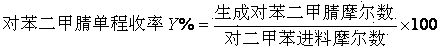Patents
Literature
148 results about "Arsenic oxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Arsenic oxide may refer to any of the following: Arsenic dioxide, As₂O₄, Arsenic trioxide, As₂O₃ Arsenic pentoxide, As₂O₅
Flat float glass
InactiveUS6846760B2High degreeLess sensitiveGlass furnace apparatusGlass rolling apparatusArsenic oxideTransmittance
This invention relates to a flat float glass that can be prestressed or transformed into a glass ceramic with high quartz mixed crystals or keatite mixed crystals. To eliminate undesirable surface defects during floating and to achieve superior characteristics of the glass or of he glass ceramic, in particular with regard to a low coefficient of thermal expansion and high light transmittance, the glass has a concentration of less than 300 ppb Pt, less than 30 ppb Rh, less than 1.5 wt. % ZnO and less than 1 wt. % SnO2, and is refined during melting without the use of the conventional fining agents arsenic oxide and / or antimony oxide.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Flat float glass
InactiveUS20020023463A1High degreeLess sensitiveGlass furnace apparatusGlass rolling apparatusArsenic oxideThermal expansion
This invention relates to a flat float glass that can be prestressed or transformed into a glass ceramic with high quartz mixed crystals or keatite mixed crystals. To eliminate undesirable surface defects during floating and to achieve superior characteristics of the glass or of he glass ceramic, in particular with regard to a low coefficient of thermal expansion and high light transmittance, the glass has a concentration of less than 300 ppb Pt, less than 30 ppb Rh, less than 1.5 wt. % ZnO and less than 1 wt. % SnO2, and is refined during melting without the use of the conventional fining agents arsenic oxide and / or antimony oxide.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Chemically and thermally pre-stressable lithium aluminosilicate float glass of high temperature resistance
ActiveCN1693247AGood quality bubblesImprove heat resistanceBase layers for recording layersGlass tempering apparatusArsenic oxideTemperature resistance
The invention provides a lithium aluminosilicate flat float glass with a high thermal stability which can be chemically and thermally tempered and is suitable for economical and environmentally friendly production. The lithium aluminosilicate flat float glass which can be chemically and thermally tempered, is refined without using a standard refining agent such as arsenic oxide and / or antimony oxide and has excellent thermal stability is constituted so as to contain 2.5-6.0 wt.% Li2O, 0<4 wt.% in total of Na2O+K2O, 0-4 wt.% B2O3, 15-30 wt.% Al2O3, 55-75 wt.% SiO2and <2 wt.% in total of TiO2+ZrO2(the undesirable crystallization of [beta]-quartz and / or keatite solid solution is prevented) as main components per the weight of the total compositions.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Glass composition
ActiveUS20090143214A1Improve glass fining effectSufficient fining effectNon-linear opticsIdentification meansArsenic oxideChemistry
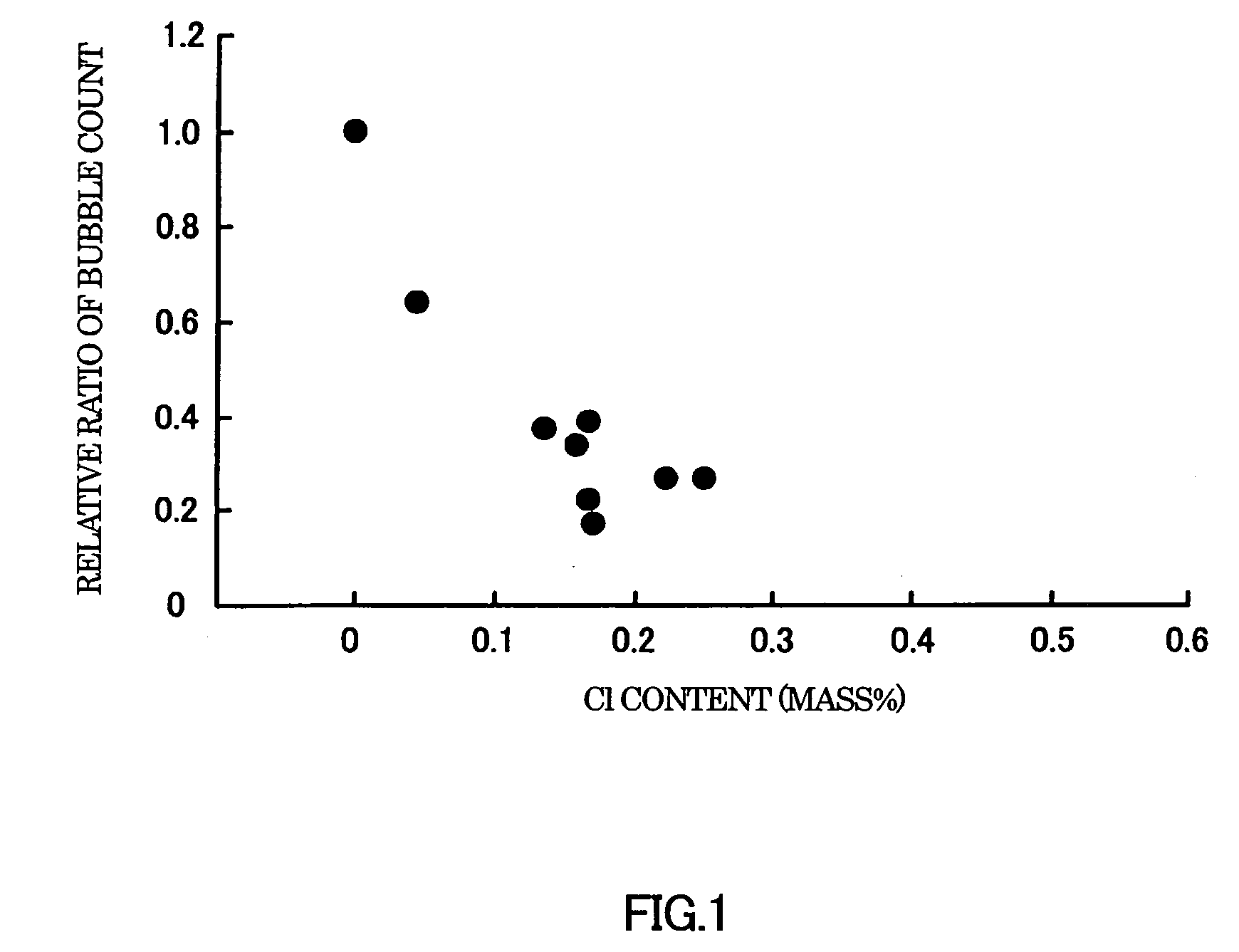
A glass composition which is reduced in the amount of residual bubbles and is produced using smaller amounts of an environmentally unfriendly component such as arsenic oxide and antimony oxide. This glass composition comprises, in terms of mass %: 40-70% SiO2; 5-20% B2O3; 10-25% Al2O3; 0-10% MgO; 0-20% CaO; 0-20% SrO; 0-10% BaO; 0.001-0.5% Li2O; 0.01-0.5% Na2O; 0.002-0.5% K2O; and 0-1.0%, excluding 0%, Cl
Owner:AVANSTRATE INC
Method for preparing high-purity arsenic
The invention relates to a method for preparing a nonmetallic material, in particular to a method for preparing high-purity arsenic, solving the problems of high production cost, low output, impossible realization of industrialization, and the like of the traditional preparation methods. The method comprises the following steps of: loading industrial arsenic into a crucible and carrying out primary sublimation and distillation in a vacuum furnace; then loading the arsenic into an oxidation furnace, and introducing oxygen into the oxidation furnace to generate arsenic oxide; loading the arsenic oxide into a crucible and carrying out secondary sublimation and distillation in the vacuum furnace; loading the arsenic oxide subjected to twice distillation into a tube furnace, introducing high-purity argon and hydrogen into the tube furnace for reducing to obtain crystallized arsenic; loading uncrystallized black arsenic and unreduced arsenic oxide into a quartz tube, putting into the vacuum furnace for separating, and reducing obtained arsenic oxide; and finally, loading separated black arsenic and all reduced crystallized arsenic into the tube furnace together, introducing high-purity argon and hydrogen into the tube furnace for carrying out hydrogen sublimation protection to obtain 6N high-purity arsenic. The method has the advantages of simple impurity removal process, low cost and high output, solves the problem of pollution, eliminates potential safety hazards and achieves the purposes of generating the high-purity arsenic without pollution.
Owner:SHANXI LONGGANG MATERIAL
Method and system for treating oxidized contaminant-containing matrix
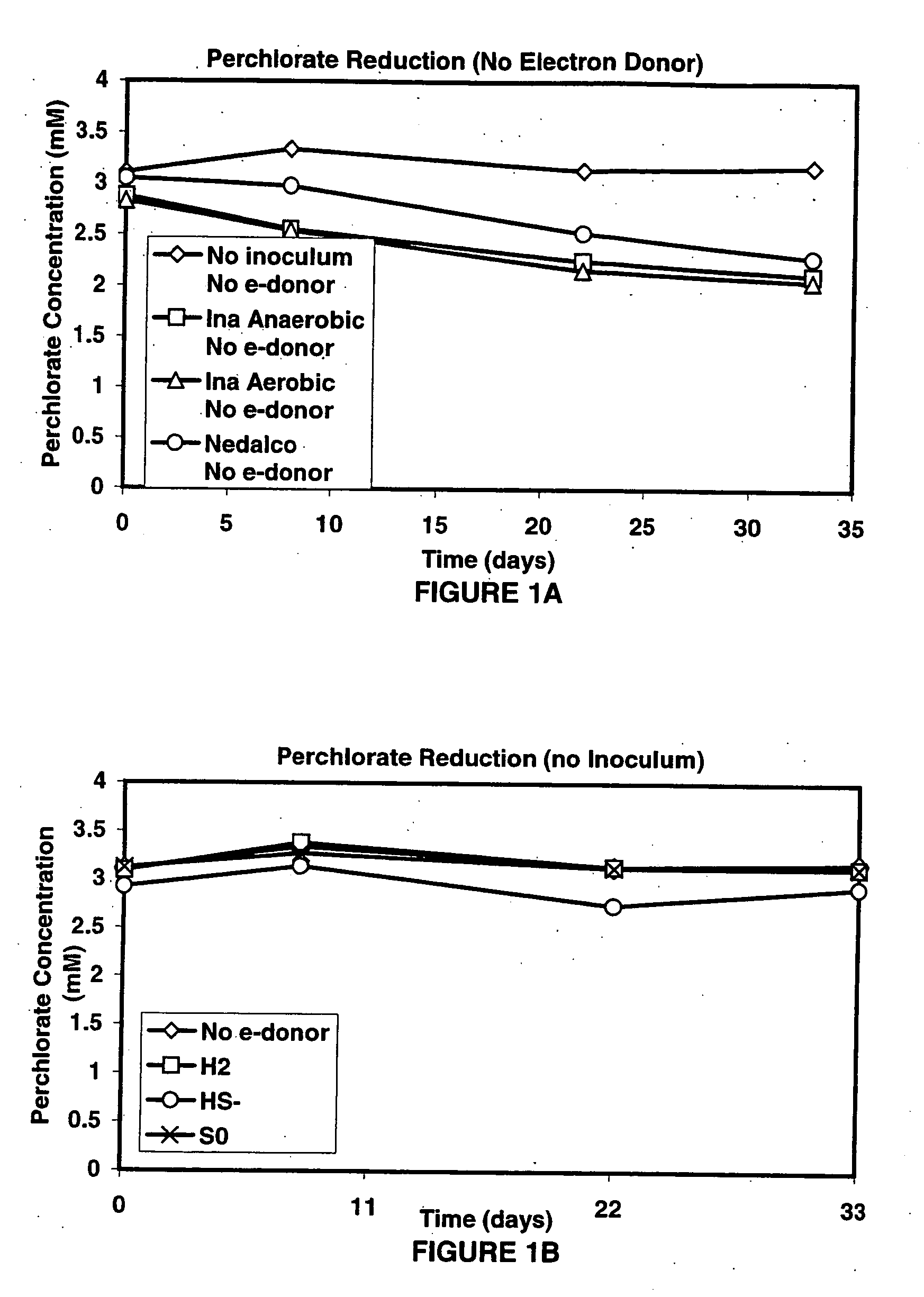
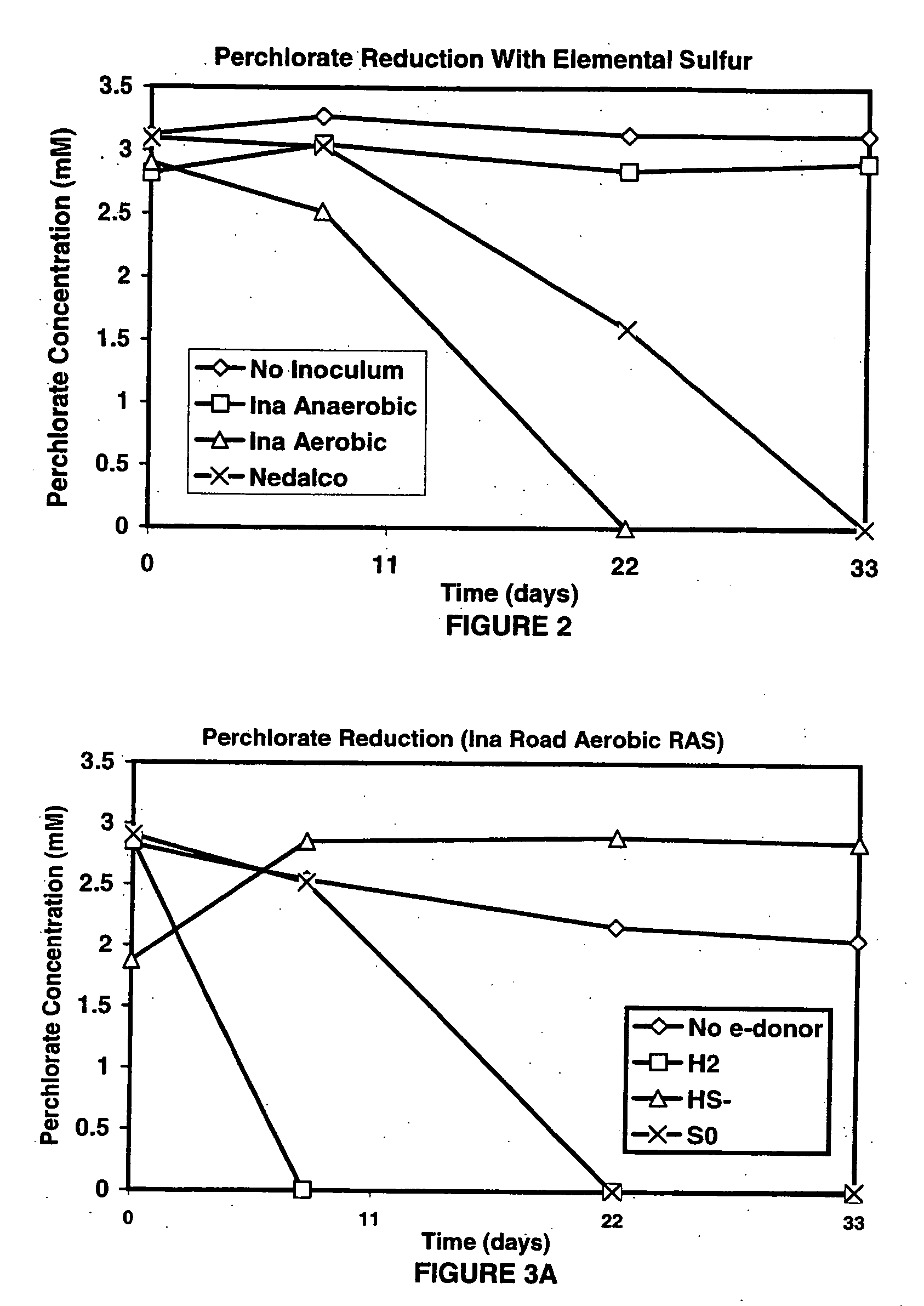
InactiveUS20060292684A1Reduce maintenanceHigh degreeWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsSulfurElectron donor
A new and useful way of treating oxidized-contaminant-containing water, soil, rock, other geological or non-geological matrix formation (such as a landfill) is provided. A bioreactor is provided that includes elemental sulfur and a microbial population capable of oxidizing sulfur and reducing pertechnate (TcO4−), arsenate (H2AsO4−), chromate (CrO42−), bromate (BrO3−), chlorite (ClO2−), chlorate (ClO3−), perchlorate (ClO4−), and uranium(VI) oxide, with biological reduction of these oxidized contaminants in the matrix containing the oxidized contaminant performed by the bioreactor, with the elemental sulfur as the electron donor.
