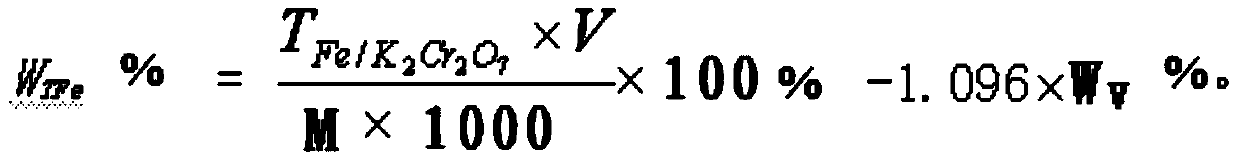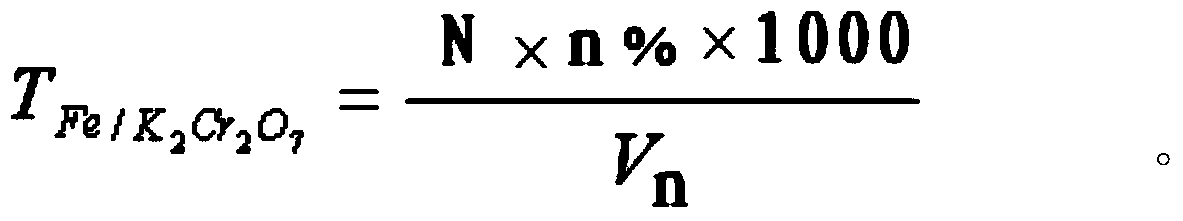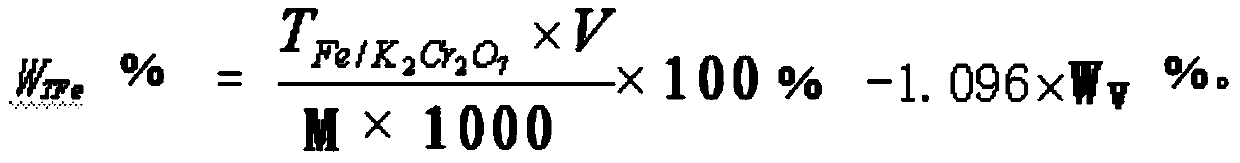Patents
Literature
464 results about "Tin(II) chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
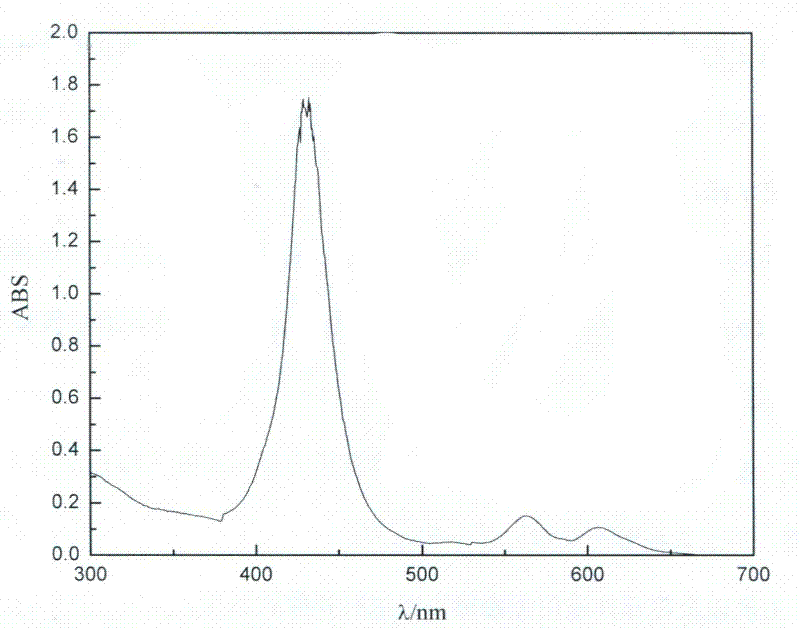
Tin(II) chloride, also known as stannous chloride, is a white crystalline solid with the formula SnCl₂. It forms a stable dihydrate, but aqueous solutions tend to undergo hydrolysis, particularly if hot. SnCl₂ is widely used as a reducing agent (in acid solution), and in electrolytic baths for tin-plating. Tin(II) chloride should not be confused with the other chloride of tin; tin(IV) chloride or stannic chloride (SnCl₄).
