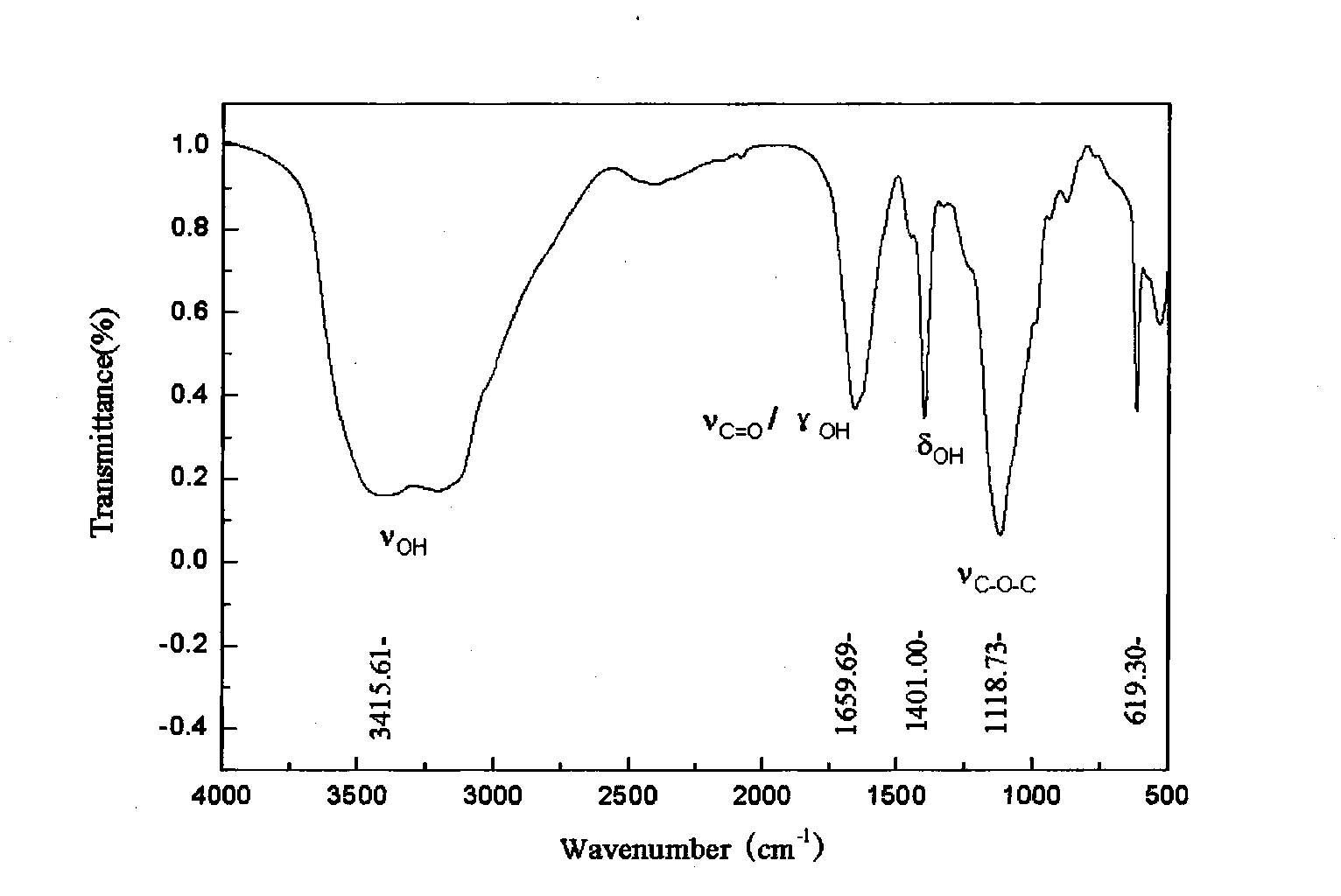
Patents
Literature
59results about How to "High flocculation activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Paenibacillus and application thereof to environmental engineering
InactiveCN101870958AImprove fermentation yieldEasy to pick upBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIonChemistry
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Preparation method for biological flocculant
InactiveCN101121920AEasy to handleNo pollution in the processFungiWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationFlocculationAspergillus
The invention discloses a method to prepare bio-flocculant. The invention is characterized in that aspergillus fermentating cultivation is adopted. The aspergillus is agitated and fermented (28-30 DEG C, pH6-7, under ventilating condition) for 48-60 hours; the fermentation broth is filtered and condensed, and then proper amount of ethanol is added into the condensed broth and centrifugal separation is conducted after stewing; the deposition is washed with ethanol and dried in vacuum to achieve a crude product of fawn flocculant. The prevention method has the advantages of simple condition of production and low cost. The bio-flocculant prepared by the method is applicable to disposing sewage containing granular contaminants or filth, and the dosage generally drops in 0.1 to 0.3 per mill. It is proved by flocculation treatment that, compared with the prior art, the invention has sound flocculation effect, low flocculant speed and small dosage; besides, the invention is environment-friendly and harmless to human body.
Owner:ENZYME ENG INST SHAANXI PROVINCE ACAD OF SCI
Exopolysaccharide generated by pseudomonas, culture method and application
ActiveCN104232548AIncrease productionGood water solubilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention relates to an exopolysaccharide generated by pseudomonas, a culture method and application. The pseudomonas sp. QL212 is preserved in common microbe center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on September 12, 2014, at the address of Institute of Microbiology of Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, Yard No. 1, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and having the preservation number of CGMCC NO.9651. The curdlan synthesized by the pseudomonas sp. QL212 serves as the exopolysaccharide; through fermentation condition optimization, the yield of curdlan is up to 5.94 g / L which is higher than the production peak of the already known pseudomonas curdlan.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Extra-cellular polysaccharide of aerobic Ruthia sp. strain metabolin and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101580550AHigh flocculation activityMicroorganism based processesSustainable biological treatmentBiotechnologyActivated sludge
The invention relates to an extra-cellular polysaccharide of aerobic Ruthia sp. strain metabolin and preparation and application thereof. An aerobic strain ZHT4-13 is separated from adhesive sludge of wild Ruditapes philippinarums in the Bohai sea offshore of China and is identified as a Ruthia sp. The aerobic strain is treated by seed culture and amplification culture, and a fermentation broth of the aerobic strain is precipitated with ethanol and separated centrifugally to obtain the extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13. The extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13 is measured to have high flocculation activity, the FR value to kaolin reaches over 80 percent, and the removal rate to hexavalent chromium ions reaches 69.3 percent; the extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13 has high activity to decolorize high-concentration wastewater, and the decolorization ratios to methylene blue, ink blue, malachite green and crystal violet reach 86.11 percent, 99.49 percent and 97.84 percent; and the extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13 plays a role of obviously improving the performance and the structure of activated sludge. The extra-cellular polysaccharide has potential value of developing a novel microbial flocculant.
