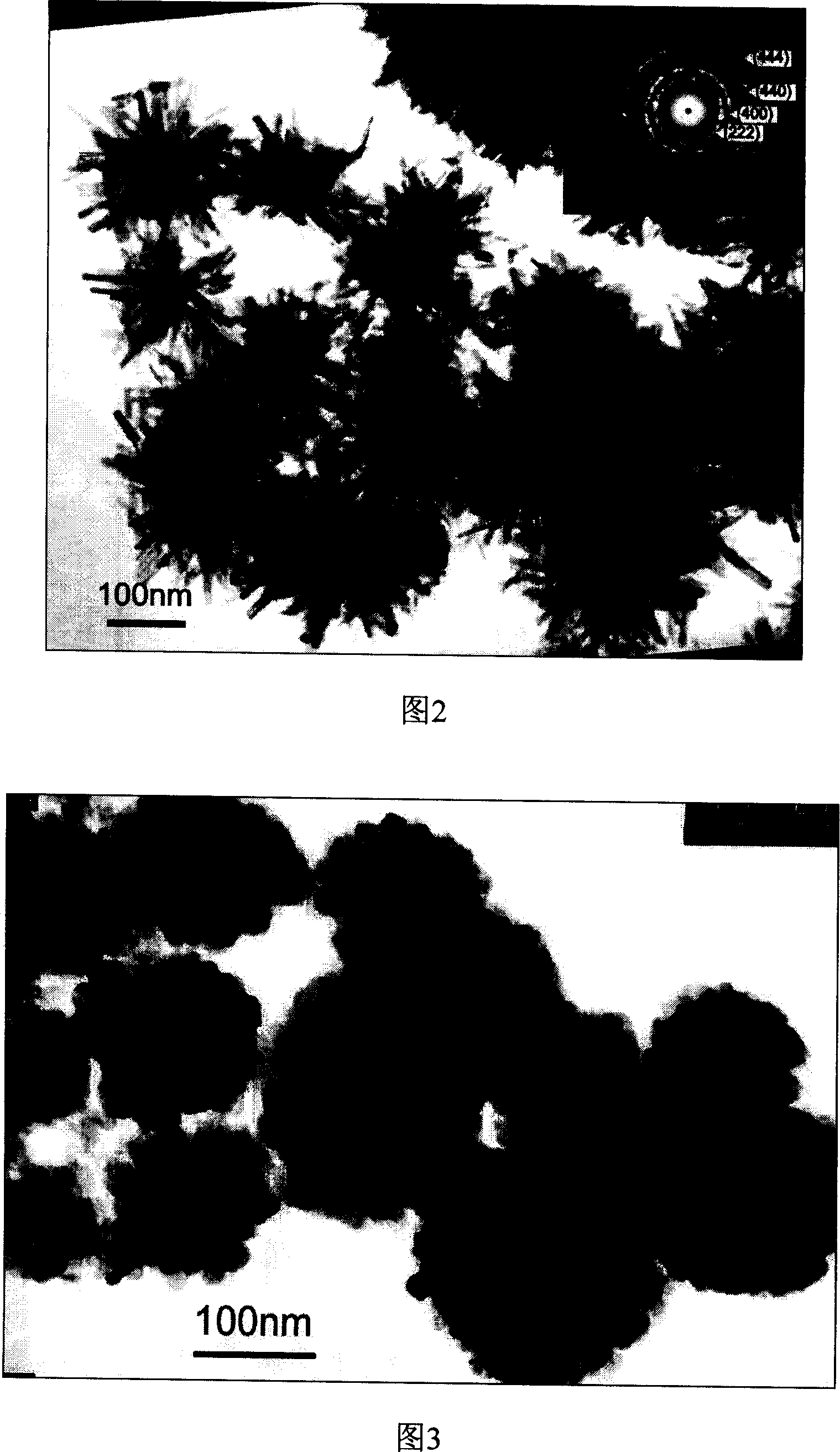
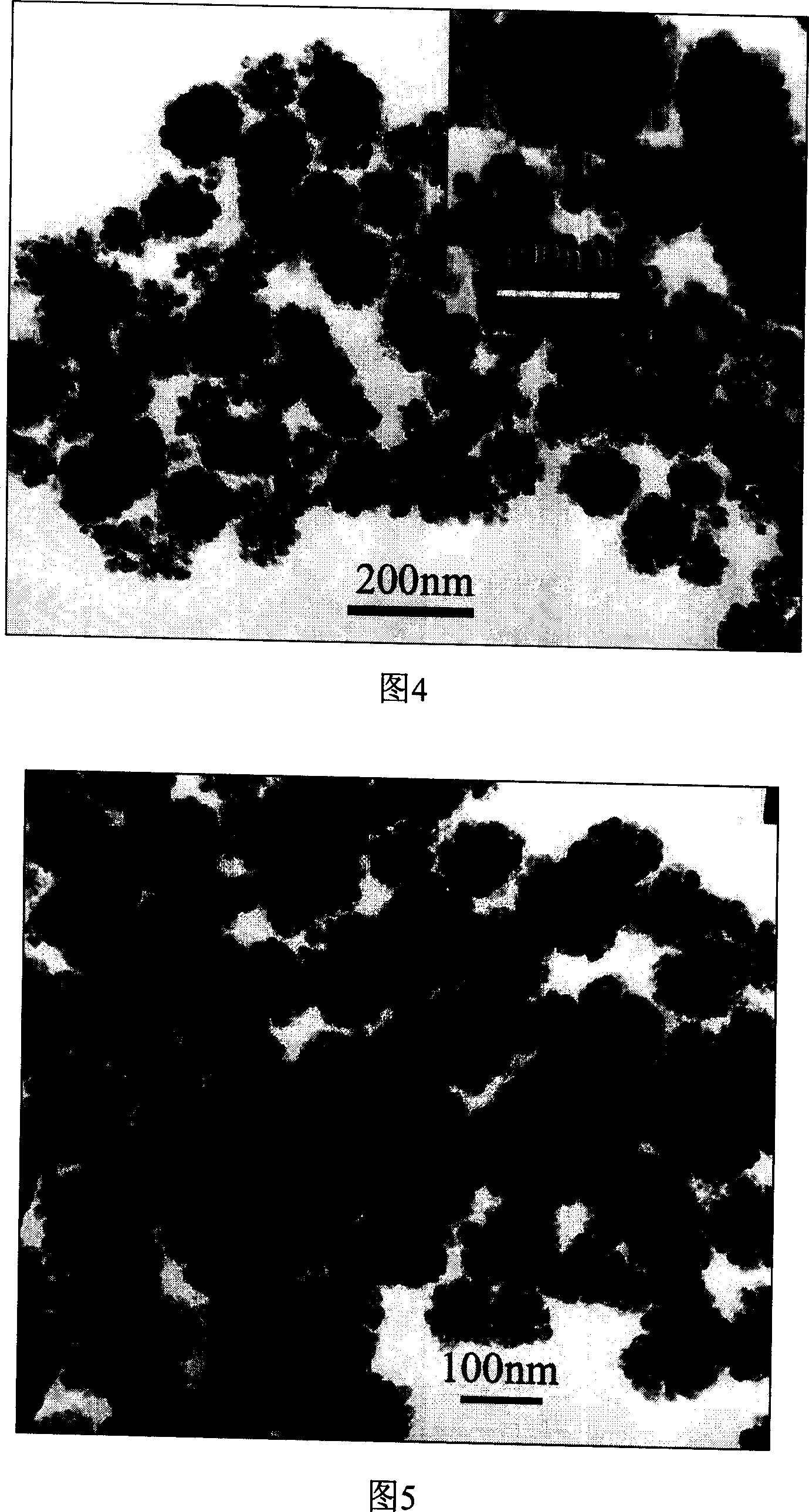
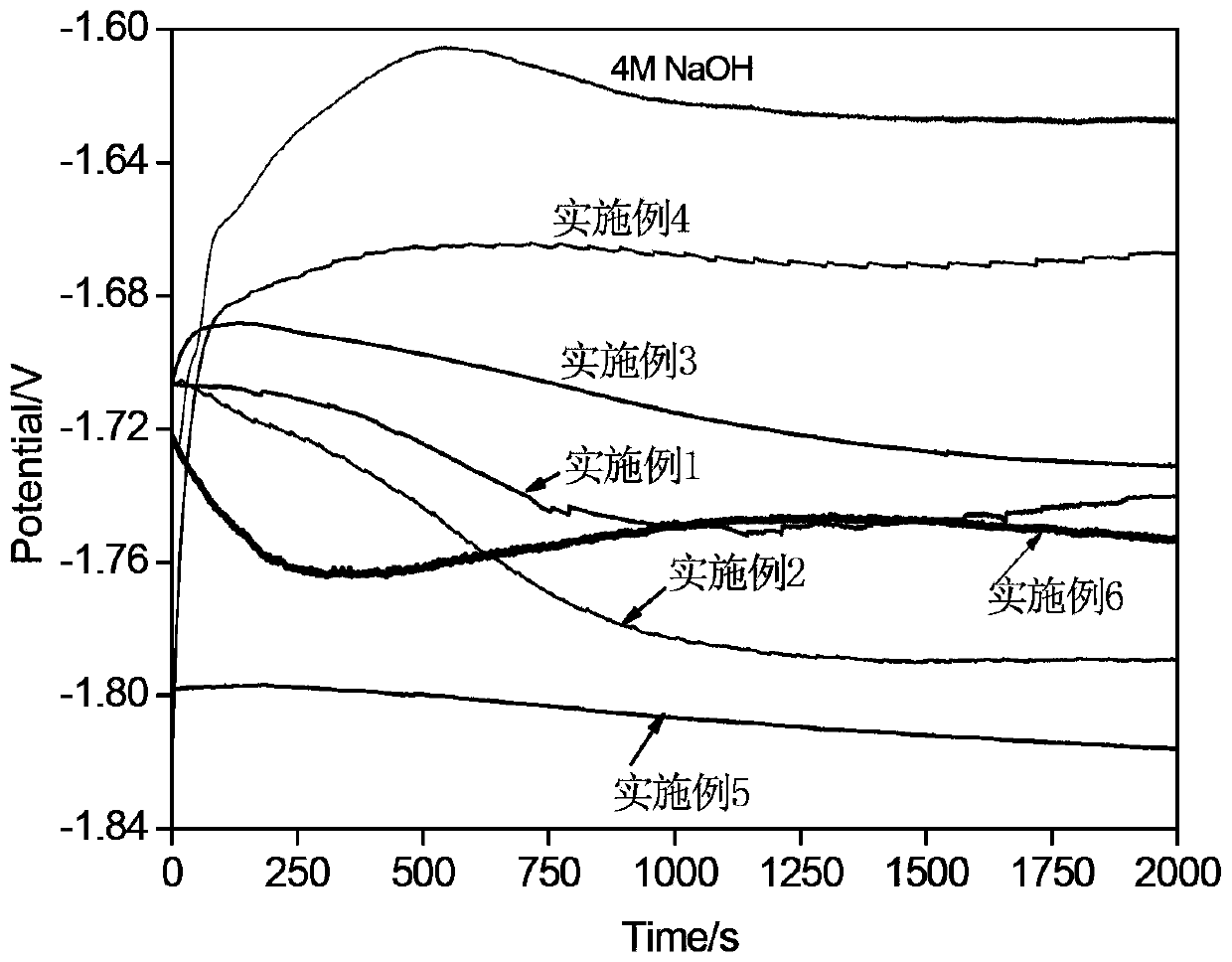
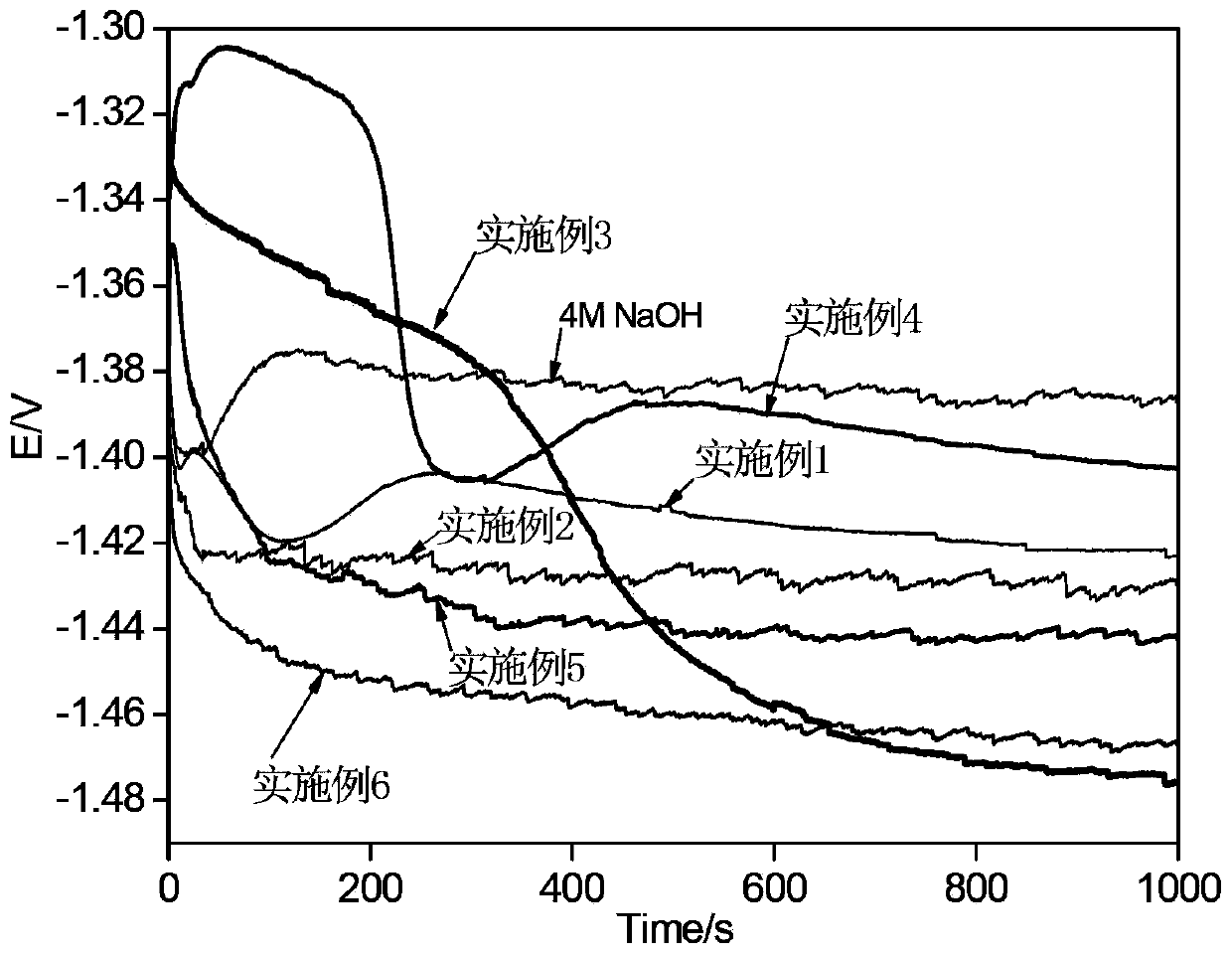
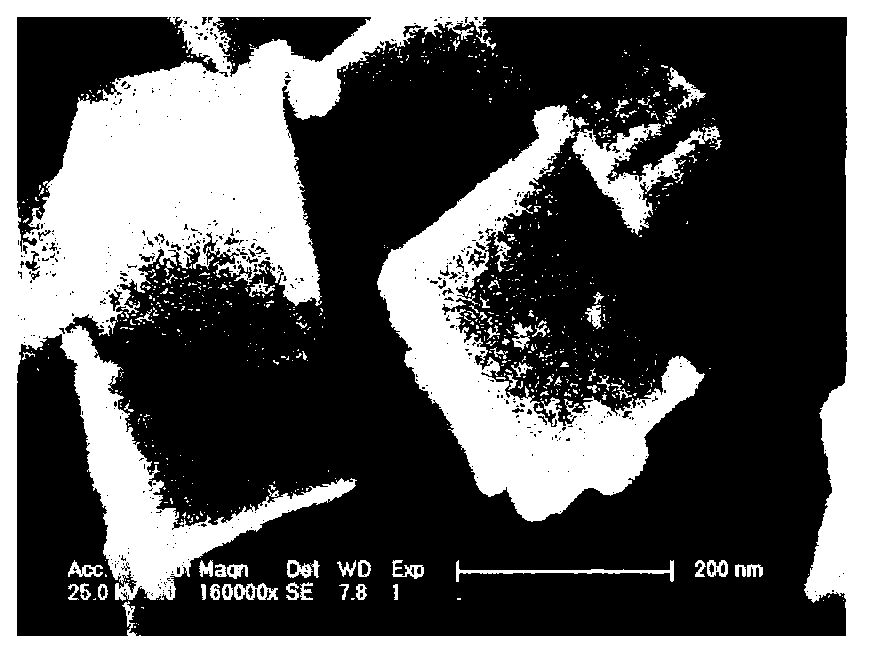
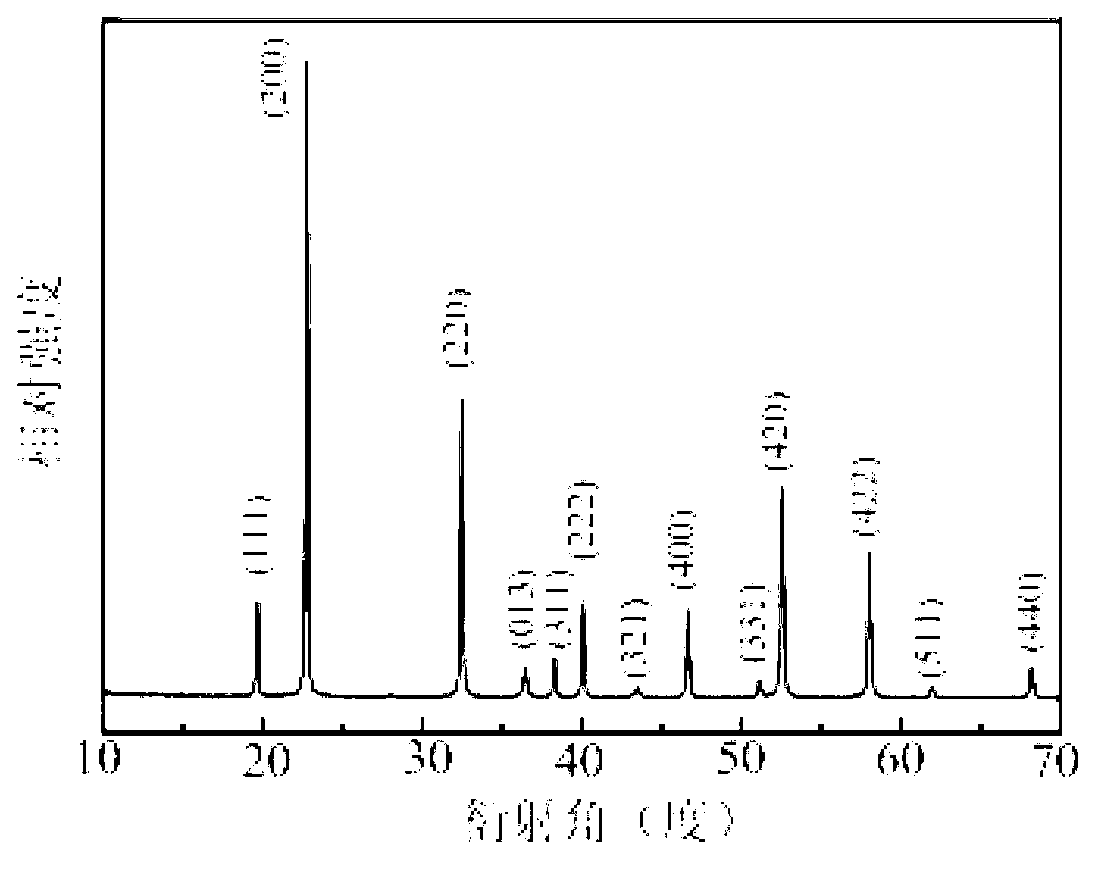
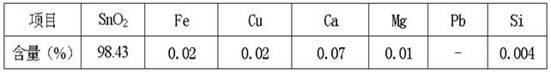
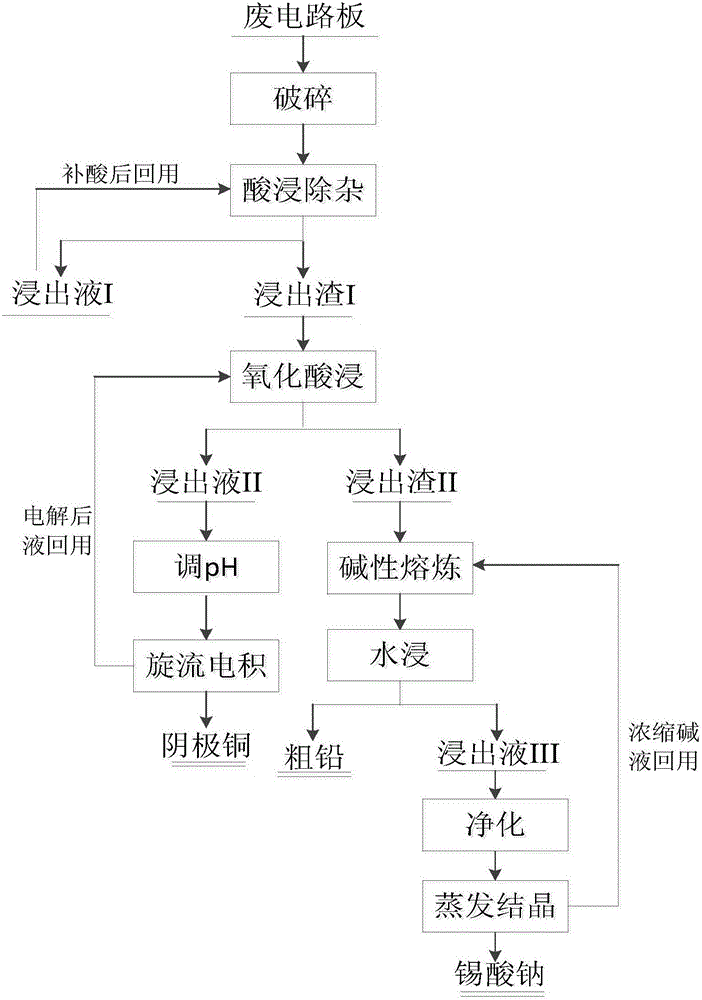
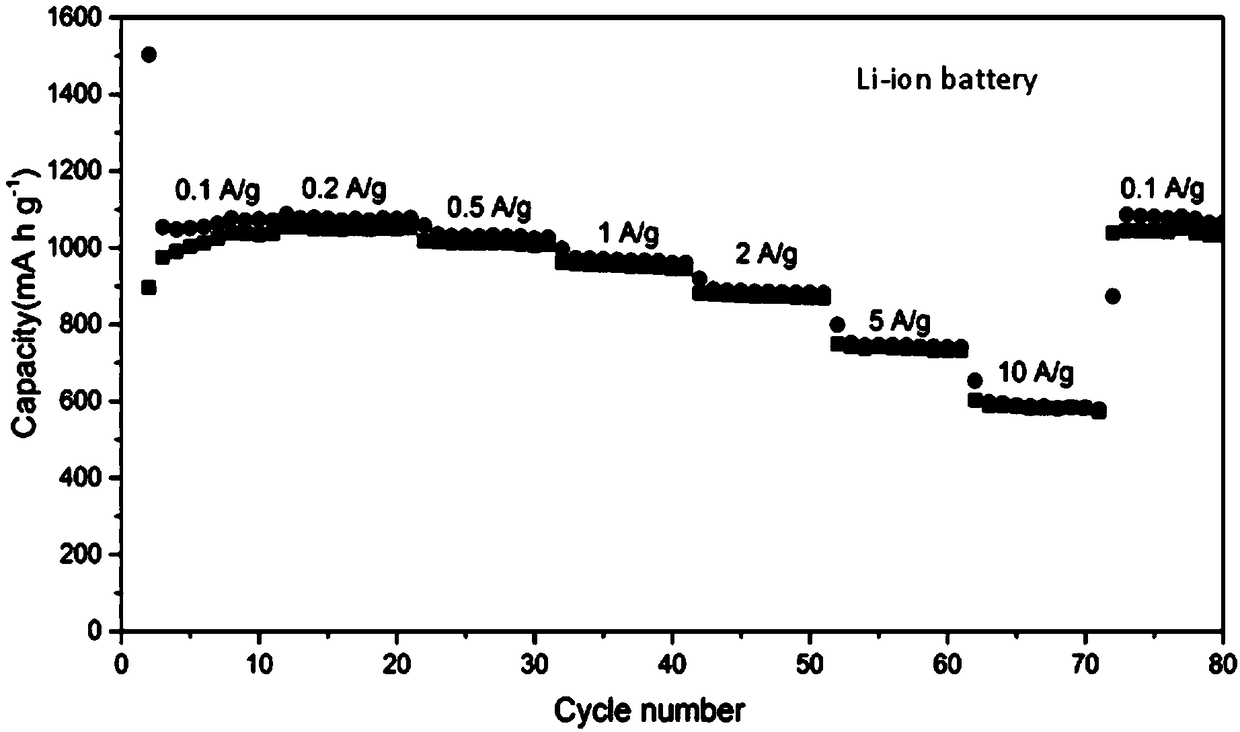
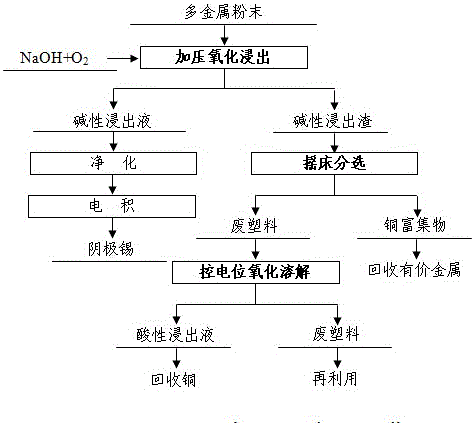
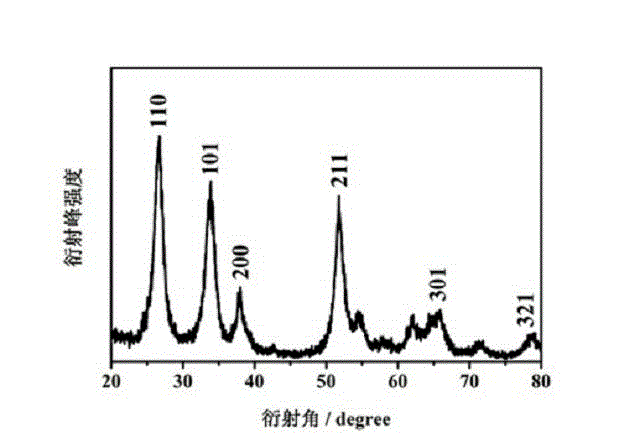
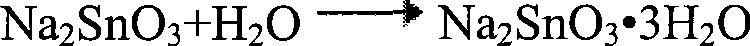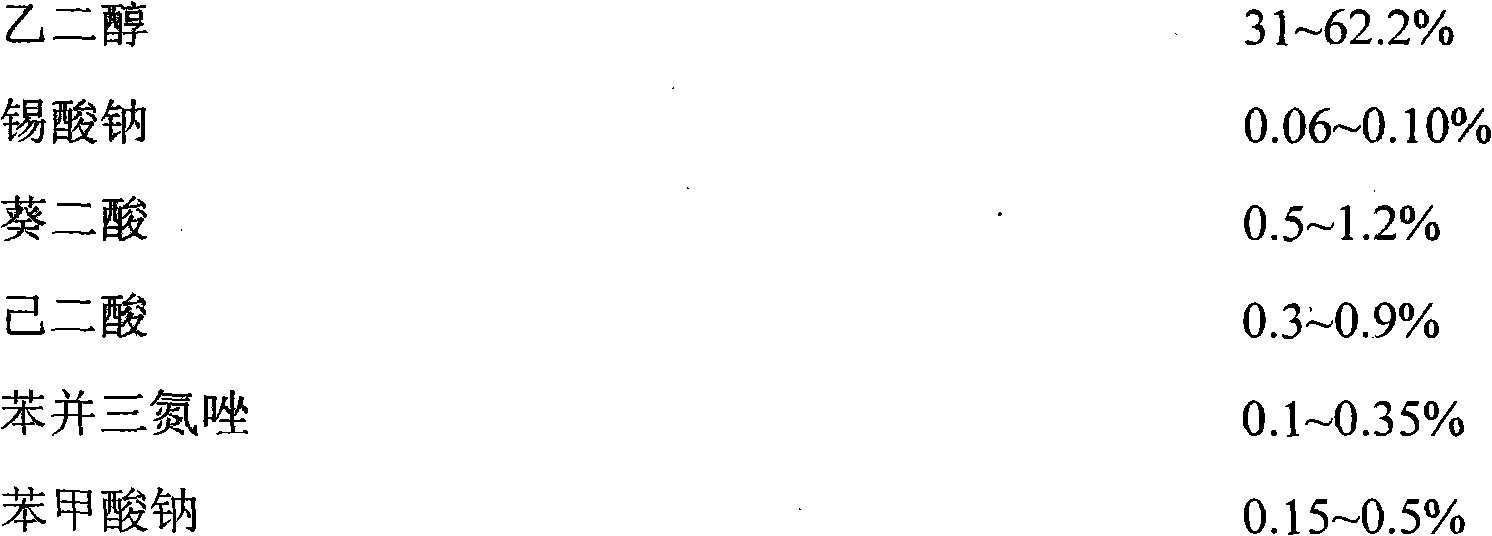Patents
Literature
288 results about "Sodium stannate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sodium stannate, formally sodium hexahydroxostannate(IV), is the inorganic compound with the formula Na₂[Sn(OH)₆]. This colourless salt forms upon dissolving metallic tin or tin(IV) oxide in sodium hydroxide, and is used as a stabiliser for hydrogen peroxide. In older literature, stannates are sometimes represented as having the simple oxyanion SnO₃²⁻, in which case this compound is sometimes named as sodium stannate–3–water and represented as Na₂SnO₃·3H₂O, a hydrate with three waters of crystallisation. The anhydrous form of sodium stannate, Na₂SnO₃, is recognised as a distinct compound with its own CAS Registry Number, 12058-66-1 , and a distinct materials safety data sheet.
