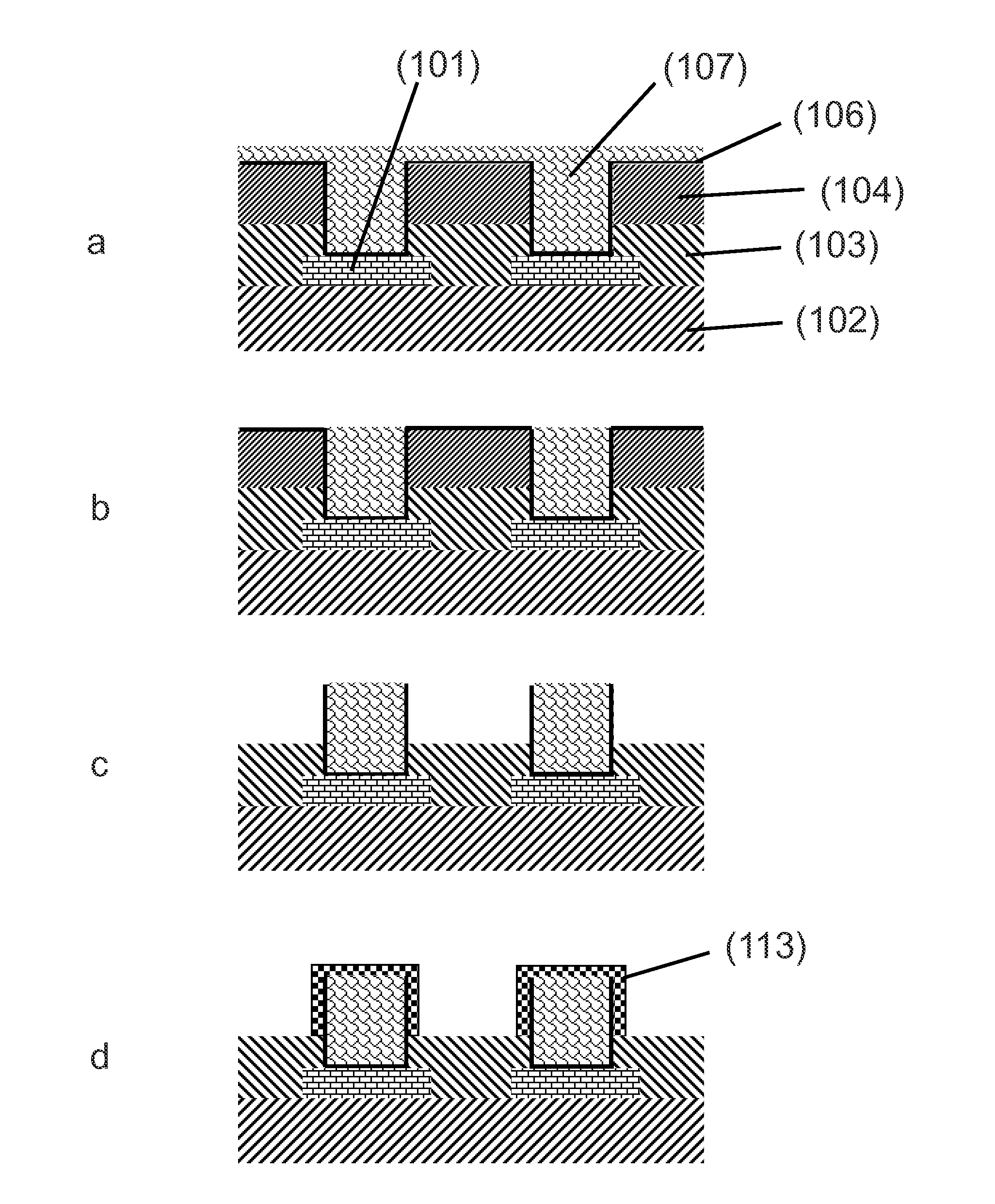
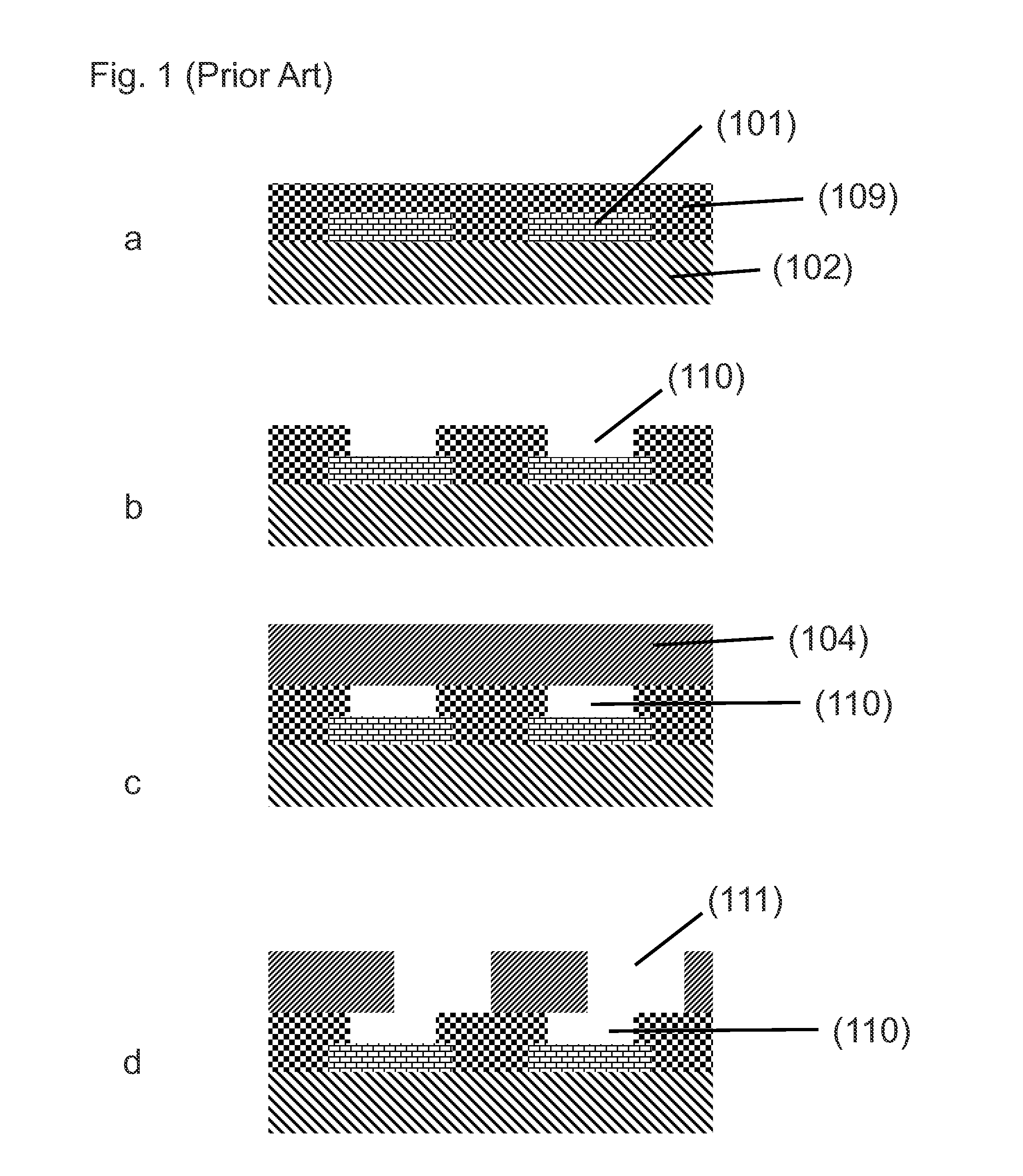
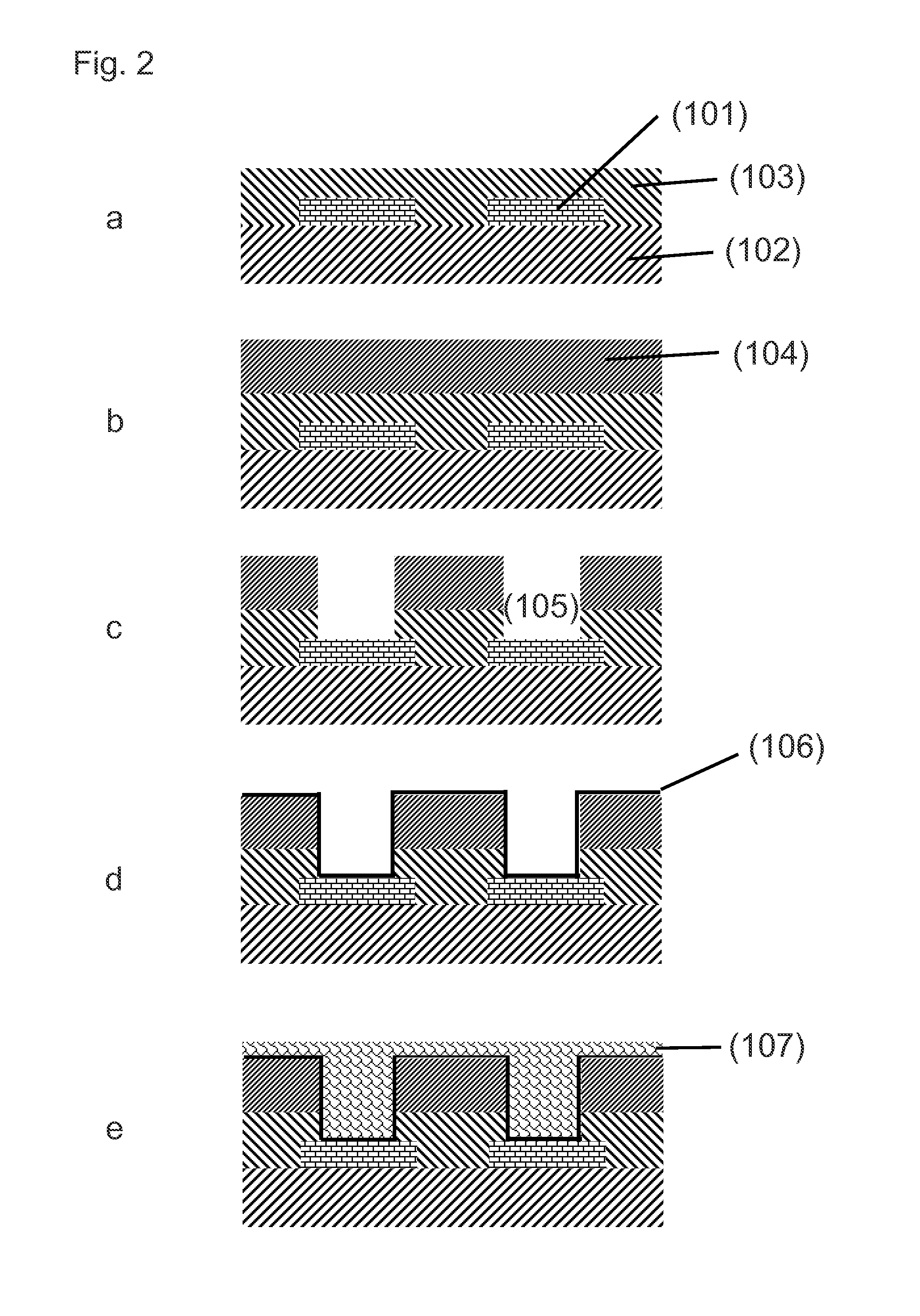
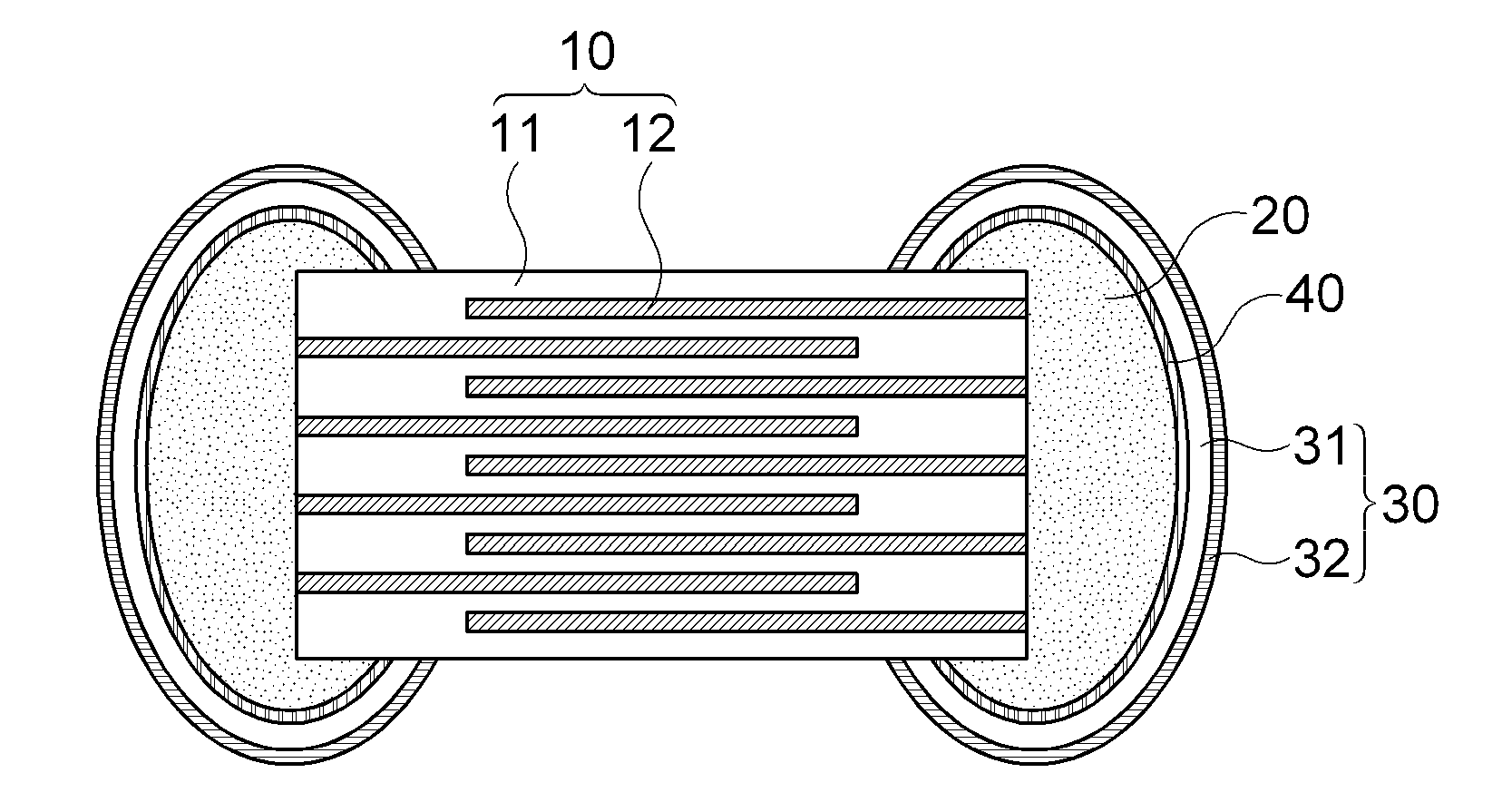
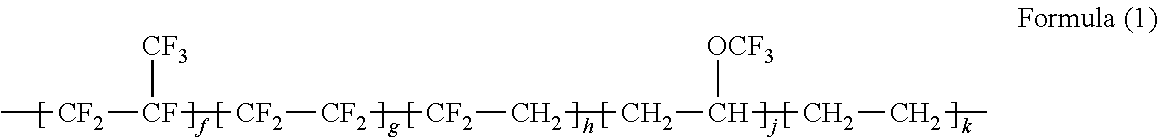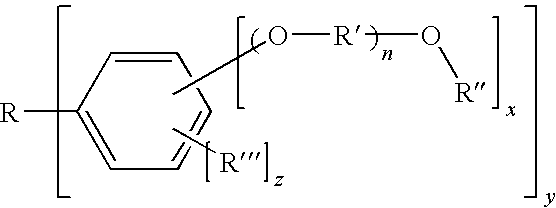Patents
Literature
169results about How to "Uniform layers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
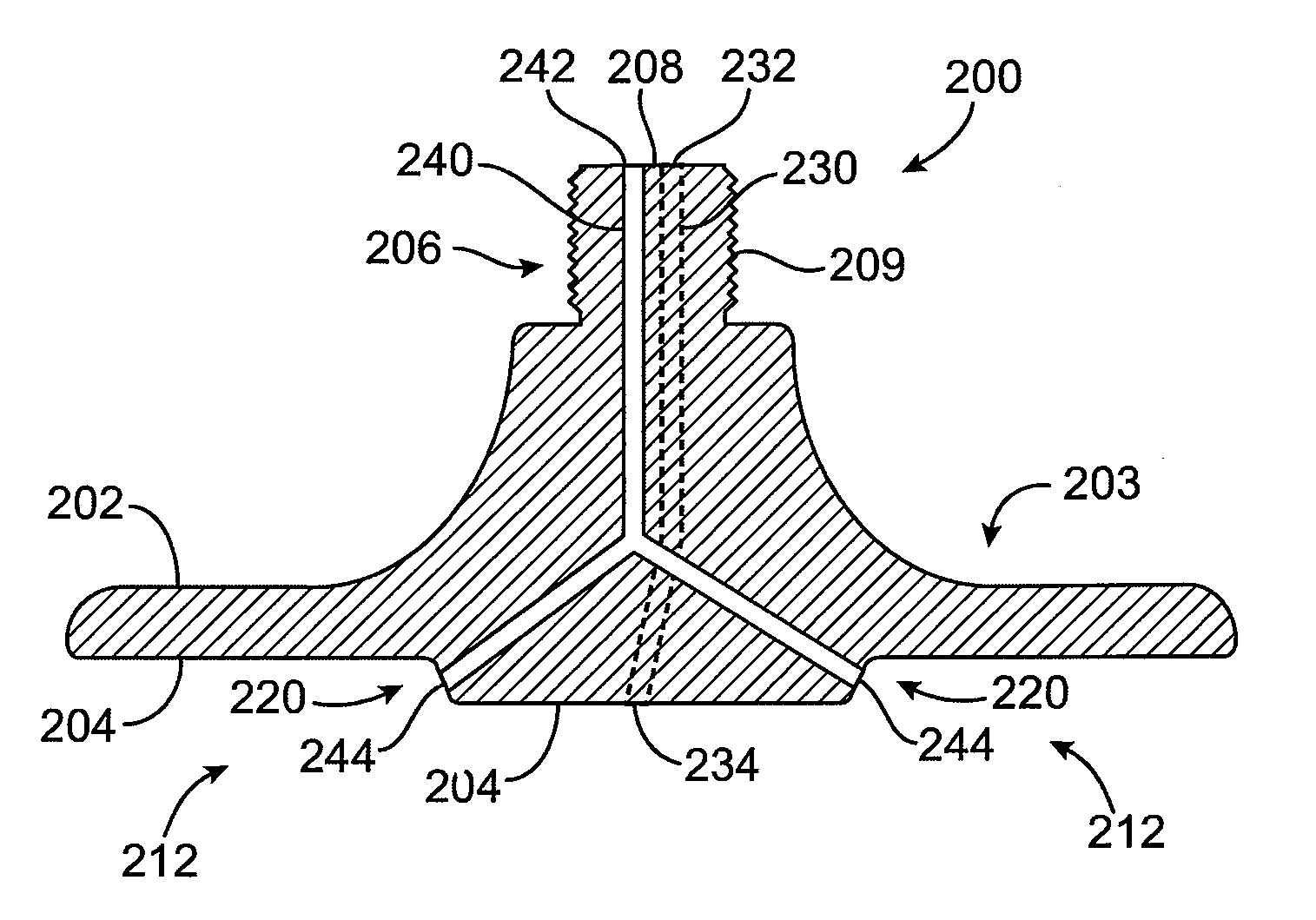
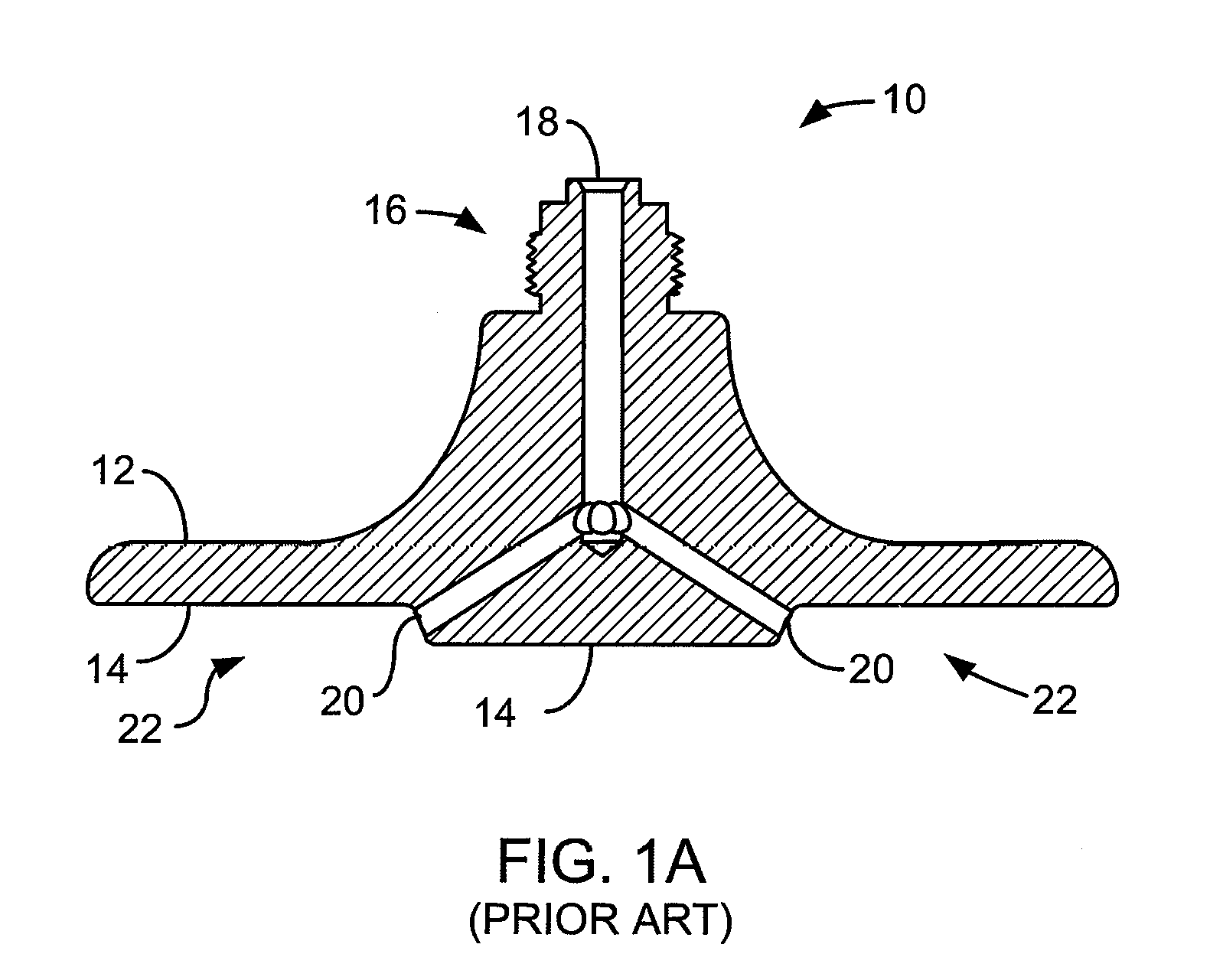
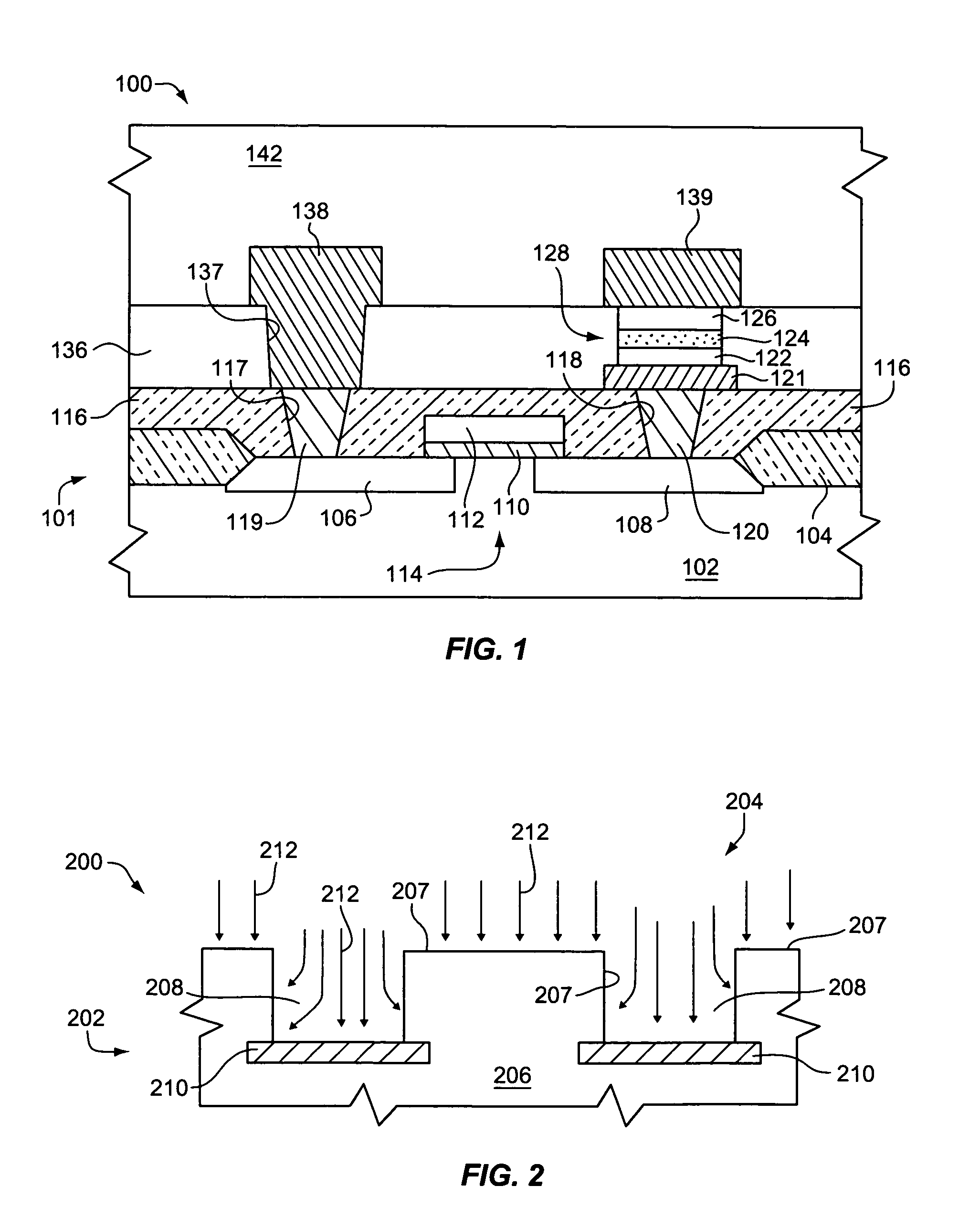
Dual top gas feed through distributor for high density plasma chamber
InactiveUS20080121177A1Improve uniformityUniform layersElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityProduct gas
A gas distributor for use in a semiconductor process chamber comprises a body. The body includes a first channel formed within the body and adapted to pass a first fluid from a first fluid supply line through the first channel to a first opening. A second channel is formed within the body and adapted to pass a second fluid from a second fluid supply line through the second channel to a second opening. The first and second openings are arranged to mix the fluids outside the body after the fluids pass through the openings.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
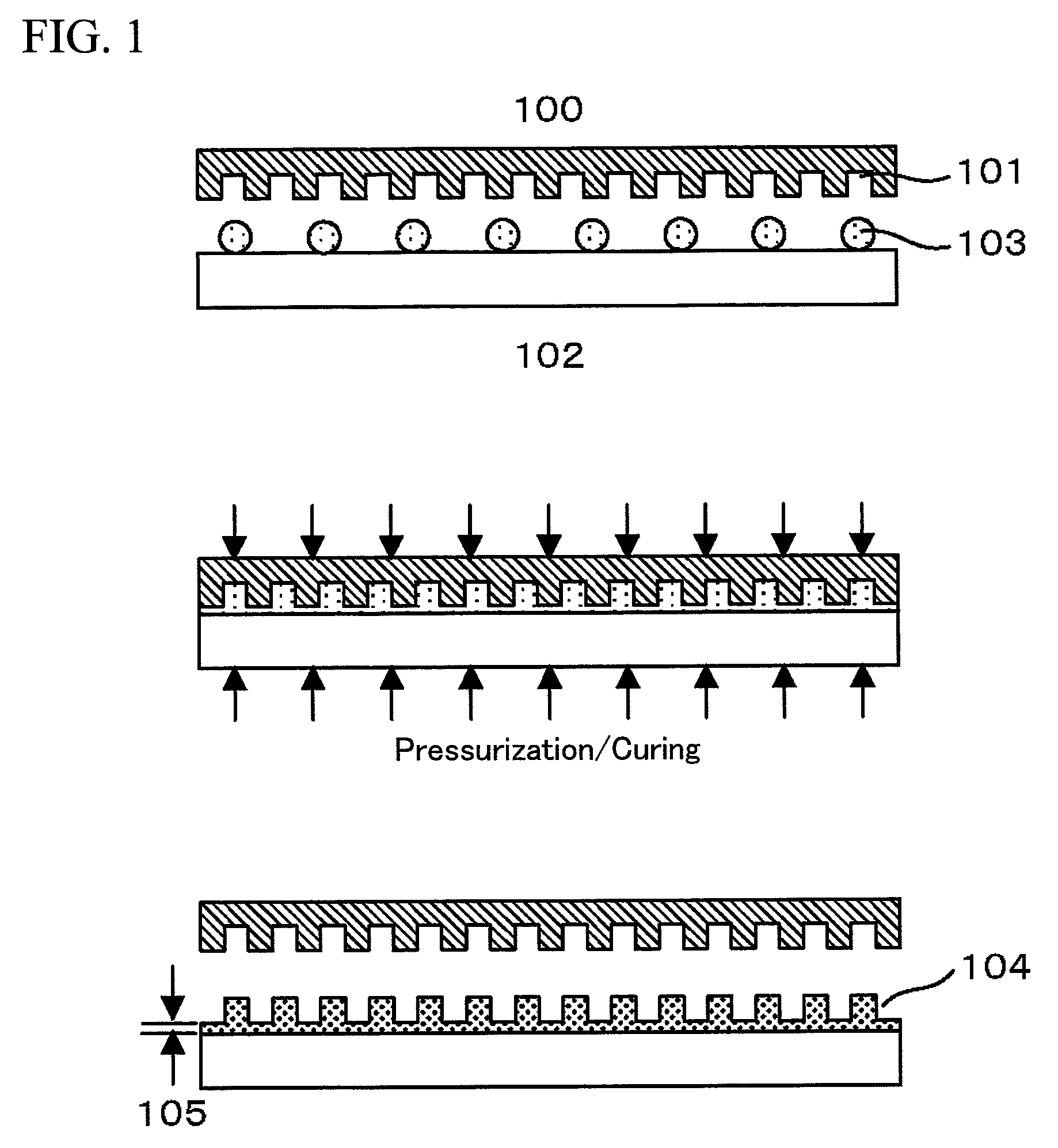
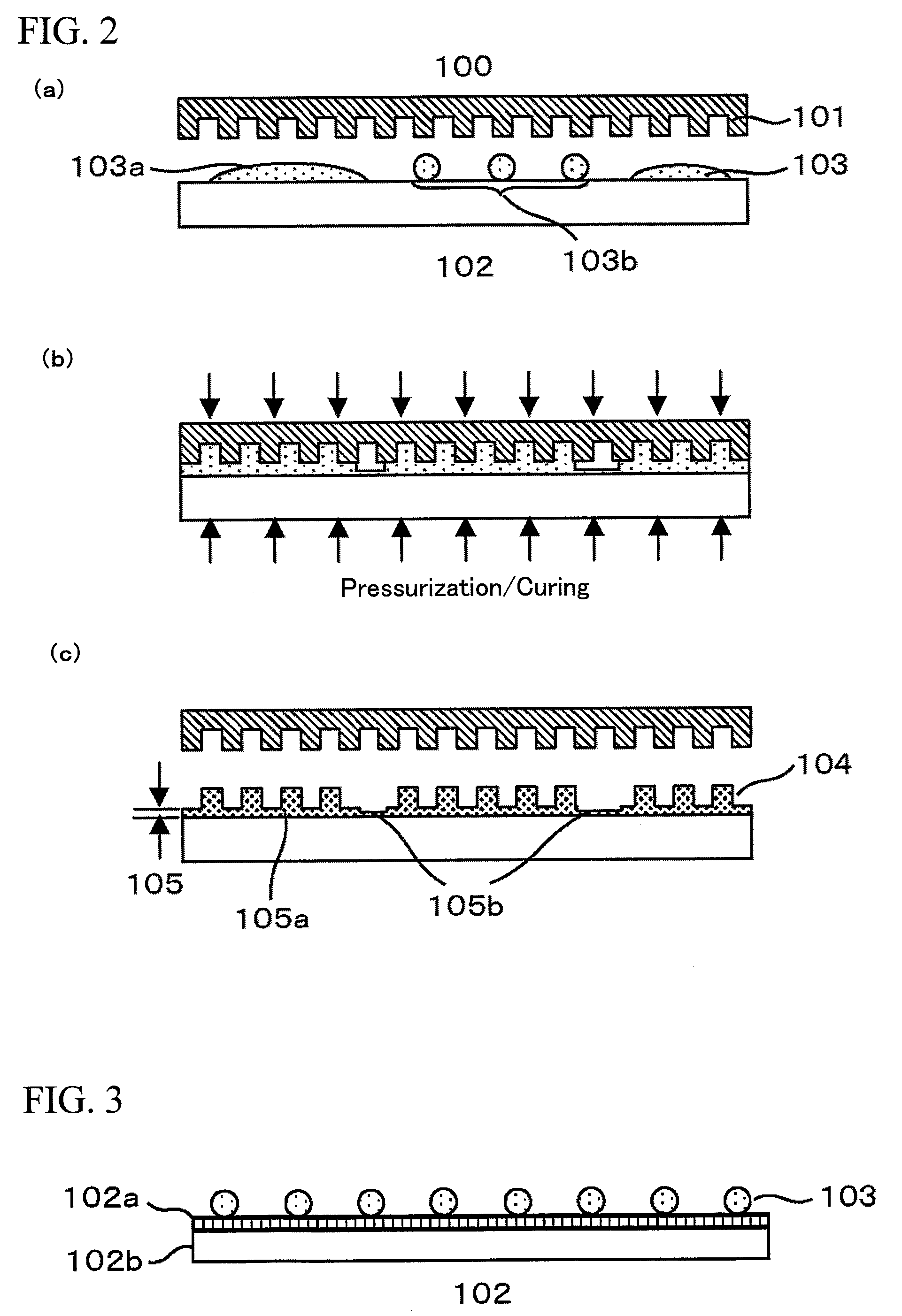
Photo nanoimprint lithography
InactiveUS20090085255A1Improve machining accuracyImprove positioning characteristicNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusResistNanoimprint lithography
The present invention is directed to providing a photo nanoimprint lithography which can form a more uniform base layer. A photo nanoimprint lithography according to the present invention includes the steps of discretely applying a photo-curable resist drop-wise onto a substrate, filling an asperity pattern of a mold with the photo-curable resist by bringing the mold having the asperity pattern formed therein into contact with the photo-curable resist, curing the photo-curable resist by irradiating the resist with a light and releasing from the mold the photo-curable resist which has been photo-cured, wherein an intermediary layer is formed on a surface of the substrate for maintaining a discrete placement of the photo-curable resist that has been instilled drop-wise on the substrate until the mold is brought into contact with the photo-curable resist that has been instilled drop-wise on the substrate.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