Owner:DALIAN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Method of preparing flocculating agent by utilizing sludge and application thereof
InactiveCN102976579AChange the body structureVarious ingredientsSludge treatmentWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationFlocculationMicroorganism
The invention relates to a preparation process of preparing a flocculating agent by utilizing sludge, and discloses a method of preparing flocculating agent by utilizing sludge and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: mutually connecting the two pretreatments of the sludge in series to change the virtual structure of the sludge, changing physical and chemical properties of the sludge particles and microbial cells in the sludge, and enabling the sludge to possess higher adsorption property of the flocculating agent. The flocculation rate to kaolin can be up to 95% above. The processing method mainly comprises the steps of adjusting the pH value, heating and centrifuging and so on. The process has the characteristics of low cost, simple process, short preparation time, convenience in application and good processing effect and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
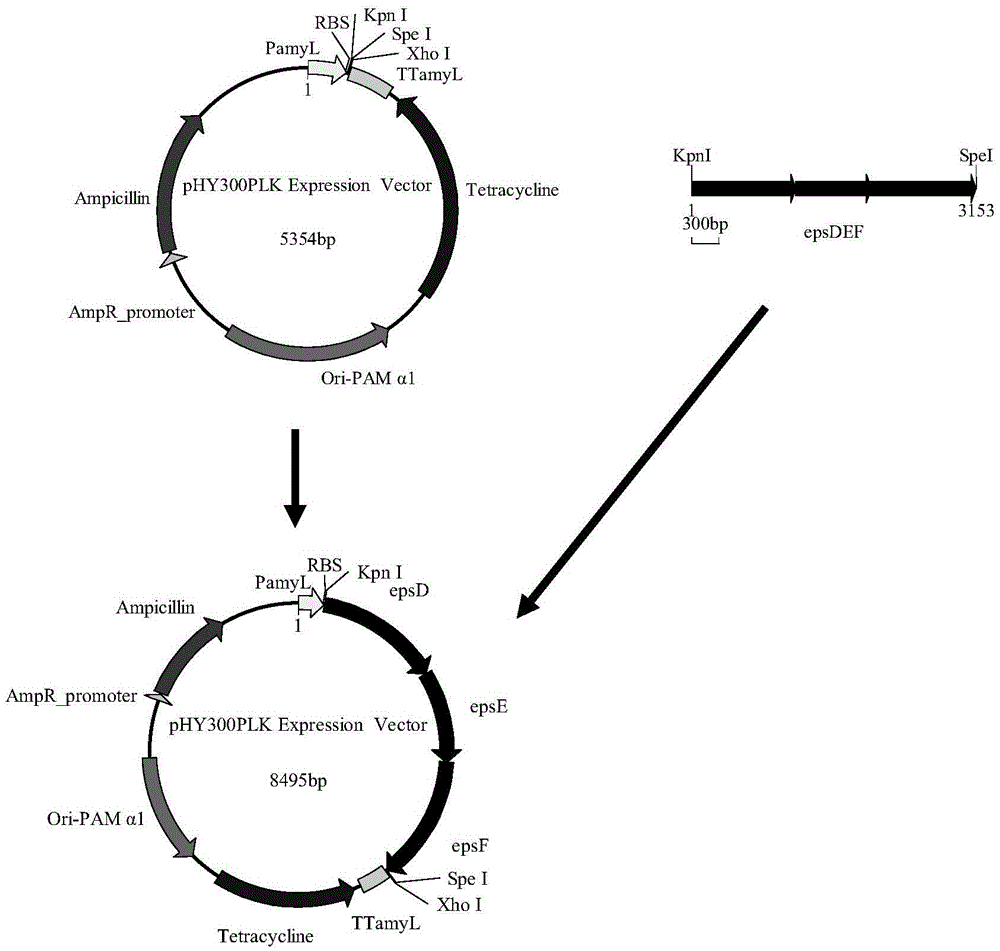
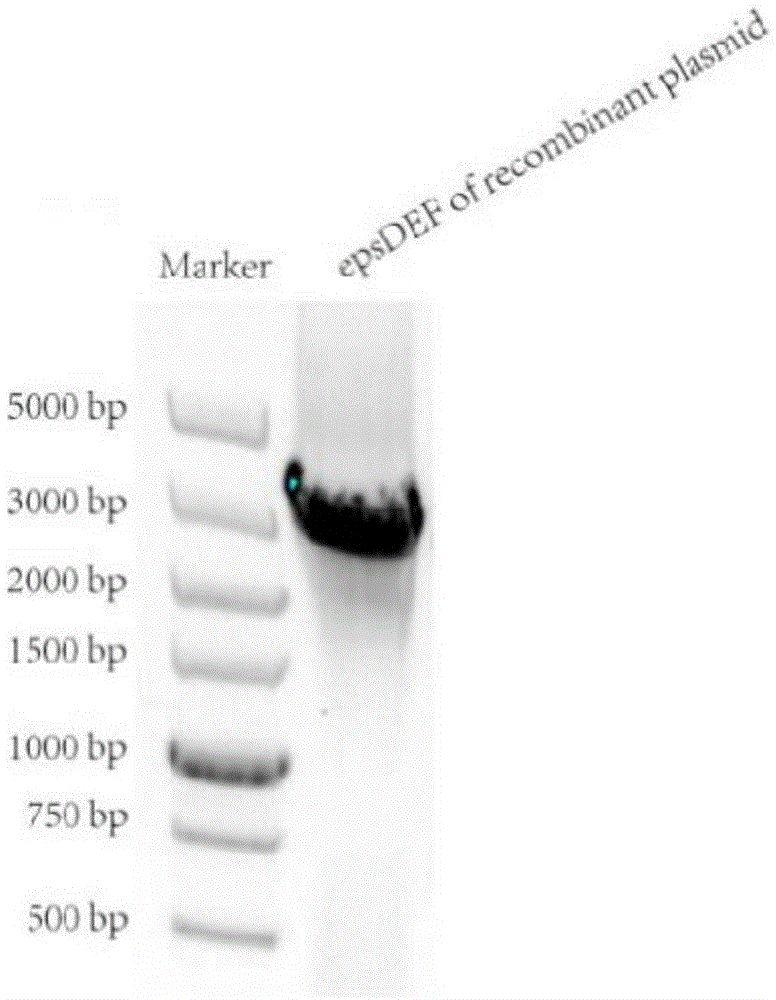
Bacillus licheniformis gene engineering bacterium capable of producing polysaccharide flocculant at high yield and establishment method thereof
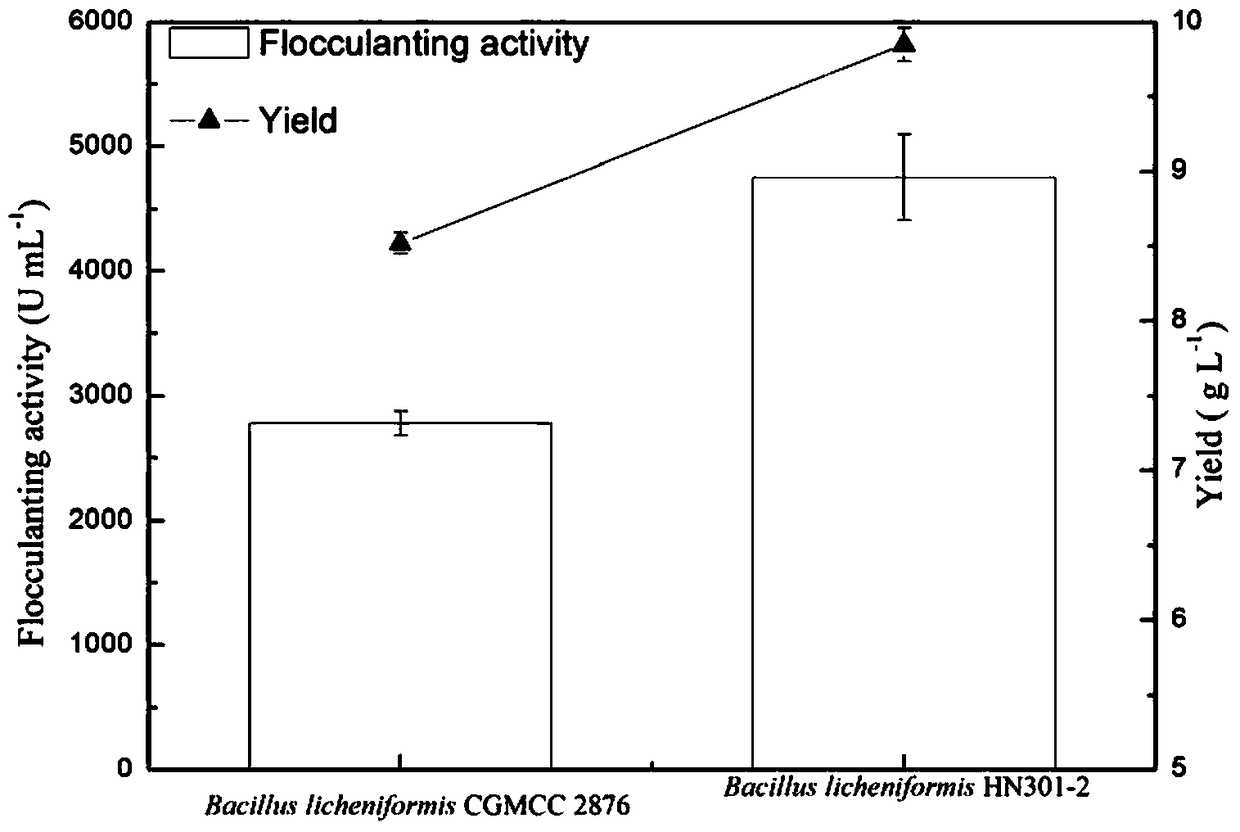
ActiveCN105624080AHigh flocculation activityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisNucleotide
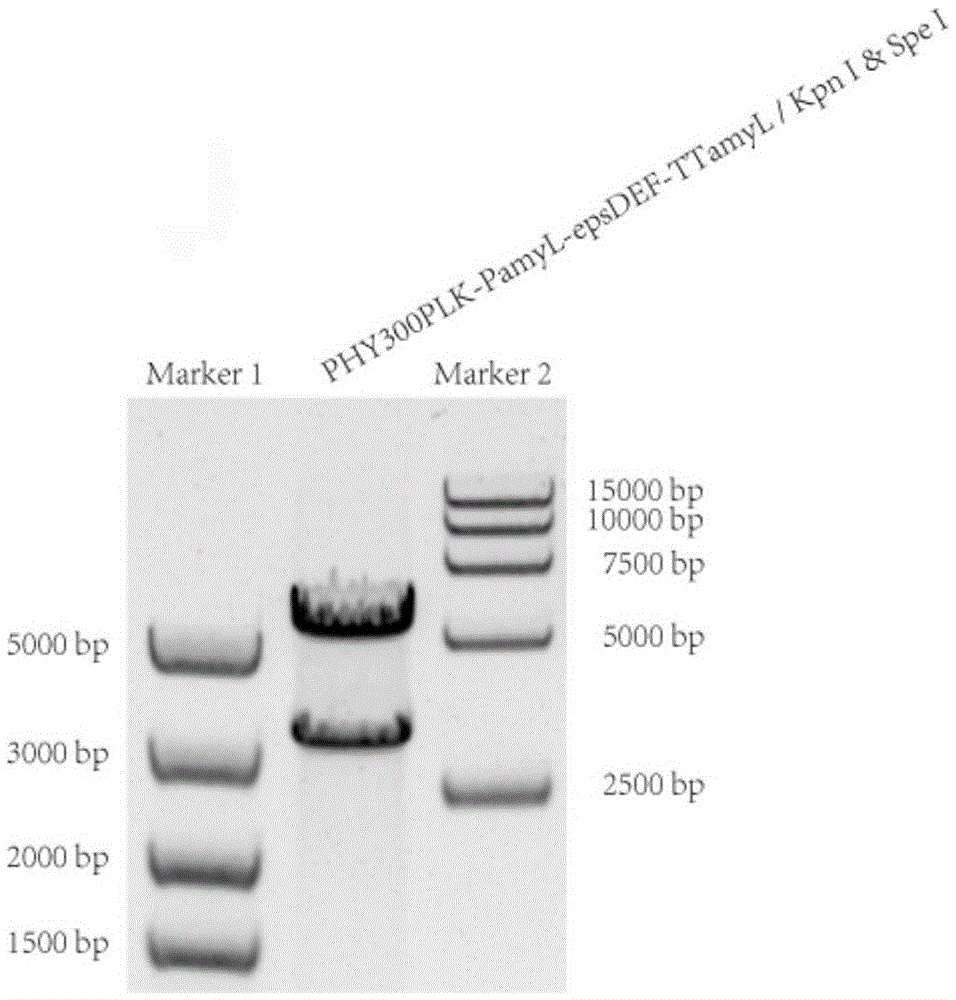
The invention relates to a Bacillus licheniformis gene engineering bacterium capable of producing a polysaccharide flocculant at high yield and an establishment method thereof, belonging to the technical fields of gene engineering and microbial fermentation. The gene engineering bacterium is formed by overexpressing epsDEF gene in Bacillus licheniformis. The nucleotide sequence of the epsDEF gene is disclosed as SEQ ID No 1 in the sequence table. The gene engineering bacterium preparation method comprises the following steps: cloning the epsDEF gene into an expression vector to obtain a recombinant expression vector, and transforming the recombinant expression vector into extracellular-polysaccharide-producing Bacillus licheniformis by electric transformation, thereby obtaining the gene engineering bacterium capable of producing a polysaccharide flocculant at high yield. The polysaccharide flocculant preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out fermentation and culture on the gene engineering bacterium, collecting the fermentation liquid, and purifying to obtain the polysaccharide flocculant. In the gene engineering bacterium fermentation process, the flocculation activity of the fermentation liquid is obviously enhanced, and the polysaccharide flocculant yield is obviously enhanced. The polysaccharide flocculant is applicable to sewage treatment and food engineering.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Bacillus licheniformis, method for preparing flocculating agent from bacillus licheniformis and application of flocculating agent