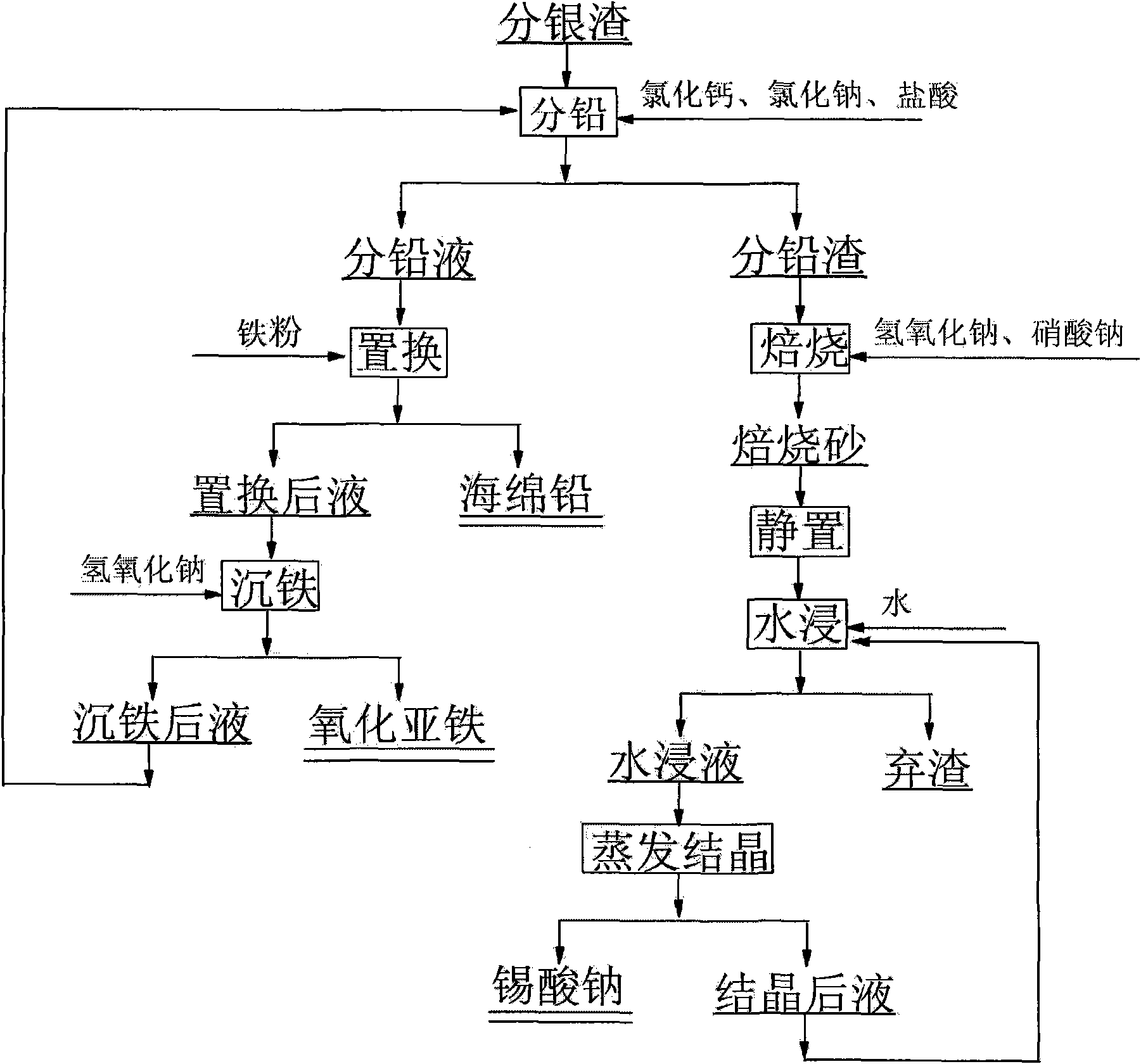
Method for recycling lead-tin in silver separating residue of copper anode slime of circuit board
ActiveCN101555550AReduce generationEmission reductionProcess efficiency improvementIron powderWastewater
The invention discloses a method for recycling lead-tin in silver separating residue of copper anode slime of a circuit board and relates to a method for recycling silver separating residue of copper anode slime of the circuit board by a wetting method. The method comprises the following steps of: stirring silver separating residue, water, hydrochloric acid, calcium chloride and sodium chloride for 0.5 to 2.0h under proper temperature according to requirements, filtering and obtaining lead separating liquid and lead separating residue; carrying out displacement to the lead separating liquid by using excess iron powder, filtering and obtaining spongy lead and displaced liquid; using sodium hydroxide to adjust pH value of the displaced liquid till the precipitate is not generated; and returning lead separating procedure after the iron is precipitated. The lead separating residue, the sodium hydroxide and sodium nitrate are mixed evenly to carry out roasting with the temperature of 350 to 500 DEG C, and then are added with water and filtered, thus obtaining the sodium stannate. Compared with the prior art, due to the adoption of a full-wetting process, the method reduces a large amount of waste gas and dusts in the process of pyrometallurgical treatment; the liquid after the iron is precipitated contains the main compositions of hydrochloric acid and sodium chloride; and the method can return acid pickling procedure, reduce discharge of waste water and lower cost, and is characterized by simple technique, no pollution and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
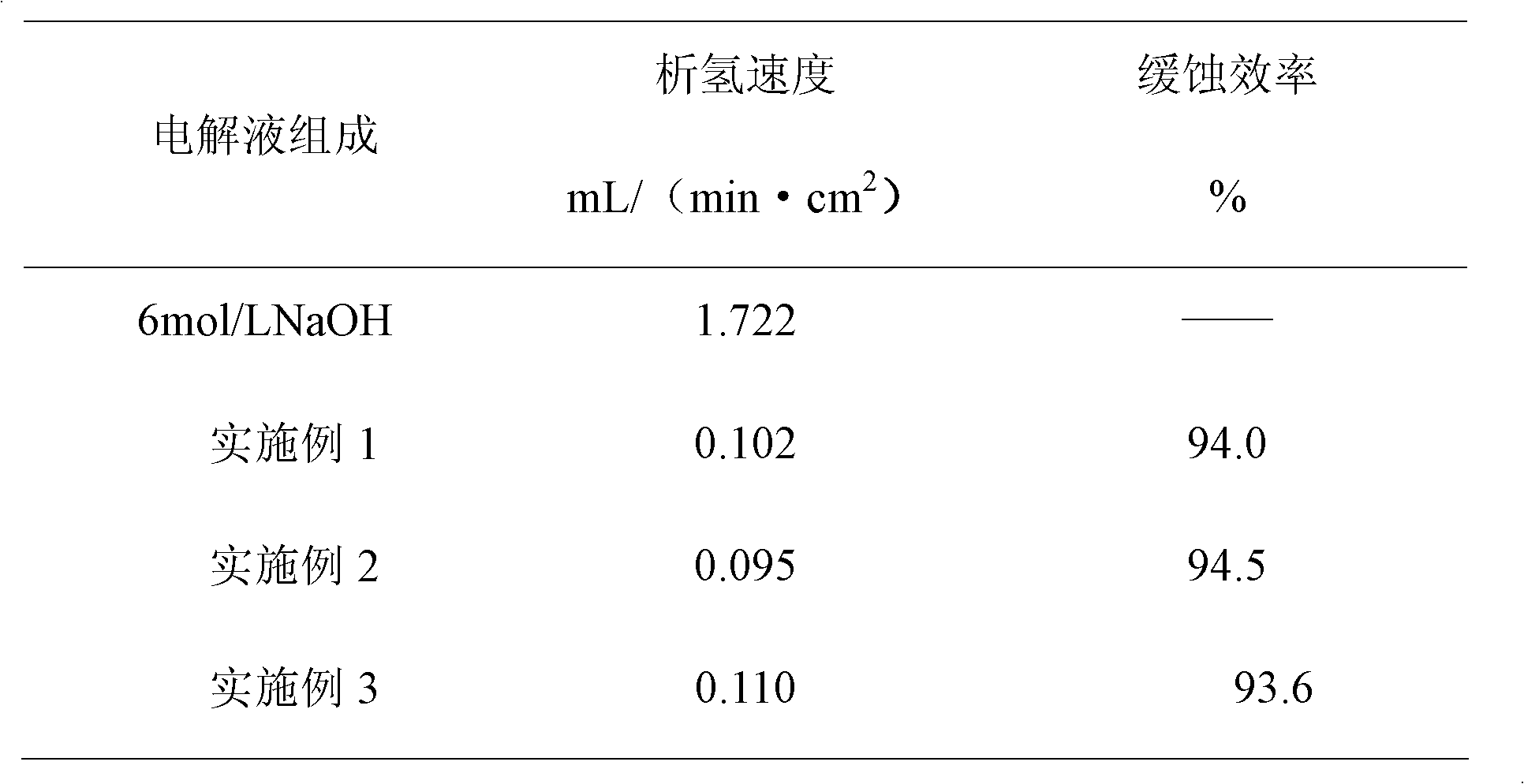
Compound corrosion inhibitor of alkaline electrolyte of alkaline aluminium battery, electrolyte and preparation method of compound corrosion inhibitor
ActiveCN102088115AExtended service lifeImprove work efficiencyAlkaline accumulatorsIndiumAluminium electrode
The invention discloses a compound corrosion inhibitor of an alkaline electrolyte of an alkaline aluminium battery, an electrolyte and a preparation method thereof. The compound corrosion inhibitor of the alkaline electrolyte of an alkaline aluminium battery is compounded by an inorganic corrosion inhibitor and an organic corrosion inhibitor, wherein the inorganic corrosion inhibitor comprises the following components based on the concentration: 0.015-0.1mol / L sodium stannate, 0.005-0.05mol / L of indium hydroxide, 0.03-0.1mol / L sodium citrate, 0.003-0.05mol / L calcium oxide and 0.02-0.1mol / L zinc oxide; the organic corrosion inhibitor comprises the following components by weight percent: 0.01-0.1wt% of chitosan derivant and 0.05-0.5wt% of organic surface active agent. The compound corrosioninhibitor can effectively prevent an aluminium electrode from corroding in an alkaline solution, and the electrochemistry performance of an aluminium anode is not affected.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
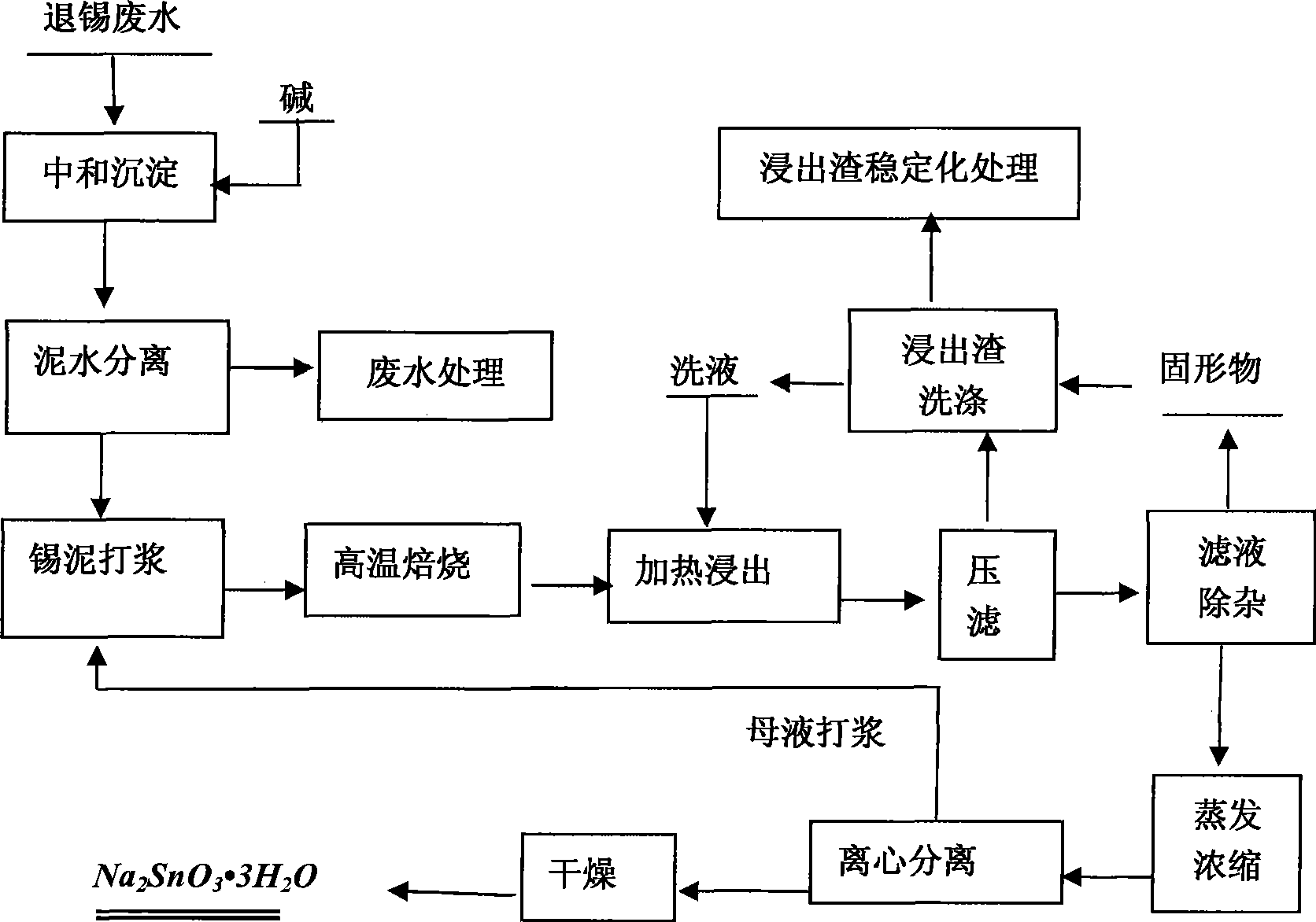
Method for preparing sodium stannate using circuit board tin-stripping wastewater
ActiveCN101497458AReduce manufacturing costRaise the gradeTin compoundsMultistage water/sewage treatmentResource utilizationSludge
The invention relates to a method for preparing sodium stannate by utilizing tin-stripping wastewater of a circuit board. Collected tin-stripping wastewater is neutralized and precipitated by adding alkali to obtain tin sludge with higher tin content; the tin sludge is beat by adding the alkali, and is subjected to high-temperature roasting and countercurrent leaching; then a leachate is subjected to filter pressing; a filtrate is subjected to evaporation, concentration and centrifugal separation after impurity removal; and 10 to 15 percent sodium hydroxide solution is used to wash the obtained product, and thus a crude sodium stannate product can be obtained and then is vacuum dried at a temperature of between 100 and 110 DEG C for 2 to 3.0 hours to obtain a sodium stannate product. The method ensures that the separation rate of tin in the tin-stripping wastewater can reach more than 99 percent, finds a novel treatment way for the tin-stripping wastewater which is produced by printed circuit board industry and is extremely difficult to treat, gives a reasonable fate for all pollutants in the tin-stripping wastewater, and realizes the resource utilization of useful components of the tin-stripping wastewater to the utmost extent when realizing the innoxious treatment of the tin-stripping wastewater.
Owner:江西东江环保技术有限公司
Universal synthesizing method for lanthanide series rare earth stannate nano powder
InactiveCN101041458AHigh purityPromote crystallizationNanostructure manufactureTin compoundsGeneral purposeNitrate
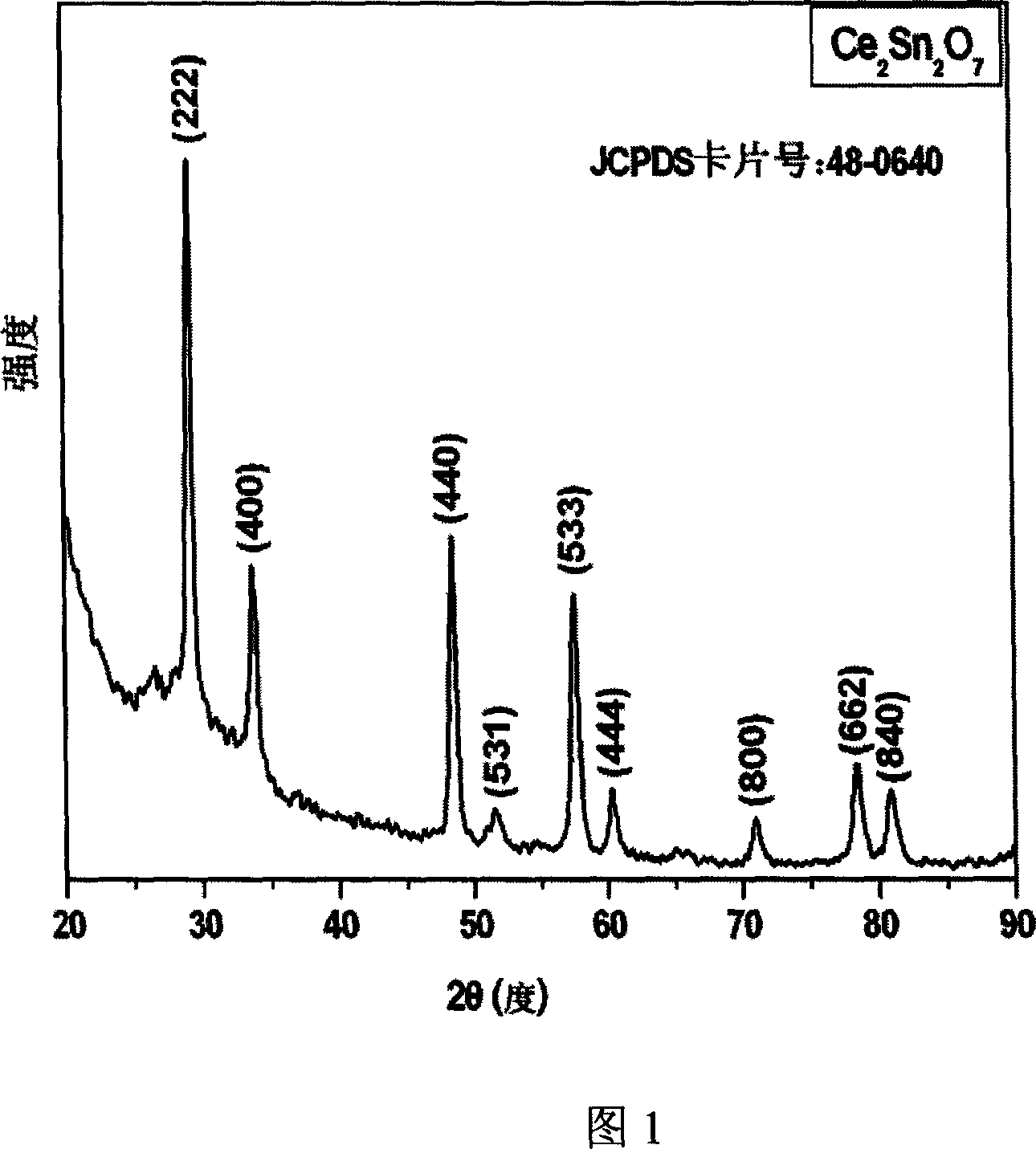
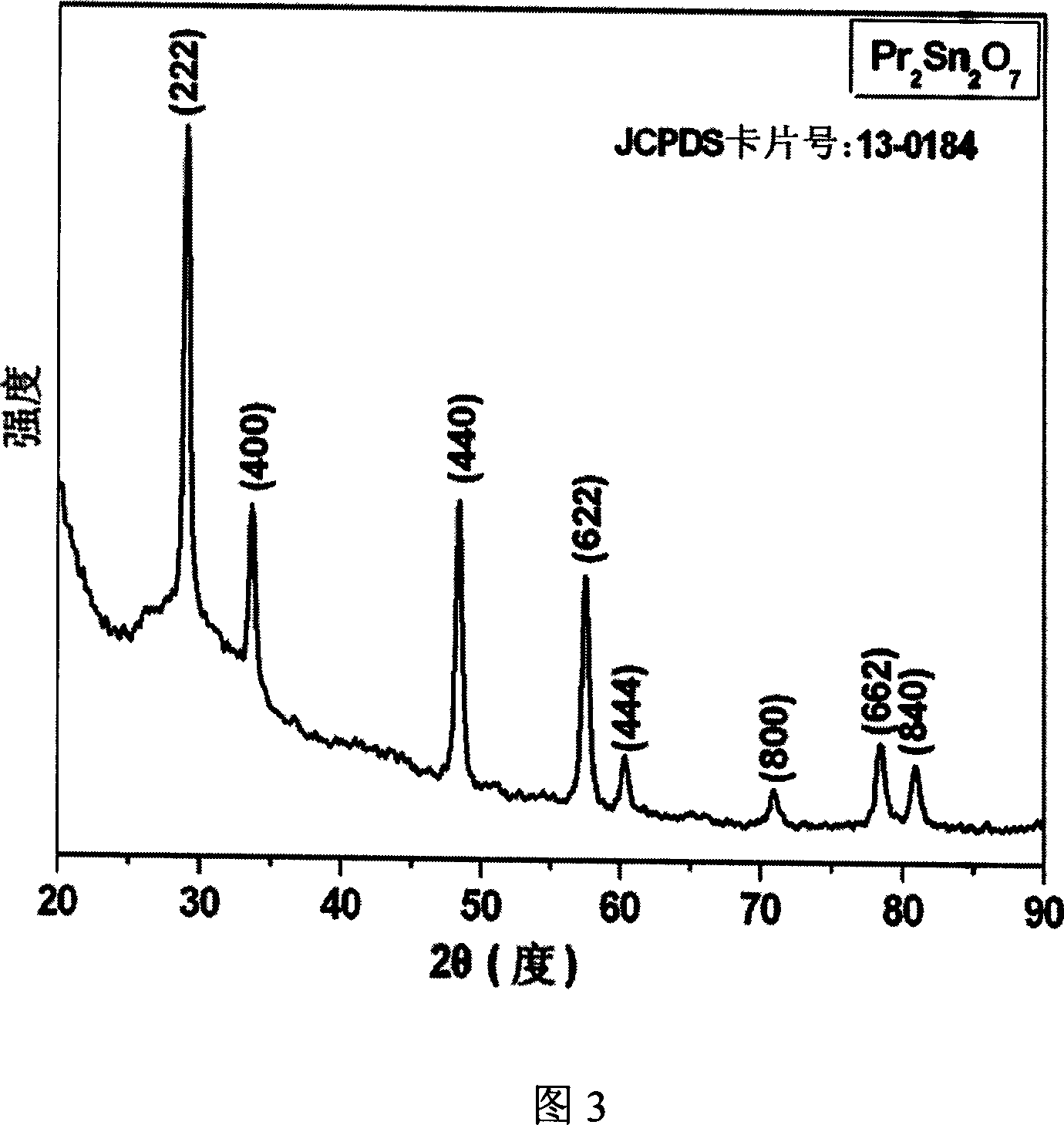
The invention discloses a general purpose synthesized method of lanthanide series rare earth stannate nanometer power, which comprises the following steps: dissolving lanthanide series rare earth nitrate (Ln(NO3)3, Ln=La-Lu) into deionized water; adding sodium stannate or potassium stannate with the same mole number; stirring; putting the final solution into autoclave; setting filling degree at 80-90%; water- annealing 4-100 h during the range of 180-250 deg.c; centrifuging and drying the treated solution at last; getting the product.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method for separating and reclaiming metal nickel and tin from waste materials containing nickel and tin
