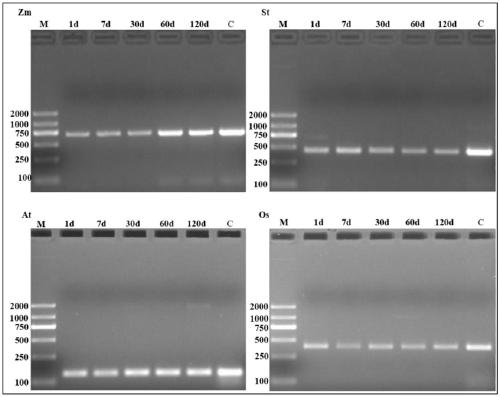
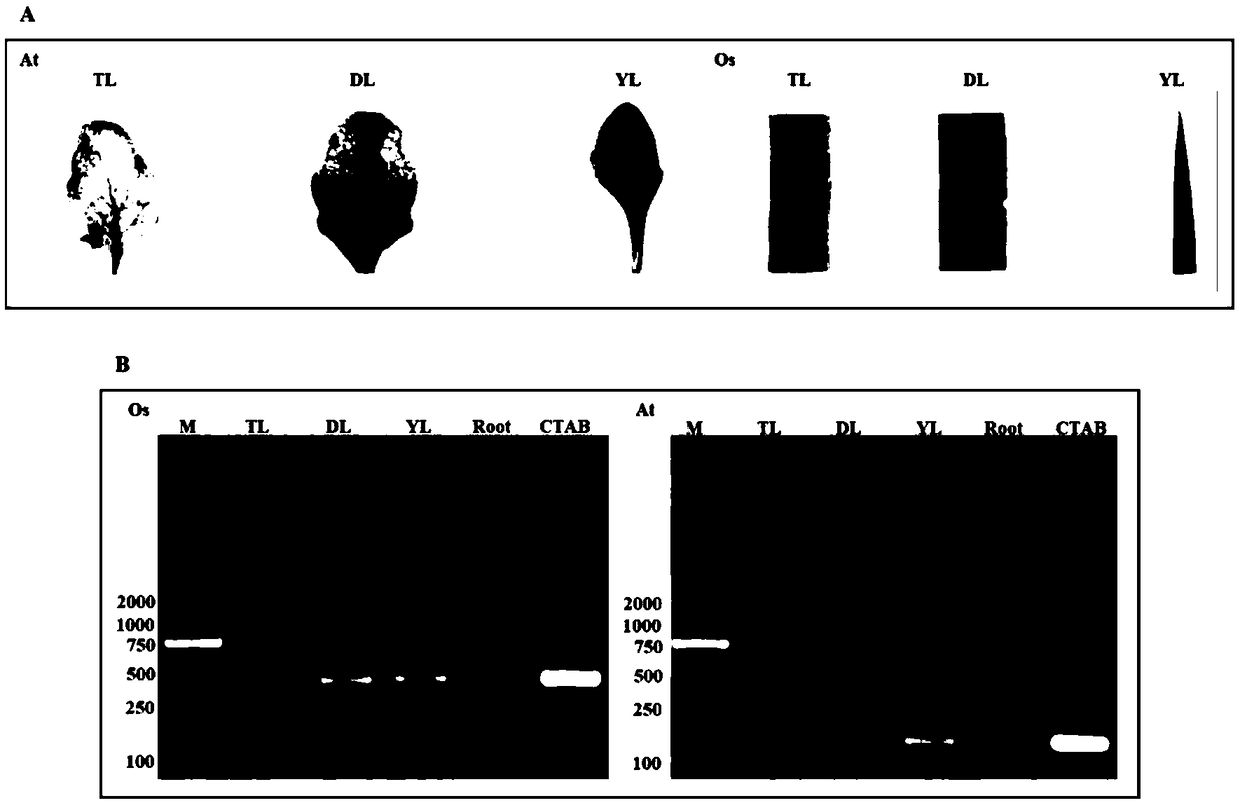
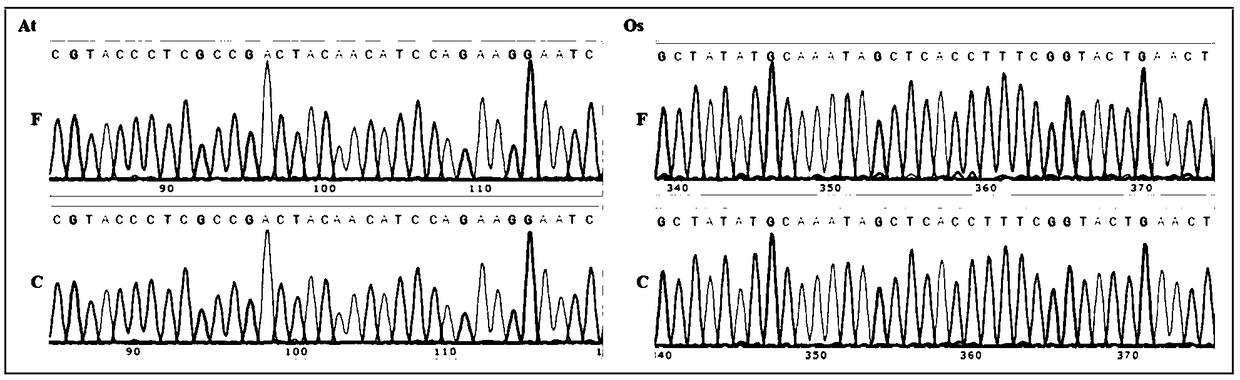
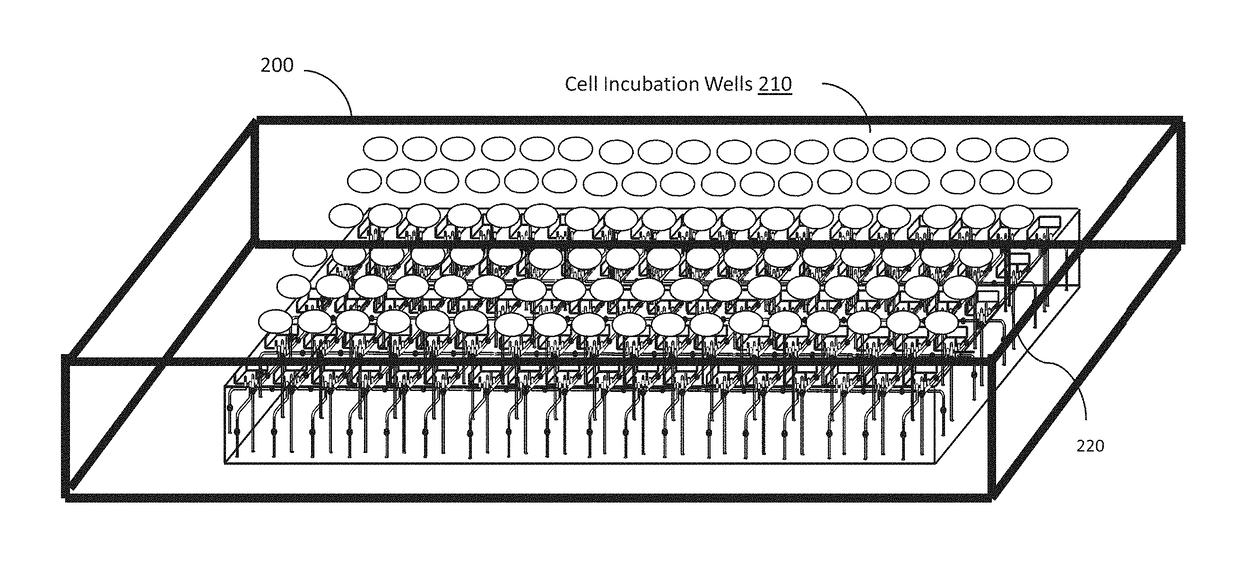
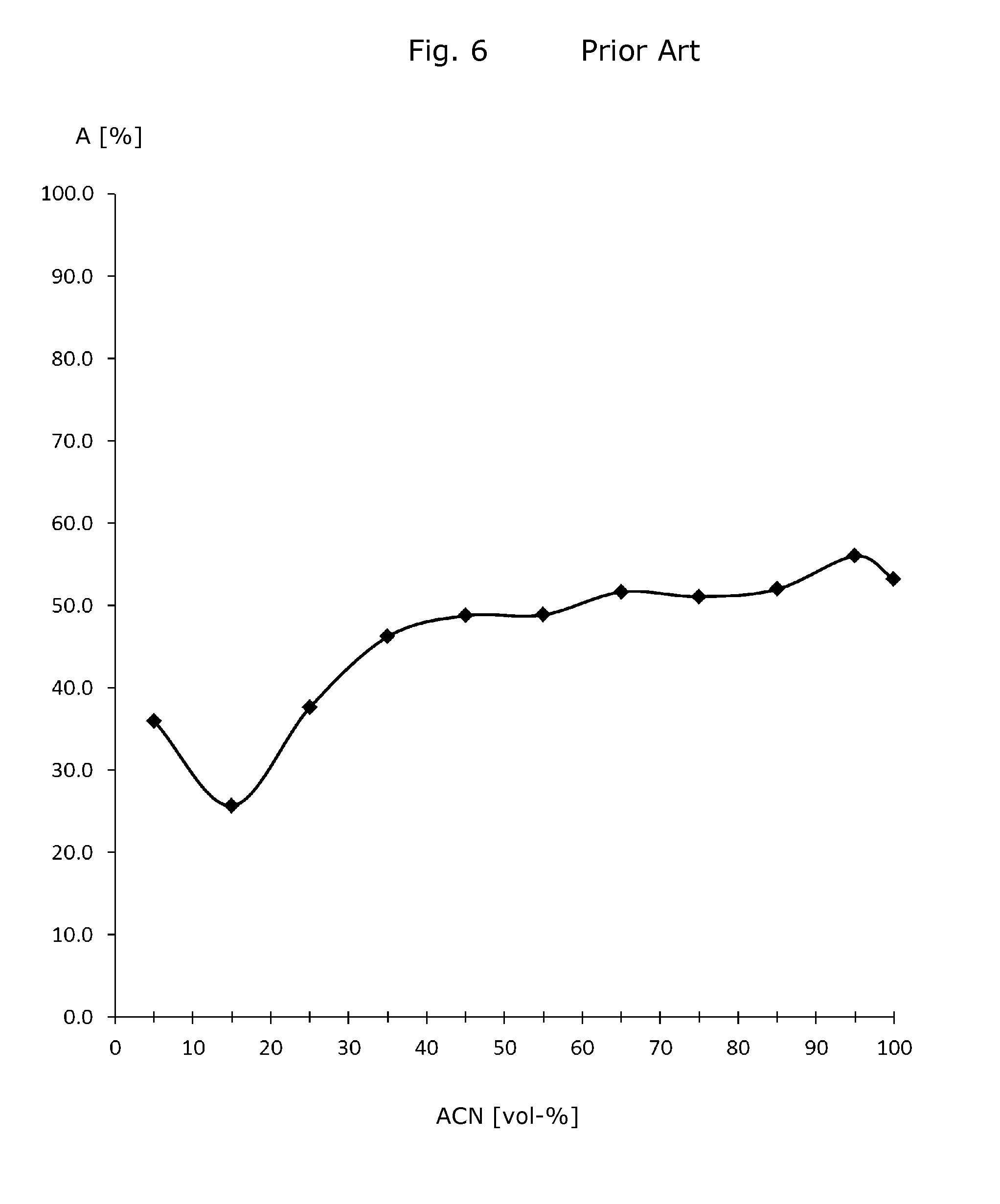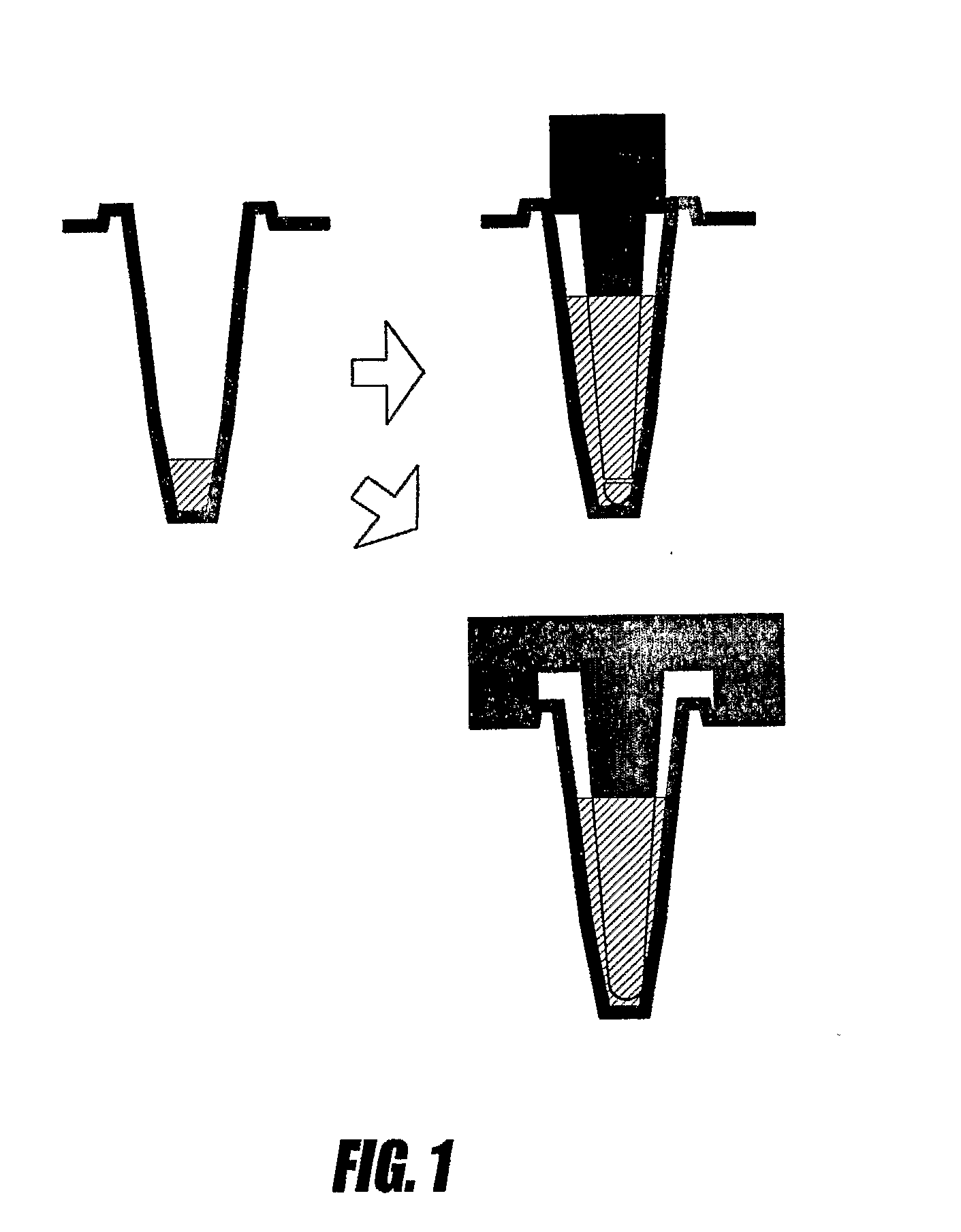Patents
Literature
31 results about "Microplate Well" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Any of the individual wells on a microwell plate.
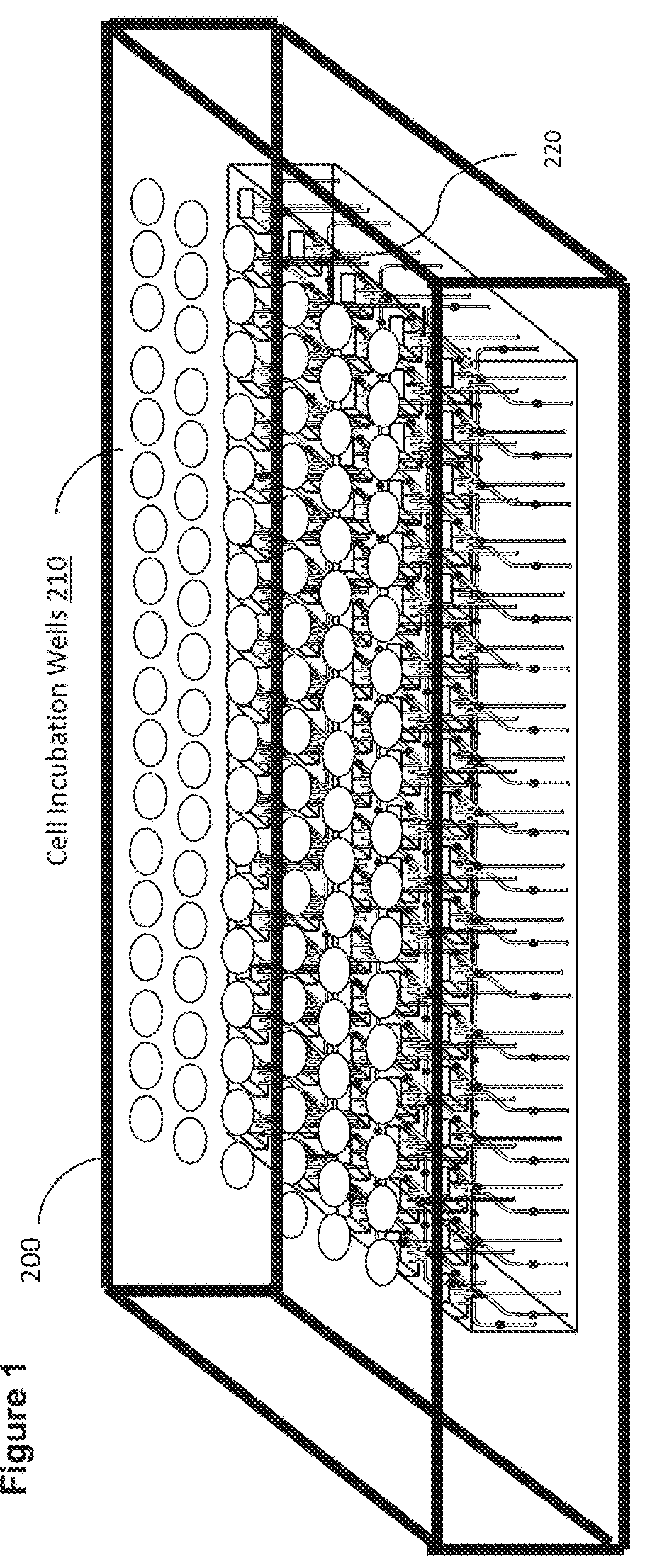
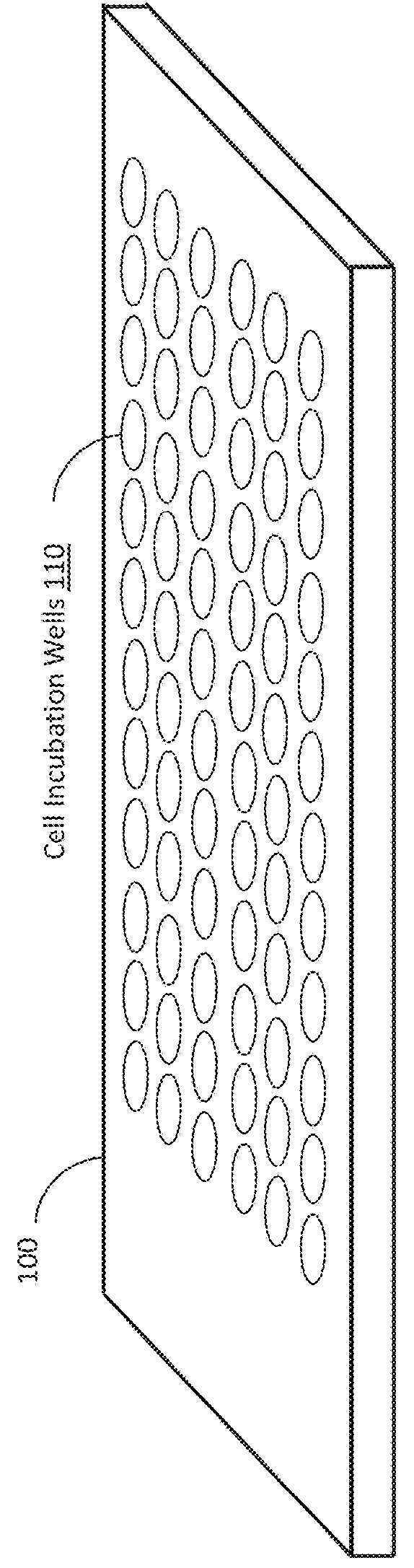
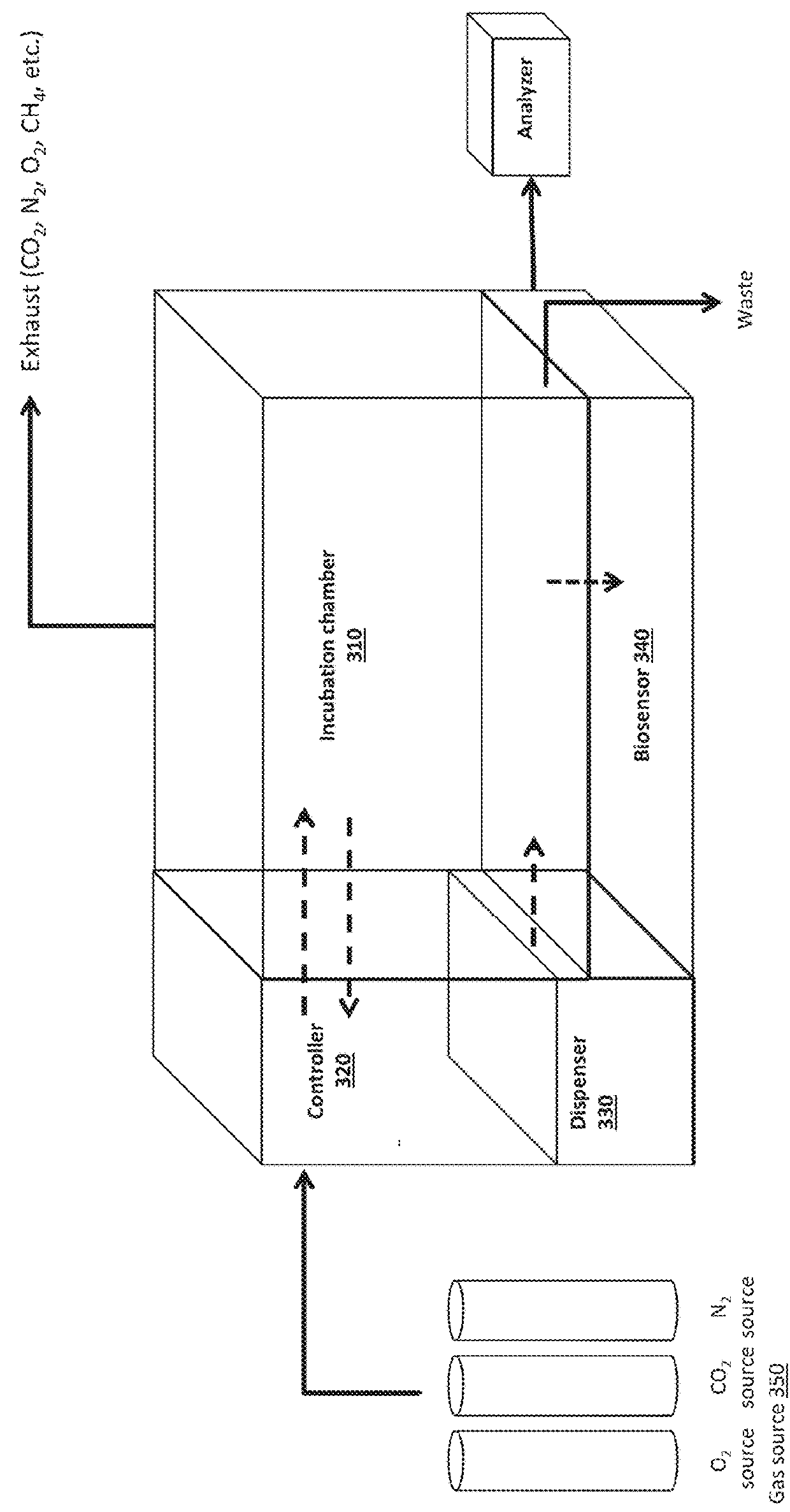
Cell Incubator and Cellular Culture Laboratory Test bed
InactiveUS20140273191A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLaboratory testLaboratory facility
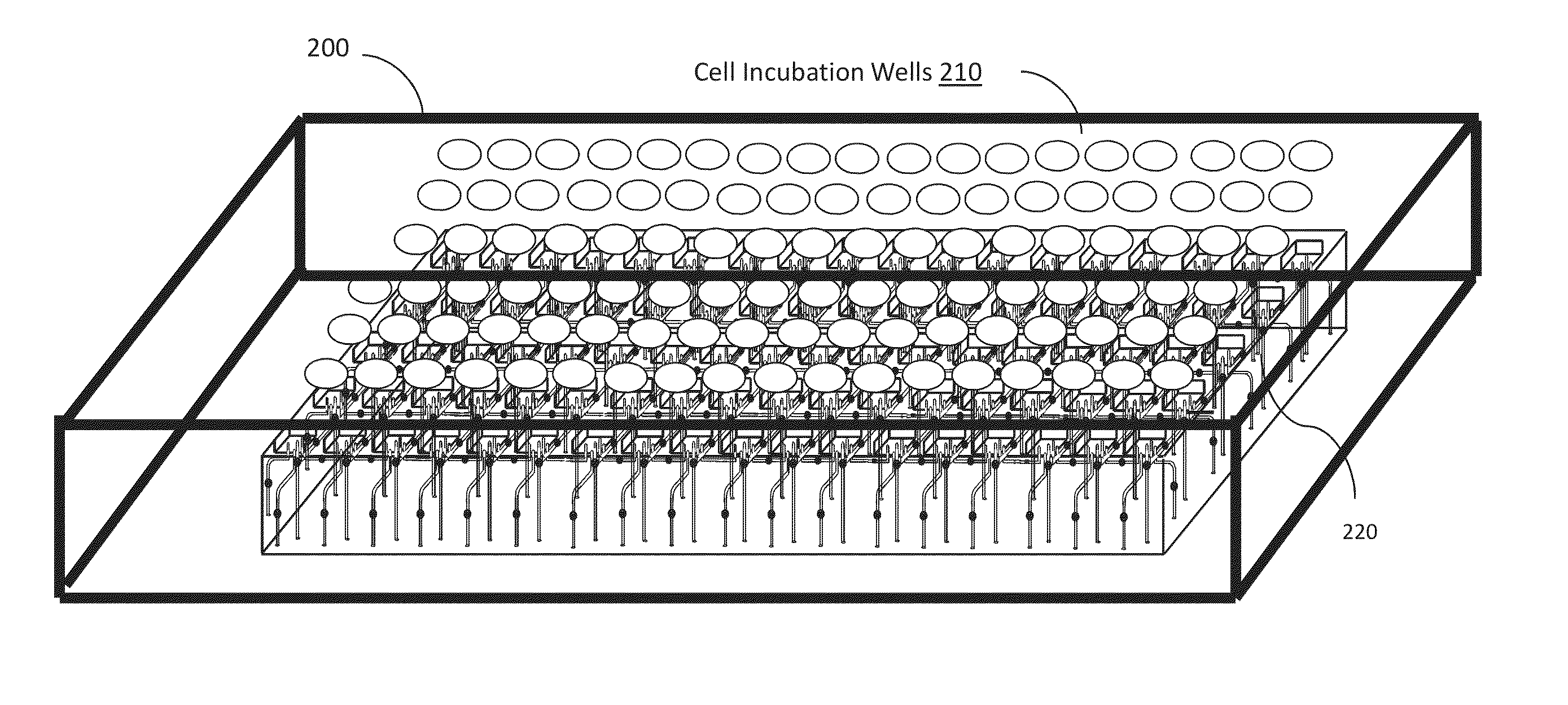
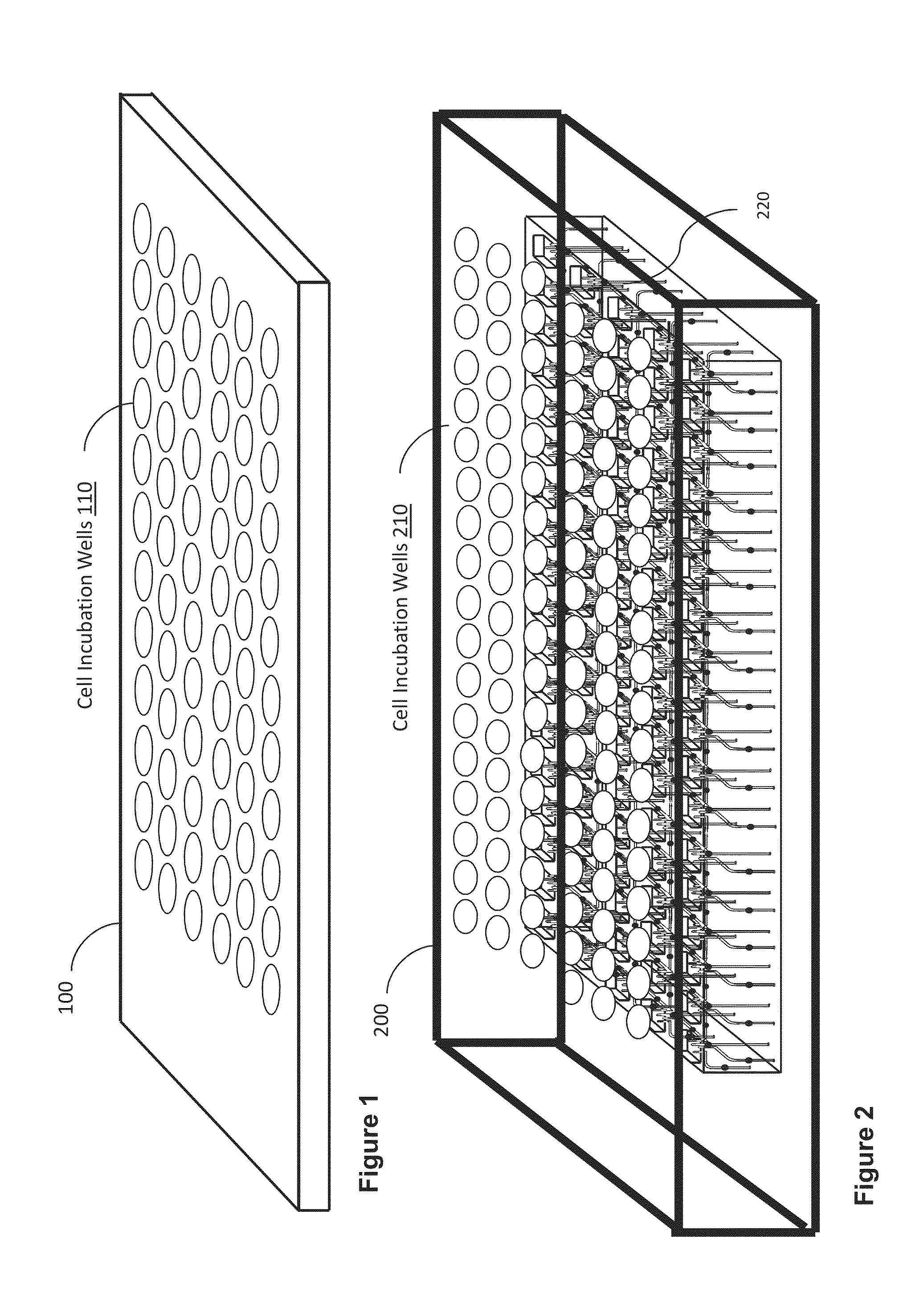
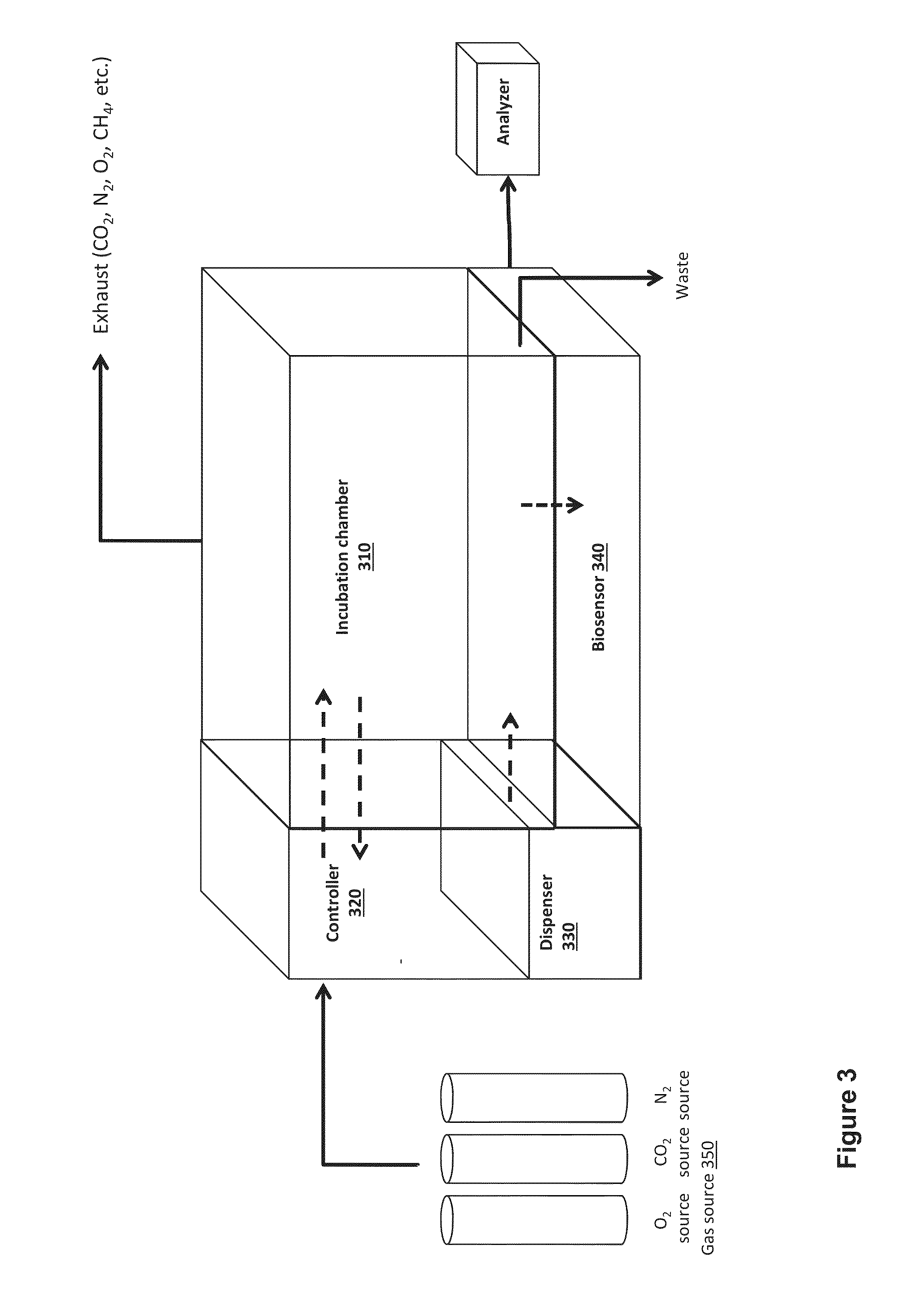
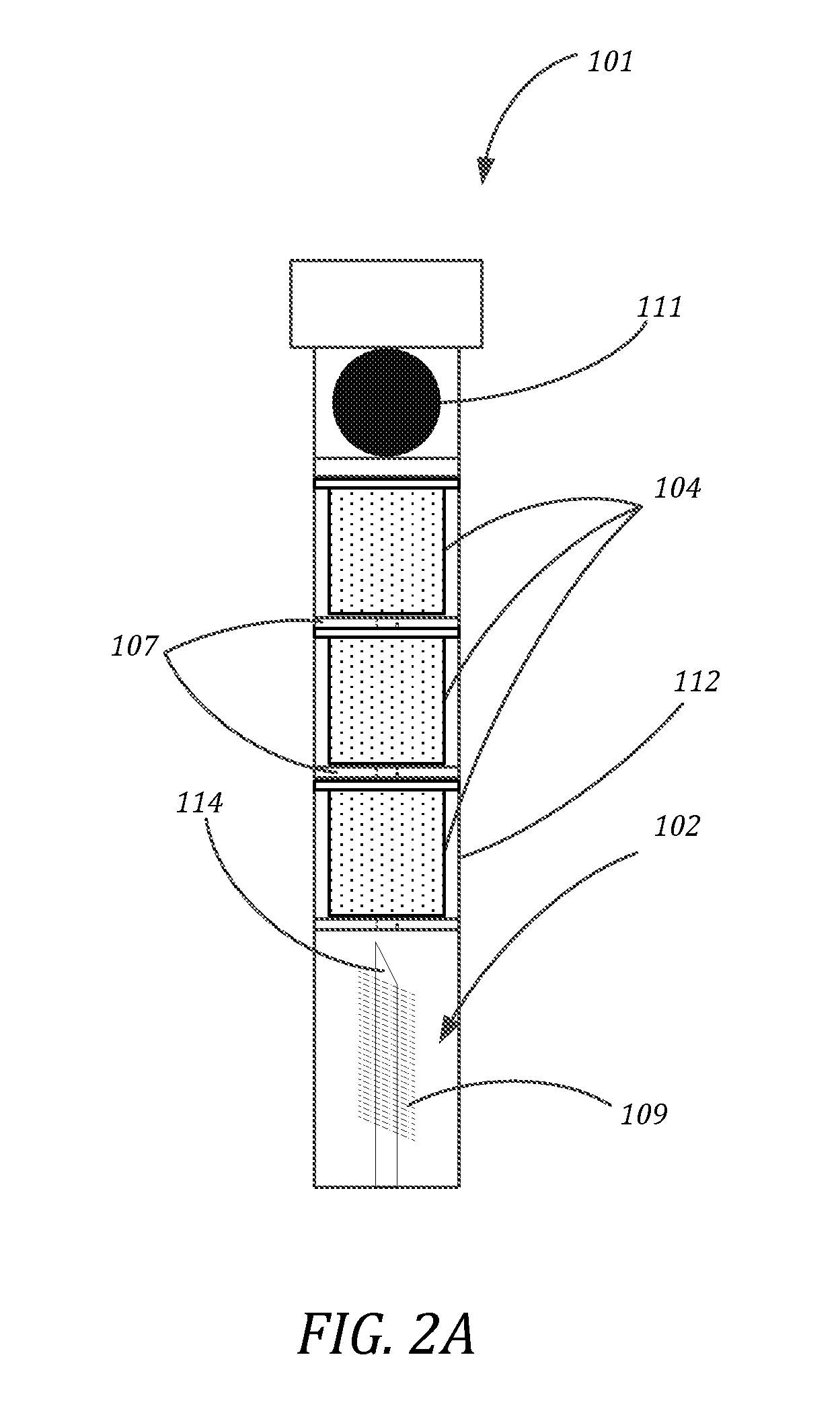
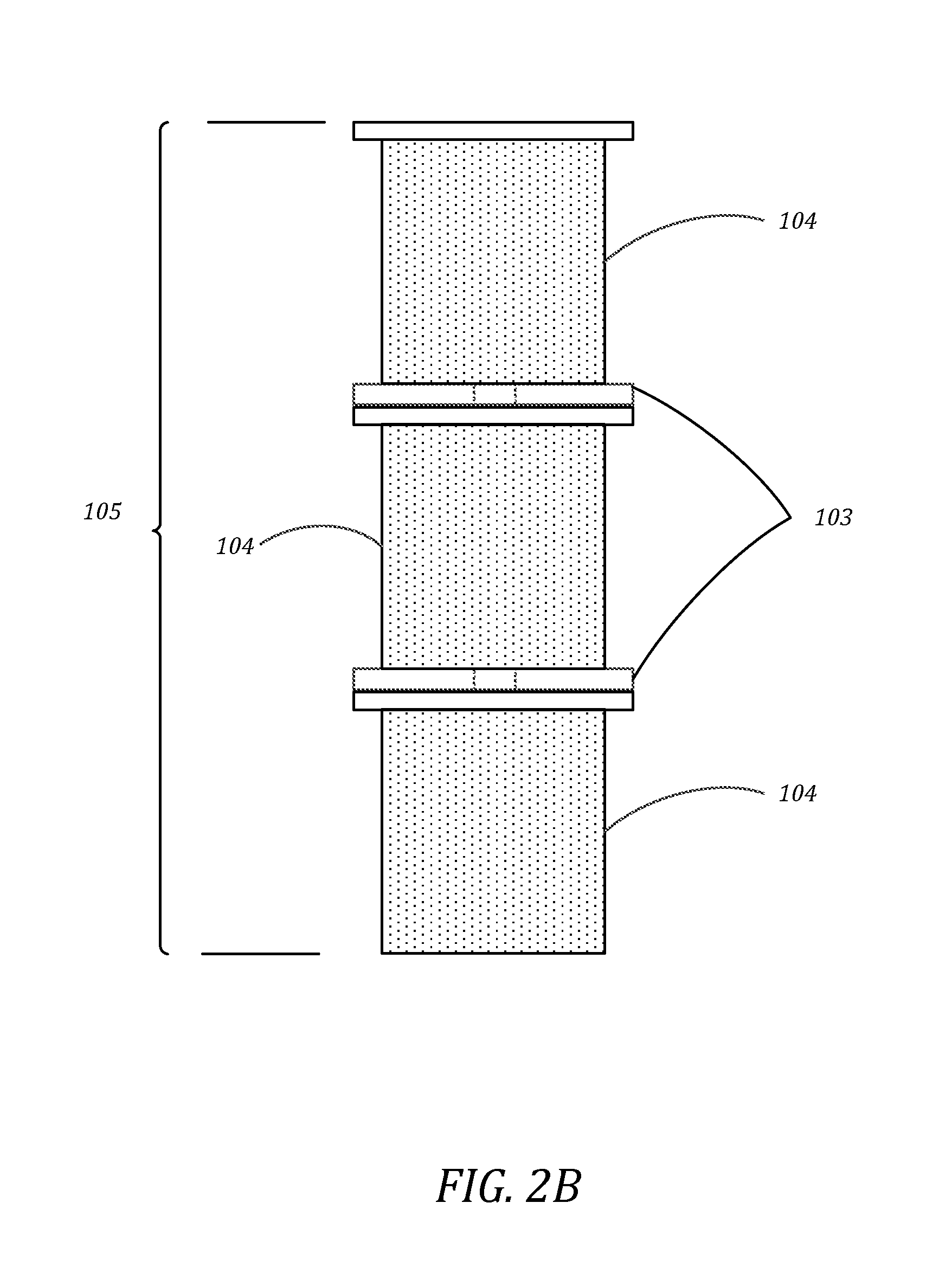
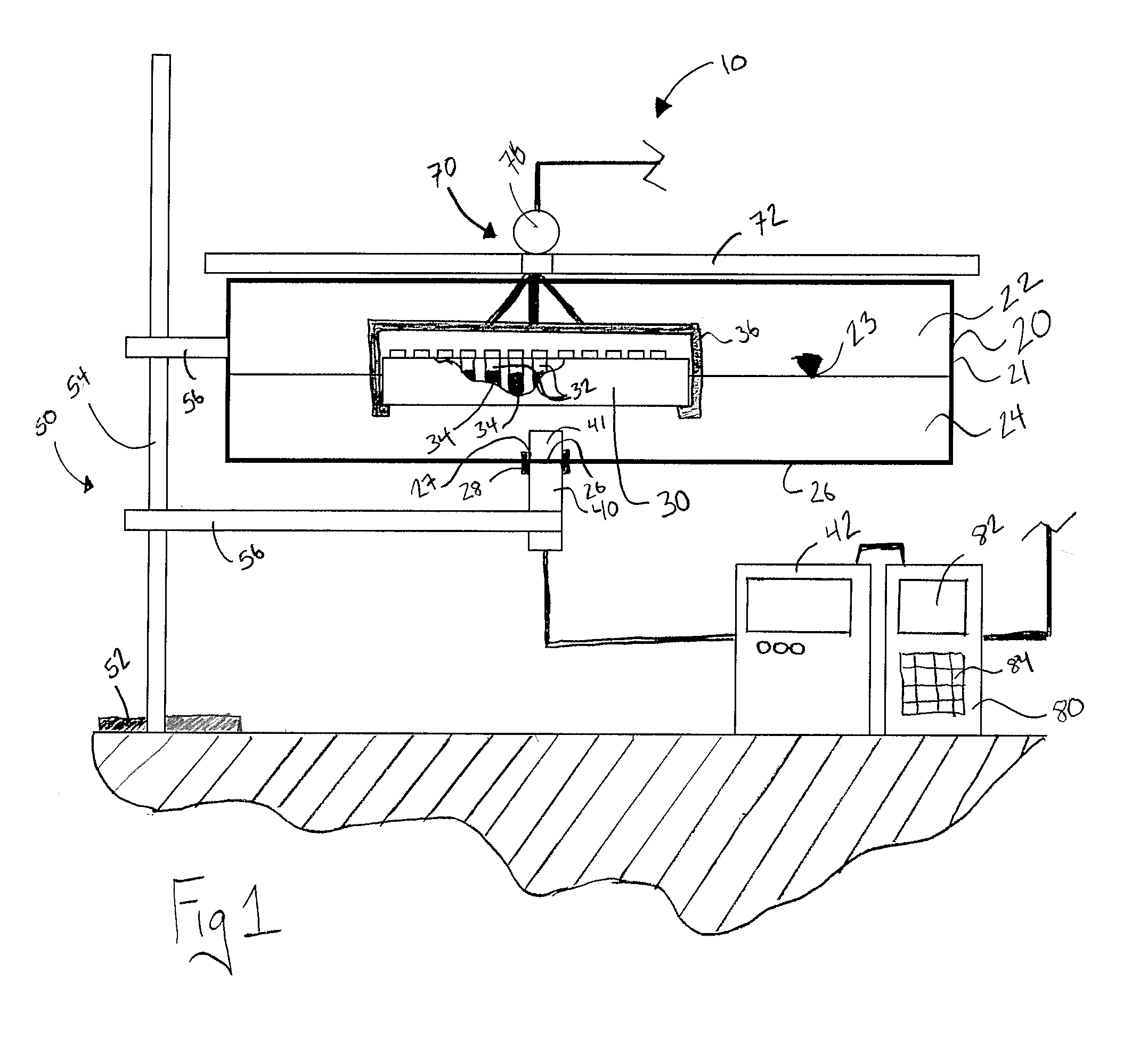
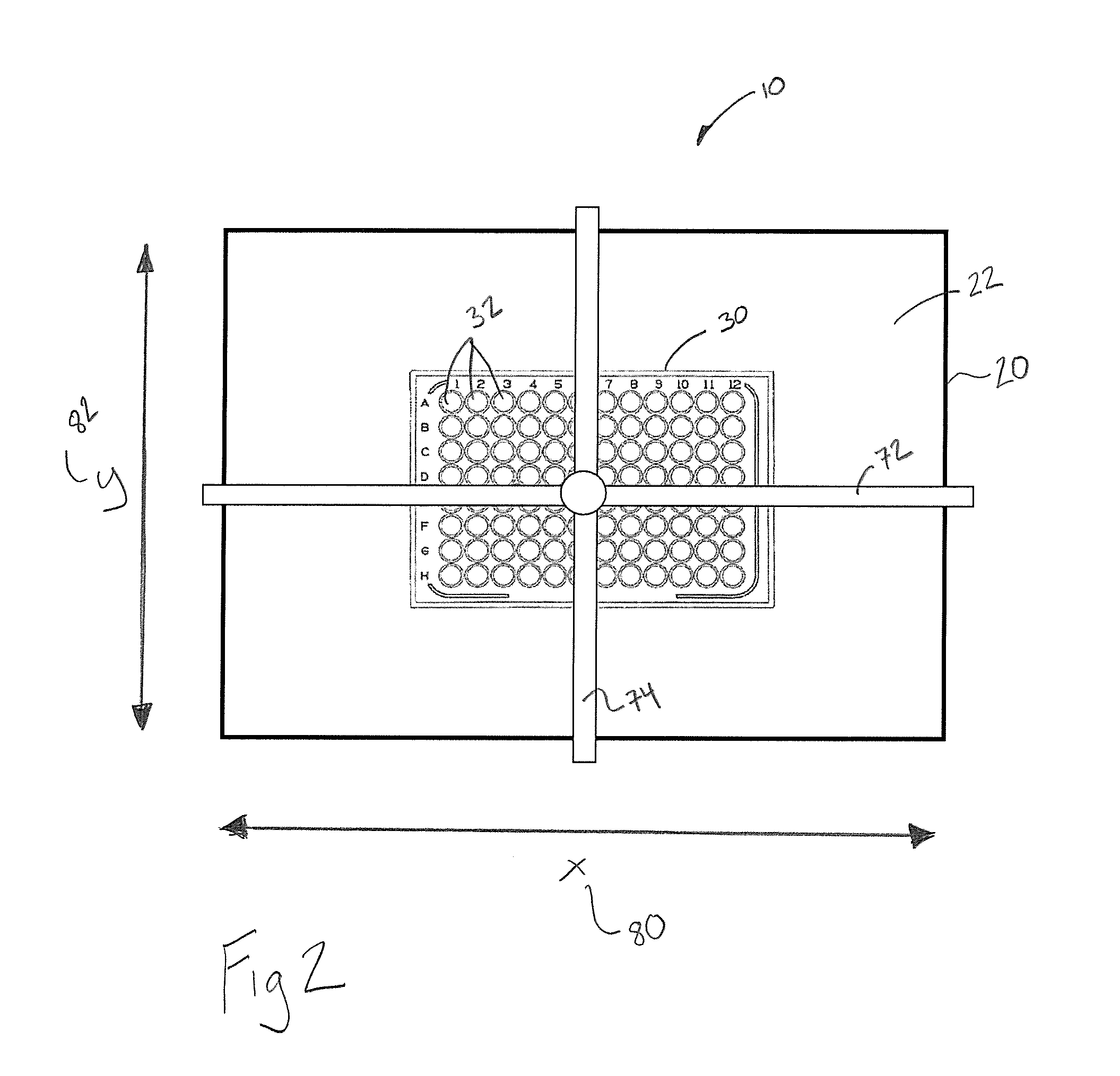
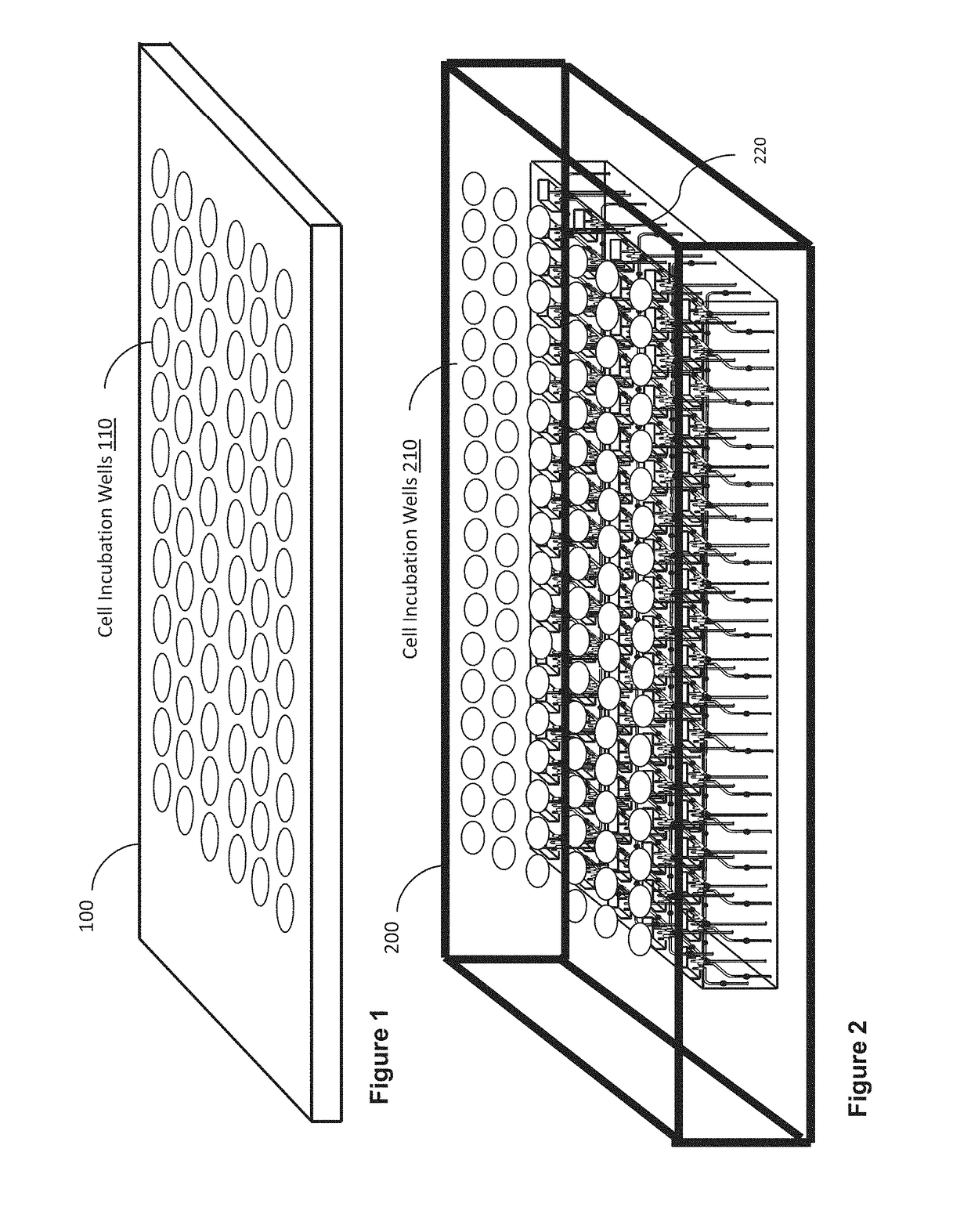
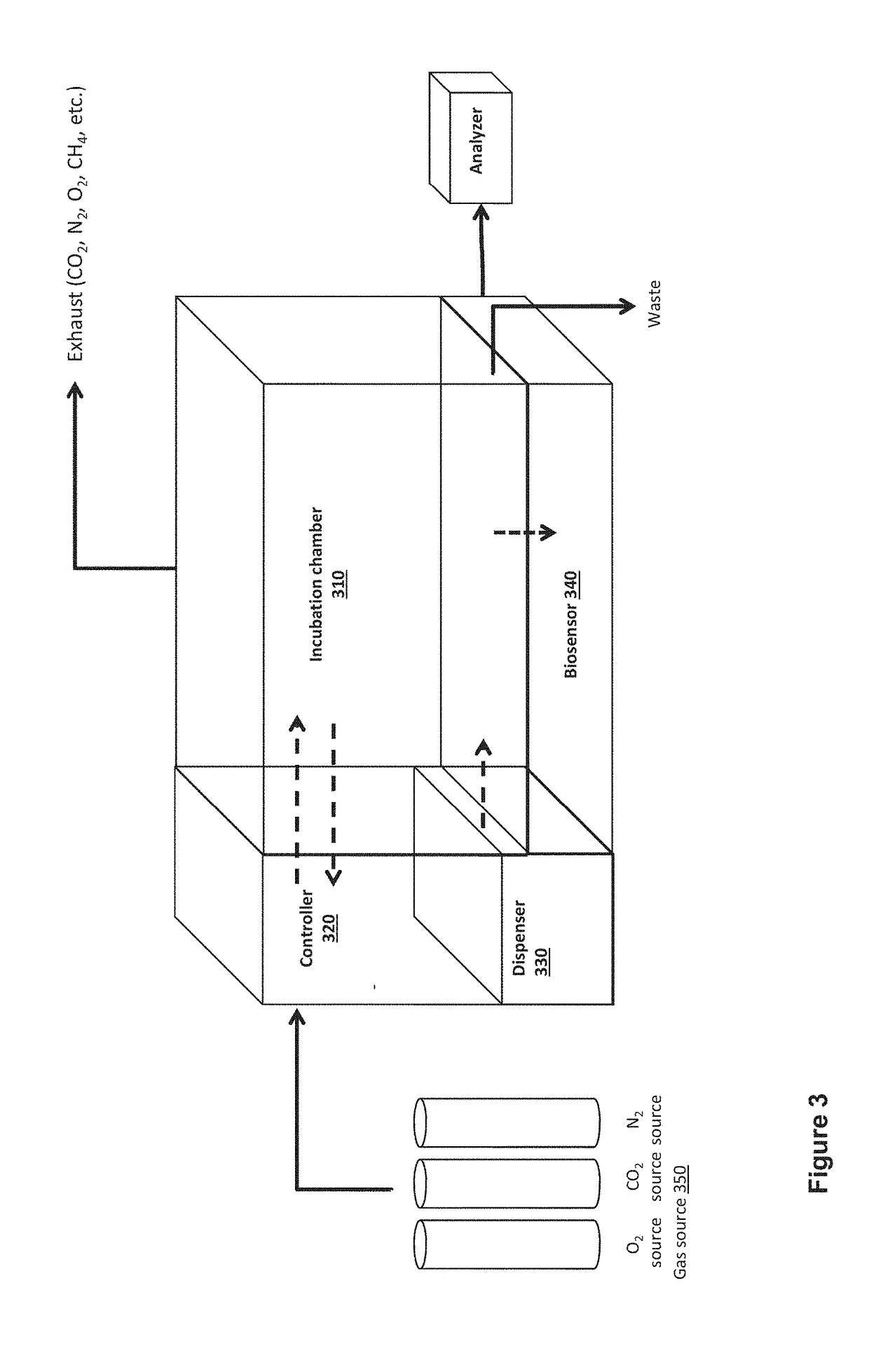
A cell incubation system and methods for using a cell incubation system are described. The incubator system comprises an incubation compartment for receiving a microplate for processing samples. The microplate comprises a plurality of wells, each of the plurality of wells including a collection chamber, and a plurality of fluidic structures coupled to the plurality of wells. The microplate further comprises a plurality of sensors coupled to the plurality of wells.
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
Direct RT-PCR on oligonucleotide-immobilized PCR microplates
InactiveUS6844158B1Simple preparation processStable outputSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTransfer cellCell layer
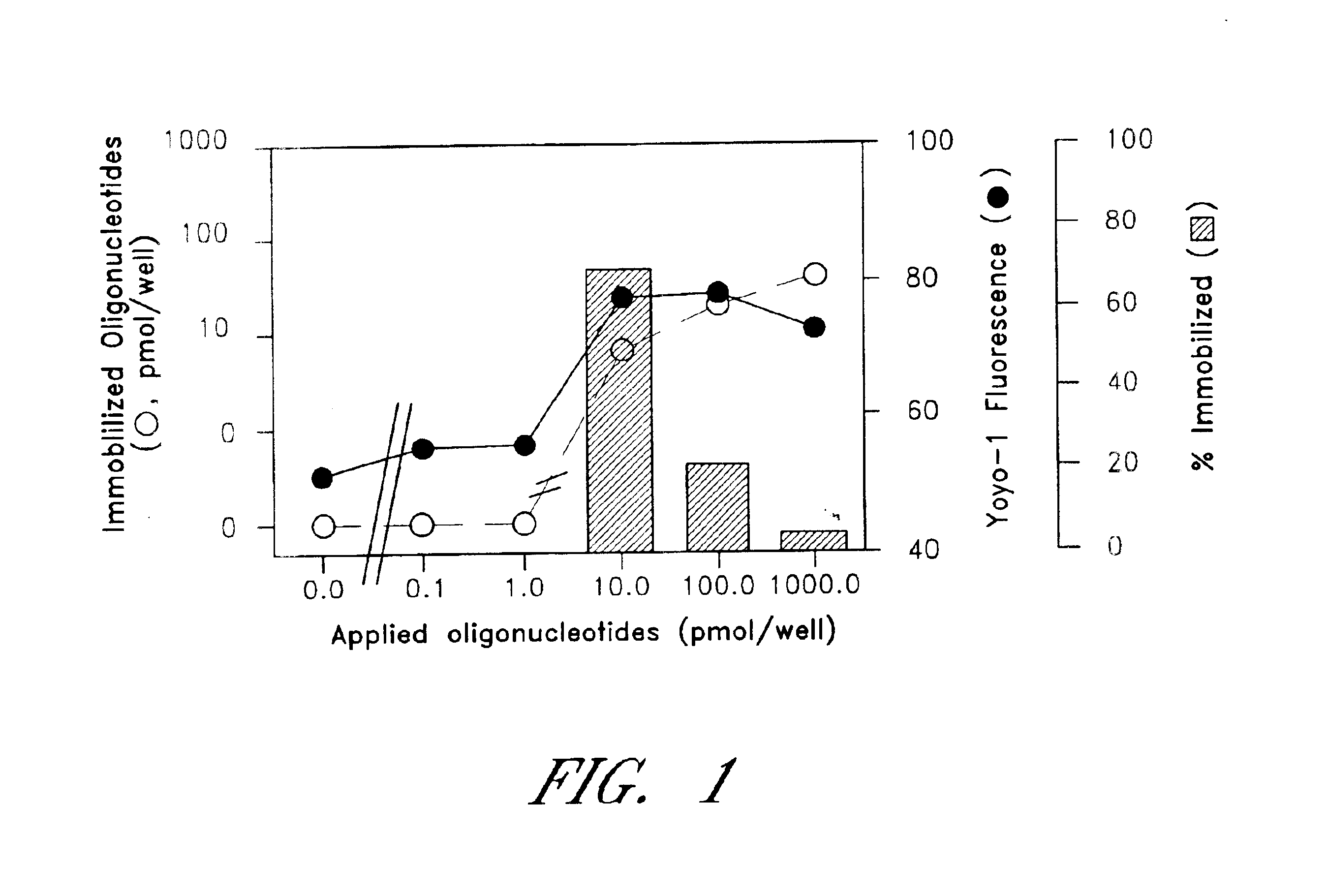
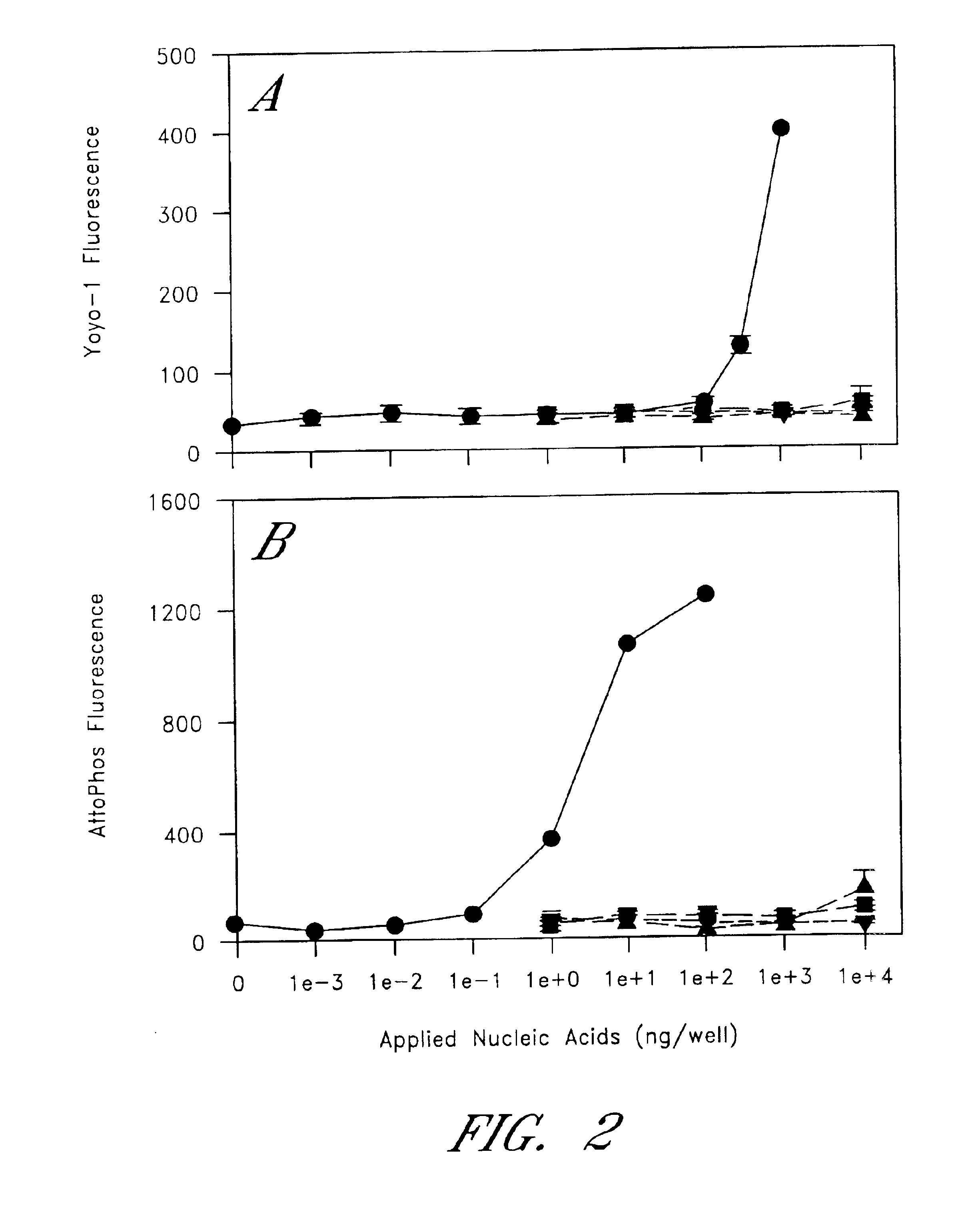
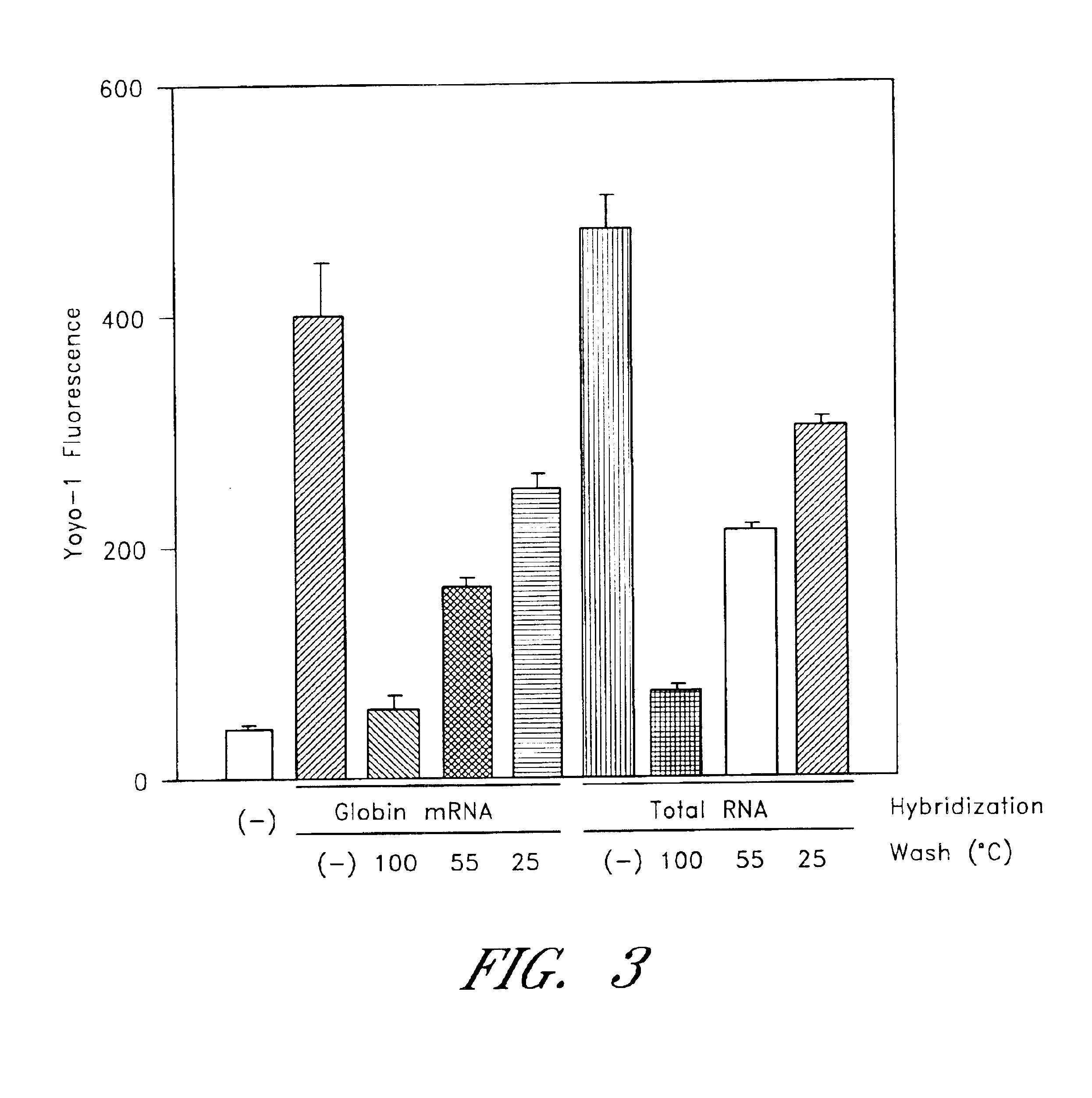
The entire process of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is simplified by using oligonucleotide-immobilized microplates made of, e.g., polypropylene, to which oligonucleotides are securely immobilized and which can be subjected to thermal cycles of PCR. RT-PCR is preferably conducted in solid-phase. Capturing of mRNA and RT-PCR can be conducted in the same plates. The cDNA synthesized from the mRNA captured on the microplates can be used more than once. Further, in combination with the microplates, a filter plate is used for the preparation of cell lysates wherein target cells are placed on the filter plate, and a lysis buffer is passed through the cell layer on the filter to transfer cell lysate directly to the microplate via well-to-well communication.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD +1
