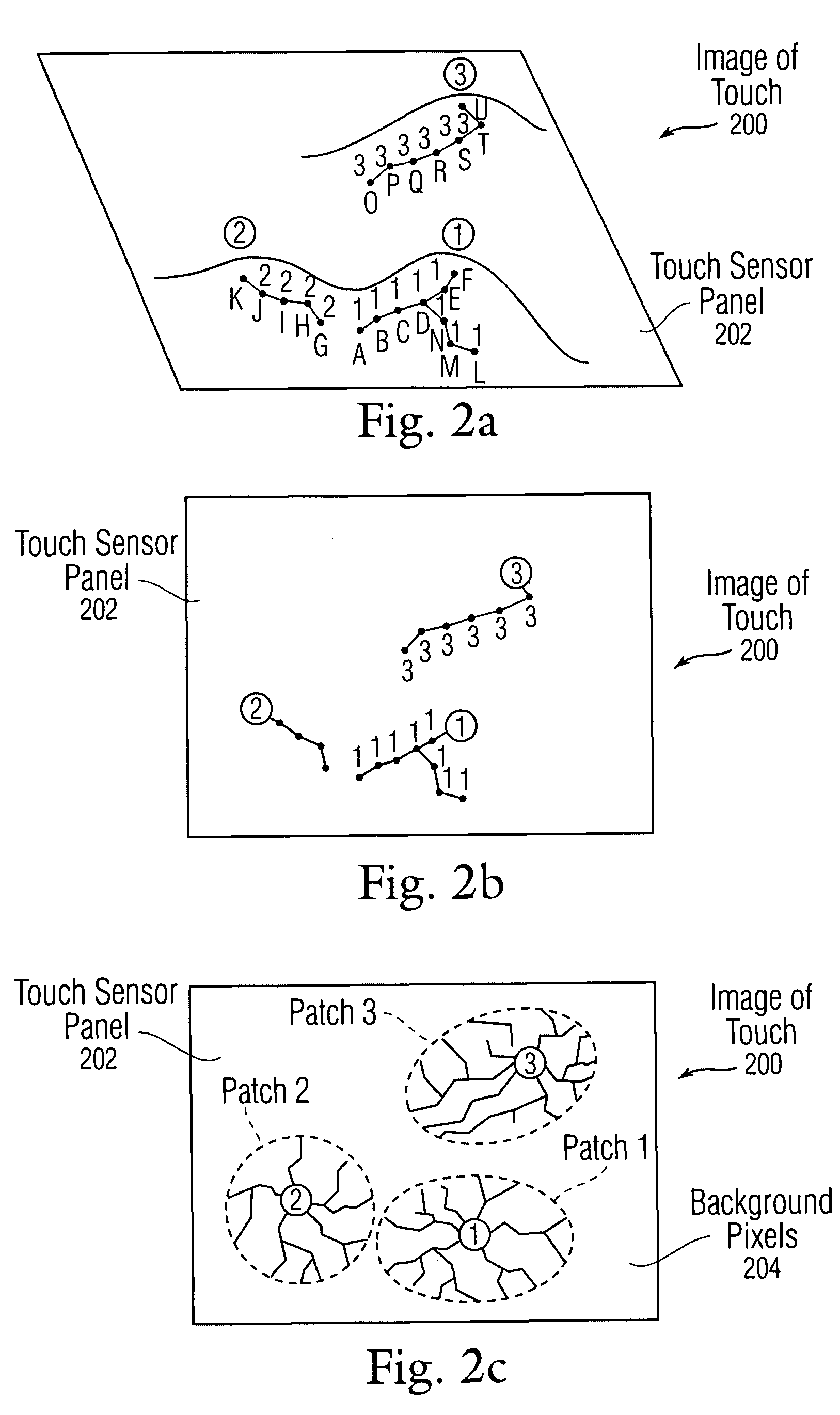
Bottom up watershed dataflow method and region-specific segmentation based on historic data
InactiveUS20080309629A1Reduce in quantityInaccurate centroid calculationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionMerge algorithm
The application of a watershed algorithm to pixels and their touch values obtained from a scan of a touch sensor panel to determine patches corresponding to images of touch is disclosed. Prior to applying the watershed algorithm, background pixels having little or no touch values can be eliminated. A primary merge algorithm can then merge adjacent patches together when the saddle point between them is shallow as compared to the peak represented by the patches. However, if two candidate patches for merging have a total number of pixels below a certain threshold, these two patches may not be merged under the assumption that the patches might have been caused by different fingertips. Conversely, if two candidate patches for merging have a total number of pixels above a certain threshold, these two patches can be merged under the assumption that the patches were caused by a single thumb or palm.
Owner:APPLE INC
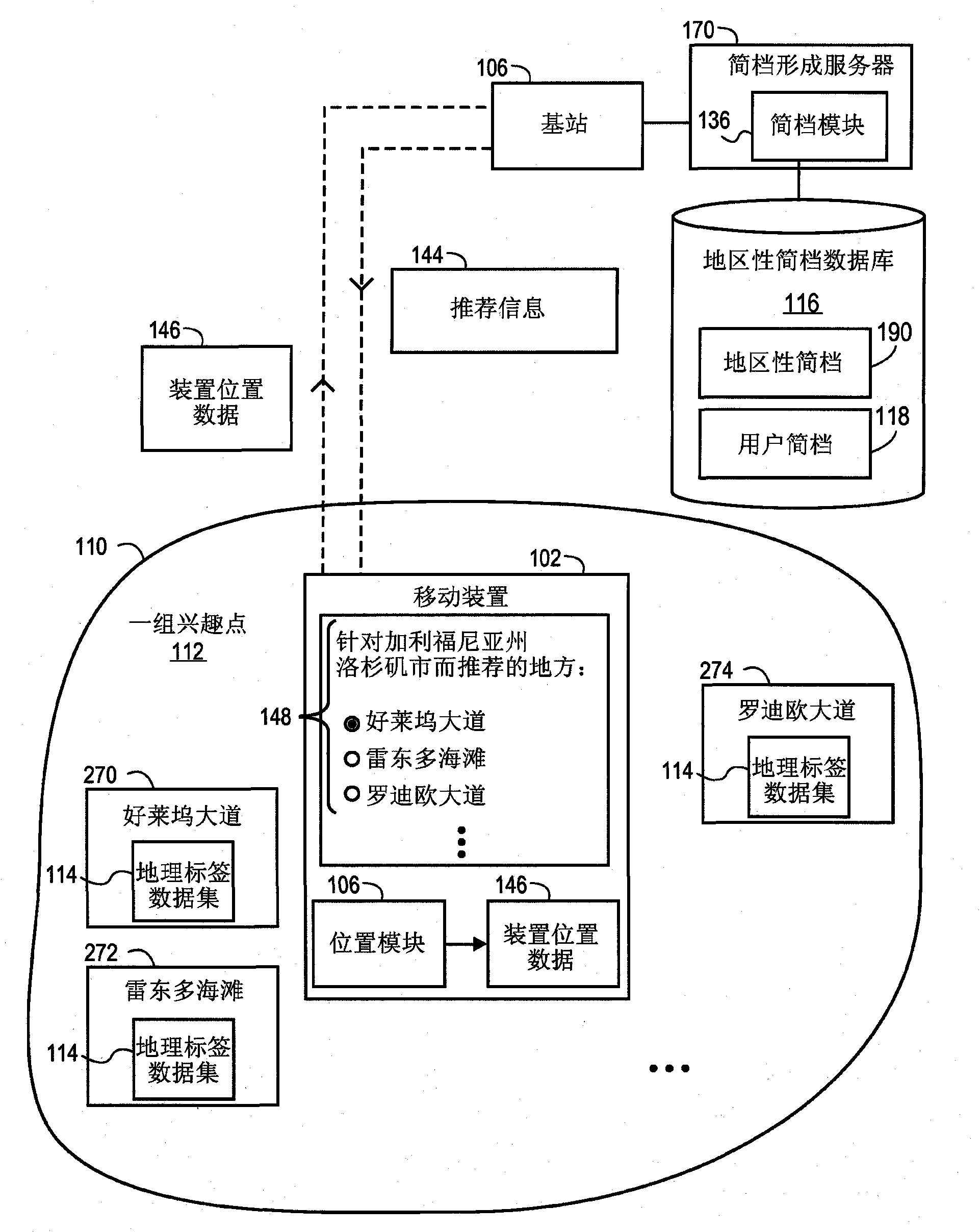
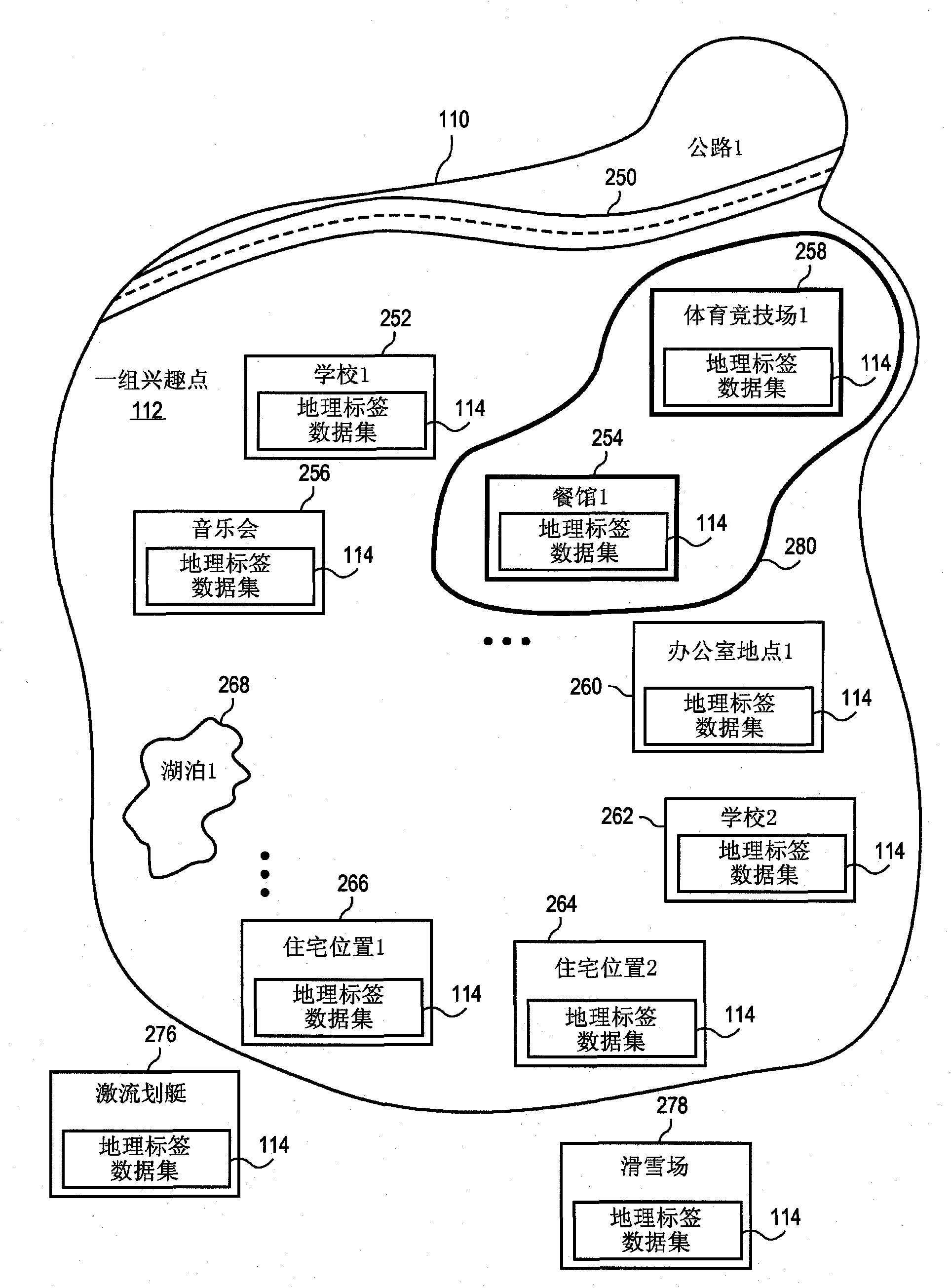
Method and apparatus for aggregating and presenting data associated with geographic locations
Implementations relate to systems and methods for aggregating and presenting data related to geographic locations. Geotag data related to geographic locations and associated features or attributes can be collected to build a regional profile characterizing a set of locations within the region. Geotag data related to the constituent locations, such as user ratings or popularity ranks for restaurants, shops, parks, or other features, sites, or attractions, can be combined to generate a profile of characteristics of locations in the region. The platform can generate recommendations of locations to transmit to the user of a mobile device, based for instance on the location of the device in the region as reported by GPS or other location service and the regional profile. Geotag data can include audio data analyzed using region-specific terms, and user recommendations can be presented via dynamic menus based on regional profiles, user preferences or other criteria.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
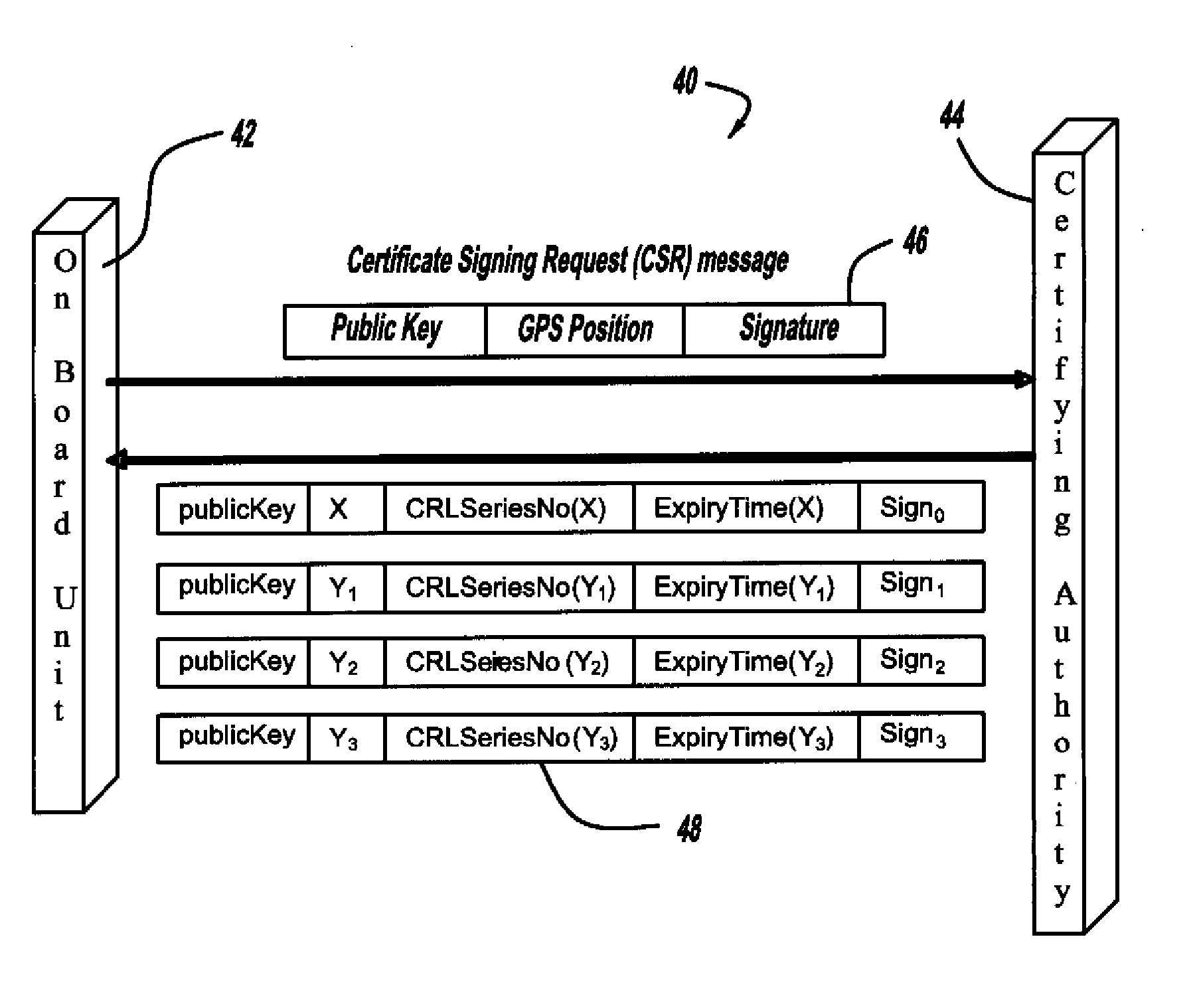
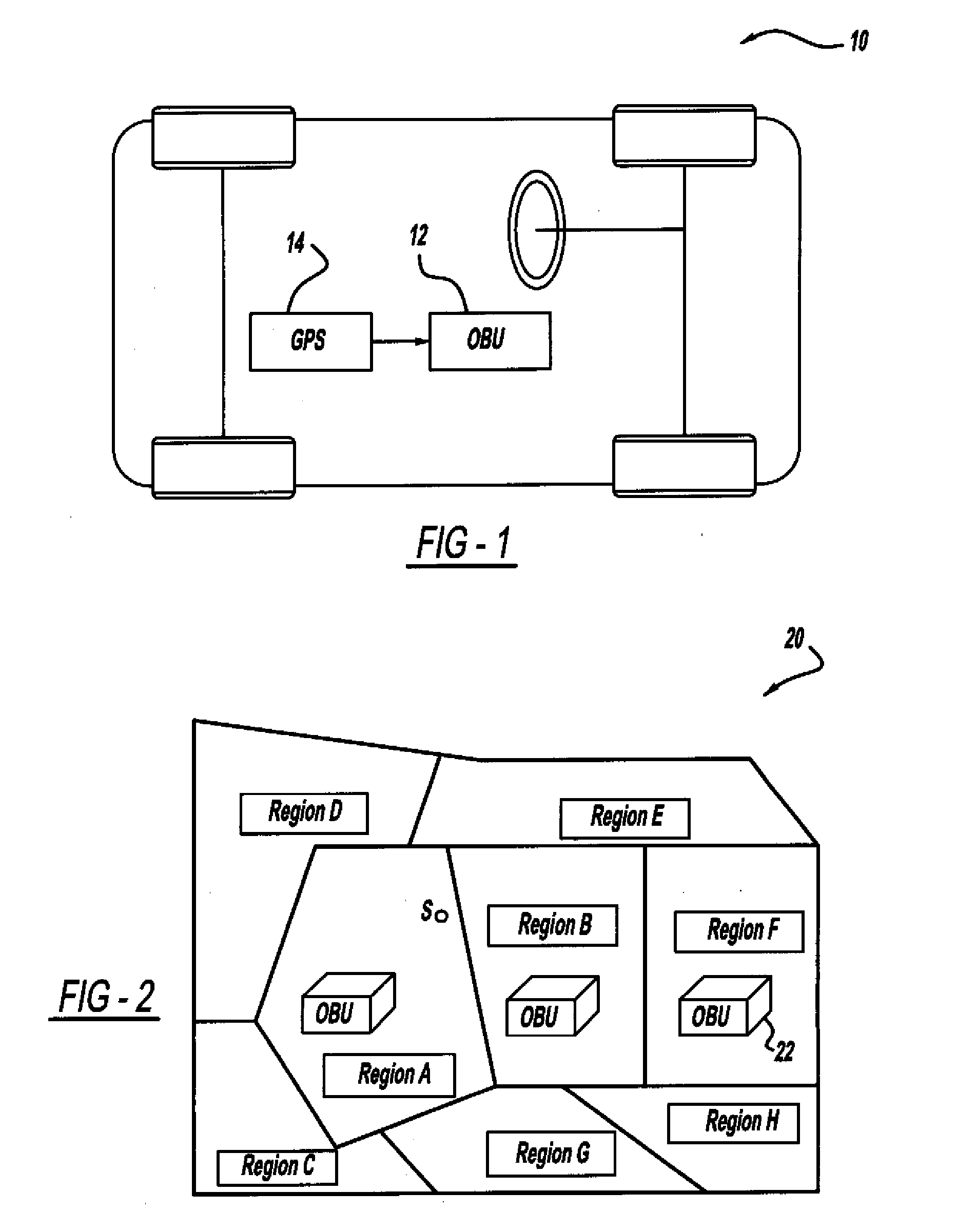
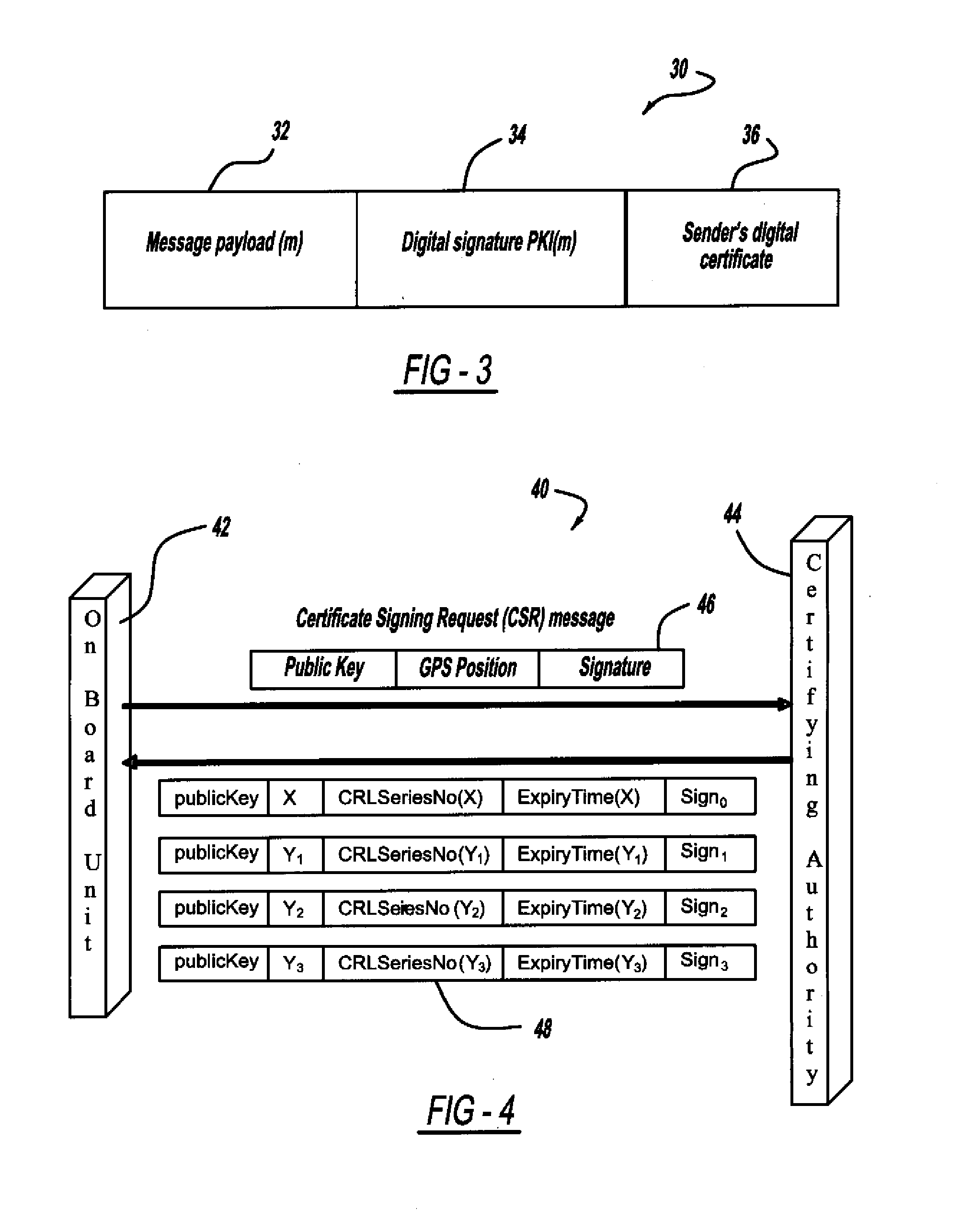
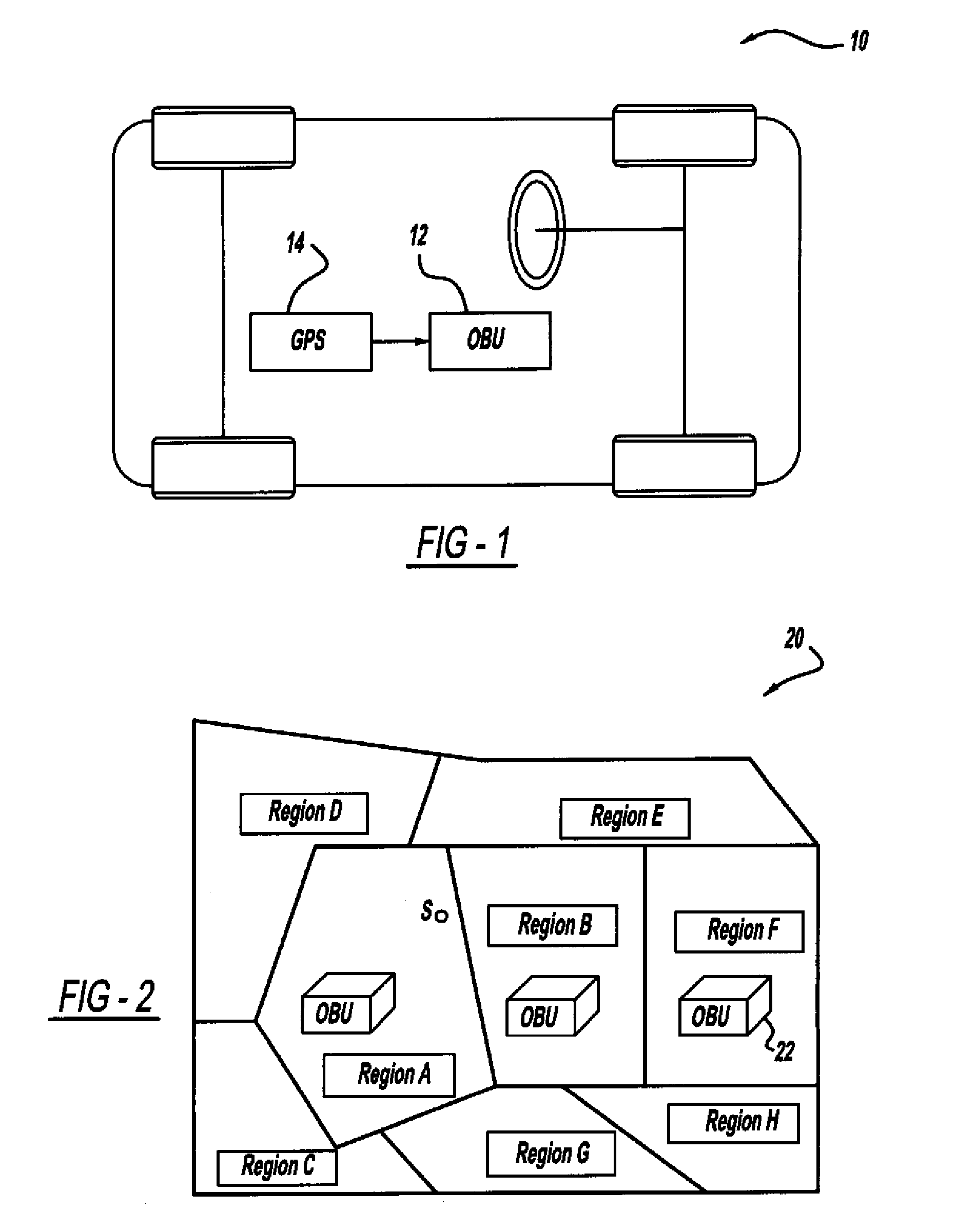
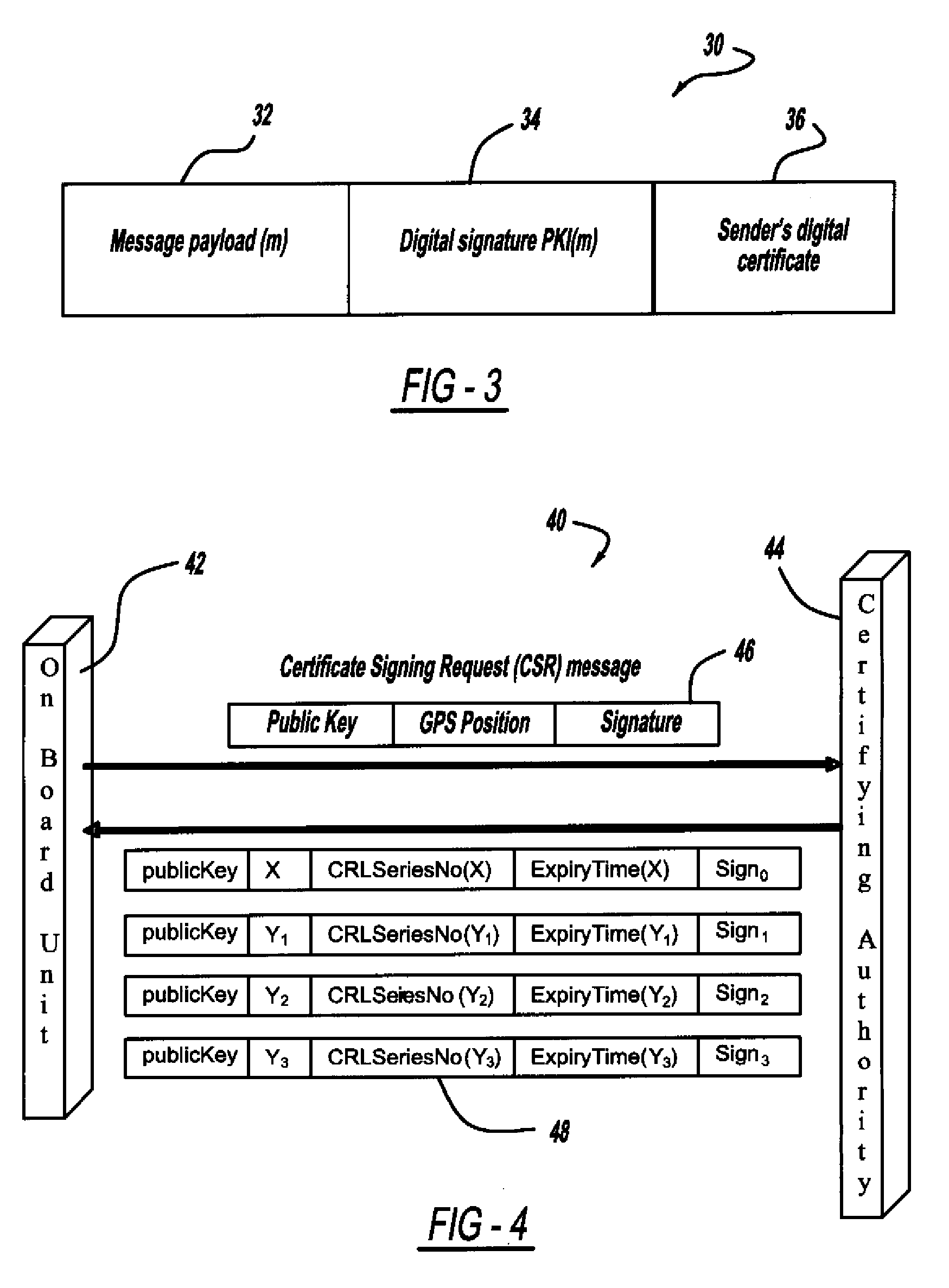
Certificate assignment strategies for efficient operation of the pki-based security architecture in a vehicular network
InactiveUS20090235071A1Small sizeReduce complexityTemperatue controlUser identity/authority verificationExpiration TimeCommunications system