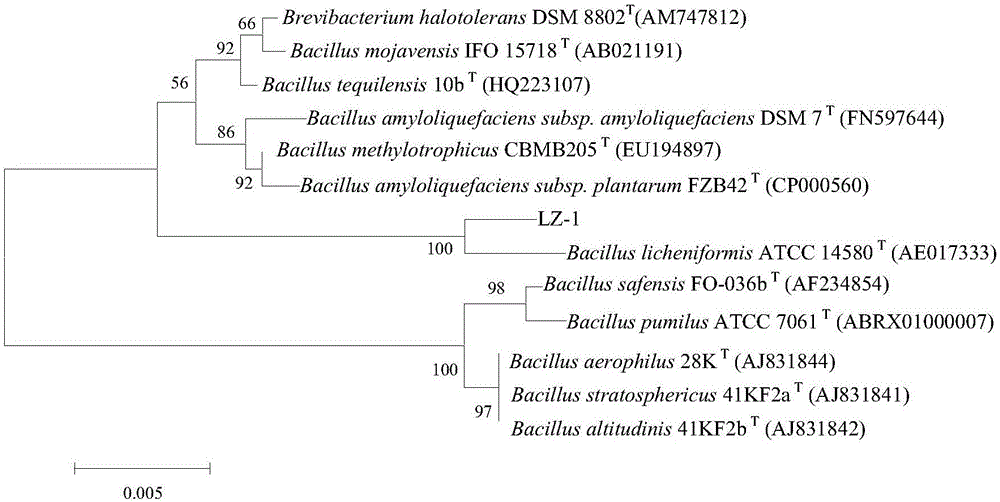
ActiveCN106244478AWide growth temperature rangeHas alkali resistanceSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningBacteriaBacillus licheniformisSludge cake
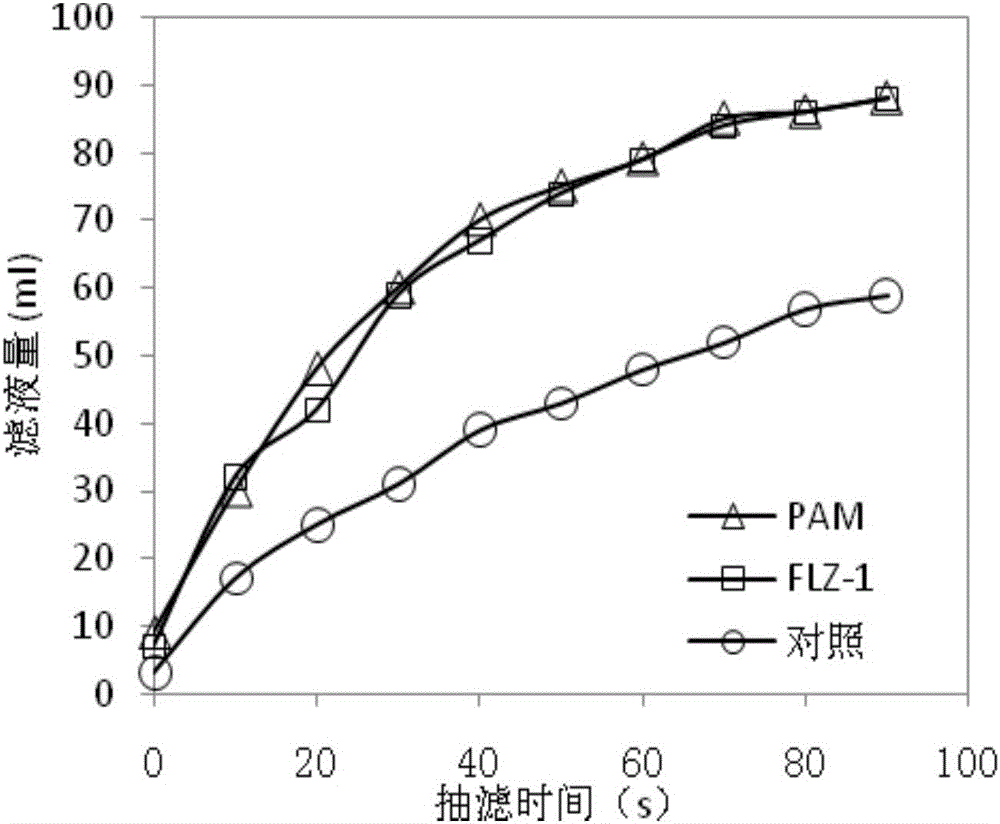
The invention relates to bacillus licheniformis, a method for preparing a flocculating agent from the bacillus licheniformis and an application of the flocculating agent. The strain is bacillus licheniformis LZ-1 which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on November 06, 2012 with preservation number of CGMCC No.6782. With the application of the bacillus licheniformis LZ-1 as well as a production method provided by the invention, a fermentation broth, which is high in flocculating activity, is obtained under the condition that an initial pH value is alkaline, and high-molecular-weight polysaccharide, which is 0.8-3.2*10<7>Da, serves as a major flocculating active ingredient. The polysaccharide flocculating agent provided by the invention has the advantages of being high in flocculating activity, low in dosage, low in production cost and the like, and the flocculating agent has a flocculating conditioning effect on sludge. The bacillus licheniformis LZ-1 fermentation broth or a product, which is extracted from the fermentation broth and contains the polysaccharide flocculating agent, can be applied to deep dewatering by sludge plate-frame pressure filtration in a mode of replacing a polyacrylamide flocculating agent, so that sewage treatment plant concentrated sludge, which is 96-98% in moisture content, is further dewatered into a sludge cake which is lower than 60% in moisture content and the size of the sludge is diminished to be 1 / 20-1 / 10 of an original size.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Extra-cellular polysaccharide of aerobic Ruthia sp. strain metabolin and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101580550BHigh flocculation activityMicroorganism based processesSustainable biological treatmentBiotechnologyActivated sludge
The invention relates to an extra-cellular polysaccharide of aerobic Ruthia sp. strain metabolin and preparation and application thereof. An aerobic strain ZHT4-13 is separated from adhesive sludge ofwild Ruditapes philippinarums in the Bohai sea offshore of China and is identified as a Ruthia sp. The aerobic strain is treated by seed culture and amplification culture, and a fermentation broth ofthe aerobic strain is precipitated with ethanol and separated centrifugally to obtain the extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13. The extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13 is measured to have high flocculation activity, the FR value to kaolin reaches over 80 percent, and the removal rate to hexavalent chromium ions reaches 69.3 percent; the extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13 has high activity to decolorize high-concentration wastewater, and the decolorization ratios to methylene blue, ink blue, malachite green and crystal violet reach 86.11 percent, 99.49 percent and 97.84 percent; and theextra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13 plays a role of obviously improving the performance and the structure of activated sludge. The extra-cellular polysaccharide has potential value of developing a novel microbial flocculant.
