Method for precisely adjusting C and Si before furnace inputting for spheroidal graphite cast iron
A technology of iron furnace and nodular graphite, which is applied in the field of metallurgy and casting, and can solve the problems of precision limitation, no physical meaning, no specific physical meaning, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
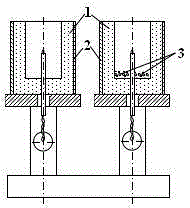
[0021] By adjusting the C content and Si content of the original molten iron, it is ensured that the final poured molten iron is in a microeutectic or eutectic state. Self-made Φ30×50mm cylindrical dry sand sampler sample cup. The material of the cup body does not contain pulverized coal and other substances that react with molten iron, and the thermocouple points are coated and protected by refractory materials such as alumina. Put an appropriate amount of forced whitening substance Te and buffering agent on the bottom of the cup through the binder, the dry sand sample cup can reduce the influence of external factors, and the test results can be very stable. In addition, during the use of this type of sample cup, the coat A steel sleeve with a wall thickness of 3mm acts to increase the strength and prevent the sample cup from collapsing when ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com