Preparation method of nickel-plated and silver-plated aromatic polyamide conductive fibers
The invention relates to a preparation method of nickel-plated and silver-plated aromatic polyamide conductive fibers, which comprises the following concrete steps of: a. washing and oil removal; b. coarsening: increasing the surface roughness and the surface wettability of fibers; c. sensitizing: soaking the fibers by adopting an aqueous solution formed by stannous chloride and hydrochloric acid; d. activation: soaking the fibers by adopting an aqueous solution formed by palladium chloride and hydrochloric acid; e. chemical nickel plating; f. sensitizing; g. activation; h. chemical silver plating; and i. coating protection. The prepared high performance nickel-plated and silver-plated aromatic polyamide conductive fibers have good electric conductivity, characteristics of heat resistance, flame retardance, light weight and high strength and functions of eliminating static electricity, conducting electricity and transmitting electrical signals. Therefore, the prepared nickel-plated and silver-plated aromatic polyamide conductive fibers can be widely applied to special departments of aviation, space flight, war industry, communication and the like and can also satisfy the clothing and equipment requirements of staffs engaging radars, television relaying and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Convenient method for preparing binder-free stannic oxide/carbon fibrofelt for negative pole of high-performance lithium ion battery
InactiveCN104319372AImprove mechanical stabilityInhibition of agglomerationCell electrodesCarbon fibersElectrospinning
The invention discloses a convenient method for preparing binder-free stannic oxide / carbon fibrofelt for a negative pole of a high-performance lithium ion battery. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: dissolving polyacrylonitrile and stannous chloride which have certain concentrations to a N'N-dimethyl formamide solution, magnetically stirring the solution of polyacrylonitrile, the stannous chloride and the N'N-dimethyl formamide solution until the solution is clarified, electrostatically spinning the solution, and finally annealing the obtained solution which is obtained at a high temperature twice to obtain Sn-SnOx uniformly loaded nanometer composite materials of the carbon fibrofelt. For a compound which is prepared by the method disclosed by the invention, since the electrostatic spinning method is adopted, nanometer particles of metal-metallic oxide are uniformly dispersed into buffer substrate carbon fiber, and the circulation specific capacity and the stability of materials for the negative pole of the lithium ion battery are effectively improved. The preparation technology disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the operation is simple, the cost is low, the efficiency is high, the large-scale and industrial production is easy to realize, and the application range is broad.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Corrosive capable of displaying ultra low carbon steel solidification arborescent structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102023112ASimplify the manufacturing processReduced finish requirementsPreparing sample for investigationTin(II) chlorideMaterials science
The invention discloses a corrosive capable of displaying an ultra low carbon solidification arborescent structure and a preparation method thereof. The corrosive is prepared from the following components: picric acid, stannous chloride, copper chloride, hydrochloric acid, surfactant, absolute ethyl alcohol and distilled water. The preparation method is as follows: taking a specified amount of the distilled water, and equally dividing the distilled water into two parts; mixing and putting solid medicament into a glass container according to fixed quantity, and adding one part of the distilledwater into the solid mixed medicament to dissolve the medicament; adding a specified amount of the absolute ethyl alcohol into another part of spare distilled water; adding a hydrochloric acid solution into the absolute ethyl alcohol solution; mixing the ethyl alcohol and the hydrochloric acid solution which are poured into an aqueous solution containing the solid medicament; fully stirring; and finally adding the surfactant to finish preparing. By utilizing the reagent provided by the invention, the solidified arborescent structure forms of ultra low C, S, P continuous casting steel billets can be displayed clearly, a finish requirement on sample surface is lowered, the sample preparation working procedure is simplified and the larbour intensity of operators is lowered.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Colloid palladium activation solution, preparation method thereof and non-metal surface activation method
InactiveCN101928937ANon-failure decompositionBreak down evenlyLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingActivation methodGlyoxylic acid
The invention provides colloid palladium activation solution which comprises colloid palladium, sodium chloride, glyoxylic acid, hydrochloric acid, stannous chloride and stabilizer for stabilizing the stannous chloride, wherein the glyoxylic acid has strong reducibility and can avoid that divalent tin ions in the activation solution are oxidized, and prolong the service life of the action solution; simultaneously, the glyoxylic acid is adsorbed on the periphery of colloid palladium particles, thereby leading the dispersion of the colloid palladium to be more uniform, avoiding the gel coagulation among the colloid particles and enhancing the activity of the activation solution. The invention provides a preparation method of the colloid palladium, and the process is simple. In addition, the adoption of the colloid palladium activation solution for activating the surface of a non-metal substrate can firstly adsorb the glyoxylic acid in the activation solution on the surface of the non-metal substrate, enhance the bonding force between the colloid palladium particles and the non-metal substrate, leading a plated coating after chemical plating to have uniform thickness and flat surface, and leading the adhesion between the plated coating and the substrate to be very high.