High capacity microarray dispensing
InactiveUS6979425B1Improve spotImprove accuracySequential/parallel process reactionsWithdrawing sample devicesAnalysis dataMicroplate Well
A high capacity microarrayer for spotting solution onto slides in an automated microarray dispensing device. A microplate indexing device automatically moves, in sequence, a plurality of microplates to a solution removal area. A dispense head accesses each microplate at the solution removal area to remove solution from the microplate. The dispense head then moves to a slide positioning station to spot slides at the slide positioning station. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the microplate indexing station has at least one input stacking chamber for stacking microplates, and at least one output stacking chamber for stacking microplates. A walking beam indexer is disposed between the at least one input stacking chamber and the at least one output stacking chamber. The walking beam indexer is for moving microplates from said at least one input stacking chamber to said at least one output stacking chamber. While at the solution removal area, a lid lifter lifts the lid off each microplate to permit the microplate to be accessed by the dispense head for solution removal. After the solution is removed, the lid lifter replaces the lid. In another preferred embodiment, there is at least one light source capable of illuminating the slides, and at least one camera operating in conjunction with the at least one light source. The at least one camera is capable of acquiring and transmitting slide image data to a computer. The computer is programmed to receive the slide image and analyze it. The computer will then generate post analysis data based on the analysis of the slide image data. The post analysis data is available for improving the spotting of the solution onto the slides. In a preferred embodiment, the slide image data includes information relating to slide alignment, information relating to spot quality, and slide identification information. In a