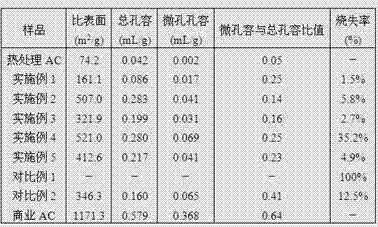
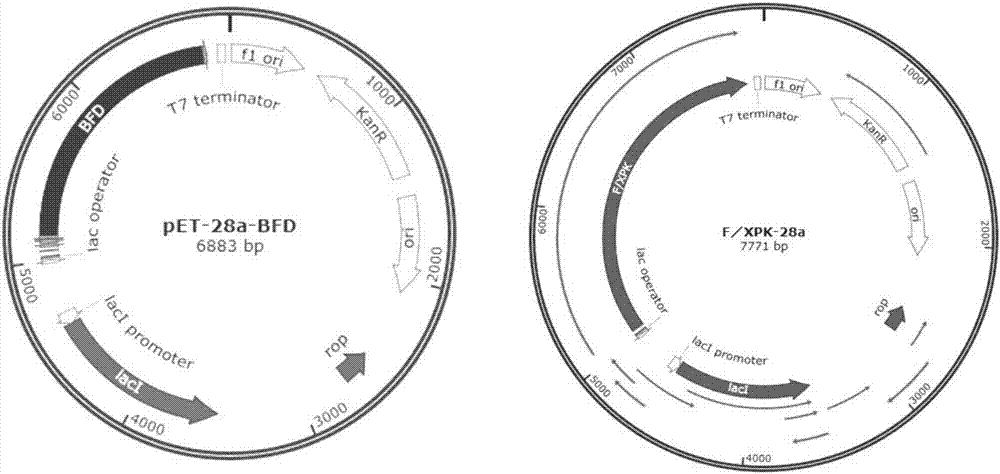
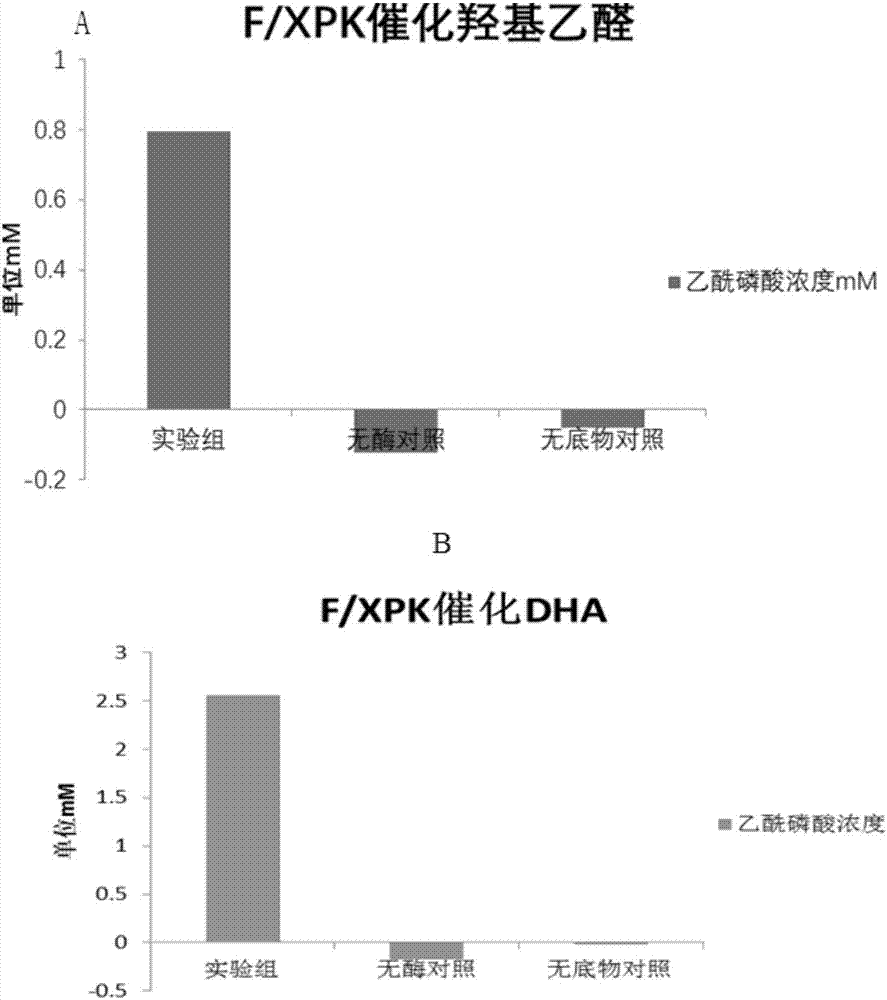
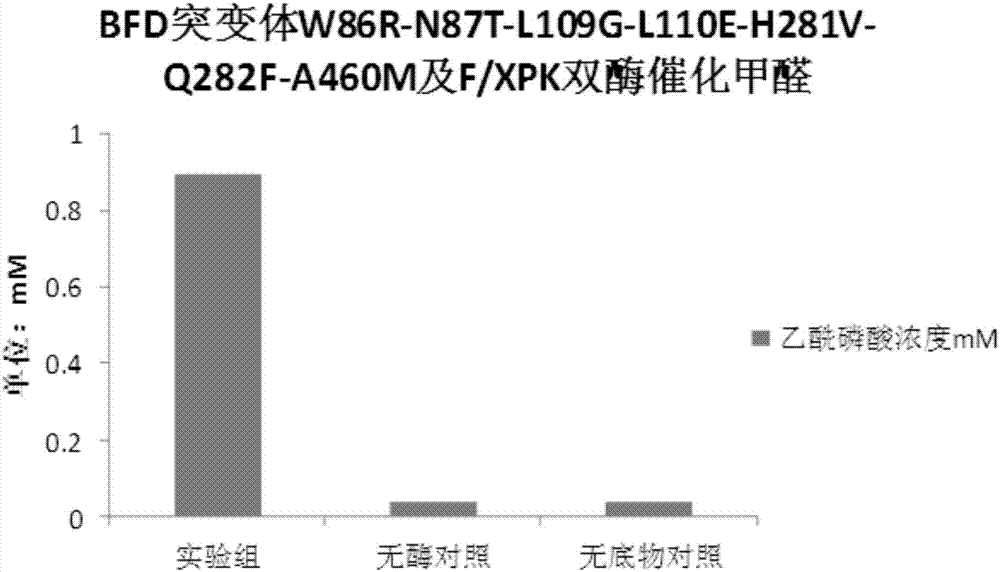
Patents
Literature
96 results about "Carbon loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
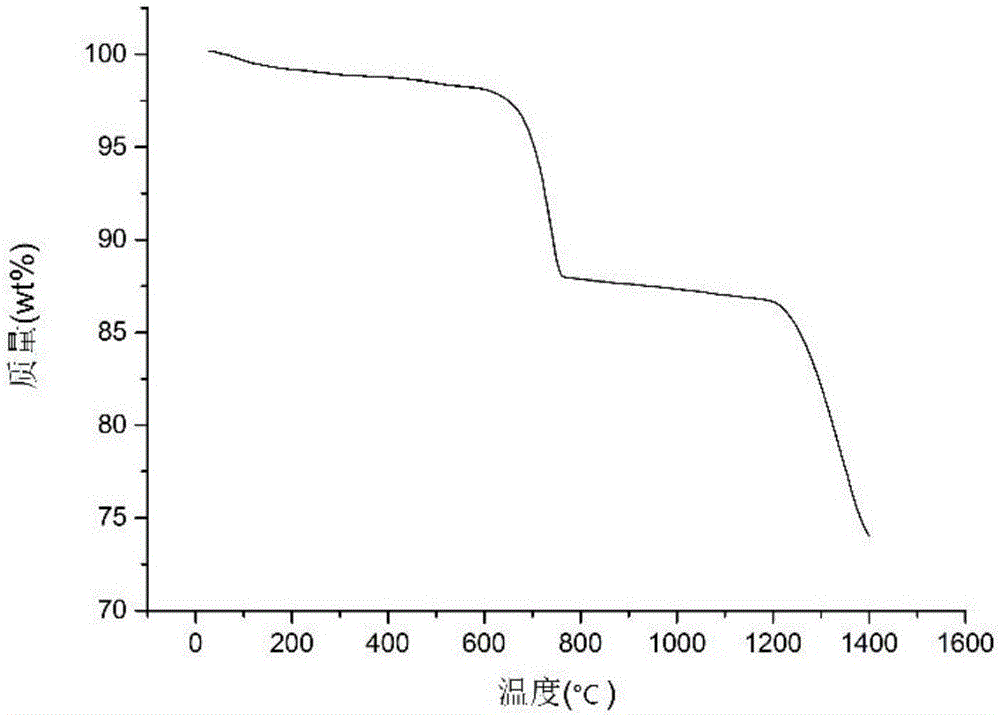
Thermally treated active carbon and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102442665ALow loss on ignitionHigh porosityCatalyst carriersCarbon compoundsActivated carbonCarbon loss
The invention discloses a thermally treated active carbon and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of: uniformly mixing active carbon which is subjected to a high temperature treatment with a pore-enlarging agent; and performing a pore-enlarging treatment at 300-1000 DEG C for 0.1-48 hours to obtain thermally treated active carbon with high mesopore and macropore rates. The active carbon obtained by the preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low carbon loss rate on ignition in the treatment process, low ratio of pore volume of micropores to total pore volume as well as high mesopore and macropore rates, and can be used as a carrier of catalysts.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for preparing high-adsorbability activated carbon by using rice hulls as raw material
The invention relates to a method for preparing high-adsorbability activated carbon by using rice hulls as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps of: providing rice hulls, carrying out acid and alkali treatment and washing the rice hulls to obtain neutral filter residue; drying the filter residue, soaking in an eutectic solution of zinc chloride and potassium chloride at 70-80 DEG C for not less than 9h; taking out the filter residue, pouring into a porcelain crucible, putting into a muffle furnace to activate at 400-800 DEG C for 1-2h; washing, filtering and washing with water to be neutral; and drying and grinding to obtain the product, wherein in the eutectic solution of the zinc chloride and the potassium chloride, the mass concentration of the zinc chloride is 20-60 percent, and the mass concentration of the potassium chloride is 2-10 percent. The invention is easy to form a thin hole structure and can manufacture activated carbon with robust holes and better adsorbability, and the activating method has less carbon loss and relative high carbon yield.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF PETROCHEMICAL TECH
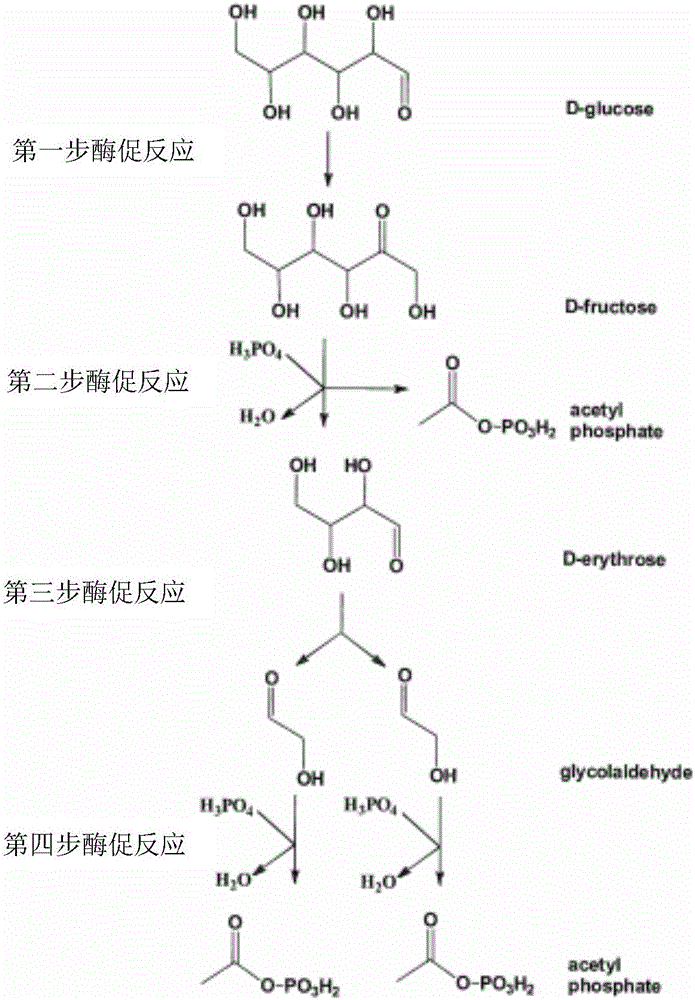
Enzyme for catalyzing formaldehyde to synthesize hydroxyl acetaldehyde and application thereof
ActiveCN106916794AEfficient aggregationNo inputFermentationCarbon-carbon lyasesPhosphate acetyltransferasePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses an enzyme for catalyzing formaldehyde to synthesize hydroxyl acetaldehyde and an application thereof. In the invention, through site-directed mutation of BFD, a mutant of the enzyme is found; and by means of the mutant of the enzyme, high-effect polymerization of the formaldehyde is achieved; meanwhile, through F / XPK, generation of acetyl phosphoric acid from the hydroxyl acetaldehyde or 1,3-dihydroxyacetone is achieved; with combination of phosphotransacetylase (Pta), a route from the formaldehyde to acetyl coenzyme A is achieved in three steps with the enzyme, thereby creating a new formaldehyde assimilation route, namely, synthesizing the acetyl coenzyme A from the formaldehyde in three steps. The route is short and is free of carbon loss and ATP input.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
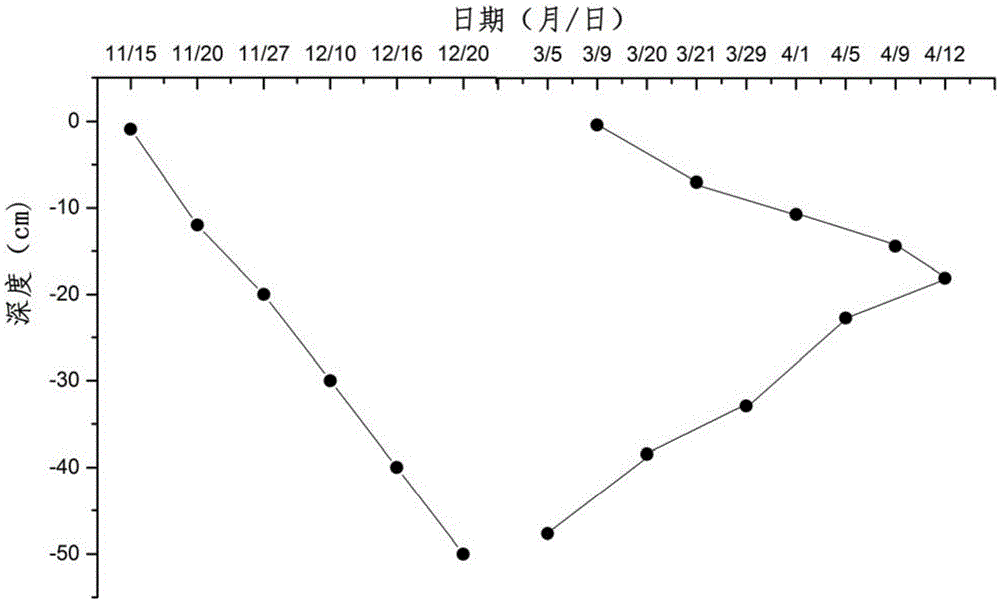
In-situ monitoring soil freeze-thawing device and method for testing soil carbon loss on basis of device
InactiveCN105572318AHigh precisionComponent separationEarth material testingSoil scienceFreezing thawing
The invention provides an in-situ monitoring soil freeze-thawing device and a method for testing the soil carbon loss on the basis of the device, and aims at solving the problems that the existing wild method can only be used for monitoring the carbon discharge flux of a whole soil ecological system and cannot be used for monitoring the contribution of a specific soil layer to the carbon discharge, and a soil freeze-thawing process cannot be really reflected by indoor freeze-thawing simulation experiments. The soil freeze-thawing device mainly comprises a temperature monitoring instrument, a soil column chamber, an air buffer chamber, a rubber sleeve and an air guide pipe. The method for testing the soil carbon loss comprises the following steps of charging in-situ soil columns of different soil layers into the soil column chamber of the freeze-thawing device; burying the soil columns into corresponding oil layers; in a freeze-thawing period, monitoring the discharge condition of gases CO2 and CH4, and comparing the soluble organic carbon DOC change condition of the corresponding soil layer before and after the freeze-thawing; further calculating the total carbon loss quantity of the freeze-thawing process. The in-situ monitoring soil freeze-thawing device and the method for testing the soil carbon loss have the advantages that the CO2 and CH4 discharge flux of different soil layers and the change angle of the DOC content in the freeze-thawing process are integrated to calculate the soil carbon loss degree; the precision is improved by 30 to 50 percent.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Regeneration method of activated carbon for treating ibuprofen decolorization process