A system and method for assigning certificates and reducing the size of the certificate revocation lists in a PKI based architecture for a vehicle wireless communications system that includes separating a country, or other area, into geographic regions and assigning region-specific certificates to the vehicles. Therefore, a vehicle need only process certificates and certificate revocation lists for the particular region that it is traveling in. Vehicles can be assigned multiple certificates corresponding to more than one region in the vehicles vicinity as advance preparation for possible travel or transmission into nearby regions. Further, the expiration time of certificates assigned to vehicles corresponding to a given geographic region can be tailored to be inversely proportional to the distance from a registered home region of the vehicle. A scalable design for a back-end certifying authority with region-based certificates can also be provided.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
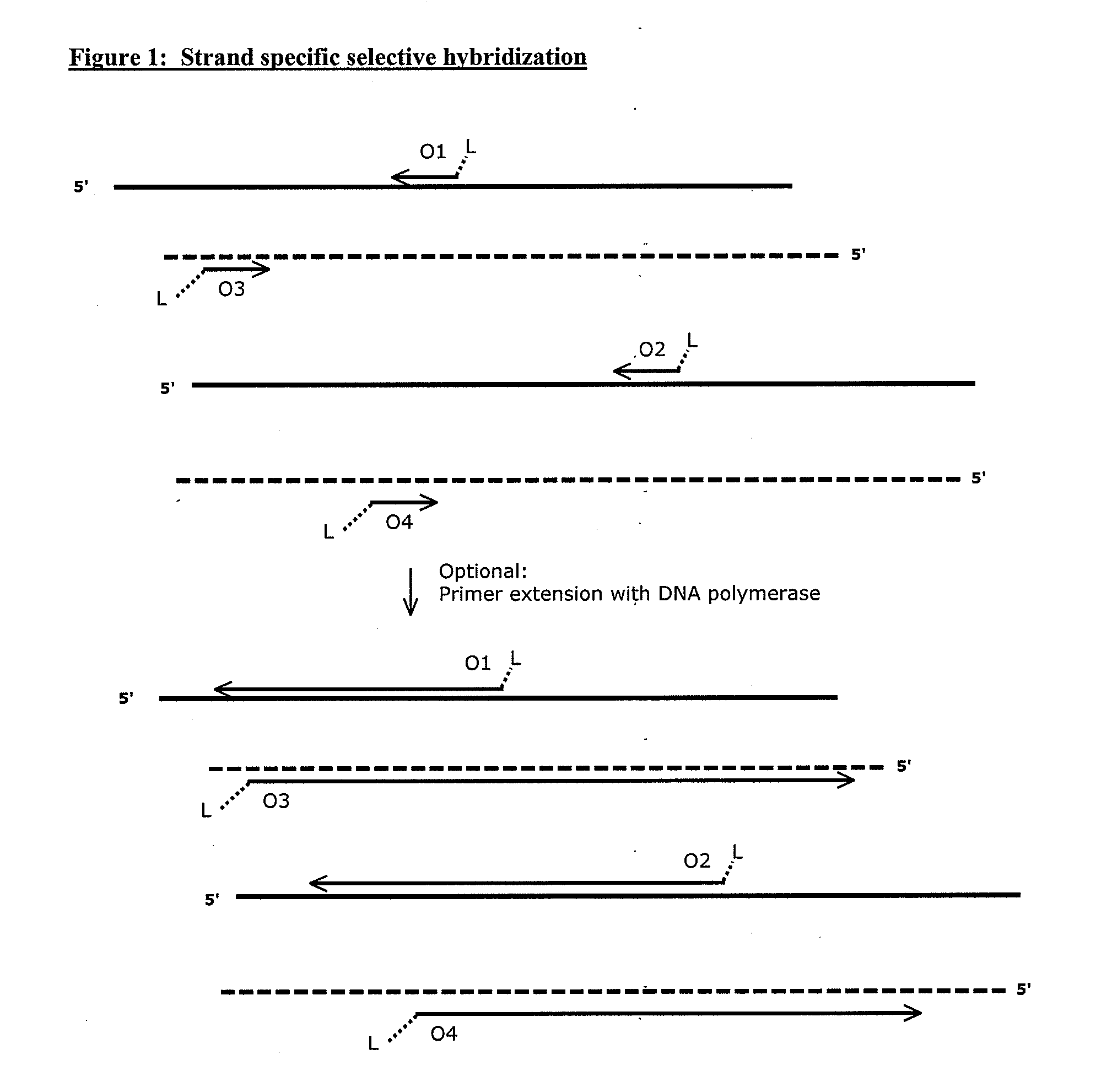
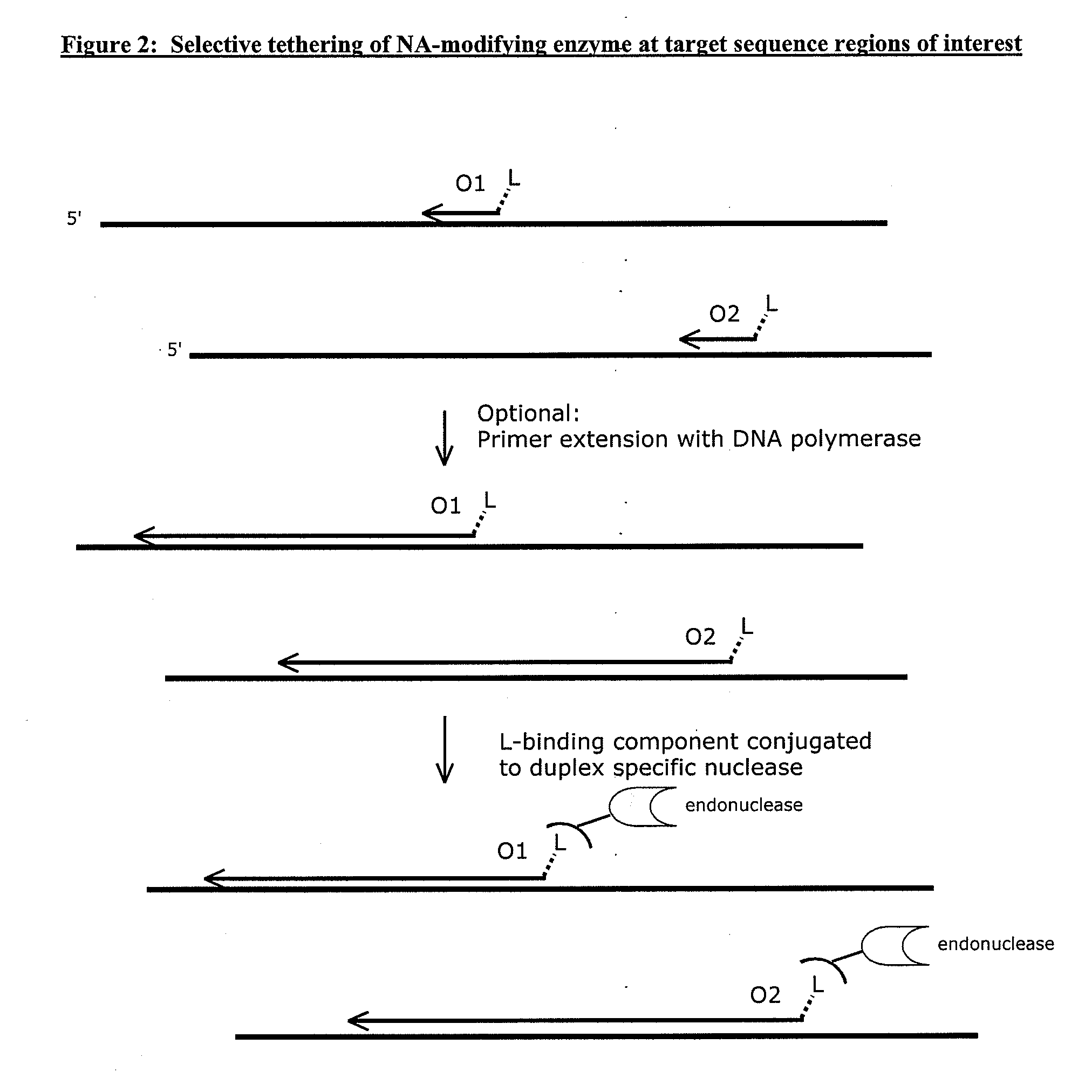
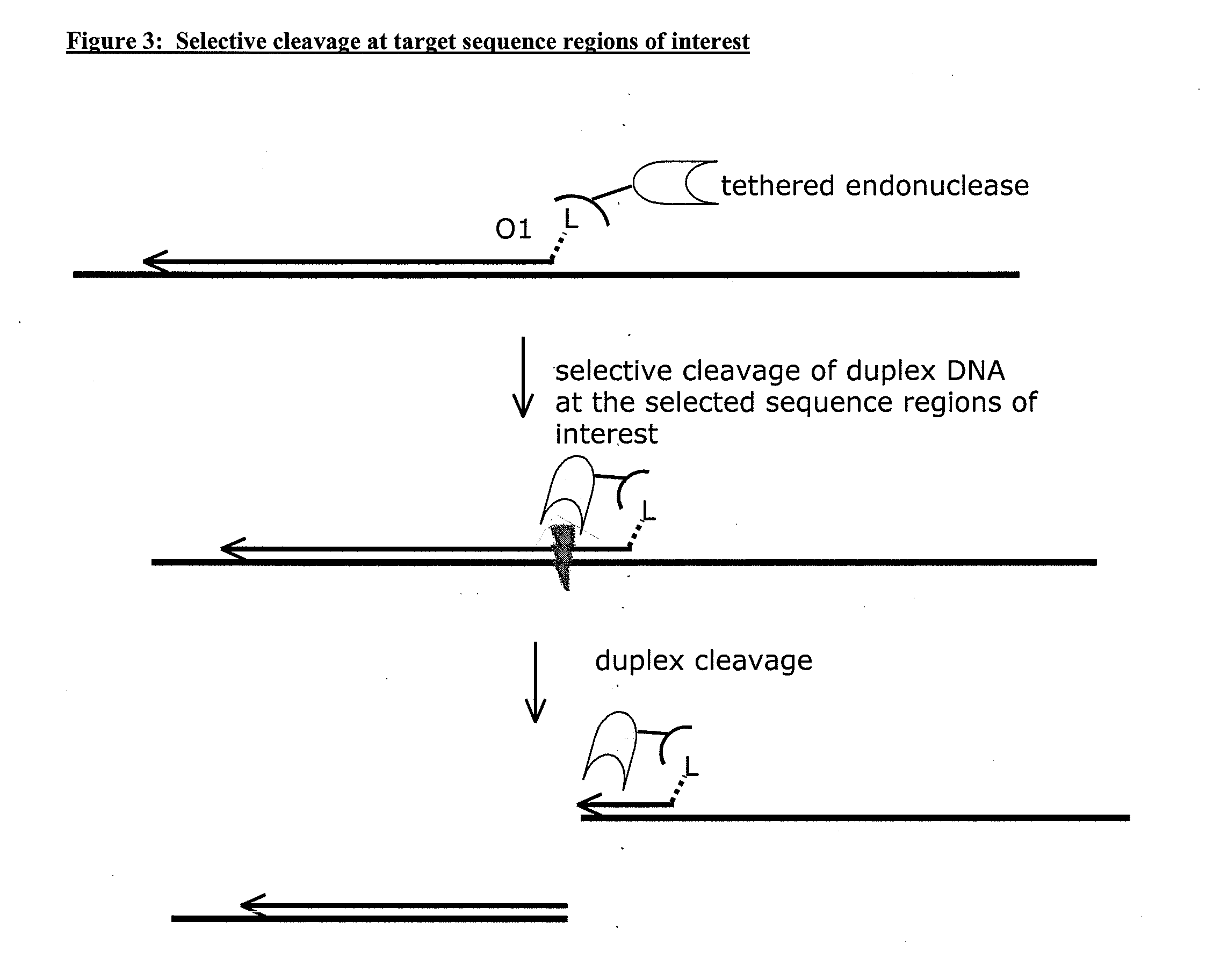
Compositions and methods for targeted nucleic acid sequence selection and amplification
InactiveUS20110105364A1Improve efficiencySuitable for automationNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingGenome wide analysis
The present invention provides novel methods, compositions, and kits for the production of amplification-ready, sequence-specific, target region-specific, and strand-specific regions of interest directly from samples containing complex DNA. The methods, composition, and kits provided herein are useful for selective target generation, genome partitioning, or user-selected enrichment of desired regions of interest. The invention described herein will enable multiplexing for genome-wide analysis with increased efficiency and is amenable to automation.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
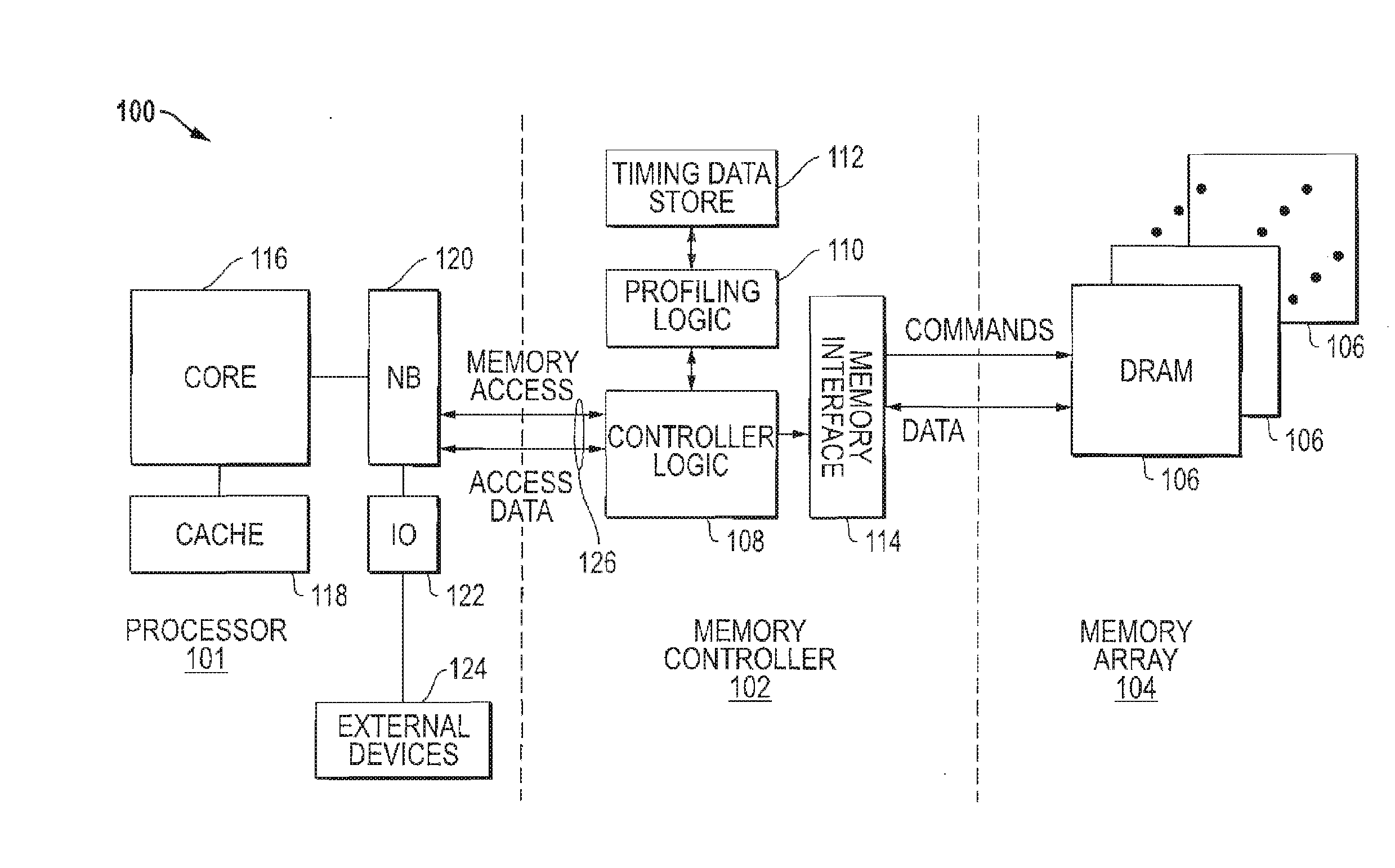
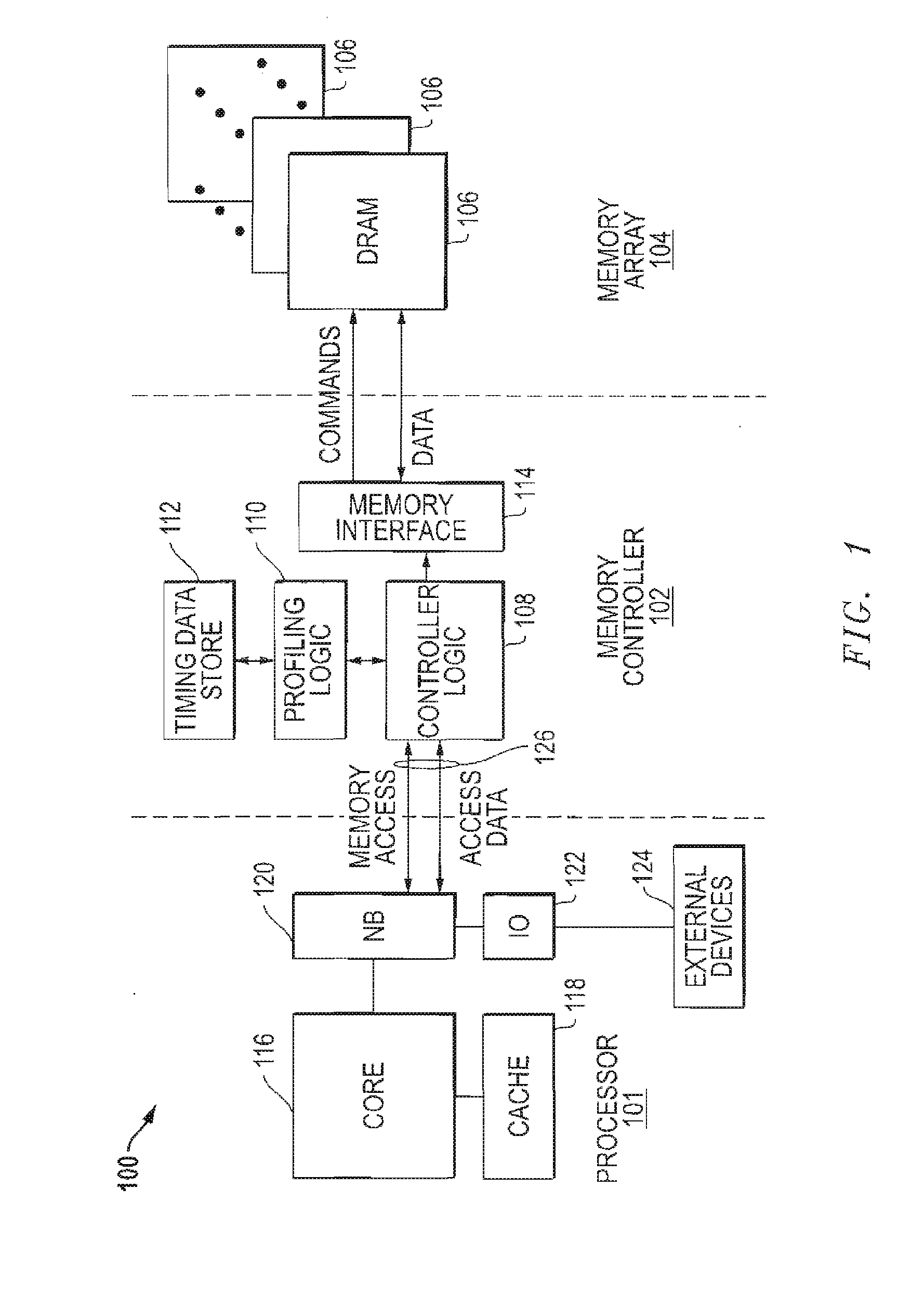
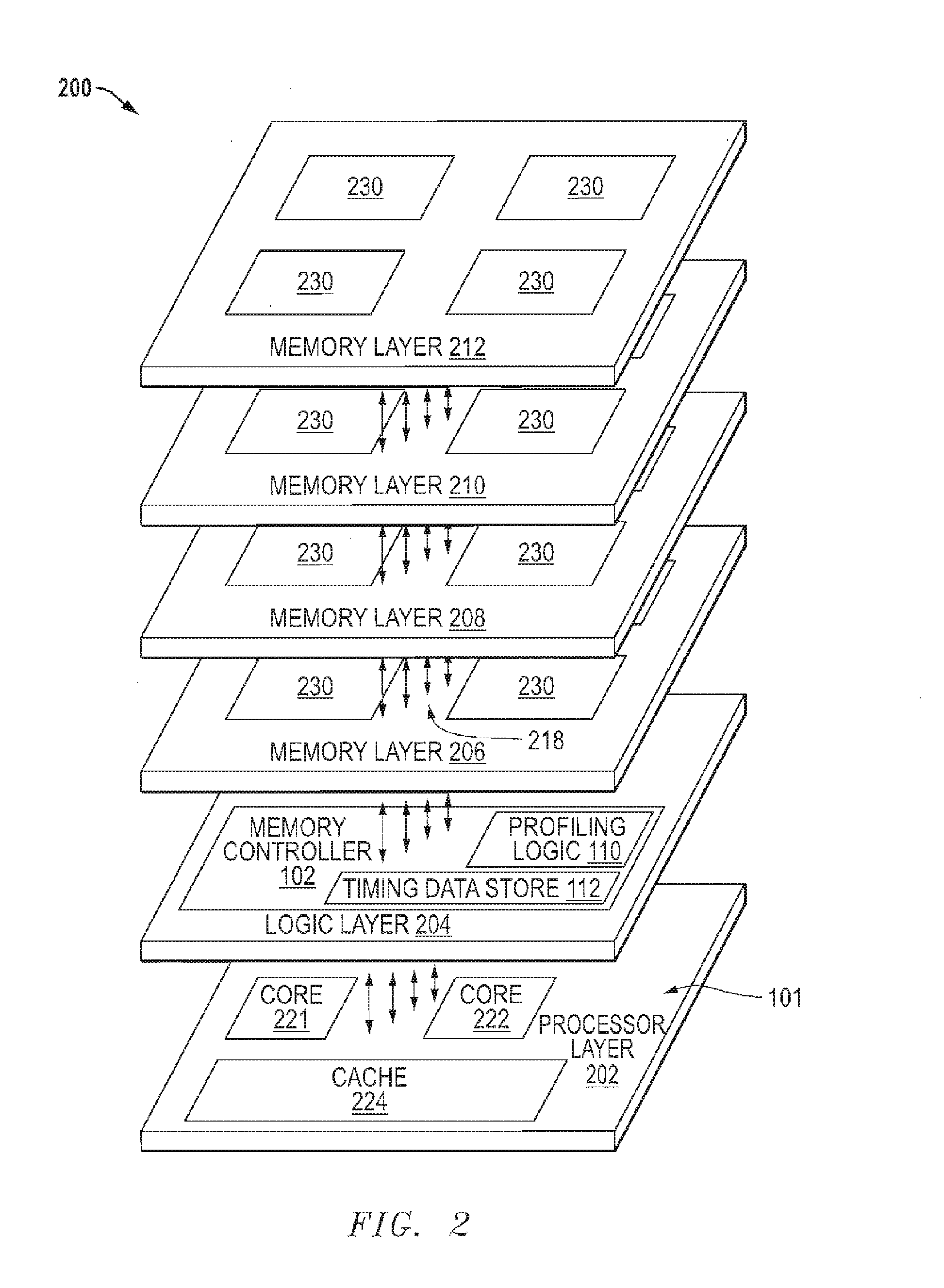
Memory system with region-specific memory access scheduling
ActiveUS20160124873A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer hardwareMemory controller
An integrated circuit device includes a memory controller coupleable to a memory. The memory controller to schedule memory accesses to regions of the memory based on memory timing parameters specific to the regions. A method includes receiving a memory access request at a memory device. The method further includes accessing, from a timing data store of the memory device, data representing a memory timing parameter specific to a region of the memory cell circuitry targeted by the memory access request. The method also includes scheduling, at the memory controller, the memory access request based on the data.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
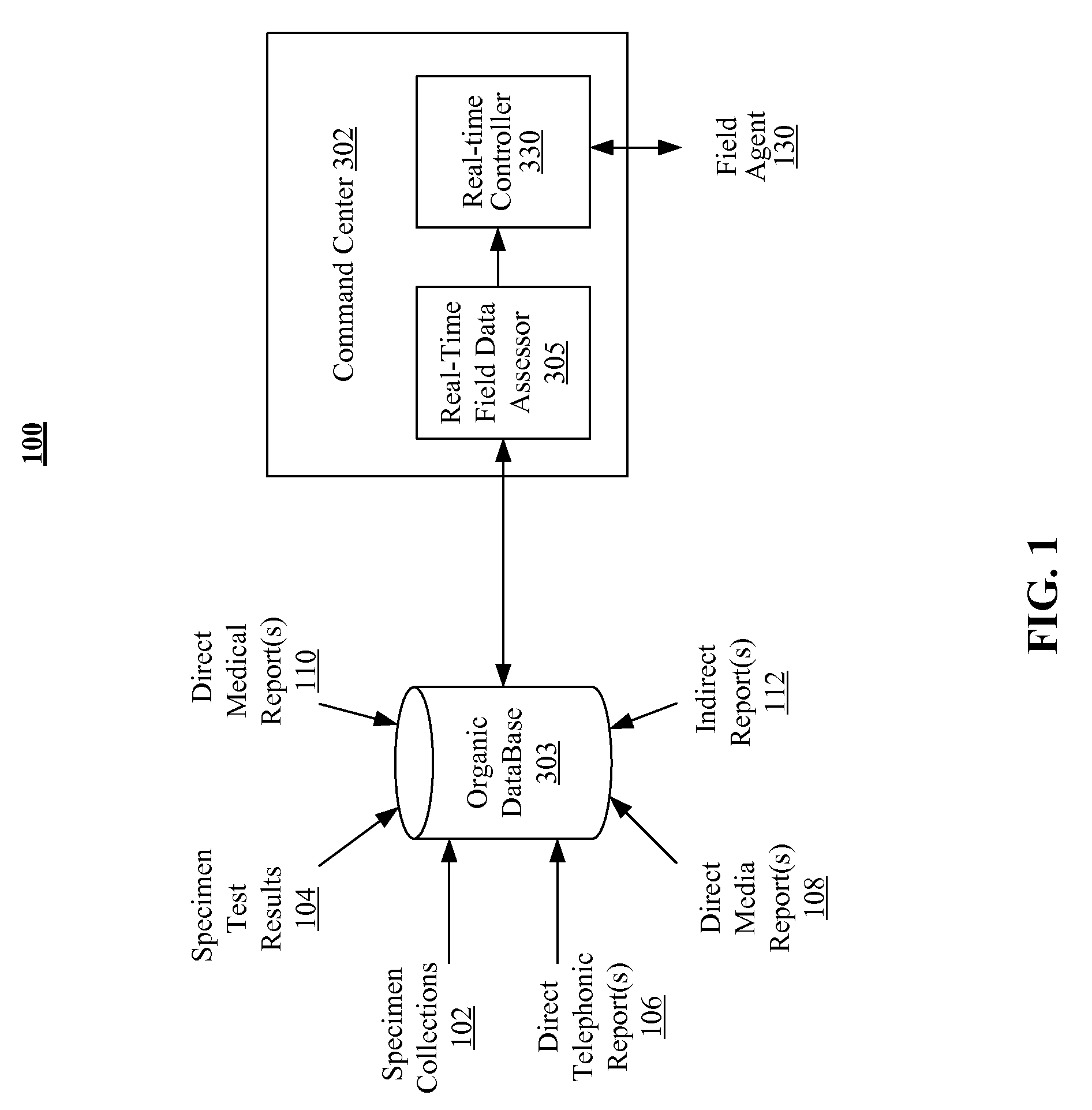
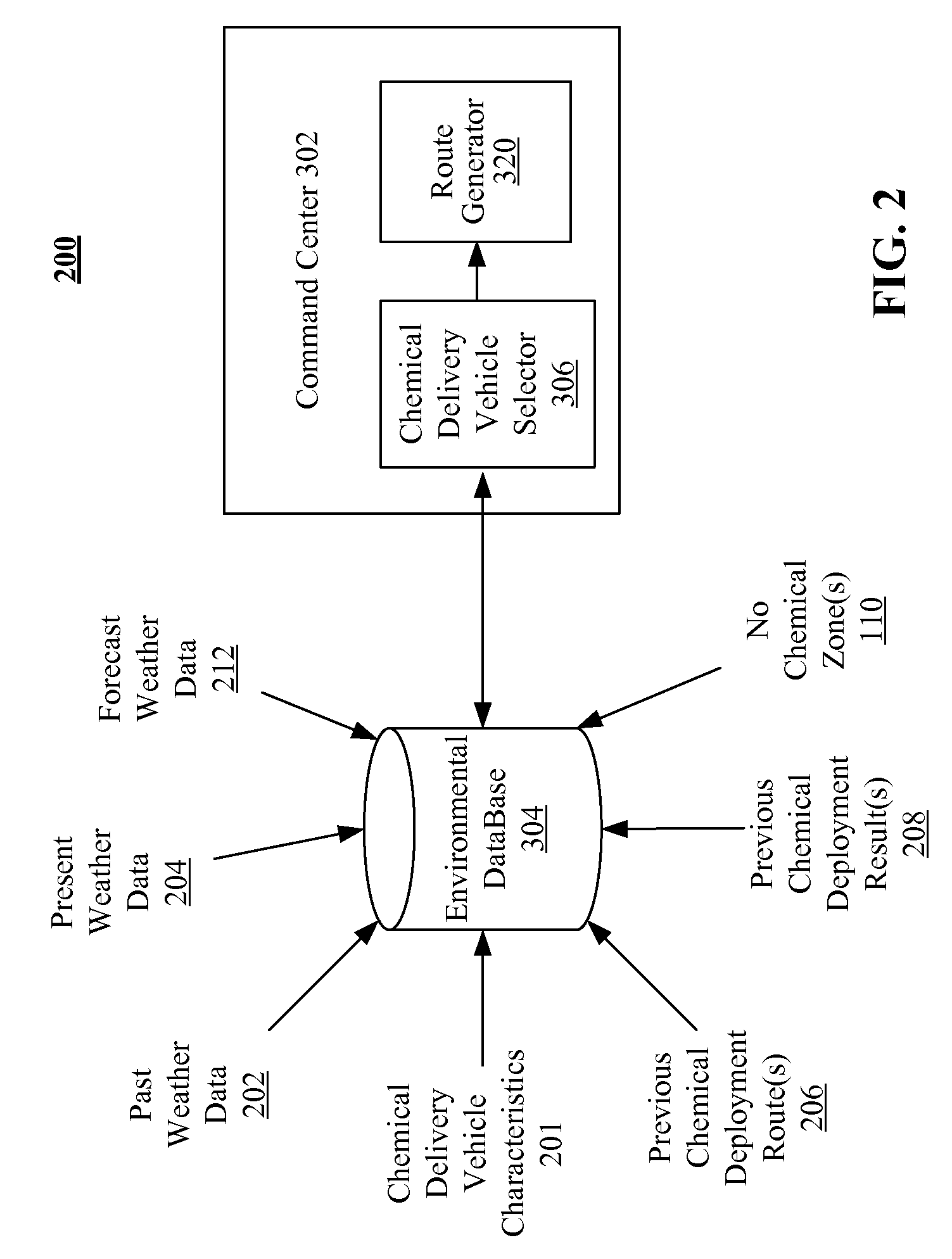
Integration of real-time field data in chemical delivery vehicle operations
