Nitrogen-retaining and carbon-retaining compost preparation method
A technology for composting and raw materials, applied in the field of environmental engineering, can solve the problems of high cost, difficulty in obtaining, and application of exogenous additives, and achieve good practical significance, environmental benefits, low cost, and the effect of increasing content.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1, the compost preparation method of nitrogen conservation, carbon conservation
[0030] (1) The raw materials for composting are fresh pig manure and corn stalks (the stalks are crushed to a length of 2-5 cm by a grinder), and mixed according to the mass of fresh base at 6.5:1. The basic properties of the initial materials are shown in Table 1.
[0031] In this embodiment, 3 treatment groups were set up, including 2 experimental groups and 1 control group, wherein the control group (CK) only had fresh pig manure and corn stalks, and no superphosphate was added. In the experimental group 1 (T1), in addition to the compost raw materials, the amount of substance added is 20% (marked as 0.20M) superphosphate (its quality is equivalent to 13.2% of the dry mass of the initial material); the experimental group 2 (T2) except the compost raw material, also add the superphosphate (its quality is equivalent to 16.5% of initial material dry mass) that the amount additi...
Embodiment 2
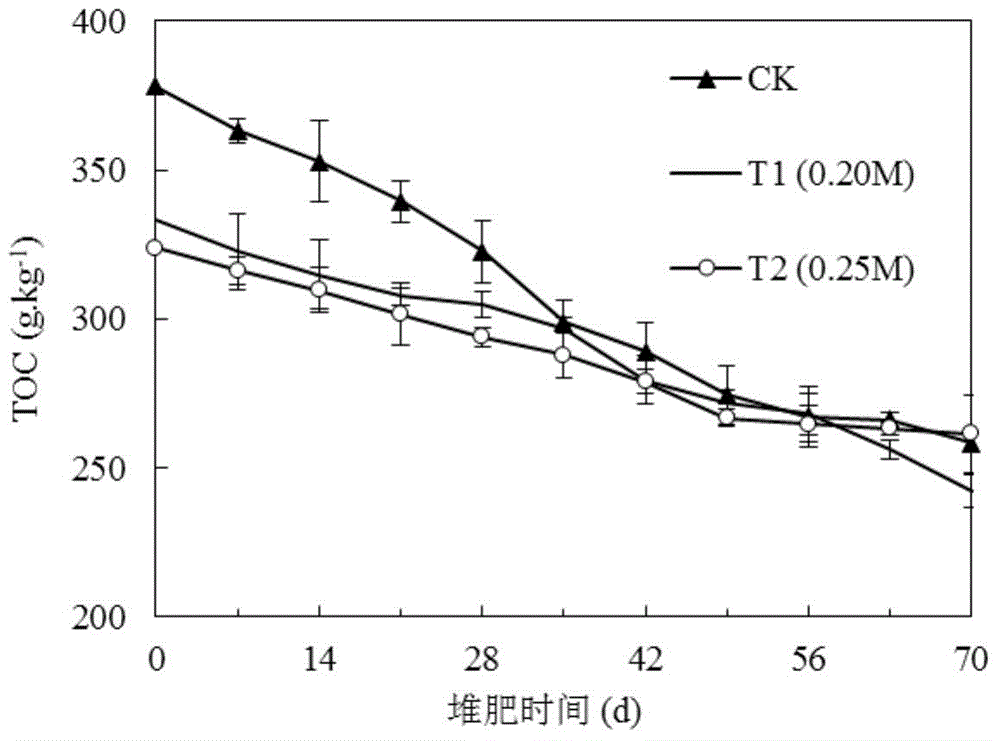
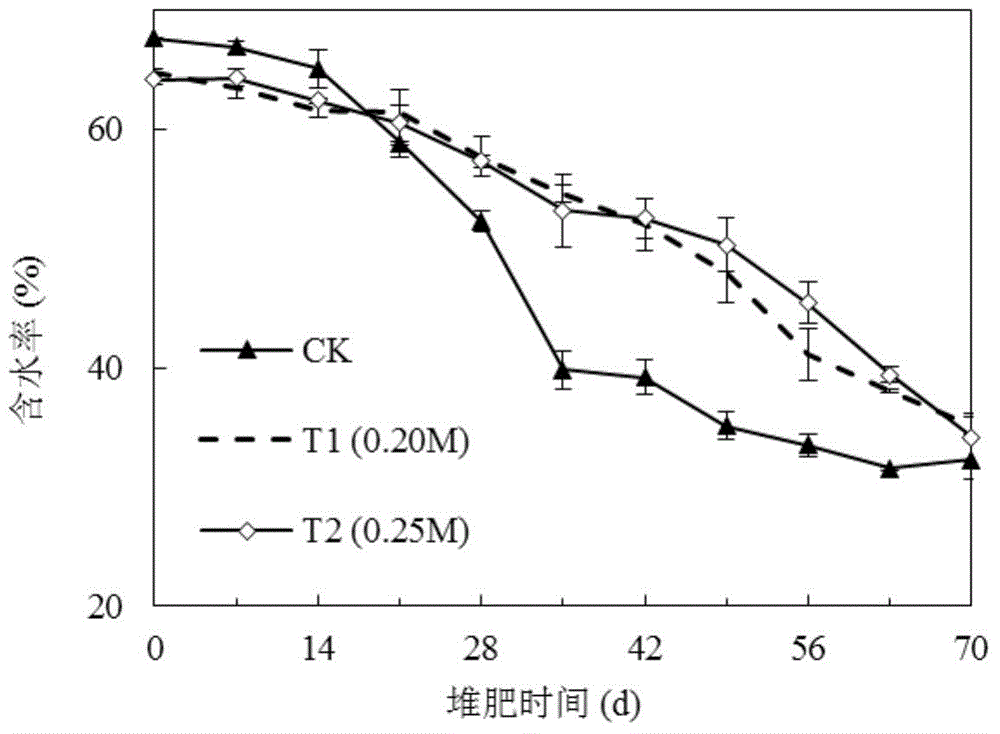
[0042] Embodiment 2, the addition of calcium superphosphate on compost carbon content, nitrogen content and compost output, quality impact in composting process
[0043] (1) Changes in temperature during composting
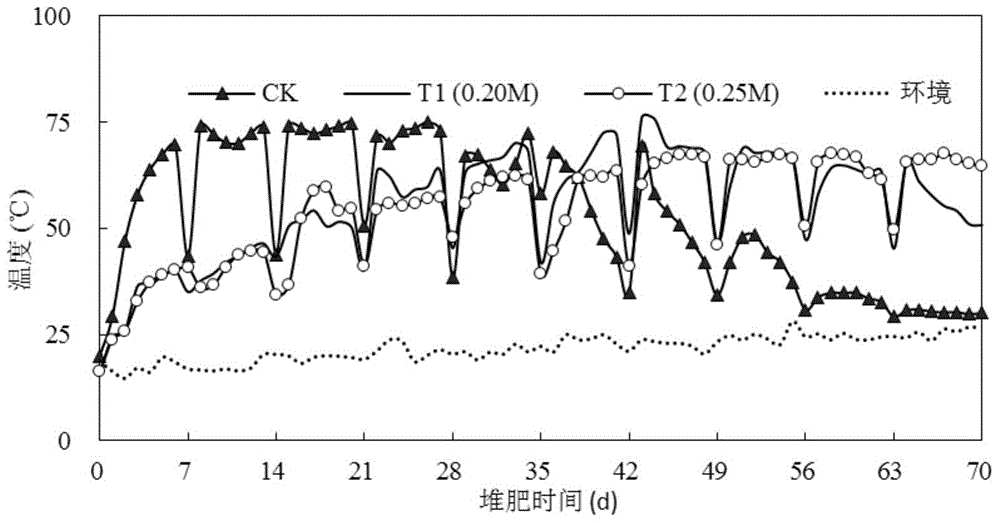
[0044] Temperature is an important indicator to reflect the degradation status of organic matter in the pile. During composting in embodiment 1, the heap body center temperature of each treatment group changes with time as figure 1 shown.
[0045] from figure 1It can be seen from the figure that the control group reached the high temperature period (>50°C) on the 3rd day of composting, while the experimental groups T1 and T2 delayed until the 15th day to reach the high temperature period of composting, which had a certain impact on the heating process of the compost. After the high temperature period lasted for about 30 days in the control group and the experimental group respectively, the temperature of the pile gradually decreased. This is because after the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com