Owner:HYDRO GEO CHEM
Method for environmentally friendly melting and refining a glass melt for an initial glass of a lithium-aluminium silicate (las) glass ceramic
The method of environmentally friendly melting and refining a glass melt of a crystallizable glass, which is used for making a lithium aluminium silicate (LAS) glass ceramic, includes the steps of providing a glass batch with a main batch composition within a lithium aluminium silicate (LAS) glass system, in which tin oxide has been added as main refining agent, but which does not contain arsenic oxide and / or antimony oxide as refining agent, formulating a raw material mixture for the glass batch for restricting the proportion of quartz sand of raw material, which is used for introducing the glass component SiO2, and refining a glass melt formed from the glass batch at temperatures of at least 1600 DEG C.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Glass Composition And Process For Producing The Same
InactiveUS20080090717A1Easy to moveLow migration rateNon-linear opticsIdentification meansArsenic oxidePhotochemistry
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
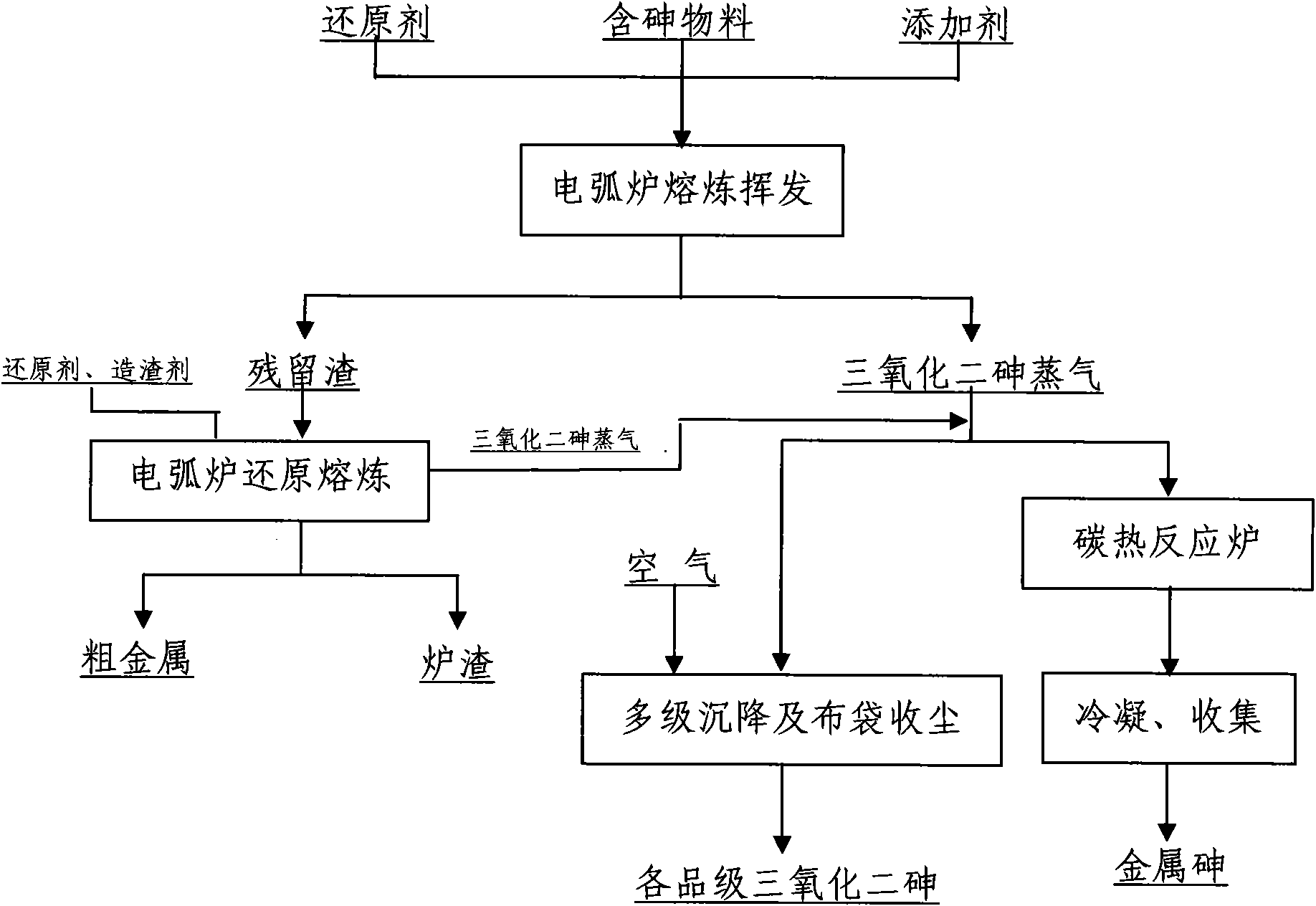
Method for treating arsenic-containing material by using electric arc furnace
InactiveCN101921921AGood environment interfaceIncrease volatilityProcess efficiency improvementSlagArsenic
The invention relates to a method for treating an arsenic-containing material and comprehensively recovering arsenic and other valuable metals by using an electric arc furnace. The method comprises the following steps of: adding a material containing arsenic trioxide into the electric arc furnace; adding a certain proportion of reducing agents and additives according to the components of the arsenic-containing material; keeping a certain pressure and temperature in the furnace to ensure that the arsenic trioxide in the material is fully volatilized; allowing the volatilized arsenic trioxide steam to pass through two paths so as to obtain high-quality arsenic trioxide and metallic arsenic respectively; and adding slag forming constituents and the reducing agents into volatilized residues for smelting to further recover the valuable metals in the residues. The method of the invention can realize the volatilization of the arsenic trioxide and the recovery and smelting of other valuable metals only by the electric arc furnace and has the advantages of strong adaptability of equipment, short flow, simple operation, good comprehensive recovery and good working environment.
Owner:YUNNAN TIN GROUP HLDG
Method for cutting LED chip
InactiveCN102097546AIncrease production capacityThere will be no edge collapseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFine working devicesEvaporationArsenic oxide
The invention provides a method for cutting an LED (Light Emitting Diode) chip, which comprises the steps of: on the back face of the chip, sawing along the middle position of two electrodes on the front face, wherein the sawing depth is 1 / 6 to 2 / 3 of the thickness of the chip, and then splitting the chip on the front face of the chip along the sawing mark by using a splitter. The method is simple in process and free from the manufacturing of a scribing slot and adopts the manner of sawing on the back face and splitting on the front face so that each side on the front face of the chip only loses the area as large as 1 micron to 5 microns of splitting width, more tube cores can be formed on each chip by splitting so as to increase the chip productivity remarkably, the chip is free from edge breaking, corner breaking, burr, cracking and other problems owing to the manner of sawing on the back face and splitting on the front face as well as incomplete sawing on the back face, and simultaneously, the method is free from the problems of pollution, arsenic evaporation and arsenic oxides and the like.
Owner:Shandong Huaguang Optoelectronics Co. Ltd.
Preparation method of terephthalonitrile through ammonium oxidation
ActiveCN103896807AHigh catalytic efficiencyEasy loadingPreparation by hydrocarbon ammoxidationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAlkali metal oxideFluidized bed
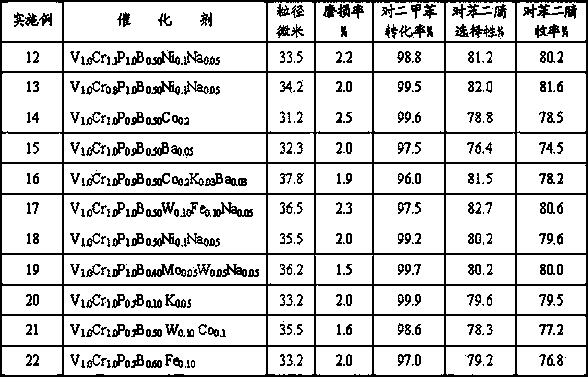
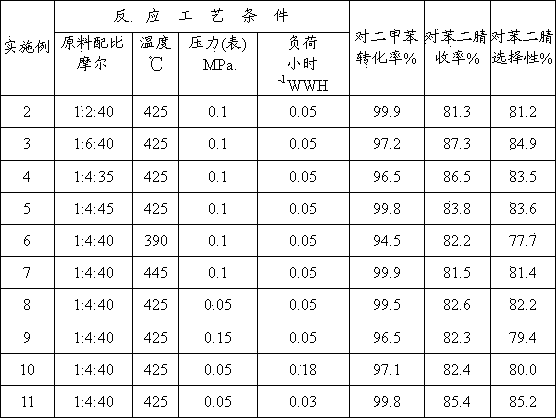
The invention relates a preparation method of terephthalonitrile through ammonium oxidation, and aims to solve the problems of low yield of terephthalonitrile, small reaction load, or difficult reaction heat dissipation in the presence of a conventional catalyst in the prior art. A fluidized bed catalyst is used to solve the problems mentioned above, wherein the fluidized bed catalyst comprises 30 to 80% of silica carrier and 20 to 70% of active component, and the active component is represented by a formula V<1.0>CrPX<c>Y<d>Z<e>O<m>; wherein the X is selected from at least one component of boron oxides and arsenic oxides, Y is selected from at least one component of alkali metal oxides and alkali earth metal oxides, Z is selected from at least one component of oxides of Ni, Co, Pb, Fe, Mo, and W. The fluidized bed catalyst well solves the problems mentioned above and is capable of being applied to the industrial terephthalonitrile production.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for smelting arsenic-containing gold concentrate
InactiveCN101078057AGood processing effectHigh recovery rateSulfur compoundsProcess efficiency improvementCooling towerArsenic oxide
A kind of smelting method of aurin mine containing arsenic, it contains the following technology steps: primary burning, second-class burning, The burning residue after burning will be added into the pickling ark with the soot separated to be pickled. The filtrate will be used to extract copper, the filter cake will be separated and cyanide residue and golden mud can be gained, and the golden mud will be smelted to extract gold bullion. The character of it is that the smoke gas, which has been catch dust by primary burning and second-class burning, will be drew arsenic in according to hop-pocket drying method. The process is as following, the smoke gas containing arsenic will enter the spray cooling tower and be quench by spraying water, the arsenic oxide will become solid and be separated out from gaseous crystal, the smoke gas will take arsenic oxide solid into bag arsenic catcher, and the arsenic oxide solid will be collected into ash bucket after being filtrated by hop-pocket, and then will be packed and finished product can be gained. The smoke gas after arsenic catching will enter the acid making system, and produce vitriol by cleanse workshop section, translation workshop section and dried absorbing workshop section, the finished vitriol product will be gained, and the off-gas will be exhaled into air. The technology of it is simple and feasible, and it is easy to operate, the coefficient of recovery and arsenic catching rate are both high, the investment of it is low, and the running cost of it is low.