A method and system for integration of real-time field data in chemical delivery vehicle operations is disclosed. Initially, information for a plurality of regions designated for chemical delivery is received at a command center, each of the plurality of regions having a defined boundary. Real-time and forecast environmental conditions are utilized in conjunction with prior and real-time field data to rank each of the plurality of regions. One or more chemical delivery vehicles are automatically selected and dispatched to one or more of the plurality of regions. When the one or more chemical delivery vehicles are within the defined boundary of one of the plurality of regions for chemical delivery, region specific chemical delivery procedures incorporating real-time environmental conditions are automatically calculated and initiated.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Methods for converting or inducing protective immunity
InactiveUS20090214533A1Reduced activityReduce functionAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsRegulatory T cellImmune complex deposition
The invention is based in part on the finding that suppressing regulatory T cell function is needed in order to convert passive immunity into active antigen-specific immunity. Generally, the methods of the invention comprise at least the combination of: (1) increasing the amount of immune complexes in the subject, wherein the immune complex comprises a target antigen and a immunoglobulin molecule comprising (i) a variable region specific to the target antigen and (ii) a Fc receptor binding region; and (2) inhibiting regulatory T cell function or decreasing / depleting the regulatory T cell population in the subject.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
X-ray computed tomography apparatus
ActiveUS7215733B2Reduce operating loadReduce exposureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayEngineering
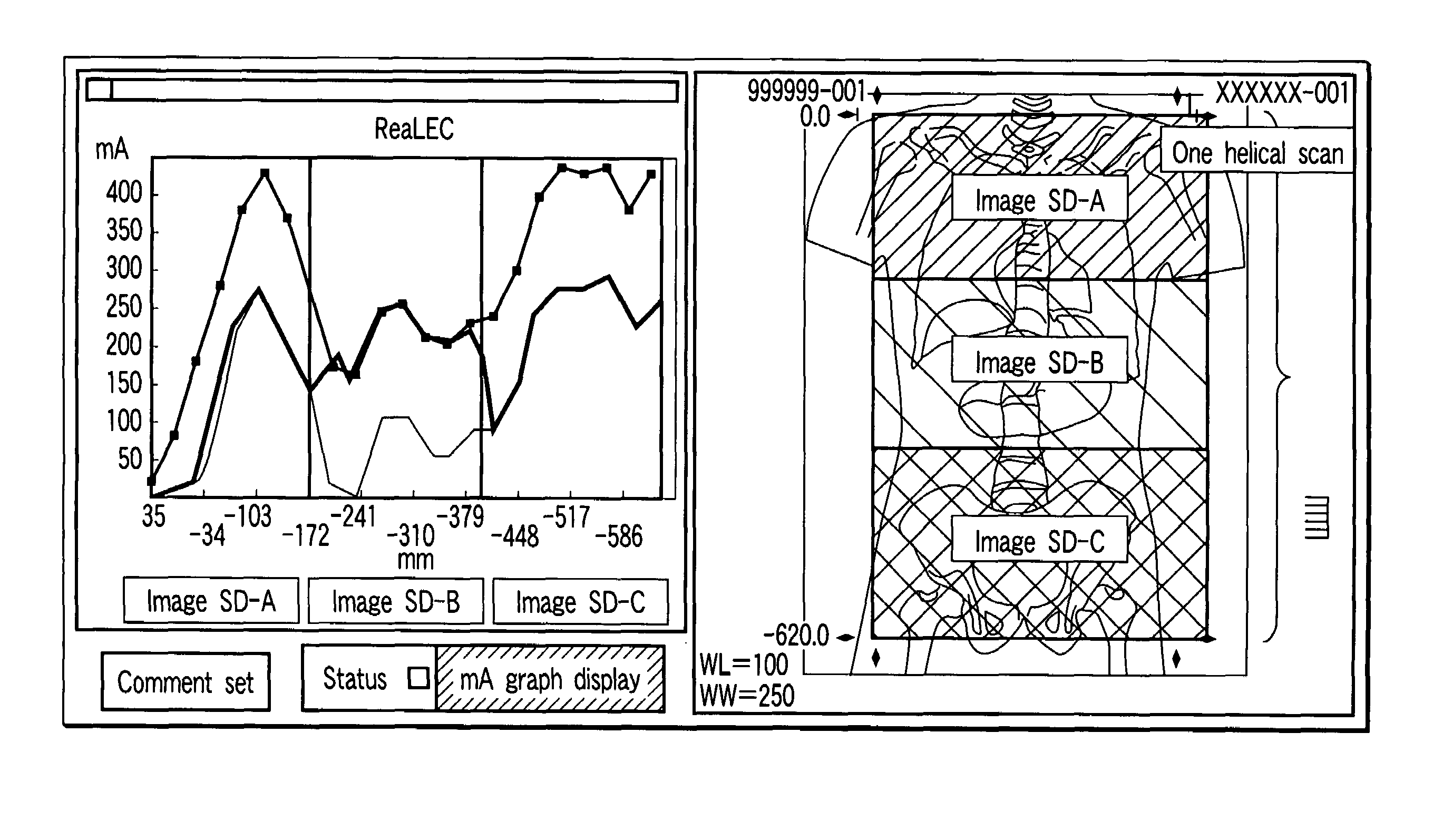
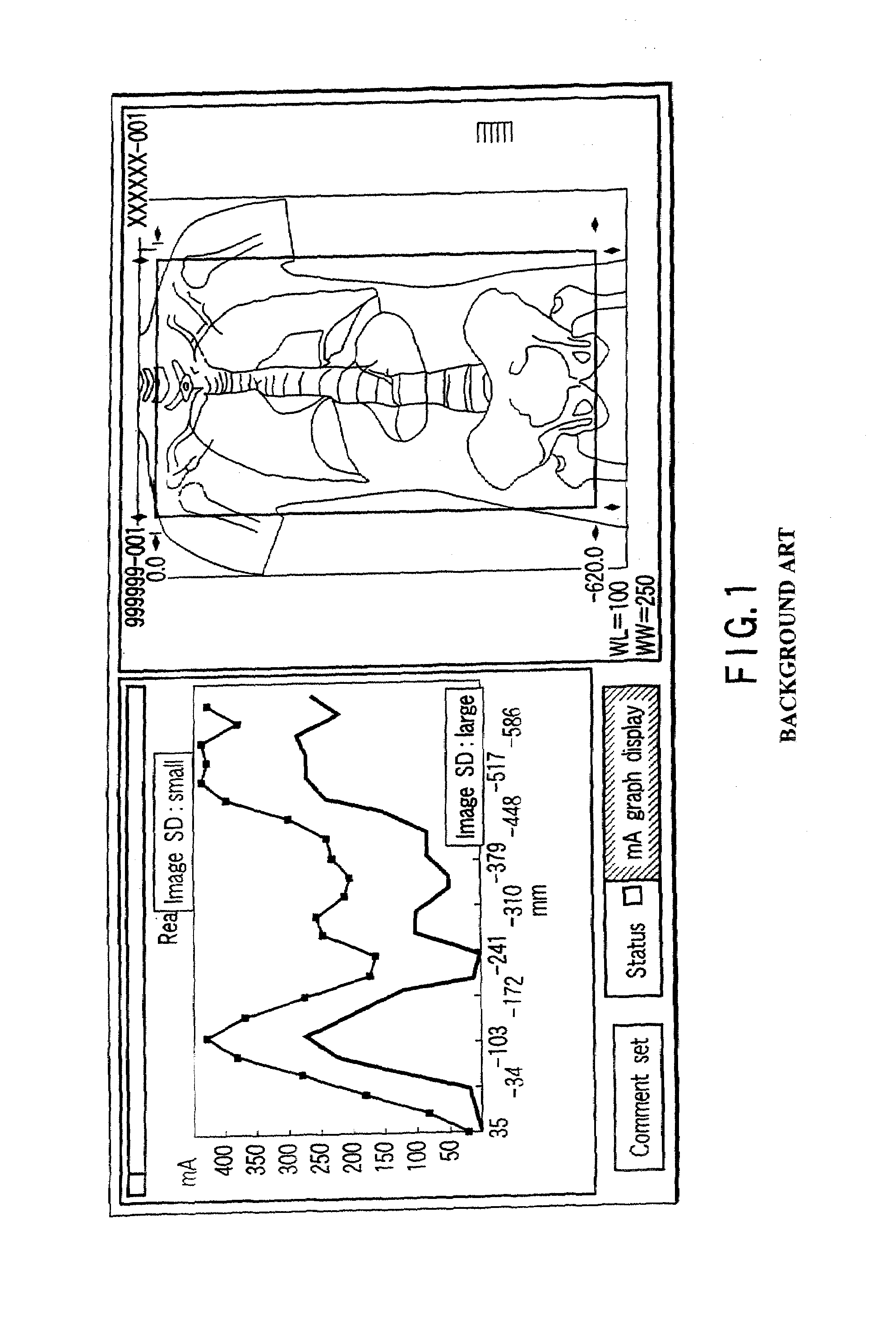
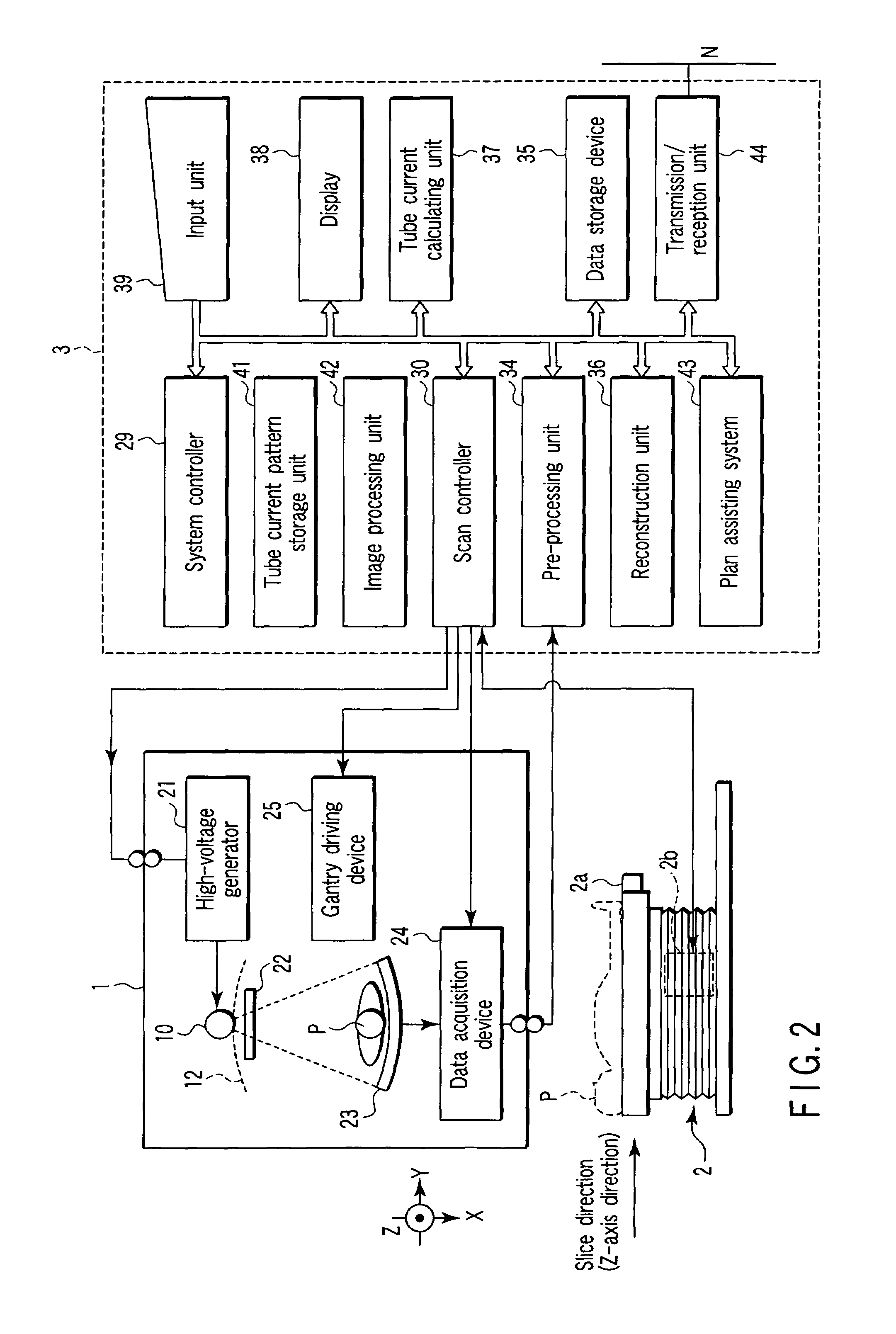
A plurality of region-specific areas are set on a scanogram, and an image SD value is set for each region-specific area. A tube current calculating unit calculates a tube current value at each position on the basis of a tube current pattern in a tube current pattern storage unit, an image SD value for each region-specific area, and a CT value at each position on the scanogram in each region-specific area. A scan controller controls X-ray emission in accordance with a calculated tube current value at each position.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method of delivering decision suport systems (DSS) and electronic health records (EHR) for reproductive care, pre-conceptive care, fertility treatments, and other health conditions
Provided are methods of delivering decision support systems (DSSs) to healthcare providers, patients, and / or consumers with or without integrated electronic health records (EHRs) for reproductive care and other health conditions. The DSS platforms of the present invention include predication models based upon de-identified data sets and customized algorithms that may be clinic specific, region specific, and / or population specific. The DSS platforms of the present invention also include methods of providing third party payments of an individual's medical bills, wherein the third party is not capable of viewing the personal health identifiers of the individual.
