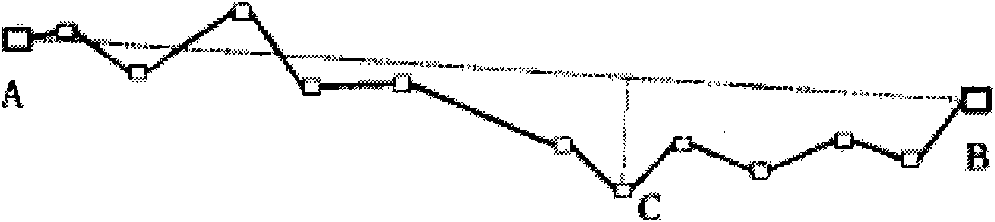Patents
Literature
222 results about "Data compaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In telecommunication, data compaction is the reduction of the number of data elements, bandwidth, cost, and time for the generation, transmission, and storage of data without loss of information by eliminating unnecessary redundancy, removing irrelevancy, or using special coding.
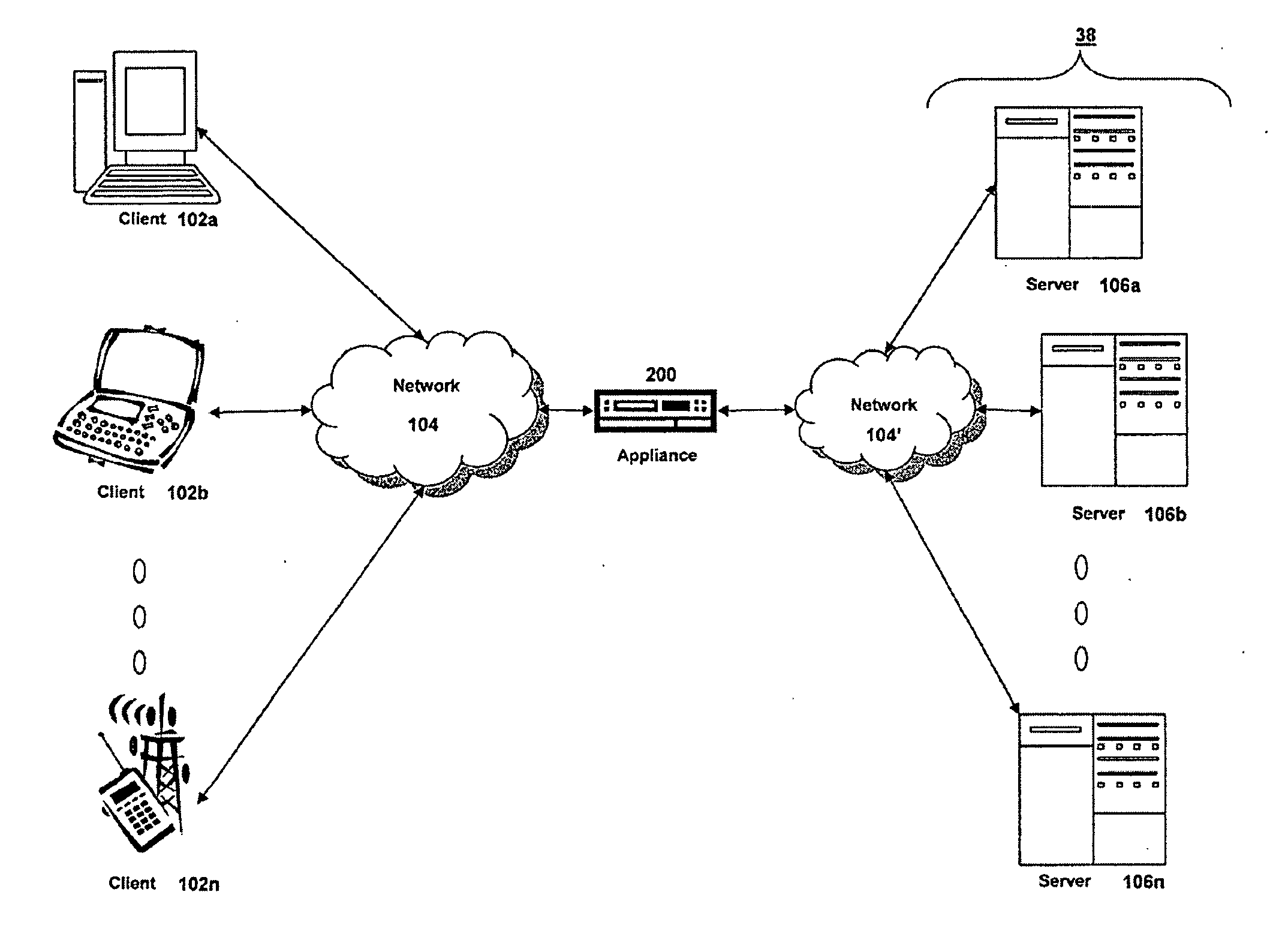
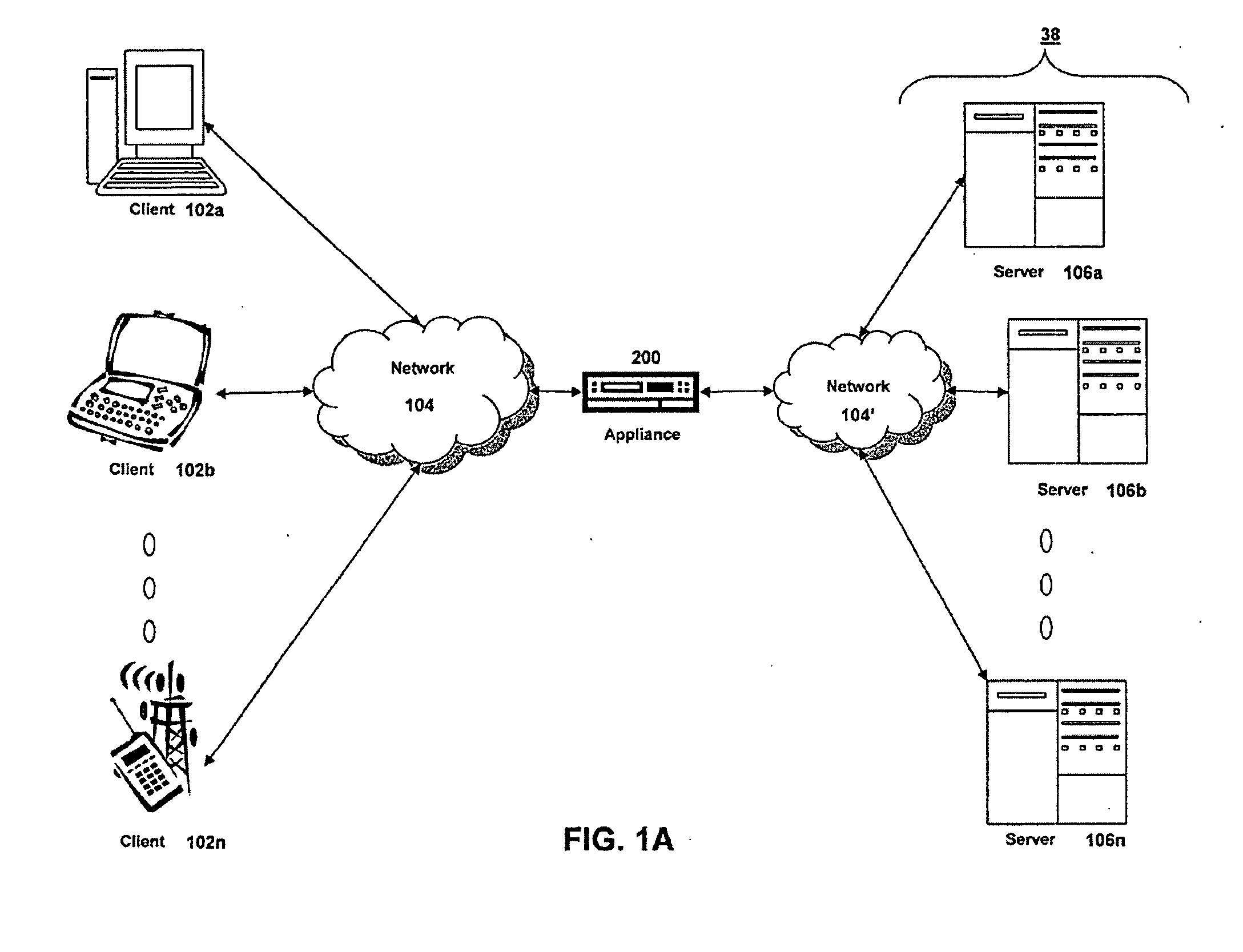
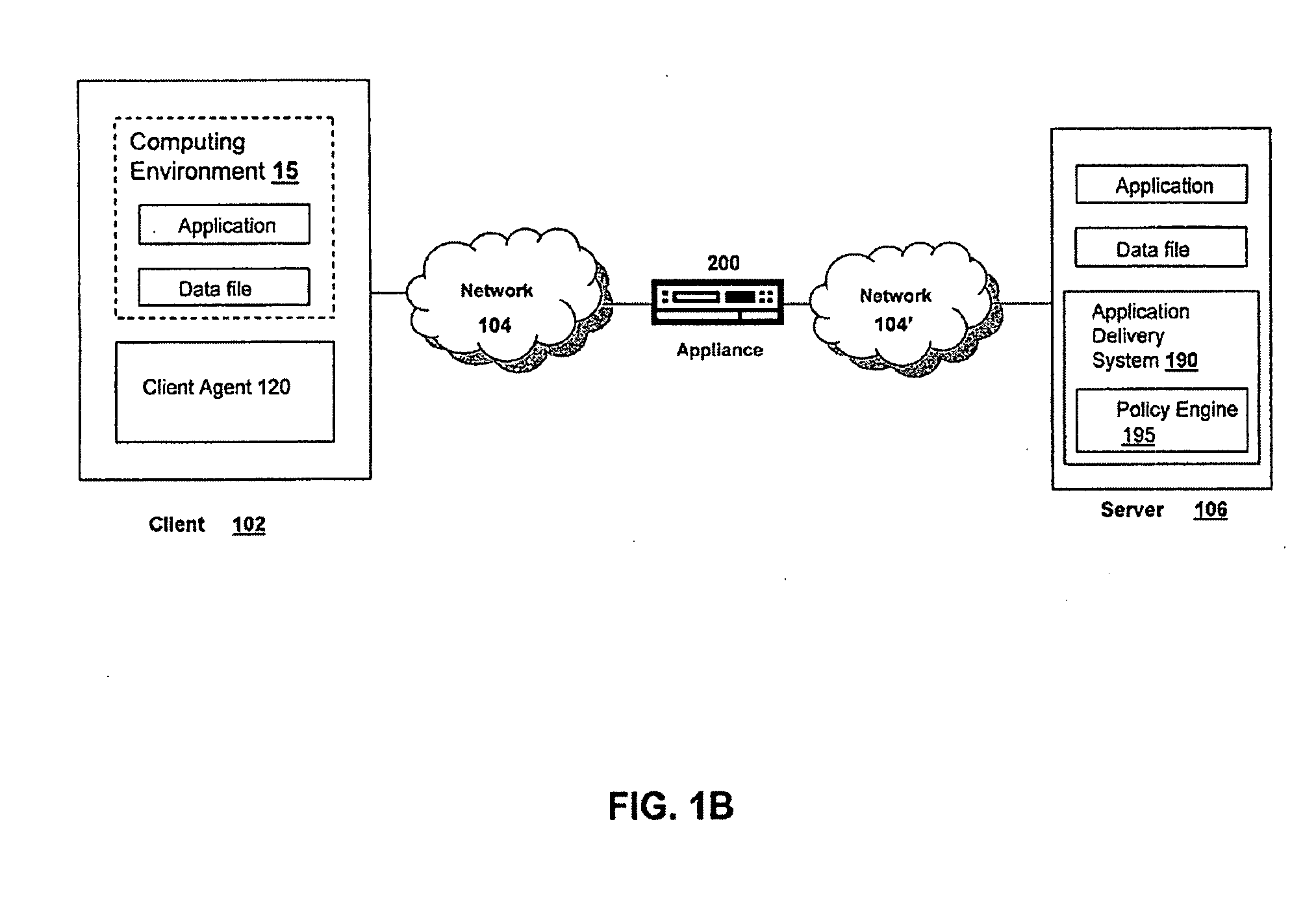
Systems and Methods of Symmetric Transport Control Protocol Compression
ActiveUS20080046616A1Reduce network latencyImprove experienceNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless network protocolsTraffic capacityData compression
A method for compressing a stream of application layer network traffic communicated over a transport layer connection of a virtual private network connection between a client and a server using an appliance. The appliance intercepts one or more transport layer packets of a stream of application network traffic communicated via a transport layer connection of a virtual private network connection between a client and a server. The appliance accumulates data from a payload of the intercepted transport layer packets, determines data accumulated for transmission should be compressed based on one or more compression trigger, and compresses the accumulated data into a self-contained compression block for transmission.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Methods and Apparatus for Reducing Storage Size
ActiveUS20080154928A1Reduce probabilitySave energyDigital data processing detailsCode conversionGraphicsData stream
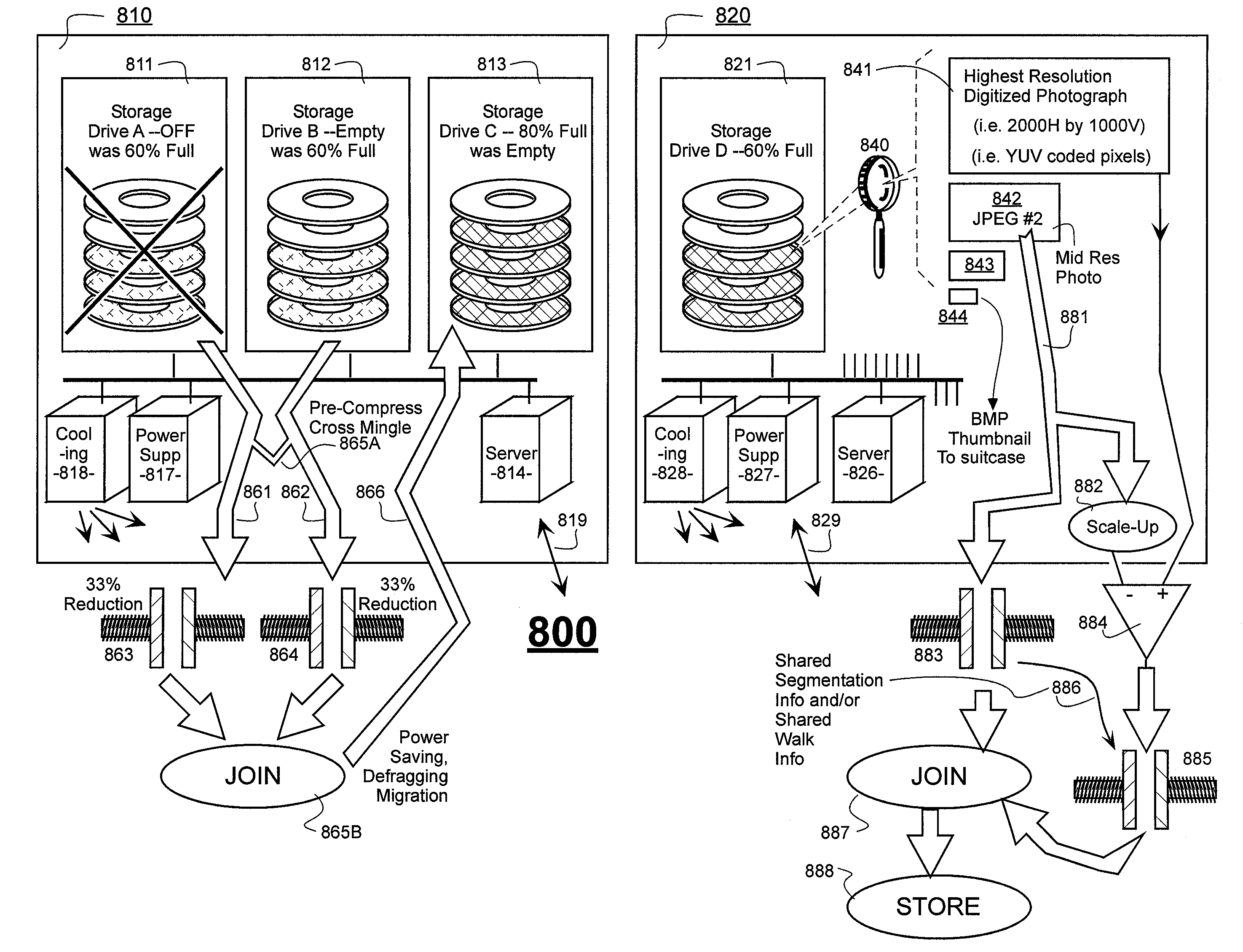
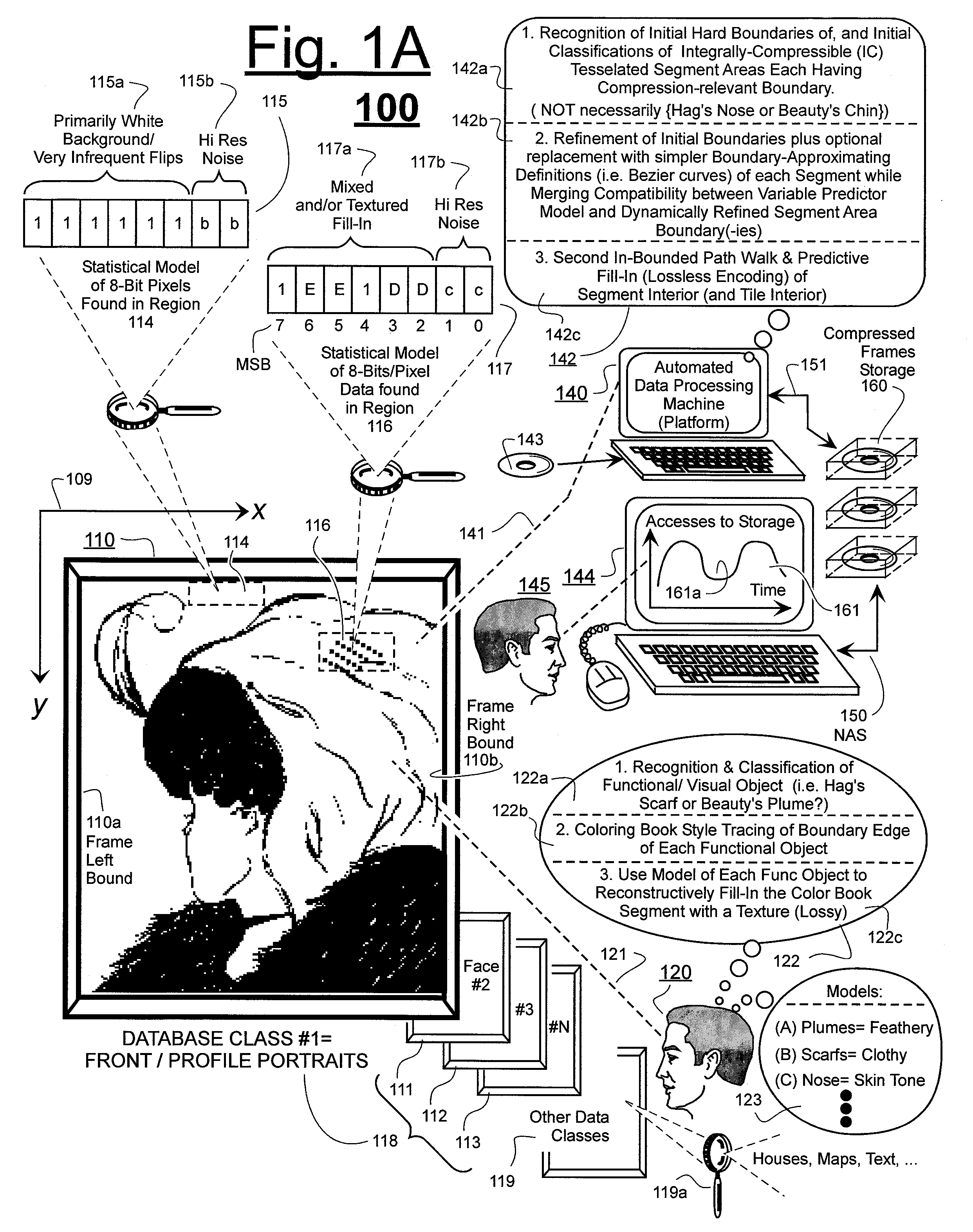
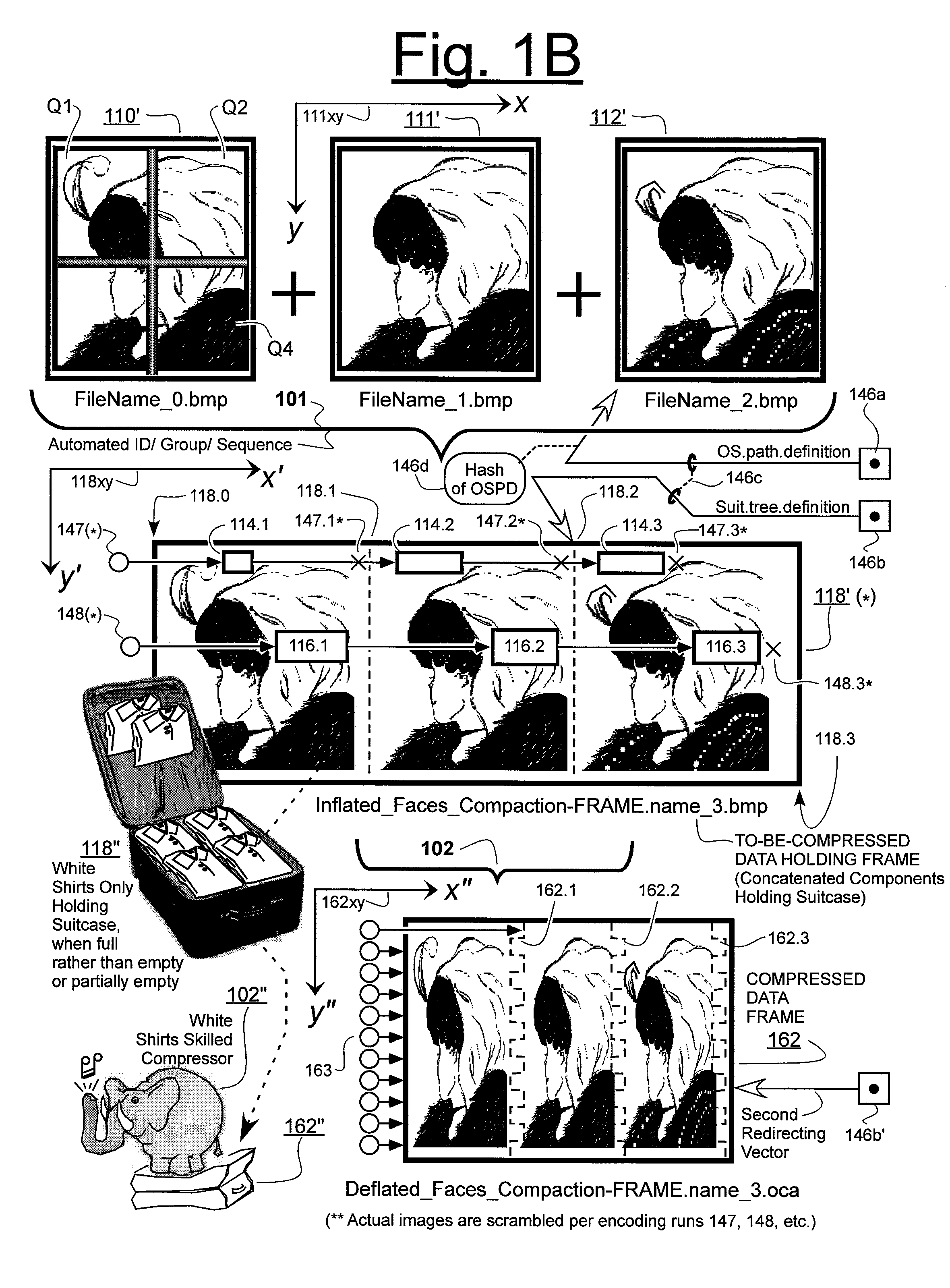
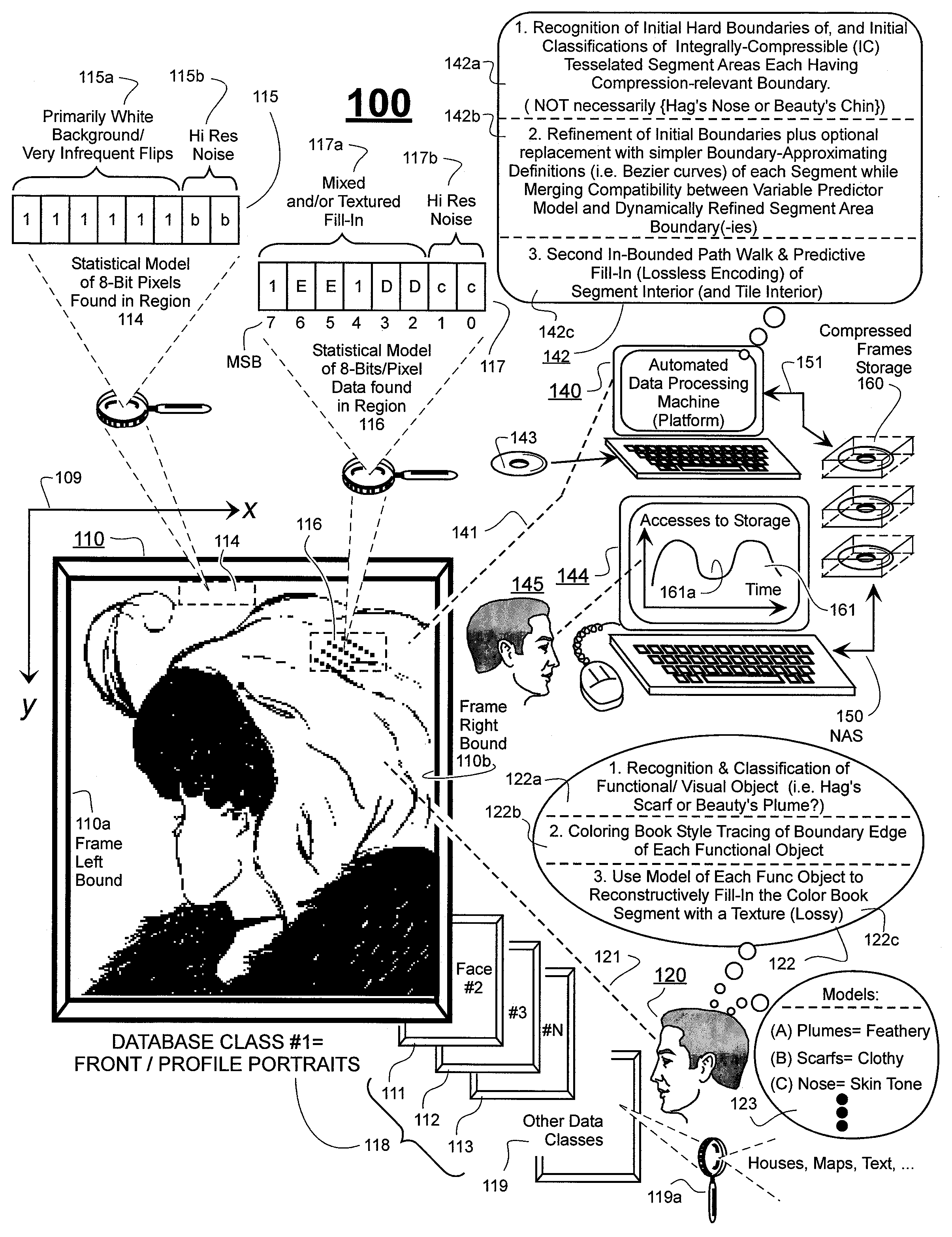
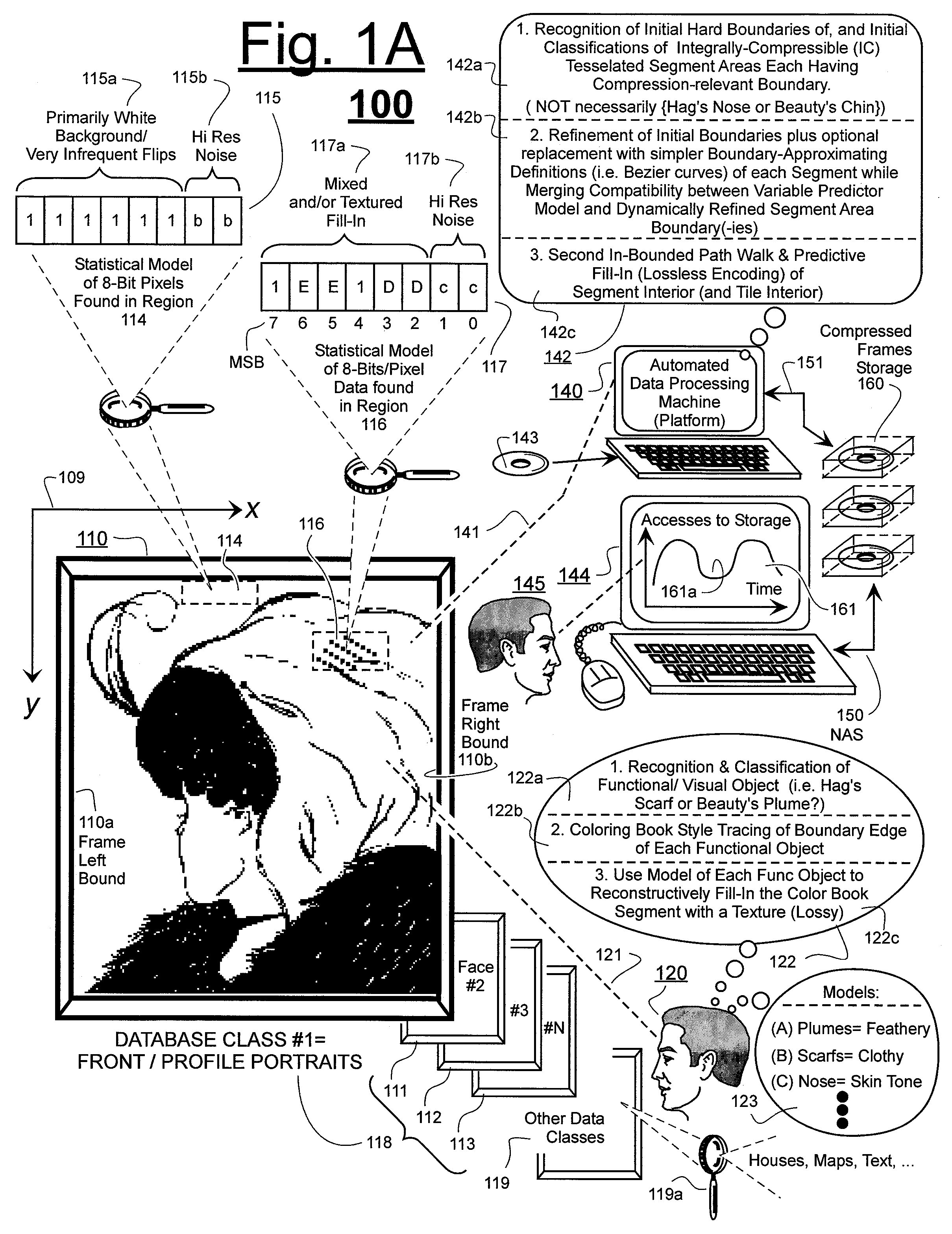
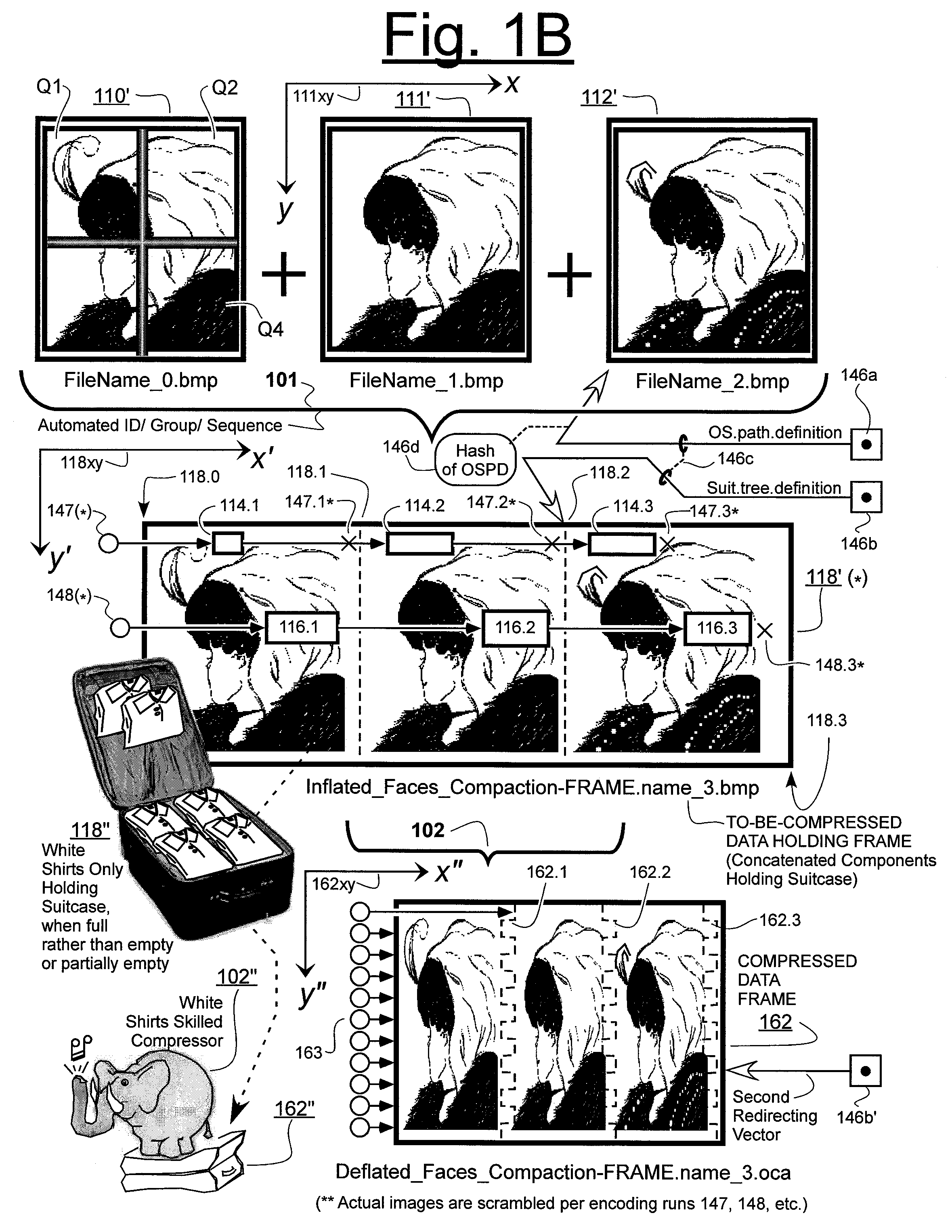
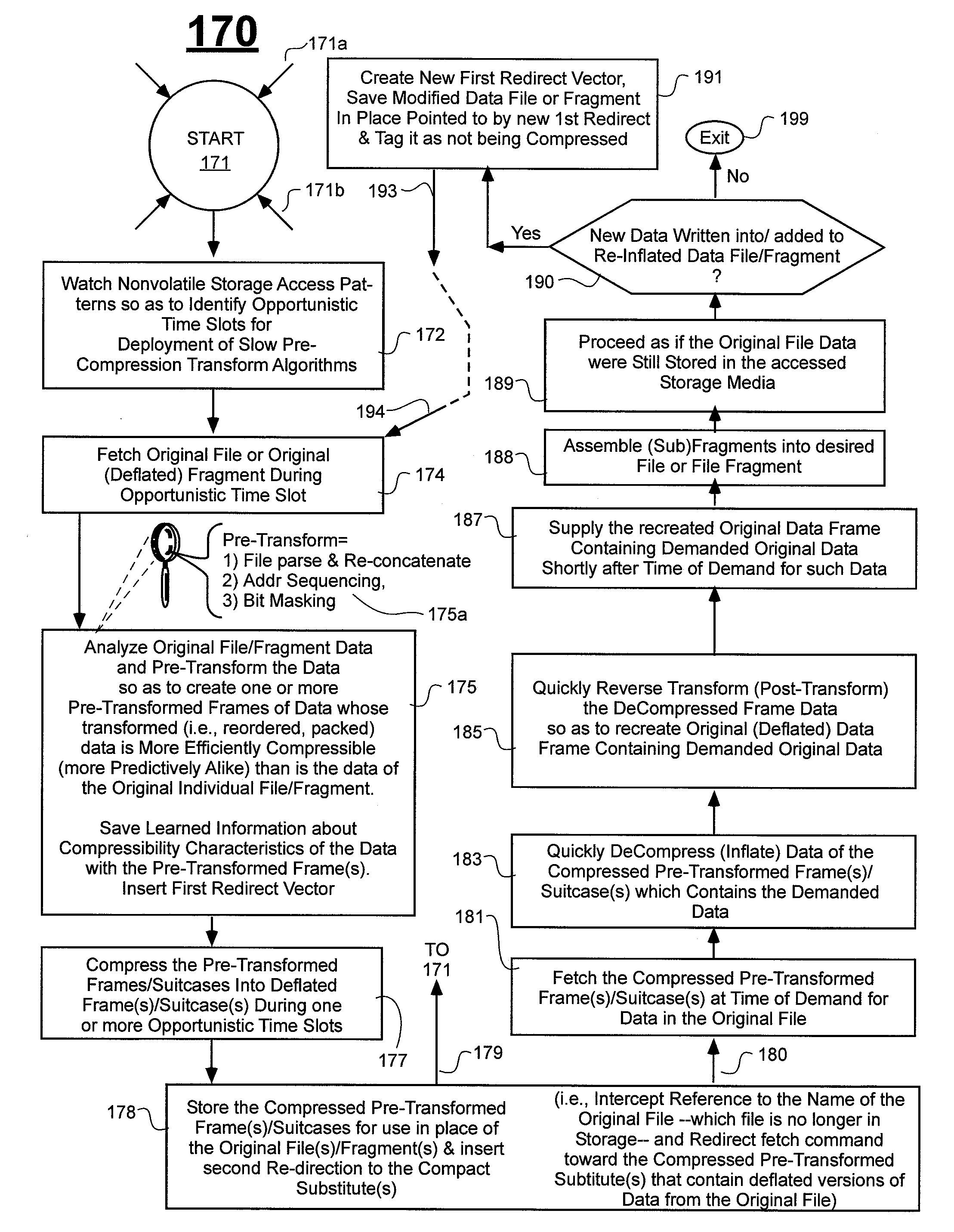
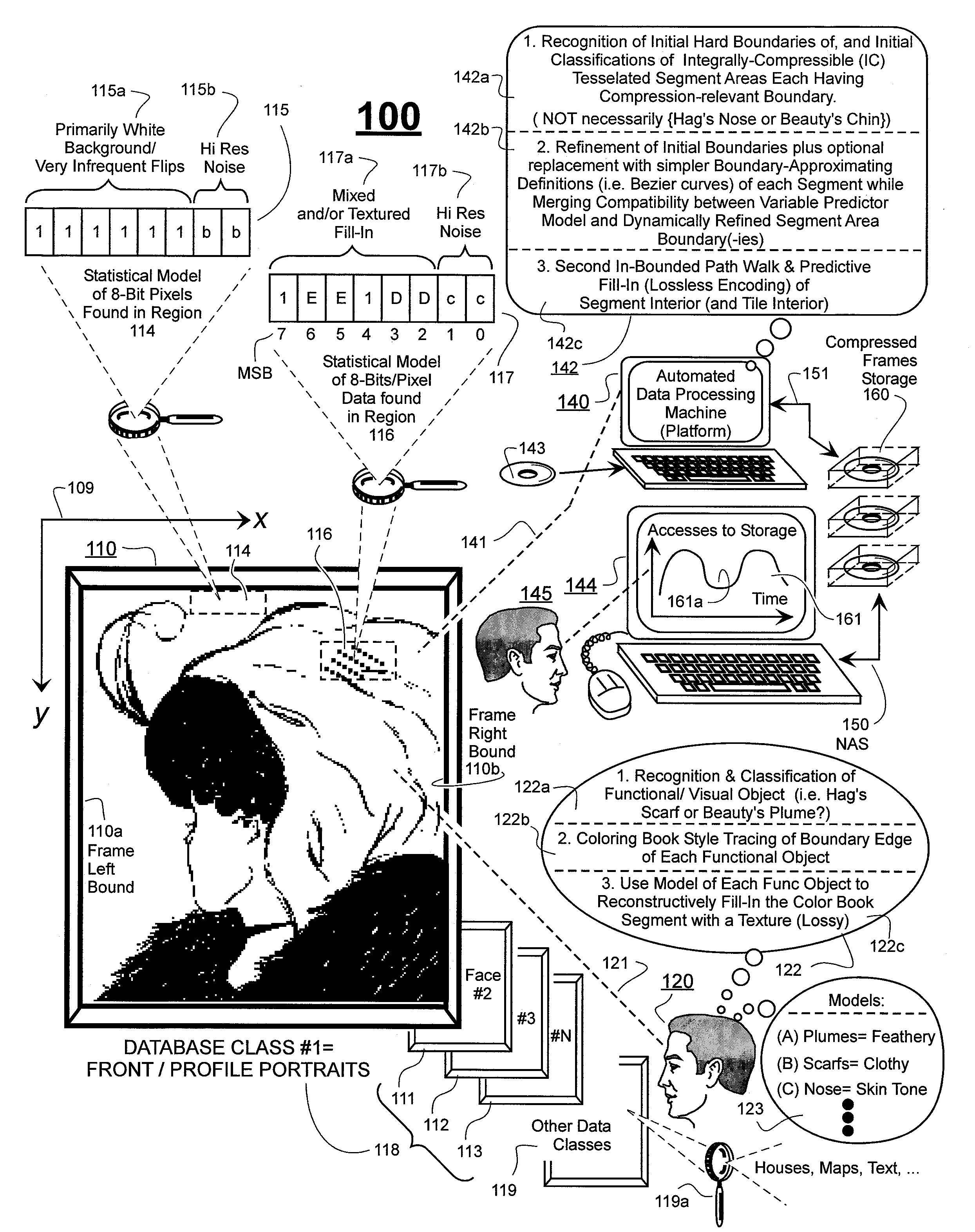
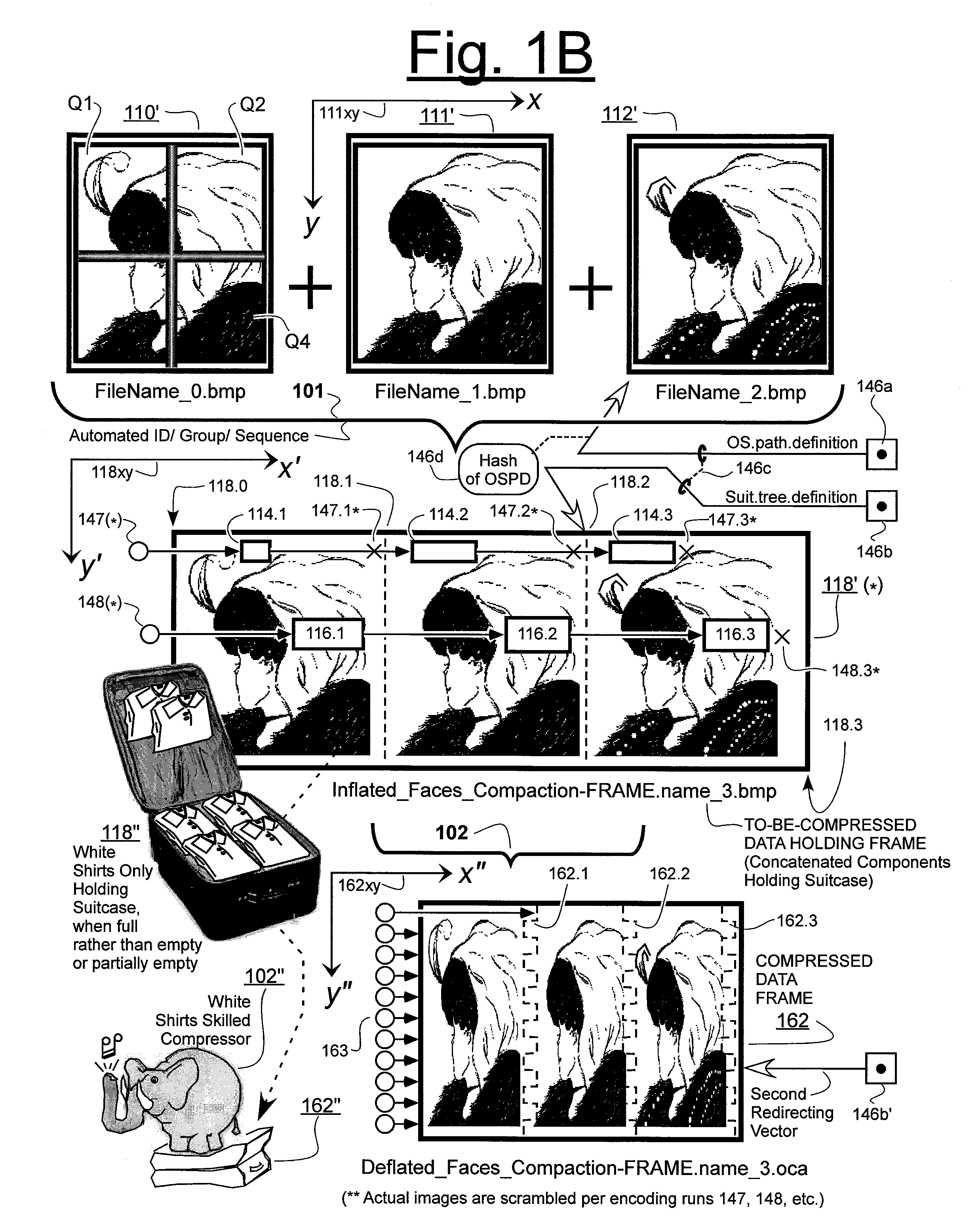
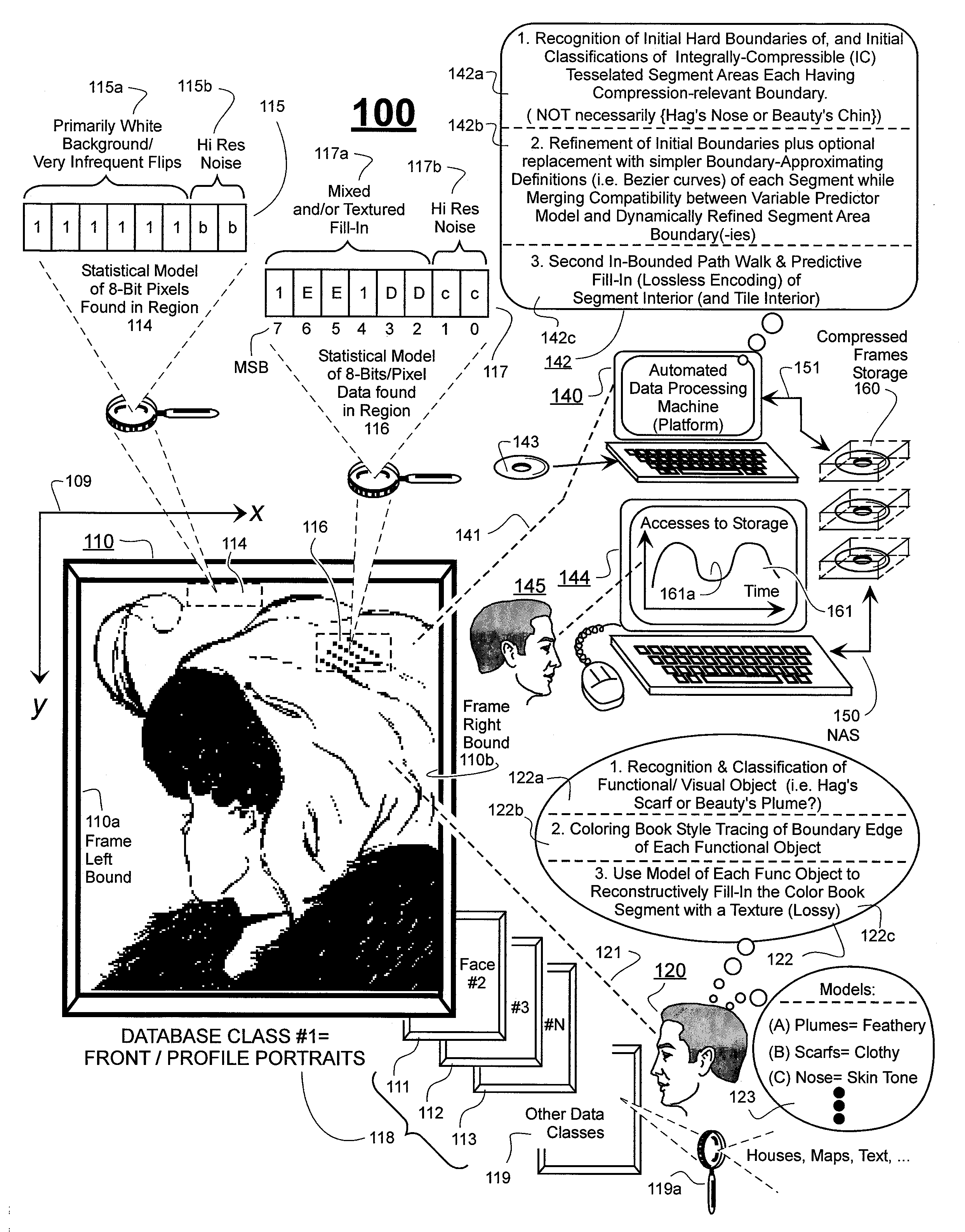
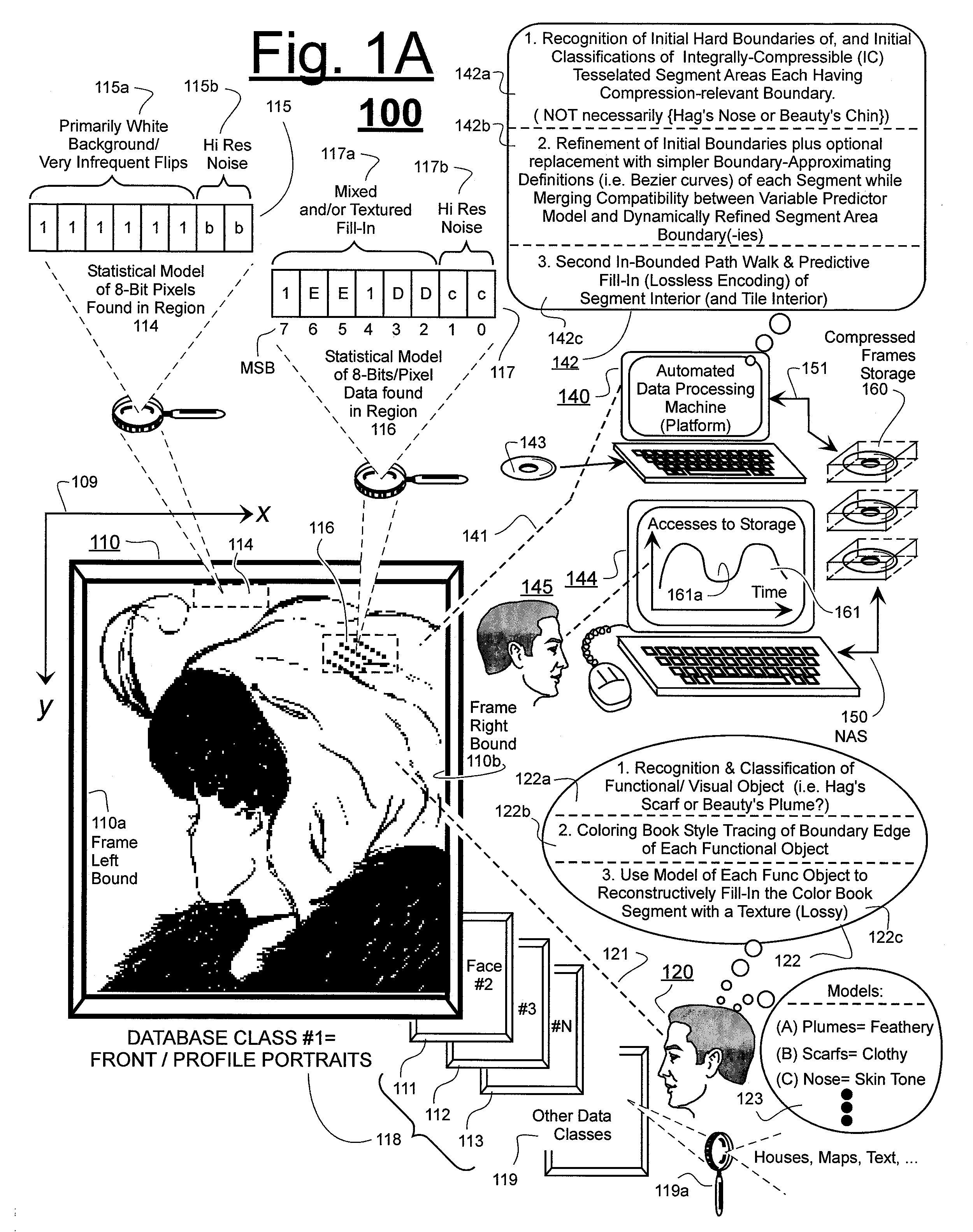
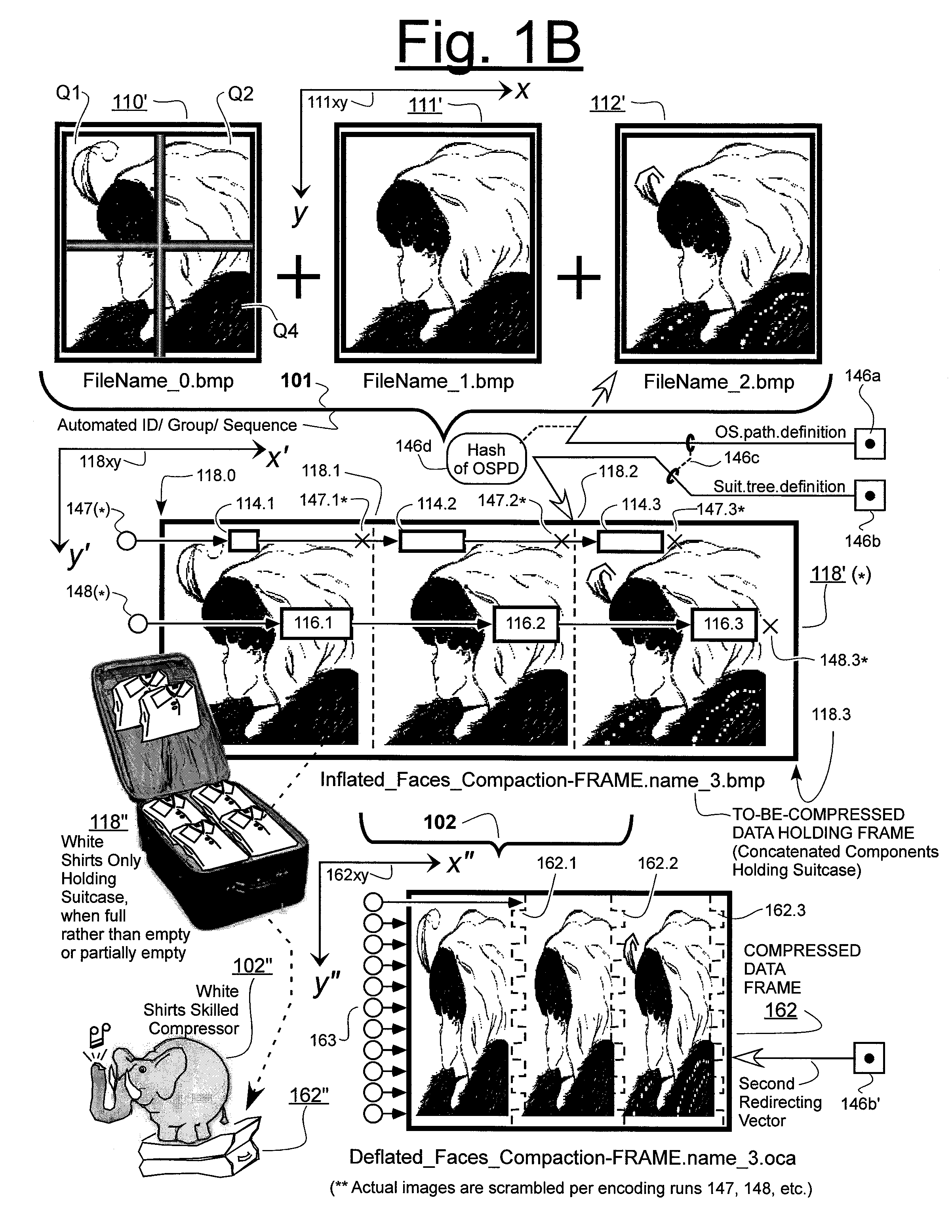
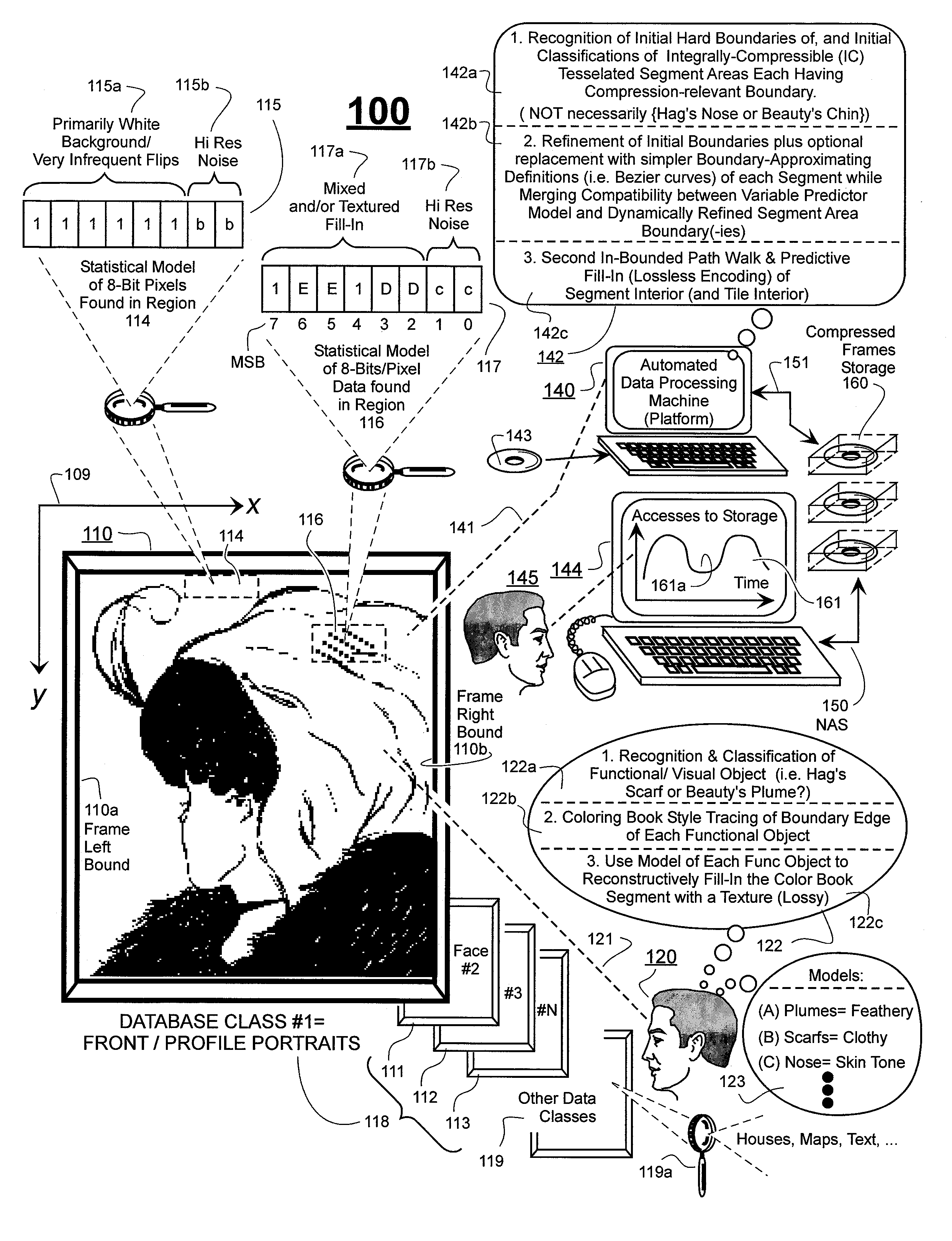
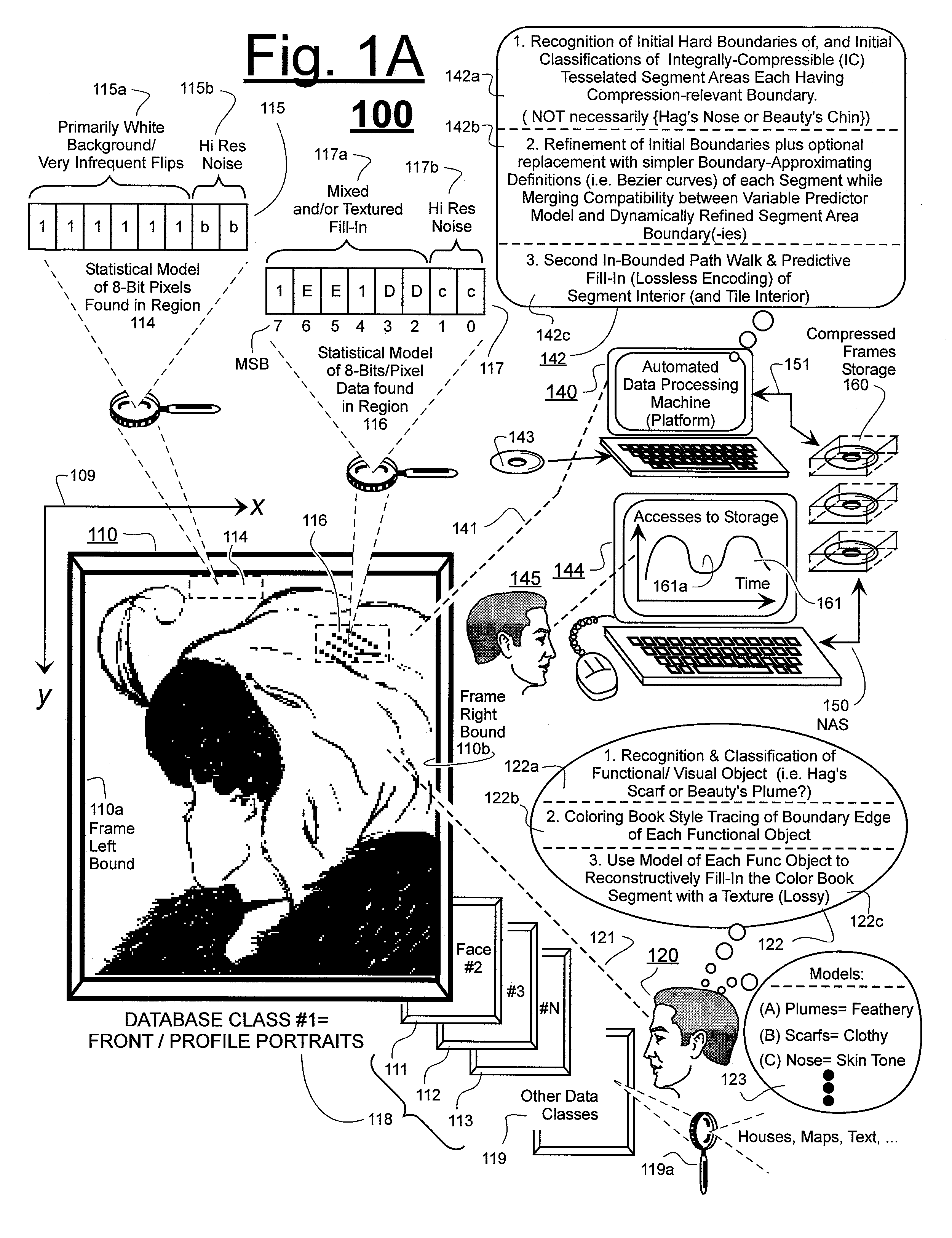
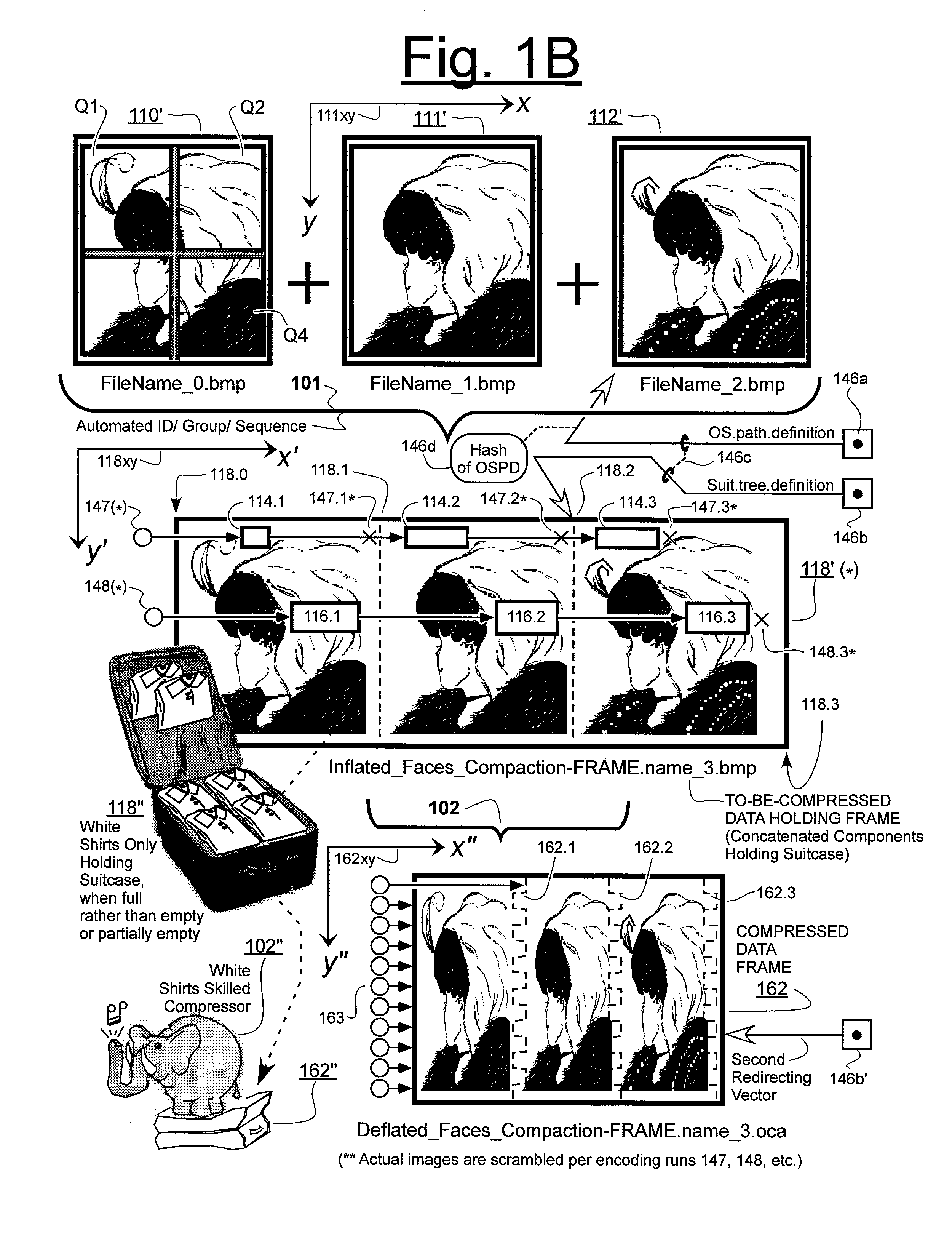
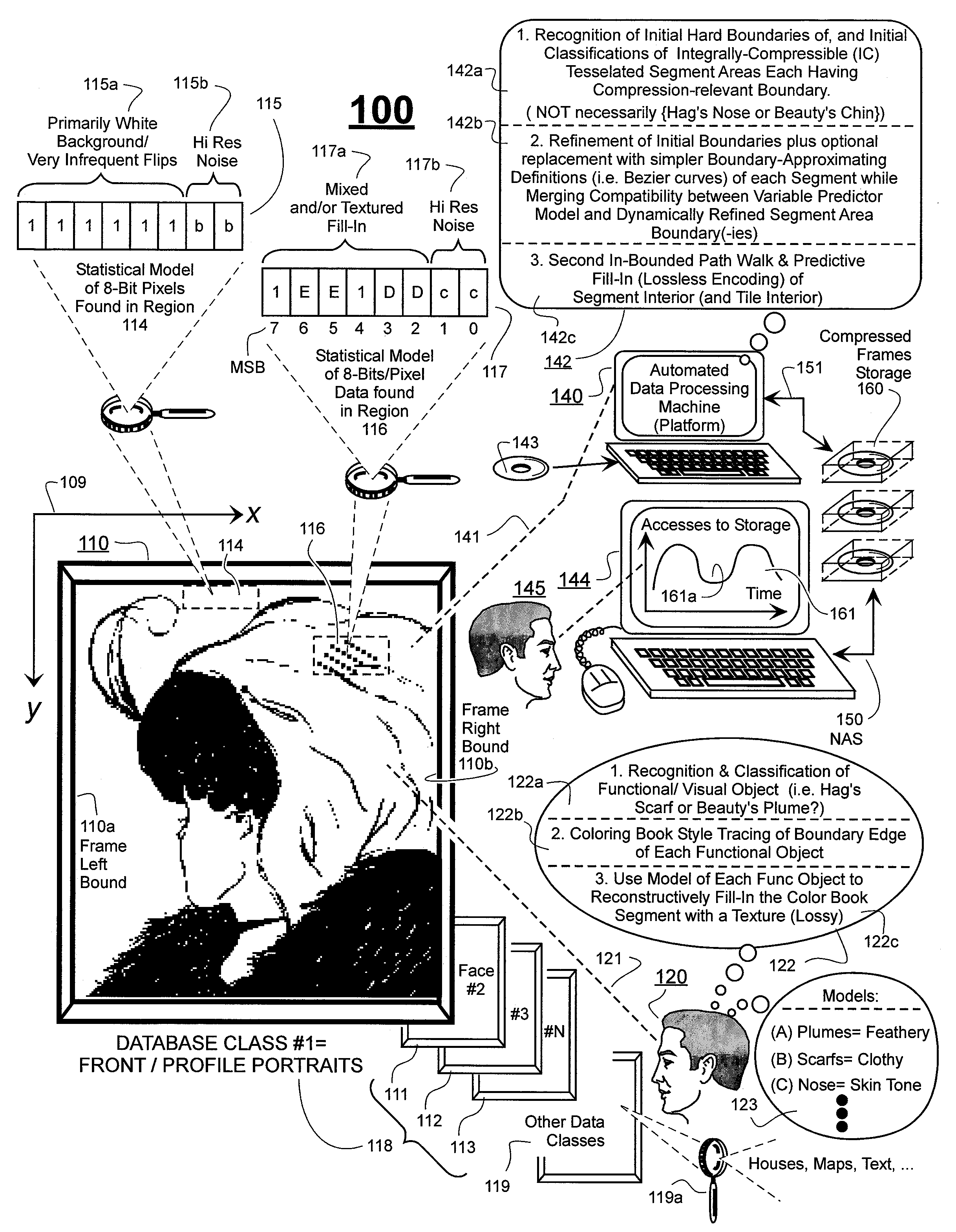
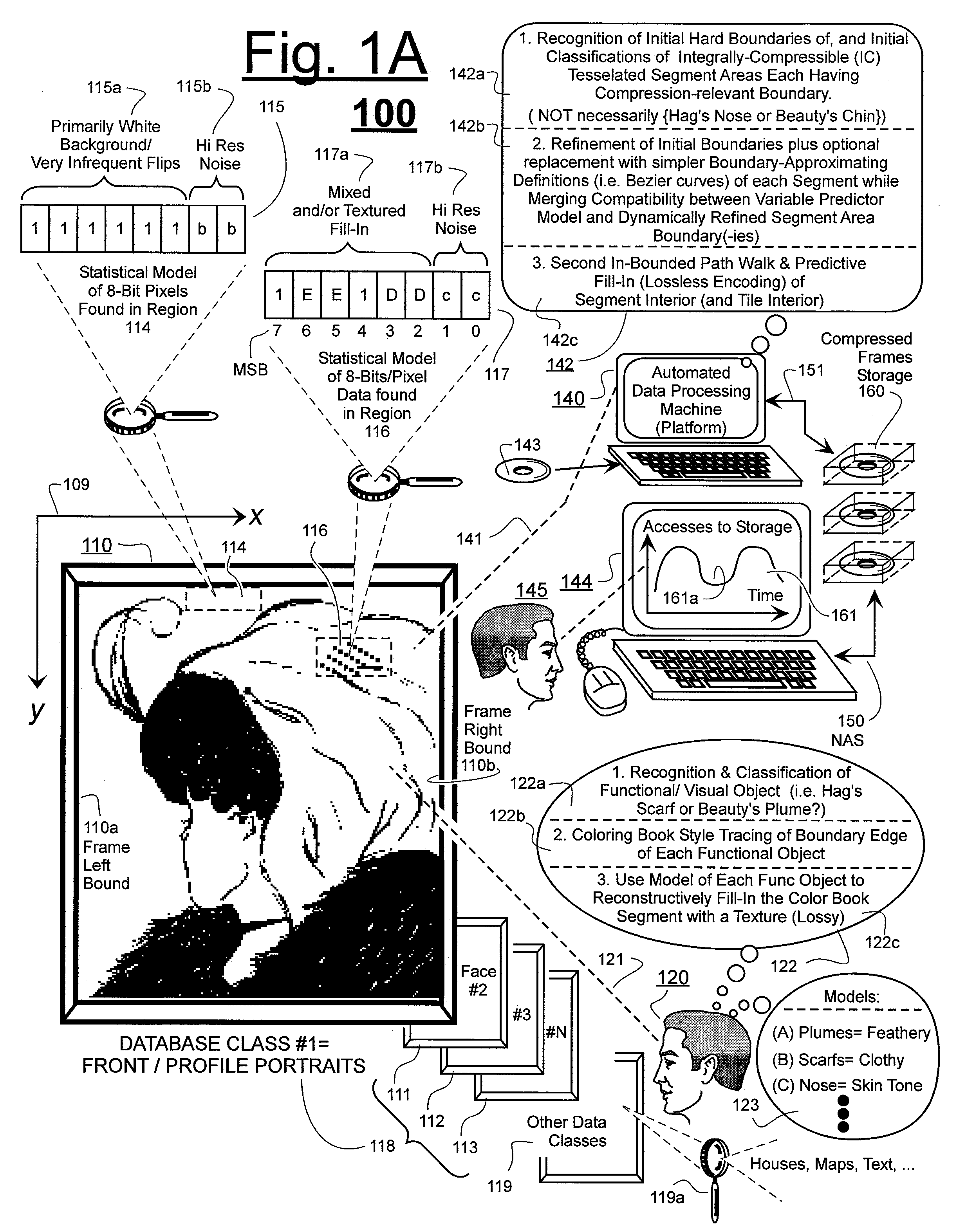
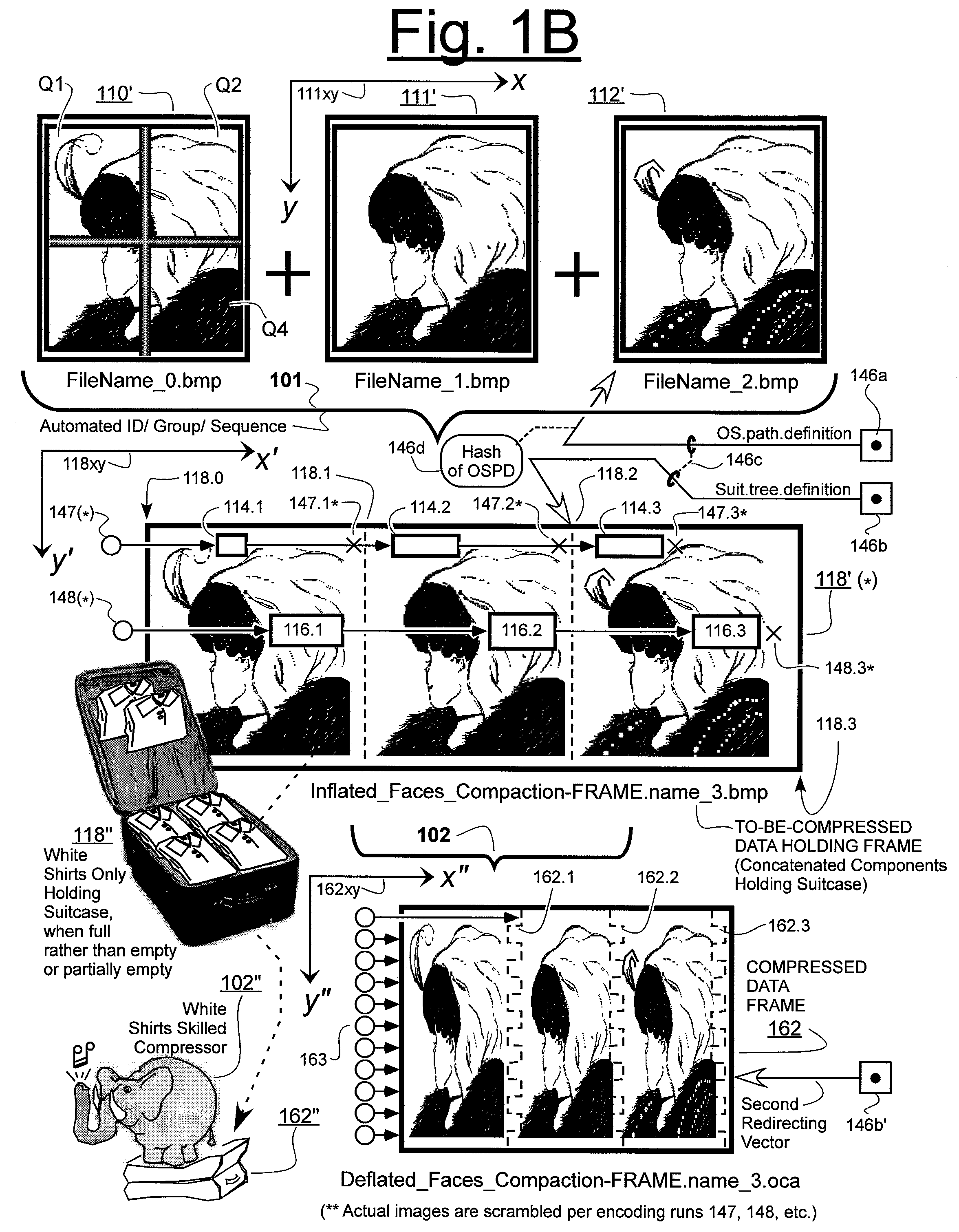
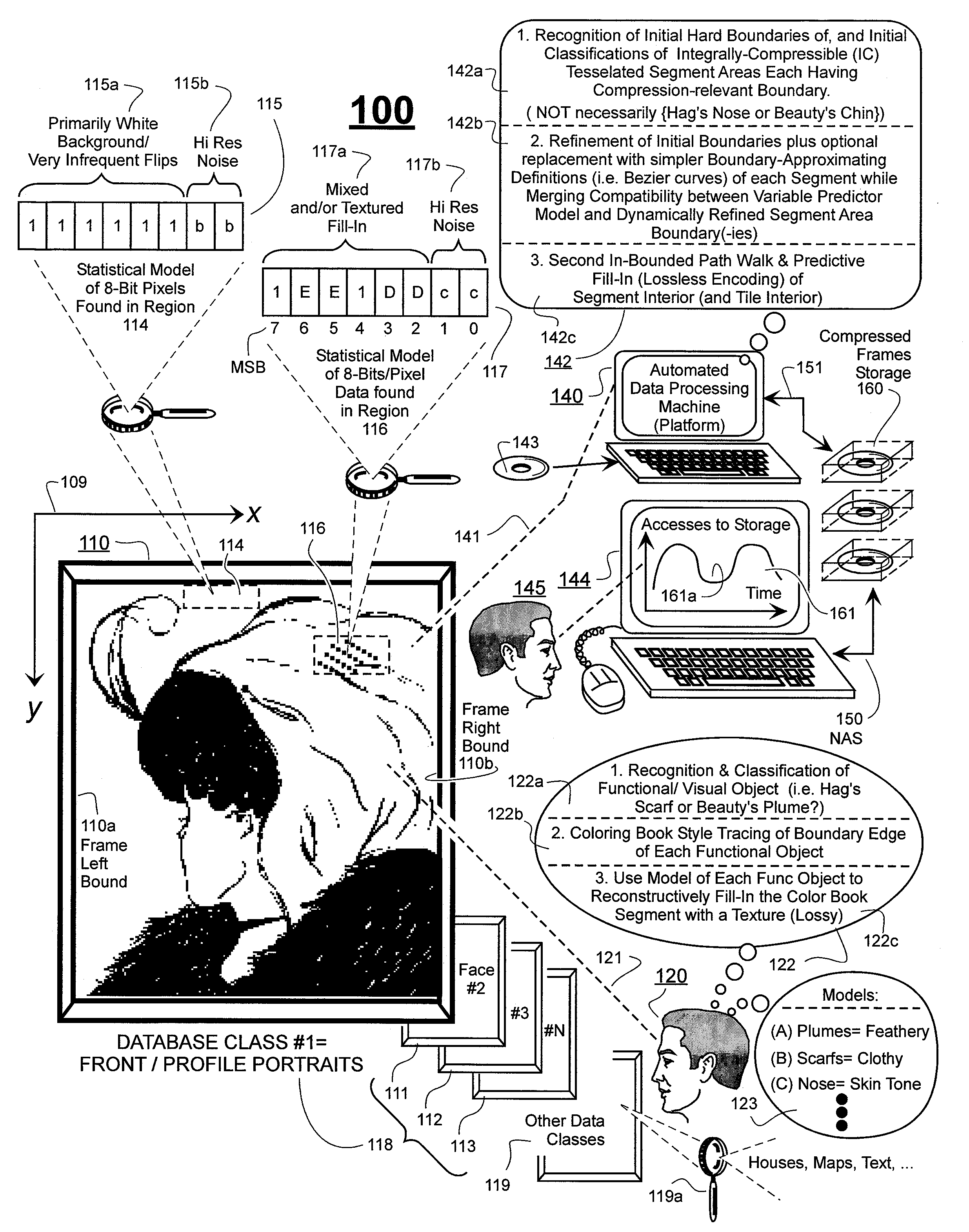
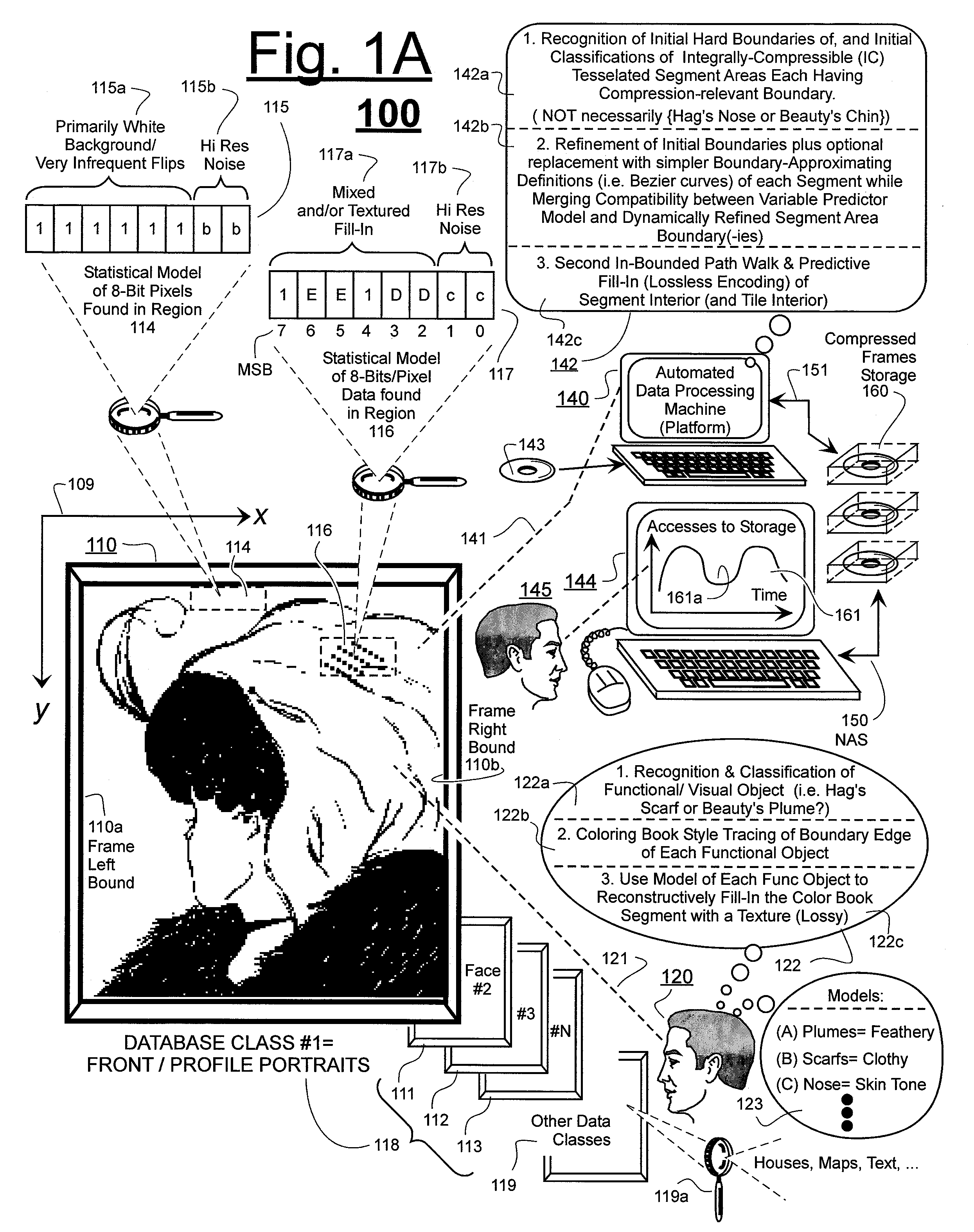
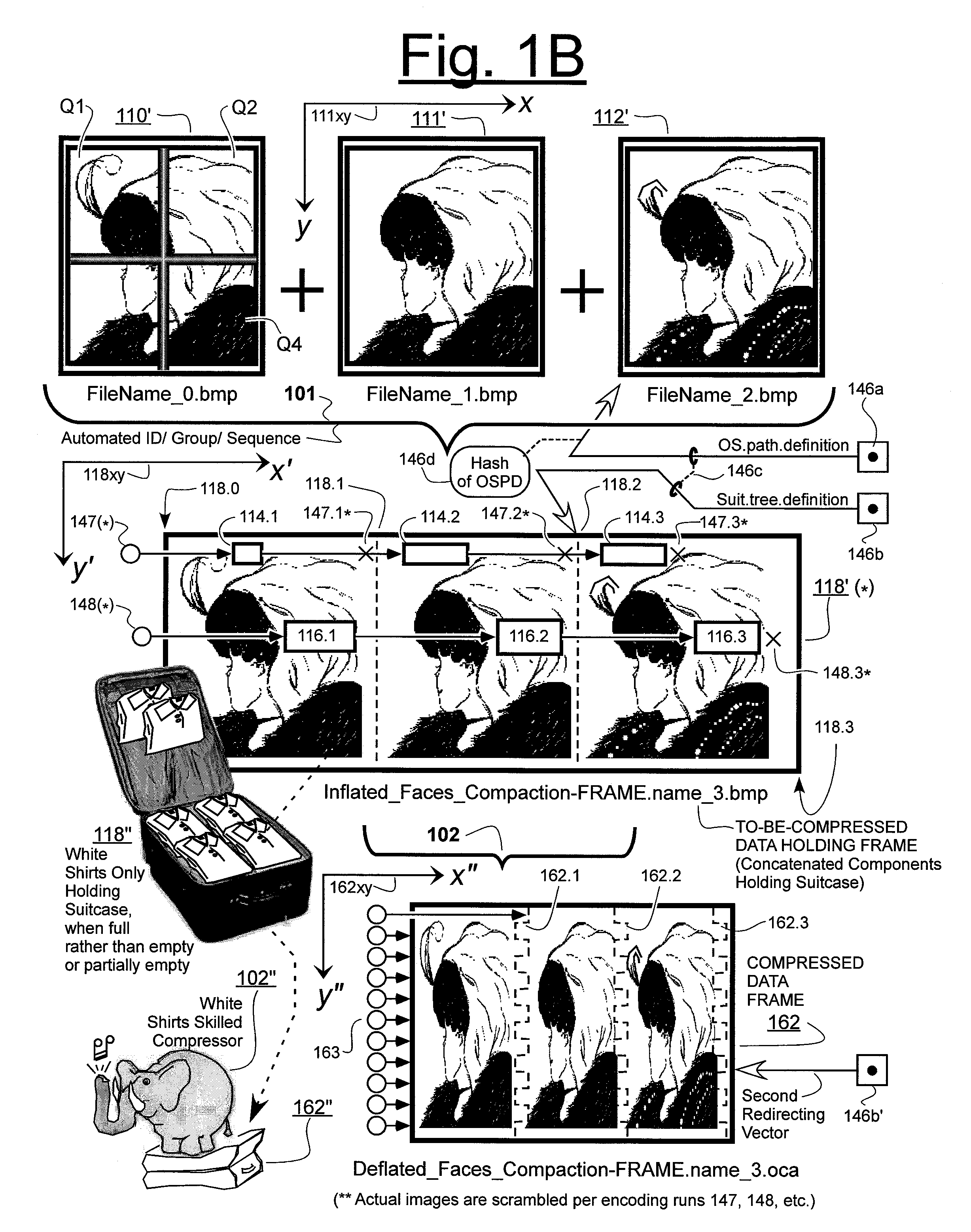
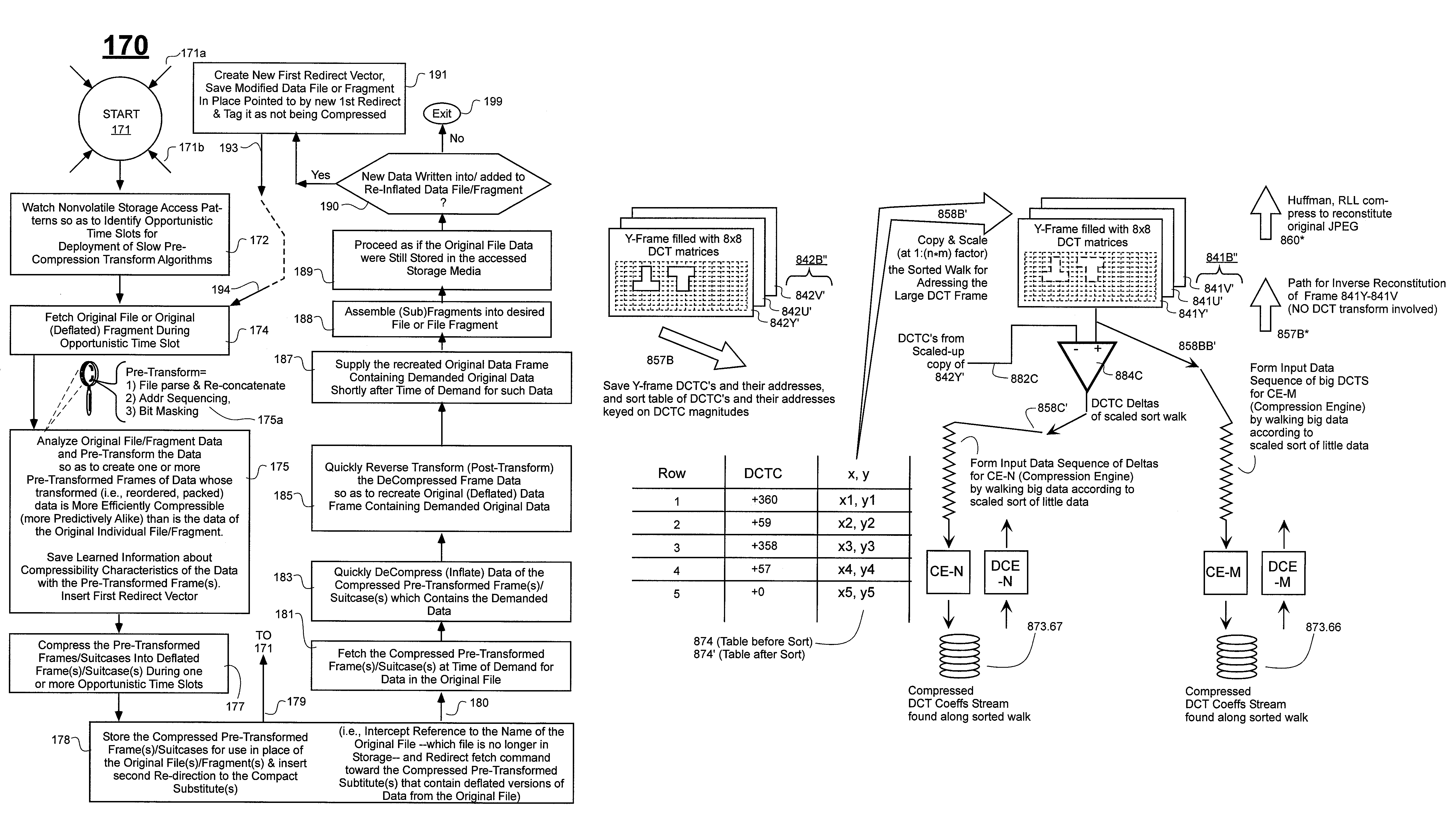
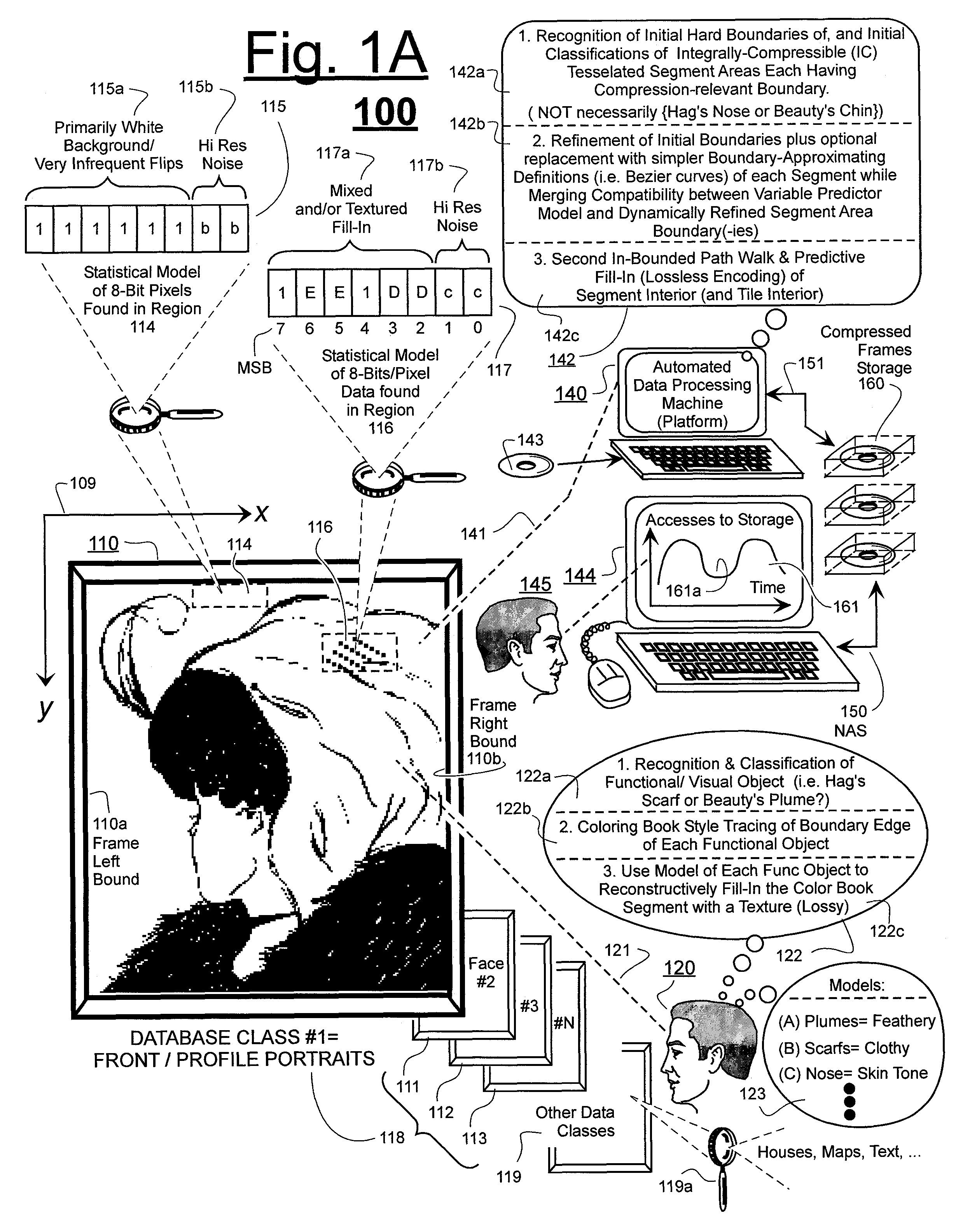
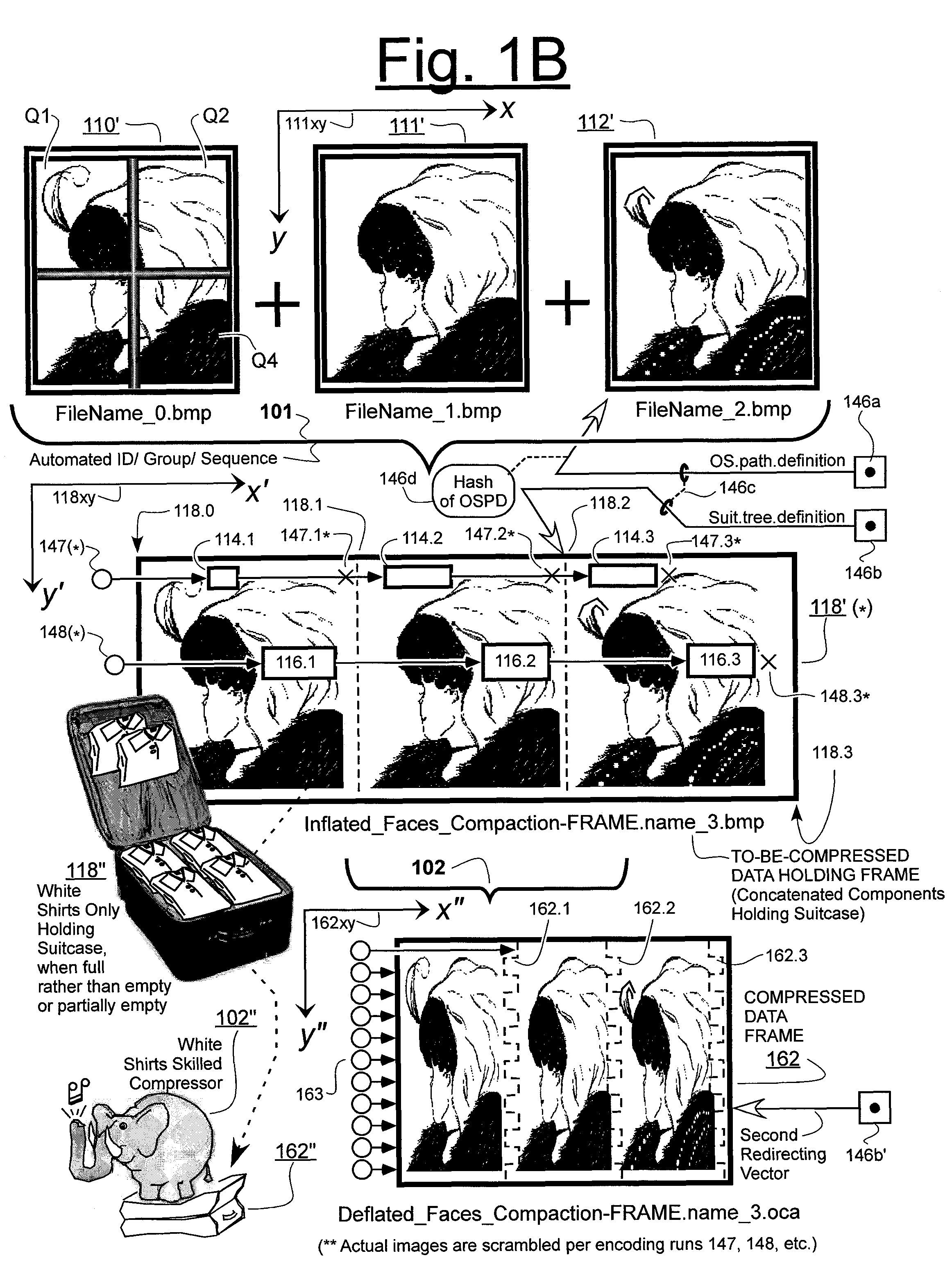
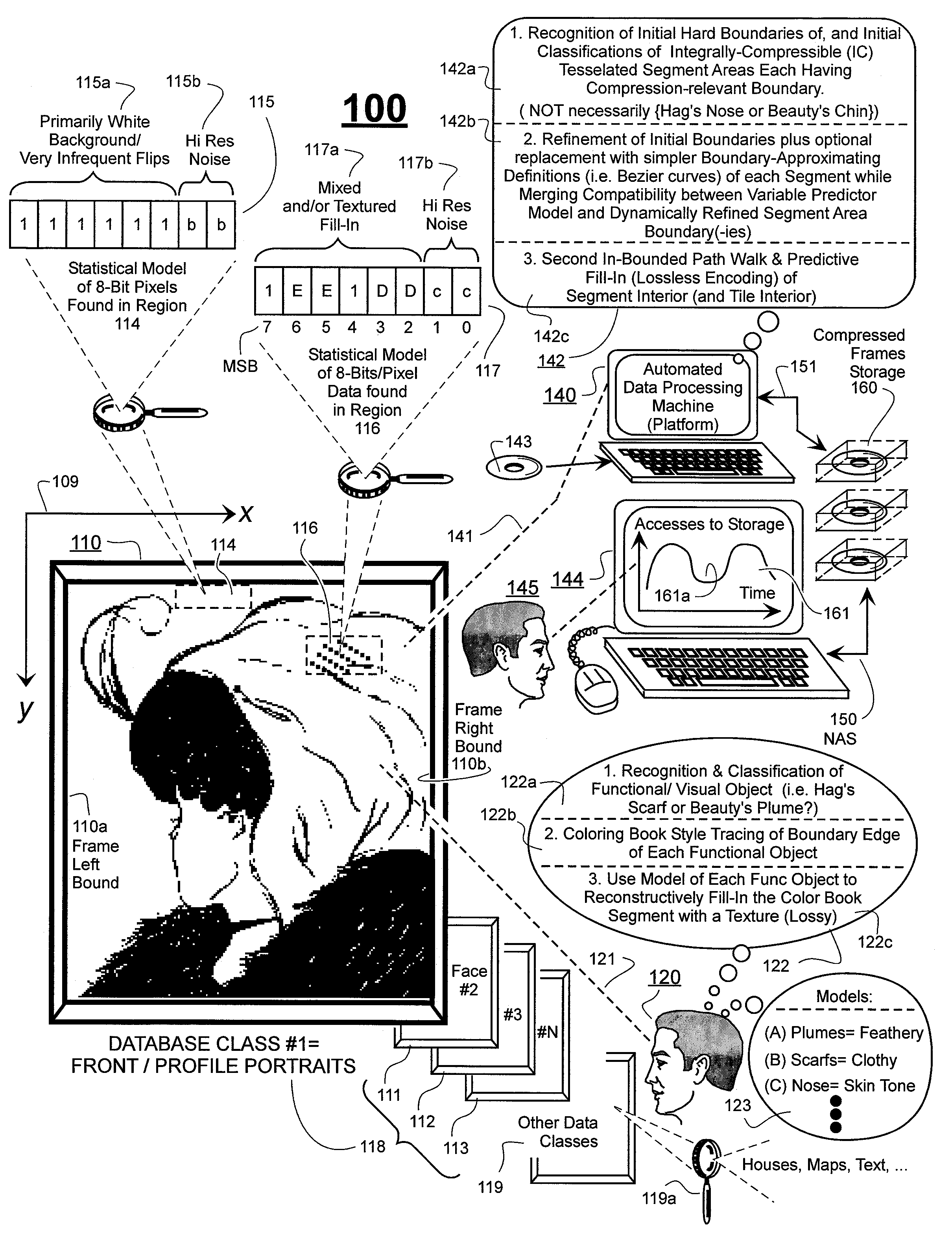
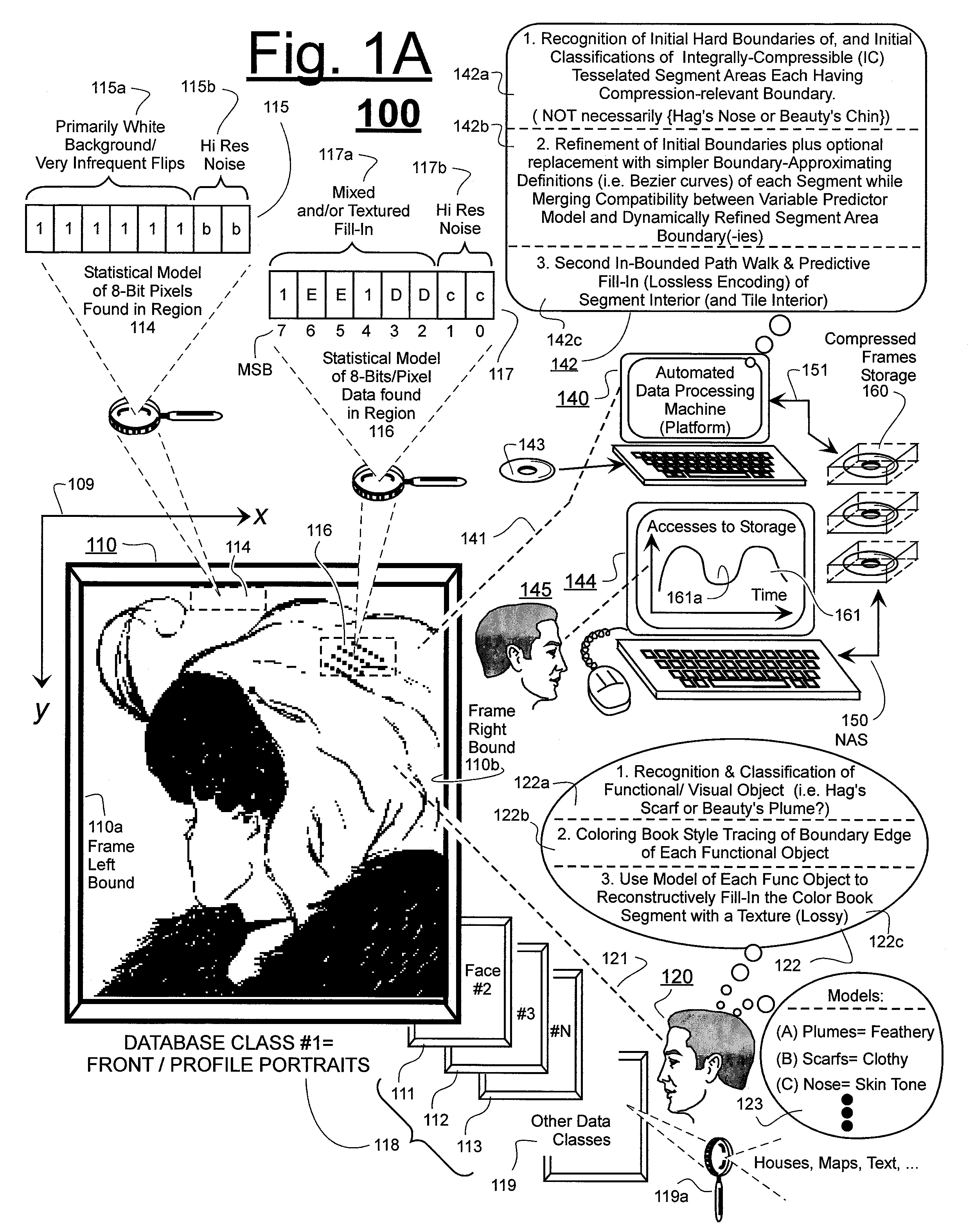
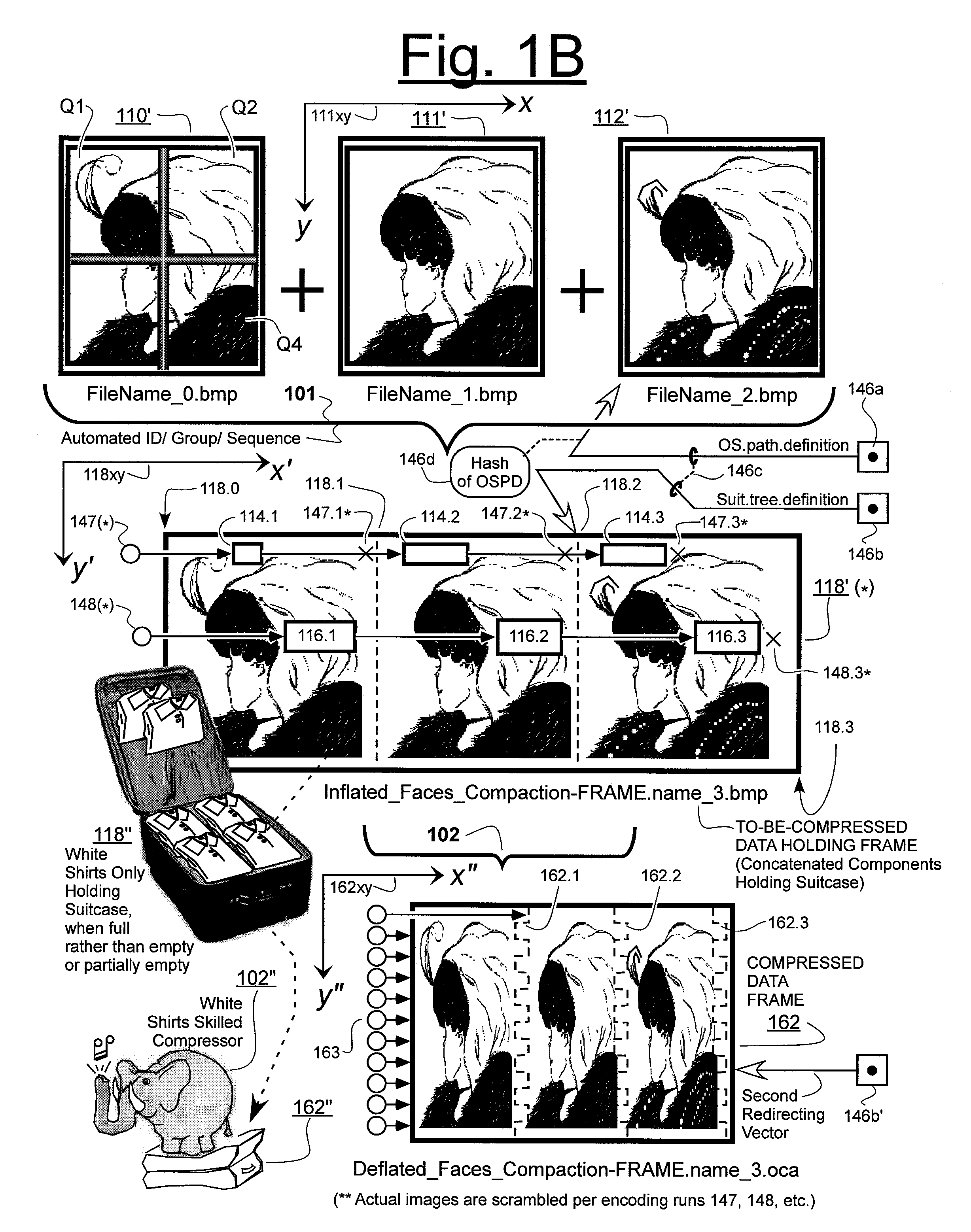
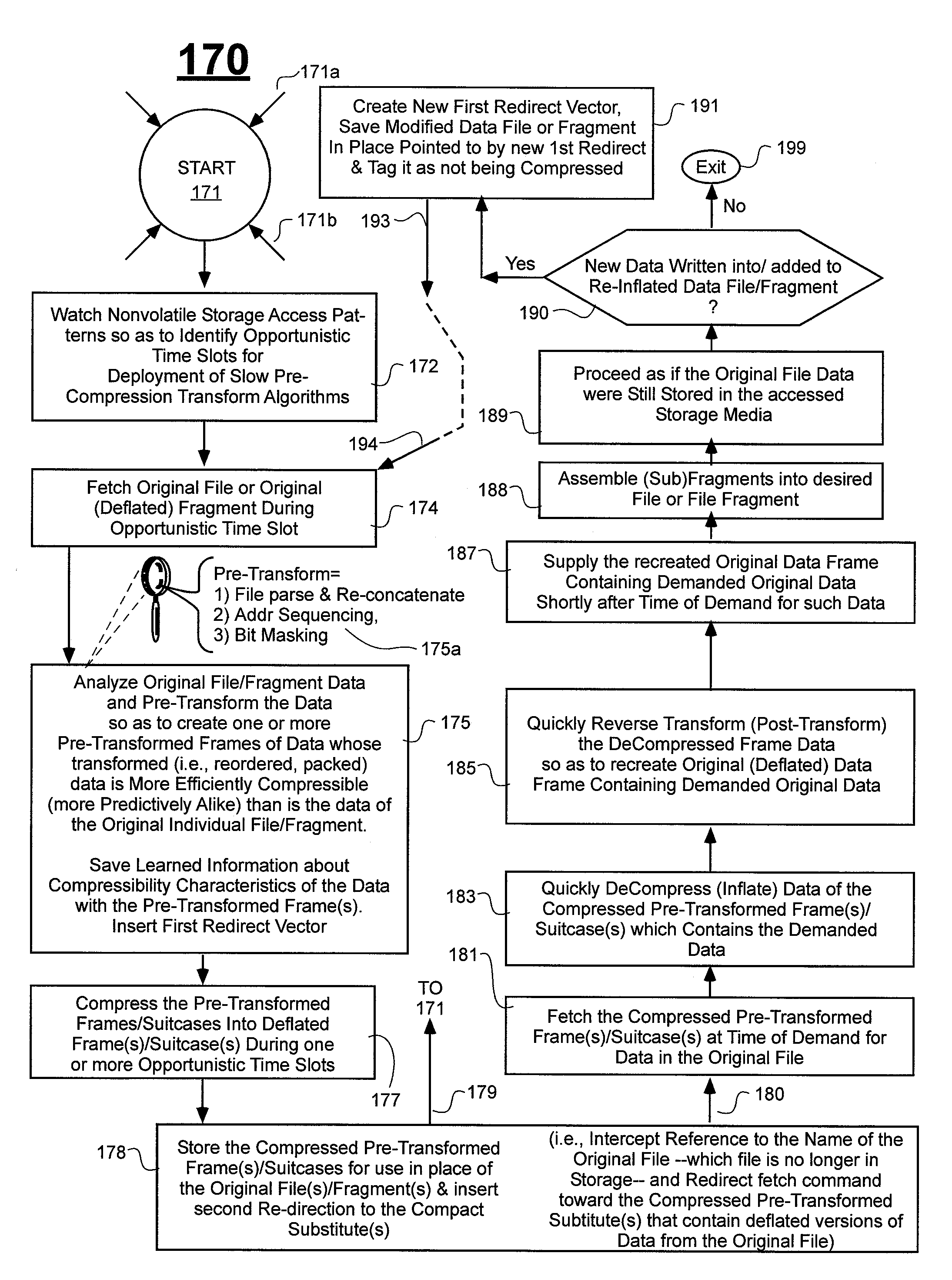
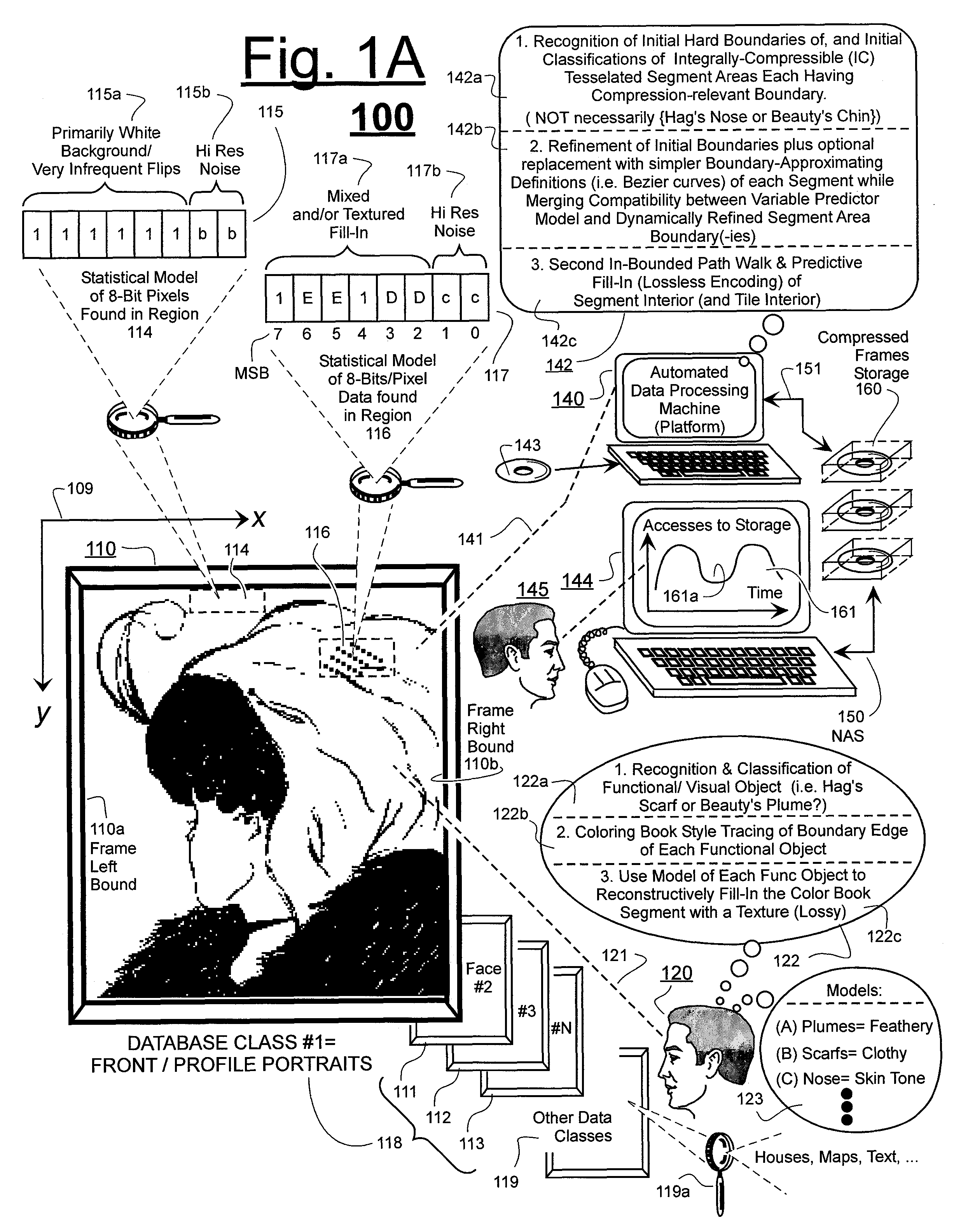
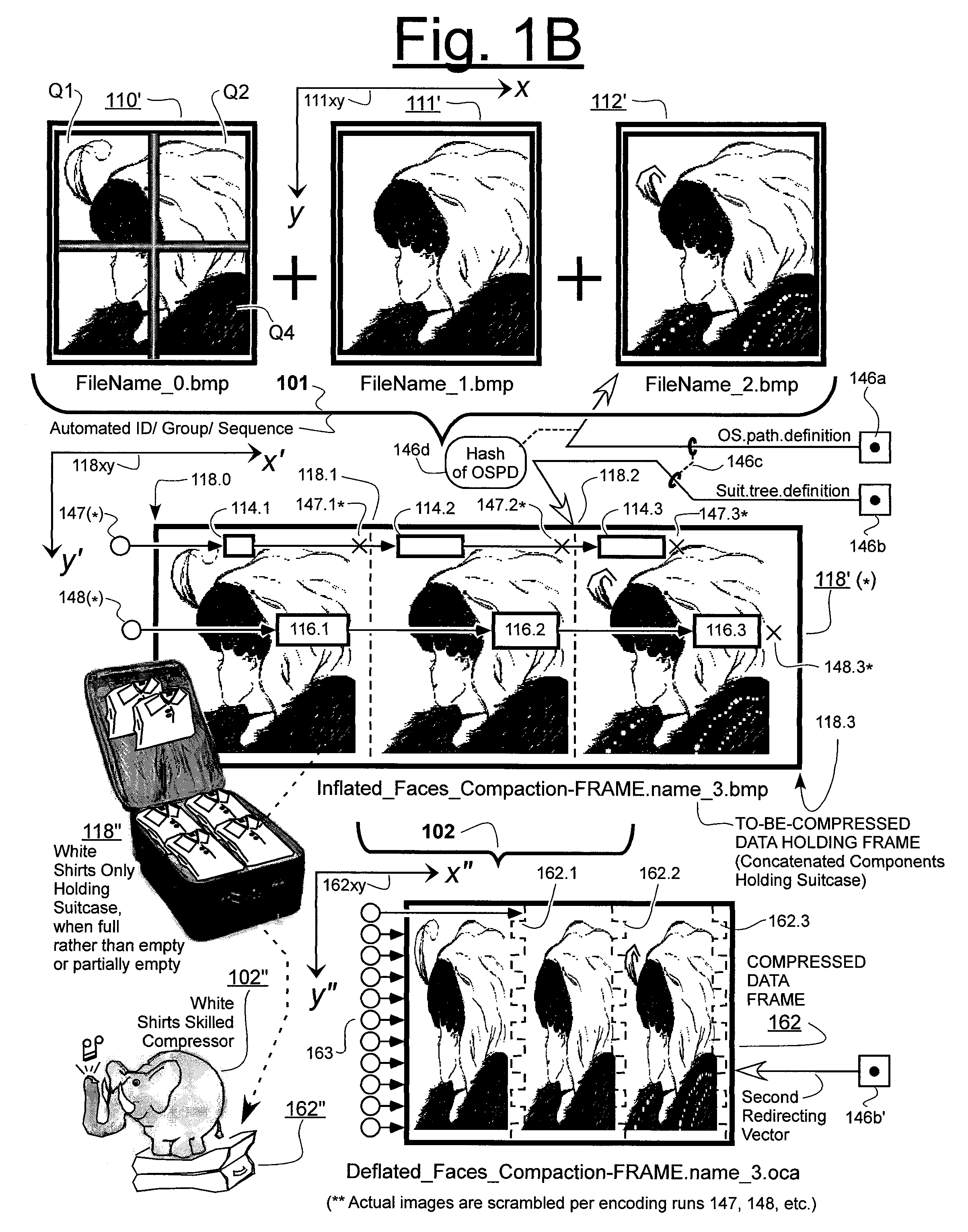
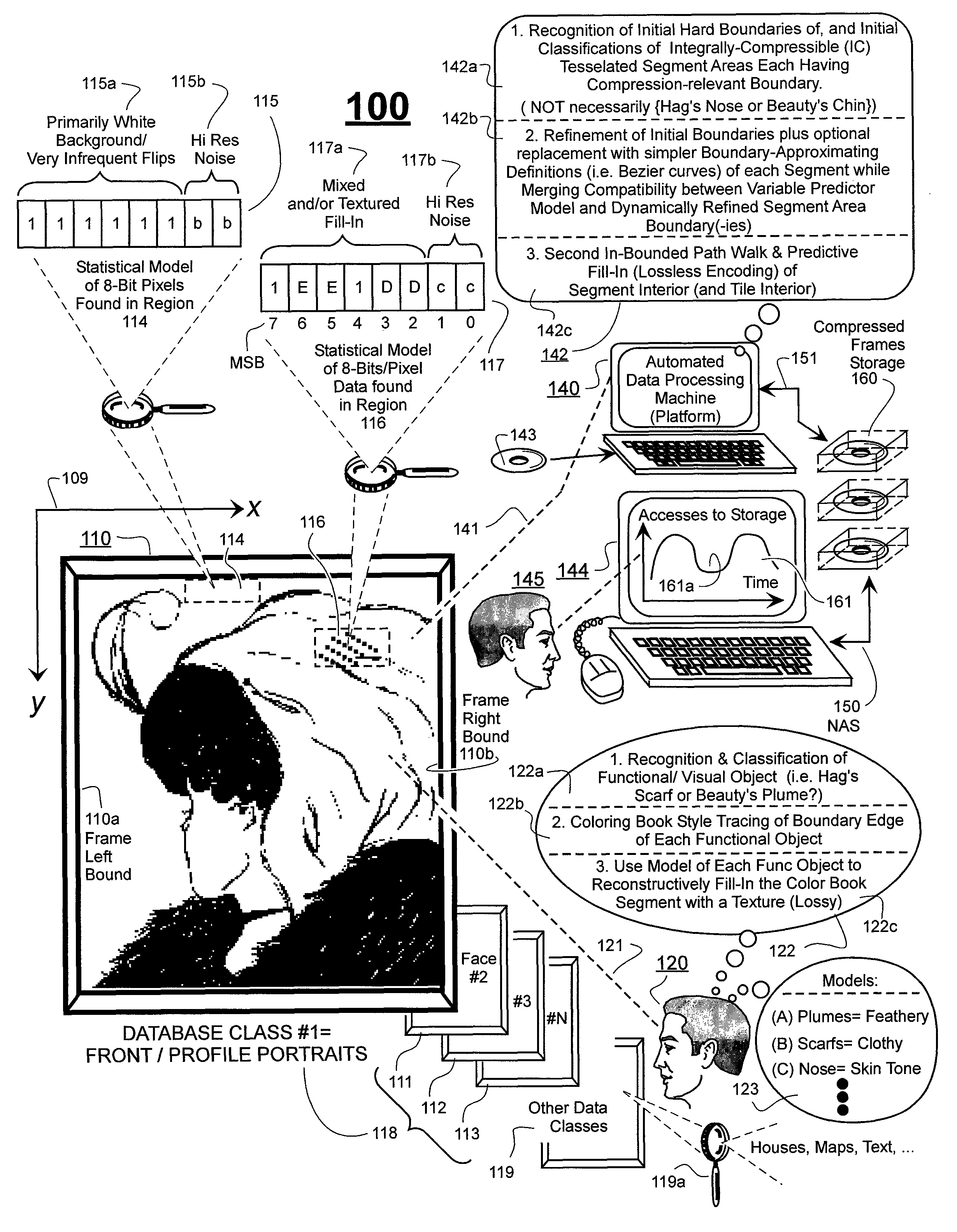
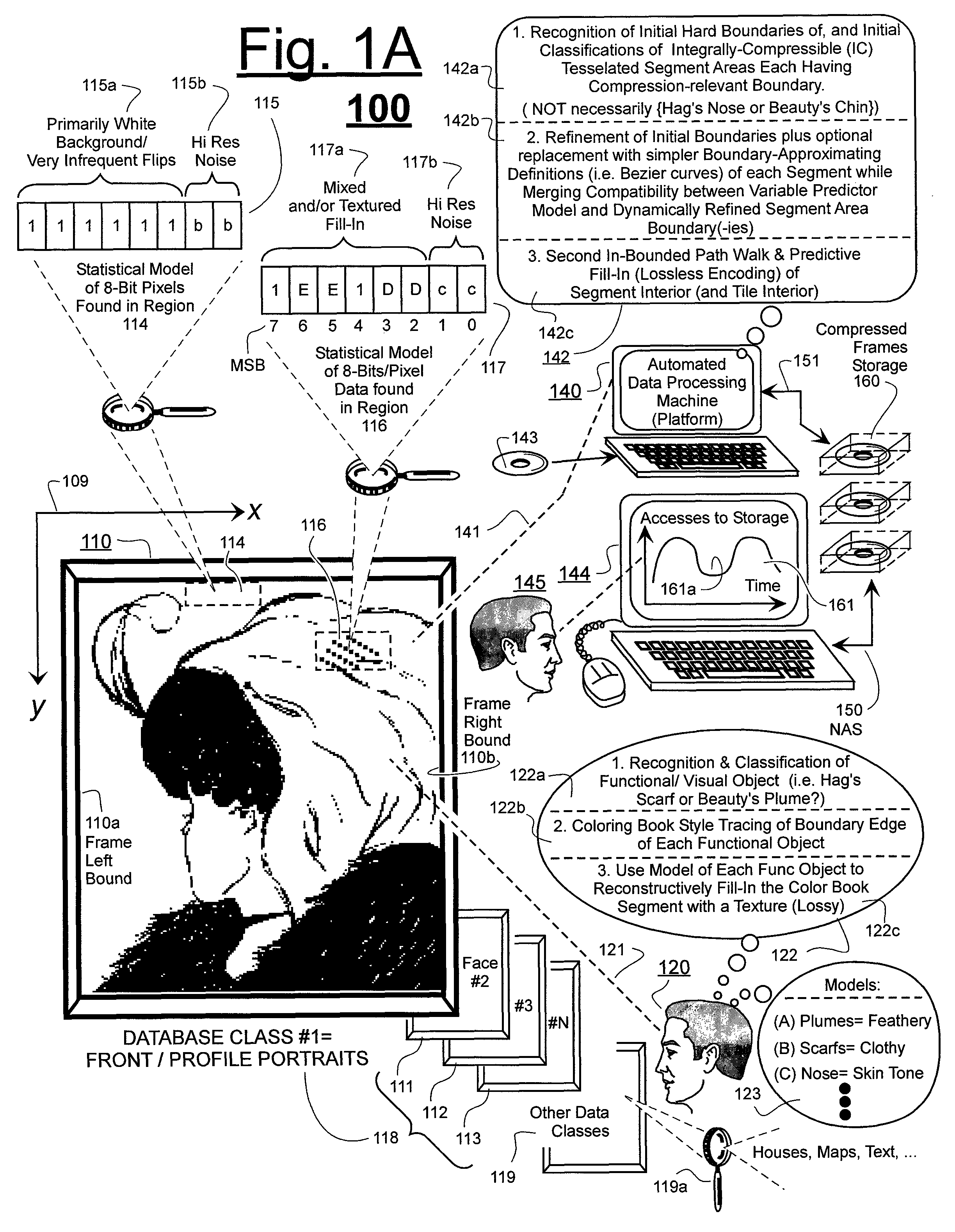
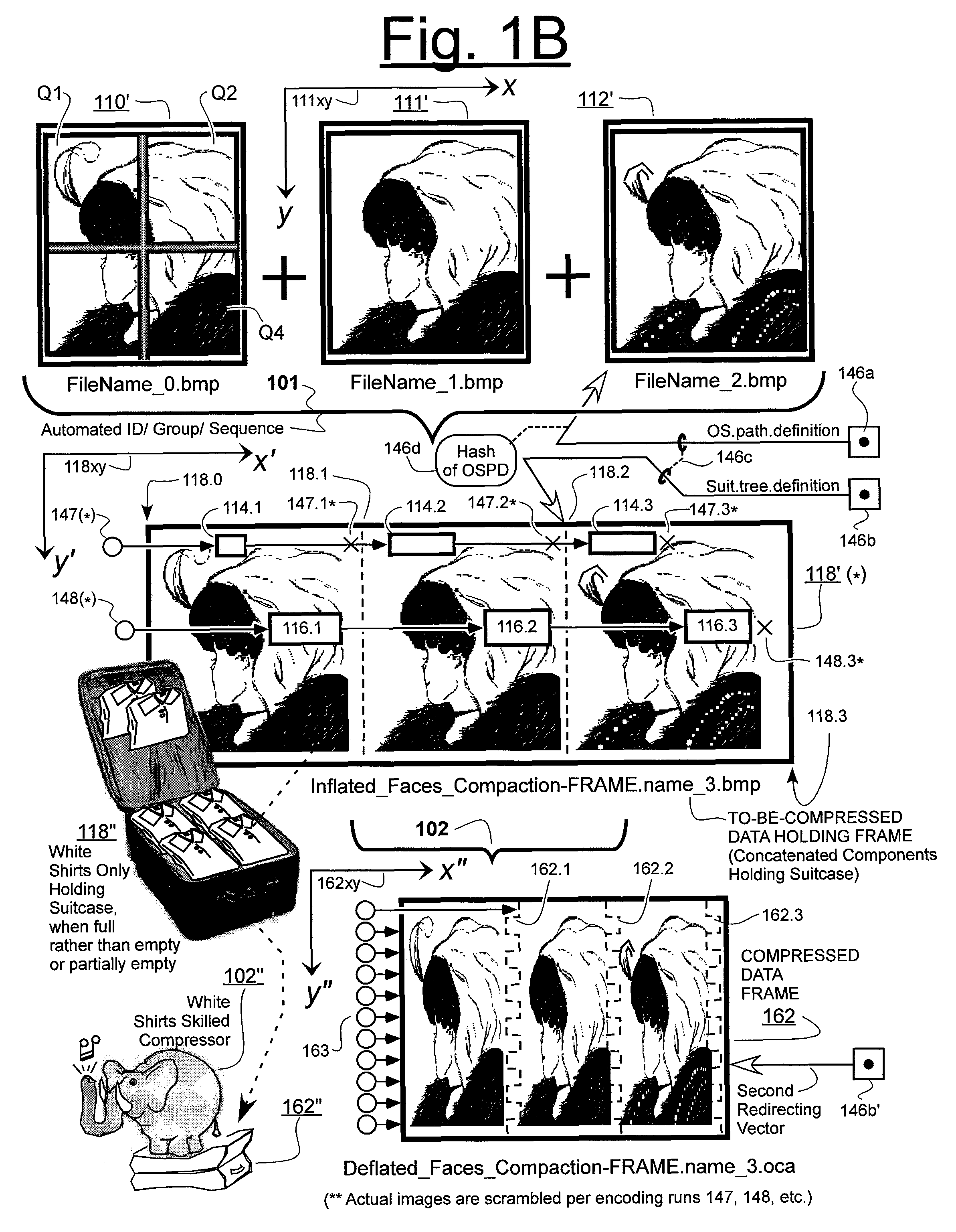
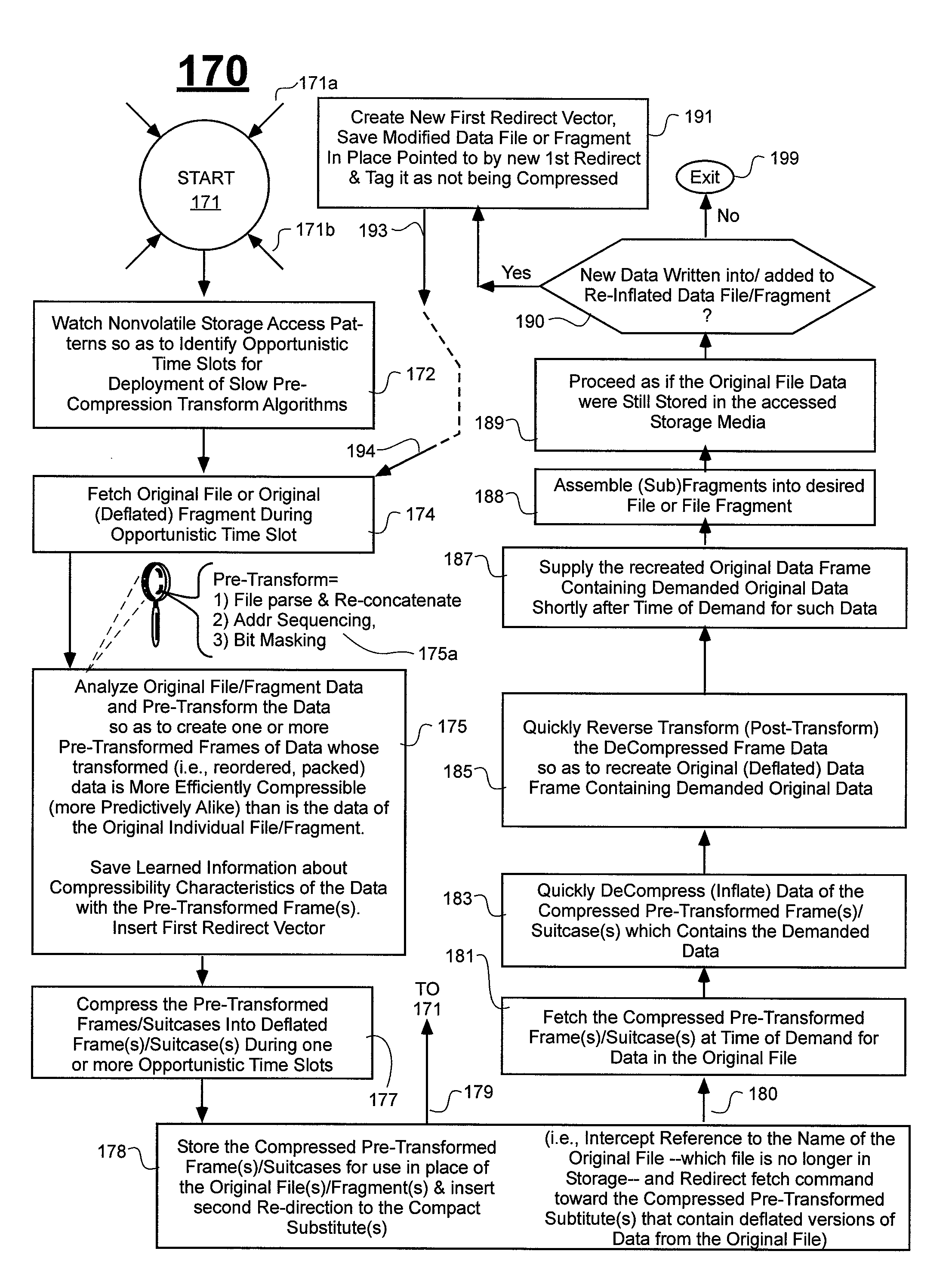
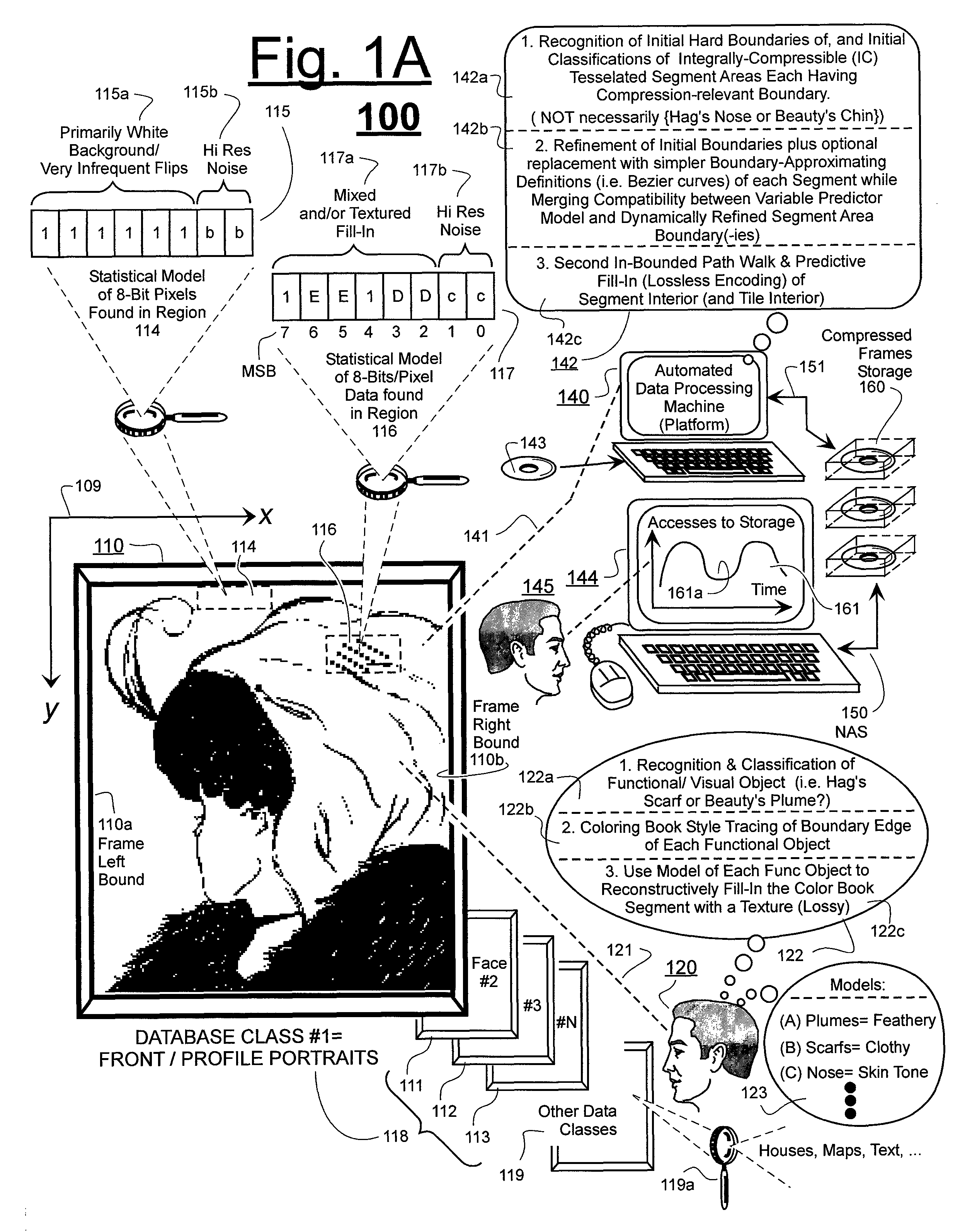
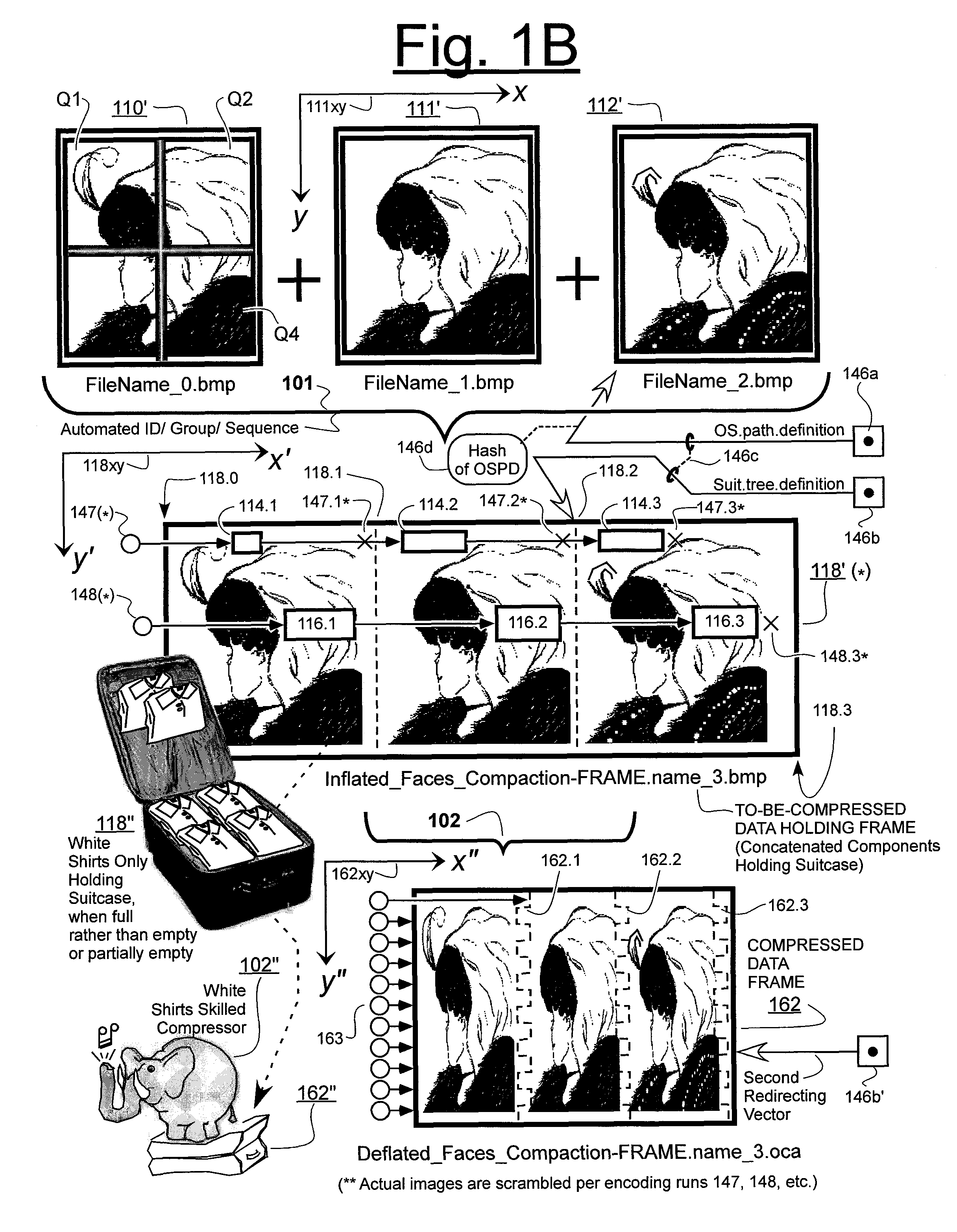
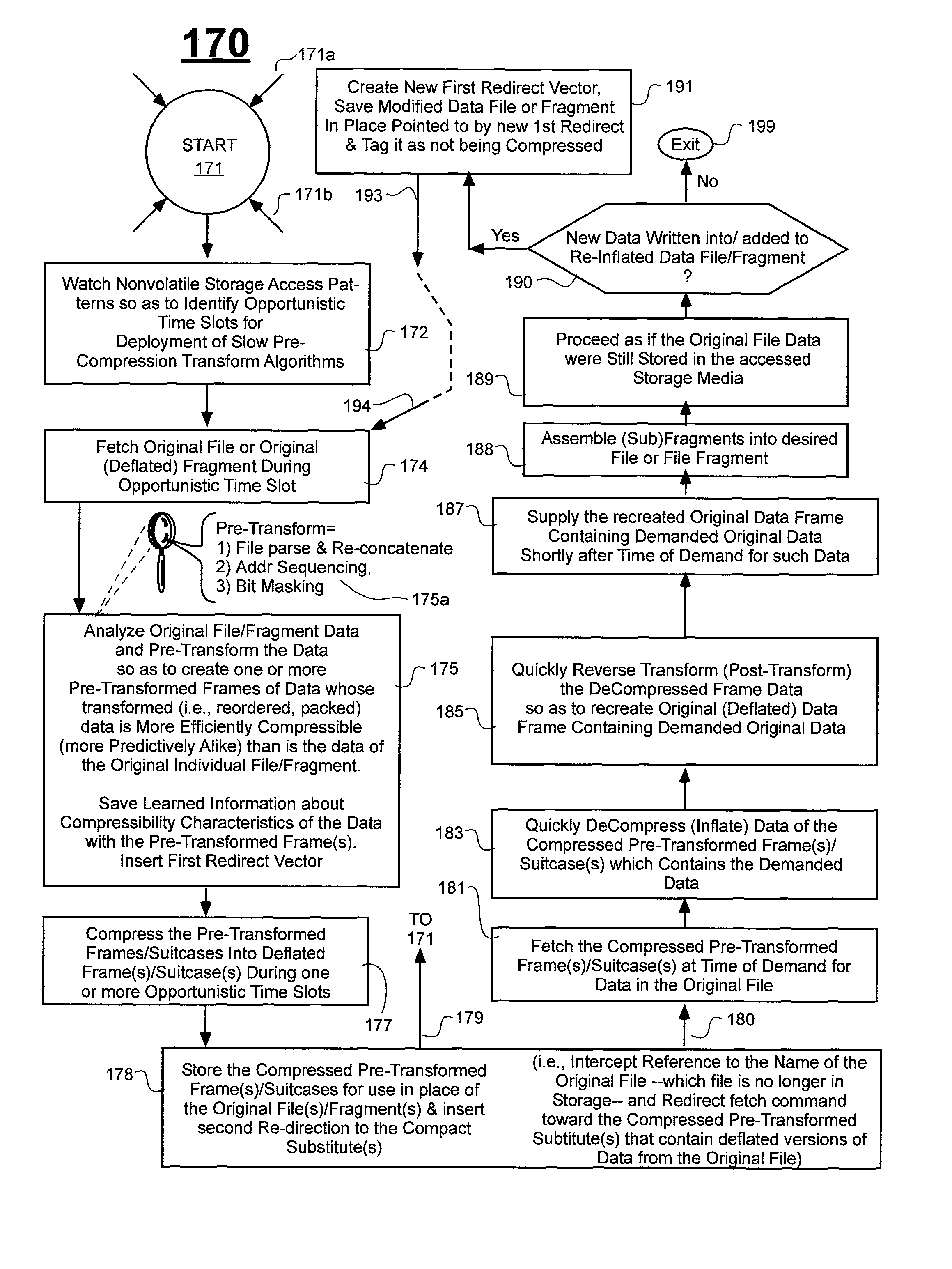
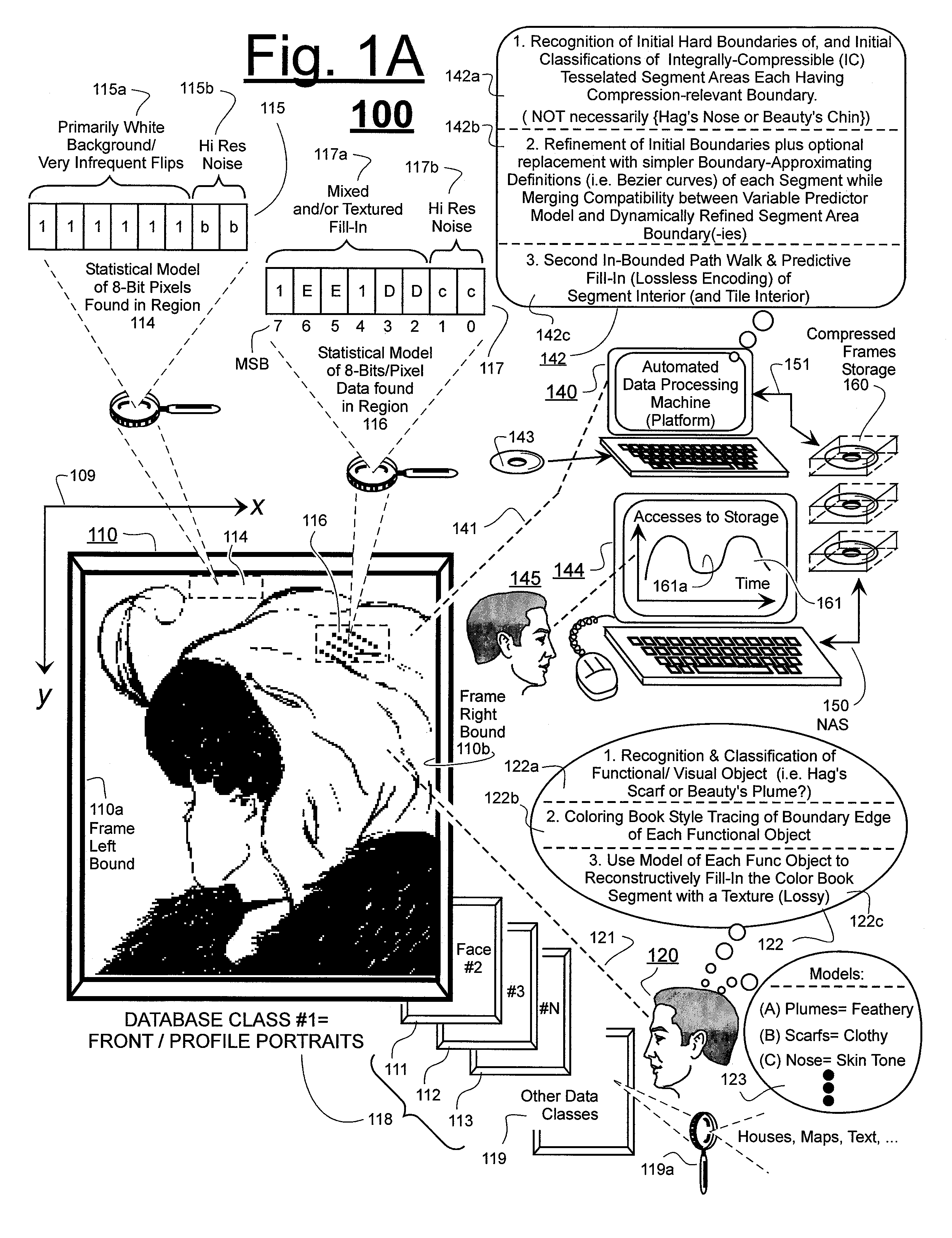
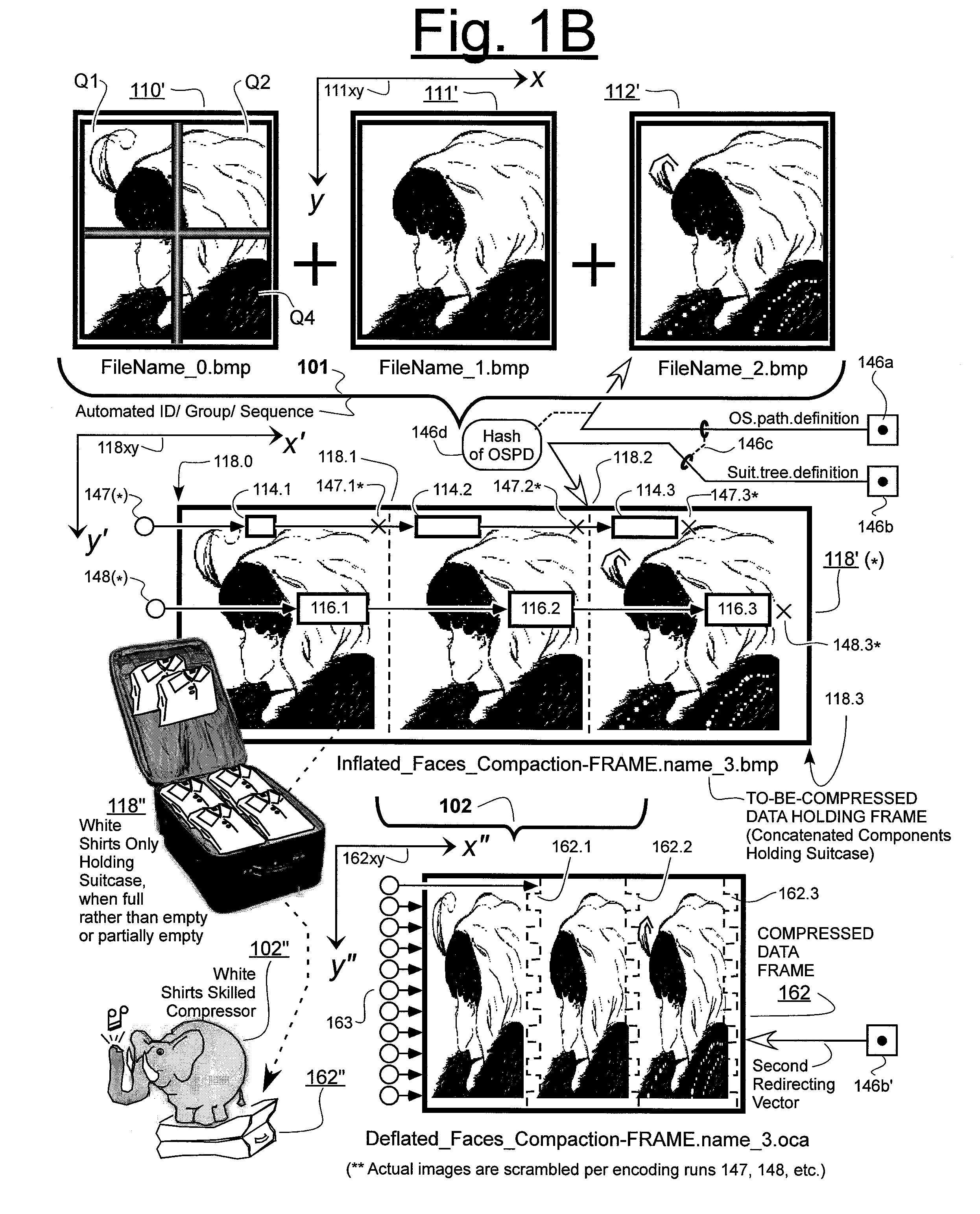
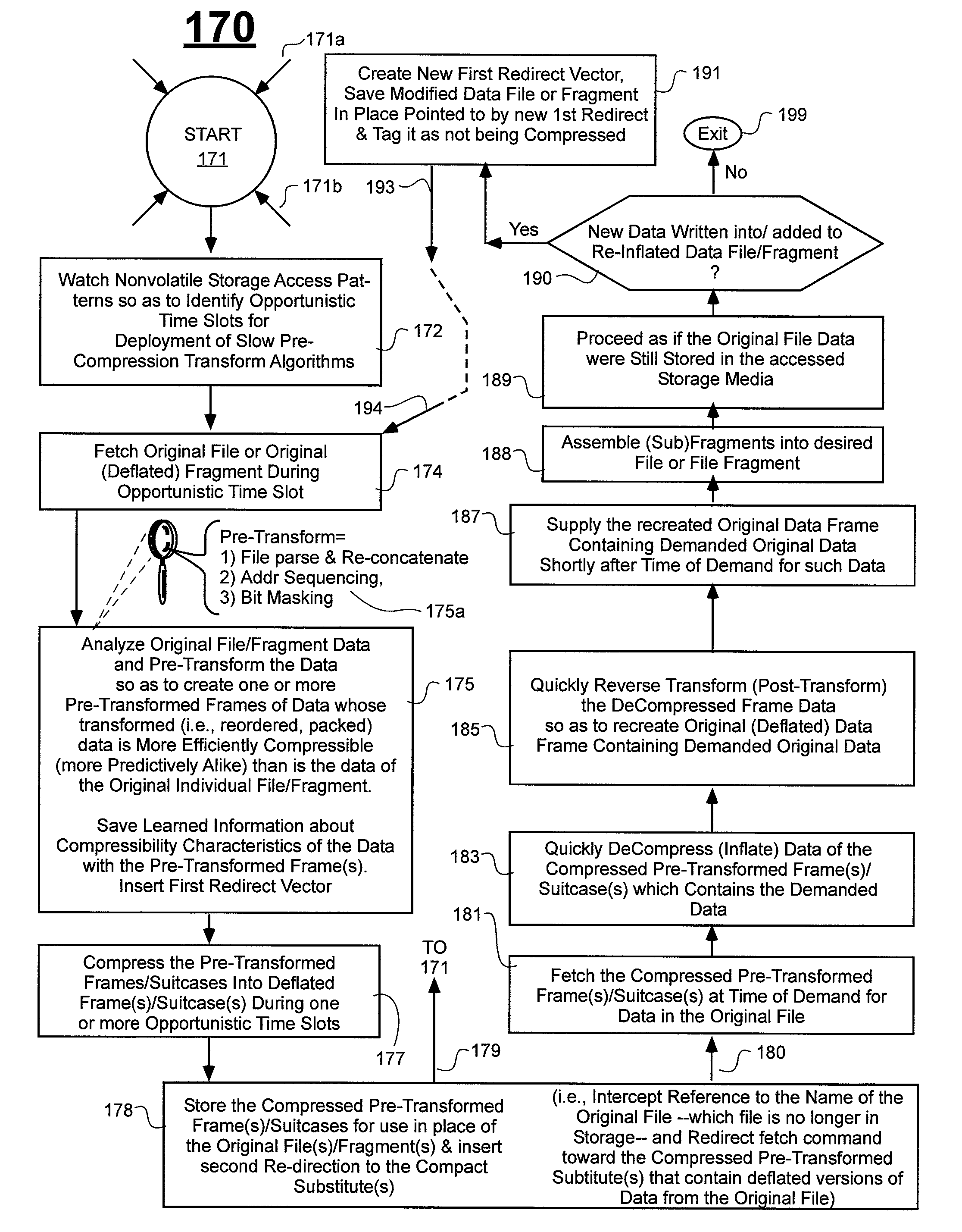
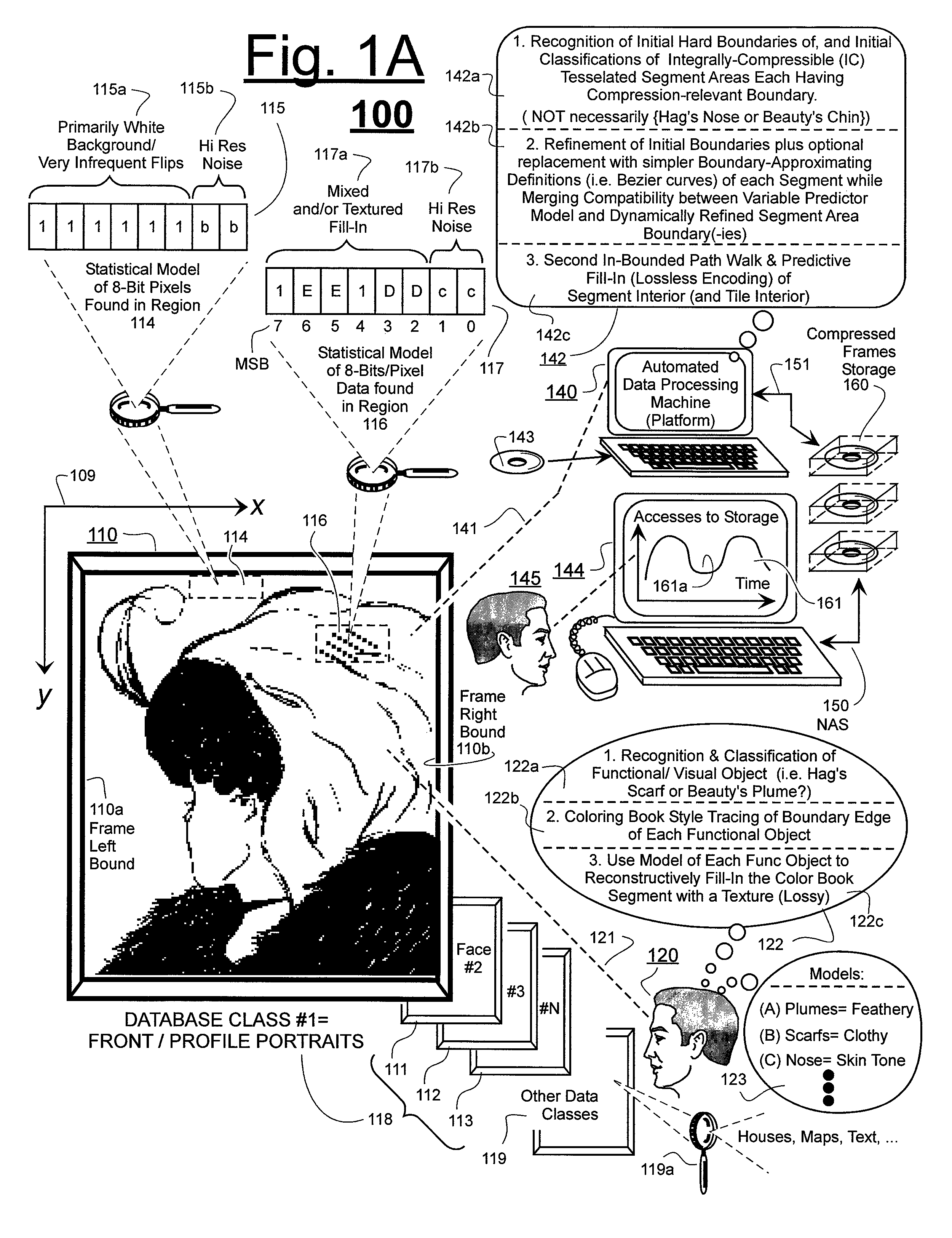
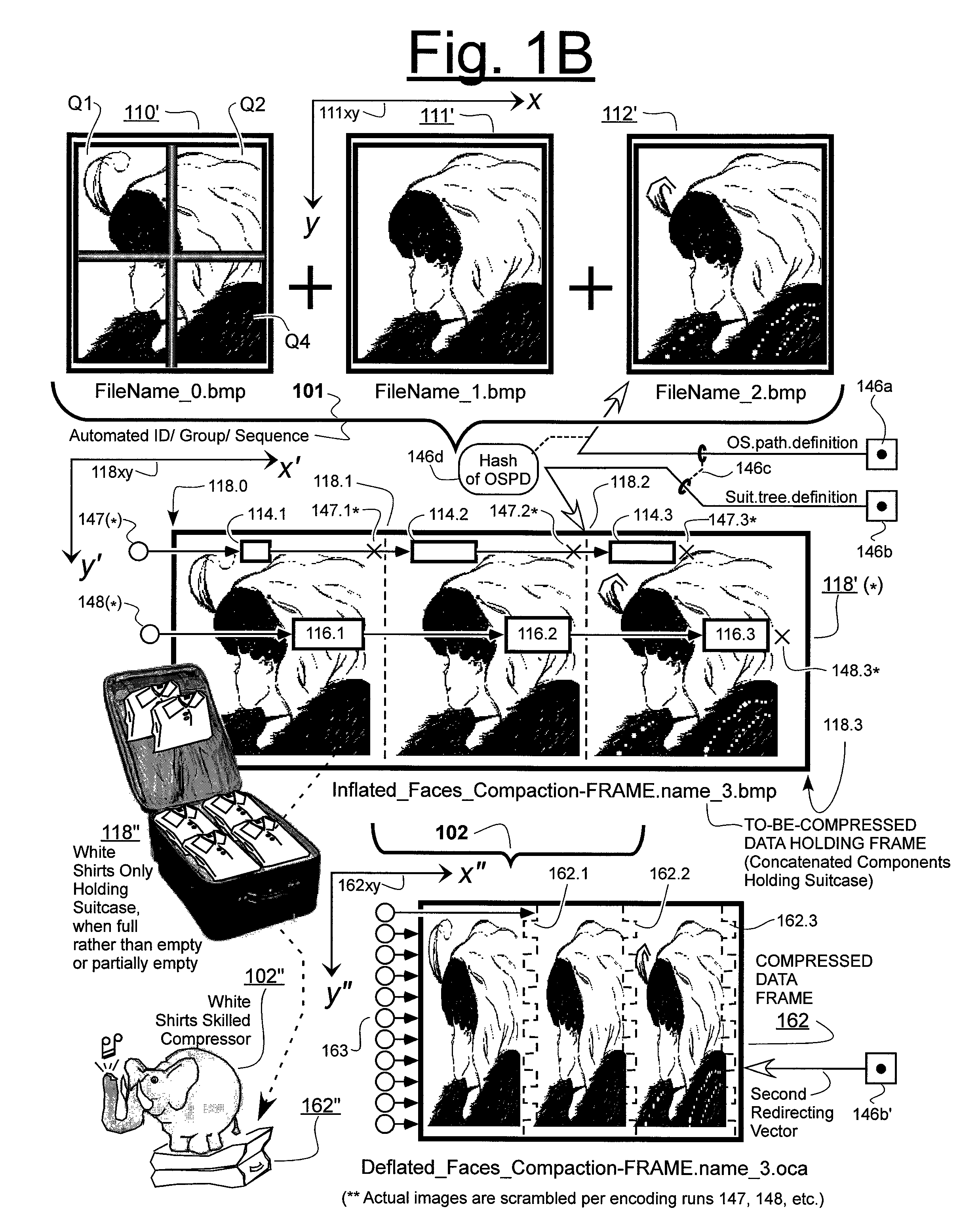