ActiveCN102553556AReduce lossesReduce energy consumptionOther chemical processesCombustible gas purificationSolventPollution
The invention relates to a regeneration method of activated carbon for treating ibuprofen decolorization process. After un-dried waste activated carbon is put in a reactor, a separator and a regeneration kettle, the pigment and other impurities are subjected to thermal decomposition by strict temperature control to realize the regeneration of activated carbon. An ethanol solution is used as an extractant, so that the problem that a novel adsorbent possibly can be introduced in a solvent regeneration process can be solved, and the ethanol solution has high selectivity of ibuprofen, and almost can not wash the pigment out at the same time, the ibuprofen can be recovered with the extractant in a recrystallized way, the regeneration is full, and no secondary pollution is generated. By the method, the pigment and other impurities can be thermally decomposed at low temperature, the energy consumption is low, the carbon loss is low and the regeneration rate is high.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Active carbon regeneration absorption device and active carbon regeneration absorption technology
ActiveCN103230786ALow costLess investmentOther chemical processesCombustible gas purificationActivated carbonWastewater
The invention relates to an active carbon regeneration absorption device. The active carbon regeneration absorption device is composed of an absorption tower system, an energy system and a tail gas absorption system, wherein waste water is pumped in the absorption tower system by a pump to enter a water distributor during waste water absorption treatment operation and flows in an active carbon bed layer through a support plate, and outlet water flows out from a baffle plate and is merged into a water outlet pipe for discharging; and during regeneration treatment process, an energy generator is opened, the active carbon bed layer is acted through an energy probe, and generated steam is discharged out from an air outlet and is discharged out through a tail gas absorber and a gas absorption column. The device has the characteristics of being simple in structure, good in safety, easy to operate, convenient to amplify and the like, and overcomes the disadvantages in the prior art that the energy dissipation area is large, the energy consumption is high, the energy utilization rate is low, the carbon loss is high, the regeneration time is long, the regeneration efficiency is low, secondary pollution is caused, and the like.
Owner:NJTECH ENVIRONMENT TECH CO LTD
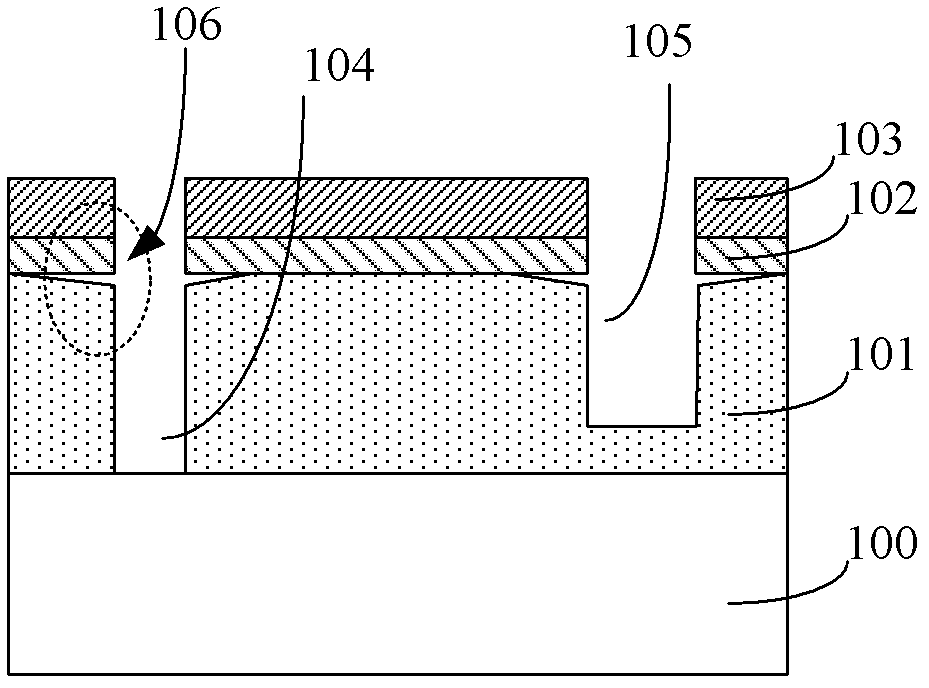
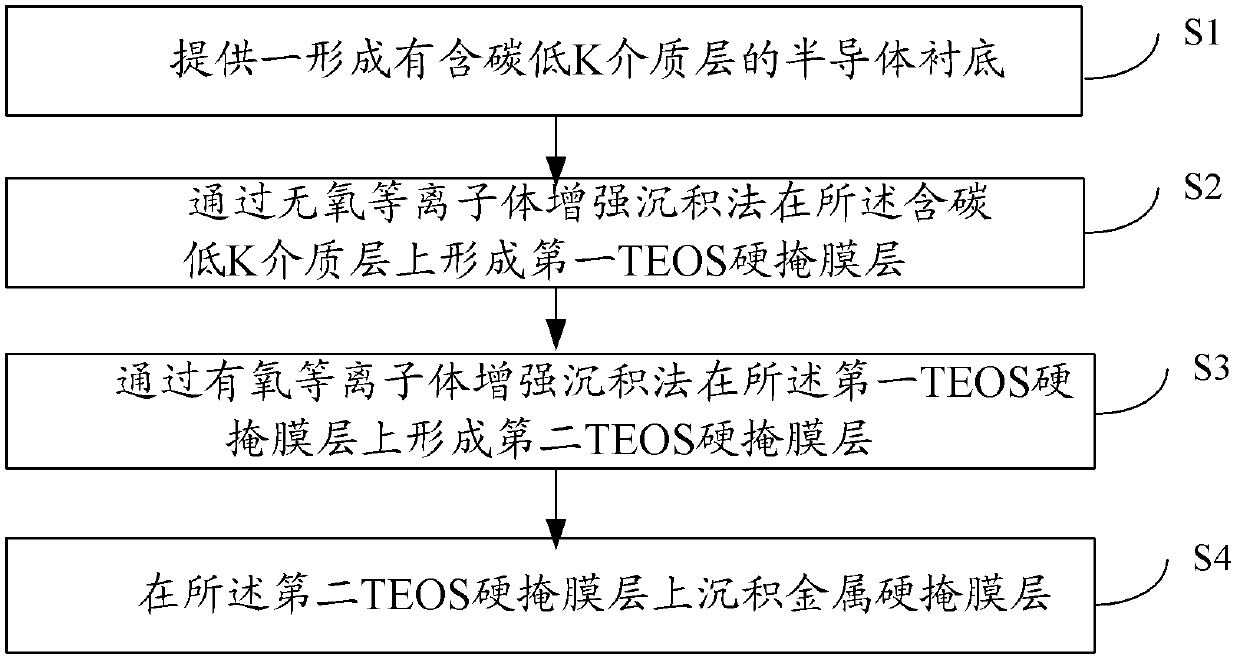
Hard mask layer structure, manufacturing method thereof and manufacturing method of semiconductor device
ActiveCN103377886AModerate Wet Etch Selectivity DifferencesIncreased process windowSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceOxygen plasma
The invention provides a hard mask layer structure, a manufacturing method thereof and a manufacturing method of a semiconductor device. Through oxygen-free plasma-enhanced deposition of a first TEOS hard mask layer over a carbon-containing low-K dielectric layer and then through oxygen plasma-enhanced deposition of a second TEOS hard mask layer, the first TEOS hard mask layer can reduce carbon loss of a surface of a lower carbon-containing low-K dielectric layer during deposition of a TEOS hard mask layer in the prior art, restrain the formation of carbon-free oxides on the interface of the lower carbon-containing low-K dielectric layer, and play the role of a buffer layer to mitigate the difference of wet etching selection ratio of the second TEOS hard mask layer, the carbon-free oxides and the carbon-containing low-K dielectric layer. Therefore cut damages on the bottom of the interface of the hard mask layer structure and the carbon-containing low-K dielectric layer after wet cleaning are avoided, and a formed through-hole and a process window of a groove are enlarged.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Novel compost rapid start/proper fermentation conditioner and use method thereof
InactiveCN102173892AImprove fermentation start timeReduce lossesBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationLivestock manureNitrogen
The invention discloses a novel compost rapid start / proper fermentation conditioner and a use method thereof. The novel conditioner comprises the following components by weigh percent: 70-90% of zeolite, 10-20% of carbon black and 2-6% of pyroligneous. During the composting of livestock manure, 5-20% of conditioner is added in a compost body to exter the effects of rapid start of compost fermentation, proper fermentation and the like; and simultaneously, in the fermentation process, the nitrogen loss can be reduced by 20-30%, the carbon loss is reduced by 10-20%, and the compost period is shortened by 10-20 days.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
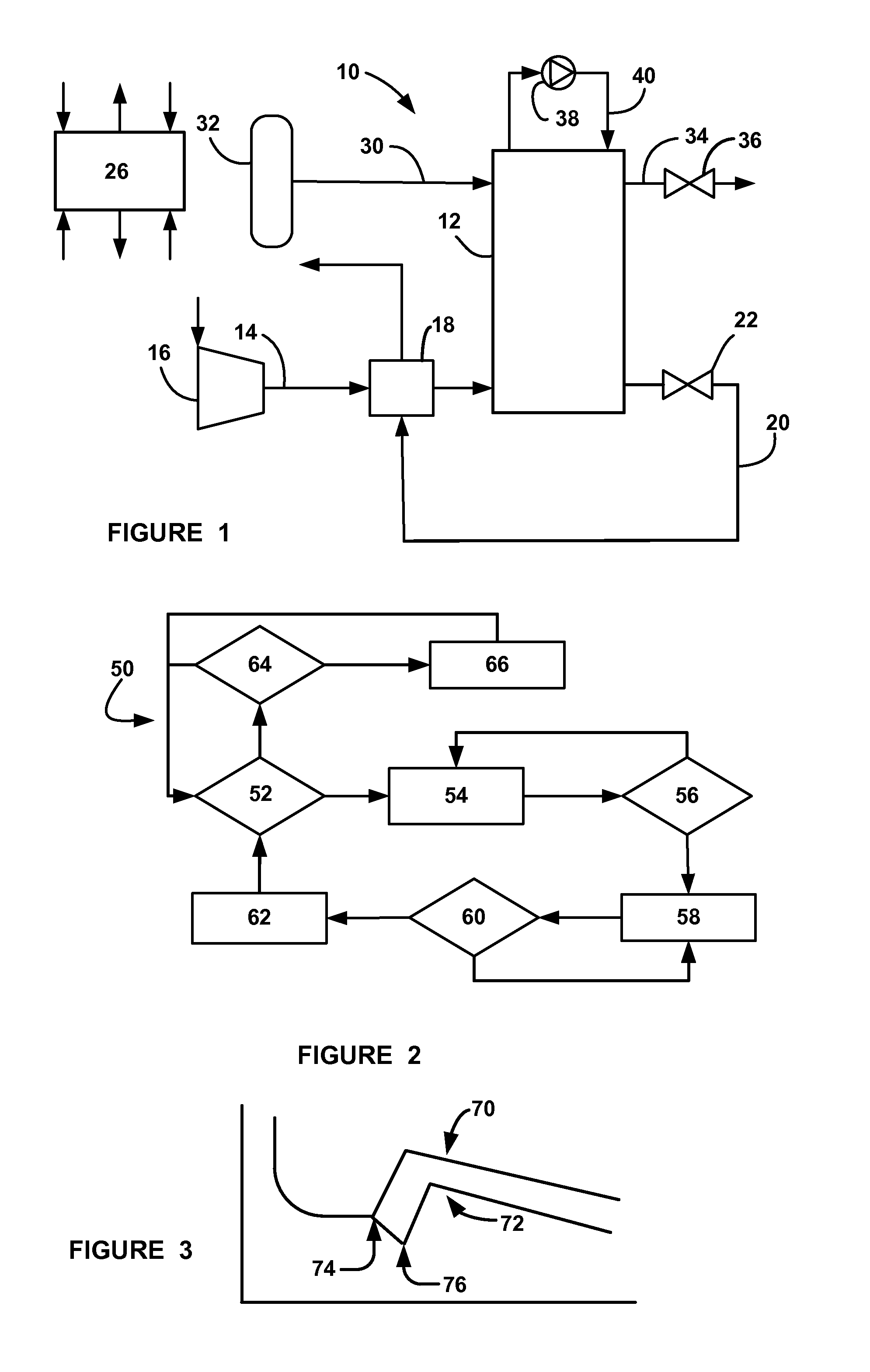
Vehicle application for air storage cathode carbon loss estimation
ActiveUS9099701B2Fuel cell auxillariesDesign optimisation/simulationHydrogen concentrationFuel cells
A system and method for estimating an amount of carbon support loss in fuel cells of a fuel cell stack in a vehicle, for example, during vehicle off-times. The system and method include estimating an amount of time that a hydrogen concentration in the fuel cell stack is zero and calculating an amount of carbon loss based on the amount of time that the hydrogen concentration in the fuel cell stack is zero.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Characterization method for quantifying carbide loss in hot spraying preparation of carbide cermet coating