Owner:UNIVFY
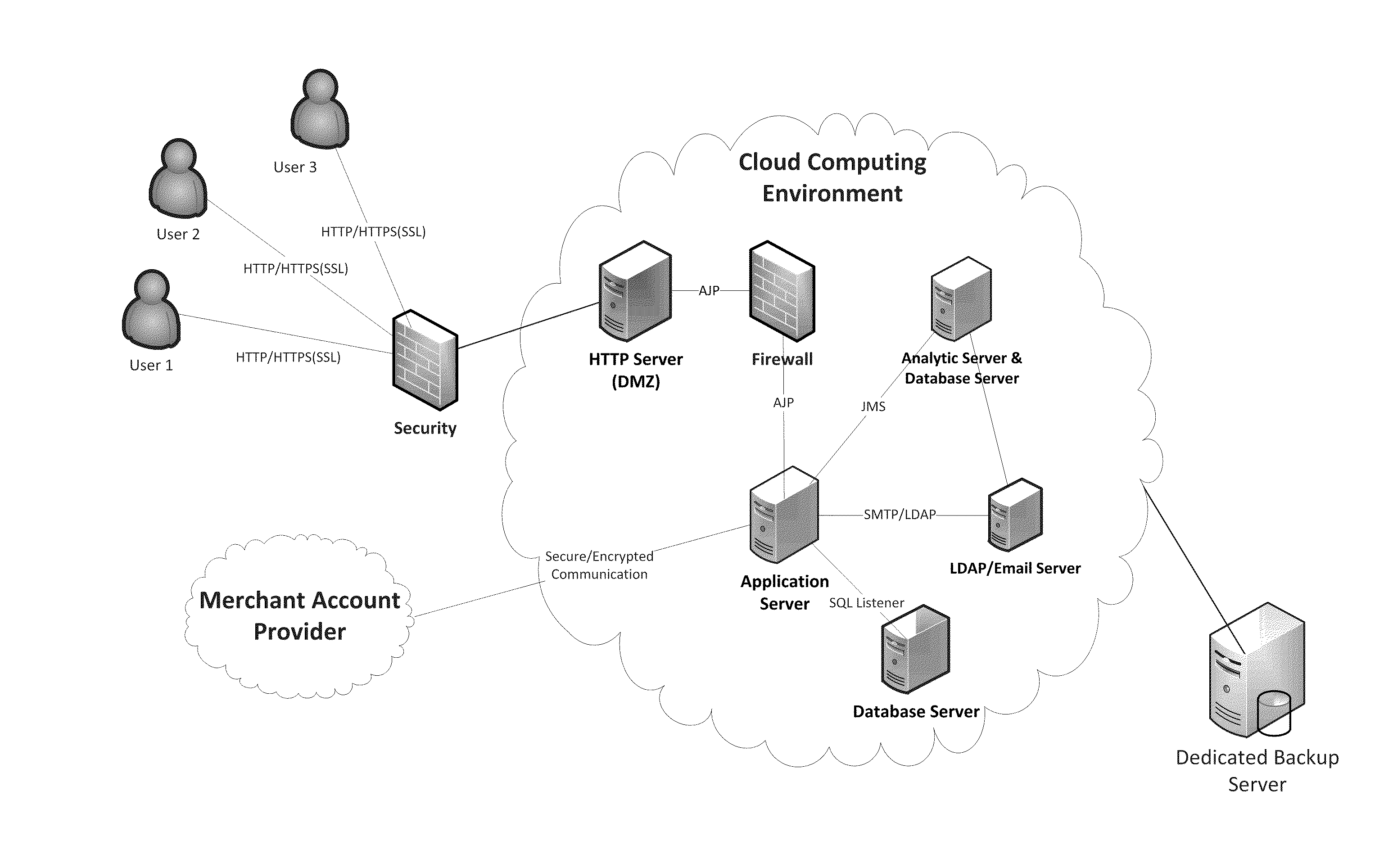
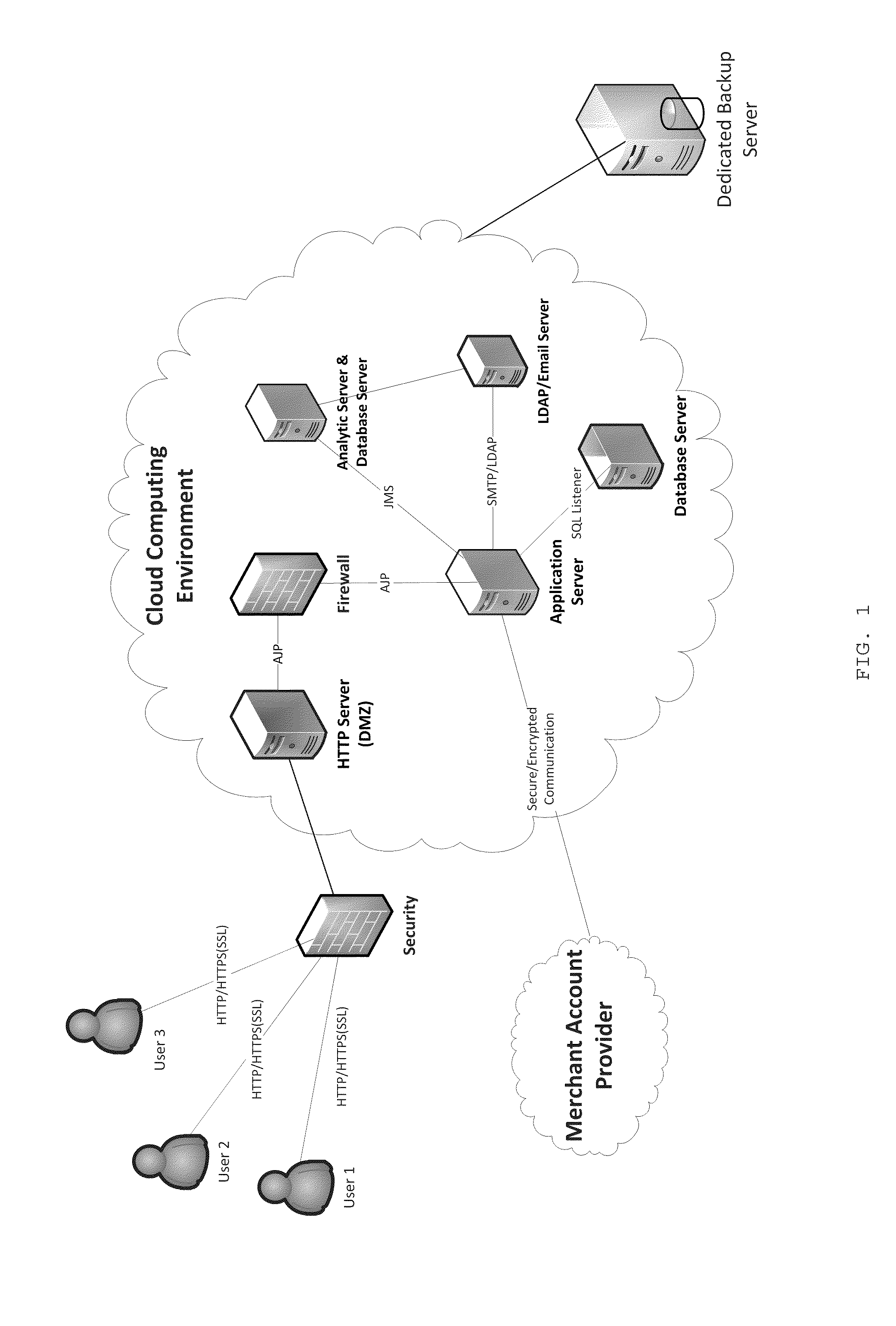
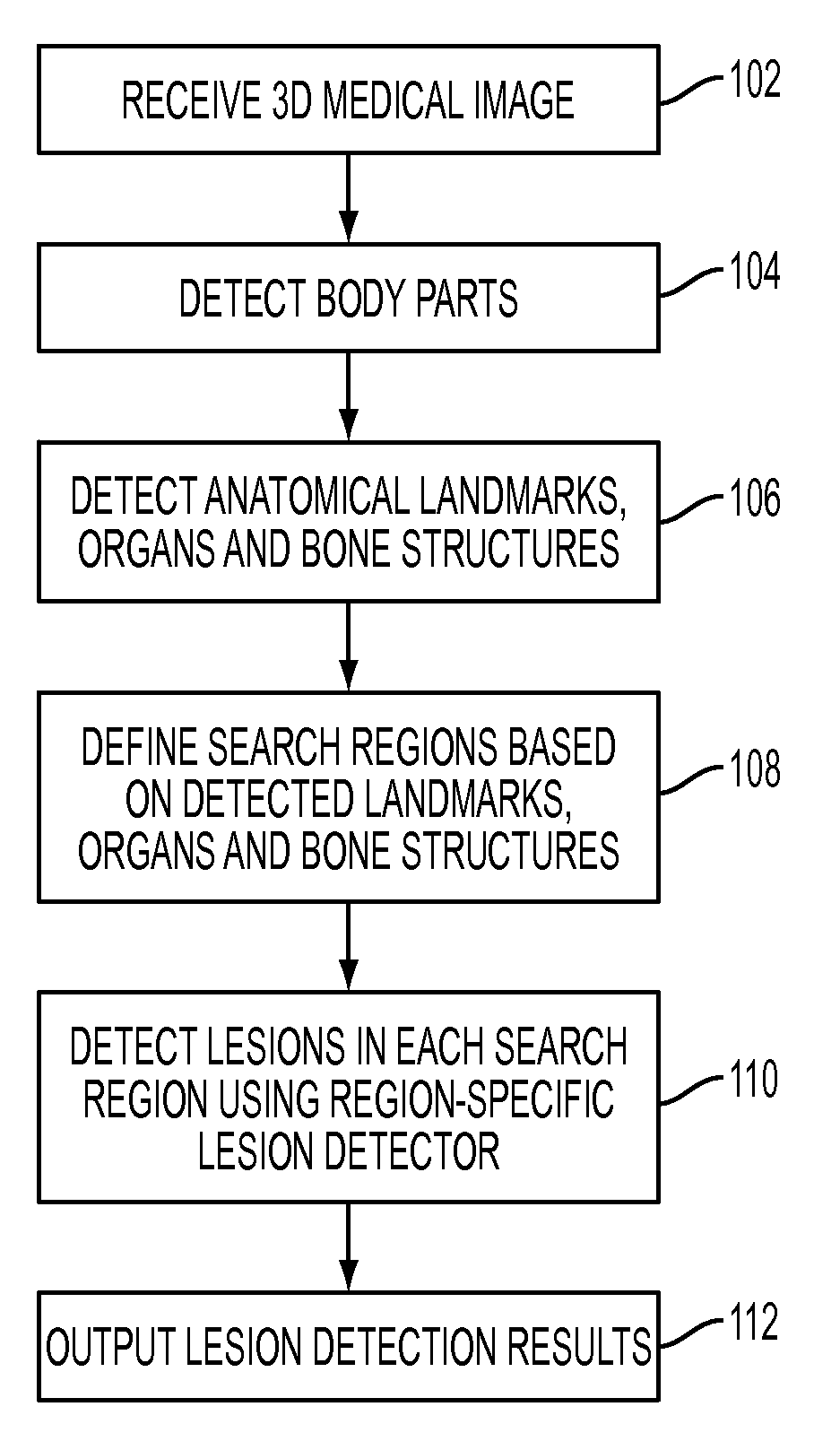
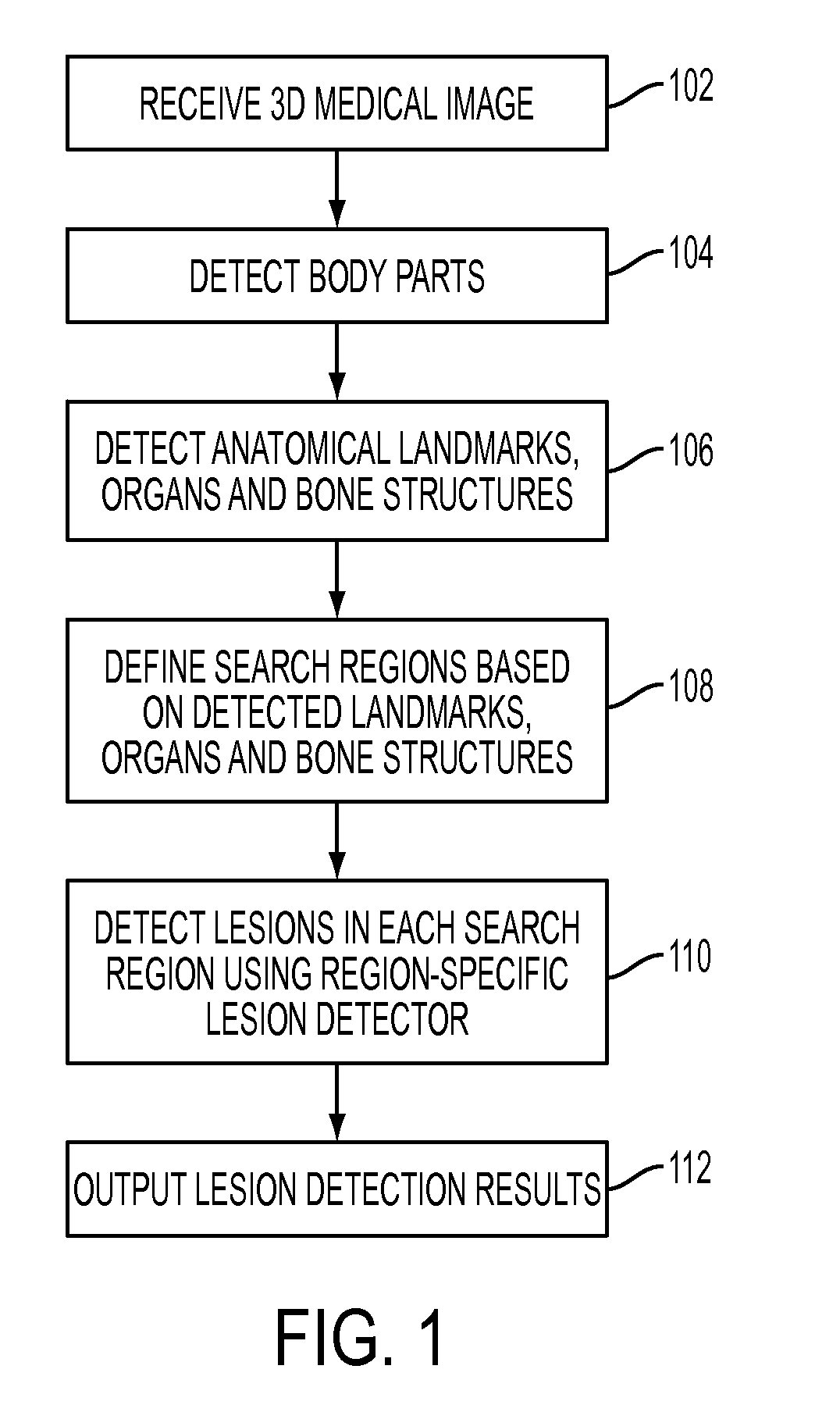
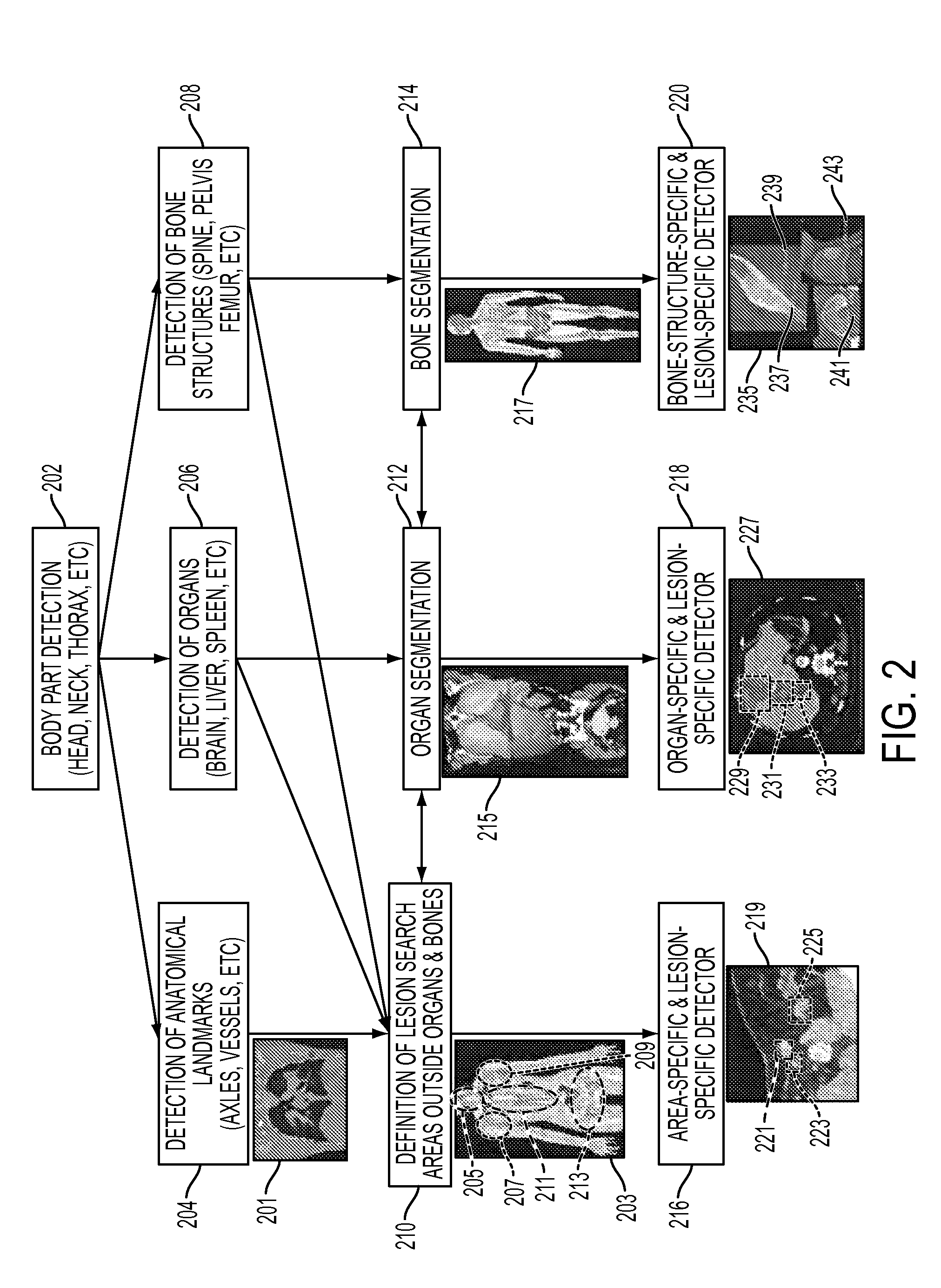
Method and System for Database-Guided Lesion Detection and Assessment
A method and system for automatically detecting lesions in a 3D medical image, such as a CT image or an MR image, is disclosed. Body parts are detected in the 3D medical image. Anatomical landmarks, organs, and bone structures are detected in the 3D medical image based on the detected body parts. Search regions are defined in the 3D medical image based on the detected anatomical landmarks, organs, and bone structures. Lesions are detected in each search region using a trained region-specific lesion detector.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Early B-cell detection for selecting vaccines
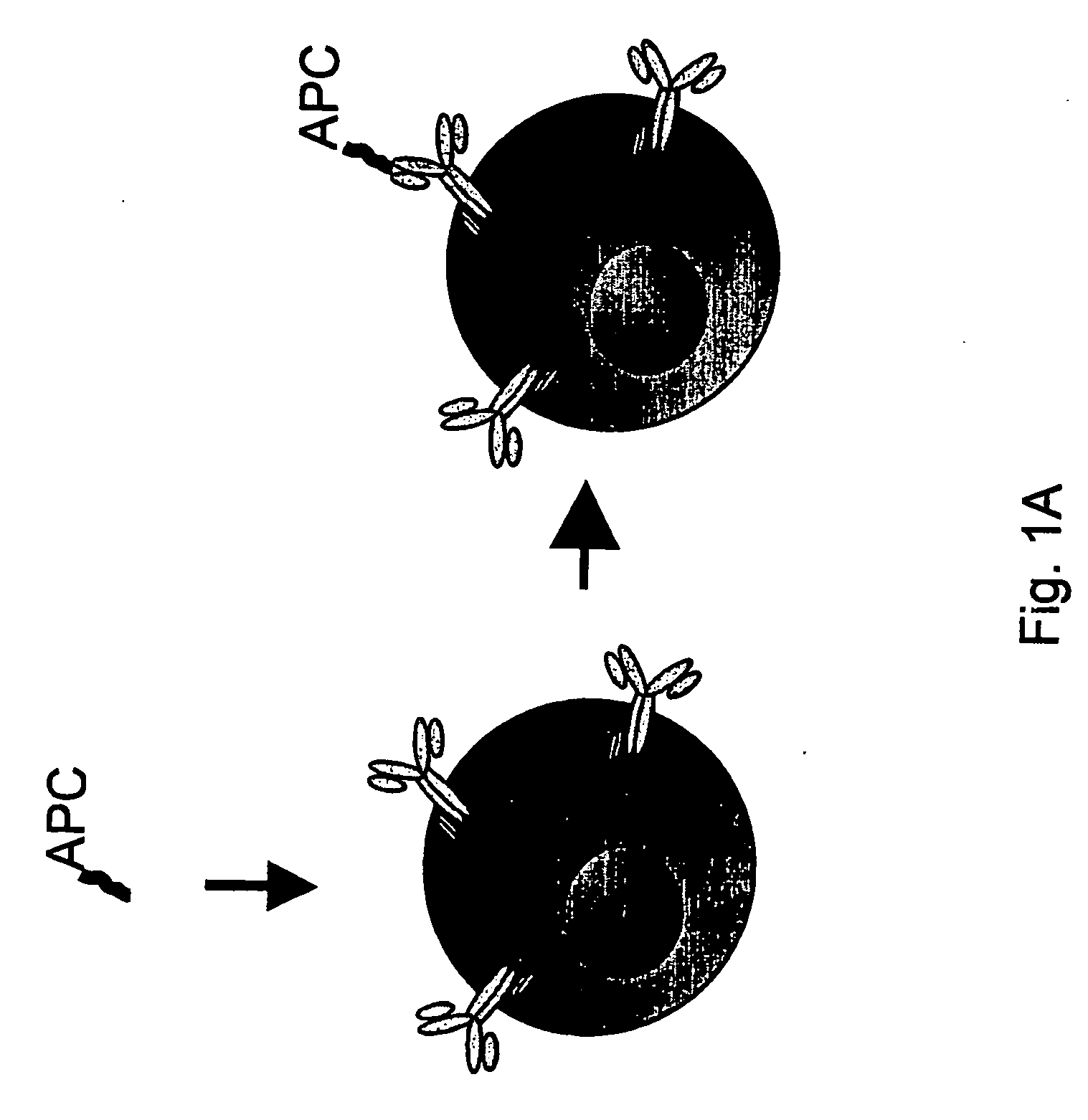
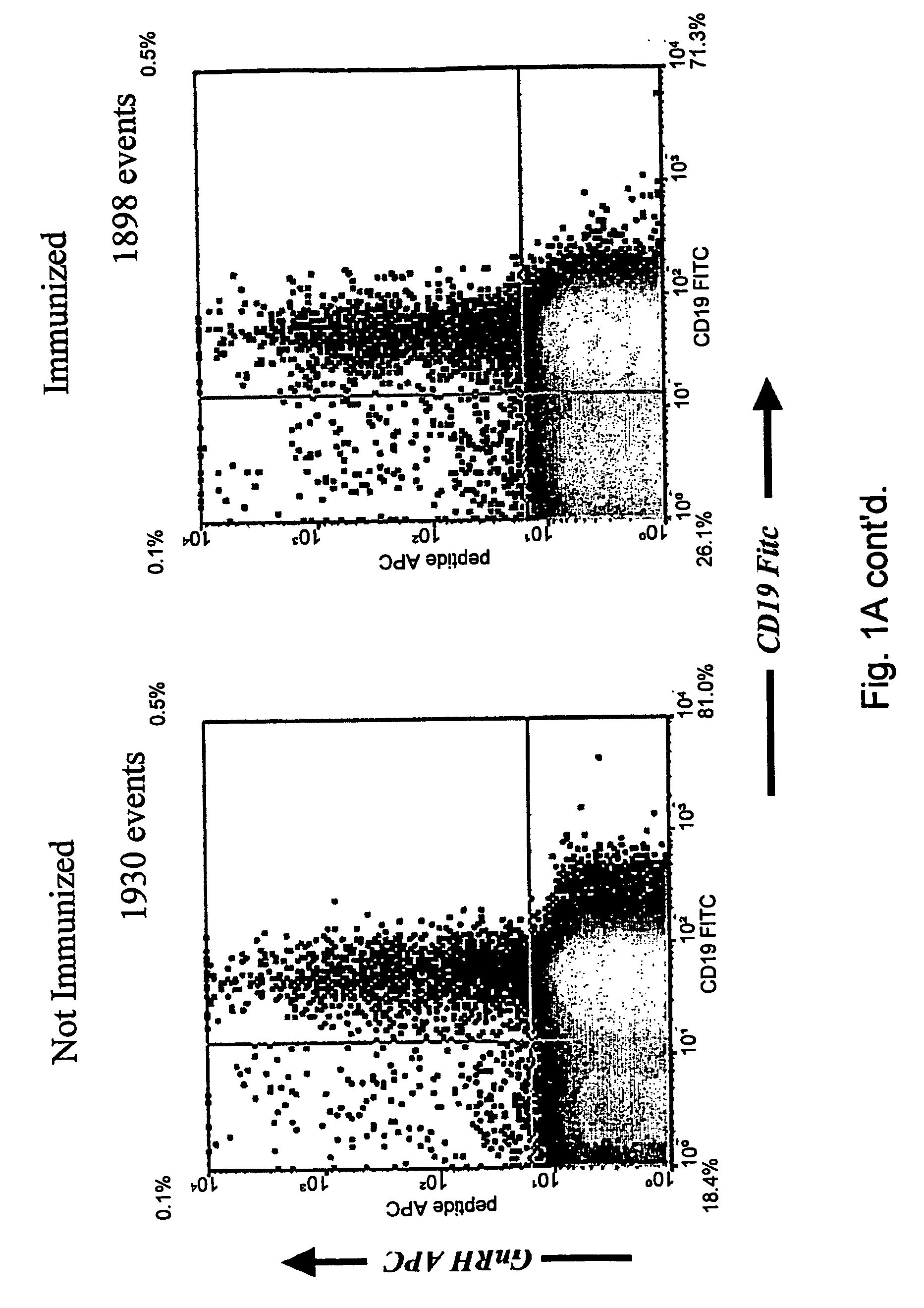
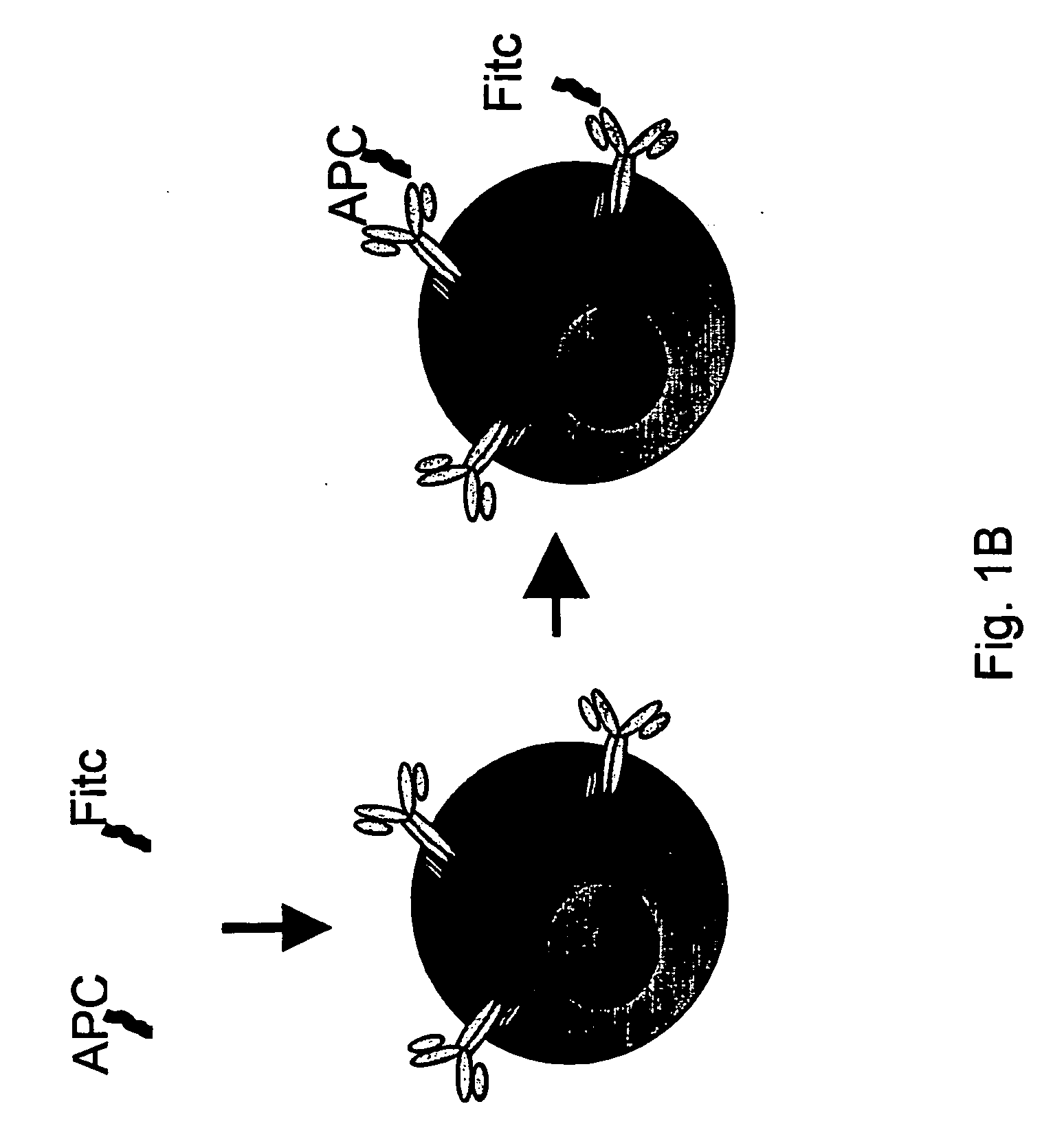
InactiveUS20070065428A1Improving immunogenicityFacilitated releaseMetabolism disorderDigestive systemRegion specificB cell
The present invention discloses an affinity-binding assay comprising a particle having at least four copies of a target molecule and at least two binding molecules specific for the target molecule, wherein a first of the binding molecules is associated with a first label and a second of the binding molecules is associated with a second label, wherein a particle having the first label and a particle having the second label are distinguishable from a particle having both the first and second labels, wherein the first and second binding molecules each comprise at least two binding regions specific for the target molecule. The present invention also discloses a composition comprising a first binding molecule associated with a first label and a second binding molecule associated with a second label, wherein the signal obtained from the first and second labels is distinguishable from the combined signal of the first and second labels, characterized in that the first and second binding molecules each comprise at least two binding regions specific for essentially the same target molecule, preferably for essentially the same epitope on the target molecule and a method for selecting a synthetic antigen from a collection of at least three antigens comprising using the disclosed composition and method. The invention further discloses an antigen obtainable by the above-described method and capable of inducing an early immune response, a kit of parts to perform the method, the use of antigens selected by the methods for use as a vaccine, and the use of antibodies and antigens as a medicament.