InactiveCN101824540AGood choiceReduce recycling costsProcess efficiency improvementTin dioxideNickel oxide hydroxide
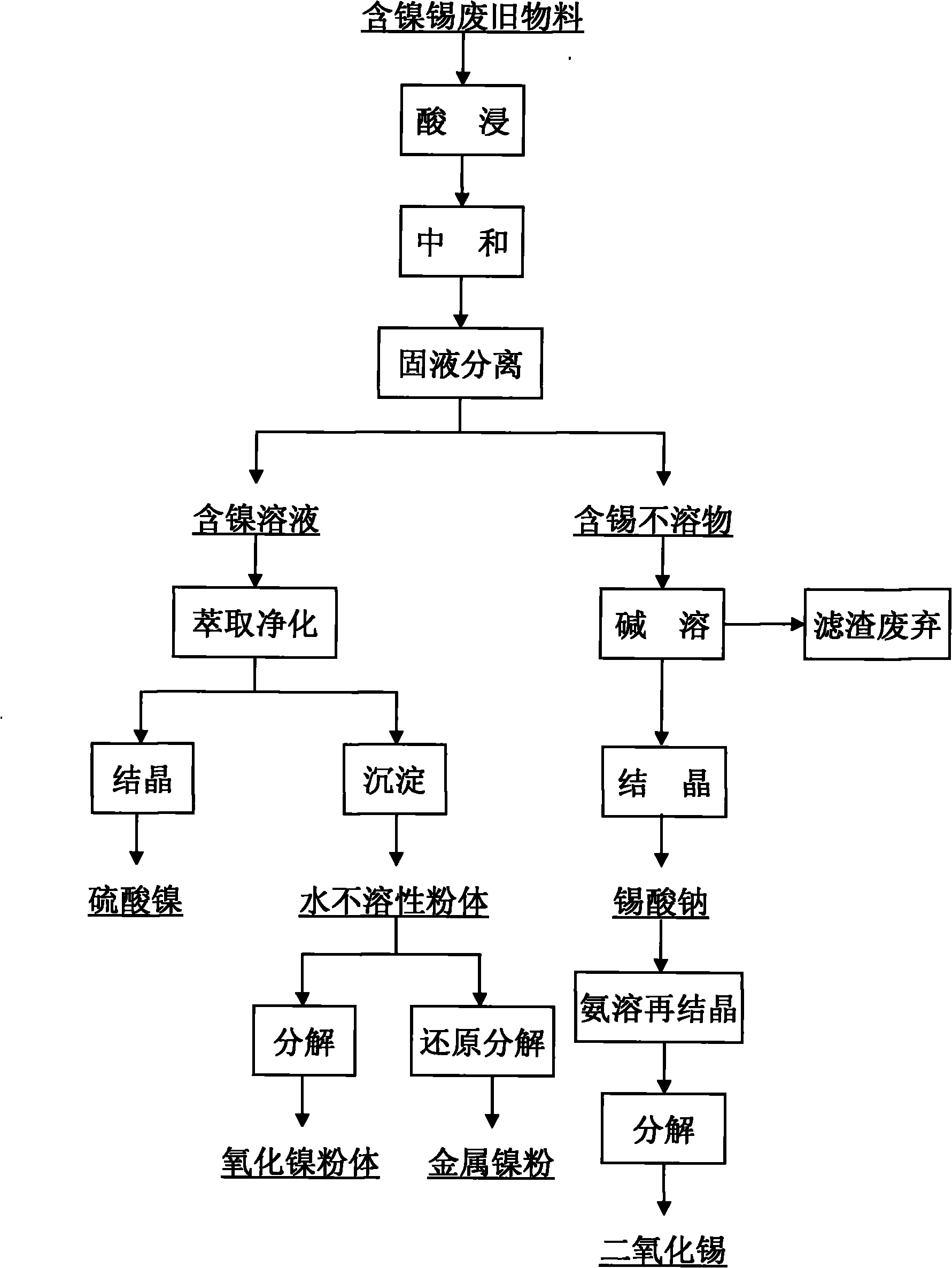
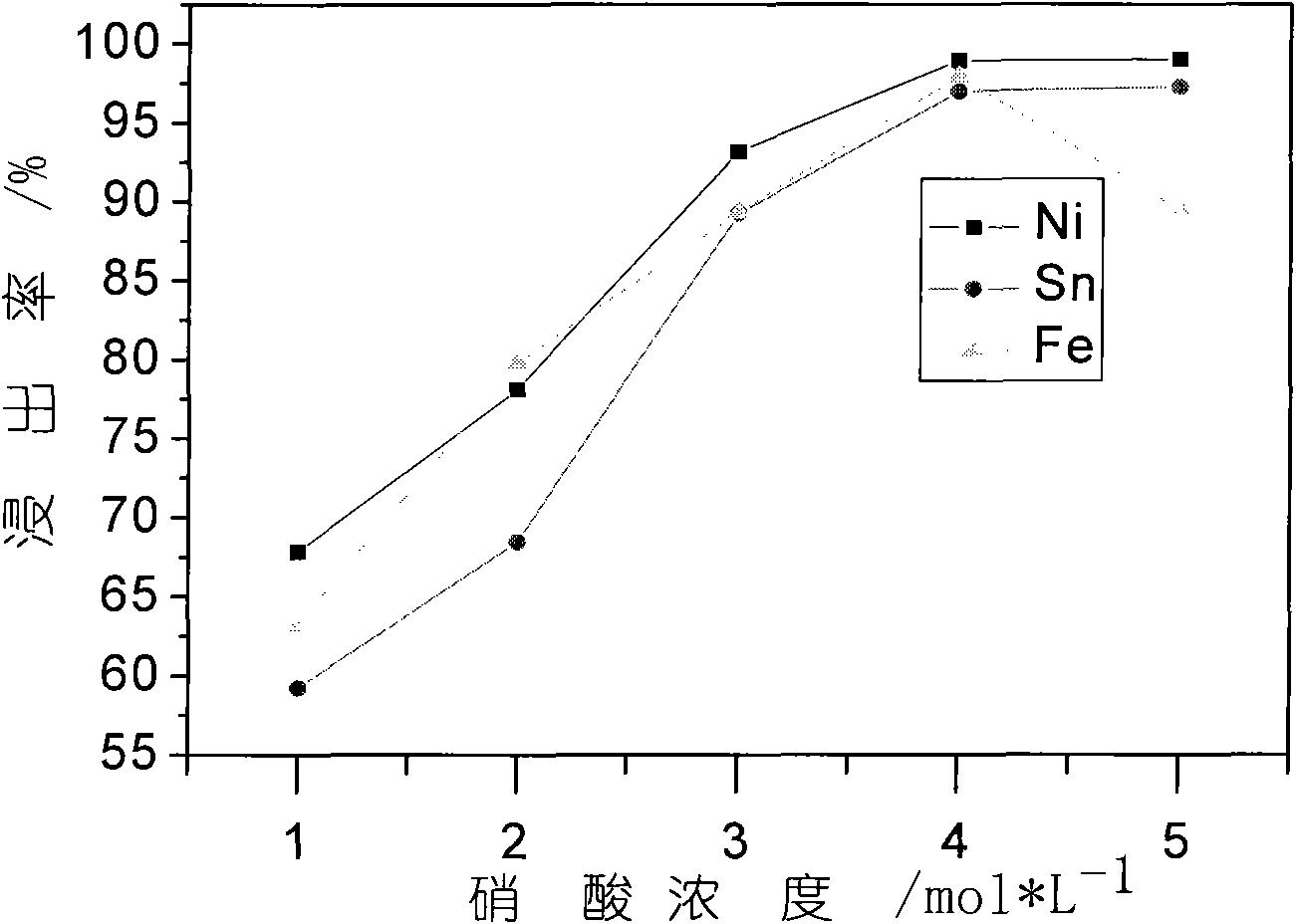
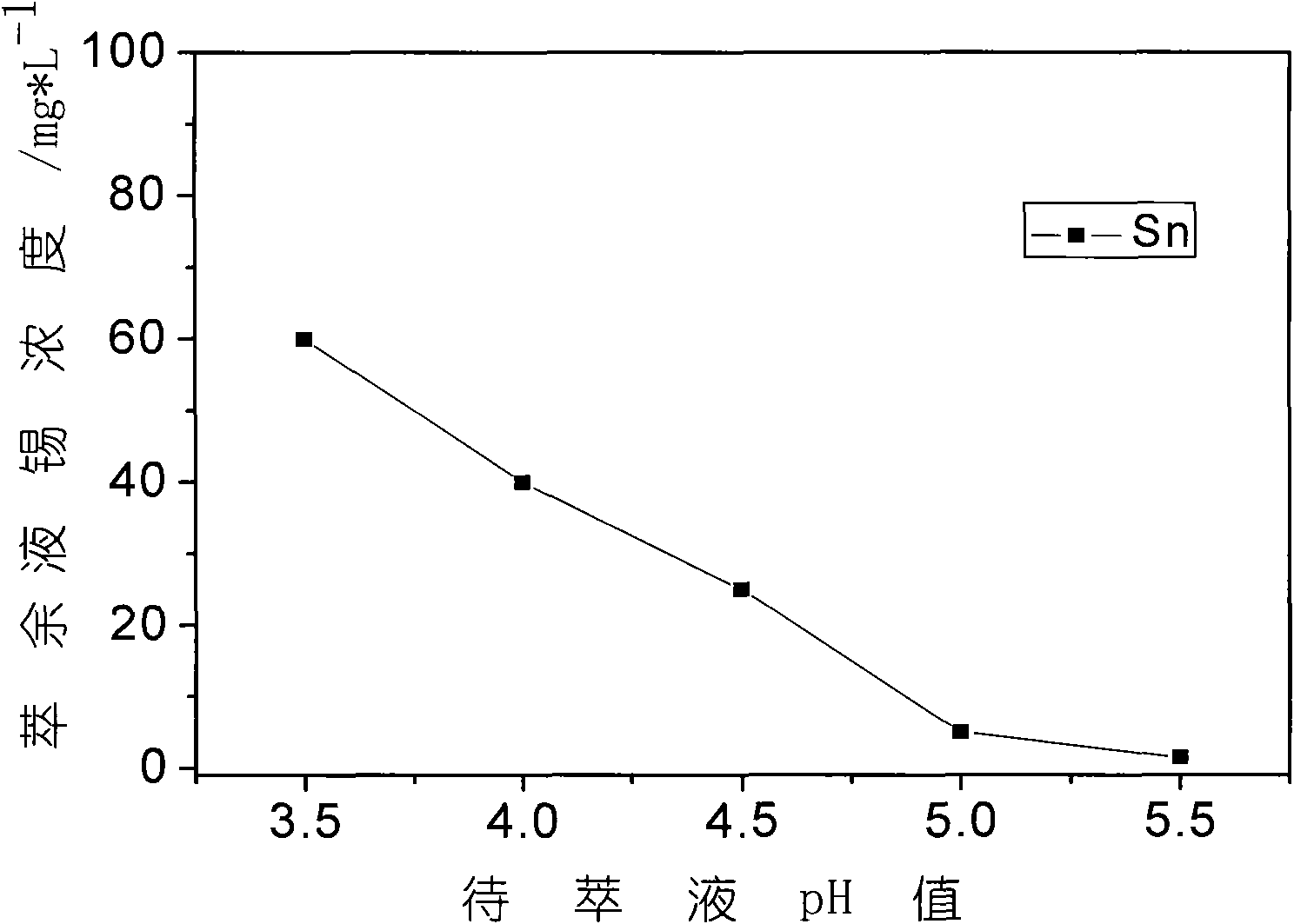
The invention discloses a method for separating and reclaiming metal nickel and tin from waste materials containing nickel and tin. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: leaching the waste materials containing the nickel and tin with acid; adjusting pH value of the materials by using an alkali substance to ensure that impurity iron and a valuable component tin are precipitated; filtering the solution to obtain nickel-containing solution and tin-containing precipitate; extracting the nickel-containing solution for impurity removal and purification, wherein purifying fluid can be directly crystallized to prepare nickel sulfate, can be precipitated and degraded to prepare nickel hydroxide, nickel carbonate and nickel oxalate powder materials, and can be further degraded or reduced to prepare nickel oxide powder and metal nickel powder; and adding sodium hydroxide solution into the tin-containing precipitate, dissolving the tin out and allowing the tin to enter the solution, recrystallizing the solution to prepare a sodium stannate product, or further crystallizing and degrading the solution to prepare a tin dioxide powder material. Acid and alkali in low price are consumables in the whole reclaiming process, and product variousness is provided, so the method has significant economic value and market competitiveness.
Owner:GUANGDONG BRUNP RECYCLING TECH
Lanthanum stannate, europium stannate and its composite stannate nanopowder synthesis method
InactiveCN1951822AAchieve synthesisThe ratio can be adjusted arbitrarilyTin compoundsRare earth metal compoundsRare earthPotassium
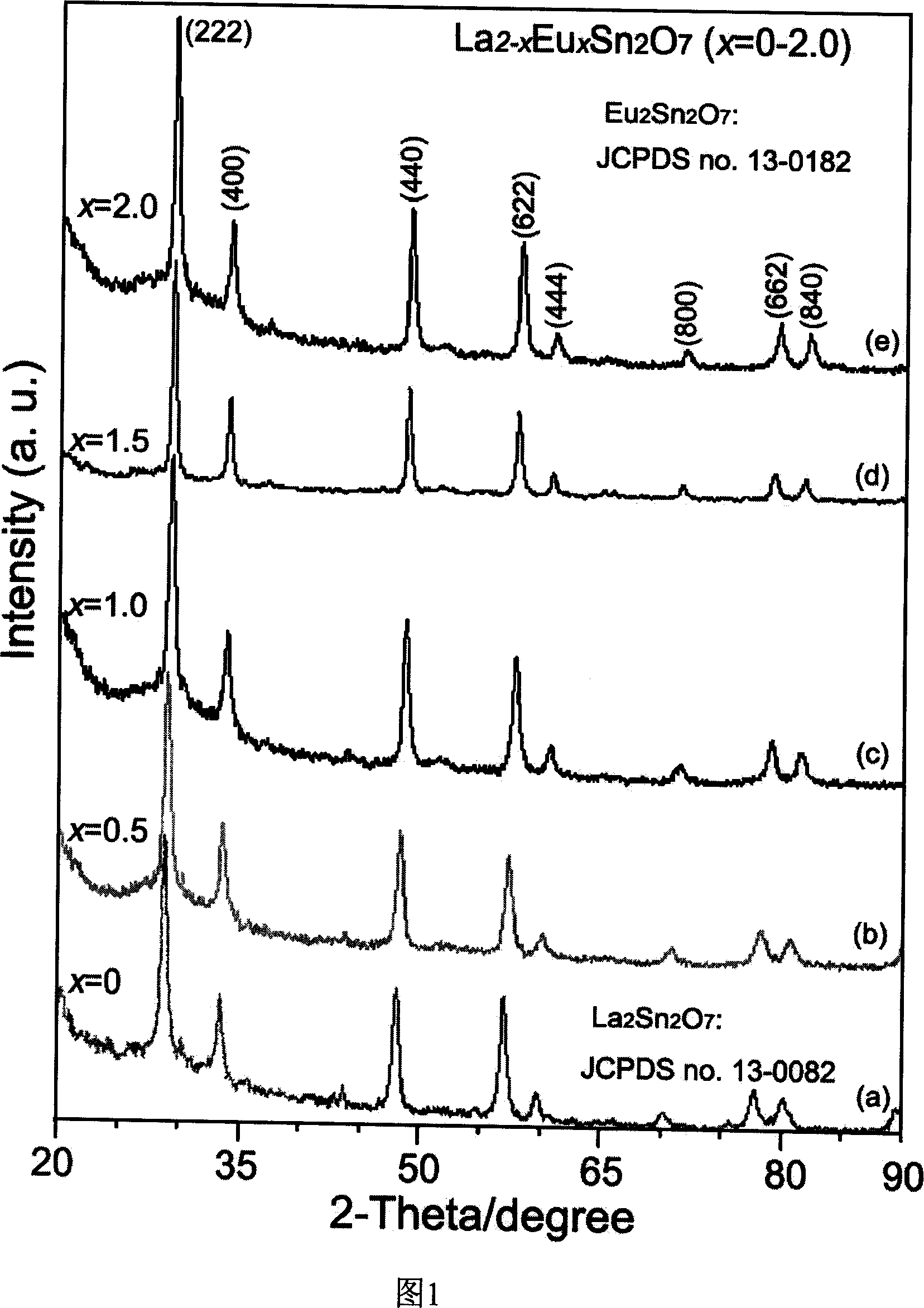
The invention discloses a synthesizing method of lanthanum stannate, europium stannate and composite stannate nanometer powder, which comprises the following steps: dissolving lanthanum stannate and europium stannate with different molar rates or lanthanum stannate or europium stannate in the deionized water; stirring; adding sodium stannate or potassium stannate with the molar weight as the sum of lanthanum stannate and europium stannate in the solution; stirring; putting terminal solution into high-pressure autoclave; setting the filling density at 80-90%; disposing for 4-30h within 180-250 deg.c through hot water; centrifuging the disposed solution; cleaning; drying the product; obtaining the product with diameter at 15-35nm. The molecular formula of the product is La2-xEuxSn2O7 (x=02), which produces single and one-phase product.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Electrolyte corrosion inhibitor for aluminum-air cell, electrolyte and preparation method
InactiveCN103633396AReduce hydrogen evolution self-corrosion rateProne to anodic polarizationFuel and primary cellsAluminum anodePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses an electrolyte corrosion inhibitor for an aluminum-air cell, an electrolyte and a preparation method, belonging to the technical field of chemical batteries. The electrolyte corrosion inhibitor mainly comprises sodium hyposulfite which has a concentration of 0.005 to 0.2 mol / L in the electrolyte and may further comprise the auxiliary additive sodium stannate which has a concentration of 0.01 to 0.03 mol / L in the electrolyte. The aluminum-air cell provided by the invention has the advantages of simple composition, low cost, safety and accordance with environmental protection requirements, can substantially reduce the hydrogen evolution self-corrosion rate of an aluminum anode, enables the open circuit potential of the aluminum anode and working potential under the condition of impressed current to undergo substantial negative transfer, allows an aluminum anode alloy to have good corrosion resistance and high electrochemical activity and meets the requirement of an alkaline aluminum-air cell for large current density discharging.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Stable electroplating solution
InactiveCN106119911AImprove stabilityIncrease temperature securityHydrogen phosphatePotassium cyanide
The invention discloses a stable electroplating solution which comprises an electroplating solution body; and the electroplating solution body is prepared from the following components: 15 to 30g / L of sodium stannate, 25 to 35g / L of sodium hydrogen phosphate, 40 to 60g / L of sodium nitrite, 25 to 40 g / L of potassium hydroxide, 15 to 25 g / L of potassium cyanide, 30 to 50 g / L of copper sulfate, 10 to 25 g / L of zinc oxide and 10 to 25 g / L of citric acid, and is obtained by adding a mixed solution of sodium stannate, sodium hydrogen phosphate and sodium nitrite into a mixed solution of potassium hydroxide, copper sulfate, potassium cyanide, zinc oxide and citric acid. Therefore, the stability of the electroplating solution can be improved; and as the components are mixed in batches, pre-reactions of the reaction liquids (components) are avoided in advance, and the temperature safety of the electroplating solution is improved.