InactiveCN101942629ARapid Quantitative DetectionFlexible quantitative detectionMolten spray coatingCarbideDeposition process
The invention discloses a characterization method for quantifying carbide loss in the hot spraying preparation of a carbide cermet coating, which comprises the following steps: comparing the carbon contents of coatings deposited under water and on a matrix under the conditions of different gas flows and oxygen flows, acquiring the change of the carbon content in the flying process of particles and after collision, and quantifying the carbon loss caused by oxidation and rebound of the particles. The method for quantifying the carbon loss of each phase in the deposition process of the carbide cermet coating based on experiment has the advantage of simple process, and can quickly, flexibly and conveniently quantify and detect the carbon loss in different phases in the hot spraying preparation process of the carbide cermet coating, thereby providing a research method for the preparation process and the performance optimization of the hot spraying carbide cermet coating structure.
Owner:JIUJIANG UNIVERSITY
Porous carbon material supported zero-valent Fe-Fe3C denitration catalyst as well as preparation method and application method thereof
ActiveCN109433236AImprove denitrification efficiencyAvoid pollutionGas treatmentPhysical/chemical process catalystsPtru catalystPorous carbon
The invention relates to a porous carbon material supported zero-valent Fe-Fe3C denitration catalyst as well as a preparation method and an application method thereof. The denitration catalyst is a Fe-Fe3C / C denitration catalyst and is prepared from components in percentage by mass as follows: 5%-15% of zero-valent Fe, 5%-10% of Fe3C and 75%-90% of C; zero-valent Fe and Fe3C are taken as active components; C is porous carbon and taken as a carrier and a reductant. The Fe-Fe3C / C denitration catalyst has simple preparation process, low cost and high low-temperature activity, which is matched with the temperature window of exhaust gas discharged from a flue of a coke oven. The low-valent Fe is used for direct catalytic reduction of NO, harm to human bodies and environment caused by ammonia escape and toxic vanadium contained in conventional denitration catalysts is avoided, and the problem of carbon loss in the process of direct denitration of carbon solid is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH LIAONING
Regeneration method for waste active carbon in itaconic acid decoloring step
ActiveCN104841409AEmission reductionHigh selectivityOther chemical processesCombustible gas purificationDistillationImpurity
The invention relates to a regeneration method for waste active carbon in an itaconic acid decoloring step, wherein the total cost, the regeneration rate and the economic benefit are relatively high. The method comprises the following steps: treating the undried waste active carbon in a reaction kettle, a separator, a distillation column and a regeneration kettle; and thermally decomposing pigments and other impurities through strict temperature control to realize the regeneration of the waste active carbon. According to the regeneration method provided by the invention, an ethanol solution is used as an extracting agent; the ethanol solution has a high selectivity on itaconic acid and the pigments are nearly not washed out; the extracting agent can be used for recovering itaconic acid by way of recrystallization; and the active carbon is fully regenerated, so that no secondary pollution is caused. The method provided by the invention can be used for thermally decomposing the pigments and other impurities at a relatively low temperature, and is low in energy consumption, small in carbon loss and high in regeneration rate.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for firing low-cobalt fine-grain hard alloy by using ordinary sintering furnace
The invention discloses a method for firing a low-cobalt fine-grain hard alloy by using an ordinary sintering furnace. The method sequentially comprises steps as follows: a low-cobalt fine-grain hard alloy blank is placed in the sintering furnace, and inert gas is introduced for dewaxing; the inert gas is kept in the sintering furnace for micro-positive-pressure sintering after dewaxing, the sintering temperature is lower than the eutectic temperature by 10-20 DEG C, and the temperature is kept for 30-120 min; vacuum pumping is performed for secondary sintering, sintering is performed at the sintering temperature ranging from 1380 DEG C to 1470 DEG C for 60-120 min at the heating speed of 5-20 DEG C / min, and sintering is finished after the temperature is reduced to the room temperature. Compared with the conventional sintering method, the method has the advantages as follows: the cobalt magnetism is increased from 4.2 to 5.2, the product finishes 80%-90% of shrinkage after sintering for the first time, the grain surface energy is quickly reduced, the sensitivity to oxygen is reduced, secondary vacuum sintering is performed after cooling and can adopt the higher heating speed, thus, the carbon loss in the furnace is reduced as much as possible, inner gas can be removed, and inner pores of the product are greatly reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HENGCHENG CEMENTED CARBIDE
Production method for low-residual-chromium-content molten steel and steel material
