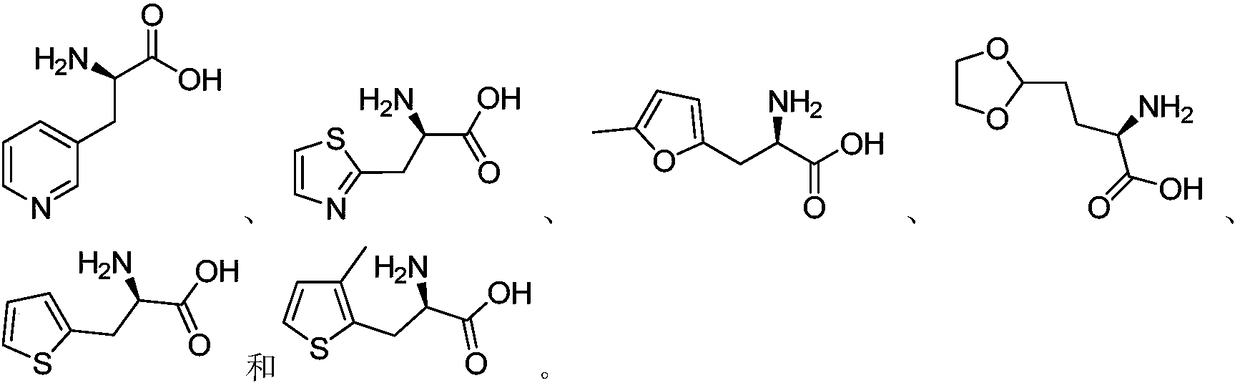
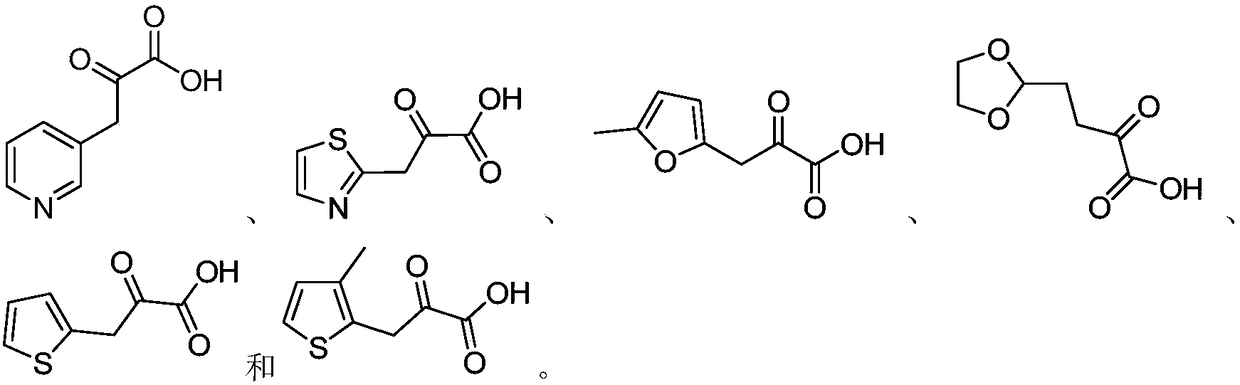
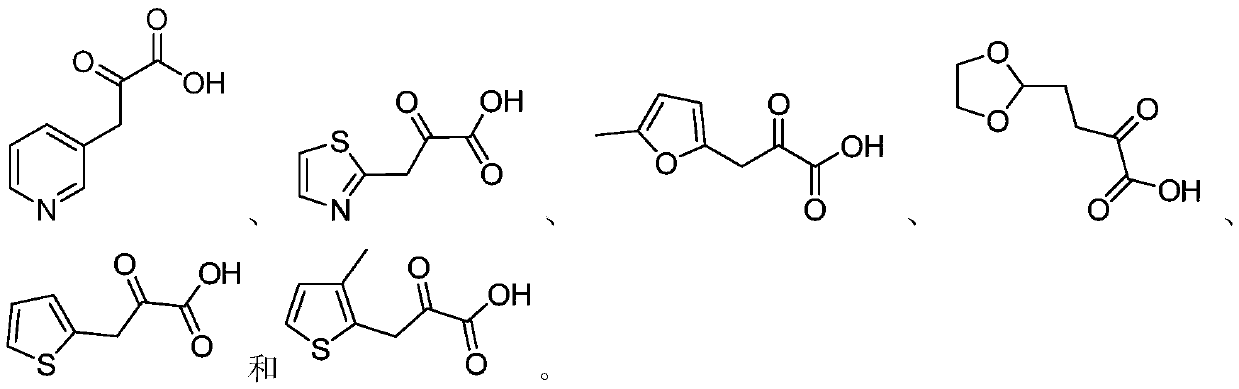
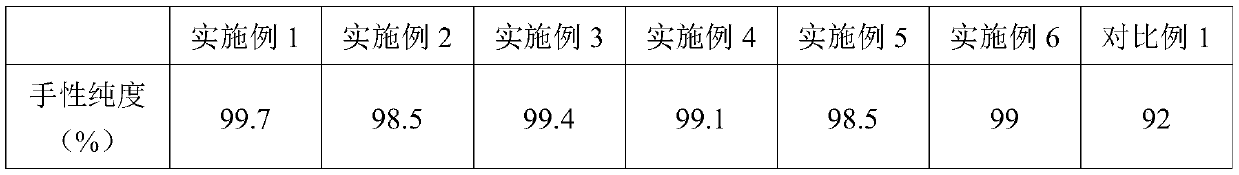
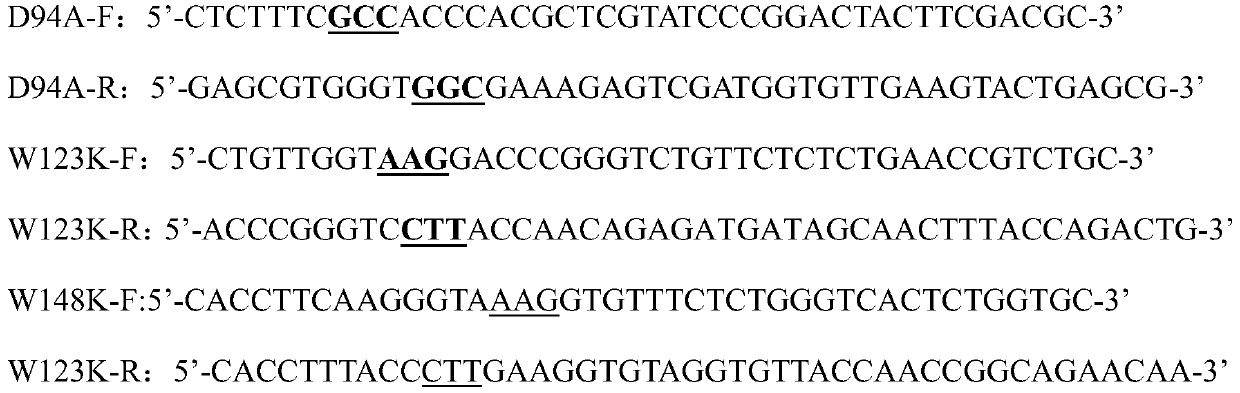Patents
Literature
32 results about "Diaminopimelic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
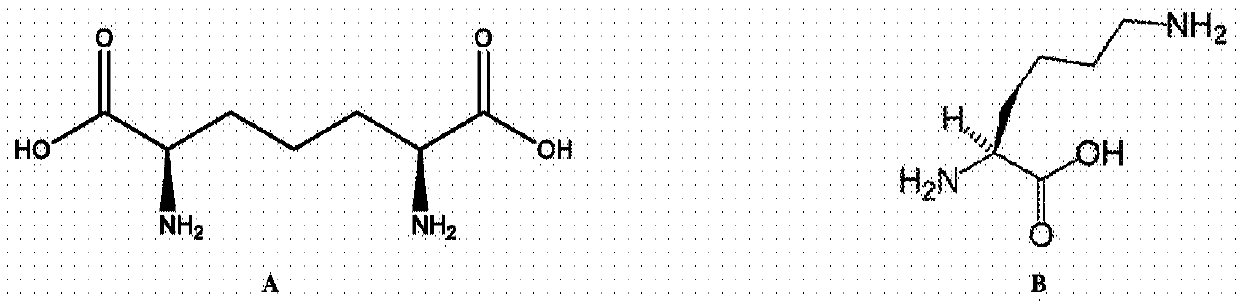
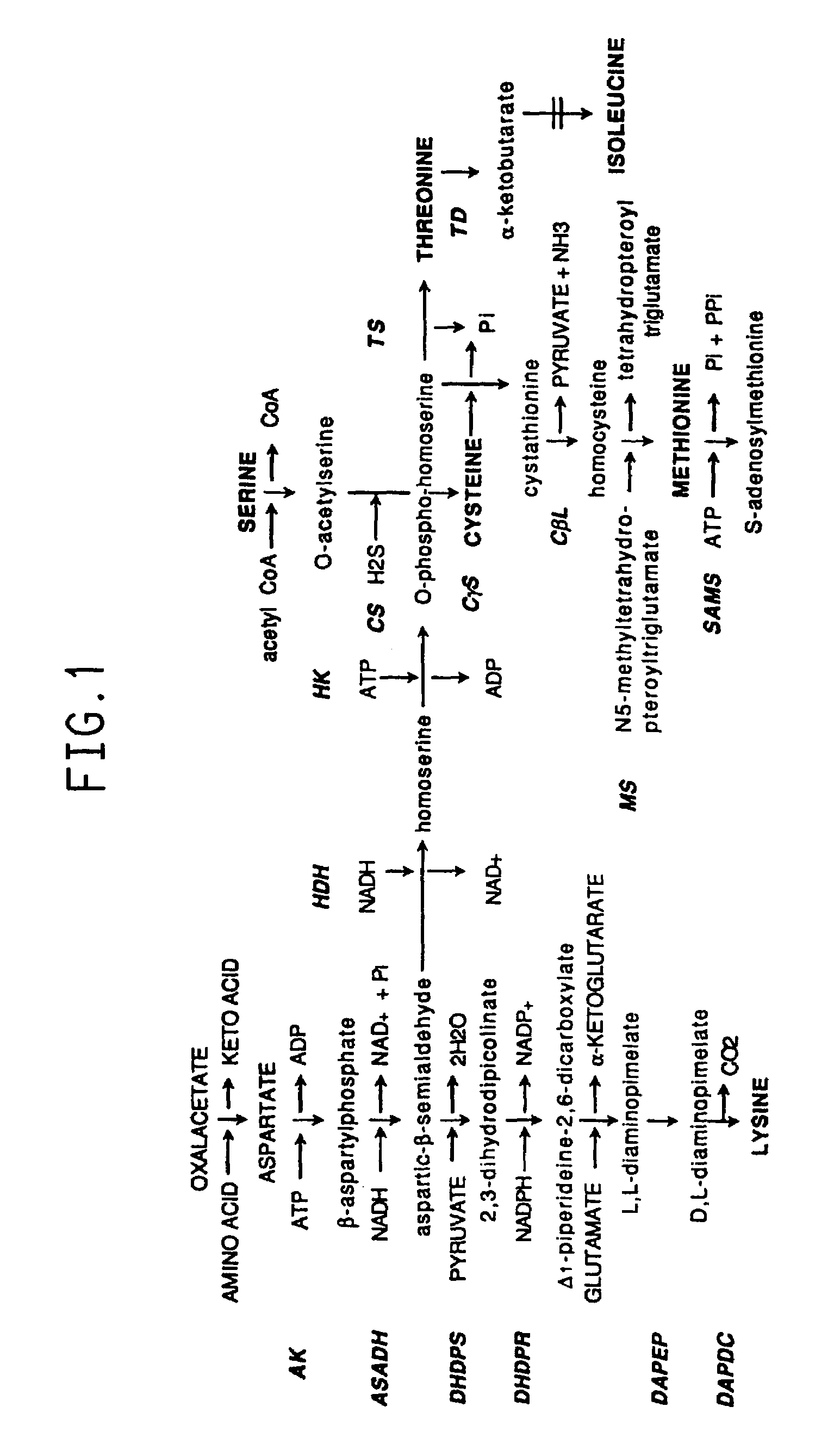
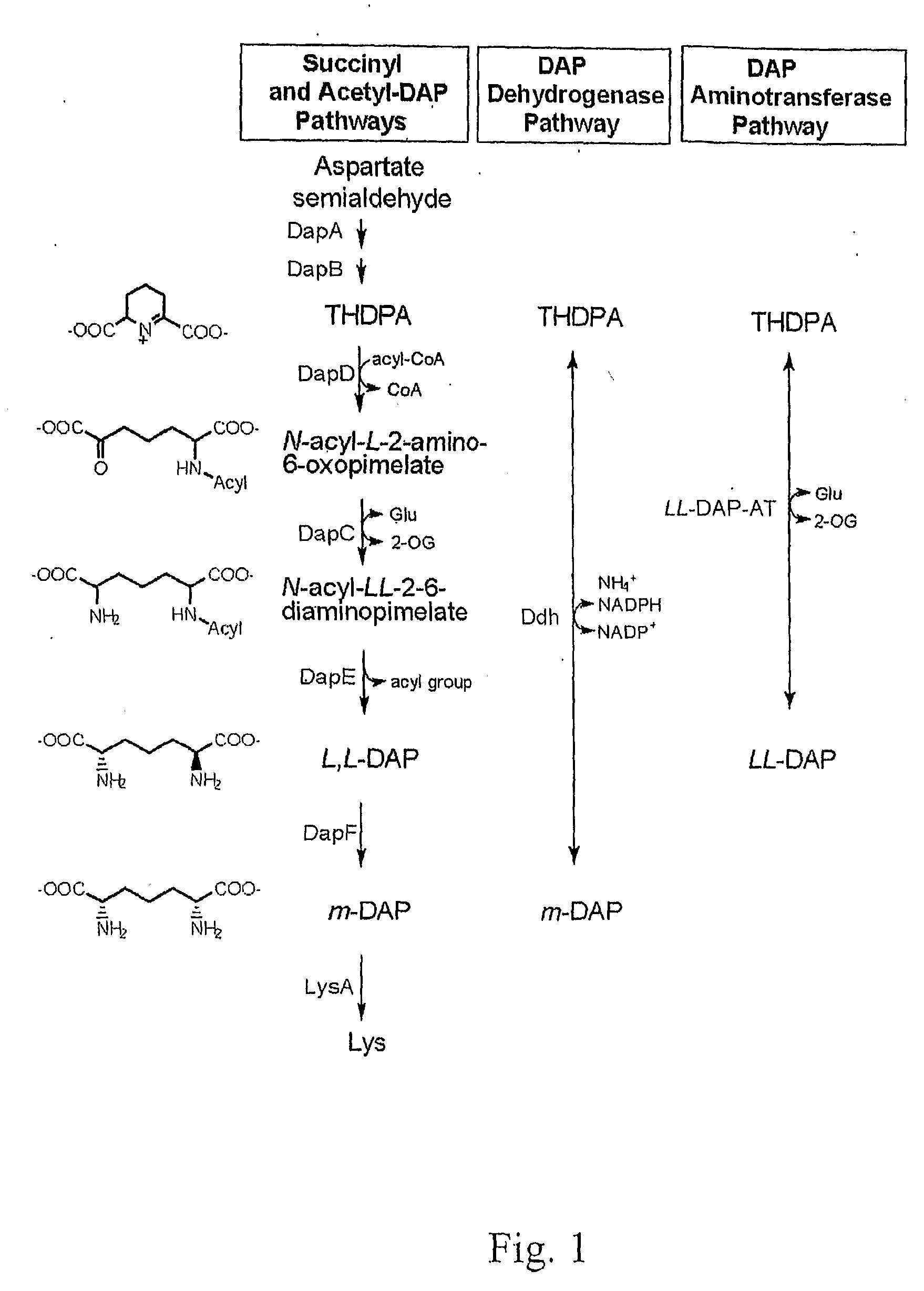
Diaminopimelic acid (DAP) is an amino acid, representing an epsilon-carboxy derivative of lysine. DAP is a characteristic of certain cell walls of some bacteria. DAP is often found in the peptide linkages of NAM-NAG chains that make up the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria. When provided, they exhibit normal growth. When in deficiency, they still grow but with the inability to make new cell wall peptidoglycan.