preferred embodiment, the analysis of the information relating to slide alignment enables the computer to make automatic adjustments to the relative positions of the at least one dispense head and the slides to increase the accuracy of the spotting. In a preferred embodiment, the analysis of the information relating to spot quality identifies a spot as pass or fail. An operator is then able to rework the spot. In a preferred embodiment, the analysis of the slide identification information enables the computer to track each slide.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Cell culture system
InactiveCN102858947AApparatus sterilizationTissue/virus culture apparatus3D cell cultureMicrotiter plate
A microtiter plate based cell culture system comprising an improved cell culture insert which is suitable and used for the cultivation of adherent cells and / or three-dimensional tissues.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
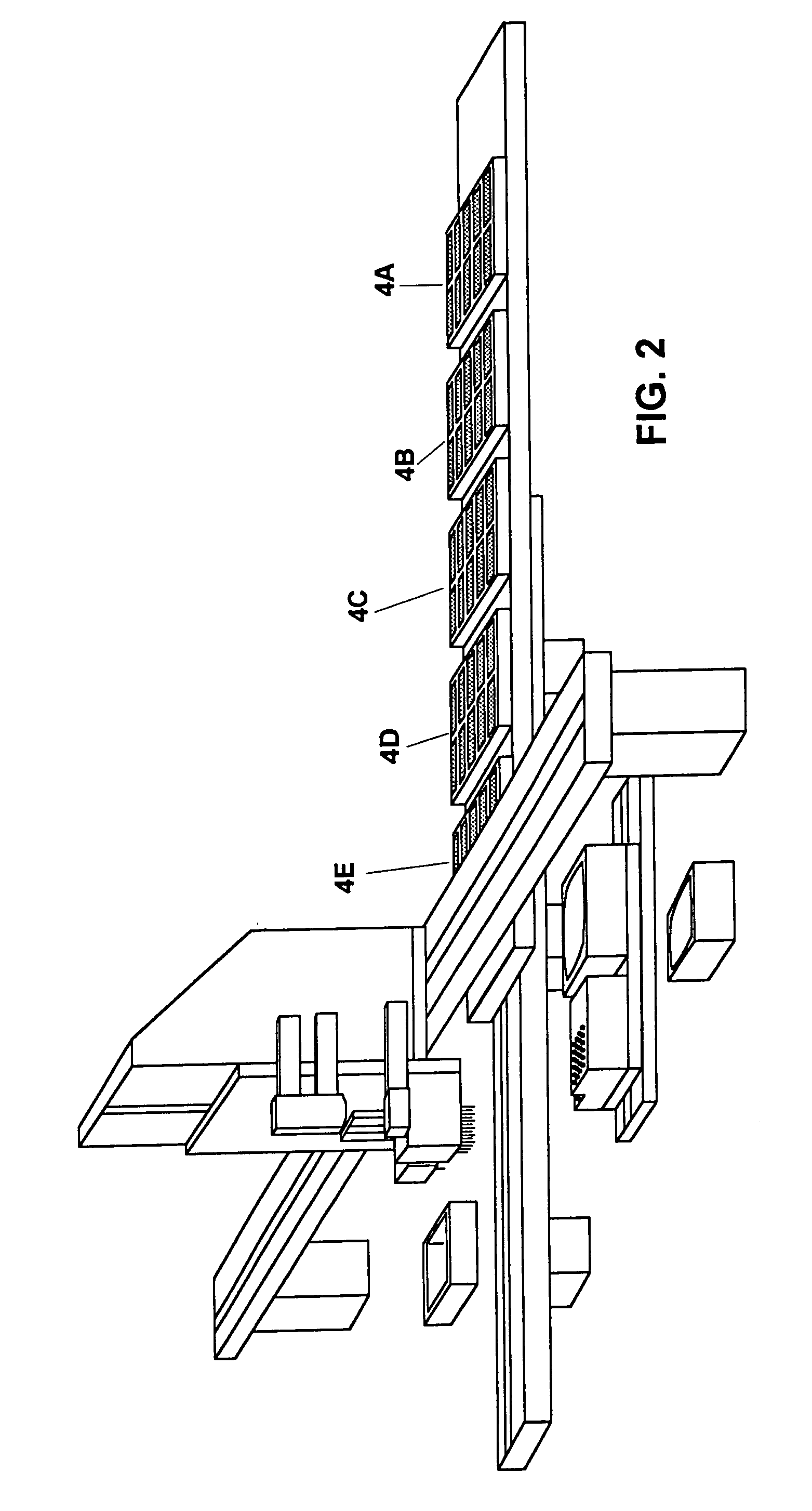
Advanced microplate, microtiter, and microarray technologies with per-well fluidics, gas exchange, electronic sensors, and imaging for cell culture and other applications
InactiveUS9994889B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringVALVE PORT
Arrangements for per-well fluidics, gas exchange, and electronic sensors for microplate, microtiter, and microarray technologies are presented. In example implementations, each individual well within in a conventional or specialized microplate can be fully or partially isolated with capping or other arrangements which can include conduits for controlled introduction, removal, and / or exchange of fluids and / or gases. Conduit networks can include small controllable valves that operate under software control, and micro-scale pumps can also be included. Conduit interconnections can include one or more of controllable-valve distribution buses, next-neighbor interconnections, and other active or passive interconnection topologies. Cap arrangements can include or provide one or more sensors of various types, including but not limited to selective gas sensors, chemical sensors, temperature sensors, pH sensors, biosensors, immunosensors, molecular-imprint sensors, optical sensors, fluorescence sensors, bioFETS, etc. Incubator interfacing and imaging are also described. The invention can be used for living cell culture or other applications.
