Salt tolerance SyDBSP gene derived from synechocystis, and uses thereof
A technology of cyanobacteria and salt tolerance, which is applied in the field of salt tolerance SyDBSP derived from cyanobacteria and its application, can solve problems such as not achieving remarkable results, achieve high application possibility, increase salt tolerance, and salt tolerance sex increasing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] Example 1: SyDBSP gene derived from Synechocystis sp. PCC6906
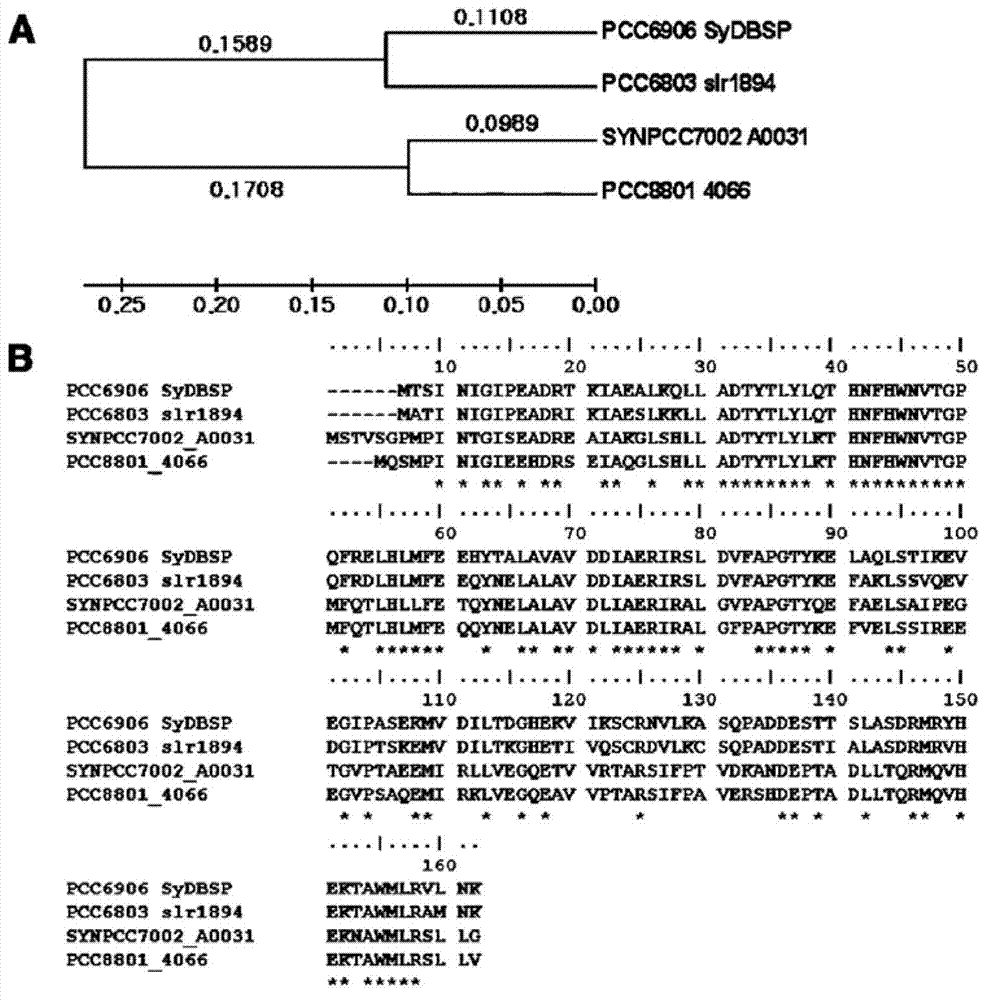
[0096] The base sequence of the SyDBSP gene derived from Synechocystis PCC6906 was isolated and determined after the genome of Synechocystis PCC6906 was isolated and all base sequence information was obtained using GS-FLX (Roche, USA). The SyDBSP gene consists of 471 nucleotides, encoding 156 amino acid sequences ( figure 1 and 2 ). The amino acid sequence of the SyDBSP gene derived from Synechocystis PCC6906 and Synechocystis PCC6803slr1894 produced in freshwater reached 80% (identity) and 91% positive (positivive), and its genetic relationship was the closest. In addition, it also showed a high genetic relationship with Synechocystis PCC7002A0031 and Cyanothece sp.PCC88014066 genes ( image 3 ).
Embodiment 2
[0097] Example 2: Screening of SyDBSP Gene Transformation Vectors and Transformed Plants Derived from Synechocystis PCC6906
[0098] In order to obtain transformed plants, from PCC6906 genomic DNA, use primers 5'-gctctagaATGACTTCAATTAATATCGGTATT-3' (SEQ ID NO.3, the Xba I site is underlined) and 5'-cgggatccCTATTTGTTCAGAACCCGGAGCAT-3' (SEQ ID NO. 4. The BamHI site is underlined) After the SyDBSP gene is amplified, it is cut with restriction enzymes. The XbaI / BamHI site of the pHC21B vector was cut with restriction enzymes, and the SyDBSP gene fragment was inserted thereinto, thereby preparing a nuclear transformation vector ( Figure 4 ). The plants introduced with the transformation vector are screened in a medium containing kanamycin as a selection marker. The selected plants use the primers of the SyDBSP gene to confirm the insertion of the SyDBSP gene by the PCR method. And, for the expression of SyDB SP gene in each transformed plant body, its expression degree was anal...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Example 3: Preparation of tobacco transformed with SyDBSP gene derived from Synechocystis sp. PCC6906
[0100] Retain and sterilize T0 generation seeds from tobacco transformed plants introduced with the SyDBSP gene derived from Synechocystis sp. , thus preserving the T1 generation seeds. Plants were obtained from the retained seeds, and genomic DNA was isolated, and the introduction of SyDBSP was confirmed by PCR and Southern blot hybridization analysis, and total RNA was isolated, and the expression level of the introduced genes was confirmed by real-time quantitative PCR. Such as Figure 5 As shown in A, among the 8 kinds of SyDBSP gene-transformed tobacco plants, 6 kinds of genes have been confirmed to have been introduced, and 5 kinds of these transformed plants have been confirmed to have inserted a copy of the gene ( Figure 5 B). In addition, in transformed tobacco plants, the overexpression of the SyDBSP gene can be confirmed by the results of real-time quan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com