ActiveCN107619899AEfficient extractionSimple processManufacturing convertersSteelmakingSmelting process
The invention provides a preparing method for low-chromium-content molten steel. The preparing method includes the following steps that firstly, molten iron is sent into a converter for the first timeof converter smelting, a cooling agent and a carburant are added in the smelting process, and low-chromium half steel is obtained; and the chromium-removed half steel obtained in the above step is sent into a converter again for the second time of converter smelting, a dephosphorizing agent is added in the smelting process, and low-chromium-content molten steel is obtained. By means of the preparing method, a duplex chromium removing technology is used for removing chromium in the molten iron, the cooling agent is added in the first converter for controlling the converter temperature, the carburant is added for supplementing carbon losses in the chromium removing process, chromium in the molten iron is removed to the maximum degree, and efficient removing of chromium is achieved; and thesecond converter is used for conducting the second time of deep chromium removing, and meanwhile conventional steelmaking tasks such as decarbonizing and dephosphorizing are completed. By means of thepreparing method, the residual Cr content of the molten steel can be controlled to be within 40 ppm, and a foundation is laid for production of high-purity steel balls. In addition, the technology issimple, extra production equipment does not need to be added, conditions are reasonable, and the method is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:攀钢集团西昌钢钒有限公司
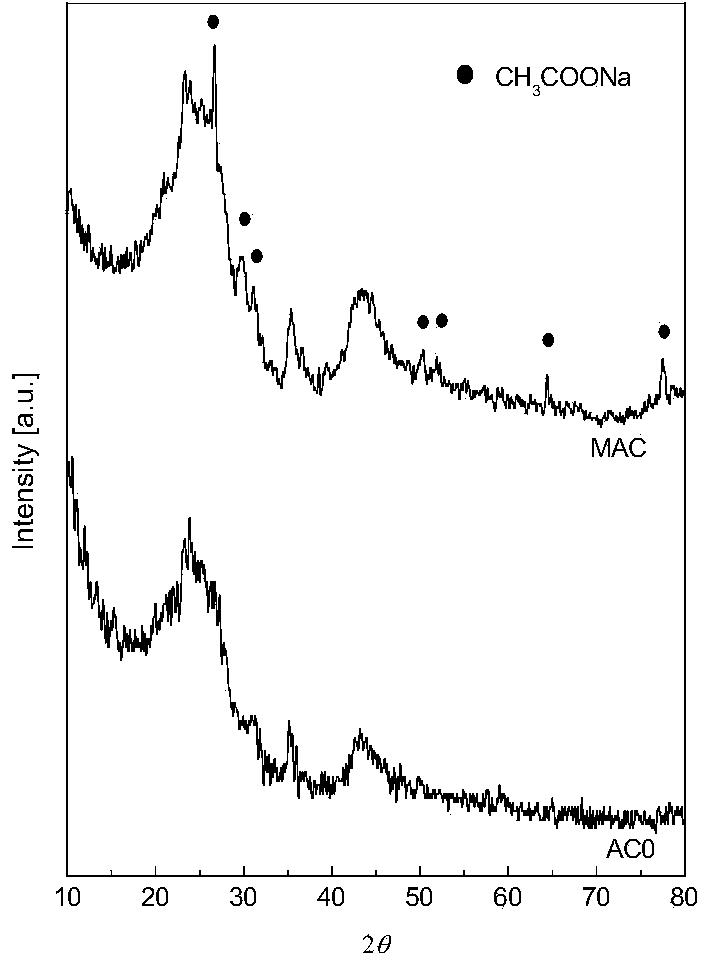
Hydrophilic active carbon modified by sodium acetate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103537260ANo loss of qualityHigh microporous contentOther chemical processesSodium acetateSodium acetrizoate
The invention discloses hydrophilic active carbon modified by sodium acetate and a preparation method thereof. The hydrophilic active carbon is formed by loading sodium acetate on the surface of the carbon framework of active carbon. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: sequentially carrying out high-temperature treatment on an active carbon raw material, soaking in a sodium hydroxide solution, drying, activating, soaking in ethyl acetate and carrying out esterolytic reaction, nitrogen purging desorption and vacuum desorption to obtain the hydrophilic active carbon. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of easiness for operation and low cost; the prepared hydrophilic active carbon has the advantages of stability in structure, large specific area, less carbon loss, high adsorption capacity and large volume on water vapors, stability in adsorption property and good reusability.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
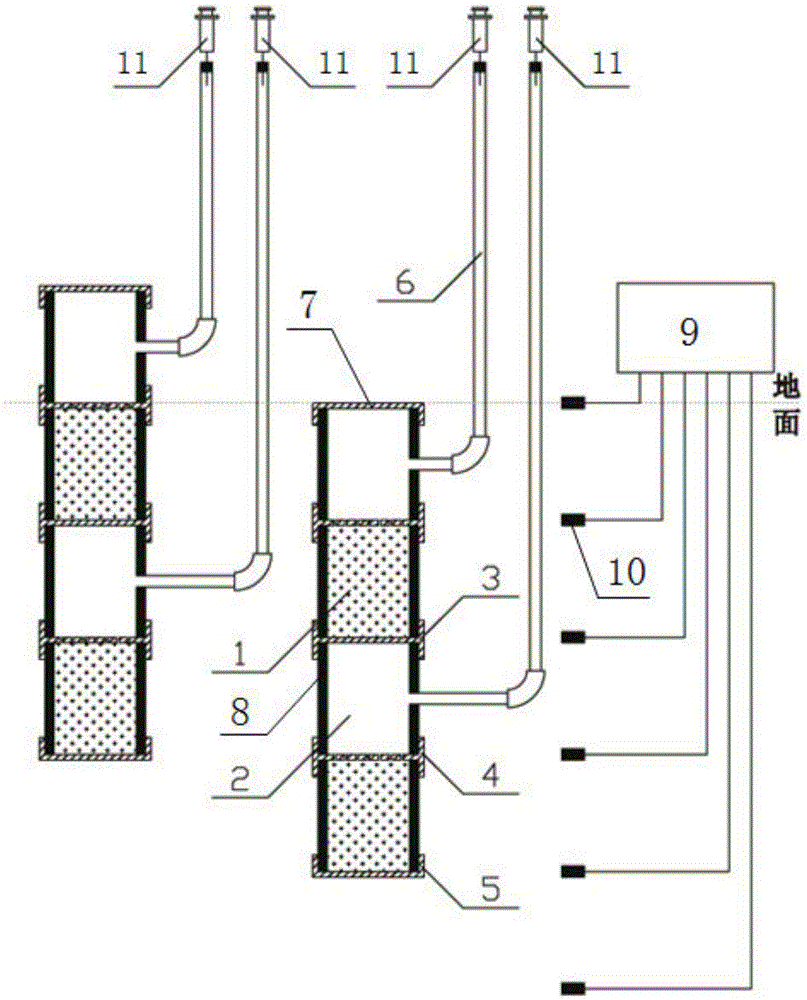
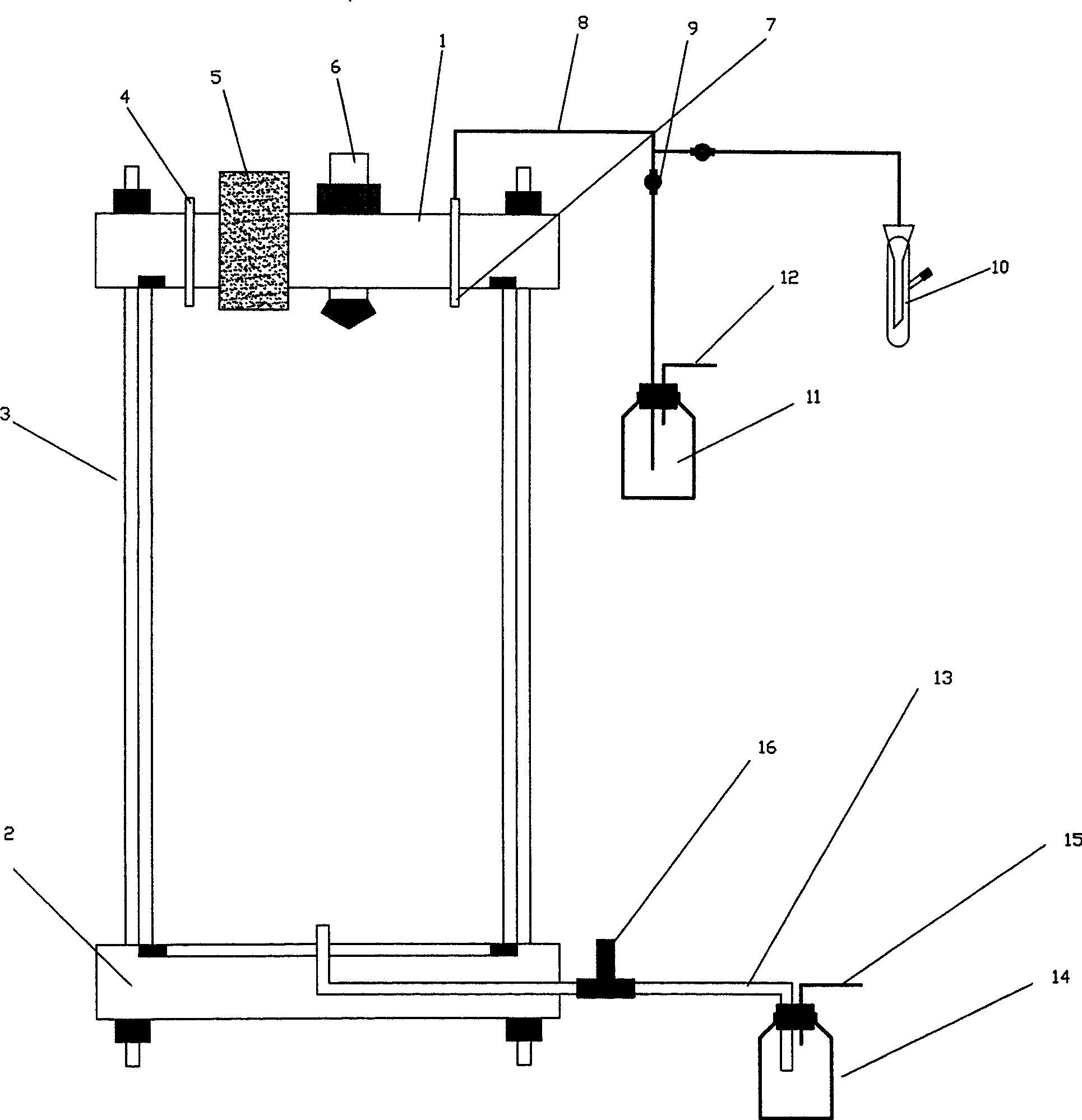
Device for dynamically detecting carbon element loss of root system of plant
The invention discloses a device for dynamically detecting the carbon loss during plant root respiration. The device comprises a closed container composed of an upper top, a lower bottom and a middle container wall. The device is characterized in that an air inlet pipe, an air outlet pipe, a rubber stopper for sealing the plant and the container, and a charging piston for adding reagent into the container are arranged at the upper top; the air outlet pipe is respectively communicated with a sample bottle and an air reservoir through guide pipes, and a three-way valve is installed on the guide pipes. The lower bottom is communicated with a liquid reservoir through a guide pipe provided with a switch. The device for dynamically detecting the carbon loss during plant root respiration can be utilized for correct detecting the respiration rate or root activity of the root, the structure is simple, the operation is convenient, the production cost is low, and the popularization and the application are convenient.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for manufacturing LiFePO (lithium iron phosphate)/lithium cobaltate composite anode
InactiveCN102306790AHigh bonding strengthImprove smoothnessCell electrodesLithium iron phosphatePolyvinylidene difluoride
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a LiFePO (lithium iron phosphate) / lithium cobaltate composite anode. The method comprises the following steps: 1, exactly weighing LiFePO, PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) and SP based on the weight ratio of 93:3.5:3.5, and adding 5-20% of lithium cobaltate by weight; 2, mixing and stirring the components weighed in the step 1 for 4-8 hours, and coating evenly by using a coating machine to manufacture an electrode plate; and 3, drying the electrode plate obtained in the step 2 in a vacuum drying oven for 11-13 hours at the temperature of 100-110 DEG C. By adding SP into the LiFePO, the electrical conductivity of the electrode is improved; by adding the PVDF into the LiFePO, the adhesive strength and firmness of an anode coating are improved; a metal ion cobalt doping way is adopted to improve the conductivity of the LiFePO material anode and avoid the influence of high temperature on carbon loss in the carbon cladding process as well as the complicated production process; the manufacturing method is simple, low in the energy consumption and high in efficiency; and the raw materials are obtained easily and the cost is low.