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
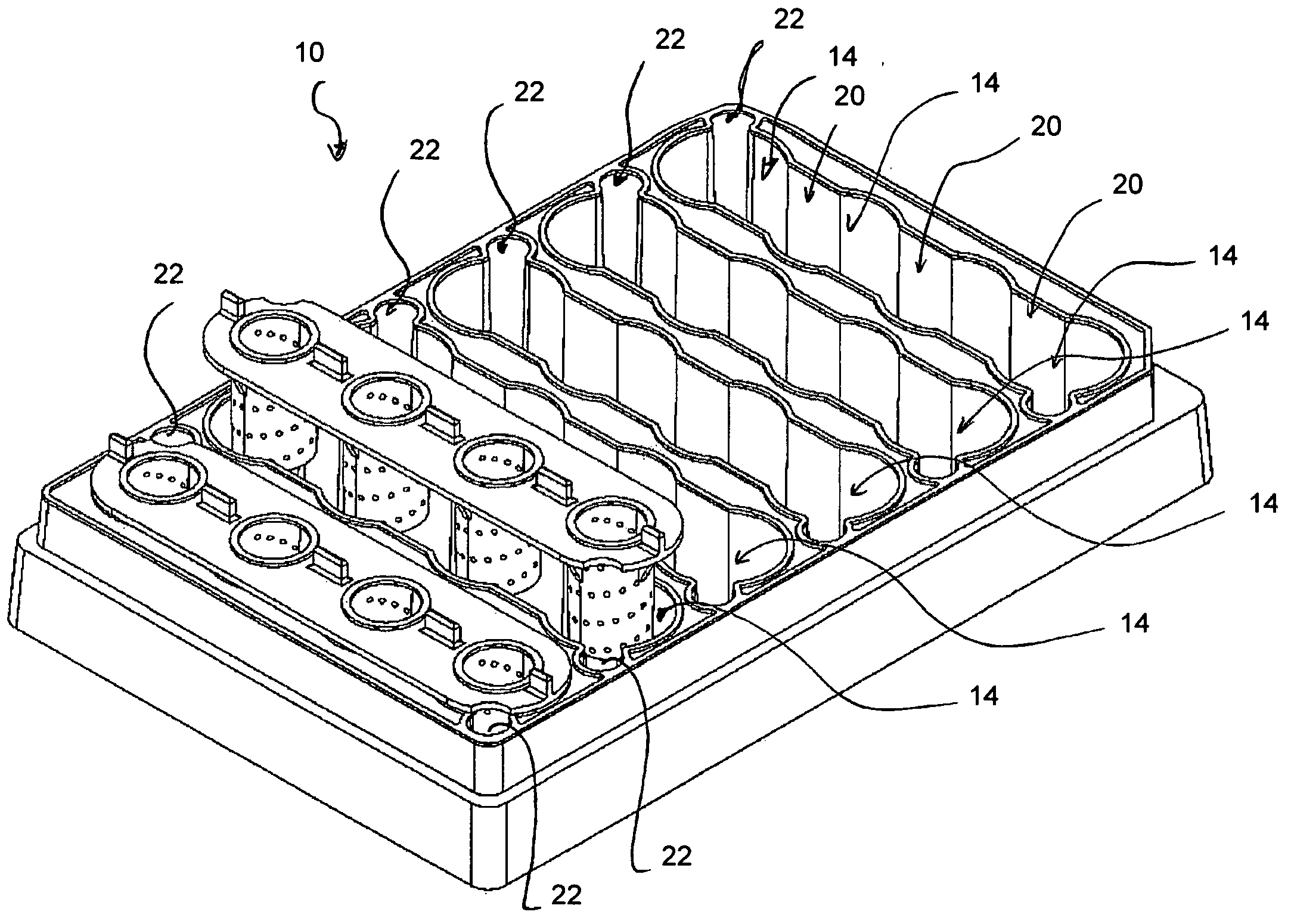
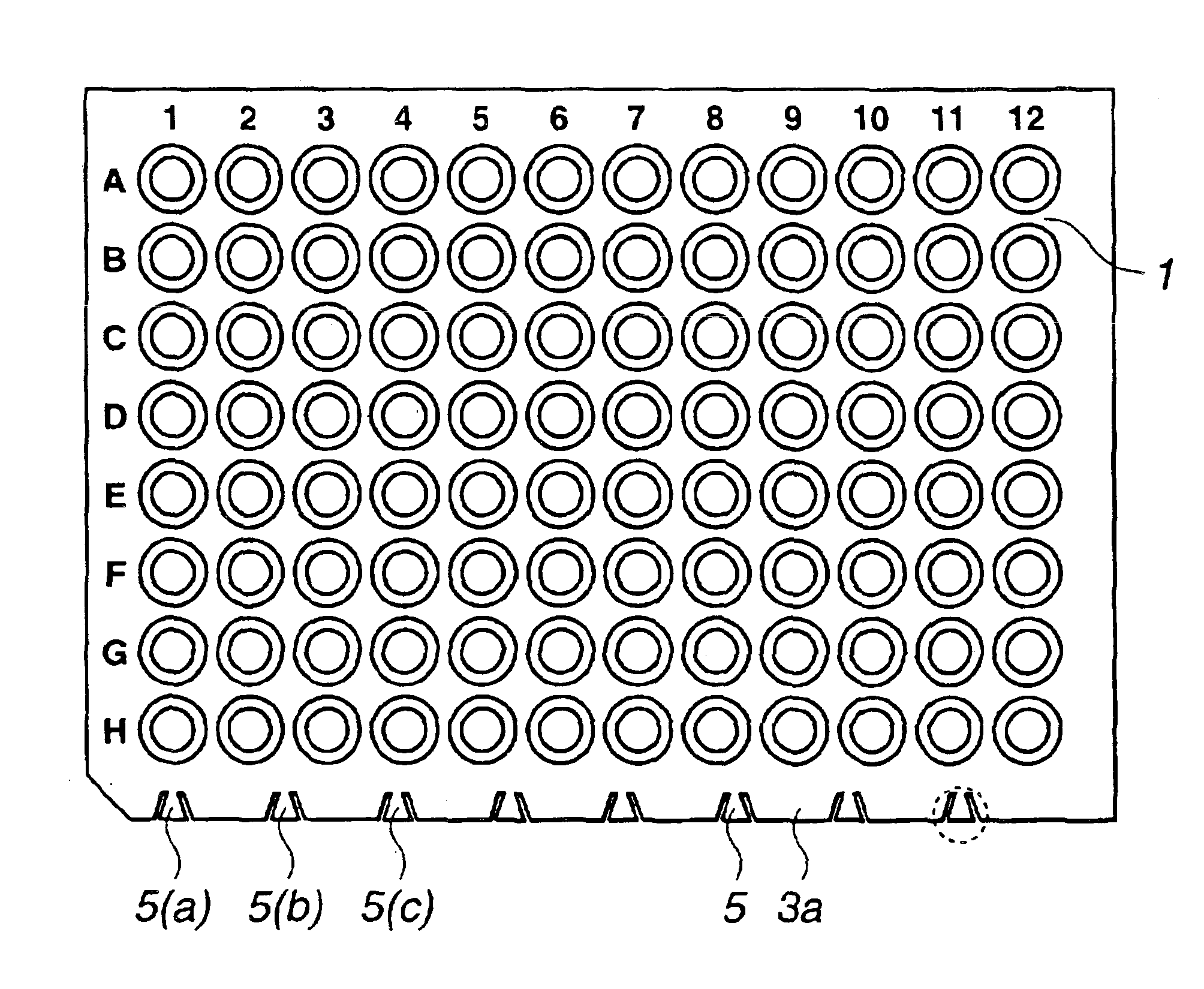
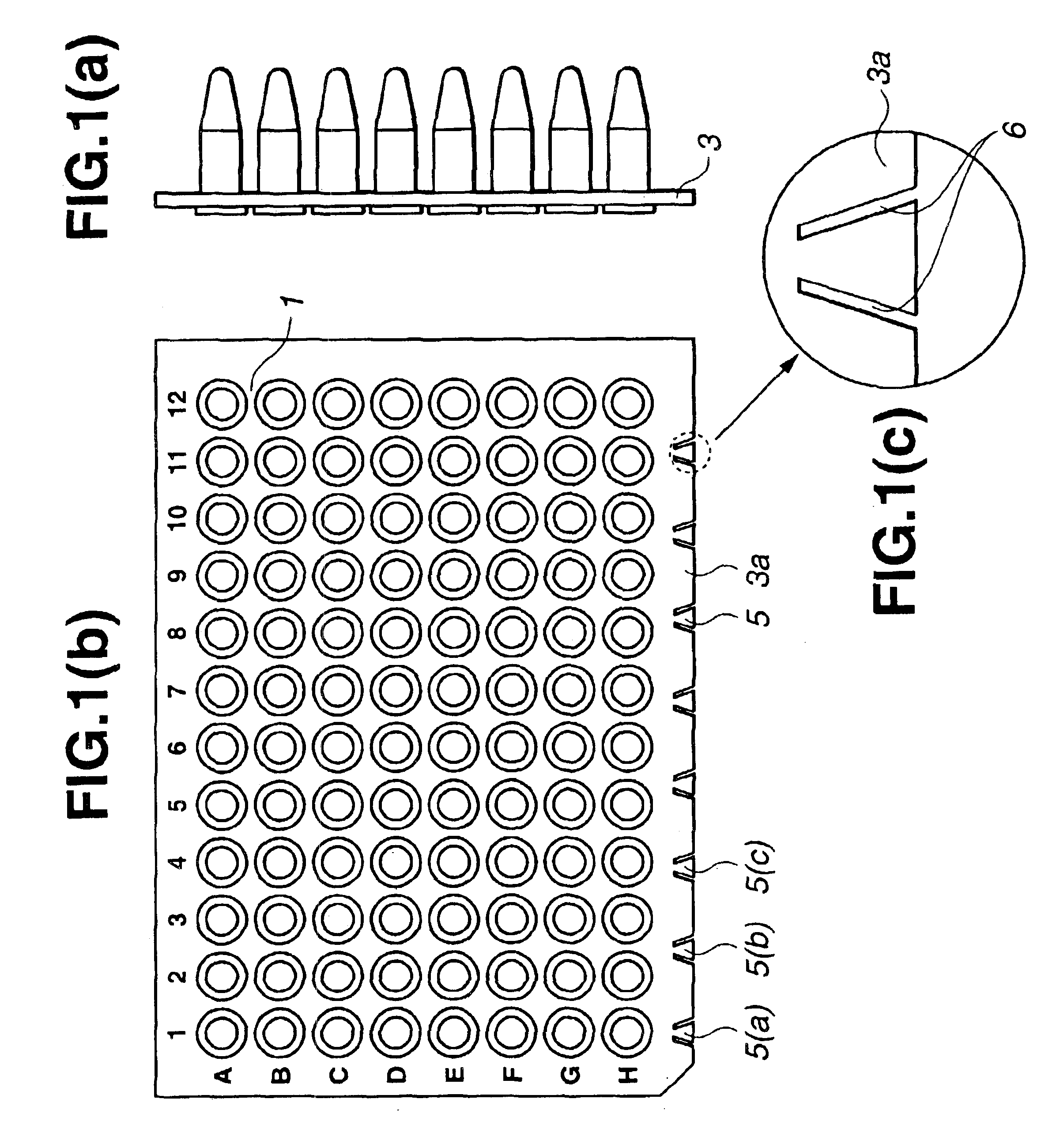
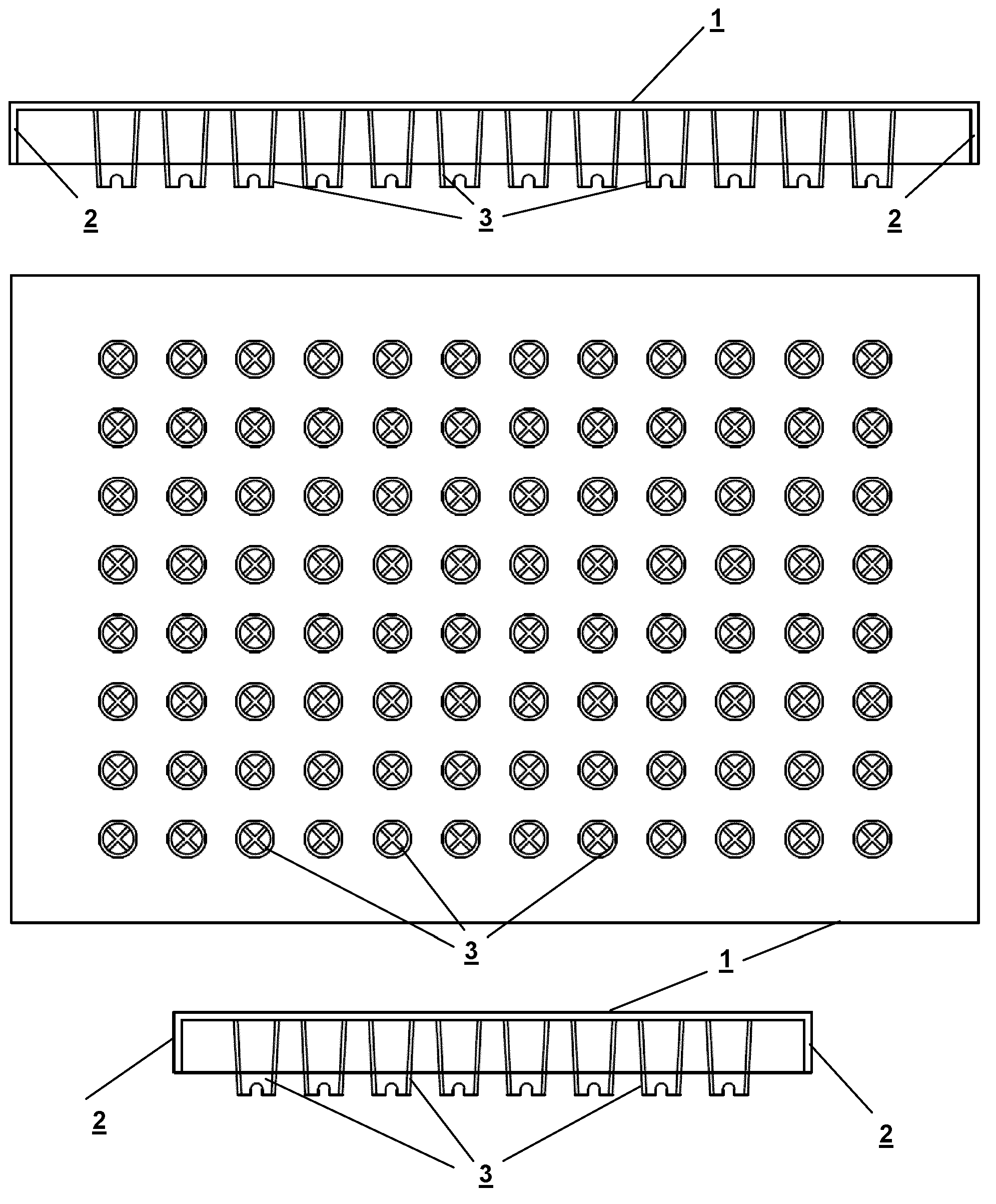
Microplate
InactiveUS6884615B2Easy to distinguishEasy to identifyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
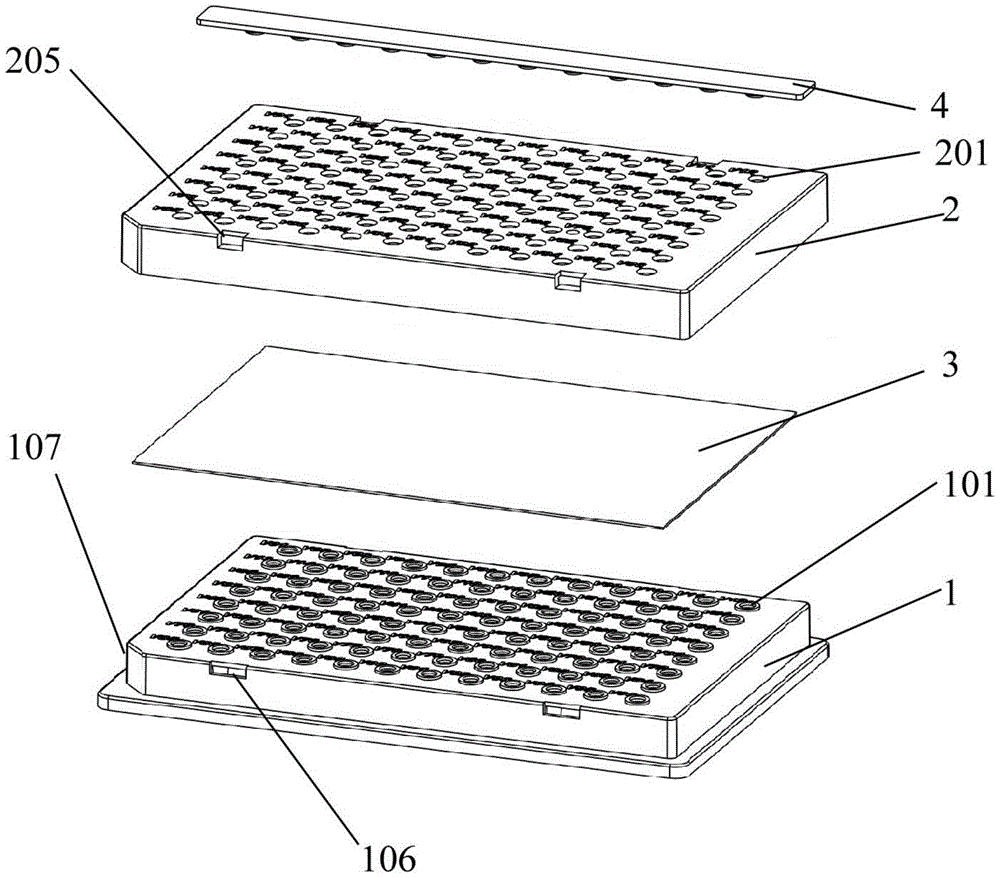
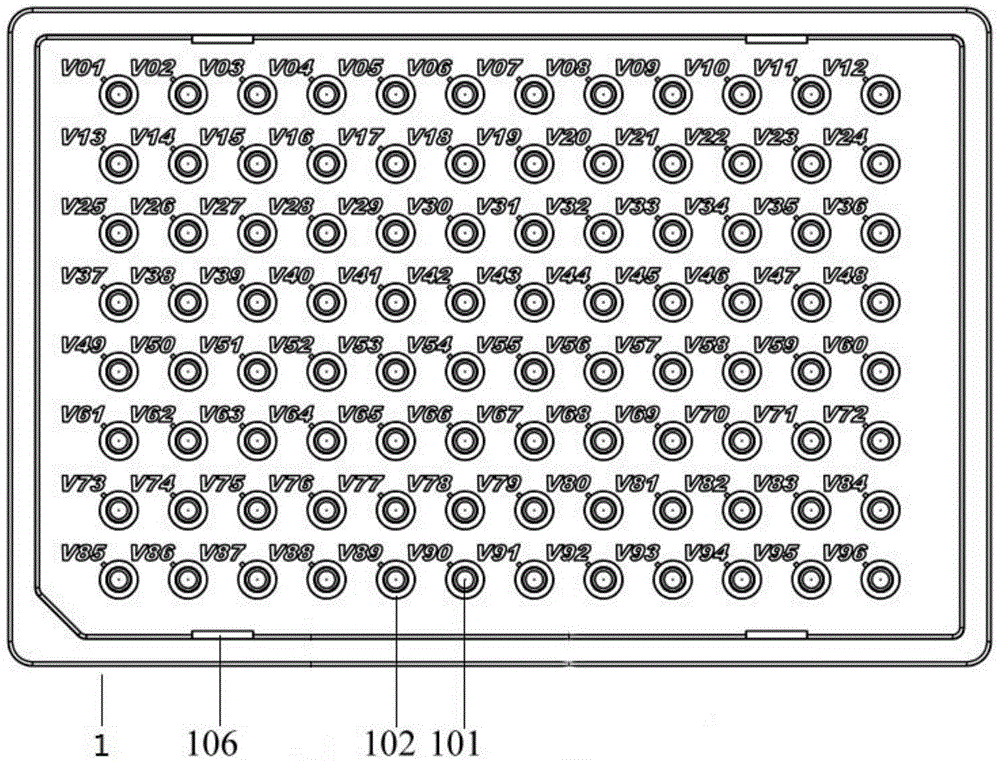
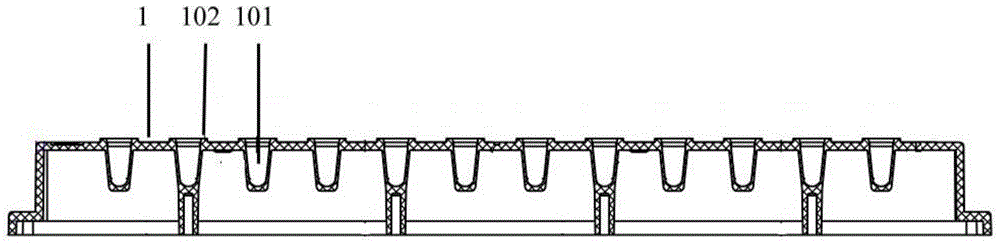
A microplate having a base and wells is disclosed. The base has mark parts at least on one edge thereof. Each mark part is defined by notches cut in the edge of the base. The wells are provided in the base and arranged in rows and columns. The mark parts can be used as indicia for identifying not only the microplate but also the wells so that the microplate and the wells can be easily identified without writing numerals or marks on the edges of the base with a felt pen or the like.
