Tricarboxylic acid cycle-free Escherichia coli chassis bacteria as well as construction method and application thereof
An Escherichia coli, tricarboxylic acid-free technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as aerobic growth limitation, complicated process, and difficult industrial application, and achieve the effects of improving enzyme catalytic efficiency, reducing carbon loss rate, and promoting synthesis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
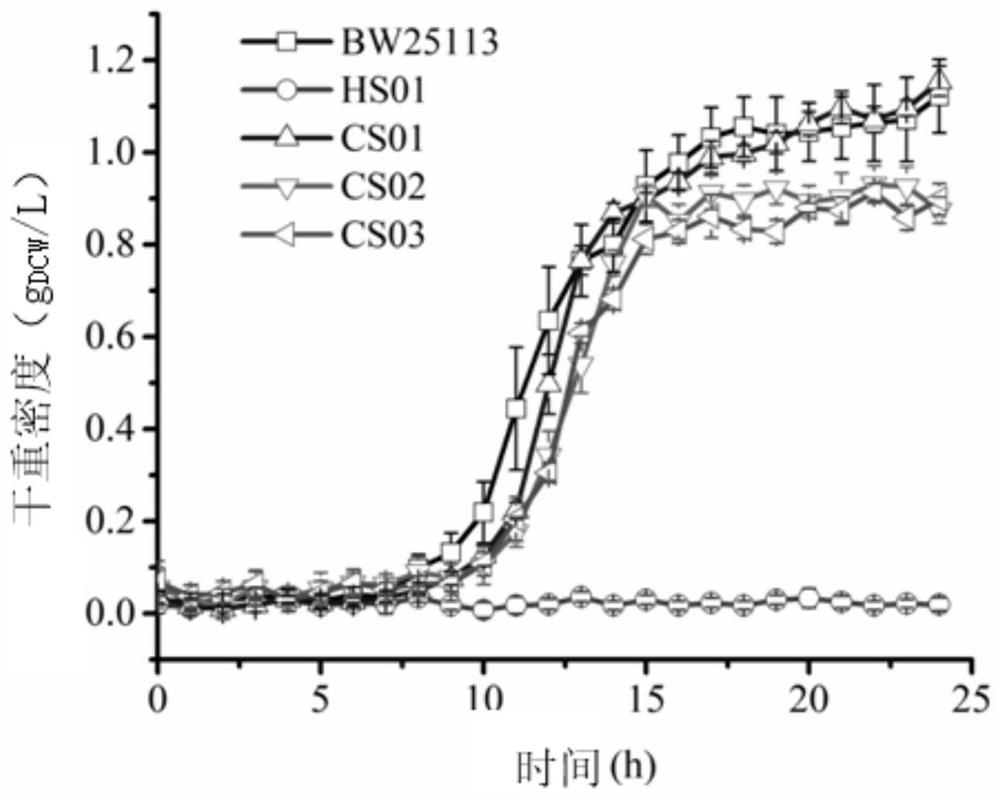
[0112] Embodiment 1, construct the Escherichia coli chassis bacterium that can grow in inorganic salt basal medium without tricarboxylic acid cycle
[0113] 1. Construction of Escherichia coli chassis bacteria without tricarboxylic acid cycle
[0114] 1. PCR amplification to obtain the erasable resistance gene selection marker element lox71-kanR-lox66
[0115] The plasmid pKD13 (GenBank: AY048744.1) was used as a template, and the primer pair composed of primer P1 and primer P2 was used for PCR amplification to obtain the selection marker element lox71-kanR-lox66 carrying the kanamycin resistance gene. Among them, the sequence of lox71 was introduced by primer P1, the sequence of lox66 was introduced by primer P2, and the size of the PCR fragment was about 1300bp, which was consistent with the target fragment.
[0116] 2. In vitro assembly of the targeting fragment dapH-dapL-patA-lox71-kanR-lox66
[0117] (1) Using the chromosomal genomic DNA of Bacillus subtilis subsp.subti...
Embodiment 2
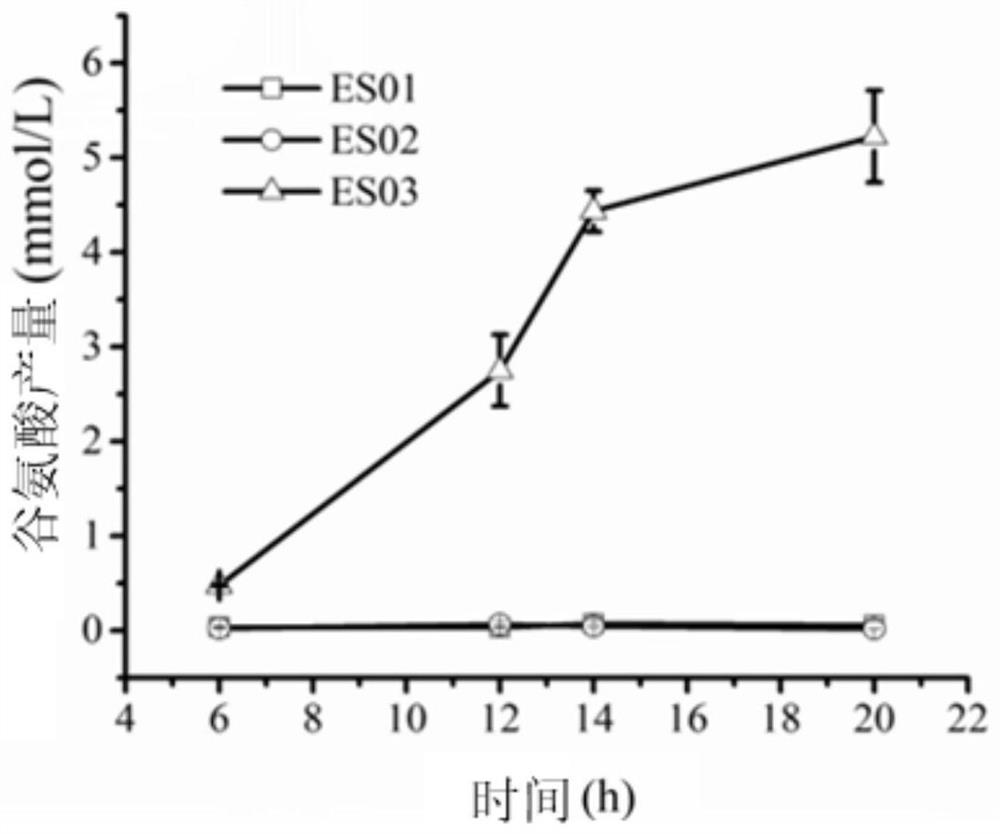
[0154] Example 2, the application of Escherichia coli chassis bacteria without the tricarboxylic acid cycle in the synthesis of the target product with α-ketoglutarate as the precursor (taking glutamic acid as an example)
[0155] α-Ketoglutarate is the precursor of many important amino acids such as glutamine and glutamic acid. Under the catalysis of glutamate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate undergoes reductive amination reaction to generate glutamate. The Escherichia coli chassis without the tricarboxylic acid cycle can be widely used in the synthesis of the target product with α-ketoglutarate as the precursor. Taking the synthesis of glutamic acid as an example, the application of Escherichia coli without the tricarboxylic acid cycle in the synthesis of the target product with α-ketoglutarate as the precursor is illustrated.