Antibiosis streptomycete
InactiveCN101463332AHigh activityFunction increaseBiocideBacteriaIntellectual propertyField experiment
The invention relates to an antibiotic streptomyces, fermentation product of which can inhibit broad spectrum fungus and protozoan, and field experiment can control crop fungus plant disease and root-knot nematode. The antibiotic streptomyces has good effect, no pollution nuisance and no residue. The antifungal agent has extremely low hazardness for the people and good performance and development prospect for medical and agricultural use. The invention is named as SIM001 antibiotic streptomyces which is Streptomyces antibioticus subspecies xi an, and is preserved as patent in the depositary institution appointed by patent office of state intellectual property office; the preservation data is April 14th, 2005, the name of the depositary institution is CGMCC, and the number of preservation is CGMCC No.1349. The whole cell hydrolysate of the antibiotic streptomyces contains L, L-DAP (Diaminopimelic acid) and no characteristic glucide; the cytoderm belongs to I type and glucide type C; one of the main antibacterial materials is polyene macrocyclic ketolide which belongs to the broad spectrum antifungal substance.
Owner:刘昶志
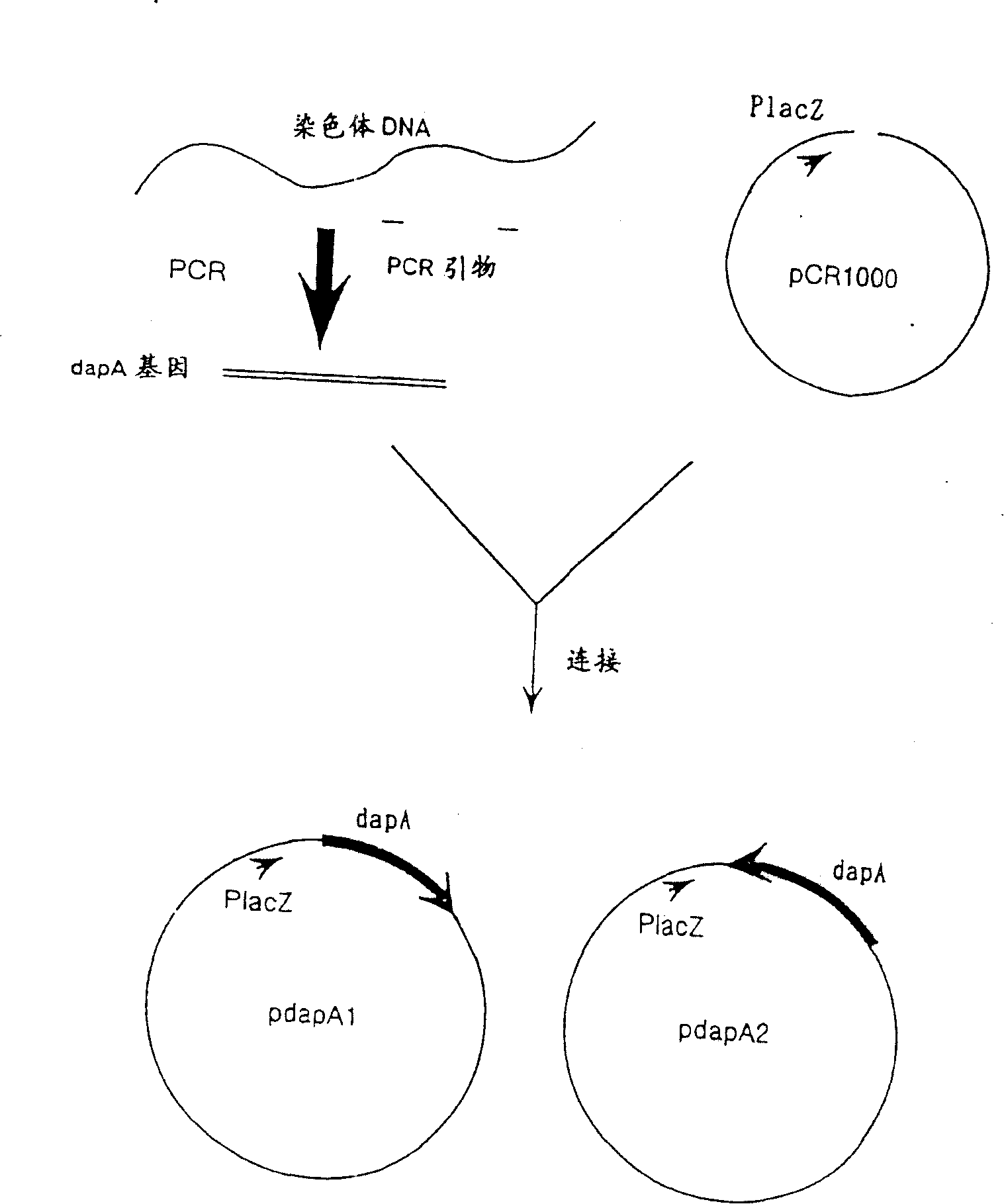
Recombinant escherichia coli and application to synthesis of tetrahydropyrimidine
InactiveCN109182236AHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideRecombinant escherichia coli
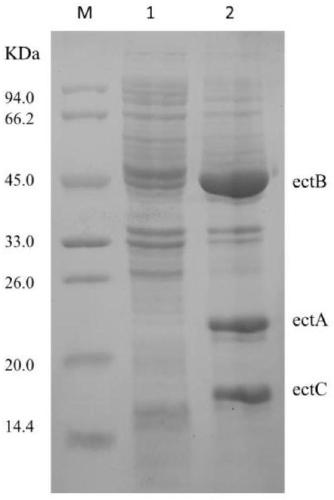
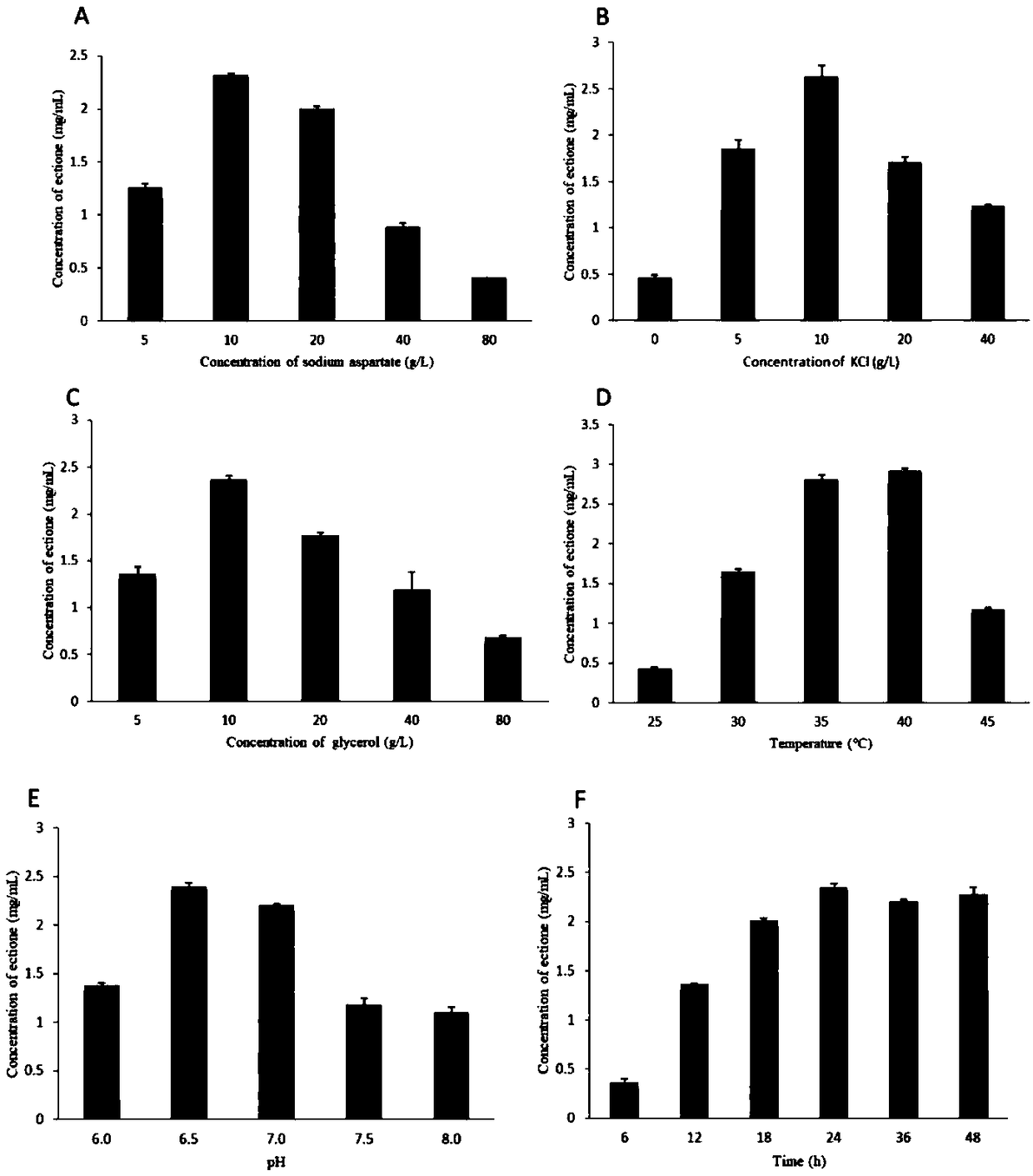
The invention provides recombinant escherichia coli and application to synthesis of tetrahydropyrimidine. The recombinant escherichia coli is obtained by knocking out a diaminapimelate decarboxylase lysA gene of escherichia coli E.coli MG1655 and introducing a tetrahydropyrimidine synthetic gene luster ectABC with a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. The nucleotide sequence of the diaminapimelate decarboxylase lysA gene is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. A thallus subjected to induced expression takes L-sodium aspartate as a substrate and the substrate is biologically converted to prepare the tetrahydropyrimidine. After conversion is carried out for 20 to 30h, the yield of the tetrahydropyrimidine reaches 2.5 to 3.5g / L, and therefore, the recombinant escherichia coli has relatively good industrial application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for production of L-lysine
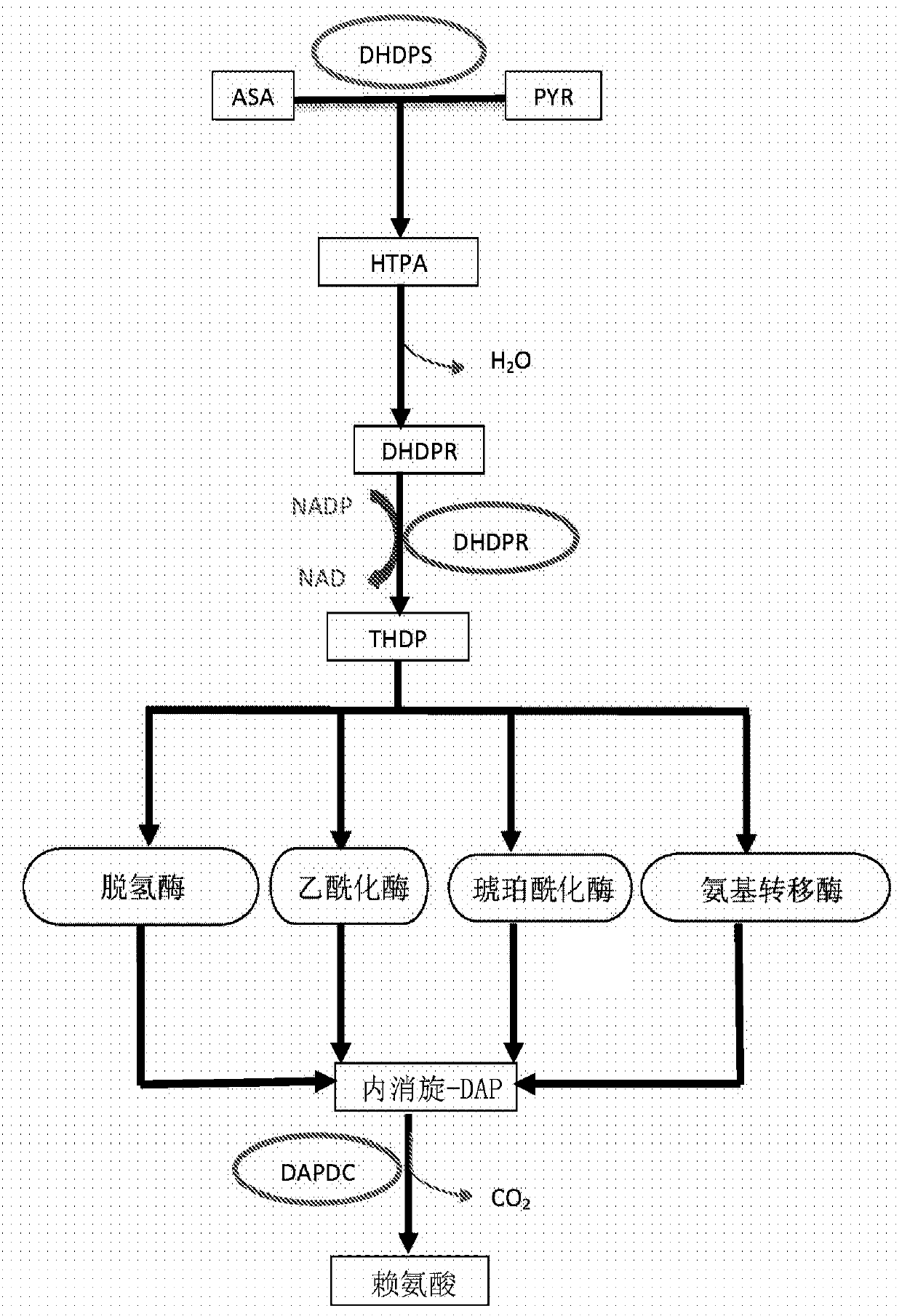
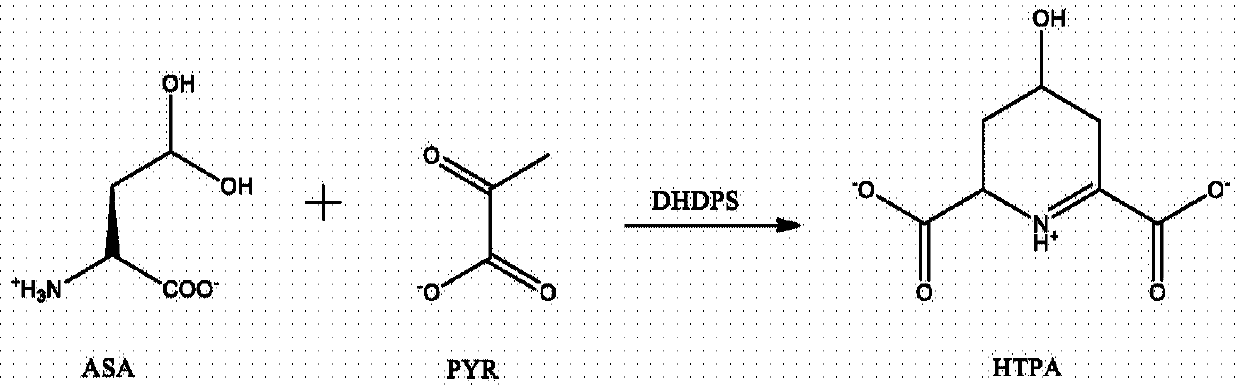
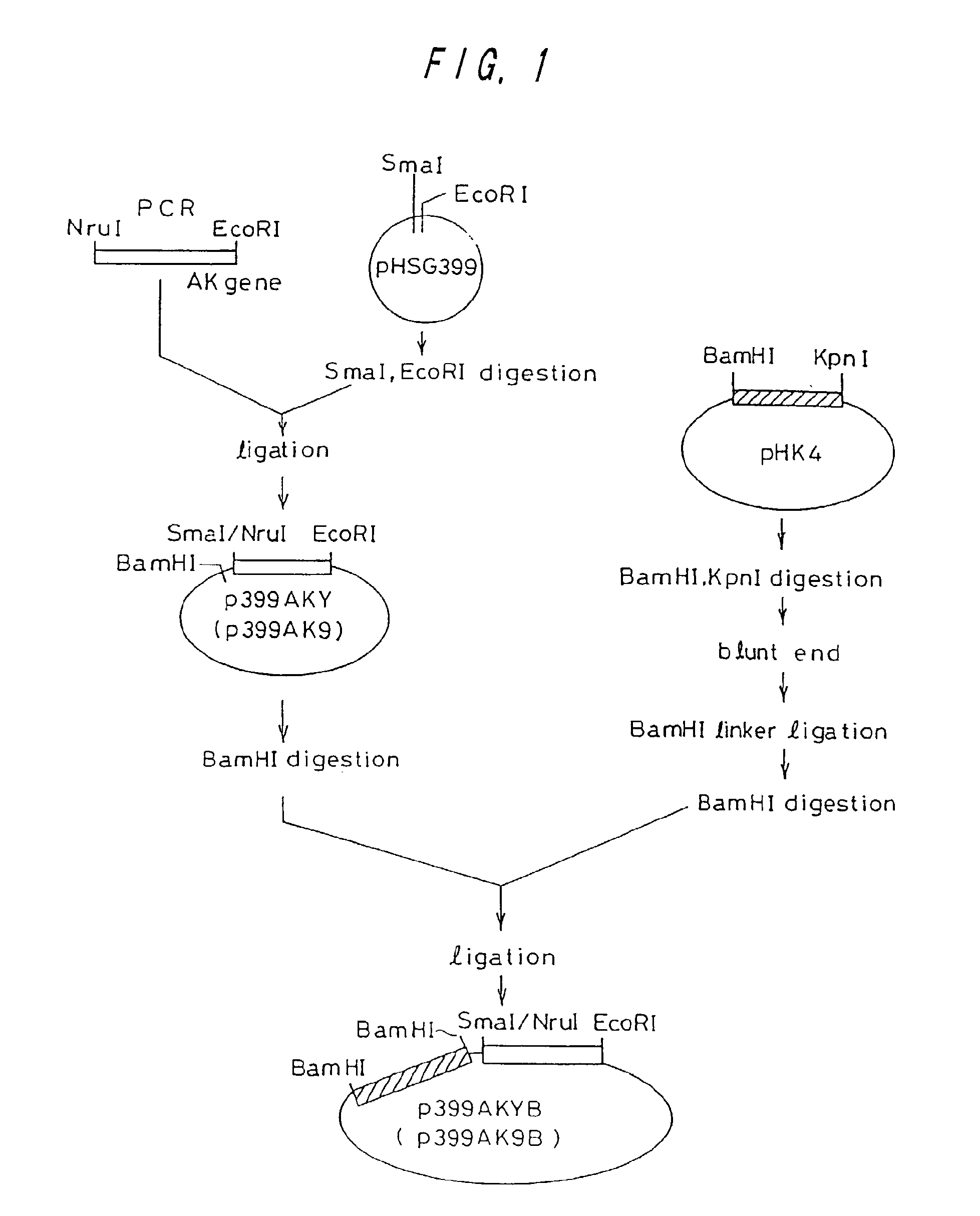
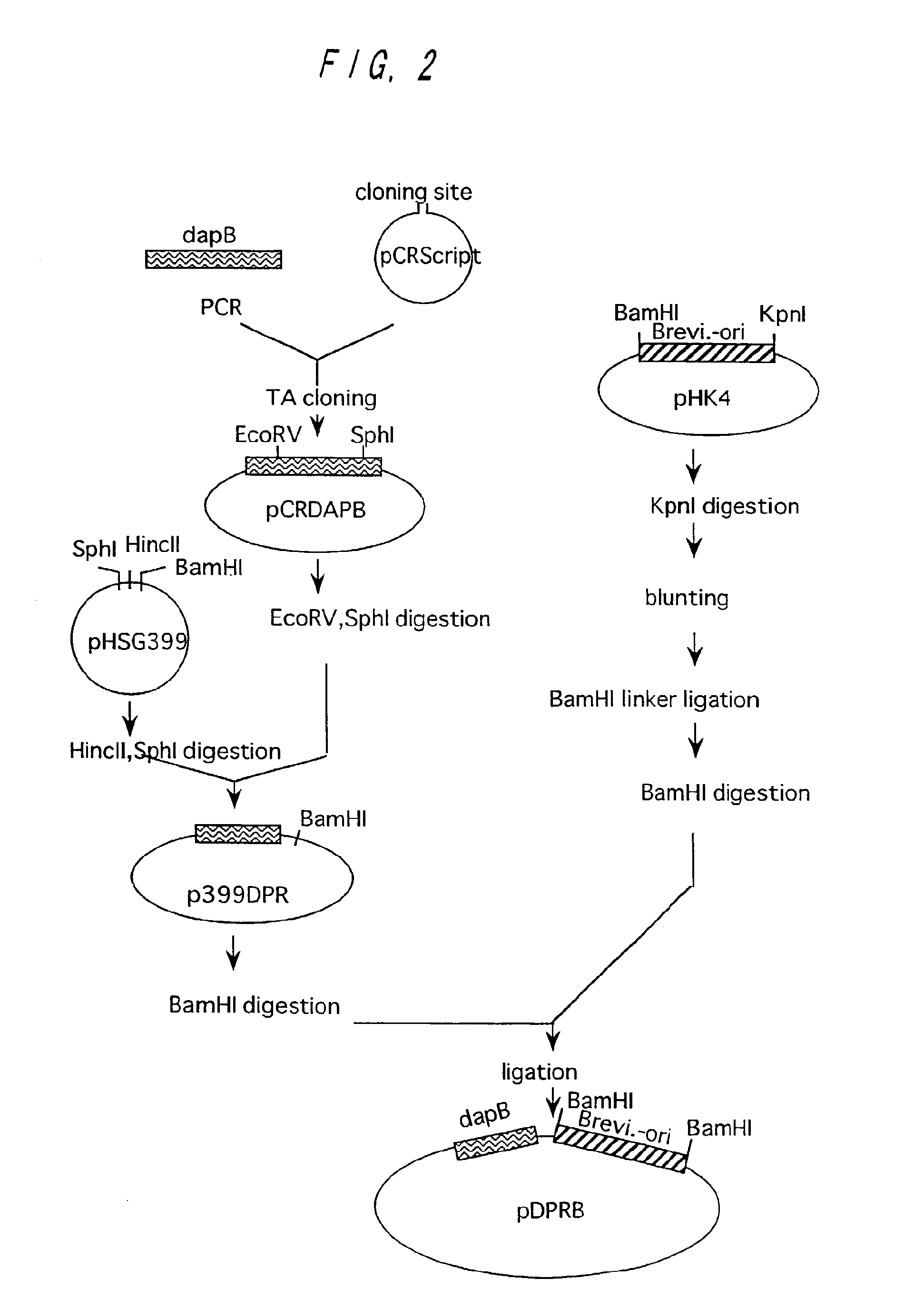
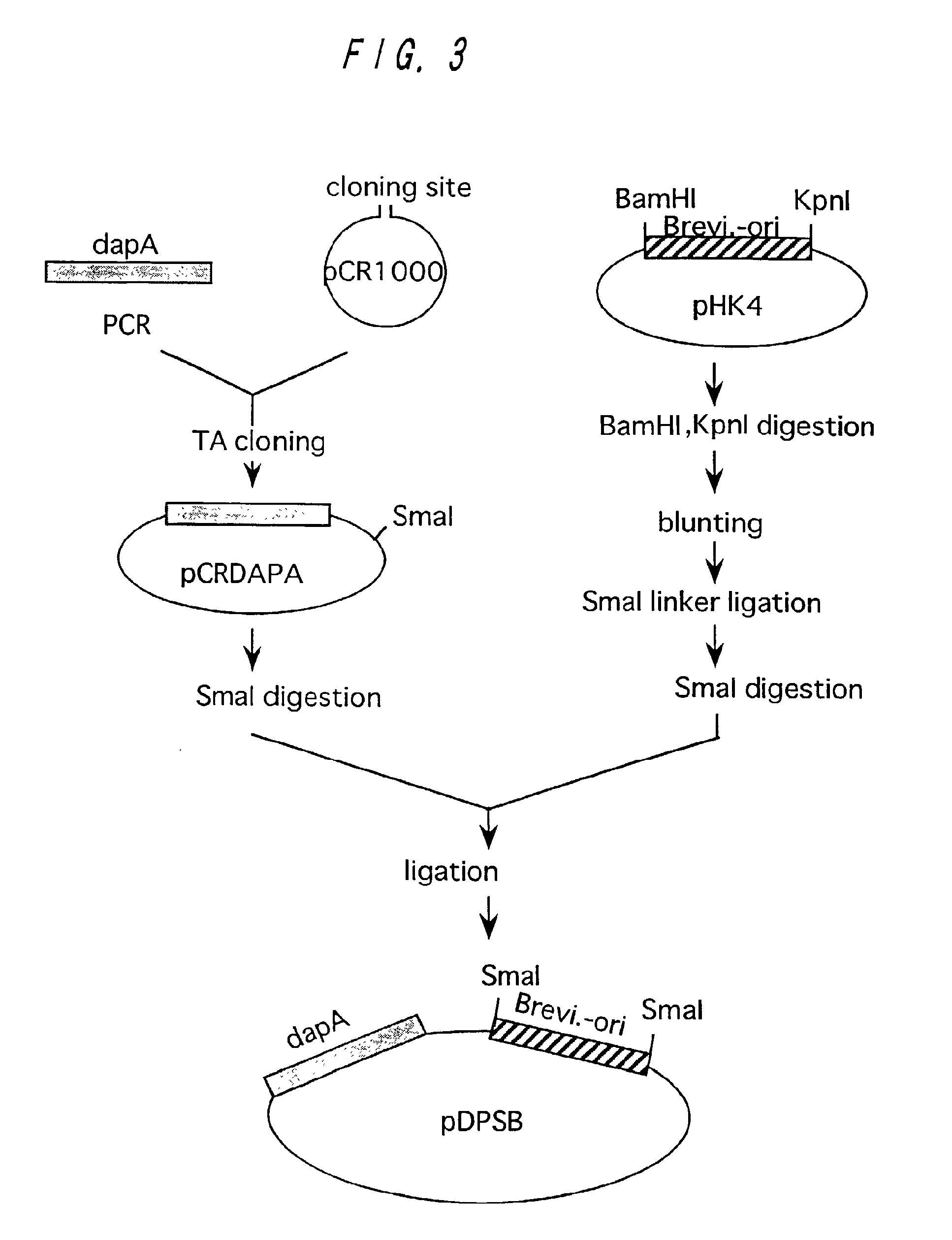
L-lysine can be produced by culturing an Escherichia coli cell in a culture medium, and collecting L-lysine from the culture medium, wherein the Escherichia coli cell is capable of producing L-lysine, is so modified that the activities of one or more enzymes involved in the synthetic pathway of meso-a,e-diaminopimelic acid (e.g., 2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine-2,6-dicarboxylate N-succinyltransferase, succinyldiaminopimelate transaminase, succinyldiaminopimelate desuccinylase, diaminopimelate epimerase) are decreased, and has a gene encoding diaminopimelate dehydrogenase introduced therein.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Ornamental plant cultivation medium, bottled ornamental plant and preparation method of bottled ornamental plant