Owner:无锡瑾宸表面处理有限公司
Composite sodium salt for producing sodium stannate from cassiterite concentrate and application of composite sodium salt
The invention discloses a composite sodium salt for producing sodium stannate from cassiterite concentrate and an application of the composite sodium salt. The composite sodium salt consists of 70%-90% of sodium carbonate, 5%-20% of sodium bicarbonate, 2.5%-5% of sodium borate and 2.5%-5% of sodium humate by mass. When the composite sodium salt is used, the composite sodium salt is ground to the particles with the size fraction of minus 0.1mm being no less than 90% by mass, the cassiterite concentrate of the fine fraction and the composite sodium salt are mixed according to the mass ratio of 1:(0.5-2), pelletized and dried, coke powder or anthracite is taken as a reducing agent, the mixture is calcined for 30 minutes-90minutes at the temperature of 800 DEG C-950 DEG C, and the cooled calcined product is ground, leached, filtered, purified, concentrated and crystallized, so that the sodium stannate product is obtained. The adopted composite sodium salt is reasonable in component, can be widely obtained, is low in price, is easy to obtain and does not cause pollution to the environment. With the composite sodium salt, the stable crystal structure of the cassiterite concentrate can be obviously damaged, and the composite sodium salt can be widely applied to various cassiterite concentrates so as to directly produce sodium stannate.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
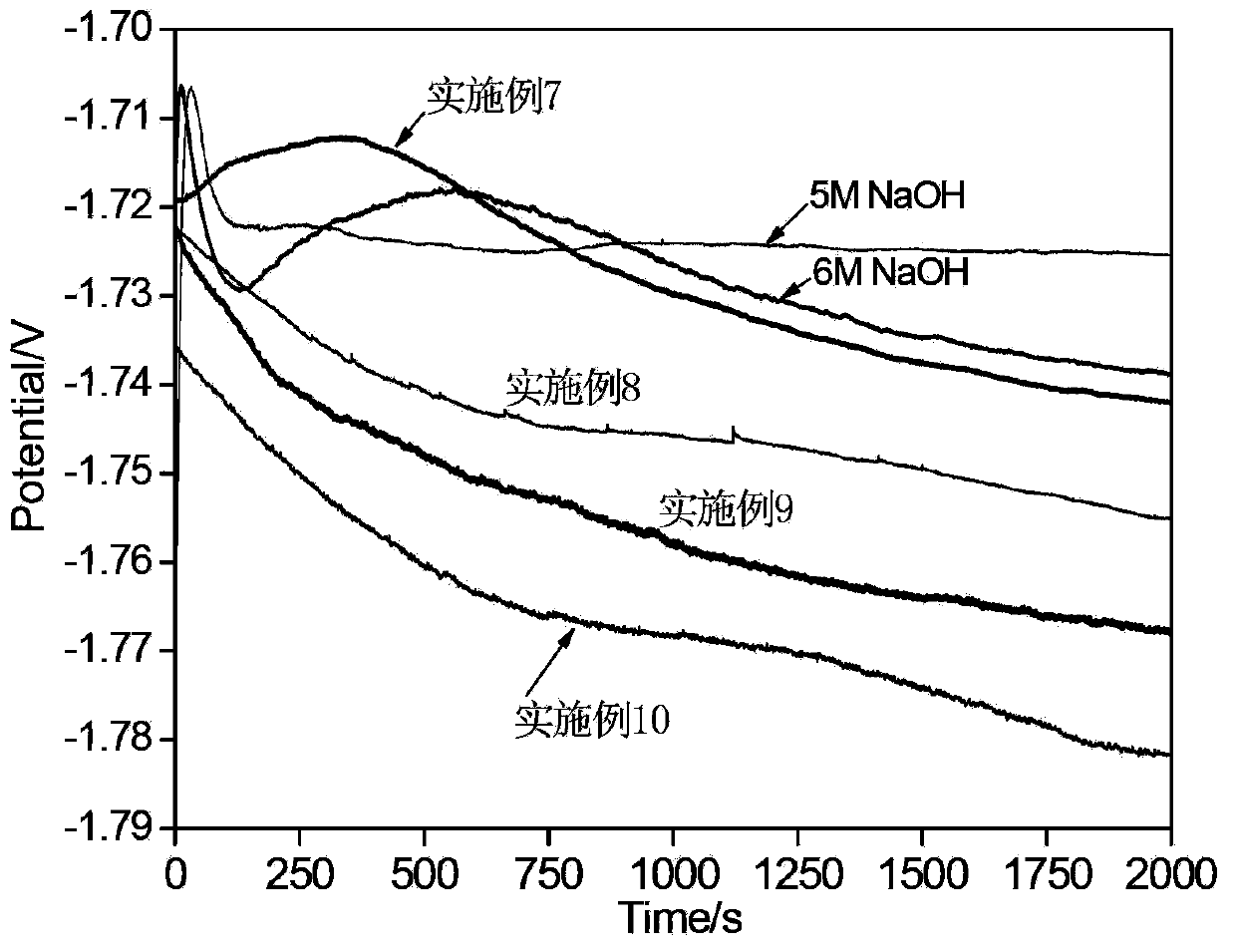
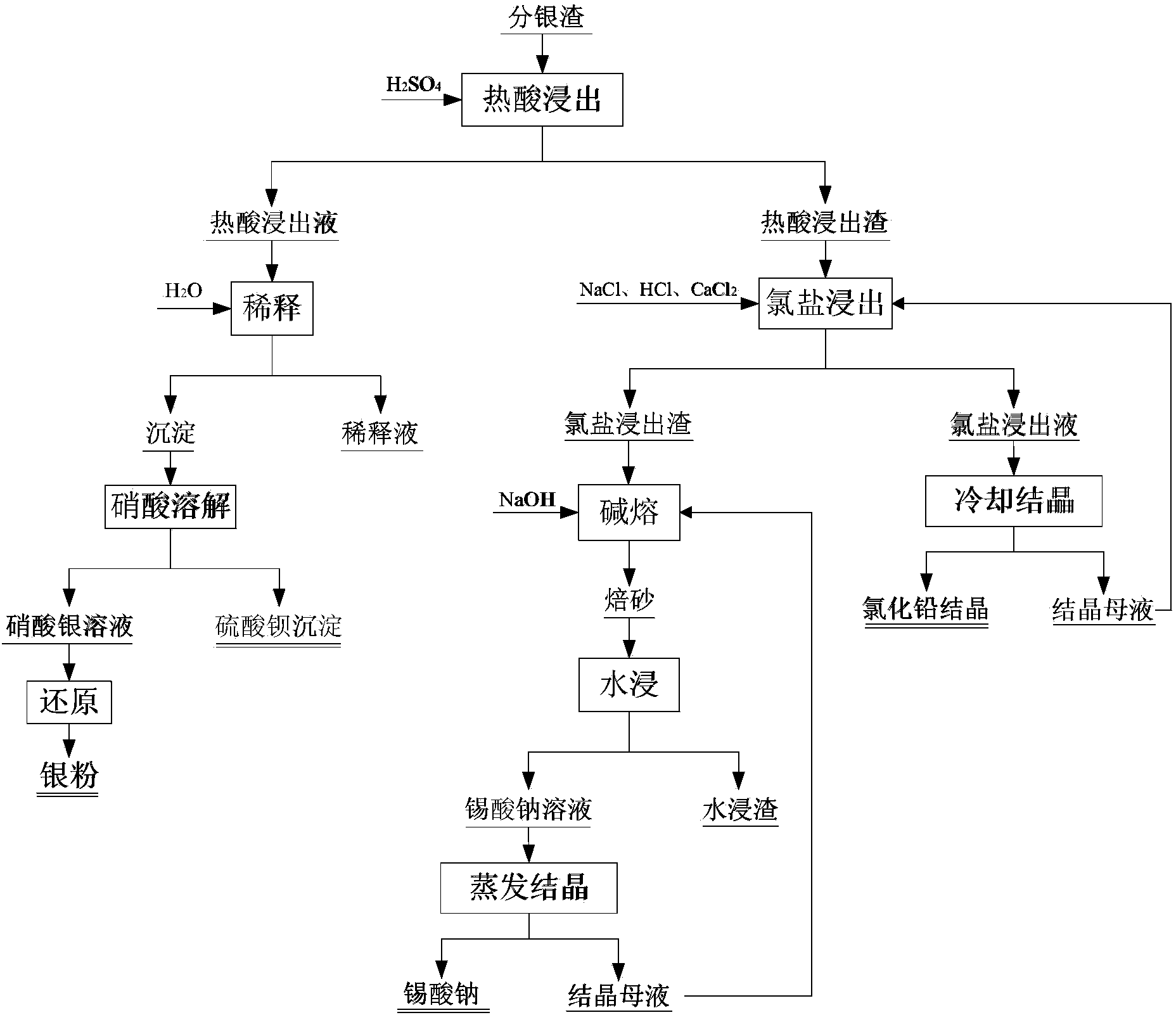
Method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from copper anode sludge silver separating slag
The invention relates to a copper anode sludge silver separating slag reutilization technique, particularly a method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from copper anode sludge silver separating slag. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out hot acid leaching on silver separating slag, filtering to obtain a hot acid leaching solution containing silver and barium and hot acid leaching slag containing tin and lead; diluting the hot acid leaching solution with water, filtering to obtain a precipitate, dissolving the precipitate with nitric acid, and filtering to obtain a barium sulfate precipitate and a silver nitrate solution; reducing the solution to obtain silver powder; leaching the hot acid leaching slag with acidic chlorine salt, filtering to obtain a chlorine salt leaching solution and chlorine salt leaching slag; cooling the chlorine salt leaching solution to crystallize and precipitate lead chloride; and carrying out alkali fusion, water immersion and evaporation crystallization on the chlorine salt leaching slag to obtain sodium stannate. The method can effectively recover all the valuable metals with higher content in the silver separating slag, and the recovery rates of the lead, silver, tin and barium are respectively up to higher than 97%, 92%, 90% and 95%. The method has the characteristics of simple technique, no emission of three wastes, high metal recovery rate and the like, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
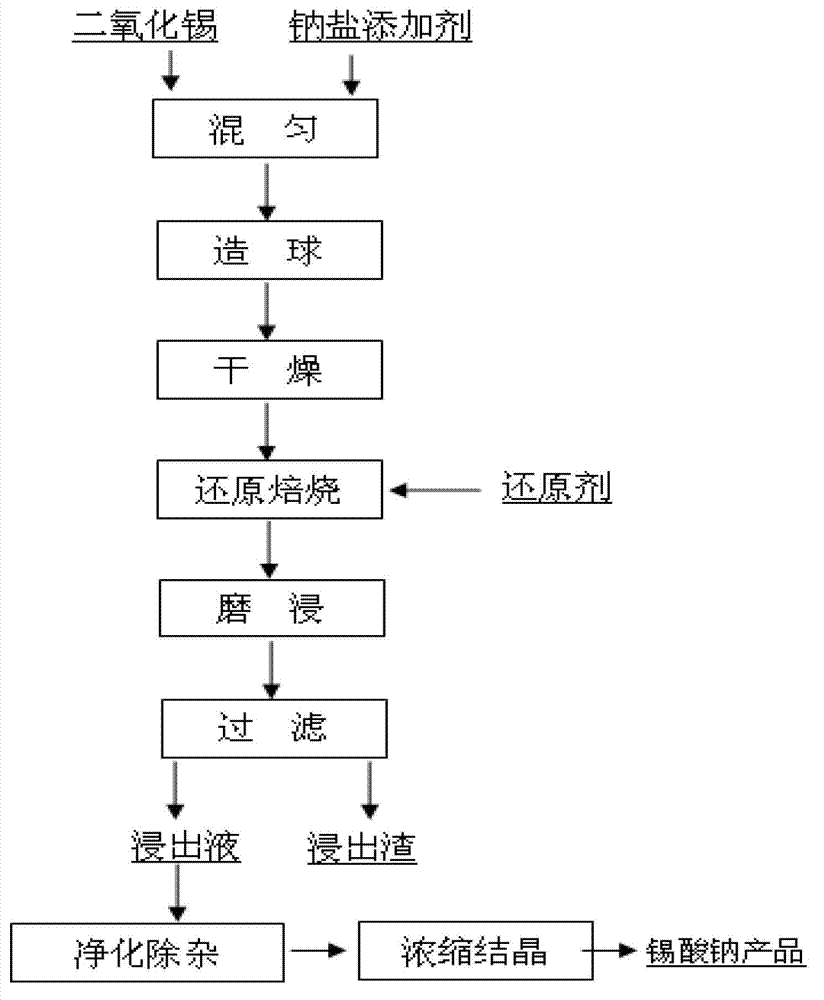
Method for preparing sodium stannate from stannic oxide and sodium salt in reduction roasting manner
The invention discloses a method for preparing sodium stannate from stannic oxide and sodium salt in a reduction roasting manner. The method comprises the following steps of firstly and respectively grinding stannic oxide and sodium salt additive to meet the following requirement that the mass percent of grinded stannic oxide and sodium salt additive with particle grade of -0.1mm is not less than 90%, and uniformly mixing grinded stannic oxide and sodium salt additive according to a mass ratio of 1:(0.8-1.6); blocking the mixture, drying and placing the mixture under reduction atmosphere to heat and roast, wherein coke powder or anthracite is served as a reduction agent, the roasting temperature is 800-950 DEG C, and the roasting time is 30-90min; and after cooling down the roasted blocks, sequentially carrying out treatments of grinding and soaking, filtering, purifying and impurity removing, and concentrating and crystallizing to obtain products of sodium stannate. Compared with the traditional sodium stannate preparation process, the method for preparing sodium stannate from stannic oxide and sodium salt in the reduction roasting manner, disclosed by the invention, has the characteristics of strong raw material suitability, high tin conversion rate, low cost, small investment, simple operation, environmental friendliness and the like; the whole reduction roasting process is carried out under a solid condition without special requirements in a roasting device; and the industrial production is easy to be realized.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing sodium stannate
InactiveCN102863015AReduce energy consumptionEasy to prepareTin compoundsPhysical chemistryPotassium hydroxide
The invention provides a method for preparing sodium stannate. According to the method, banca tin, hydrogen peroxide and potassium hydroxide which serve as raw materials are synthesized in one step to form the sodium stannate. The method comprises the following steps of: putting the banca tin and 10 to 40 percent sodium hydroxide solution into a reaction kettle, stirring, adding 5 to 30 percent hydrogen peroxide into the system, and reacting at the temperature of between 60 and 100 DEG C for 1 to 6 hours; and filtering, concentrating a filtrate under reduced pressure, filtering, and drying a filter cake to obtain the sodium stannate, wherein the yield of the sodium stannate is up to 99.5 percent. The method has the characteristics of simple preparation process, energy conservation, environment friendliness and the like and can be used for industrial production, the generation of harmful gases of ammonia gas and the like is avoided, and the sodium stannate is prepared at low temperature under normal pressure.