Owner:SHANDONG HUMON SMELTING
Glass for sealing with metal or alloy
The invention relates to a glass for sealing with metal or alloy, wherein the mol ratio of its constituents being, 70.0% to 80.0% of silicon oxide, 0.0% to 4.0% of aluminium oxide, 12.0% to 19.0% of boron oxide, 0.0% to 4.0% of lithium oxide, 0.0% to 6.0% of sodium oxide, 0.0% to 8.0% of potassium oxide, 0.0% to 6.0% of magnesium oxide, 0.0% to 6.0% of calcium oxide, 0.0% to 6.0% of strontium oxide, 0.0% to 6.0% of barium oxide, 0.0% to 6.0% of zinc oxide, 0.0% to 6.0% of arsenic trioxide, 0.0% to 1.0% of cerium oxide. The glass has similar expansion coefficient, low air bubble generating number and low glass liquid phase temperature with the sealing metal.
Owner:铂京光电股份有限公司
Glass composition and process for producing glass composition
ActiveUS20090131238A1Sufficient fining effectLow costGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusArsenic oxideChloride
A glass composition which is reduced in the amount of residual bubbles and is produced using smaller amounts of an environmentally unfriendly component such as arsenic oxide and antimony oxide. This glass composition contains, in terms of mass %: 40-70% SiO2; 5-20% B2O3; 10-25% Al2O3; 0-10% MgO; 0-20% CaO; 0-20% SrO; 0-10% BaO; 0-0.5% Li2O; 0-1.0% Na2O; 0-1.5% K2O; and 0-1.5%, excluding 0%, Cl, Li2O+Na2O+K2O exceeding 0.06%. The glass composition can be produced suitably using, for example, a chloride as part of the raw glass materials.
Owner:AVANSTRATE INC
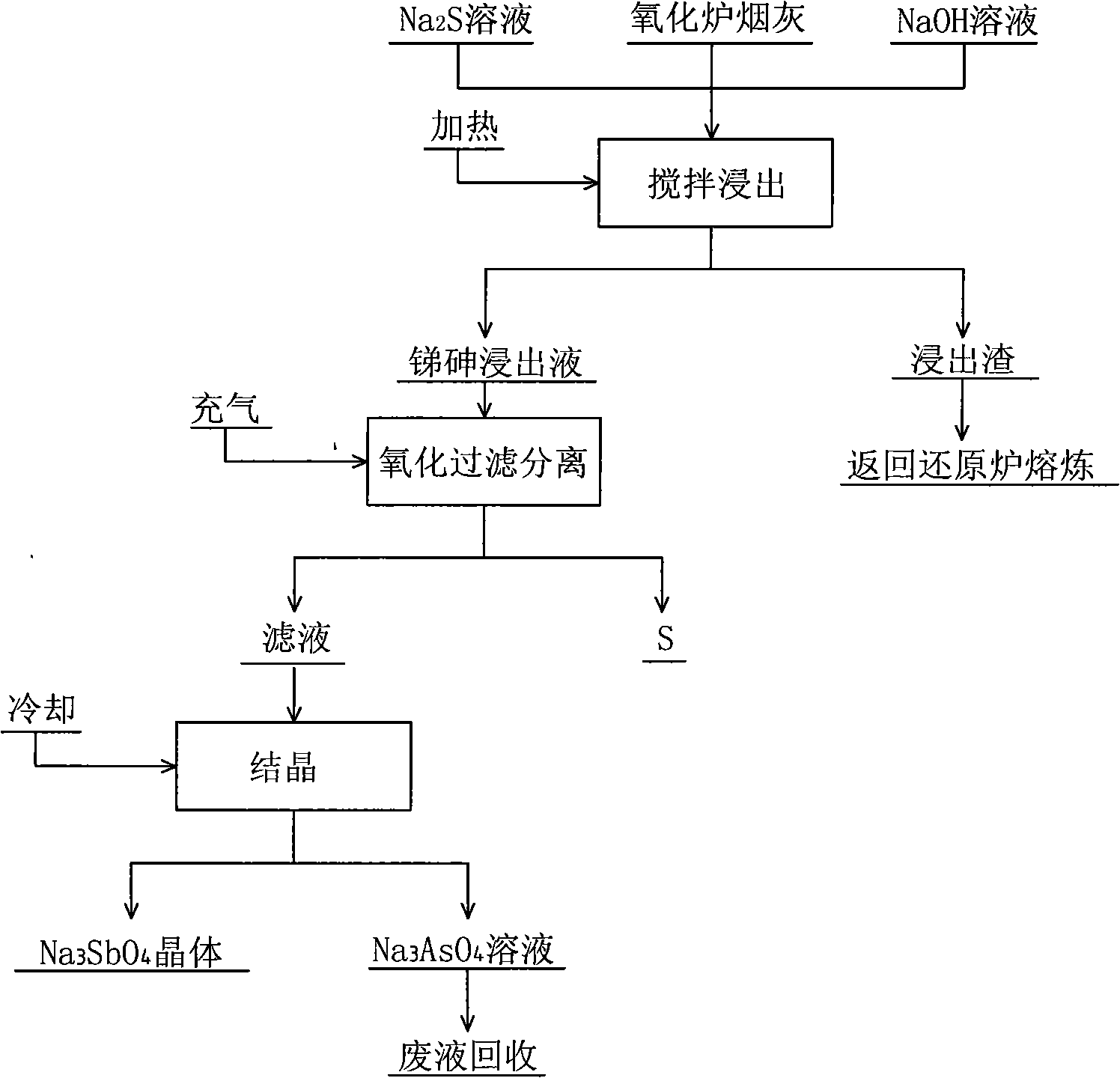
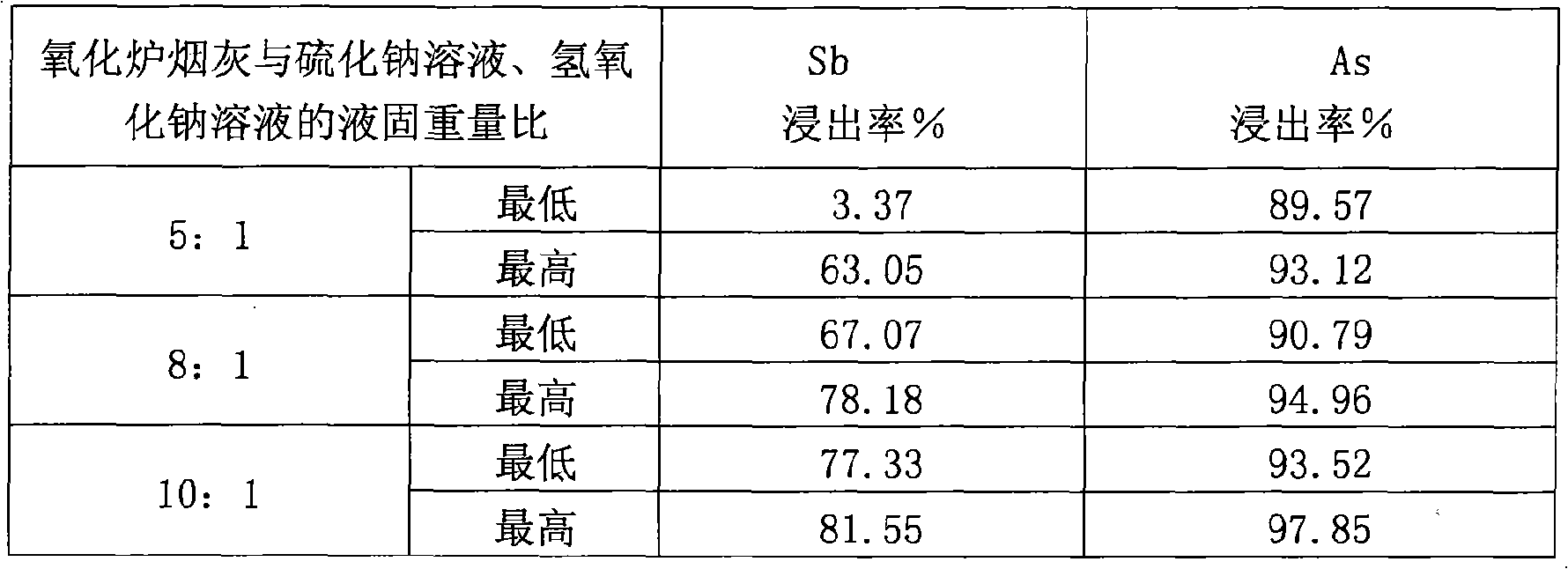
Oxidation oven ash hydrometallurgical leaching process
InactiveCN101328539AEasy to removeEfficient separationProcess efficiency improvementArsenic oxideSoot
The invention provides a leaching process of the oxidation oven soot wet method, belonging to the treatment on side products of soot generated in the smelting process technical field. In the process, antimony oxide and arsenic oxide in the oxidation oven soot are simultaneously leached out by the reducing capacity of sodium sulphide first, and generated sodium thioadtimonate and sodium sulfarsenate enter leaching liquid; filter residues are returned for silver smelting reduction smelting; the leaching liquid is passed through air, the sodium thioadtimonate is oxidized into sodium antimonate, free sulfurs in the sodium antimonate are