Owner:深圳市新合富力科技有限公司
Non-mercury catalyst for production of vinyl chloride and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102069000AAvoid pollutionEase of mass productionPhysical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by halogen halide additionBarium dichlorideCopper chloride
The invention discloses a non-mercury catalyst for the production of vinyl chloride and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the fields of chemical catalyst and the preparation thereof. The non-mercury catalyst of the invention uses cocoanut active charcoal as carrier and stannous chloride as main active substance, wherein the weight percentage of stannous chloride is 15%-30%; and at least one additive of barium chloride, zinc chloride and copper chloride is added and the total additive weight percentage is 0.5-2%. By using the non-mercury catalyst, the environmental pollution caused by the mercury-containing catalyst can be avoided; the large-scale production can be benefited, the conversion rate and selectivity of the catalyst can be increased, the yield of the product can be increased; by increasing the quality of the carrier, technical guarantee can be provided for the large-scale production device of vinyl chloride, the loss of the active matter can be slowed down, the service life of the catalyst can be prolonged; and the use efficiency of the catalyst can be increased by 500%.
Owner:YIBIN TIANYUAN GRP CO LTD
Preparation method of silicon dioxide/silver core-shell composite powder for high temperature electronic paste
ActiveCN103231072AGood dispersionUniform sizeConductive layers on insulating-supportsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingDispersityHydrogen Nitrate
The invention provides a preparation method of silicon dioxide / silver core-shell composite powder for high temperature electronic paste and belongs to the technical field of electronic paste. The preparation method includes: manufacturing silicon dioxide nano-particles firstly, adding a hydrogen nitrate solution to adjust pH value, adding a stannous chloride solution after centrifugal cleaning, adding silicon dioxide microspheres in a silver ammonia solution to be soaked under the condition of ultrasound and then performing centrifugal separation, and enabling a layer of silver nano-particles to be generated on the surfaces of the silicon dioxide microspheres; adding silver nitrate and a dispersing agent under the condition of stirring, and then adding ascorbic acid to obtain silver-plated silicon dioxide composite powder; and removing reaction residues by using a deionized water centrifugal sedimentation and ultrasonic dispersion cycle cleaning mode to obtained the silicon dioxide / silver core-shell composite powder. The preparation method of the silicon dioxide / silver core-shell composite powder for the high temperature electronic paste is simple to operate and low in cost, and particles obtained by the preparation method are remarkable in core-shell structure, even in particle size, high in solid content, ordered in height, good in dispersity and have various application prospects in the aspects of biological sterilization, chemistry, optical materials, electronic paste and the like.