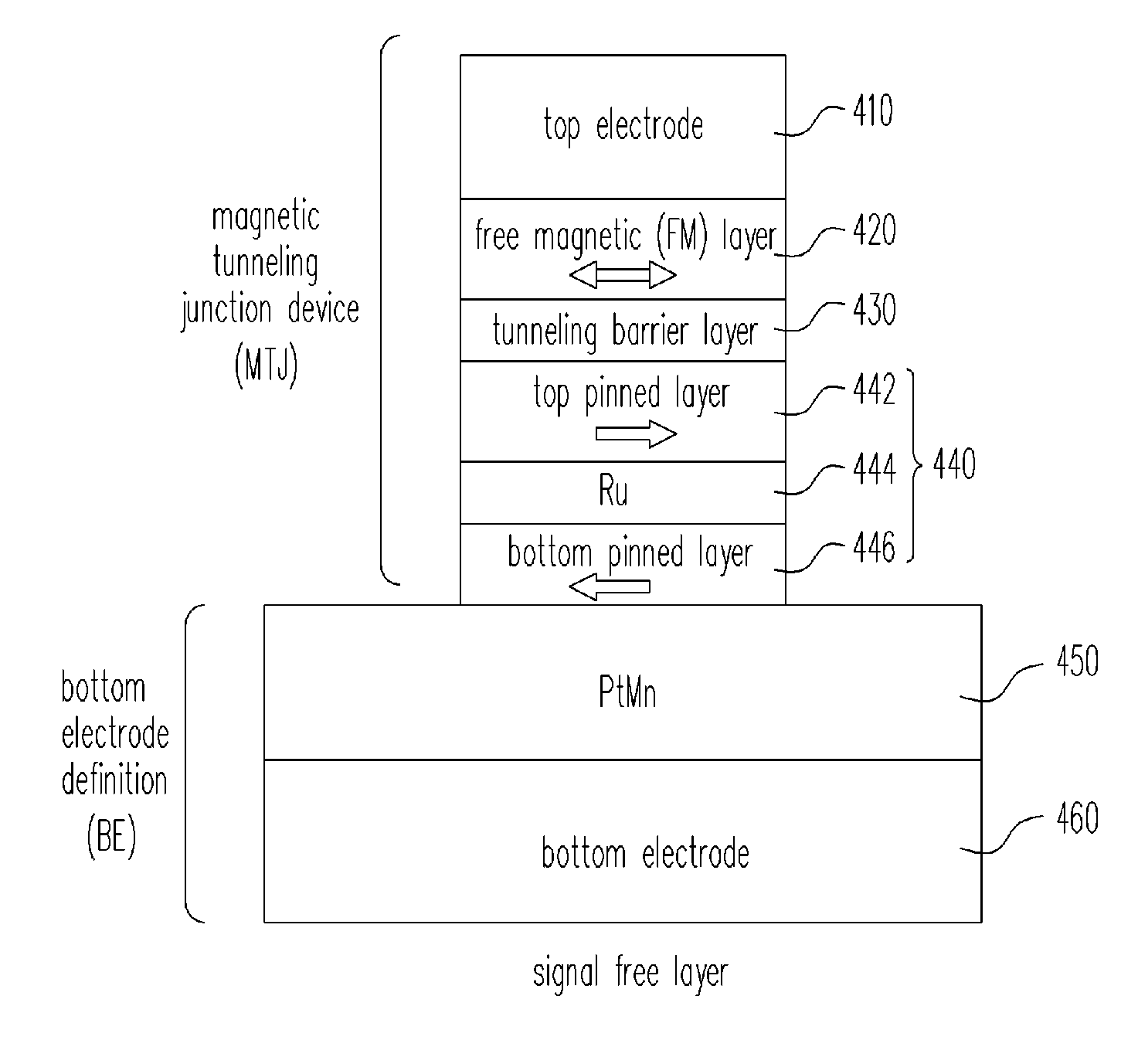
Magnetic memory cell and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20070187785A1Eliminate deviationUniformly manufactureMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesPhysicsBias field
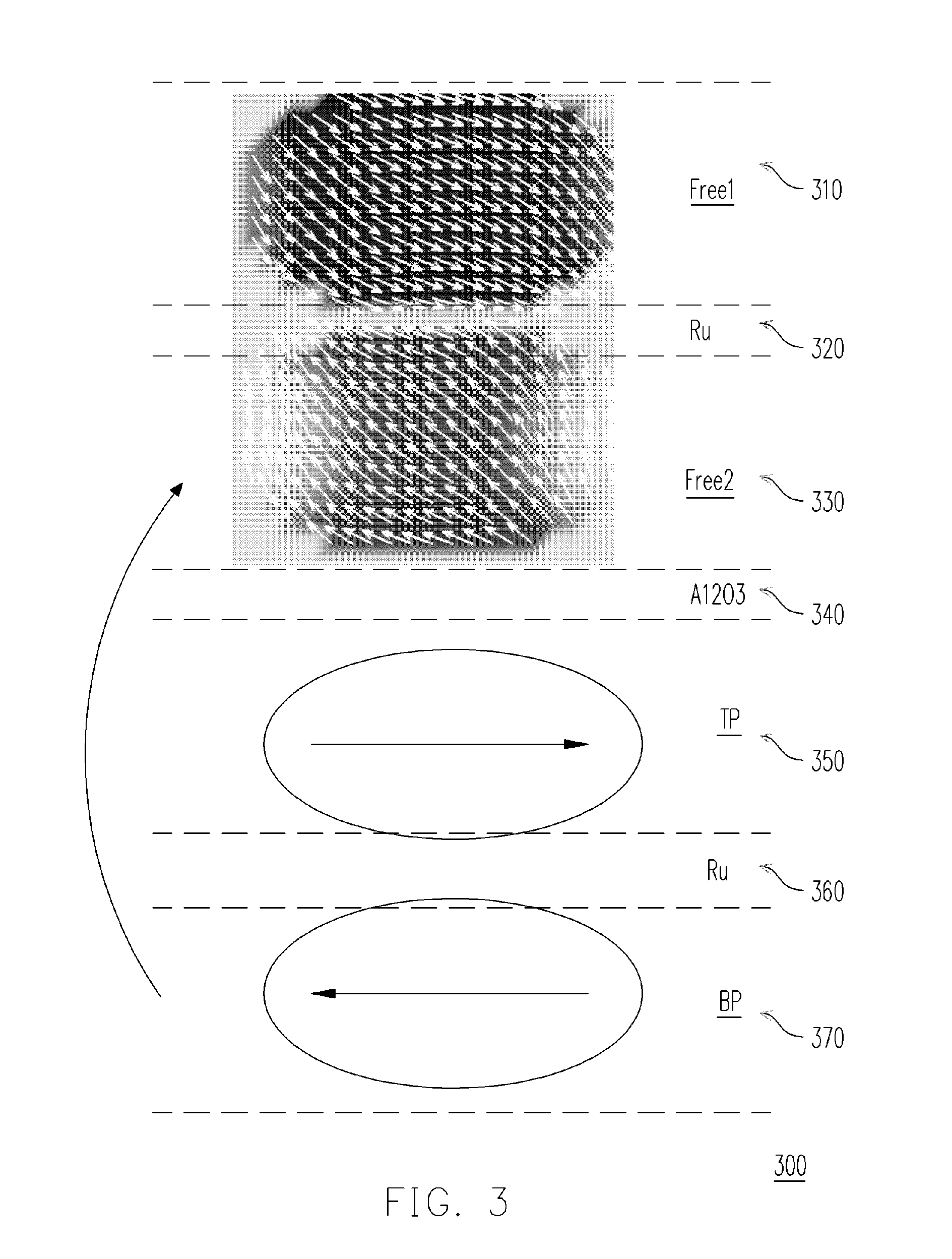
A magnetic memory cell and a manufacturing method for the magnetic memory cell are provided. In the magnetic memory cell, a pinned layer of a magnetic bottom electrode can be formed with sizes different from the free layer. The wider magnetic bottom electrode produces a preferable uniform bias field that will create a normal magnetization vector distribution in the end domain of the free layer, and thus achieving a preferred switching property. The above process can also be achieved through self-alignment. In addition, by adjusting the bias field of the bottom electrode, uniform field distribution over entire free layer can be significantly improved, and thus the magnetic memory cell will have a very low writing toggle current.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Group-iii nitride compound semiconductor device and production method thereof, group-iii nitride compound semiconductor light-emitting device and production method thereof, and lamp
InactiveUS20090194784A1Improve in-plane uniformityLower Level RequirementsSolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingRocking curveInter layer
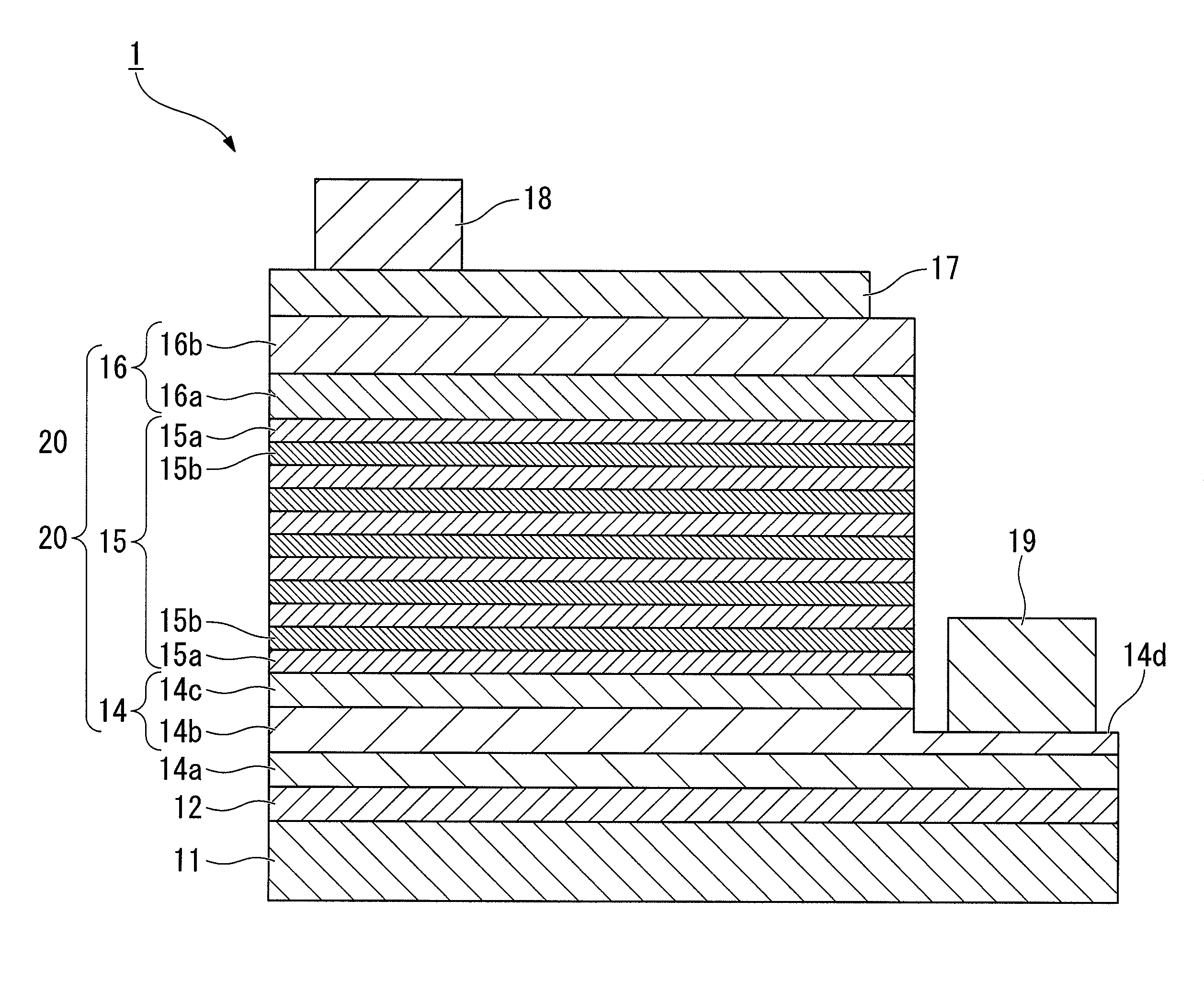
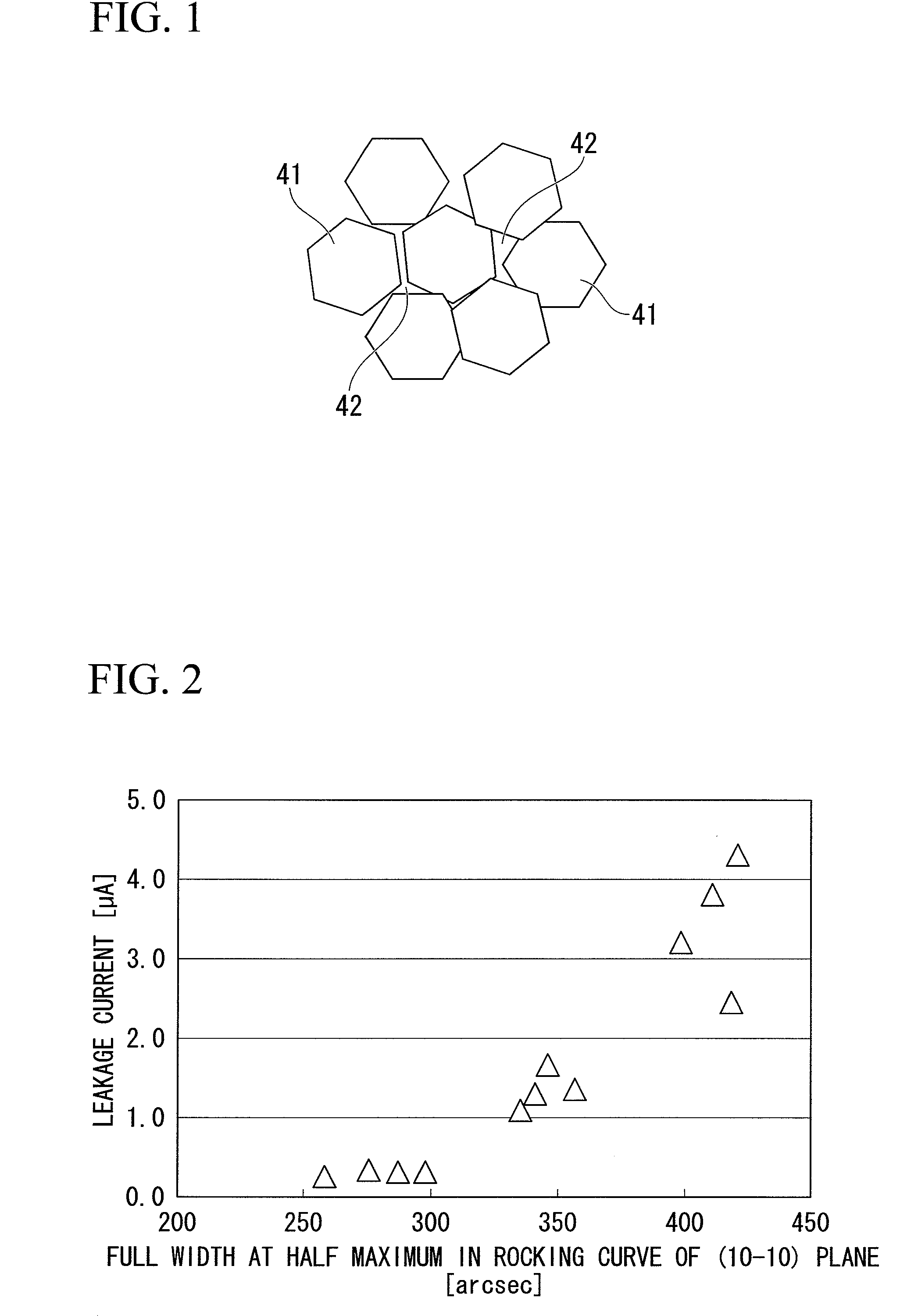
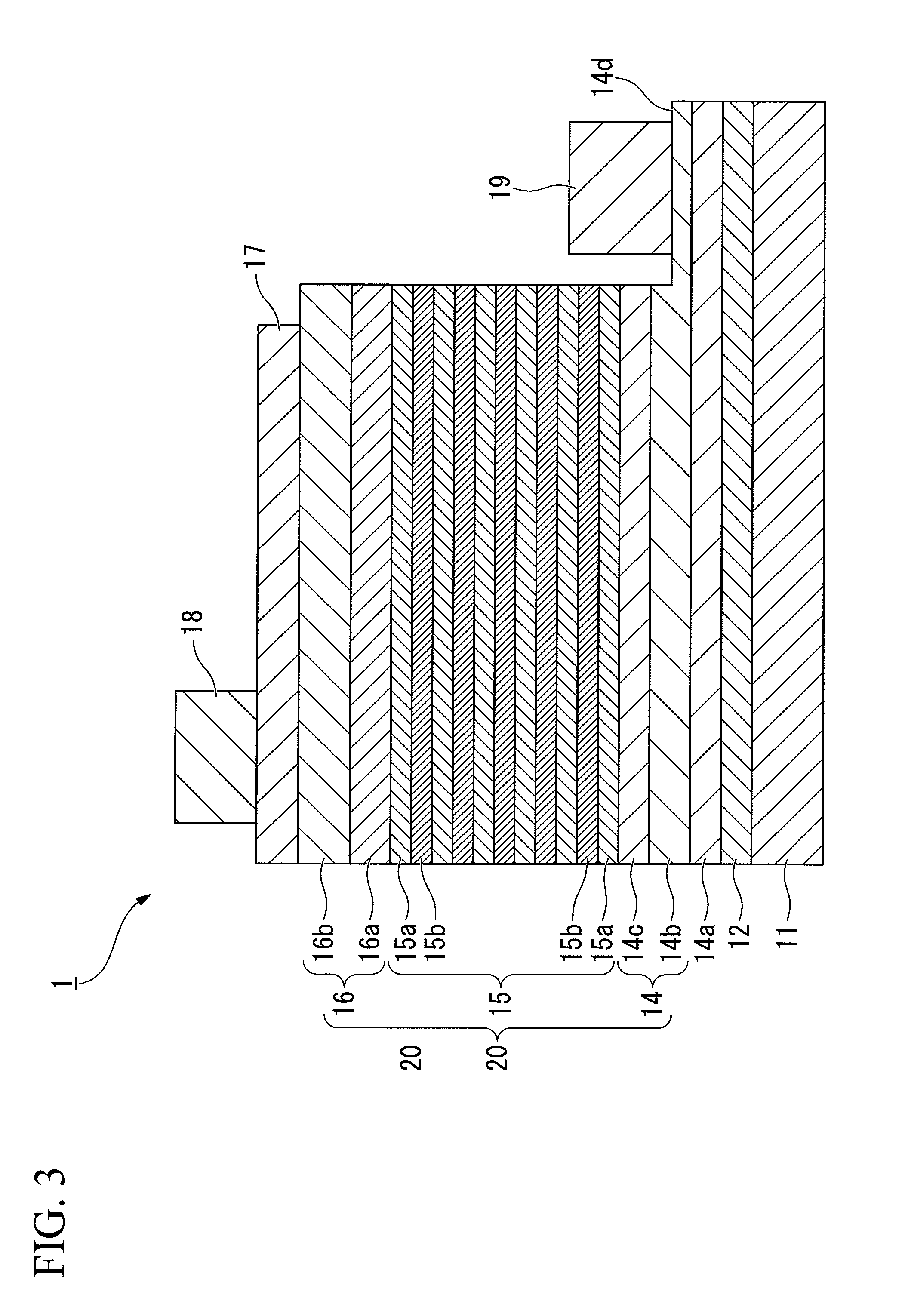
A group-III nitride compound semiconductor device of the present invention comprises a substrate, an intermediate layer provided on the substrate, and a base layer provided on the intermediate layer in which a full width at half maximum in rocking curve of a (0002) plane is 100 arcsec or lower and a full width at half maximum in rocking curve of a (10-10) plane is 300 arcsec or lower. Also, a production method of a group-III nitride compound semiconductor device of the present invention comprises forming the intermediate layer by using a sputtering method.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
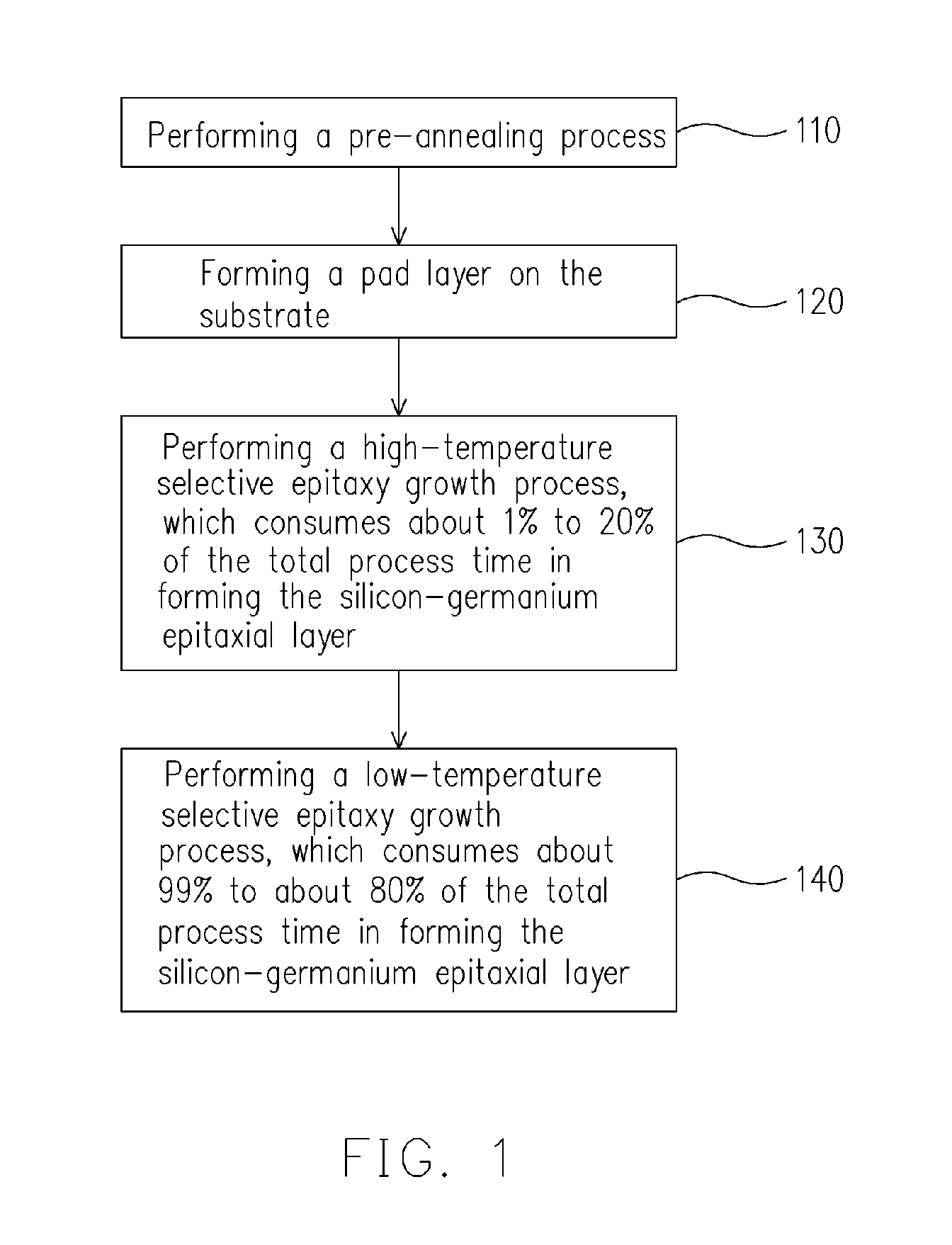
Method for forming silicon-germanium epitaxial layer
InactiveUS20080076236A1Uniform layersImprove throughputSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesComputer scienceProcess time
