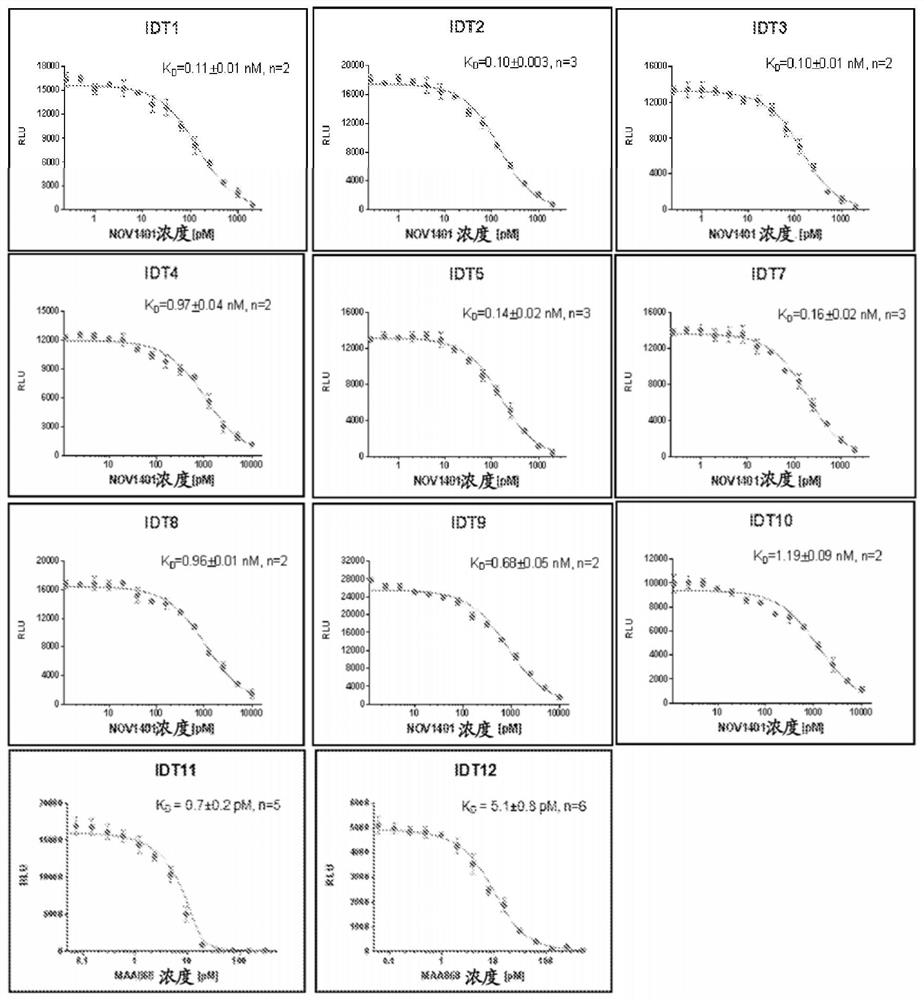
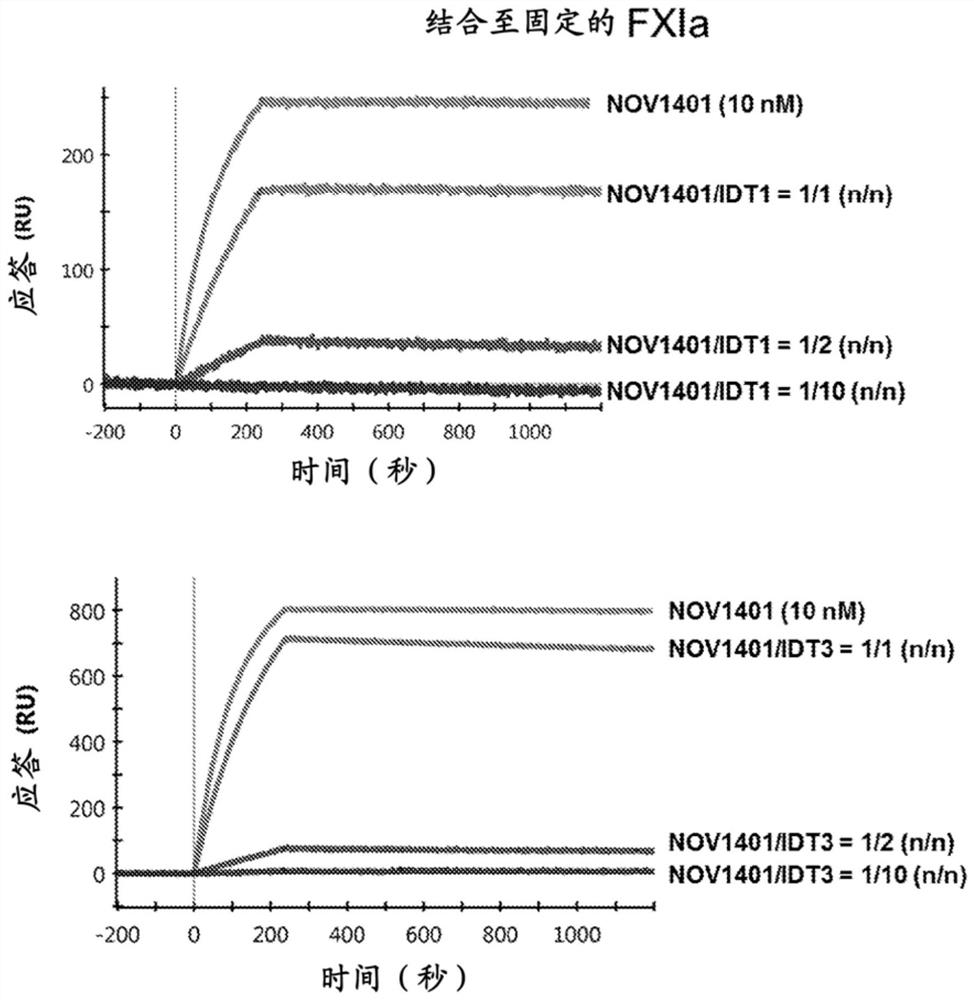
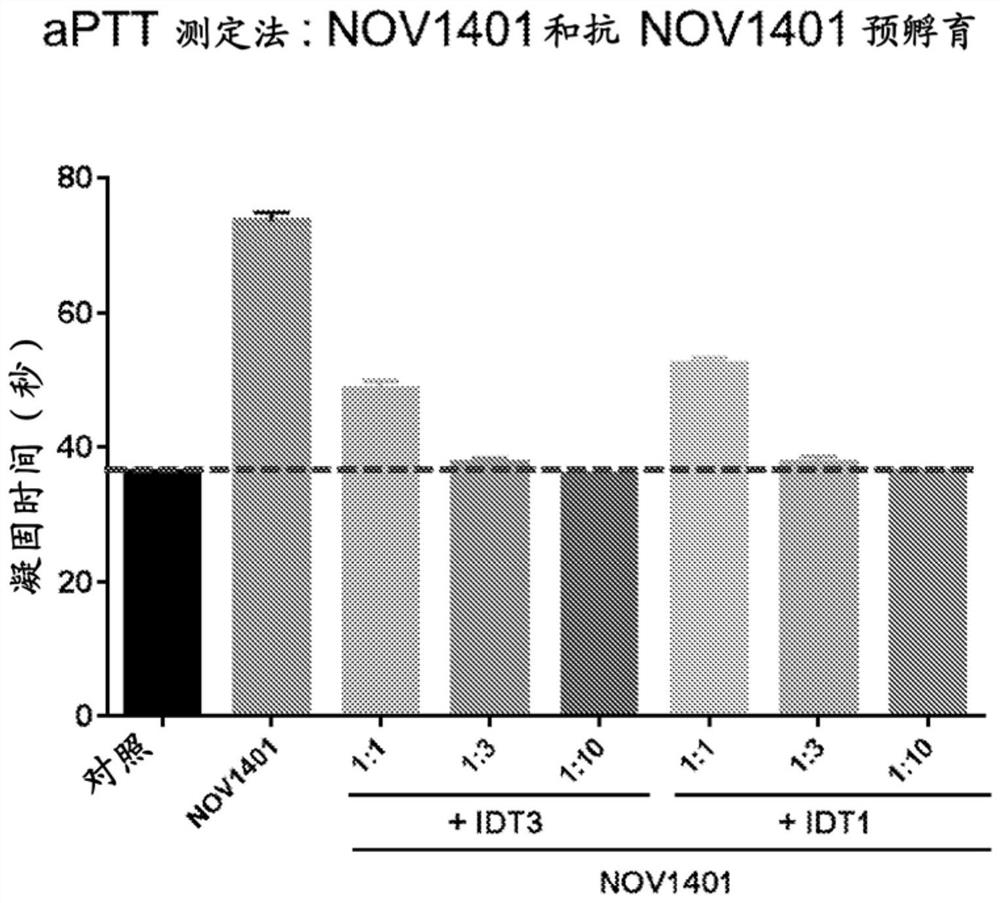
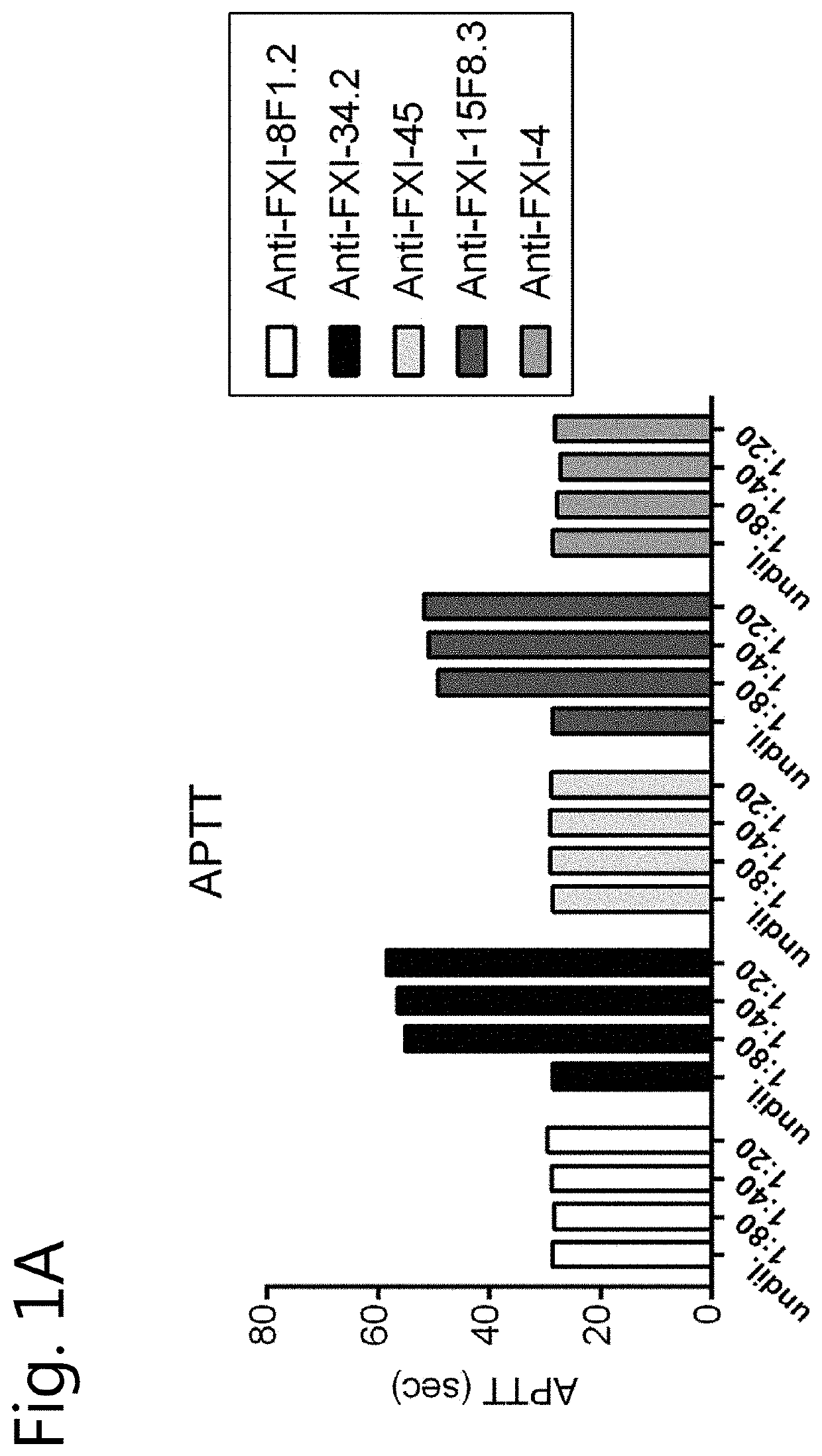
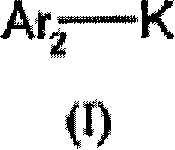Patents
Literature
40 results about "Factor XI" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
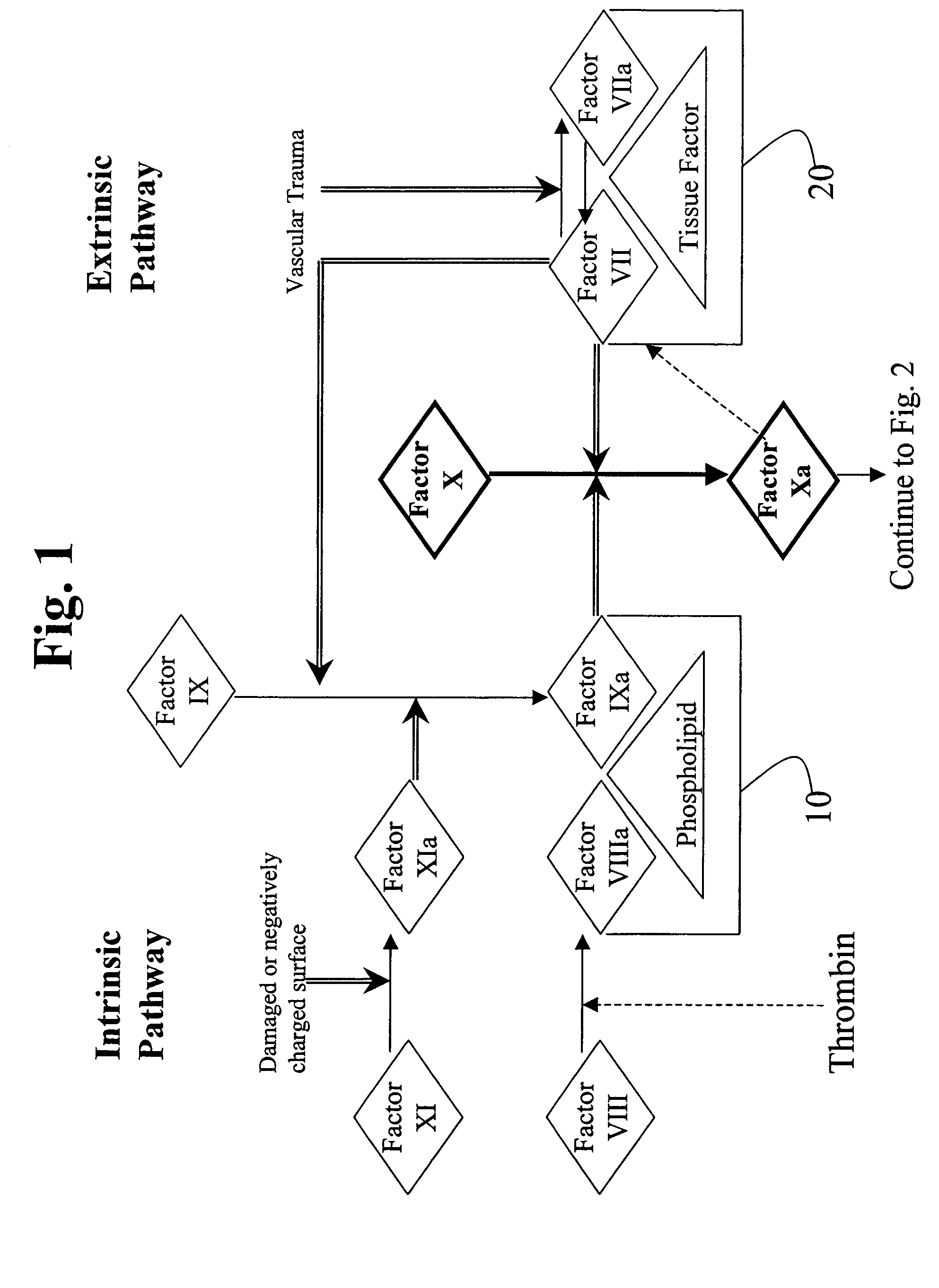
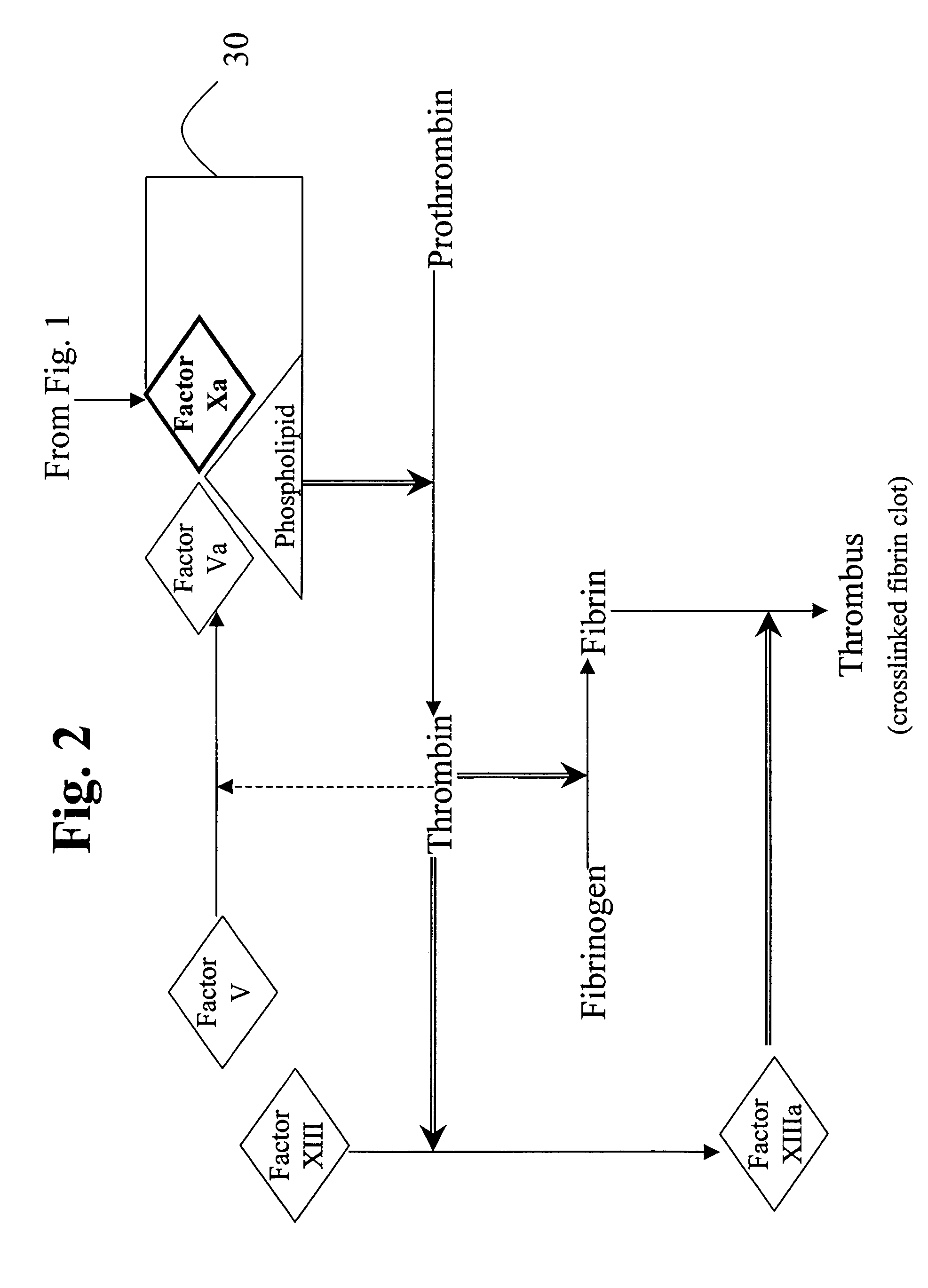
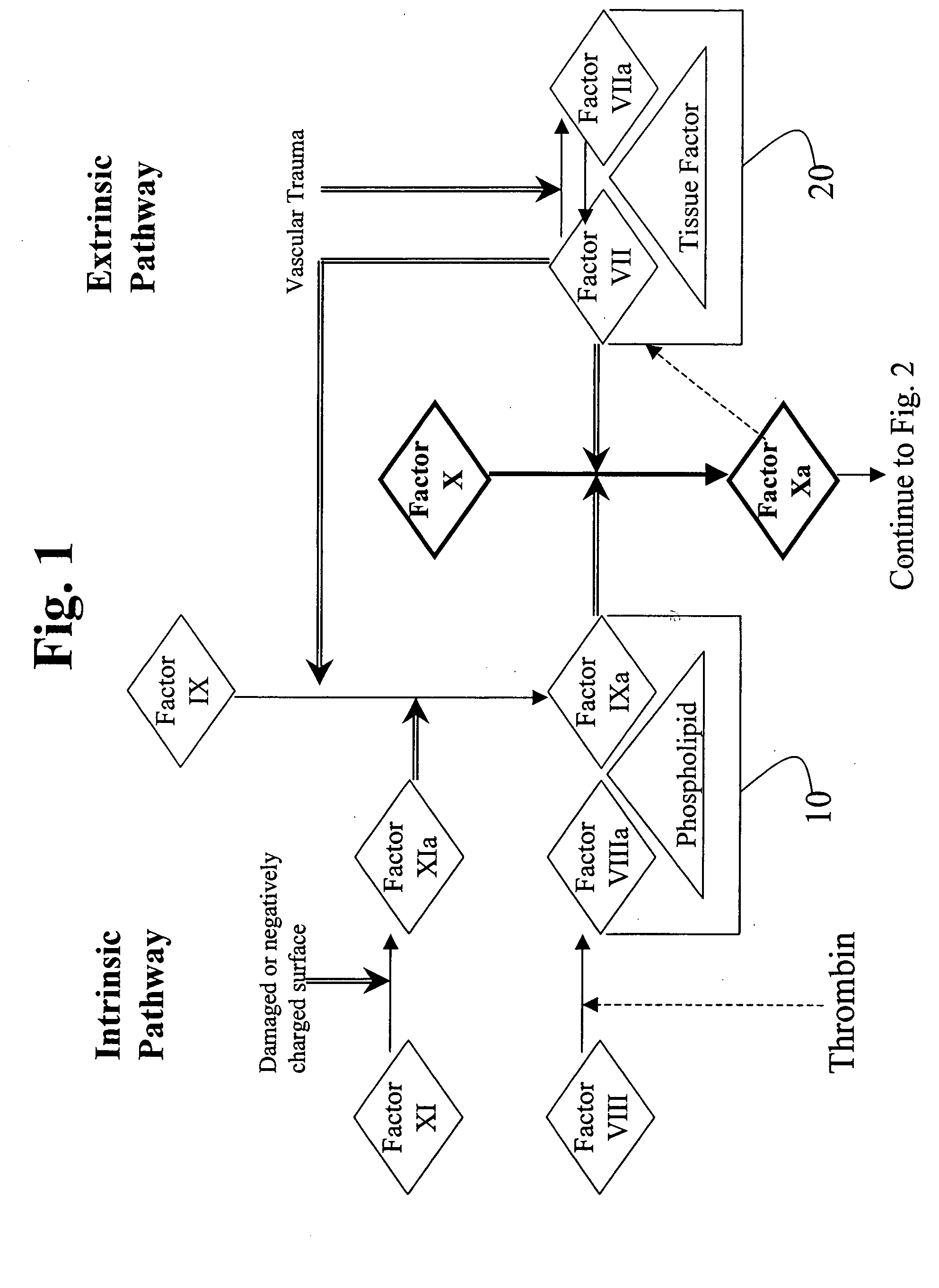
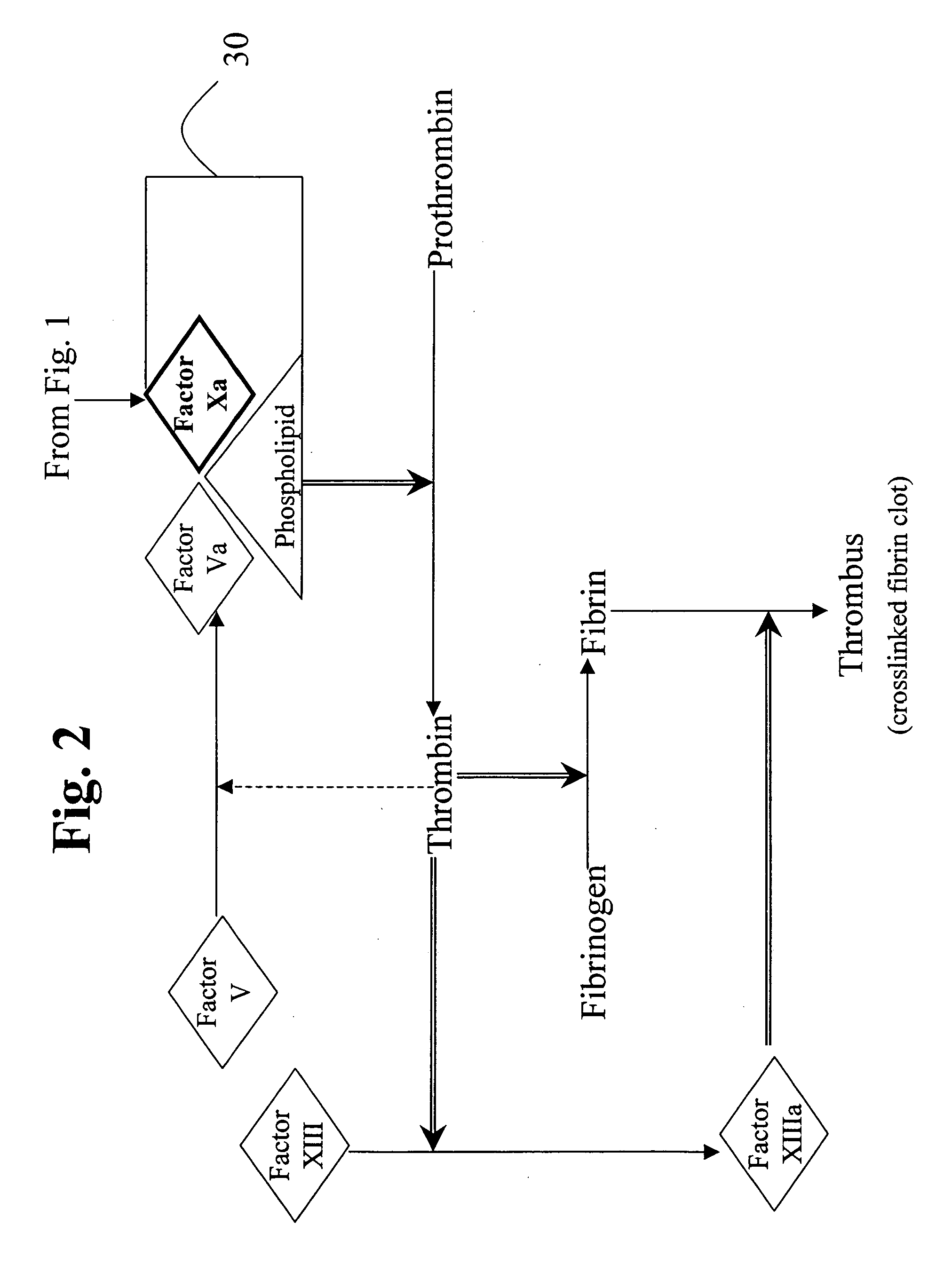
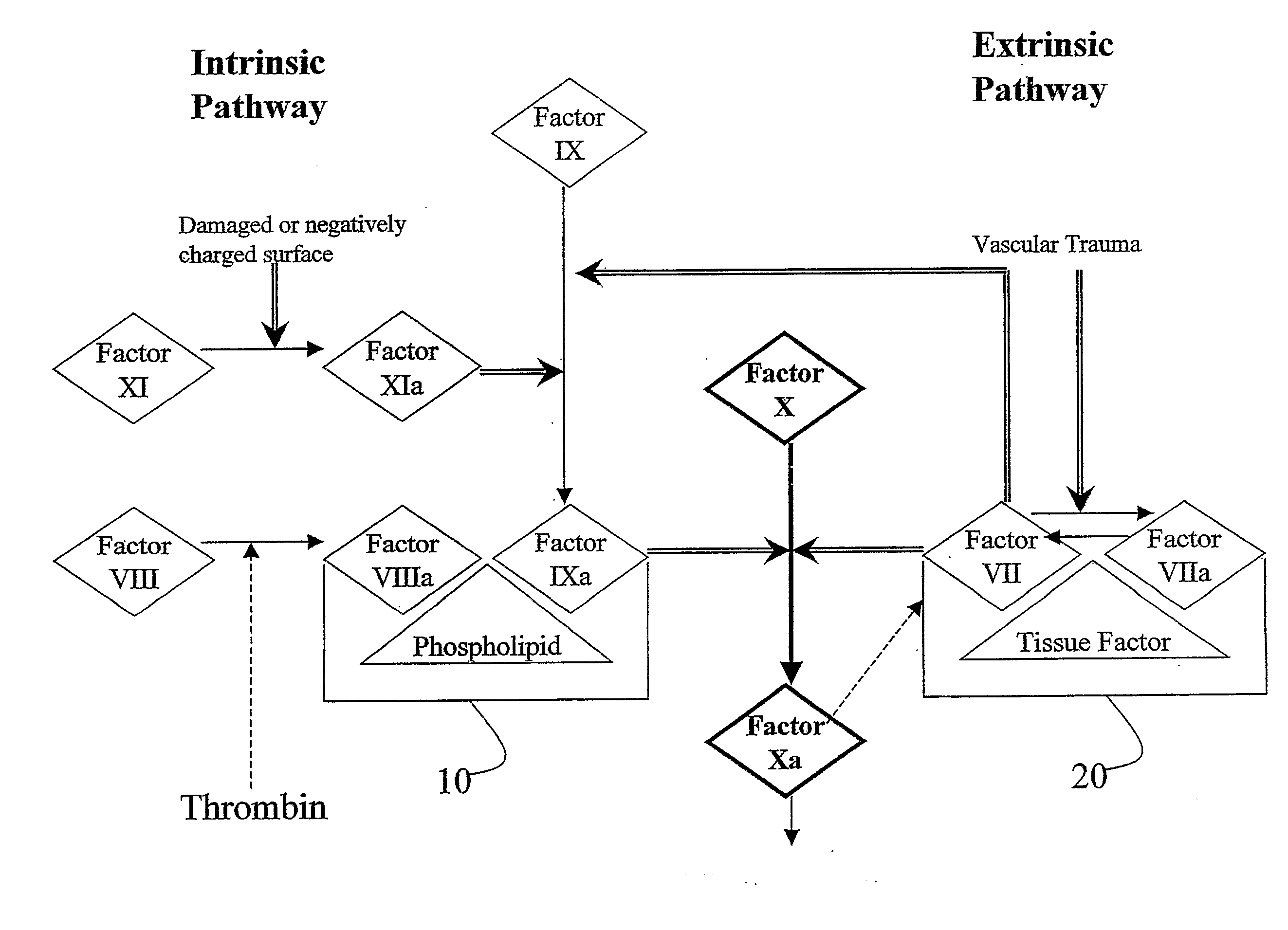
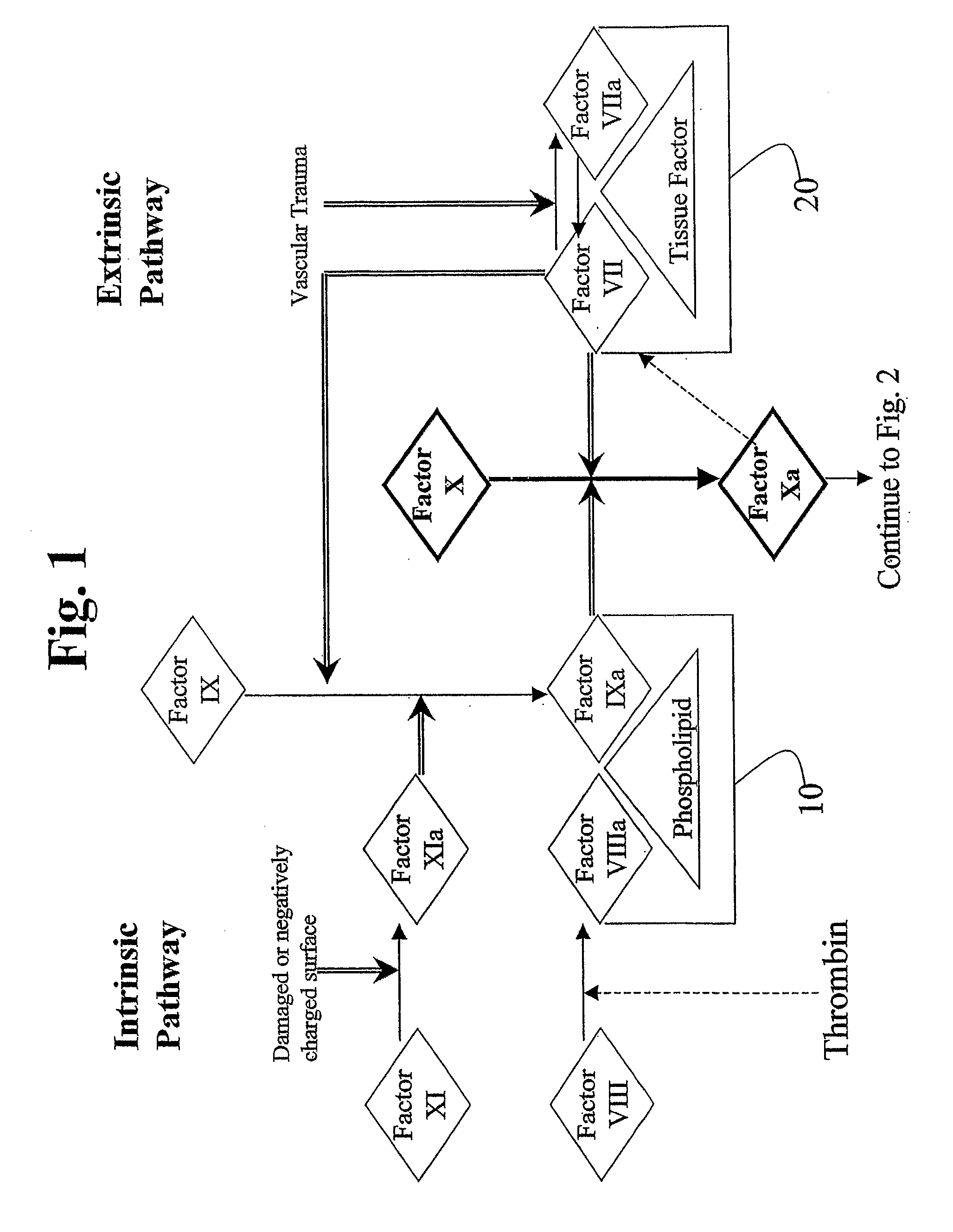
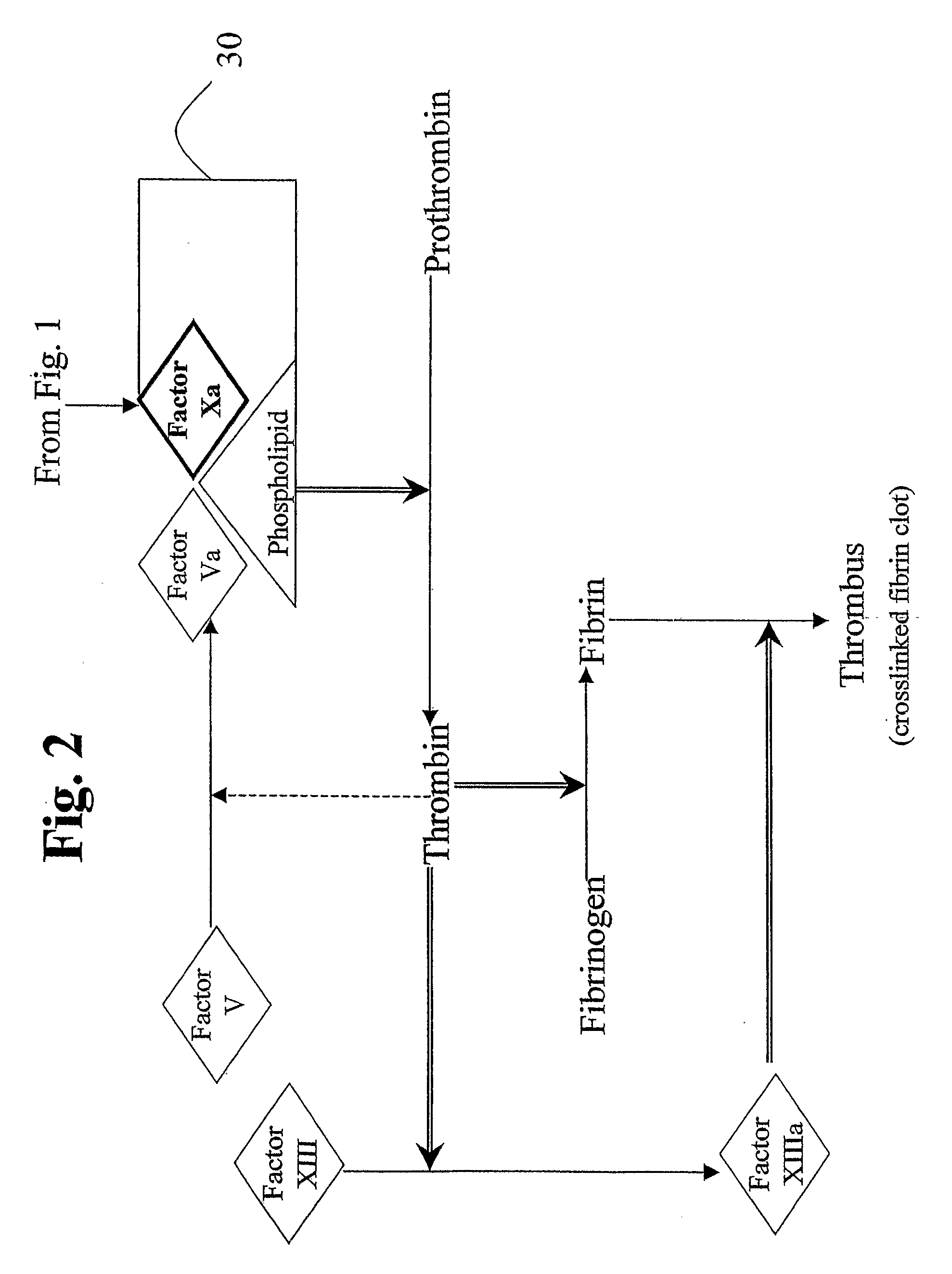
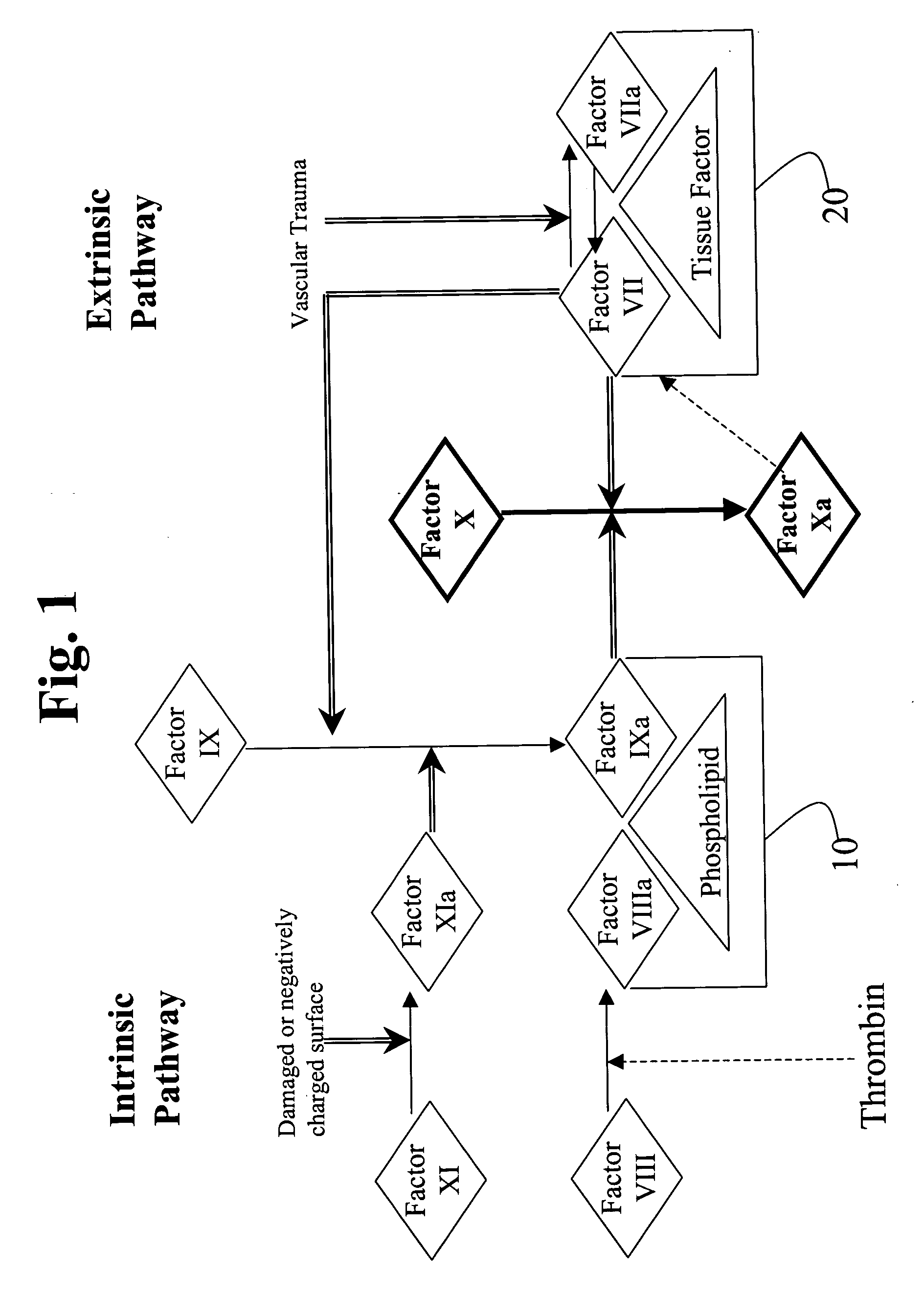
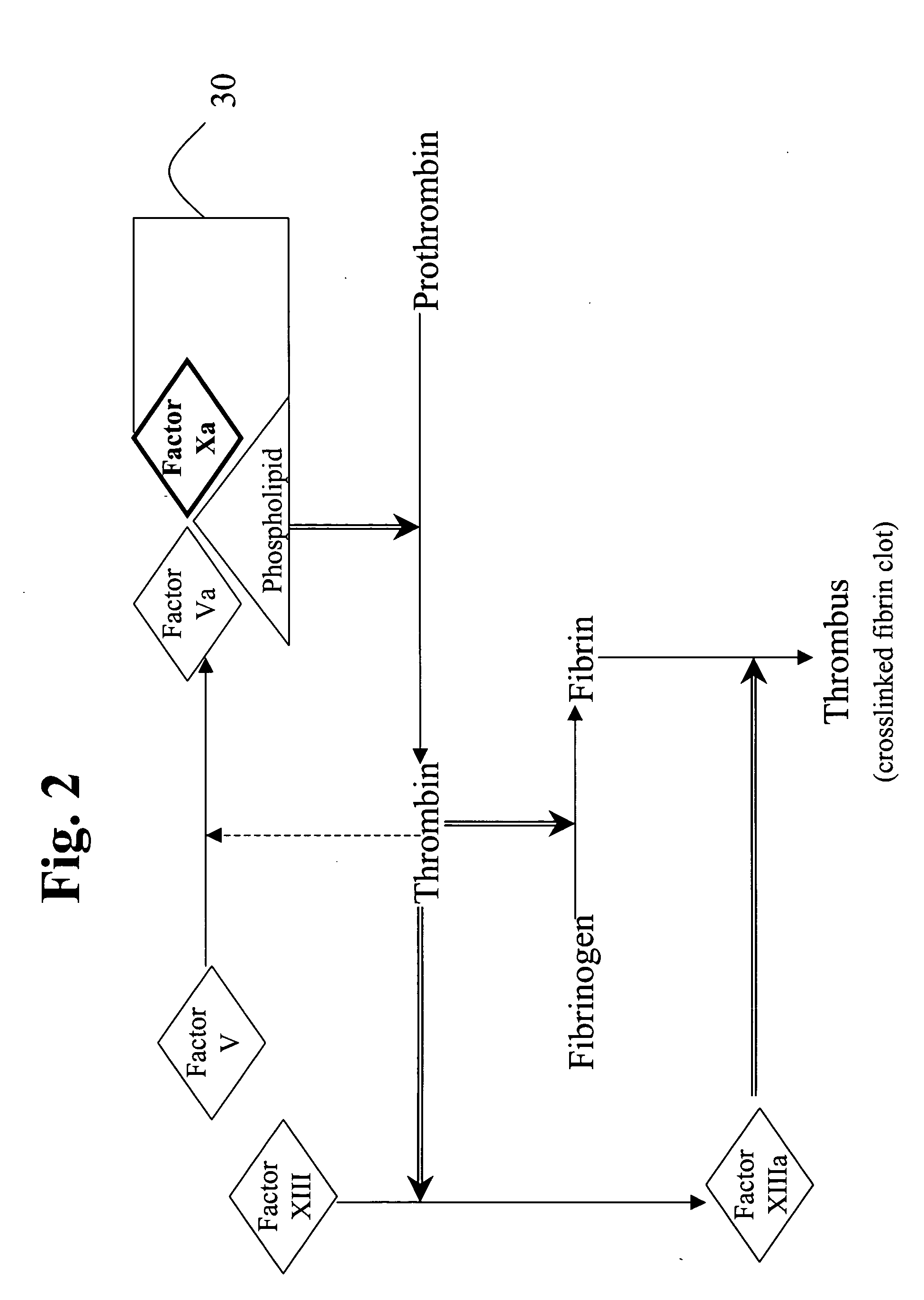
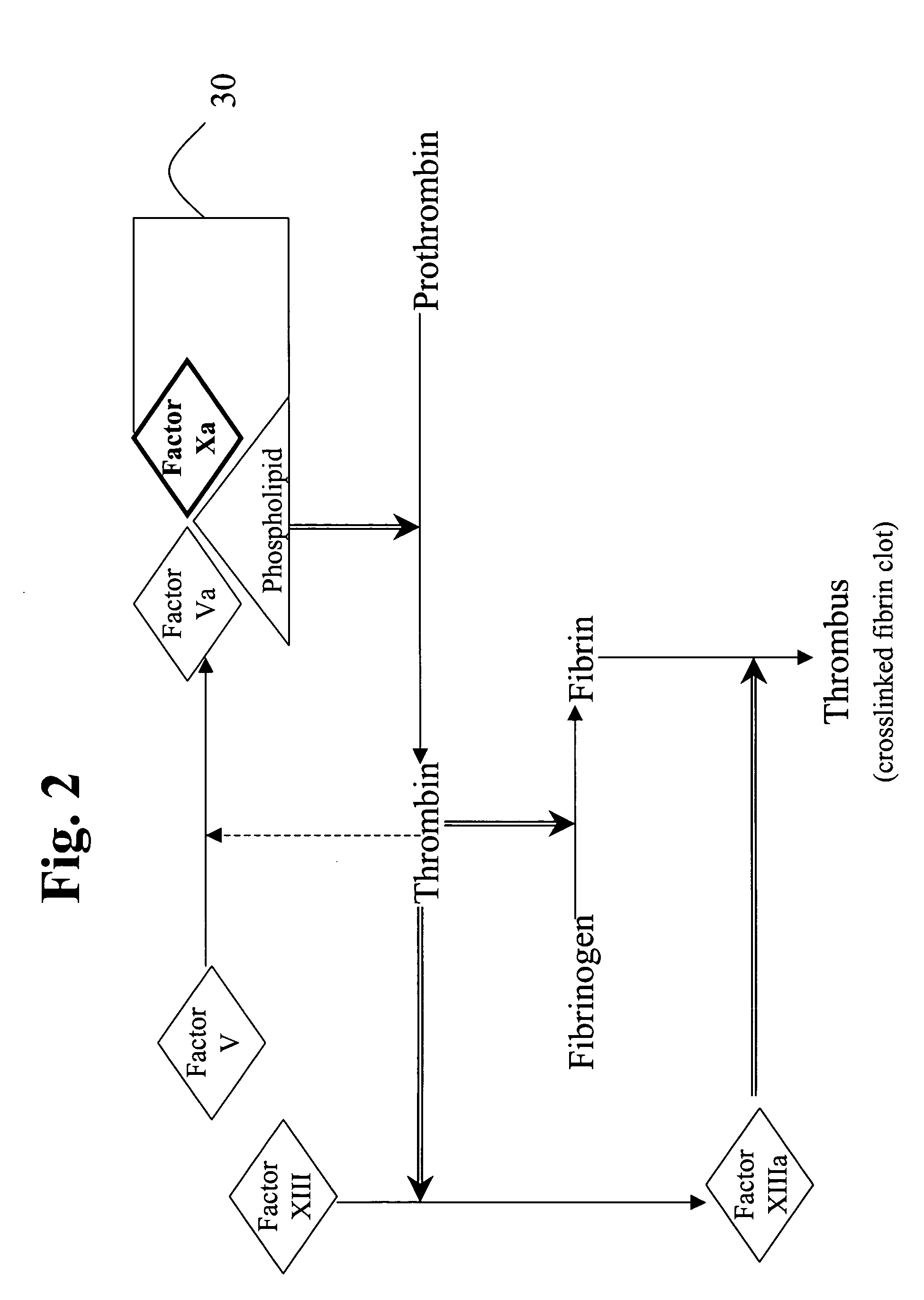
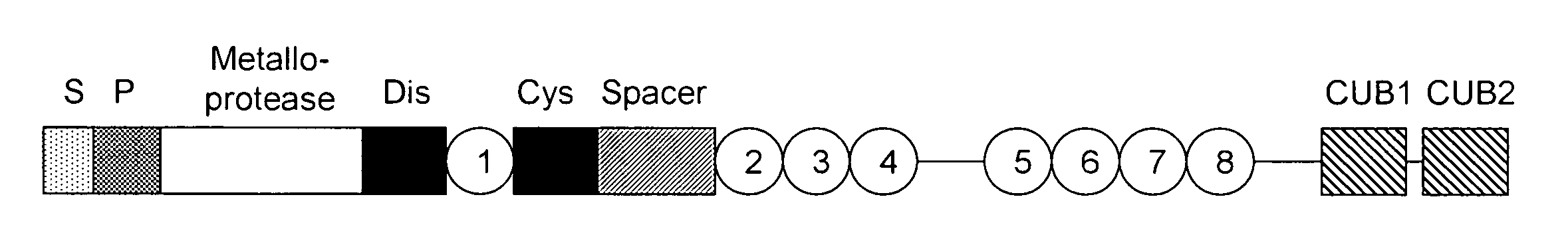
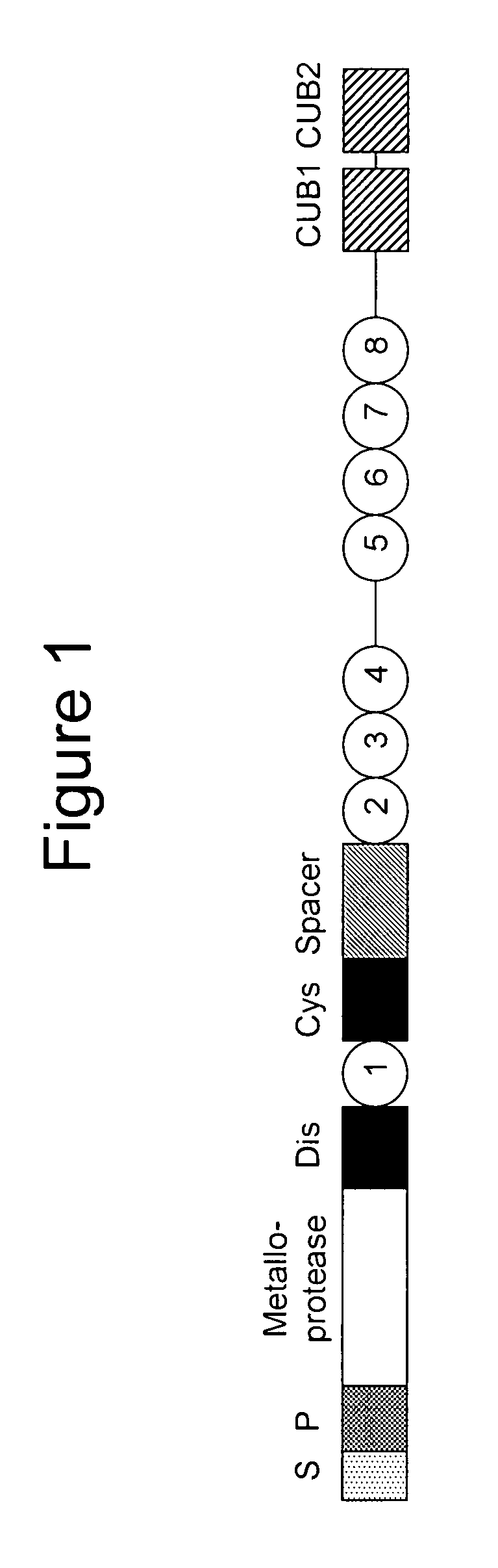
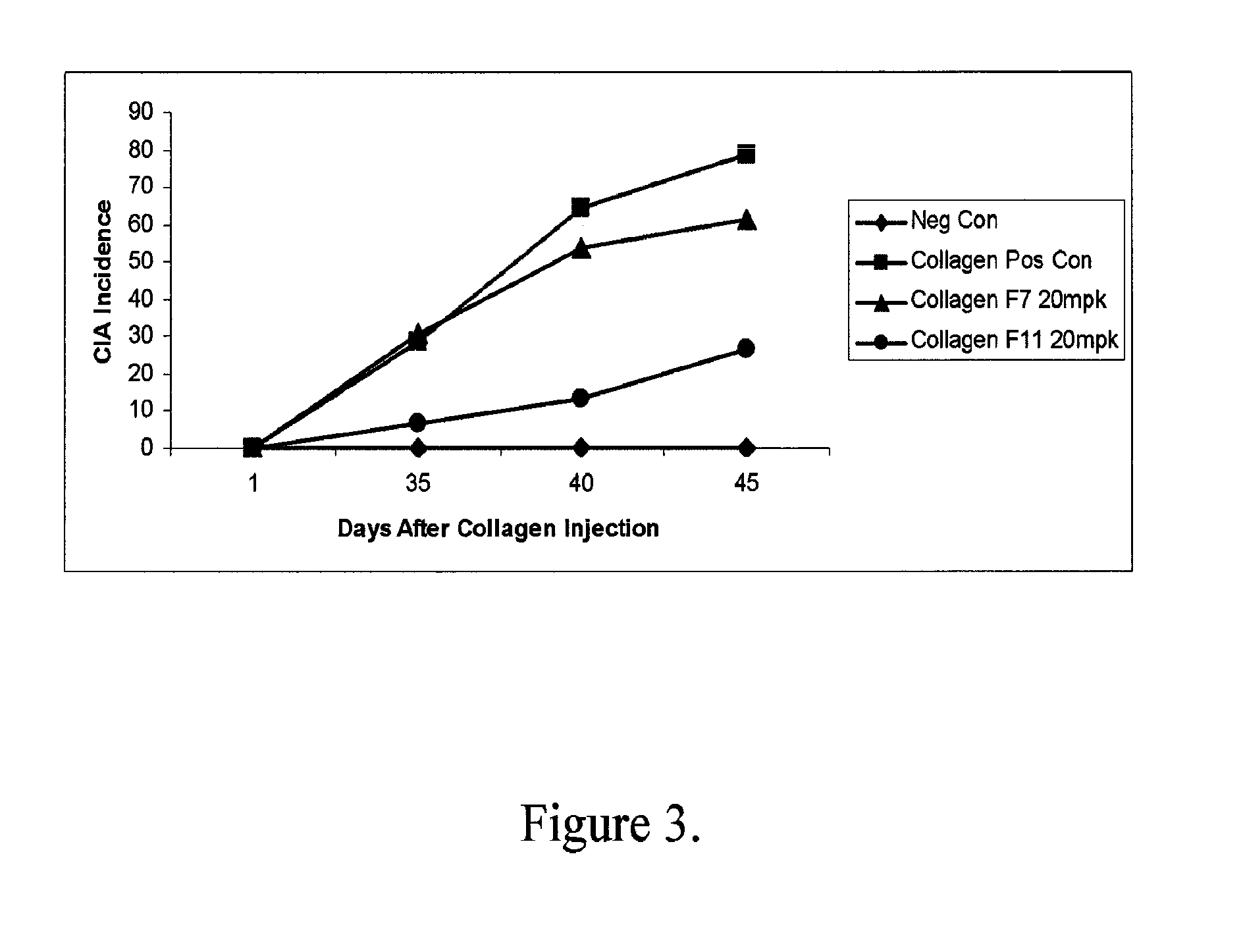
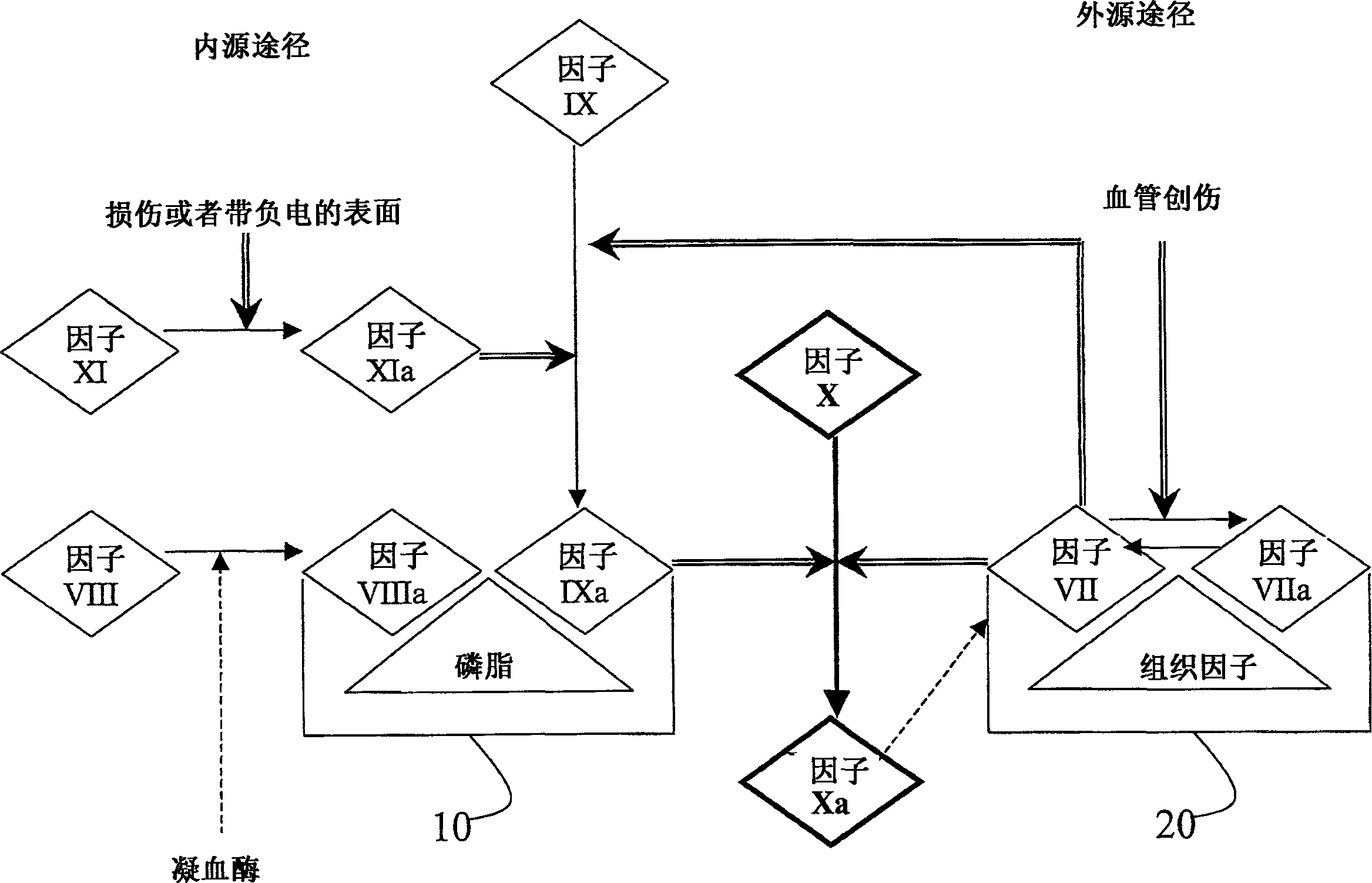
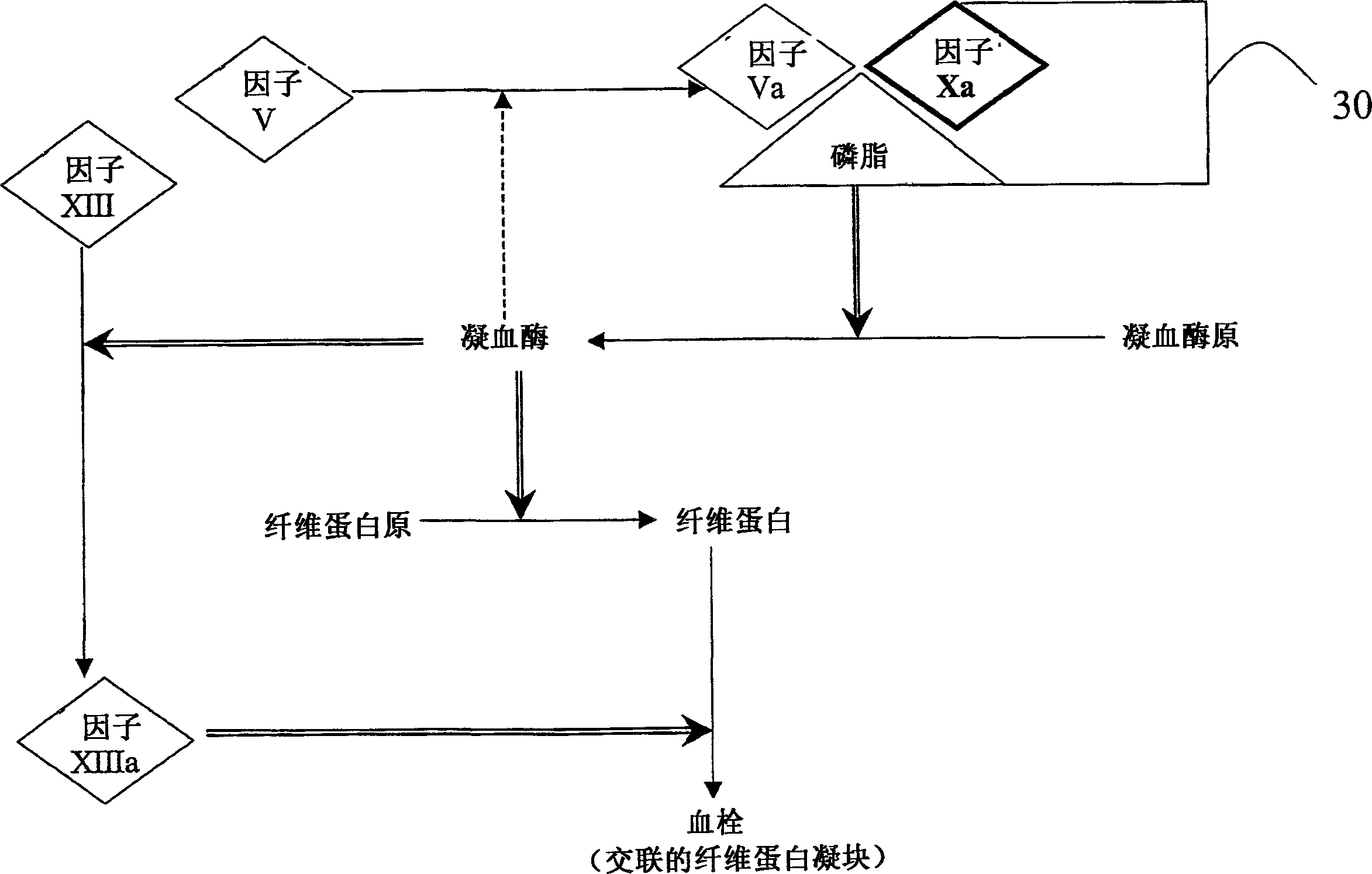
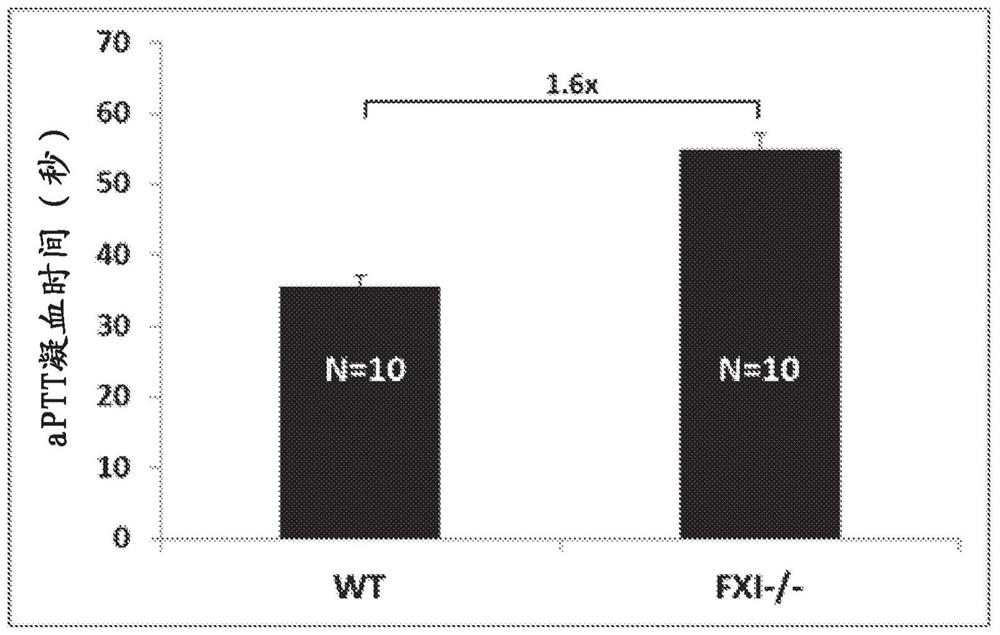
Factor XI or plasma thromboplastin antecedent is the zymogen form of factor XIa, one of the enzymes of the coagulation cascade. Like many other coagulation factors, it is a serine protease. In humans, Factor XI is encoded by the F11 gene.
Aryl and heteroaryl compounds, compositions, and methods of use