Owner:FUTABA CORPORATION
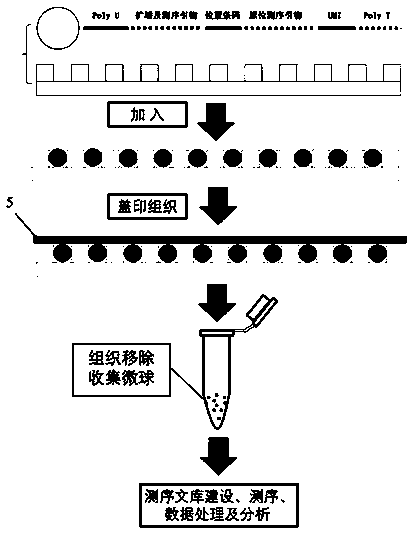
Space transcriptome detection chip and method
InactiveCN109762728AHigh resolutionNo damageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell specificMicrosphere
The invention provides a space transcriptome sequencing chip and method. The chip and the method are used for determining one or more single cell sequences in different space positions in tissues. Thechip comprises a micropore plate and coding sequencing microspheres, wherein the micropore plate is provided with the coding sequencing microspheres. The method comprises the steps of coupling with the microspheres using a plurality of random codes, wherein each random code comprises a molecular marker and a position marker barcode; the molecular marker can detect sequence information of single cells of the tissues, and the position markers are used for recording space position information of the single cells of the tissues. Based on the detection chip and the detection method, the single-cell specific transcriptome information of the tissues can be analyzed and detected, and the spatial positions of thousands of single cells in the tissues can be simultaneously detected.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
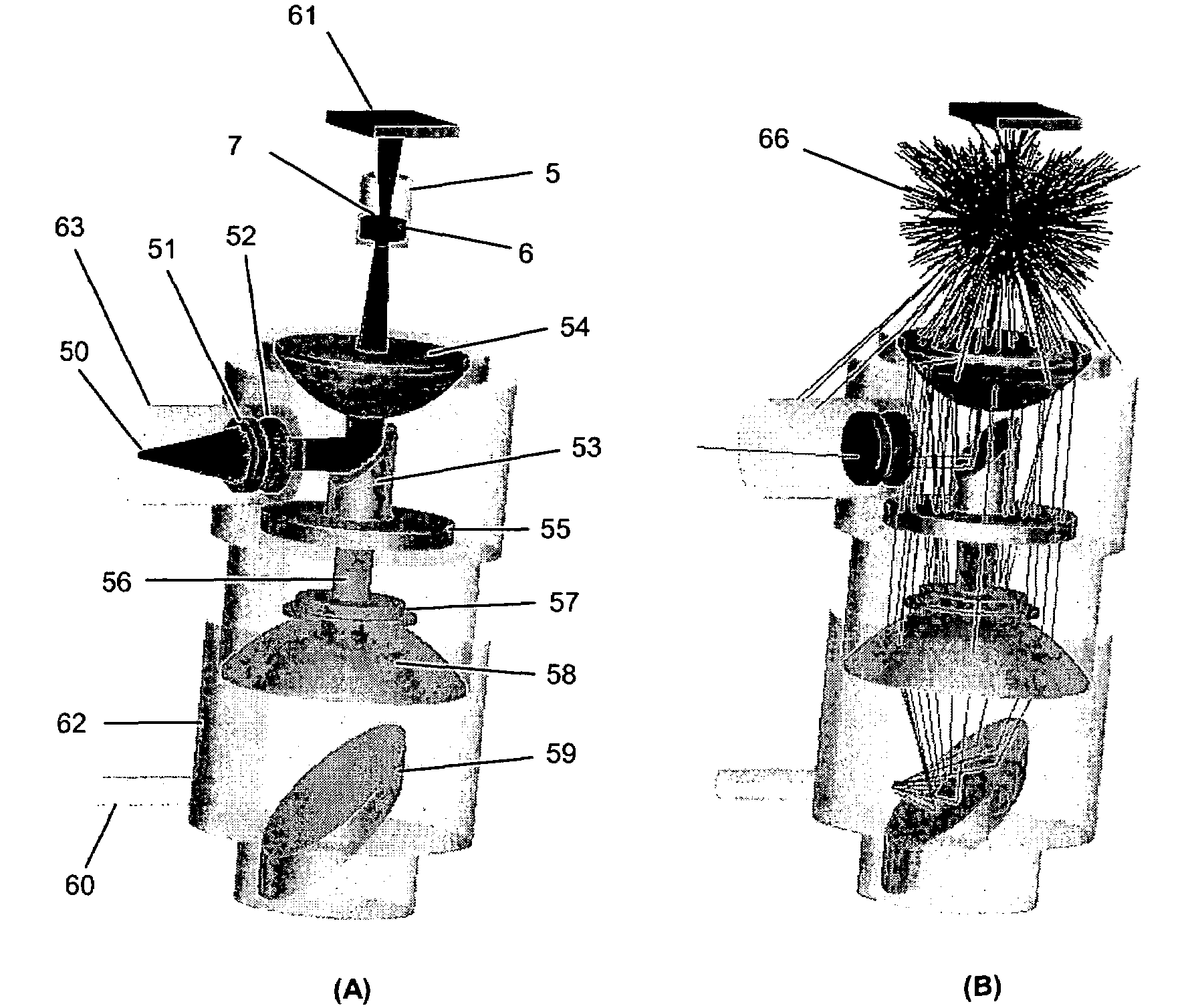
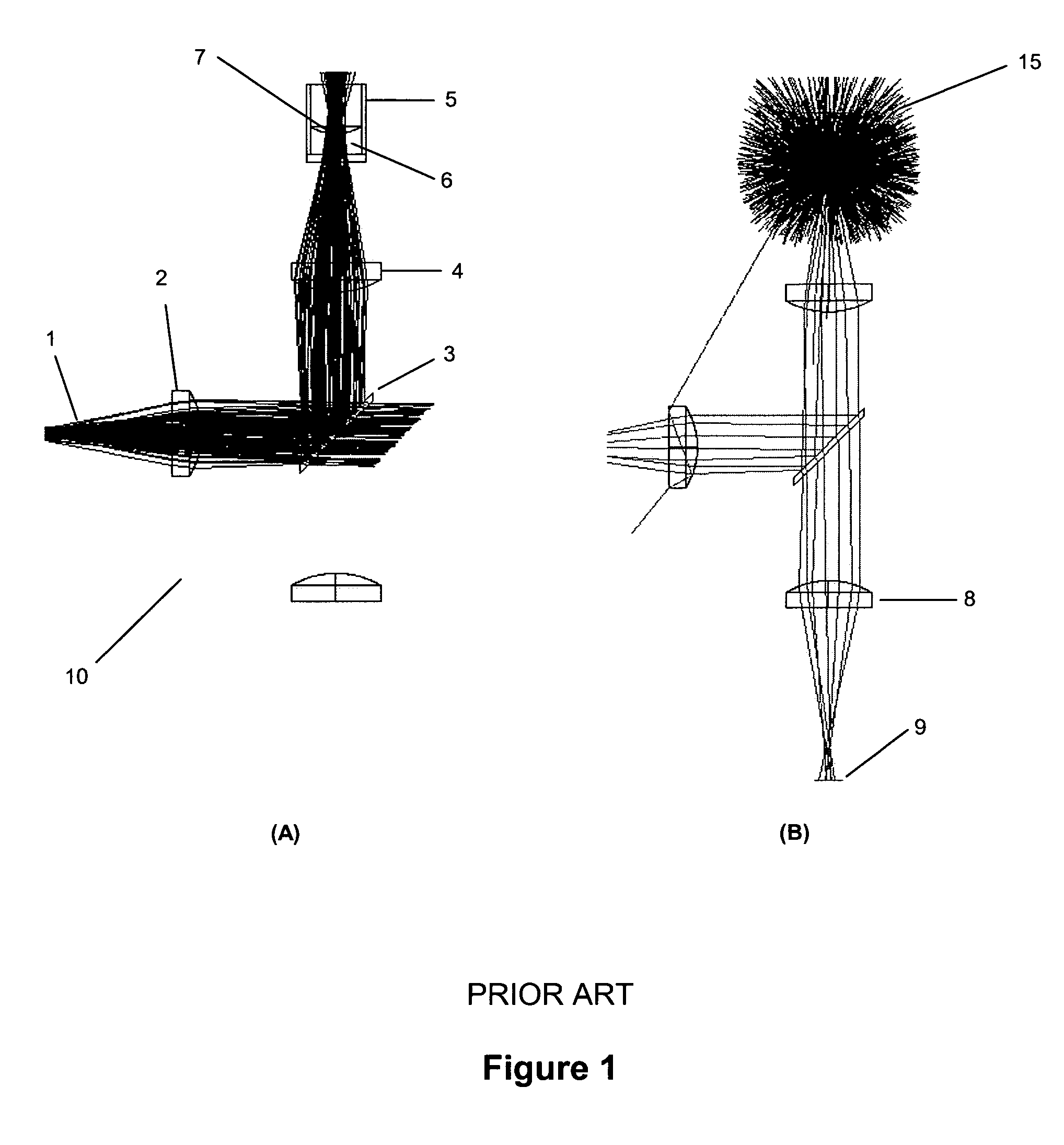
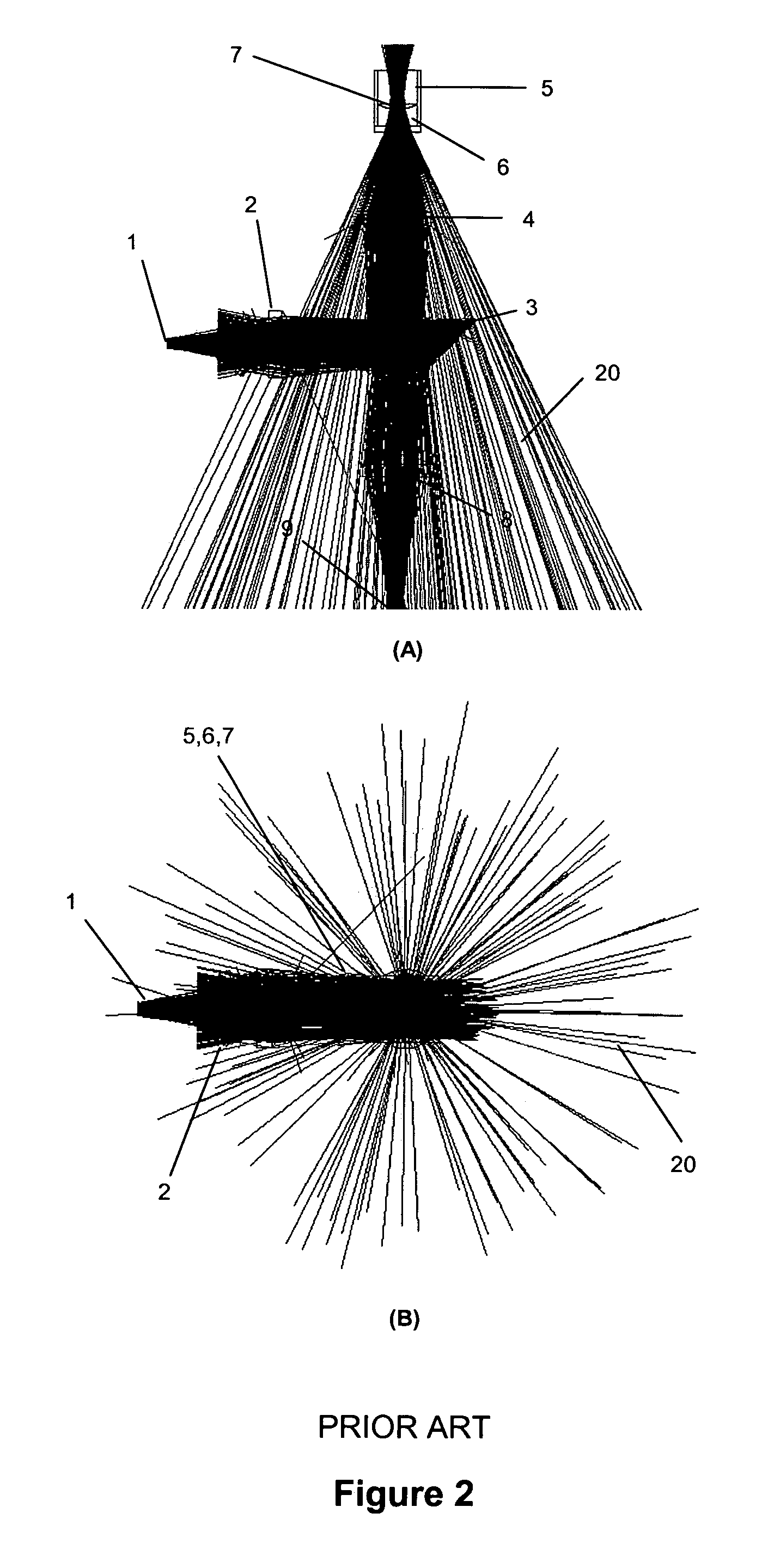
Optical system
InactiveUS20060119845A1Attenuation bandwidthReduce the numberRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFiberExcitation beam
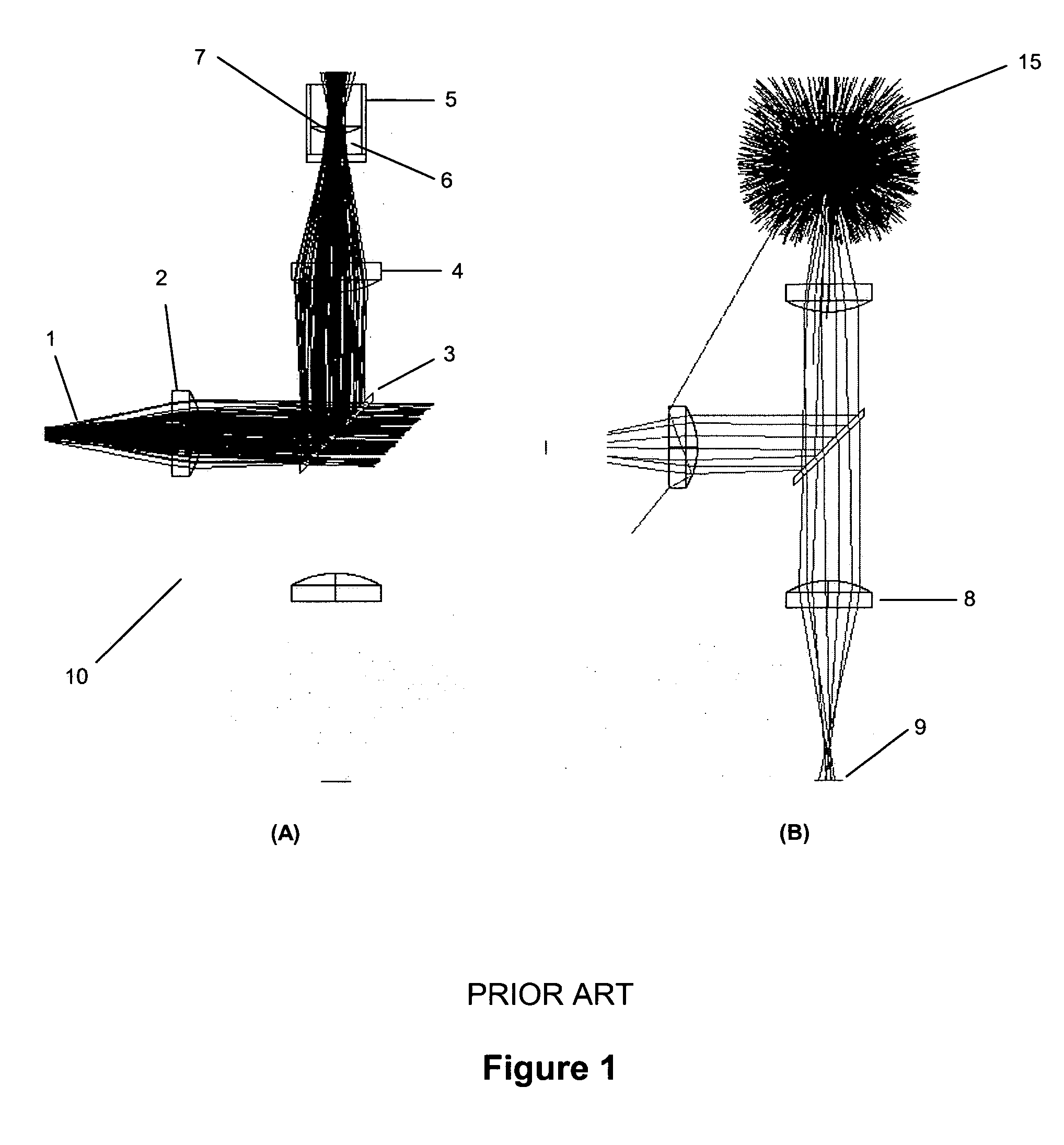
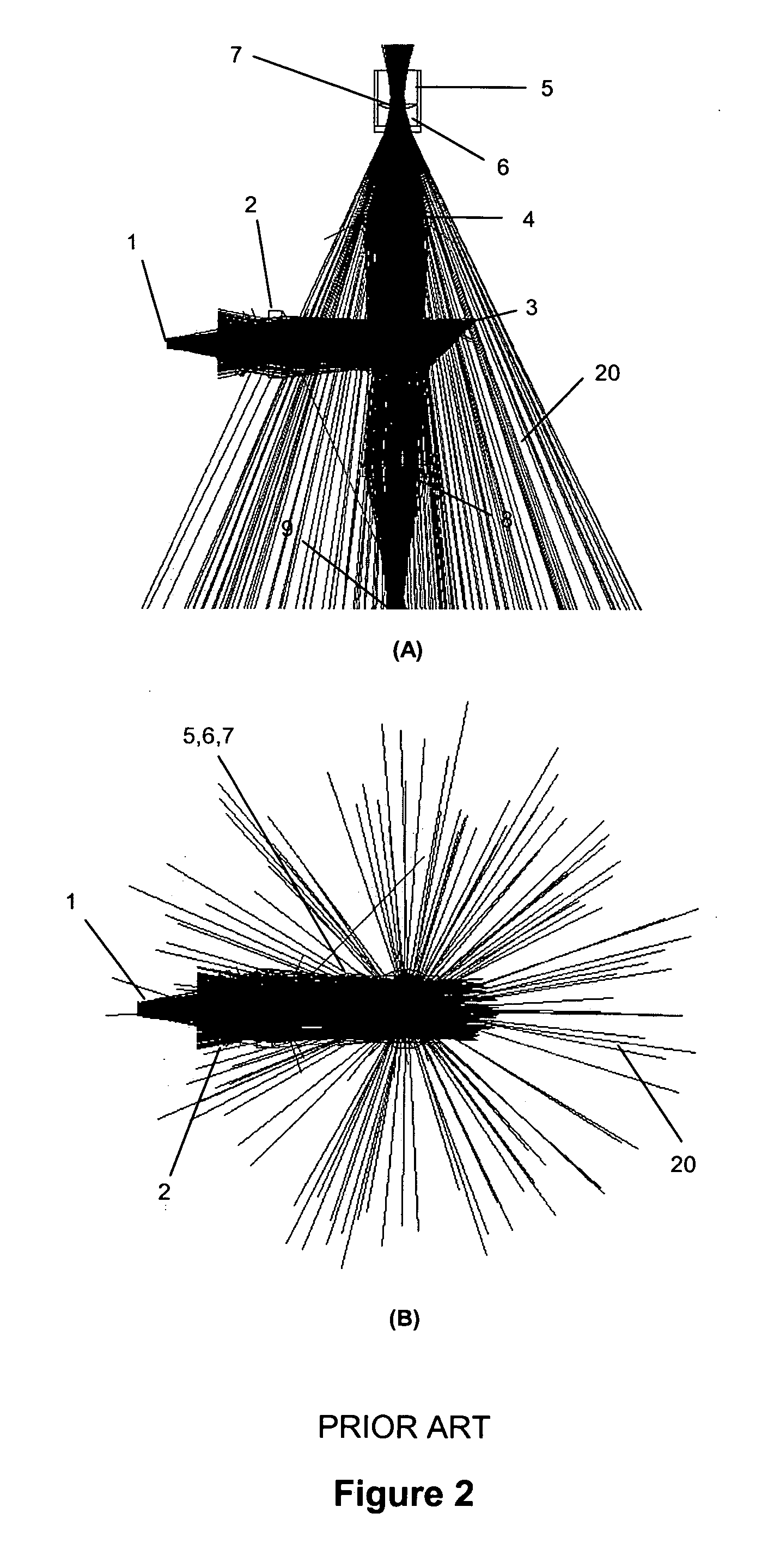
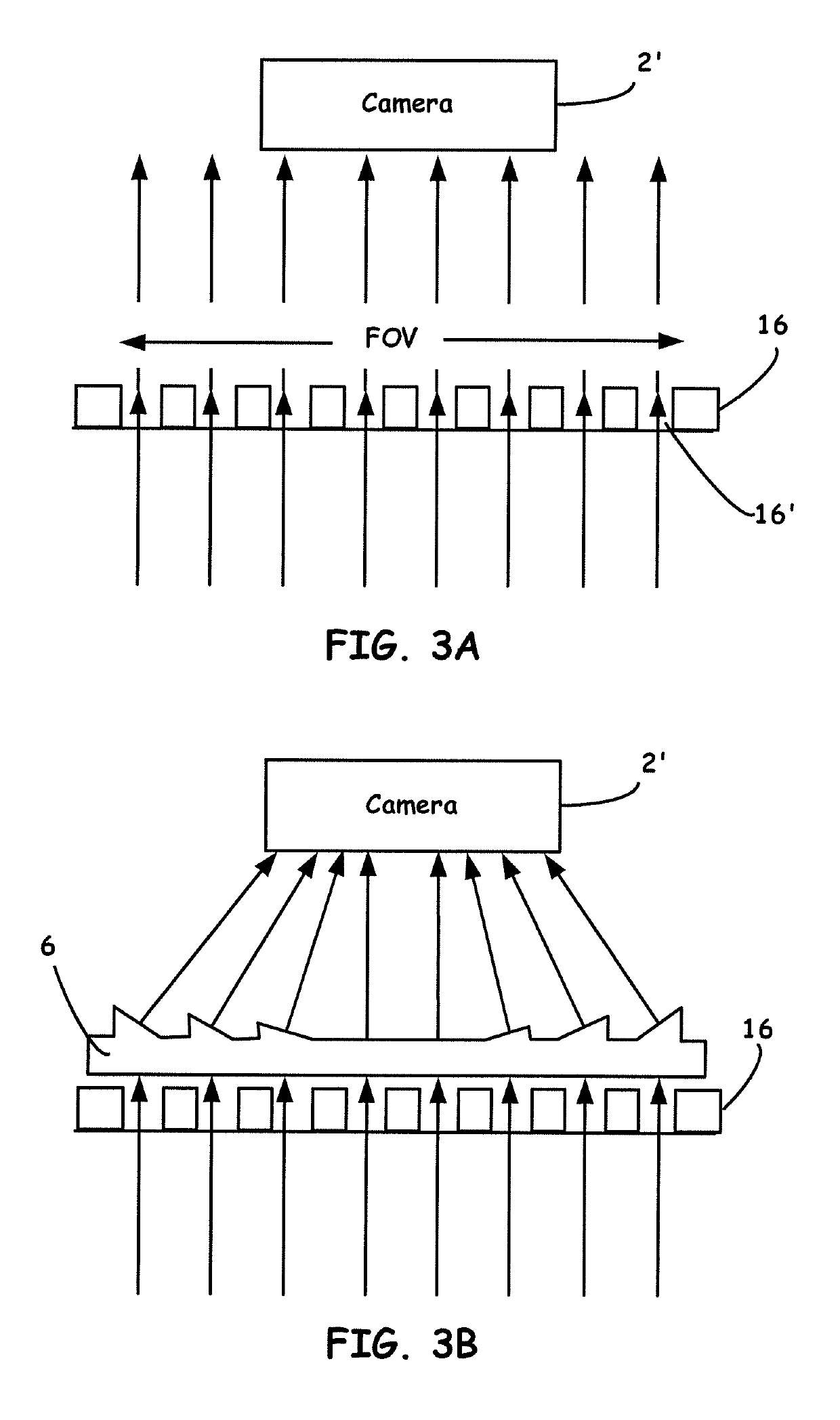
An optical system is provided for achieving enhanced rejection of scattered excitation light and superior signal-to-noise performance when reading microplate wells. The optical system uses an axial configuration in which the excitation beam incident upon the sample propagates along the axis of the microplate well. Excitation light from a light source, such as a lamp or fiber optic bundle, is collimated into a beam using a lens. A reflective pick-off mirror is then used to reflect the collimated excitation beam upward along the well axis. A focusing lens, with a diameter exceeding the diameter of the collimated excitation beam, is used to focus the excitation beam in the well. The same broad lens is used to collimate the emitted fluorescent light, of which a large percentage propagates axially past the pick-off mirror towards a second focusing lens that focuses the emission beam onto the face of a fiber optic bundle. The emitted light is later filtered and detected using at a position that is optically shielded from the aforementioned optical system. The optical system is incorporated into a microplate reader or automated assay instrument in order to provide a compact assembly for sensitive fluorescence measurements either above or below the microplate. The optical system further enables the simultaneous measurement of absorbance and fluorescence in a compact optical configuration.