InactiveCN106069764APromote rootingDoes not hinder growthHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGrowth plantKanamycin
The invention is applicable to the technical field of plant cultivation, and provides an ornamental plant cultivation medium, a bottled ornamental plant and a preparation method of the bottled ornamental plant. A formula of the ornamental plant cultivation medium is as follows: a 1 / 2MS cultivation medium is used as a basic material, meanwhile 1.8-2.3 g / L of agar, 7-9 g / L of phytagel, 48-53 mg / L of diaminopimelic acid, 9.5-10.5 [mu]mol / L of PQQ and 23-26 mg / L of kanamycin are added, and then the pH value of the ornamental plant cultivation medium is adjusted to be 6.5-6.9. The provided cultivation medium can be used for accelerating plant growth, is also relatively firm, is suitable for long-time plant growth, and is particularly suitable for being used as the cultivation medium of the bottled ornamental plant; the plant is relatively vigorous in growth, relatively strong in stability, better in ornamental value and longer in growth cycle.
Owner:WUHAN ZHONGKE HAOYU SCI & TECH
Process for the production of beta-lysine
InactiveCN101400799AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseTransketolase
Process for the production of -lysine by constructing a recombinant microorganism which has a deregulated lysine 2,3-aminomutase gene and at least one deregulated gene selected from the group (i) which consists of aspartokinase, aspartatesemialdehyde dehydrogenase, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydrodipicolinate reductase, tetrahydrodipicolinate succinylase, succinyl-amino-ketopimelate transaminase, succinyl-diamino-pimelate desuccinylase, diaminopimelate epimerase, diaminopimelate dehydrogenase, arginyl-tRNA synthetase, diaminopimelate decarboxylase, pyruvate carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, transketolase, transaldolase, 6-phosphogluconolactonase, fructose 1,6-biphosphatase, homoserine dehydrogenase, phophoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, succinyl-CoA synthetase, methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, provided that if aspartokinase is deregulated as gene (i) at least a second gene (i) other than aspartokinase has to be deregulated, and cultivating said microorganism.
Owner:BASF SE
Process for the production of beta-lysine
InactiveUS20090029425A1FermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseTransketolase
Process for the production of -lysine by constructing a recombinant microorganism which has a deregulated lysine 2,3-aminomutase gene and at least one deregulated gene selected from the group (i) which consists of aspartokinase, aspartatesemialdehyde dehydrogenase, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydrodipicolinate reductase, tetrahydrodipicolinate succinylase, succinyl-amino-ketopimelate transaminase, succinyl-diamino-pimelate desuccinylase, diaminopimelate epimerase, diamino-pimelate dehydrogenase, arginyl-tRNA synthetase, diaminopimelate decarboxylase, pyruvate carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, transketolase, transaldolase, 6-phosphogluconolactonase, fructose 1,6-biphosphatase, homoserine dehydrogenase, phophoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, succinyl-CoA synthetase, methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, provided that if aspartokinase is deregulated as gene (i) at least a second gene (i) other than aspartokinase has to be deregulated, and cultivating said microorganism.