This invention provides aryl and heteroaryl compounds, methods of their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds, and their use in treating human or animal disorders. The compounds of the invention may be useful as antagonists, or partial antagonist of factor IX and / or factor XI and thus, may be used to inhibit the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. The compounds may be useful in a variety of applications including the management, treatment and / or control of diseases caused in part by the intrinsic clotting pathway utilizing factor IX and / or XI.
Owner:TRANSTECH PHARMA INC
Aryl and heteroaryl compounds, compositions, methods of use
This invention provides aryl and heteroaryl compounds, methods of their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds, and their use in treating human or animal disorders. The compounds of the invention may be useful as antagonists, or partial antagonist of factor IX and / or factor XI and thus, may be used to inhibit the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. The compounds may be useful in a variety of applications including the management, treatment and / or control of diseases caused in part by the intrinsic clotting pathway utilizing factor IX and / or XI.
Owner:TRANSTECH PHARMA
Aryl and Heteroaryl Compounds, Compositions, Methods of Use
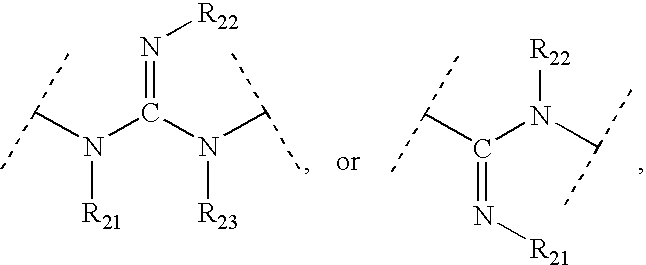
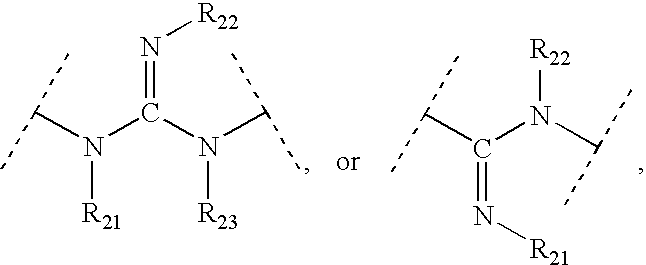
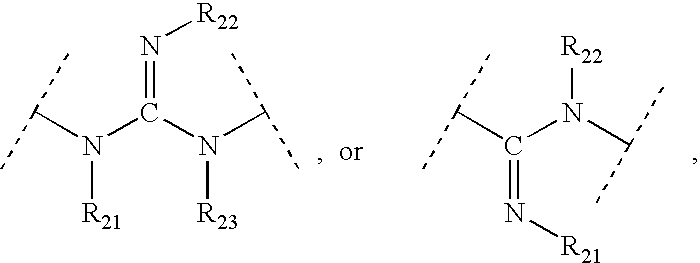
This invention provides aryl and heteroaryl compounds of formula (X). The compounds of the invention may be useful as antagonists, or partial antagonist of factor IX and / or factor XI and thus, may be used to inhibit the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. Formula (X) wherein R102 is selected from the group consisting of —C(O)OH, —C(O)OCH3, —C(O)O-t-butyl, —C(O)NH—OCH2-phenyl, C(O)NHOH, and —C(O)NHSO2CH3; and wherein R101, R103, R104 and Y are as defined herein.
Owner:TRANSTECH PHARMA INC
Aryl and heteroaryl compounds, compositions, and methods of use
This invention provides aryl and heteroaryl compounds, methods of their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds, and their use in treating human or animal disorders. The compounds of the invention may be antagonists, or partial antagonist of factor IX and / or factor XI and thus, may be useful for inhibiting the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. The compounds may be useful in a variety of applications including the management, treatment and / or control of diseases caused in part by the intrinsic clotting pathway.