Owner:DALIAN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Multi-functional composite bioflocculant for wastewater treatment
InactiveCN102557211AHigh activityEasy to handleWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationTherapeutic effectChemistry
The invention discloses a multi-functional composite bioflocculant for wastewater treatment. The composite bioflocculant is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 15 to 30 percent of aluminum polychlorid, 5 to 20 percent of ferrous sulfate, 5 to 20 percent of sodium hydrogen phosphate, 5 to 10 percent of magnesium sulfate, 2 to 5 percent of potassium chloride, 2 to 5 percent of zinc chloride, 1 to 2 percent of calcium carbonate and 50 percent of microbial flocculant. The composite bioflocculant has the characteristics of high-efficiency flocculation, easiness for microbial degradation and environment friendliness, also has certain microbial growth factors, and can be used for the growth and succession of microorganisms in the subsequent biochemical treatment process of wastewater as well as quick and mass propagation in severe environments, accelerate biochemical reaction and improve the treatment effect of biochemical systems.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Method for extracting bioflocculant
InactiveCN102399823AHigh flocculation activityLow costMicroorganismsFermentationChemistryHigh activity
The invention relates to a method for extracting a bioflocculant. The method is characterized by extracting the flocculant from activated sludge, has the advantages of wide source and low cost, comprising the following steps: screening the activated sludge and extracting bacterial strains with best activity, culturing in a glucose medium, and then carrying out extraction on the supernatant liquor in the medium by acetone process, ethanol process or CTAB process. The obtained flocculant has high activity, high yield, no secondary pollution to the environment, and very good potential of large scale production.
Owner:SHANGHAI HAIDI GARDENING
Industrial sewage treatment adsorbent
InactiveCN106830163AEasy to passImprove adsorption capacityWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationAdhesiveSorbent
The invention discloses an industrial sewage treatment adsorbent. The industrial sewage treatment adsorbent comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-40 parts of attapulgite, 30-40 parts of argil, 20-30 parts of expanded graphite cyclodextrin compound, 10-18 parts of bamboo charcoal, 10-20 parts of carbon nanotube, 5-10 parts of retinervus luffae fructus, 8-18 parts of adhesive, 20-35 parts of flocculant and 3-5 parts of oxidizing bactericide. According to the invention, industrial sewage treatment is performed by means of the attapulgite clay; and the industrial sewage treatment adsorbent can adsorb wastewater containing heavy metal, is high in effect and low in cost, and achieves considerable economic benefits.
