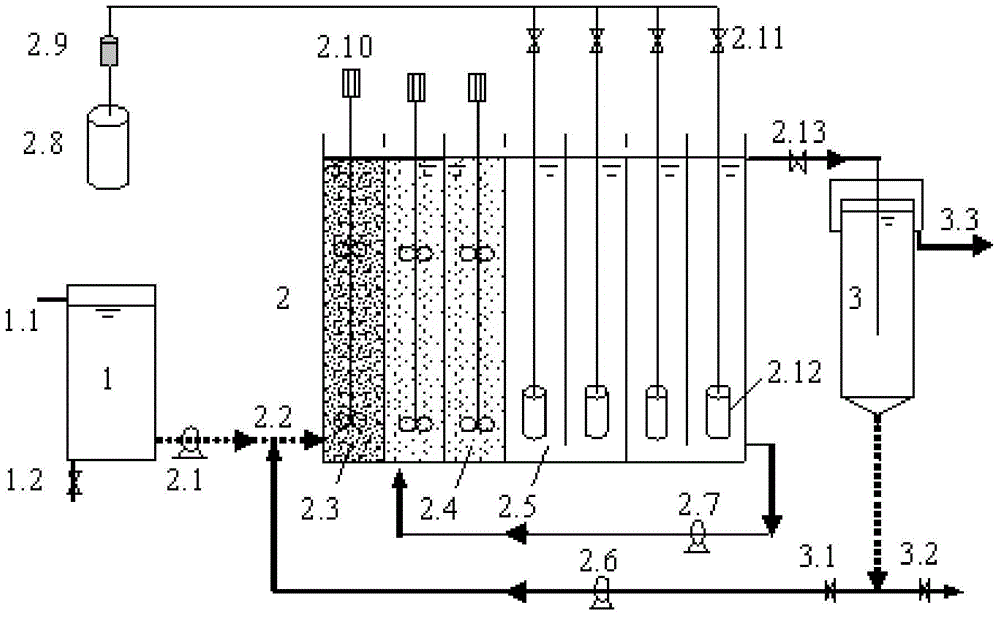
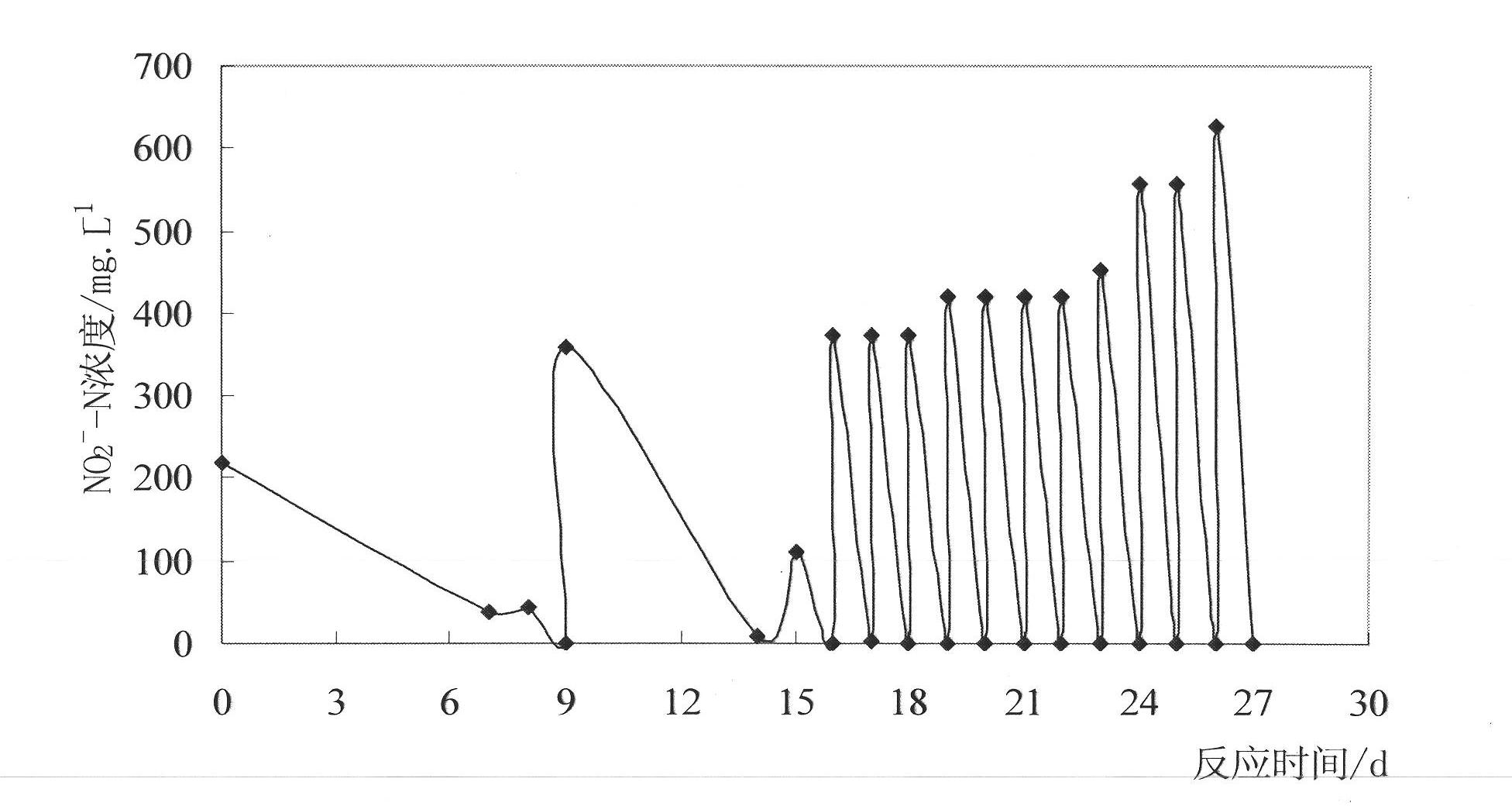
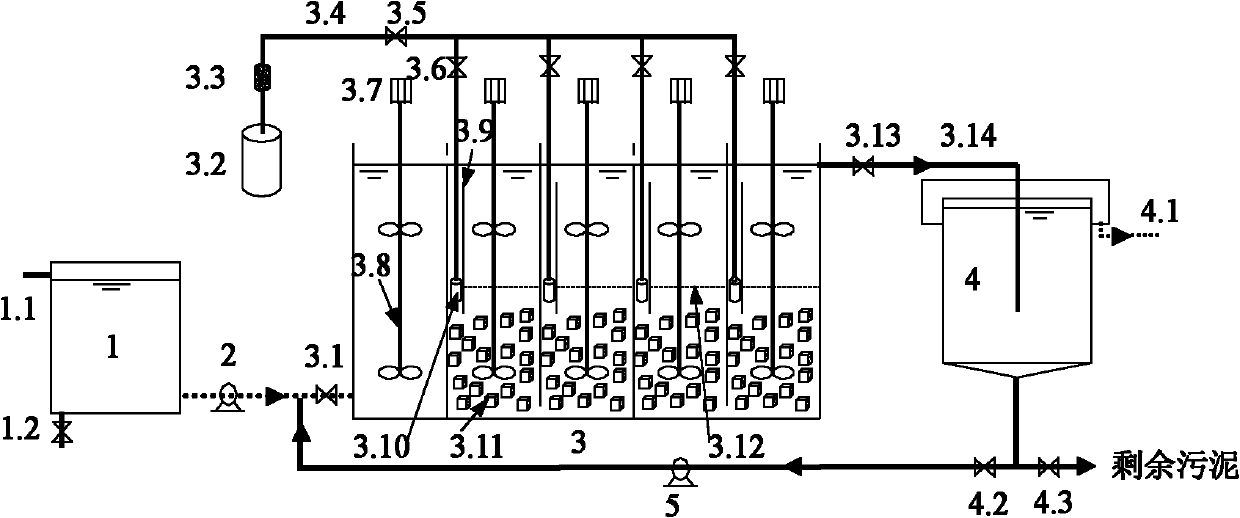
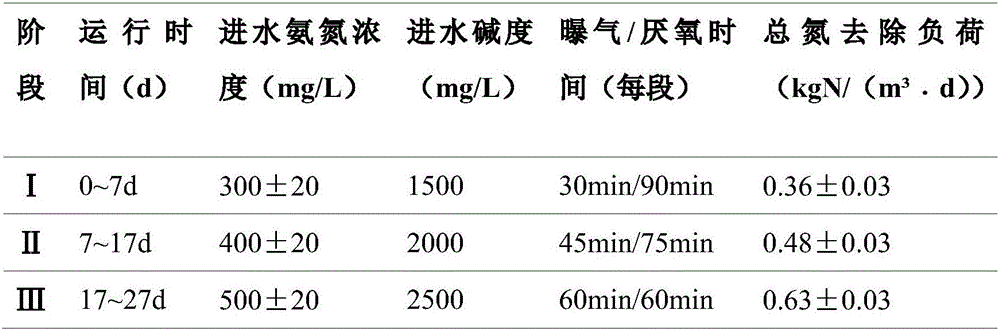
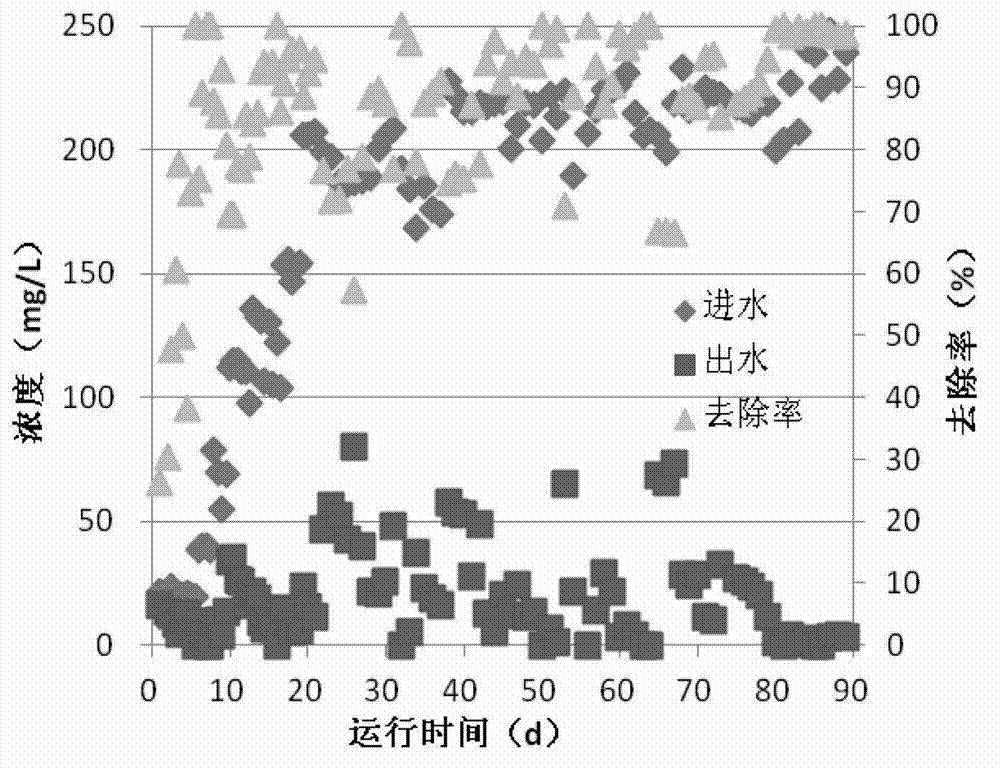
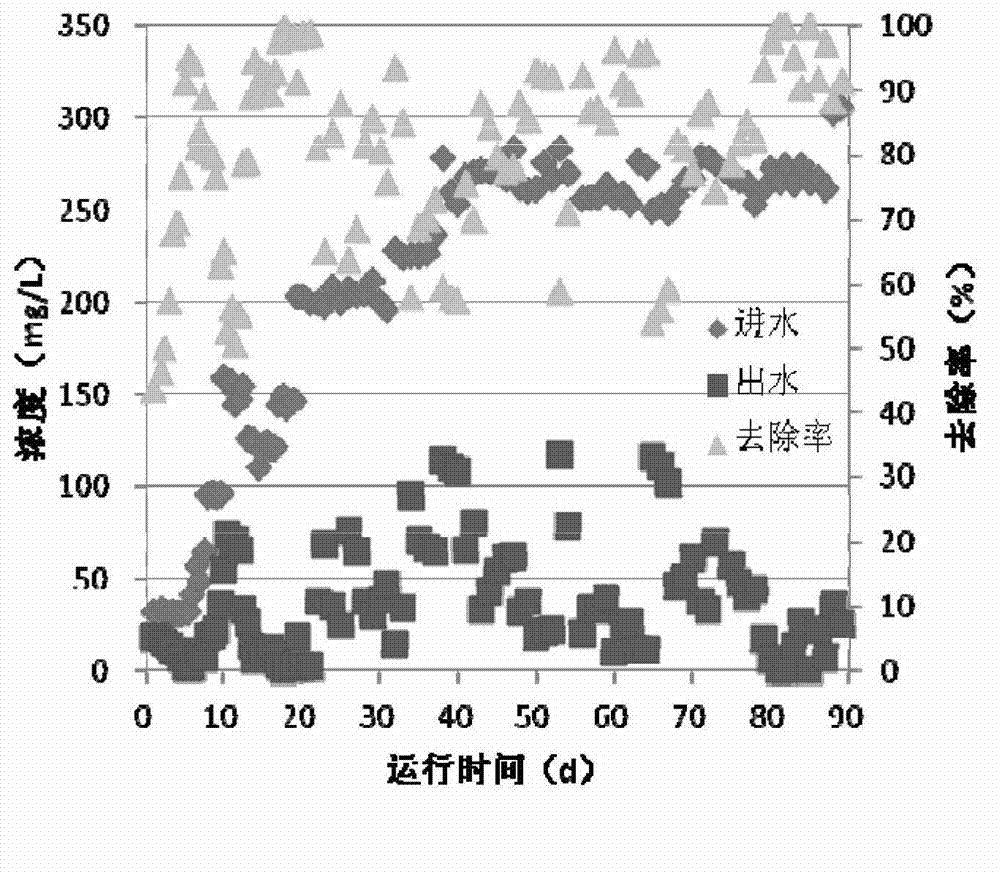
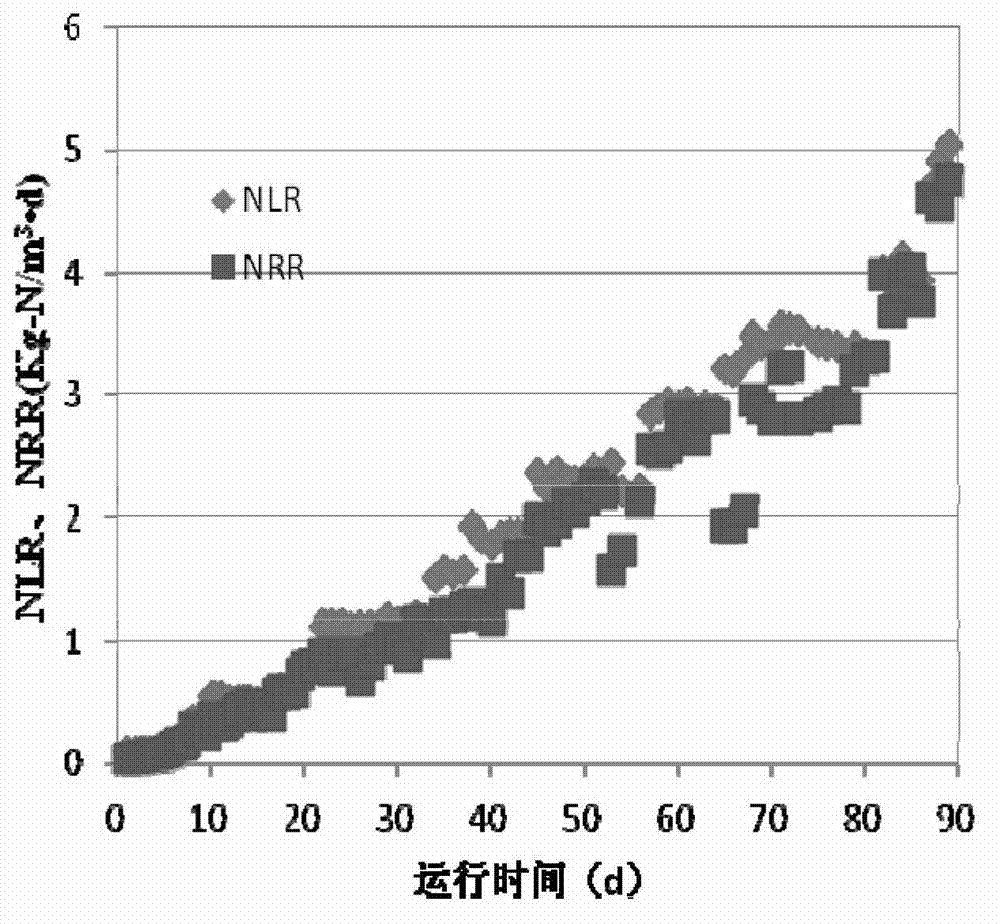