Owner:VTV THERAPEUTICS LLC
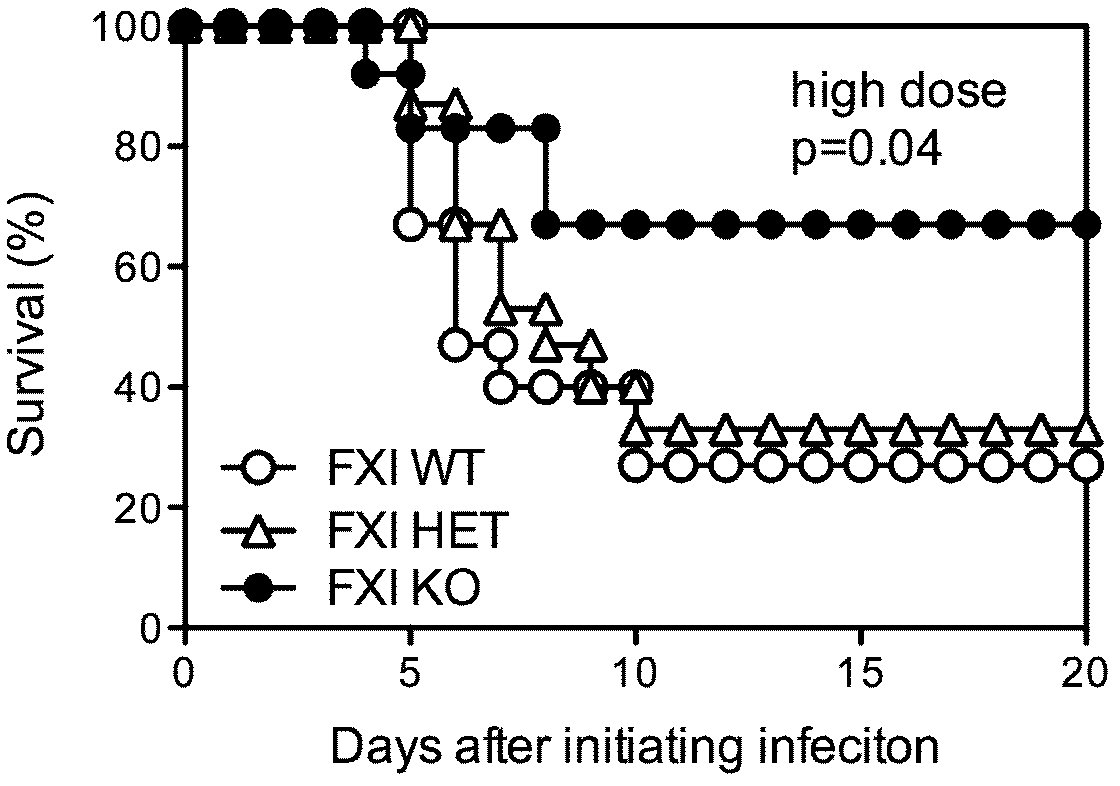
Therapeutic use of factor XI
InactiveUS20050181978A1Shorten clotting timeGood hemostasisPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood disorderMedicineFactor XI
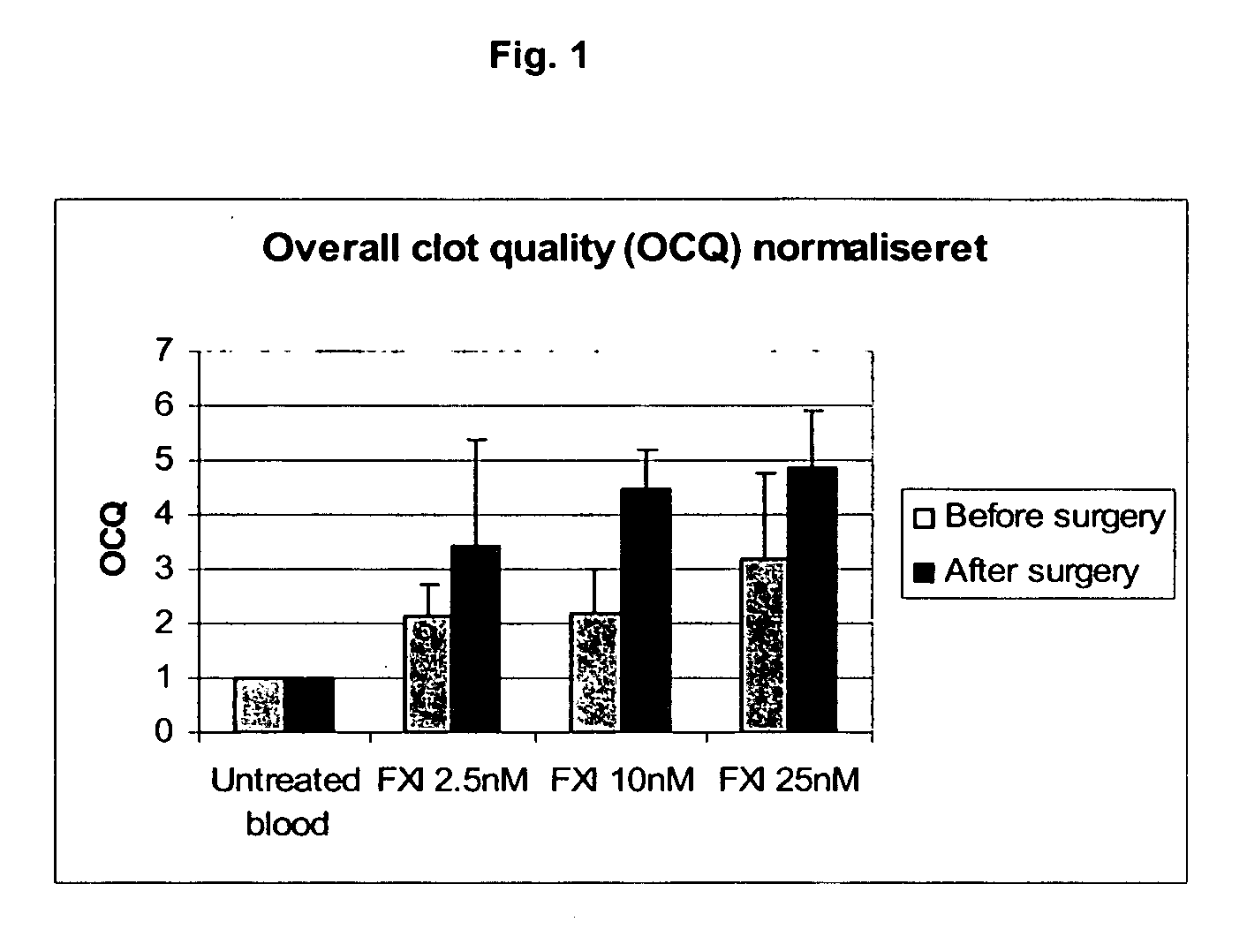
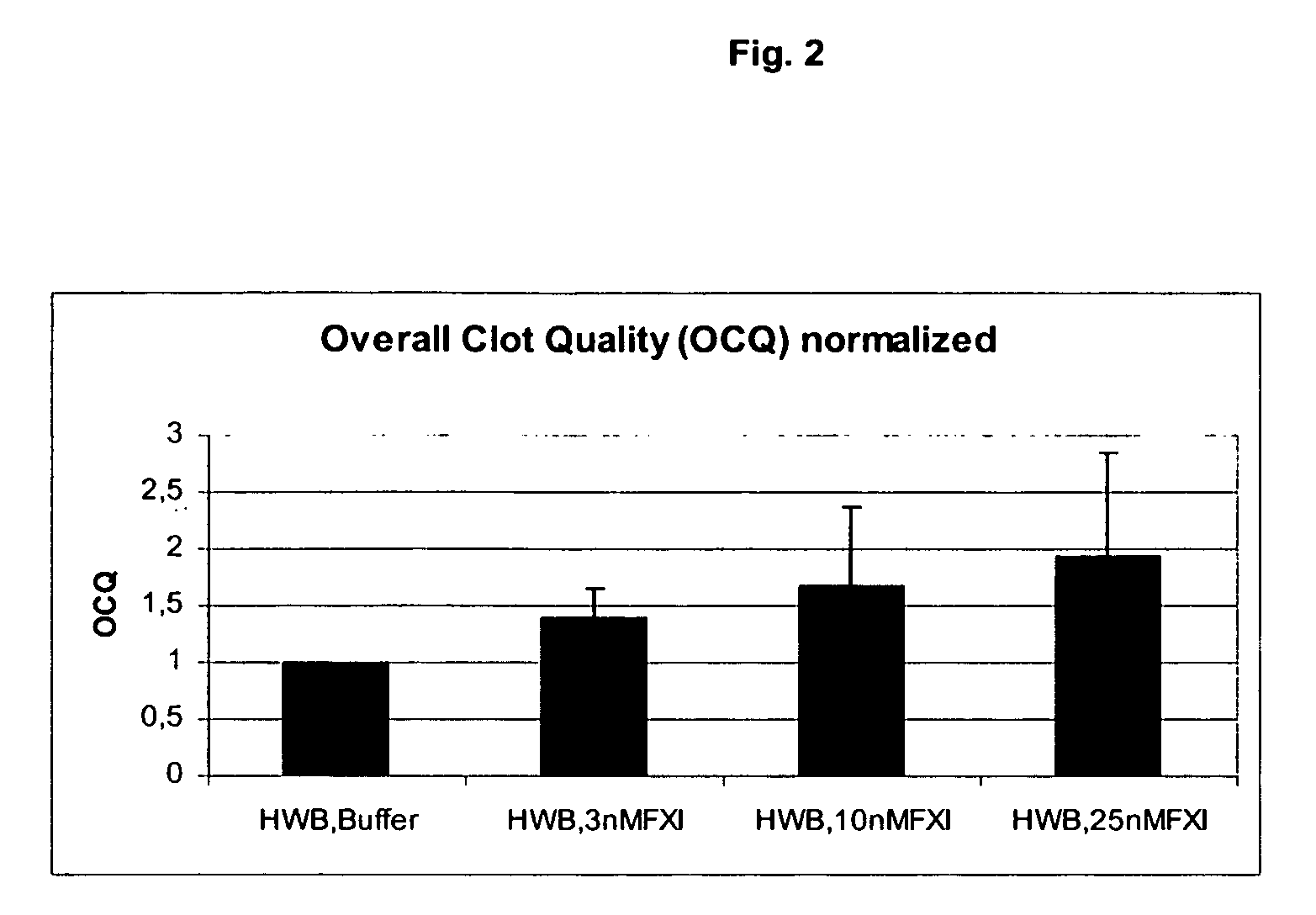
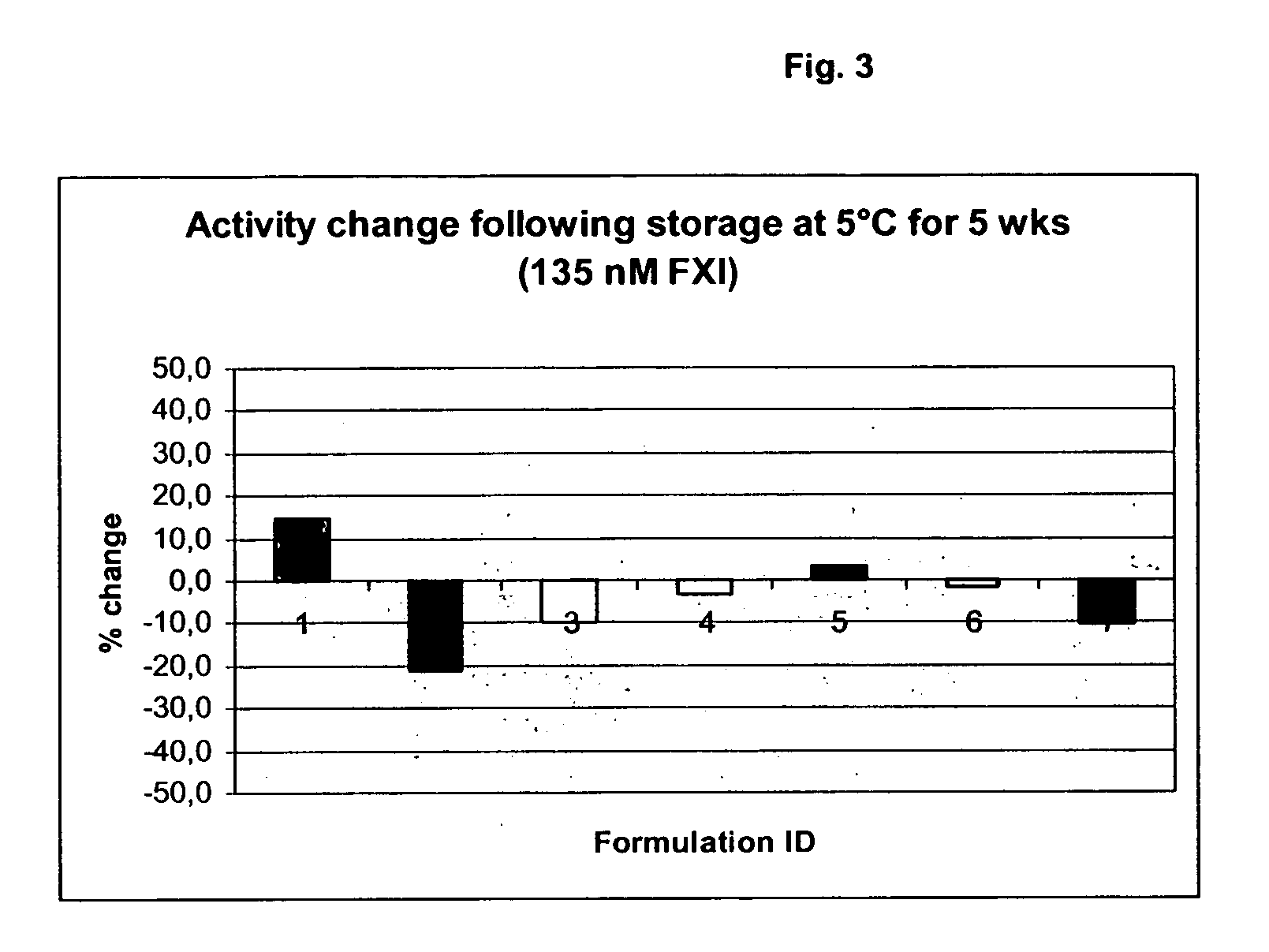
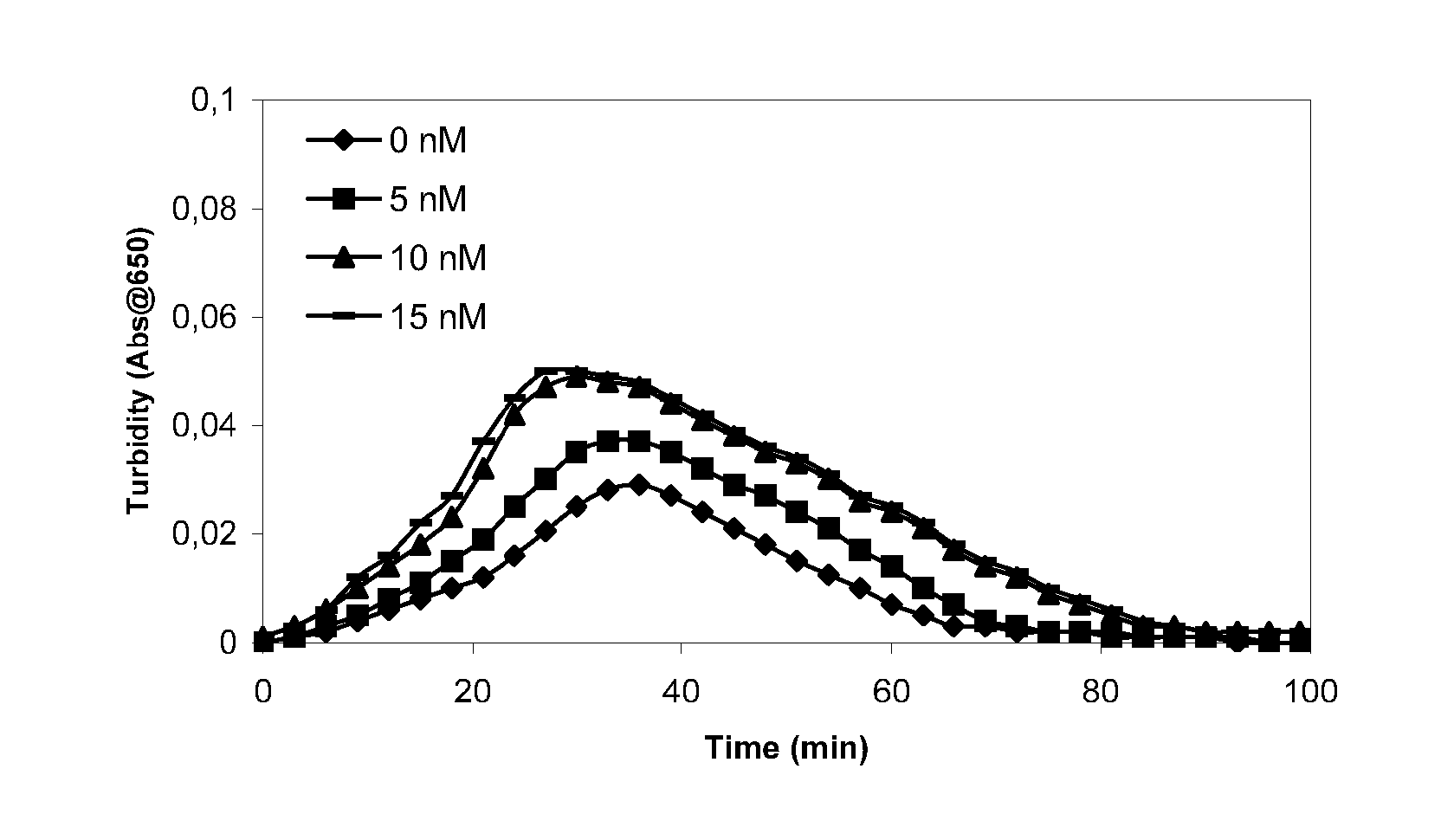
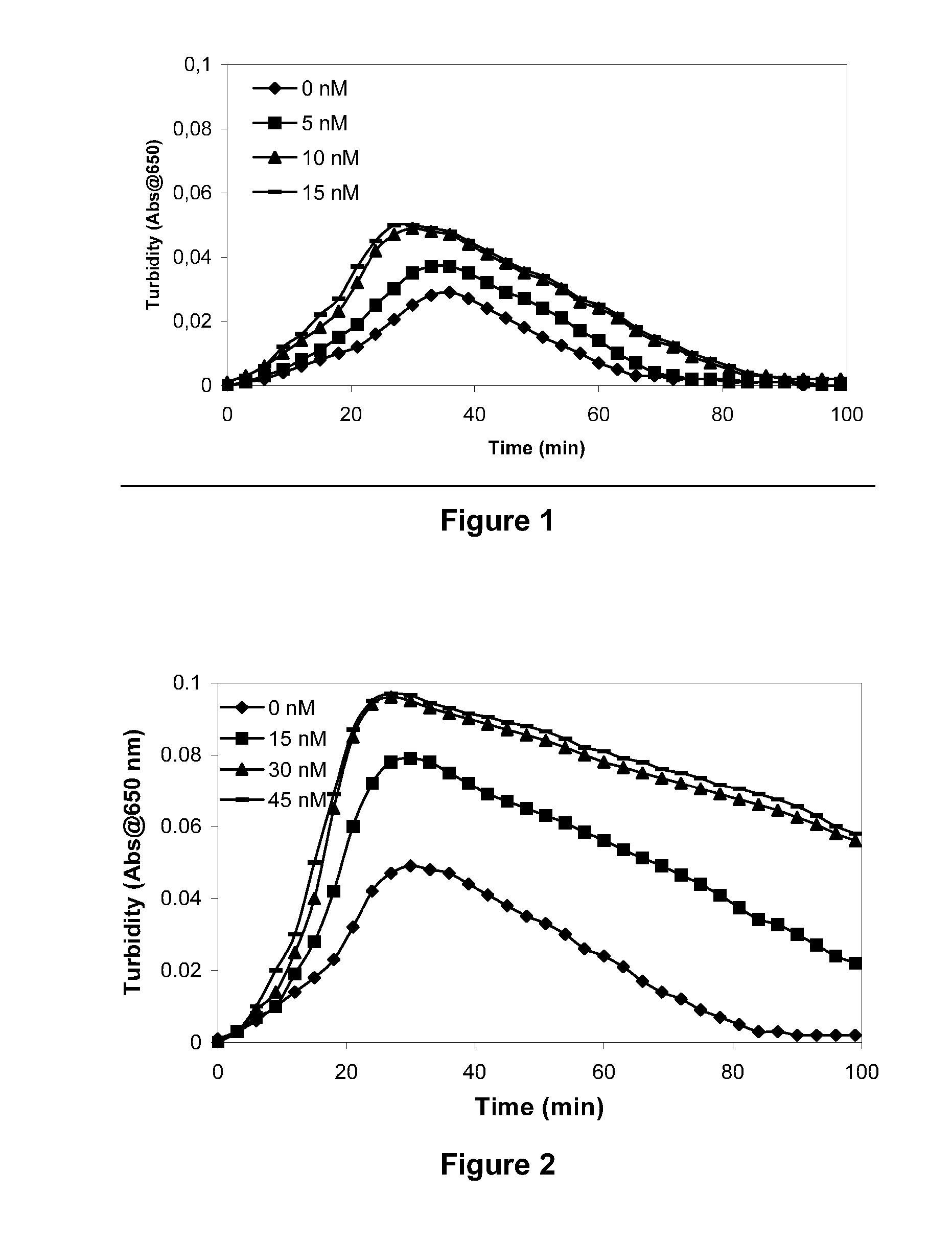
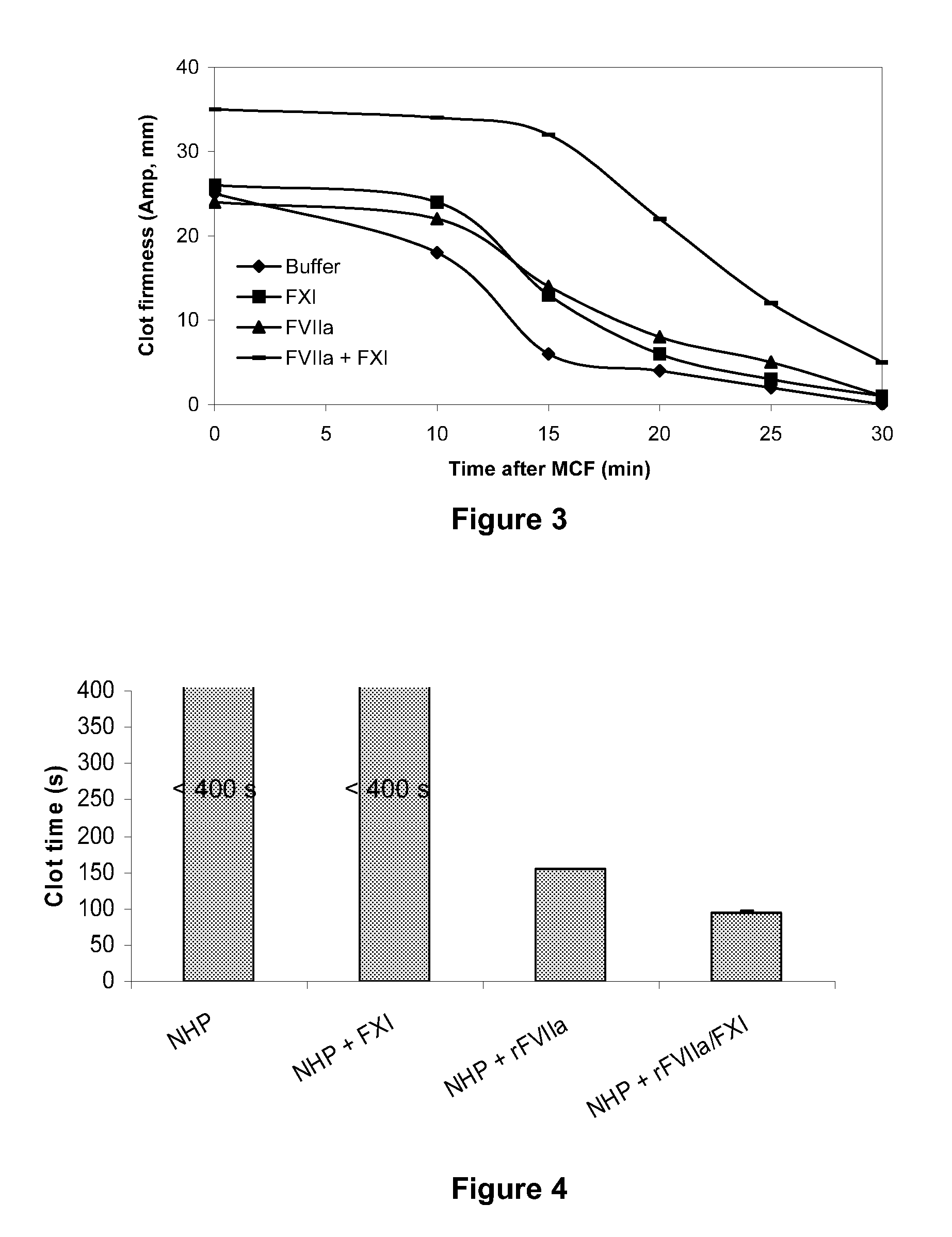
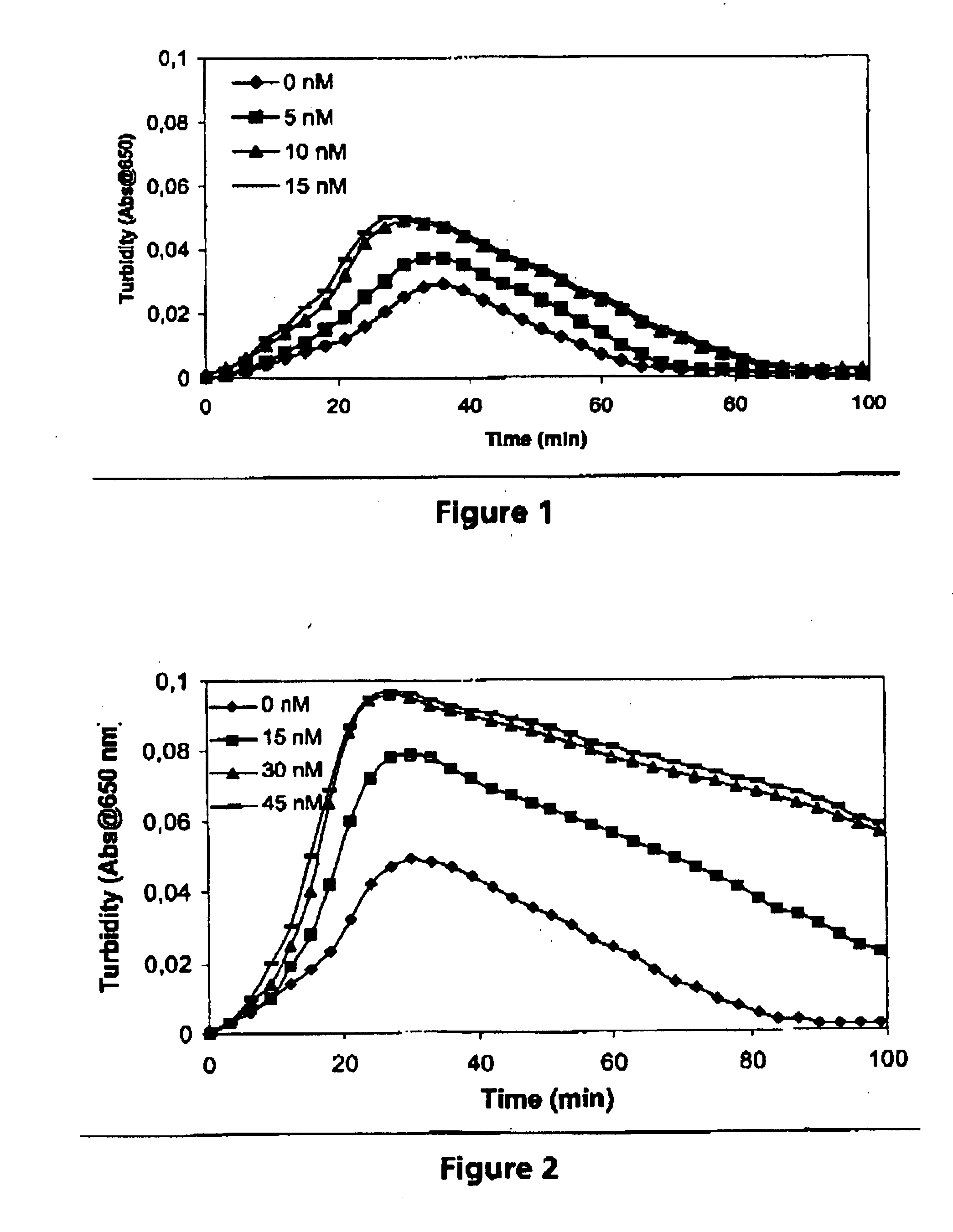
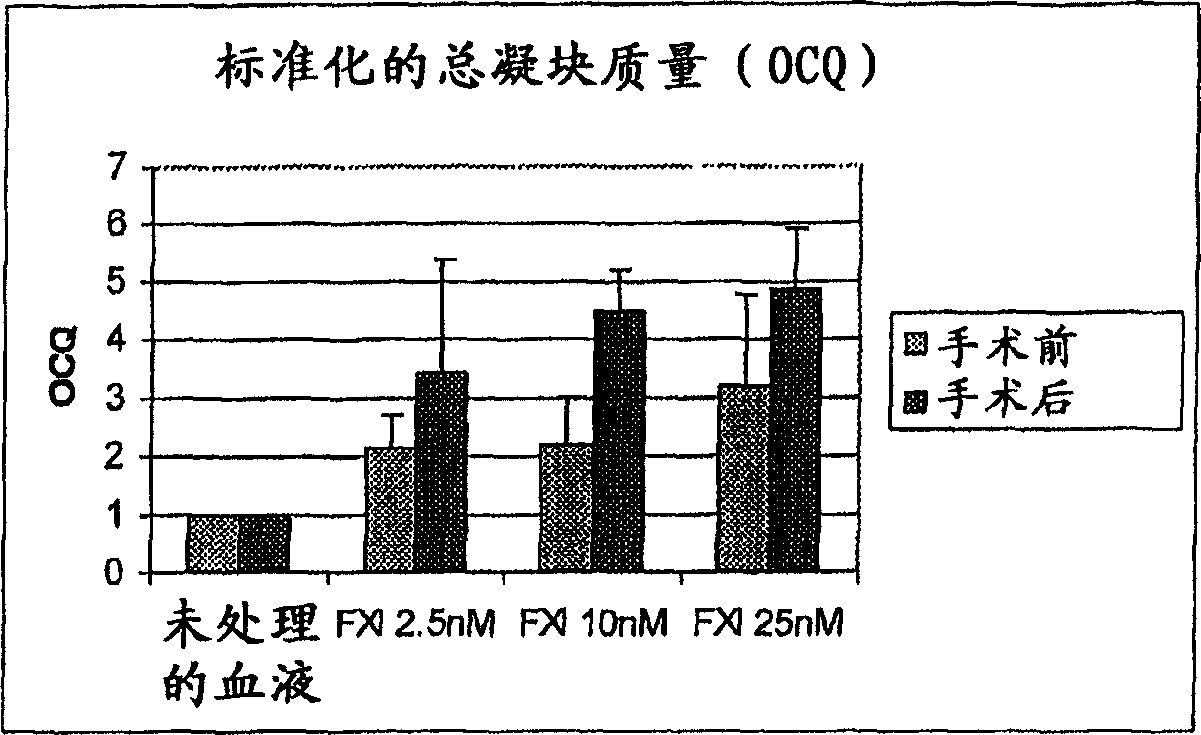
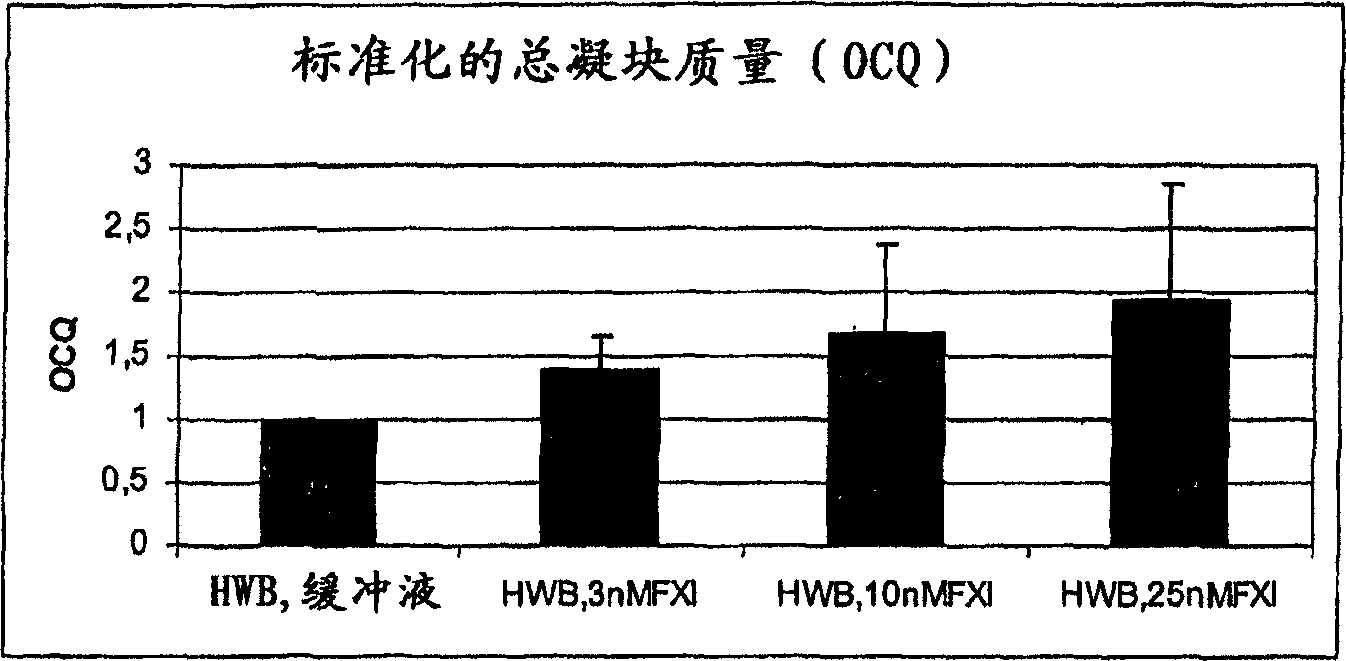
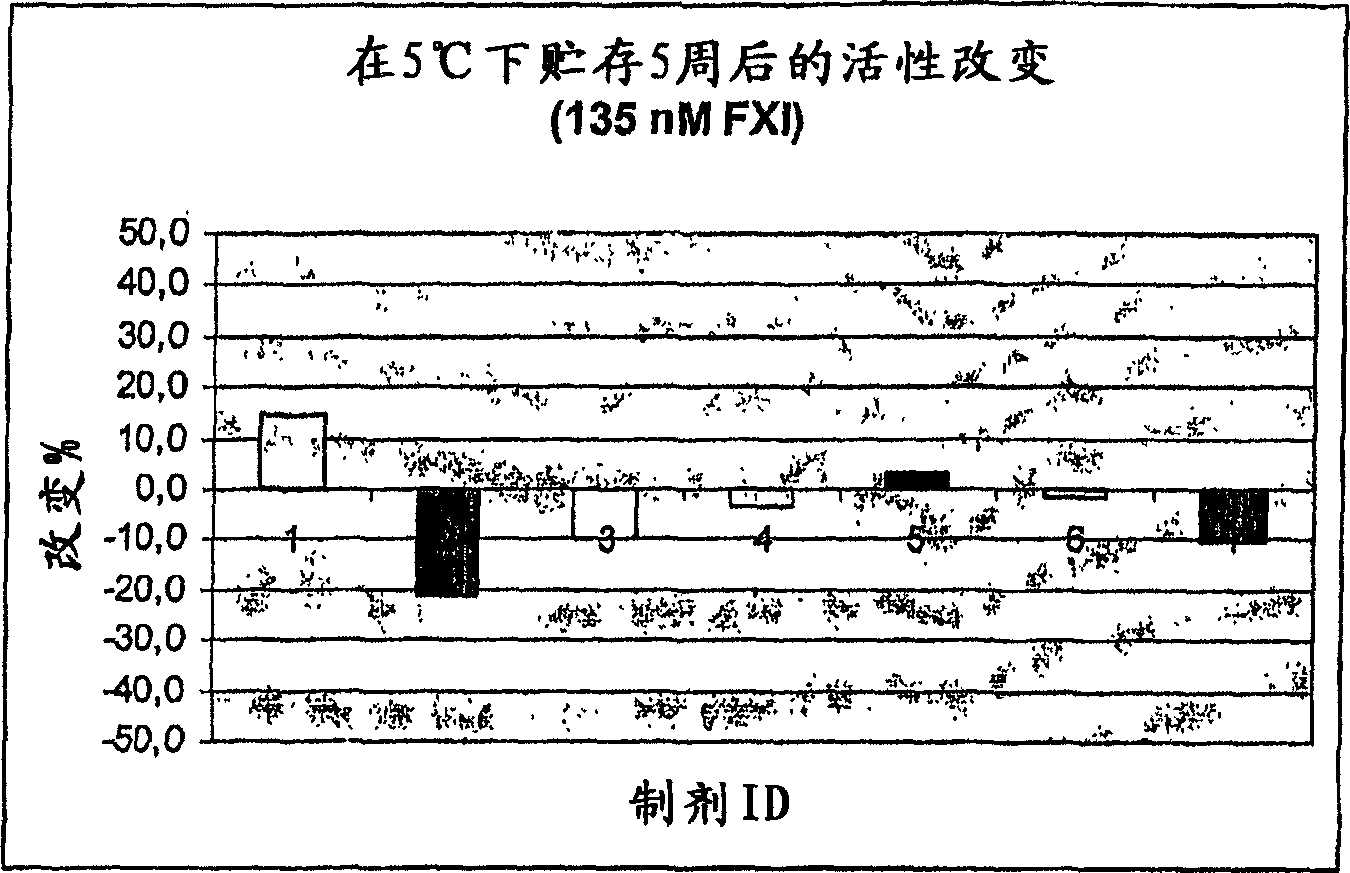
The present invention provides methods and compositions for treating bleeding episodes. The methods are carried out by administering to a patient in need thereof a preparation comprising a factor XI polypeptide, in an amount effective for such treatment. The methods of the invention result in one or more of: reduced clotting time; enhancement of hemostasis; increase in clot lysis time; increase in clot strength; and / or increase in overall clot quality (OCQ) in said patient.