separated by filtering; the mixed filtrate of the sodium antimonate and the sodium sulfarsenate has coarse sodium antimonate crystals extracted by condensed crystallization; and the remained sodium sulfarsenate liquid is taken as waste liquid for reclaiming treatment, so that the effective separation of Pb and Ag and Sb and As is realized. The process of the invention can effectively reduce the quantity of soot returned to the oven for smelting, improving the capability of a reducing furnace for treating anode mud and achieving the double-win aims of improving the efficiency of the reducing furnace and reducing environmental pollution.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
Transparent, dyed cooktop
ActiveUS9156727B2Easy to operateOperational securityStoves/ranges topsHot plates heating arrangementsInfraredDisplay device
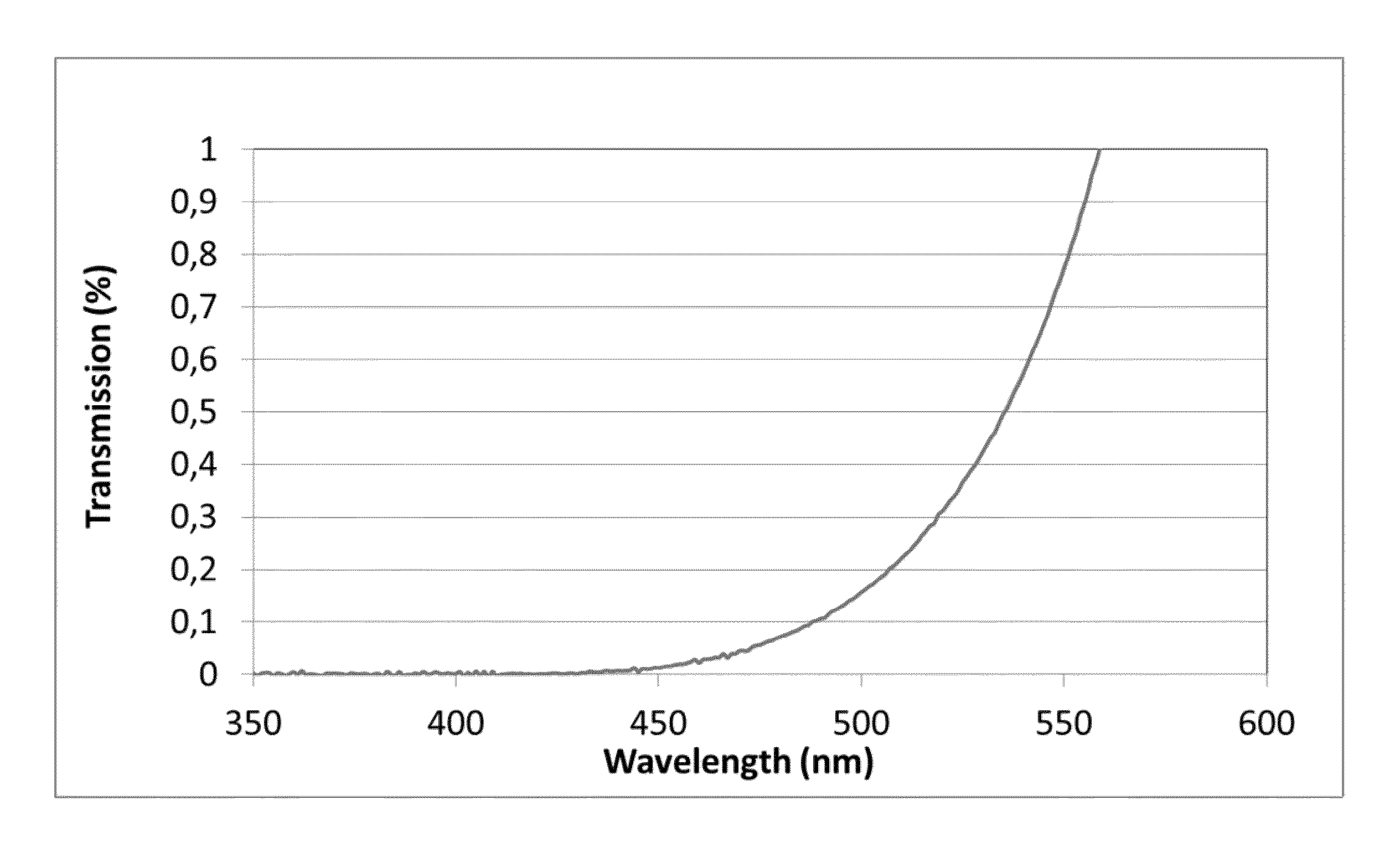
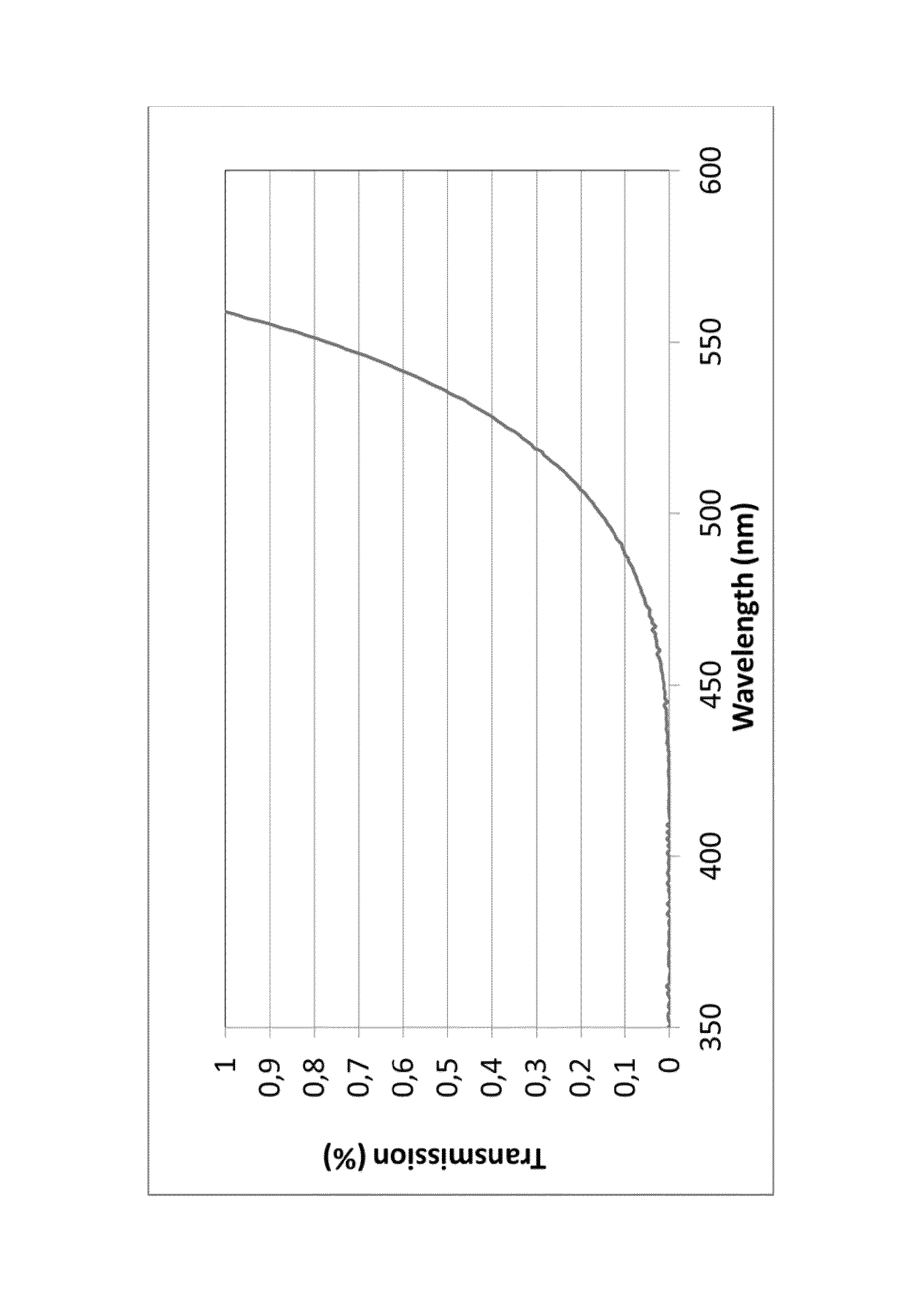
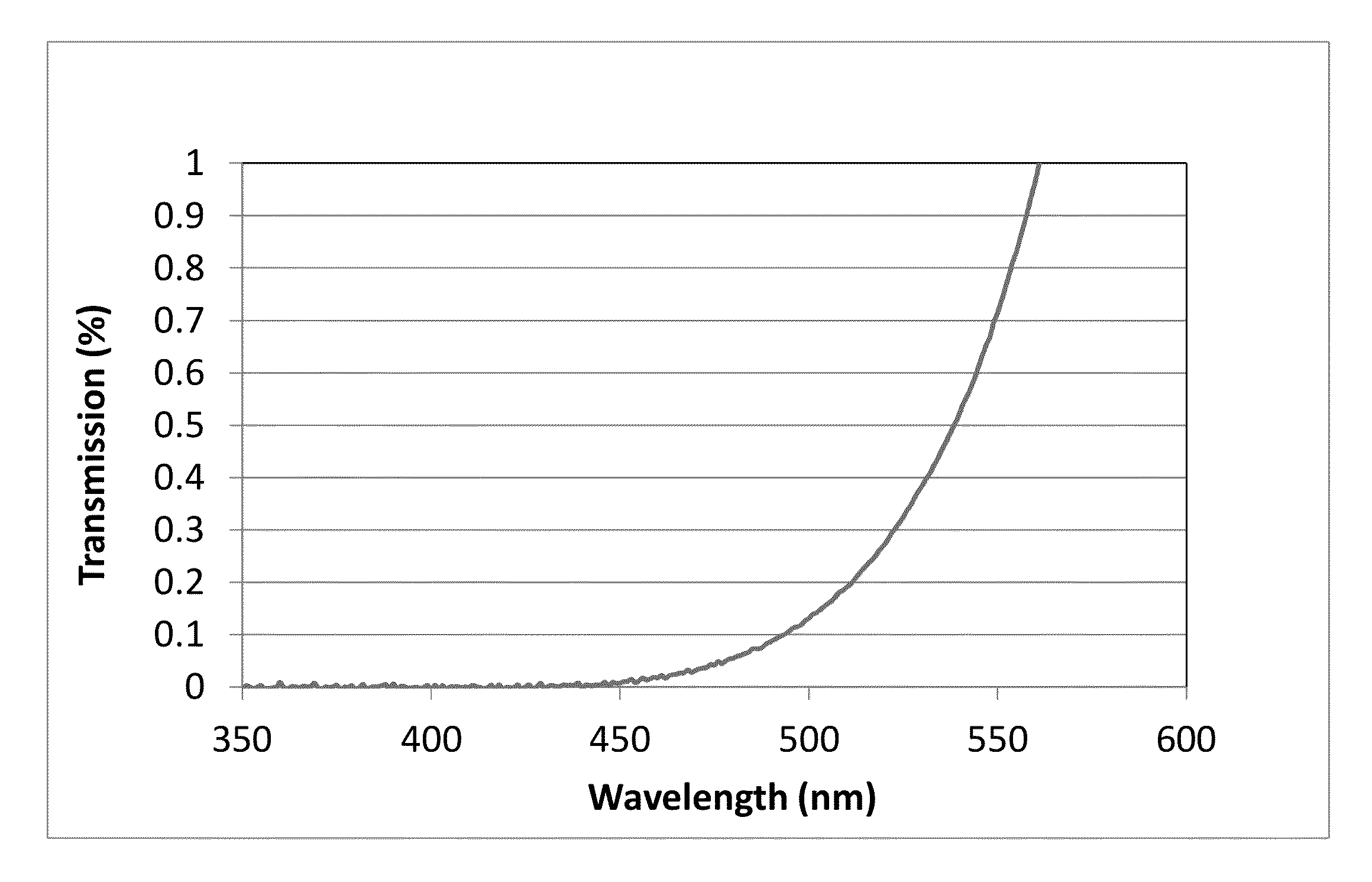
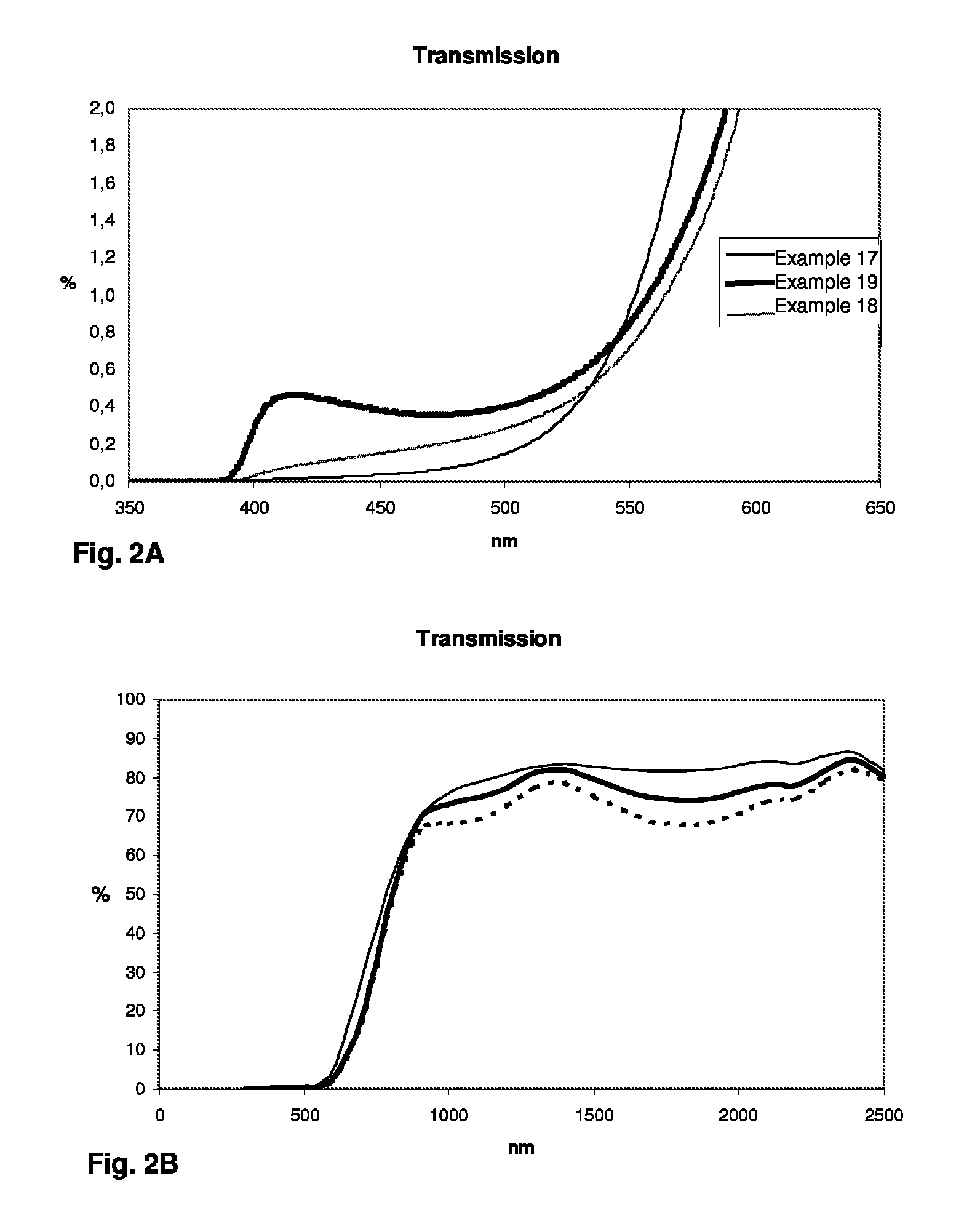
A transparent, dyed cooktop is provided that has improved color display capability. The cooktop is made of a glass ceramic having high quartz mixed crystals as the predominant crystal phase, wherein the glass ceramic comprises none of the chemical refining agents arsenic oxide and / or antimony oxide, except for inevitable trace amounts. The glass ceramic has transmission values of greater than 0.1% in the range of visible light over the entire wavelength range greater than 450 nm, light transmission in the visible range of 0.8 to 5%, and transmission in the infrared at 1600 nm of 45-85%. The glass ceramic also includes a display apparatus that has a display device which is designed to display different operating conditions with different colors and / or symbols.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Method and composition for sequestration of arsenic
A method for sequestrating arsenic oxides, comprising forming an insoluble and stable glass incorporating a fully oxidized form of arsenic generated by oxidation of an initial lower oxide of arsenic and stabilization by calcium salt formation. The glass composition for sequestration of arsenic comprises from 50 to 75% silica; from 0.5 to 3% Al2O3; from 1 to 15% MnO; from 5 to 15% CaO; from 1 to 20% As2O5 and from 8 to 14% Na2O, less than four percent of iron oxides, magnesium oxide and other oxides.