Prediction-based compression engines are spoon-fed with sequentially efficiently compressible (SEC) streams of input data that make it possible for the compression engines to more efficiently compress or otherwise compact the incoming data than would be possible with streams of input data accepted on a TV-raster scan basis. Various techniques are disclosed for intentionally forming SEC input data streams. Among these are the tight packing of alike files or fragments into concatenation suitcases and the decomposition of files into substantially predictably consistent (SPC) fragments or segments that are routed to different suitcases according to their type. In a graphics-directed embodiment, image frames are partitioned into segment areas that are internally SPC and multidirectional walks (i.e., U-turning walks) are defined in the segment areas where these defined walks are traced during compression and also during decompression. A variety of pre-compression data transformation methods are disclosed for causing apparently random data sequences to appear more compressibly alike to each other. The methods are usable in systems that permit substantially longer times for data compaction operations than for data decompaction operations.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Methods and Apparatus for Reducing Storage Size
ActiveUS20080050027A1Reduce probabilitySave energyCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationGraphicsData stream
Prediction-based compression engines are spoon-fed with sequentially efficiently compressible (SEC) streams of input data that make it possible for the compression engines to more efficiently compress or otherwise compact the incoming data than would be possible with streams of input data accepted on a TV-raster scan basis. Various techniques are disclosed for intentionally forming SEC input data streams. Among these are the tight packing of alike files or fragments into concatenation suitcases and the decomposition of files into substantially predictably consistent (SPC) fragments or segments that are routed to different suitcases according to their type. In a graphics-directed embodiment, image frames are partitioned into segment areas that are internally SPC and multidirectional walks (i.e., U-turning walks) are defined in the segment areas where these defined walks are traced during compression and also during decompression. A variety of pre-compression data transformation methods are disclosed for causing apparently random data sequences to appear more compressibly alike to each other. The methods are usable in systems that permit substantially longer times for data compaction operations than for data decompaction operations.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Methods and Apparatus for Reducing Storage Size
ActiveUS20080050025A1Save energyPacked tightlyImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsData stream
Prediction-based compression engines are spoon-fed with sequentially efficiently compressible (SEC) streams of input data that make it possible for the compression engines to more efficiently compress or otherwise compact the incoming data than would be possible with streams of input data accepted on a TV-raster scan basis. Various techniques are disclosed for intentionally forming SEC input data streams. Among these are the tight packing of alike files or fragments into concatenation suitcases and the decomposition of files into substantially predictably consistent (SPC) fragments or segments that are routed to different suitcases according to their type. In a graphics-directed