Owner:ROJKJAER RASMUS +4
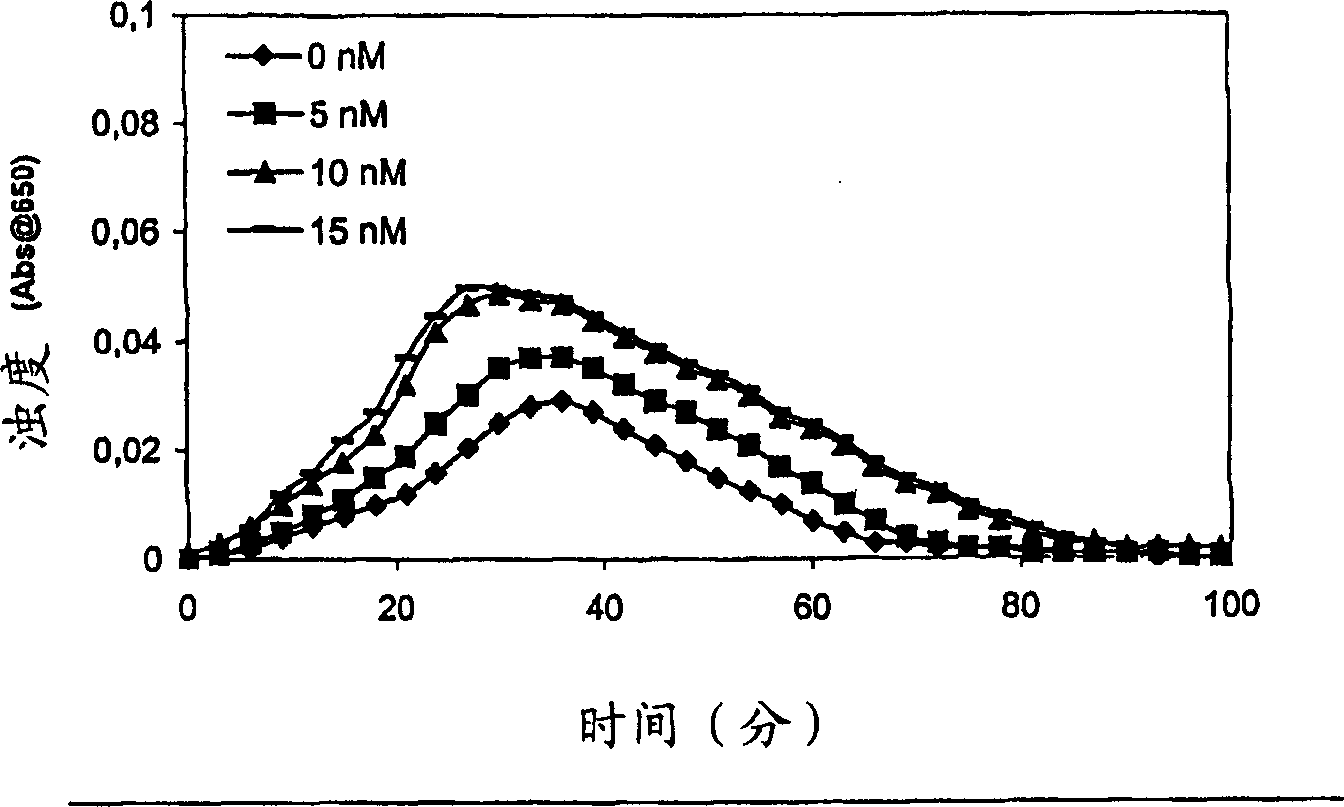
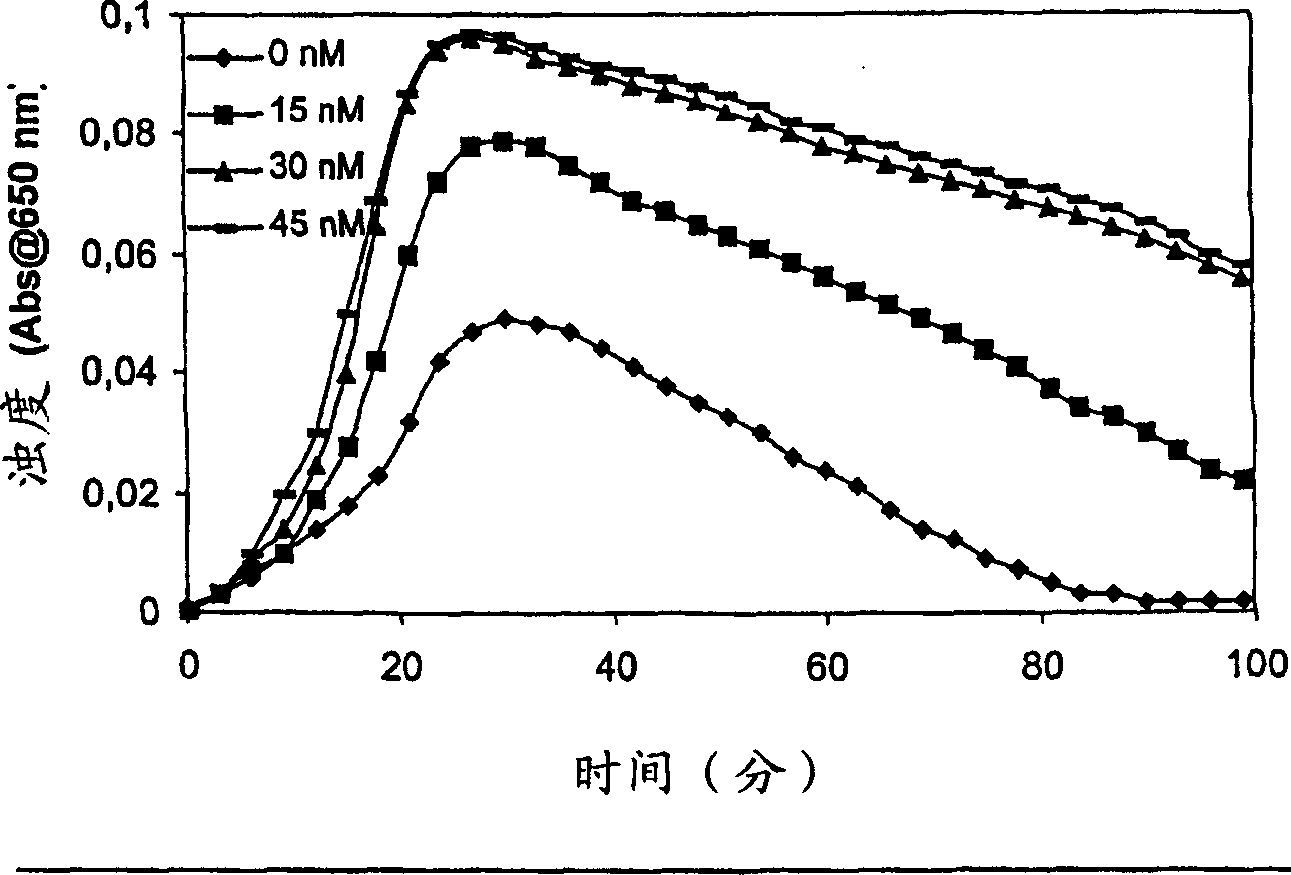
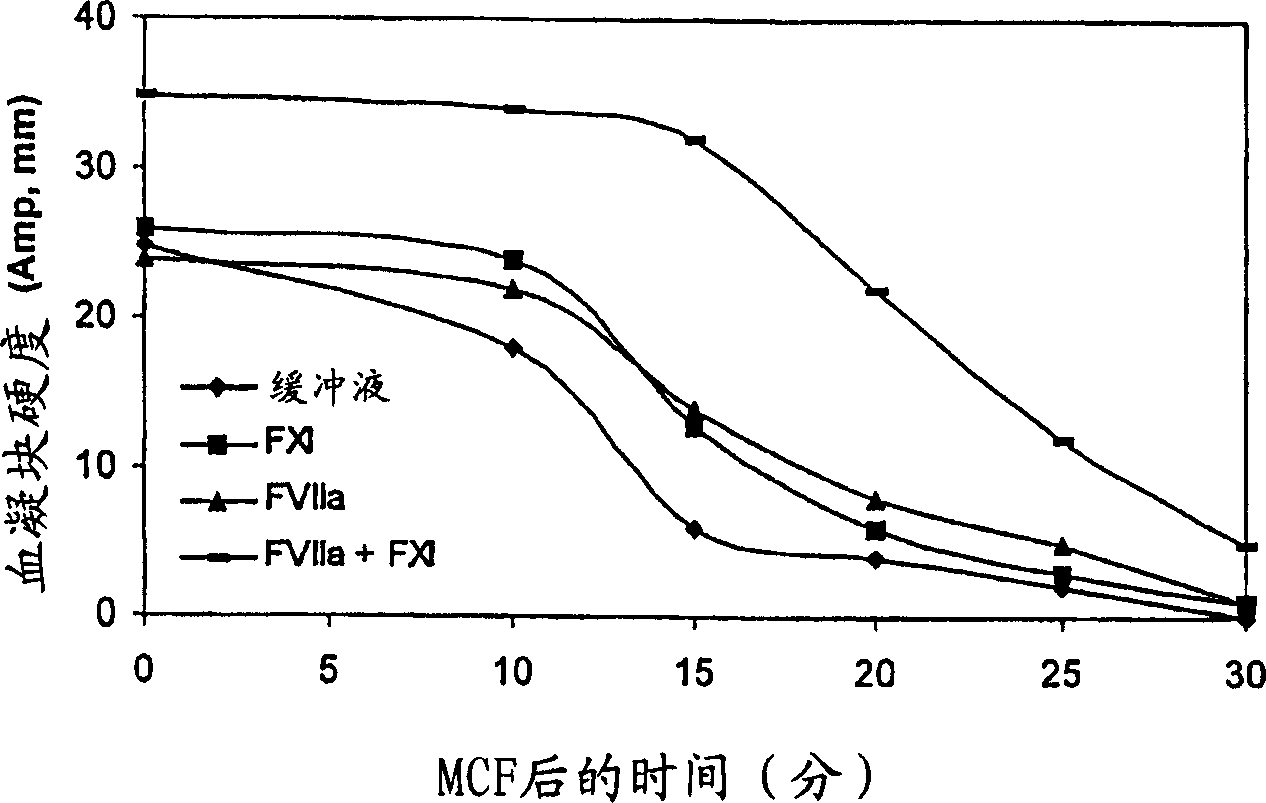
Pharmaceutical Compositions Comprising Factor VII Polypeptides and Factor XI Polypeptides
InactiveUS20080058266A1Easy to useEffectivelyPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesFactor XIPharmaceutical drug
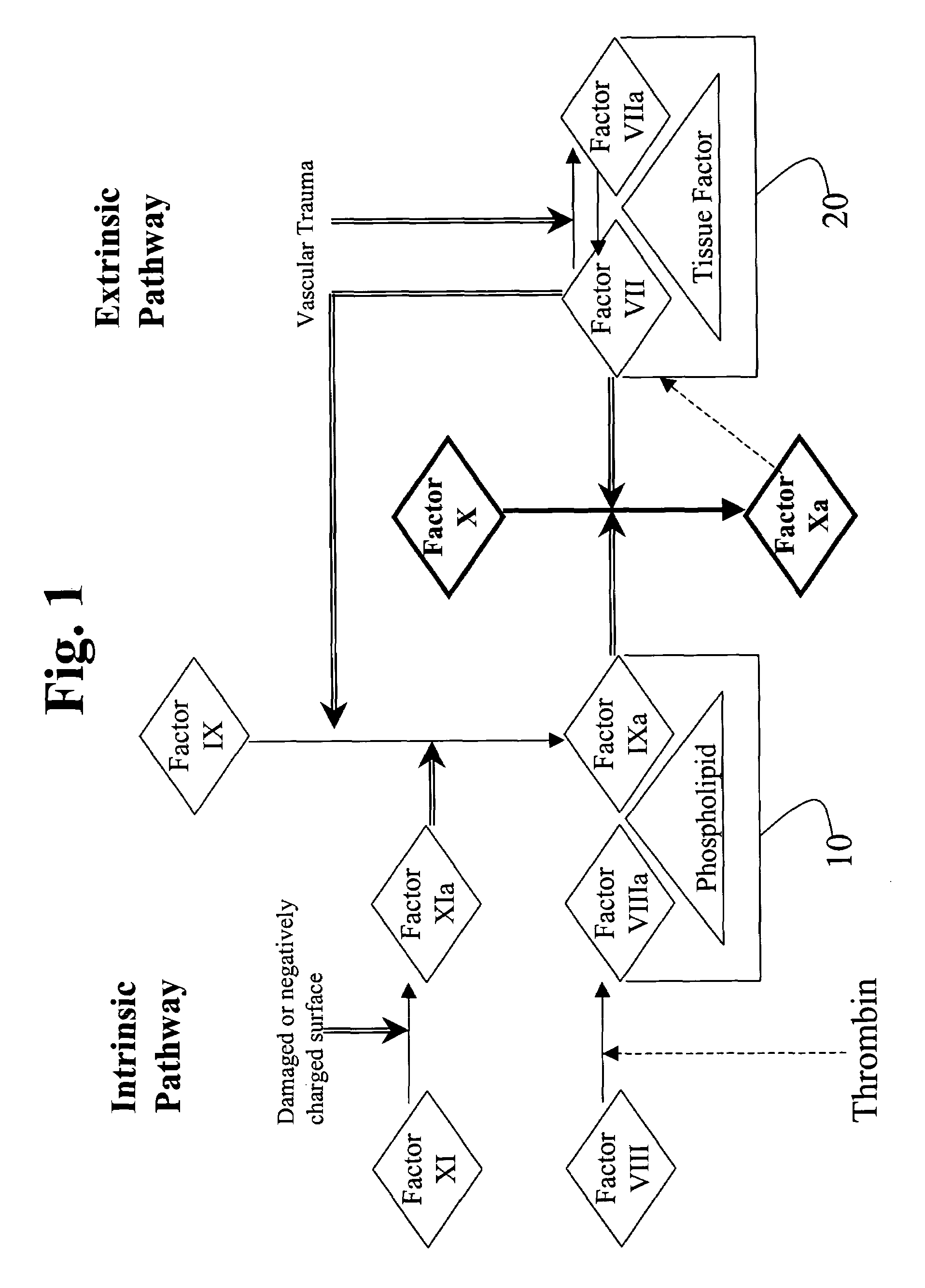
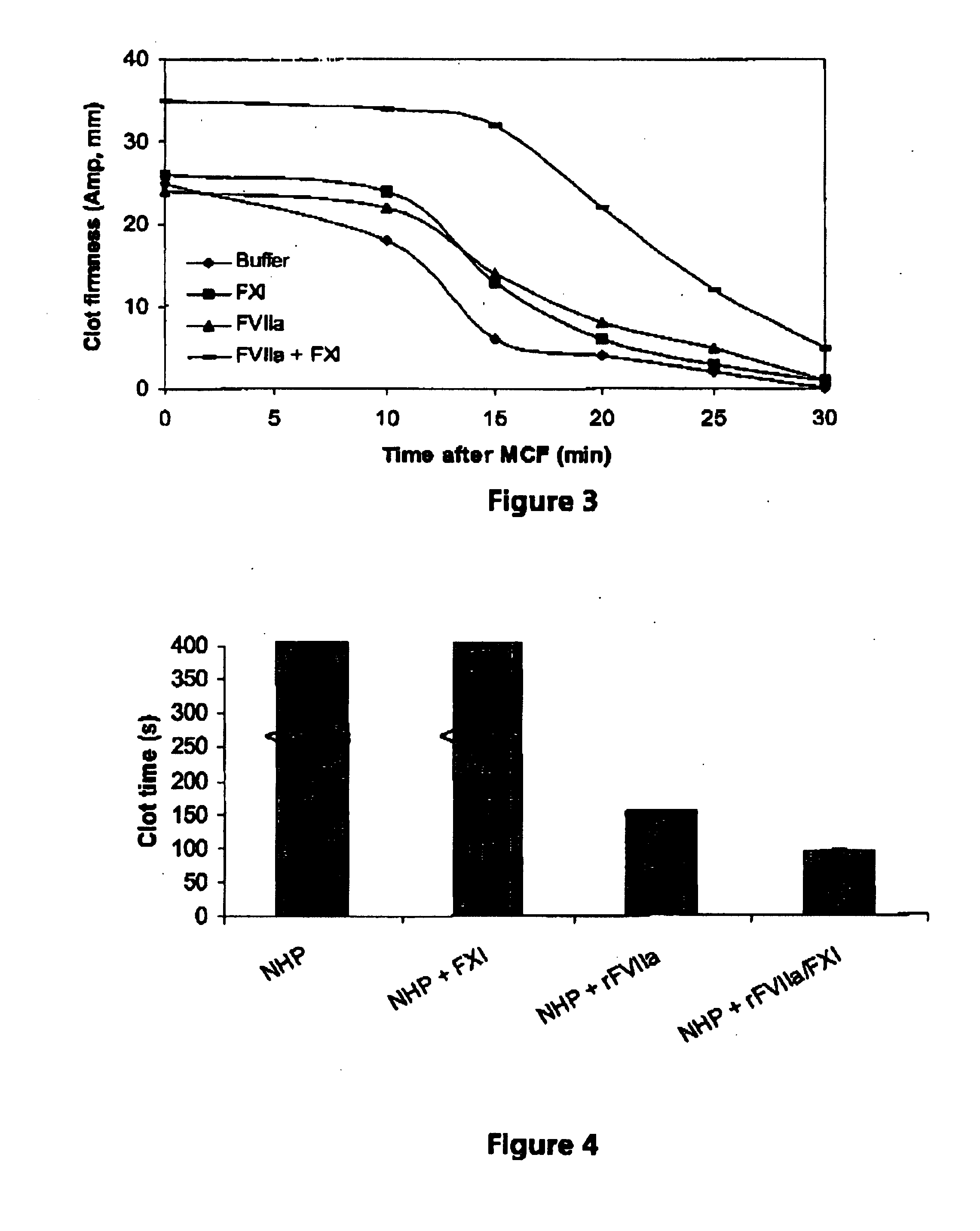
Compositions comprising a factor VII or factor VII-related polypeptide and a factor XI or factor XI-related polypeptide, kits comprising the same, and methods of using such compositions (e.g., in the treatment of bleeding conditions) are provided
Owner:NOVO NORDISK HEALTH CARE AG
Methods for Treating Bleeding Disorders
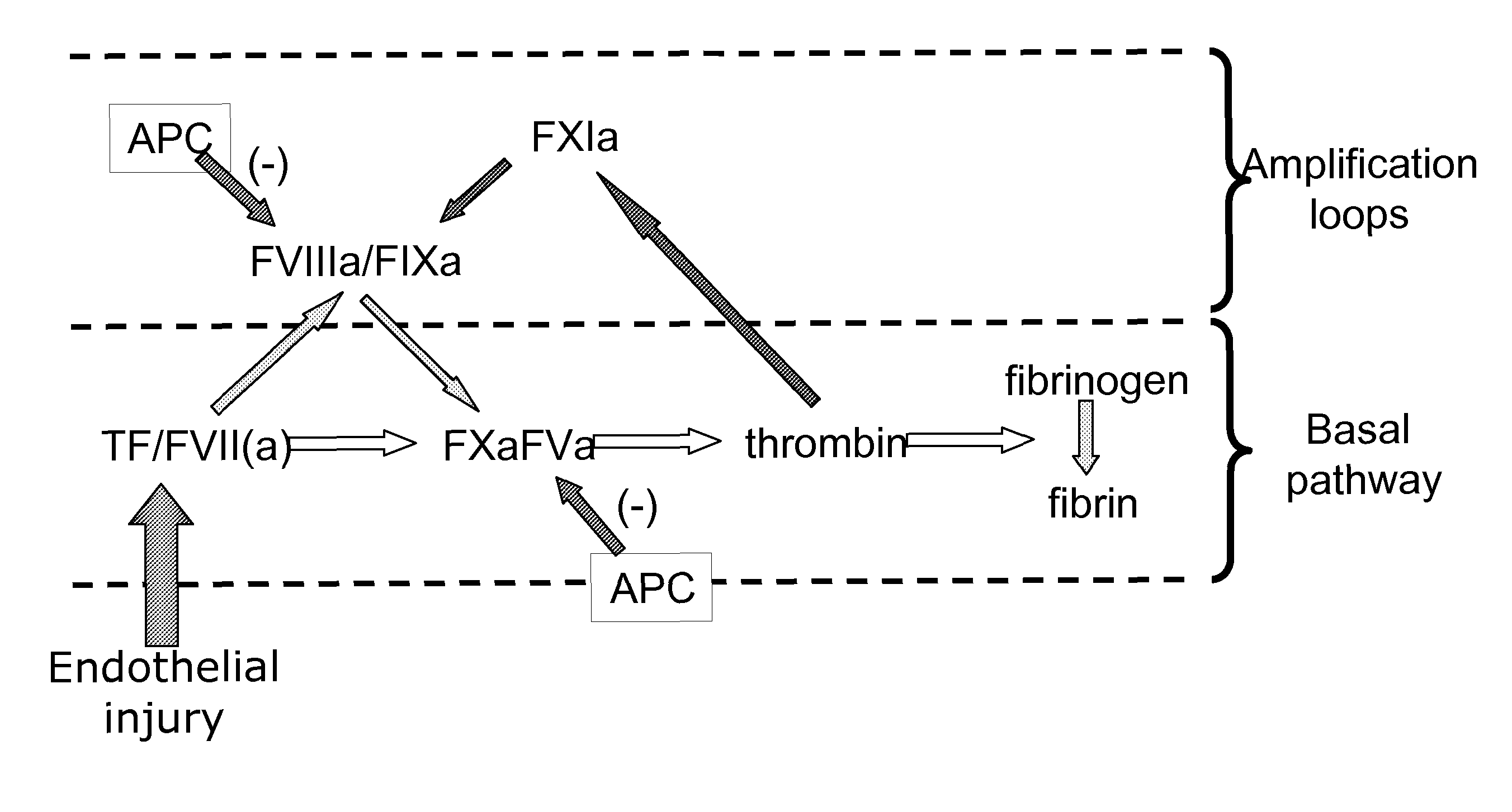
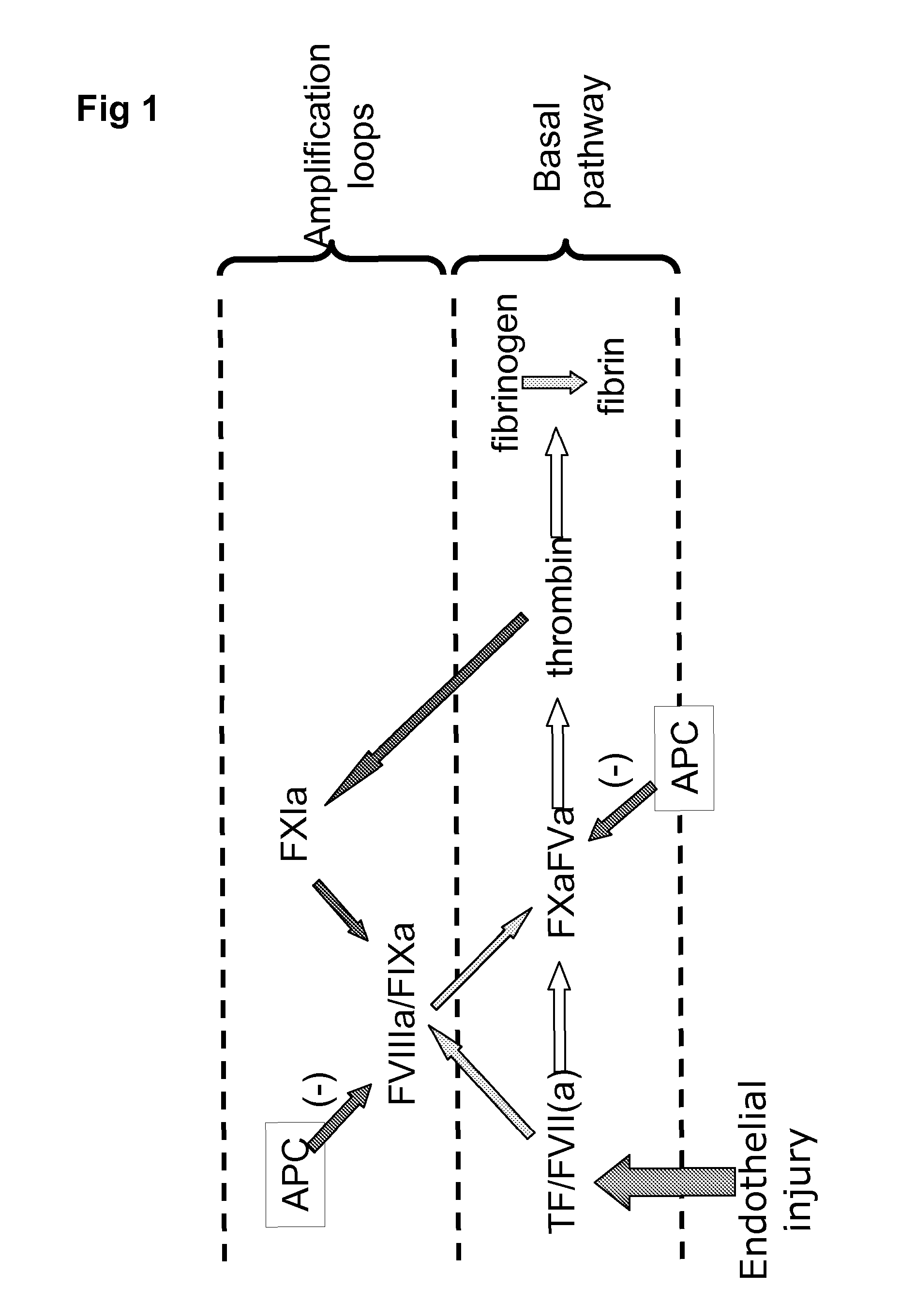
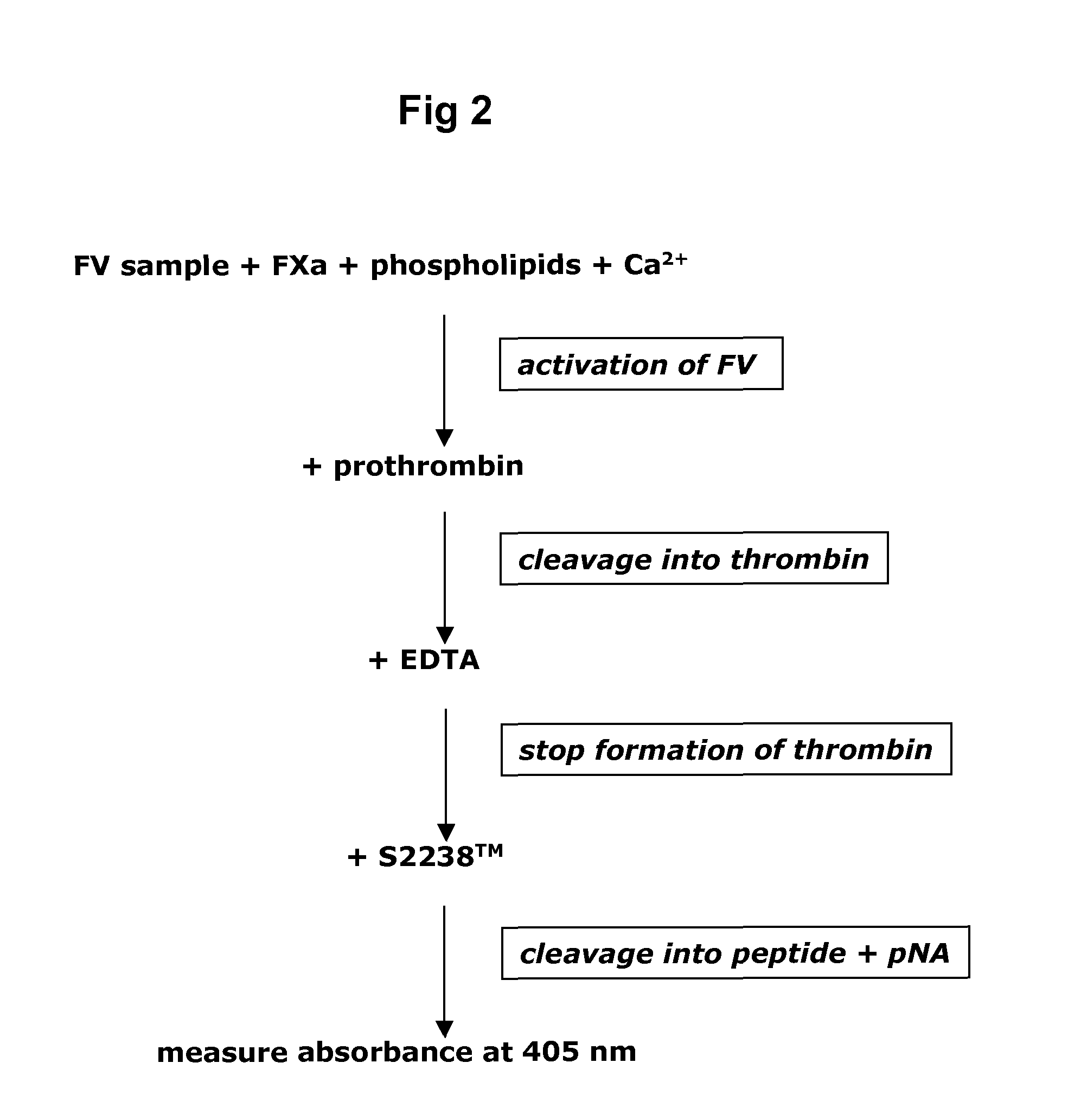
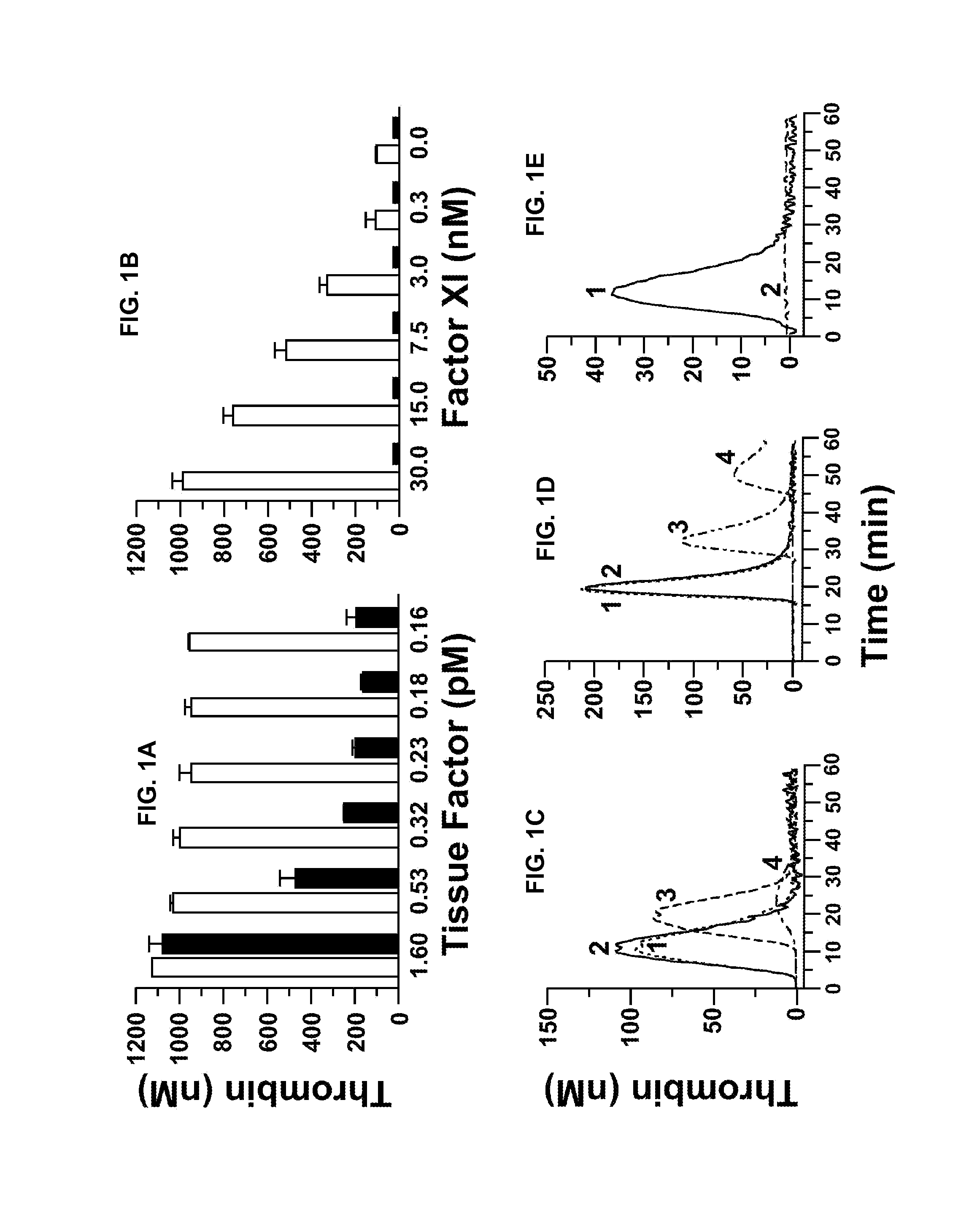
A method of factor XI-dependent blood coagulation enhancement in a subject in need of enhanced blood coagulation comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a composition comprising a non-anticoagulant sulfated polysaccharide (NASP) to the subject. A method of factor XI-dependent blood coagulation enhancement in a subject in need of enhanced blood coagulation comprising: (i) selecting a subject that is not deficient for factor XI; and (ii) administering a therapeutically effective amount of a composition comprising a non-anticoagulant sulfated polysaccharide (NASP) to the subject, wherein the NASP enhances blood coagulation in a factor XI-dependent manner. A method of identifying a non-anticoagulant sulfated polysaccharide (NASP) which is capable of enhancing blood coagulation in dependence on FXI, the method comprising: a) combining a blood or plasma sample comprising activation competent FXI with a composition comprising a sulfated polysaccharide and measuring the clotting or thrombin generation parameters of the blood or plasma sample; b) combining a corresponding blood or plasma sample deficient in activation competent FXI with a composition comprising the sulfated polysaccharide and measuring the clotting or thrombin generation parameters of the blood or plasma sample; and c) comparing the clotting or thrombin generation parameters of the blood or plasma samples as determined in steps (a) and (b) with each other, wherein a decrease in the clotting time of the blood sample or an increase in peak thrombin or decrease in peak time of the plasma sample comprising activation competent FXI compared to the clotting time of the blood sample or peak thrombin or peak time of the plasma sample deficient in activation competent FXI is indicative of a NASP which is capable of enhancing blood coagulation in dependence on FXI.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Aryl and heteroaryl compounds, compositions, and methods of use
This invention provides aryl and heteroaryl compounds, methods of their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds, and their use in treating human or animal disorders. The compounds of the invention may be antagonists, or partial antagonist of factor IX and / or factor XI and thus, may be useful for inhibiting the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. The compounds may be useful in a variety of applications including the management, treatment and / or control of diseases caused in part by the intrinsic clotting pathway.
Owner:VTV THERAPEUTICS LLC
Local curved surface change factor based scattered point cloud data compaction processing method
InactiveCN104616349AImprove search efficiencyOvercoming the results of reduced efficiencyImage generation3D modellingFactor basePoint cloud
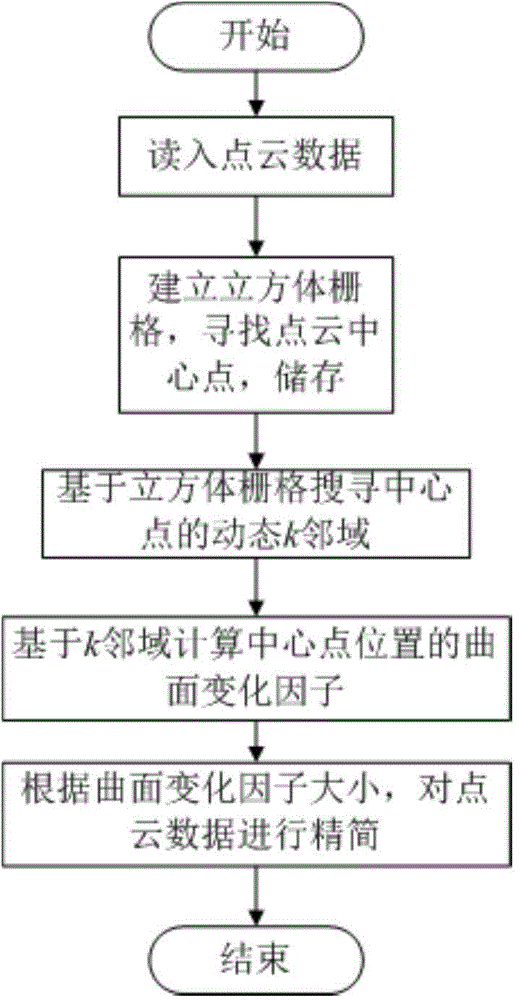
The invention discloses a local curved surface change factor based scattered point cloud data compaction processing method. The local curved surface change factor based scattered point cloud data compaction processing method comprises the steps of 1 reading measured point cloud data, 2 calculating a central point of a point cloud, 3 searching dynamic K neighborhood points of the central point based on cubic grids and accordingly establishing the topological relation of scattered point cloud, 4 adopting a variance component method to calculate curved surface change factors of a k neighborhood of the central point, 5 determining the compaction rate of each cubic grid in the k neighborhood of the central point and performing even compaction in within a k neighborhood range. The topological relation of the scattered point cloud is established by establishing the dynamic K neighborhood point information of the scattered point cloud. Complicated curvature calculation is replaced by the curved surface change factors. The compaction ratio is adjusted according to the curved surface change factors Xi, even compaction within the k neighborhood range is achieved, the detail characteristic of high curvature can be protected, and planar characteristic of low curvature is also protected when the compaction degree is high. Point cloud data processing and curved surface reconstruction efficiency and accuracy are improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising factor VII polypeptides and factor XI polypeptides