Owner:BASF AG
Salmonella choleraesuis double-gene-deletion strain free of resistance marker and application thereof
InactiveCN102732442AImprove securityClear genetic backgroundBacteriaMicroorganism based processesVirulent characteristicsExogenous antigen
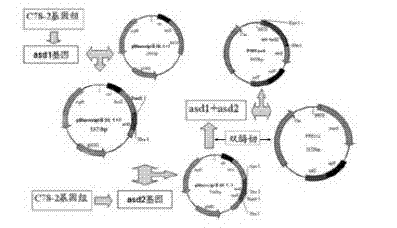
The invention relates to a Salmonella choleraesuis double-gene-deletion strain free of a resistance marker, Salmonella choleraesuis C7822 (with an accession number of CCTCC NO: M2011402 ). The strain is obtained by carrying out deletion of the asd gene, one of the important nutrition and metabolism genes of Salmonella choleraesuis, on Salmonella choleraesuis C7821 (with an accession number of CCTCC NO: M2010102 ) which has undergone deletion of the crp virulence gene. The gene-deletion strain C7822 loses the capability of synthesizing diaminopimelic acid (DAP), so the strain cannot survive in a DAP negative environment. After plasmids containing the asd gene are transformed into C7822, the asd gene in the plasmids can form a complementary gene with C7822, which enables C7822 to regain the capability of surviving in a DAP negative environment. The double-gene-deletion strain C7822 obtained in the invention has distinct genetic background, strong security and no resistance marker and can stably carry and express exogenous antigens; the double-gene-deletion strain is a good carrying vector and expression strain for exogenous antigens and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Compounds and methods for the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory disease
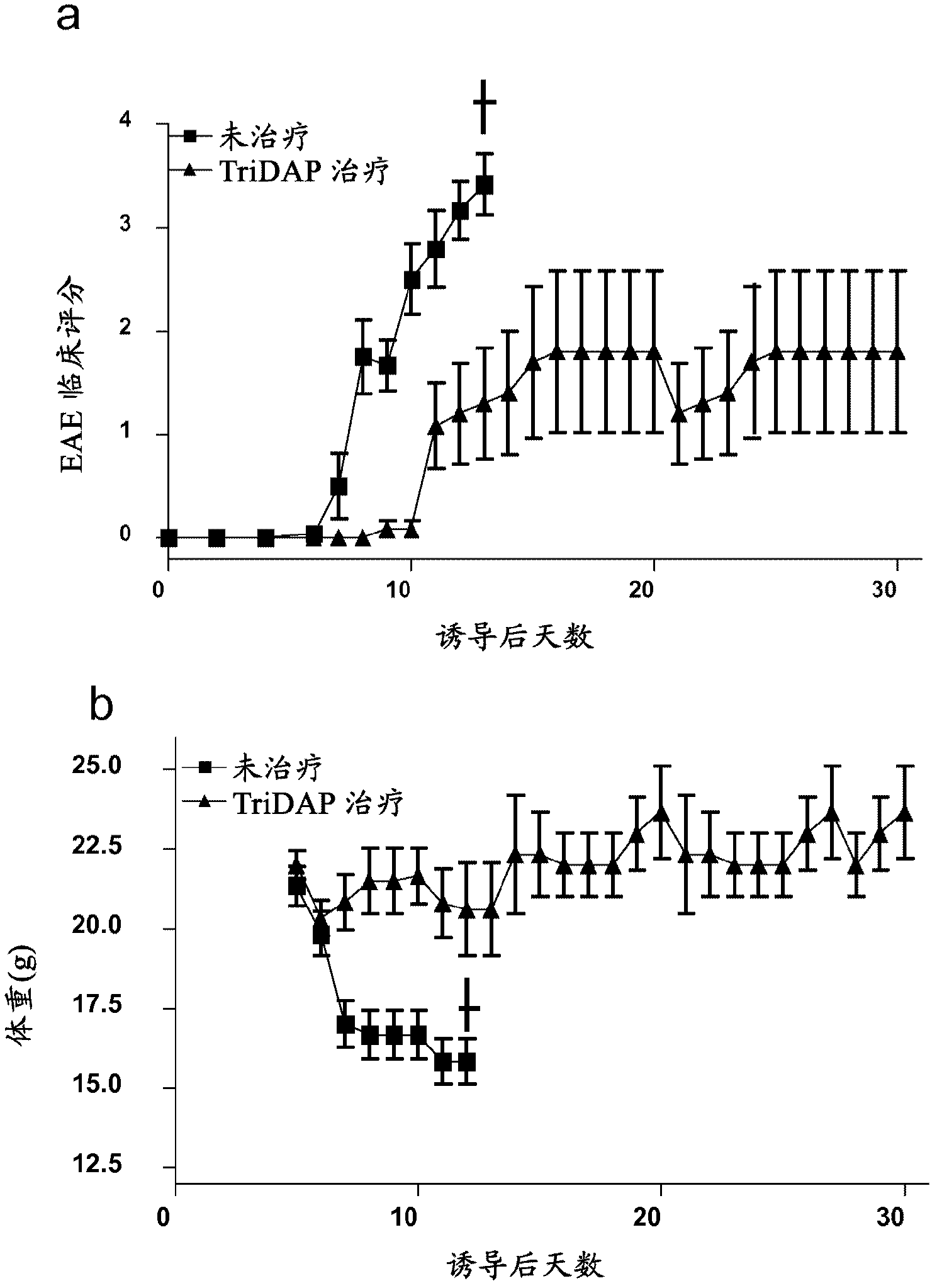
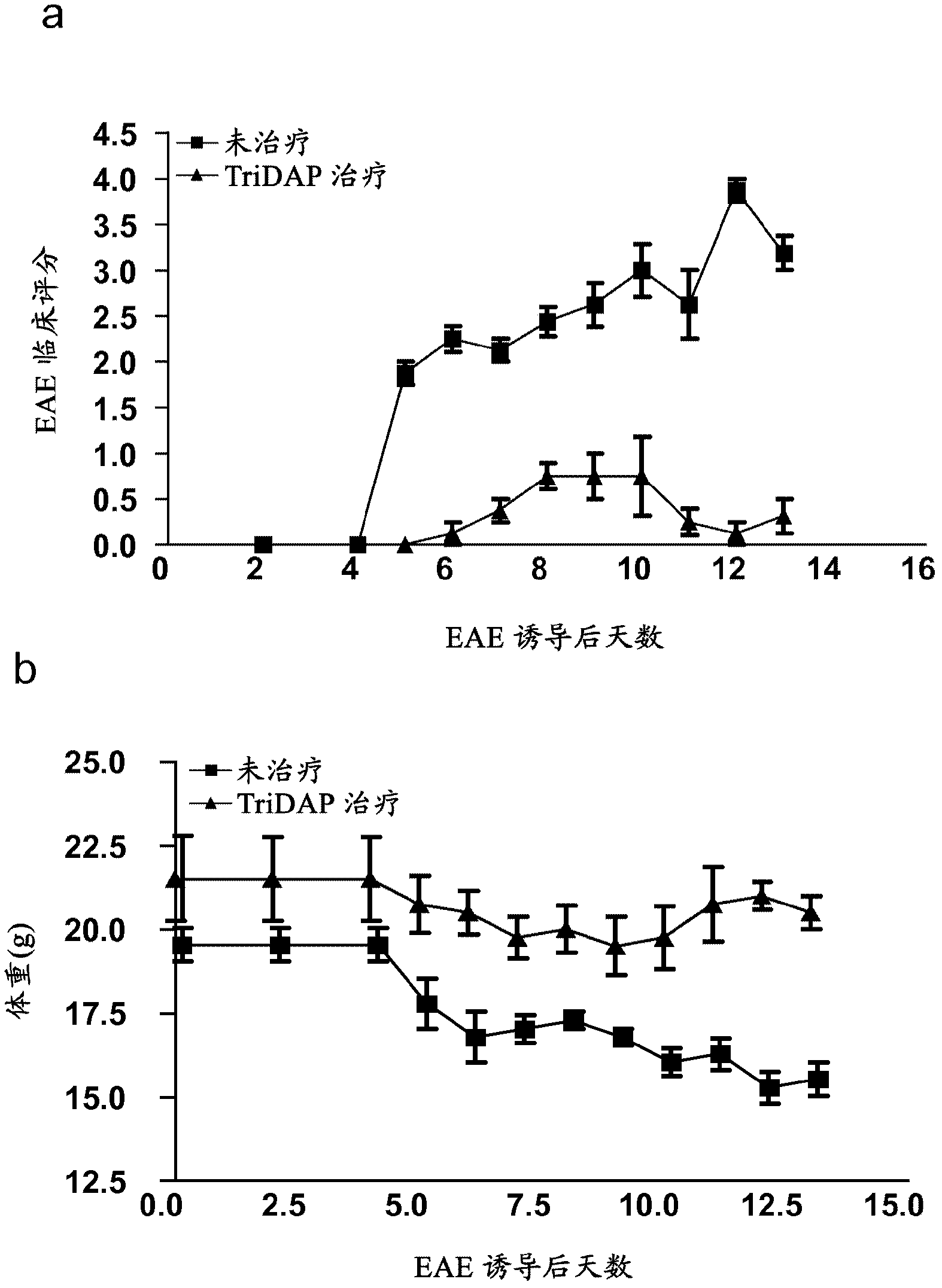
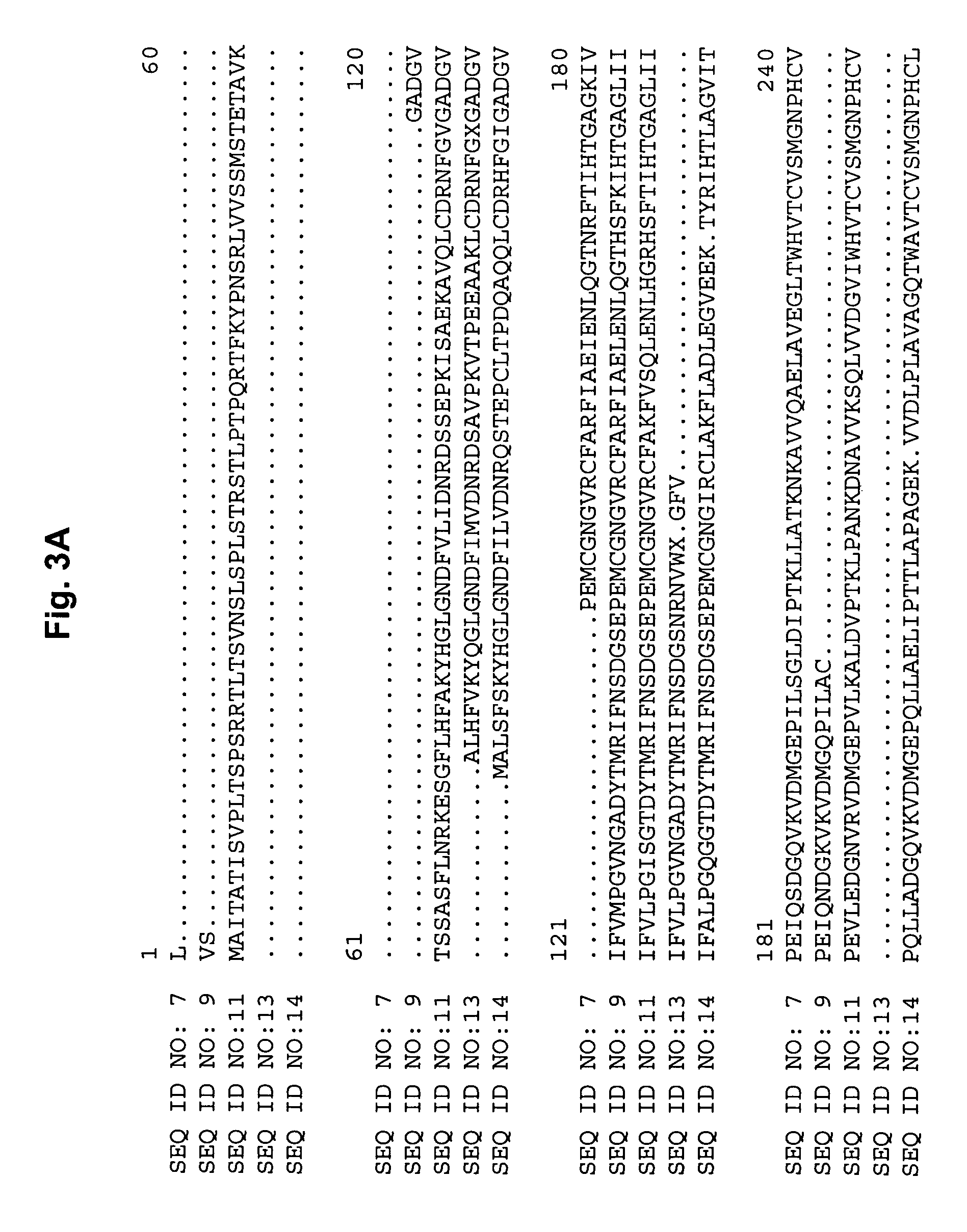
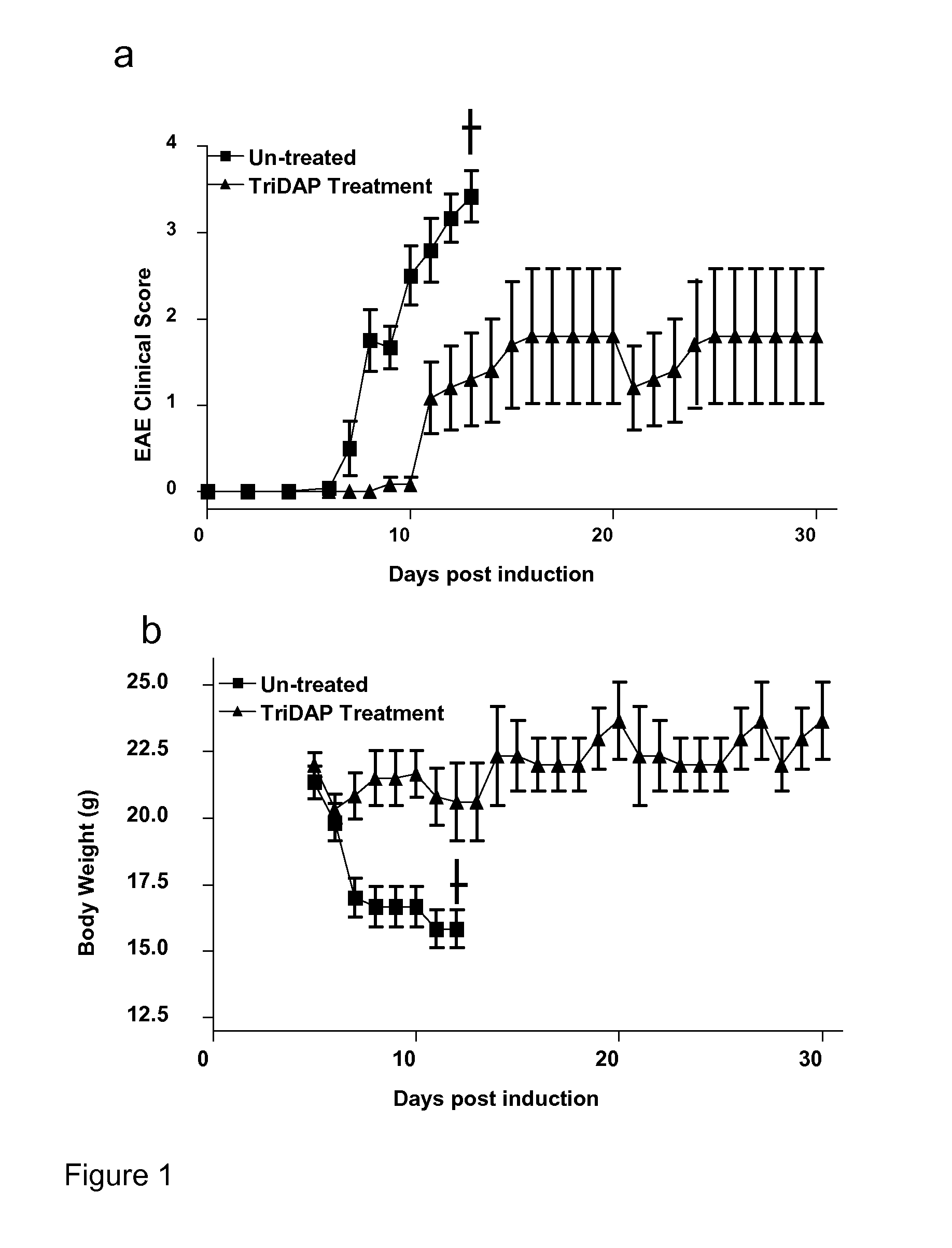
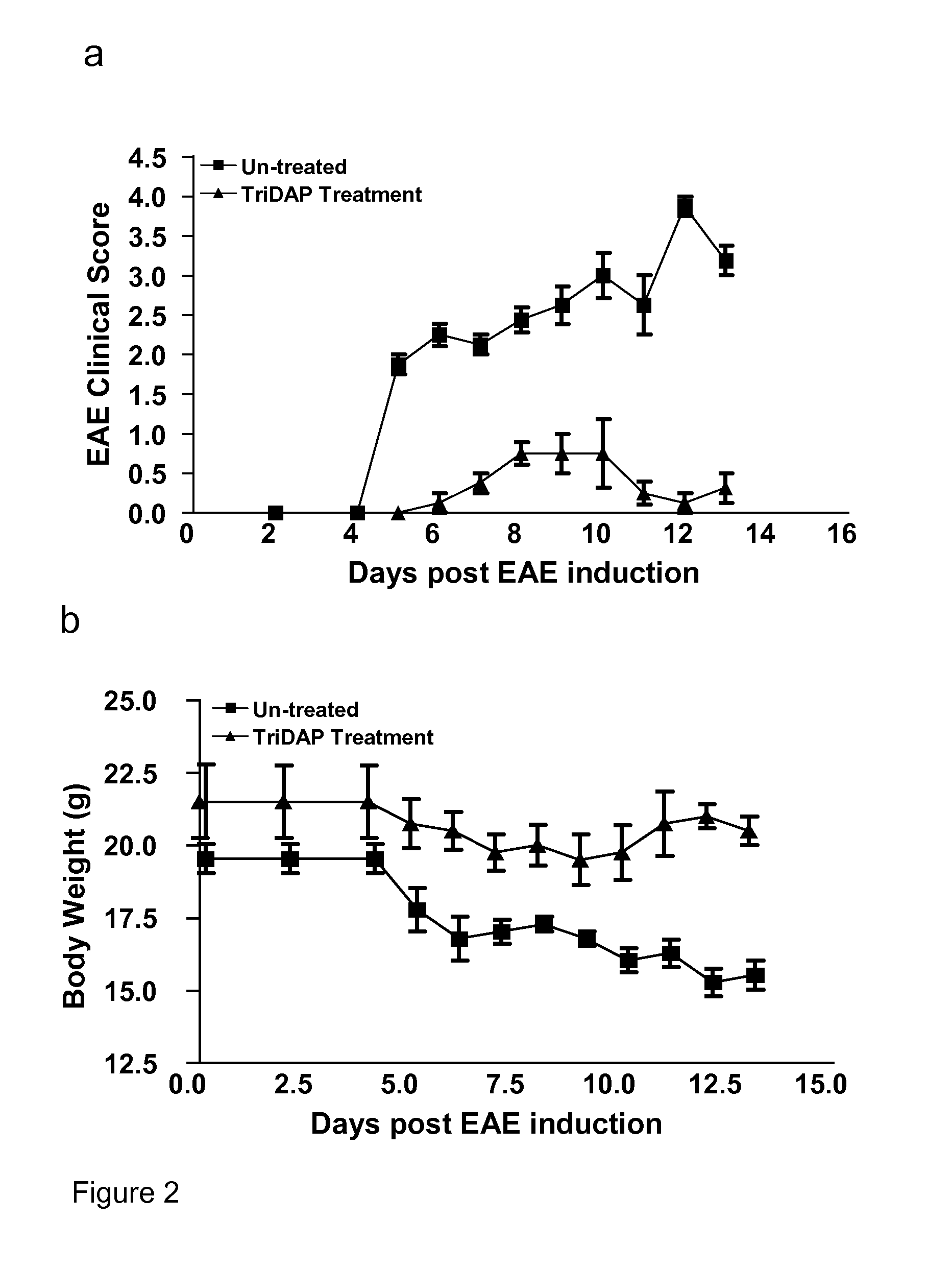
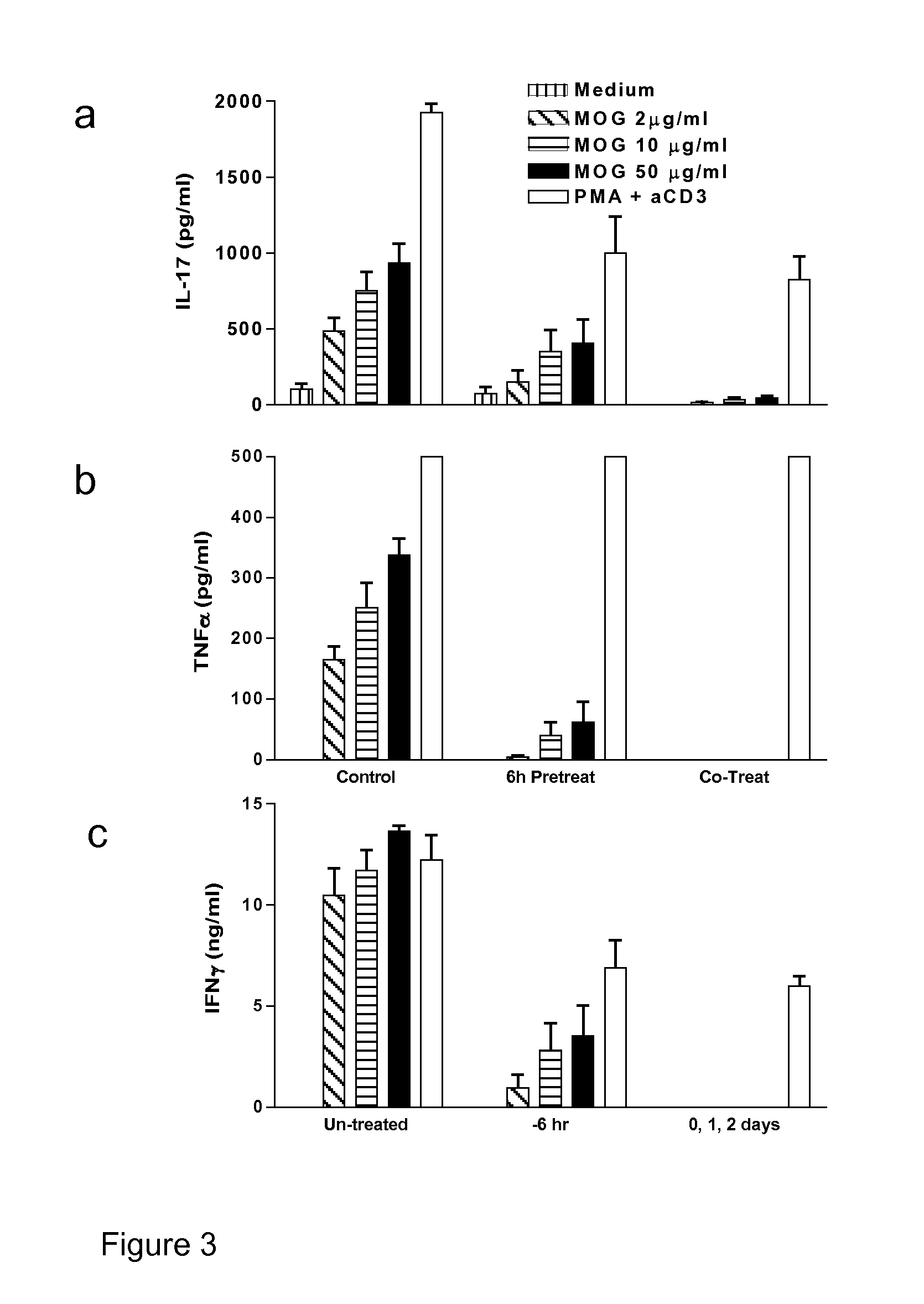
The present invention provides a method and composition for the treatment and prevention of an autoimmune disease such a multiple sclerosis which is mediated by autoreactive T cells. The administration of a NOD-1 agonist is shown to mediate an anti-inflammatory immune response. NOD-1 agonists suitable for use in the methods and compositions of the invention include diaminopimelic acid (DAP)-containing muropeptide compounds such as Tri-DAP and M-TriDAP.
Owner:都柏林伊丽莎白女皇神学院院长、研究员及专家协会
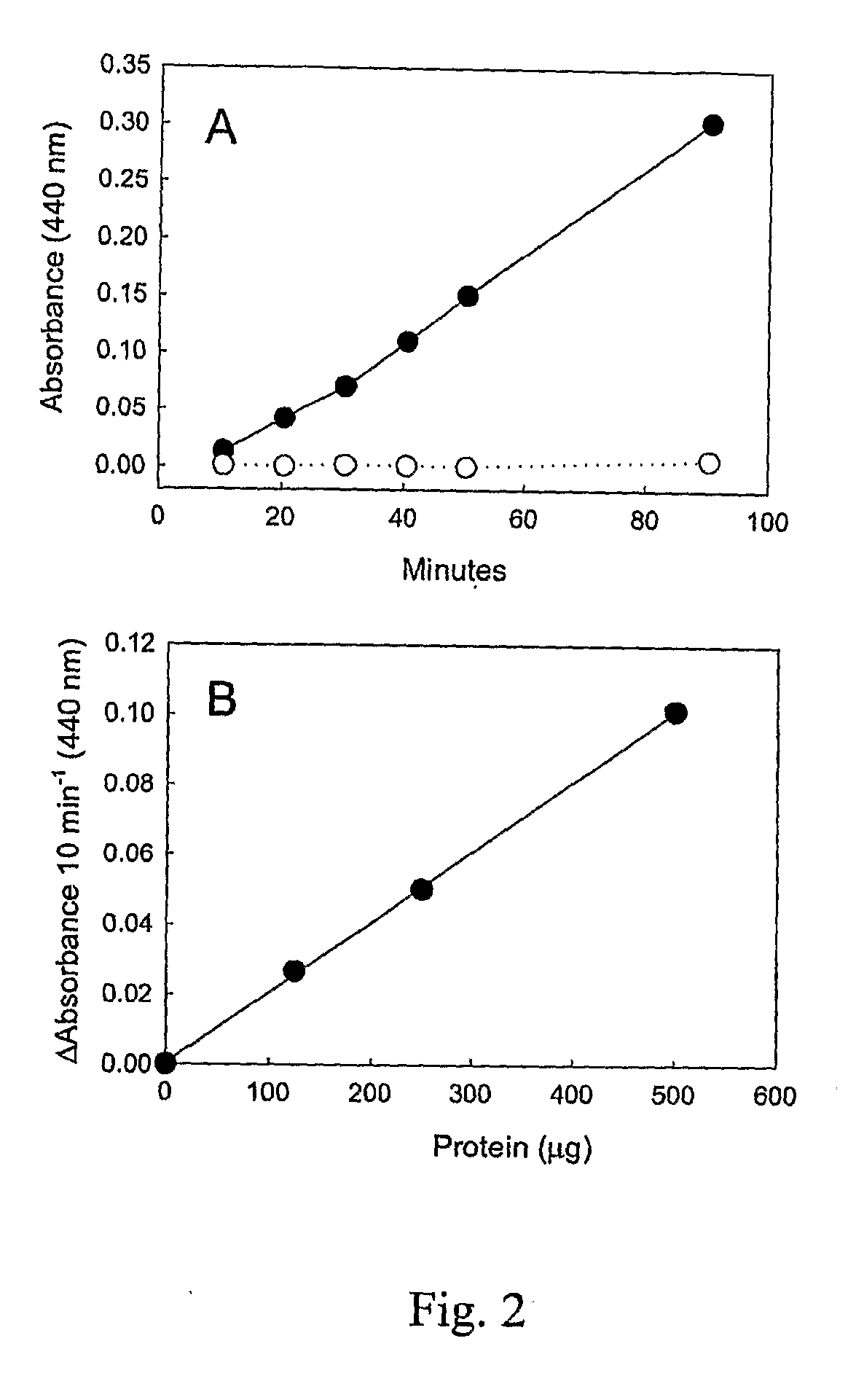
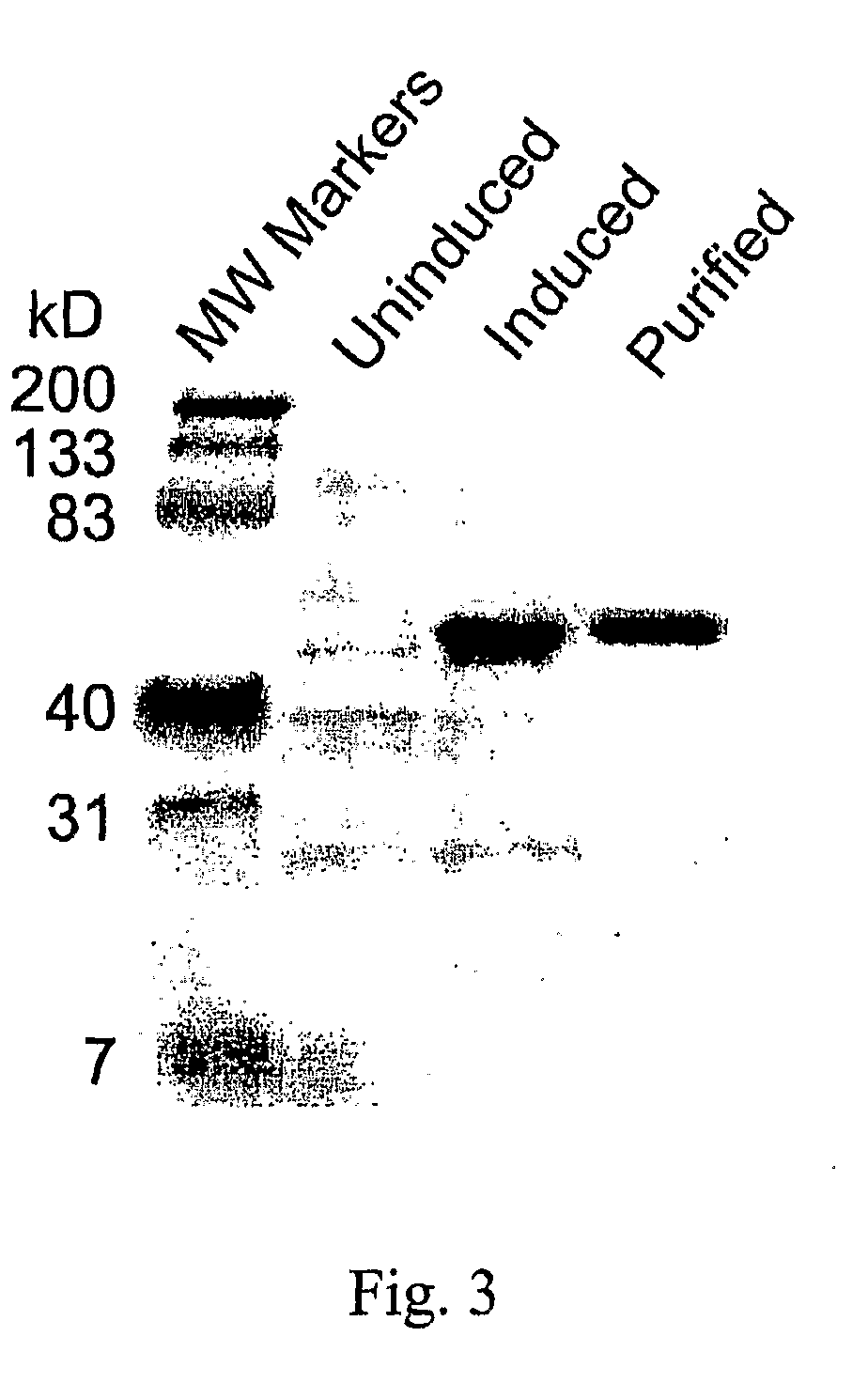
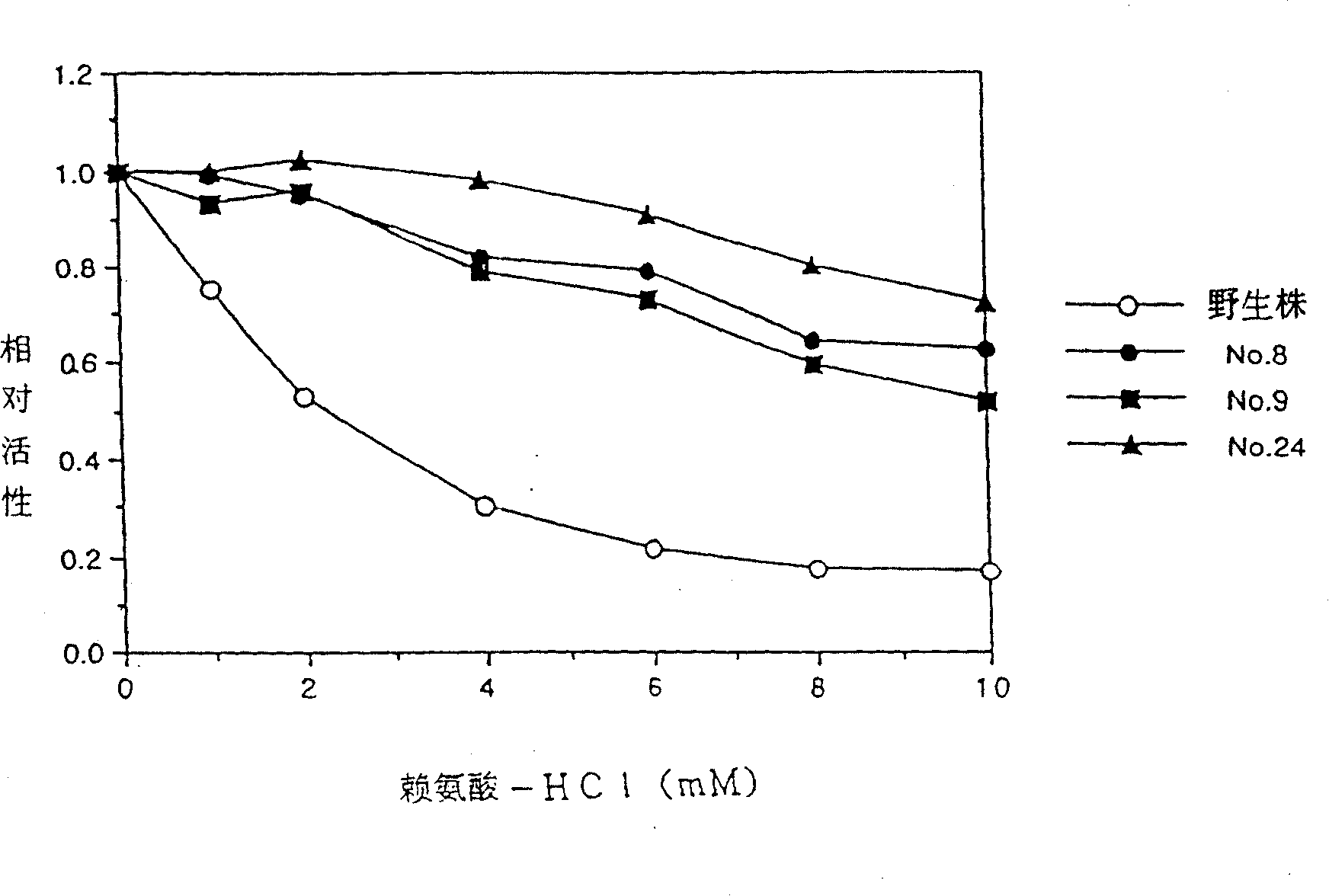
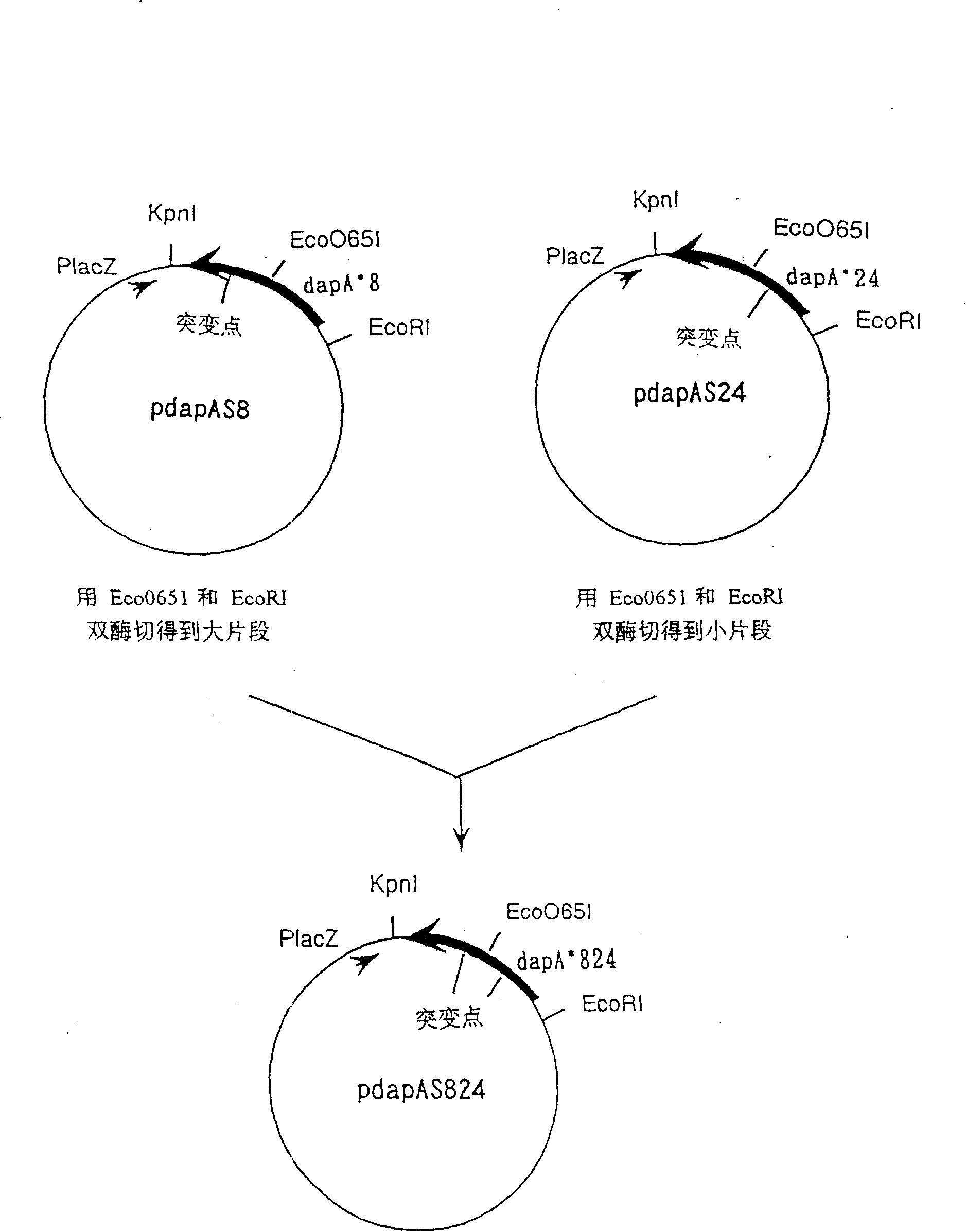
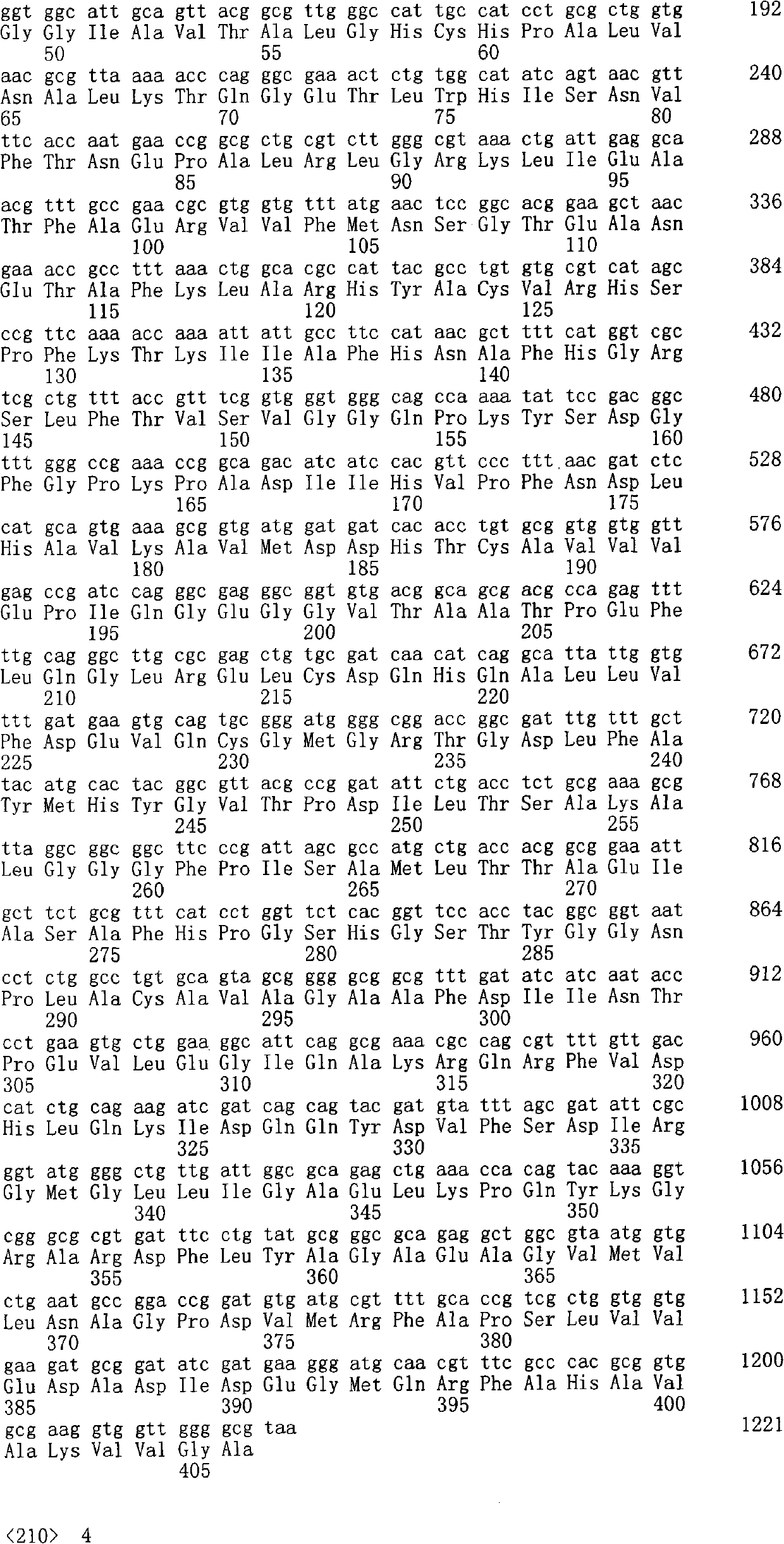
