Biological mothballing system suitable for synechococcus elongatus, and construction method and application of biological mothballing system
A construction method and technology of Synechococcus, applied in the field of biological storage systems, can solve the problems of strain growth impact, strain death, long time, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
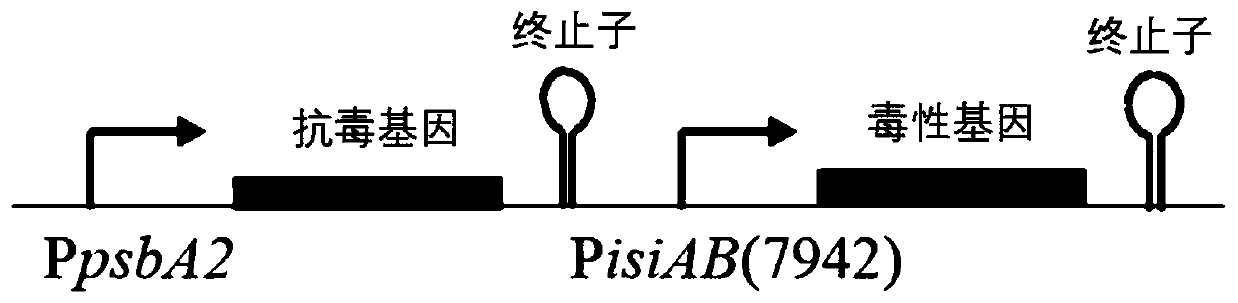
[0022] (1) In vitro amplification of the target gene
[0023] A bacterial genome extraction kit was used to extract the Synechococcus 7942 genome as a template,
[0024] Take the sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 6 as the upstream primer of the sepA2 gene,
[0025] Take the sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 7 as the downstream primer of sepA2 gene,
[0026] Take the sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 8 as the upstream primer of the sepT2 gene,
[0027] Take the sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 9 as the downstream primer of the sepT2 gene,
[0028] Take the sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 10 as the upstream primer of PisiAB promoter,
[0029] Use the sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 11 as the downstream primer of the PisiAB promoter to perform PCR amplification;