Owner:PEPSCAN SYST +1
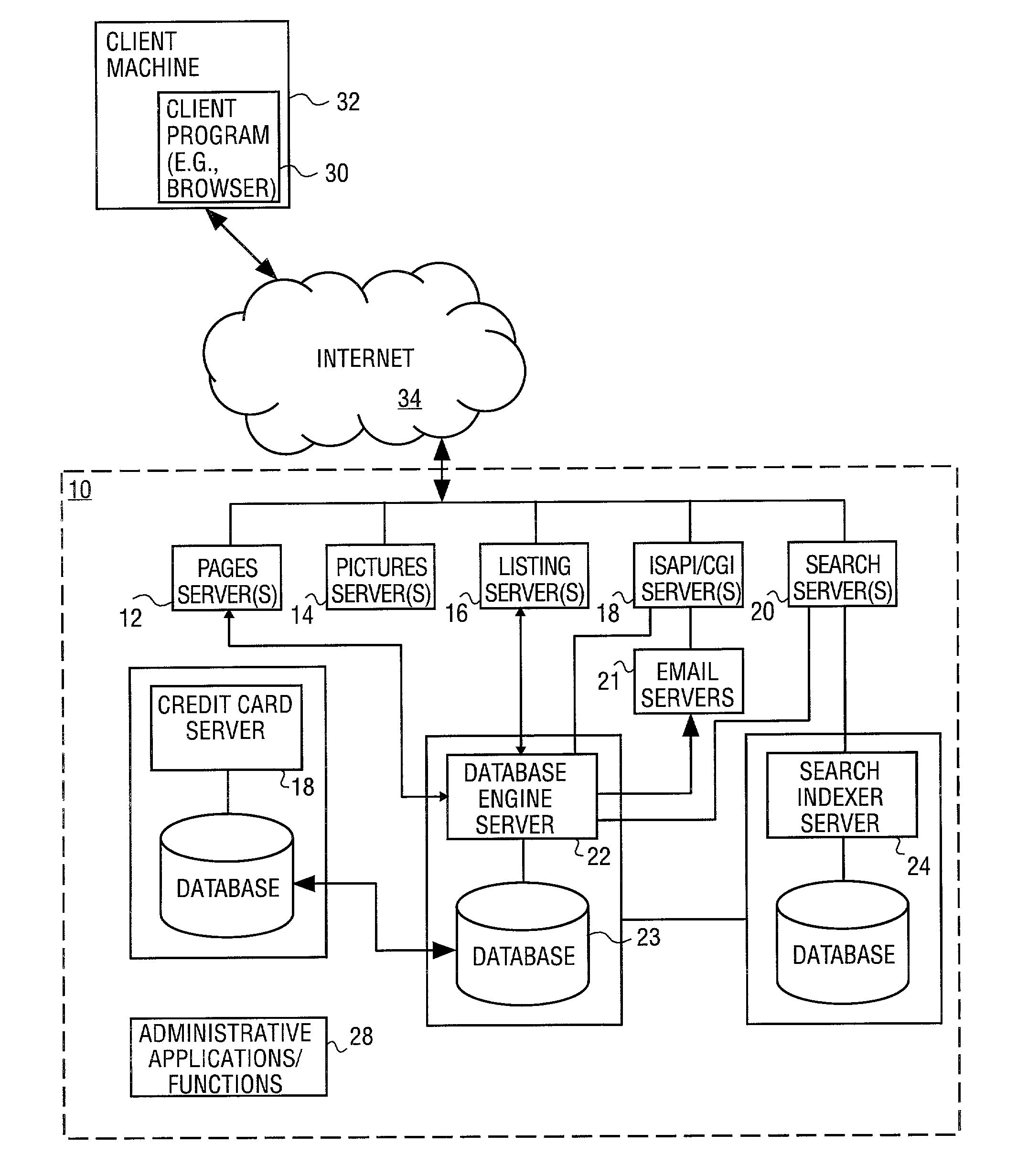
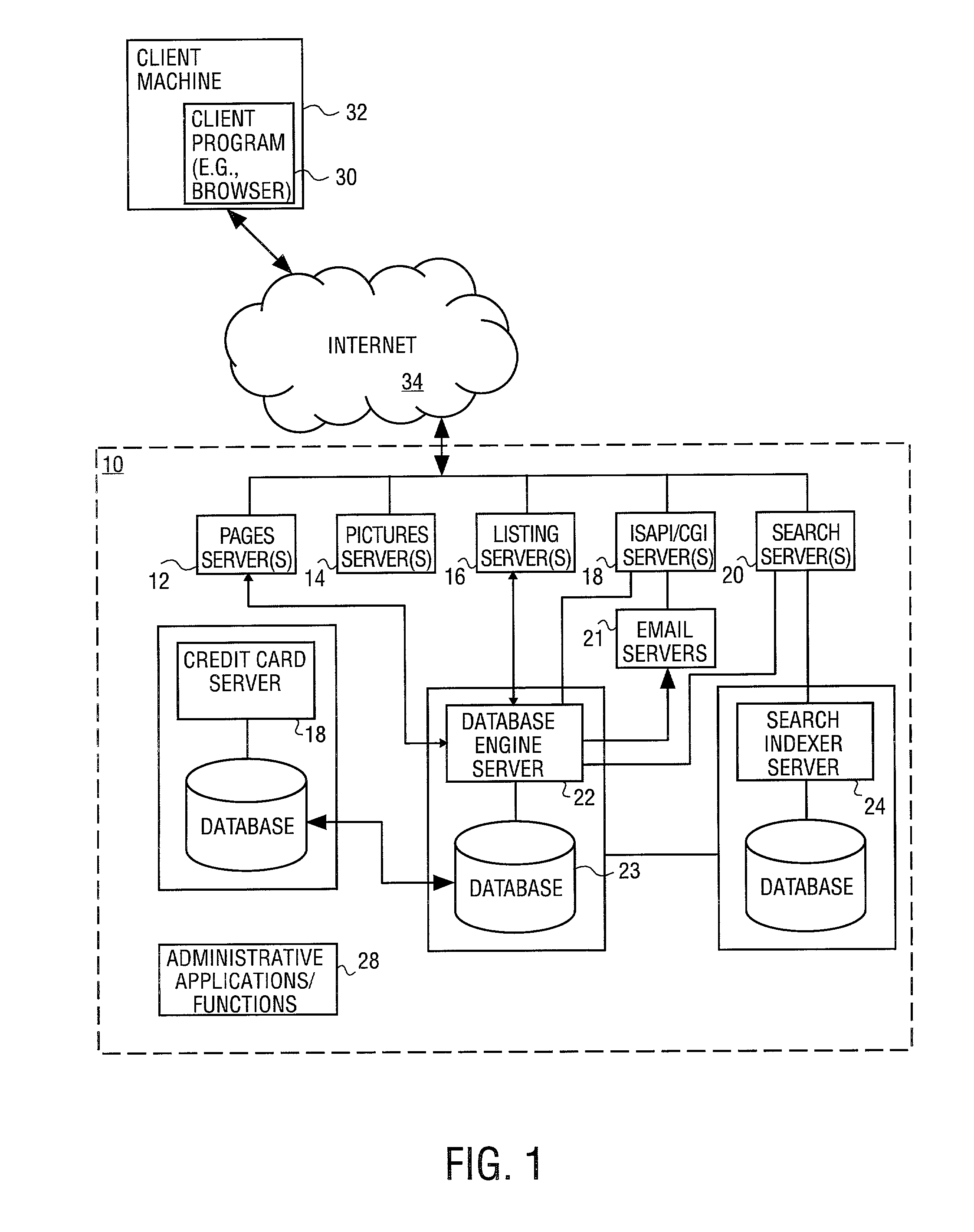
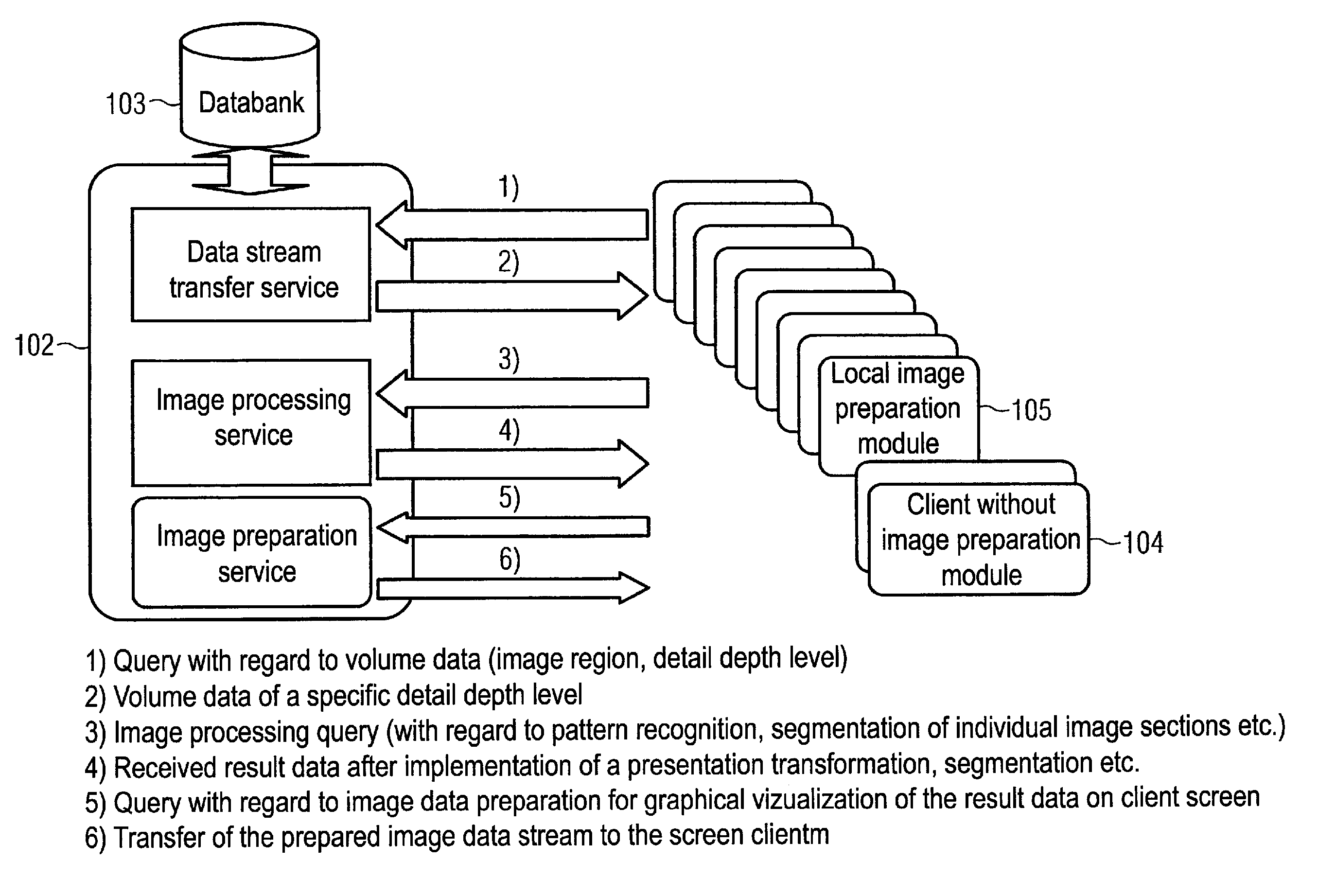
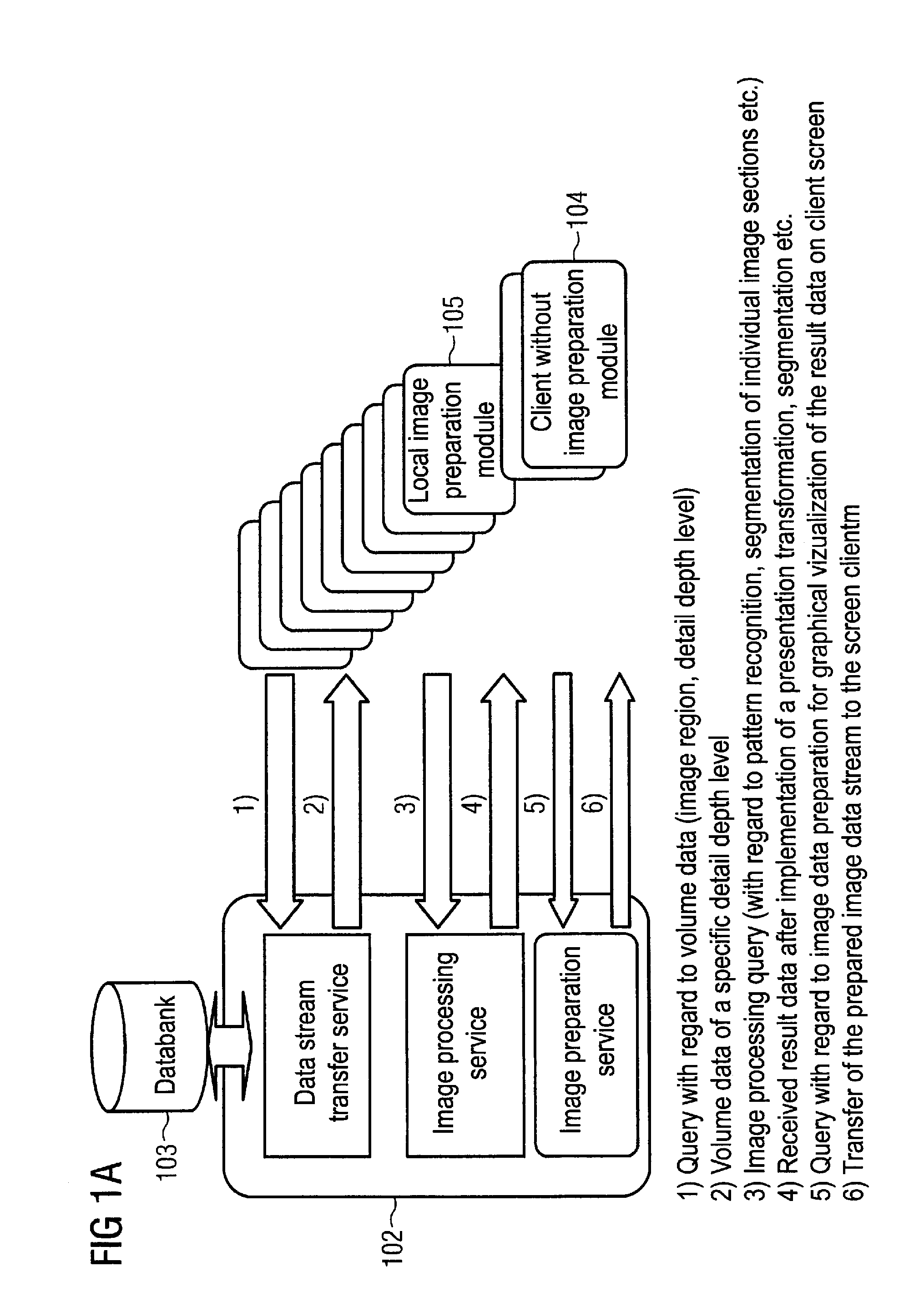
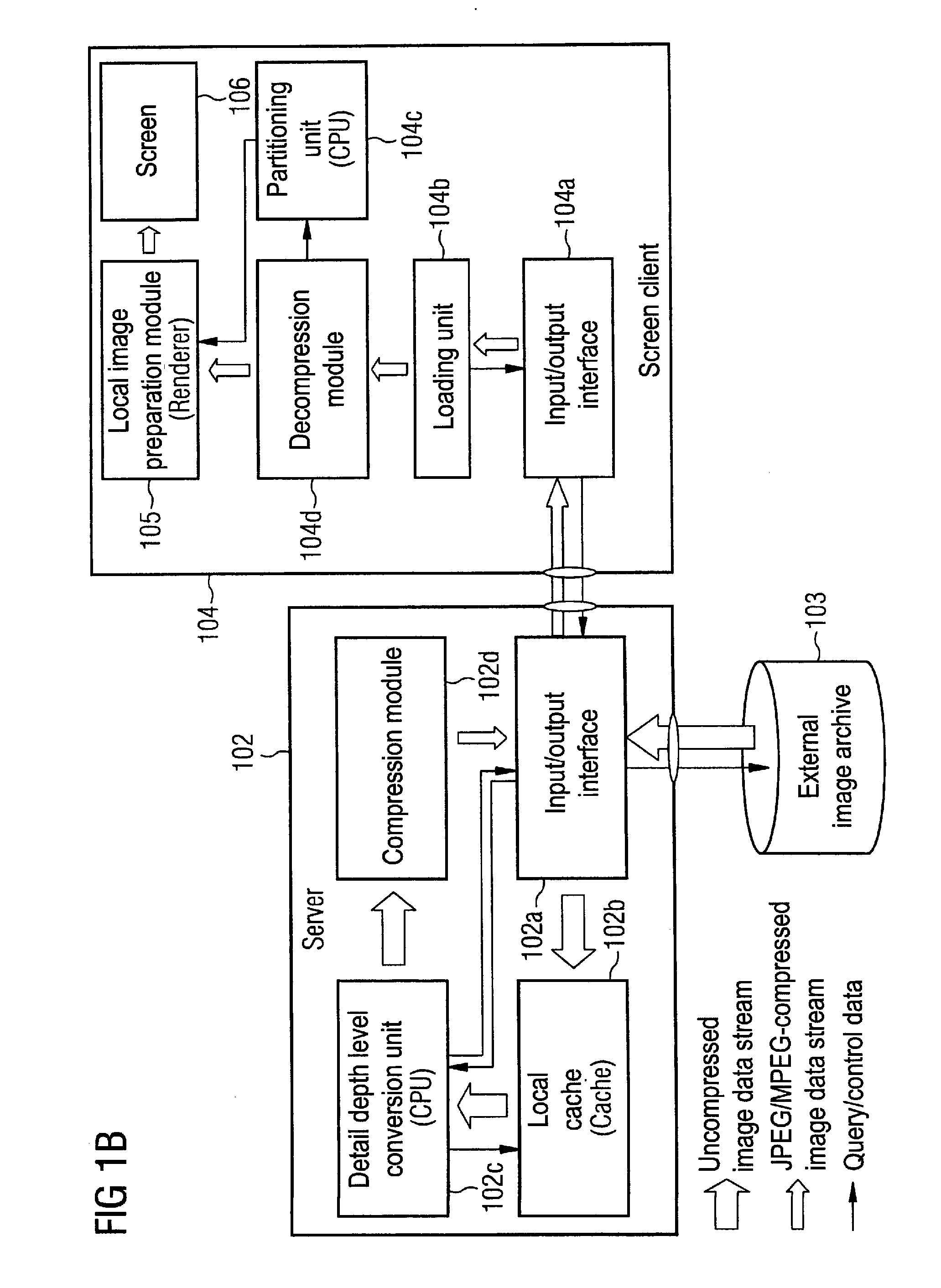
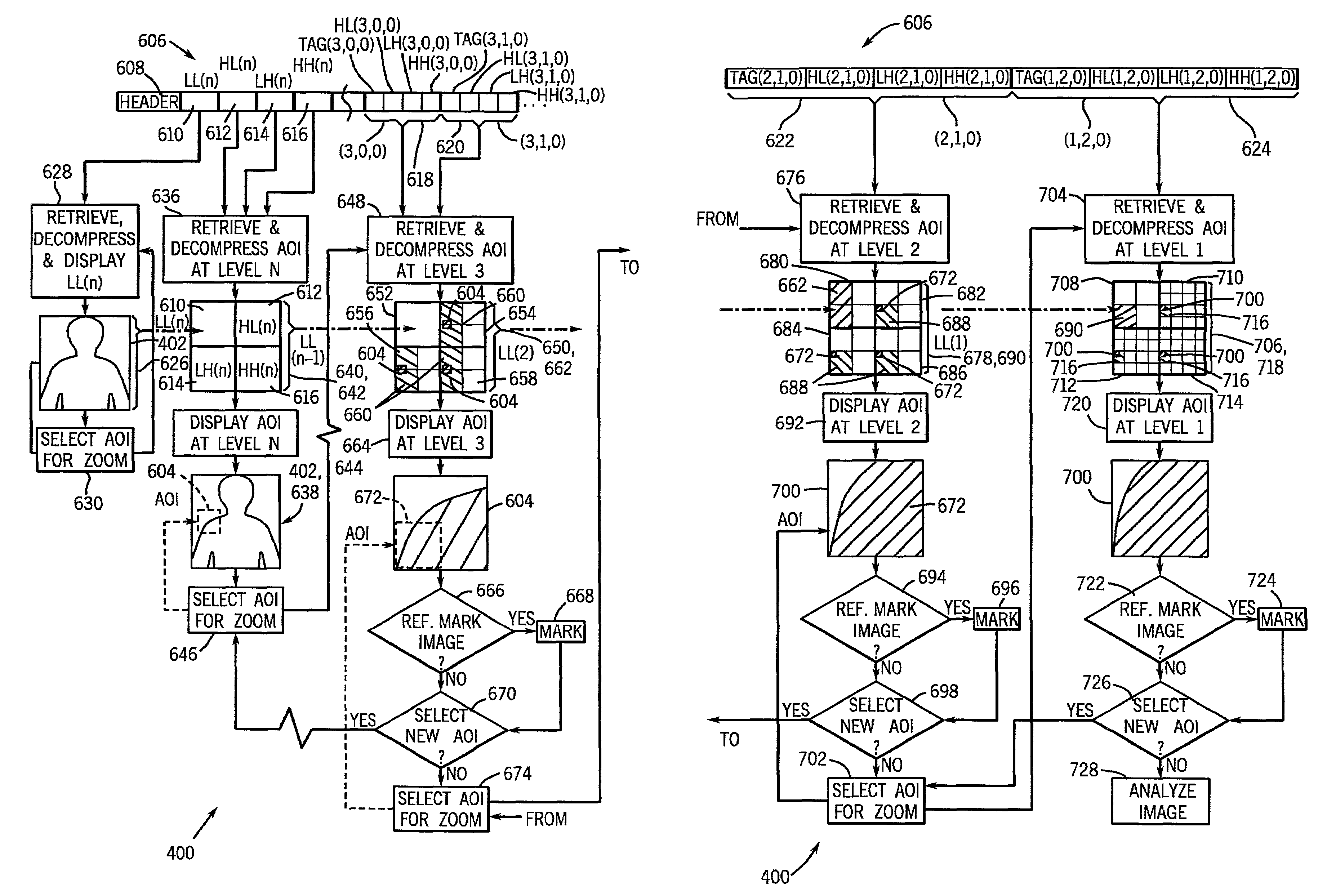
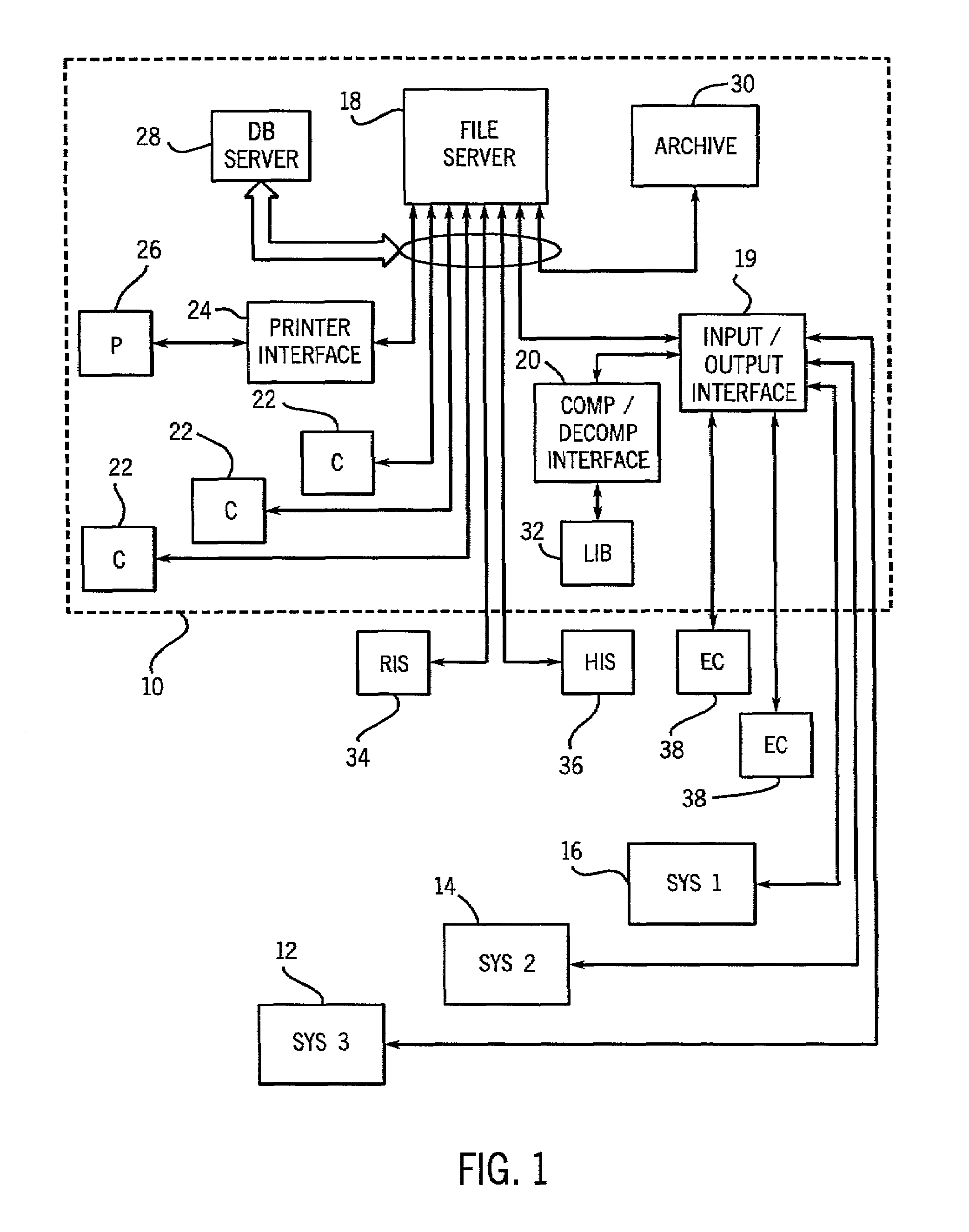
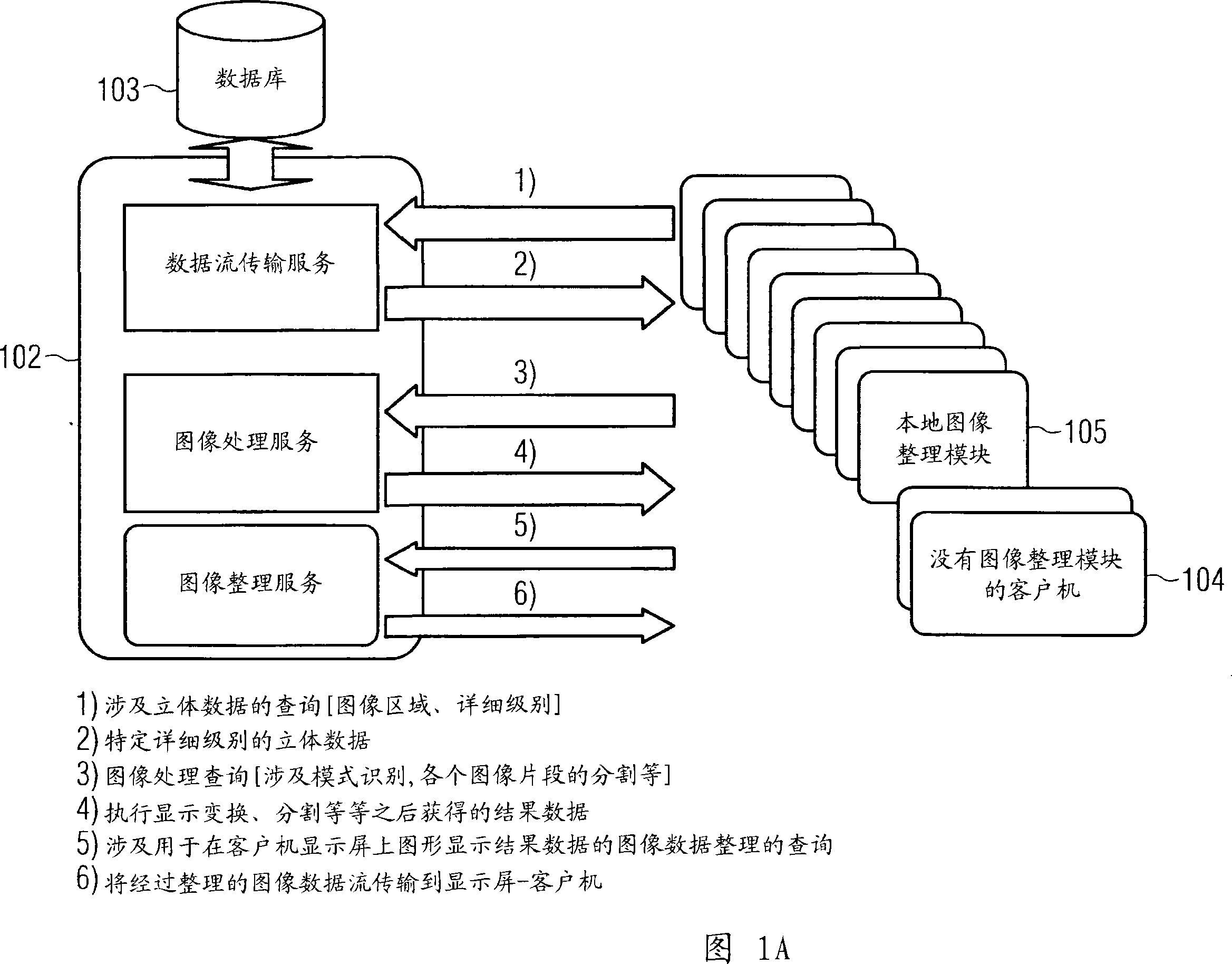
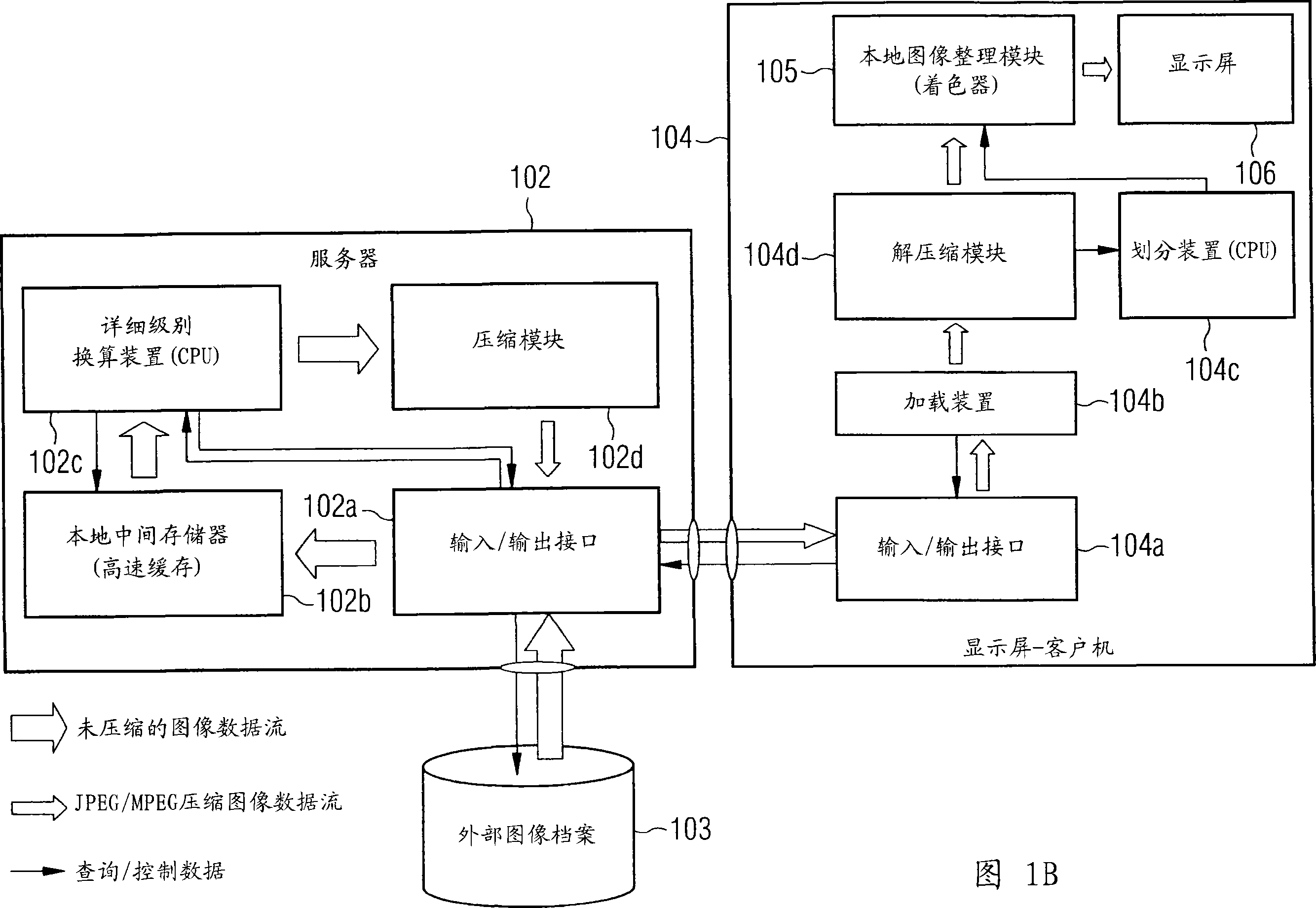
Depth detail level adjustment of multi-dimensional image data with a client/server-based image rendering system
InactiveUS20080069458A1Simple working processReduce decreaseCharacter and pattern recognitionImage data processing detailsGraphicsImage post processing
In a client / server-based image archiving, image retrieval and image rendering system and method for storage, retrieval and graphical visualization of multi-dimensional digital image data such as assessment of medical image data, the detail depth level of volume data received via a data transfer network, to be shown in graphical form, is adjustable by the compressed volume data of subjects to be presented being stored with a highest-possible resolution (predetermined by an imaging system) in a databank administered by a server and directly accessibly only by this server. Although the client / server-based image archiving, image retrieval and image rendering system is able to offer volume data with this highest possible resolution to any point of the system at the request of a screen client, volume data are transferred to a screen client in a compressed form only up to a specific, spatially-variable, region-specific, or subject-specific detail depth level and are presented at the requesting screen client in graphical form. Complicated image rendering and image post-processing algorithms are implemented by the server.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method and system for listing items globally and regionally, and customized listing according to currency or shipping area
InactiveUS20100131510A1Digital data processing detailsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsRegion specificDatabase
A method to facilitate network-based commerce includes determining a site that a user accesses, the site being one of multiple sites operated by a network-based commerce facility. A category list available for the site is retrieved, the category list identifying categories of offerings available via the site. The category list is communicated to the user. The site is a regional site, and the category list is a region-specific category list.
Owner:EBAY INC
Method for recognizing image of carcinoma bone metastasis in bone scan
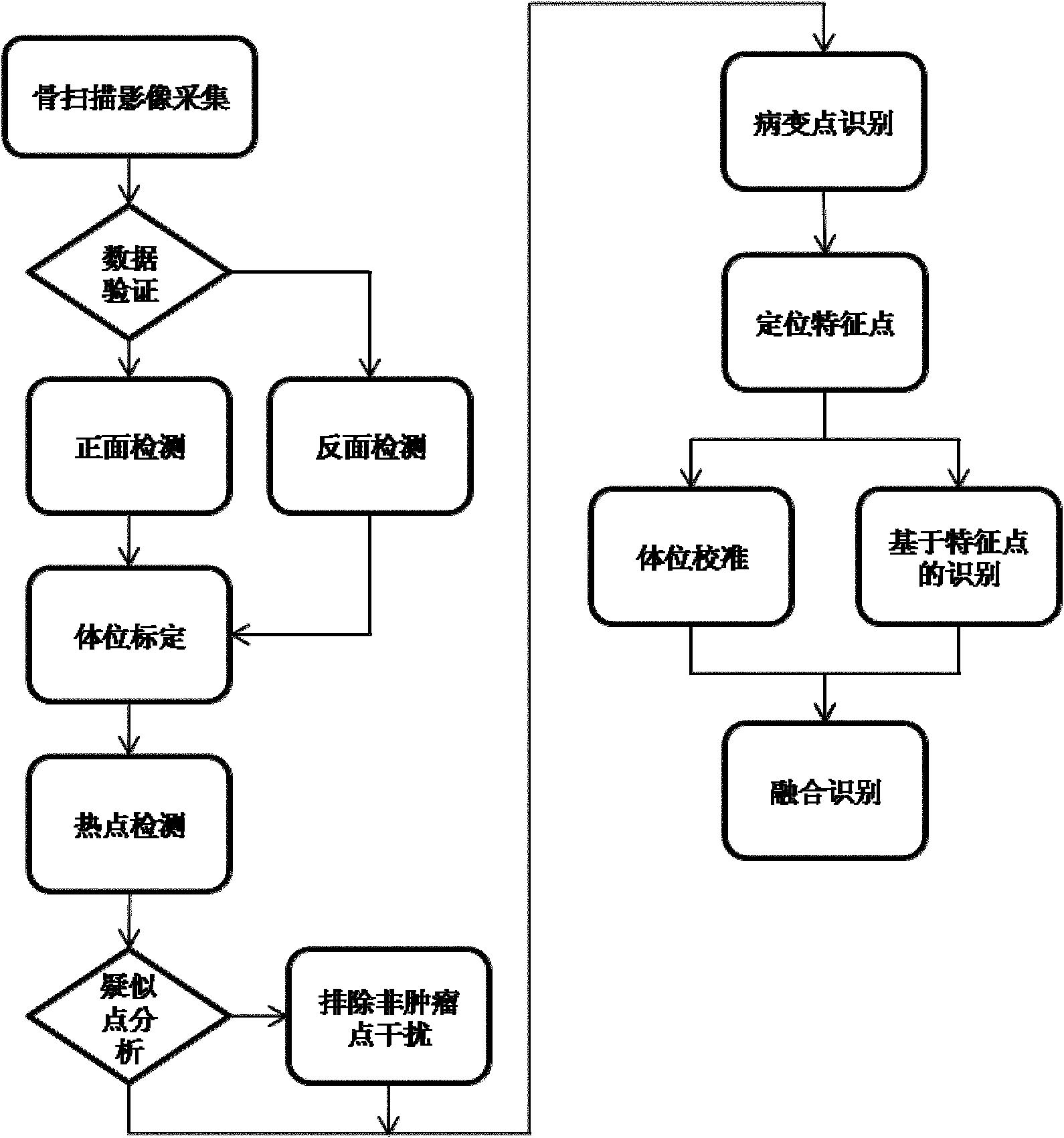
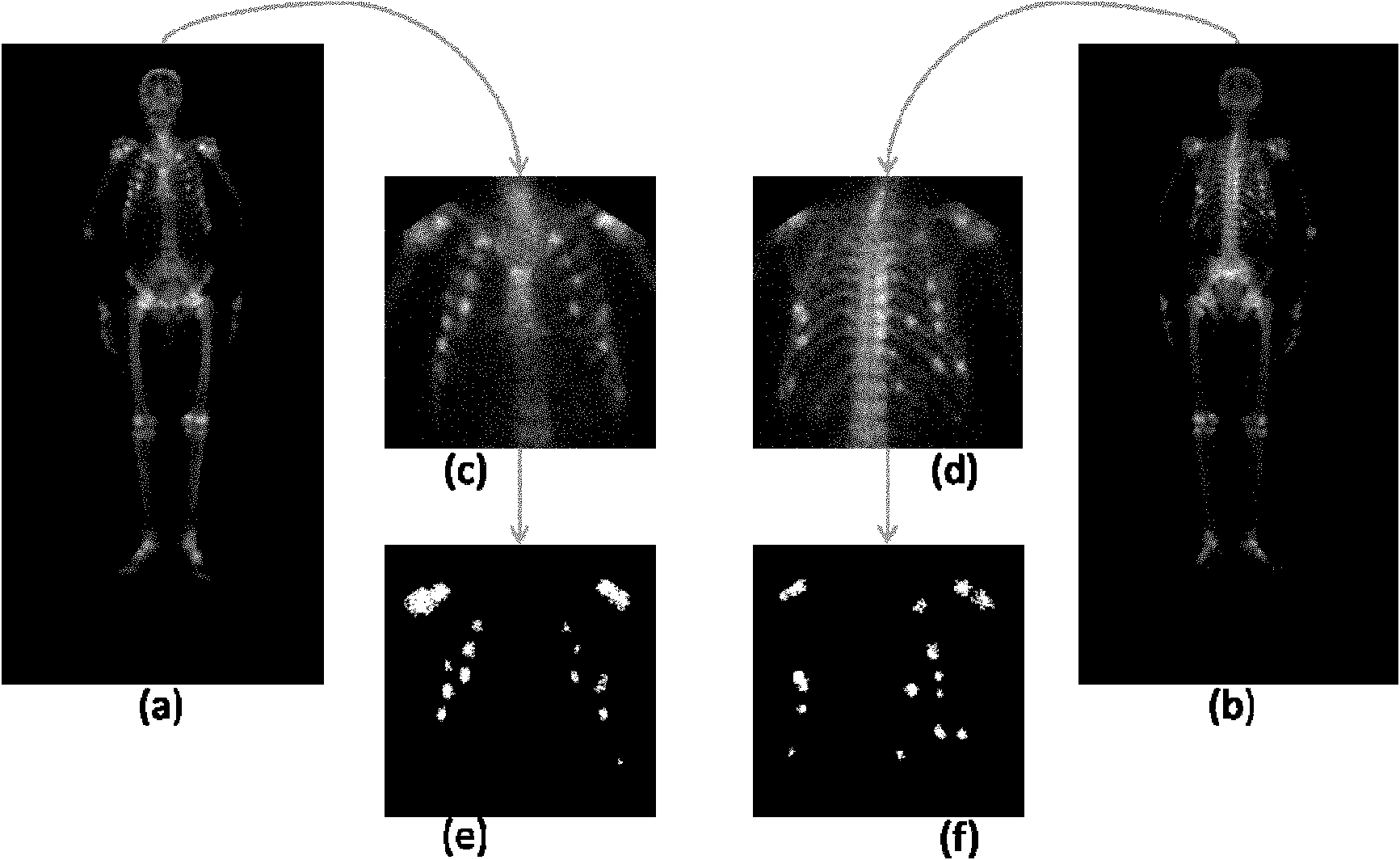
InactiveCN102096804APrecise positioningAccurate identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsHuman bodyLymphatic Spread
The invention provides a method for recognizing an image of carcinoma bone metastasis in bone scan in the technical field of image processing. The method comprises the following steps of: detecting positive information and negative information by extracting a whole body bone scan image of a human body; finding out a reference point according to image information, positioning a key part of the human body, and dividing the image into a plurality of main blocks; extracting a hot spot region by using an adaptive region-specific and characteristic-maximum-based (ARC) hot spot detection algorithm of each region; extracting a characteristic vector according to a hot spot detection result and the original image; using a support vector machine (SVM) training model according to the extracted characteristic vector; testing and modifying an obtained classifying model, and simultaneously performing checking, matching and human body calibration on a recognition result so as to obtain a correct diagnosis report. Compared with other methods of recognizing the image of carcinoma bone metastasis, the hot spot detection precision and patient recognition accuracy are improved, the blank in the new developing field of China is recovered, and a uniform diagnosis standard on carcinoma bone metastasis diagnosis in China is established.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
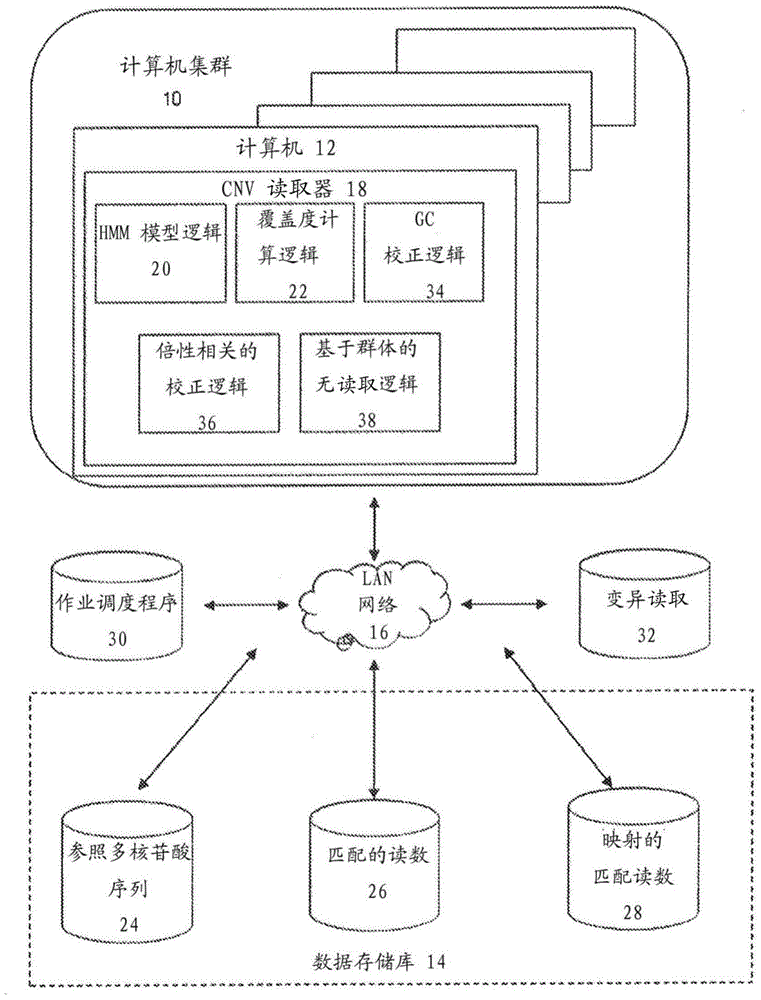
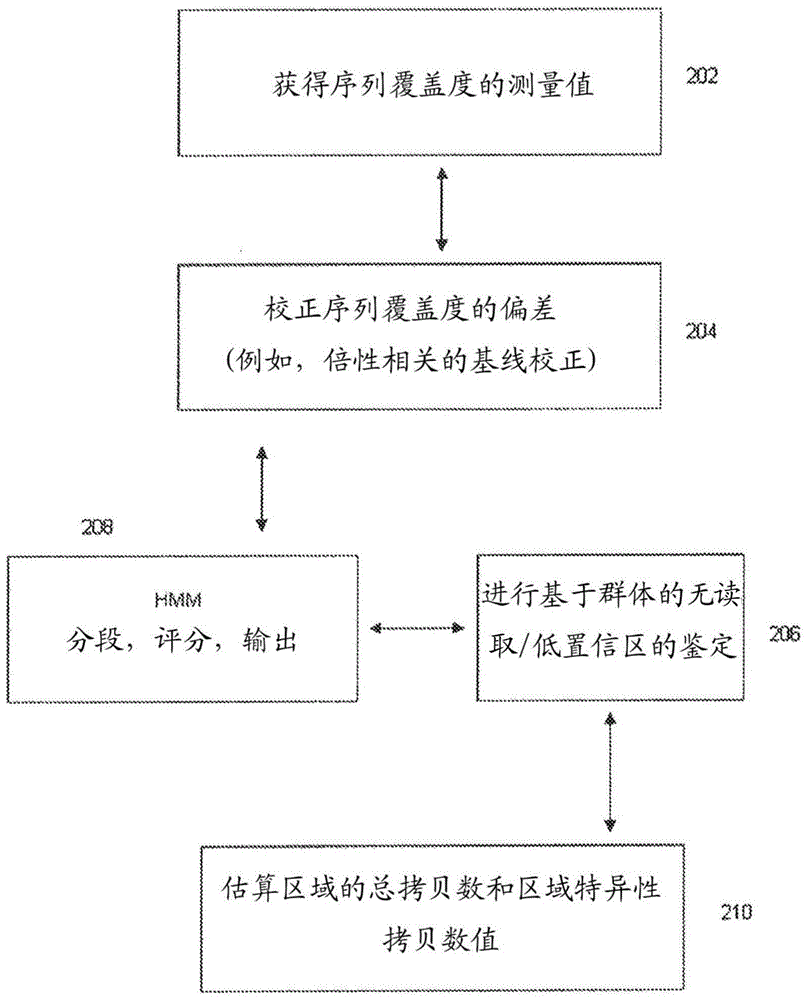
Methods for determining absolute genome-wide copy number variations of complex tumors
Methods for interpreting absolute copy number of complex tumors and for determining the copy number of a genomic region at a detection position of a target sequence in a sample are disclosed. In certain aspects, genomic regions of a target sequence in a sample are sequenced and measurement data for sequence coverage is obtained. Sequence coverage bias is corrected and may be normalized against a baseline sample. Hidden Markov Model (HMM) segmentation, scoring, and output are performed, and in some embodiments population-based no-calling and identification of low-confidence regions may also be performed. A total copy number value and region-specific copy number value for a plurality of regions are then estimated.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Image tessellation for region-specific coefficient access
The present technique addressably handles image data, which is decomposed and tessellated into a plurality of tessellated sub-band blocks. The tessellated sub-band blocks may be addressed by an array of indices, which identify specific data blocks of the image data by decomposition level and spatial coordinates of the tessellated sub-band blocks. Accordingly, a desired region of the image data at multiple resolutions can be identified and individually handled for storage, transmission, retrieval, and display. The desired region also can be reference marked based on the array of indices.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
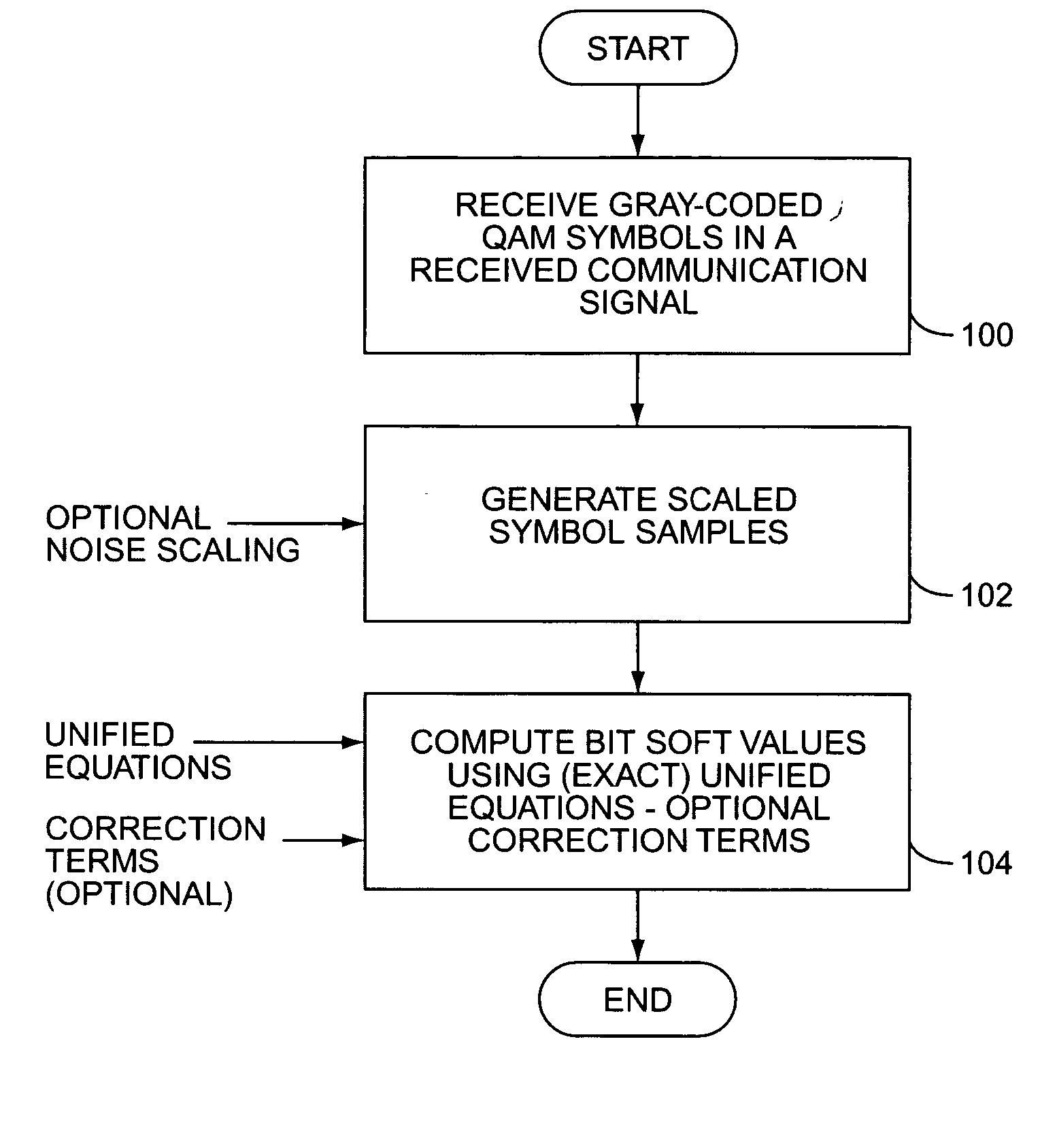
Fast soft value computation methods for gray-mapped QAM
InactiveUS20050141628A1Other decoding techniquesDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionSymbol of a differential operatorGray map
A method and apparatus use unified equations to provide computationally efficient but exact solutions to bit soft value computations for Gray-coded QAM symbols in a received communication symbol as compared to carrying out region-specific equations that are keyed to particular regions of a nominal modulation constellation. Such unified equations further may include one or more correction terms that compensate the bit soft value computations for the effects on symbol samples of more than one “nearest” neighbor in the nominal modulation constellation. While the computations offer particular advantages for receivers making use of the HS-DSCHs used in WCDMA, the method and apparatus can be used in essentially any wireless receiver or system employing Gray-coded QAM.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