embodiment, image frames are partitioned into segment areas that are internally SPC and multidirectional walks (i.e., U-turning walks) are defined in the segment areas where these defined walks are traced during compression and also during decompression. A variety of pre-compression data transformation methods are disclosed for causing apparently random data sequences to appear more compressibly alike to each other. The methods are usable in systems that permit substantially longer times for data compaction operations than for data decompaction operations.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Methods and Apparatus for Reducing Storage Size
ActiveUS20080152235A1Reduce probabilitySave energyDigital data information retrievalCode conversionGraphicsData stream
Prediction-based compression engines are spoon-fed with sequentially efficiently compressible (SEC) streams of input data that make it possible for the compression engines to more efficiently compress or otherwise compact the incoming data than would be possible with streams of input data accepted on a TV-raster scan basis. Various techniques are disclosed for intentionally forming SEC input data streams. Among these are the tight packing of alike files or fragments into concatenation suitcases and the decomposition of files into substantially predictably consistent (SPC) fragments or segments that are routed to different suitcases according to their type. In a graphics-directed embodiment, image frames are partitioned into segment areas that are internally SPC and multidirectional walks (i.e., U-turning walks) are defined in the segment areas where these defined walks are traced during compression and also during decompression. A variety of pre-compression data transformation methods are disclosed for causing apparently random data sequences to appear more compressibly alike to each other. The methods are usable in systems that permit substantially longer times for data compaction operations than for data decompaction operations.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Optimization of storage and transmission of data
InactiveUS20110314070A1Improve efficiencyImprove optimizationMultiple digital computer combinationsFile/folder operationsApplication softwareData storing
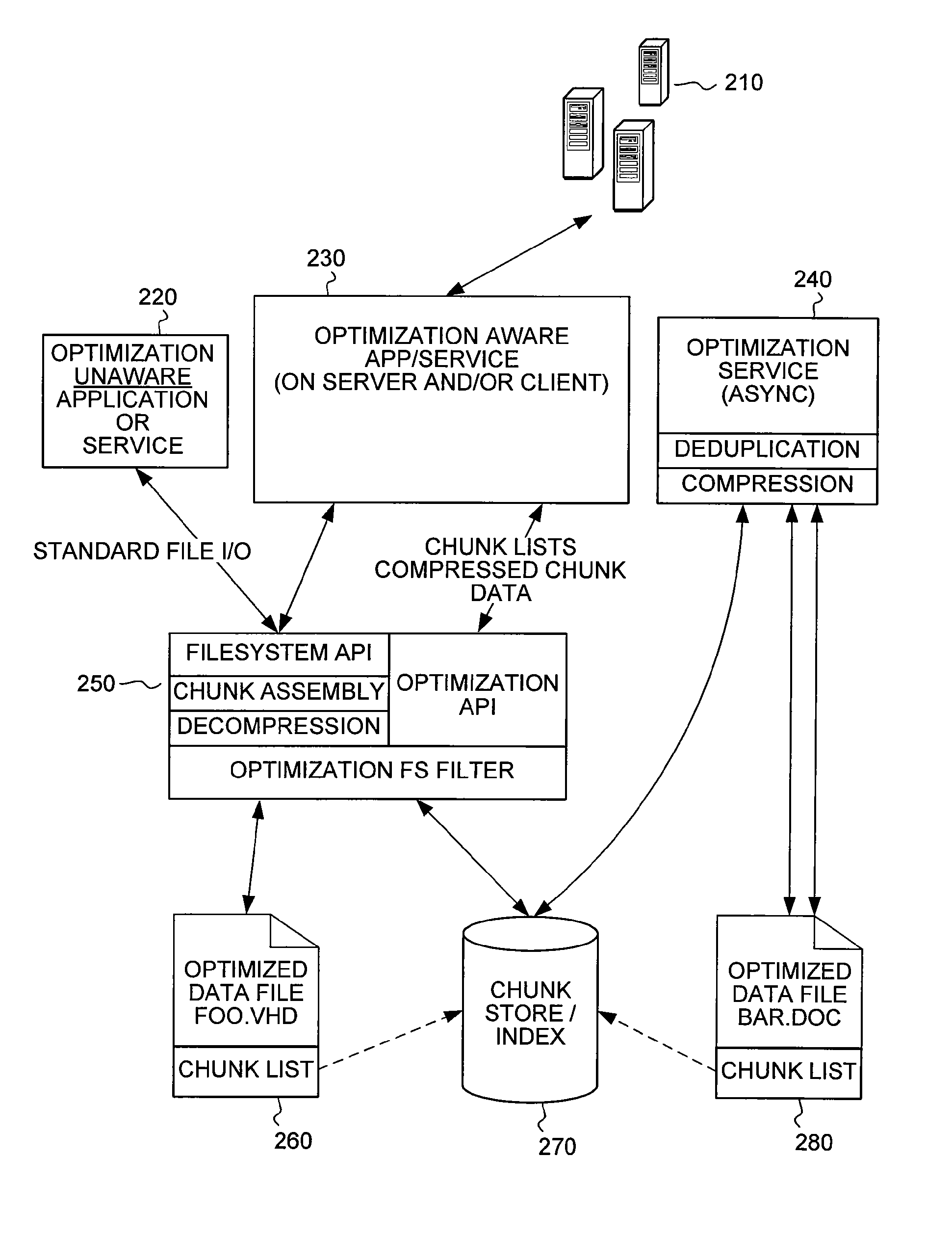
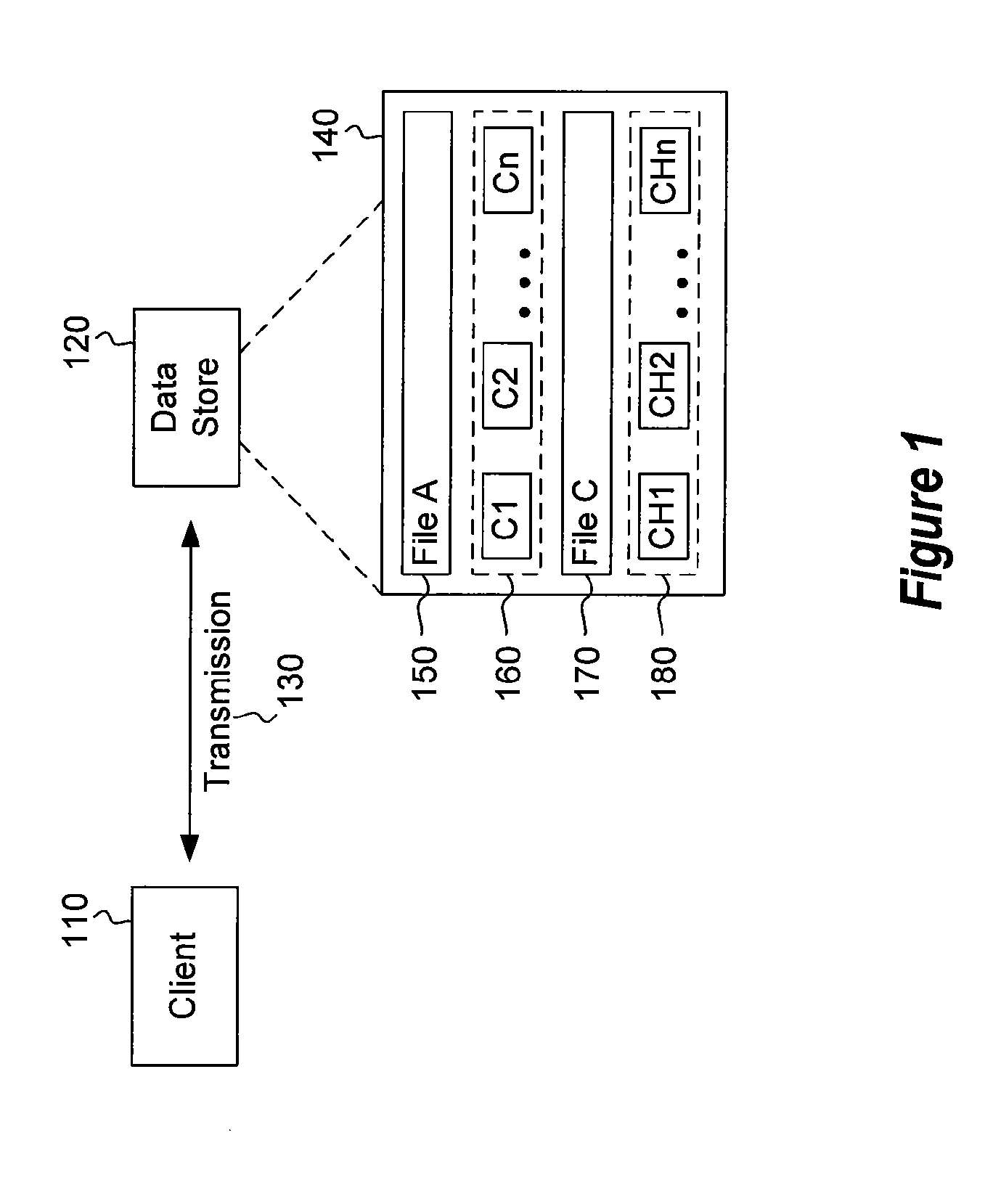
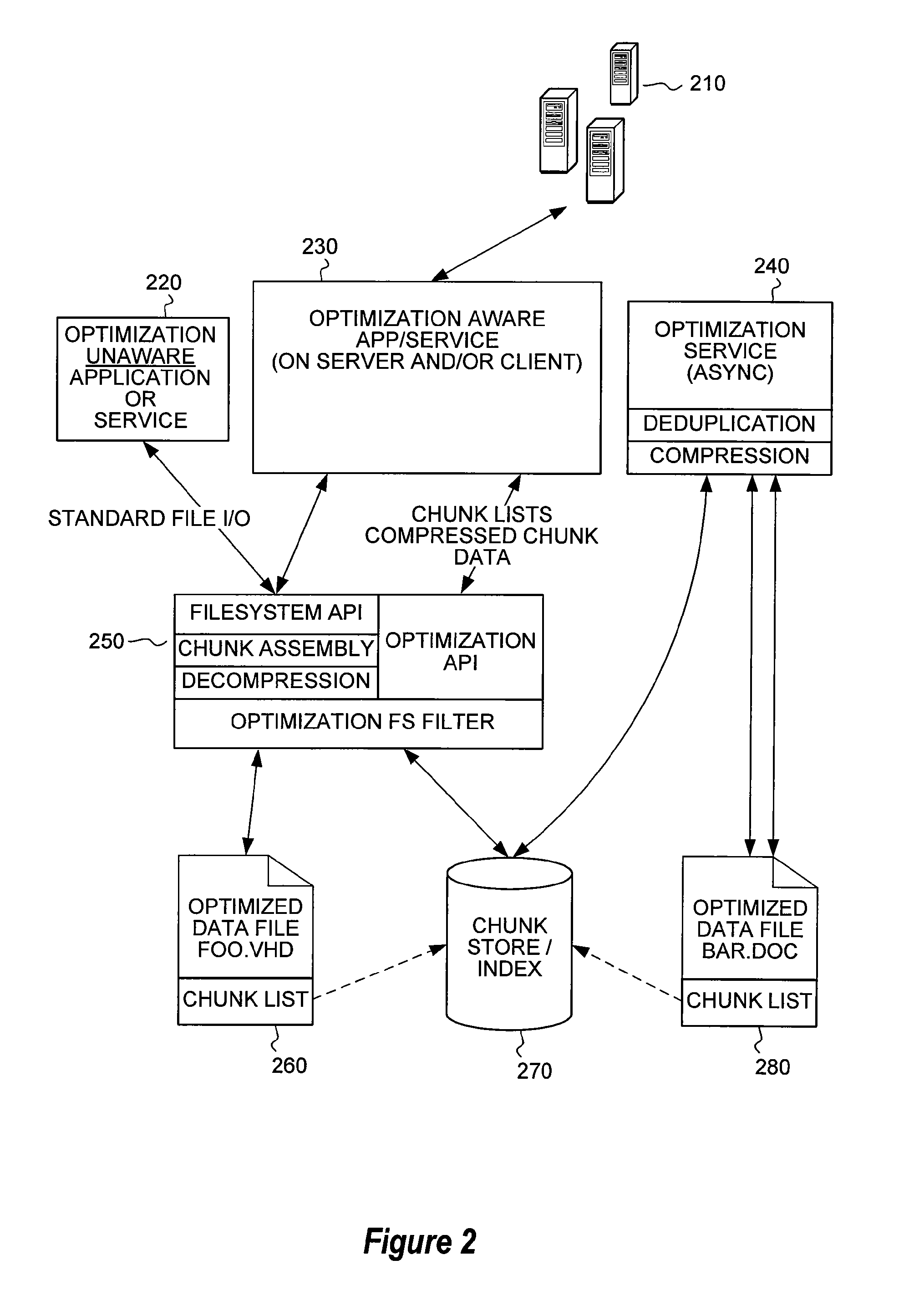
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for end-to-end optimization of data storage and transmission of data. Details of how data is stored within a data store are exposed to clients and applications. Clients and applications are enabled to makes requests to data stores to obtain data as it is actually stored upon within the data store to eliminate redundant processing of the requested data. Compression and de-duplication of data within a data store are leveraged to increase the efficiency and reduce latency of data transmitted over a LAN or WAN.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods and Apparatus for Reducing Storage Size
ActiveUS20080050047A1Reduce probabilitySave energyCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsData transformation