Owner:QINGDAO QIANYUN HIGH TECH NEW MATERIAL
Nitrogen-retaining and carbon-retaining compost preparation method
InactiveCN105523797AIncrease contentImprove conversion rateBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationTotal nitrogenOxygen
The invention discloses a nitrogen-retaining and carbon-retaining compost preparation method. The method comprises the following steps: under the action of an additive, compost raw materials are subjected to aerobic fermentation, such that the compost is obtained. The additive is calcium superphosphate. The amount of substance of phosphorus element in calcium superphosphate is 20-25% of the amount of substance of total nitrogen of the compost raw materials. The compost is a mixture of fresh pig manure and corn stalks. The compost preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of low cost and simple operation. While nitrogen loss and carbon loss during a composting process are controlled, the compost product can reach the requirements of an organic fertilizer industry standard. With the method, compost product nutrient content can be improved, an agricultural organic waste-to-fertilizer conversion rate can be improved, and greenhouse gas emission during the composting process can be reduced. Therefore, energy saving and emission reduction of the preparation process are realized. The method has good practical significance and environment benefit.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Regeneration method of low-carbon-loss activated carbon
ActiveCN106512973AEfficient regenerationHigh adsorption valueOther chemical processesCombustible gas purificationActivated carbonPre treatment
The invention discloses a regeneration method of low-carbon-loss activated carbon. Activated carbon is pretreated by iron or an iron compound as a catalyst at lower temperature, and the synergic actions of dilution and ultrasonic washing are performed; and thus, the regenerated activated carbon with high adsorptive value is obtained under the conditions of low energy consumption and mild conditions, and the carbon loss can be reduced to a large extent.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
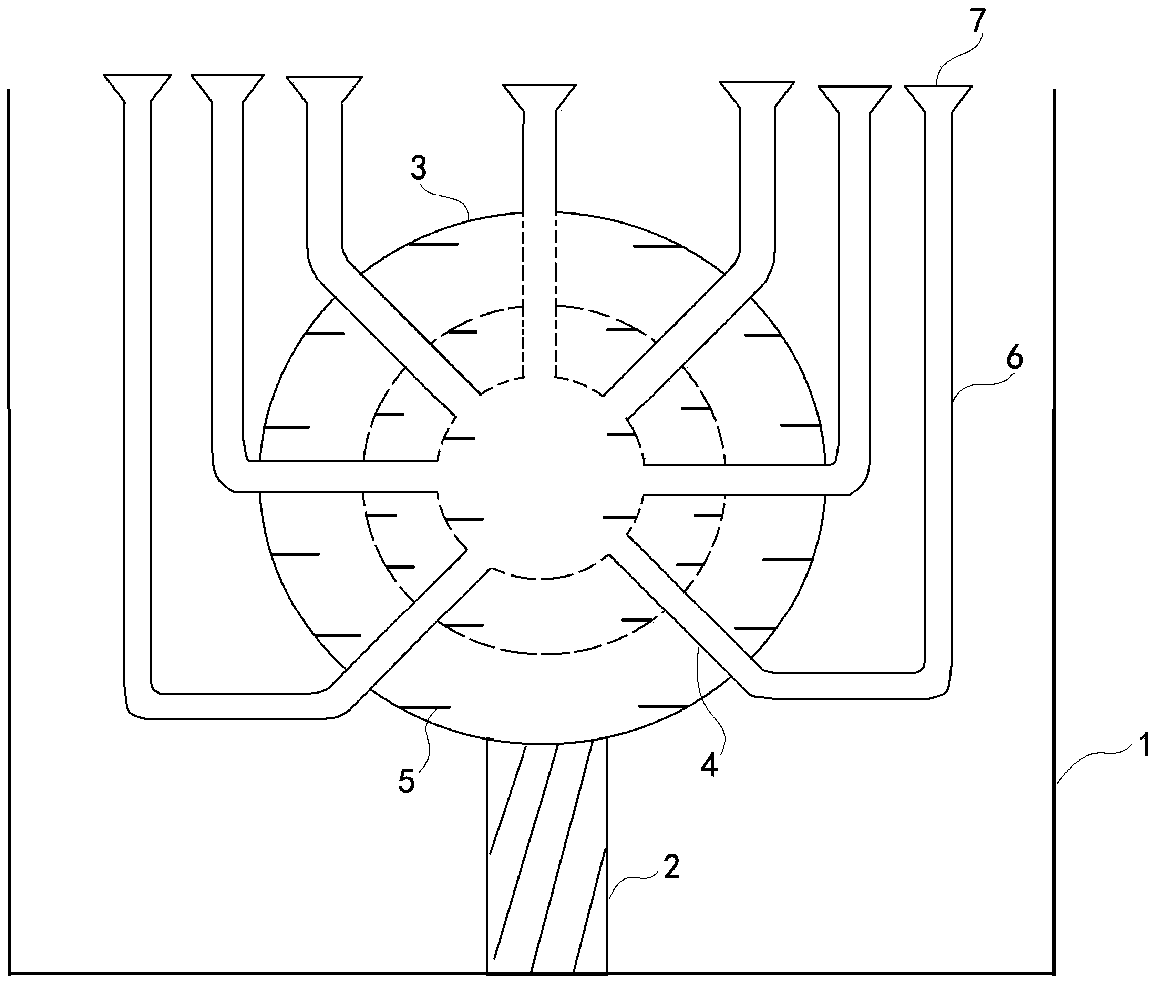
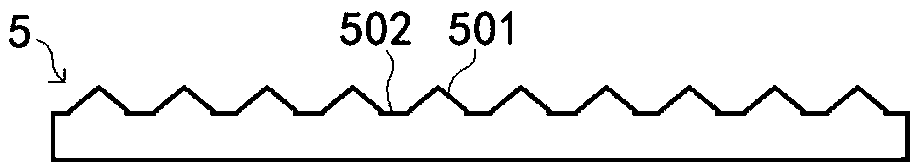
Device for detecting carbon content of fly ash
The invention discloses a device for detecting the carbon content of fly ash, and relates to the technical field of detection of carbon content of fly ash. The device comprises a storage container; anignition mechanism is arranged in the storage container, and comprises a plurality of spherical ignition shells and a plurality of connecting cylinders; the spherical ignition shells are sequentiallynested with one another; the connecting cylinders penetrate from the spherical ignition shell on the outmost layer to the interiors of the spherical ignition shell on the innermost layer; vent pipesare led out from the end parts of the connecting cylinders and then expand upwards vertically; the upper ends of the vent pipes are communicated with the lower ends of vents; the vents are channels ofwhich the internal diameters are gradually expanded from bottom to top; and the bottom end of the spherical ignition shell on the outmost layer is connected to the bottom of the storage container through a supporting pillar. The invention aims to overcome the defect that in the conventional technical scheme that the carbon content of fly ash is measured on the basis of an ignition carbon loss method, the measurement accuracy is lower, and provides the device for detecting the carbon content of the fly ash. The measurement accuracy of the carbon content of the fly ash is improved.
Owner:义乌市添诚科技有限公司
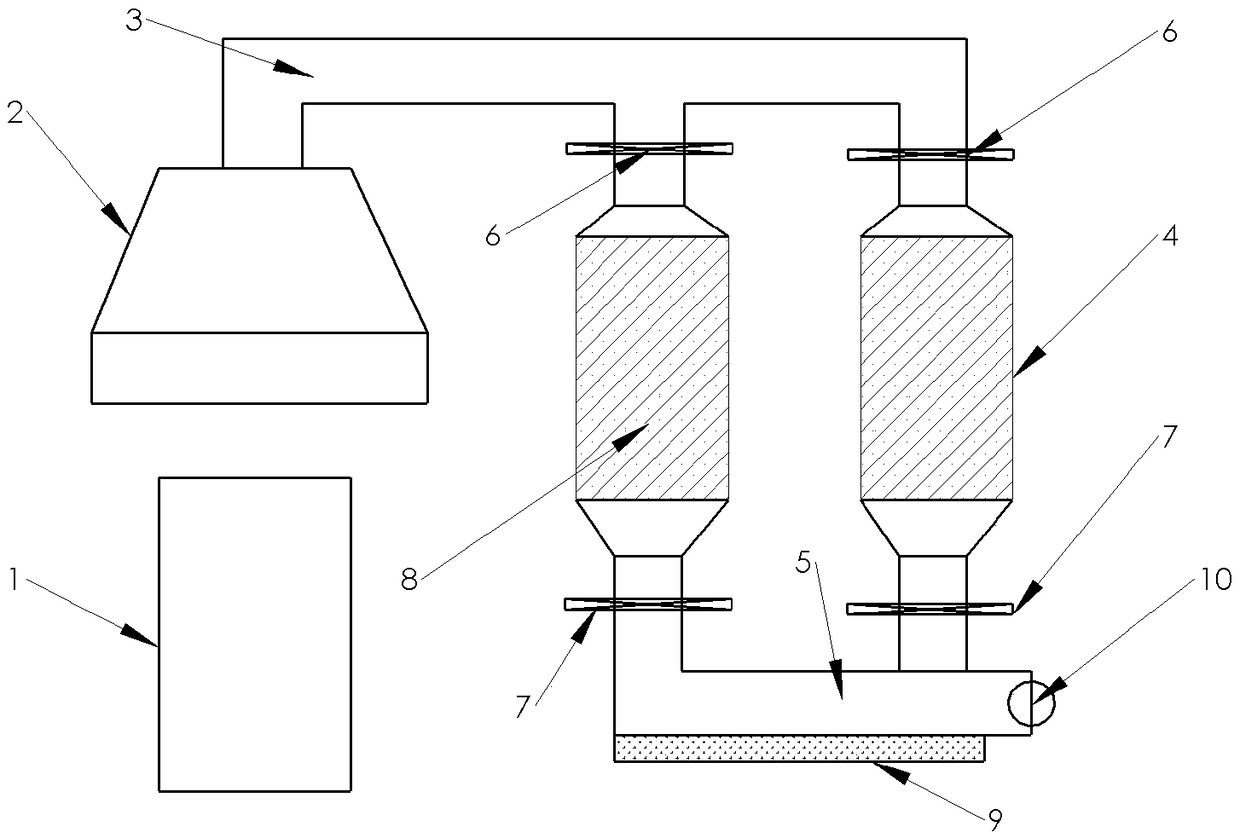
Device for using high-temperature converter gas and increasing heat value and use method of device
InactiveCN108707718AReduce the temperatureSimple methodIncreasing energy efficiencyExhaust gas handlingFlue gasProcess engineering
The invention relates to a device for using high-temperature converter gas and increasing the heat value. The device comprises a movable flue gas hood, a fixed flue, a carbon loss reactor, a water-cooling elbow and a dust removal tank; the movable flue gas hood is arranged above a converter; one end of the fixed flue is connected with the movable flue gas hood; the other end of the fixed flue is connected with the carbon loss reactor; the lower end of the carbon loss reactor is connected with the water-cooling elbow; the dust removal tank is arranged below the water-cooling elbow; a flue gas analysis meter is arranged at the tail of the water-cooling elbow; the carbon loss reactor is filled with one or more of coke, machine-pressed charcoal and semi-coke with the lumpiness not lower than 10 mm; and valves are mounted at the upper end and the lower end of the carbon loss reactor. A method is simple and easy to implement, the carbon loss reactor, is arranged on the basis of an original gasification cooling pipeline, the temperature of the high-temperature converter gas is reduced from 1,500-1,600 DEG C to 800-950 DEG C by the aid of the carbon loss reaction absorbing a large quantityof heat, meanwhile, CO is enriched, the content of CO in the converter gas is increased from 50%-70% to more than 80%, and subsequent application is facilitated.