Meso-diaminopimelic acid dehydrogenase mutants with improved catalytic efficiency
ActiveCN110499301AHigh catalytic activityHigh catalytic efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMeso-diaminopimelic acid
The invention discloses meso-diaminopimelic acid dehydrogenase mutants with improved catalytic efficiency, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. According to the invention, single-site / double-site mutation is carried out on meso-diaminopimelic acid dehydrogenase shown as SEQ ID NO.2, and mutant enzymes D94A, W123K, D94A / W123K and W148K are successfully expressed and purified in escherichia coli. Enzyme activity measurement finds that the three meso-diaminopimelic acid dehydrogenase mutants have higher catalytic activity than the wild type, for example, the efficiencies of catalyzing phenylpyruvic acid by the mutant enzymes DAPDH-D94A, DAPDH-W123K and DAPDH-D94A / W123K are respectively improved by 3.5 times, 1.5 times and 1.3 times, and the enzyme activity of key enzymes issuccessfully improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Metabolite composition for pre-operative early warning of kidney delayed graft function of donor donated after cardiac death and screening method of compsition
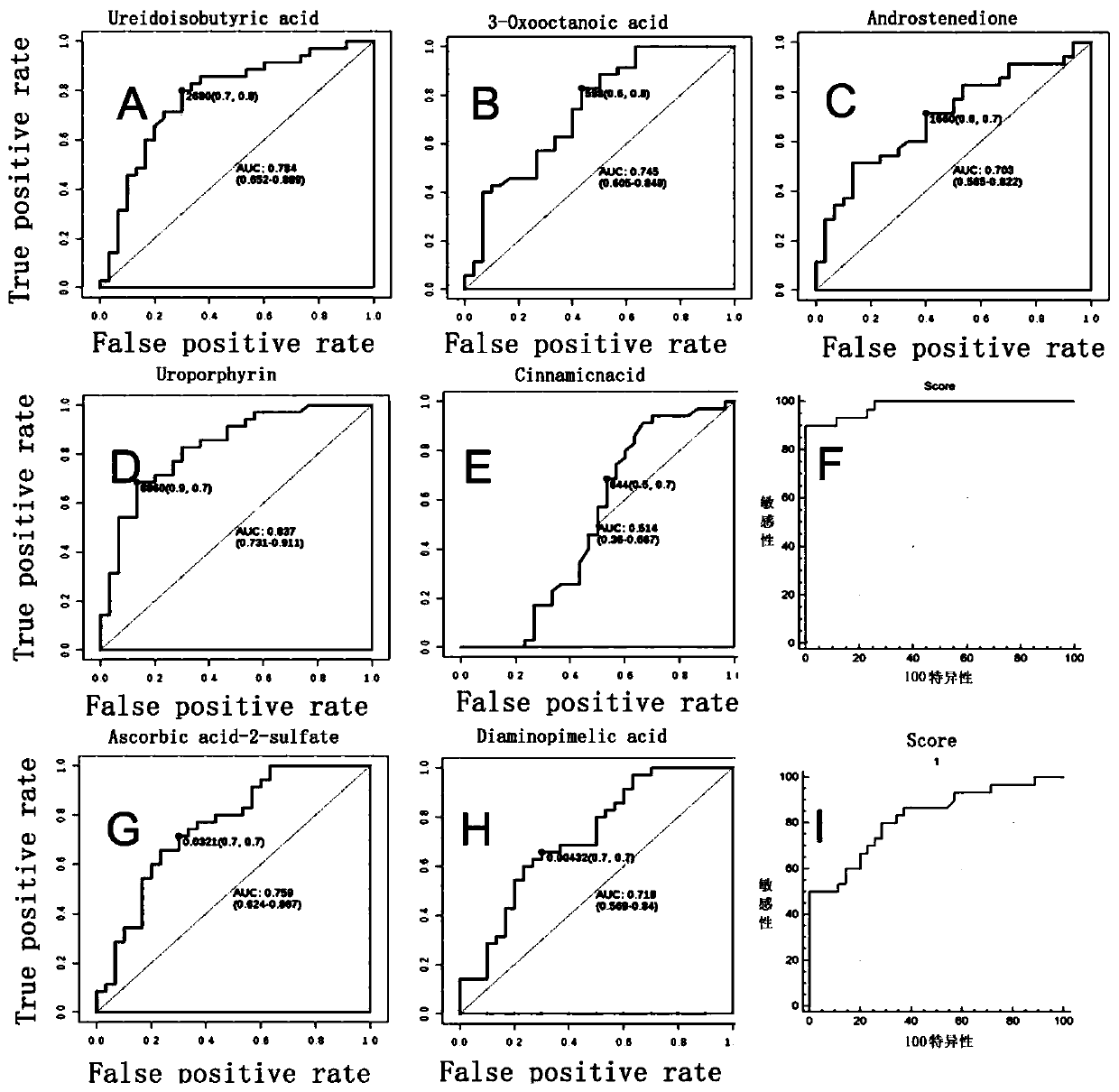
ActiveCN111060607AReduction of delayed recoveryComponent separationChemical machine learningPhysiologyMetabolome
The invention discloses a metabolic composition for pre-operative early warning of kidney delayed graft function of a donor donated after cardiac death. The metabolic composition is prepared from oneor more selected from seven metabolites including ascorbic acid, diaminopimelic acid, cinnamic acid, isobutyl-isobutyrate, androstenedione, 3-oxocaprylic acid and uroporphyrin. The invention further discloses a screening method of the metabolic composition. In the screened metabolic composition, the binding indication rate of ascorbic acid and diaminopimelic acid is 0.823, and the binding indication rate of cinnamic acid, isobutyl-isobutyrate, androstenedione, 3-oxocaprylic acid and uroporphyrin is 0.98.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Heterocyclic inhibitors of lysine biosynthesis via the diaminopimelate pathway
InactiveCN110621315AAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiaminopimelate biosynthesisDiaminopimelic acid pathway