Owner:NOVX SYST CANADA
Sequential delivery device and method
ActiveUS20150024384A1BuildBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReagentMicroplate Well
A reagent delivery device includes a reagent delivery column with a housing receiving reagent storage elements that can move, and a breaching element coupled to the housing. The device includes an actuation member that during operation forces the reagent storage elements toward the breaching element. Breaching the storage elements releases the reagent. The breaching element and / or the housing are configured to communicate reagent between the reagent storage element and a target chamber coupled to the housing. The breaching element can be a needle, a blade, or a combination thereof. Multiple reagent delivery columns can be coupled to microplate wells for larger scale reagent delivery and processing. Biasing elements such as a spring and a counterweight can be directly or indirectly coupled to the housing and / or the reagent storage elements, resisting and / or moderating movement of the reagent elements.
Owner:PEYVAN KIANOOSH
Compressible Transparent Sealing for Open Microplates
InactiveUS20090285719A1Heating or cooling apparatusLaboratory glasswaresEngineeringMechanical engineering
An apparatus for sealing a microplate, wherein the apparatus comprises a microplate having a first surface and an opposing second surface. A plurality of wells is formed in the first surface of the microplate, wherein each of the plurality of wells is sized to receive an assay therein. A sealing cover is disposed over the microplate adjacent the plurality of wells and is compliant to accommodate variations between the sealing cover and the microplate and / or distribute loads evenly therebetween.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Microplate reader with lid lifter for microplates
A microplate reader comprises a housing; at least one optical measuring / detection device; a microplate support; a moving unit; and an integrated lid holding apparatus. The lid holding apparatus is arranged to move the microplate lid and / or the microplate support is arranged to move the microplate in one respective, in an at least approximately vertical direction for moving the microplate lid away from the microplate. The lid holding apparatus is arranged inside the housing as a magnetic lifter and comprises a non-array arrangement of at least one permanent magnet, or at least three electromagnets, or at least one switchable permanent magnet. Each microplate lid to be moved away from the microplate comprises magnetizable material.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG
Optical system
InactiveUS7324202B2Attenuation bandwidthReduce the numberRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationExcitation beamFiber bundle
An optical system is provided for achieving enhanced rejection of scattered excitation light and superior signal-to-noise performance when reading microplate wells. The optical system uses an axial configuration in which the excitation beam incident upon the sample propagates along the axis of the microplate well. Excitation light from a light source, such as a lamp or fiber optic bundle, is collimated into a beam using a lens. A reflective pick-off mirror is then used to reflect the collimated excitation beam upward along the well axis. A focusing lens, with a diameter exceeding the diameter of the collimated excitation beam, is used to focus the excitation beam in the well. The same broad lens is used to collimate the emitted fluorescent light, of which a large percentage propagates axially past the pick-off mirror towards a second focusing lens that focuses the emission beam onto the face of a fiber optic bundle. The emitted light is later filtered and detected using at a position that is optically shielded from the aforementioned optical system. The optical system is incorporated into a microplate reader or automated assay instrument in order to provide a compact assembly for sensitive fluorescence measurements either above or below the microplate. The optical system further enables the simultaneous measurement of absorbance and fluorescence in a compact optical configuration.
Owner:NOVX SYST CANADA
Microplate sampling adapter
InactiveCN103282481AMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresMicroorganismCell culture media
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Dual-amplification method of template linear amplification and multi-biotin signal amplification
InactiveCN102485906ALow costReliable dataMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LMicrotiter plate
The invention relates to a dual-amplification method of template linear amplification and multi-biotin signal amplification. The method comprises steps that: nucleic acid is separated from a specimen; T7RNA polymerase linear amplification is carried out, such that an RNA product is obtained; the RNA product obtained through linear amplification is captured onto a microtiter plate, and signal amplification is carried out. The method is advantaged in low cost and more reliable data. With the method, the sensitivity and the detection time are similar to those of a PCR method.
Owner:武汉中帜生物科技股份有限公司
System and Method for Ultrasonic Sample Preparation
InactiveUS20150037808A1Avoid problemsPromotes even distributionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsActuatorAcoustics
A system and method for ultrasonic sample preparation, includes a vessel having a wall defining an inner volume. An ultrasonic probe is disposed in the inner volume of the vessel. A microplate having a plurality of sample wells is also disposed in the inner volume of the vessel. An actuator is connected to the microplate and is configured to move the microplate relative to the ultrasonic probe in the inner volume to facilitate uniform distribution of ultrasonic energy.
Owner:SONICS & MATERIALS
Microplate sampling adapter
InactiveUS20130260410A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrowell PlateCell culture media
The present invention relates to adapters for microplates. The adapters allow sampling from a liquid growth medium in a microplate well after a microorganism has formed a dense layer of biomass on the surface of the growth medium. The adapters also allow easy transfer of a surface-grown microorganism from all wells of a microplate in one go, when inserted before the microorganism form the layer and then removed after incubation and layer-formation, which also enables easy sampling of the growth medium in the