Owner:昆明高聚科技有限公司
Silvered aramid conductive fiber and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a silvered aramid conductive fiber and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method is conducted according to the steps as follows: a. coarsening: coarsening the aramid fiber through putting the fiber into a mixed solution of sodium hydroxide, absolute ethanol and the balance of water, and neutralizing the fiber by rinsing; b. hydrolyzing: hydrolyzing the coarsened aramid fiber by putting the fiber into an acid solution; c. activation of palladium salt: activating the hydrolyzed aramid fiber subjected to activation of palladium salt in step b by putting the fiber into a mixed solution of hydrochloric acid, palladium chloride, stannous chloride and the balance of water; d. reducing: reducing the palladium salt activated aramid fiber in step c by putting the fiber into a mixed solution of hydrochloric acid, sodium hypophosphite and the balance of water; e. chemical silvering: chemical silvering the reduced aramid fiber in step d by putting the fiber into a chemical silvering solution of silver nitrate, sodium hydroxide, aqua ammonia, a complex agent, a reducing agent and the balance of water; f. drying: drying the chemical silvered aramid fiber in step e in the conventional manner to obtain the silvered aramid conductive fiber.
Owner:TIANNUO PHOTOELECTRIC MATERIAL
Method for preparing nano metal pipe by template chemical plating process
The preparation method of nano metal tube by utilizing template chemical plating process includes the following steps: (1) adopting nano carbon fibre or nano polymer fibre as chemical plating template, and cleaning the surface of nano carbon fibre or nano polymer fibre; (2) in strong acid solution making surface coarsening modification; (3) under the condition of ultrasonic stirring soaking the above-mentioned modified fibre material in surfactant solution, then making activation treatment in hydrochloric solution of stannous chloride and palladium dichloride; (4) making chemical plating treatment in chemical plating liquor; (5) oxidating and removing template; and (6) reducing metal oxide and obtaining nano metal tube under the condition of hydrogen atmosphere.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
In-situ etching method for preparing hollow tin-based oxide/carbon composite nano-material
InactiveCN103346299AEfficient removalPromote crystallizationCell electrodesCarbon compositesTin dioxide
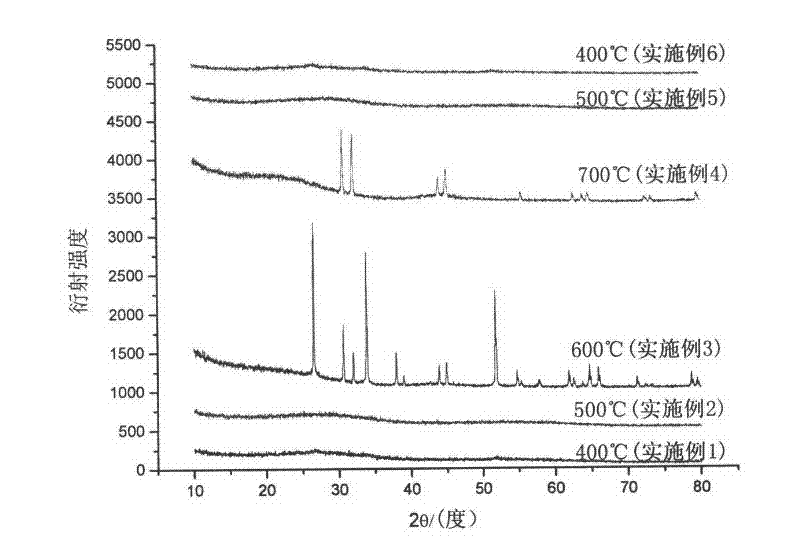
The invention relates to a preparation method of a hollow tin-based oxide / carbon composite nano-material, and belongs to the technical field of material synthesis and electrochemistry. The method comprises: taking a carbon coated silica composite material as a template, stannous chloride (SnCl2-H2O(1 / 2)) as a tin source, urea as an alkali source, and water as a solvent, adopting a simple in-situ etching hydrothermal crystallization method for generation of a stannic oxide