Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and application thereof on aquiculture
A technology for dissolving starch spores and bacilli, which is applied in the field of agricultural microorganism applications to achieve the effect of improving aquaculture environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Isolation, screening and cultivation of strains
[0020] Sampling: At three different sampling points in the polluted river ditch, remove about 5mm thick surface mud from the bottom sludge, put the mud into a beaker, seal the mouth with plastic wrap and bring it back to the room for rapid separation.
[0021] Separation: Dilute the sludge with sterile water at a ratio of 1:4, treat it in a water bath at 80°C for 15 minutes, draw 100 μL of the sludge, spread it on a starch medium plate, and incubate at 37°C.
[0022] Purification: After 2 days of plate culture, select the strains that produce hydrolysis circles around them and streak them on the NA medium, and select dry single colonies with irregular, irregular colony edges, and rough surfaces to continue streak culture. After streak culture for 5 generations That is, pure strains were obtained.
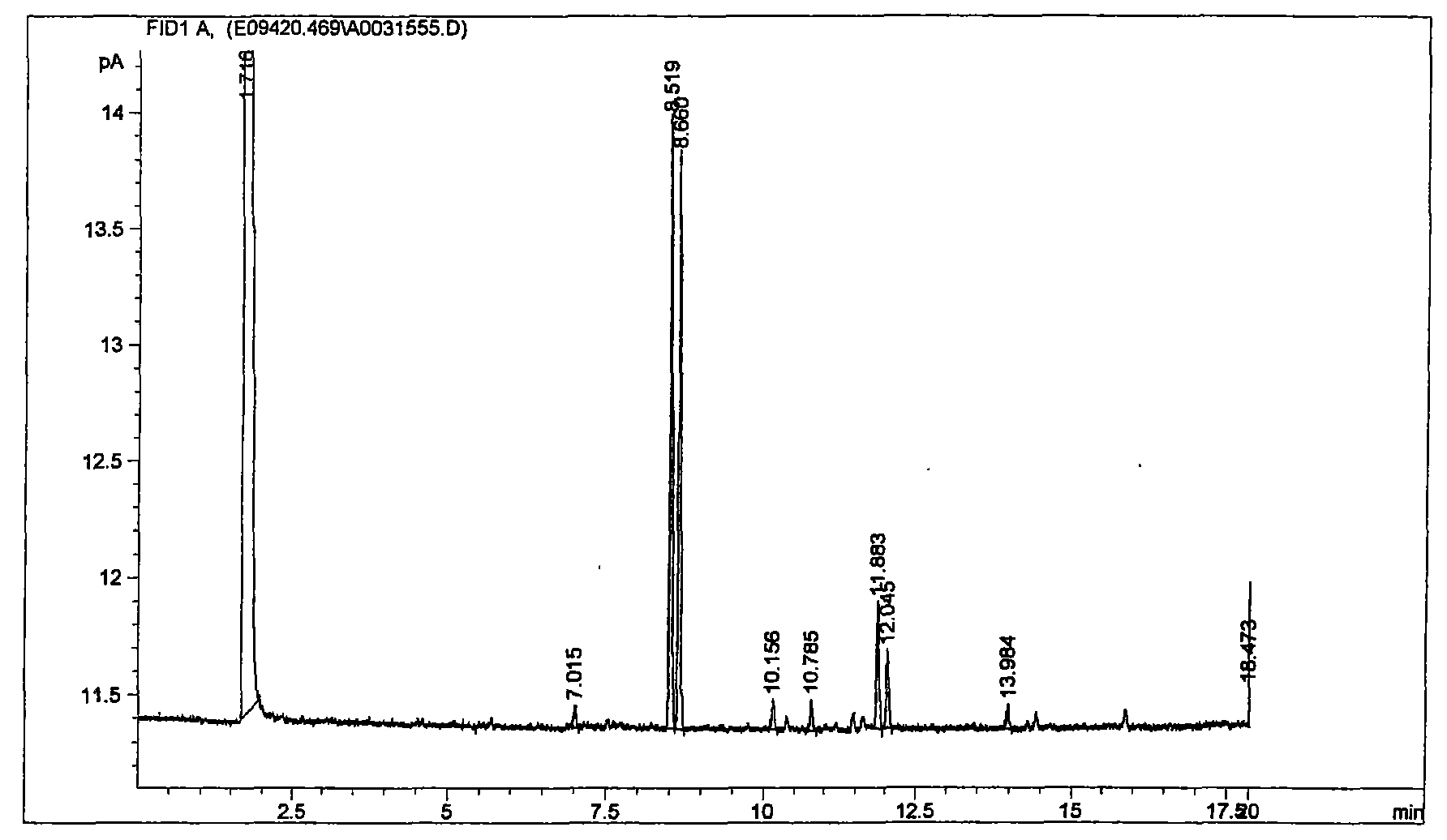
[0023] Screening: Spot the purified strains on the starch medium, measure the colony size (C) and the size of the hydrolysi...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Identification characteristics of strains
[0027] 1. Morphological observation and staining reaction of bacteria
[0028] On the broth medium, the colonies are close to cream color, opaque, wrinkled after 2 days of culture, and the edges are irregular; under the microscope, they are rod-shaped (0.7-0.8μm×2-3μm), Gram staining is positive, and the spores are oval Medial, flagella lateral.