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Method for extracting DNA from plant genome and optimizing amplification system
InactiveCN109055355AEasy to operateShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationPlant tissueRapid identification
The invention discloses a method for extracting DNA from plant genome and optimizing an amplification system. The method comprises the following steps: taking a plant tissue sample which is 3-5mm longand 2-3 mm wide into a micro-pore plate; adding zirconia balls into the micro-pore plate; adding a DNA extracting solution into the micro-pore plate; and sealing the micro-pore plate, putting the sealed micro-pore plate onto a tissue grinding apparatus to be ground to form sample tissue liquid; taking the sample tissue liquid as a PCR reaction template to perform PCR amplification. The method canbe applied to quick extraction of DNA from various plant genomes, meets research of the plant molecular biology and the genetics, and rapid identification of genetically modified crops.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
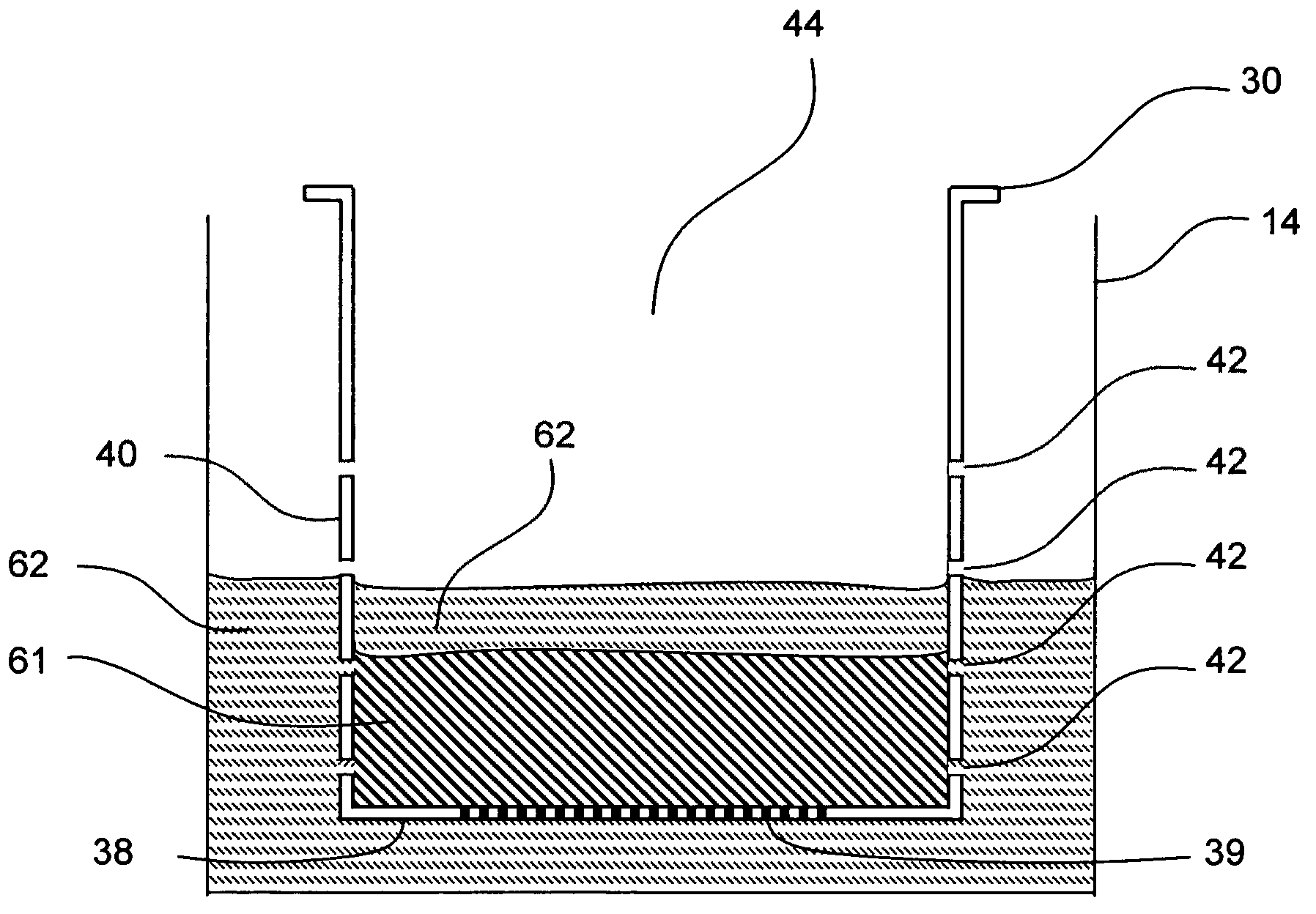
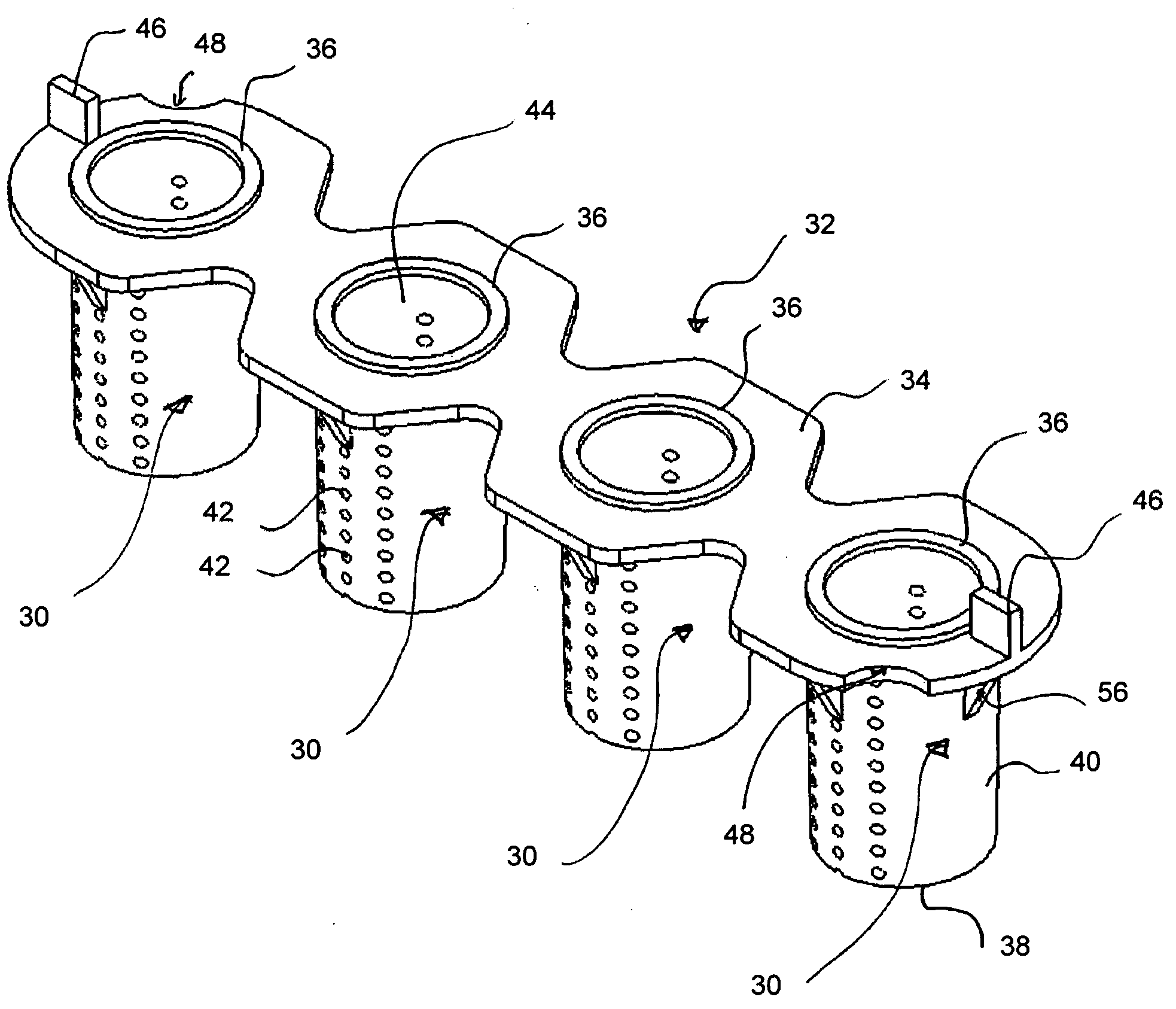
Cap arrangements providing per-well fluidics and gas exchange for advanced microplate, microarray, and microtiter technologies
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
Method for rapidly determining titer of bacteriophage of Enterobacter sakazakii
InactiveCN101775444AEasy to measureRapid determinationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEnterobacterBacteriophage
The invention relates to a method for rapidly determining the titer of bacteriophage of Enterobacter sakazakii, comprising the following steps of: A. preparing a bacteriophage concentration gradient suspension; B. preparing an Enterobacter sakazakii suspension; C. sequentially adding an Enterobacter sakazakii culture solution, the Enterobacter sakazakii suspension in the step B and the acteriophage concentration gradient suspension in the step A in a micropore plate; and D. scanning and determining in real time, scanning and determining a growth curve in a dynamics determining mode in real time under a certain culture temperature and wave length by utilizing a microplate reader. By using the determining method, the titer of the bacteriophage of the Enterobacter sakazakii can be simply, rapidly and efficiently determined.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
A prism array based portable microplate reader
ActiveUS20190091695A1Reduce analysisBiological particle analysisColor/spectral properties measurementsPrismField of view
The methods and configurations herein provide for analysis of microplate based assays. Certain aspects include: an optical illumination panel; a plurality of sample wells configured to receive light from the optical illumination panel, and wherein the plurality of sample wells is configured with a first field of view; at least one aperture array configured to isolate directed light therethrough the plurality of sample wells; at least one optical array configured to receive optical information from the plurality of sample platforms, wherein the at least optical array comprises an array of individual microprisms configured with equal apex angles at distal equidistances along a row, wherein the individual microprism apex angles decrease toward the center of the row culminating in at least one flat surface along a center portion of the row; and a detector configured to capture the optical information with a second field of view as provided by the at least one optical array.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
A microporous plate for encapsulating a small amount of liquid
ActiveCN104841501BEasy to operateAvoid cross contaminationLaboratory glasswaresMicrotiter plateEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of biological instruments, in particular to a micro-porous plate for packaging micro liquid. The micro-porous plate comprises a micro-porous plate body and a micro-porous plate cover which is matched with the micro-porous plate body; the micro-porous plate body is provided with a plurality of micro-porous cavities; the micro-porous plate cover is provided with plate holes corresponding to the micro-porous cavities; a plate sealing film is arranged between the micro-porous plate body and the micro-porous plate cover; the micro-porous plate cover is provided with a sealing plate which is matched with the micro-porous plate cover. The micro-porous plate is convenient to transport, and cross infection among liquids can be effectively avoided; moreover, convenience is brought to observation and positioning, automatic operation can be satisfied, and the working efficiency is increased.
Owner:HANGZHOU BERRYGENOMICS GENE DIAGNOSIS TECH
Sorptive Extraction Layer for Immobilized Liquid Extraction
ActiveUS20140356976A1Optimizes affinity and also extraction efficiency and overall recoveryPositive influence on the analyte partition ratioWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationBiological pumpCopolymer composition
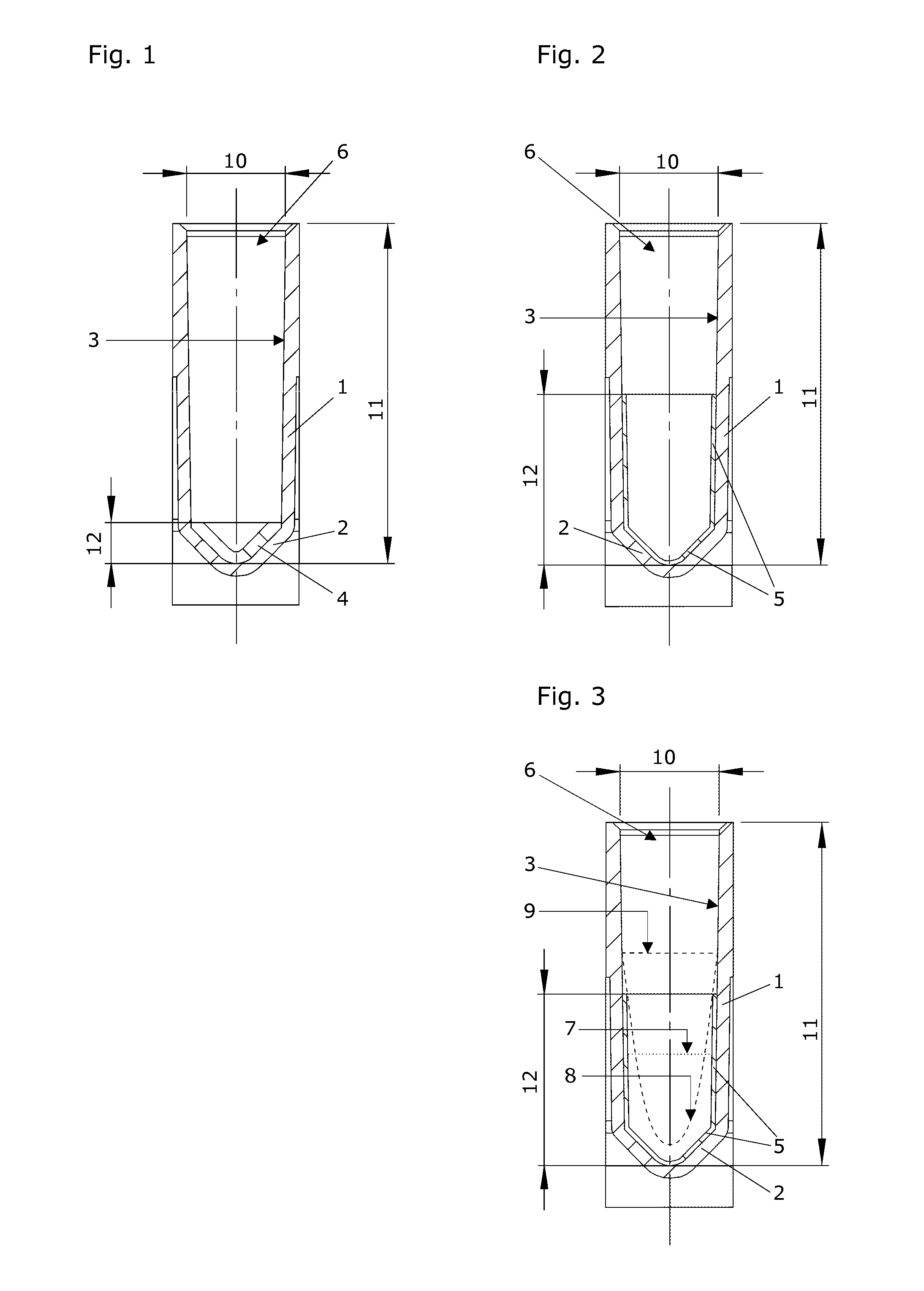
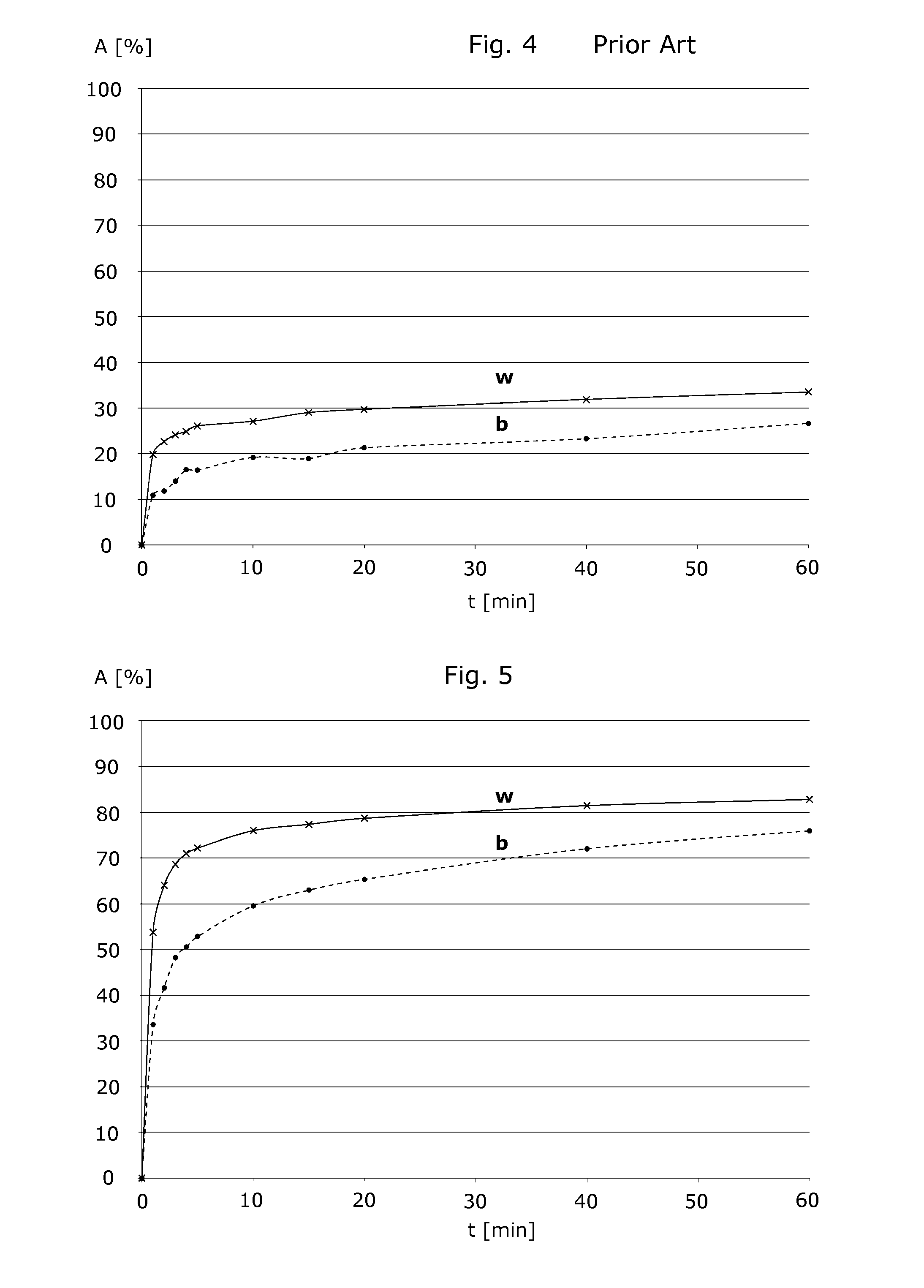
A sorptive extraction layer for immobilized liquid extraction of target molecules preferably from biological samples is disclosed. The sorptive extraction layer is mainly composed of ethylene-acrylate-copolymer. Preferably, microplate wells are at least partially coated with such a sorptive extraction layer. There is also disclosed a method of extracting target molecules preferably from biological samples. According to this method, immobilized liquid extraction is carried out with a sorptive extraction layer which is mainly composed of ethylene-acrylate-copolymer.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG
Method of minimizing reagent consumption in microplate-based reactions
InactiveUS20090263837A1Increase surface areaMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresReagentAnalytical chemistry
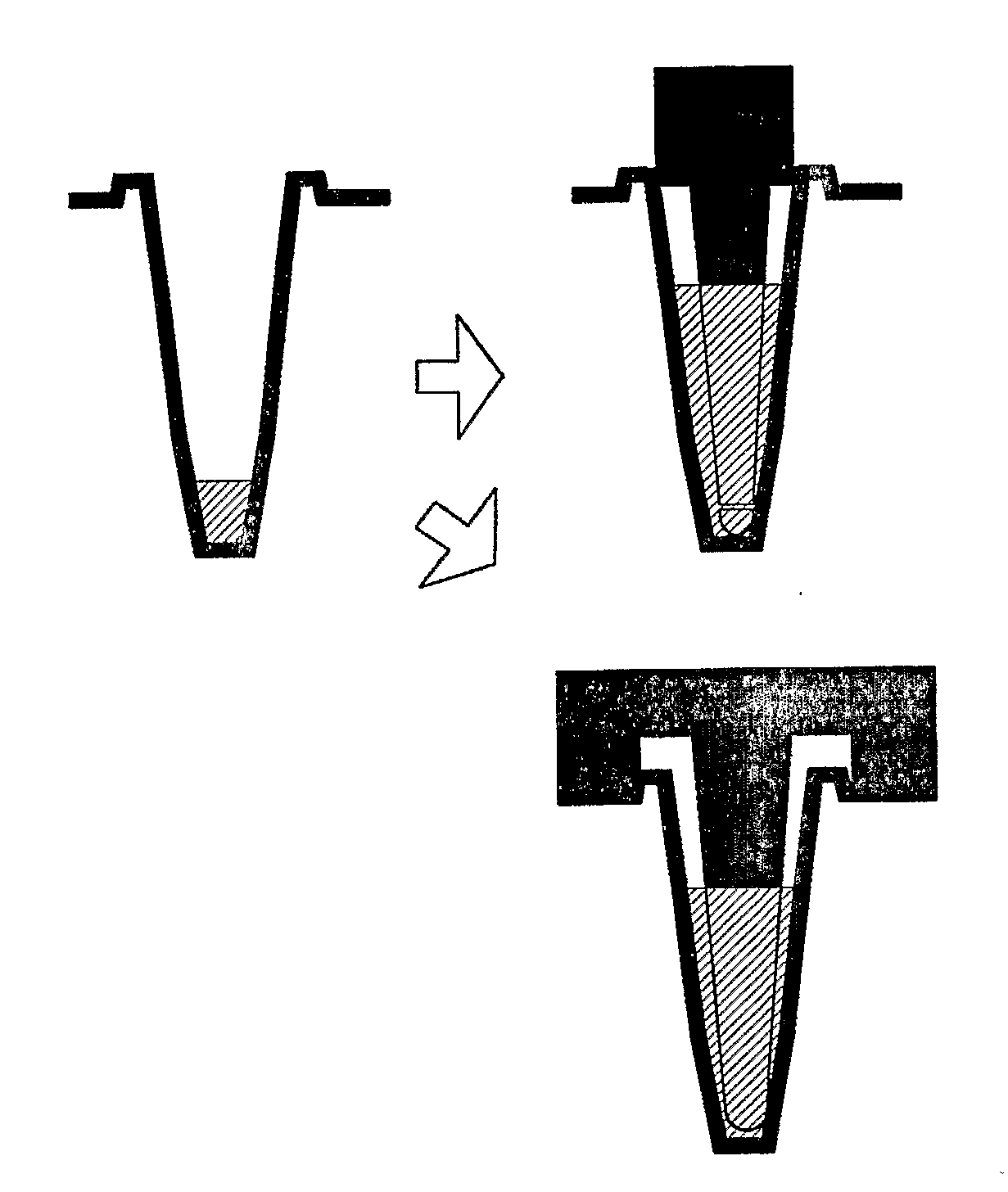
A method is provided for performing a reaction, such as the synthesis of concentrated cDNA, in the wells of a microplate while minimizing the volume of the solution of reagents required to perform the reaction. In the method, a pestle is inserted into the well of a microplate to which a substance has been immobilized. A volume of reagent solution is introduced into the well that is insufficient to cover the portion of the well onto which the substance is immobilized. The insertion of the pestle displaces reagent solution and increases the surface area of the solution in contact with the portion of the well to which the substance has been immobilized when the pestle is inserted.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD +1