The present invention relates to certain heterocyclic compounds of formula (1) that have the ability to inhibit lysine biosynthesis via the diaminopimelate biosynthesis pathway in certain organisms. As a result of this activity these compounds can be used in applications where inhibition of lysine biosynthesis is useful. Applications of this type include the use of the compounds as herbicides.
Owner:LA TROBE UNIVERSITY
Method of producing l-lysine
InactiveUS20110065153A1Improve the L-lysine-producing ability and the growth speed of a coryneform bacteriumImprove scalabilityBacteriaTransferasesDiaminopimelate decarboxylaseDiaminopimelate dehydrogenase
The ability and speed with which a coryneform bacterium can produce L-lysine are improved when the coryneform bacterium contains an aspartokinase in which feedback inhibition by L-lysine and L-threonine is substantially desensitized. This is accomplished by successively enhancing the DNA coding for dihydrodipicolinate reductase, the DNA coding for dihydrodipicolinate synthase, the DNA coding for diaminopimelate decarboxylase, and the DNA coding for diaminopimelate dehydrogenase.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Identification method of red nocardia cell wall skeleton
ActiveCN104111303AEasy to separateImprove reliabilityComponent separationMeso-diaminopimelic acidN-Butanol
The invention discloses an identification method of red norcardia cell wall skeleton. The method comprises the following steps: (1) sample spotting: using at least two silica-gel G thin-layer plates, spotting a proper amount of an alanine reference solution and a test sample solution on the first thin-layer plate; then spotting a proper amount of a meso-diaminopimelic acid reference solution and a test sample solution on the second thin-layer plate; (2) development: soaking the first thin-layer plate into a developing solvent composed of n-butanol-glacial acetic acid-water according to a volume ratio of 8:3:1, soaking the second thin-layer plate into a developing solvent composed of sodium dodecyl sulfate-n-butanol-n-hexane-water according to a volume ratio of 6:25:6:20; wherein the distance between the surface of the developing solvent to the bottom edge of the thin layer plate is in a range of 0.5 to 1.0 cm and the sample spots cannot be emerged by the developing solvent; sealing the top cover, when the developing solvent reaches the two thirds of the total length of the thin-layer plate, taking out the thin-layer plate, drying; (3) color developing; (4) observation. The identification method has the advantages of clear color development, high separation degree, and high reliability.