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Preparation method of tungsten carbide coating with micro-nano structure
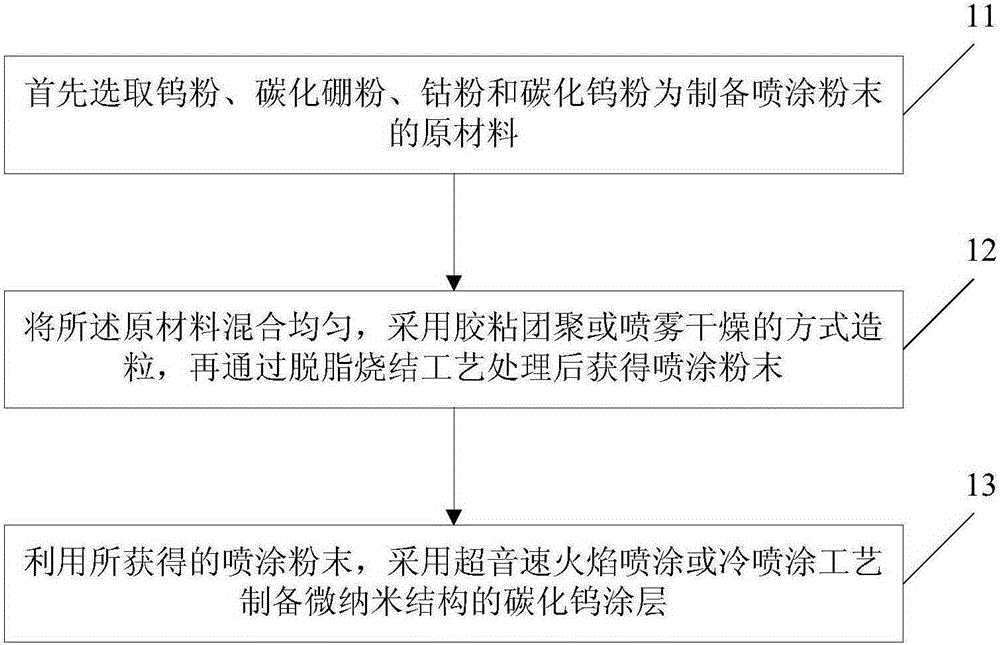
ActiveCN105316617AEvenly distributedLess carbon lossMolten spray coatingPressure inorganic powder coatingMicro nanoBoron carbide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a tungsten carbide coating with a micro-nano structure. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, a tungsten powder, a boron carbide powder, a cobalt powder and a tungsten carbide powder are taken as raw materials for preparing a spraying powder, wherein the tungsten powder accounts for 20 to 86.7 percent of the total weight, the boron carbide powder accounts for 1.2 to 10 percent of the total weight, the cobalt powder accounts for 8 to 25 percent of the total weight, and the tungsten carbide powder accounts for 30 to 75 percent of the total weight; the raw materials are mixed evenly, a way of glue agglomeration or spray drying is adopted for granulation, and then the spraying powder is obtained through degreasing-sintering fabrication processing; and the tungsten carbide coating with the micro-nano structure is prepared by using the obtained spraying powder, adopting supersonic speed flame spraying or a cold spraying process. The method is simple in process, nanophase distribution is even, carbon loss is less, nano tungsten carbide is contained in the coating, the coating with the micro-nano structure is formed, and the coating with the micro-nano structure is relatively high in hardness and good in toughness.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY +1
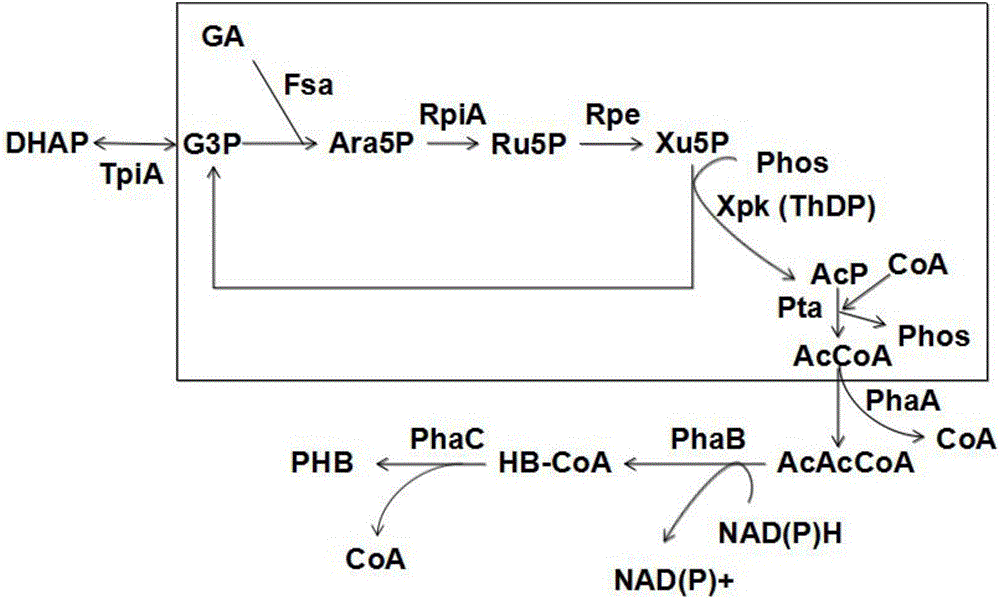
New way for synthesizing acetyl coenzyme A and derivative product thereof using glycolic aldehyde
ActiveCN106755172AHigh affinityIncrease enzyme activityFermentationPhosphoric acidBatch fermentation
The invention discloses a new way for synthesizing acetyl coenzyme A and a derivative product thereof using glycolic aldehyde. The method comprises reaction that glycolic aldehyde reacts with 3-glyceraldehyde phosphate under enzyme catalysis to generate 5-phosphoric acid arabinose, wherein the enzyme is selected from aldolase, transaldolase and isozyme thereof and mutate enzyme. The method is relatively high in catalytic rate; the theoretical yield of carbon of a reaction route is 100%; the carbon loss avoided; G3P, an enzyme and a coenzyme all can be recycled; the reaction efficiency is relatively high; and the cost is reduced. In addition, the coenzymes RpiA and Rpe from a pentose phosphate pathway are high in affinity with a substrate and high in catalytic activity. According to the method, more obvious advantages are developed in the production processes, of in vitro continuous polyenzyme catalysis, fed-batch fermentation and continuous fermentation, capable of controlling the substrate level.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A flue gas desulphurization and regeneration method for an ordered graded porous carbon material
ActiveCN107473219AGuaranteed orderOvercoming the presence of blind holesGas treatmentCarbon compoundsPorous carbonBiological activation
A flue gas desulphurization and regeneration method for an ordered graded porous carbon material is disclosed. Phenolic resin and a triblock copolymer are adopted as raw materials to prepare a porous polymer, and then activation is performed by utilizing nitrogen and ammonia to obtain a microporous-mesoporous graded carbon structure. When the carbon material is applied in flue gas desulphurization techniques, the sulfur capacity of activated carbon can be effectively increased, H2SO4 that is a byproduct is more liable to be separated from pore structures, and 80% or above of the H2SO4 can be separated out by adopting a water washing method and is far higher than water washing regeneration efficiencies at present. A high-temperature reaction between H2SO4 and carbon is avoided so that a regeneration process is nearly free of carbon loss.