Methods and systems for controlling liquids in multiplex assays
ActiveUS20110269641A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsChemical analysis using titrationEngineeringMicroplate Well
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
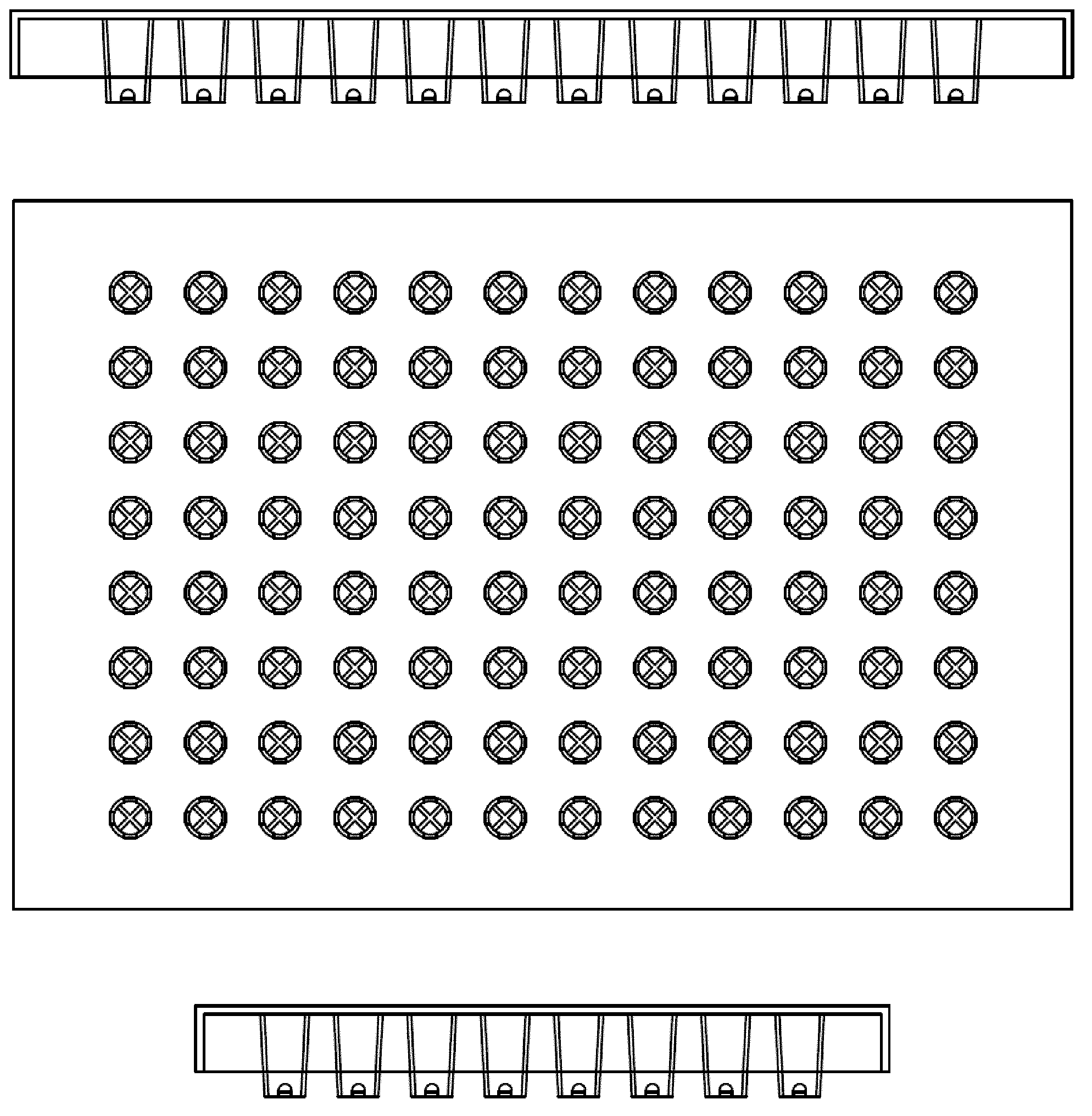
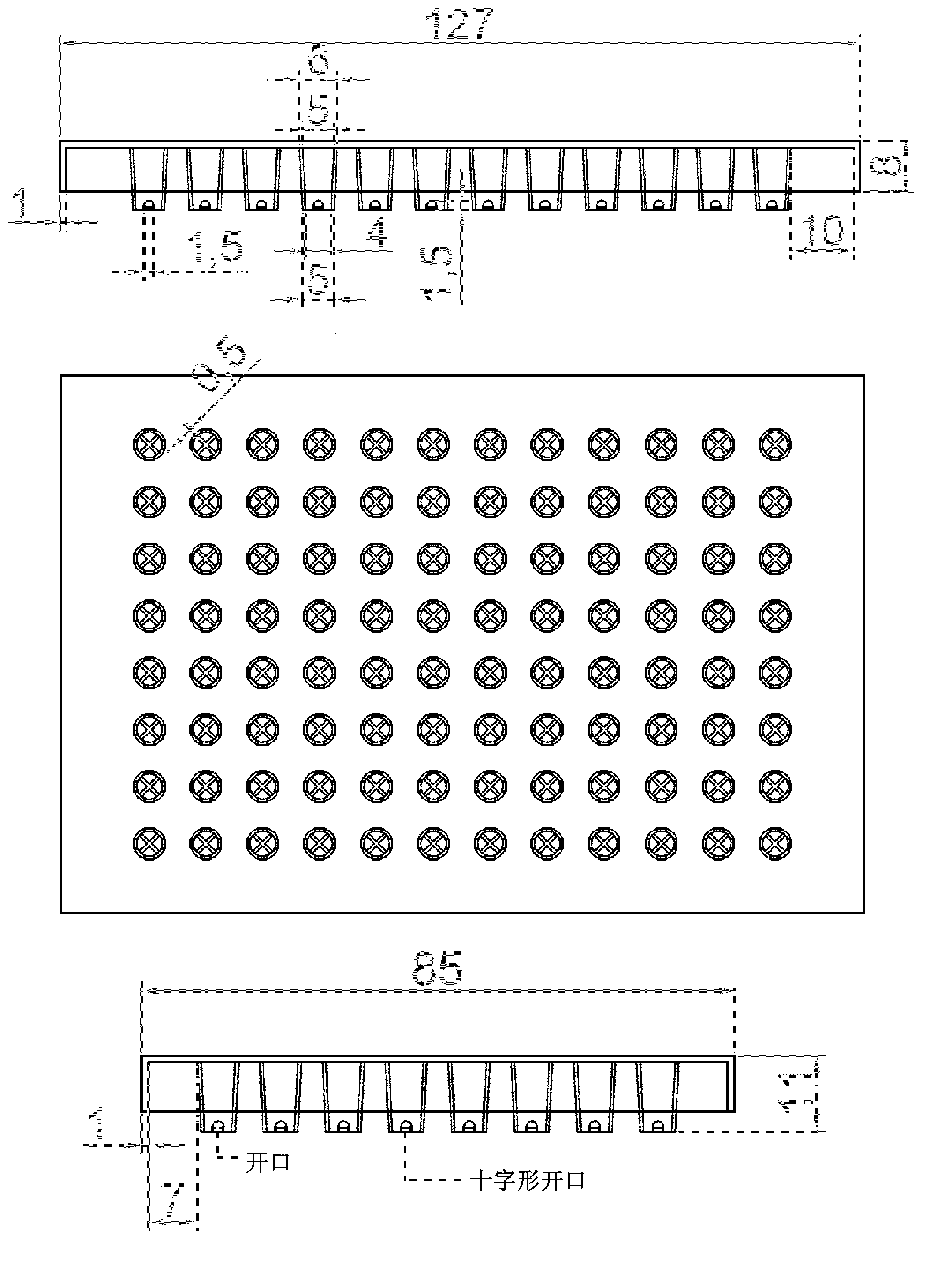
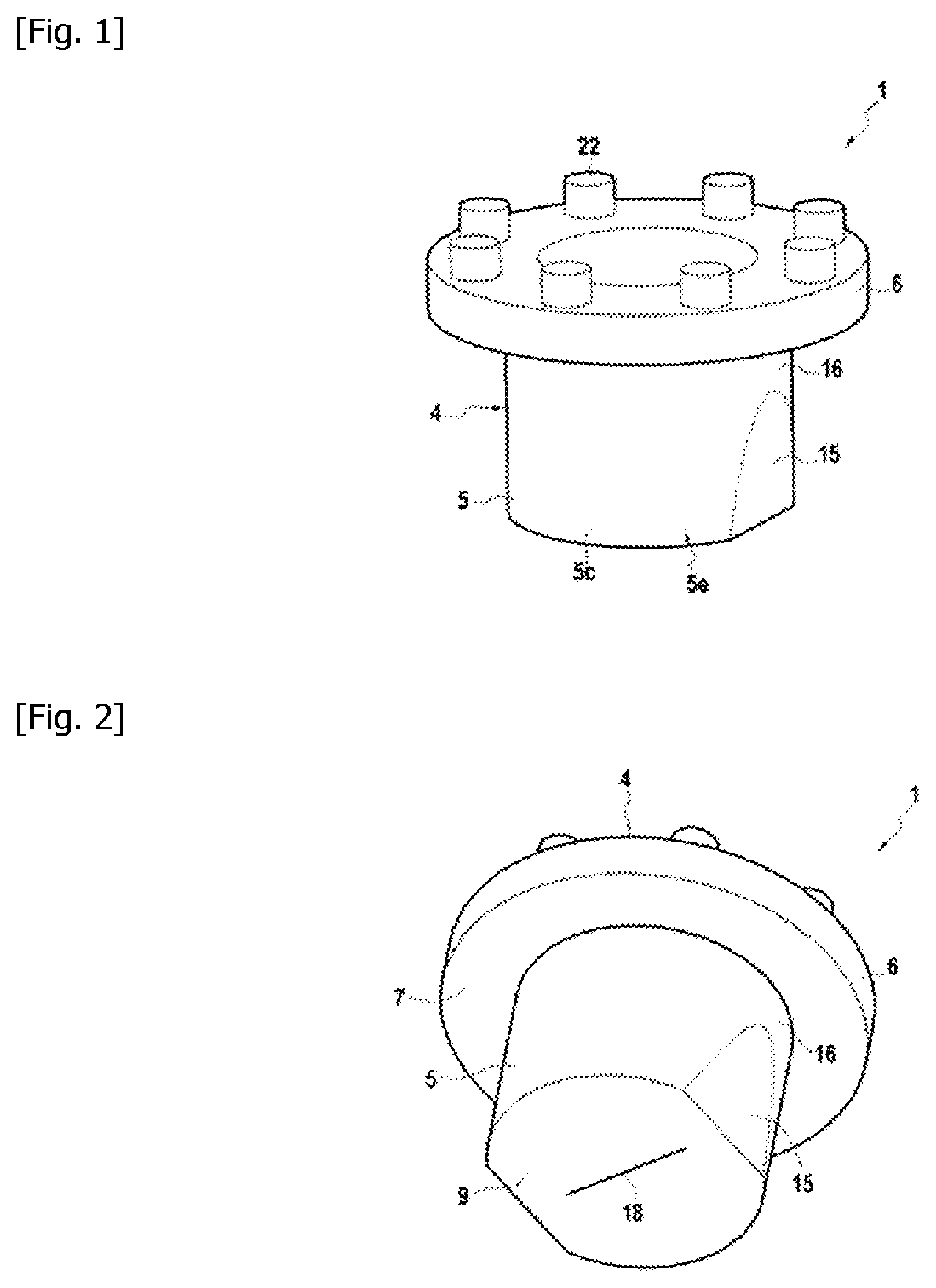
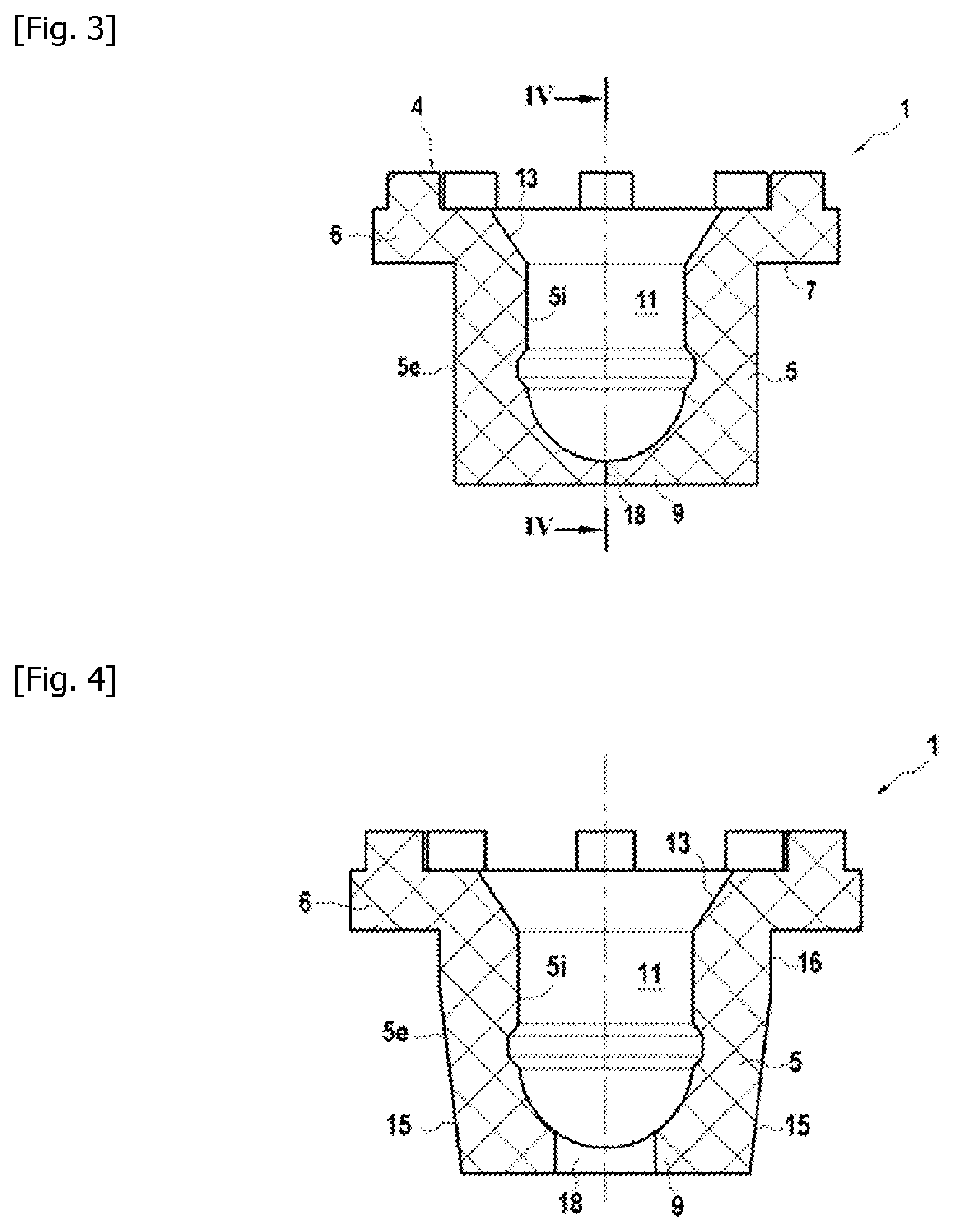
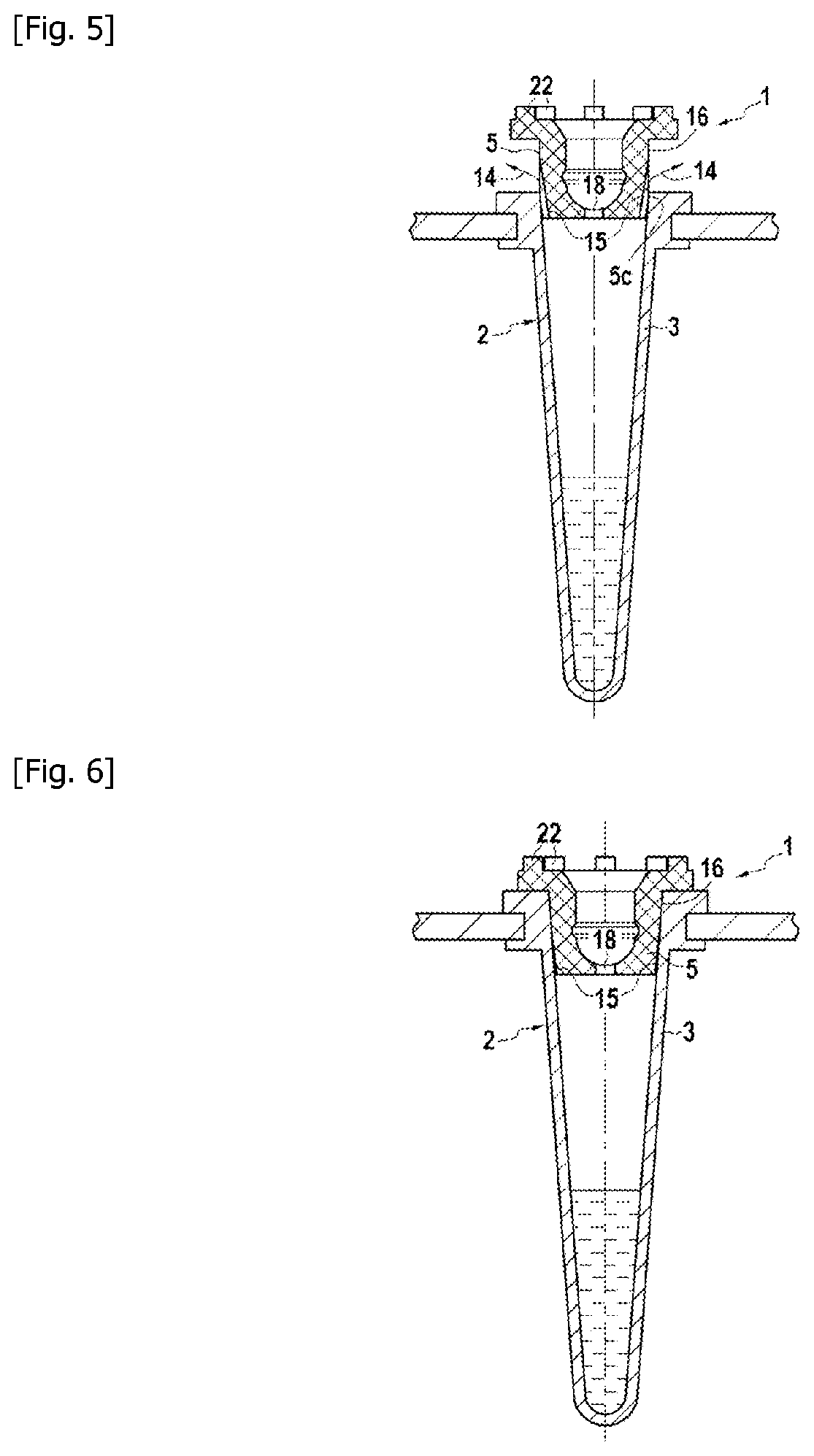
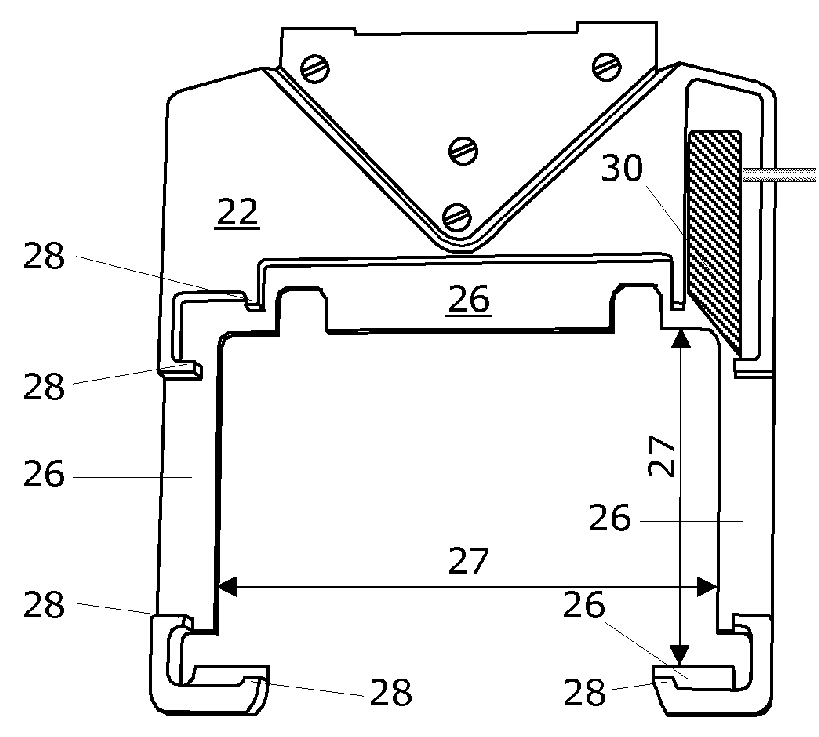
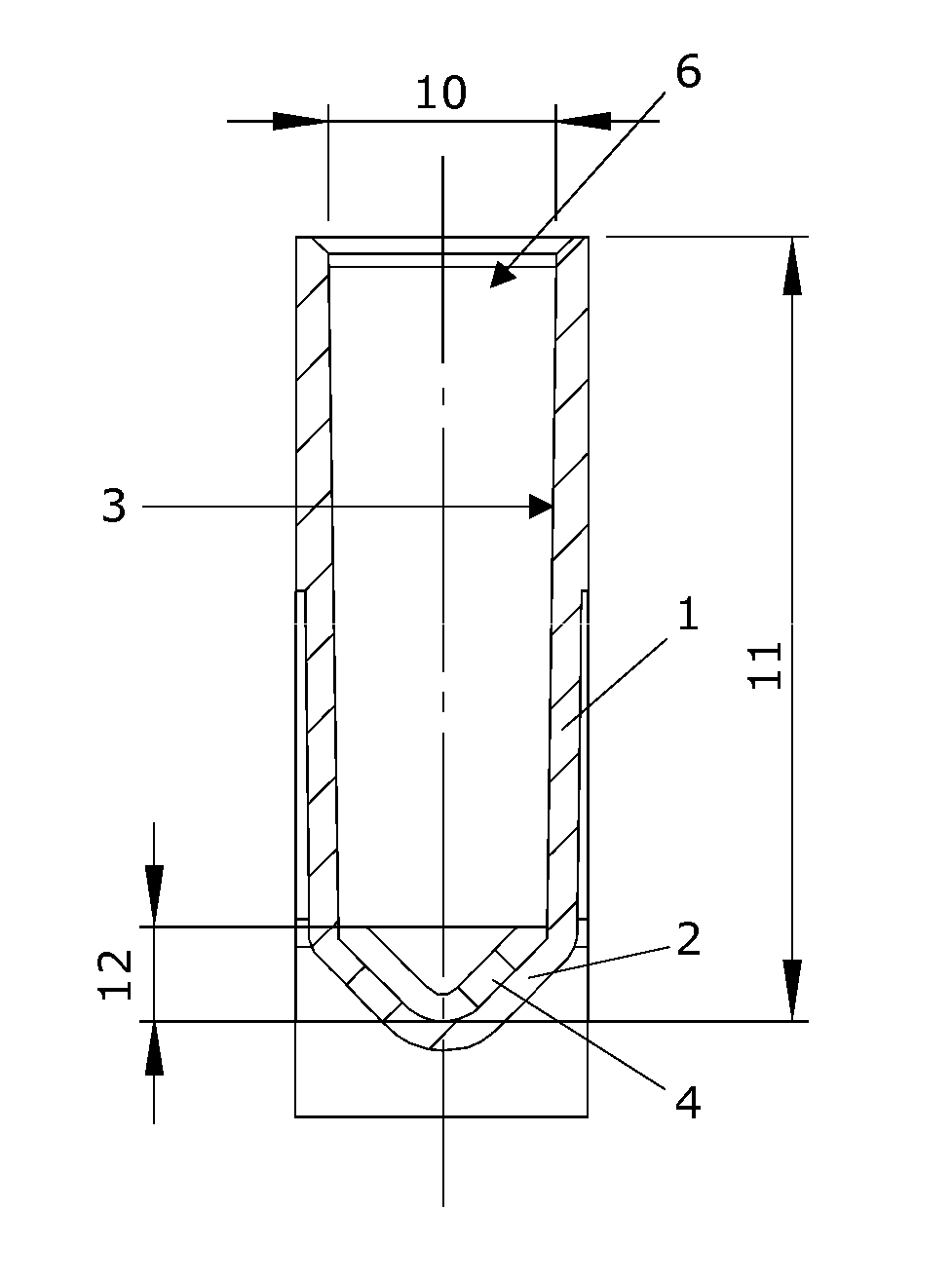
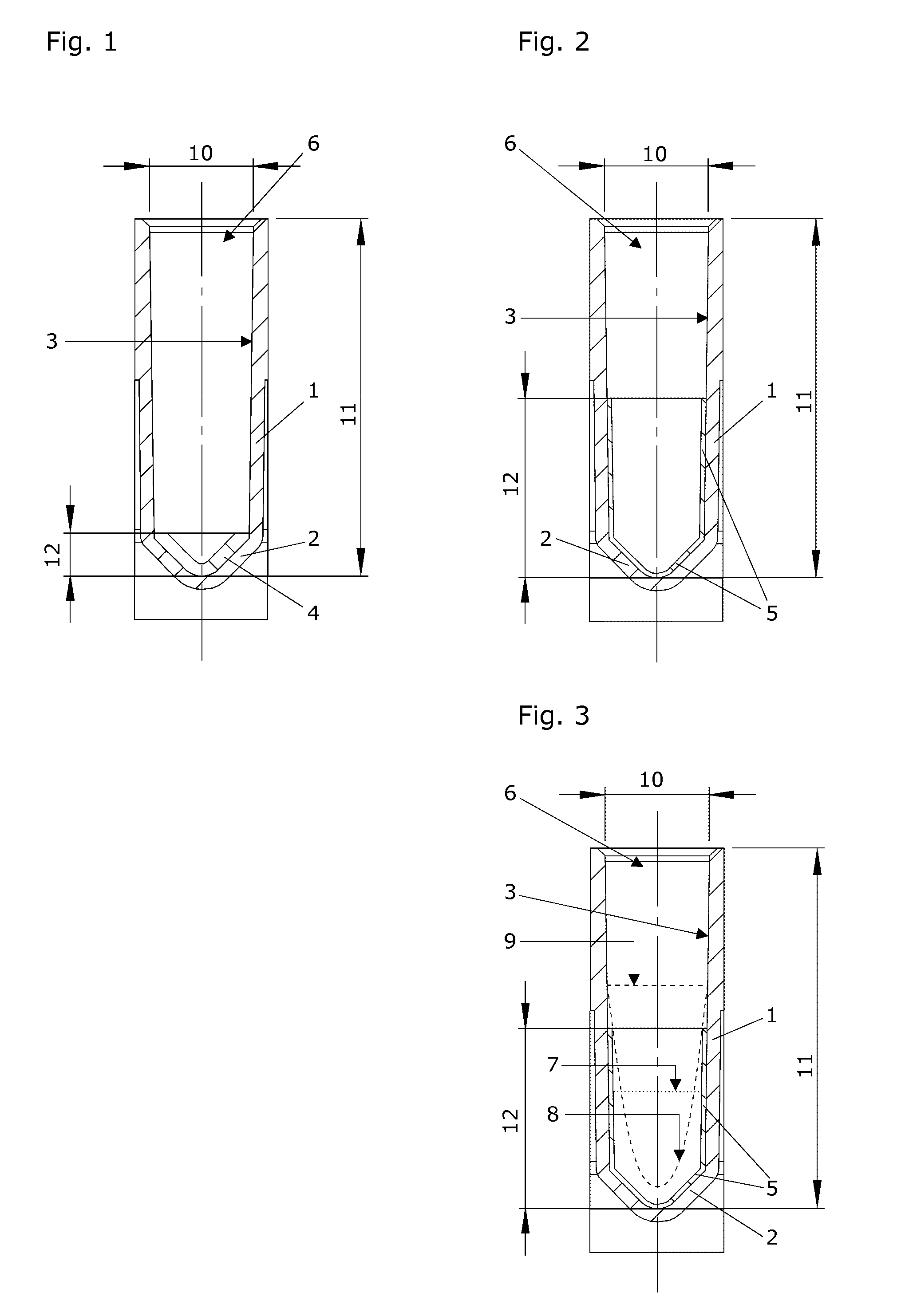
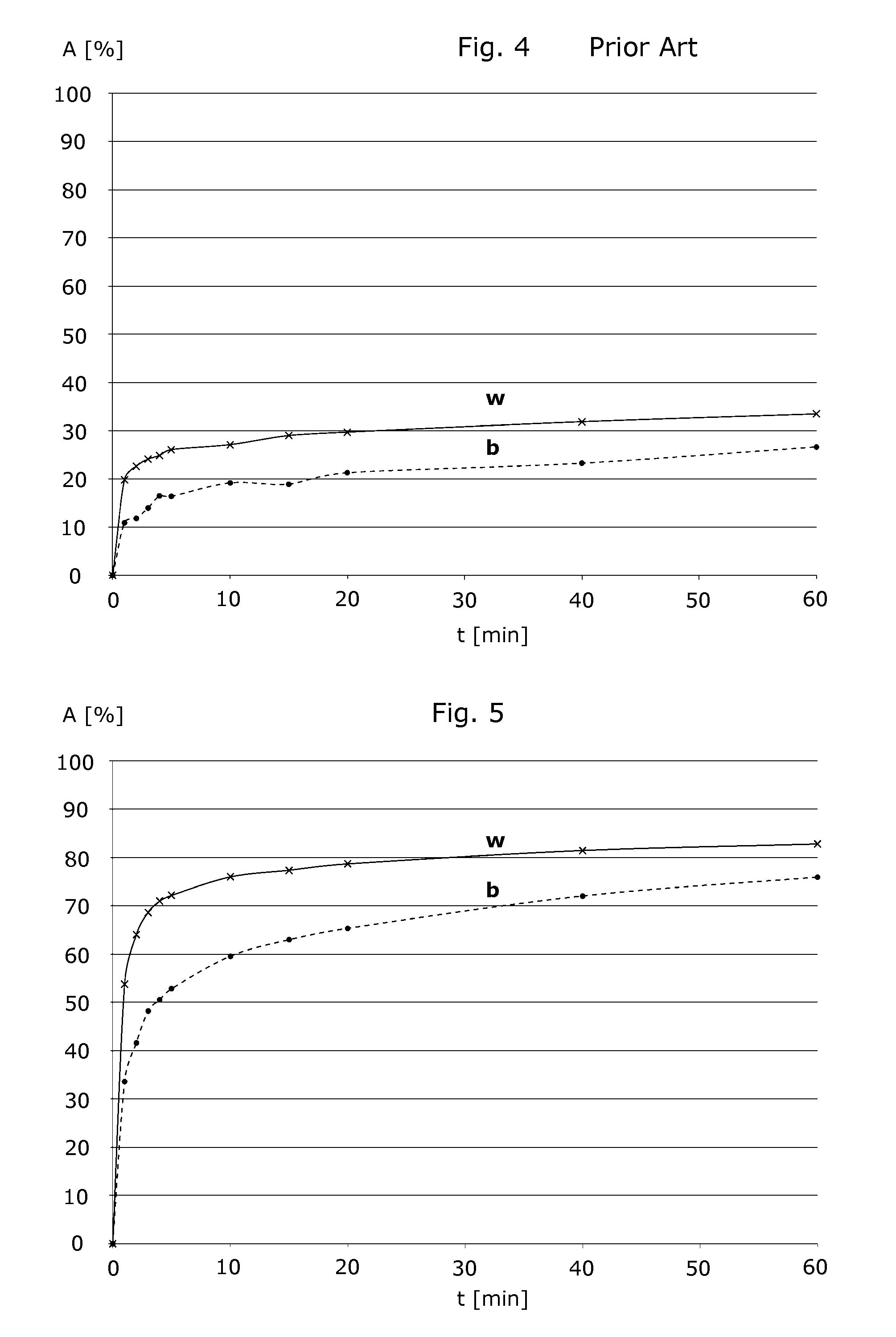
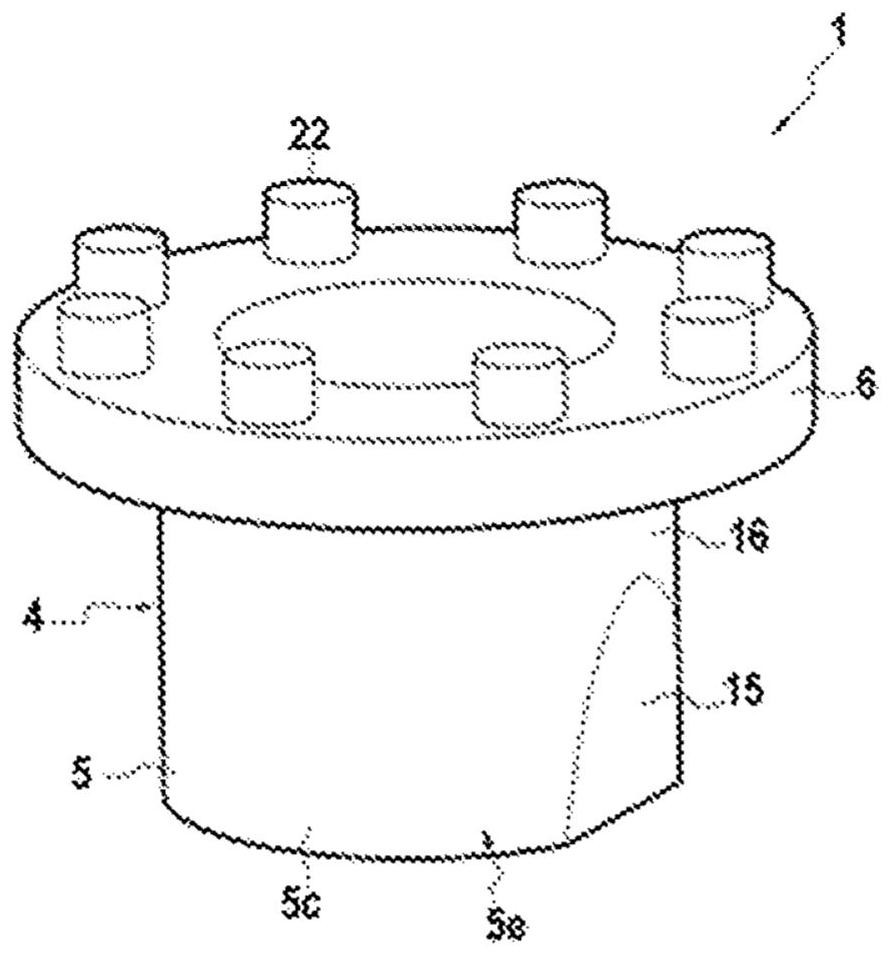
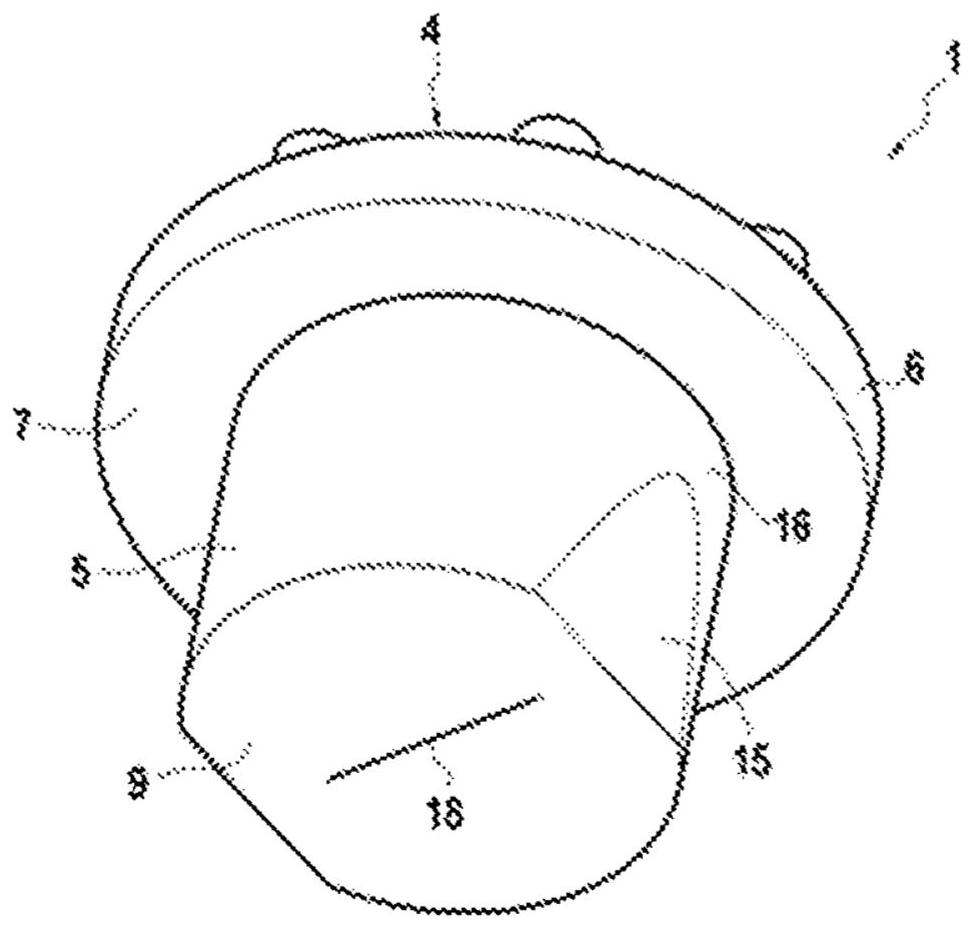
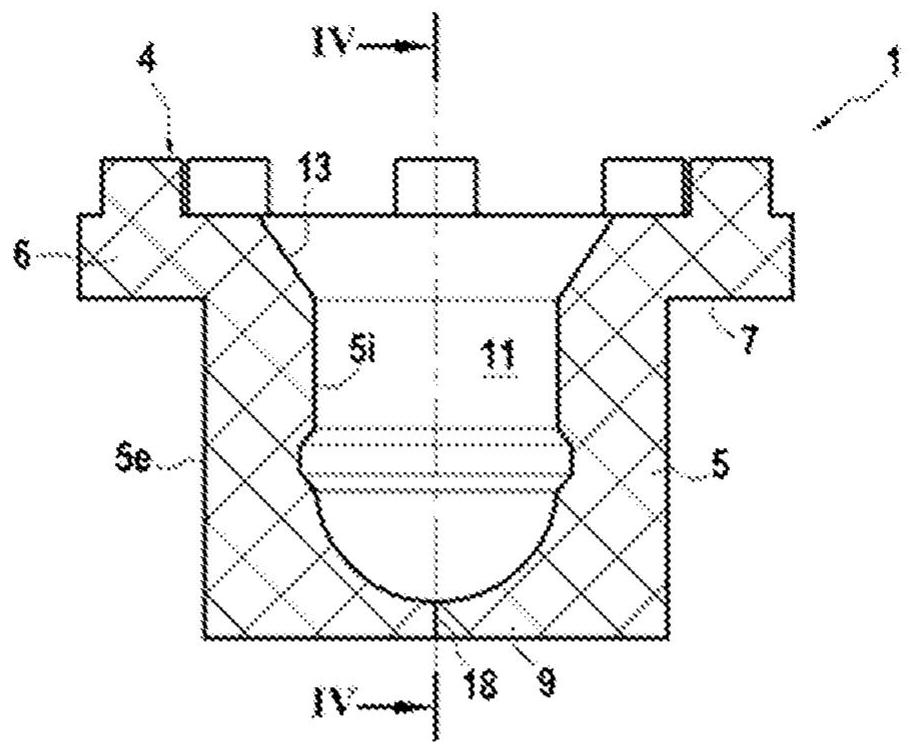
Closure element for a microplate well having vents and a slot, and method for the use thereof
An obturation element (1) for a well receiving a chemical or biological solution to be analyzed, including for each well, a plug (4) including an insertion sleeve (5) in the form of a cylinder provided with two truncated areas (15) arranged in a symmetrically opposite manner on the outside of the sleeve to form vents, this insertion sleeve (5) being provided with a bottom wall (9) in which a through-cutout (18) is arranged, oriented radially in the direction of the two truncated areas (15).
Owner:BIOMERIEUX SA
Influenza A virus subtype parting detection high-flux kit
ActiveCN109136406AFast throughputFlux sensitiveMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerMagnetic bead
The invention discloses an influenza A virus subtype parting detection high-flux kit which comprises a micropore plate, a micropore plate cover, a main electromagnetic chuck, a carboxyl magnetic beadand a reverse primer, wherein the micropore plate cover is matched with the micropore plate, the main electromagnetic chuck is detachably arranged at the bottom of the micropore plate, the carboxyl magnetic bead is connected with a magnetic bead connection forward primer, and a 5' end of the reverse primer is provided with a fluorescent mark. The micropore plate comprises a plurality of micropores, annular projections with inner diameters matched with those of the micropores are arranged on the micropore plate cover, the micropore plate and the micropore plate cover can be placed into a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) instrument, and a PCR tube and a PCR frame are replaced. The kit is high in repeatability and sensitivity, good in specificity and convenient and rapid to operate, and RT-PCR(reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) results are detected without electrophoresis.
Owner:浙江以和细胞生物科技有限公司
A heating and oscillating magnetic separation device
ActiveCN104117429BMagnetic Separation GuaranteeGuaranteed heated incubationMagnetic separationMagnetite NanoparticlesPush pull
The invention discloses a heating and oscillating magnetic separation device, which comprises three main modules, namely a magnetic separation module, a heating module and a vibration module. The magnetic separation module includes linear motors, lead screws, magnet brackets, and permanent magnets. The heating module includes electromagnetic pushers, springs, support plates, support columns, heating tanks, and heating films. The vibration module includes vibration motors and eccentric hammers. The device drives the magnet bracket to move on the lead screw through a linear motor, thereby driving the permanent magnet to move up and down, and controls the relative position of the permanent magnet and the microporous plate to realize the reunion and dispersion of magnetic nanoparticles; the electromagnetic push-pull device pushes the support plate up and down Movement, and then drive the heating tank to move up and down through the support column, and control the distance between the heating tank and the hole wall of the microplate to realize the function of heating and closing. Finally, a fully functional, compact and easy-to-integrate biological sample processing device based on magnetic separation is realized, and the automation of the entire experimental process can be realized by using the robotic arm device.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Microplate reader with incubation device
ActiveUS9964556B2Eliminate disadvantagesEasy to disassembleBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOptical axisEvaporation
Microplate reader has measuring space, action source, measuring device for biological structure signals of microplate wells, transport support for positioning wells in relation to an optical axis of the device and controller for the action source, the measuring device and the transport support. An incubation apparatus with a frame accommodates a microplate with wells having bottoms for reducing liquid evaporation. The frame has a first opening surrounded by an inner wall for the microplate and an outer wall parallel to the inner wall and connected thereto by an intermediate bottom so that a channel is formed and the intermediate bottom for accommodating a liquid adjusted to the content of the microplate wells. The incubation apparatus has a support surface with a second opening for a microplate and, as a result, at least a portion of the well bottoms is freely accessible by the second opening.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG
Sorptive extraction layer for immobilized liquid extraction
ActiveUS9200991B2Optimizes affinity and also extraction efficiency and overall recoveryPositive influence on the analyte partition ratioComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationBiological pumpCopolymer composition
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG
Closure element for a microplate well having vents and a slot, and method for the use thereof
ActiveCN113825566AMake sure to closeClosuresClosure using stoppersMicrowell PlateStructural engineering
The invention relates to a closure element (1) for a well for receiving a chemical or biological solution to be analysed, comprising, for each well, a plug (4) comprising an insertion skirt (5) taking the form of a cylinder provided with two truncated regions (15) formed in a symmetrically opposite manner on the outside of the skirt to form vents, this insertion skirt (5) being provided with an end wall (9) in which there is formed a through-cutout (18) oriented radially in the direction of the two truncated regions (15).
Owner:BIOMERIEUX SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com