Prediction-based compression engines are spoon-fed with sequentially efficiently compressible (SEC) streams of input data that make it possible for the compression engines to more efficiently compress or otherwise compact the incoming data than would be possible with streams of input data accepted on a TV-raster scan basis. Various techniques are disclosed for intentionally forming SEC input data streams. Among these are the tight packing of alike files or fragments into concatenation suitcases and the decomposition of files into substantially predictably consistent (SPC) fragments or segments that are routed to different suitcases according to their type. In a graphics-directed embodiment, image frames are partitioned into segment areas that are internally SPC and multidirectional walks (i.e., U-turning walks) are defined in the segment areas where these defined walks are traced during compression and also during decompression. A variety of pre-compression data transformation methods are disclosed for causing apparently random data sequences to appear more compressibly alike to each other. The methods are usable in systems that permit substantially longer times for data compaction operations than for data decompaction operations.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Large-data storage and optimization method
InactiveCN103440244AStable big data storage optimization methodEfficient big data storage optimization methodSpecial data processing applicationsRedundant operation error correctionData compressionParallel computing
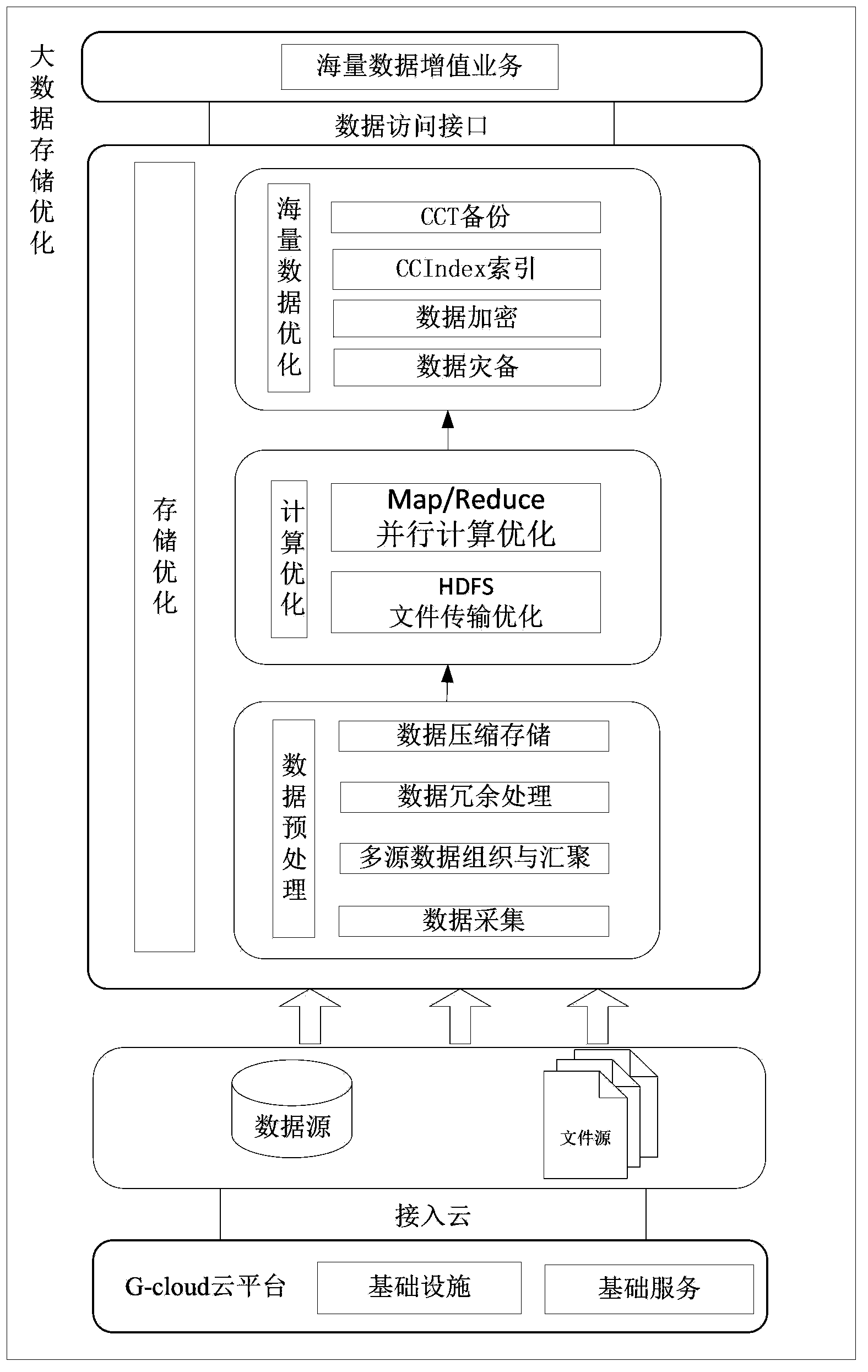
The invention relates to the technical field of data processing, in particular to a large-data storage and optimization method facing to sea-cloud coordination. The method comprises the following steps of data preprocessing, calculation optimization and mass data optimization, wherein the step of data preprocessing comprises data collection, multi-source data organization and gathering, data redundant processing and data compression storage; the calculation optimization comprises HDFS (hadoop distributed file system) file transmission and optimization and Map / Reduce parallel calculation and optimization; and the step of mass data optimization comprises data backup for disaster recovery, data encryption, CC index and CCT backup. The large-data storage and optimization method disclosed by the invention can be applied to large-data storage of a cloud platform.
Owner:GUANGDONG ELECTRONICS IND INST
Methods and Apparatus for Reducing Storage Size
ActiveUS20080050029A1Save energyPacked tightlyCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingGraphicsData stream
Prediction-based compression engines are spoon-fed with sequentially efficiently compressible (SEC) streams of input data that make it possible for the compression engines to more efficiently compress or otherwise compact the incoming data than would be possible with streams of input data accepted on a TV-raster scan basis. Various techniques are disclosed for intentionally forming SEC input data streams. Among these are the tight packing of alike files or fragments into concatenation suitcases and the decomposition of files into substantially predictably consistent (SPC) fragments or segments that are routed to different suitcases according to their type. In a graphics-directed embodiment, image frames are partitioned into segment areas that are internally SPC and multidirectional walks (i.e., U-turning walks) are defined in the segment areas where these defined walks are traced during compression and also during decompression. A variety of pre-compression data transformation methods are disclosed for causing apparently random data sequences to appear more compressibly alike to each other. The methods are usable in systems that permit substantially longer times for data compaction operations than for data decompaction operations.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Methods and Apparatus for Reducing Storage Size