Owner:TIANJIN CHENGJIAN UNIV
Method for precisely adjusting C and Si before furnace inputting for spheroidal graphite cast iron
To achieve optimal control over the content of C and Si of spheroidal graphite cast iron, the invention discloses a method for precisely adjusting C and Si before furnace inputting for the spheroidal graphite cast iron. The method comprises the steps that firstly, according to the final content of C, the content of Si needs to minus Si content increasing ingredients subjected to inoculation, base iron is smelted, and after being smelted, the base iron pours a thermoanalysis empty sample cup and a white cast sample cup; secondly, the activated carbon equivalent (ACEL) of molten iron is determined according to the liquid phase temperature TL of a grey cast cooling curve, the activated silica equivalent (ASiE) is determined according to the eutectic temperature TE of a white cast cooling curve, and the content of activated carbon (AC) is obtained through backstepping; thirdly, the balance temperature Teq of a Si-O-C deoxygenation reaction is calculated through the AC and the ASiE, and the silicon carbon loss state is judged according to the difference of the balancing temperature Teq and the molten iron temperature Ta; fourthly, the empty sample cup is poured again, and C and Si are adjusted according to the ACEL of the molten iron at the time; and fifthly, the ACEL of the finally-nodulized molten iron is verified and can be adjusted again in the next batch. The method is used for the fields of casting detection and metallurgy.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Genetically engineered bacterium used for combined production of succinic acid and isoprene, and construction method thereof
InactiveCN106635936ANo wasteAtom economyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium used for combined production of succinic acid and isoprene, and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The genetically engineered bacterium contains the gene of an enzyme needed in simultaneous overexpression of isoprene synthetic route in escherichia coli and pyruvate carboxylase gene. The invention also provides the construction method and the application method of the genetically engineered bacterium. The genetically engineered bacterium is capable of realizing combined production of succinic acid and isoprene, avoiding carbon loss in isoprene biosynthesis process, improving atom economy, reducing emission of carbon dioxide, and possesses high environmental benefits.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Gasification system for carbon-containing fuel
ActiveCN103710046ARealized lossAchieve reductionEnergy inputCombined combustion mitigationSyngasSlag
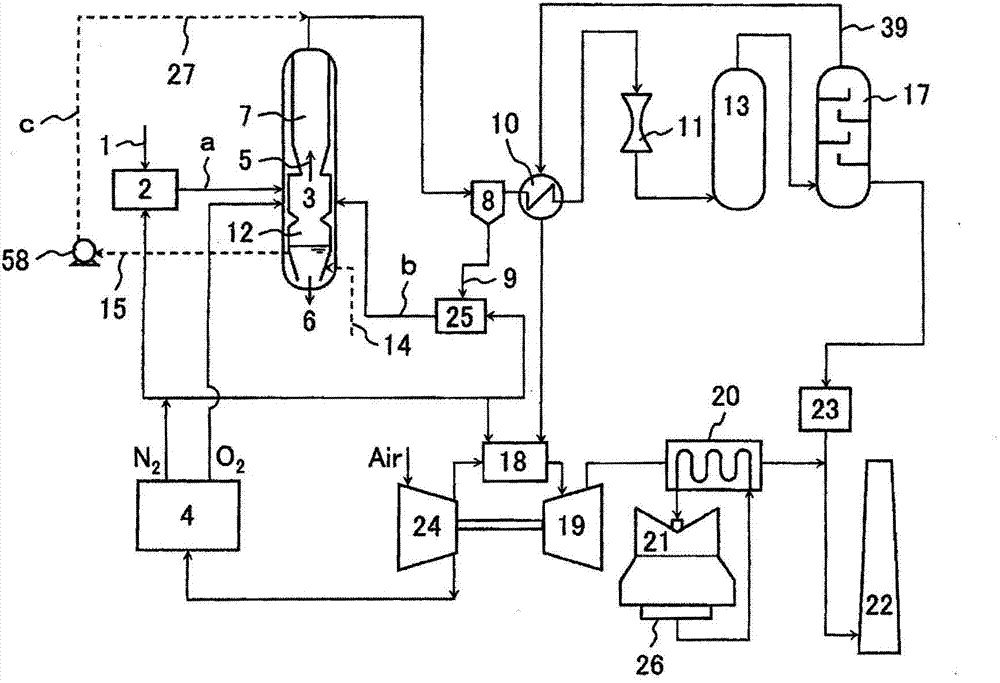
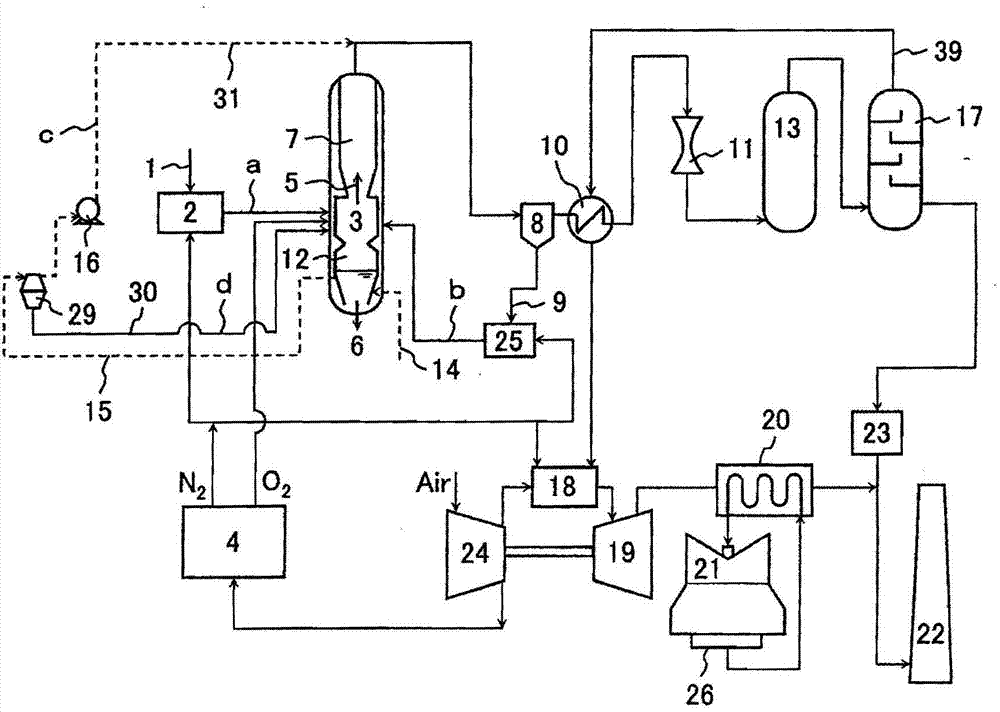
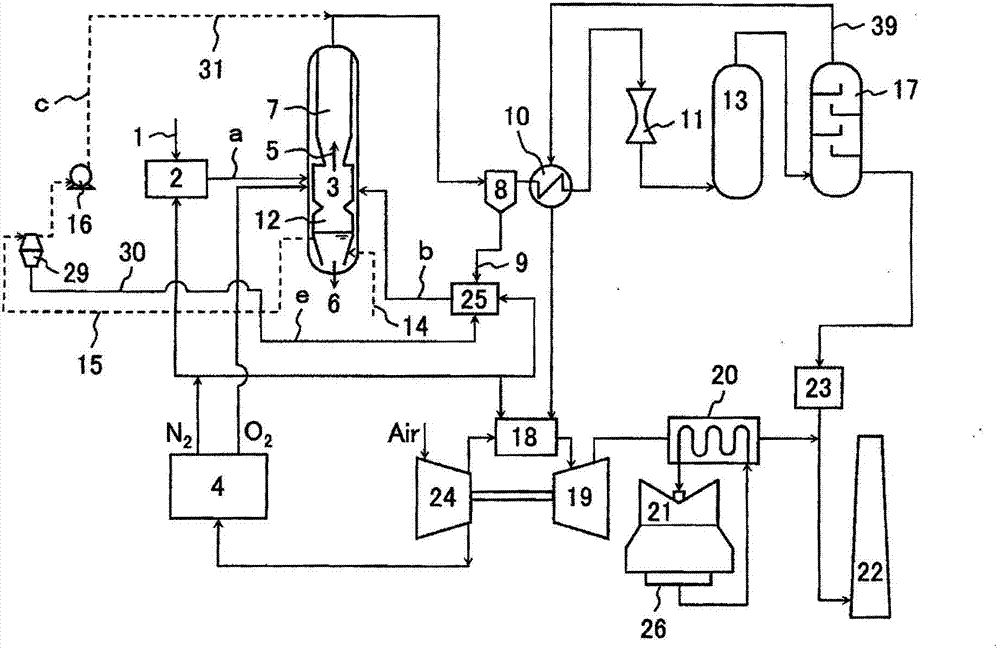
The present invention provides a gasification system for carbon-containing fuel that achieves both the utilization of high-temperature waste water and waste heat generated by a gasifier and the reduction in the equipment and construction costs of the gasifier. In a gasifier (3) for gasifying carbon-containing fuel, high-temperature water is pulled out from a slag-cooling water pool (12) at the bottom of the gasifier, and fed to the downstream side of the gasifier or the upstream side of a dust removing part (8) through a water supply system (c) so as to be mixed with a syngas, thereby cooling the syngas. Thus, a heat recovery part (7) of the syngas can be miniaturized or eliminated. The high-temperature water pulled out from the slag-cooling water pool is easily evaporated while being mixed with the syngas, such that the syngas can be cooled with high efficiency. Solids in the high-temperature water pulled out from the slag-cooling water pool are recovered by the duct removing part with the syngas, and fed into the gasifier again. Thus, the utilization of the waste heat of the high-temperature water is realized, and the carbon loss and waste material are reduced.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD +1
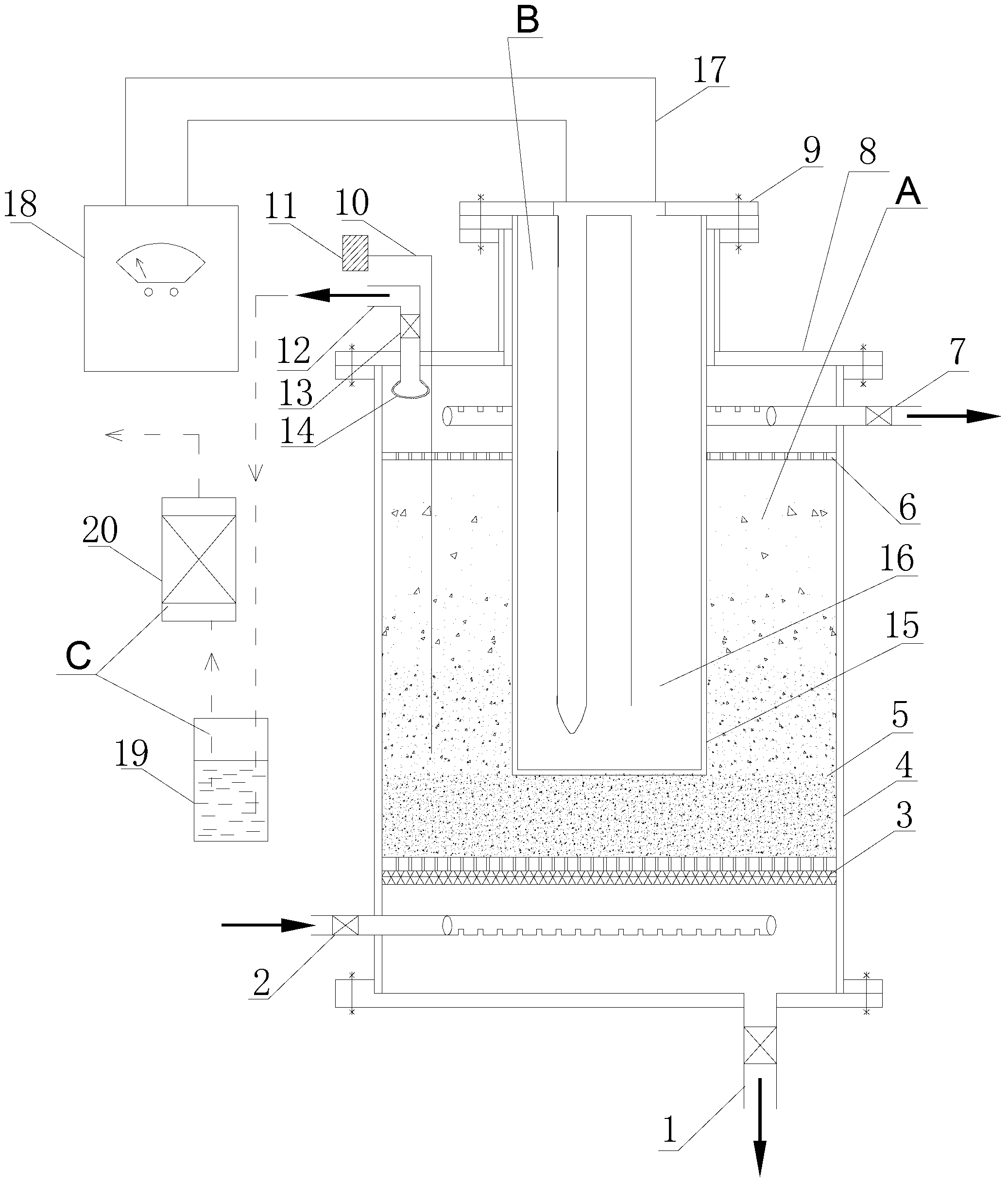
Filtering and back-flushing method of ceramic filter element of water purifier
InactiveCN101954242ALighten the burden of filtrationGuaranteed filtration accuracySemi-permeable membranesWater dischargeFiltration
The invention relates to the water treatment industry, in particular to the aspect of deep filtration and purification of drinking water. The invention discloses a filtering and back-flushing method of a ceramic filter element of a water purifier. The pipeline of a water treatment device comprises a water path switcher and a ceramic filter element device controlled by the water path switcher; the water path switcher is provided with a back-flushing water discharge port; an inflow / outflow water switch port of a connection disk of the water path switcher is serially communicated in the pipeline of the water treatment device; an inflow / outflow water switch port of a controlled disk of the water path switcher is communicated with a water inlet and a water outlet of the controlled ceramic filter element device; a sealed switch interface is formed between the connection disk and the controlled disk, and related water switch ports are formed at corresponding equational switch positions respectively; and a filtering channel and a back-flushing channel of the controlled ceramic filter element device are formed through relative shift of the positions of the water switch ports on the connection disk and the controlled disk respectively. The invention has the advantages of effectively eliminating influence of carbon loss on the drinking water and prolonging the service life of the rear fine filter element, along with simple and practical structure, low cost and good filtering and back-flushing effect.
