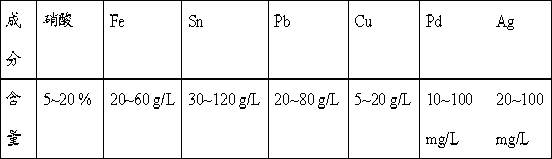Processing method for waste liquid from stripping tin scolding
A treatment method and waste liquid technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as environmental impact, waste, and comprehensive utilization of unfavorable resources, and achieve process The process is reasonable and practical, reducing waste and reducing pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
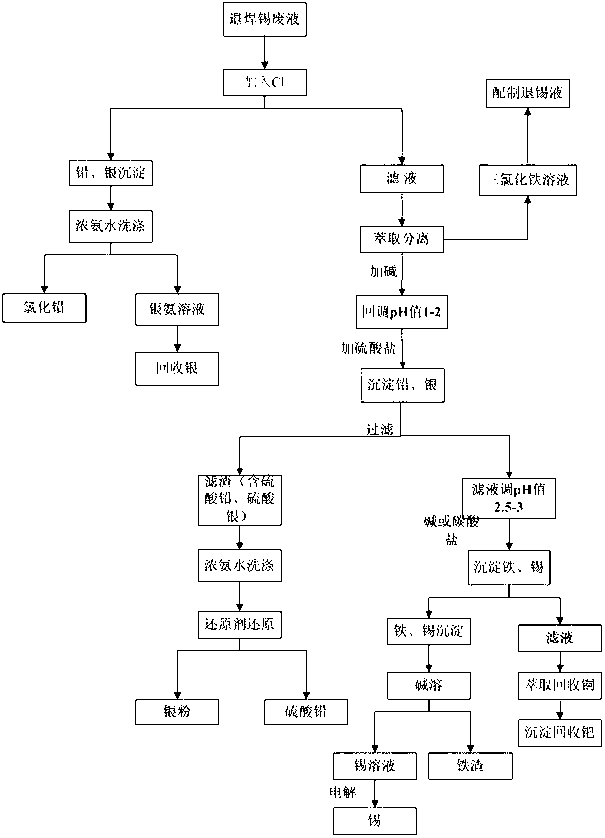
[0026] The processing method of described desoldering waste liquid, comprises the steps:
[0027] 1. Add sodium chloride solution to the waste soldering solution so that the concentration of chloride ions in the solution is 2 mol / L, mix and stir at a temperature of 30 °C, and the reaction time is 1 hour, then filter the solution , the filter residue includes lead chloride precipitation and a small amount of silver chloride, the filter residue uses strong ammonia water, the concentration of commonly used strong ammonia water is 25~28% ammonia water, washing and dissolving silver chloride precipitation, washing liquid reclaims silver, obtains purer chlorine Lead;
[0028] 2. Extract the ferric iron from the filtered filtrate with N235 extractant, back-extract the organic phase loaded with ferric iron with water, and the back-extraction solution is ferric chloride solution, which can be returned to prepare tin stripping solution;
[0029] 3. Adjust the pH of the solution to 1.0~...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The processing method of described desoldering waste liquid, comprises the steps:
[0035] 1. In the waste soldering solution, add calcium chloride to react, so that the concentration of chloride ions in the solution is 4 mol / L, mix and stir at a temperature of 10 ℃, the reaction time is 4 hours, and then filter the solution , filter residue comprises lead chloride precipitation, and a small amount of silver chloride, and filter residue washes and dissolves silver chloride precipitation with 25% strong ammonia water, and washing solution reclaims silver, obtains relatively pure lead chloride;
[0036] 2. Extract the ferric iron from the filtered filtrate with N235 extractant, back-extract the organic phase loaded with ferric iron with water, and the back-extraction solution is ferric chloride solution, which can be returned to prepare tin stripping solution;
[0037] 3. Adjust the pH of the solution to 1.0~2.0 with alkali, then add sulfate, the ratio of the moles of sul...
Embodiment 3
[0042] The processing method of described desoldering waste liquid, comprises the steps:
[0043] 1. In the waste soldering solution, add potassium chloride to react, so that the concentration of chloride ions in the solution is 3 mol / L, mix and stir at a temperature of 20 ℃, and the reaction time is 2 hours, then filter the solution, The filter residue includes lead chloride precipitate and a small amount of silver chloride. The filter residue is washed with concentrated ammonia water to dissolve the silver chloride precipitate, and the silver is recovered from the washing solution to obtain relatively pure lead chloride;
[0044] 2. Extract the ferric iron from the filtered filtrate with N235 extractant, back-extract the organic phase loaded with ferric iron with water, and the back-extraction solution is ferric chloride solution, which can be returned to prepare tin stripping solution;
[0045]3. Adjust the pH of the solution to 1.0~2.0 with alkali, and then add sulfate to ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com