ActiveUS20080050026A1Save energyPacked tightlyCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingGraphicsData stream
Prediction-based compression engines are spoon-fed with sequentially efficiently compressible (SEC) streams of input data that make it possible for the compression engines to more efficiently compress or otherwise compact the incoming data than would be possible with streams of input data accepted on a TV-raster scan basis. Various techniques are disclosed for intentionally forming SEC input data streams. Among these are the tight packing of alike files or fragments into concatenation suitcases and the decomposition of files into substantially predictably consistent (SPC) fragments or segments that are routed to different suitcases according to their type. In a graphics-directed embodiment, image frames are partitioned into segment areas that are internally SPC and multidirectional walks (i.e., U-turning walks) are defined in the segment areas where these defined walks are traced during compression and also during decompression. A variety of pre-compression data transformation methods are disclosed for causing apparently random data sequences to appear more compressibly alike to each other. The methods are usable in systems that permit substantially longer times for data compaction operations than for data decompaction operations.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
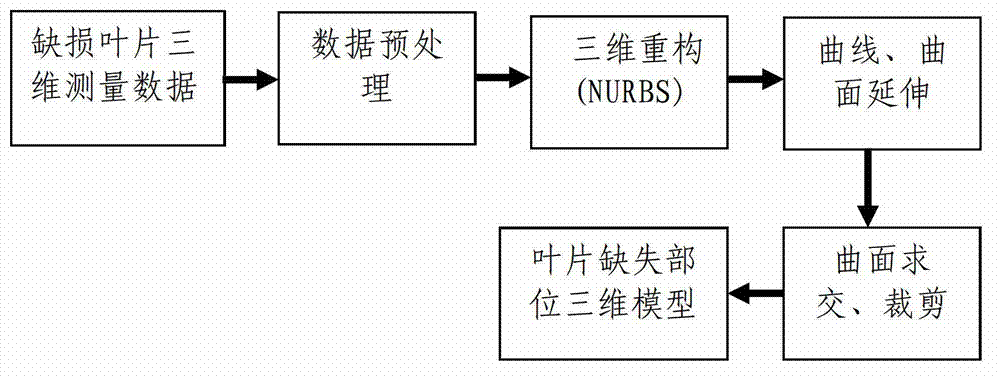
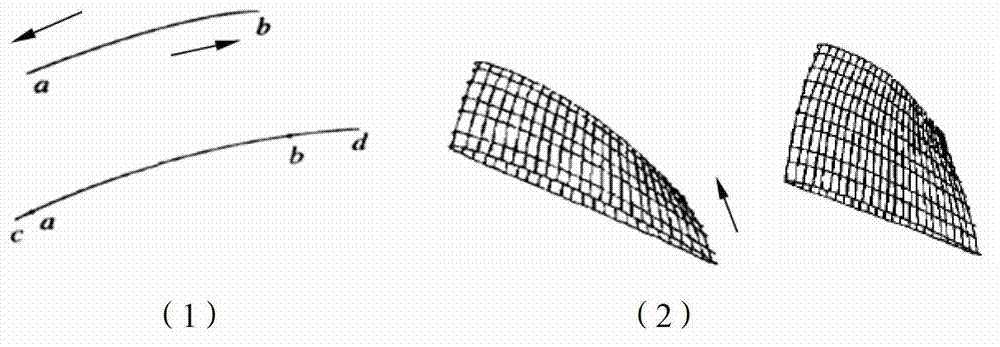
Three-dimensional model rebuilding method of aviation engine blade tip missing parts
InactiveCN103093065AHigh precisionHigh-precision restorationGeometric CADEngine fuctionsAviationPoint cloud
The invention discloses a three-dimensional model rebuilding method of aviation engine blade tip missing parts. The three-dimensional model rebuilding method adopts the following process steps: 1) picking out abraded blades appropriate for being repaired in an extension mode and cutting the abraded parts flat; 2) measuring the blades to be repaired with a high-accuracy digitization three-dimensional measurement instrument to acquire three-dimensional point cloud data of the parts to be repaired; then conducting denoising, data compaction and data pre-processing on the point cloud data; 3) rebuilding the abraded blades to be with the rebuilding accuracy >=0.02mm by adopting a non-uniform rational B-spline (NURBS) method; 4) extending curved surfaces and rebuilding a three-dimensional model of missing parts of the abraded blades with rebuilding accuracy+ / - 0.02mm; and 5) conducting intersection and cutting a plurality of extended NURBS curved surfaces to acquire the three-dimensional model of the missing parts of the abraded blades. An analytical method, a partition method, a tracking method or an implicit function method is adopted by the algorithm of intersection of the curved surfaces.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Dynamic monitoring system and method for aerial quick response
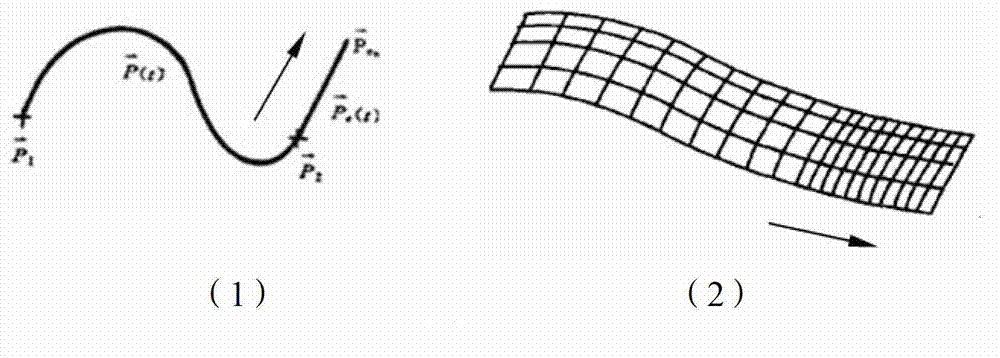
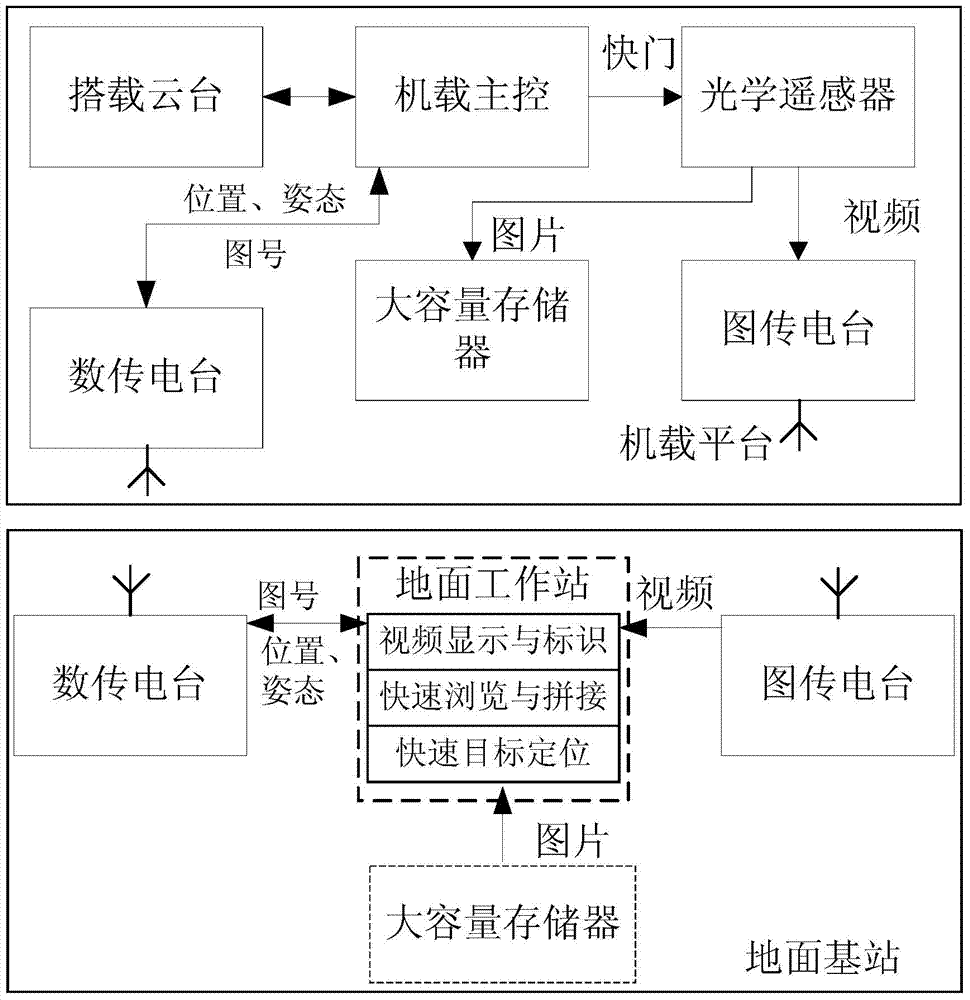
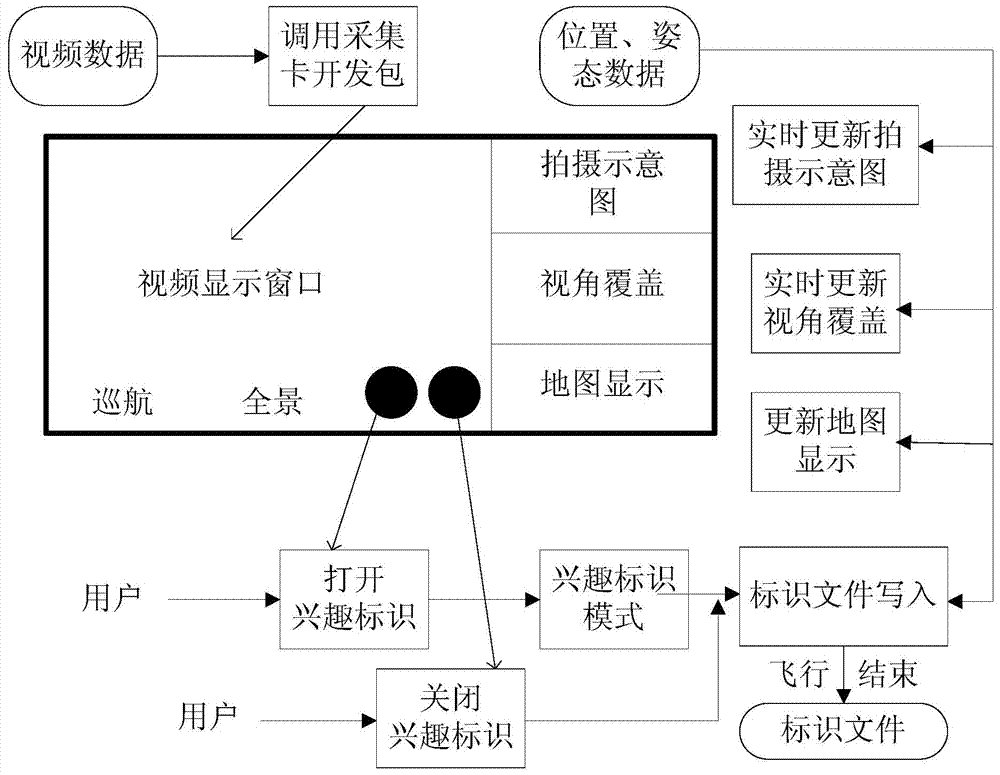
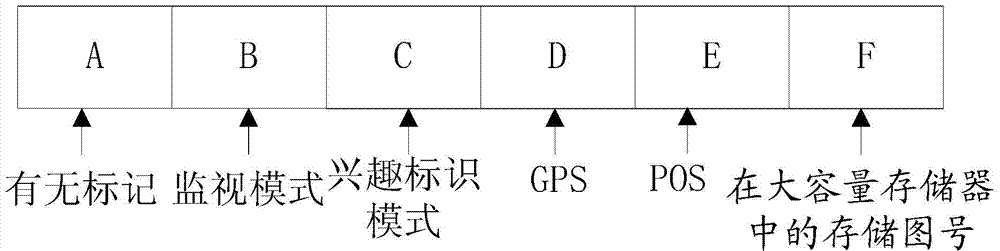
ActiveCN103942273AReduce workloadQuick responseGeometric image transformationPicture taking arrangementsDynamic monitoringData acquisition