Owner:安徽其霖环境工程技术有限公司
Engineering bacterium with overexpressed uridine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase gene and establishment thereof
ActiveCN105624176AIncrease productionHigh flocculation activityWater contaminantsTransferasesEscherichia coliUridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase
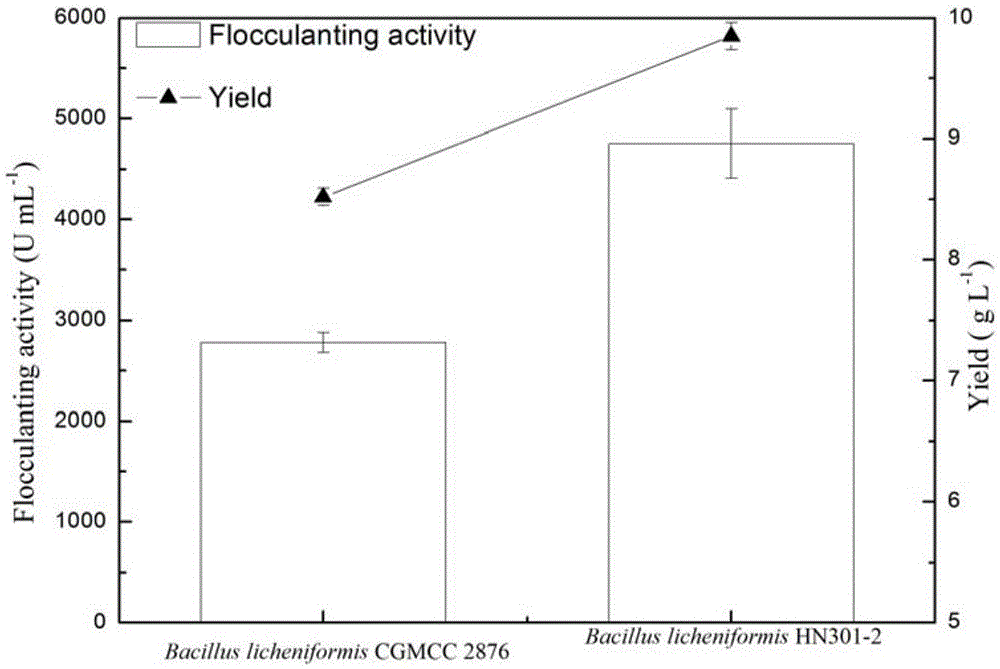
The invention relates to an engineering bacterium with overexpressed uridine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase gene and establishment thereof, belonging to the technical fields of gene engineering and microbial fermentation. By cloning the key enzyme uridine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase gene in the polysaccharide flocculant synthesis route, an Escherichia coli-Bacillus shuttle plasmid is utilized to establish a recombinant expression vector. The recombinant plasmid is transformed into Bacillus licheniformis by electric transformation to establish recombinant Bacillus licheniformis HN301-2; and compared with the initial strain, the polysaccharide flocculant yield of the recombinant Bacillus licheniformis is enhanced by 15.6%, and the fermentation liquid flocculation activity is enhanced by 70%. The engineering bacterium is hopeful to be used in industrial production of polysaccharide flocculants, and can enhance the yield and lower the cost.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for preparing biological flocculent by biological hydrogen-making waste liquid
InactiveCN1613789AEfficient removalHigh flocculation activityWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationLiquid wasteHydrogen
A method for producing biological flocculent by biological hydrogen waste liquid is carried out by: 1) mixing producing fungus substratum of hydrogen waste liquid and flocculent to prepare culturing solution, and circulating acclimating flocculent by rich and poor nutritive alternating method; 2) transferring acclimated bacterial strain to biological hydrogen waste liquid at temperature 30deg.C, culturing at table speed 140r / min, and finishing acclimating to obtain biological flocculent when flocculating ratio>50%. It achieves high efficiency and safety, and more effective.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for preparing biological sludge amendment and application thereof
InactiveCN101144076AReduce the cost of trainingHigh yieldFungiOn/in inorganic carrierMedicineBiochemical engineering
The present invention in particular relates to a preparation method of biological type sludge conditioning agent and the application thereof. The biological type sludge conditioning agent is prepared by using aspergillus sojae (Aspergillus sojae) as raw material, and the obtained sludge conditioning agent can be applied to the sludge dewatering. The coagulation activity of the conditioning agent of the present invention is high, the cost is low, the dosage output is high, the stability is strong, the applicable range is wide, and the present invention has the biological degradability and the environmental friendliness, and the second pollution is not caused.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Carrier-free immobilized culture method of microbial flocculating agent
InactiveCN102174582ALow costHigh flocculation activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismSucrose
The invention discloses a carrier-free immobilized culture method of a microbial flocculating agent. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: adding self-flocculating bacteria spore suspension in a volume which is 0.1 to 1 percent of the volume of a culture medium into the culture medium, wherein each millimeter of suspension contains 106 self-flocculating bacteria spores; putting the culture medium into a shaking bed, and performing culture and fermentation, wherein the culture conditions comprise that the revolution speed is 150 to 180 revolutions per minute, the temperature is 20 to 30 DEG C and the pH is 3.5 to 10.5; and standing after the suspension is cultured for 24 to 120 hours, and separating mycelium pellets generated by the self-flocculating bacteria and the fermentation solution, wherein the solid part is the mycelium pellets, and the liquid part is the microbial flocculating agent. Sucrose is used as a carbon source, sodium nitrate is used as a nitrogen source, the self-flocculating bacteria generate stress reaction by using the characteristic that the self-flocculating bacteria can form the mycelium pellets and improving the salt concentration of the culture medium, and the purpose of generating the microbial flocculating agent by the self-flocculating bacteria is fulfilled. The microbial flocculating agent prepared by the method has the advantages of low cost, extensive production conditions and high flocculating activity, and can be used for treating multiple kinds of printing and dyeing wastewater.
Owner:JINGGANGSHAN UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing microbial flocculant by protoplast fusion technology
InactiveCN102241437ACost efficientThe implementation process is simpleHybrid cell preparationBiological water/sewage treatmentChemistrySucrose
The invention provides a method for preparing a microbial flocculant by a protoplast fusion technology, and belongs to the field of flocculant preparation. The method is characterized by (1) protoplast producing bacterium LV-1 regeneration conditions and preparation steps, specifically comprising carrying out an activation operation in a liquid complete medium (CM) for 5 to 10 hours based on an inoculation amount of 0.5 to 2%, adding 2 to 6 mol / L of glycine into the liquid complete medium before enzymolysis to carry out a treatment for 5 to 15 hours, carrying out an enzymolysis process in a water bath for 1 to 4 hours at a temperature of 37 DEG C and an enzyme concentration of 0.05 to 0.2 mg / mL, and coating a regeneration template containing cane sugar as a stabilizer, and (2) protoplast fusion strain LV-2 fermentation and flocculation conditions, specifically comprising a cane sugar content of 8 to 12 g / L, a lactose content of 5 to 10 g / L, an ammonium nitrate content of 0.4 to 1.2 g / L, a peptone content of 0.4 to 1.2 g / t, an extract yeast content of 0.1 to 0.4 g / L, a culture temperature of 20 to 40 DEG C and an optimal adding amount of 0.2 to 2%. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of high effectiveness, simple process, board application scope, low cost and good biological safety.
