Halomonas sp. capable of degrading phenols and high-throughput screening method and application thereof
A medium halophilic bacteria and screening method technology, applied in the moderate halophilic bacteria degrading phenol and its high-throughput screening and application field, can solve the problem of large reagent consumption, monotonous and cumbersome screening methods, and high screening efficiency low level problem
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
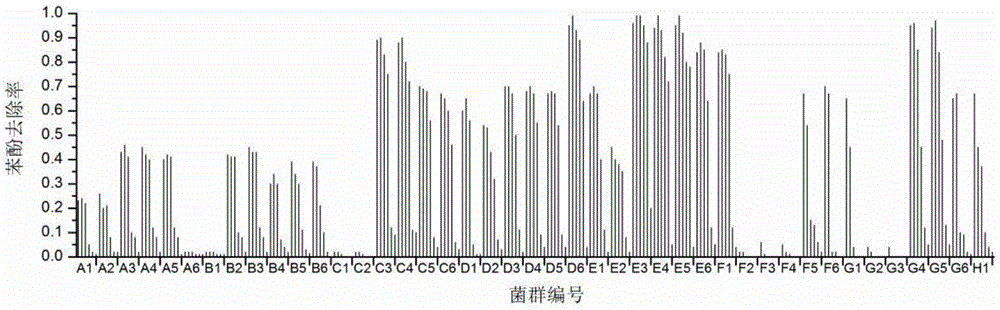
[0103] 43 environmental samples were collected from 8 environments polluted by high salinity and organic matter (Table 6). First enrich in 125-mL serum bottles according to step (1) of the screening method, and then transfer 3 times to obtain the bacterial population without sediment.
[0104] Table 6 Sample collection information
[0105]
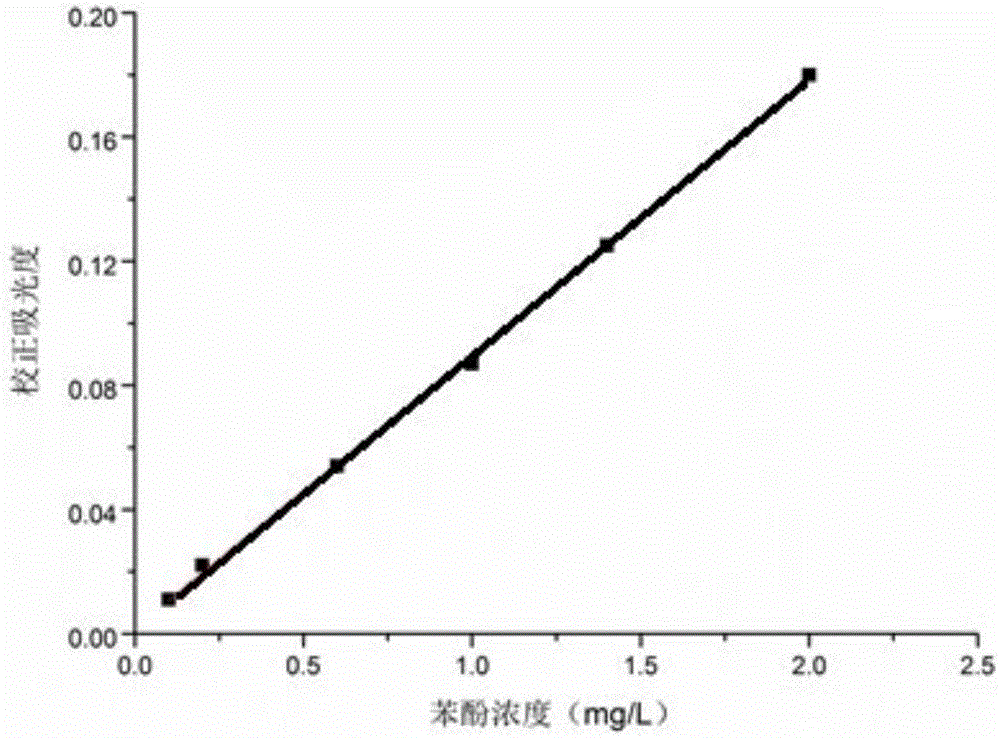
[0106] The 43 cultures (No: A1–H1) were respectively transferred to 48-well deep-well plates according to step (2) of the screening method, and cultured at 30°C and 200rpm for 72h. According to step (3) of the screening method, the remaining phenol concentration in the deep well plate was determined by using a 96-well microplate reader plate spectrophotometric method based on 4-aminoantipyrine colorimetry. Transfer 200 μL of the bacterial solution in the 48-well deep-well plate to a 96-well microplate reader plate, centrifuge the whole 96-well microplate reader plate at 2500×g for 20 min, transfer the supernatant to a new 96-well micro...