Owner:FUJIAN SHANHE PHARMA
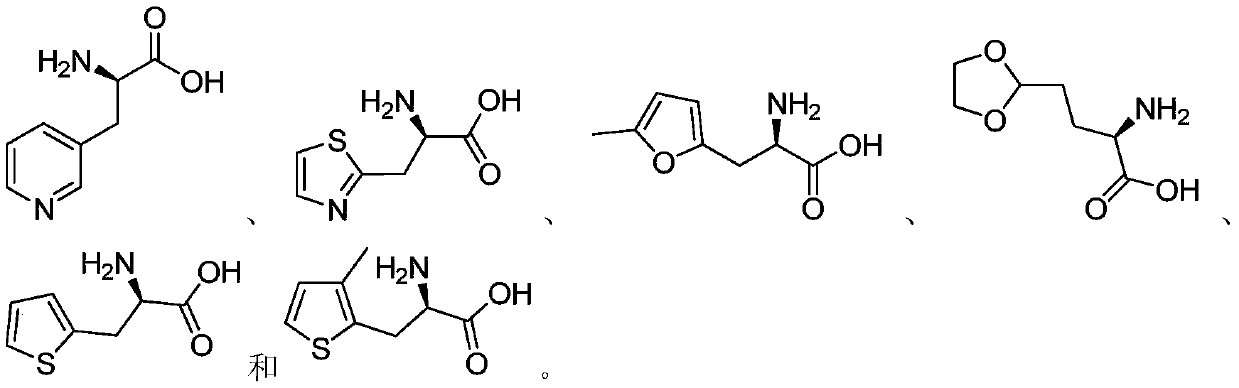
Synthetic method of D-heterocyclic amino acid, kit and application
ActiveCN108300744AImprove conversion rateHigh chiral purityFermentationChemical compoundDiaminopimelate dehydrogenase
The invention provides a synthetic method of D-heterocyclic amino acid, a kit and an application. The synthetic method comprises the step that a keto acid compound of D-heterocycles is transformed into D-heterocyclic amino acid by diaminopimelic acid dehydrogenase shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The keto acid compound of D-heterocycles is transformed into D-heterocyclic amino acid by diaminopimelic acid dehydrogenase, so that non-natural chiral amino acid with higher transformation rate and higher ee can be obtained, the synthetic method based on diaminopimelic acid dehydrogenase adopts stable technological conditions and mild reaction conditions, the whole production process is simple to operate, less pollution is produced, and one new way of thinking is provided for artificial synthesis of D-heterocyclic amino acid.
Owner:ASYMCHEM LAB TIANJIN +1
Plant amino acid biosynthetic enzymes
InactiveUS7022895B2Inhibitory activityBacteriaTransferasesAntisense OrientationS-Adenosyl-l-methionine
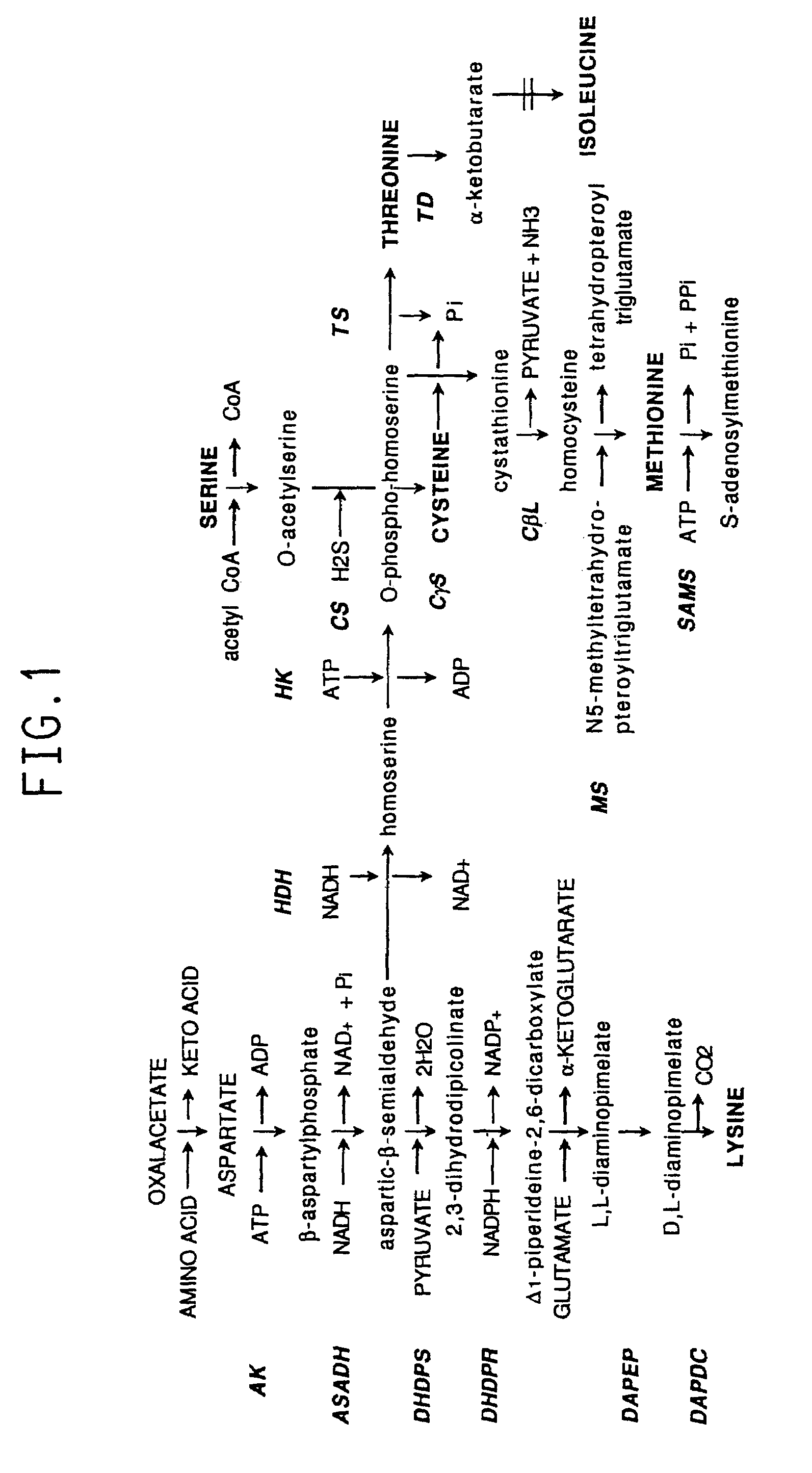
This invention relates to an isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a plant enzyme that catalyze steps in the biosynthesis of lysine, threonine, methionine, cysteine and isoleucine from aspartate, the enzyme a member selected from the group consisting of: dihydrodipicolinate reductase, diaminopimelate epimerase, threonine synthase, threonine deaminase and S-adenosylmethionine synthetase. The invention also relates to the construction of a chimeric gene encoding all or a portion of the enzyme, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the chimeric gene results in production of altered levels of the enzyme in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Compounds and methods for the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory disease
InactiveUS20110294736A1T cell activationAvoid excessive secretionNervous disorderAntipyreticAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
The present invention provides a method and composition for the treatment and prevention of an autoimmune disease such a multiple sclerosis which is mediated by autoreactive T cells. The administration of a NOD-1 agonist is shown to mediate an anti-inflammatory immune response. NOD-1 agonists suitable for use in the methods and compositions of the invention include diaminopimelic acid (DAP)-containing muropeptide compounds such as Tri-DAP and M-TriDAP.
Owner:TRINITY COLLEGE DUBLIN
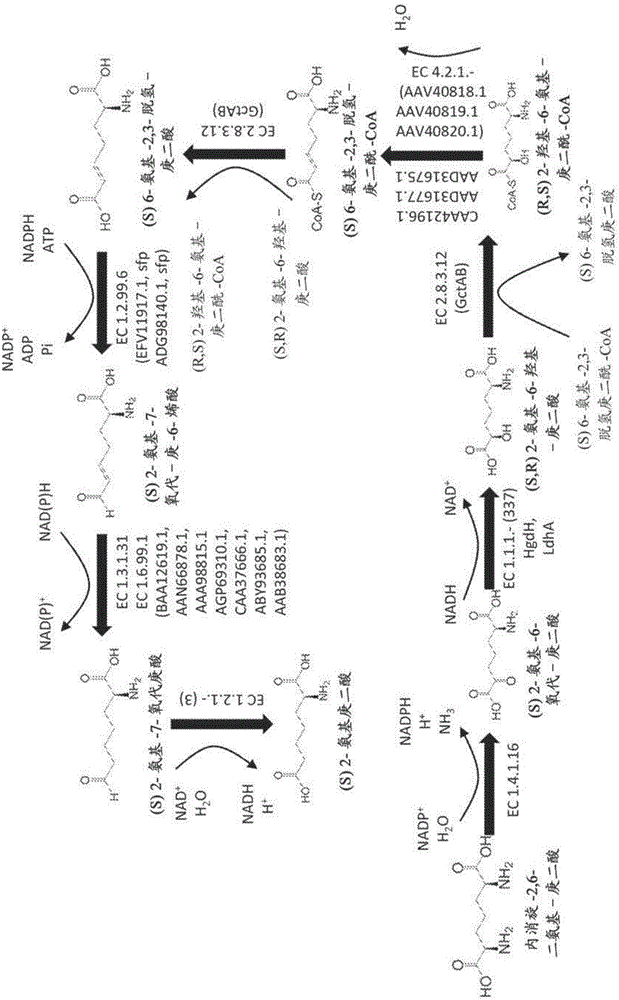
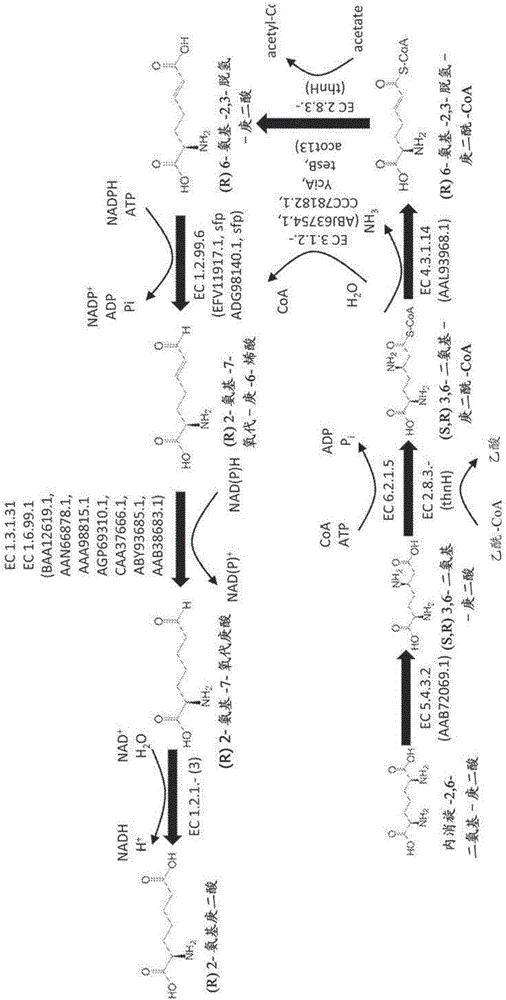
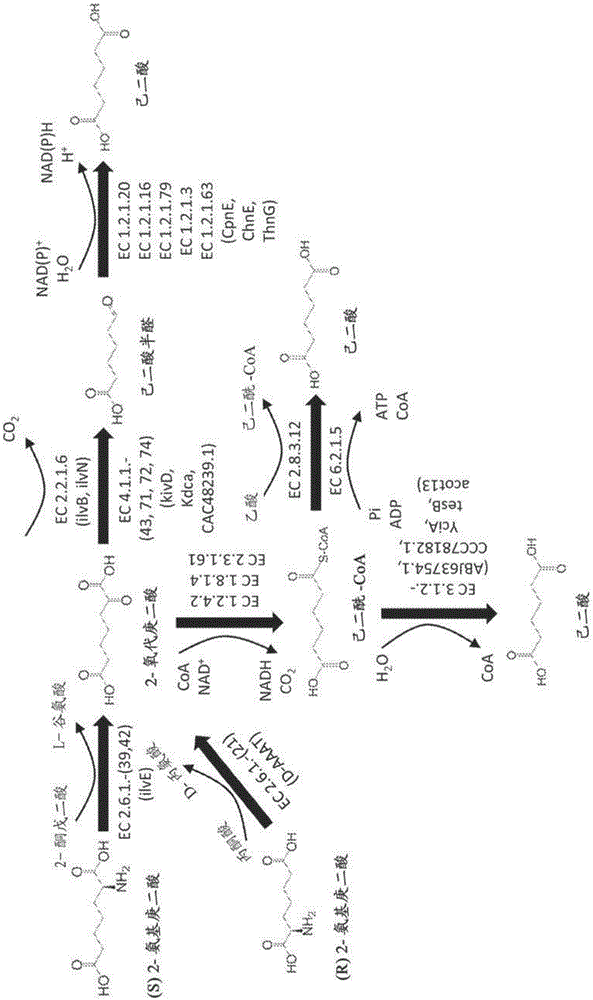
Methods of producing 6-carbon chemicals using 2,6-diaminopimelate as precursor to 2-aminopimelate
The document describes biochemical pathways for producing 2- aminopimelate from 2,6-diaminopimelate, and methods for converting 2- aminopimelate to one or more of adipic acid, adipate semialdehyde, caprolactam, 6- aminohexanoic acid, 6-hexanoic acid, hexamethylenediamine, or 1,6-hexanediol by decarboxylating 2-aminopimelate into a six carbon chain aliphatic backbone and enzymatically forming one or two terminal functional groups, comprised of carboxyl, amine or hydroxyl group, in the backbone.
Owner:INVISTA TEXTILES (U K) LTD
Screening method of medicine for treating citrus huanglongbing
ActiveCN110923289ALow costImprove screening efficiencyBiocideHydrolasesMacromolecular dockingScreening method
The invention provides a screening method of a medicine for treating citrus huanglongbing. The method comprises the following steps: 1) performing database comparison to obtain a succinyl diaminoheptanedioic acid desuccinylase gene sequence of Asia species of citrus huanglongbing; 2) carrying out mutation on amino acids at the fifth site and the fifteenth site of the succinyl diaminoheptanedioic acid desuccinylase protein sequence of the Asia species of citrus huanglongbing; 3) constructing a dimer protein with two active centers; 4) scoring molecular docking; 5) screening alternative compoundmolecules; 6) preparing a medicament for transfusion of citrus huanglongbing trees; 7) treating the sick trees; 8) taking phloem tissues of diseased branches, and extracting total DNA; and 9) selecting the alternative compound molecules with the most reduced germ concentration as target compound molecules by a PCR method. According to the screening method of the medicine for treating the citrus huanglongbing, the compound capable of treating the plant huanglongbing is obtained by molecular biological analysis and field screening.