A method for forming a SiGe epitaxial layer is described. A first SEG process is performed under a first condition, consuming about 1% to 20% of the total process time for forming the SiGe epitaxial layer. Then, a second SEG process is performed under a second condition, consuming about 99% to 80% of the total process time. The first condition and the second condition include different temperatures or pressures. The first and the second SEG processes each uses a reactant gas that includes at least a Si-containing gas and a Ge-containing gas.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
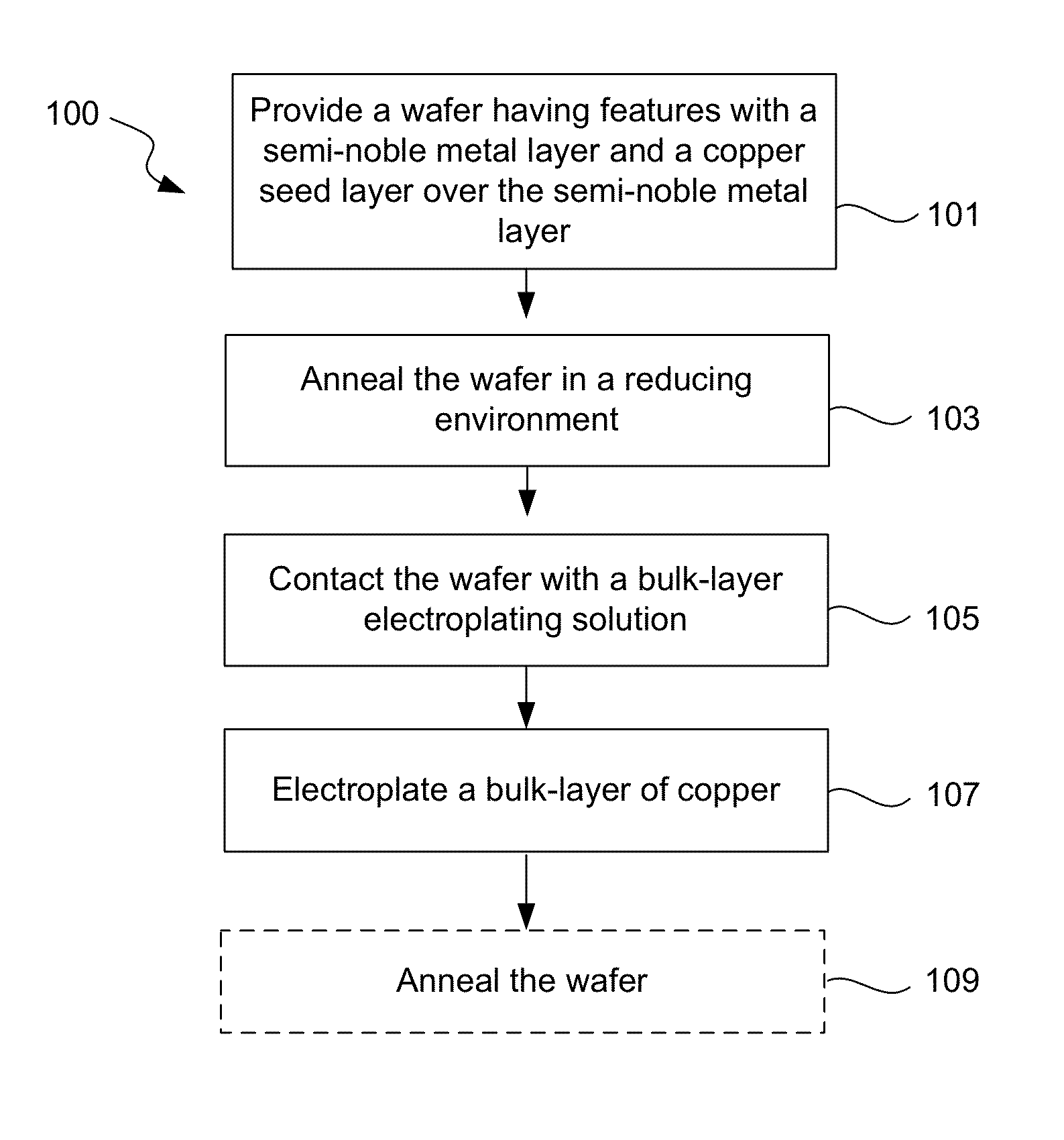
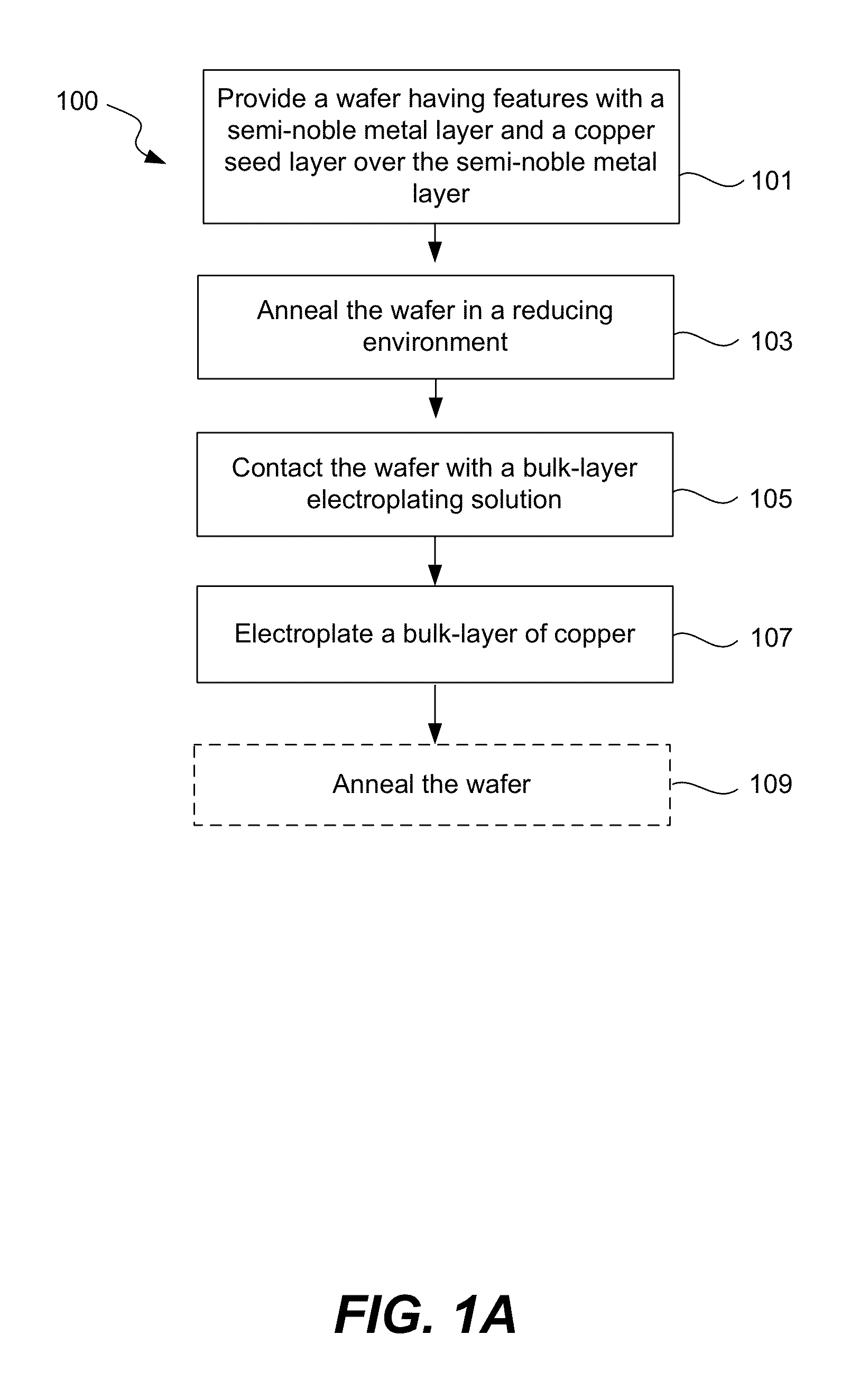
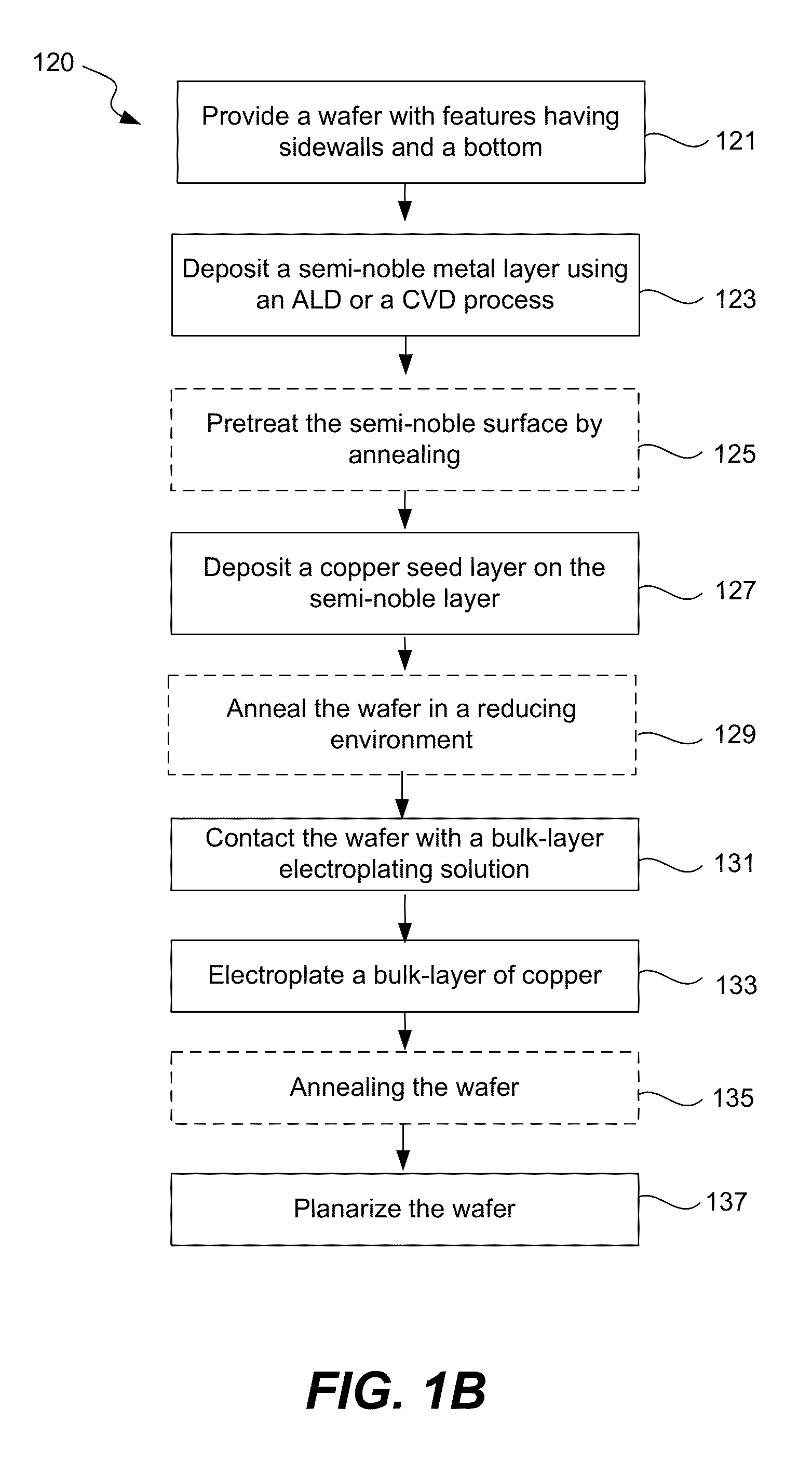
Copper electroplating process for uniform across wafer deposition and void free filling on semi-noble metal coated wafers
InactiveUS8513124B1Expand coverageImprove nucleationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorElectroplating
Disclosed are methods of depositing a copper seed layer to be used for subsequent electroplating a bulk-layer of copper thereon. A copper seed layer may be deposited with different processes, including CVD, PVD, and electroplating. With electroplating methods for depositing a copper seed layer, disclosed are methods for depositing a copper alloy seed layer, methods for depositing a copper seed layer on the semi-noble metal layer with a non-corrosive electrolyte, methods of treating the semi-noble metal layer that the copper seed layer is deposited on, and methods for promoting a more uniform copper seed layer deposition across a semiconductor wafer.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Imaging member for offset printing applications
ActiveUS20140060352A1Uniform layersFree from defectPlaten pressesPlate printingSurface layerPerfluoropolyether
An imaging member includes a surface layer comprising a fluoroelastomer-perfluoropolyether composite formed from a reaction mixture comprising a fluoroelastomer and a perfluoropolyether compound. Methods of manufacturing the imaging member and processes for variable lithographic printing using the imaging member are also disclosed.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method to form solder deposits and non-melting bump structures on substrates
InactiveUS20130105329A1Uniform layersReduce in quantitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetal alloySubstrate surface