Owner:DUNDEE SUSTAINABLE TECH
High-strength alkali-aluminosilicate glass
InactiveCN103443041AThin material handlingInput/output processes for data processingAlkali ionsArsenic oxide
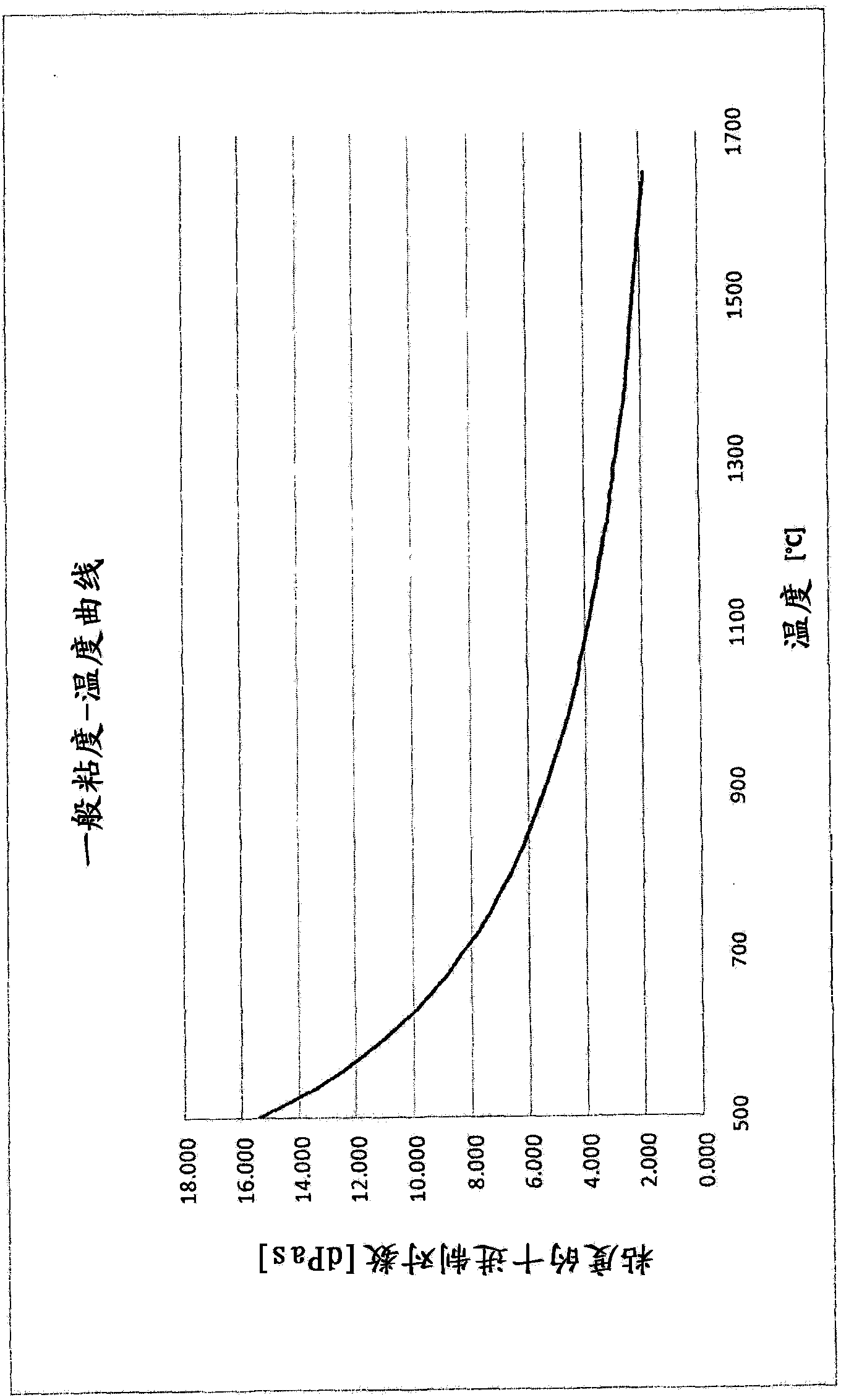
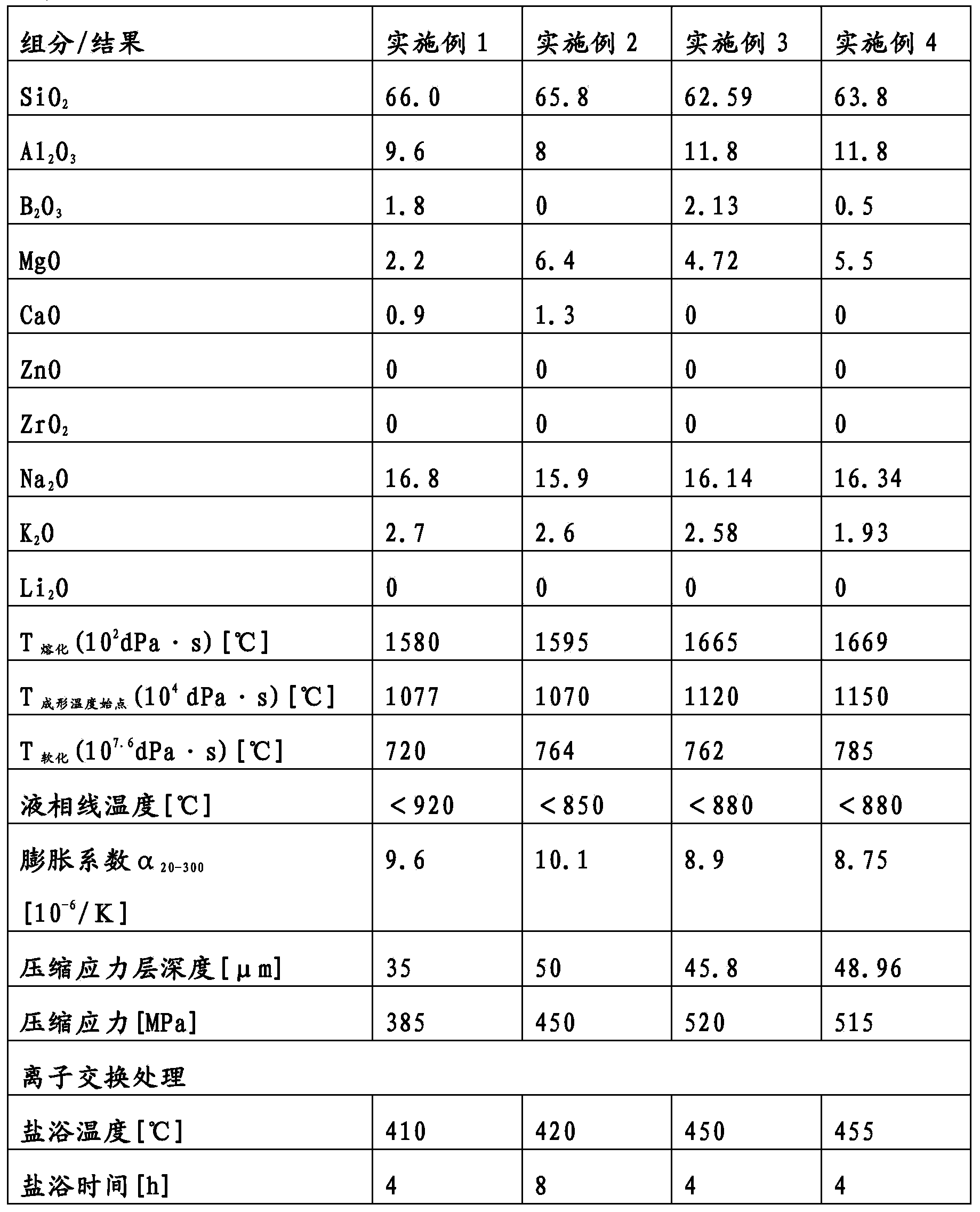
The invention provides high-strength alkali-aluminosilicate glass. The alkali-aluminosilicate glass is characterized by excellent meltability, fineability and processibility. The alkali-aluminosilicate glass is showed in the following formula: 60.5 to 69.0 weight percent of SiO2; 7.0 to 11.8 weight percent of Al2O3; 0 to 4.0 weight percent of B2O3; 2.0 to 8.5 weight percent of MgO; 0 to 4.0 weight percent of CaO; 0 to 5.0 weight percent of ZnO; 0 to 3.0 weight percent of ZrO2; 15.0 to 17.5 weight percent of Na2O; 0 to 2.7 weight percent of K2O; 0 to 2.0 weight percent of Li2O; and 0 to 1.5 weight percent of a fining agent such as As2O3, Sb2O3 CeO2, SnO2, Cl-, F-, (SO4) 2- and combinations thereof. The glass allows for adequate conditions for an alkali ion exchange treatment in a short time period (4 to 8 hours) and can also be produced according to the established, continuous, vertically downward directed drawing process such as the overflow down-draw method or the fusion method, the die slot or the slot down-draw method, or combinations thereof. The viscosity-temperature profile of the glass allows the use of the conventional fining agents in combination at the lowest amounts possible and additionally allows the production of the glass that are free of or contain only small amounts of either or both of antimony oxide and arsenic oxide.
Owner:KORNERSTONE MATERIALS TECH +1
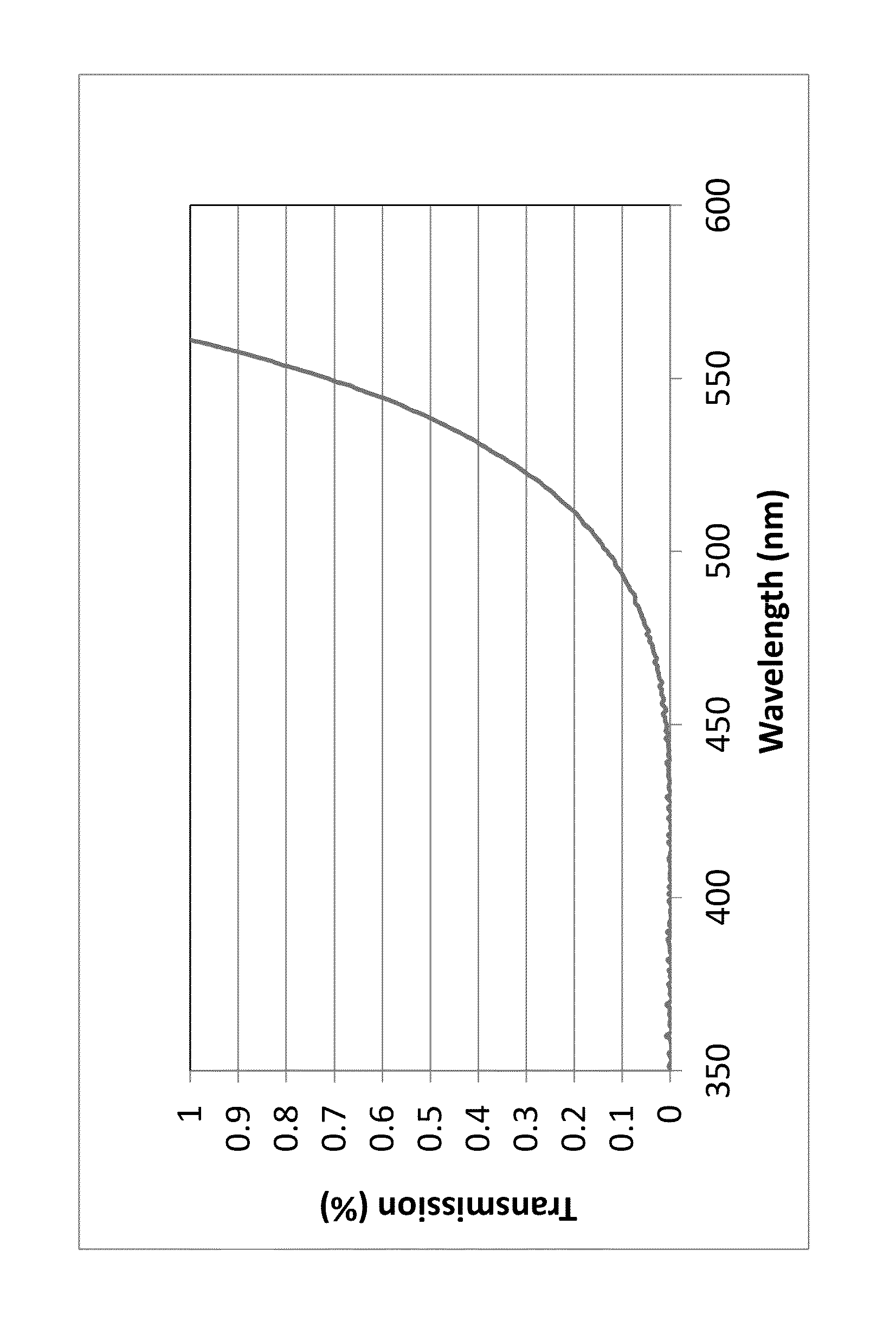
Β-quartz glass-ceramics with a controlled transmission curve and a high iron oxide content; articles comprising said glass-ceramics, and precursor glasses
β-quartz lithium aluminosilicate (LAS) glass-ceramics contain neither arsenic oxide nor antimony oxide, are fined with tin oxide and include vanadium oxide, chromium oxide and a high iron oxide content (>950 ppm), and have a controlled transmission curve. Articles such as cook-tops can be made from such glass-ceramics.