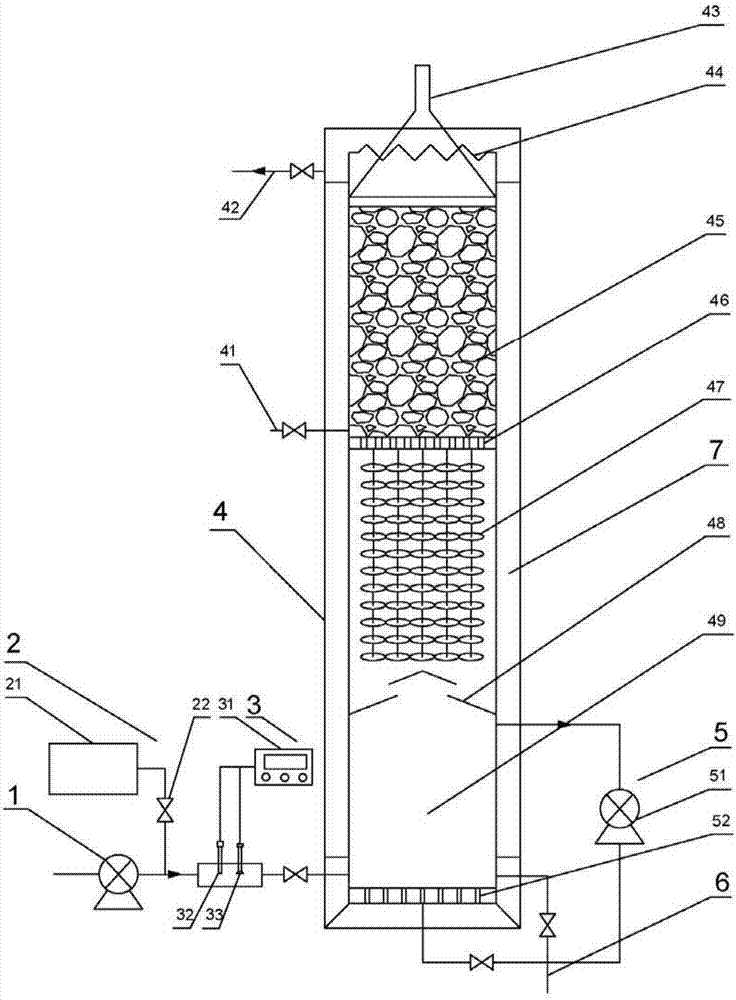
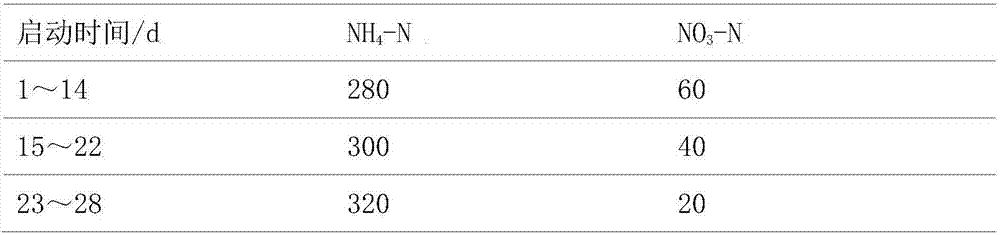
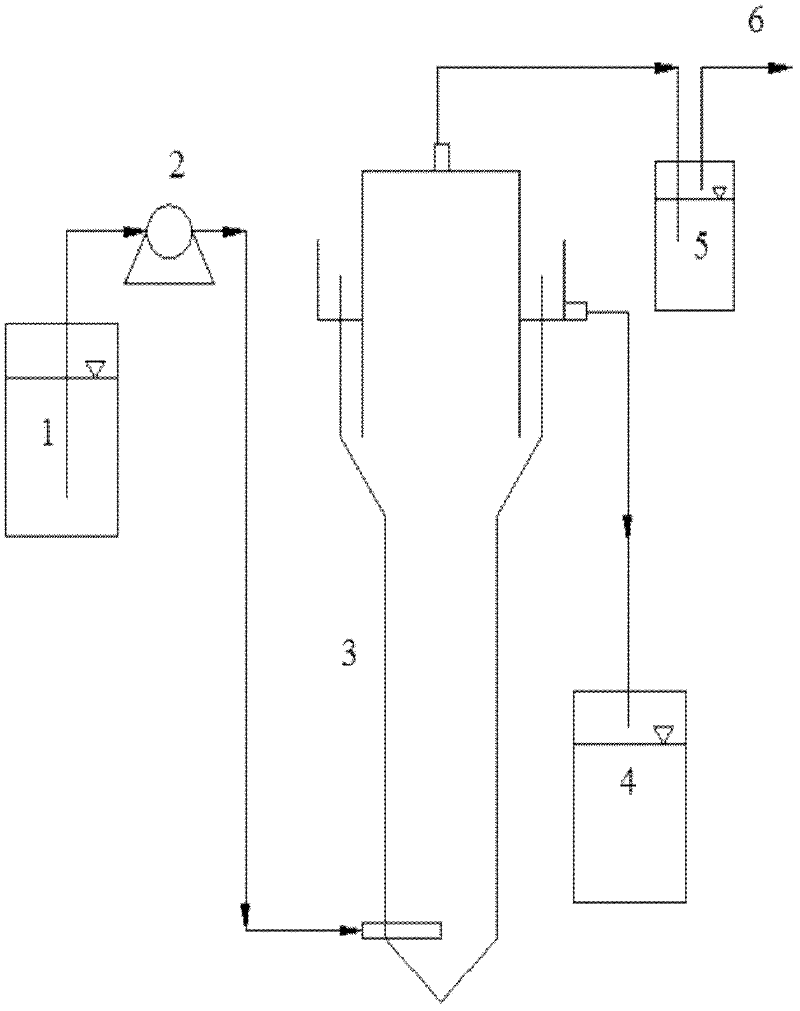
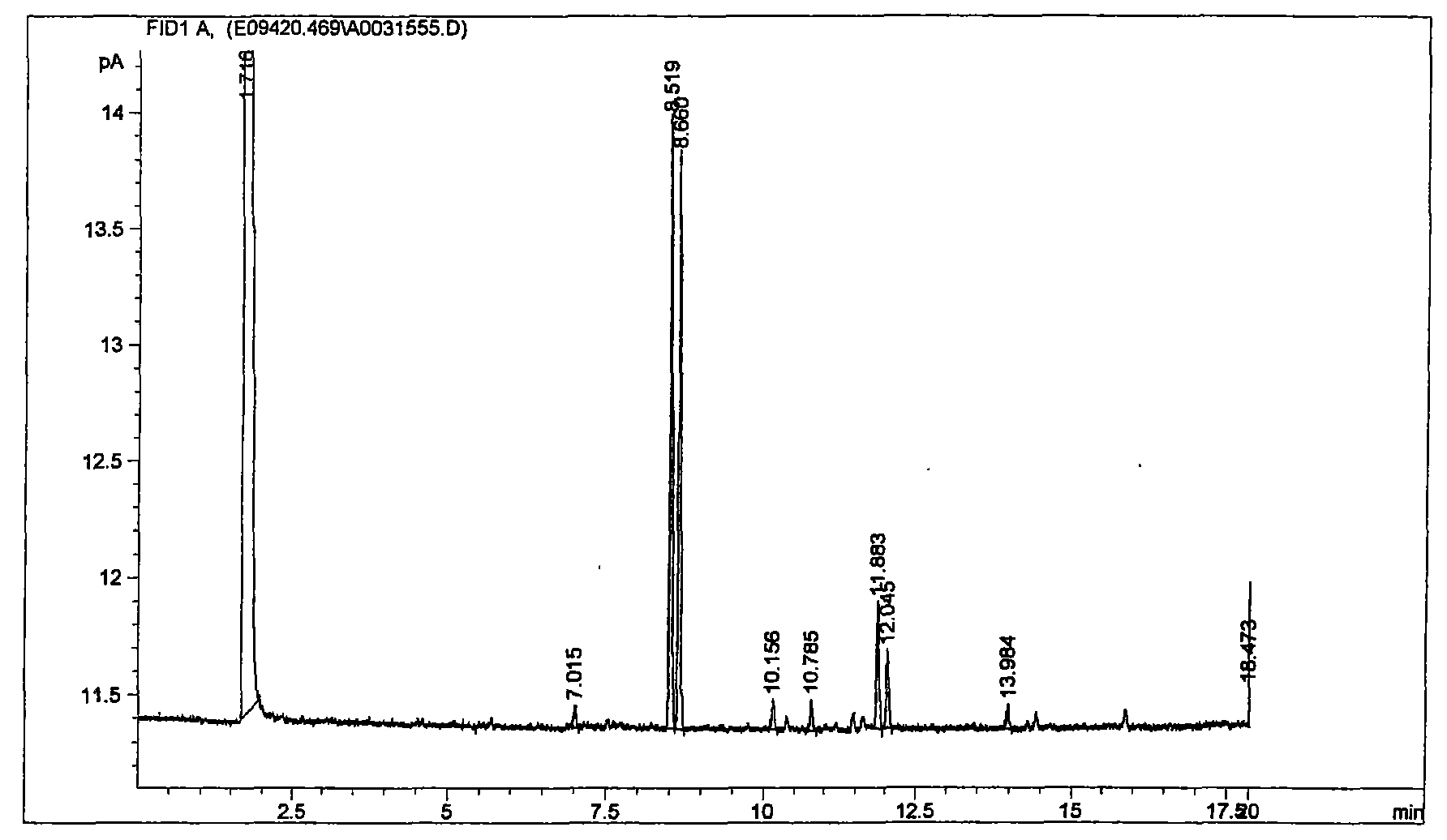
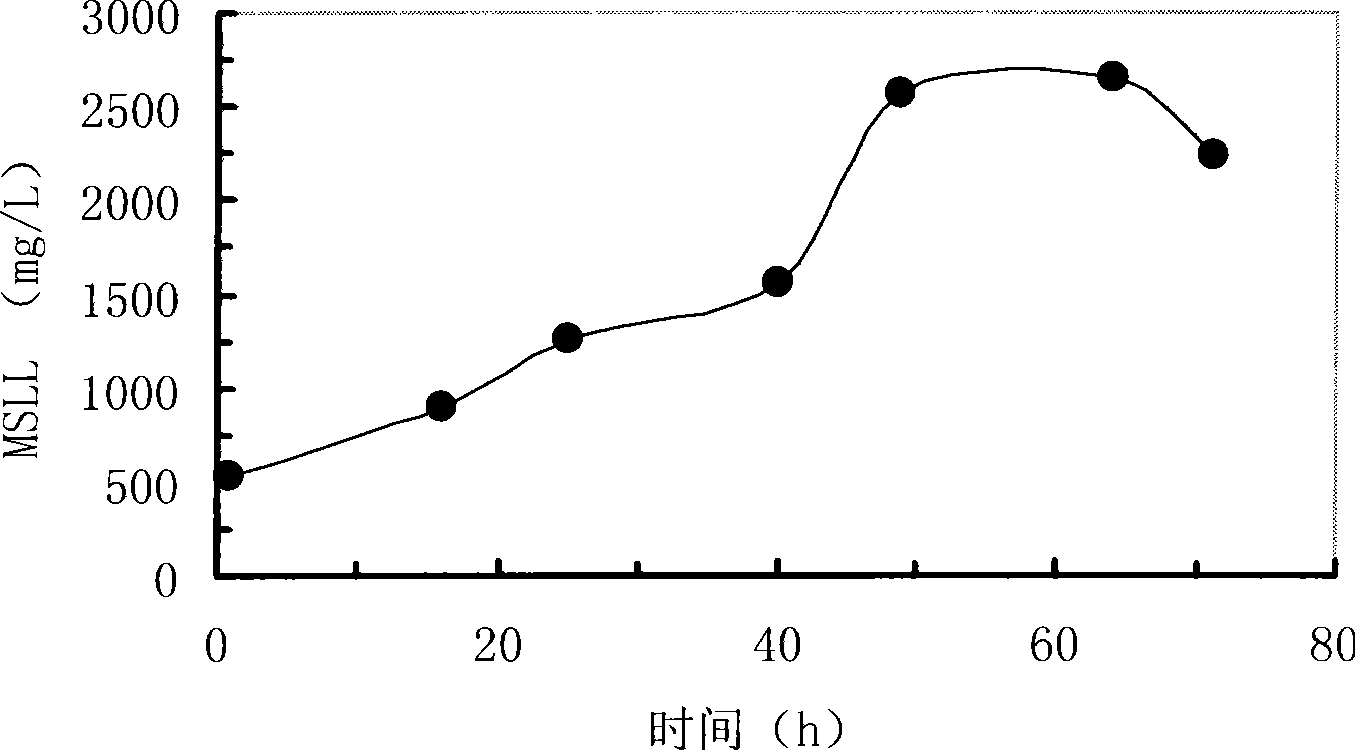
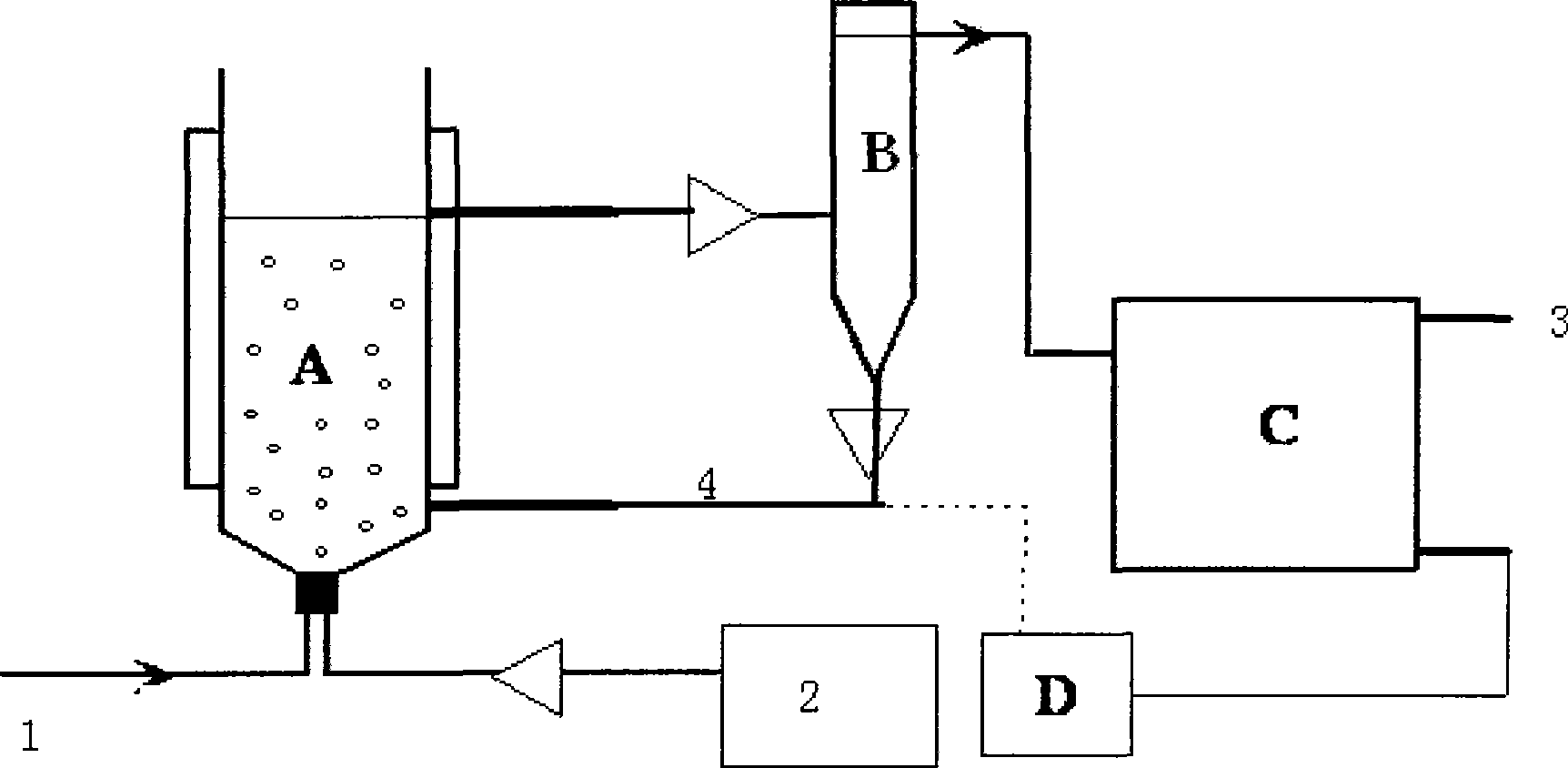
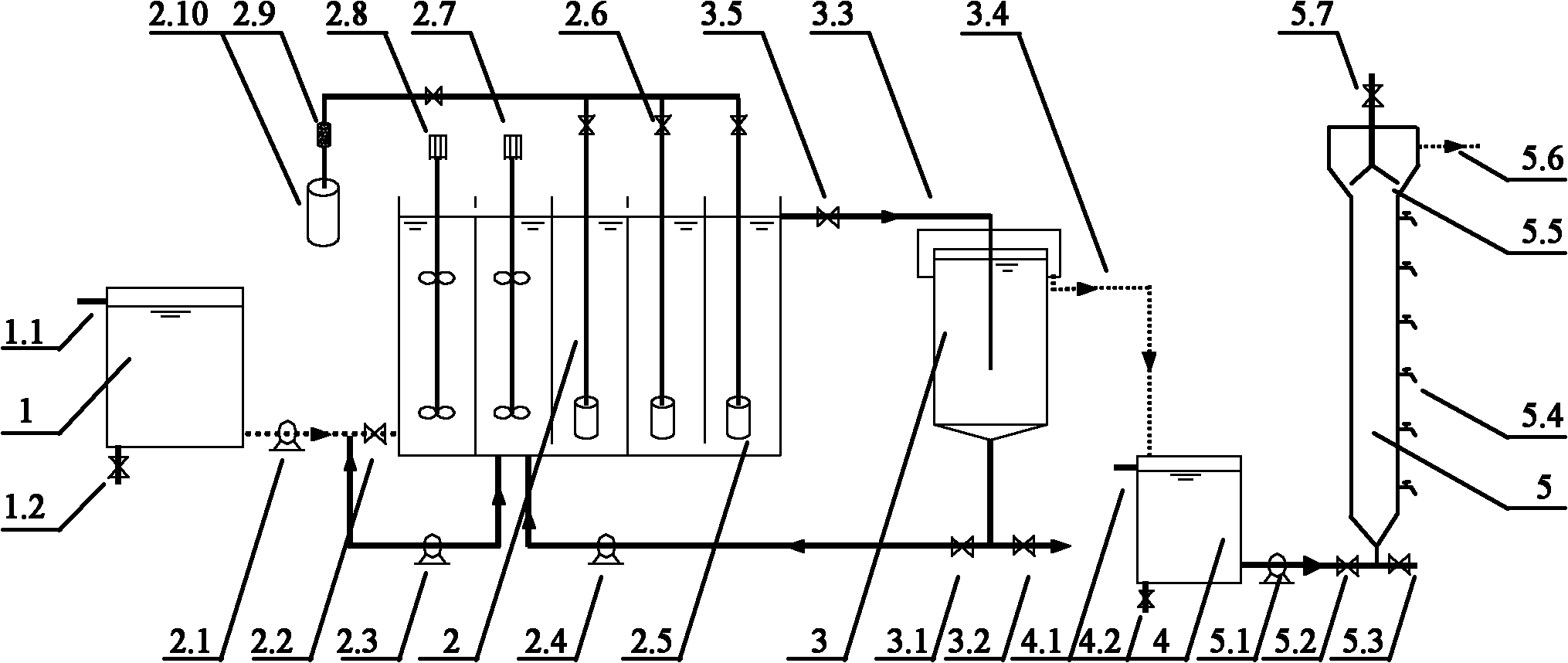
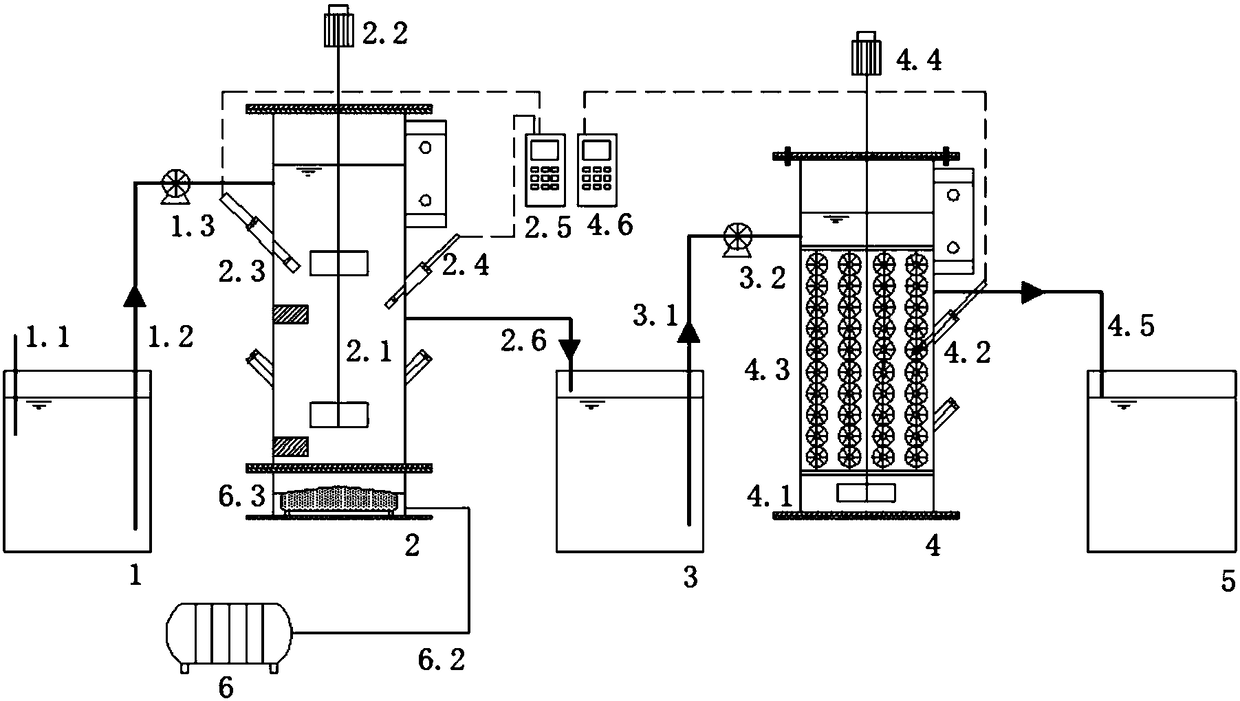