Described is a method of forming a metal or metal alloy layer onto a substrate comprising the following steps i) provide a substrate including a permanent resin layer on top of at least one contact area and a temporary resin layer on top of the permanent resin layer, ii) contact the entire substrate area including the at least one contact area with a solution suitable to provide a conductive layer on the substrate surface and i) electroplate a metal or metal alloy layer onto the conductive layer.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
Multilayer ceramic capacitor and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20130088810A1Uniform layersFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsCeramic capacitorDielectric layer
Disclosed herein are a multilayer ceramic capacitor and a method for manufacturing the same. The multilayer ceramic capacitor includes: a capacitor main body having dielectric layers and inner electrodes laminated therein; external electrodes and plating layers formed on a surface of the capacitor main body; and electroless plating layers formed between the external electrodes and the plating layers.According to the examples of the present invention, the electroless plating layer is formed before the plating layer is formed on the external electrode, thereby solving non-plating problems when the plating layer made of nickel or the like is formed on the external electrode. Therefore, soldering defects due to nickel non-plating or the like can be solved at the time of mounting, and thus, a multilayer ceramic capacitor having high reliability can be provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Method of fabricating a dual damascene copper wire
ActiveUS6849541B1Improve conductivityImprove overhang phenomenonSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCopper wireOptoelectronics
A method of forming at least one wire on a substrate. The substrate includes at least one conductive region. An insulating layer is disposed on the substrate. At least one recess in the insulating layer exposes the conductive region. A barrier layer is formed on a surface of the insulating layer and the recess first. A continuous and uniform conductive layer is then formed on a surface of the barrier layer. A seed layer is thereafter formed on a surface of the conductive layer. Finally, a metal layer filling up the recess is formed on a surface of the seed layer.