InactiveUS20070027077A1Improved and reliable and widely applicableGood coagulationPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesFactor XIPharmaceutical drug
Compositions comprising a factor VII or factor VII-related polypeptide and a factor XI or factor XI-related polypeptide, kits comprising the same, and methods of using such compositions (e.g., in the treatment of bleeding conditions) are provided
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Use of Anti-factor xi antibodies for prevention of thrombus formation
InactiveUS20110159006A1Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseFactor XI
The present invention relates to binding molecules such as antibodies that specifically bind plasma coagulation factor XI and that inhibit factor XI activation and / or activity. The factor XI-binding molecules of the invention may used in methods for preventing or treating diseases, disorders and / or conditions that are mediated by factor XI activation and / or wherein inhibition of factor XI has a beneficial effect.
Owner:HACK ERIK
Complementation of factor xi deficeincy by factor v mutants
InactiveUS20100144620A1Restore clottingMeet growth requirementsPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesHaemophilia CFactor XI
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Methods and kits for measuring ADAMTS13/FXI complexes
InactiveUS20060073535A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide substrateAdamts13 activity
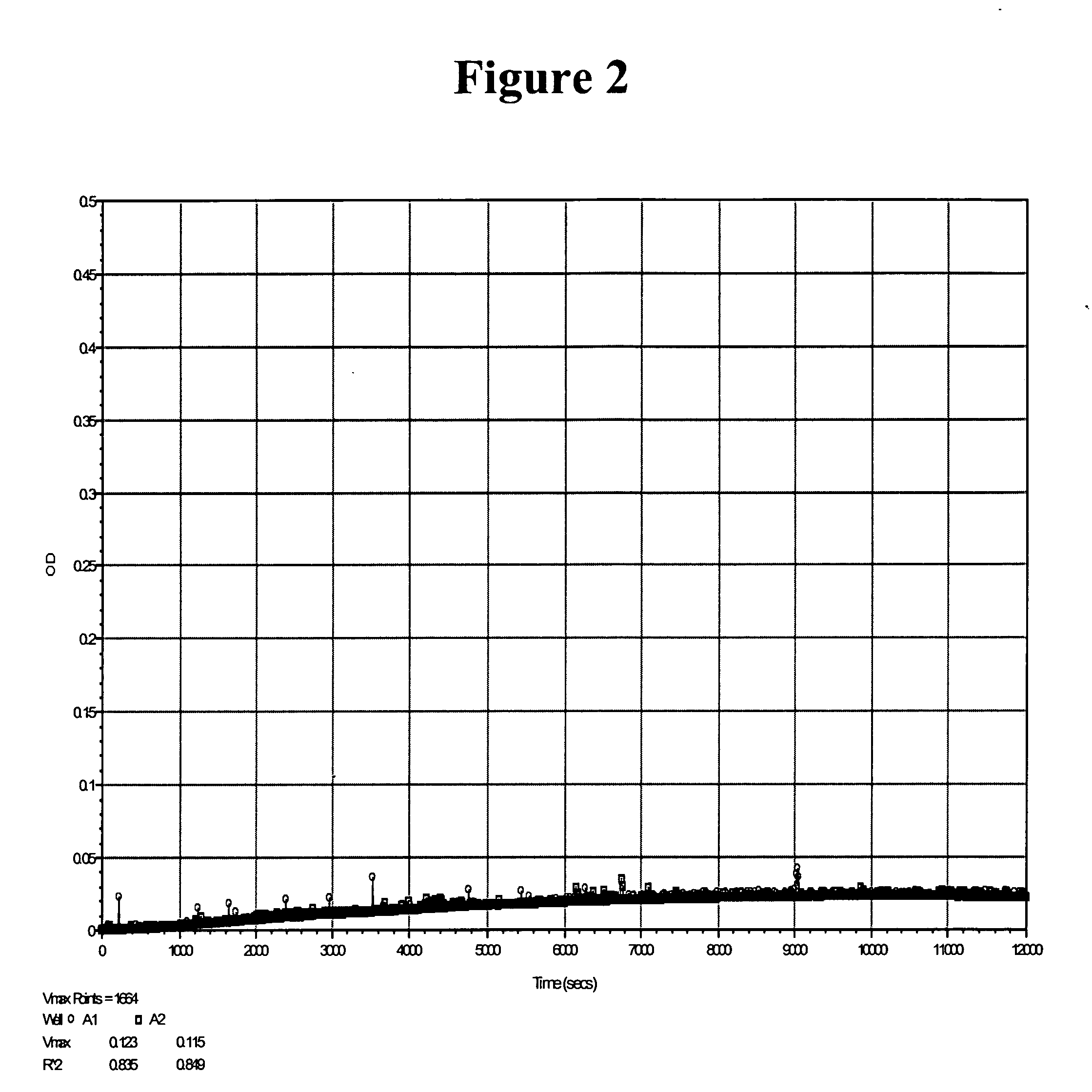
Provided are assays and kits to detect ADAMTS13 activity using peptide substrates and ADAMTS13 / Factor XI complexes using ELISA. These assays and kits can be used for diagnostic applications and to evaluate treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). Also provided is a novel form of ADAMTS13 found on platelets.
Owner:AMERICAN DIAGNOSTICA
Methods and kits for detecting and measuring ADAMTS13/FXI complexes
InactiveUS20080138837A1Inhibit and enhance formationMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisHemostatic DisordersPeptide substrate
Provided are assays and kits to detect ADAMTS13 activity using peptide substrates and ADAMTS13 / Factor XI complexes using ELISA. These assays and kits can be used for diagnostic applications and to evaluate treatment of thrombotic or hemostatic disorders, for example, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). Also provided is a novel form of ADAMTS13 found on platelets, and anti-ADAMTS13 antibodies.
Owner:AMERICAN DIAGNOSTICA
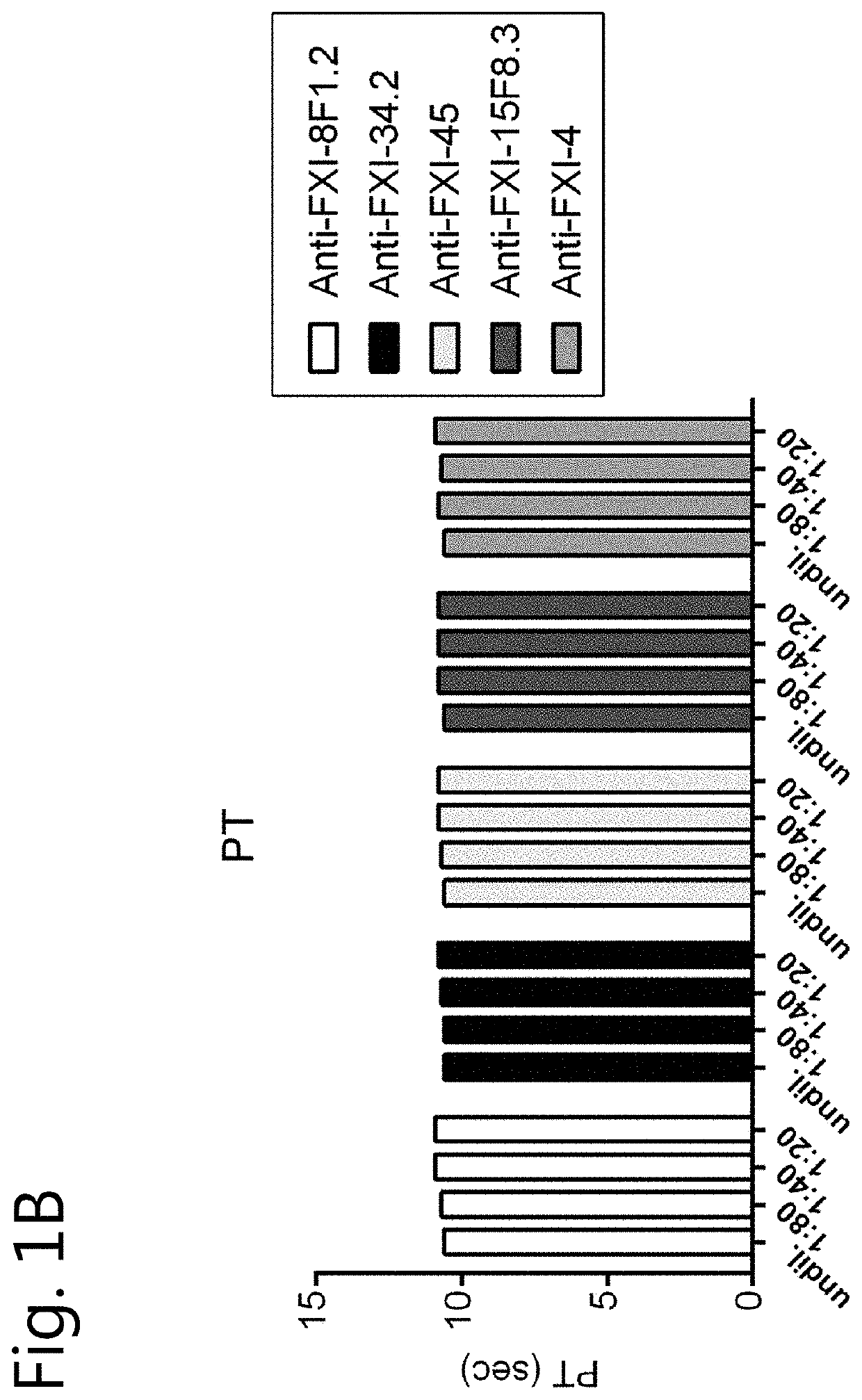
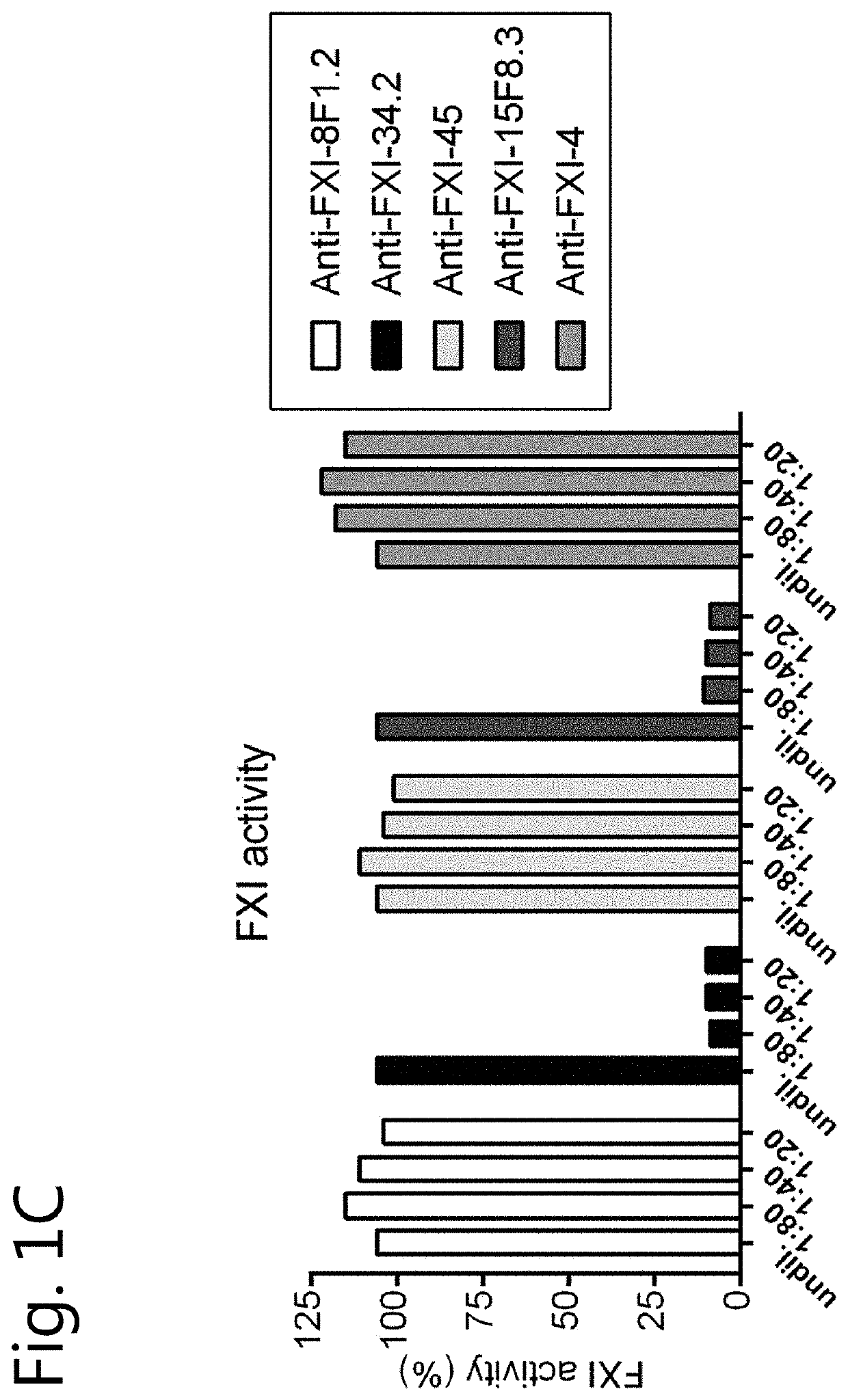
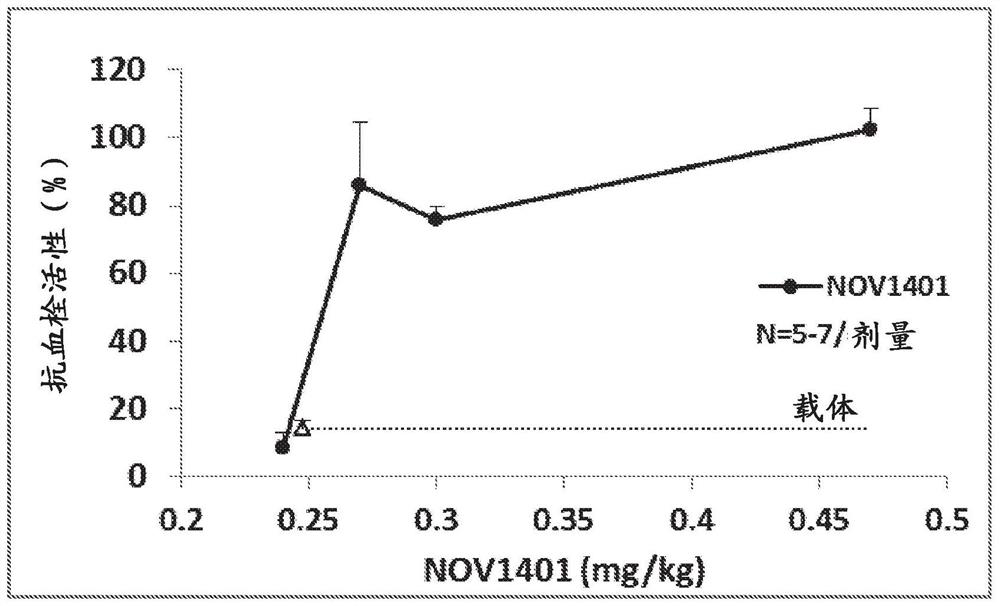
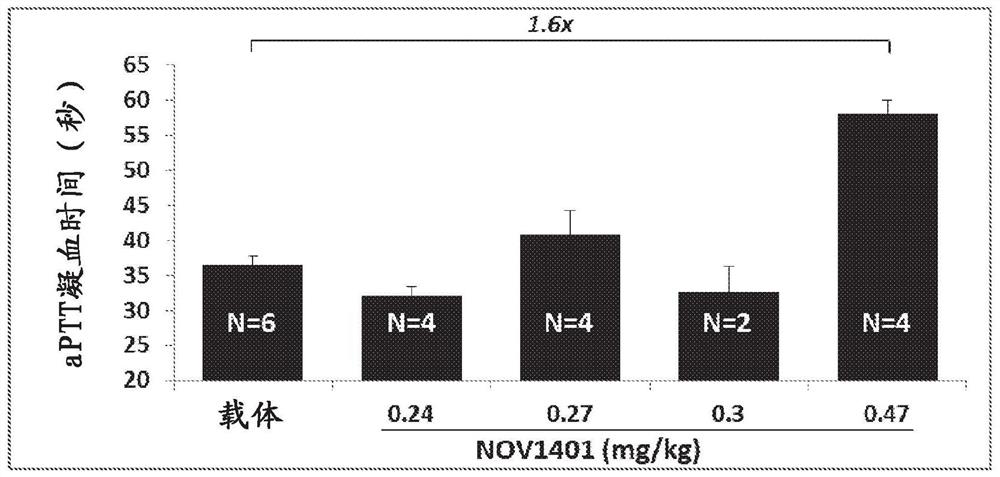
Anti-fXI antibodies and methods of use
ActiveUS8940883B2Inhibition of activationImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAnimal cellsFactor XIBiological activation
Disclosed herein are monoclonal antibodies specific for factor XI (fXI) that prevent activation of fXI by factor XIIa (fXIIa). The monoclonal antibodies are universal fXI antibodies, capable of binding all mammalian species tested. The anti-fXI monoclonal antibodies prolong clotting time in mammalian plasmas. Moreover, administration of the fXI monoclonal antibodies disclosed herein results in inhibition of thrombosis without altering hemostasis in animal models of thrombosis. Thus, provided herein are monoclonal antibodies specific for fXI that block activation of fXI by fXIIa, compositions and immunoconjugates comprising such antibodies and their methods of use.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV +1
Target spot for treating septicemia
InactiveCN102600471AImprove living conditionsLow side reaction rateAntibacterial agentsGenetic material ingredientsAspirinSide effect
The invention discloses a target spot for treating septicemia, belonging to the technical field of treatment of septicemia. The target spot is Factor XI or Factor XII, and can block a Factor XI or Factor XII expression in a septicemia patient body so as to treat septicemia. According to the invention, an antibody-14E11for blocking the Factor XI expression is a novel medicine for treating septicemia after the APC (aspirin compound tablet), and due to the special position of Factor XI on a clotting cascade chain, the occurrence rate of side effects should be obviously lower than that of the APC.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
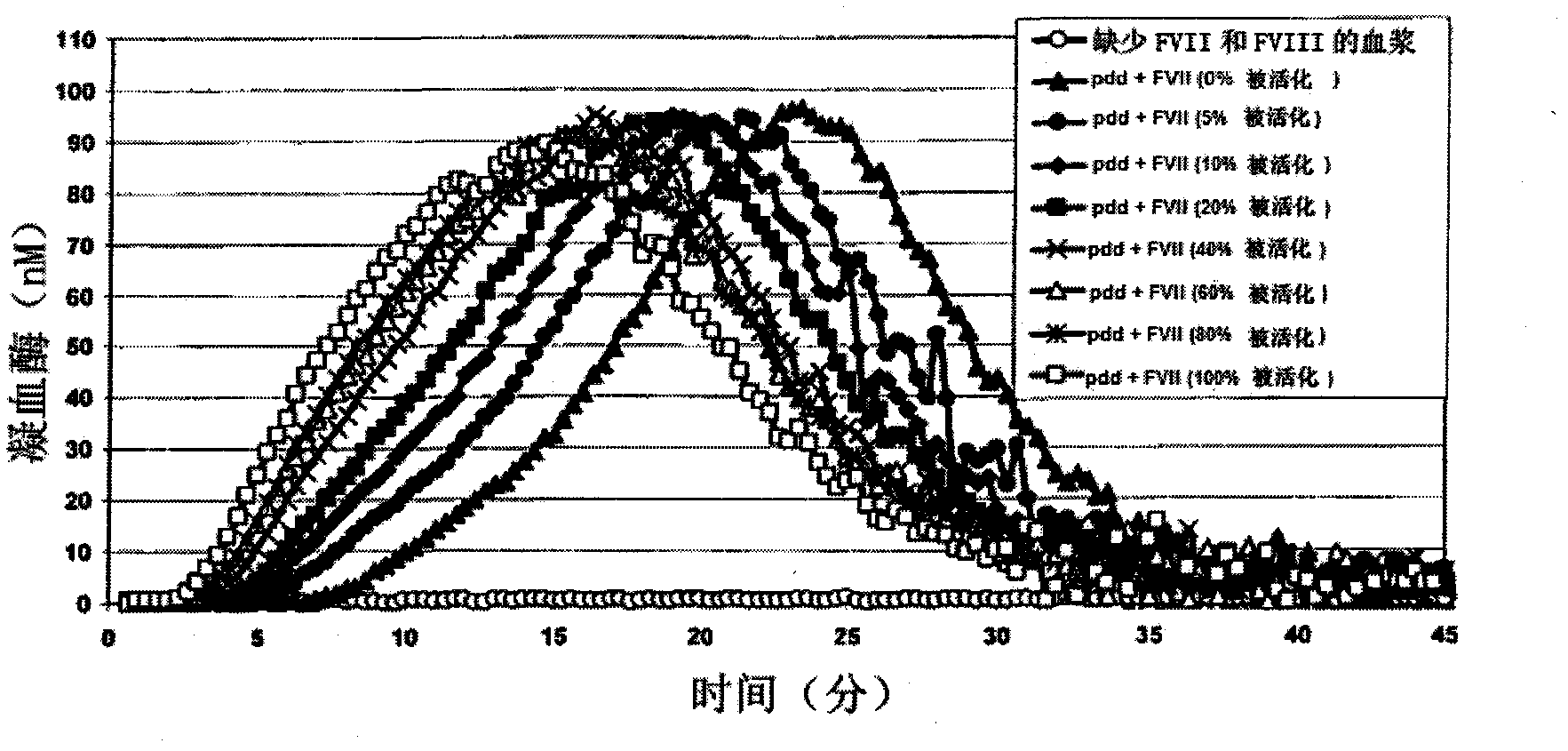
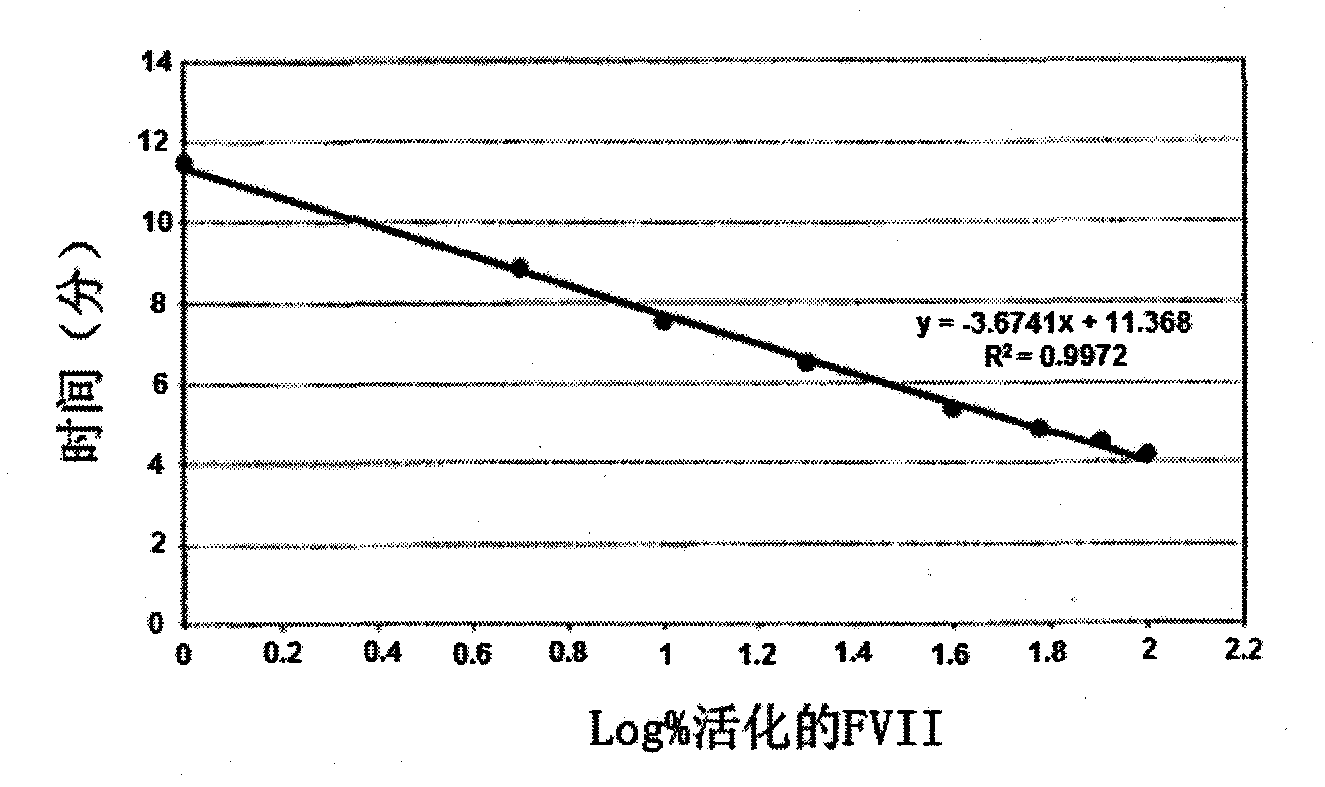
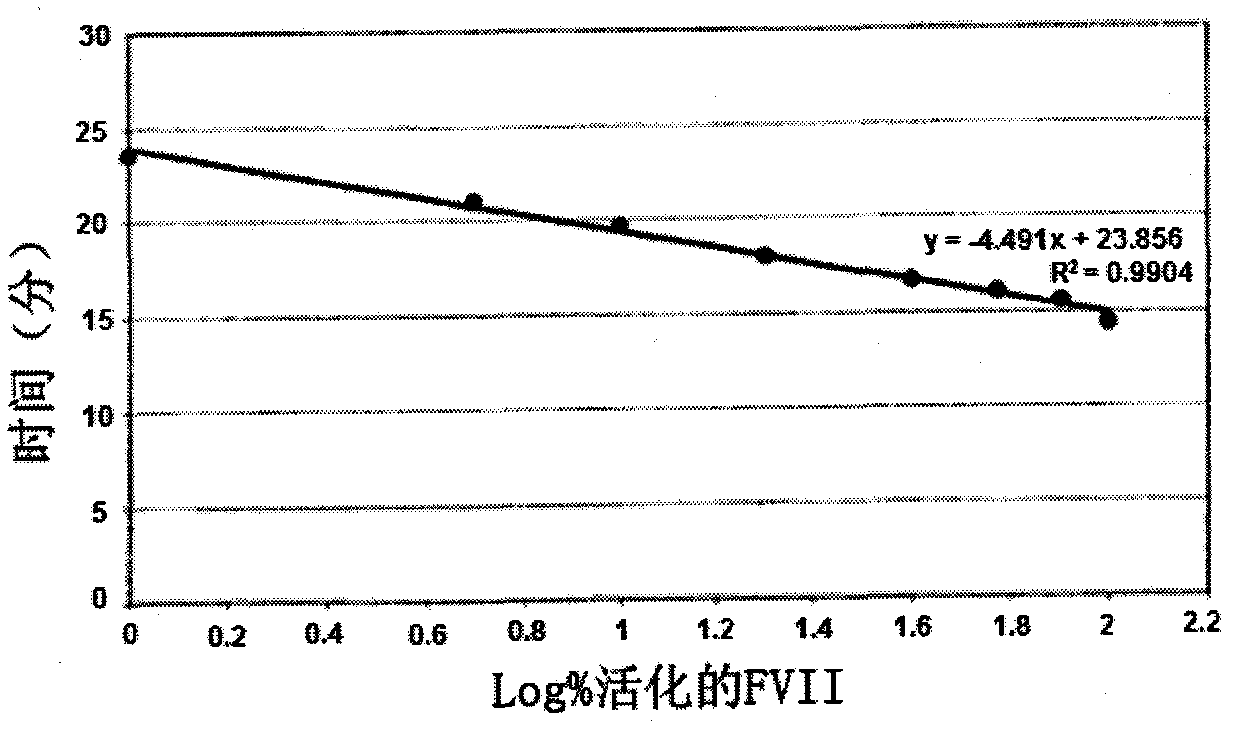
Method for measuring activated factor VII level in a sample
InactiveCN102084254AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisTest sampleFactor XI