Owner:SHANGHAI GREEN LIFE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Compound oil paint flocculating agent where bacterial cellulose shell-core structures are added
InactiveCN106587374AReduce manufacturing costHigh flocculation activityPaint waste treatmentWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsMicrosphereFermentation
The invention discloses a compound oil paint flocculating agent where bacterial cellulose shell-core structures are added. The following steps including the first step of strain separation and purification, the second step of strain screening, the third step of strain fermentation and cultivation and the fourth step of compound magnetic microsphere preparation are included. The preparation process is simple, the compound oil paint flocculating agent can be suitable for industrialized large-scale production, can be repeatedly used and can reduce cost, the problems that the flocculating efficiency is poor and sediment sinks in circulating water are effectively solved, and the long-term effective safe operation of the circulating water is ensured.
Owner:TIANCHANG YINHU PAINT
Industrial ammonia-nitrogen organic wastewater treatment agent and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112777744AImprove adsorption performanceIncrease roughnessWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesIndustrial wastewater treatmentEnvironmental chemistry
The invention relates to an industrial ammonia-nitrogen organic wastewater treatment agent and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of industrial wastewater treatment. By arranging a self-made zeolite carrier and multiple functional microorganisms, modifying the natural zeolite, compounding the microorganisms and cooperating with each other, the ammonia nitrogen and COD in the industrial ammonia nitrogen organic wastewater are effectively removed finally, the turbidity of the wastewater is remarkably reduced, and the treatment agent has a wide application prospect.
Owner:ZHENJIANG HEYUN IND WASTEWATER DISPOSAL CO LTD
Method for preparing compound flocculating agent
ActiveCN101693561BStable flocculationGood flocculation effectWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationMetalWater treatment
Owner:江苏中鹏环保集团有限公司
Low-production-cost polydopamine compound oil paint flocculant
InactiveCN106587375AReduce common ingredientsStable common ingredientsWater treatment compoundsSpecific water treatment objectivesFlocculationMicrosphere
The invention discloses a low-production-cost polydopamine compound oil paint flocculant which is prepared by the following steps: (1) separation and purification of strains; (2) screening of the strains; (3) fermentation cultivation of the strains; and (4) preparation of compound magnetic microspheres. The flocculant has the beneficial effects that the flocculation speed is high, the settling time is long, the feeding quantity is small, common components in oil paint can be stably coagulated, the wastewater treatment cost can be lowered, and the application prospects are wide.
Owner:TIANCHANG YINHU PAINT
Preparation method of microbial sewage purification treatment agent
InactiveCN111115849AHigh flocculation activityImprove adsorption capacityWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationBiotechnologyCarboxyl radical
The invention discloses a preparation method of a microbial sewage purification treatment agent, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. According to the invention, a culture medium containing a bacillus natto liquid is prepared from soybean milk, wherein gamma-polyglutamic acid is rich, the gamma-polyglutamic acid can be complexed with metal salt ions in water pollutants to obtain gamma-polyglutamate, the adsorbent has the advantages of biodegradability, good biocompatibility, high water-retaining property and the like, the polypeptide structure of the gamma-polyglutamic acid and carboxyl and amino groups rich in a molecular chain are extremely similar to physiological properties of microorganisms, the gamma-polyglutamic acid is extremely easy to coexist with microorganisms, a space reserved after the gamma-polyglutamic acid is biologically degraded provides a space for subsequent microorganism growth, and the quantity of active microorganisms on the adsorbent is increased, so that the biofilm culturing quantity of the adsorbent microorganisms is increased, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:王小龙
Method for preparing bioflocculant and use thereof
InactiveCN101906439ASimple production processShort fermentation cycleMicroorganism based processesFermentationActivated sludgeFruit juice
The invention discloses a method for preparing a bioflocculant and use thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: (a) performing fermentation culture on penicillium funiculosum to obtain fermentation liquor and centrifuging the fermentation liquor to remove mycelium to obtain supernate; and (b), mixing the supernate with ethanol and centrifuging the mixture to obtain the bioflocculant. The bioflocculant can be used for treating activated sludge, fly ash, charcoal, ink, muddy water, river sediment suspension, kaoline suspension, manure water, dyeing and printing wastewater and / or fruit juice.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND
Preparation method for biological flocculant
InactiveCN100549159CEasy to handleNo pollution in the processFungiWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationFlocculationParticulates
A preparation method of a biological flocculant, the present invention is characterized in that the fermentation culture of Aspergillus is adopted, and the fermentation culture is stirred for 48 to 60 hours under the conditions of temperature of 28-30° C., pH of 6-7 and ventilation; the fermentation liquid is filtered and concentrated, Ethanol was added to the concentrated solution, and after standing, centrifugation was performed, and the precipitate was washed with ethanol and dried in vacuum to obtain a crude flocculant in light yellow brown. The preparation method of the invention has the advantages of simple production conditions and low cost. The prepared biological flocculant is suitable for sewage treatment containing granular impurities or dirt, and the dosage is generally in the range of 0.1‰ to 0.3‰. It has been proved by the flocculation treatment of sewage that compared with the existing technology, it has the advantages of good flocculation effect, fast flocculation speed, low dosage, no pollution to the environment, and no toxic effect on the human body.
Owner:ENZYME ENG INST SHAANXI PROVINCE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing microorganism flocculant
InactiveCN101327975BGood flocculation effectSimple methodWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationMicroorganismLiquid medium
The invention relates to a method for preparing a microbial flocculant which is characterized by: preparing the microbial flocculant through the steps of the preparation of liquid medium, the fermentation culture of the strain, the preparation of the flocculant crude product and flocculant refined product using the delftia acidovorans as the stain resource for preparing the microbial flocculant. The mehtod finds the delftia acidovorans capable of generating the microbial flocculant with a stable flocculability and a good flocculating effect for the first time in China. The screened flocculanthas advantages of high flocculating activity, few dosage, short fermentation time, simple extraction technology, which greatly reduces the production cost. The method for preparing the flocculant is simple and easy to apply. The experiment of wastewater treatment shows that the flocculating effect is ideal after using the flocculant.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Preparation method and application for immobilized microorganism flocculant
InactiveCN102583680AGood flocculation effectHigh flocculation activityWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationMicroorganismFlocculation
The invention provides a preparation method and application for immobilized microorganism flocculant. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing aqueous solution containing 0.5-2% of sodium alginate, 0.5-1.5% of polyvinyl alcohol and 0.5-1.5% of gelatin according to the mass concentration; after the mixture is fully dissolved, adding Geotrichum candidum to ensure that the Geotrichum candidum accounts for 3-6wt% of the solution; evenly stirring; dripping into 0.05-0.15mol / L of CaCl2 solution prepared in advance; standing for 3-5h; and carrying out suction filtering and washing to obtain the immobilized microorganism flocculant. The immobilized microorganism flocculant has the advantages of high flocculation activity, small use amount, no secondary pollution and the like when being used for treating water, the mineralization flocculation rate for the underground karst water is about 70%, and the maximum hardness flocculation rate can be about 60%.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Method for preparing microbial flocculant through enteromorpha hydrolysate fermentation
InactiveCN105039417AReduce manufacturing costOptimize production methodsMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for preparing a microbial flocculant through enteromorpha hydrolysate fermentation. The method comprises the steps of preparation of liquid strain, fermentation and product aftertreatment. The fermentation process comprises the steps that 1, fresh enteromorpha is cleaned, salt, sediment and unwanted algae are removed, then the fresh enteromorpha is smashed and added to a hydrolysis tank, water is added to regulate acidity, alkali is added for neutralization, filter pressing and clarification are conducted, and then a hydrolysate is obtained; 2, the hydrolysate is diluted till the sugar concentration of reducing sugar is 15-30 g / L, fermentation liquor is prepared and added to a fermentation tank, and high-temperature sterilization and cooling are conducted; 3, a seed solution is inoculated into the fermentation tank for fermentation, and fermentation is ended after the content of residual sugar in the fermentation liquor is reduced to the level below 3 g / L. According to the method, enteromorpha is used as the raw material, microbial flocculant fermentation is directly conducted after acid hydrolysis filtration, the production method is simple, production cost is low, grain is saved, and waste is turned into wealth.