Owner:YUNNAN TIN
Vehicle engine fluid
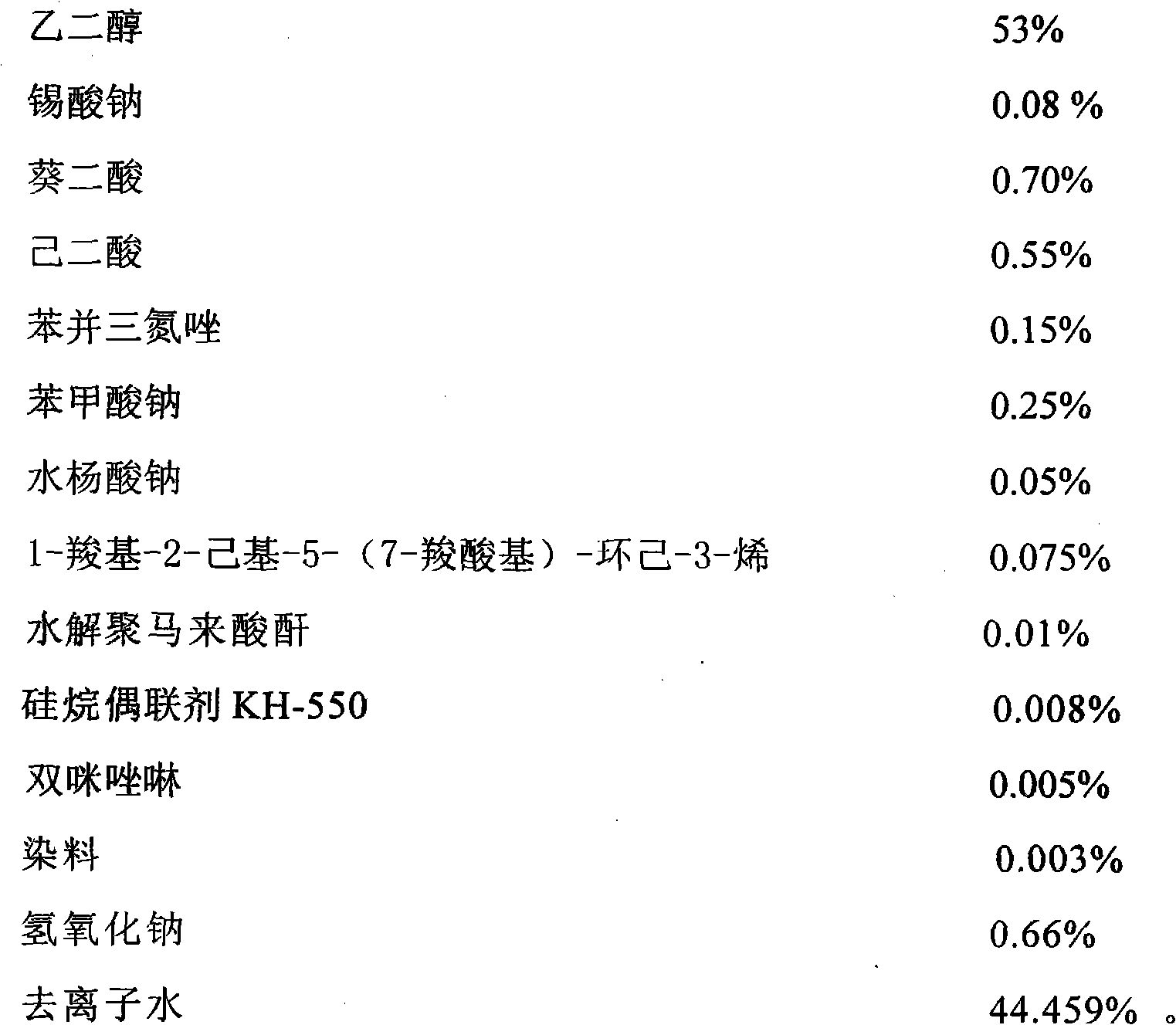
InactiveCN102093852AImprove thermal stabilityInhibition formationHeat-exchange elementsAdipic acidSebacic acid
The invention discloses a vehicle engine fluid, relating to an engine fluid for a vehicle engine cooling system. The vehicle engine fluid is composed of glycol, sodium stannate, sebacic acid, adipic acid, benzotriazole, sodium benzoate, sodium salicylate, 1-carboxyl-2-hexyl-5-(7-carboxyl)-hexamethylene-3-alkene, hydrolyzed polymaleic anhydride, silane coupling agent KH-550, bis-imidazoline, dye, sodium hydroxide, deionzied water and the like. The vehicle engine fluid has the advantages of good corrosion effect, stable property, excellent corrosion inhibition property, no precipitate and no toxicity, and is not easy to volatilize, can be well absorbed on the surface of metal so as to form an absorption film, and can effectively inhibit corrosion of an antifreeze solution on soldering tin; and the selected additive is cheap and available and has good economic benefits and social benefits, and the like. The vehicle engine fluid can be widely applied to a cooling system of a vehicle engine, especially is used as a vehicle antifreeze solution in a low-temperature region.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for separating tin, antimony, bismuth, arsenic and copper from tin electrolytic anode mud
InactiveCN102399989AImprove leaching rateEasy to recycleProcess efficiency improvementLiquid wasteTin dioxide
The invention provides a method for separating tin, antimony, bismuth, arsenic and copper from tin electrolytic anode mud. The method comprises the following steps of: grinding the tin electrolytic anode mud finely, mixing the tin electrolytic anode mud with an oxidizing agent, adding a NaOH solution, stirring the mixture at a certain temperature under certain pressure, and thus obtaining dissolved serous fluid; and filtering to obtain a sodium stannate solution, cooling naturally to room temperature, filtering, decomposing the obtained filtrate by introducing carbon dioxide or adding NaHCO3, filtering, and thus obtaining an alkali solution and stannic oxide. By the method, the problem of difficulty in separation of the tin and the antimony in the tin anode mud is solved, and other valuable metals in the tin anode mud can be subsequently recovered smoothly; compared with a method for processing the anode mud by an acid method, the method has the obvious advantage that: the discharging of waste liquid and waste gas is avoided in the process of utilizing the anode mud comprehensively; and the method has a short process, makes simple equipment used, is energy-saving and environment-friendly and is worthy of being applied and popularized.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
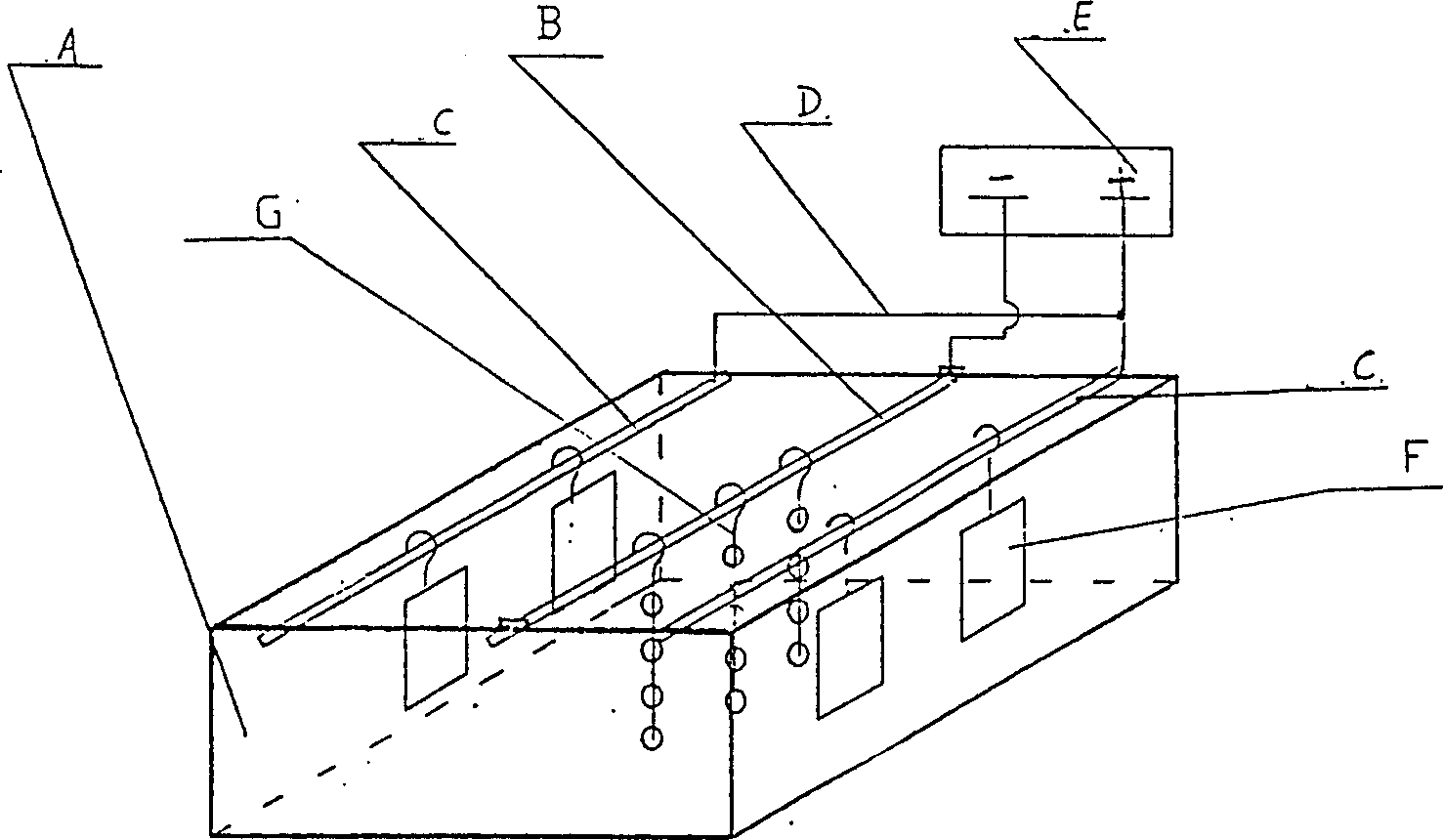
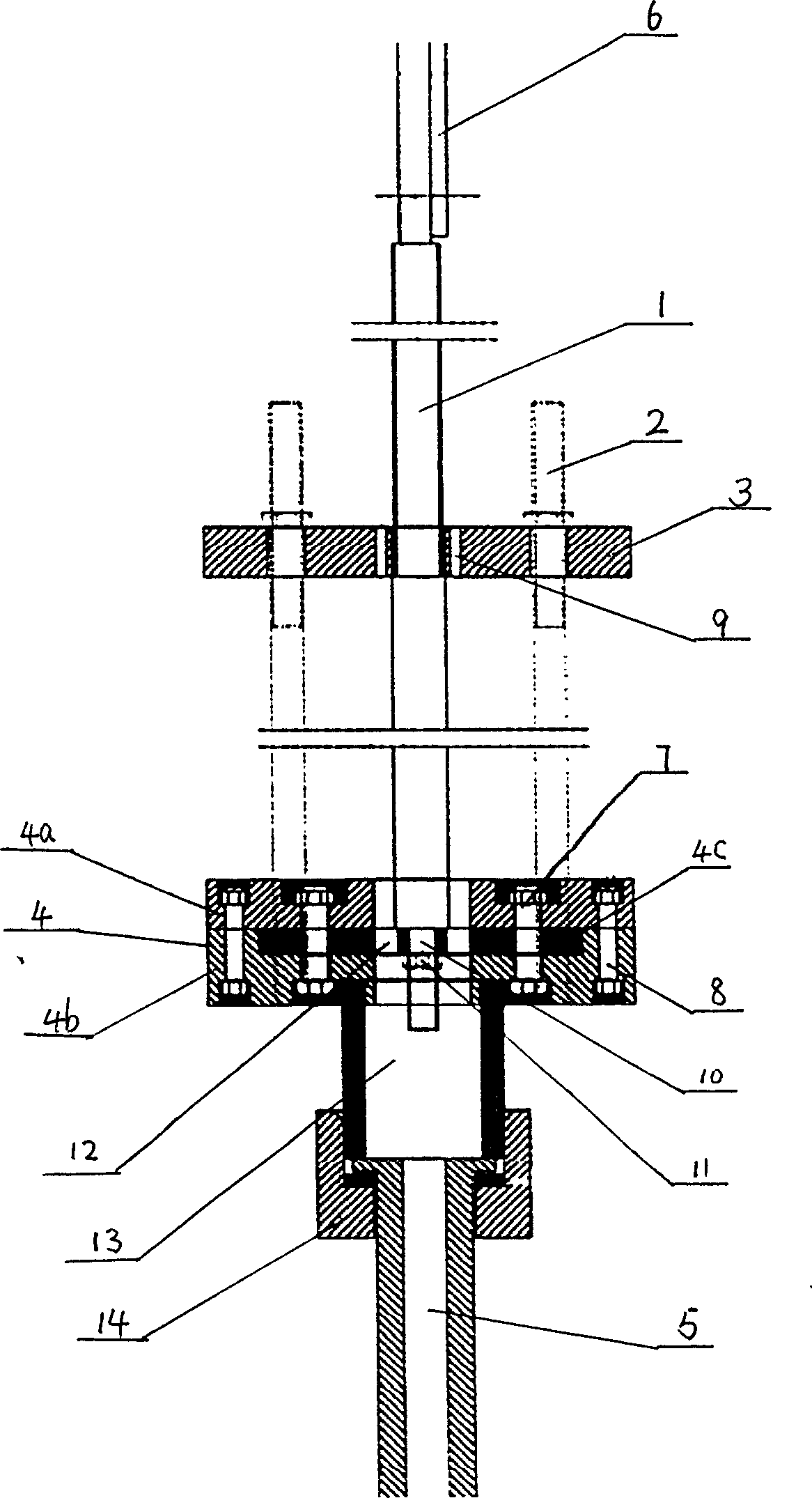
Technique method for electroplating inner surfaces of gear wheel holes and dedicated equipments
A technology and special apparatus for electroplating the inner surface of gear hole is disclosed. The said technology features use of bipolar electroplating method. Its electroplating liquid contains cuprous cyanide, sodium stannate, sodium cyanide and sodium hydroxide. A central anode rod of said special apparatus passes through several gears to hange them in the electroplating liquid for electroplating them after DC is applied across anode and cathode. Its advantages are uniform plated layer and high productivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Preparation method of submicron hydroxy zinc stannate cubic material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a submicron hydroxy zinc stannate cube, the size of which is 100-300 nanometers. According to the preparation method, raw materials, including cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide, n hexanol, cyclohexane and deionized water, are selected to form a microemulsion; the microemulsion reacts with zinc sulfate and sodium stannate which are used as reactants to respectively prepare a microemulsion containing zinc sulfate and a microemulsion containing sodium stannate; the two microemulsions are mixed to react and undergo aging, centrifugation, washing and drying so as to obtain submicron hydroxy zinc stannate cubic particles, which can be used as photocatalysis, gas-sensitive and flame retardation materials and the like. The method can be adopted to synthesize the size-controllable hydroxy zinc stannate cubic material at room temperature. The production technology is simple, requires low cost and causes no environmental pollution.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for co-producing sodium stannate and stannic oxide by solder removing liquid
The invention discloses a method for co-producing sodium stannate and stannic oxide by solder removing liquid, comprising the following steps: separating tin in the solder removing liquid, recovering copper, transforming copper into sodium stannate, preparing sodium stannate and preparing stannic oxide. The method of the invention features in low processing cost, simple technical process and device structure, and high product purity and can prepare sodium stannate and stannic oxide.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
Method for recycling valuable metal in waste circuit board
The invention discloses a method for recycling valuable metal in a waste circuit board. The method includes the following steps that the waste circuit board is subject to smashing and reselection to prepare multi-metal powder; a dilute acid solution is added into the multi-metal powder, agitation leaching is carried out, filtering is carried out, and leaching slag I and leaching liquid I are obtained; an acid solution is added into the leaching slag I according to the liquid-solid mass ratio of the acid solution to the leaching slag I being 10-40:1, then an oxidizing agent is added, agitation leaching is carried out, filtering is carried out after leaching is finished, and leaching slag II and leaching liquid II are obtained; the leaching liquid II is subject to cyclone electrodeposition to obtain cathode copper and an after-electrolysis solution; alkali and a reducing agent are added into the leaching slag II, smelting is carried out under the condition that the temperature ranges from 400 DEG C to 600 DEG C, water leaching is carried out, filtering is carried out, and lead bullion containing precious metal and leaching liquid III are obtained; and the leaching liquid III is purified and is subject to evaporation and concentration to obtain a concentrated alkali solution and sodium stannate crystals. According to the method for recycling the valuable metal in the waste circuit board, the procedure is short, the efficiency is high, the cost is low, cleanness is achieved, and pollution is avoided.