Owner:EUROKERA SOC & NOM COLLECTIF
Β-quartz glass-ceramics with a controlled transmission curve and a high content of iron oxide and of tin oxide; articles in said glass-ceramics, precursor glasses
β-quartz lithium aluminosilicate (LAS) glass-ceramics contain neither arsenic oxide nor antimony oxide, are fined with tin oxide and include vanadium oxide, chromium oxide and a high iron oxide content (>1500 ppm), and have a controlled transmission curve. Articles such as cook-tops can be made from such glass-ceramics.
Owner:EUROKERA SOC & NOM COLLECTIF
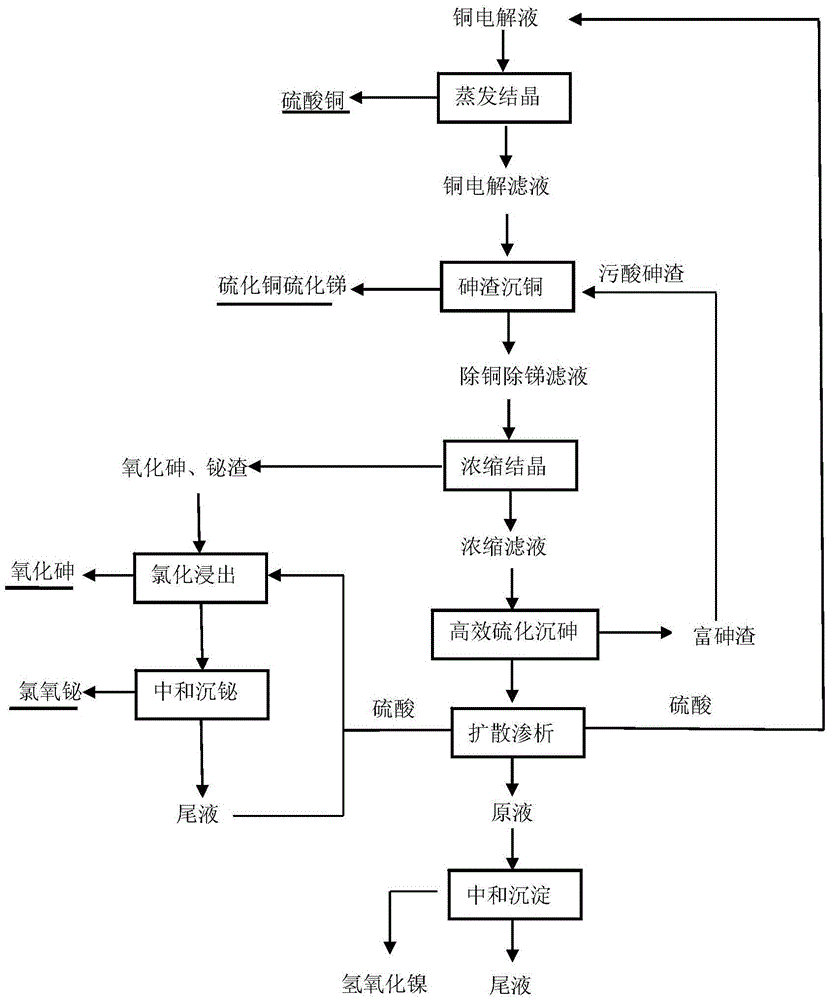
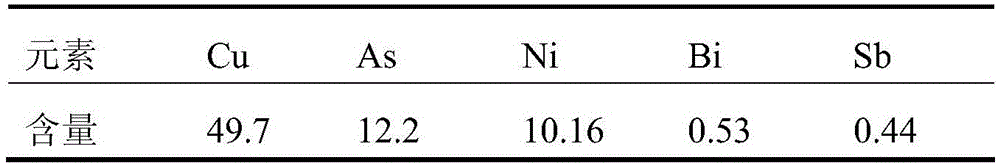
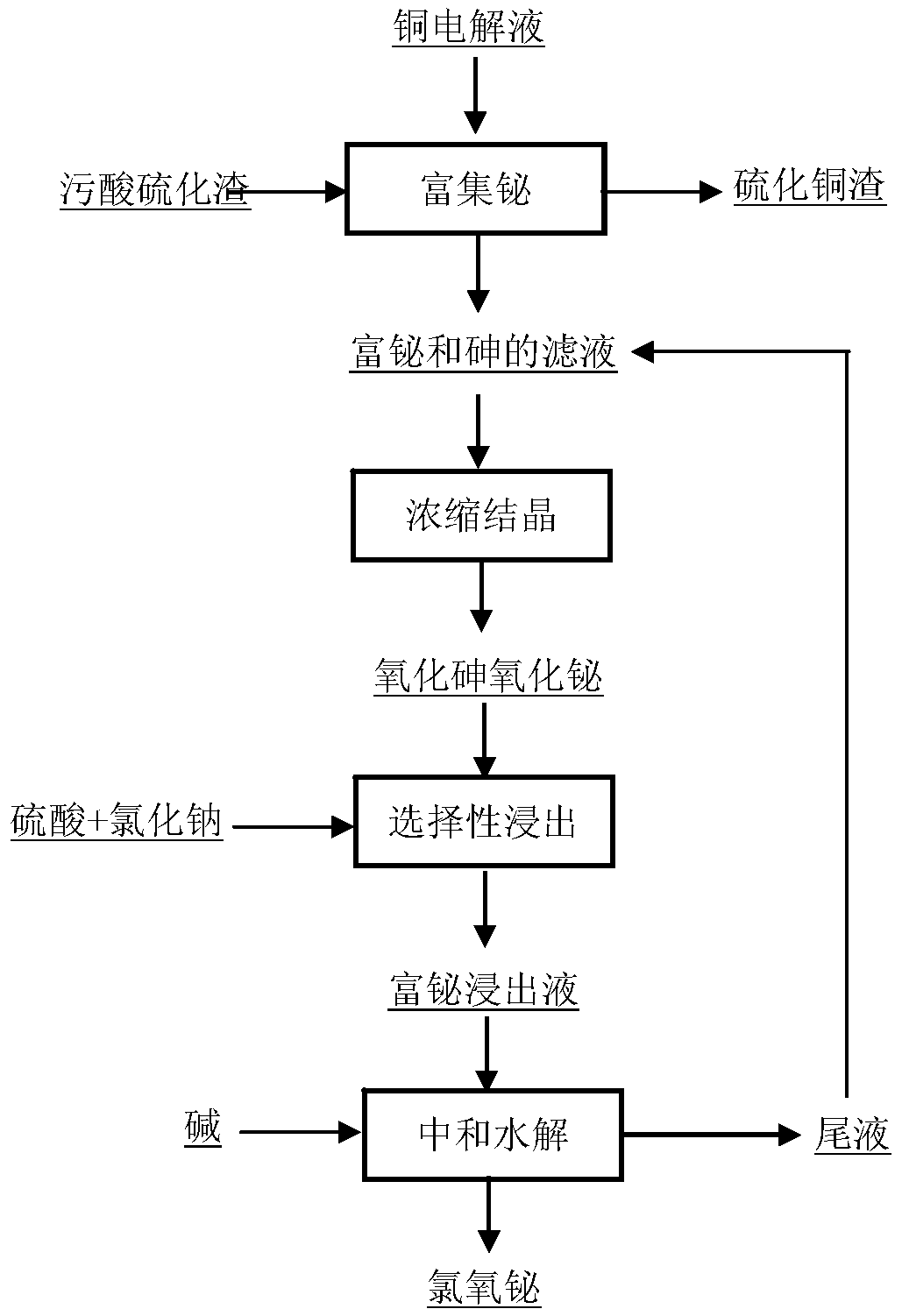
Method for purifying and recovering valuable metal by copper electrolyte
ActiveCN105603190AReduce manufacturing costSimple processProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisSlag
The invention discloses a method for purifying and recovering valuable metal by copper electrolyte. The method comprises the following steps: (1) evaporating, crystallizing and filtering the copper electrolyte to recover copper sulfate; (2) adding arsenic sulfide slag into copper electrolysis filtrate, and filtering to recover copper sulfide and antimony sulfide after a reaction is finished; (3) evaporating, crystallizing and filtering the copper electrolysis filtrate to separate arsenic oxide and bismuth oxide; (4) selectively leaching and recovering bismuth in the step (3); (5) efficiently vulcanizing the copper electrolysis filtrate for deep arsenic removal; (6) performing diffusion dialysis on the copper electrolysis filtrate to separate and recover sulfuric acid; (7) recovering nickle in a diffusion dialysis stock solution by adopting a neutralization precipitation method. The method adopts a wet method in the whole process, is efficient, environment-friendly and energy-saving, and has better application value.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
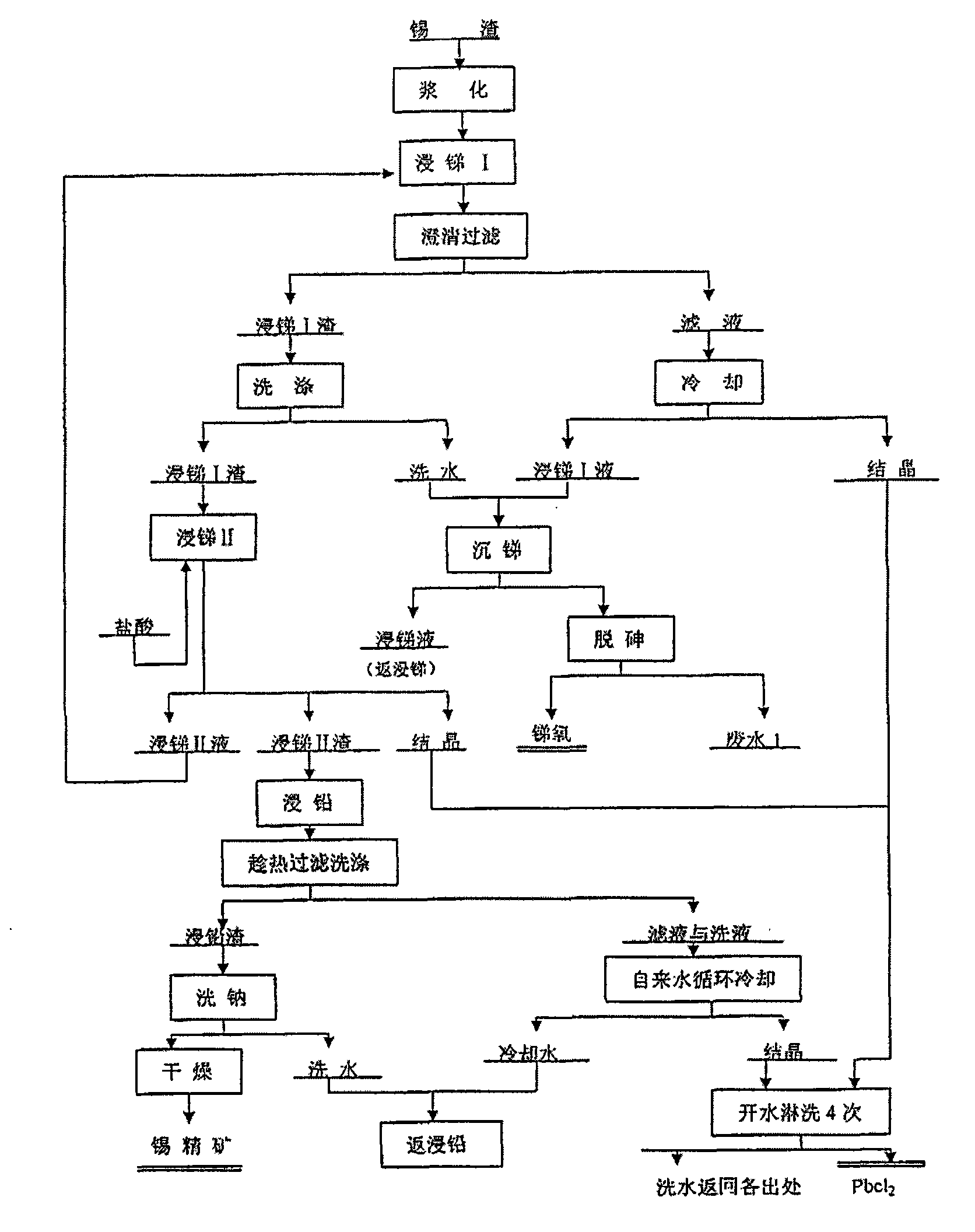
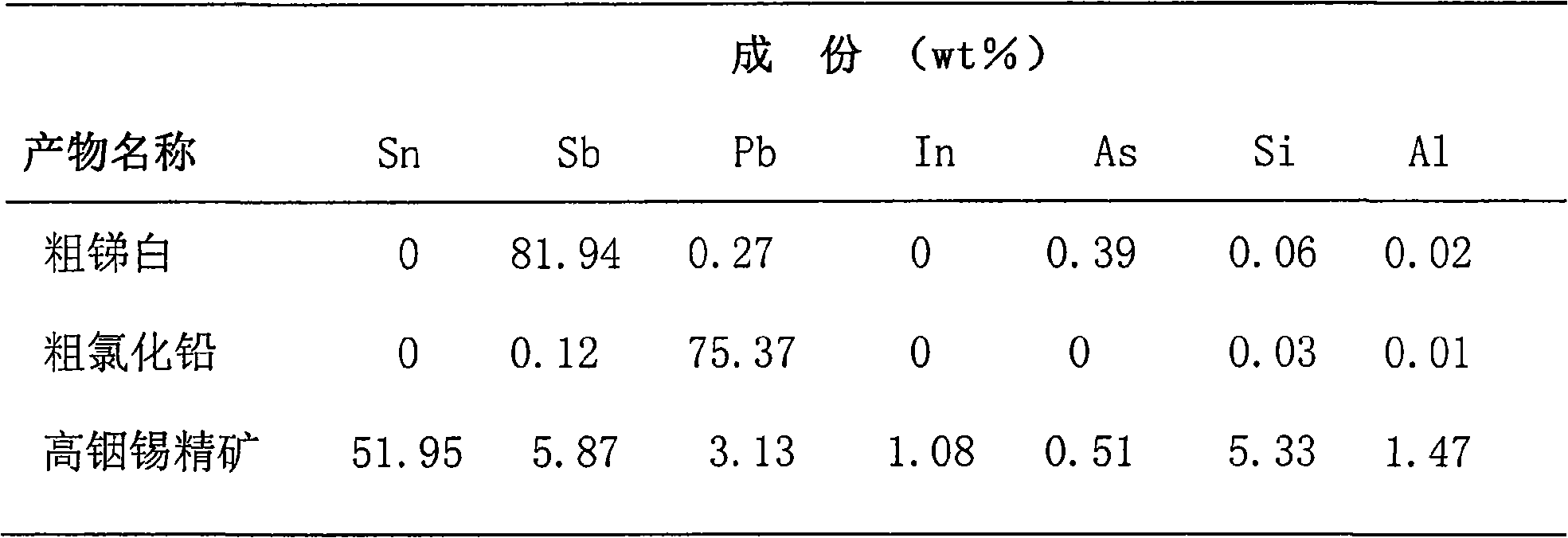
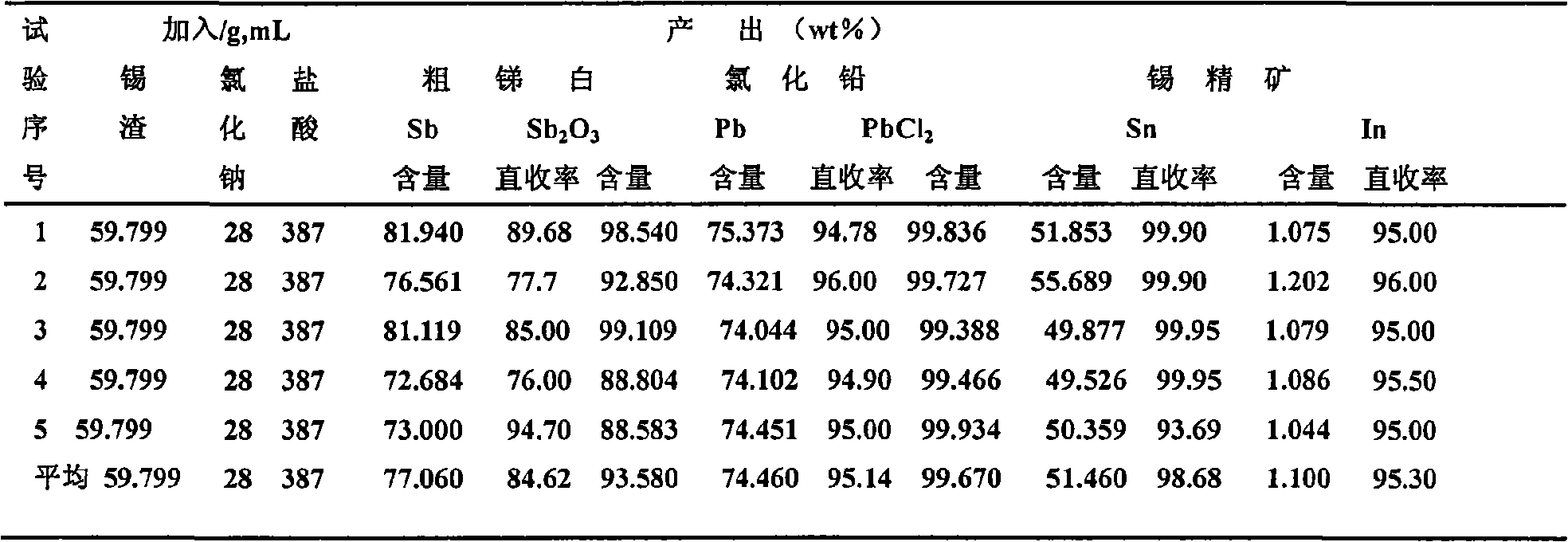
Method for recovering tin, antimony and lead and enriching indium from tin residue
InactiveCN101660053ASolve the problem of comprehensive collection and recyclingAvoid circulation lossProcess efficiency improvementIndiumArsenic oxide
The invention relates to a method for recovering tin, antimony and lead and enriching indium from tin residue, which comprises the following steps: tin residue powder containing tin, antimony, lead, indium and arsenic oxide uses mixed liquor of hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride and hydrazine hydrate as a leaching agent, carries out electric potential control and two step countercurrent to recoverleached antimony, one-step leaching agent is neutralized and hydrolyzed to output crude antimony oxide, lead can be leached by sodium chloride solution in two-step leaching residue; after lead is leached, the liquor is cooled and crystallized to obtain lead chloride; after lead is leached, sodium is washed out in residue to obtain high indium tin concentrate containing 49.52-55.69wt% of tin and 1.04-1.2wt% of indium. The purities of crude antimony oxide and crude lead chloride are respectively 93.58wt% and 99.67wt%; the recovery efficiencies of tin, antimony, lead and indium respectively reach up to 98.68wt%, 84.616wt%, 95.136wt%, and 95.3wt%. The method has the advantages of short flow, good separation effect and good working conditions.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Glass composition and process for producing glass composition
ActiveUS7786035B2High yieldReduce usageGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusArsenic oxideChloride
A glass composition which is reduced in the amount of residual bubbles and is produced using smaller amounts of an environmentally unfriendly component such as arsenic oxide and antimony oxide. This glass composition contains, in terms of mass %: 40-70% SiO2; 5-20% B2O3; 10-25% Al2O3; 0-10% MgO; 0-20% CaO; 0-20% SrO; 0-10% BaO; 0-0.5% Li2O; 0-1.0% Na2O; 0-1.5% K2O; and 0-1.5%, excluding 0%, Cl, Li2O+Na2O+K2O exceeding 0.06%. The glass composition can be produced suitably using, for example, a chloride as part of the raw glass materials.