[0030] Using the bacterial genome extraction kit to extract the Synechocystis 6803 genome as a template, the sequences shown in SEQ ID No. 12 and SEQ ID No. 13 are respectively the PpsbA2 promoter upstream and downstream primers for PCR amplification;
[003...
Embodiment 2
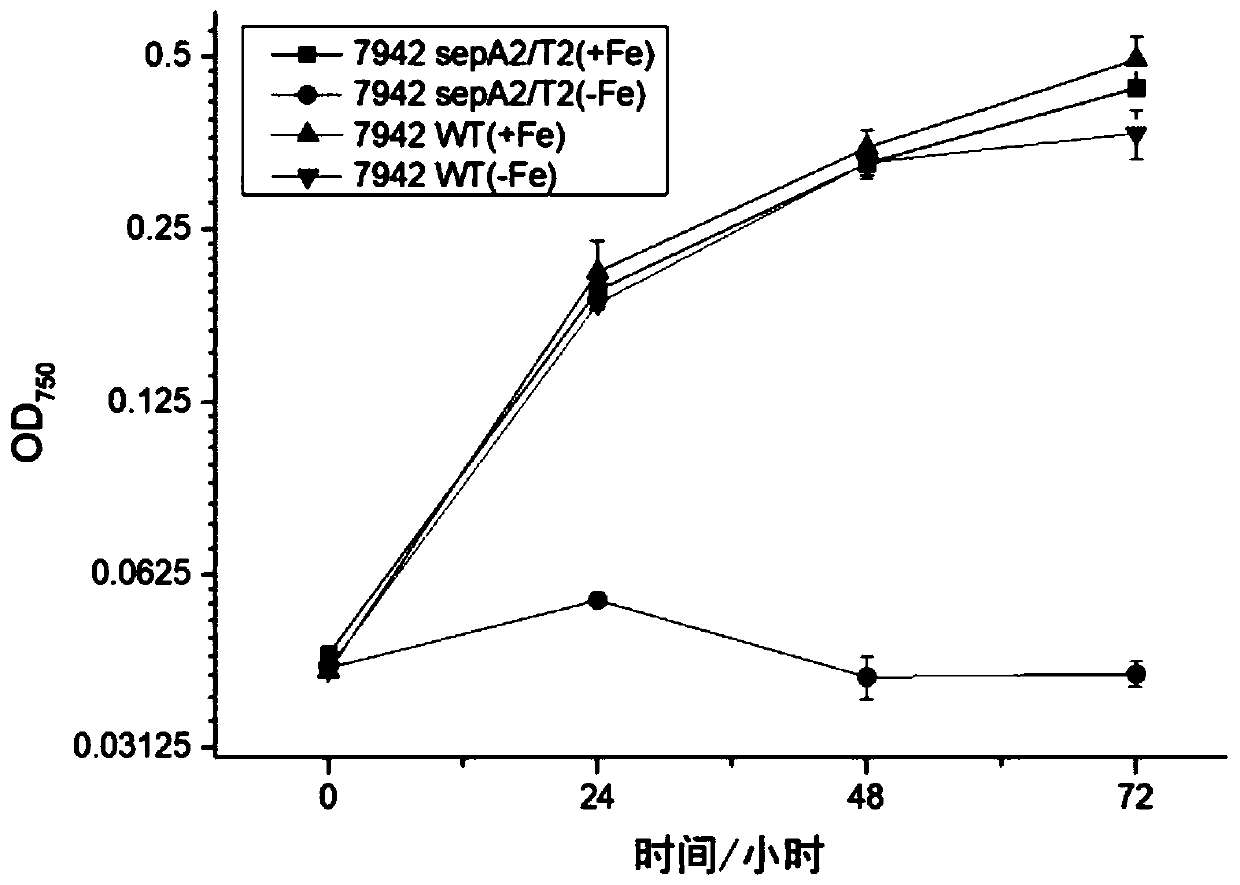
[0047] The growth curves of Synechococcus 7942 wild-type and mutant strains in normal liquid medium BG11 and iron-deficiency liquid medium BG11 were determined.
[0048] The Synechococcus 7942 (wild strain WT) and the mutant strain 7942-sepA2 / T2 obtained in Example 1 were cultured in normal liquid medium BG 11 and liquid medium BG 11 containing deferoxamine 100 μM, and the setting parameter of the shaker was light. Intensity 200μmolphotons m -2 s -1 , The speed is 160rpm, and the temperature is 37°C.
[0049] The steps are: take OD during vaccination 750nm Add 5 mL of 0.2 fresh cells to 20 mL of culture medium, make 3 parallel samples for each group, measure the absorbance at 750 nm with a 96-well plate microplate reader, measure it every 24 hours, and draw a growth curve ( figure 2 ).
[0050] From figure 2 It can be observed that in the normal liquid medium BG 11, the growth status of the wild strain and the mutant strain is almost the same, while in the medium induced by iron ...