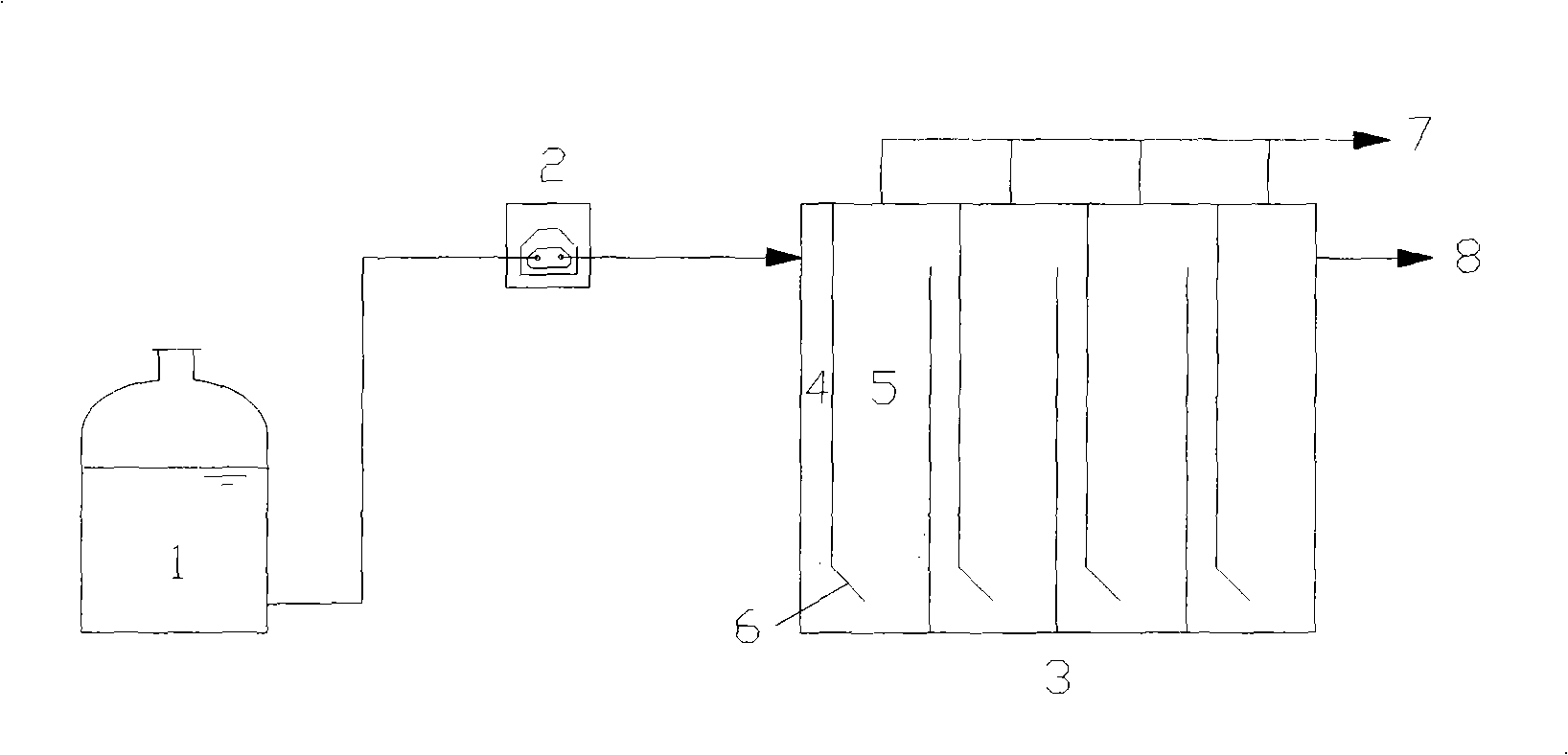
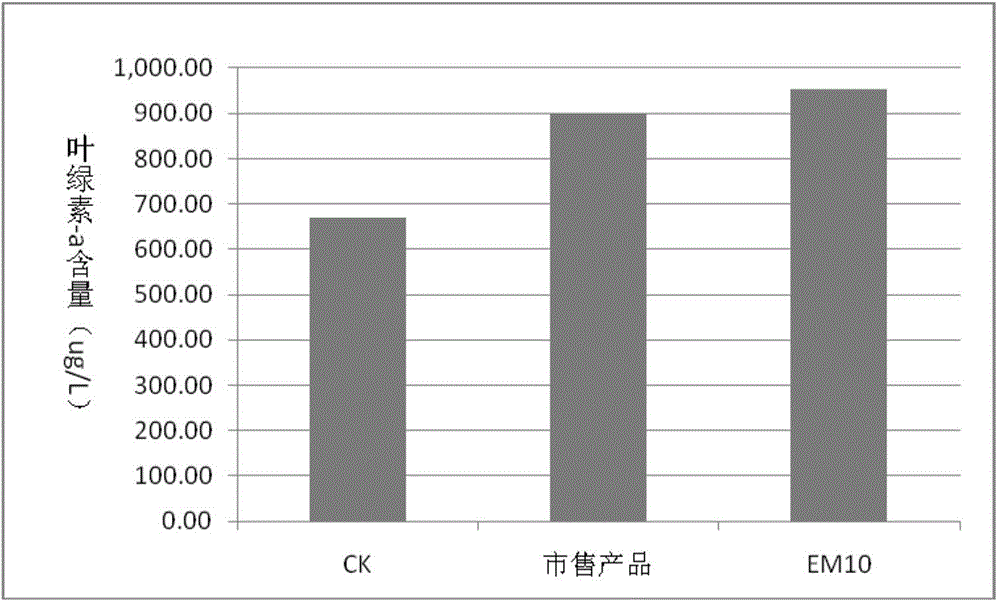
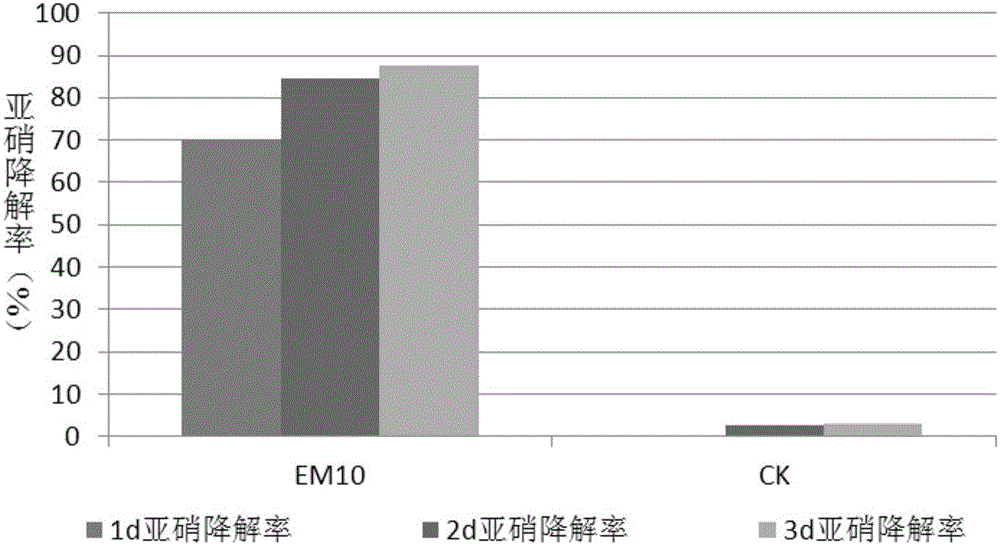
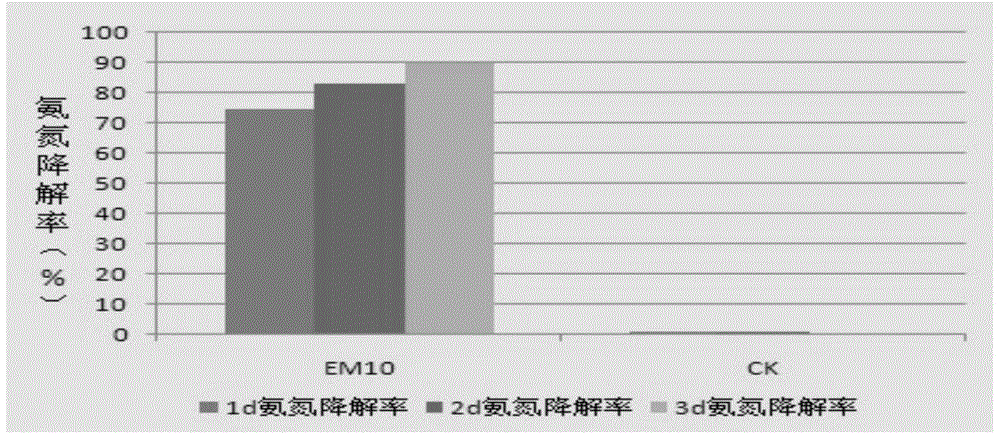
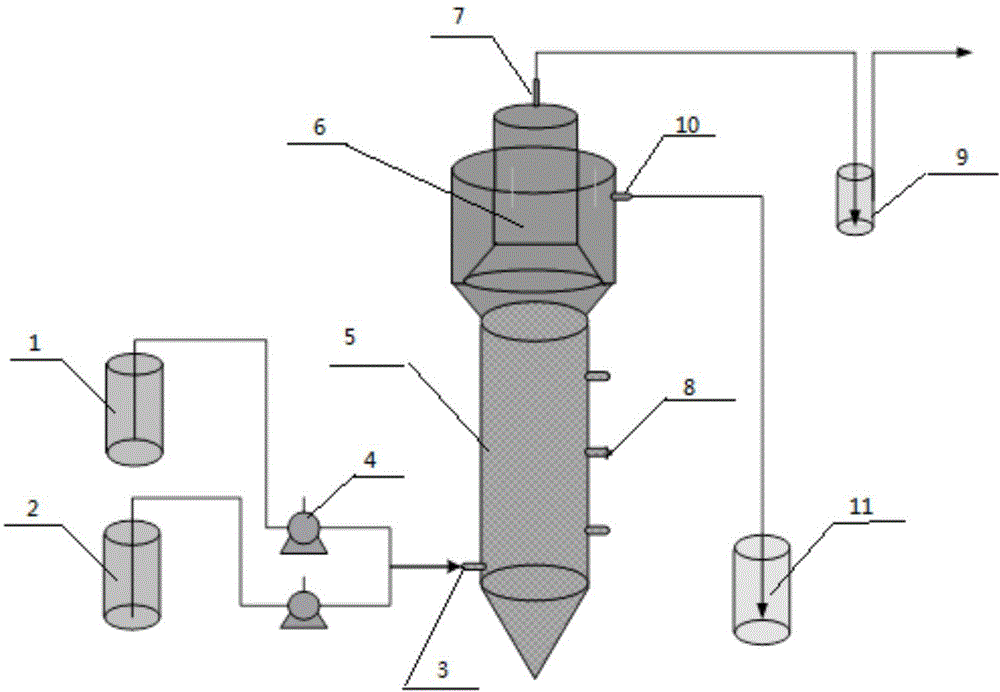
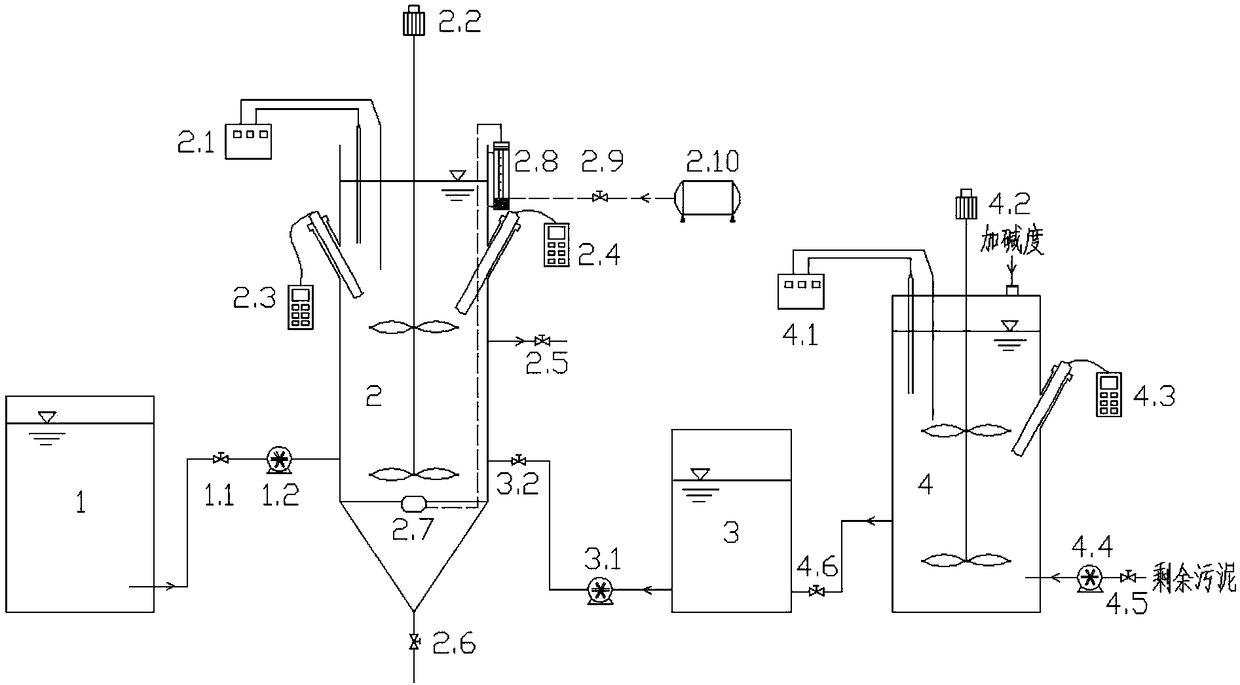
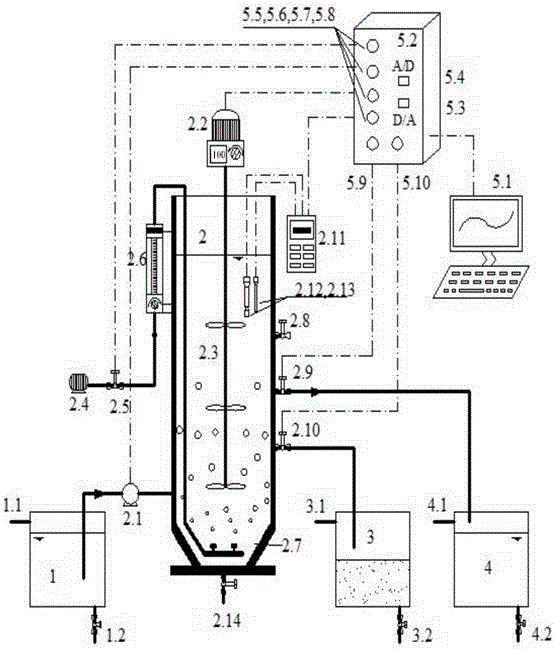
Patents
Literature
968 results about "Nitrite nitrogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nitrite is the nitrogen oxoanion formed by loss of a proton from nitrous acid. It has a role as a human metabolite. It is a nitrogen oxoanion, a member of reactive nitrogen species and a monovalent inorganic anion.