Owner:广西自贸区西江资源循环科技产业股份有限公司
Method of recycling silver-containing soldering tin slag
ActiveCN104046784AEfficient separationEfficient enrichmentProcess efficiency improvementSlagEconomic benefits
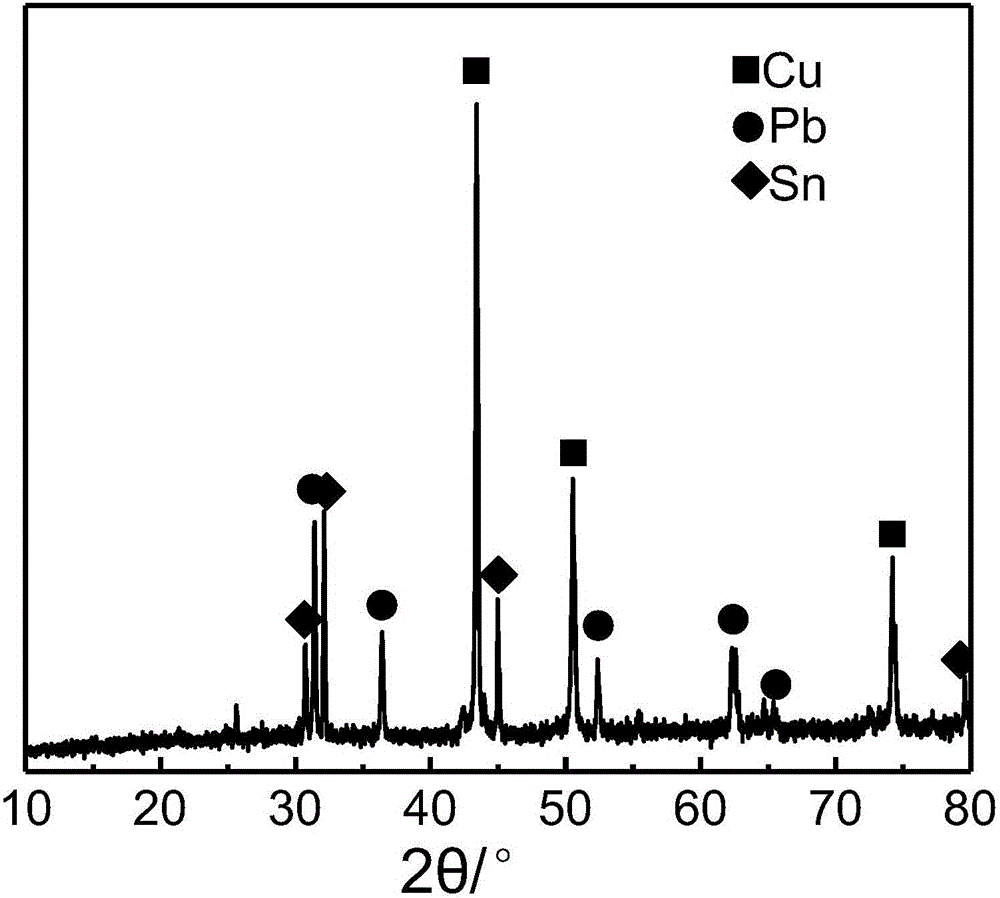
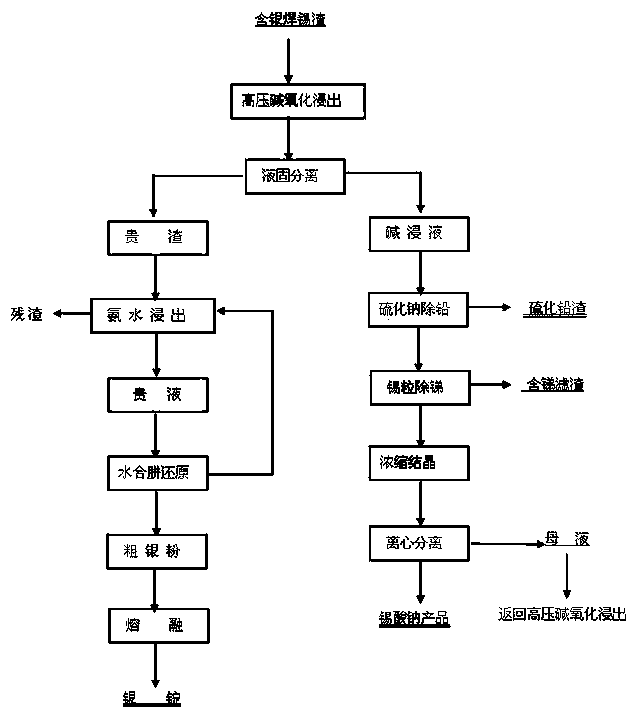
The invention relates to a method of recycling silver-containing soldering tin slag and belongs to the technical field of metallurgy and chemical engineering. The method comprises the steps of carrying out high pressure alkaline oxidation leaching and solid-liquid separation, purifying to remove impurities, concentrating and crystallizing, separating silver from expensive slag and the like. Due to the adoption of the method, industrial-grade sodium stannate, lead slag sulfide and silver ingot products are respectively recovered and the method has the advantages of high metal recovery rate, good economic benefits, no secondary pollution and the like.
Owner:YANGZHOU NINGDA NOBLE METAL CO LTD
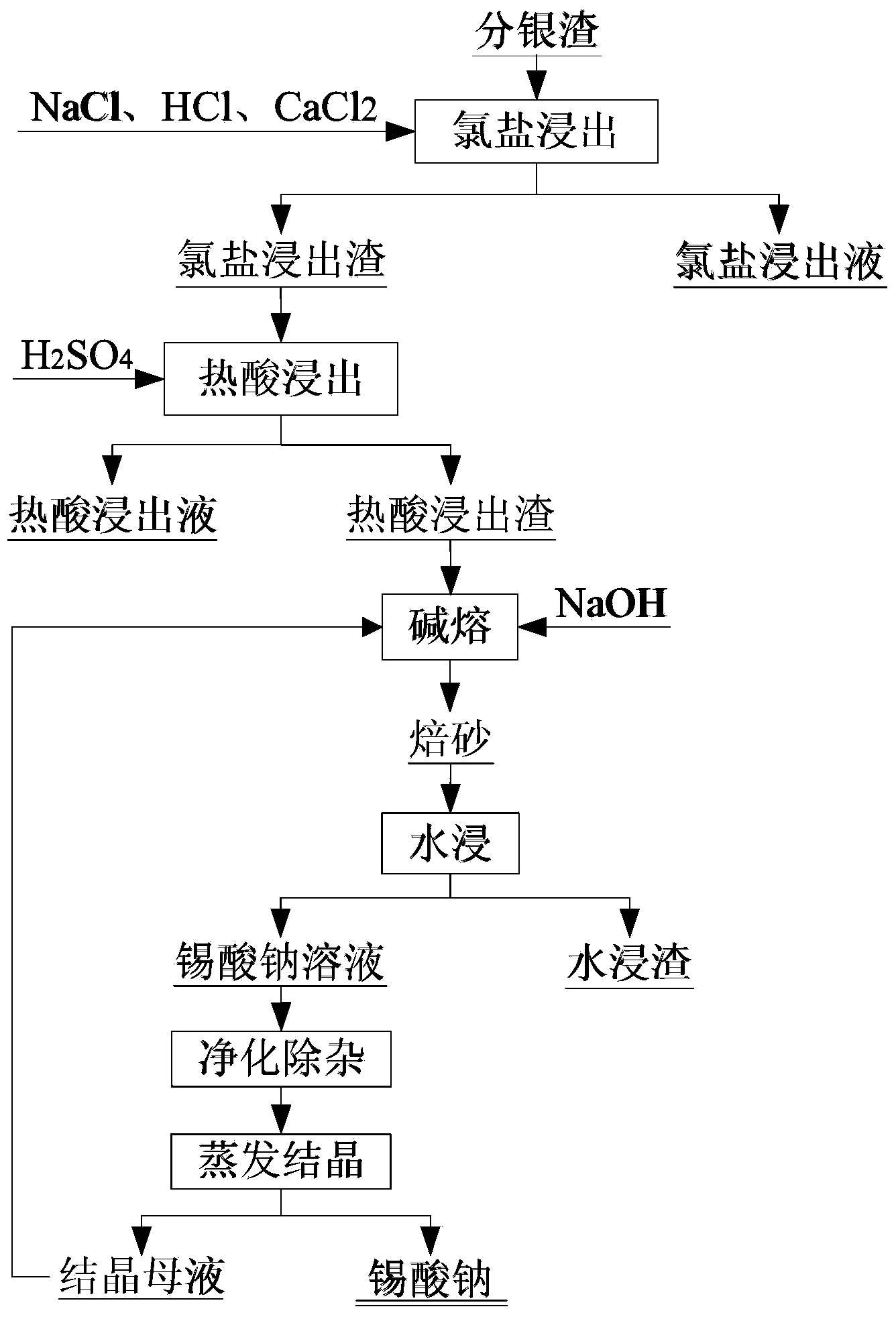
Method for preparing sodium stannate from copper anode mud silver separation residue
InactiveCN103966451AIncrease contentHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementCopperCopper anode
The invention relates to a copper anode mud silver separation residue reuse technique, and in particular relates to a method for preparing sodium stannate from copper anode mud silver separation residues. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, leaching the silver separation residues in an acid chlorine salt system so as to leach out lead and silver and feeding lead and silver into a liquid, retaining metals such as tin and barium in the residues, further performing thermal acid leaching on the filtered chlorine salt leaching residues, leaching out barium and feeding into a thermal acid leaching liquid, and retaining tin in thermal acid leaching residues; further performing alkali fusion and water leaching on the thermal acid leaching residues to obtain a sodium stannate solution and water leaching residues; and purifying the sodium stannate solution to remove residual impurities such as lead, copper and antimony, and subsequently performing evaporative crystallization to obtain a sodium stannate product. By adopting the method, tin in the copper anode mud silver separation residues can be effectively opened and recycled to prepare a qualified sodium stannate product, the tin recycling rate is greater than 90%, and the method has the characteristics of short process route, simple equipment, high recycling rate and the like, and is particularly applicable to preparation of sodium stannate from copper anode mud silver separation residues obtained in the copper sulphide ore or scrap copper production process.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
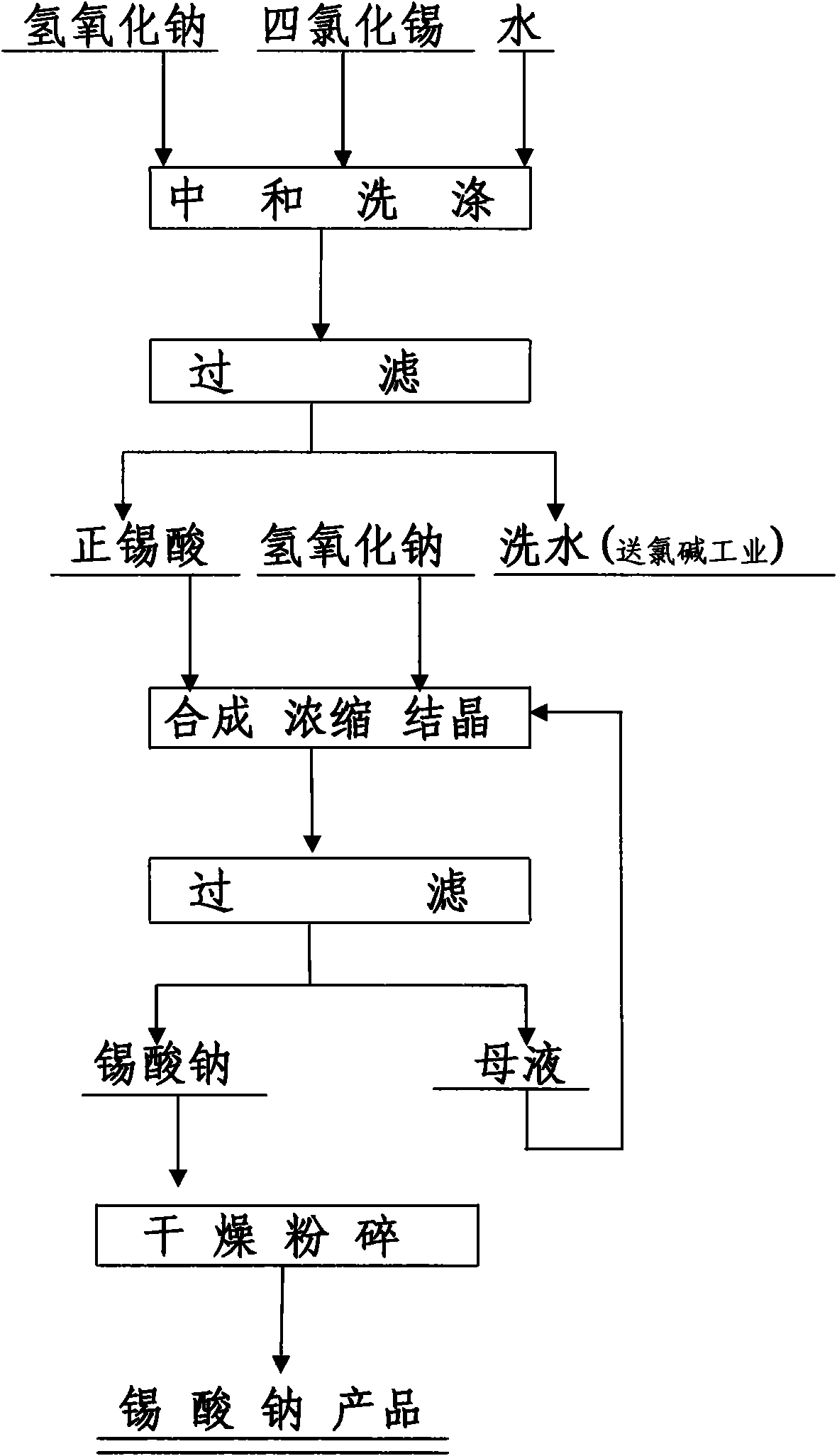
Method for producing sodium stannate
The invention belongs to a technique for producing inorganic compound sodium stannate, and more particularly relates to a method for preparing the sodium stannate by adopting stannic chloride. The technique comprises the steps: (1) neutralizing stannic chloride by alkali, obtaining precipitate and washing by water, solid-liquid separation, and obtaining stannic acid; (2) synthesizing the sodium stannate by using the stannic acid and sodium hydroxide, concentrating, crystallizing, filtering, drying and crushing the sodium stannate, and obtaining the product of sodium stannate. The method has easy operation and complete reaction of all steps, simplifies the process flow, can improve the direct recovery rate of tin, and reduces the production cost, thus being capable of producing the sodium stannate in industrialized scale.
Owner:YUNNAN TIN GROUP HLDG
Cyanide-free and nickel-free electroplating method for copper-tin alloy
InactiveCN104674314AReduce poisonHelp the marketLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSuperimposed coating processCopper platingCyanide
The invention discloses a cyanide-free and nickel-free electroplating method for a copper-tin alloy. The method comprises the following steps: sequentially performing chemical copper plating, cyanide-free copper electroplating, sulfate copper electroplating, cyanide-free copper-tin alloy electroplating and lead-free chromium electroplating on a base material, wherein the electroplating solution of cyanide-free copper electroplating comprises 10-20g / l copper pyrophosphate and 230-280g / l sodium pyrophosphate; the electroplating solution of cyanide-free copper-tin alloy electroplating comprises 240-280g / l potassium pyrophosphate, 12-17g / l copper pyrophosphate and 10-20g / l sodium stannate; and the electroplating solution of lead-free chromium electroplating comprises 20-24g / l trivalent chromium and 65-85g / l boric acid. The electroplated parts are subjected to non-phosphorus oil removal, chemical copper plating, cyanide-free copper preplating, sulfate copper plating, cyanide-free copper-tin alloy plating and lead-free chromium plating, the requirement of constructing environment protection industry and intensive economy in China is met, cancerogenic substances are not contained in production, and the environmental pollution is further reduced.