Owner:MARLIN SEMICON LTD
Reverse pulse plating composition and method
A composition and method for electroplating a metal on a substrate. The composition has a chloride to brightener concentration ratio of from 20:1 to 125:1. The method of electroplating, which employs the composition, employs pulse patterns that improve physical properties of metal surfaces.
Owner:SHIPLEY CO LLC
Cleaning unit, slit coating apparatus having the same and method of coating substrate
A cleaning unit of this invention includes a body and a cleaning member. The body includes an upper face. The upper face subsides to form a receiving recession for receiving a slit nozzle of the slit coater. The receiving recession includes a sidewall and a bottom face. The sidewall includes a first injection hole. A cleaning material is sprayed via the injection hole. The cleaning member eliminates dregs of the material attached on the slit nozzle of the slit coater. The cleaning member is attached on the bottom face of the receiving recession. According to the present invention, the slit nozzle is effectively cleared, so that the substrate is uniformly coated with the photosensitive layer, and the photosensitive layer is not scratched.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
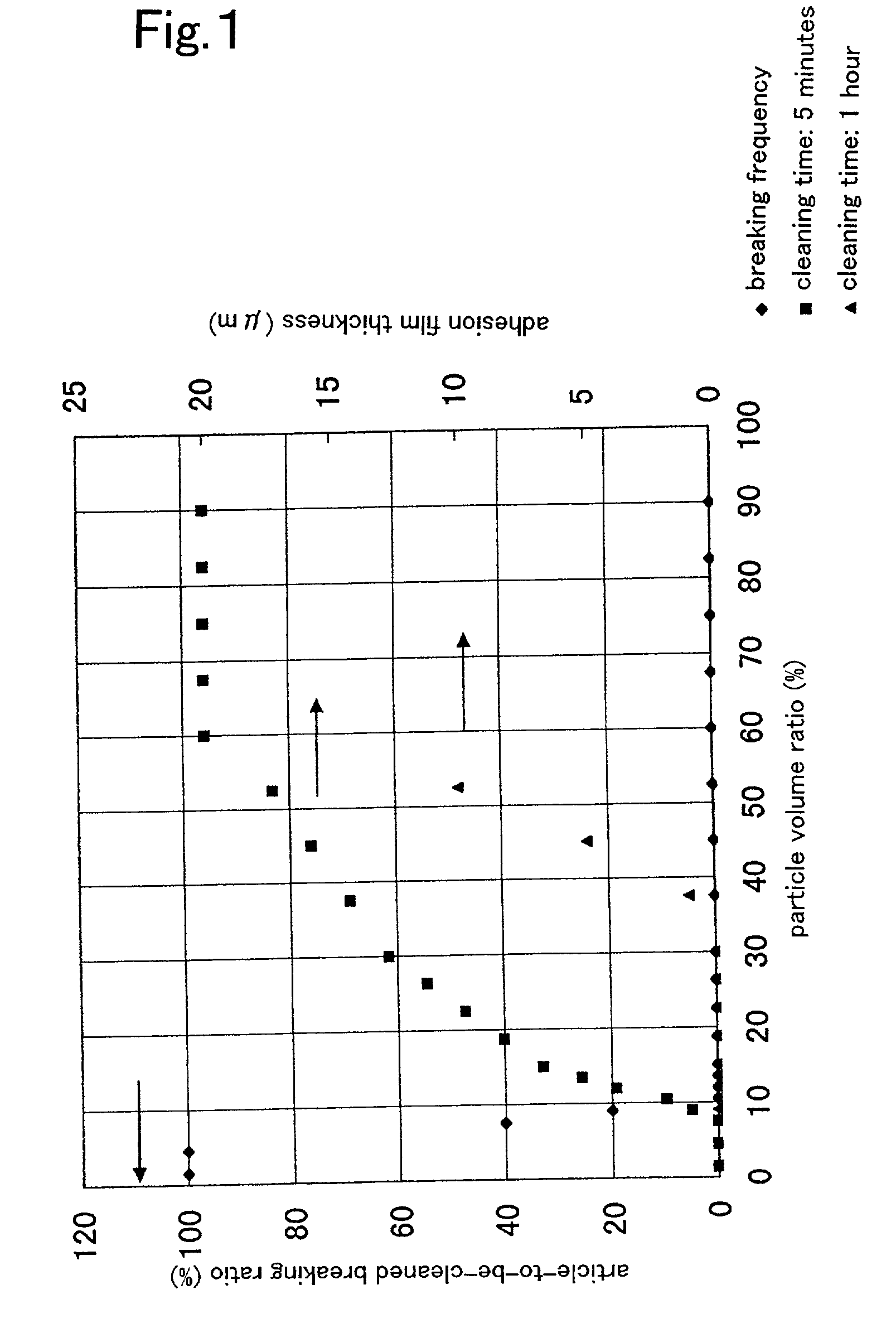
Ultrasonic cleaning method
InactiveUS20020185150A1Effectively cleaned and clearedLarge kinetic energyElectrostatic cleaningDetergent materialsMegasonic cleaningEngineering
A ultrasonic cleaning method is provided that performs ultrasonic cleaning without breaking a small and low-strength article-to-be-cleaned. It is a ultrasonic cleaning method that performs ultrasonic cleaning of an article-to-be-cleaned by a combination of a ultrasonic wave transmission medium and particles having a larger specific gravity than the ultrasonic wave transmission medium. The article-to-be-cleaned is cleaned by allowing at least a part of the article-to-be-cleaned to be in contact with a cleaning layer formed with the ultrasonic wave transmission medium and the particles where the mixing ratio of the particles to the ultrasonic wave transmission medium is 10 to 60 vol %, and imparting a ultrasonic wave to the cleaning layer. The particles mutually restrict their movements in a particle group thereby preventing the kinetic energy from becoming excessively large, and exhibit a frictional force and an impinging force suitable for removing the contaminant adhering to the surface without breaking the low-strength article-to-be-cleaned.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Magnetoresistive sensor with a free layer stabilized by direct coupling to in stack antiferromagnetic layer