Embodiment 2
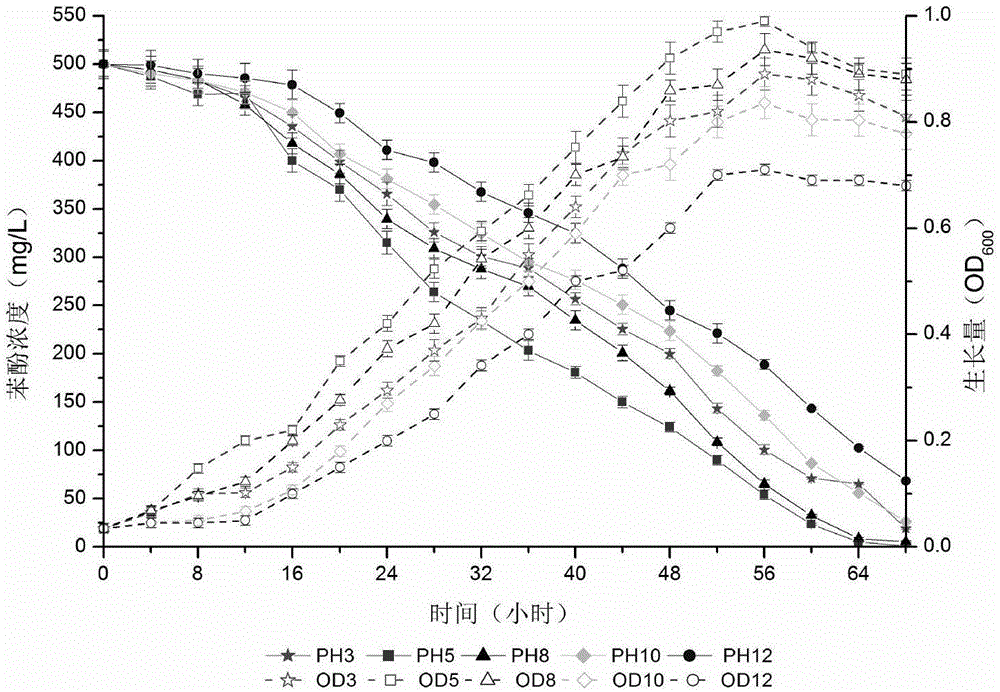
[0113] Halomonassp.PH4-5 was inoculated into MSM medium containing 500 mg / L phenol and 3%-12% (w / v) sodium chloride to investigate the degradation of phenol.
[0114] Halomonassp.PH4-5 optimal growth and degradation salinity is 5%. After the strain was grown in MSM medium containing 500 mg / L phenol for 68 hours, the phenol removal rates were 96.2%, 99.8% at 3%, 5%, 8%, 10%, and 12% (w / v) NaCl , 98.9%, 94.7% and 86.3% (see image 3 ). The strain has a removal rate of more than 94% for 500mg / L phenol in the salinity range of 3%-10%, and can degrade high-concentration phenol in a wide salinity range, reflecting the advantages of moderate halophilic bacteria. It can be used for biological treatment of high-salt phenolic wastewater.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com