Preparation method of tungsten carbide coating with micro-nano structure
A micro-nano structure, tungsten carbide technology, applied in coating, metal material coating process, pressure inorganic powder coating and other directions, can solve the problem of high cost of nano-tungsten carbide coating and the lack of effective solution for nano-tungsten carbide dispersion and retention. and other problems, to achieve the effect of uniform distribution of nano-phase, high hardness and less carbon loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
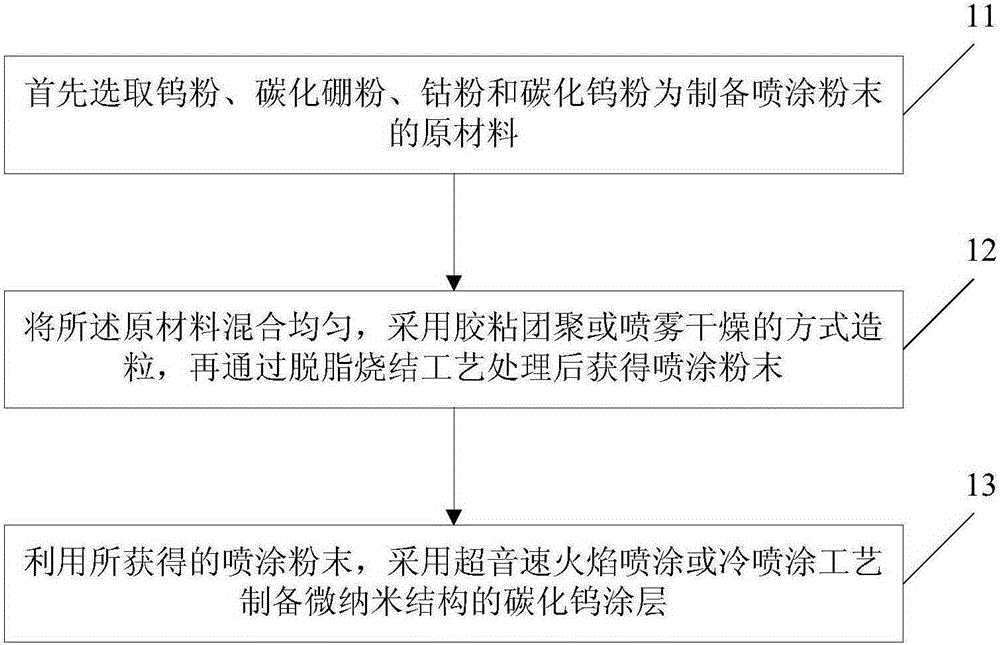
[0030] Embodiment 1, with tungsten powder, boron carbide, cobalt powder, tungsten carbide powder as raw material, wherein tungsten powder accounts for 40%, boron carbide accounts for 4.6%, cobalt powder accounts for 8%, tungsten carbide accounts for 47.4%; Tungsten powder D 50 ≤1 micron, boron carbide D 98 ≤2 microns, cobalt powder D 50 ≤1.5 microns, tungsten carbide D 50 = 0.8 ~ 1.5 microns;
[0031] The above raw materials are mixed evenly, granulated by adhesive agglomeration or spray drying, and then sprayed powder is obtained by degreasing and sintering process, and the maximum sintering temperature is 1250°C;
[0032] Select the particle size range of the spraying powder according to the conventional particle size, and prepare the coating by supersonic flame spraying process; among them, oxygen: 56 cubic meters per hour, kerosene 28 liters per minute, and spraying distance of 380 mm, to obtain a tungsten carbide coating containing micro-nano structure .
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2, with tungsten powder, boron carbide, cobalt powder, tungsten carbide powder as raw material, wherein tungsten powder accounts for 80%, boron carbide accounts for 5.1%, cobalt powder accounts for 12%, tungsten carbide accounts for 8%; Tungsten powder D 50 ≤0.8 microns, boron carbide D 98 ≤1 micron, cobalt powder D 50 ≤1.0 micron, tungsten carbide D 50 = 1.0 ~ 1.5 microns;
[0034] The above raw materials are mixed evenly, granulated by adhesive agglomeration or spray drying, and then sprayed powder is obtained by degreasing and sintering process, and the maximum sintering temperature is 1300°C;
[0035] Select the particle size range of the spraying powder according to the conventional particle size, and prepare the coating by supersonic flame spraying process; among them, oxygen: 38 cubic meters per hour, kerosene 20 liters per minute, and spraying distance of 360 mm, to obtain a tungsten carbide coating containing micro-nano structure .
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3, with tungsten powder, boron carbide, cobalt powder, tungsten carbide powder as raw material, wherein tungsten powder accounts for 60%, boron carbide accounts for 6%, cobalt powder accounts for 15%, tungsten carbide accounts for 19%; Tungsten powder D 50 ≤0.8 microns, boron carbide D 98 ≤2 microns, cobalt powder D 50 ≤1.0 micron, tungsten carbide D 50 = 1.5 ~ 2.5 microns;
[0037] The above raw materials are mixed evenly, granulated by adhesive agglomeration or spray drying, and then sprayed powder is obtained by degreasing and sintering process, and the maximum sintering temperature is 1350°C;
[0038] Select the particle size range of the spraying powder according to the conventional particle size, and prepare the coating by supersonic flame spraying process; among them, oxygen: 50 cubic meters per hour, kerosene 27 liters per minute, spraying distance 390 mm, to obtain a tungsten carbide coating containing micro-nano structure .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com