Hydrothermal synthesis method of tin dioxide nano material
A nanomaterial, tin dioxide technology, applied in tin oxide, nanotechnology, nanotechnology and other directions, can solve the problems of uneven structure and performance, and achieve the effect of low cost, uniform morphology and high specific surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] 1. Weigh 5 mmol of stannous sulfate (SnSO 4 ), add it into 60 ml deionized water, mix well, and stir at room temperature for 30 min;
[0020] 2. Weigh 1 mmol tetrapropylammonium hydroxide (TPAOH) with an electronic balance and add it to 40 ml deionized water, mix well, and stir at room temperature for 30 min. Add this solution dropwise to the above solution, then put it in a water bath at 80 °C, and stir it magnetically for 4 h;
[0021] 3. Pour the above mixed solution into a 100 ml autoclave lined with polytetrafluoroethylene, and crystallize at 180 °C for 24 h;
[0022] 4. After the reaction is completed, the product is taken out from the reactor, and through conventional steps such as centrifugation, washing, drying, and roasting, the tin dioxide nanomaterial of the multi-level structure prepared by the present invention is obtained.
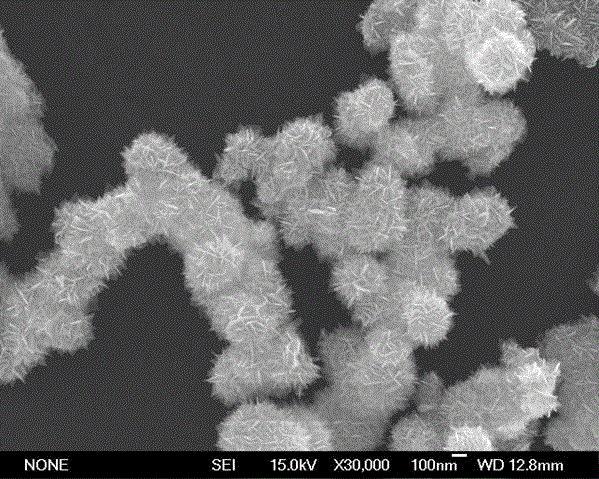
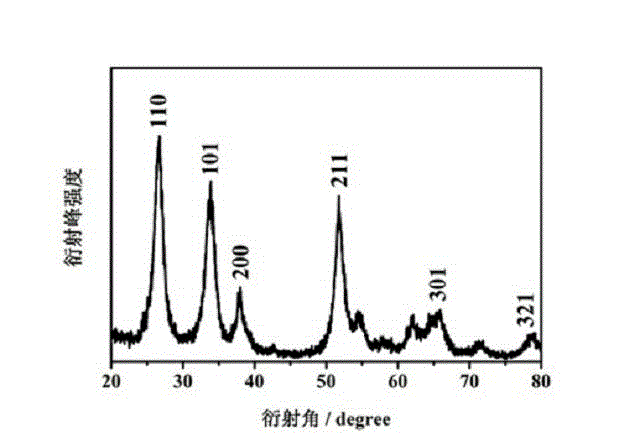
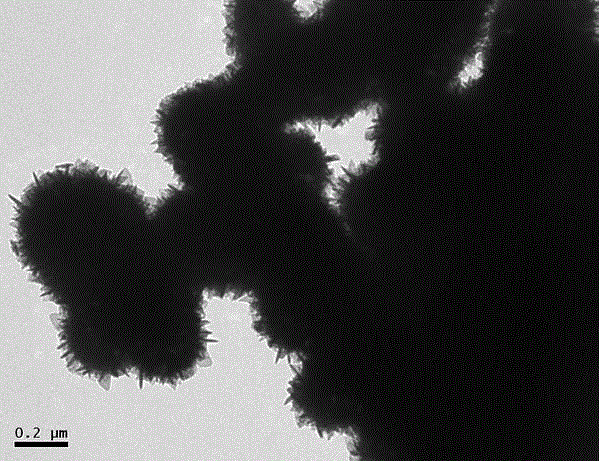
[0023] The prepared samples were characterized for their physical properties, and some of the results are shown in...
Embodiment 2
[0025] The implementation process is the same as in Example 1 except for the following differences.
[0026] 1. Weigh 2.5 mmol of stannous sulfate with an electronic balance, and add it into a mixed solution of water and ethanol with a total volume of 60 ml (wherein V H2O / V ethanol =1:1), stirring at room temperature for 30 min;
[0027] 2. Use an electronic balance to weigh 0.5 mmol tetrapropylammonium hydroxide (TPAOH) and add it to a mixed solution of water and ethanol with a total volume of 40 ml (wherein V H2O / V ethanol =1:1), stirred at room temperature for 30 min. Add this solution dropwise to the above solution, then put it in a water bath at 80 °C, and stir it magnetically for 4 h;
[0028] 3. Pour the above mixed solution into a 100 ml autoclave lined with polytetrafluoroethylene, and crystallize at 170 °C for 30 h.
[0029] Obtained result has obvious difference with embodiment 1, and the obtained SnO 2 It is a solid spherical structure, some agglomerated,...
Embodiment 3
[0031] The implementation process is the same as in Example 1 except for the following differences.
[0032] 1. Weigh 5 mmol of stannous chloride with an electronic balance, add it to 60 ml of deionized water, mix well, and stir at room temperature for 30 min.
[0033] 2. Weigh 1.5 mmol tetrapropylammonium hydroxide (TPAOH) with an electronic balance and add it to 40 ml deionized water, mix well, and stir at room temperature for 30 min. This solution was added dropwise to the above solution, and then it was placed in a water bath at 80 °C and stirred magnetically for 6 h.
[0034] The obtained result is quite different from Example 1, the difference is that the obtained SnO 2 It is a burr-like hollow spherical structure with uniform appearance and good monodispersity, and its particle size is about 180 nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com