Method for extracting heavy metals from secondary flying ash generated during burning wastes
A secondary fly ash and waste incineration technology, applied in the field of heavy metal extraction, can solve the problem of low leaching efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
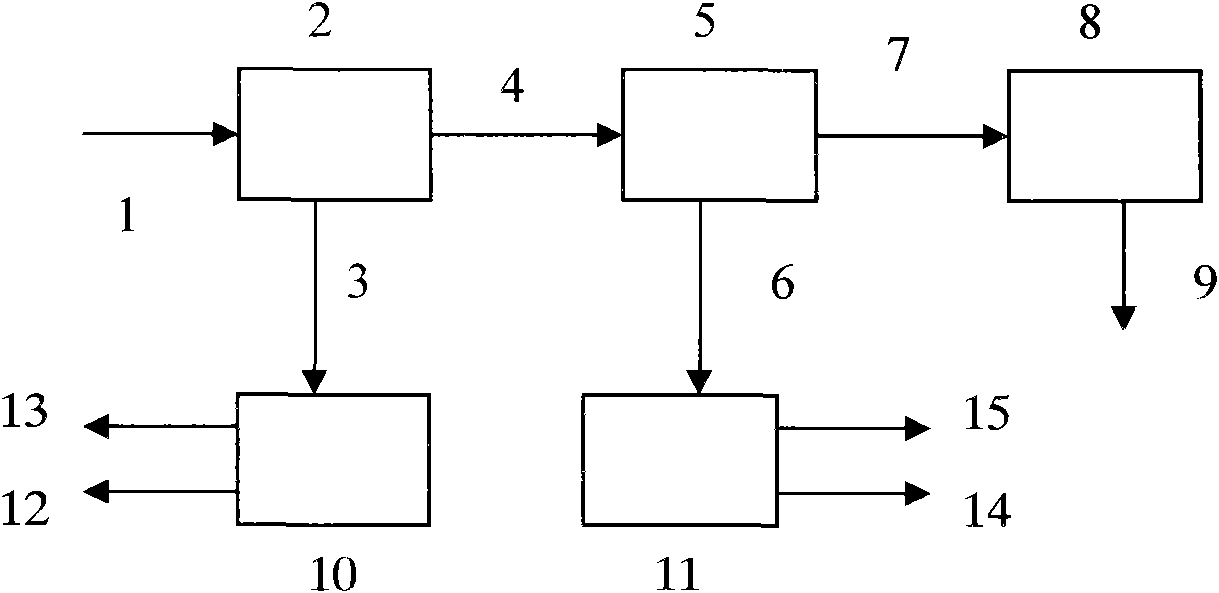
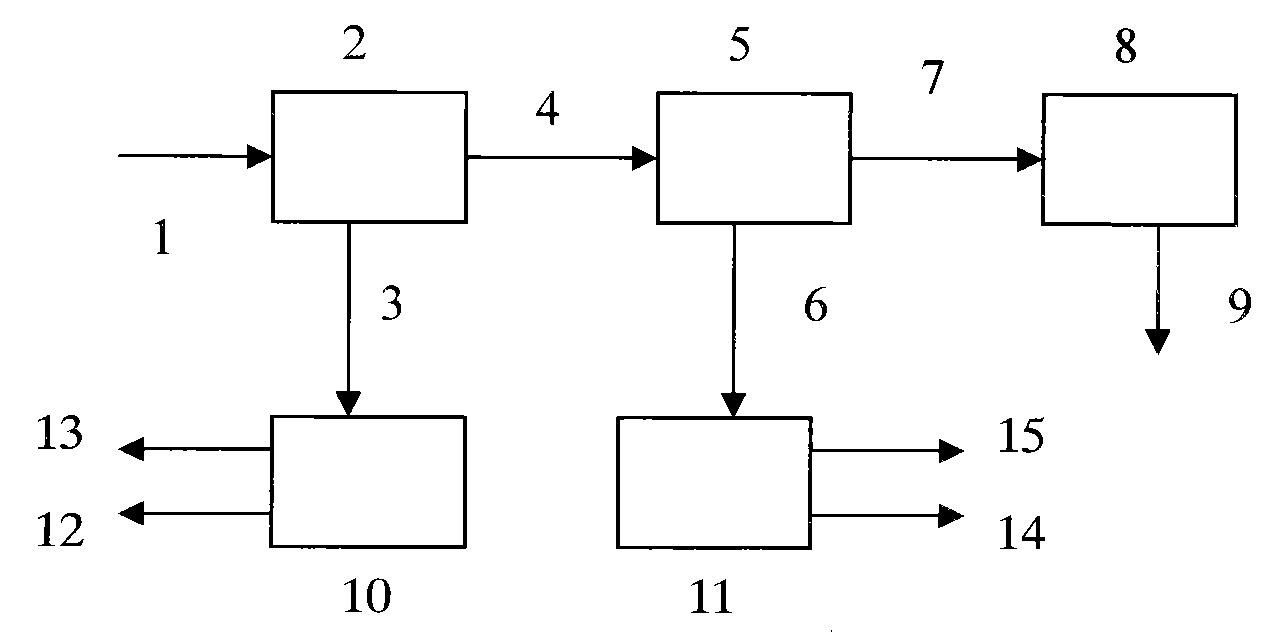
[0017] Such as figure 1 As shown, the secondary fly ash 1 is slowly added into the washing tank 2 through a screw feeder, the mass ratio of gray to water is 1:2, stirred and washed at 80°C for 90 minutes; then naturally settled for 2 hours, and the solid and liquid are separated to obtain Supernatant 3 and washing residue 4. Washing residue and concentrated hydrochloric acid are mixed in equal volumes, heated and extracted in acid extraction reactor 5 for 30 minutes to obtain extract 6 and extraction residue 7, and the extraction residue is mixed with lime with a weight concentration of 10%, and stirred in lime neutralization pool 8 Homogenously, a stabilized solid residue 9 was obtained.
[0018] The supernatant 3 contains high concentrations of copper chloride and zinc chloride, and is evaporated in the evaporator 10 to obtain condensed water 12 and solid powder 13 of copper chloride and zinc chloride. The extract 6 is distilled under reduced pressure in the vacuum still 1...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Such as figure 1 As shown, the secondary fly ash 1 is slowly added into the water washing tank 2 through the screw feeder, the mass ratio of gray to water is 1:3, stirred and washed at 60°C for 30 minutes; then naturally settled for 4 hours, and the solid and liquid are separated to obtain Supernatant 3 and washing residue 4. Washing residue and concentrated hydrochloric acid are mixed in equal volumes, heated and extracted in acid extraction reactor 5 for 1 hour to obtain extract 6 and extraction residue 7, and the extraction residue is mixed with lime with a weight concentration of 10%, and stirred in lime neutralization pool 8 Homogenously, a stabilized solid residue 9 was obtained.
[0021] The supernatant 3 contains high concentrations of copper chloride and zinc chloride, and is evaporated in the evaporator 10 to obtain condensed water 12 and solid powder 13 of copper chloride and zinc chloride. The extract 6 is distilled under reduced pressure in the vacuum sti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com