The invention relates to a dynamic monitoring system and method for an aerial quick response. The dynamic monitoring method comprises the steps that the dynamic monitoring system is built, aerial photography data are classified and marked while real-time monitoring is conducted, and retrieval, browsing and post treatment, including splicing and target positioning, of images of interest can be quickly completed after a flight mission is accomplished. According to the dynamic monitoring system and method for the aerial quick response, a data acquisition process during a flight and a data processing process after the flight are related through interest marks, and fast retrieval of the aerial photography data is greatly facilitated; meanwhile, through the strategy that original high-resolution images and size-compressed images are connected, as a result, it is guaranteed that the data compaction process is quick, and reconnaissance application value of high-resolution detail information is retained.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Methods and apparatus for reducing storage size
ActiveUS7885988B2Reduce probabilitySave energyDigital data processing detailsCode conversionGraphicsData stream
Prediction-based compression engines are spoon-fed with sequentially efficiently compressible (SEC) streams of input data that make it possible for the compression engines to more efficiently compress or otherwise compact the incoming data than would be possible with streams of input data accepted on a TV-raster scan basis. Various techniques are disclosed for intentionally forming SEC input data streams. Among these are the tight packing of alike files or fragments into concatenation suitcases and the decomposition of files into substantially predictably consistent (SPC) fragments or segments that are routed to different suitcases according to their type. In a graphics-directed embodiment, image frames are partitioned into segment areas that are internally SPC and multidirectional walks (i.e., U-turning walks) are defined in the segment areas where these defined walks are traced during compression and also during decompression. A variety of pre-compression data transformation methods are disclosed for causing apparently random data sequences to appear more compressibly alike to each other. The methods are usable in systems that permit substantially longer times for data compaction operations than for data decompaction operations.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
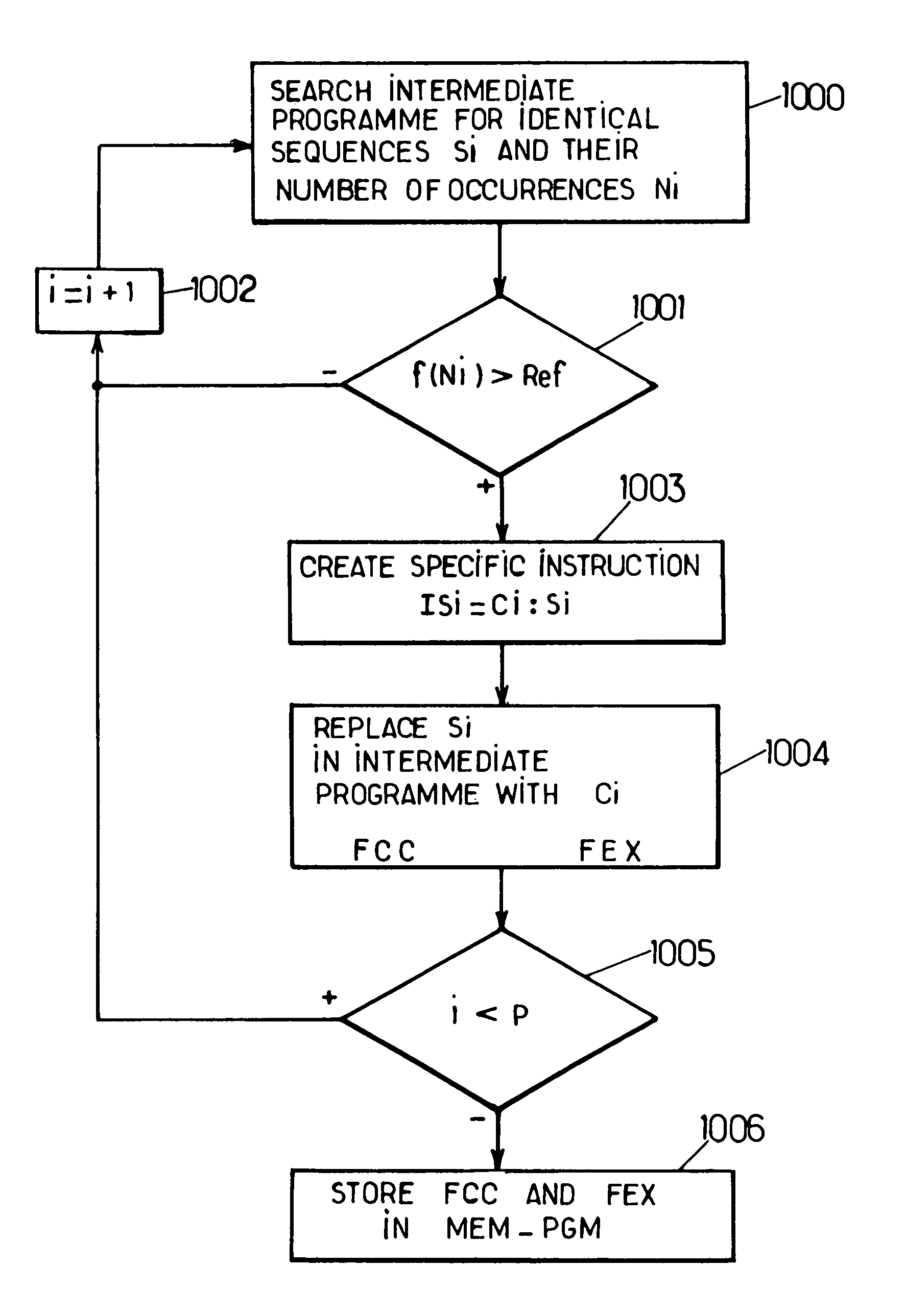
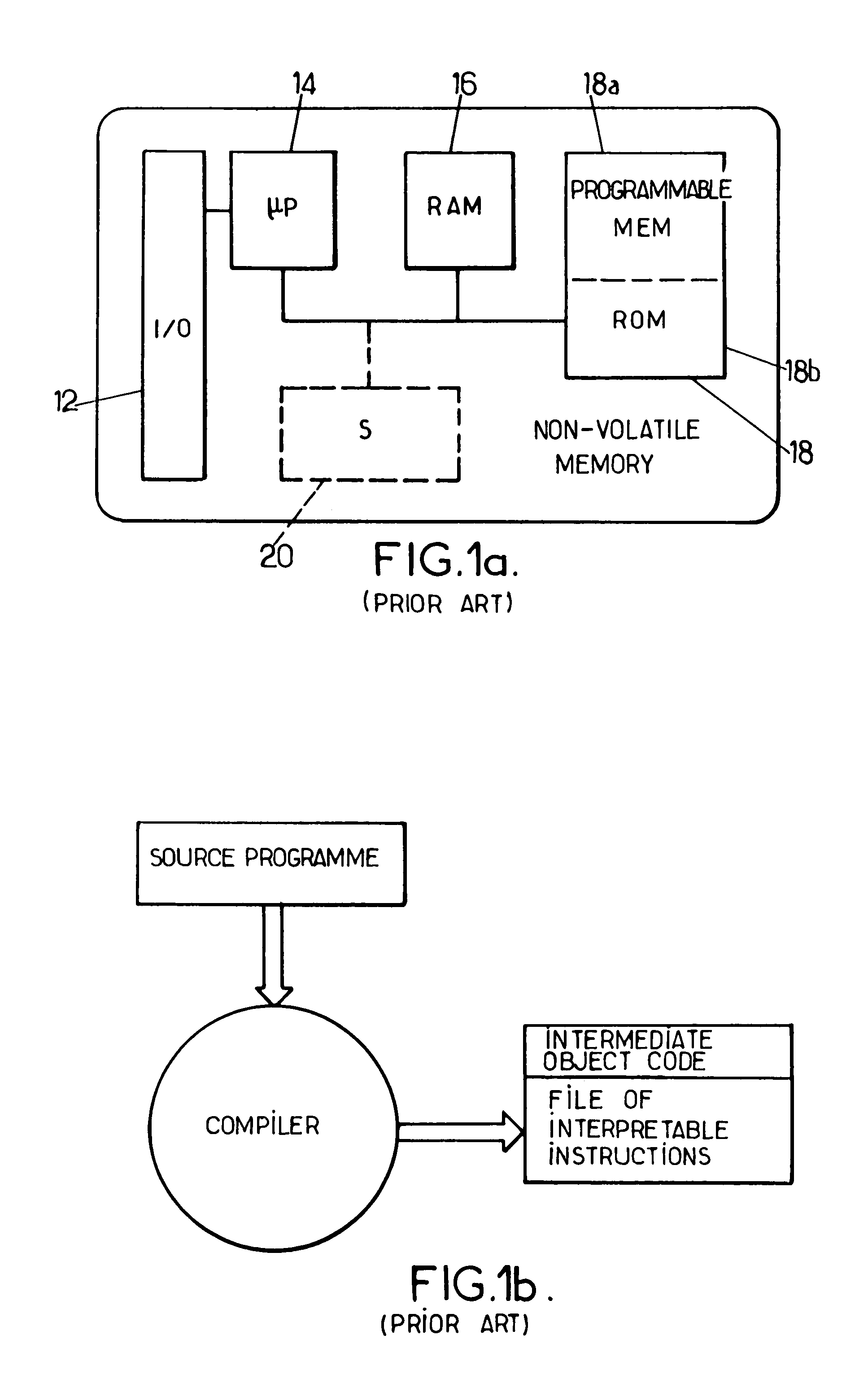
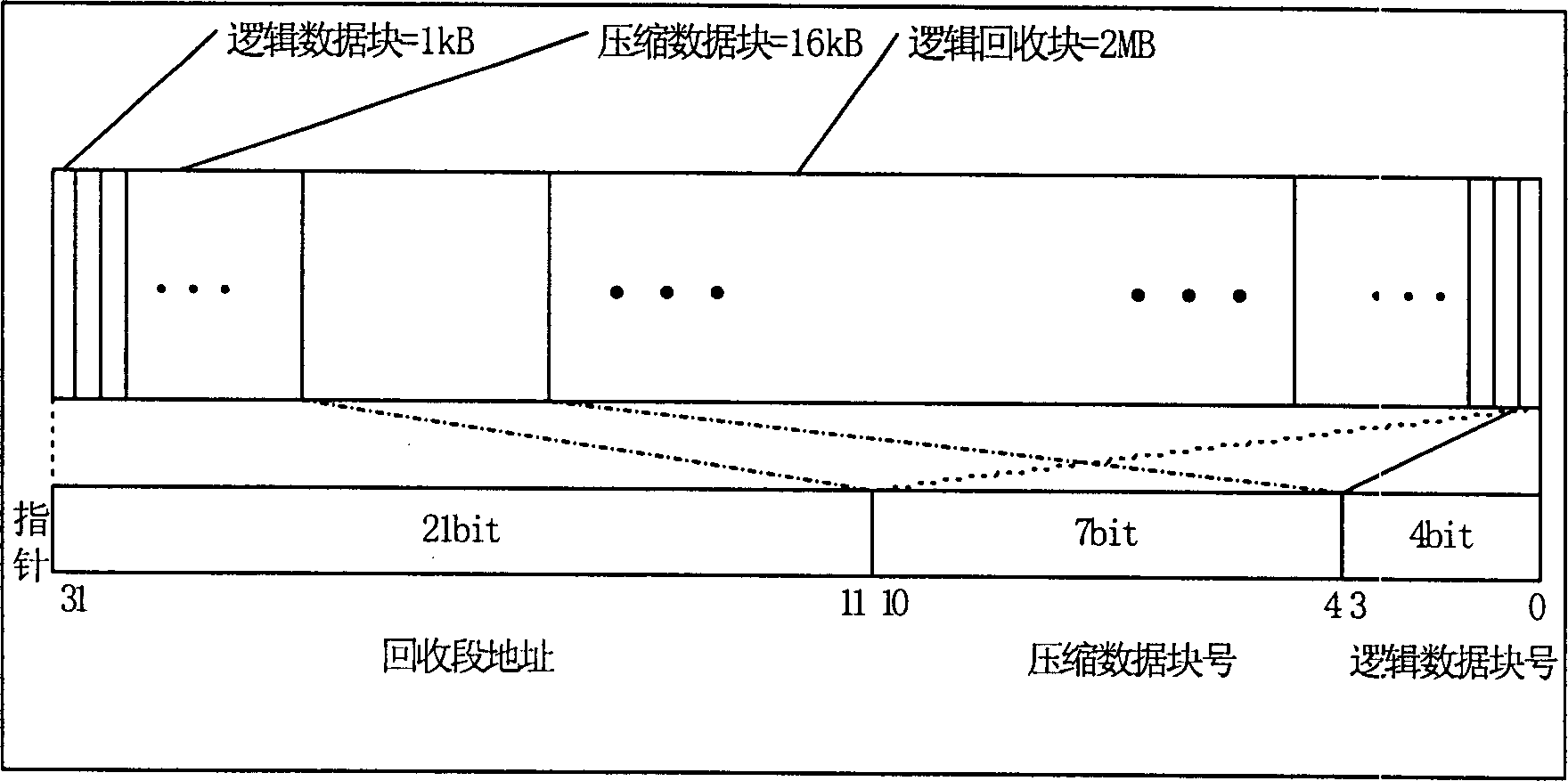
Data compaction method for an intermediate object code program executable in an onboard system provided with data processing resources and corresponding onboard system with multiple applications
The invention concerns a data compaction method and system for an intermediate program. The method consists in searching the program (1000) for identical sequences (Si) and counting Ni number of occurrences of each sequence (Si), a comparison test (1001) to find the superiority of a function f(Ni) to a reference value enables to generate (1003) a specific instruction of a specific code (Ci) with which the sequence (Si) is associated, replacing (1004) each occurrence in the sequence (Si) by the specific code (Ci) in the intermediate program to create a compacted intermediate program (FCC) with which an executing file (FEX) is associated. The invention is applicable to multiple application portable objects such as microprocessor cards, onboard systems of the like.