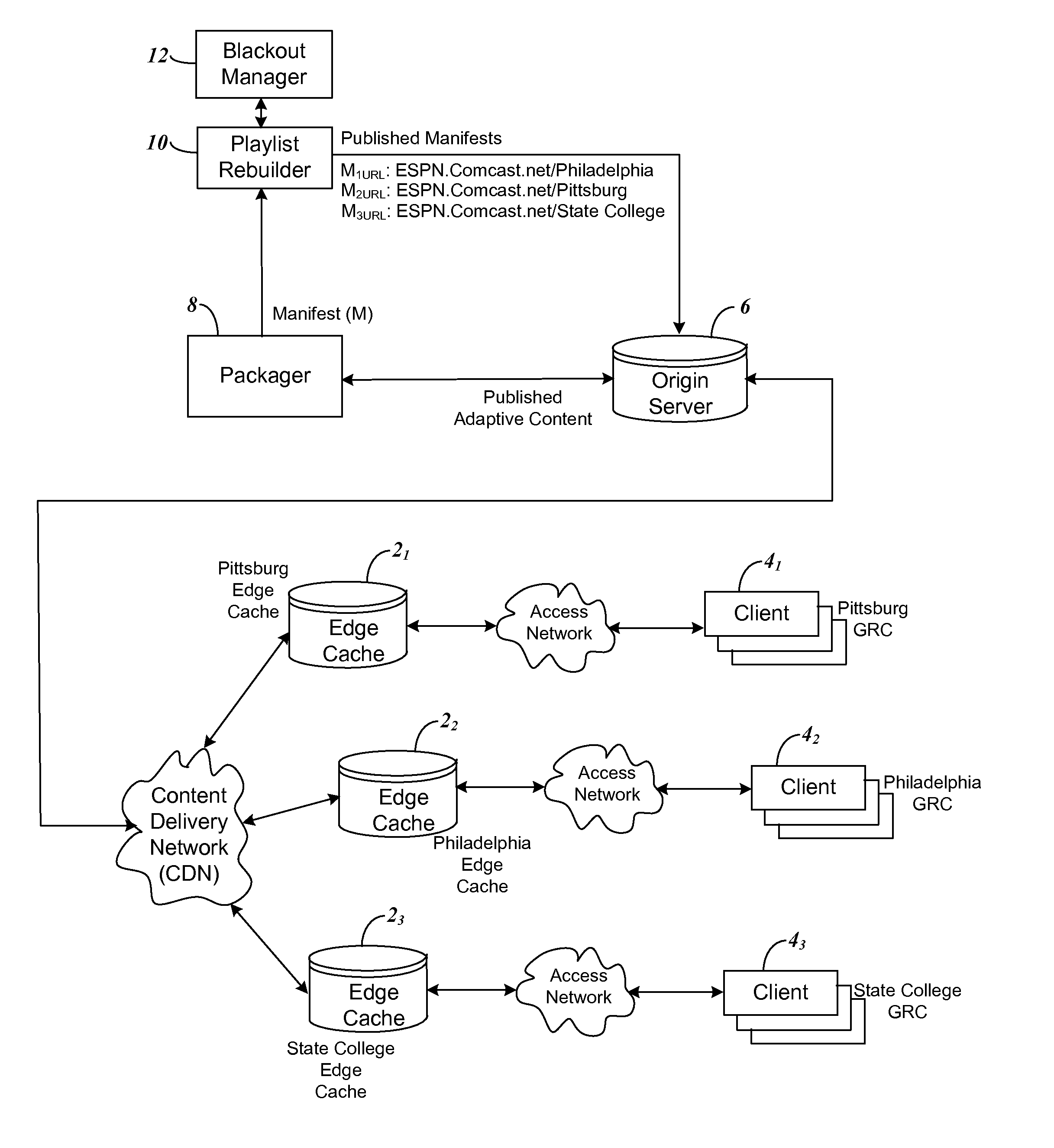
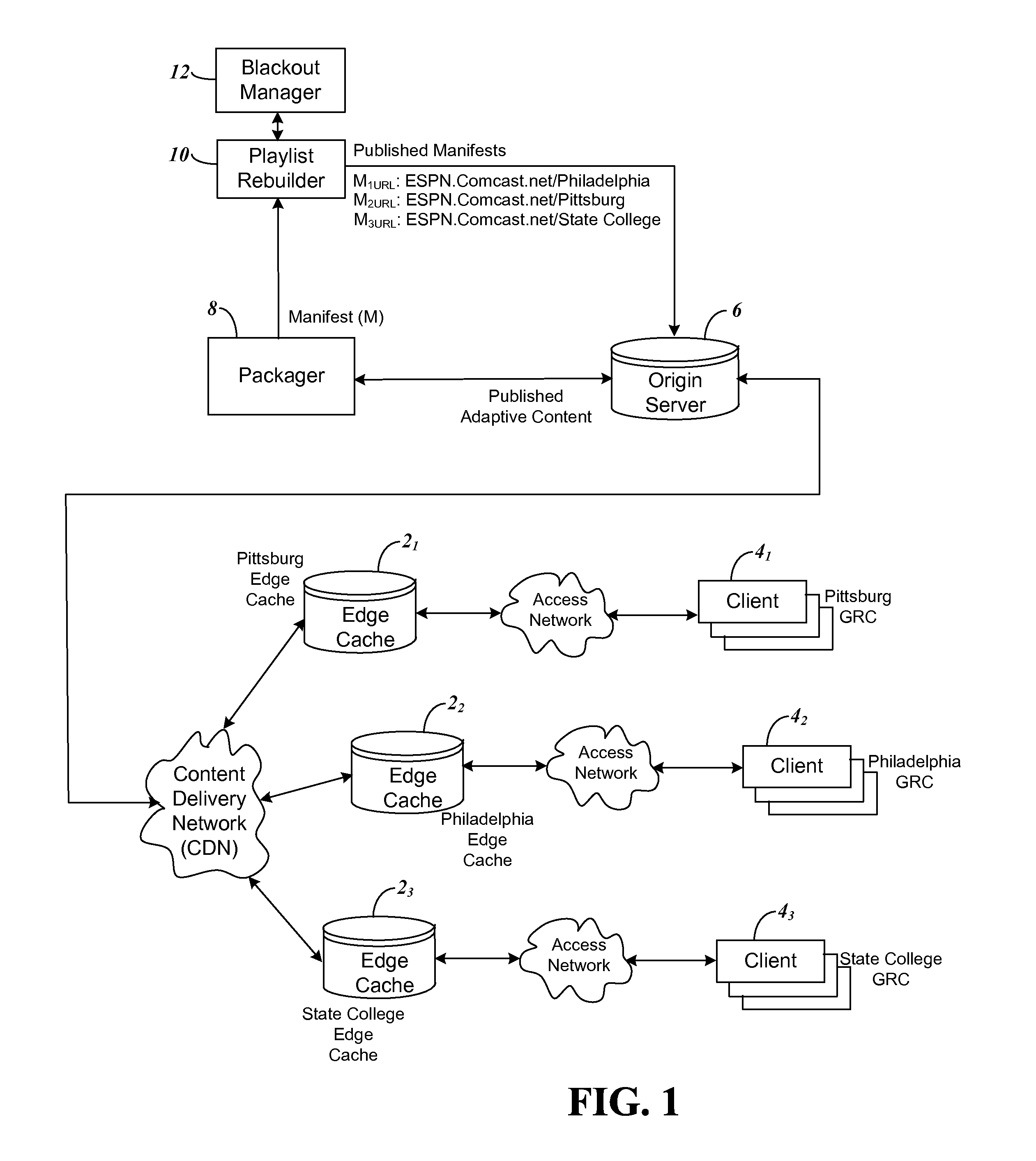
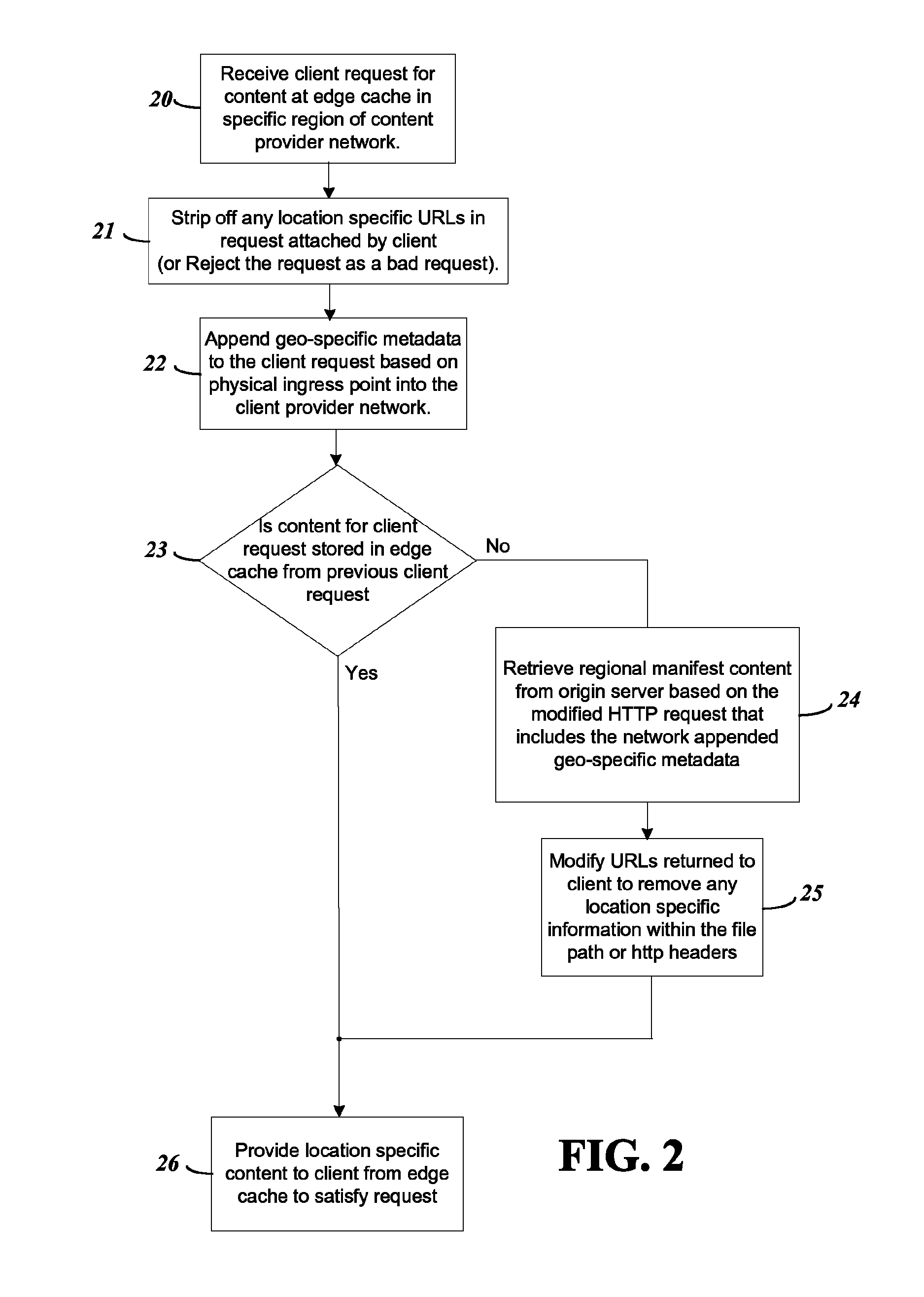
Location specific video content retrieval enabling regional blackouts to be maintained
ActiveUS8561102B1Inhibitory contentAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsManifest fileGeolocation
A video content delivery system is provided for set top boxes (STBs) that may be relocated as well as mobile clients using the Internet to retrieve content manifest files pertaining to the geographic area in which they are located. To provide this system, the edge cache in each geo-location region of a content provider is configured to append location specific metadata to a client's original HTTP request for content, making the request geo-location or region specific. The specific metadata appended by the edge cache in each region prevent clients from bypassing blackout or other content restrictions by moving from a non-restricted area and sending inaccurate location information. In another feature of the system to prevent client bypassing of blackout restrictions, the edge cache when communicating with the STB removes any location specific information which the client provides.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Data Presentation for Navigation System
InactiveUS20080312814A1Reduced space requirementsReduce processing timeInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlResult listRegion specific
Owner:MITAC INT CORP
Certificate assignment strategies for efficient operation of the PKI-based security architecture in a vehicular network
InactiveUS8090949B2Small sizeReduce complexityTemperatue controlUser identity/authority verificationExpiration TimeCommunications system
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
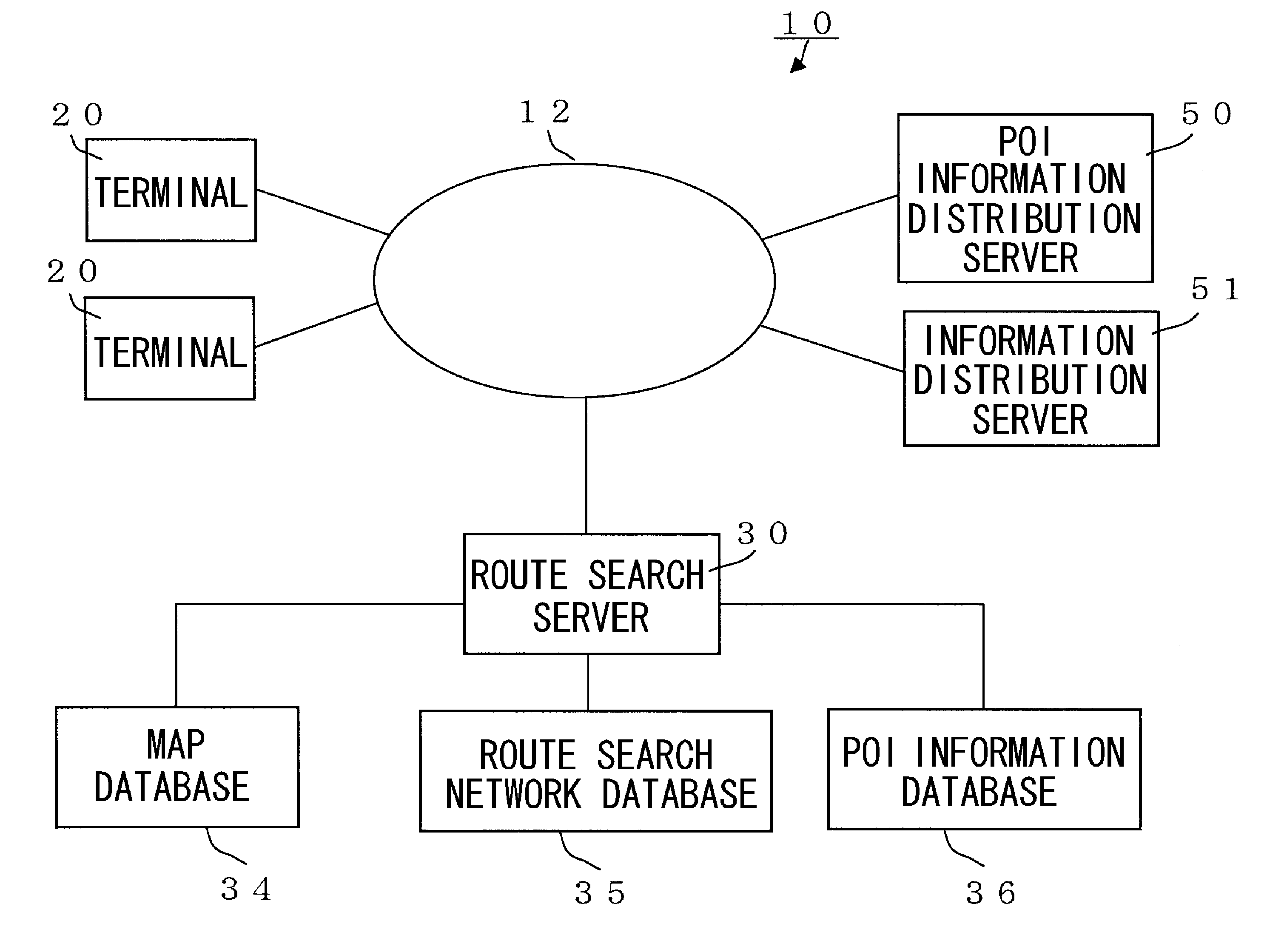
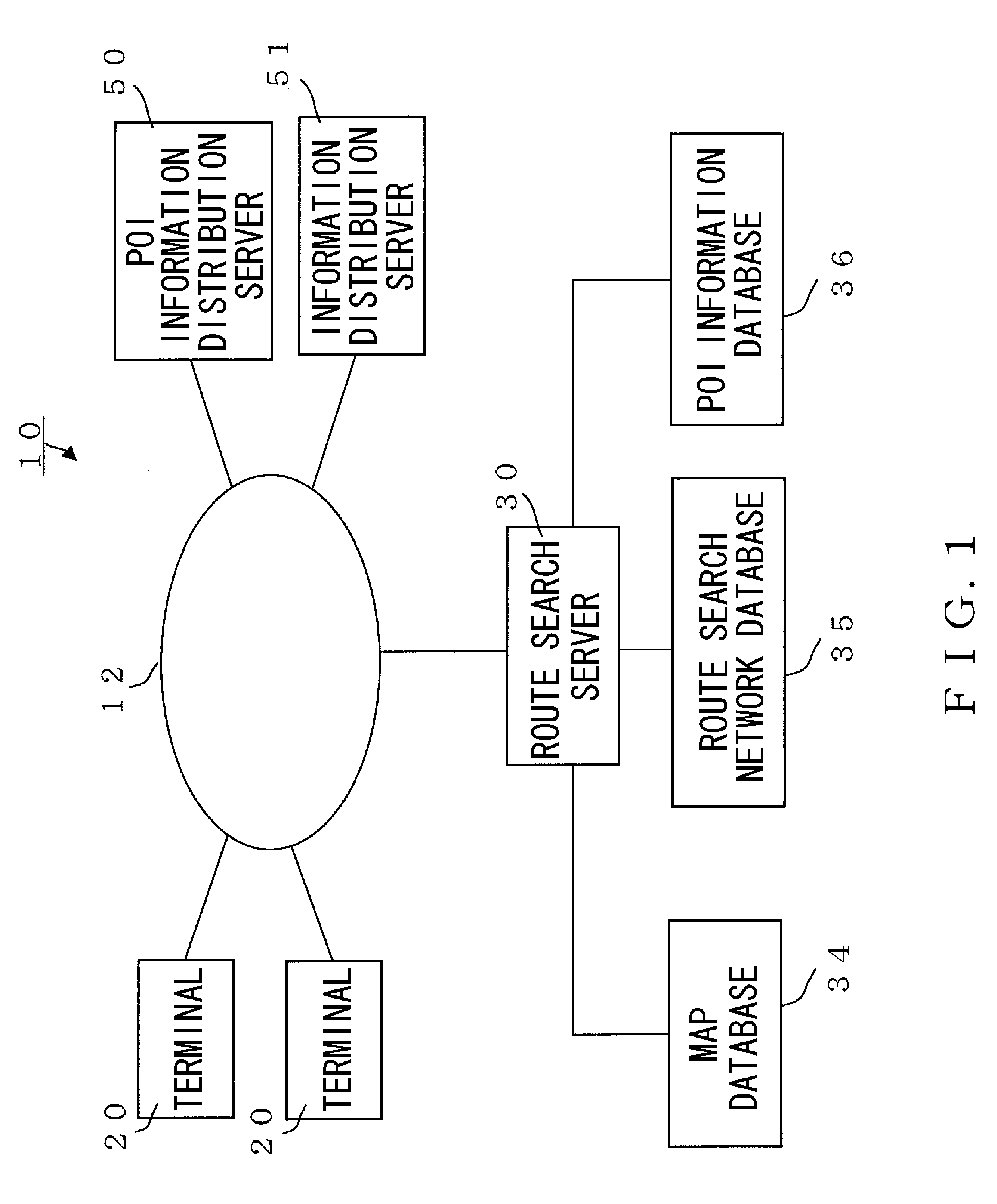
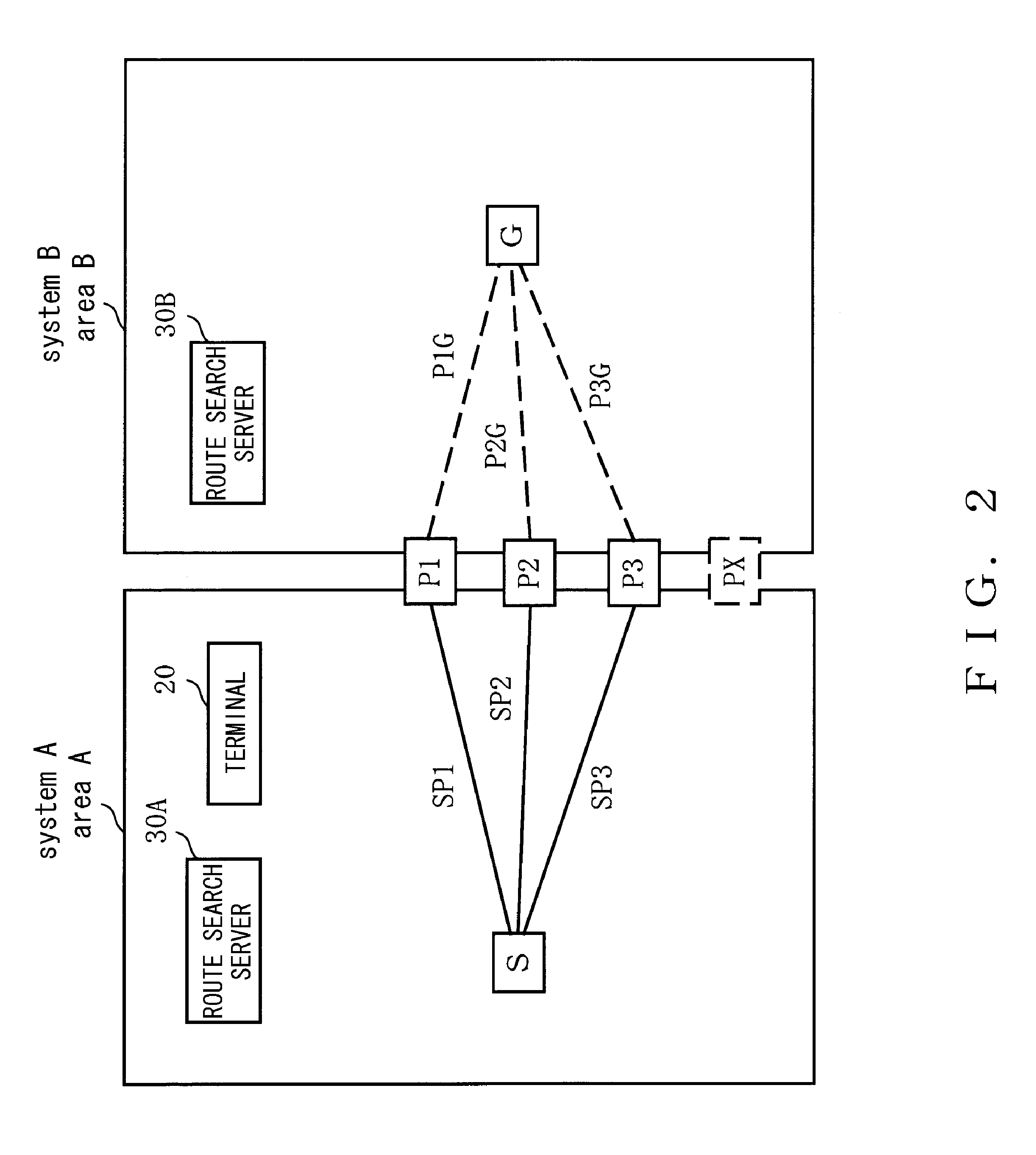
Route guidance system, route search server, route guidance method, and terminal
ActiveUS20110040479A1Smooth transferTime requiredInstruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsGuidance systemRoute search
First and second route guidance systems provided with country or region-specific map data or route search network data are linked. If the departure place and the destination are in different areas, a first route guidance system (A) extracts a candidate connection which is the border between the different areas to transmit it to a second route guidance system (B). The first and second route guidance systems search the optimum route from the departure place to the candidate connection and the optimum candidate route from the candidate connection to the destination, respectively and provide the required time and link data to their respective route guidance systems. The first or second route guidance system determines a recommended route with the smallest total of the required time out of candidate routes connected at the candidate connection and provides the recommended route data including the link data from the first route guidance system (A) to a terminal (20). The terminal (20) requests route guidance to the first or second route guidance system on the basis of the recommended route data depending on the area in which it is located.
