Quick counting method for microcystis aeruginosa
A microcystis aeruginosa, counting method technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based method, microorganism determination/inspection, biochemical equipment and method, etc. Counting and other issues to achieve the effect of improving detection efficiency and accuracy, simple pretreatment, and reducing sample loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
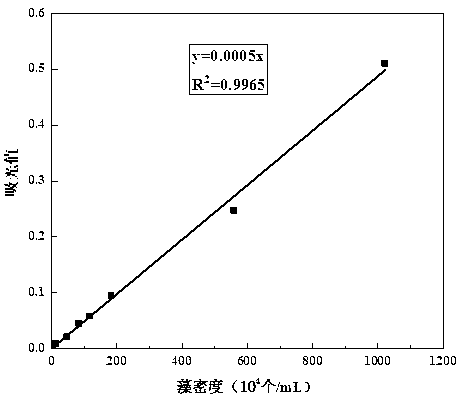
[0028] According to the rapid counting method of Microcystis aeruginosa of the present invention, at first establish a calibration curve or a regression equation between the algae liquid absorbance and the cell density of Microcystis aeruginosa, the specific steps are as follows:
[0029] 1. Preparation of algae solution. Microcystis aeruginosa was cultured with sterilized BG-11 in a light incubator, and the culture conditions were: light intensity 40μE·(m 2 s) -1 , temperature 25°C, light-to-dark ratio 12h: 12h, shake regularly 3 times a day. After culturing for 7-10 days, take 1ml of the algae liquid and dilute it 2, 5, 8, 10, 20, 50, 100, 1000 times with sterilized BG-11 medium respectively.
[0030] 2. Cell count. Accurately count the cells of each concentration with a microscope, repeat 5 times for each sample, and take the average value to obtain the cell density C i .
[0031] 3. Measure the absorbance. Add the algae solution of the blank group and different conce...
Embodiment 2
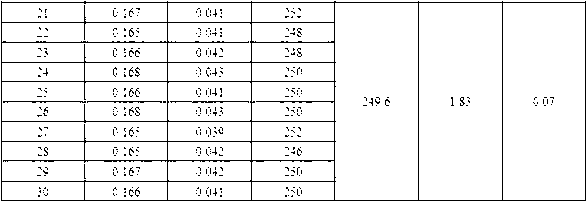
[0038] According to the calibration curve or regression equation established in Example 1, the rapid counting method of Microcystis aeruginosa of the present invention is used to measure the cell density of the algae liquid, and compared with the flow cytometer counting method, the specific steps are as follows:
[0039] 1. Preparation of algae solution. Microcystis aeruginosa was cultured with sterilized BG-11 in a light incubator, and the culture conditions were: light intensity 40μE·(m 2 s) -1 , temperature 25°C, light-to-dark ratio 12h: 12h, shake regularly 3 times a day. After culturing for 10 days, take 1ml of algae fluid and dilute it with sterilized BG-11 medium to make algae fluid with three concentration gradients of high, medium and low, and add sterilized BG-11 to the blank group.
[0040] 2. Cell count. The cell densities of the algae liquid in the high, medium and low concentration gradients were 9.64×10 by precise counting using a flow cytometer. 4 pcs / mL, 5...
Embodiment 3
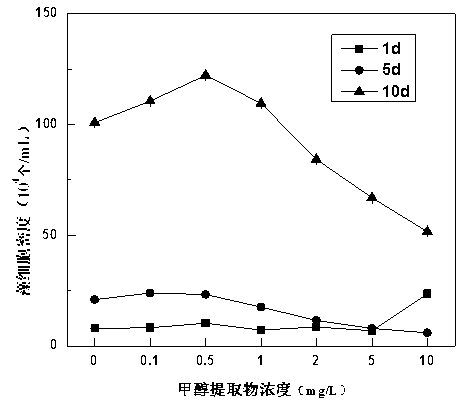
[0049] According to the rapid counting method of Microcystis aeruginosa of the present invention, the impact of rice straw methanol crude extract on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa is studied, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0050] 1. Sample preparation. Take 50g of crushed dry rice straw (passed through a 40-mesh sieve) and place it in a 1L Erlenmeyer flask, add 500ml of analytically pure methanol, ultrasonically treat for 1 hour at room temperature, and repeat twice. After the extraction, the residue was removed, the particle interference was removed through a 0.22 μm filter membrane, and the extract was obtained by rotary evaporation at 65° C. and weighed.
[0051] Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was used to dilute the methanol extract (experiments have confirmed that when the proportion of DMSO added is less than 1%, it has no effect on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Hong Yu, Hu Hongying, Huang Jingjing, Sakoda A, Sagehashi M. Different Effects of solvent e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com