InactiveUS20060187591A1Improve the immunityDecreased specular scatteringRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsDirect couplingMagnetic moment
A magnetoresistive sensor having a free layer biased by an in stack bias layer that comprises a layer of antiferromagnetic material. The bias layer can be IrMnCr, IrMn or some other antiferromagnetic material. The free layer is a synthetic free layer having first and second magnetic layers antiparallel coupled across an AP coupling layer. The first magnetic layer is disposed adjacent to a spacer or barrier layer and the second magnetic layer is exchange coupled with the IrMnCr bias layer. The bias layer biases the magnetic moments of the free layer in desired directions parallel with the ABS without pinning the magnetic moments of the free layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
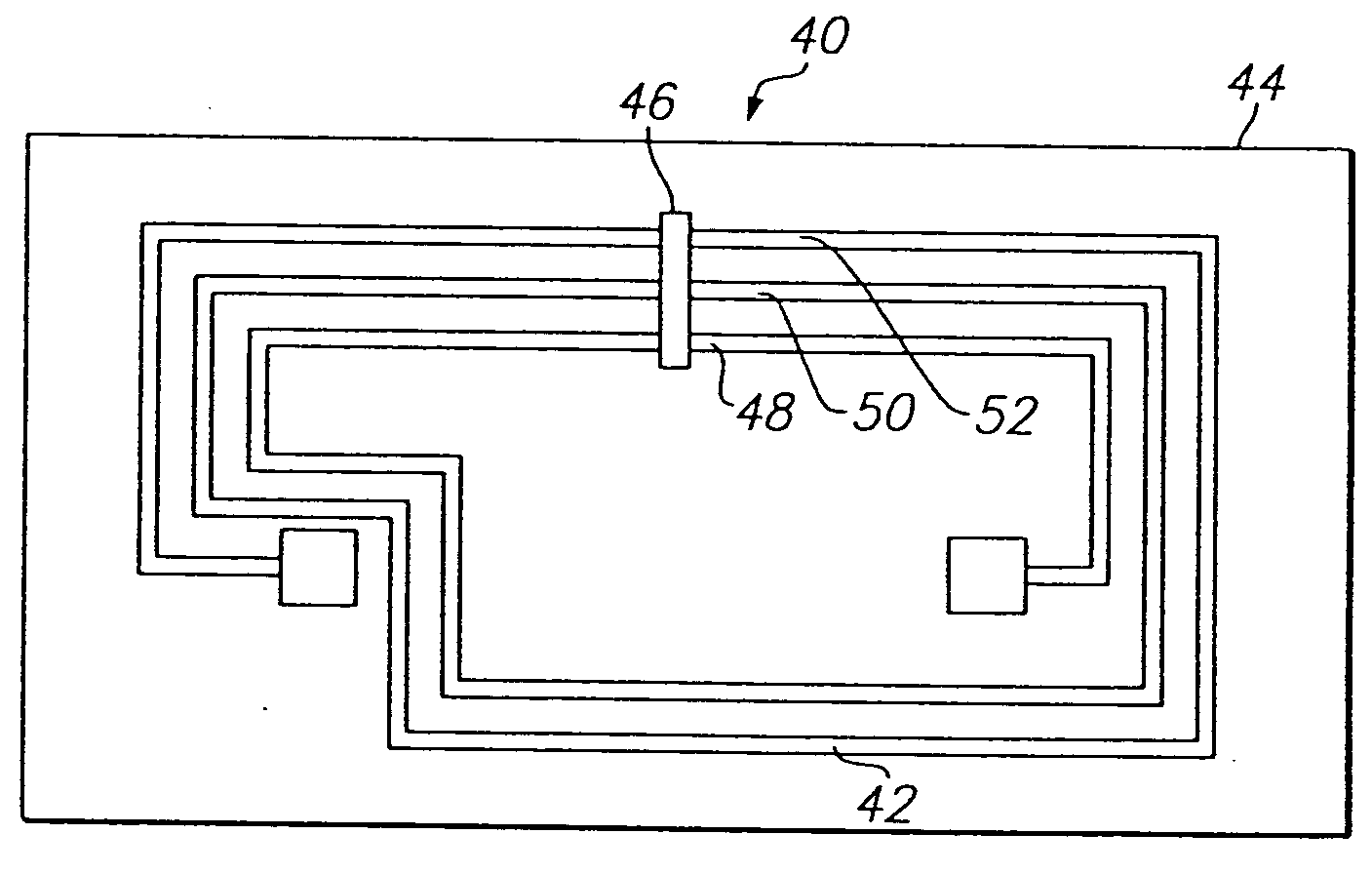
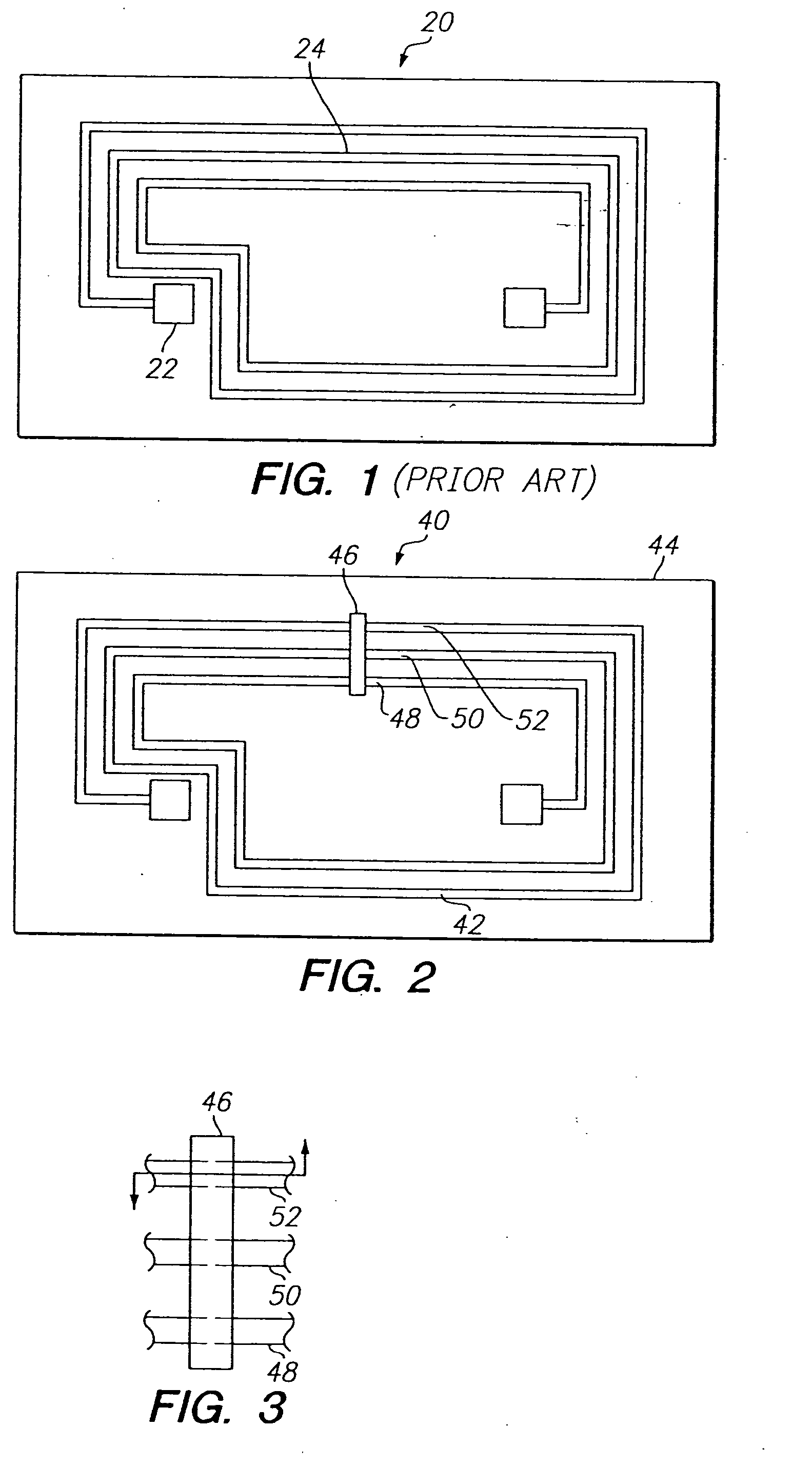
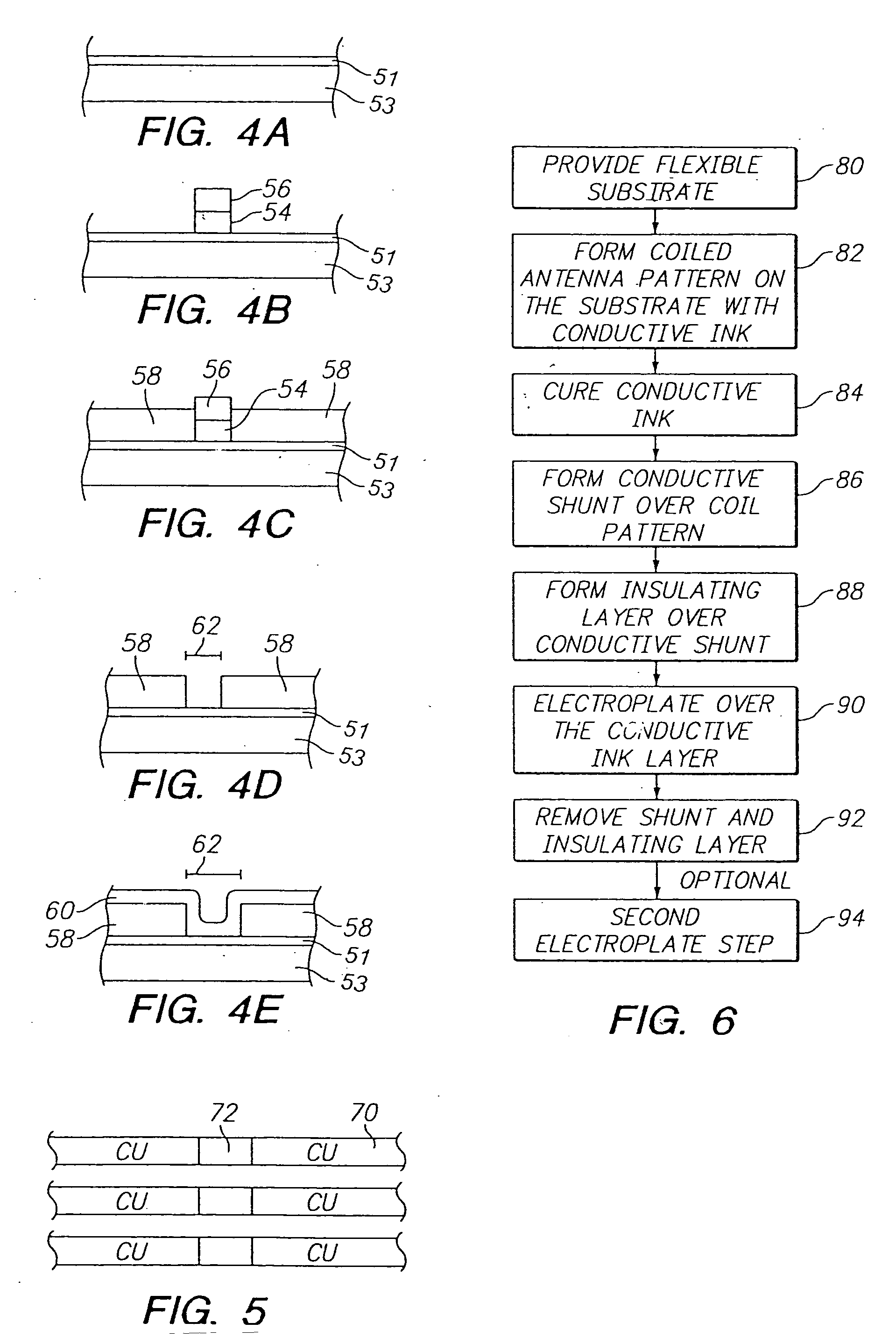
Method for forming radio frequency antenna
InactiveUS6933892B2Uniform platingResistanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsRadio frequencyElectroplating
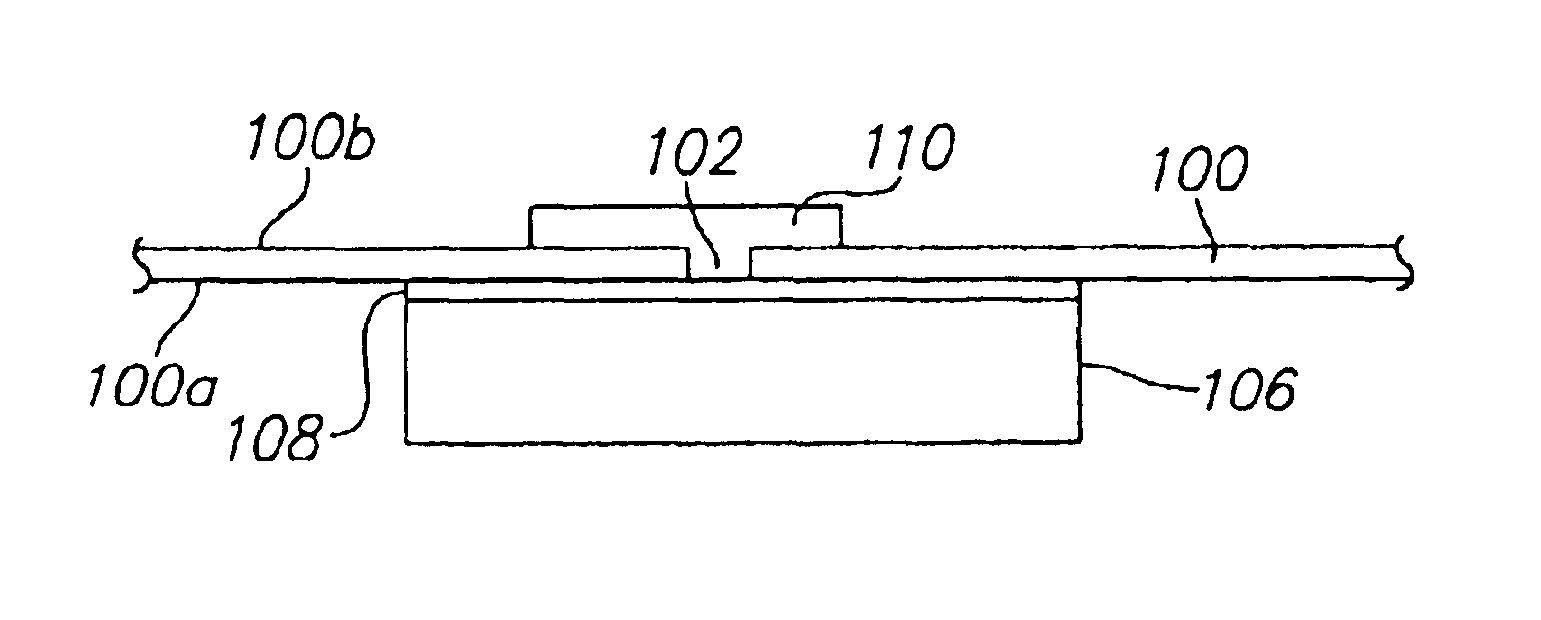
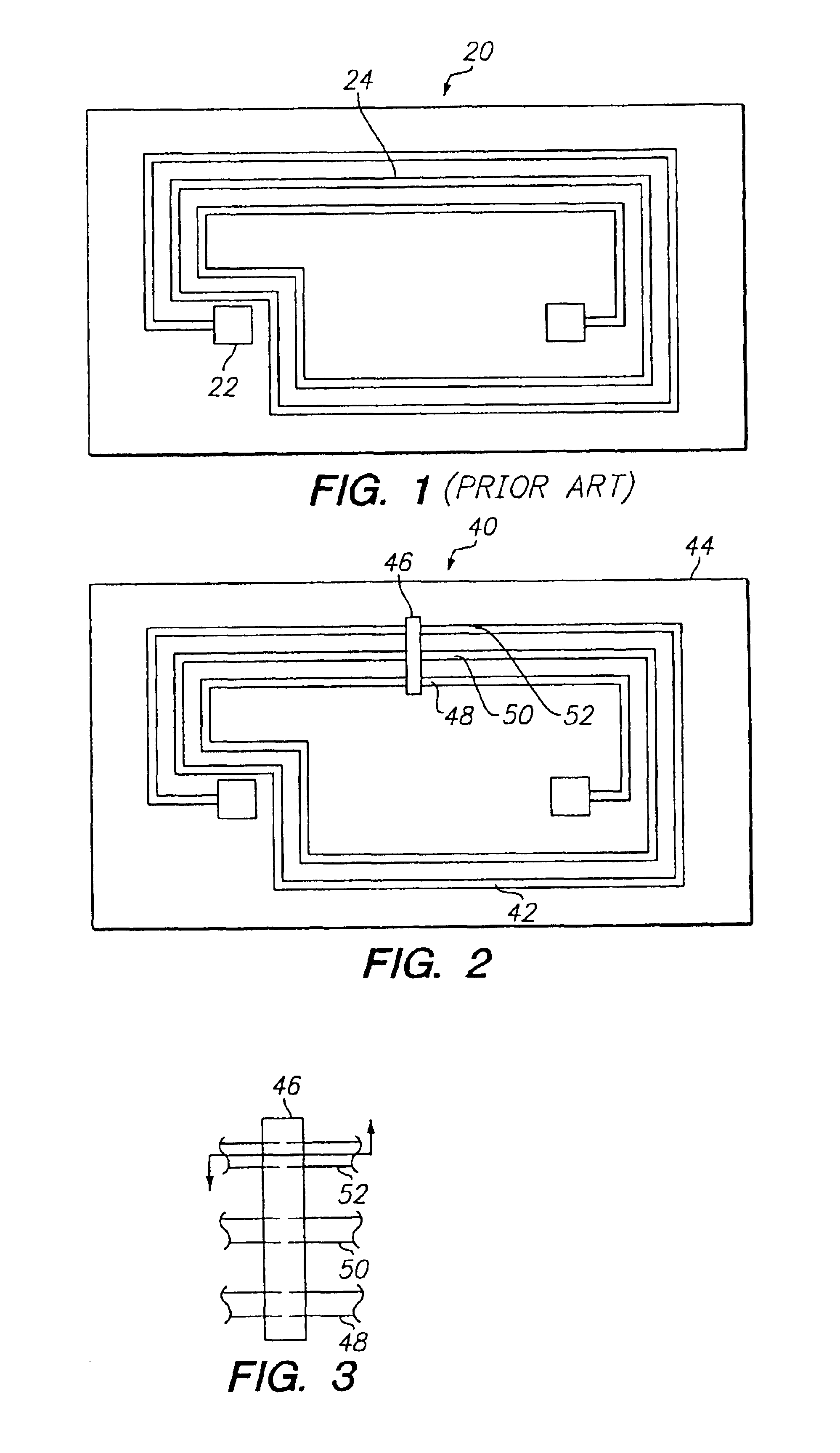
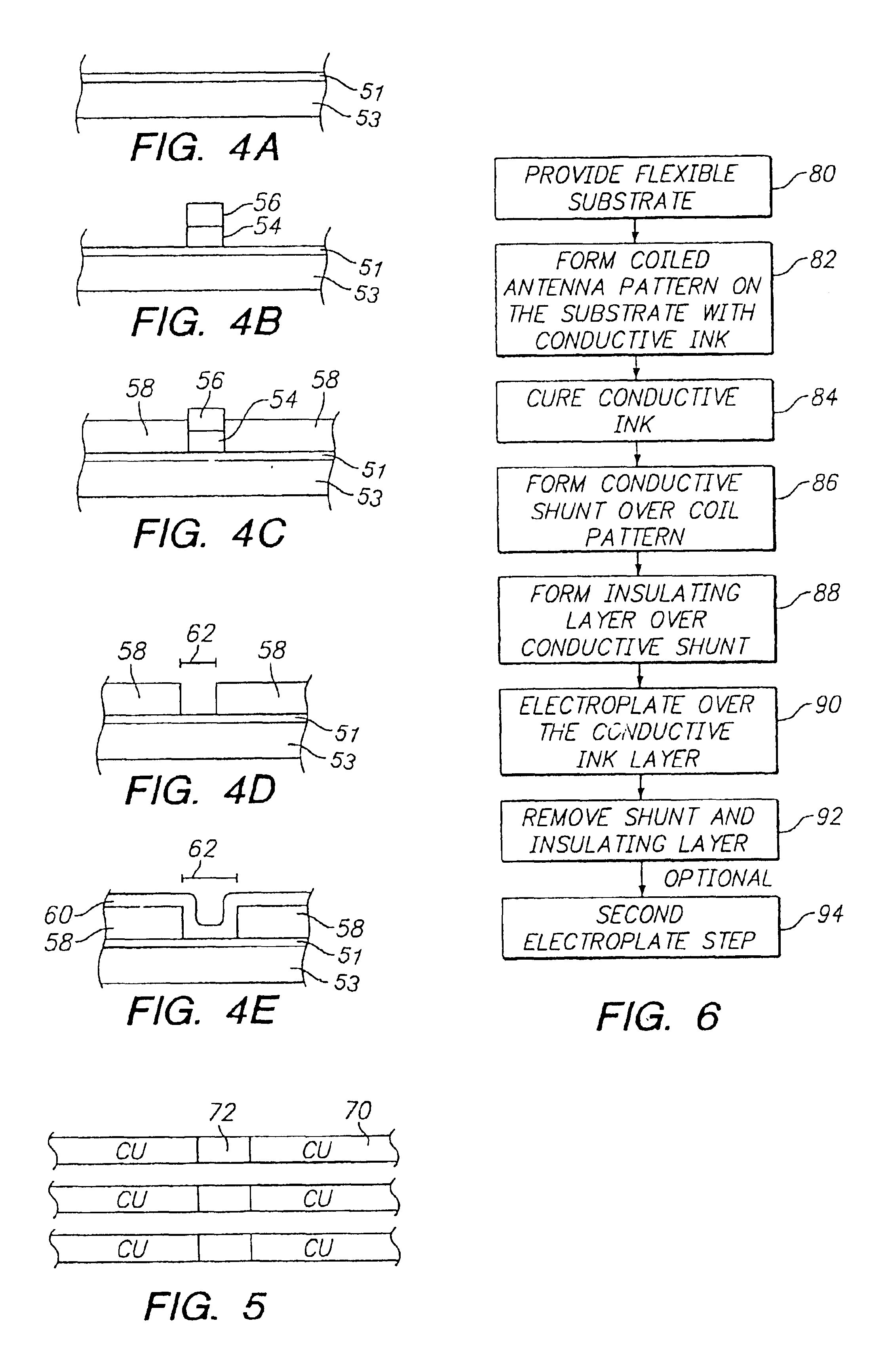
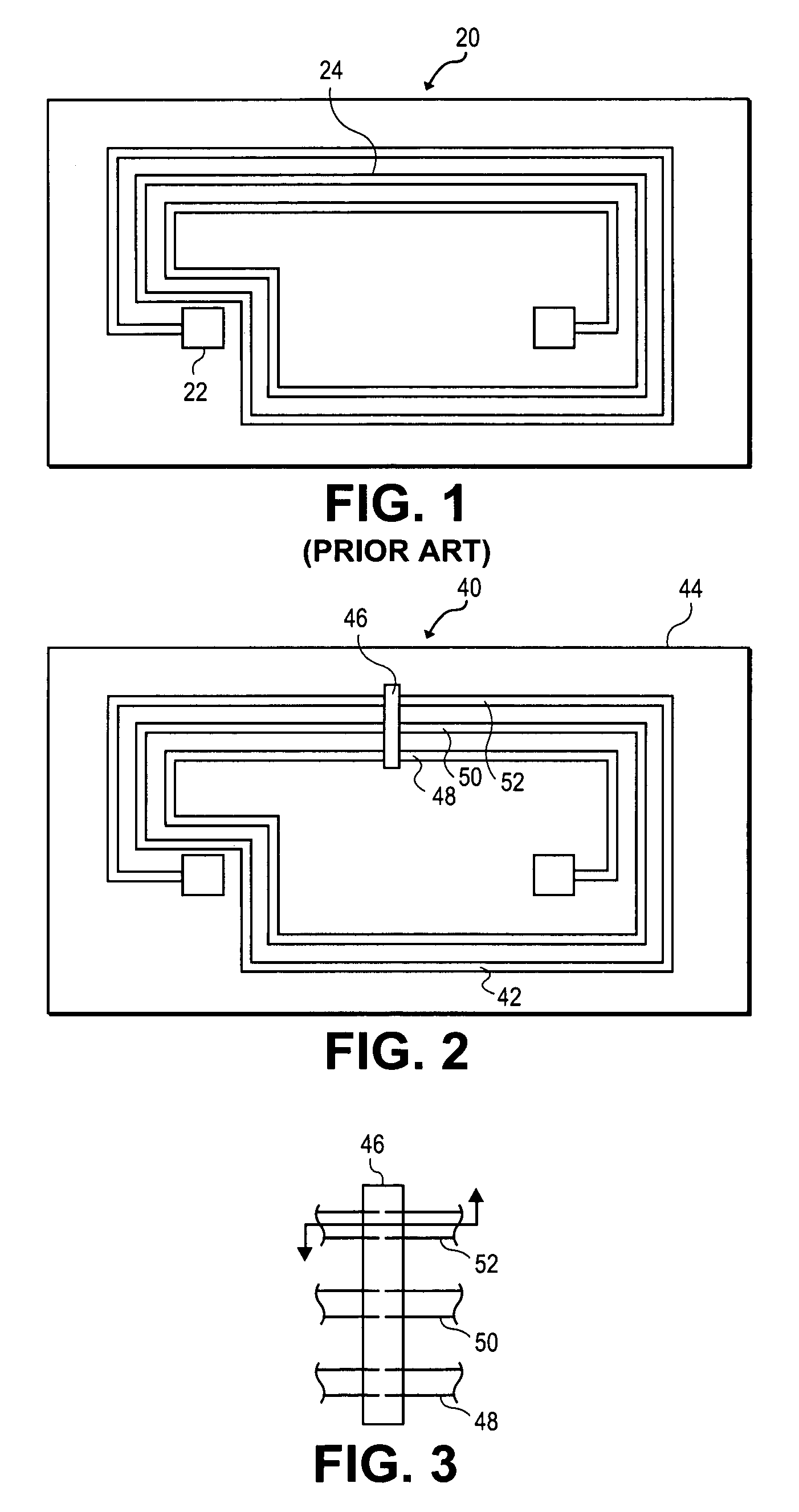
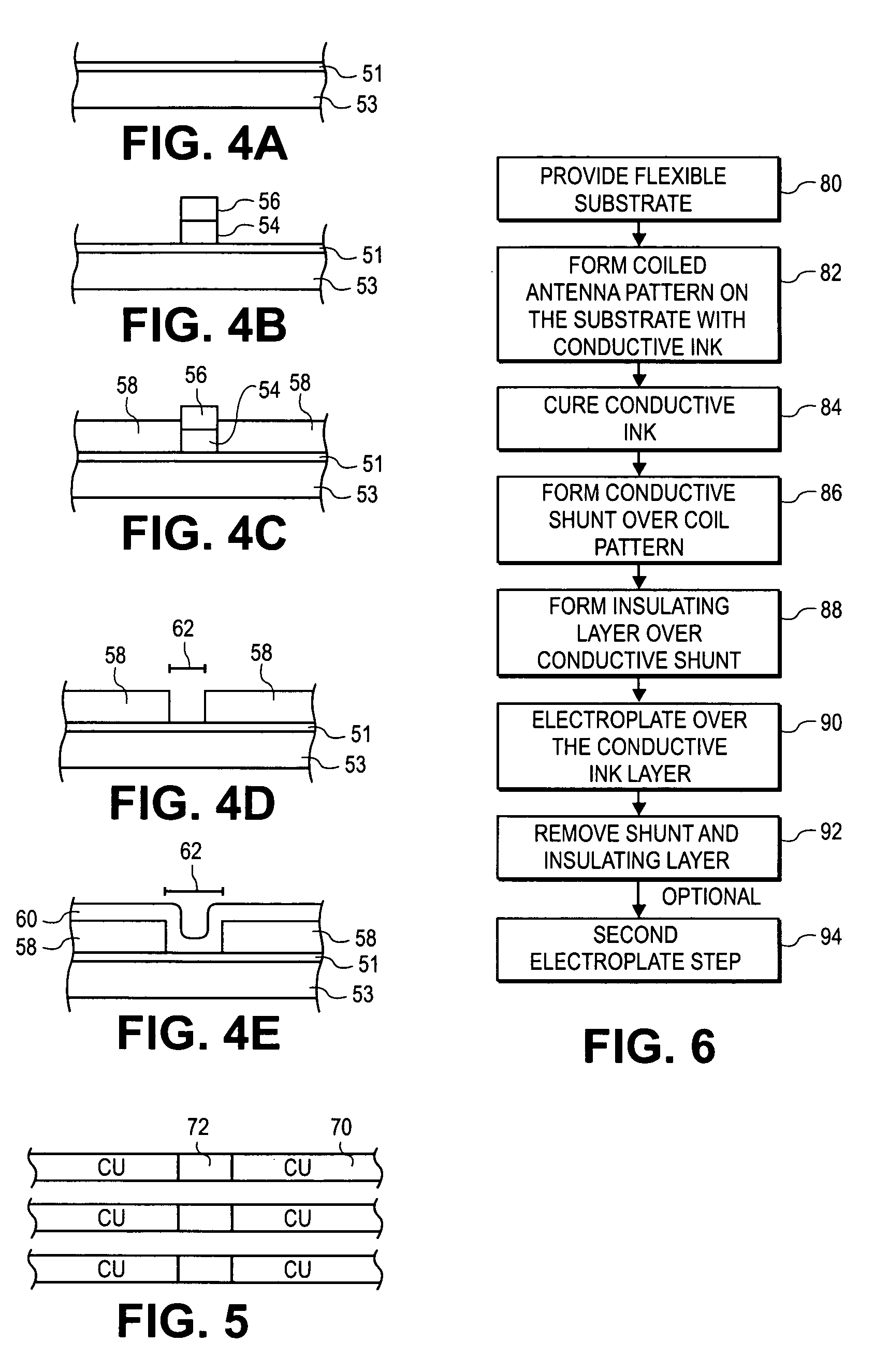
A metalized circuit suitable for application as a radio frequency antenna is produced by forming an antenna coil pattern on a flexible substrate. The antenna coil pattern is formed using a conductive ink which is patterned on the substrate. The conductive ink is cured and an electrical-short layer is formed across the coils of the conductive ink pattern. An insulating layer is formed over top of the electrical-short layer, a metal layer electroplated on top of the conductive layer, and then the electrical-short layer is removed. The use of the electrical-short layer during the electroplating allows for the voltage at the different points on the conductive ink layer to be relatively similar, so that a uniform electroplate layer is formed on top of the conductive ink layer. This results in a better quality radio frequency antenna at a reduced cost.