[0029] 2. Physiological and biochemical characteristics of the strain
[0030] The strain was inoculated on a Biolog Microplate GP plate and cultured for 24 hours to detect its carbon source utilization. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0031] Table 1 The utilization of carbon source by bacterial strains
[0032] α-Cyclodextrin
[0033] Inulin
[0034] As can be seen from Table 1, strains can utilize the following types of 95 carbon sources: β-Methyl-D-Glucoside, α-Methyl-D-Glucoside, α-D-Glucose, Tween 80, Tween 40, Turanose, Sucrose , N-Acetyl-D-Glucosami...
Embodiment 3
[0078] The water purification function of embodiment 3 bacterial strains
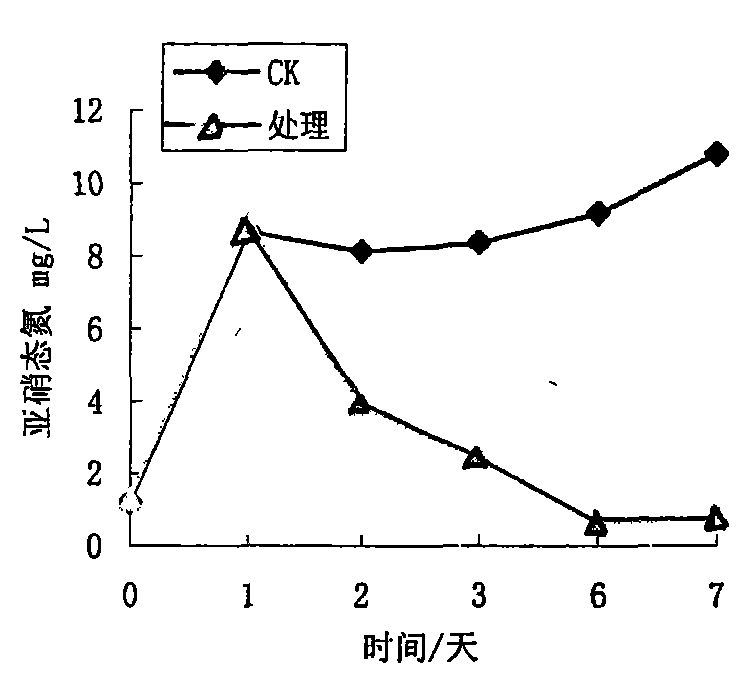
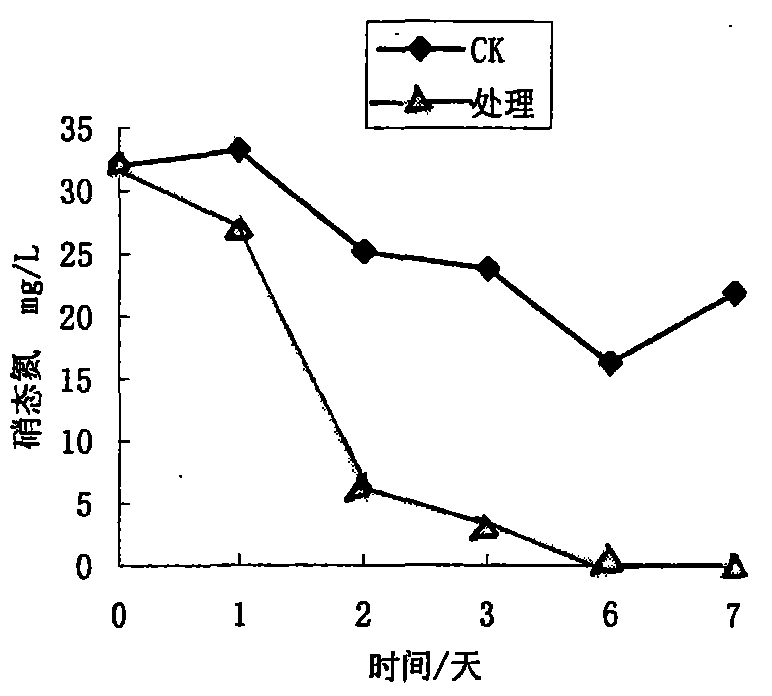
[0079] The simulated aquaculture water is configured indoors, and centrifuged bacterial cells are added to the tank so that the bacteria content in the water is 10 7 CFU·L -1 On the day of adding bacteria and on the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 6th, and 7th days after adding bacteria, take water and immediately take water to measure the content of nitrite and nitrate in the water.
[0080] From figure 2 and image 3 It can be seen that the bacteria can basically completely degrade nitrite nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen in the water on the sixth day of the test.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com