Owner:CP8 TECH SA
Vector data compaction and compression method and corresponding decompression method
InactiveCN101561819AThin compression worksSimplify data volumeSpecial data processing applicationsVirtual screenLossless compression
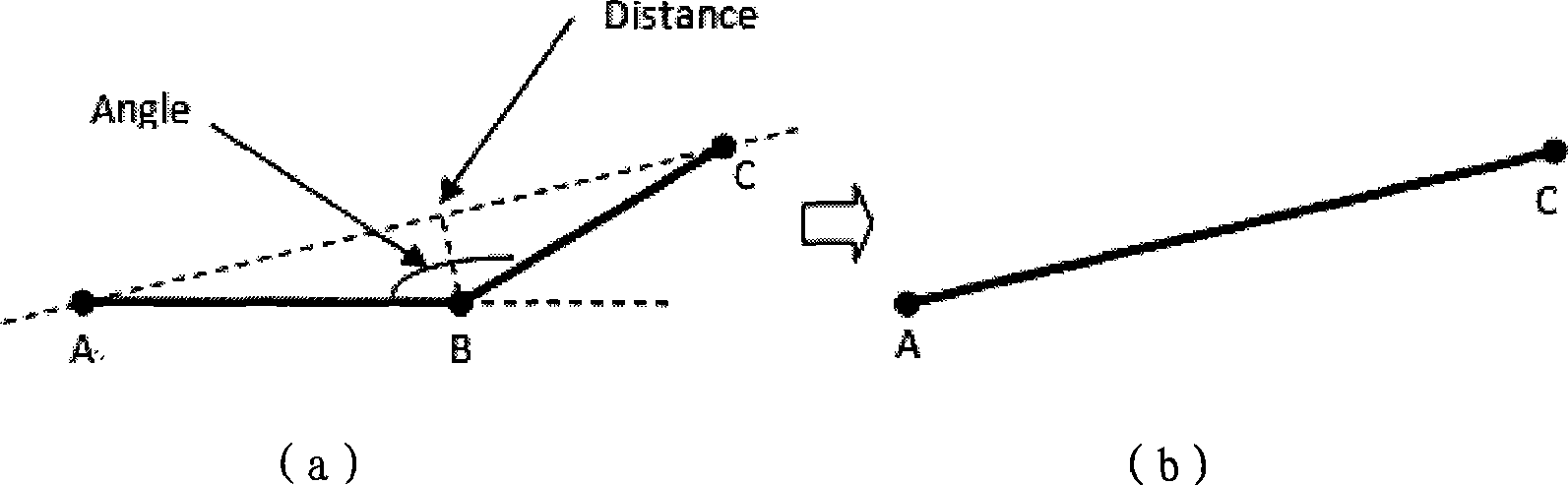
The invention relates to the technical field of geographical information systems and provides a vector data compaction and compression method based on virtual screen mapping theory as well as a corresponding decompression method. The vector data compaction and compression method includes the following steps of: determining the size of a virtual screen; conducting Douglas compaction on segmental arc coordinate; conducting virtual screen mapping on the coordinate; conducting offset storage and compression on the segmental arc coordinate; and packing data after compaction and compression and conducting general lossless compression. The methods can be widely applied to the vector data compaction and compression in the fields of GIS, Web, GIS, MovingGIS and car navigation, and can compact and compress the volume of vector data dramatically on condition of meeting visual fidelity.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
Wireless multi-person motion data collector and collection method
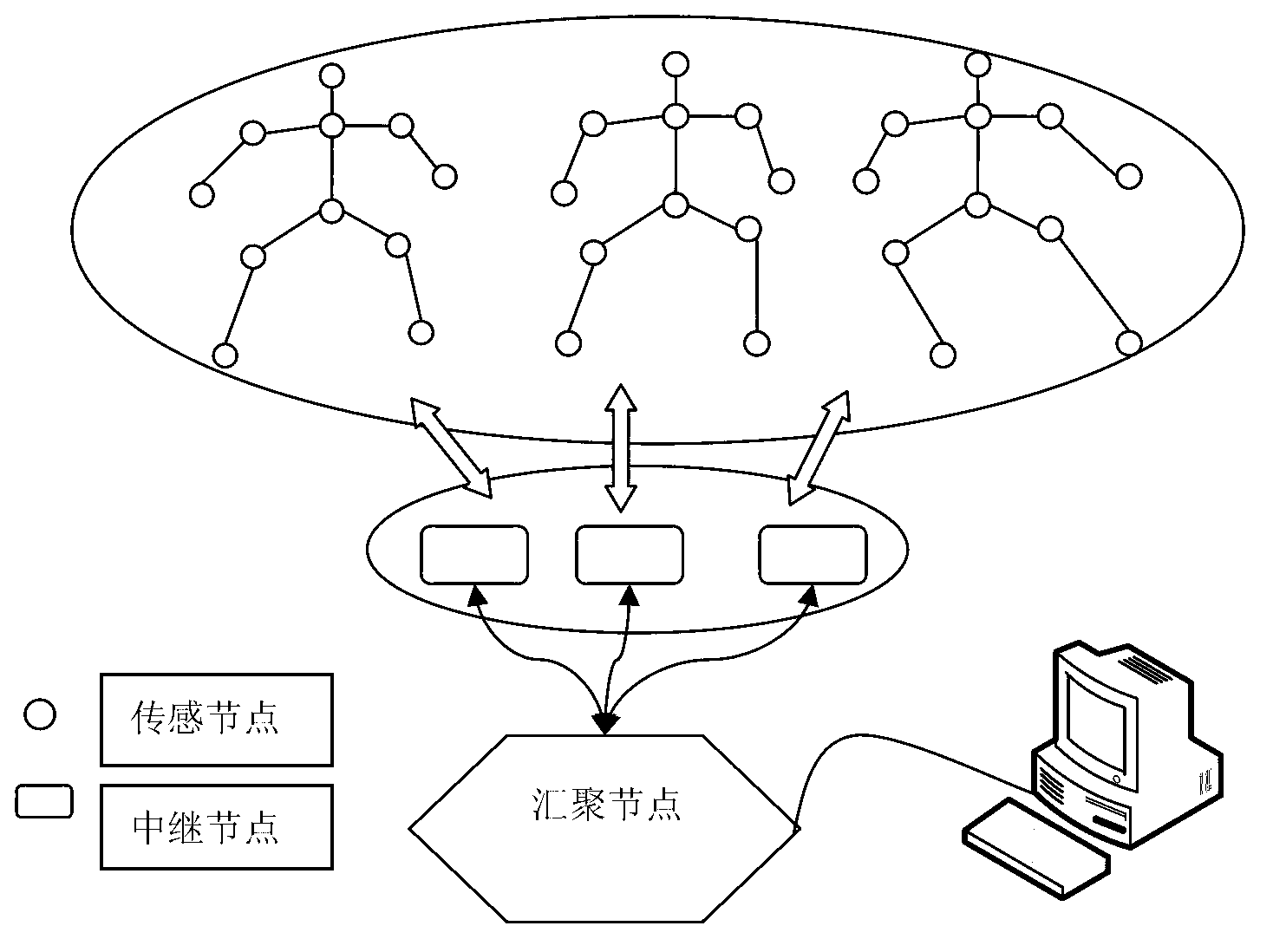
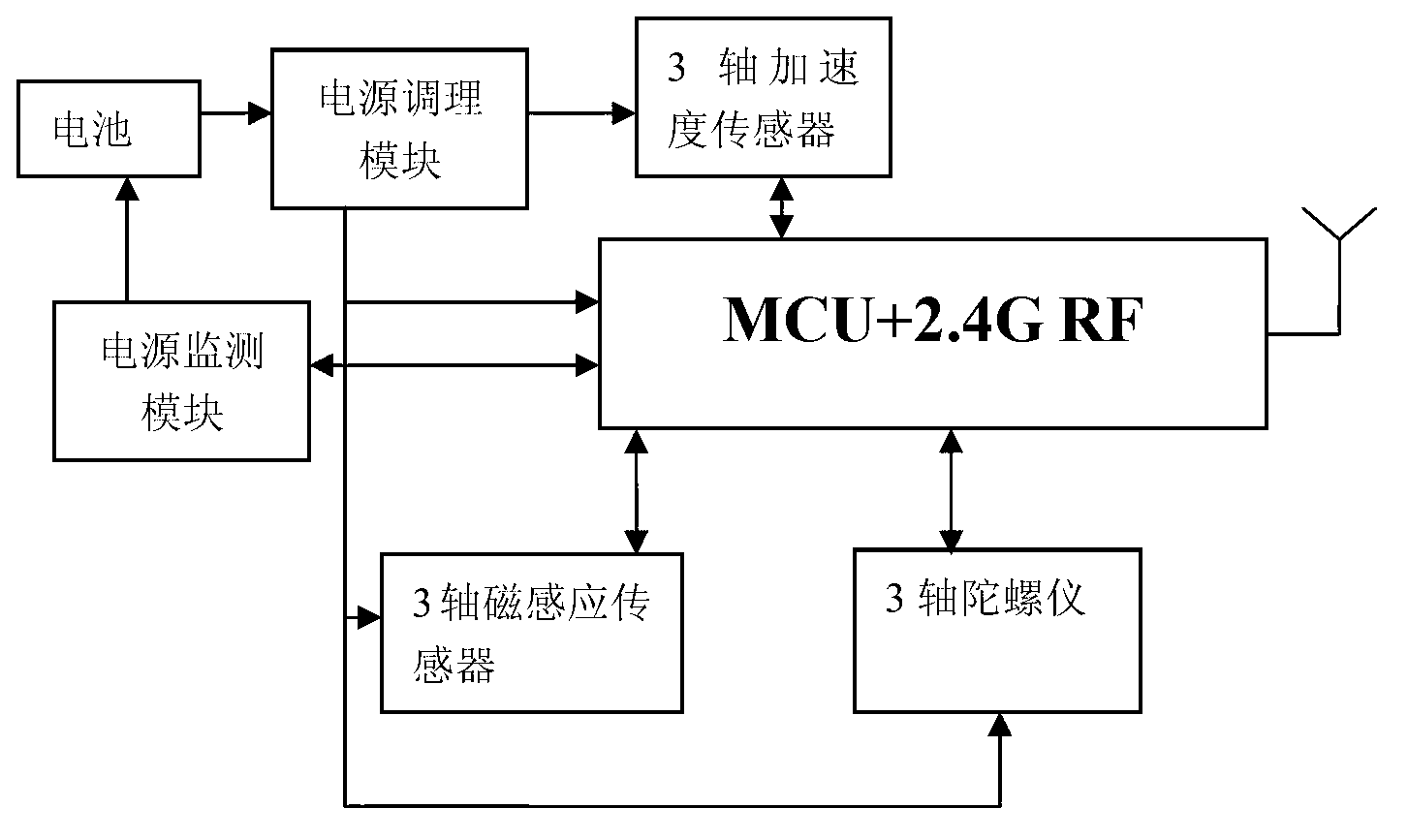
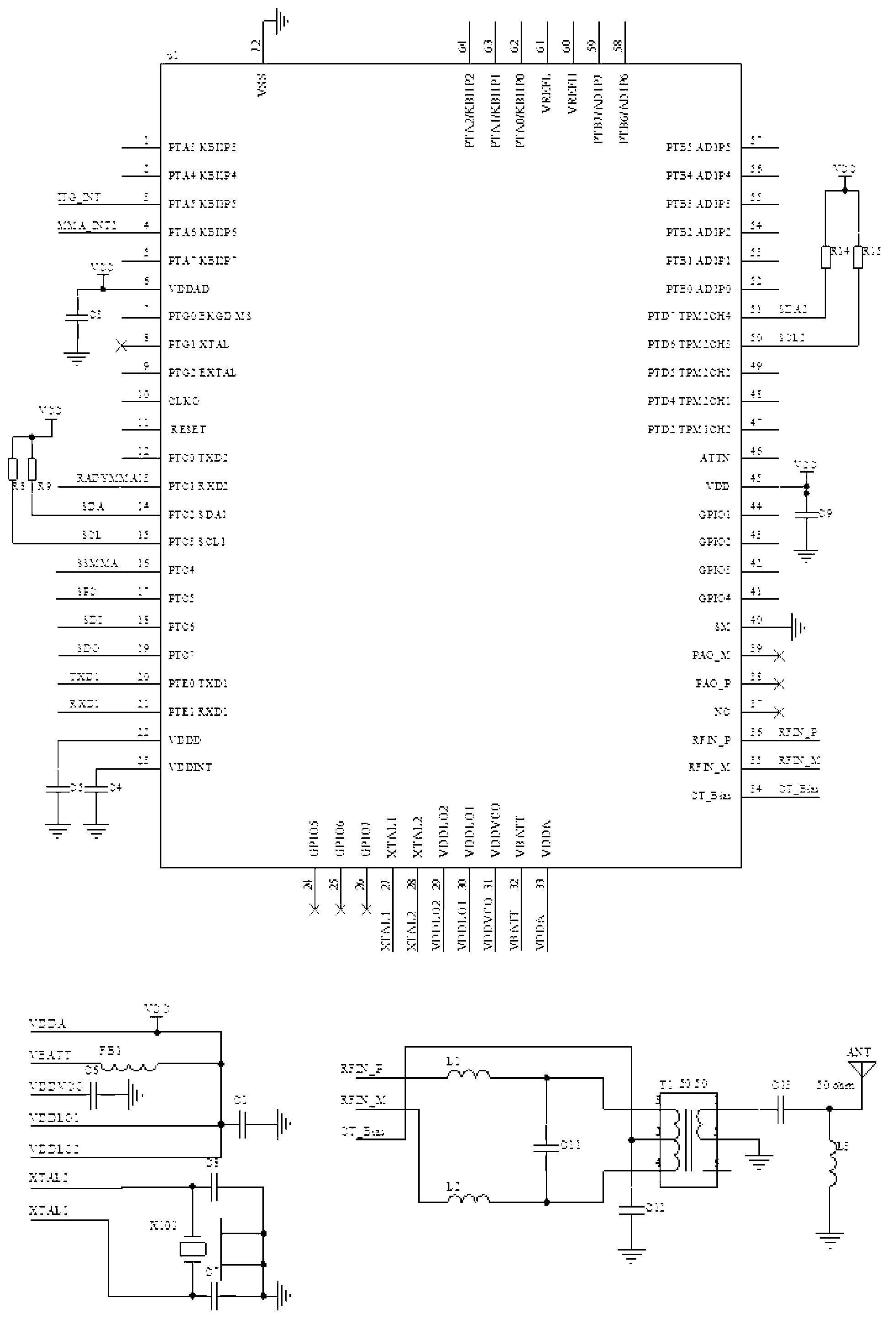
InactiveCN103079289AGuaranteed high performance requirementsReduce areaNetwork topologiesHigh level techniquesData compressionGyroscope
The invention discloses a wireless multi-person motion data collector and a collection method. The wireless multi-person motion data collector comprises tens of data sensing nodes, six data relay nodes and a data convergence node, wherein the data sensing nodes are adhered to each motion key position of the human body; each human body motion data is periodically collected by a high-precision acceleration sensor, a magnetic sensor and a gyroscope; compressed sensing data is wirelessly transmitted to the data relay nodes; the data relay nodes are in charge of integrating data and transmitting the data to the data convergence node; the data convergence node is in wired connection with six data relay nodes; and the data is periodically uploaded to a computer. According to the invention, the motion data of 2-4 people can be simultaneously and wirelessly collected, and the invention has the characteristics of high precision, high data rate and low power consumption and is widely suitable for occasions, such as virtual man-machine interaction, virtual games and limb medical rehabilitation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods and apparatus for reducing storage size
ActiveUS7936932B2Reduce probabilitySave energyCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingGraphicsData stream
Prediction-based compression engines are spoon-fed with sequentially efficiently compressible (SEC) streams of input data that make it possible for the compression engines to more efficiently compress or otherwise compact the incoming data than would be possible with streams of input data accepted on a TV-raster scan basis. Various techniques are disclosed for intentionally forming SEC input data streams. Among these are the tight packing of alike files or fragments into concatenation suitcases and the decomposition of files into substantially predictably consistent (SPC) fragments or segments that are routed to different suitcases according to their type. In a graphics-directed embodiment, image frames are partitioned into segment areas that are internally SPC and multidirectional walks (i.e., U-turning walks) are defined in the segment areas where these defined walks are traced during compression and also during decompression. A variety of pre-compression data transformation methods are disclosed for causing apparently random data sequences to appear more compressibly alike to each other. The methods are usable in systems that permit substantially longer times for data compaction operations than for data decompaction operations.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Methods and apparatus for reducing storage size
ActiveUS7974478B2Reduce probabilitySave energyCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingGraphicsData stream
Prediction-based compression engines are spoon-fed with sequentially efficiently compressible (SEC) streams of input data that make it possible for the compression engines to more efficiently compress or otherwise compact the incoming data than would be possible with streams of input data accepted on a TV-raster scan basis. Various techniques are disclosed for intentionally forming SEC input data streams. Among these are the tight packing of alike files or fragments into concatenation suitcases and the decomposition of files into substantially predictably consistent (SPC) fragments or segments that are routed to different suitcases according to their type. In a graphics-directed embodiment, image frames are partitioned into segment areas that are internally SPC and multidirectional walks (i.e., U-turning walks) are defined in the segment areas where these defined walks are traced during compression and also during decompression. A variety of pre-compression data transformation methods are disclosed for causing apparently random data sequences to appear more compressibly alike to each other. The methods are usable in systems that permit substantially longer times for data compaction operations than for data decompaction operations.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Map data simplifying method oriented to mobile equipment
InactiveCN101400138AImprove display effectReduce data volumeInstruments for road network navigationStore-and-forward switching systemsService domainData stream
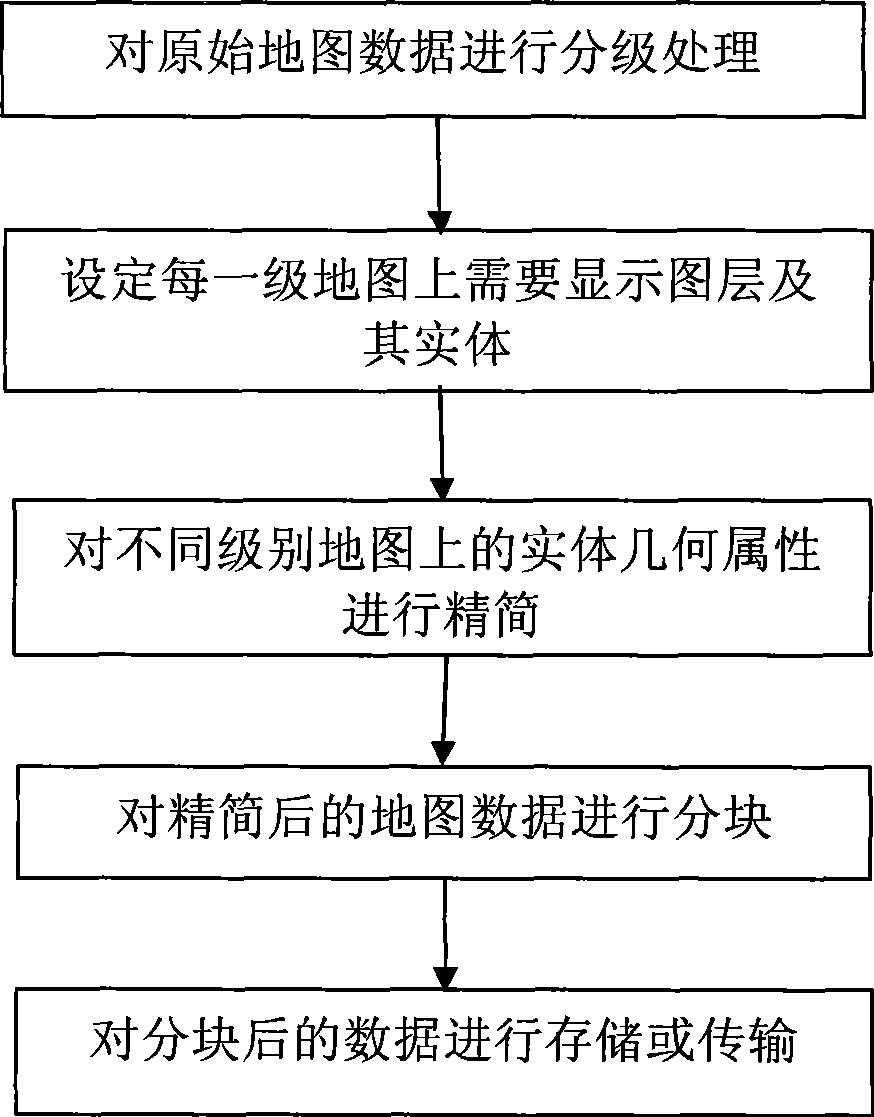
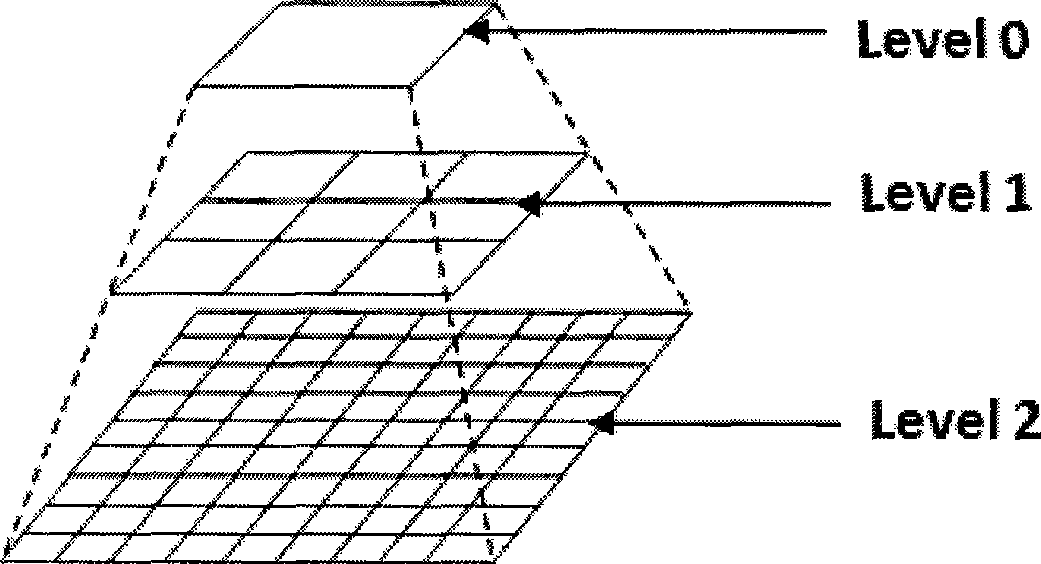
The invention discloses a map data compaction method facing to mobile devices, belonging to the map service field facing to the mobile device. The method comprises: 1) according to the requirement of map display in mobile application, determining map display levels facing to the mobile device; 2) according to the map display level, setting map layers and entity thereof to be displayed on the corresponding level map; 3) simplifying geometric attributes of the displayed entity on each level of the map; 4) partitioning the displayed map of the simplified map on each level, wherein the size of the partition is fixed as 255 coordinate unit*255 coordinate unit, the side of the partitioned coordinate unit of the data partition in different levels can be adjustable; 5) adopting binary data flow to storing and transmitting the partitioned map data. Compared with the prior art, the invention has small data volume and high plotting performance on the basis of ensuring better map display effect.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
System and method for data feed acceleration and encryption
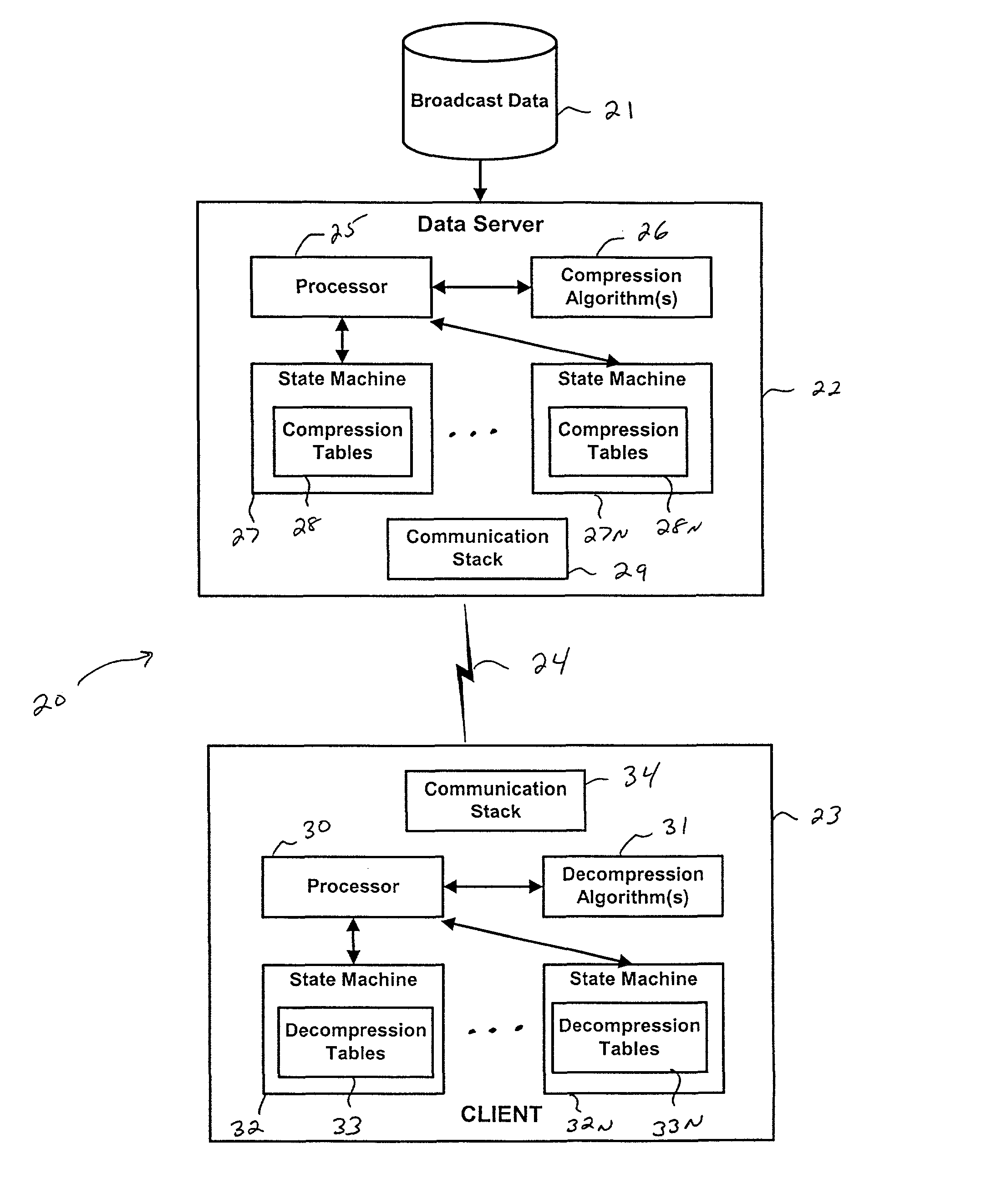
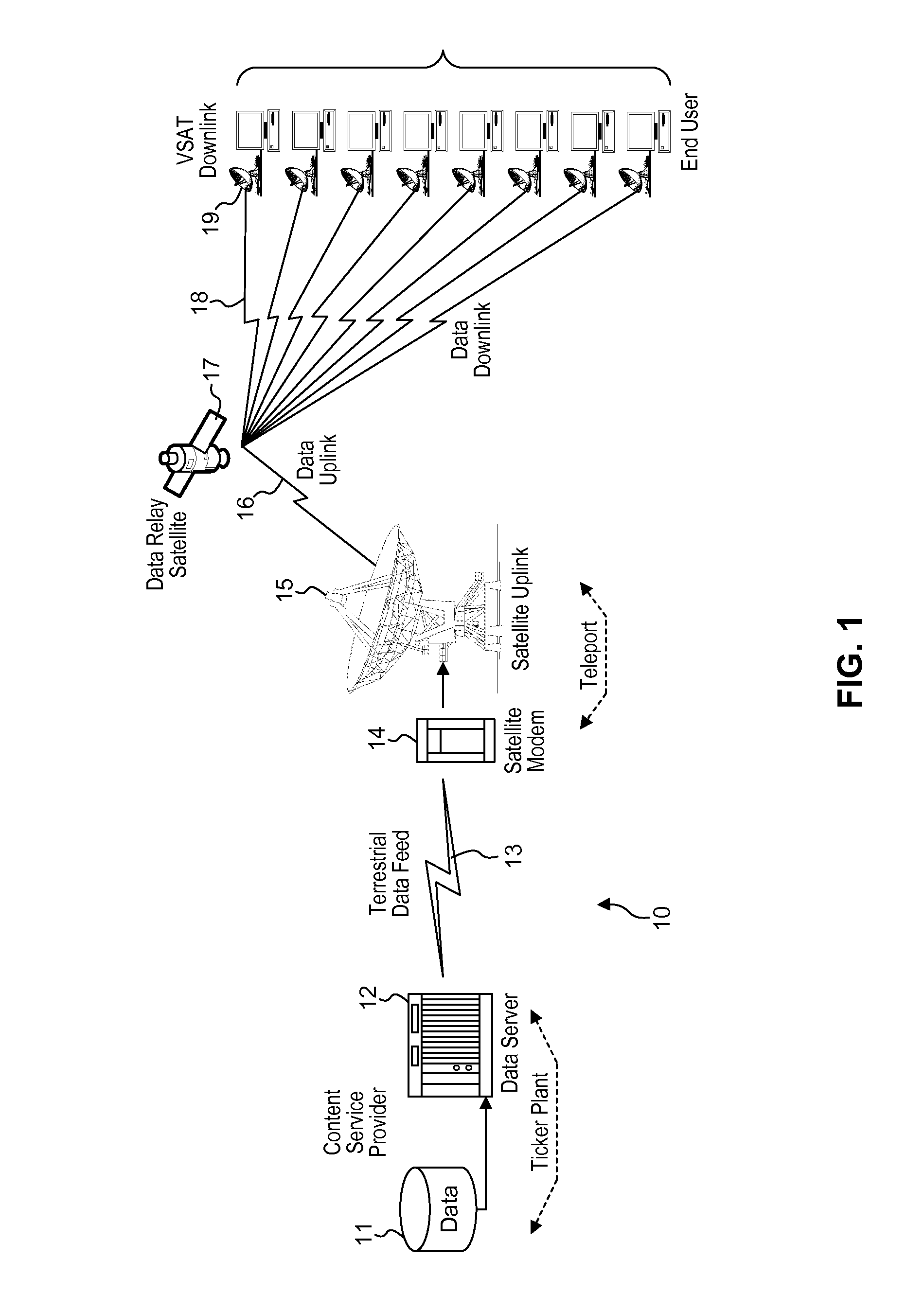
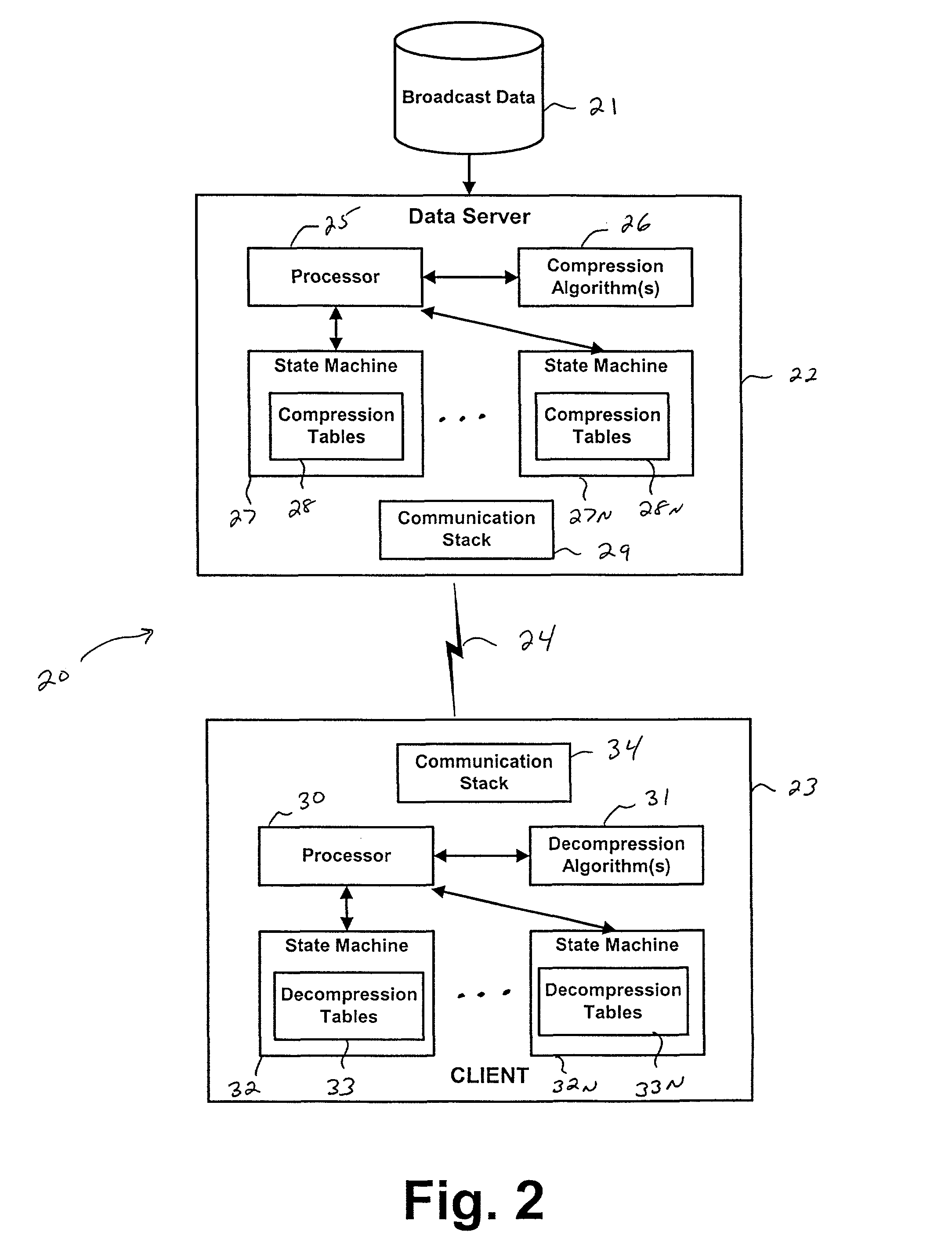
InactiveUS9143546B2Improve communication bandwidthIncrease effective bandwidthSpecial service provision for substationSecure transmissionBroadcast data
Systems and methods for providing accelerated transmission of broadcast data, such as financial data and news feeds, over a communication channel using data compression and decompression to provide secure transmission and transparent multiplication of communication bandwidth, as well as reduce the latency associated with data transmission of conventional systems.