Owner:RCD TECHNOLOGY
Ultrafiltration membranes and methods of making and use of ultrafiltration membranes
InactiveUS20070084788A1Minimizing flow restrictionUniform layersMembranesSemi-permeable membranesCelluloseProtein solution
An inherently hydrophobic polymer membrane substrate having its surface rendered hydrophilic with a hydroxyalkyl cellulose and having a throughput greater than about 1500 L / m2 is provided. A process for making the membrane also is provided which includes a step of autoclaving in boiling water and / or steam or submerging in boiling water. The membrane is useful for removing virus from a protein solution.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Metal powder atomization manufacturing processes
PendingUS20190001416A1Improve liquidityEasy to useTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusMetal powder
There are provided reactive metal powder atomization manufacturing processes. For example, such processes include providing a heated metal source and contact the heated metal source with at least one additive gas while carrying out the atomization process. Such processes provide raw reactive metal powder having improved flowability. The at least one additive gas can be mixed together with an atomization gas to obtain an atomization mixture, and the heated metal source can be contacted with the atomization mixture while carrying out the atomization process. Reactive metal powder spheroidization manufacturing processes are also provided.
Owner:AP&C ADVANCED POWDERS & COATINGS
Textured imaging member
InactiveUS20140060360A1Uniform layersFree from defectPlaten pressesDiffusing elementsEngineeringRadiation
An imaging member includes a surface layer comprising a matrix material, an aerogel component, and a radiation-absorbing filler. Methods of manufacturing the imaging member and processes for variable lithographic printing using the imaging member are also disclosed.
Owner:XEROX CORP +1
Substrate structure of liquid crystal display and method of forming alignment layer
InactiveUS20060172091A1Uniform layersImprove film propertiesLiquid crystal compositionsRadiation applicationsLiquid-crystal displayWater layer
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Method for forming radio frequency antenna
InactiveUS20050078035A1Uniform platingResistanceAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsRadio frequencyElectroplating
A metalized circuit suitable for application as a radio frequency antenna is produced by forming an antenna coil pattern on a flexible substrate. The antenna coil pattern is formed using a conductive ink which is patterned on the substrate. The conductive ink is cured and an electrical-short layer is formed across the coils of the conductive ink pattern. An insulating layer is formed over top of the electrical-short layer, a metal layer electroplated on top of the conductive layer, and then the electrical-short layer is removed. The use of the electrical-short layer during the electroplating allows for the voltage at the different points on the conductive ink layer to be relatively similar, so that a uniform electroplate layer is formed on top of the conductive ink layer. This results in a better quality radio frequency antenna at a reduced cost.
Owner:SQUARE 1 BANK
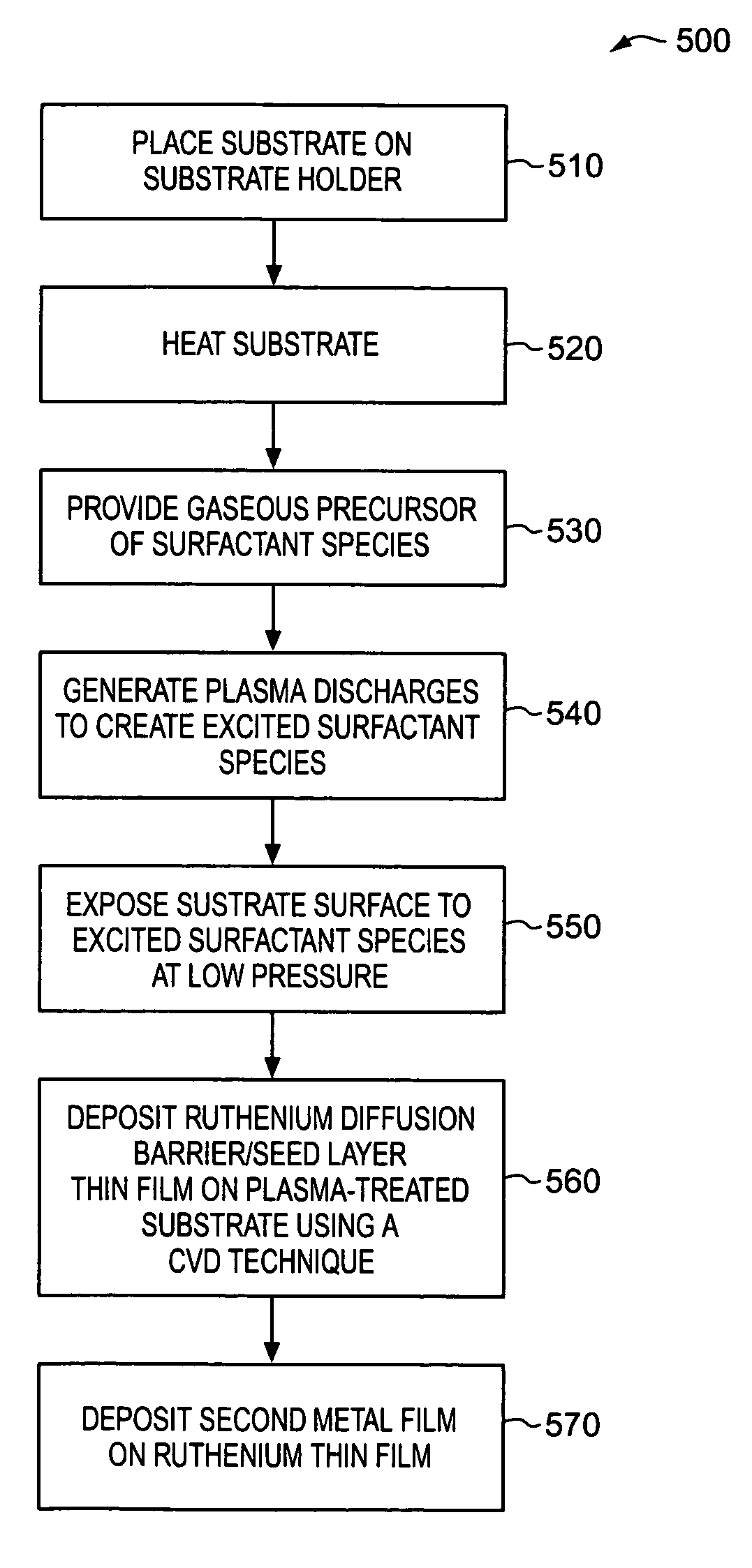
Surface treatment using iodine plasma to improve metal deposition
ActiveUS7041596B1Increase depositionShorten the timePretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumIodine
An excited surfactant species is created by generating plasma discharge in a surfactant precursor gas. A surfactant species typically includes at least one of iodine, led, thin, gallium, and indium. A surface of an integrated circuit substrate is exposed to the excited surfactant species to form a plasma-treated surface. A ruthenium thin film is deposited on the plasma-treated surface using a CVD technique.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Imaging member for offset printing applications
InactiveUS20140060363A1Uniform layersFree from defectPlaten pressesCeramic shaping apparatusEngineeringSurface layer
An imaging member includes a surface layer comprising a silicone rubber and an infrared-absorbing filler. Methods of fabricating the imaging member and processes for variable lithographic printing using the imaging member are also disclosed.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Slurry compositions for selectively polishing silicon nitride relative to silicon oxide, methods of polishing a silicon nitride layer and methods of manufacturing a semiconductor device using the same
InactiveUS8043970B2Reduce rateSuppress and reduce damagePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesDevice materialSlurry
Slurry compositions for selectively polishing silicon nitride relative to silicon oxide, methods of polishing a silicon nitride layer and methods of manufacturing a semiconductor device using the same are provided. The slurry compositions include a first agent for reducing an oxide polishing rate, an abrasive particle and water, and the first agent includes poly(acrylic acid). The slurry composition may have a high polishing selectivity of silicon nitride relative to silicon oxide to be employed in selectively polishing a silicon nitride layer in a semiconductor manufacturing process.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
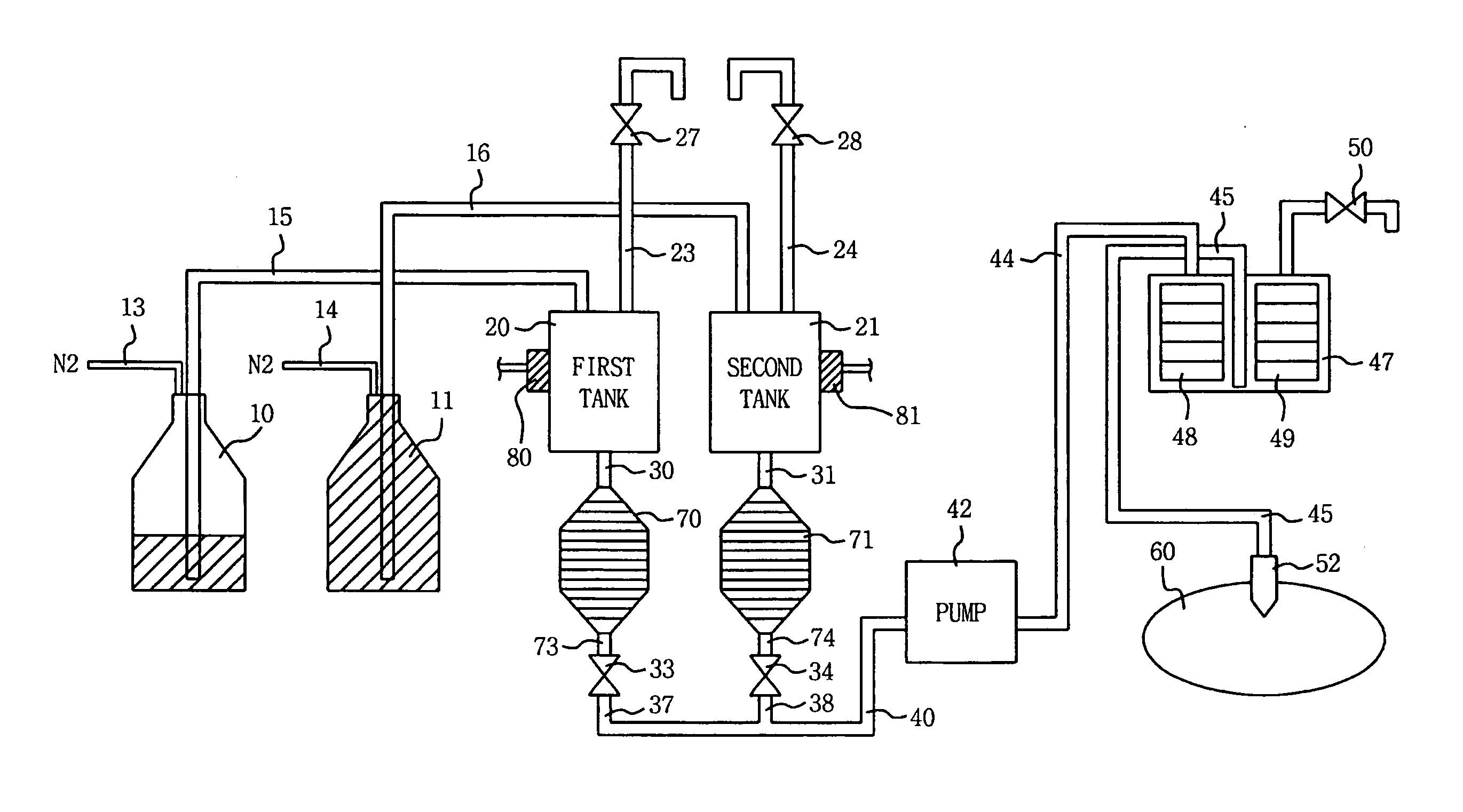
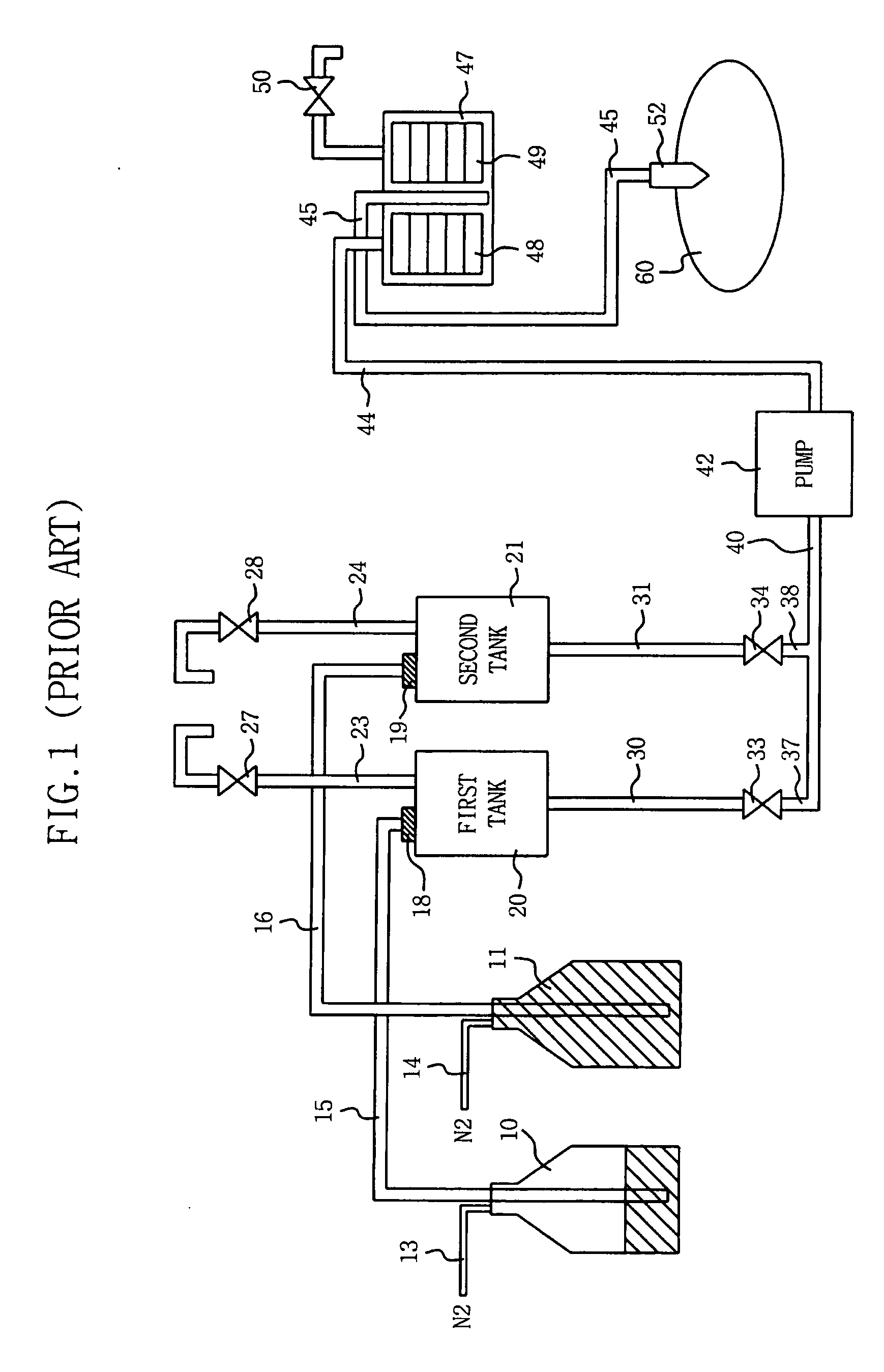
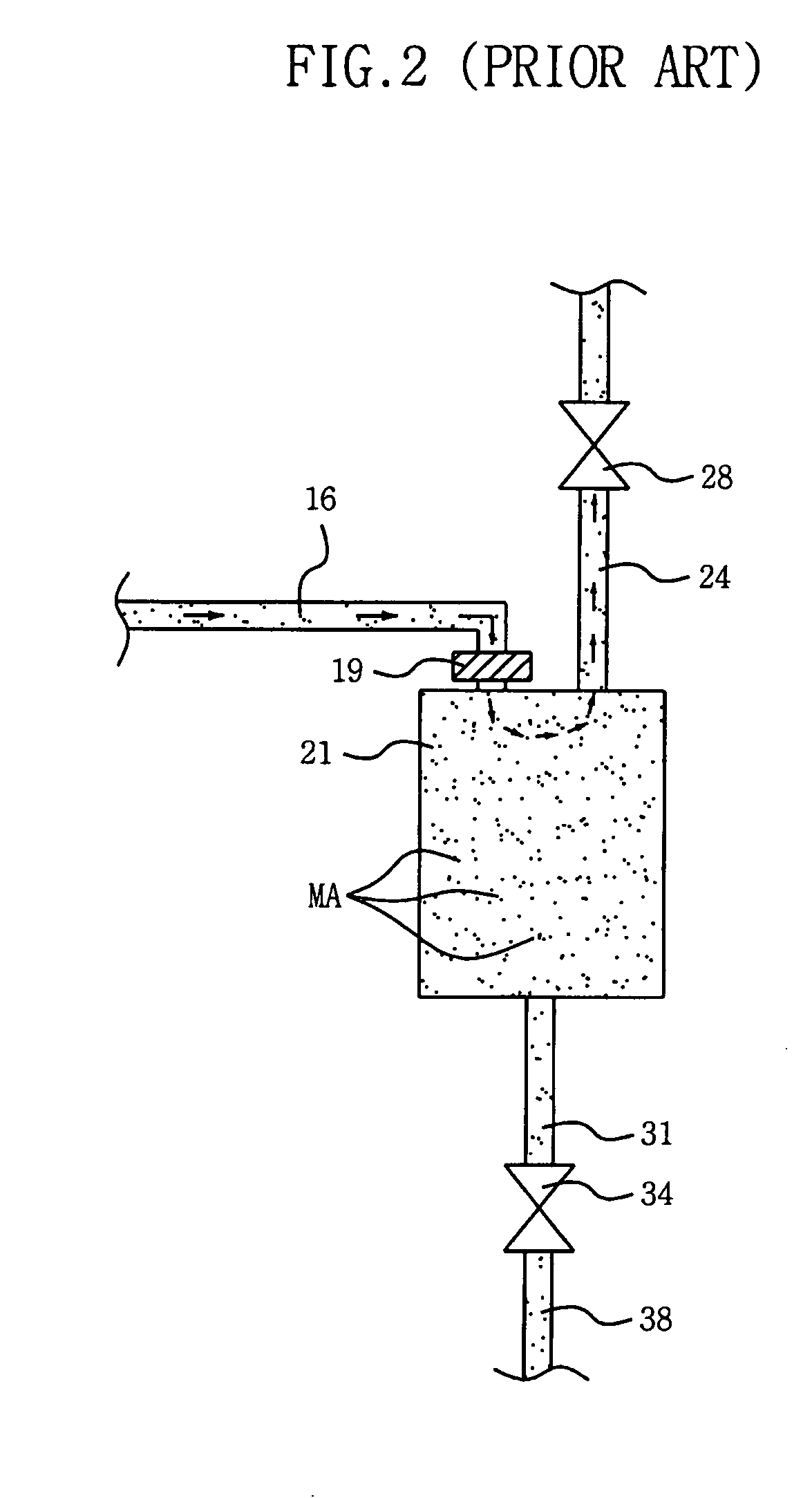
Apparatus and method of dispensing photosensitive solution in semiconductor device fabrication equipment
ActiveUS20050224132A1Uniform layersReduce the presence of air bubblesLiquid degasificationLiquid fillingBuffer tankSemiconductor
A method of and apparatus for dispensing photosensitive solution. substantially reduces the amount of air bubbles in the photosensitive solution during the dispensing operation. The photosensitive solution dispensing apparatus includes at least one supply vessel that contains the solution, a respective buffer tank that buffers the solution supplied from each supply vessel, a filter unit for filtering the solution, a pump for pumping the solution pumped from the buffer tank to the filter unit, a dispensing nozzle connected to the filter unit, and a dedicated bubble removal filter that is interposed between the buffer tank and the pump. The bubble removal filter is configured to remove air bubbles from the solution before the solution flows into the pump and is dispensed through the nozzle.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for forming radio frequency antenna
InactiveUS7298331B2ResistanceUniform platingSimultaneous aerial operationsPrinted circuit aspectsRadio frequencyElectroplating
A metalized circuit suitable for application as a radio frequency antenna is produced by forming an antenna coil pattern on a flexible substrate. The antenna coil pattern is formed using a conductive ink which is patterned on the substrate. The conductive ink is cured and an electrical-short layer is formed across the coils of the conductive ink pattern. An insulating layer is formed over top of the electrical-short layer, a metal layer electroplated on top of the conductive layer, and then the electrical-short layer is removed. The use of the electrical-short layer during the electroplating allows for the voltage at the different points on the conductive ink layer to be relatively similar, so that a uniform electroplate layer is formed on top of the conductive ink layer. This results in a better quality radio frequency antenna at a reduced cost.