Deepness denitrogenation method for treating organic wastewater in high concentration
ActiveCN101050026AGuaranteed emission standardsThe process route is compactWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesHigh concentrationTotal nitrogen
This invention discloses a method for deep denitrification treatment of high-concentration organic wastewater. The apparatus comprises an anaerobic decarbonization zone, an aerobic nitrosation / anaerobic ammoxidation denitrification zone, and a traditional nitrification / denitrification zone. In the anaerobic decarbonization zone, an anaerobic bioreactor is utilized to perform anaerobic biotreatment on the organic pollutants in raw water to remove the majority of organic matters. In the aerobic nitrosation / anaerobic ammoxidation denitrification zone, ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen are removed in the form of nitrogen gas. In the traditional nitrification / denitrification zone, nitrate in the water discharged from the aerobic nitrosation / anaerobic ammoxidation denitrification zone is subjected to denitrification and removed in the form of nitrogen gas. Excess organic matters are subjected to aerobic bioreaction and removed. The method can ensure COD; total nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen contents in the treated water are qualified for discharge. The method has such advantages as high decarbonization and denitrification efficiency, low energy consumption, and high running stability.
Owner:BEIJING MUNICIPAL RES INST OF ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION
Sphingomonas strain and application thereof in water treatment
InactiveCN102168054APromote degradationReduce concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIndustrial waste waterWater source
The invention belongs to the technical fields of environmental engineering and bioengineering and particularly relates to a sphingomonas strain and applications thereof in the aspects of shortcut nitrification-denitrification of nitrogen-containing industrial waste water and domestic sewage and treatment of a polluted water source. The sphingomonas strain is separated from a Taihu water in China,is a local strain and has high safety; and the strain can be grown in a basic medium, wherein in the basic medium, CO2 is used as a carbon source and energy or CO2 and an organism are used as a mixedcarbon source and energy, and ammonia nitrogen or nitrate nitrogen is used as a nitrogen source. The bacterium liquid, the dormancy cell and the immobilized strain of the sphingomonas can decompose ammonia nitrogen into nitrite nitrogen and simultaneously can decompose the ammonia nitrogen into nitrogen, can be used as denitrification microorganism for converting the ammonia nitrogen into the nitrite nitrogen and the nitrogen, thereby achieving the shortcut nitrification-denitrification. The strain can rapidly decompose the ammonia nitrogen and is suitable for treating the nitrogen-containingindustrial waste water and domestic sewage as well as polluted water source.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Autotrophic nitrogen removal method for biological phosphorus removal of urban sewage based on short-cut denitrification for providing nitrite
ActiveCN104556376AReduced oxygen demandReduce operating energy consumptionTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSludgeAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
The invention discloses an autotrophic nitrogen removal method for biological phosphorus removal of urban sewage based on short-cut denitrification for providing nitrite. The method comprises the following steps: firstly feeding urban sewage into an anaerobic zone of a biological phosphorus removal nitrogen removal reactor, wherein short-cut denitrification is firstly carried out on denitrifying bacteria on a biological membrane so as to reduce nitrate nitrogen in return sludge to nitrite nitrogen, anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria on the biological membrane further convert nitrite nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen into nitrogen while anaerobic phosphorus release is carried out on phosphorus-accumulating bacteria in floc sludge; then feeding the sewage into the anaerobic zone again, wherein short-cut denitrification is carried out on the denitrifying bacteria on the biological membrane so as to reduce nitrate nitrogen in return sludge to nitrite nitrogen, and anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria on the biological membrane further convert nitrite nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen into nitrogen; then feeding the sewage into an aerobic zone and ammonia oxidizing bacteria and nitrite oxidizing bacteria in the floc sludge oxidize residual ammonia nitrogen in the sludge to nitrate nitrogen; and finally, implementing residual phosphorus removal and autotrophic nitrogen removal of urban sewage of a continuous flow, wherein the treatment energy consumption of an urban sewage plant is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Nitrous acid-type denitrification bacteria strain and application thereof
ActiveCN102465105ACarbon savingSimple processBacteriaTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesHigh concentrationNitrous acid
The invention relates to a bacteria strain for short-cut denitrification and an application thereof. The short-cut denitrification bacteria strain is arthrobacter creatinolyticus FDN-1 and is preserved in Ordinary Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on March 11, 2010, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 3657. The bacteria strain can directly adopt nitrite nitrogen as a substrate to complete the short-cut denitrification process. When the arthrobacter creatinolyticus FDN-1 is used for processing ammonia-contained waste water, the technique is simple, high denitrification activity can be still obtained under the condition that low-concentration organic carbon source exists, and at the same time the high-concentration organic carbon source can be withstood. When the bacteria strain is in use, the system is rapid to start, and a vast application prospect can be realized in the denitrification treatment process of different types of waste water.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Device and method for denitrification of single stage autotroph in low-cellulose nitrate (CN) high-ammonia nitrogen waste water
ActiveCN102101720AAchieve separationEasy to controlTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesCelluloseSludge
The invention discloses a device and a method for denitrification of single stage autotroph in low-cellulose nitrate (CN) high-ammonia nitrogen waste water. The device comprises a raw water tank, a water inlet pump, a reactor, a secondary sedimentation tank and a sludge reflux pump, wherein overcurrent holes are arranged in the water flow direction of the reactor in an up-and-down alternative form and connected with various grid chambers, an anoxic zone grid chamber is arranged at the front end of the reactor, and an aerobic zone grid chamber is arranged at the back end of the reactor; the anoxic zone grid chamber is provided with a stirrer and an agitator blade; the aerobic zone grid chamber is provided with the stirrer, the agitator blade, an aeration riser pipe and an intermediate perforated clapboard; and the aeration riser pipe is internally provided with an aeration head, and sponge filling material is filled below the intermediate perforated clapboard, wherein filling ratio is 30-50%. In the method, shortcut nitrification is achieved above the aerobic zone through low dissolved oxygen (DO is 0.5 <-1>mg / L) and free ammonia (FA) inhibition so that ammonia nitrogen is converted to nitrite nitrogen; and anoxicammoxidation biomembrane acts on the lower part of the aerobic zone, the nitrite nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen are converted to nitrogen, thereby achieving denitrification of autotroph. The method has the advantages of low oxygen consumption, less sludge output and no extra carbon source.