The present invention relates to a method for measuring the activated factor VII level in a sample to be tested, including the steps of: a) mixing said test sample with a plasma free of factor VII (FVII) and free of at least another factor selected from among factor VIII (FVIII), factor IX (FIX), and factor XI (FXI), the test sample + plasma having a final FVII + FVIIa concentration of 10 pM to 80 pM; b) adding initiating components from the thrombin generation reaction; c) obtaining a thrombogram when carrying out a thrombin generation test (TGT) on the mixture from step b); d) comparing at least one of the thrombogram parameters from step c) with a homologous parameter obtained from standard thrombograms established on the basis of standard samples, the activated factor VII level of which is known and varies with each standard sample; e) deducing, from step d), an activated factor VII level measurement in the test sample.
Owner:LFB BIOTECH
Factor XI antibodies and methods of use
ActiveCN107922505AImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAntibody ingredientsAntigen Binding FragmentFactor XI
The present invention relates to monoclonal antibodies and antigen binding fragments thereof that bind to human Factor XI and activated Factor XI ("Factor XIa"), and pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treatment comprising the same.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
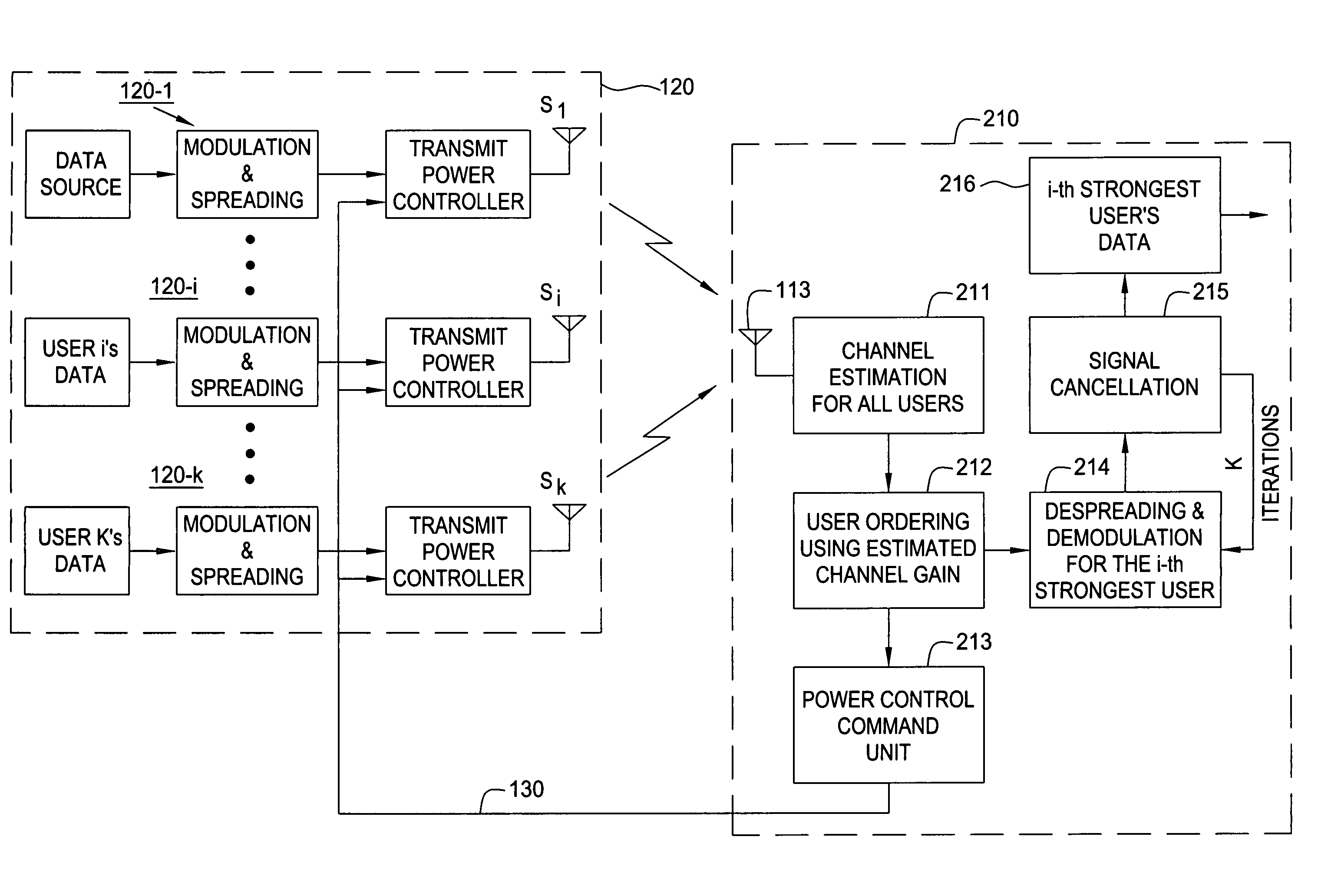
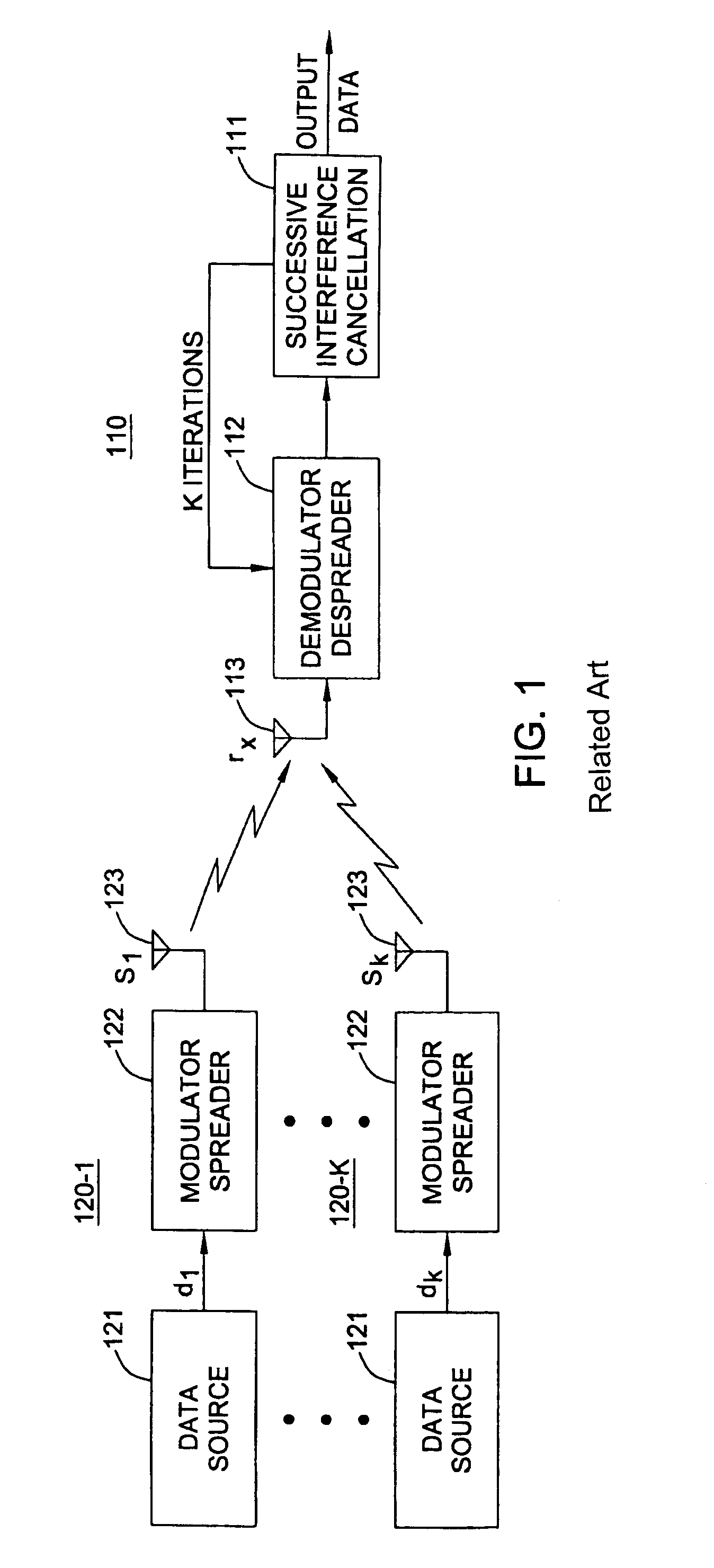
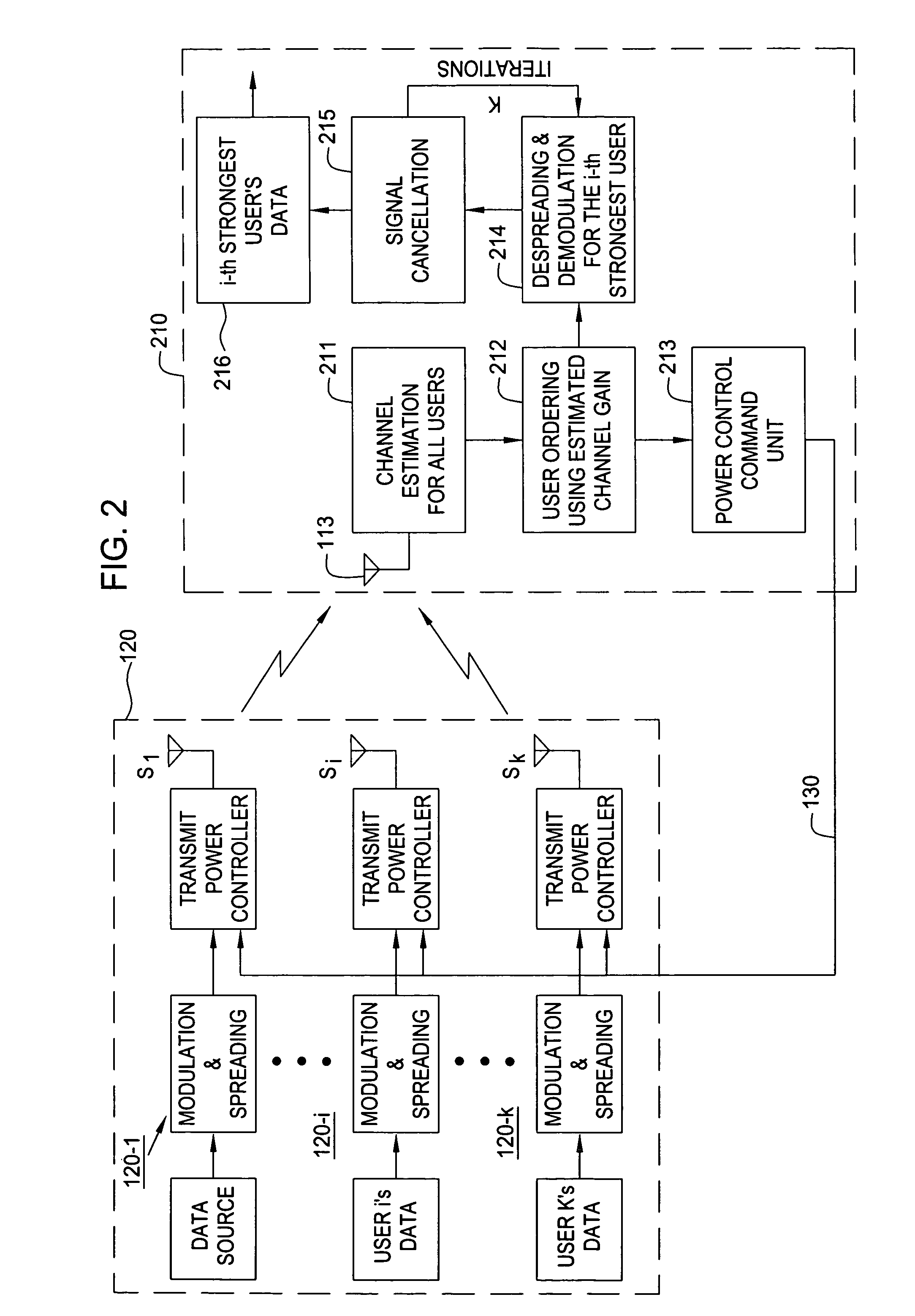
Transmit power adaptation for CDMA communication systems using successive interference cancellation
Transmit power adaptation for DS / CDMA systems is disclosed for a CDMA system that utilizes a successive interference cancellation receiver on fading channels. The transmission power is adapted in response to channel variations to achieve an arbitrary power profile for received signal powers at the system base station. That is, the received signal powers are distributed with some factor xi's given as:SRi=SR(1)xi, (i=2, 3, . . . , K and x1=1)where K is the number of users and SR(i) is the received signal power of the user having the ith strength, and wherein user strengths are ranked in the order of estimated channel gains. The factor xi gives a measure of the disparity between the received power levels. The channel is estimated at both the transmitter and receiver. In one embodiment, the factors, xi, for distributing the signal powers are selected such that the average BER for each user is minimized. In another embodiment, the factors, xi, for distributing the signal powers are selected such that, after successive interference cancellation, an instantaneous BER for all users is equal.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
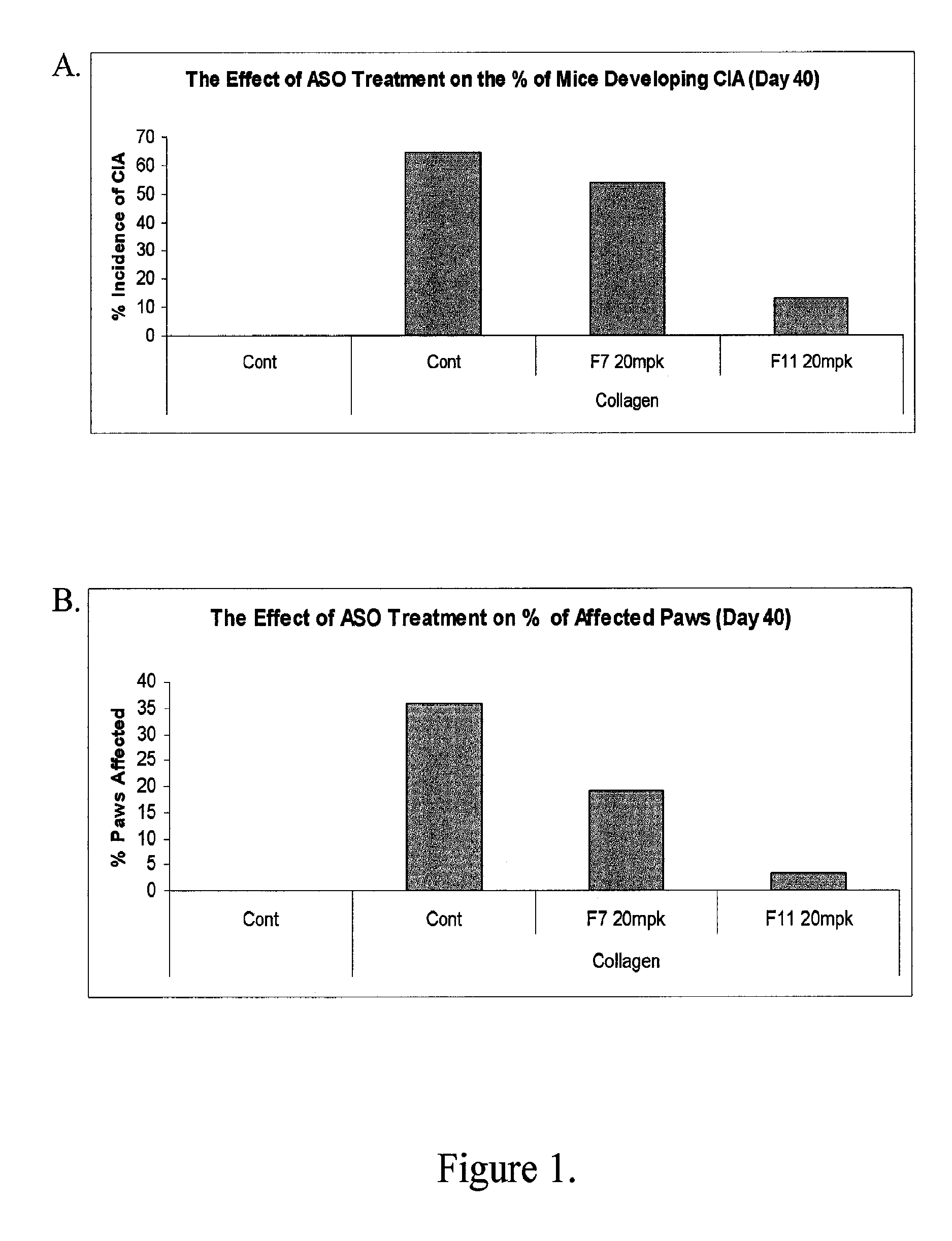
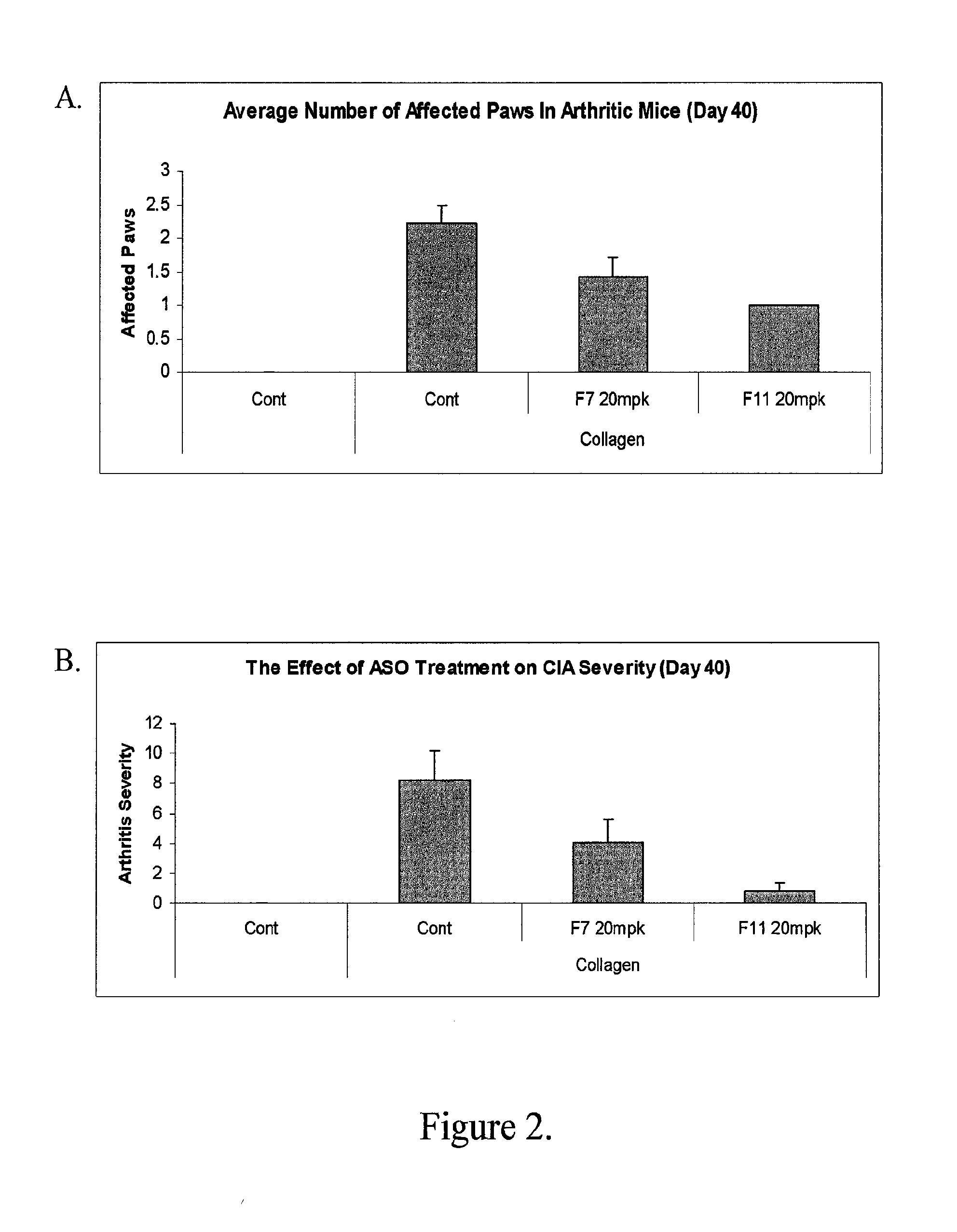
Modulation of inflammatory responses by factor xi
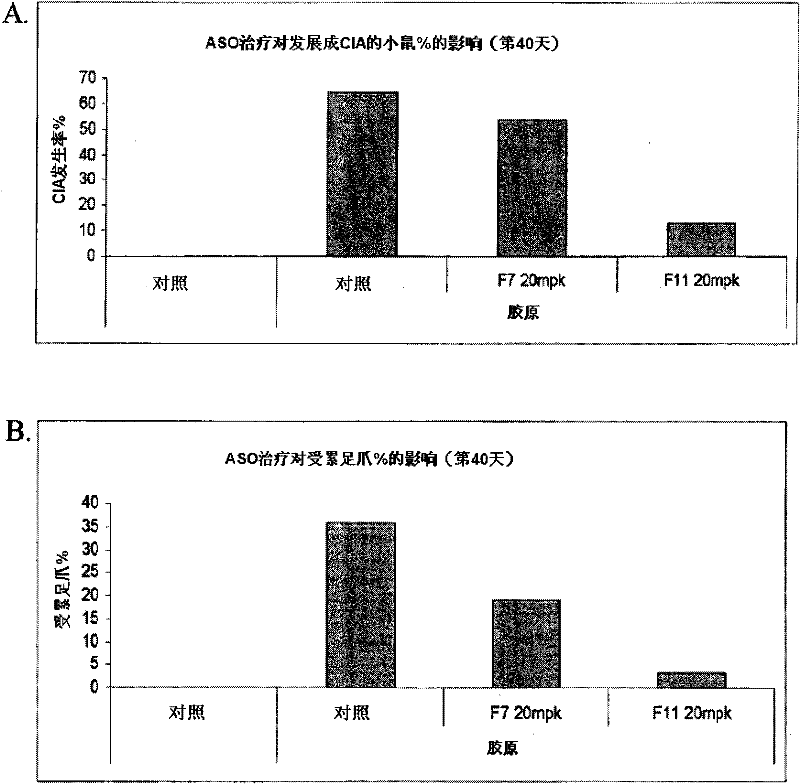
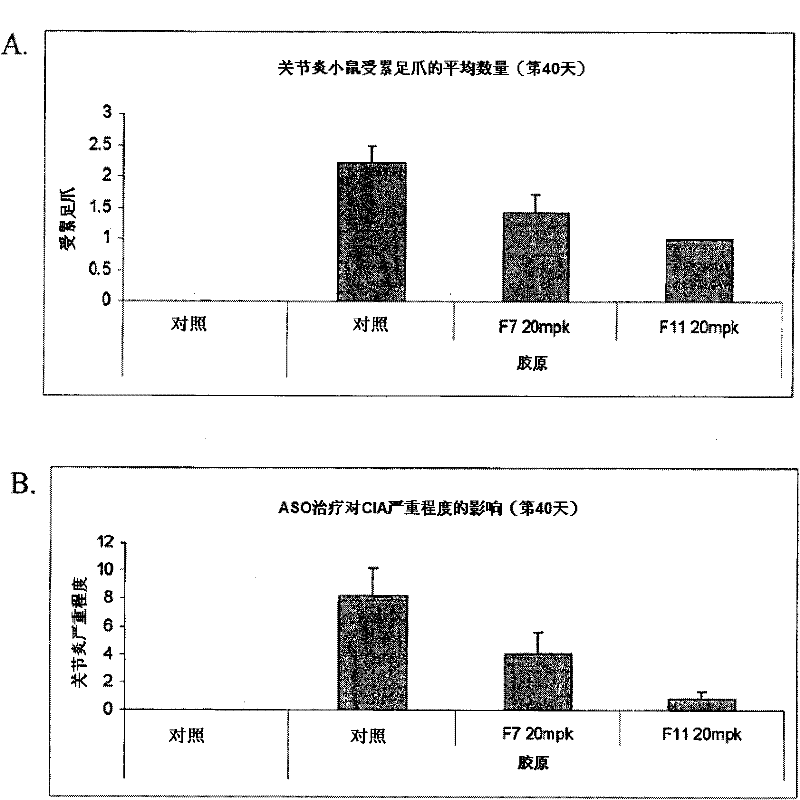
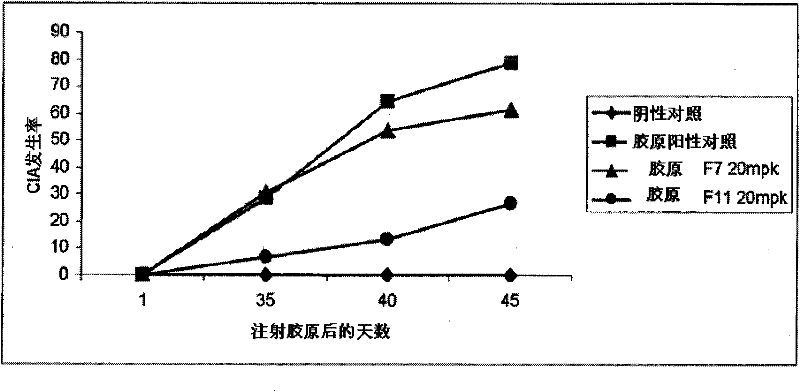
InactiveUS20120083522A1Inhibit the inflammatory responseImprove inflammationOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsFactor XIArthritis
Disclosed herein are antisense compounds and methods for modulating Factor XI and modulating an inflammatory disease, disorder or condition in an individual in need thereof. Inflammatory diseases in an individual such as arthritis and colitis can be ameliorated or prevented with the administration of antisense compounds targeted to Factor XI.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
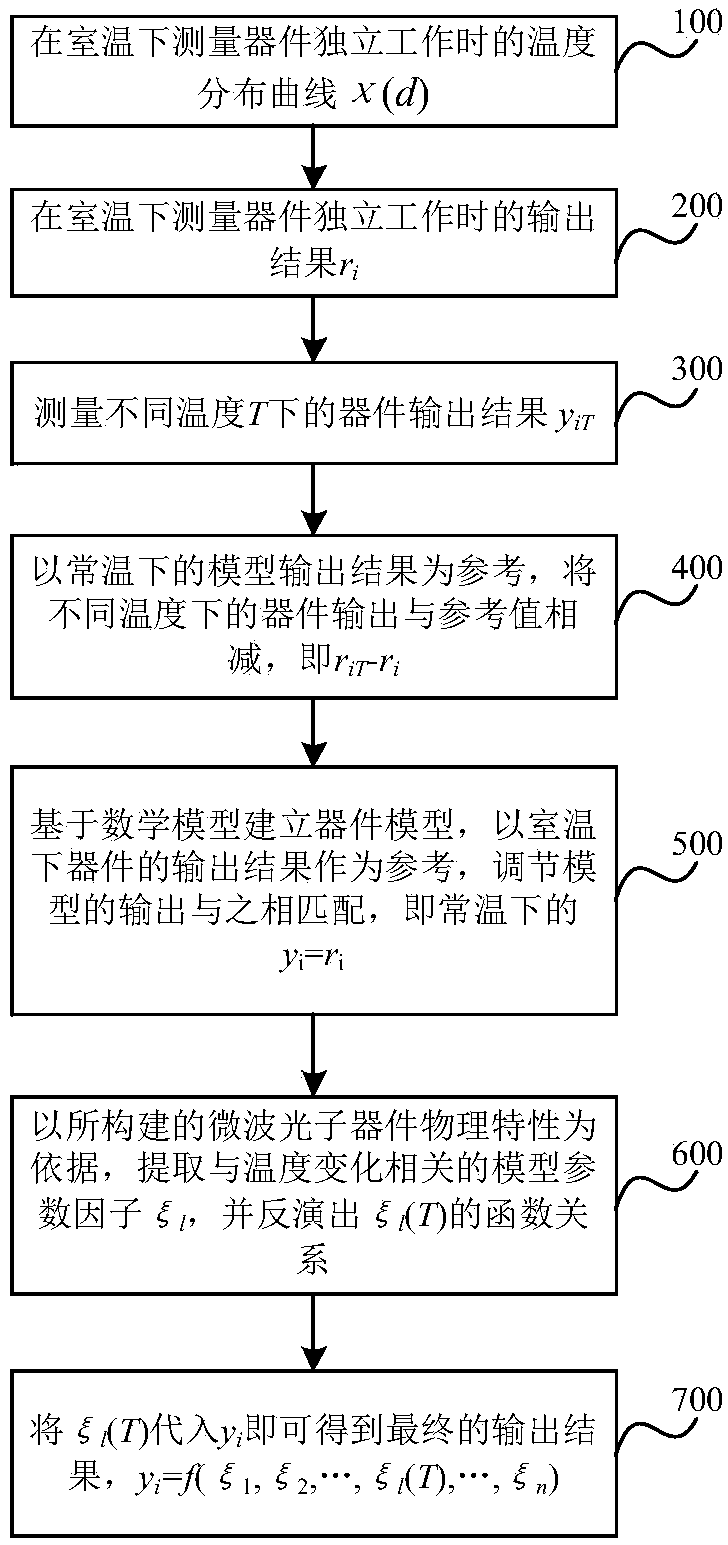
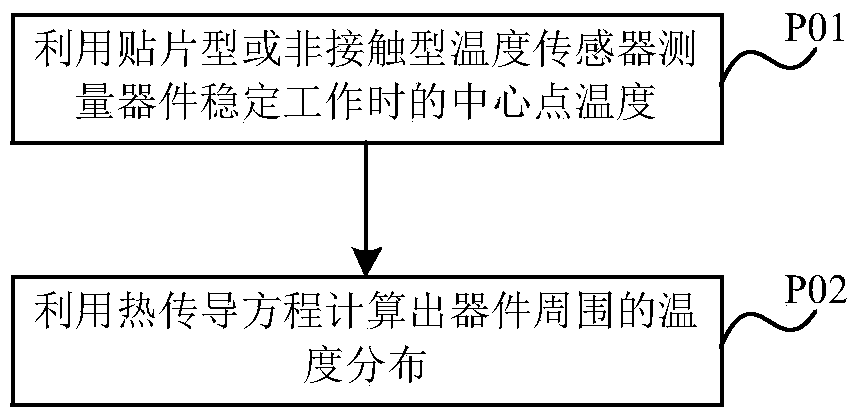
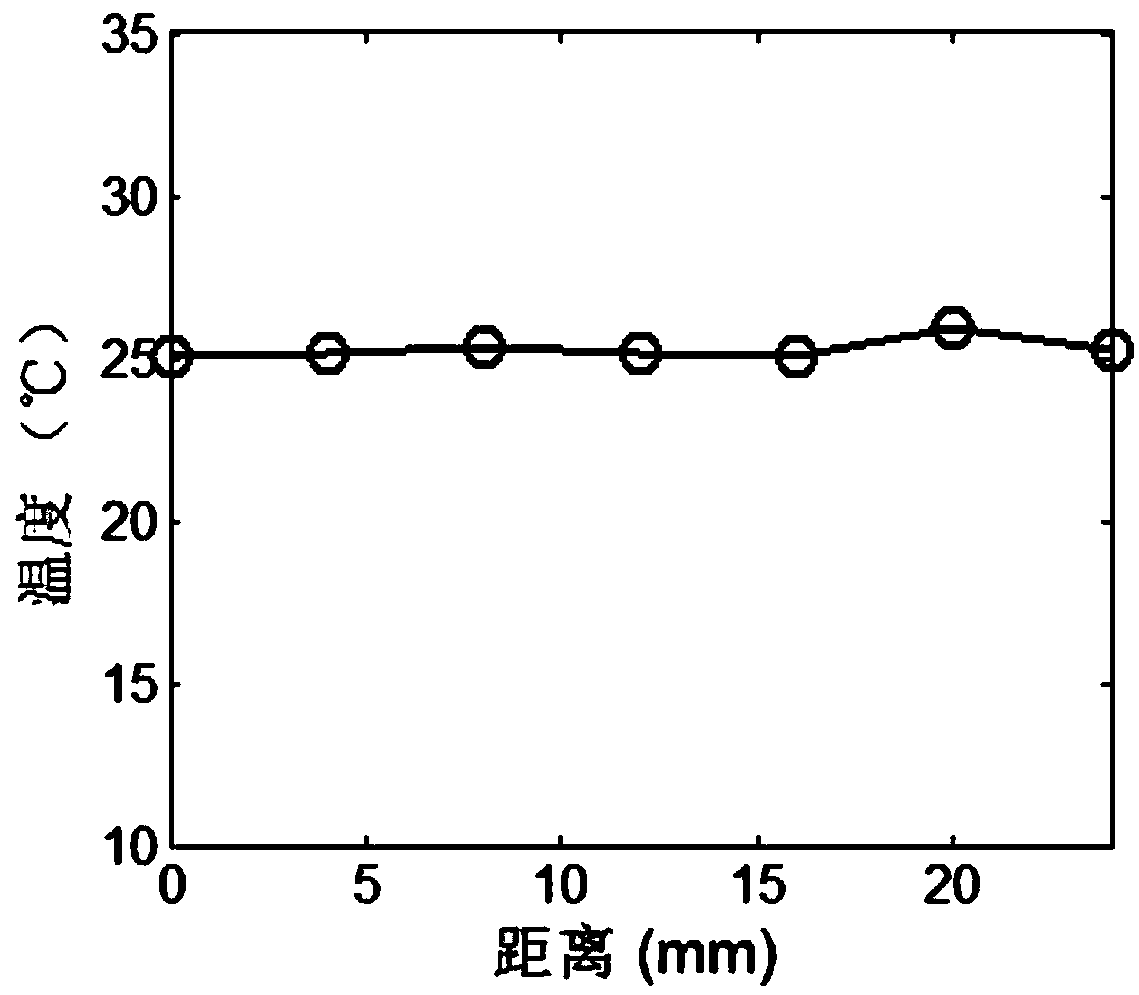
A microwave photonic device modeling method based on electromagnetic field and temperature field coupling
ActiveCN109635519AHigh precisionRapid modelingSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelEngineering
The invention relates to the field of modeling of integrated devices, and discloses a microwave photonic device modeling method based on electromagnetic field and temperature field coupling. The method comprises the following steps: measuring a temperature distribution curve of a device during independent work and an output result ri during independent work at room temperature; Measuring device output results riT at different temperatures T; Taking an output result which works independently at room temperature as a reference to obtain the influence of the temperature on the output result of the device; Establishing an ideal mathematical model output by the device, and adjusting parameters to enable an output result of the mathematical model to be the same as an output result independentlyworking at room temperature; Extracting a temperature factor Xi in the mathematical model and the influence of the temperature on the output result of the device, and inverting a function relation Xi(T) between the temperature factor and the temperature; And substituting the temperature factor Xi and the function relationship Xi (T) into the mathematical model to complete the calculation of the model output characteristic. Aiming at the field of high-integration modeling and simulation, the influence of temperature on the modeling precision of the device can be solved, the modeling speed is high, and the precision is high.
Owner:SOUTHWEST CHINA RES INST OF ELECTRONICS EQUIP
Therapeutic use of factor XI