Owner:青岛美能达生物科技有限公司
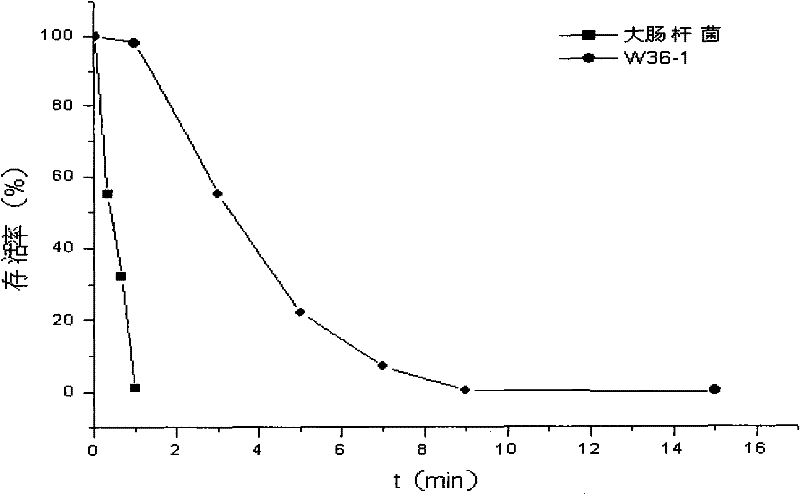
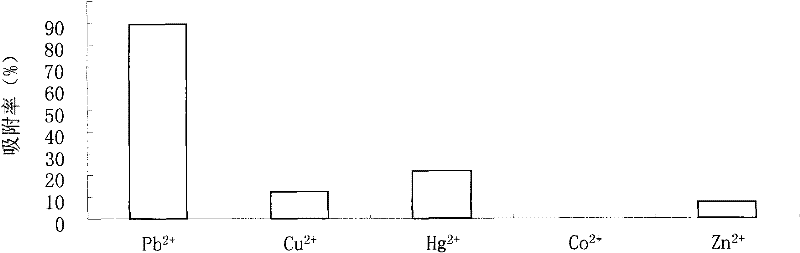
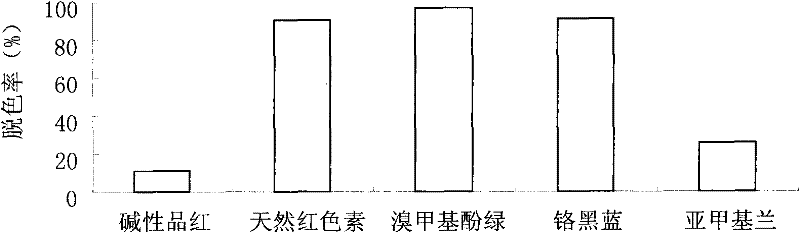
Radiation resistant pantoea sp. W36-1 and application thereof in environmental engineering
InactiveCN101864379BHigh flocculation activityHigh decolorization rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRadiation resistantPolysaccharide
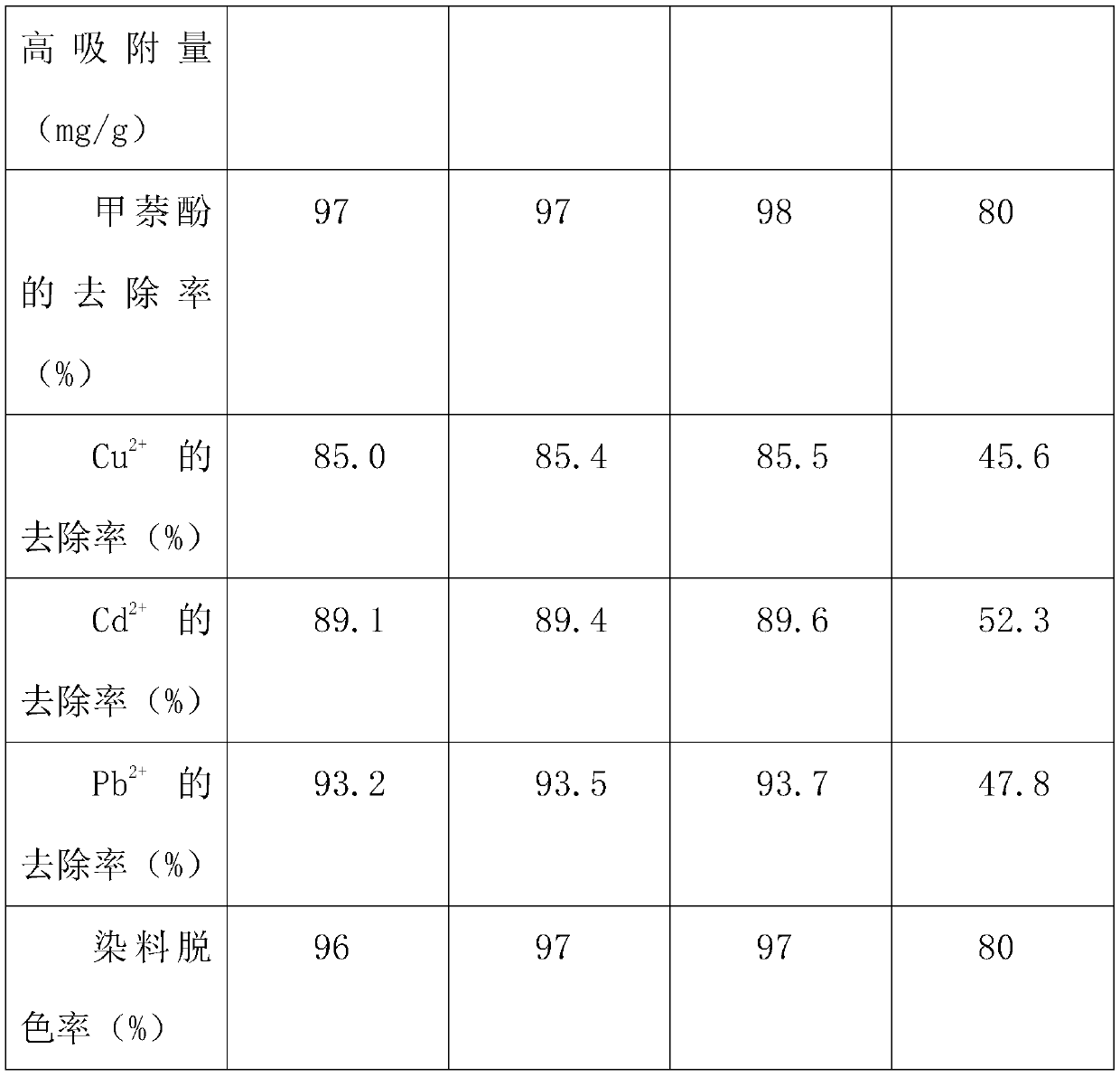
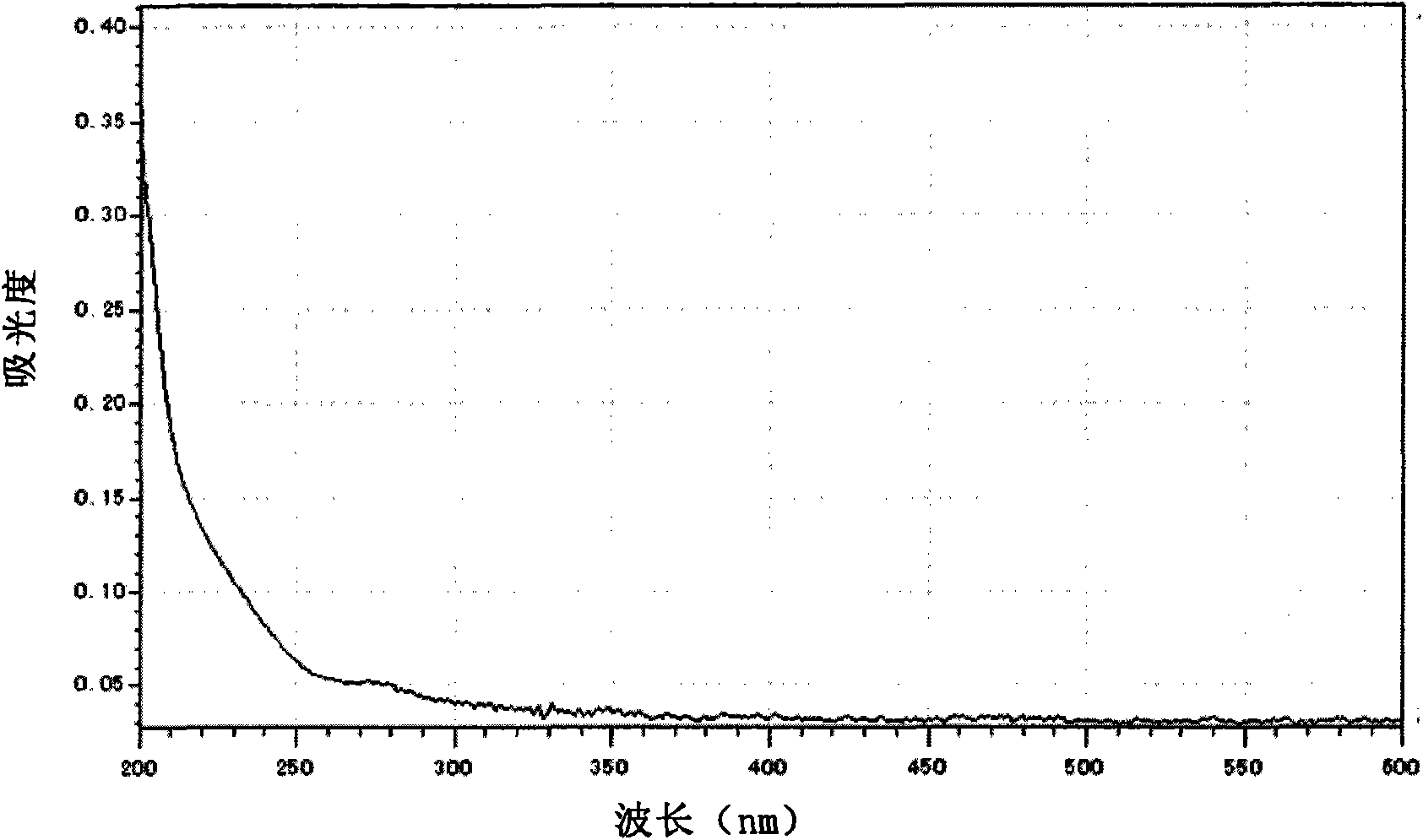
The invention discloses pantoea sp. W36-1, of which the preservation number is CGMCC No. is 3701, a flocculant prepared by the pantoea sp. W36-1 and application of the flocculant in removal of suspensions, dyeing agents and heavy metal in waste water. Extracellular products of the bacteria have an obvious absorption peak at 200 to 250nm, and polysaccharide solution can remove 54.89 percent of free groups in the bacteria. The method for preparing the pantoea sp. W36-1 comprises the following steps of: performing fermentation culture of the bacteria strain for 48 hours, centrifuging 100ml of fermentation solution at a rotation speed of 6,000r / min for 10 minutes, adding absolute ethanol, of which the volume is 1.5 times that of supernatant, into the supernatant, uniformly mixing the absoluteethanol and the supernatant standing the mixed solution at the temperature of 4 DEG C overnight, centrifuging the precipitate, washing the precipitate by 70-percent ethanol for 2 to 3 times, and thendrying the precipitate to obtain the finished product. The flocculent activity of the fermentation culture product of the pantoea sp. W36-1 is 81.7 to 83.15 percent, the yield of the pantoea sp. W36-1 is 6g / L and can be widely used for removing suspensions, dyeing agents, heavy metal and the like in waste water.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Starch-based polymer composite flocculant for sewage treatment and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112194759AStir wellFiber richWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationPotassium persulfateHexamethylenediamine
The invention relates to the technical field of polymer flocculant materials for sewage treatment, in particular to a starch-based polymer composite flocculant and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the composite flocculant comprises the following steps: drying potato peels in the sun and crushing the potato peels to obtain potato peel powder, adding distilled water to preparea turbid liquid, and adding a NaOH solution to activate chemical functional groups of the potato peel powder to obtain a solution A; adding hexamethylenediamine into the solution A, and conducting reacting at 40-60 DEG C for 1-2 hours to obtain a solution B; and adding a cross-linking agent dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride and an initiator potassium persulfate into the solution B, conducting reacting at 30-60 DEG C for 2-3 hours, adding polyaluminium chloride accounting for 0.5-2% of the total mass of the system, and carrying out sufficient and uniform stirring to obtain a starch-based polymer composite flocculant product. The potato peel is used as a raw material and is cheap and easy to obtain; and flocculation activity is good, and a sedimentation rate is favorably improved.