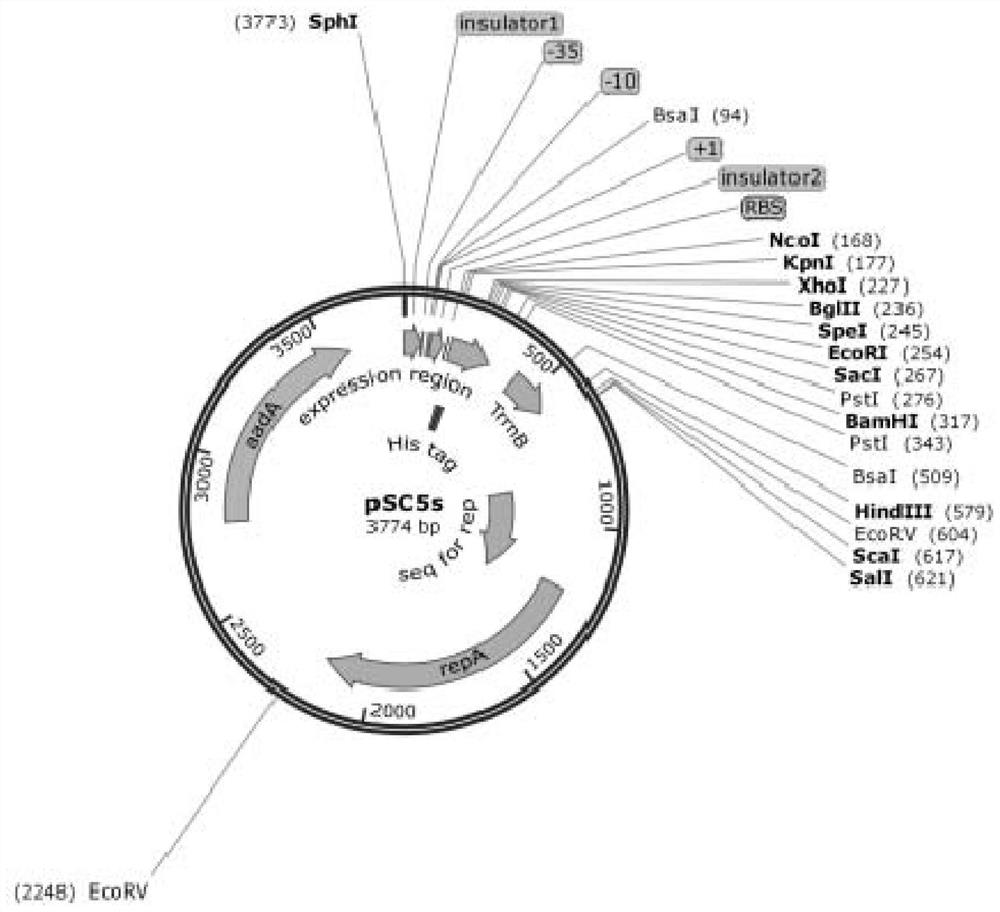
[0156] 1. Construction of engineering bacteria producing glutamate
[0157] 1. Using the genomic DNA of the BW25113 strain as a template, PCR amplif...
Embodiment 3
[0174] Embodiment 3, the application of Escherichia coli chassis bacteria without tricarboxylic acid cycle in the synthesis reaction catalyzed by α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase (to synthesize deacetoxycephalosporin (G-7-ADCA ) for example)
[0175] α-ketoglutarate is the co-substrate of a series of α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases such as hydroxylase and expandase. Synthetic reactions catalyzed by ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases. Taking the synthesis of G-7-ADCA as an example, the application of Escherichia coli without tricarboxylic acid cycle in the synthesis reaction catalyzed by α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase is illustrated below.
[0176] 1. Construction of engineering strains
[0177] 1. Using the plasmid pDB1s-DAOCS (recorded in the Chinese Invention Patent Literature, Publication No. CN104805047A) as a template, PCR amplification was performed using primers P31 and P32 to obtain the gene encoding deacetoxycephalosporin synthase scDAOCS. The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com