based nano-material and successful removing of the silica template at the same time, to obtain the tin-based oxide / carbon composite nano-material with a hollow spherical structure and homogeneous morphology. In the method, the raw material ratio of the tin source and urea is the key of the method. And more important, by simple control of the subsequent heat treatment temperature, the carbon composite nano-materials of stannous oxide (SnO) and of tin oxide (SnO2) with two totally different crystal phases can be obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Freeze-etching agent of ultra-low-carbon steel casting billet macrograph grain structure, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102401759ALow S.P contentEasy to distinguishPreparing sample for investigationFreeze EtchingGlass vessel
The invention discloses a freeze-etching agent of ultra-low-carbon steel casting billet macrograph grain structure, and a preparation method thereof. The freeze-etching agent is prepared from materials of: 30 to 50g of ferric chloride, 0.5 to 1.2g of stannous chloride, 2 to 3 parts of trinitrophenol, 10 to 20ml of sodium alkyl phenyl sulfonate, 200 to 500ml of absolute alcohol, and 600 to 1000ml of hydrochloric acid. Solid agents of the formulation are mixed and placed into a glass vessel according to the ratio; 1500 to 2000ml of distilled water is divided into two parts; one part is added to the solid mixed agents, and the other part is preserved for later use; absolute alcohol is added to the preserved part of distilled water; hydrochloric acid is added to the alcohol solution; sodium alkyl phenyl sulfonate is added to the aqueous solution containing agents such as ferric chloride, and the mixture is uniformly stirred; the alcohol + hydrochloric acid solution is then added to the aqueous solution containing the agents such as ferric chloride; the solution is sufficiently stirred, such that the freeze-etching agent is prepared. With the freeze-etching agent, the form of the ultra-low-carbon continuous casting steel billet macrograph grain structure can be clearly shown. The freeze-etching agent provided by the invention has advantages of high detection speed, low pollution, and convenient operation. Also, the freeze-etching agent is energy-saving.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
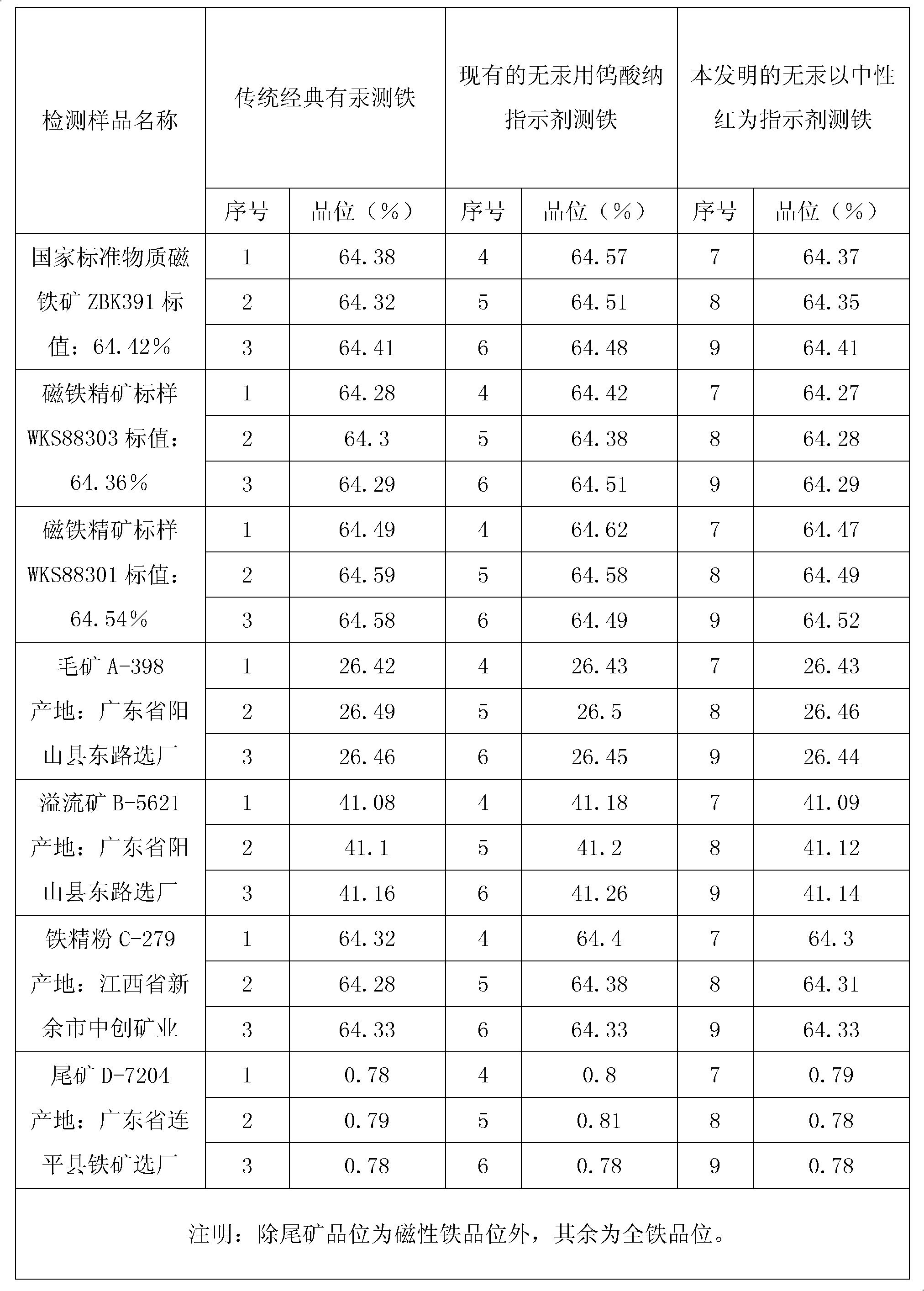
Novel method for measuring iron without mercury
InactiveCN102608112AEliminate pollutionGood reproducibilityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPhosphoric acidColor changes