Owner:NAVITIME JAPAN CO LTD
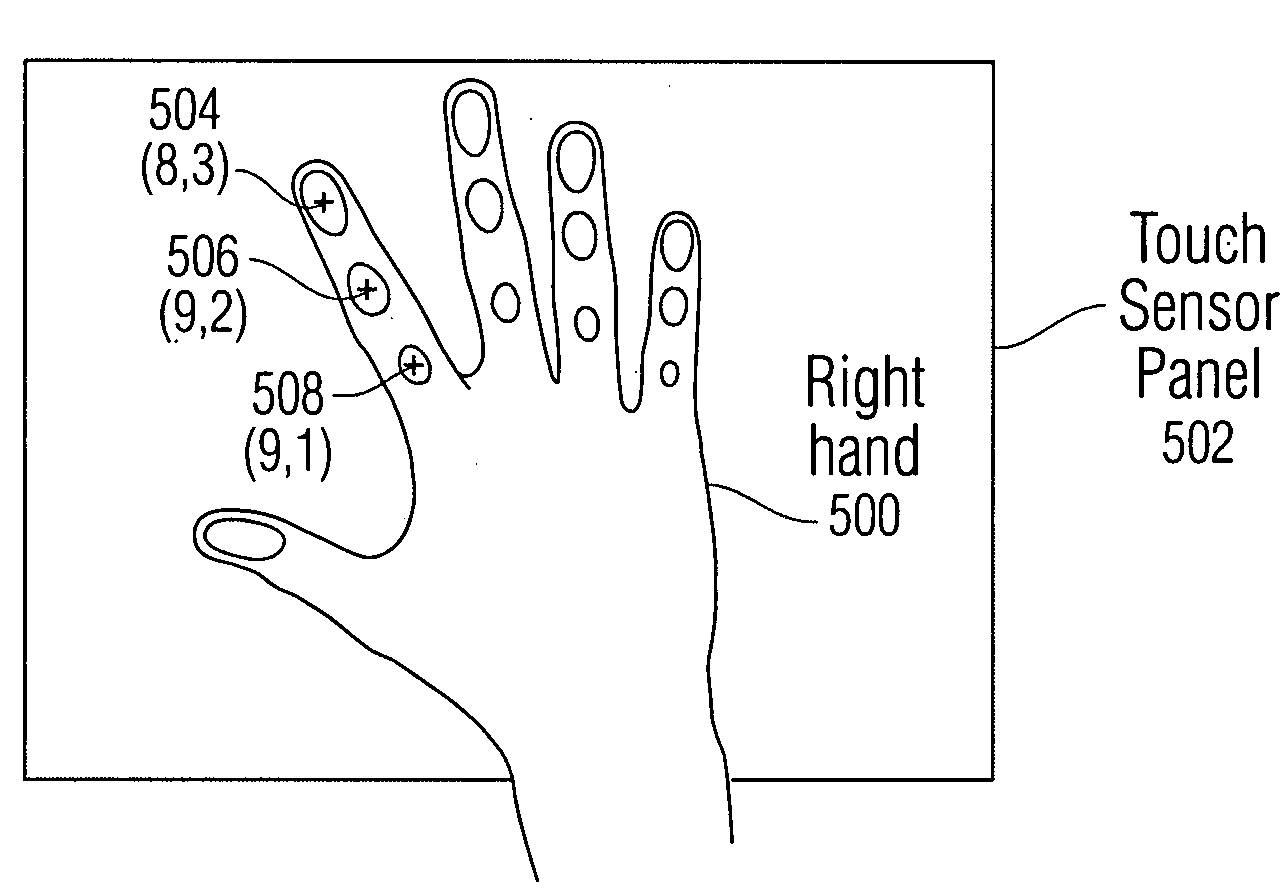
Bottom-up watershed dataflow method and region-specific segmentation based on historic data to identify patches on a touch sensor panel
InactiveUS7916126B2Reduce the numberReduce in quantityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionMerge algorithm
The application of a watershed algorithm to pixels and their touch values obtained from a scan of a touch sensor panel to determine patches corresponding to images of touch is disclosed. Prior to applying the watershed algorithm, background pixels having little or no touch values can be eliminated. A primary merge algorithm can then merge adjacent patches together when the saddle point between them is shallow as compared to the peak represented by the patches. However, if two candidate patches for merging have a total number of pixels below a certain threshold, these two patches may not be merged under the assumption that the patches might have been caused by different fingertips. Conversely, if two candidate patches for merging have a total number of pixels above a certain threshold, these two patches can be merged under the assumption that the patches were caused by a single thumb or palm.
Owner:APPLE INC
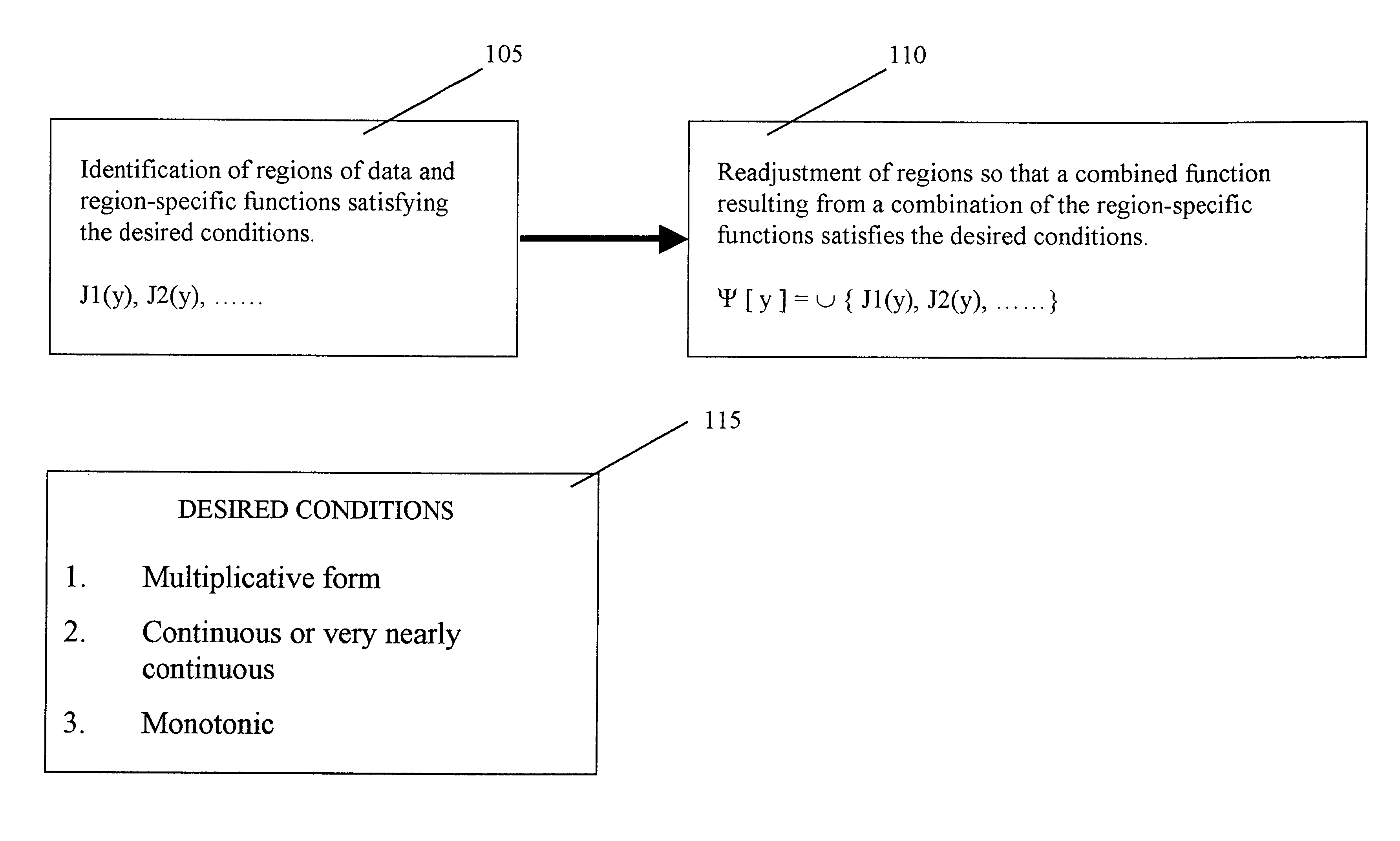
Employing a combined function for exception exploration in multidimensional data
There is provided a method for providing a function for use in detecting a presence of an exception in multidimensional data. The method comprises the steps of (a) partitioning the multidimensional data into at least a first region and a second region; (b) assigning a first region-specific function to the first region and a second region-specific function to the second region; and (c) determining a combined function from the first region-specific function and the second region-specific function. The combined function is used to calculate an expected value of the multidimensional data for distinguishing the presence of an exception.
Owner:IBM CORP
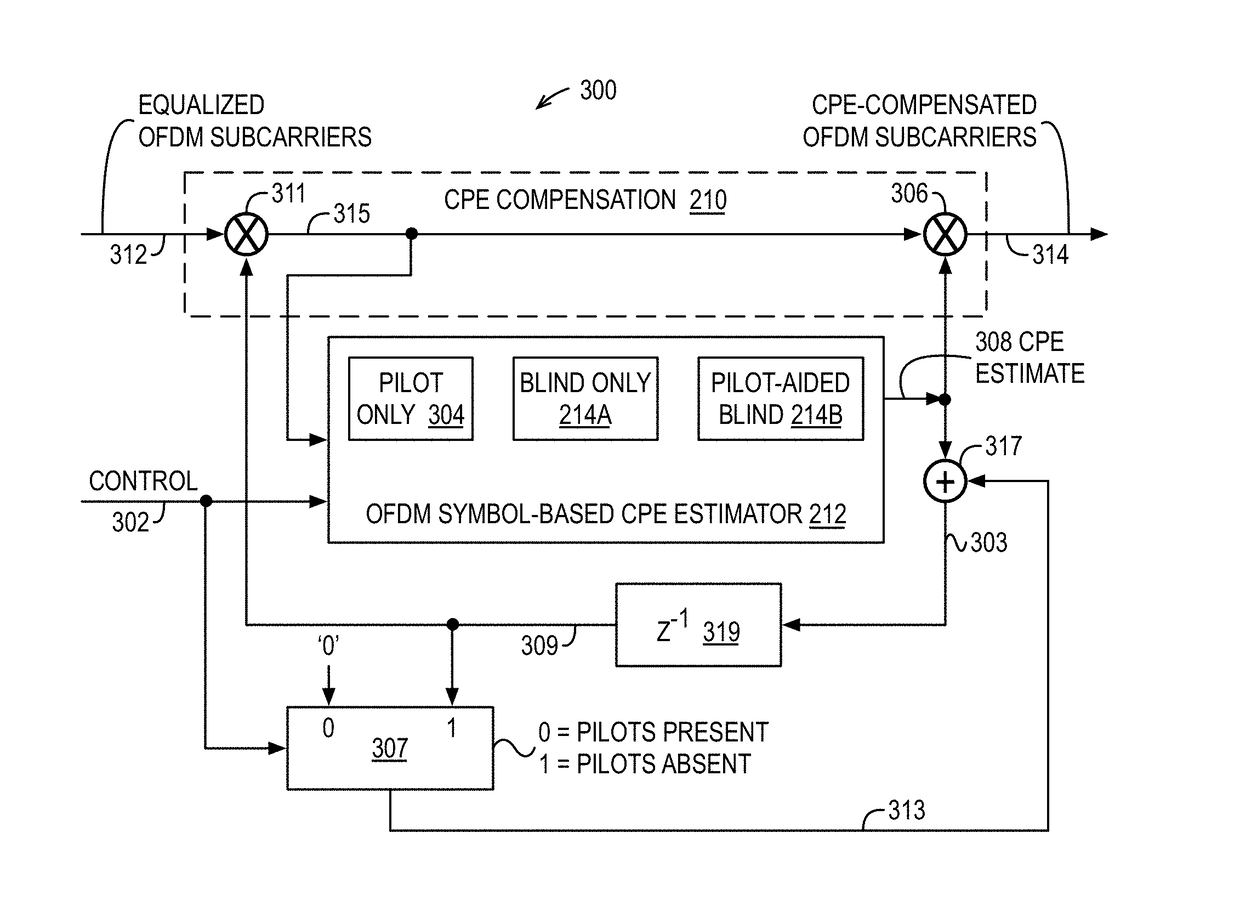
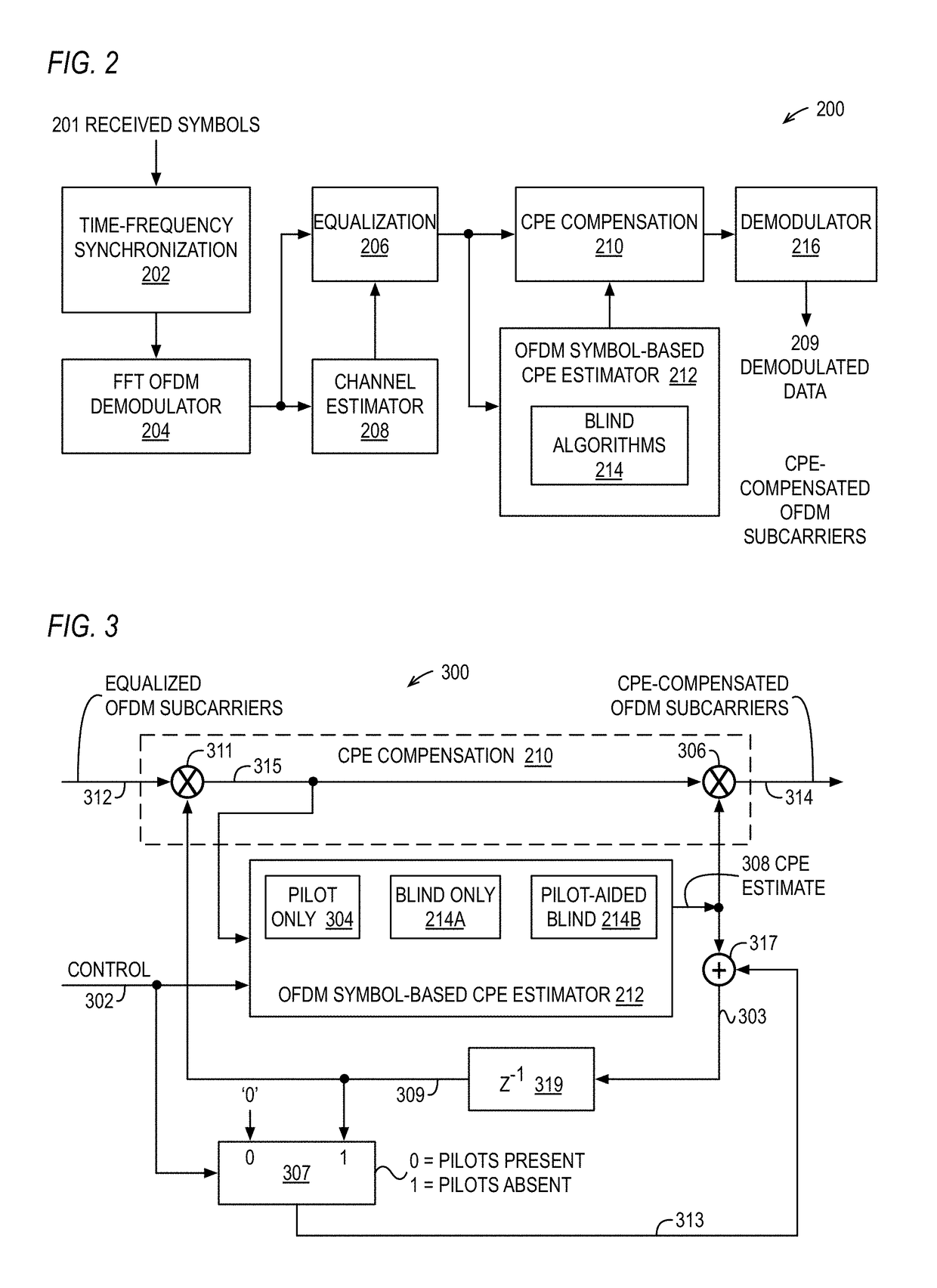
Common phase error (CPE) compensation for frequency division multiplex (FDM) symbols in wireless communication systems
A wireless device receives a frequency division multiplexed (FDM) symbol of constituent equalized FDM data subcarriers. A modulation scheme constellation diagram is subdivided into two or more regions. For each of the regions, a subset of the subcarriers that fall within the region are extracted and a respective region-specific CPE estimate is computed thereon. The respective region-specific CPE estimates are averaged to produce an overall CPE estimate used to compensate the subcarriers. Furthermore, a first CPE estimate is computed using pilot symbols embedded in a first received FDM symbol and is used to compensate the subcarriers. A following second FDM symbol that has no embedded pilot symbols is compensated using the first CPE estimate, and a second CPE estimate is computed using a blind estimation method on the second FDM symbol compensated subcarriers, which are compensated using the second CPE estimate.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
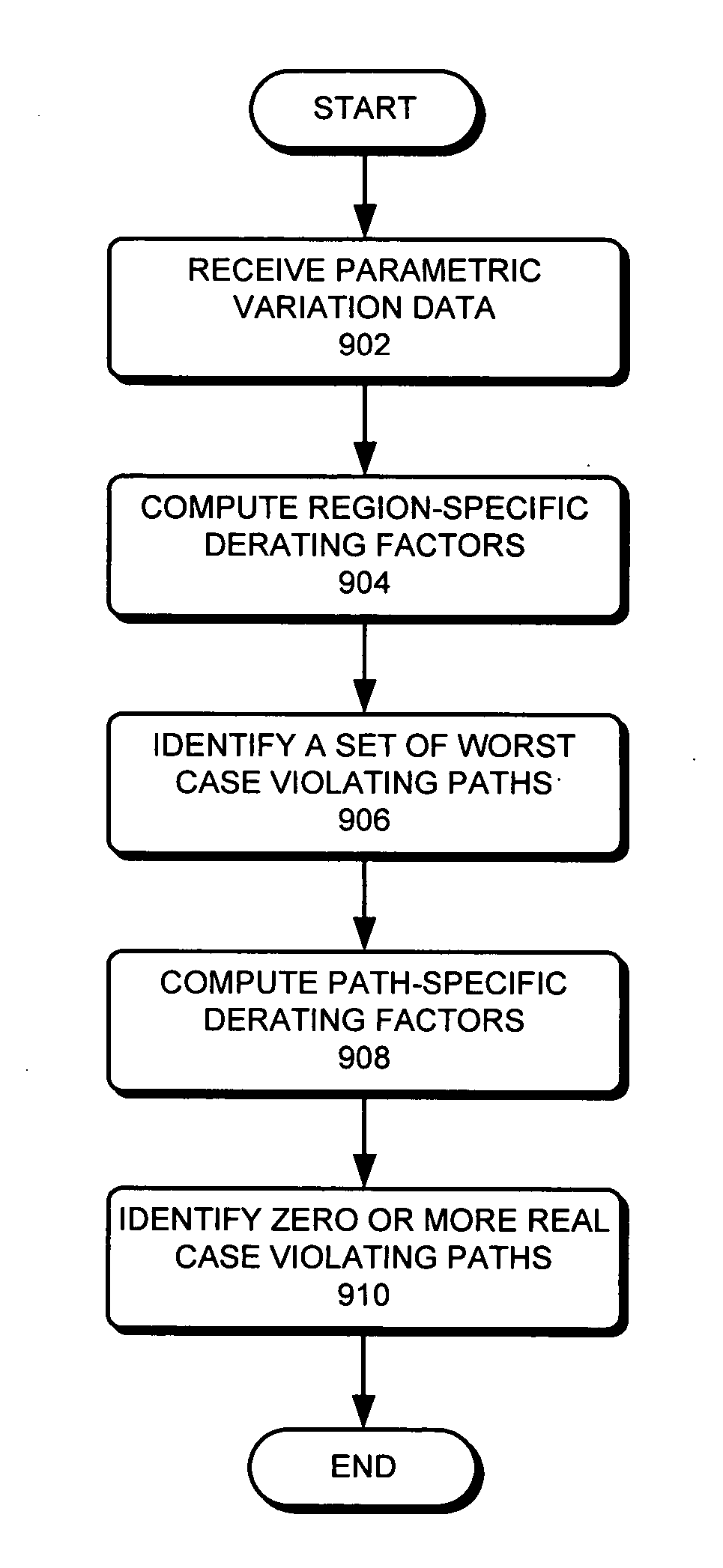
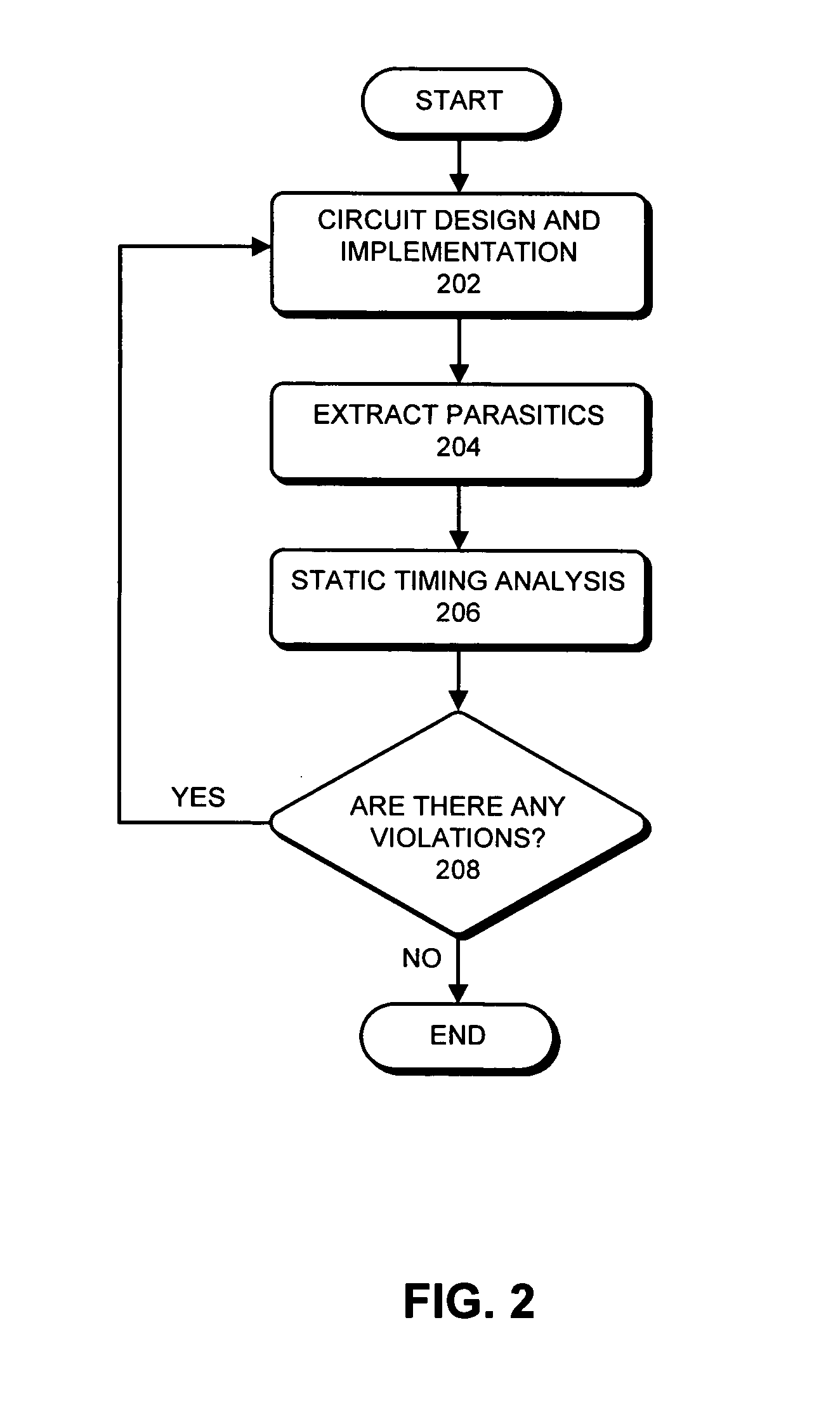
Method and apparatus for reducing timing pessimism during static timing analysis
ActiveUS20060090150A1Reduces timing pessimismSave computation timeComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStatic timing analysisAlgorithm
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that reduces timing pessimism during Static Timing Analysis (STA). During operation, the system receives parametric variation data which describes the on-chip variation of timing-related parameters. Next, the system computes region-specific derating factors using the parametric variation data. The system then identifies a set of worst-case violating paths using the region-specific derating factors. Next, the system computes path-specific derating factors for one or more paths in the set of worst-case violating paths using the parametric variation data and the path properties. Finally, the system identifies zero or more realistic-case violating paths from the set of worst-case violating paths using the path-specific derating factors.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Depth detail level adjustment of multi-dimensional image data with a client/server-based image rendering system
The invention relates to image archive, image retrieval and image coloring system based on client computer or server for storing, calling and graphing visual multi-dimensional digital image data. For example, the doctor can check and diagnose the image data of displayed internal organ, skeleton and muscle organization of awaiting inspection patient. The invention relates to display screen client and the method executed by it for setting detail level of stereo image data displayed by graph and received by data transport network. Constringent stereo data of awaiting displaying object is stored in the database visited directly only by server management with as much as possible slender resolution predetermined by the image system. Stereo data is provided by detail level changing with position especially, being special to region or object with the constringent form, and transported to the display screen client and displayed by the graph on it. Furthermore, image coloring and treatment algorithm after graphing can be executed on the server.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com