Owner:REALTIME DATA
Dynamic compensation method for three-dimensional laser distance metering data of mobile robot in moving process
The invention provides a dynamic compensation method for three-dimensional laser data in a moving process, and belongs to the technical field of autonomous environmental perception of a mobile robot. The method is mainly characterized in that a three-dimensional laser data acquisition manner in the moving process is improved, and a reasonable data compaction method is adopted to improve algorithm execution efficiency. Therefore, the dynamic compensation method adopts a dynamic data matching method to correct robot position and posture errors caused by a mileage recorder, and improve the accuracy of the three-dimensional laser data obtained in the moving process; on the other hand, a plane extraction method is adopted to filter out disordered laser data, so as to reduce matched laser point quantity, and ensure that the dynamic compensation method can be carried out on-line in real time. The dynamic compensation method can be used in the fields such as structured scene reconstruction of the mobile robot.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Methods and apparatus for reducing storage size
ActiveUS7970216B2Reduce probabilitySave energyCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationGraphicsData stream
Prediction-based compression engines are spoon-fed with sequentially efficiently compressible (SEC) streams of input data that make it possible for the compression engines to more efficiently compress or otherwise compact the incoming data than would be possible with streams of input data accepted on a TV-raster scan basis. Various techniques are disclosed for intentionally forming SEC input data streams. Among these are the tight packing of alike files or fragments into concatenation suitcases and the decomposition of files into substantially predictably consistent (SPC) fragments or segments that are routed to different suitcases according to their type. In a graphics-directed embodiment, image frames are partitioned into segment areas that are internally SPC and multidirectional walks (i.e., U-turning walks) are defined in the segment areas where these defined walks are traced during compression and also during decompression. A variety of pre-compression data transformation methods are disclosed for causing apparently random data sequences to appear more compressibly alike to each other. The methods are usable in systems that permit substantially longer times for data compaction operations than for data decompaction operations.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
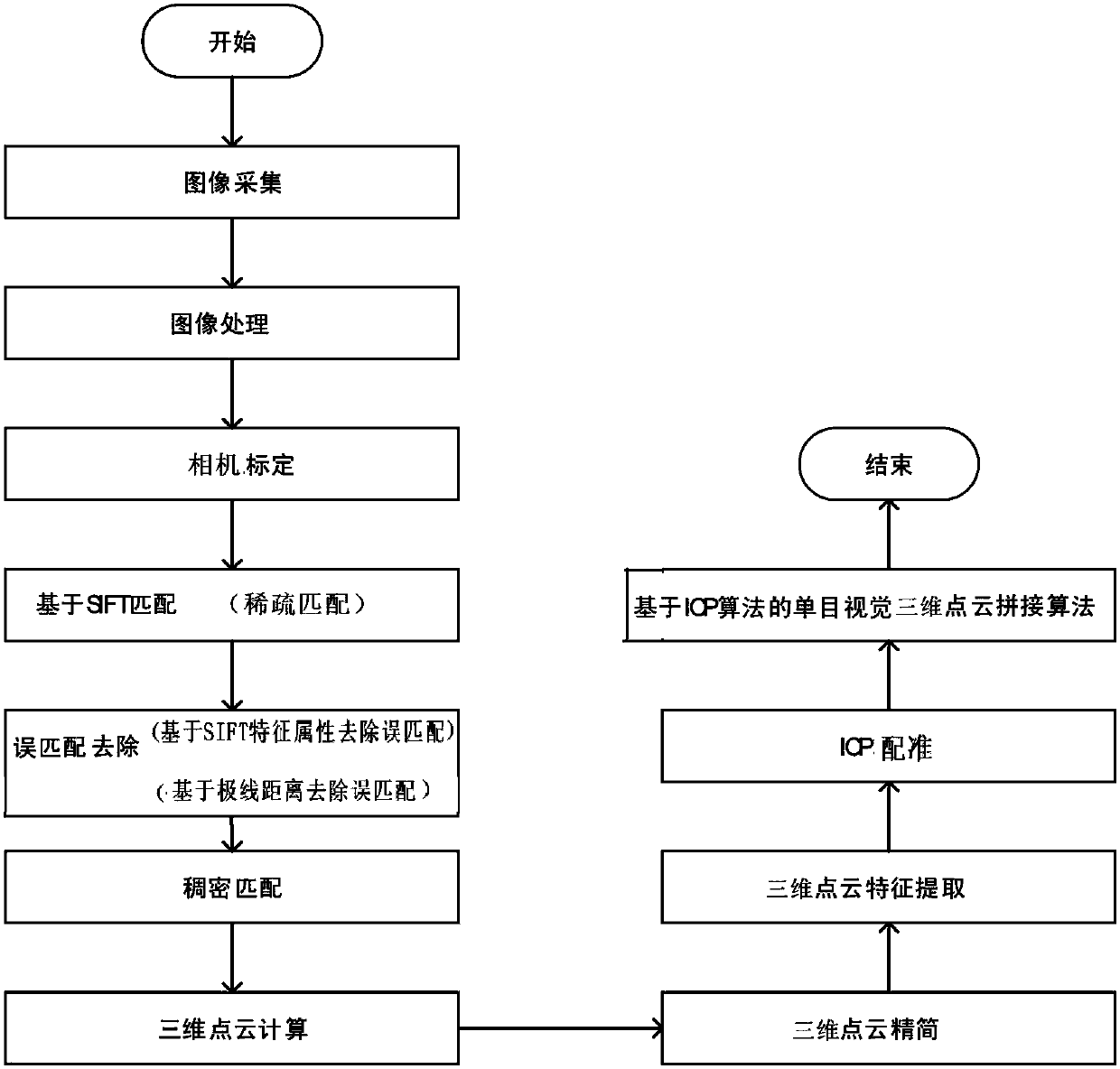
Method and system for generation of three-dimensional panoramic image based on zooming stereoscopic vision
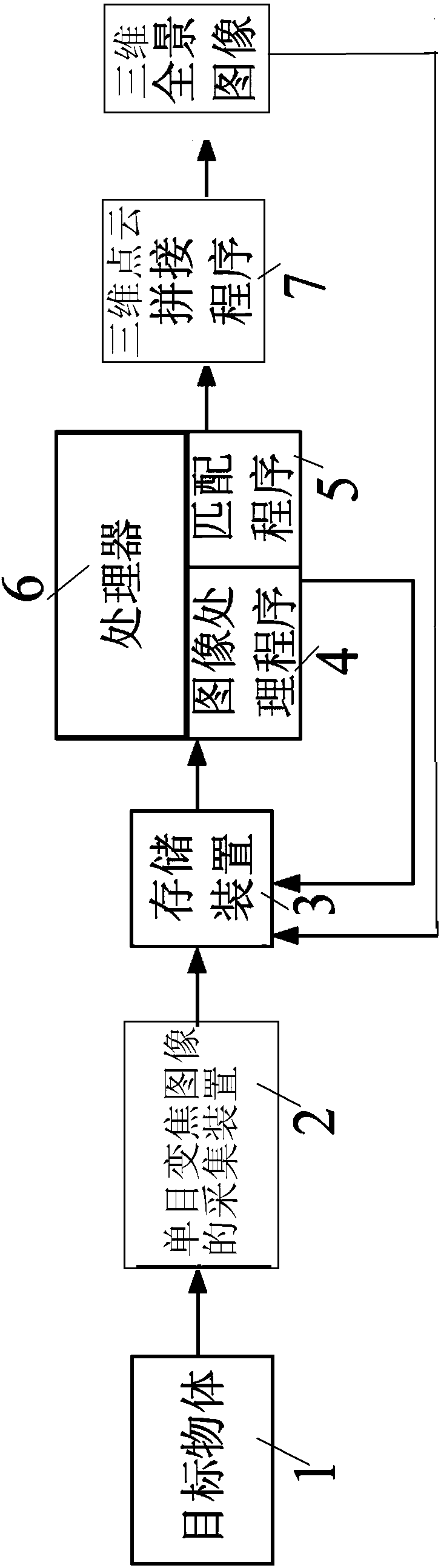
ActiveCN107833181AHow to break the shooting angle can not meet the demandSimple hardware compositionImage enhancementImage analysisVisual perceptionImage based
The present invention provides a method and a system for generation of a three-dimensional panoramic image based on zooming stereoscopic vision. The method employs two-dimensional images shot in different focal lengths to perform accurate image processing and analysis, employs an algorithm to calculate three-dimensional point cloud data of the image and performs point cloud data compaction, registration and splicing to finally generate a three-dimensional panoramic image. The system comprises two portions consisting of hardware and software, wherein the hardware comprises a monocular zooming image collection device, a storage device and a processor, and the software portion comprises an image processing program, a matching program and a splicing program. The implementation method can perform camera calibration, and a point cloud splicing method capable of graying, image enhancement, image feature extraction, dense matching, three-dimensional point cloud calculation, three-dimensional monocular vision can perform three-dimensional reconstruction of the image; and moreover, a mode is broken that a traditional camera shooting angle cannot satisfy demands, and the method and the systemfor generation of the three-dimensional panoramic image based on zooming stereoscopic vision can perform omnibearing appearance of basic construction of a target object.
Owner:SHENYANG LIGONG UNIV
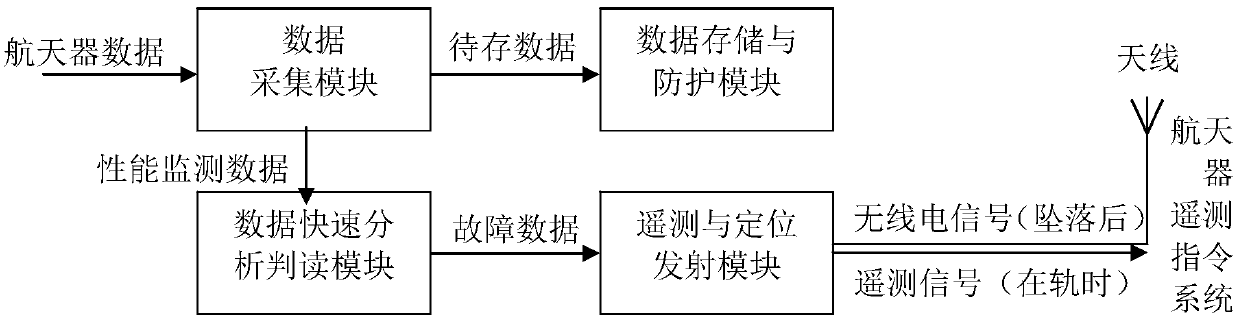
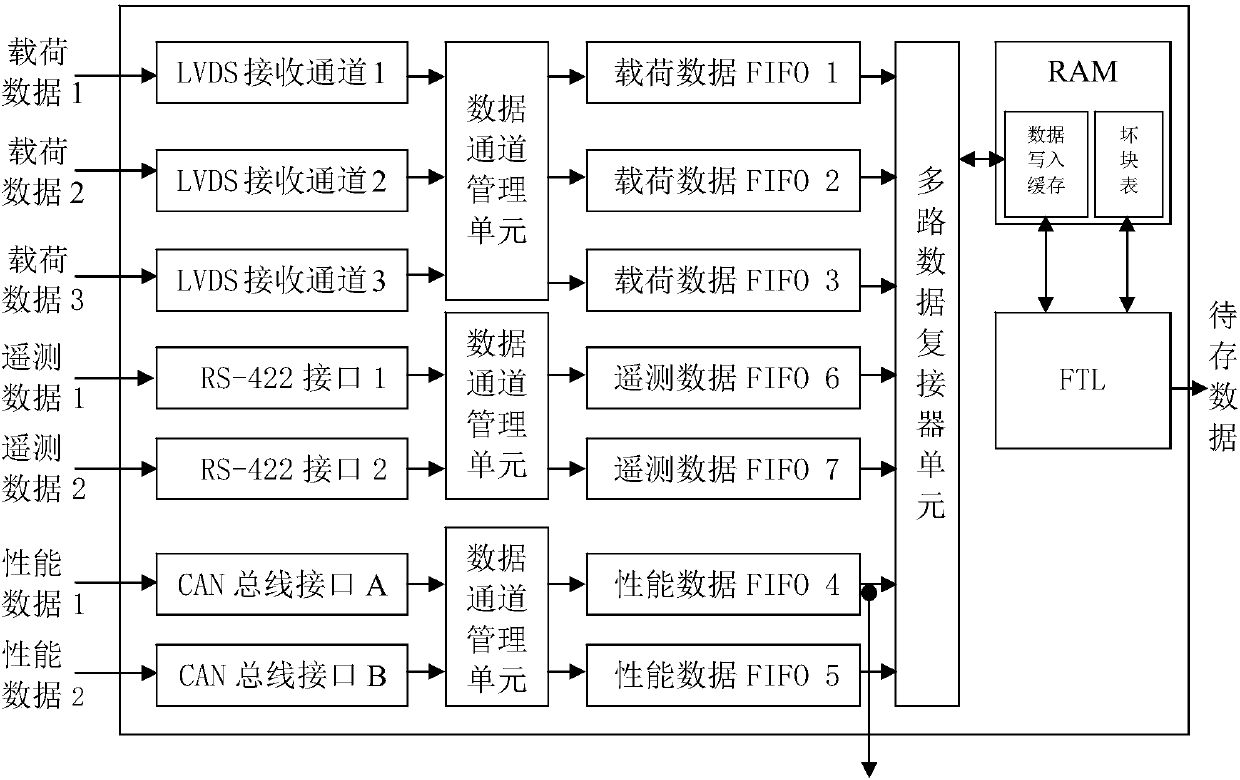
Flight data analytic recording device, system and method for spacecraft
PendingCN107945314AMonitoring statusAssess your healthRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesTotal factory controlData compressionData acquisition
The invention provides a flight data analytic recording device, system and method for a spacecraft. The flight data analytic recording device is mounted in the spacecraft and comprises a data acquisition module, a data storage and protection module, a rapid data analysis and interpretation module and a telemetering and location transmitting module, wherein the data acquisition module acquires multiple spacecraft data, sends the to-be-stored data to the data storage and protection module, and sends performance monitoring data to the rapid data analysis and interpretation module; the data storage and protection module compresses and stores the to-be-stored data; the rapid data analysis and interpretation module quickly interprets the performance monitoring data on line and outputs failure data to the telemetering and location transmitting module; and the telemetering and location transmitting module downloads the failure data and is simultaneously used for transmitting an emergency locating signal after the spacecraft is in contact with the ground. The on-orbit state of the spacecraft can be monitored, failures can be diagnosed, data are downloaded to the ground, and the state of thespacecraft can be analyzed when the spacecraft falls on Earth.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
Large thin-walled component complex curved surface mirroring processing method
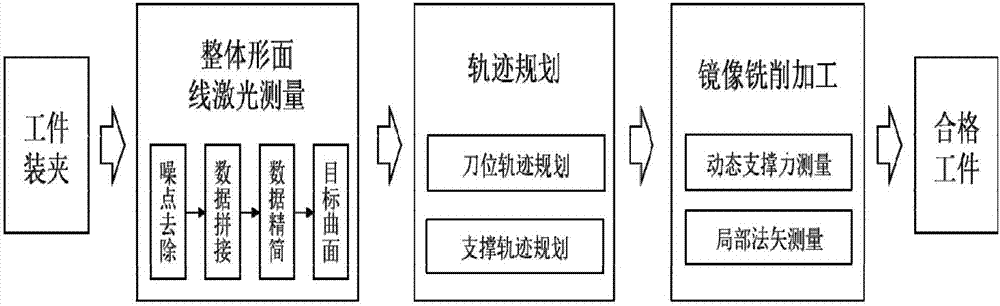
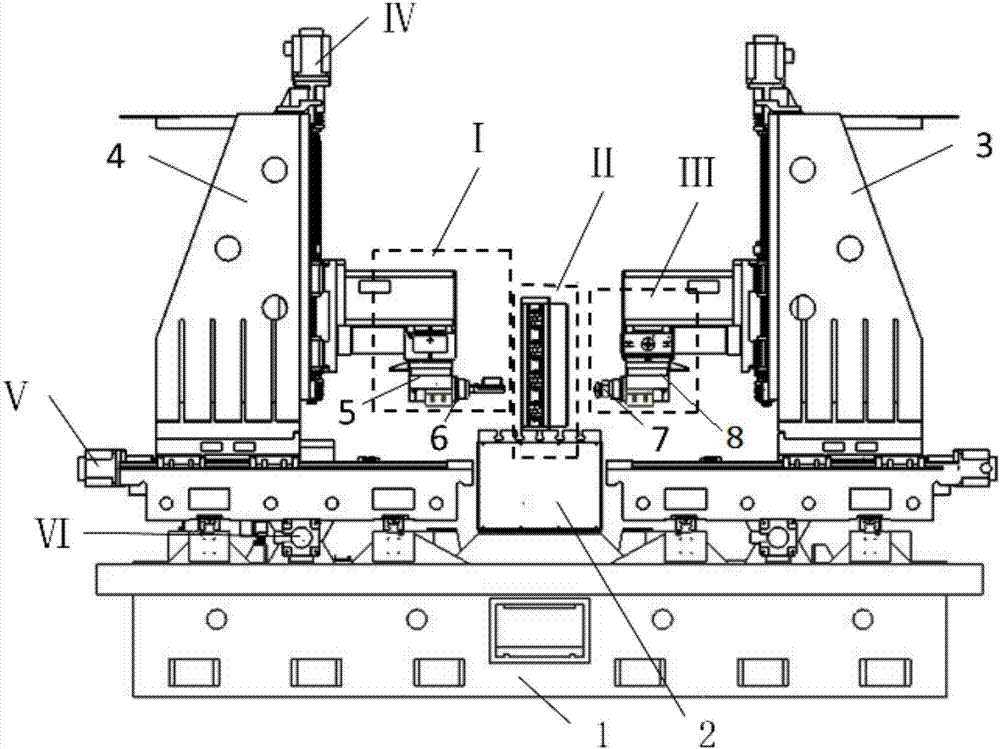
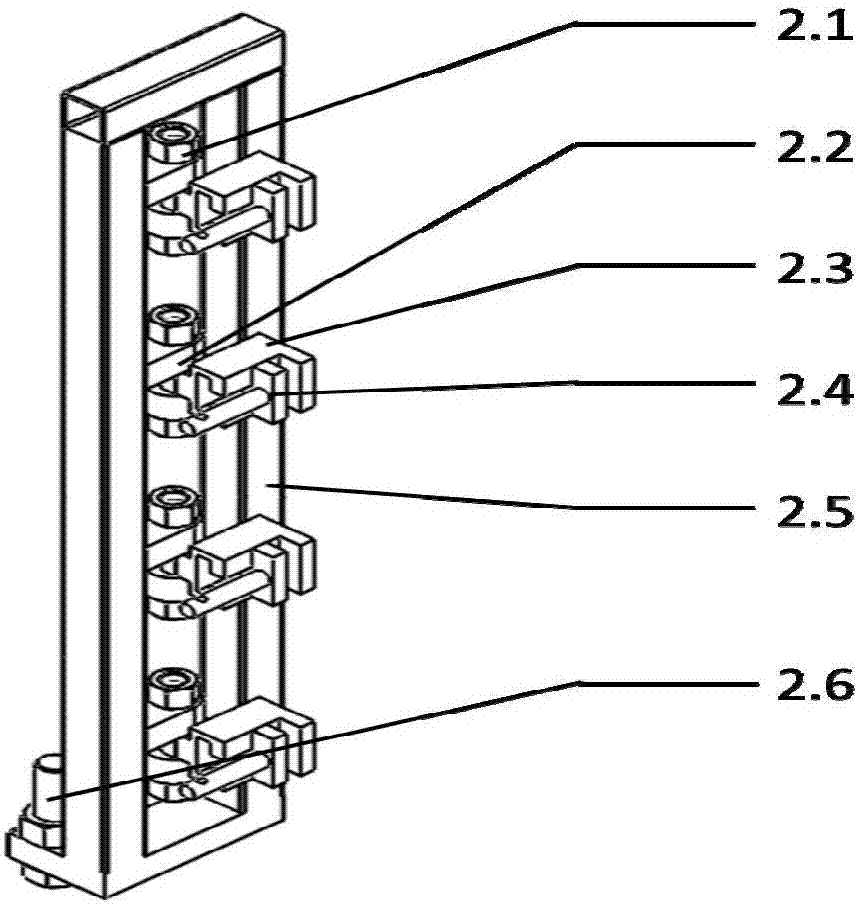
ActiveCN107976955AGuaranteed mirror relationshipGuaranteed measurement - mirror image processingNumerical controlLaser sensorSuperficial mass
The invention relates to a large thin-walled component complex curved surface mirroring processing method, and belongs to the technical field of large thin-walled component processing, and especiallyrelates to a large thin-walled component complex curved surface mirroring processing method. An employed processing device is laid in a bilaterally symmetrical structure, the specially-produced processing device is employed to carry out measuring and mirroring processing, a line laser sensor is employed to measure a workpiece, a current vortex sensor is employed to measure displacement with respect to the workpiece surface, and a piezoelectric transducer is employed to measure the value of a support force. Noise removal, data compaction, data splicing are carried out on measured data, and a target curved surface is generated. Processing path planning and support path planning are carried out, a local normal vector and a dynamic support force are measured, and mirroring milling is carried out. According to the invention, after once clamping installation, measuring and mirroring processing can be carried out on the thin-walled component, and the large thin-walled component complex curvedsurface mirroring processing method is good in measuring real-time performance, high in accuracy and convenient to use. Accurate milling of thin-walled components can be achieved, the processing precision is high, and the surface quality is high after processing.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Automatic compressing/decompressing file system and its compressing algorithm
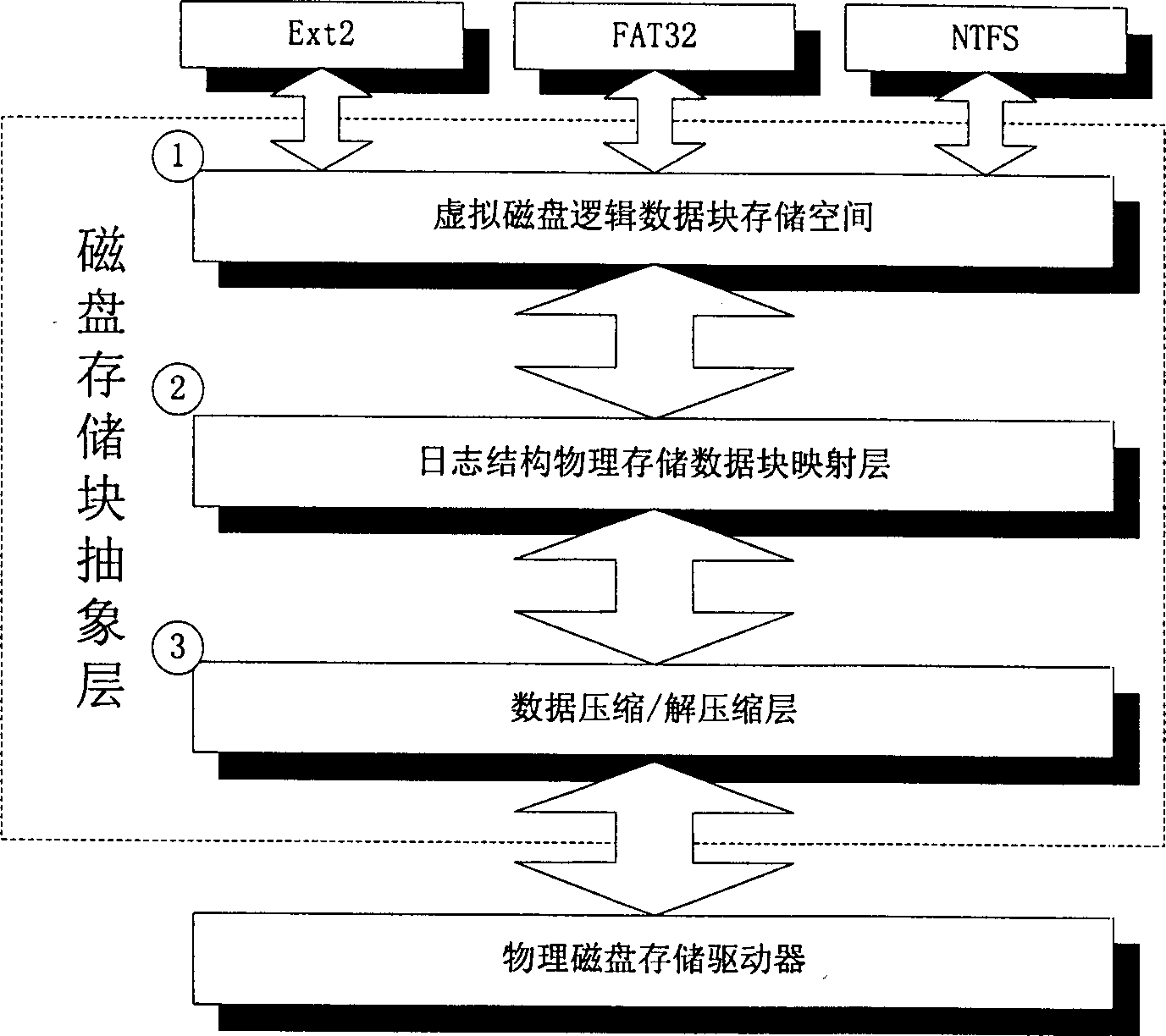
InactiveCN1425986AInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFile systemComputer module
The automatic compressing / decompressing file system and its compressing algorithm features that one magnetic disc storage block abstract layer integrated to physical memory hardware is added into common file system and physical memory of storing compressed data to separate common file system from compressed disc data and support multiple file system modules. The magnetic disc storage block abstract layer contains virtual disc logic data block storing space, long structure physical storing data block mapping layer and data compressing / decompressing layer. In the system data compressing algorithm, each new character is created with two characters available in dictionary. The present invention is especially suitable for embedded system and can raise greatly the utilization of embedded equipment resource, especially memory resource, and improve its performance.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methods and apparatus for reducing storage size
ActiveUS7961960B2Reduce probabilitySave energyDigital data information retrievalCode conversionGraphicsData stream
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
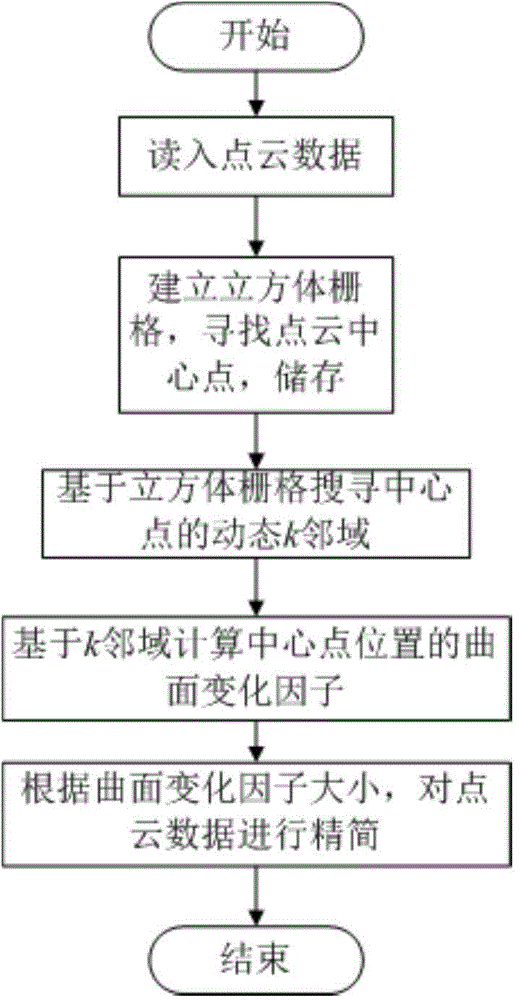
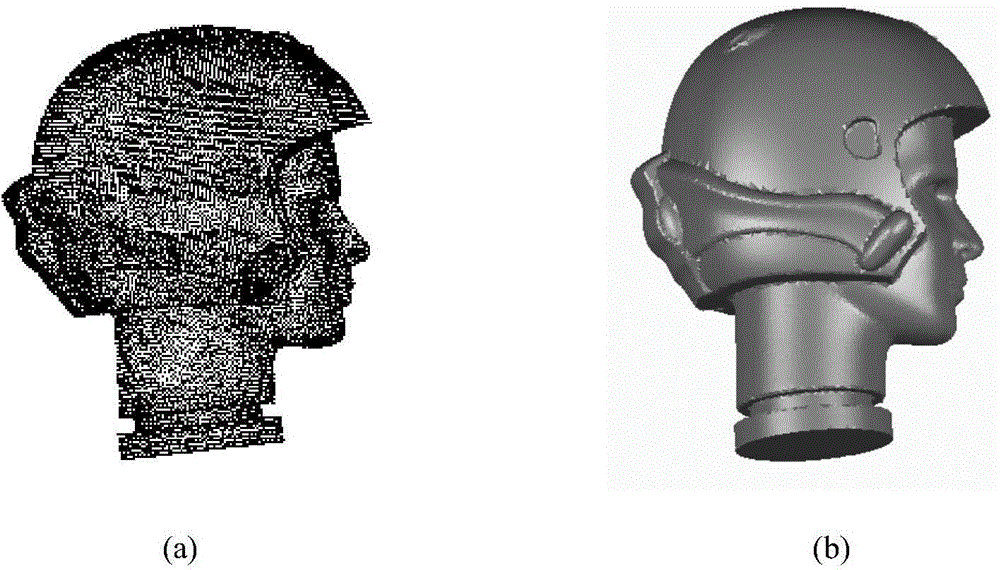
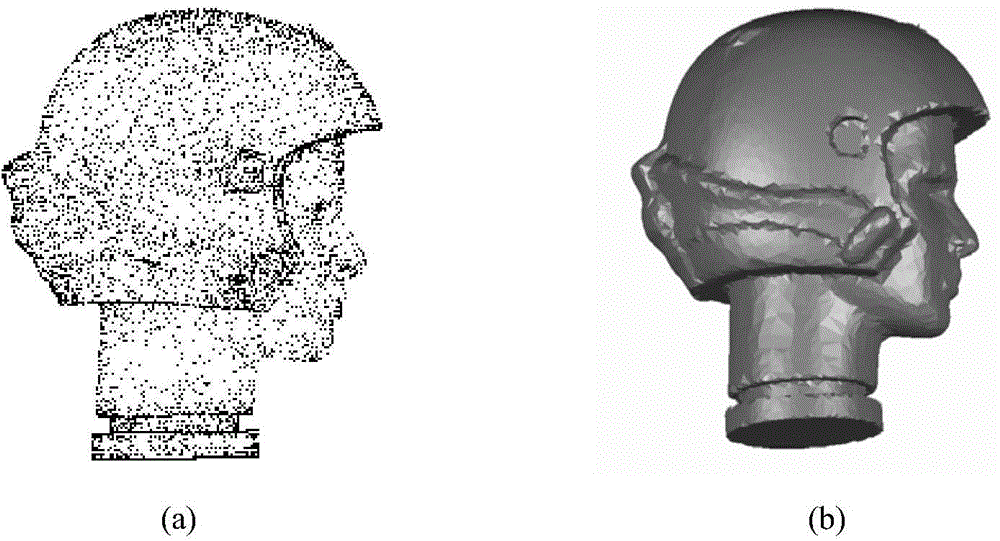
Local curved surface change factor based scattered point cloud data compaction processing method
InactiveCN104616349AImprove search efficiencyOvercoming the results of reduced efficiencyImage generation3D modellingFactor basePoint cloud
The invention discloses a local curved surface change factor based scattered point cloud data compaction processing method. The local curved surface change factor based scattered point cloud data compaction processing method comprises the steps of 1 reading measured point cloud data, 2 calculating a central point of a point cloud, 3 searching dynamic K neighborhood points of the central point based on cubic grids and accordingly establishing the topological relation of scattered point cloud, 4 adopting a variance component method to calculate curved surface change factors of a k neighborhood of the central point, 5 determining the compaction rate of each cubic grid in the k neighborhood of the central point and performing even compaction in within a k neighborhood range. The topological relation of the scattered point cloud is established by establishing the dynamic K neighborhood point information of the scattered point cloud. Complicated curvature calculation is replaced by the curved surface change factors. The compaction ratio is adjusted according to the curved surface change factors Xi, even compaction within the k neighborhood range is achieved, the detail characteristic of high curvature can be protected, and planar characteristic of low curvature is also protected when the compaction degree is high. Point cloud data processing and curved surface reconstruction efficiency and accuracy are improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Methods and apparatus for reducing storage size
Prediction-based compression engines are spoon-fed with sequentially efficiently compressible (SEC) streams of input data that make it possible for the compression engines to more efficiently compress or otherwise compact the incoming data than would be possible with streams of input data accepted on a TV-raster scan basis. Various techniques are disclosed for intentionally forming SEC input data streams. Among these are the tight packing of alike files or fragments into concatenation suitcases and the decomposition of files into substantially predictably consistent (SPC) fragments or segments that are routed to different suitcases according to their type. In a graphics-directed embodiment, image frames are partitioned into segment areas that are internally SPC and multidirectional walks (i.e., U-turning walks) are defined in the segment areas where these defined walks are traced during compression and also during decompression. A variety of pre-compression data transformation methods are disclosed for causing apparently random data sequences to appear more compressibly alike to each other. The methods are usable in systems that permit substantially longer times for data compaction operations than for data decompaction operations.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Methods and apparatus for reducing storage size
ActiveUS7961959B2Reduce probabilitySave energyCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingGraphicsData stream
Prediction-based compression engines are spoon-fed with sequentially efficiently compressible (SEC) streams of input data that make it possible for the compression engines to more efficiently compress or otherwise compact the incoming data than would be possible with streams of input data accepted on a TV-raster scan basis. Various techniques are disclosed for intentionally forming SEC input data streams. Among these are the tight packing of alike files or fragments into concatenation suitcases and the decomposition of files into substantially predictably consistent (SPC) fragments or segments that are routed to different suitcases according to their type. In a graphics-directed embodiment, image frames are partitioned into segment areas that are internally SPC and multidirectional walks (i.e., U-turning walks) are defined in the segment areas where these defined walks are traced during compression and also during decompression. A variety of pre-compression data transformation methods are disclosed for causing apparently random data sequences to appear more compressibly alike to each other. The methods are usable in systems that permit substantially longer times for data compaction operations than for data decompaction operations.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com