Owner:AVANSTRATE INC
Black high-strength microcrystalline glass and its preparation method
The invention discloses a black high-strength microcrystal glass, which comprises the following parts: 70% SiO2, 3. 5% Lithia, 17% alumina, 0.1%-0.5% ferric trioxide, 0.5%- 1% cobalt trioxide, 0.5%-1% nickel trioxide, 3. 1% -3. 5% at least one of titania, zirconia and phosphorus pentoxide, 1%-1. 5% at least one of magnesia, zinc oxide, barium oxide and boric oxide, 2. 0%-2. 1% potassium oxide and or sodium oxide and 1% arsenic oxide and or antimony oxide. The making method of microcrystal glass comprises the following steps: grinding evenly; adding reducer to allocate composite material; fusing under 1580 -1650 deg. c; shaping; annealing; coring under 600-800 deg. c for 1-4h; heating to 700-1000 deg. c to crystallize for 1-12h.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
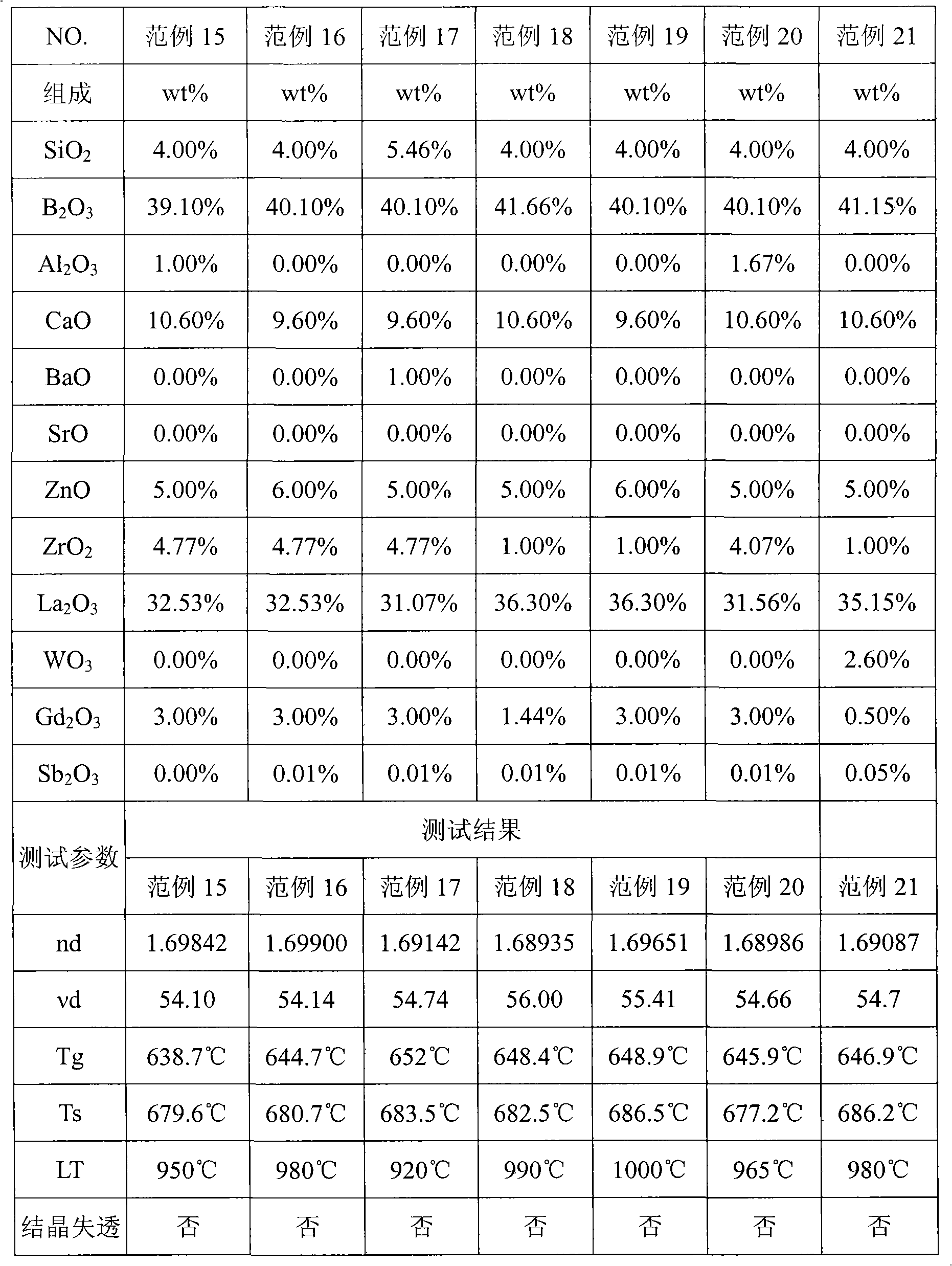
Optical glass
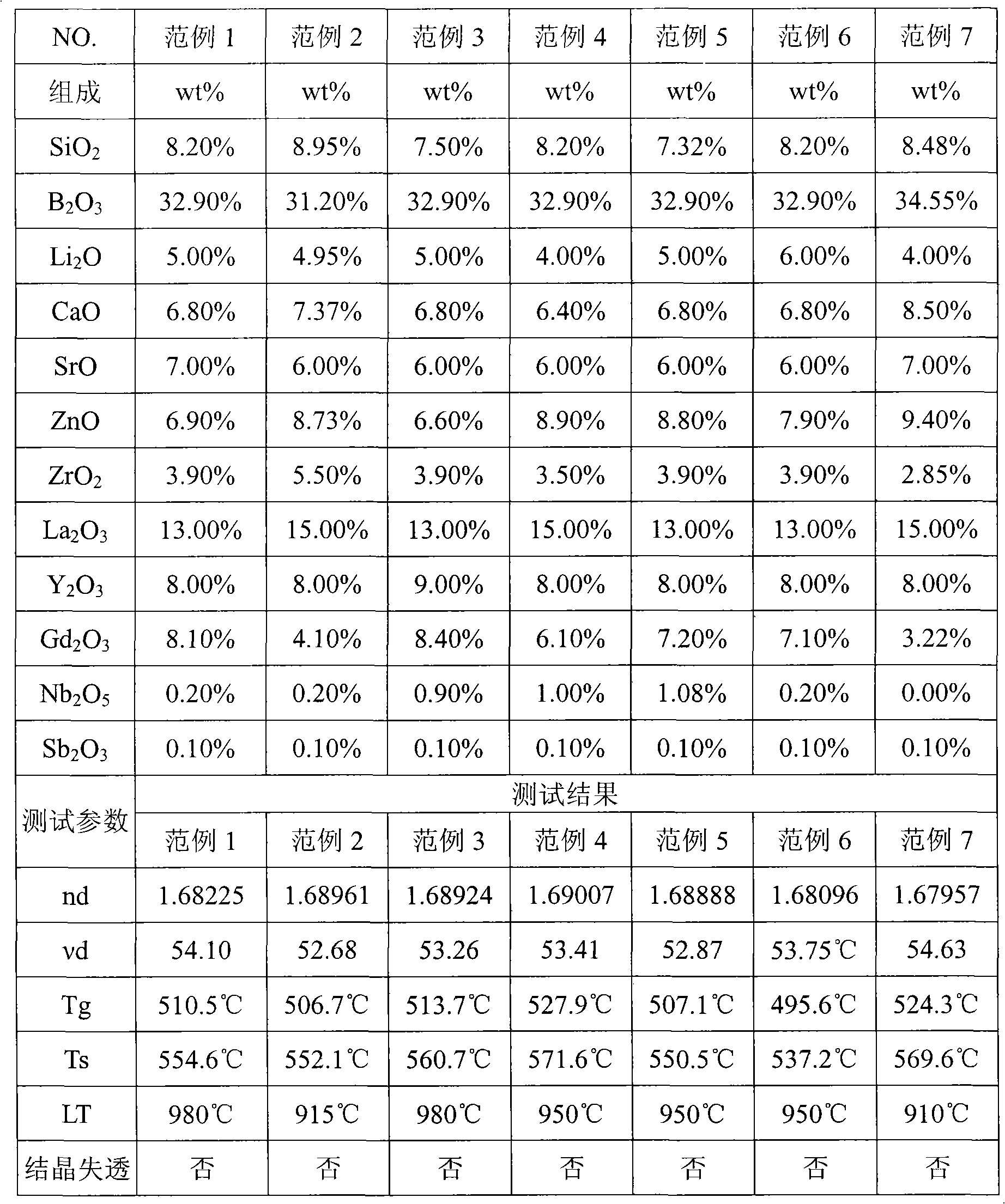
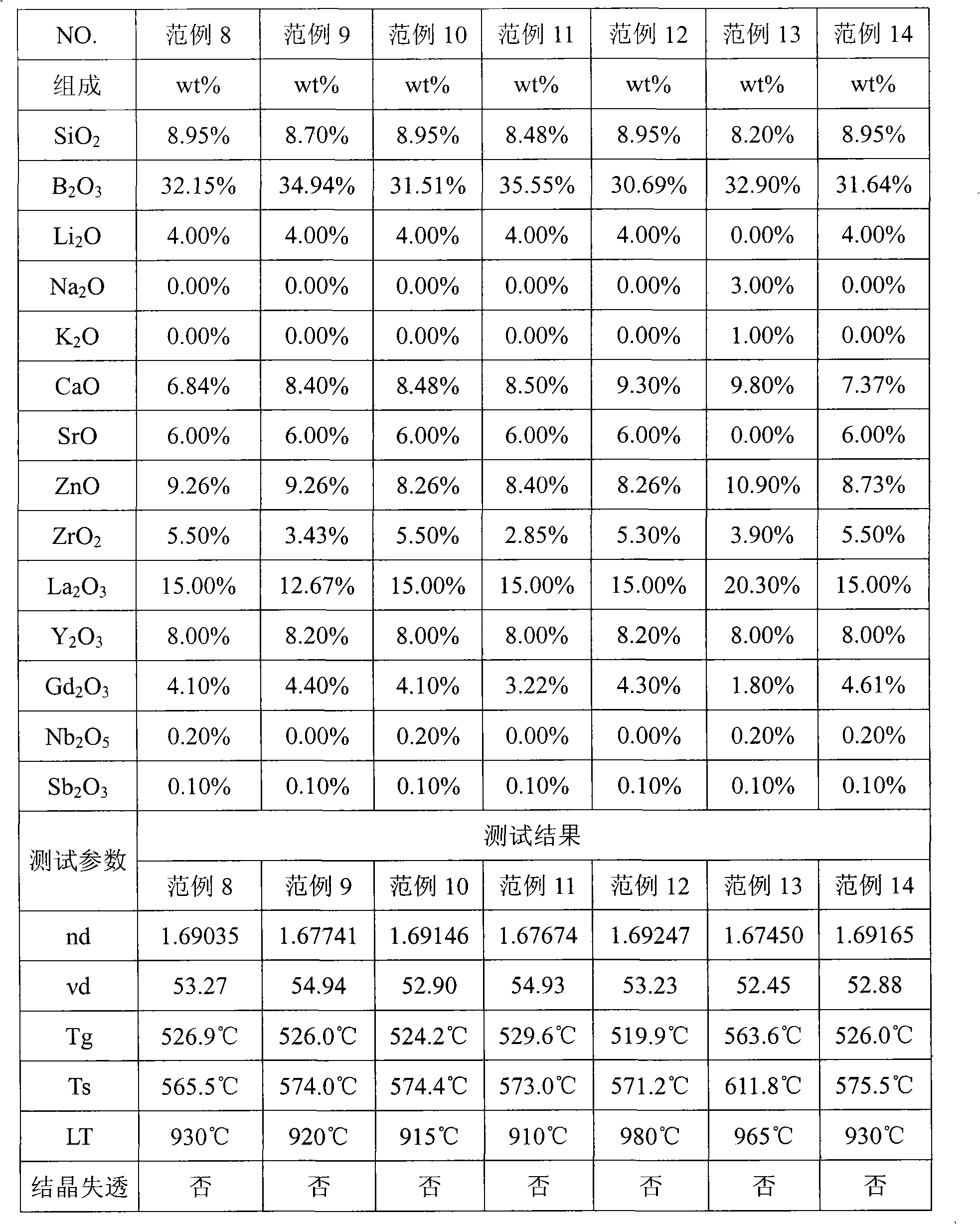
The invention provides optical glass which comprises substances according to the following weight percentage: 2 to 11 percent of SiO2; 28 to 45 percent of B2O3; 2 to 15 percent of CaO; 3 to 18 percent of ZnO; 1 to 8 percent of ZrO2; 9 to 40 percent of La2O3; 0.5 to 11 percent of Gd2O3; preferably, the optical glass further comprises 0 to 10 percent of Y2O3, 0 to 3 percent of Al2O3, not more than 8 percent of the total amount of R2O (R is at least one of Li, Na or K ), 0 to 5 percent of R'O(R' is at least one of Mg, Sr or Ba), 0 to 3 percent of WO3, 0 to 2 percent of Nb2O5 and 0 to 1 percent of Sb2O3. The optical glass of the invention does not comprise components which is harmful to the environment such as lead oxide, arsenic oxide, etc. and has the refractive index between 1.66 and 1.72, the abbe number between 51 and 56, the liquid-phase temperature LT which is less than or equal to 1000 DEG C and the melting temperature of raw materials which is less than or equal to 1300 DEG C, so the optical glass can be easily produced on scale and can be not easy to lead to the bad phenomenon of crystallization and devitrification in the production of a blank pre-mold body or precise molding lens.
Owner:ASIA OPTICAL CO INC
Low-temperature molding optical glass
The low temperature molded optical glass consists of P2O5 9-25 wt%, GeO2 1-20 wt%, Nb2O5 12-28 wt%, TiO2 1-7 wt%, Bi2O 30-55 wt%, WO3 0-38 wt%, SiO2 0-3 wt%, B2O3 0-5 wt%, Al2O3 0-2 wt%, Ta2O5 0-3 wt%, Sb2O3 0-1 wt%, R2O not more than 13 wt%, where R is Li, Na and / or K, and XO not more than 15 wt%, where X is Ca, Sr, Ba and / or Zn. The low temperature molded optical glass contains no lead oxide, arsenic oxide and other environment harming components, and has easy production and no devitrification within the temperature range near the softening point.
Owner:ASIA OPTICAL CO INC
Glass composition and process for producing glass composition
InactiveCN101243020AReduce usageImprove yieldNon-linear opticsIdentification meansArsenic oxideChloride
The present invention provides a glass composition that uses a small amount of arsenic oxide or antimony oxide, which has a large environmental load, and has few residual bubbles. The glass composition contains, in mass %, SiO2: 40-70%, B2O3: 5-20%, Al2O3: 10-25%, MgO: 0-10%, CaO: 0-20%, SrO: 0-20 %, BaO: 0-10%, Li2O: 0-0.5%, Na2O: 0-1.0%, K2O: 0-1.5%, Cl: more than 0% and 1.5% or less, Li2O+Na2O+K2O is more than 0.06% scope. The glass composition can preferably be produced by using chloride as part of the glass raw material.
Owner:AVANSTRATE INC
Method for enriching and recycling bismuth from waste acid sulfide residues
ActiveCN105568002AAchieve reductionReduce processing costsProcess efficiency improvementArsenic oxideSulfide