Owner:彭永臻
Preparation method and application of immobilized bacteria for improving denitrification efficiency of constructed wetland
InactiveCN102392011AHigh mechanical strengthImprove stabilityTreatment using aerobic processesSustainable biological treatmentConstructed wetlandIndustrial waste water
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of immobilized bacteria for improving the denitrification efficiency of a constructed wetland. 1. The preparation steps are as follows: 1) screening and culturing aerobic denitrification strains which are screened out of the constructed wetland in a thermotank; 2) selecting aerobic denitrification bacteria in slope conservation, inoculating into a sterile enrichment culture medium and aerating to get bacterial suspension; 3) using sodium alginate-polyvinyl alcohol to embed so as to get the immobilized aerobic denitrification bacteria; and 4) taking pellets of the aerobic denitrification bacteria out of a refrigerator, washing with double distilled water or physiological saline, soaking in the physiological saline, and aerating to activate the immobilized pellets. 2. An application of the immobilized bacteria in the constructed wetland is as follows: filling the immobilized pellets into a simulation column of the constructed wetland for performing waste water denitrification treatment. The preparation method of the immobilized bacteria is simple, the production cost is low, the application in the industrial waste water treatment is easy, the denitrification efficiency is high, the accumulation amount of nitrite nitrogen is low, and the service life is long.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Method for quickly starting oxygen-poor ammonia oxidizing biofilter
InactiveCN101830569AQuick changeLow running costBiological water/sewage treatmentHydroxylamineSludge
The invention relates to a method for quickly starting an oxygen-poor ammonia oxidizing biofilter, and relates to a method for biological denitrification of waste water, which comprises the following steps of: (1) inoculating an anaerobic denitrification biomembrane biofilter, and after a denitrification biomembrane is cultured, converting the anaerobic denitrification biomembrane biofilter into an oxygen-poor environment for cultivating oxygen-poor ammonia oxidizing bacteria; (2) taking inorganic carbon NaHCO3 as a carbon source, taking NH4Cl as a nitrogen source of ammonia nitrogen, taking NaNO2 as the nitrogen source of nitrite nitrogen, taking KH2PO4 as a phosphorus source, and controlling the pH value to be alkalescent, wherein the concentration is low-matrix, and the temperature is room temperature; adding hydroxylamine, and inducing and inoculating sludge to be converted towards an oxygen-poor ammonia oxidizing biomembrane; and (3) taking the biofilter as a reactor, and taking ceramsite as filter materials. In the method, the oxygen-poor ammonia oxidizing bacteria are applied to the sewage denitrifying technology to realize the shortest denitrification of nitrogen, so the problems of a large number of required carbon sources and neutralizers, large energy consumption and large sludge producing amount in the conventional biological denitrifying technology are solved.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Staphylococcus cohnii and applications thereof
ActiveCN103103142AHigh reductase activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHigh concentration
The invention relates to a strain of Staphylococcus cohnii, and applications thereof. The strain is Staphylococcus cohnii FSDN-C, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on July 14, 2011, wherein a preservation number is CGMCCNO.5062. According to the present invention, the strain can adopt nitrite nitrogen as a substrate to complete short time denitrification denitrogenation, wherein organic pollutants can be removed during denitrogenation; when the Staphylococcus cohnii FSDN-C is adopted to treat ammonia-containing wastewater, characteristics of simple process, and high concentration organic carbon source tolerance are provided; after the strain is poured, the system is rapidly started; and the strain has broad application prospects in various wastewater denitrogenation treatment processes.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Bacterial strain used for short-cut denitrification for nitrogen removal and its application
ActiveCN102465106ASimple processStart fastBacteriaTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesHigh concentrationBacterial strain
The invention relates to a bacterial strain used for short-cut denitrification for nitrogen removal and its application. The bacterial strain used for short-cut denitrification for nitrogen removal is flavobacterium mizutaii FDN-2, which is preserved in China general microbiological culture collection center on March 11, 2012 and has a preservation number of CGMCC NO.3659. The bacterial strain can directly utilize nitrite nitrogen as a substrate to complete a short-cut denitrification process. When treating ammonia-containing wastewater with the flavobacterium mizutaii FDN-2 of the invention,the process is simple, and the flavobacterium mizutaii FDN-2 can tolerate a high concentration organic carbon source. When the flavobacterium mizutaii FDN-2 in the invention is put into use, a systemcan be rapidly initiated, so that the flavobacterium mizutaii FDN-2 boasts very broad application prospects in various nitrogen removal processes of wastewater.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Kocuria palustris strain and applications thereof
ActiveCN103103141AFast growthIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHigh concentration
The invention relates to a Kocuria palustris strain and applications thereof. The strain is Kocuria palustris FSDN-A, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on July 14, 2011, wherein a preservation number is CGMCCNO.5061. According to the present invention, the strain can adopt nitrite nitrogen or nitrate nitrogen as a substrate to complete a denitrification process; when the Kocuria palustris FSDN-A is adopted to treat ammonia-containing wastewater, characteristics of simple process, high denitrogenation activity, and high concentration organic carbon source tolerance are provided; after the strain is poured, the system is rapidly started; and the strain has broad application prospects in wastewater denitrogenation treatment processes, and is especially suitable for treatment of wastewater containing nitrogen oxides and organic pollutants.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Rapid start method for integrated autotrophic denitrification system
ActiveCN106673205AExtend the aeration timeReduce hypoxic timeWater treatment parameter controlTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSequencing batch reactorMass ratio
The invention relates to a rapid start method for an integrated autotrophic denitrification system and belongs to the technical field of treatment of sewage with high ammonia nitrogen. An SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) is inoculated with short-cut nitrification sludge and anammox sludge according to the mass ratio of (1: 3) to (1: 1), and the concentration of mixed sludge is 3,000mg / L to 4,000mg / L. The dissolved oxygen is controlled to be 0.3mg / L to 0.5mg / L by adopting an intermittent aeration operating mode, and the accumulation amount of nitrite nitrogen at the end of aeration is 20mg / L to 30mg / L; in each cycle, three aeration and hypoxic stages are set at intervals; each cycle has six stages, i.e., water inlet, aeration / hypoxic reaction, stirred degassing, precipitating, water outlet and standing. In a starting process, the concentration of dissolved oxygen is controlled unchanged, the balance of supply and consumption of nitrite nitrogen is maintained through a method of stagewise prolonging aeration stage time and shortening hypoxic stage time, and the rapid increase of denitrification load is achieved. When the initial ammonia nitrogen concentration in the reactor reaches 300mg / L, the balance of supply and consumption of nitrite nitrogen is maintained by means of shortening the hypoxic stage time. According to the method, the starting speed is high, the total-nitrogen removal load is high, and the operation is stable.
Owner:SHANGHAI YIKE ENVIRONMENT TECH CO LTD
Cultivation method of anammox granular sludge
ActiveCN103043788AAccelerated enrichment growthPromote formationTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesWater concentrationNitrogen
The invention discloses a cultivation method of anammox granular sludge, and belongs to the field of water treatment. The cultivation method solves the technical problems that the existing high-efficiency anammox granular sludge is difficult to cultivate, and the cultivation time is long. The method comprises the following steps that 1, aerobic granular sludge and anammox seed sludge are simultaneously inoculated into an EGSB (expanded granular sludge bed) reactor; 2, nitrogenous simulated waste water is supplied to the EGSB reactor, the hydraulic retention time is kept for 12h, and concentrations of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen in intake water are gradually increased until successful start when the synchronous removal rate of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen is above 80%; and 3, intake water concentrations of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen are kept stable, the hydraulic retention time is gradually shortened up to 2.6h when the synchronous removal rate of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen is above 80%, and then the cultivation of the anammox granular sludge is completed. With the method, the reactor can be started successfully within about 20 days, and the high-efficiency anammox granular sludge can be obtained within about 89 days.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CIVIL ENG & ARCHITECTURE
UBF reactor used for coupled denitriding via anaerobic ammonia oxidation-sulfur-based autotrophic denitrification, and system and denitriding method thereof
ActiveCN107162184AReduce outputReduce aerationWater contaminantsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesChemistryNitrite nitrogen
The invention discloses a UBF reactor used for coupled denitriding via anaerobic ammonia oxidation-sulfur-based autotrophic denitrification, and a system and a denitriding method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of waste water processing. The denitriding method is suitable to be used for processing high mmonia nitrogen low C / N waste water, partial nitrification is used for providing all reaction substrates of anaerobic ammonia oxidation, marcasite is used for providing electron donors of sulfur-based autotrophic denitrification; porous limestone is taken as a supporting framework of a limestone filling layer; and nitrite nitrogen generated via nitrosation, and nitrate nitrogen generated via nitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation are taken as electron acceptors. The denitriding method is high in ammonium-nitrogen removal rate; operation stability is high; compared with conventional nitration-denitrification denitriding method, the denitriding method possesses following advantages: no extra organic matter is added as the electron donor, marcasite is ued for providing the electron donors of sulfur-based autotrophic denitrification bacteria, cost is low, controllability is high, effluent is stable, sludge yield is low, and energy consumption is low.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Operating method for high-efficient anaerobic ammonium oxidation reactor
ActiveCN102515348AAvoid matrix inhibitionEasy to interceptTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesAmmoniacal nitrogenLow load
The invention discloses an operating method for a high-efficient anaerobic ammonium oxidation reactor. The method comprises the steps of (1) inoculating anaerobic granular sludge in an anaerobic reactor, the wherein the anaerobic granular sludge accounts for 30-90% of total volume of the reactor; and (2) taking nitrogenous simulating wastewater as reaction inflowing water, wherein the temperatureof the reactor is controlled to be in 18-37 DEG C; and in a reactor starting stage, remaining hydraulic power for 12-48h, adjusting reaction operating conditions according to concentration of ammonianitrogen and / or nitrite nitrogen, operating the anaerobic reactor for 30-150d, and forming high-efficient anaerobic ammonium oxidation granular sludge enriched with anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria. The method improves total nitrogen load of the reactor in a way that the load is increased gradually by lower load so as to be beneficial to stable increasing of domestication enrichment and nitrogen removing rate of the anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria, can effectively avoid matrix restraining of anaerobic ammonium oxidation and is beneficial to reducing process operating cost when the reactor operates under a room temperature condition.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and application thereof on aquiculture
InactiveCN101792723AReduce contentEasy to separateBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementSludgeWater quality
The invention relates to Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and application thereof on aquiculture. The bacterial strain is separated from the substrate sludge of a polluted brook, is identified as the Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and is collected in Microscobial Culture Collection of China. The bacterial strain can normally grow within the temperature of 20 to 45 DEG C and within the pH value of 5.0 to 10.0; the bacterial strain can reach the fermentation terminal point when being inoculated on a broth culture medium the initial pH value of which is 7.0 according to inoculum concentration of 1:20 and cultured for 18 hours at the speed of 150r.min-1 at the temperature of 39 DEG C. The invention is characterized in that the bacterial strain can enable the content of nitrate nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen, COD and the like in a culture water body to be obviously lowered, has no harm to people and livestock and can be produced on a large scale for improving the aquiculture environment. The Bacillus amyloliquefaciens has obvious degradation function on main pollutants in a simulate culture water body and can be made into a micro-ecology preparation for purifying the culture water body.
Owner:TIANJIN CITY AGRI BIO TECH RES CENT
Anaerobic multi-stage aerobic-anoxic dephosphorization and denitrification process
ActiveCN101439908AImprove nitrogen removal efficiencyIncrease concentrationTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSludgeNitration
The invention relates to multistage anaerobic, aerobic and anoxic dephosphorization and denitrogenation technology, which is mostly suitable for treating urban domestic sewage. The sewage is divided into two parts, namely approximately 30 percent of the sewage is mixed with return sludge and enters into an anaerobic tank, and most of the sewage exceeds the anaerobic tank and directly enters into an anoxic tank for denitrogenation in a multipoint mode; after denitrogenation is completed, the mixed solution is mixed with a small part of the sewage and enters into a secondary settling tank for sludge-water separation; and denitrogenation reaction is continuously completed during sludge-water separation; and the return sludge and nitrite nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen of discharged water are reduced, and residual sludge is discharged regularly. The multistage anaerobic, aerobic and anoxic dephosphorization and denitrogenation technology has high phosphor and nitrogen removal rate, reduces the capacity of a structure, saves investment, fully utilizes carbon sources and simultaneously reduces direct oxygen consumption because the sewage does not directly enter into an aerobic tank and then the carbon sources in the sewage do not directly contact oxygen, and improves the catch rate of air bubbles and obviously saves the aeration cost due to ultrahigh sludge concentration in the aerobic tank under the condition of blast aeration.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +1
Aerobic denitrifying bacterium and application thereof in wastewater treatment
ActiveCN103667168AEasy to trainNo accumulationMicroorganism based processesOn/in organic carrierDenitrifying bacteriaWastewater
The invention discloses an aerobic denitrifying bacterium and application thereof in wastewater treatment. The applicant selects an aerobic denitrifying bacterium through enrichment, Pseudomonas stutzeri JH-1, CCTCC NO: M2013488 from a wet land. The bacterium can be used for treating wastewater with high NO3<->, reaches the highest removing rate of 99.6%, avoids the accumulation of nitrite nitrogen, meanwhile can remove COD in organic wastewater with the highest removing rate of 60%-80%; compared with other reported aerobic denitrifying bacteria for wastewater treatment, the bacterial strain provided by the invention can efficiently treating wastewater, achieves the removal rate of nitrate nitrogen of 99.6% after 24 h and the denitriding rate of 22.6 mg. L<-1>.h<-1>, which is 1.51-4.57 times of that of the reported bacterial strains, can be independently used or solidified for wastewater treatment, and is widely applied.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Rotating biological-cathode microbiological fuel cell and sewage treatment method thereof
InactiveCN101817587AEven contactBiochemical fuel cellsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesFiberCarbon fibers
The invention relates to a rotating biological-cathode microbiological fuel cell and a sewage treatment method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment and resource recycling in environment engineering. The invention is characterized in that a cathode is made of carbon fibers and fixed to a circular ring. The outer layer of the rotating cathode biomembrane mainly comprises aerobic nitrifiers for completing the short-range nitrification of ammonia nitrogen. In the inner layer of the cathode biomembrane, nitrite nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen are used as electron acceptors, an electrode is an electron donor and used for denitrification. The structure of a reactor realizes controllable rotation speed of the cathode, controllable distance between the cathode and the anode, and controllable submerging proportion of the cathode biomembrane, and has the advantages of flexible operation, and convenient regulation and control. The rotating biological-cathode microbiological fuel cell can realize control on dissolved oxygen in a single-chamber reactor; and thus, the invention reduces the internal resistance of the cell, accelerates the biomembrane renewing, realizes the short-range nitrification and denitrification, synchronously completes decarburization and denitrification with low consumption and high efficiency, and extracts chemical energy from pollutants to form electric energy output.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for cultivating nitrosobacteria flora and method for treating wastwater containing ammonia nitrogen
ActiveCN101434915AImproving the Efficiency of Removing Ammonia Nitrogen in Biochemical TreatmentSimple processBacteriaWater contaminantsHigh concentrationCulture fluid
The invention discloses a culture method of a nitrosomonas sp. flora and a treatment method of waste water containing ammonia nitrogen. The ammonia nitrogen concentration and the pH value of a matrix are increased during an enrichment process, and free NH3 with higher concentration is maintained, thereby gradually achieving the purposes of eliminating nitrobacter sp. and enriching nitrosomonas sp. and obtaining a nitrosomonas sp. flora. Then, the obtained nitrosomonas sp. flora is taken as seeds, the expanded culture is carried out by utilizing self-prepared ammonia nitrogen waste water or high ammonia nitrogen waste water as a culture liquid, the nitrosomonas sp. flora after the expanded culture is inoculated into a biochemical treatment pool for improving the removal efficiency of ammonia nitrogen by biochemical treatment, or the nitrosomonas sp. flora after the expanded culture is directly used for removing the ammonia nitrogen of the ammonia nitrogen waste water, and the optimal proposal is used in the aerobic nitrification stage of the shortcut nitrification-denitrification process for accumulating nitrite nitrogen as an electron acceptor for denitrification directly. The method has simple process and outstanding effect of treating the waste water containing the ammonia nitrogen.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Low-carbon urban sewage biological phosphorus removal and autotrophic biological nitrogen removal device and method
ActiveCN102101746AReduce doseEmission reductionEnergy based wastewater treatmentMultistage water/sewage treatmentOxygenChemistry
The invention discloses a low-carbon urban sewage biological phosphorus removal and autotrophic biological nitrogen removal device and a low-carbon urban sewage biological phosphorus removal and autotrophic biological nitrogen removal method. The device comprises a raw water tank, a biological phosphorus removal and half shortcut nitrification reactor, a secondary sedimentation tank, an intermediate water tank and an anammox reactor, wherein the biological phosphorus removal and half shortcut nitrification reactor is a university of cape town (UCT) reactor without internal returning of digestive fluid; the secondary secondary sedimentation tank is a radial-flow sedimentation tank; and the anammox reactor is an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor. The method comprises: introducing urban sewage first to the anaerobic zone of the biological phosphorus removal and half shortcut nitrification reactor for phosphorus release, then to an anoxic zone of the biological phosphorus removal and half shortcut nitrification reactor for denitrification and phosphorus absorption and finally to an aerobic zone for aerobic phosphorus absorption and half shortcut nitrification; subjecting mixed liquid containing ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen to sludge and water separation in the secondary sedimentation tank; and introducing the water to the anammox UASB reactor for autotrophic biological nitrogen removal under anammox action. When the method is used, process aeration can be reduced, energy consumption can be reduced, and carbon source is saved. The method is suitable for treating low-carbon sewage.