Owner:SQUARE 1 BANK
Ultrafiltration membranes and methods of making and use of ultrafiltration membranes
ActiveUS20100159143A1Minimizing flow restrictionUniform layersMembranesSemi-permeable membranesCelluloseProtein solution
An inherently hydrophobic polymer membrane substrate having its surface rendered hydrophilic with a hydroxyalkyl cellulose and having a throughput greater than about 1500 L / m2 is provided. A process for making the membrane also is provided which includes a step of autoclaving in boiling water and / or steam or submerging in boiling water. The membrane is useful for removing virus from a protein solution.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Phase retarder film containing TiO2
InactiveUS6097460AExcellent evaporation layer in uniformitySmall sizeLayered productsPolarising elementsDielectricPhase retardation
A phase retarder film is provided wherein at least one oblique evaporation layer comprising an inorganic dielectric mainly containing TiO2 is formed on at least one surface of a transparent polymer film with an intermediate layer between, the evaporation layer having positive refractive index anisotropy and a principal optic axis tilted 20 degrees to 70 degrees from a normal direction to said transparent polymer film. The phase retarder film is suitable for improving viewing angle characteristics of the TN-LCD.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Photosensitive compound and photoresist composition including the same
InactiveUS20090155714A1High resolutionDry resistanceOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationResistHydrogen atom
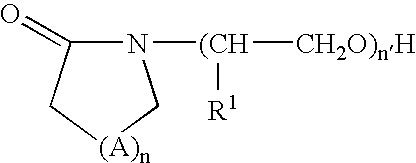
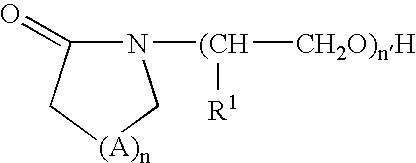
A photosensitive compound whose size is smaller than conventional polymer for photoresist, and which has well-defined (uniform) structure, and a photoresist composition including the same are disclosed. The photosensitive compound represented by the following formula. Also, the present invention provides a photoresist composition comprising 1 to 85 wt % (weight %) of the photosensitive compound; 0.05 to weight parts of a photo-acid generator with respect to 100 weight parts of the photosensitive compound; and 10 to 5000 weight parts of an organic solvent.In the formula, n is 0 or 1, x is 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, y is 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6, z is 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4, R, R′ and R″ are independently hydrocarbon group of 1 to 30 carbon atoms, preferably 2 to 20 carbon atoms, and R′″ is a hydrogen atom or hydrocarbon group of 1 to 30 carbon atoms, preferably 2 to 20 carbon atoms.
Owner:DONGJIN SEMICHEM CO LTD
Copper reflow process
InactiveUS20030139033A1Improve adhesionSimple modelSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInterconnectionCopper
A manufacturable method for forming a highly reliable electrical interconnection. An electrical interconnection pattern is first formed in a dielectric layer on a semiconductor substrate as recessed regions in the dielectric layer. A conductive layer primarily comprising copper is thereafter deposited over the surface and in the recessed regions of the dielectric layer. The conductive layer is then reflowed to fill the recessed regions of the dielectric layer with substantially no void formation. This reflow process may also be used to improve the step coverage of any such copper layer deposited over the surface of a substrate to be used in conjunction with alternate techniques for forming electrical interconnections including photoresist patterning and etch.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Process for laying a strip continuously on a toroidal surface
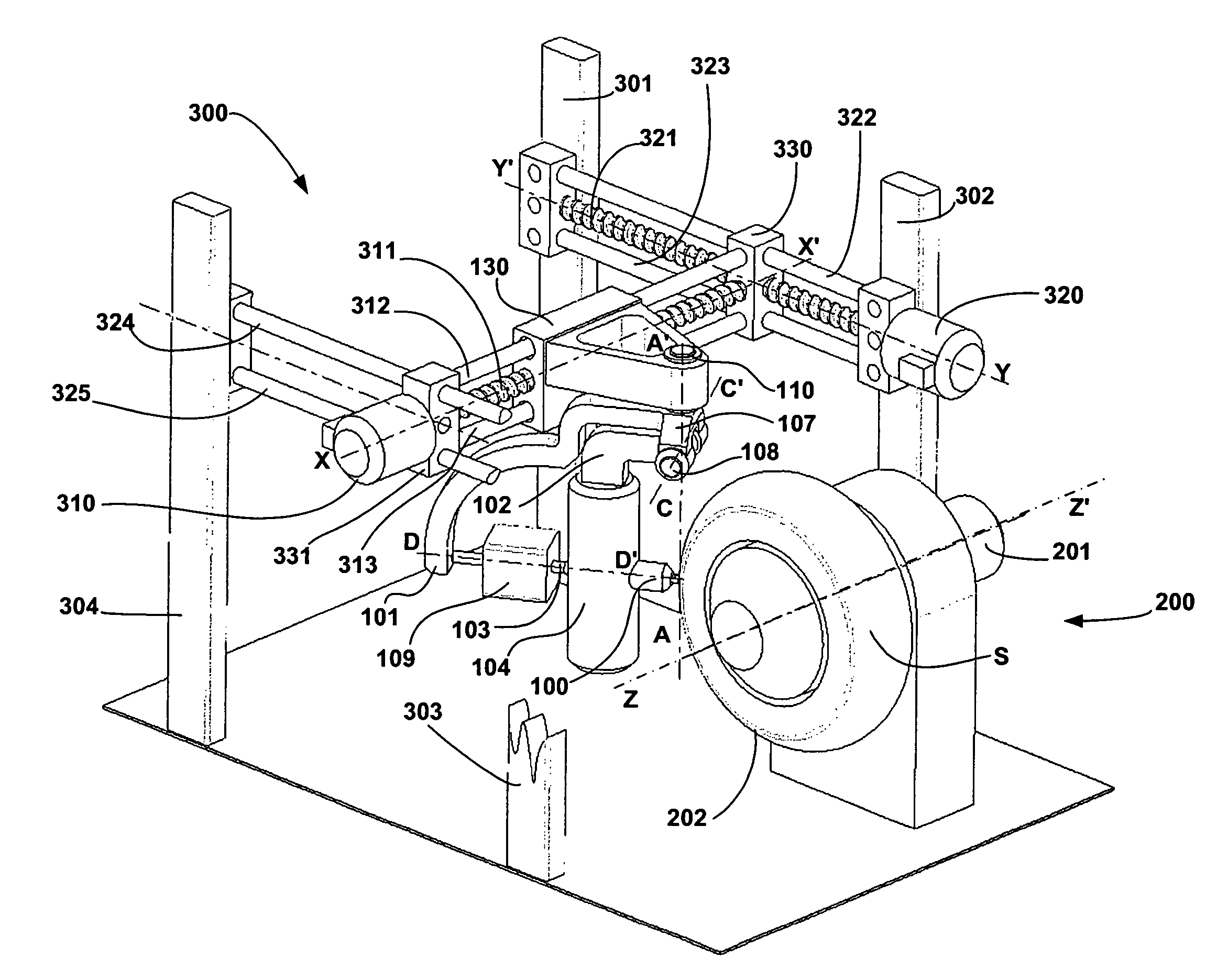
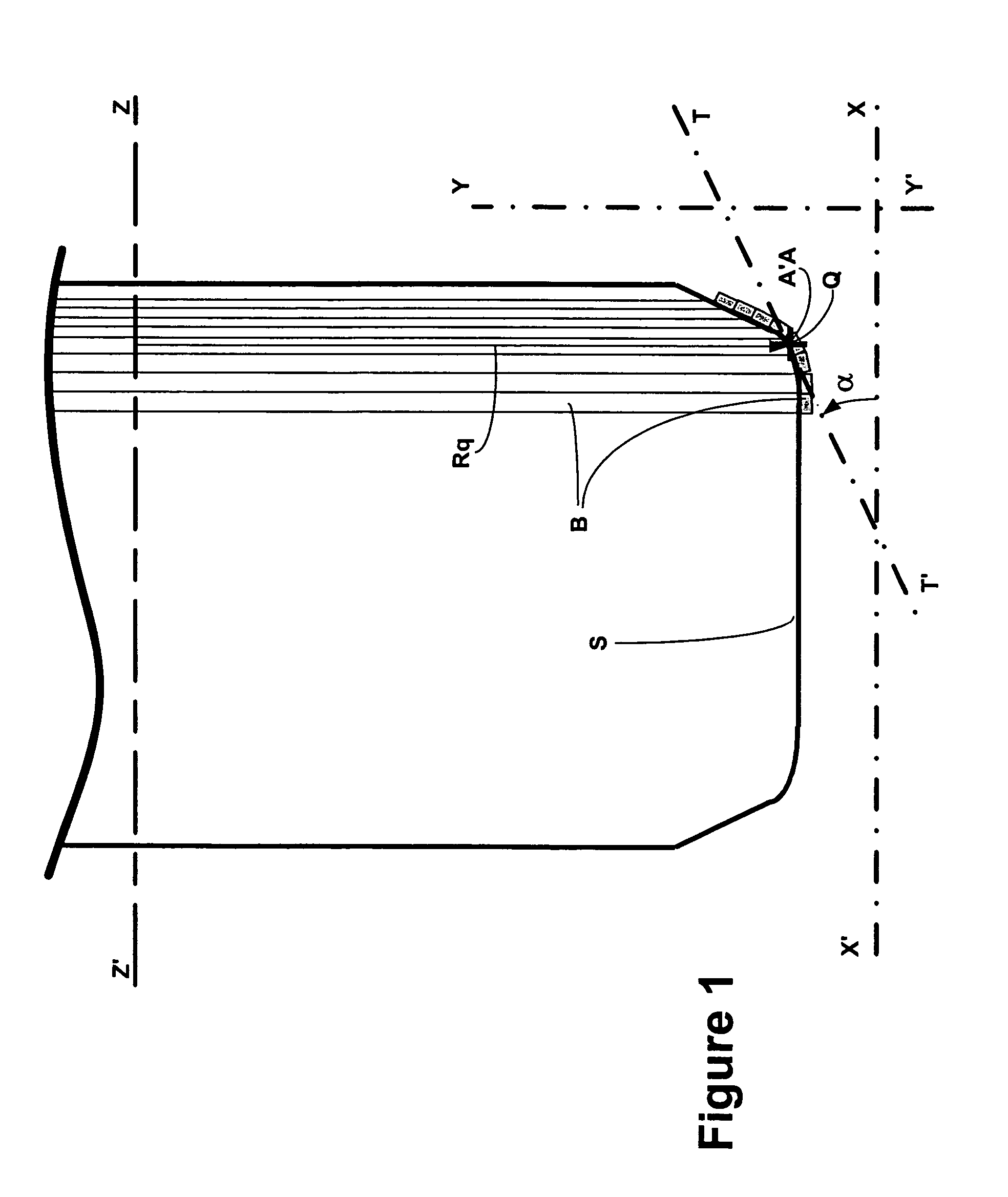
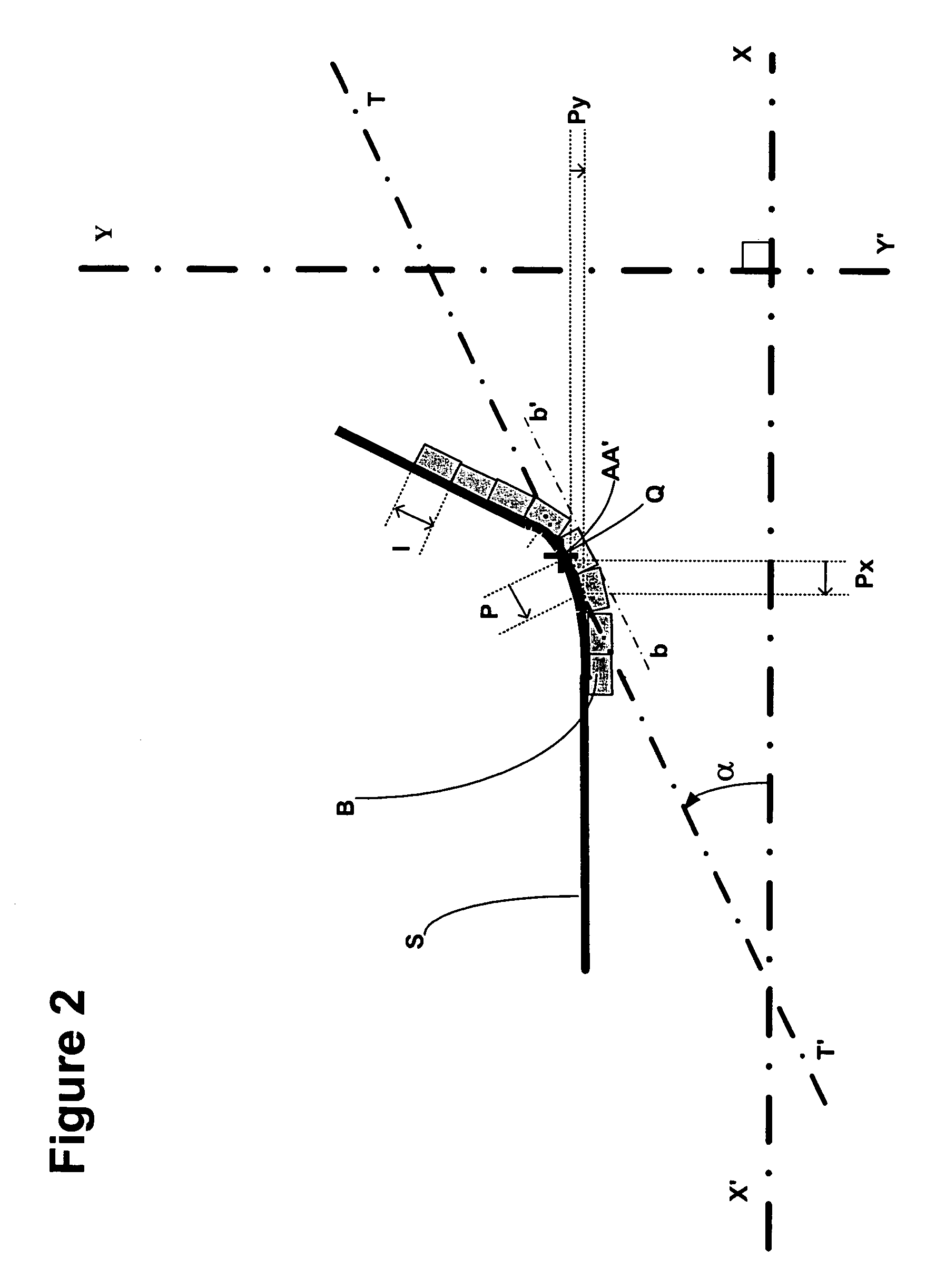
A mechanism for laying a strip on a receiving surface rotating about a first axis. The mechanism includes a laying head moving along a second axis oriented parallel to the axis of rotation of the surface and along a third axis oriented parallel to a radial direction passing through the point of contact between the receiving surface and a strip applicator of the laying head. The laying head is rotatable about a front axis oriented substantially perpendicular to the second and third axes and passing through the contact point. the laying includes a device for estimating the value of the of the angle α formed by a tangent to the transverse profile of the surface and the second axis. The movements of the laying head are determined by the value of the angle α in such a way as to displace the laying head in a direction parallel to the tangent following the transverse profile of the receiving surface.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com