Method for recycling lead-tin in silver separating residue of copper anode slime of circuit board
A technology for copper anode slime and silver separation slag is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, which can solve problems such as short treatment process flow, and achieve the effects of simple and easy process, reduction of waste water discharge and cost reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
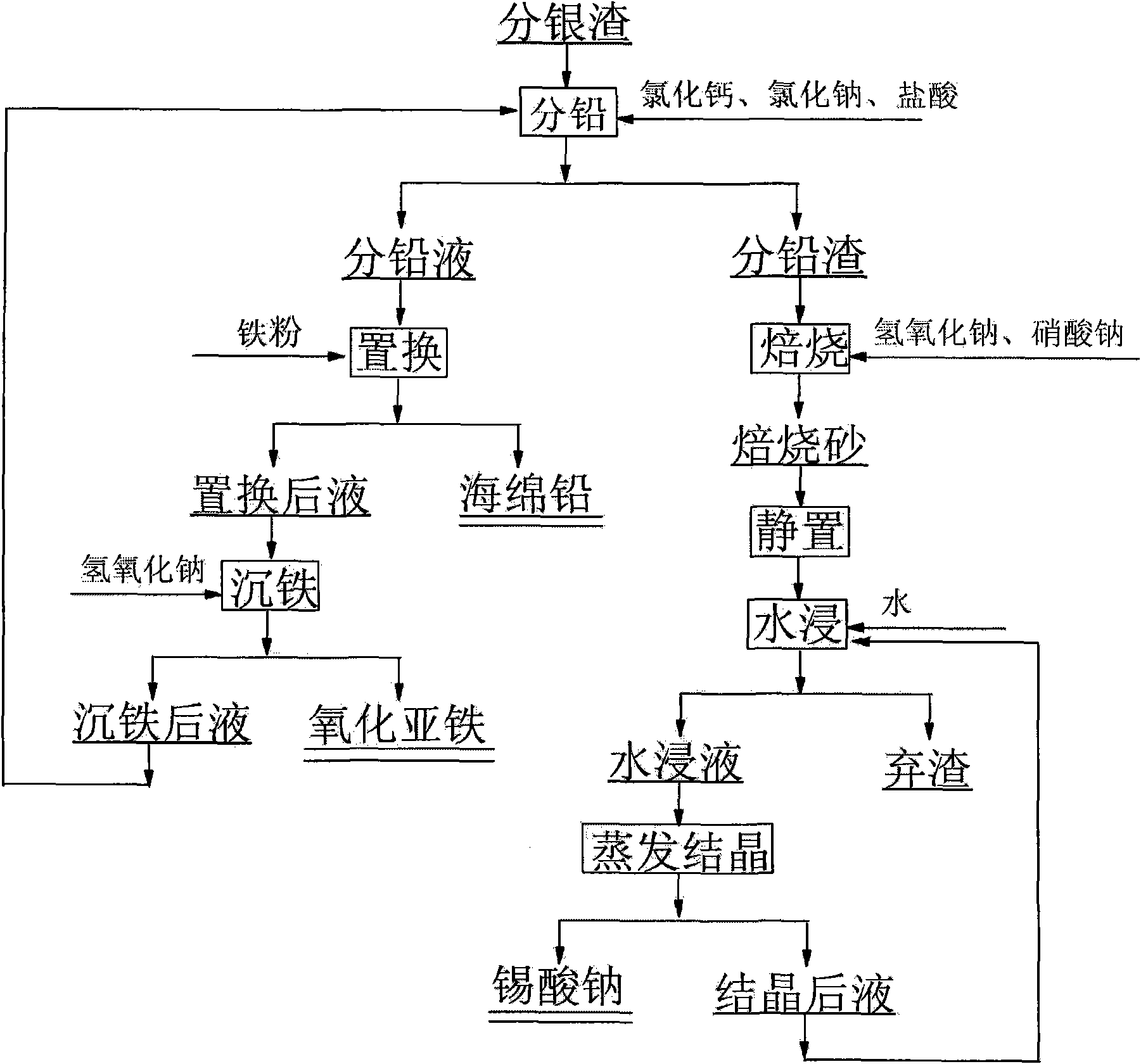
[0012] Add 250g of water, 20g of hydrochloric acid, 50g of calcium chloride, and 30g of sodium chloride to 50g of silver slag, and stir at 80°C for 0.5h; filter to obtain lead liquid and lead slag, replace lead liquid with excess iron powder, and filter to obtain Sponge lead and liquid after replacement, adjust the pH value of the liquid after replacement with sodium hydroxide until no precipitation occurs, and return the liquid after iron sinking to the lead separation process; add 5g of sodium hydroxide and 1g of sodium nitrate to the lead residue, and mix well; roast at 350°C 1.5h; place the calcined sand in the air for 24h, add 150g of water, stir for 0.5h, and filter to obtain sodium stannate. The lead recovery rate is 95.3%, and the tin recovery rate is 98.2%.
Embodiment 2
[0014] Add 100g of silver-separating slag to Example 1, 200g of iron-sinking liquid, 500g of water, 25g of hydrochloric acid, 70g of calcium chloride, 100g of sodium chloride, and stir for 1 hour at 75°C; Replace excess iron powder, filter to obtain sponge lead and replaced liquid, adjust the pH value of the replaced liquid with sodium hydroxide until no precipitation occurs, and return the liquid after iron sinking to the lead separation process; add 20g of sodium hydroxide and nitric acid to the lead slag Sodium 4g, mix evenly; roast at 420°C for 1h; place the roasted sand in air for 30h, add 400g of water, stir for 1h, filter to obtain sodium stannate. The lead recovery rate is 93.7%, and the tin recovery rate is 99.1%.
Embodiment 3
[0016] Add 50g of silver-separating slag to Example 2, 200g of the solution after iron precipitation, 50g of water, 5g of hydrochloric acid, 30g of calcium chloride and 20g of sodium chloride, and stir for 2h at 95°C; Replace excess iron powder, filter to obtain sponge lead and replaced liquid, adjust the pH value of the replaced liquid with sodium hydroxide until no precipitation occurs, and return the liquid after iron sinking to the lead separation process; add 7g of sodium hydroxide and nitric acid to the lead slag Sodium 2g, mixed evenly; roasted at 450°C for 2h; put the calcined sand in the air for 48h, add 250g of water, stir for 0.5h, filter to obtain sodium stannate. The lead recovery rate is 94.1%, and the tin recovery rate is 97.8%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com