Owner:CHENDU NEW KELI CHEM SCI CO LTD
A kind of anti-high temperature floc producing strain and its cultivation and application method
InactiveCN103820358BHigh flocculation activityEasy to breedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismFruit tree
A high-temperature resistant floc-producing strain and its cultivation and application methods belong to the field of microbiology. Preserved by the General Microbiology Center (CGMCC) of the China Council for the Collection of Microbial Cultures, preservation number: CGMCC? No.2040, classification name: Paenibacillus? sp. Date of preservation: May 11, 2007. The high-temperature-resistant Paenibacillus strain screened from fruit tree soil is the first new strain discovered in China. After being heated at 40 to 80°C for 5 to 60 minutes, it is cultured through aerobic fermentation at 25 to 35°C. The fermentation liquid is used as a flocculant for kaolin suspensions. When the ratio is 0.01% to 0.2% (v / v), the flocculation rate is 88% to 97%. When the Paenibacillus and its fermentation liquid provided by the invention are used as kaolin suspension flocculant, the cultivation operation process is simple, the cost is low, the flocculation activity is high, the usage is low, and there is no secondary pollution.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Engineering bacteria and construction of overexpressing uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase gene
ActiveCN105624176BIncrease productionHigh flocculation activityWater contaminantsTransferasesBiotechnologyUridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase
The invention relates to an engineering bacterium with overexpressed uridine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase gene and establishment thereof, belonging to the technical fields of gene engineering and microbial fermentation. By cloning the key enzyme uridine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase gene in the polysaccharide flocculant synthesis route, an Escherichia coli-Bacillus shuttle plasmid is utilized to establish a recombinant expression vector. The recombinant plasmid is transformed into Bacillus licheniformis by electric transformation to establish recombinant Bacillus licheniformis HN301-2; and compared with the initial strain, the polysaccharide flocculant yield of the recombinant Bacillus licheniformis is enhanced by 15.6%, and the fermentation liquid flocculation activity is enhanced by 70%. The engineering bacterium is hopeful to be used in industrial production of polysaccharide flocculants, and can enhance the yield and lower the cost.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com