Owner:杜也兵
Kiln method for producing phosphoric acid and light aggregate
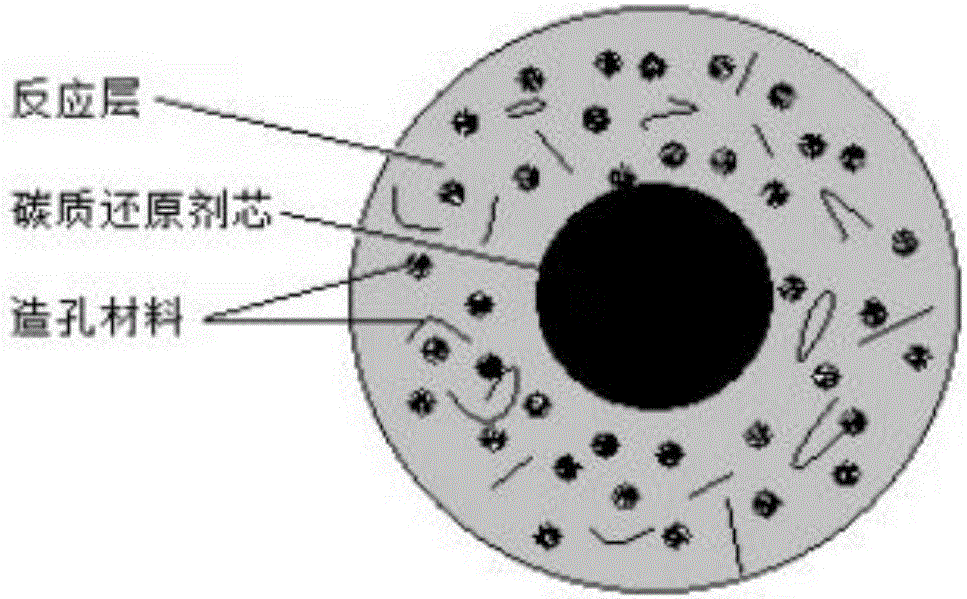
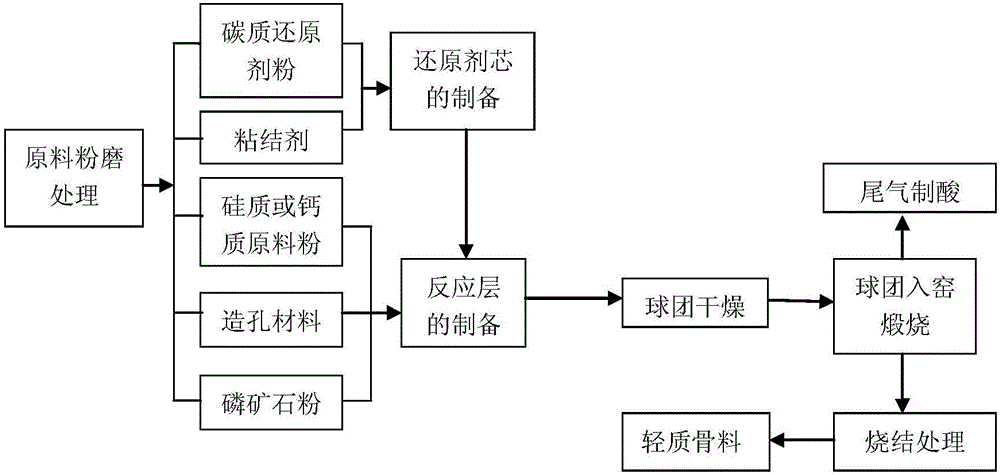
ActiveCN106517120AReduce breakageEffective protectionPhosphoric acidReaction layerCalcium in biology
The invention discloses a kiln method for producing phosphoric acid and light aggregate. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: raw material pretreatment: preparing the following raw materials: carbon reducing agent powder, an adhesive, phosphate ore powder, silicon raw material powder / calcium raw material powder, and pore forming material powder; adding carbon reducing agent powder and the adhesive into a pelletizer, mixing, and sieving, wherein the oversize product is the produced reducing agent cores; adding the reducing agent cores, phosphate ore powder, silicon raw material powder / calcium raw material powder, and pore forming material powder into the pelletizer, mixing to prepare green pellets with an outer reaction layer; delivering the green pellets to a kiln, calcining the green pellets at a constant temperature, naturally cooling to obtain light aggregate, and burning the gas from the kiln to prepare phosphoric acid. The provided method can produce phosphoric acid and light aggregate for preparing concrete, effectively solves the problem of carbon loss in the conventional kiln method for producing phosphoric acid, effectively overcomes the problem that a large amount of slag is hard to process, and is very practical.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
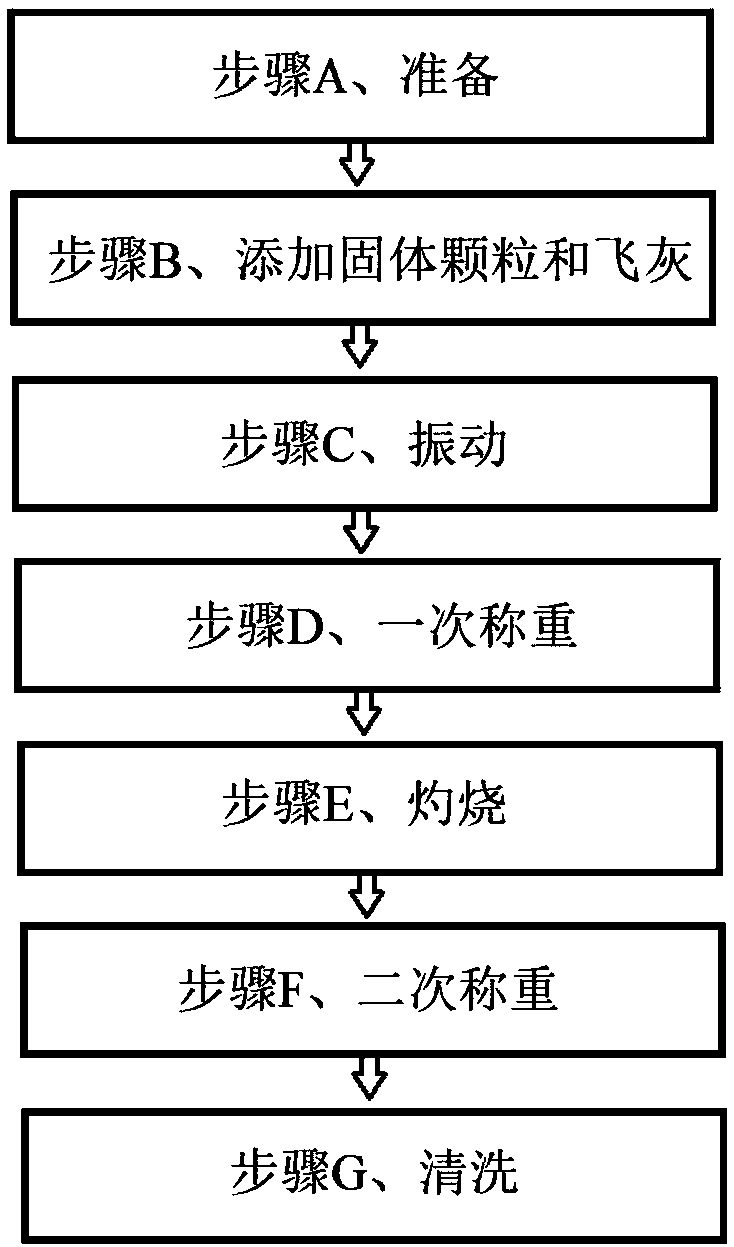
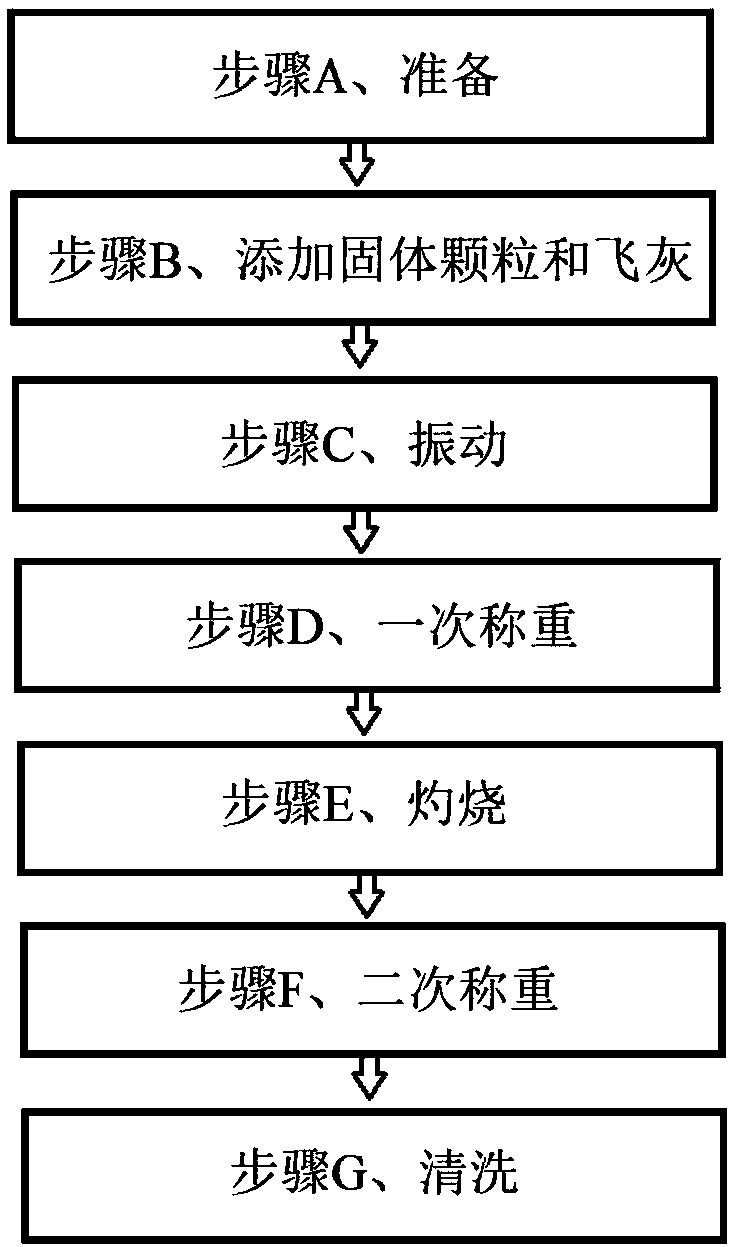
Carbon content detection method of fly ash of boiler
ActiveCN109100257APlay a role in ventilationPlay the role of supporting the skeletonWeighing by removing componentSolid particleFly ash
The invention discloses a carbon content detection method of fly ash of a boiler, and relates to the technical field of detection of the carbon content of the fly ash. The carbon content detection method of the fly ash of the boiler comprises the following steps: Step A, preparation; Step B, adding of solid particles and the fly ash; Step C, vibration; Step D, primary weighing; Step E, burning; Step F, secondary weighing; and Step G, cleaning. The invention aims to overcome the shortcoming of relatively low measurement accuracy of an existing technical scheme of measuring the carbon content ofthe fly ash based on a burning carbon loss method, and the carbon content detection method of the fly ash of the boiler is provided, so that the accuracy of measuring the carbon content of the fly ash is improved.
Owner:当涂县护河镇感湾劳务服务有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com