Owner:温兵
Dressing-metallurgy combined treatment method for waste printed circuit board multi-metal powder
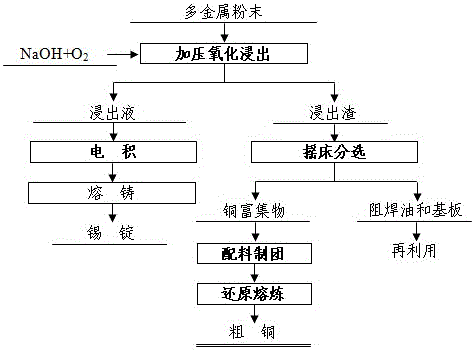
ActiveCN106381391AEfficient removalAvoid pollutionProcess efficiency improvementSmelting processOxygen
The invention provides a dressing-metallurgy combined treatment method for waste printed circuit board multi-metal powder. According to the dressing-metallurgy combined treatment method for the waste printed circuit board multi-metal powder, oxidizing leaching of the multi-metal powder is conducted in an alkaline system containing a catalyst through feeding of oxygen, tin is dissolved into a leaching solution in a sodium stannate form, and meanwhile copper is separated from a residual plastic matrix; a copper-enriched object and waste plastic are generated from the leaching solution in a shaking table separation manner, and the copper-enriched object generates crude copper through reduction smelting after material blending. The essence of the dressing-metallurgy combined treatment method for the waste printed circuit board multi-metal powder is that the waste printed circuit board multi-metal powder is treated in a chemical dressing and thermometallurgy combined manner. It is effectively avoided that the tin is reduced and mixed with the crude copper, the environmental pollution problem caused in the smelting process of the waste plastic is eliminated, and the environmental pollution caused in the process of recycling the copper from the multi-metal powder is completely eradicated through the source treatment measure.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
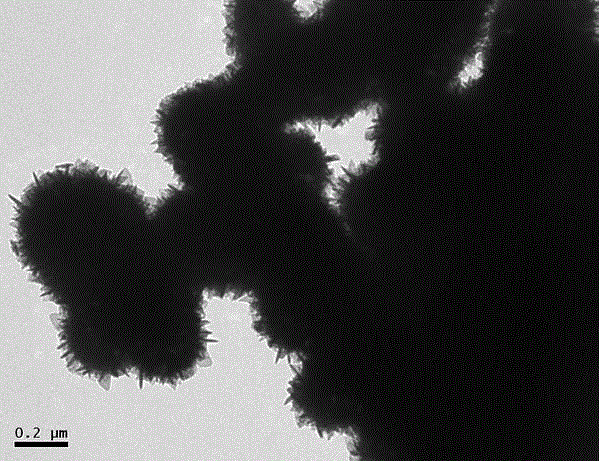
Preparation method of tin dioxide self-assembly nanostructure microsphere
The invention discloses a preparation method of a tin dioxide self-assembly nanostructure microsphere, belonging to the preparation method of inorganic advanced nanometer materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: a, adding sodium stannate trihydrate and surfactant to a mixed solvent of alcohol and water, and then adding ethanolamine, wherein the mol ratio of the sodium stannate trihydrate to the surfactant is 1:2-1:3, the volume ratio of the alcohol to the water in the mixed solvent is 1:3.5-3:1, the amount of the added ethanolamine is 2-5ml in each 1mmol sodium stannate trihydrate; b, mixing the solvent and the solute at the step a by using a glass bar to obtain a uniformly distributed mixed solution; c, arranging the obtained mixed solution of the step b into areaction kettle to carry out the hydrothermal reaction for 1-48h at 140-200 DEG C, and then naturally cooling to the room temperature after the reaction is finished; and d, centrifugally washing the obtained precipitation of the step c with water and anhydrous alcohol to obtain the tin dioxide self-assembly nanostructure microsphere. In the preparation method, the synthesis is carried out under the condition of solvent heat, the method is simple; and the tin dioxide self-assembly nanostructure microsphere has the advantages of low cost, even structure, uniform size distribution, universality and controllability, and also provides wide application prospect for gas sensitive devices.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for preparing molybdenum disulfide/stannic sulfide composite material of hollow structure
InactiveCN108807878AReduce stackingHigh magnificationCell electrodesSecondary cellsSodium-ion batteryLithium-ion battery
The invention relates to a method for preparing a molybdenum disulfide / stannic sulfide composite material of a hollow structure. The method comprises the following steps: dispersing sodium molybdate,sodium stannate, thioacetamide and a silicon dioxide template into water and ethanol, carrying out uniform ultrasonic mixing, carrying out a hydrothermal reaction in a polytetrafluoroethylene reactionkettle so as to obtain a molybdenum disulfide-stannic sulfide composite material with a template, and finally etching with hydrofluoric acid so as to remove the template, thereby obtaining the molybdenum disulfide / stannic sulfide composite material of the hollow structure. The molybdenum disulfide / stannic sulfide composite material of the hollow structure, which is prepared by using the method, has good reaction activity, has a synergistic effect in an electrode reaction, can be used as an electrode material and applied to lithium ion batteries and sodium ion batteries, is capable of greatlyimproving rate capability and circulation stability of the batteries, has the potential of being an excellent energy storage material and can be widely applied to lithium ion batteries and sodium ionbatteries.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Chemical mineral dressing pretreatment method for waste printed circuit board multi-metal powder
ActiveCN106381392AEfficient removalAvoid pollutionProcess efficiency improvementWet separationPretreatment methodControl manner
The invention provides a chemical mineral dressing pretreatment method for waste printed circuit board multi-metal powder. According to the chemical mineral dressing pretreatment method for the waste printed circuit board multi-metal powder, oxidizing leaching of the waste printed circuit board multi-metal powder is conducted in an alkaline system containing a catalyst through feeding of oxygen, tin is dissolved into a leaching solution in a sodium stannate form, copper is separated from a residual plastic matrix at the same time, and the tin is recycled from the leaching solution through an electro-deposition method; and a copper-enriched object and waste plastic are generated from leaching residues in a shaking table separation manner, and the waste plastic is oxidized and dissolved in a sulfuric acid solution in a potential-controlled manner, so that copper mixed with the waste plastic is completely dissolved. The essence of the chemical mineral dressing pretreatment method for the waste printed circuit board multi-metal powder is that the waste printed circuit board multi-metal powder is treated in the chemical mineral dressing manner combining alkaline pressurized oxidation leaching and shaking table separation, effective removal of the tin and the plastic in the multi-metal powder is achieved at the same time, and high-quality raw materials are provided for following-up recycling of copper. The content of the plastic in the copper-enriched object is smaller than 0.1%, and the environmental pollution caused in the following-up copper recycling process is completely eradicated through the source treatment measure. The content of the copper in the waste plastic is smaller than 0.1%, and dispersed loss of heavy metal and secondary pollution are avoided.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Hydrothermal synthesis method of tin dioxide nano material
InactiveCN103332726ALarge specific surface areaUniform shapeMaterial nanotechnologyTin oxidesTin dioxideGas detector
The invention relates to a hydrothermal synthesis method of a tin dioxide nano material, belonging to the technical field of inorganic chemistry and material synthesis. The hydrothermal synthesis method is characterized by comprising the following step of: with stannous sulfate (SnSO4) as a tin source and water as a solvent, preparing the tin dioxide nano material with flower-like characteristic and uniform morphology through a simple hydrothermal process under the auxiliary crystallization action of small molecular alkali tetrapropylammonium hydroxide (TPAOH), wherein the tin source of the raw materials can be stannous chloride (SnCl2), sodium stannate (Na2SnO3) or the like and the SnO2 nano material with uniform morphology can be obtained by using the tin source. The method has the advantages of simpleness in operation, controllable conditions, easiness in obtainment of the raw materials, no addition of organic solvents in the reaction process, large specific surface area of the prepared material, uniform morphology, good crystallinity and the like and has wider application prospects in the fields such as lithium batteries, gas sensors, photocatalysis, solar cells and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Glass powder, preparation method of glass powder, conductive silver slurry and preparation method of conductive silver slurry
ActiveCN102674696AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyEasy to prepareNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialCable/conductor manufactureSilver pasteBismuth telluride
The invention provides glass powder which contains 5-30% of sodium stannate, 1-20% of sodium metaborate, 1-20% of sodium silicate and 40-70% of bismuth telluride by mass. The glass powder overcomes the traditional shortcomings, does not require processes such as high temperature melting and quenching and can be obtained by simply directly mixing components evenly. A preparation method of the glass powder is simple, and the glass powder is excellent in performance. Conductive silver slurry is further provided. The conductive silver slurry contains 65-90% of the glass powder, 1-10% of sliver powder and 5-30% of organic carrier by mass.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
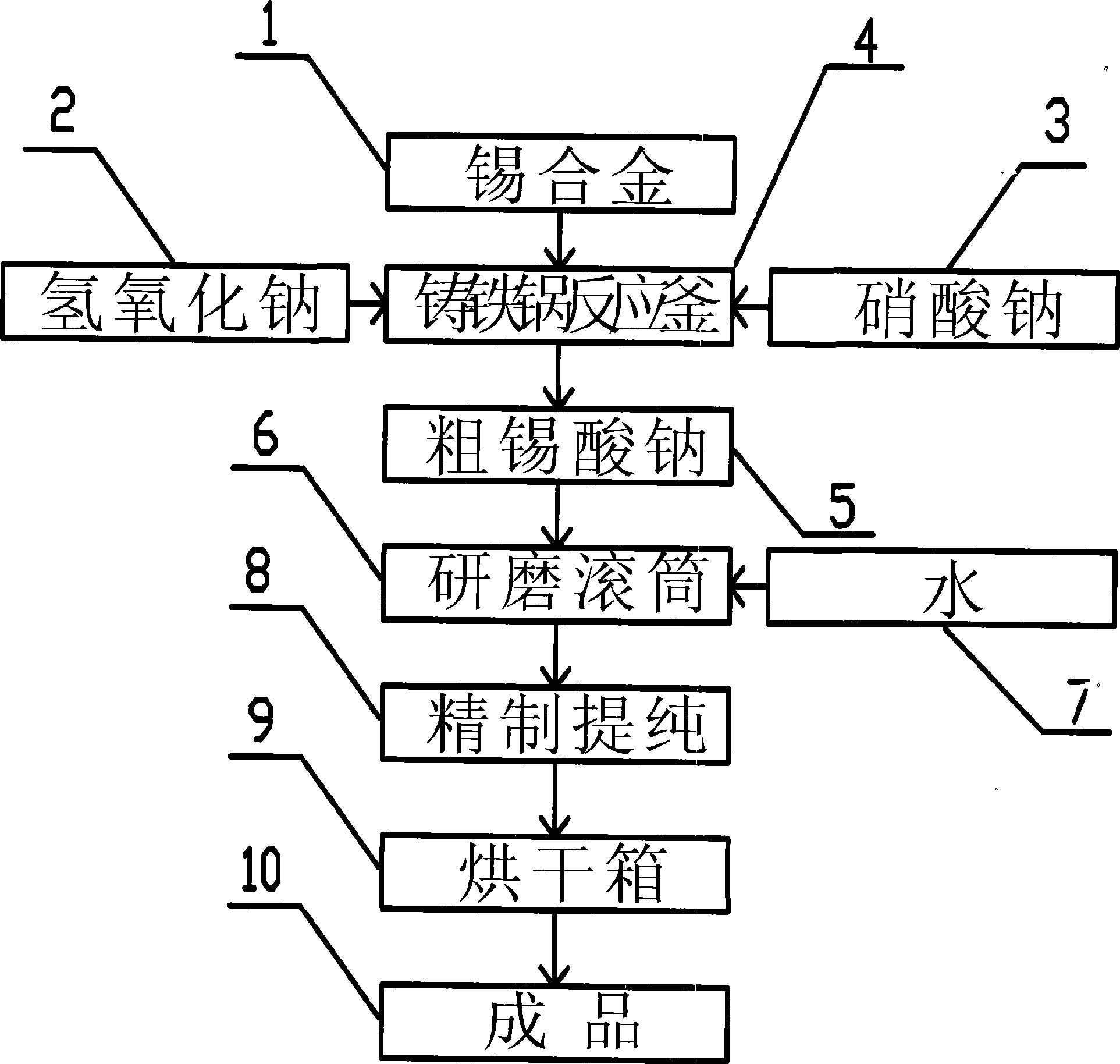
Method for producing sodium stannate by using tin and tin alloy
The invention discloses a method for producing sodium stannate by using tin and tin alloy, which comprises the following steps: (1) the tin and the tin alloy have chemical reaction with sodium hydroxide and oxidizer at a temperature of between 300 and 550 DEG C to obtain granular coarse sodium stannate; the reaction course comprises that the sodium hydroxide and the oxidizer are added to molten tin and tin alloy step by step until the reaction is completely finished; (2) the granular coarse sodium stannate is dissolved in water; (3) the solution is purified finely; and (4) the fully purified sodium stannate solution is condensed, separated and dried to obtain finished products. The method is used for producing the sodium stannate by using the tin and the tin alloy.
Owner:上饶旭日冶炼厂
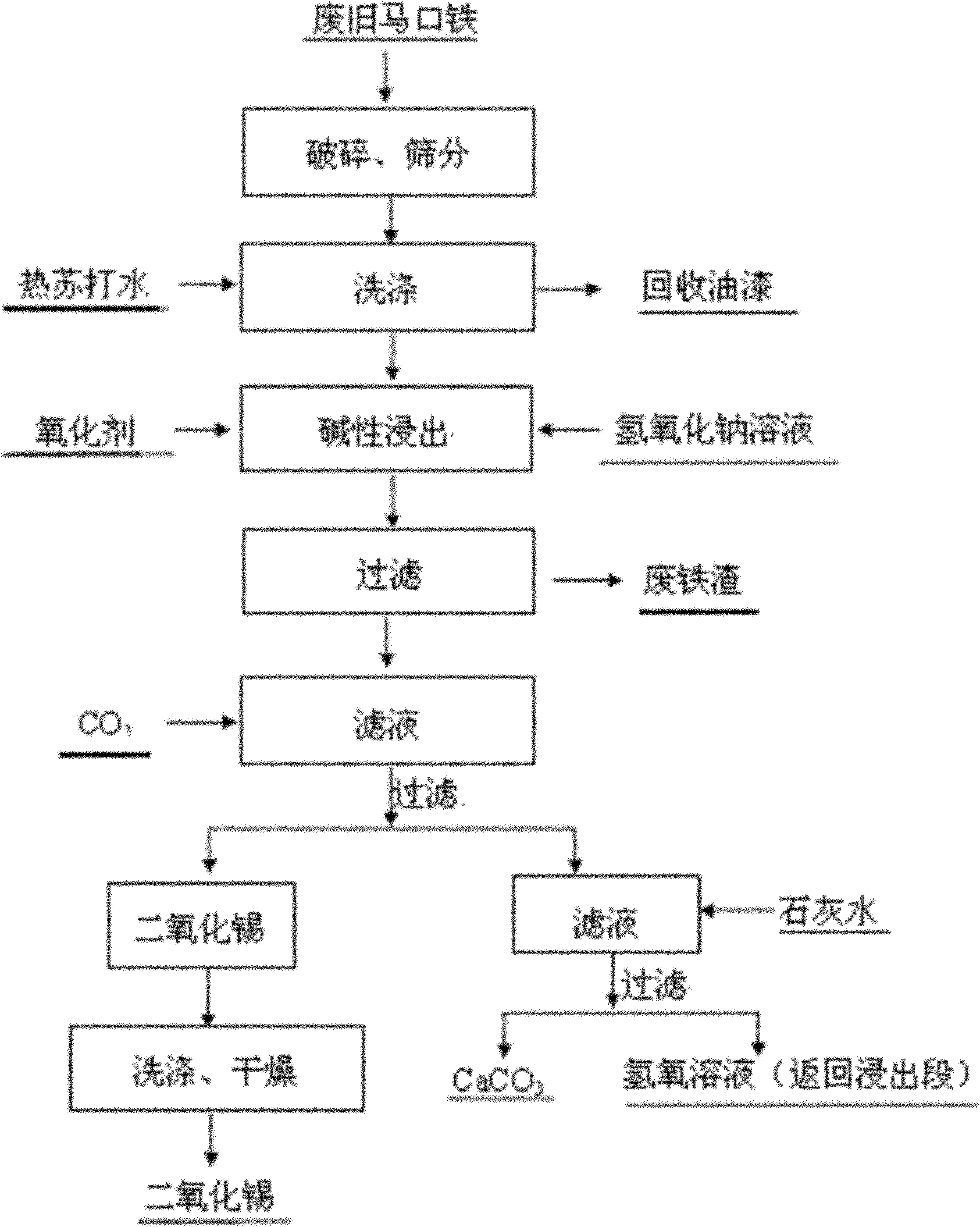
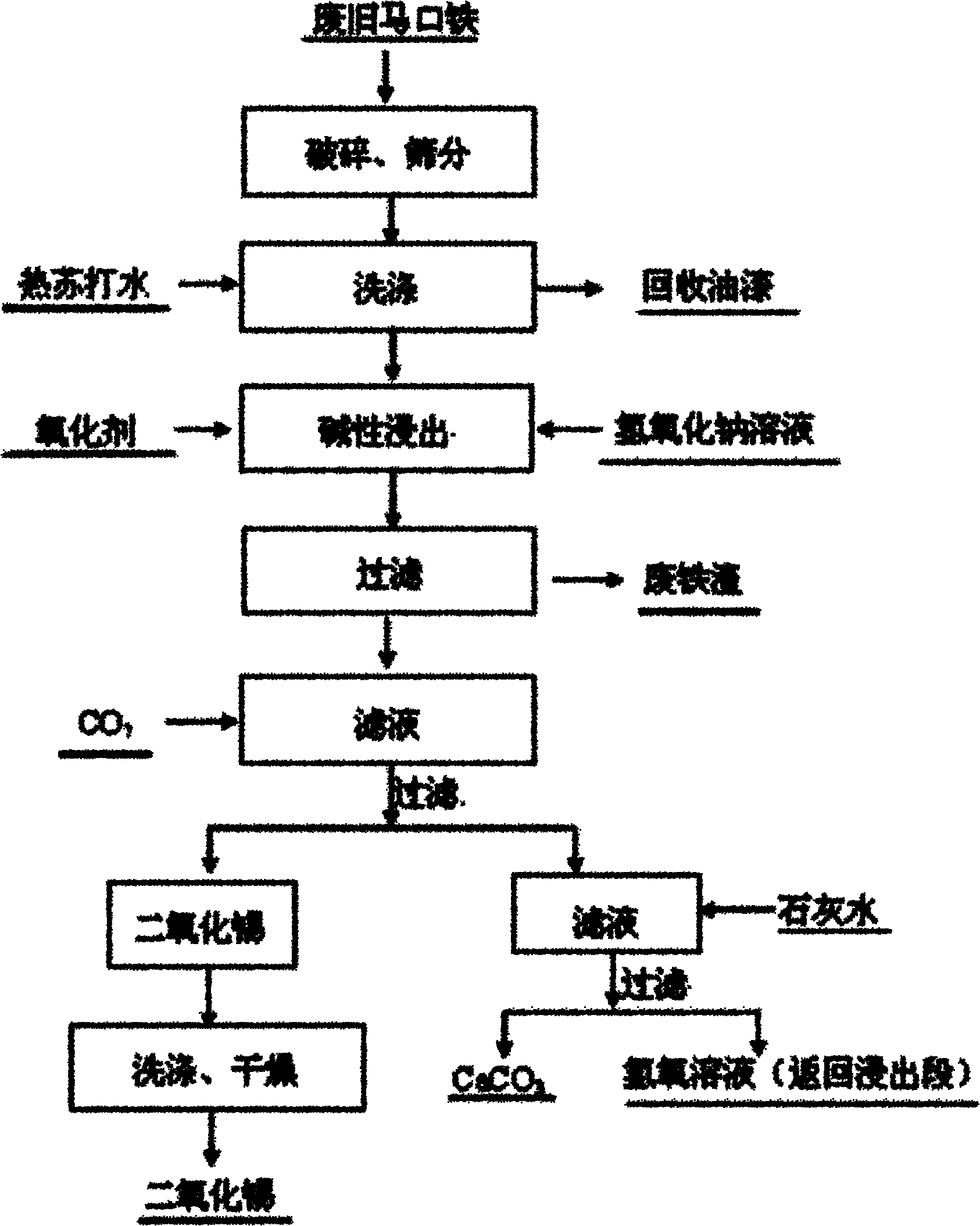
Method for separating tin from waste tinplate and preparing tin dioxide
ActiveCN102102150ASimple preparation processLow costProcess efficiency improvementTin dioxideMarket competition
The invention discloses a method for separating tin from waste tinplate and preparing tin dioxide. The method comprises the following steps: (1) grinding waste tinplate, screening; (2) washing the screen underflow with soda water; (3) filtering the washed material, leaching filter residue with sodium hydroxide solution and oxidant, filtering the leachate, wherein the filtrate is sodium stannate solution; and (4) introducing carbon dioxide in the sodium stannate solution, filtering, and washing to obtain the tin dioxide product. The preparation method of the invention has low cost and pollution and remarkable economic value and market competition.
Owner:GUANGDONG BRUNP RECYCLING TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com