Owner:彭永臻
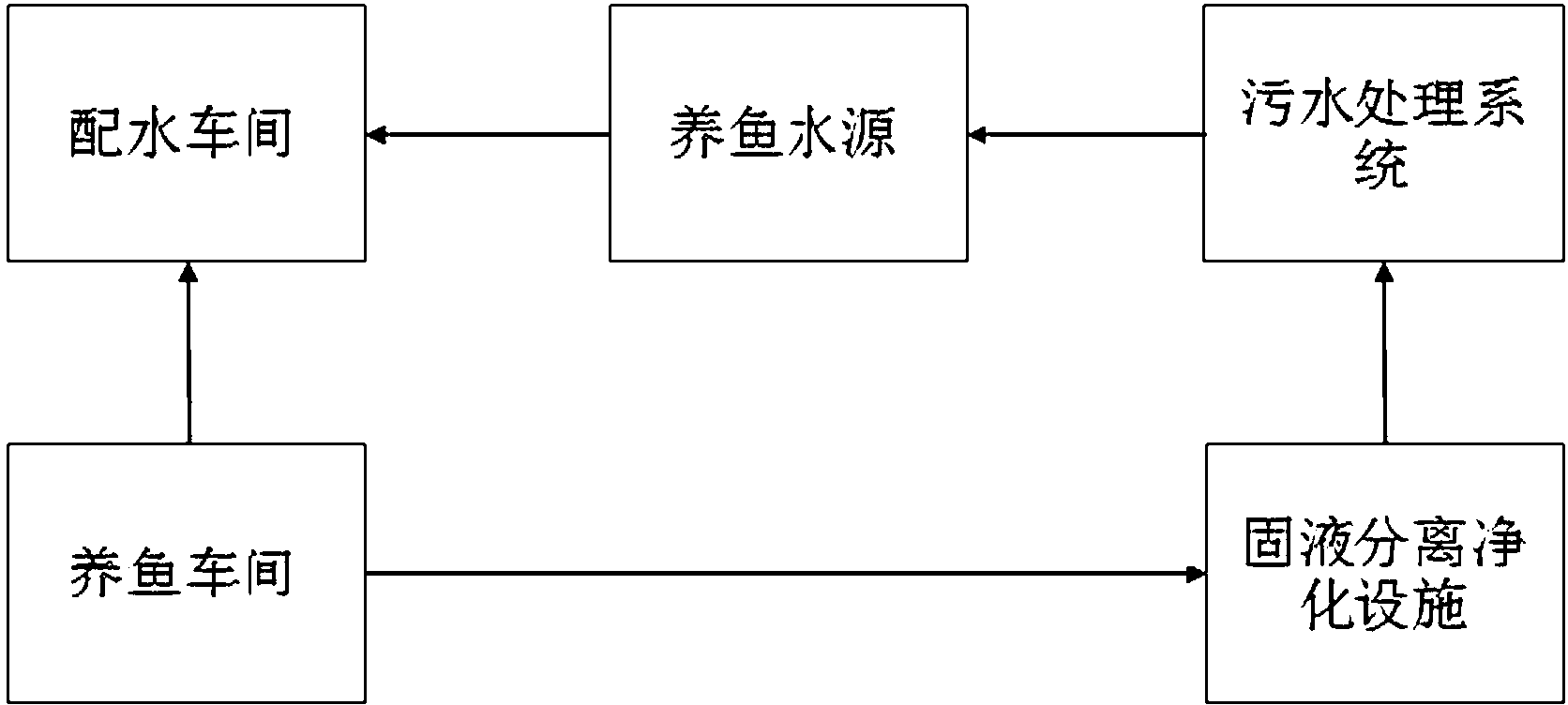
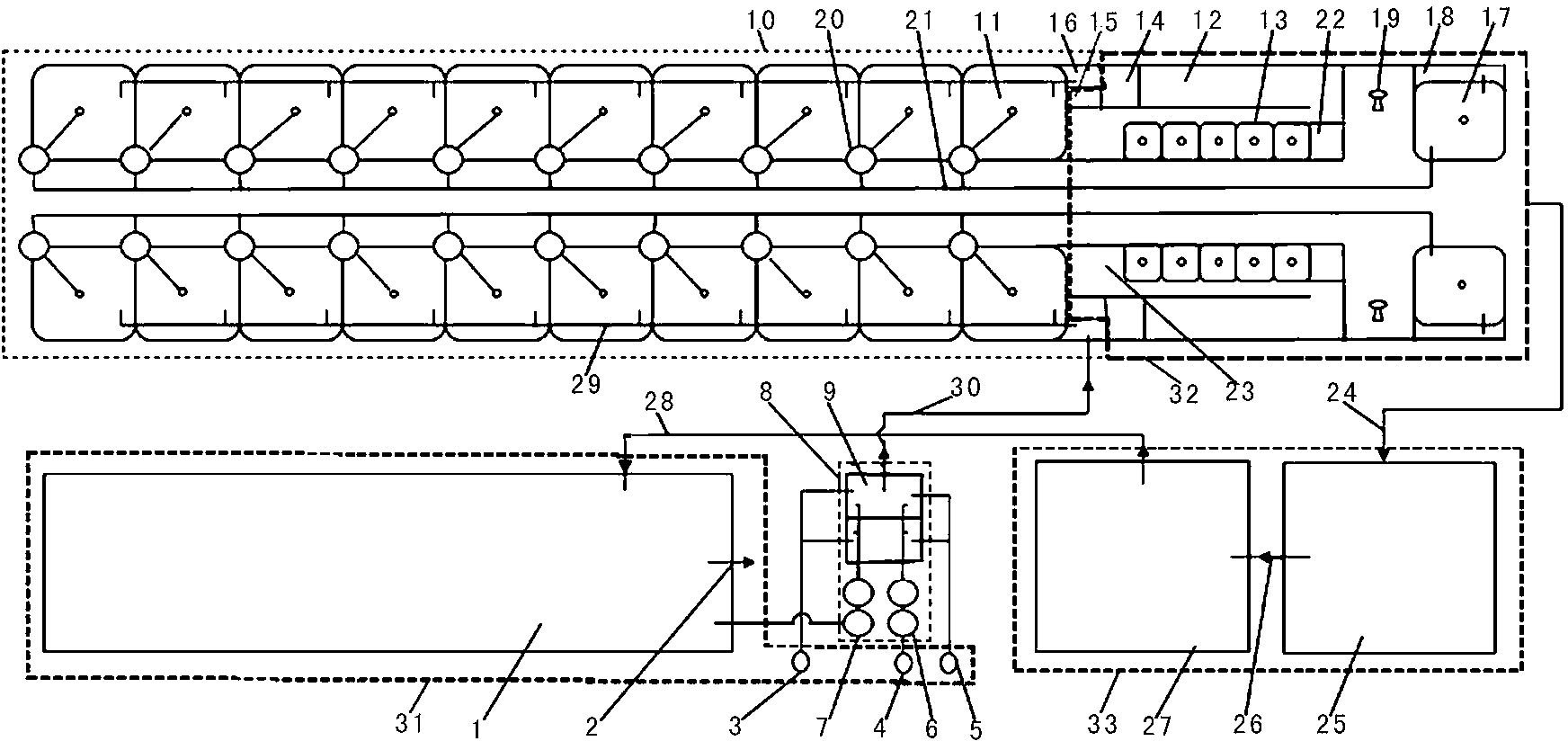
Ecotype enclosed method for culturing fish through circulation water
InactiveCN103238554AEasy to interceptEasy to sinkPisciculture and aquariaFiltrationUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses an ecotype enclosed method for culturing fish through circulation water. Natural seawater, underground salt water, underground fresh water and geothermal water are mainly utilized and mixed, and an industrial culture foundation for producing pollution-free healthy seafood is built and used. A solid-liquid separation purification device is used for replacing sand filtration of a biological filter, ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen are degraded after water passing through a biological film on biological filler in the biological filter, and the total purification rate of water body particles is over 99%. An aeration pond is arranged to conduct aeration and oxygenation on a culture water body to enable the content of dissolved oxygen in water in a fish culture pond to be kept at 8-14mg / L, finally the water body is sterilized through ultraviolet light, clean ecological water is input into the fish culture pond, and the return water in the fish culture pond is purified repeatedly and utilized in a circulating mode. Sewage discharged from a culture system is purified by an open-air pond and flows back to a water storage sedimentation pond to achieve zero-discharge complete enclosed circulation water factory-like fish culture.