The present invention provides methods and compositions for treating bleeding episodes. The methods are carried out by administering to a patient in need thereof a preparation comprising a factor XI polypeptide, in an amount effective for such treatment. The methods of the invention result in one or more of: reduced clotting time; enhancement of hemostasis; increase in clot lysis time; increase in clot strength; and / or increase in overall clot quality (OCQ) in said patient.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Agkistrodon acutus anticoagulant factor XI polypeptide and application thereof
ActiveCN113773377AStrong inhibitory activityProlonged thromboplastin timePeptide/protein ingredientsProtease inhibitorsAntithrombotic AgentAgkistrodon acutus
The invention belongs to the field of polypeptides in biochemistry, and relates to an agkistrodon acutus anticoagulant factor XI polypeptide and application thereof. According to the polypeptide, a Kunitz type polypeptide sequence is screened from an agkistrodon acutus snake venom transcriptome database, the Kunitz type polypeptide sequence is constructed and expressed to obtain the polypeptide with antithrombotic activity, and the polypeptide can be applied to preparation of antithrombotic drugs.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Aryl and heteroaryl compounds, compositions, and methods of use
This invention provides aryl and heteroaryl compounds, methods of their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds, and their use in treating human or animal disorders. The compounds of the invention may be useful as antagonists, or partial antagonist of factor IX and / or factor XI and thus, may be used to inhibit the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. The compounds may be useful in a variety of applications including the management, treatment and / or control of diseases caused in part by the intrinsic clotting pathway.
Owner:TRANSTECH PHARMA INC
Modulation of inflammatory responses by factor xi
InactiveCN102458480APrevent and/or improve inflammatory responseImprove inflammatory responseOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsDiseaseFactor XI
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Reversal binding agents for anti-factor XI/XIA antibodies and uses thereof
PendingCN111902427AImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAntinoxious agentsAntiendomysial antibodiesFactor XI
The present disclosure relates to reversal agents, which specifically bind to anti-Factor XI and / or anti-Factor XIa antibodies, and reverse one or more anticoagulant effects of the anti- Factor XI and / or anti-Factor XIa antibodies, as well as to methods of use thereof, such as methods for reversing anticoagulant effects of such anti-Factor XI and / or anti-Factor XIa antibodies, and to related methods for managing bleeding or bleeding risks.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Monoclonal antibodies against the active site of factor XI and uses thereof
ActiveUS11059905B2Reduces chromogenic activityImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAntibody ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesFactor XI
The present invention provides novel anti-factor XI (FXI) antibodies and compositions comprising such antibodies. The anti-FXI antibodies of the invention specifically bind to the active center of FXI and inhibit the functional activity of FXI. The invention further provides humanized versions of the anti-FXI antibodies that are useful in the prevention and treatment of conditions in which pathological thrombus formation or thrombo-embolism are involved. The invention further provides nucleic acid molecules encoding the anti-FXI antibodies, cells expressing the anti-FXI antibodies and methods for producing the anti-FXI antibodies.
Owner:PROTHIX BV
Factor XI antibodies and methods of use
PendingCN114380914AImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAntibody ingredientsAntigenAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention relates to monoclonal antibodies and antigen-binding fragments thereof that bind to human coagulation factor XI and activated coagulation factor XI ("coagulation factor XIa"), and pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treatment comprising the same.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
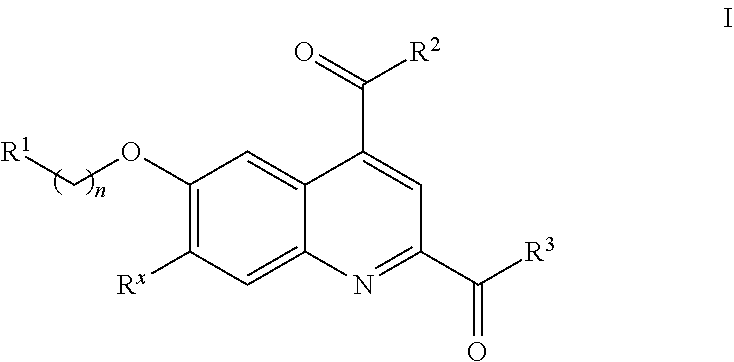
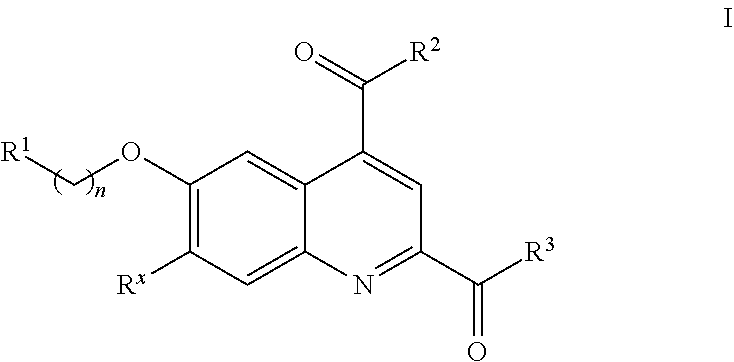
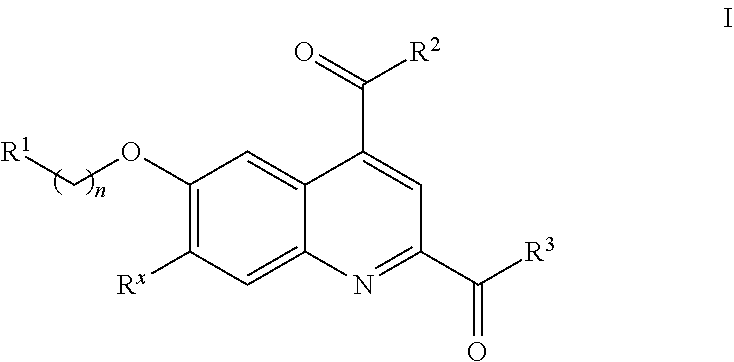
Factor xi activation inhibitors
The present invention provides a compound of Formula (I) and pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more said compounds, and methods for using said compounds for treating or preventing thromboses, embolisms, hypercoagulability or fibrotic changes. The compounds are selective Factor XI activation inhibitors.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Pharmaceutical composition comprising factor VII polypeptides and factor XI polypeptides
The present invention relates to compositions comprising factor VII or factor VII-related polypeptides and factor XI or factor XI-related polypeptides, and their use for the treatment of bleeding episodes.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com