Owner:BEIJING UNION UNIVERSITY
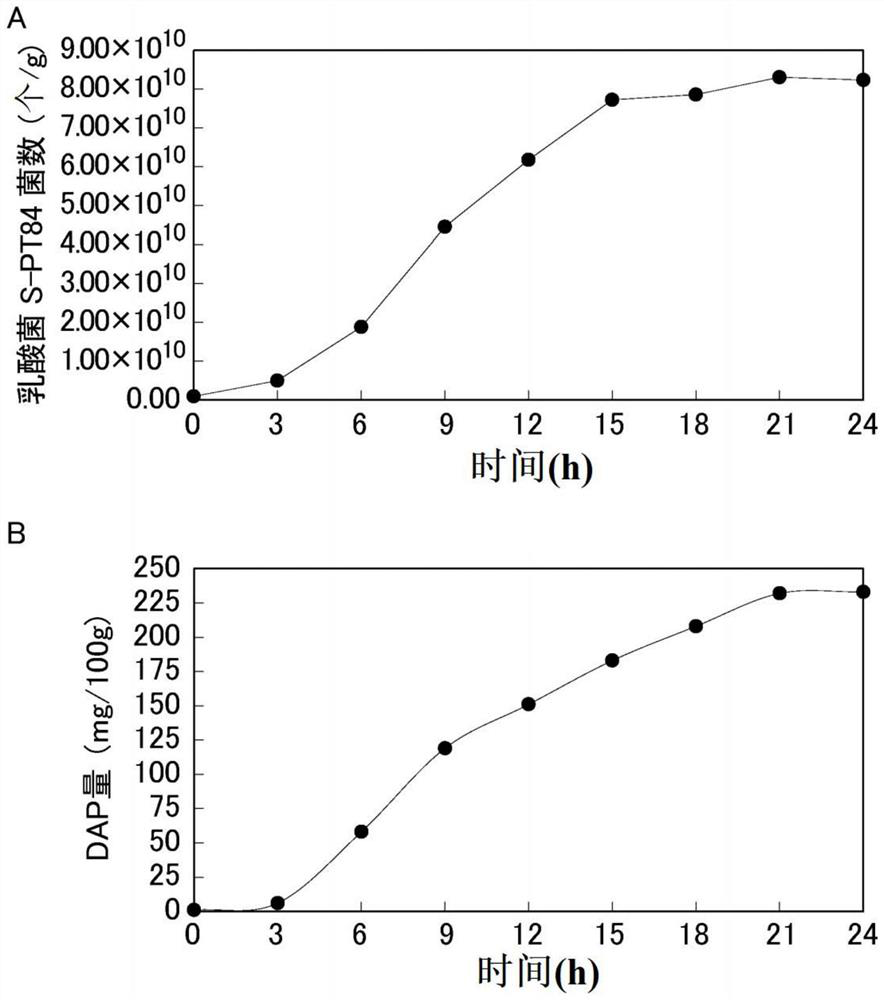
Method for quantifying diaminopimelic acid-containing bacteria
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a novel method with which it is possible to quantify diaminopimelic acid-containing bacteria contained in a test sample. The present invention relates to a method for quantifying diaminopimelic acid-containing bacteria contained in a sample to be detected, the method being characterized by comprising: determining the amount of diaminopimelic acid derived from the diaminopimelic acid-containing bacteria in the sample to be detected as an index, and determining the amount of diaminopimelic acid derived from the diaminopimelic acid-containing bacteria in the sample to be detected; and a step for quantifying the bacteria containing diaminopimelic acid.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
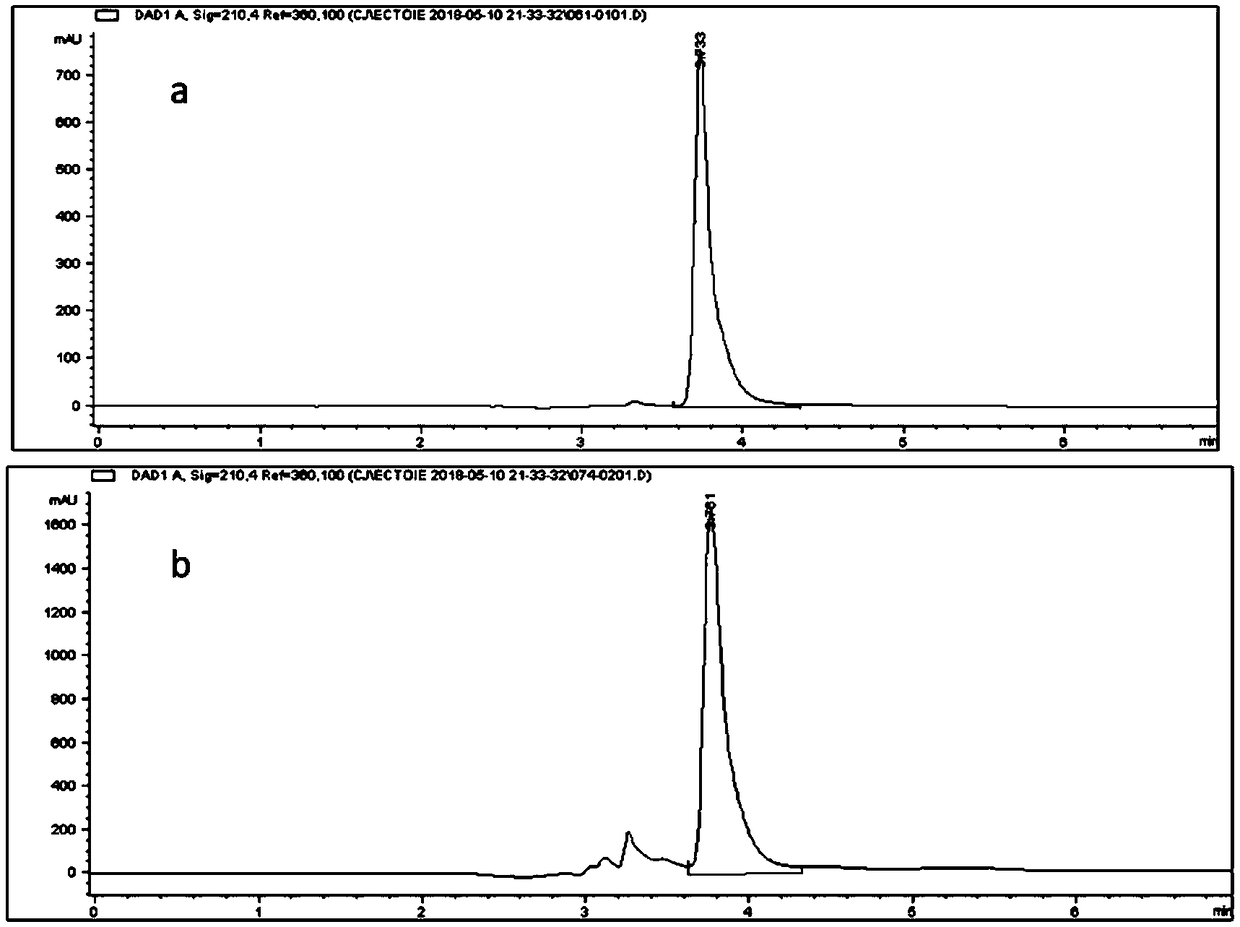
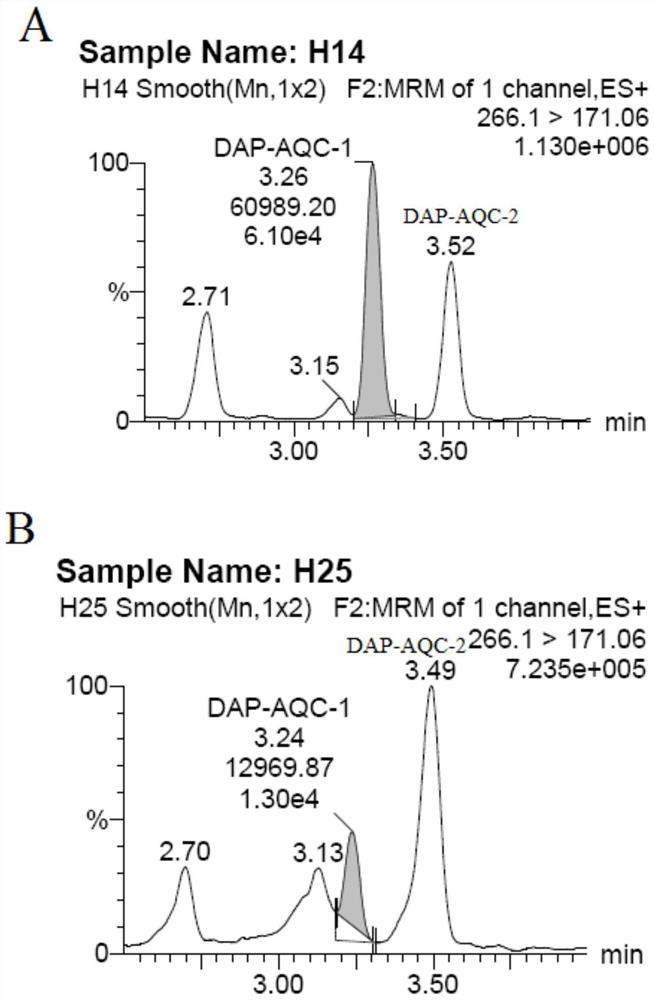
Serum diaminopimelic acid detection kit based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, detection method and application
ActiveCN113341023ARapid quantitationQuantitatively accurateComponent separationInternal standardQuinoline
The invention discloses a serum diaminopimelic acid detection kit based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, a detection method and application, and belongs to the technical field of biological detection. The detection kit comprises an extraction reagent and a derivatization reagent; the extraction reagent comprises a DAP standard substance and a DAP isotope internal standard substance, and the derivatization reagent comprises a borate buffer solution and 6-aminoquinoline-N-succinimide methyl ester (AQC). Through research and development of the kit, the content of DAP in serum / plasma can be relatively rapidly and accurately quantified, and the repeatability is good. And the detection accuracy and stability can be improved by using the isotope internal standard. And the detection sensitivity can be improved by utilizing derivatization.
Owner:FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF DALIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Method for preparing high-efficiency maigre feed for livestock and poultry from Chinese herbal medicine
InactiveCN109744370ANo resistanceImprove disease resistanceFood processingAnimal feeding stuffHerbal preparationsAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-efficiency maigre feed for livestock and poultry from Chinese herbal medicine. The production process comprises the steps of 1) preparation of mainfeed, 2) detection of main feed harmful substances, 3) crushing of the main feed, 4) screening of the Chinese herbal medicine, 5) extraction and purification of the Chinese herbal medicine, 6) preparation of a Chinese herbal preparation, 7) preparation of premix feed by taking collagen, diaminopimelic acid, microelements, humic acid, amino acid, an acidifying agent, decavitamin, an enzymic preparation and probiotics as additives, wherein the main feed comprises a large amount of raw materials including wheat and bean pulp, the Chinese herbal medicine comprises chuanxiong rhizome, poria cocos and the like, and the high-efficiency maigre feed has the advantages of not containing antibiotics and improving the quality of livestock and poultry products.
Owner:张涛
Tricarboxylic acid cycle-free Escherichia coli chassis bacteria as well as construction method and application thereof
PendingCN113817761AReduce loss rateEasy to synthesizeBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses tricarboxylic acid cycle-free Escherichia coli chassis bacteria as well as a construction method and application thereof. The preparation method of the Escherichia coli chassis bacteria comprises the following steps: increasing the expression quantity and / or activity of tetrahydropyridine dicarboxylic acid: N-acetyltransferase, N-acetyl diaminopimelic acid deacetylase, N-acetyl diaminopimelic acid aminotransferase, O-acetyl homoserine thiolase and homoserine: O-acetyltransferasein host bacteria (Escherichia coli or mutant Escherichia coli), reducing the expression quantity and / or activity of tetrahydropicolinic acid: N-succinyltransferase and homoserine: O-succinyltransferase in the host bacteria, and obtaining the tricarboxylic acid cycle-free Escherichia coli chassis bacteria. Experiments prove that the Escherichia coli chassis bacteria can reduce the carbon loss rate and improve the capability of synthesizing a target product by taking central metabolic intermediates (such as acetyl coenzyme A, pyruvic acid and alpha-ketoglutaric acid) as precursors. The tricarboxylic acid cycle-free Escherichia coli chassis bacteria and the preparation method have an important application value.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compositions and methods for modulating lysine production
InactiveUS20090158455A1High in lysineSpeed up the conversion processBacteriaSugar derivativesLysine biosynthesisDiaminopimelic acid
Compositions and methods which modulate LL-diaminopimelate aminotransferase are disclosed. Also provided are compositions and methods for enhancing lysine biosynthesis in a cell.
Owner:GILVARG CHARLES +2
Process for producing L-lysine by fermenting
A bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia, which is transformed by introducing, into its cells, a DNA coding for a dihydrodipicolinate synthase originating from a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia having mutation to desensitize feedback inhibition by L-lysine and a DNA coding for an aspartokinase III originating from a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia having mutation to desensitize feedback inhibition by L-lysine; preferably a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia in which a dihydrodipicolinate reductase gene and a diaminopimelate dehydrogenase gene originating from Brevibacterium lactofermentum (or a succinyldiaminopimelate transaminase gene and a succinyldiaminopimelate deacylase gene) are further enhanced, is cultivated in an appropriate medium, L-lysine is produced and accumulated in a culture thereof, and L-lysine is collected from the culture.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for production of L-lysine
ActiveCN101765659BIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaRecombinant DNA-technologyEscherichia coliDiaminopimelate dehydrogenase
L-lysine is produced by culturing the following Escherichia coli having L-lysine-producing ability in a medium modified to reduce the endogenous One or more enzymes of the racemic α,ε-diaminopimelic acid synthesis pathway, such as 2,3,4,5-tetrahydropyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid N-succinyltransferase, The activity of succinyldiaminopimelate transaminase, succinyldiaminopimelate desuccinylase or diaminopimelate epimerase, and a gene encoding diaminopimelate dehydrogenase is introduced therein.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Synthesis method, kit and application of d-heterocyclic amino acid
ActiveCN108300744BImprove conversion rateHigh chiral purityFermentationDiaminopimelate dehydrogenaseKeto acid
Owner:ASYMCHEM LAB TIANJIN +1
A method for identifying the cell wall skeleton of Nocardia rubrum
ActiveCN104111303BEasy to separateImprove reliabilityComponent separationMeso-diaminopimelic acidN-Butanol
The invention discloses an identification method of red norcardia cell wall skeleton. The method comprises the following steps: (1) sample spotting: using at least two silica-gel G thin-layer plates, spotting a proper amount of an alanine reference solution and a test sample solution on the first thin-layer plate; then spotting a proper amount of a meso-diaminopimelic acid reference solution and a test sample solution on the second thin-layer plate; (2) development: soaking the first thin-layer plate into a developing solvent composed of n-butanol-glacial acetic acid-water according to a volume ratio of 8:3:1, soaking the second thin-layer plate into a developing solvent composed of sodium dodecyl sulfate-n-butanol-n-hexane-water according to a volume ratio of 6:25:6:20; wherein the distance between the surface of the developing solvent to the bottom edge of the thin layer plate is in a range of 0.5 to 1.0 cm and the sample spots cannot be emerged by the developing solvent; sealing the top cover, when the developing solvent reaches the two thirds of the total length of the thin-layer plate, taking out the thin-layer plate, drying; (3) color developing; (4) observation. The identification method has the advantages of clear color development, high separation degree, and high reliability.
Owner:FUJIAN SHANHE PHARMA
Antibiosis streptomycete
InactiveCN101463332BHigh activityFunction increaseBiocideBacteriaIntellectual propertyField experiment
The invention relates to an antibiotic streptomyces, fermentation product of which can inhibit broad spectrum fungus and protozoan, and field experiment can control crop fungus plant disease and root-knot nematode. The antibiotic streptomyces has good effect, no pollution nuisance and no residue. The antifungal agent has extremely low hazardness for the people and good performance and developmentprospect for medical and agricultural use. The invention is named as SIM001 antibiotic streptomyces which is Streptomyces antibioticus subspecies xi an, and is preserved as patent in the depositary institution appointed by patent office of state intellectual property office; the preservation data is April 14th, 2005, the name of the depositary institution is CGMCC, and the number of preservation is CGMCC No.1349. The whole cell hydrolysate of the antibiotic streptomyces contains L, L-DAP (Diaminopimelic acid) and no characteristic glucide; the cytoderm belongs to I type and glucide type C; one of the main antibacterial materials is polyene macrocyclic ketolide which belongs to the broad spectrum antifungal substance.
Owner:刘昶志
A culture medium for ornamental plants, a bottled ornamental plant and a production method thereof
InactiveCN106069764BPromote rootingDoes not hinder growthPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGrowth plantKanamycin
The invention is applicable to the technical field of plant cultivation, and provides an ornamental plant cultivation medium, a bottled ornamental plant and a preparation method of the bottled ornamental plant. A formula of the ornamental plant cultivation medium is as follows: a 1 / 2MS cultivation medium is used as a basic material, meanwhile 1.8-2.3 g / L of agar, 7-9 g / L of phytagel, 48-53 mg / L of diaminopimelic acid, 9.5-10.5 [mu]mol / L of PQQ and 23-26 mg / L of kanamycin are added, and then the pH value of the ornamental plant cultivation medium is adjusted to be 6.5-6.9. The provided cultivation medium can be used for accelerating plant growth, is also relatively firm, is suitable for long-time plant growth, and is particularly suitable for being used as the cultivation medium of the bottled ornamental plant; the plant is relatively vigorous in growth, relatively strong in stability, better in ornamental value and longer in growth cycle.
Owner:WUHAN ZHONGKE HAOYU SCI & TECH
Plant amino acid biosynthetic enzymes
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com