Owner:天津市兴盛海淡水养殖有限责任公司
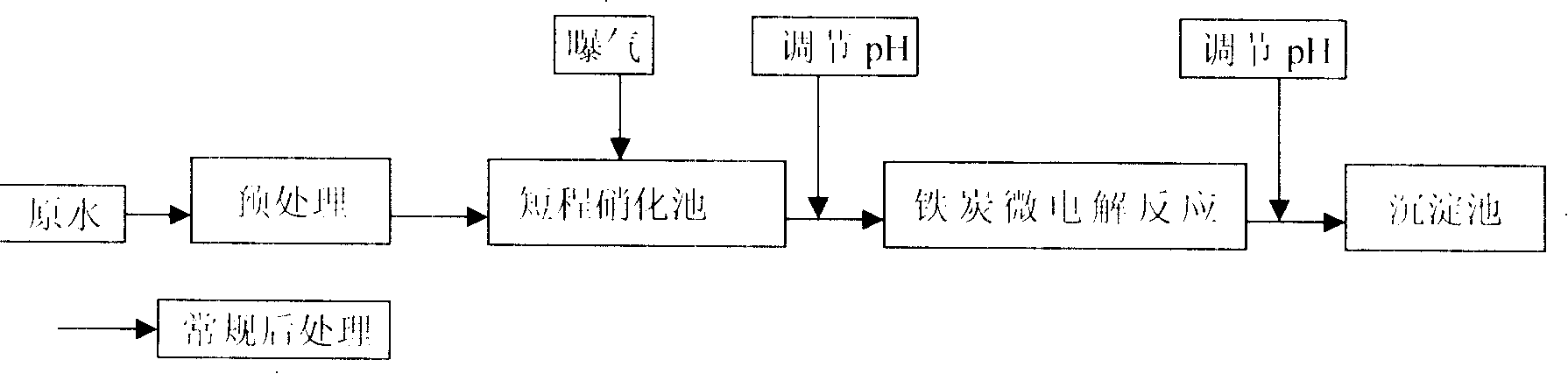
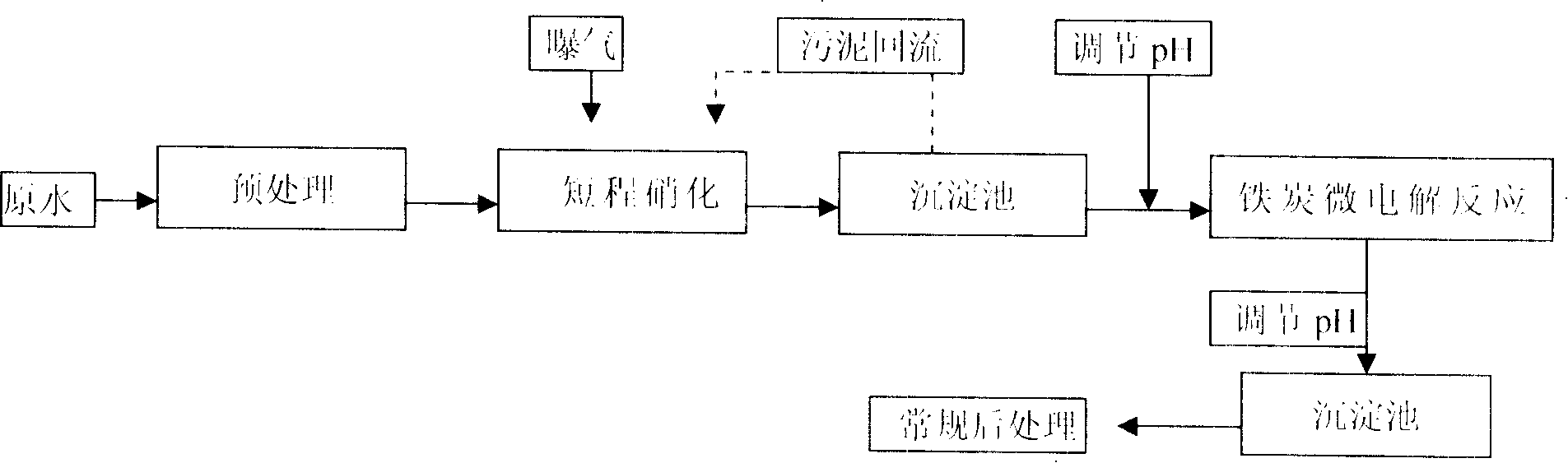
Energy-saving process for treating high ammonia nitrogen waste water
InactiveCN101195513AHigh removal rateReduce consumptionTreatment using aerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentElectrolysisWater quality
In the invention discloses an energy-saving treatment method of high strength ammonia wastewater, which comprises procedures of pre-processing, short-cut nitrification, micro-electrolysis and after-treatment. The method is characterized in that firstly wastewater is preprocessed to transform Kjeldahl nitrogen into amino nitrogen, then the wastewater enters a main body of the process to be processed. In a short-cut nitrification tank, the amino nitrogen in the wastewater is nitrated and controlled to a nitrite nitrogen stage, then a micro-electrolysis reactor is employed to replace anaerobic denitrification or ammonoxidation process to be denitrified, the nitrite nitrogen and organic pollutants in the wastewater are highly effectively degraded and are further subsequently processed by employing biological method and physicochemical oxidation method, and outlet water of the wastewater reaches standards. The method makes full use of water quality of raw water, the additional medicament consumption is saved, the process flow is shortened, and the process operation is simplified. Compared with the conventional denitrification process, the denitrification rate is increased, the total nitrogen removal rate reaches 60%-75%, and the treatment effect of degrading hardly degradable organics is remarkably increased. The treatment cost of wastewater per ton by employing novel method can be reduced by 30-50%.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH LIAONING
Technology for treating domestic sewage by realizing partial short-cut nitrification, sludge fermentation coupling denitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation in sequencing batch reactor
ActiveCN108585202AEasy to upgradeAchieve reductionTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSustainable biological treatmentSequencing batch reactorNitration
The invention discloses a technology for treating domestic sewage by realizing partial short-cut nitrification, sludge fermentation coupling denitrification and anaerobic ammonia oxidation in a sequencing batch reactor, and belongs to the field of the sewage sludge biological treatment. The technology comprises an inlet water tank, a partial short-cut nitrification reactor (PN-SBR), an intermediate water tank, an anaerobic ammonia oxidation coupling sludge fermentation and denitrification reactor (ASFD-SBR), and an outlet water tank. The partial short-cut nitrification is performed in the partial short-cut nitrification reactor (PN-SBR), and a part of ammonia nitrogen in raw water is converted to nitrite nitrogen. The influent ammonia nitrogen and the nitrite nitrogen are converted to a nitrogen gas and a little of nitrate nitrogen by anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria in the anaerobic ammonia oxidation coupling sludge fermentation and denitrification reactor (ASFD-SBR), and the generated nitrate nitrogen is reduced to the nitrogen gas by a carbon source generated by sludge fermentation, wherein static bed filler is used for retaining the anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria, and denitrification and sludge fermentation processes are performed in floc sludge. The technology is capable of saving energy consumption, and simultaneously realizing the deep denitrification of theurban domestic sewage in a low carbon nitrogen ratio (C / N) and the recycling of the sludge.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for anaerobic ammonia oxidation treatment of low-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater
ActiveCN101525179AAchieving oxidative denitrificationIncrease concentrationWater contaminantsWaste based fuelPeristaltic pumpAnaerobic bacteria
The invention relates to a method for the anaerobic ammonia oxidation treatment of low-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater. The method is characterized in that sludge containing anaerobic bacteria is inoculated into an anaerobic traverse baffle reactor under an anaerobic condition; the alkalescent ammonia nitrogen wastewater with 10 to 20mg / L of the concentrations of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen enters the anaerobic traverse baffle reactor by an inlet water storage bottle, and a constant-current peristaltic pump is used for controlling the hydraulic stay time to be from 24 hours to 48 hours and the reaction temperature to be from 25 DEG C to 30 DEG C; if anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria become dominant flora and both the removal rates of the ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen reach 80 percent for 5 days, the anaerobic traverse baffle reactor is successfully started; then, other low-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater enters the anaerobic traverse baffle reactor by the inlet water storage bottle, and the hydraulic stay time is controlled to be from 12 hours to 48 hours; and finally, both the removal rates of the ammonia nitrogen and the nitrite nitrogen can reach about 80 percent.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
Composite microecological preparation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105462872AGood cooperation and symbiosisImprove immune activityFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyStaphylococcus lactis
The invention provides a composite active bacterial preparation which is used for aquatic products and has the water improving and fertilizing functions and a preparation method thereof by applying a modern bioengineering technology mainly for the problem that in existing aquaculture, the water quality of a pond is poor. The composite microecological preparation is prepared by mixing bacillus subtilis, bacillus megatherium, bacillus amyloliquefaciens, bacillus licheniformis, enterococcus faecium, lactobacillus brevis, lactobacillus plantarum, lactococcus lactis and saccharomyces cerevisiae through liquid-submerged fermentation. In the liquid preparation, microorganisms are in a dormant state and are stable and easy to preserve, after the preparation is put into water, the dormant strains can quickly resuscitate, harmful substances such as nitrite nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen in the water are quickly decomposed, good algae growth is facilitated, harmful algae reproduction is inhibited, and therefore the purpose of improving the water quality of the culture water is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING DABEINONG TECH GRP CO LTD +2
Swamp Rhodopseudomonas of using nitrite nitrogen in high effect, and application
This invention relates to a kind of photosynthetic bacterium that has a high assimilation utility to nitrite nitrogen. More specifically, this invention provides a Rhodopseudomonas palustris strain that can assimilate nitrite nitrogen, and its r ejuvenation, preservation, biological detection and application. The photosynthetic bacterium is a kind of biological water purifier and biological fertilizer, and can be used in controlling the content of nitrite nitrogen in water body for aquaculture, improve environmental pollution, and eliminate cinnamic acid and benzoic acid. The photosynthetic bacterium can be used as nitrogen-fixing biological fertilizer and cucumber growth promoter.
Owner:珠海市农科中心有限公司
Method for cultivating anaerobic ammonium oxidation granular sludge
ActiveCN101830558AIncrease biomassGuaranteed stabilityWater contaminantsWaste based fuelAnaerobic reactorOxygen
The invention provides a method for cultivating anaerobic ammonium oxidation granular sludge. The method comprises the steps of: mixing and putting two or three kinds of anaerobic methanogenic granular sludge, nitrification aerobic granular sludge and hypoxia denitrification granular sludge into an upflow anaerobic reactor; pumping simulate waste water containing ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen to start; keeping the temperature of 25 to 35 DEG C in the reactor and the pH value of 7.5 to 8.0 without dissolved oxygen, and keeping hydraulic detention time of 8 to 24 hours; and stabilizing for a period of time to obtain the anaerobic ammonium oxidation granular sludge from the reactor. The invention has the advantages of having good hydraulic performance and microbial activity of the anaerobic ammonium oxidation granular sludge cultivated by the method, and greatly improving the operation effectiveness and the operation stability of the reactor.
Owner:江苏清材智能制造有限公司
Rapid culture method of simultaneous desulfidation and denitrogenation granular sludge
ActiveCN104891650AGood granularityStrong impact resistanceWaste based fuelTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSulfideChemistry
The invention discloses a rapid culture method of simultaneous desulfidation and denitrogenation granular sludge. The method is characterized in that an upflow anaerobic sludge bed reactor is adopted, anaerobic ammoxidation granular sludge and methanogenesis granular sludge are adopted as inoculation sludge, model wastewater containing ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen is adopted as inlet water, and the method comprises the following steps: adding sulfide into the model wastewater, adding inorganic salts and trace elements for maintaining the growth of microbes, gradually improving the concentrations of matrixes in the inlet water and / or shortening the hydraulic retention time in order to adjust the running of the reactor, and culturing under anaerobic and shady conditions at 30-37DEG C under the pH value of the inlet water of 7.5-8.0. The sludge obtained in the invention has the advantages of obvious granularity, strong impact resistance, high processing efficiency, saving of the occupied are through cooperating with a UASB reactor, simplification of the desulfidation and denitrogenation process, and low investment and running cost, and is suitable for treating wastewater containing ammonia nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen and sulfides of the light industry, the pharmacy industry, the oil refining industry and the leather making industry.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for achieving partial short-cut nitrification-Anammox/denitrification of sewage by using sludge fermentation materials
ActiveCN108439595ARealize deep denitrificationAchieve reductionTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesAmmonia-oxidizing bacteriaNitrogen gas
The invention provides a method for achieving partial short-cut nitrification-Anammox / denitrification of sewage by using sludge fermentation materials, and belongs to the field of treatment of sewagesludge. A device used by the method comprises a raw water tank, an SBR reactor, a sludge fermentation material storage tank and a residual sludge fermentation tank. The method comprises mixing residual sludge fermentation materials with domestic sewage for treating, and achieving the short-cut nitrification by using the sludge fermentation materials, wherein the inhibition of the sludge fermentation materials on nitrite oxidizing bacteria is far greater than the inhibition of the sludge fermentation materials on ammonia oxidizing bacteria. The method is specifically characterized in that in ananaerobic phase, polyphosphate accumulating bacteria are used for releasing phosphorus by using the sludge fermentation materials and carbon sources in raw water, and storing the inner carbon sources, in an aerobic phase, the partial short-cut nitrification is achieved through real-time control on DO and pH, in an anoxic phase, anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria are used for converting ammonianitrogen and nitrite nitrogen into nitrogen and nitric nitrogen, and heterotrophic bacteria are used for reducing residual nitrite nitrogen and the generated nitric nitrogen into nitrogen by using theinner carbon sources. Through the method, the aeration intensity is reduced; meanwhile, the deep denitrification of the domestic sewage with a low C / N ratio and the reduction of exogenous sludge areachieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Device and method capable of realizing simultaneous phosphorus and nitrogen removal from sewage in low C/N ratio by coupling enhanced biological phosphorus removal with simultaneous shortcut nitrification and denitrification
ActiveCN105923772AHigh degree of enrichmentAerobic phosphorus uptakeWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesAmmonia-oxidizing bacteriaLow oxygen
The invention discloses a device and a method capable of realizing simultaneous phosphorus and nitrogen removal from sewage in a low C / N ratio by coupling enhanced biological phosphorus removal with simultaneous shortcut nitrification and denitrification and belongs to the field of biological sewage treatment. After entering an SBR coupling enhanced biological phosphorus removal with simultaneous shortcut nitrification and denitrification, sewage is first subjected to anaerobic stirring, and GAOs (glycogen-accumulating organisms) and PAOs (phosphorus-accumulating organisms) absorb organic carbon sources from the sewage and synthesize an internal carbon source PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates) to be stored in bodies; then the sewage is subjected to low-oxygen aeration stirring, AOB (ammonia oxidizing bacteria) play a role in shortcut nitrification to convert ammonia nitrogen into nitrite nitrogen, and the PAOs decompose the PHA for aerobic phosphorus accumulation so as to create a hypoxic microenvironment beneficial to that the GAOs and the PAOs use the nitrite nitrogen produced during shortcut nitrification for endogenous denitrification and denitrifying phosphorus removal respectively. The method coupling enhanced biological phosphorus removal with simultaneous shortcut nitrification and endogenous denitrification is capable of realizing simultaneous phosphorus and nitrogen removal from the sewage in the low C / N ratio without addition of a carbon source, so that oxygen consumption and energy consumption are reduced and urban sewage treatment costs are saved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com