Embodiment 3
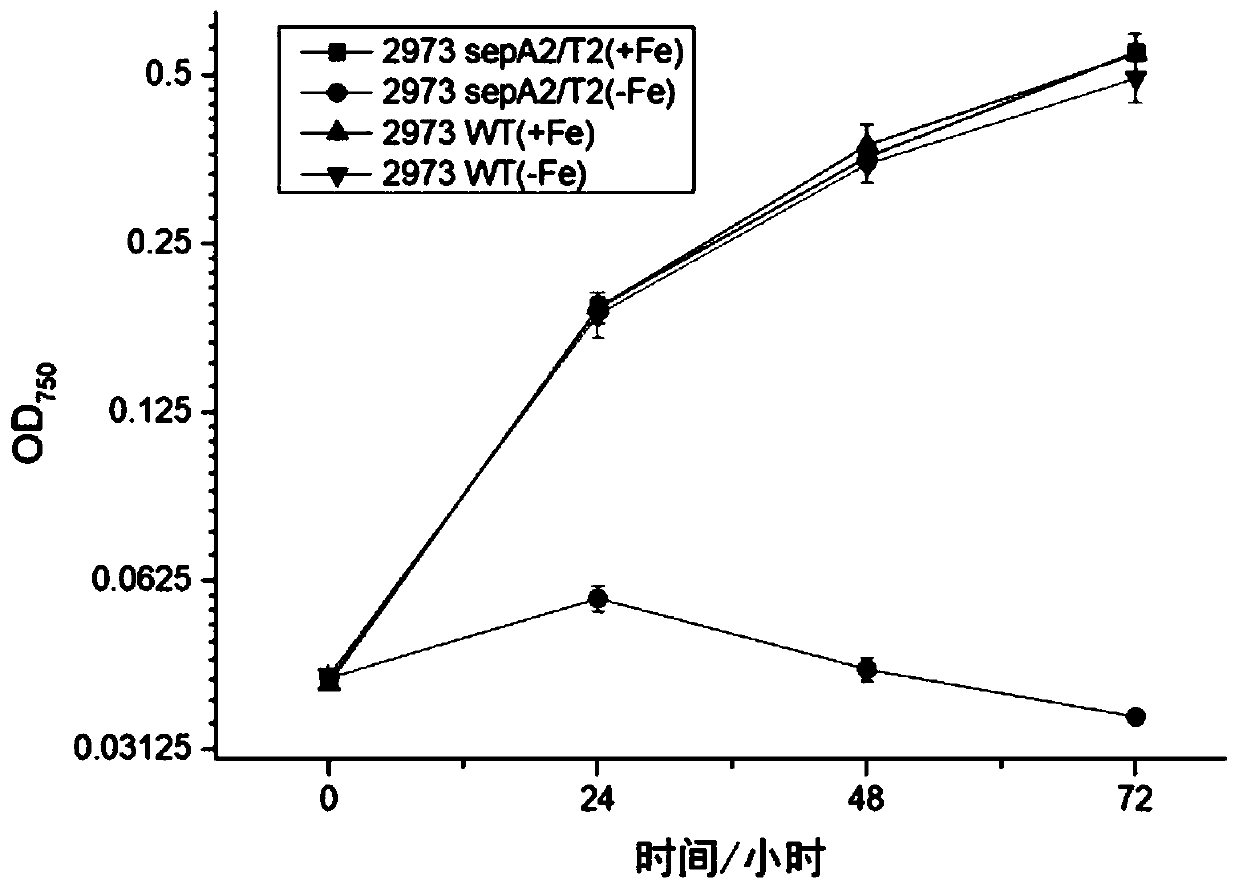
[0052] The growth curves of Synechococcus 7942 wild-type and mutant strains in normal liquid medium BG11 and iron-deficiency liquid medium BG11 were determined.
[0053] The Synechococcus 2973 (wild strain WT) and the mutant strain 2973-sepA2 / T2 obtained in Example 1 were cultured in normal liquid medium BG 11 and liquid medium BG 11 containing deferoxamine 100 μM, and the setting parameter of the shaker was light. Intensity 200μmolphotons m -2 s -1 , The speed is 160rpm, and the temperature is 37°C.
[0054] The steps are: take OD during vaccination 750nm Add 5 mL of 0.2 fresh cells to 20 mL of culture medium, make 3 parallel samples for each group, measure the absorbance at 750 nm with a 96-well plate microplate reader, measure it every 24 hours, and draw a growth curve ( figure 2 ).
[0055] From figure 2 It can be observed that in the normal liquid medium BG 11, the growth status of the wild strain and the mutant strain is almost the same, while in the medium induced by iron ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com