The invention discloses a method for enriching and recycling bismuth from waste acid sulfide residues. The method comprises the following steps: 1) adding the waste acid sulfide residues into copper electrolyte, controlling reaction conditions, introducing bismuth and arsenic in the waste acid sulfide residues into a solution, replacing and enriching sulfides in copper waste acid sulfide residues in electrolyte to obtain copper sulfide residues; 2) evaporating and concentrating the solution which is rich in bismuth and arsenic in step 1), and separating out a mixture of bismuth oxide and arsenic oxide from the solution by crystallizing the solution after cooling the solution; 3) adding sodium chloride into sulfuric acid to selectively leach bismuth in the mixture of the bismuth oxide and the arsenic oxide, and filtering the mixture to bismuth-rich leaching liquor; and 4) regulating the pH value of the bismuth-rich leaching liquor for neutralizing and hydrating the bismuth-rich leaching liquor to generate bismuth chloride oxide precipitates, standing the bismuth chloride oxide precipitates for certain time, filtering the bismuth chloride oxide precipitates to obtain bismuth chloride oxide and tail liquor, and returning the tail liquor into a solution which is rich in bismuth and arsenic in the step 1) for circulating. The method not only can realize recycling waste acid sulfide residues in a smelting system, but also efficiently enriches and recycles the bismuth, and has a relatively high practical value.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Transparent, dyed cooktop having improved color display capability, and method for producing such a cooktop
ActiveUS9061937B2Improve color displayHigh glass throughputDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusArsenic oxideTransmittance
Transparent, dyed cook top or hob with improved color display capability, consisting of a glass ceramic with high quartz mixed crystals as predominant crystal phase, whereby the glass-ceramic contains none of the chemical refining agents arsenic oxide and / or antimony, with transmission values of greater than 0.1% in the range of the visible light within the entire wavelength range greater than 450 nm, a light transmission in the visible of 0.8-2.5% and a transmission in the infrared at 1600 nm of 45-85%.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Treatment method for arsenical waste liquid
ActiveCN105177316AShort-term arsenic extraction technology approachReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementLiquid wasteArsenic pollution
The invention provides a treatment method for arsenical waste liquid, which comprises the following steps: (A) performing sulfurization treatment of arsenical waste liquid to obtain arsenic-sulfur-copper mixed slag; (B) performing concentrated sulfuric acid oxidation treatment of the arsenic-sulfur-copper mixed slag to obtain sulfur precipitate and mother liquid; (C) recycling the sulfur precipitate to prepare concentrated sulfuric acid and / or a sulfurization agent, performing crystallization treatment of the mother liquid to separate out arsenic oxide, and continuing to perform purification treatment of arsenic oxide; and (D) enabling the mother liquid subjected to crystallization treatment to circulate back to step (A) to be mixed with arsenical waste liquid repeatedly, and directly extracting elemental copper from the mother liquid when the copper element enrichment concentration in the mother liquid is up to 100-120 g / L. The treatment method for arsenical waste liquid, provided by the embodiment of the invention, is simple, is easy to operate has mild operation conditions, realizes safe and innocent treatment of arsenic pollution, can recycle elemental metal from waste liquid and creates a certain economic value.
Owner:HUNAN LEIENMENGTE ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCE SCI & TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com