The invention relates to a novel method for measuring iron without mercury, which comprises the following steps of: decomposing a test sample through mixed acid of hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid; taking neutral red and sodium diphenylaminesulfonate as indicators; measuring the iron through a SnCl2-TiCl3-K2Cr2O7 volumetric method; reducing Fe<3+> of phi Fe<3+> / Fe<2+>=+0.76V through tin bichloride with phi Sn<4+> / Sn<2+>=+0.16V; adding neutral red reagent when the solution is flavescent, i.e. the solution still contains a small amount of Fe<3+>; taking the color change of the neutral red as an indicator indicating that Fe<3+> is completely reduced to be Fe<2+> according to the principle that the neutral red is reduced to be colorless after the Fe<3+> is reduced completely, and the neutral red reagent is blue in the Fe<3+> solution; dropping titanium trichloride with phi Ti<4+> / Ti <3+>=+0.1V until blue is disappeared; removing excess titanium trichloride through oxidation by a 5.000g. L<-1> sodium diphenylaminesulfonate-potassium dichromate standard solution method; and finally, calculating ion grade of the test sample.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Analysis method for phosphor in high temperature alloy
InactiveCN1880946AEliminate the effects ofAnalytical results are reliableMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationDielectricFluohydric acid
The invention discloses a phosphor analyzing method in the high-temperature alloy, which is characterized by the following: heating to dissolve sample through compound acid such as azotic acid and hydrochloric acid or azotic acid, hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric acid (or microwave sample-fusing furnace); adding perchloric acid to heat until smoke; dripping hydrochloric acid to remove chromium; adding complex citrate in the alkali dielectric; adding complex niobium, tantalum, zirconium, hafnium, titanium, vanadium, tungsten fluohydric acid in the azotic acid dielectric; extracting phosphor through butanol-chloroform composite agent and ammonium molybdate; reextracting organic phase through hydrochloric solution of tin chloride; testing absorbance of water phase at 680nm. The invention eliminates influence of high-content interference element, whose result is accurate and reliable with testing greatest lower limit as 0.0002%(m / m).
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for measuring total iron content in directly-reduced iron
InactiveCN102323133AEasy to operateImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationPotassium fluorideTest sample
The invention provides a method for measuring the total iron content in directly-reduced iron. The method comprises the following steps of: adding potassium fluoride solution and mixed acid of sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid into a directly-reduced iron test sample, heating to dissolve the test sample, and thus obtaining dissolving solution; adding hydrochloric acid solution and stannous chloride solution into the dissolving solution, heating until the dissolving solution is boiled, cooling to room temperature, and thus obtaining sample solution to be measured; and directly measuring the total iron content in the directly-reduced iron by a titration method in the prior art. The method is convenient to operate and is high in accuracy rate of the measured total iron content and high in stability, repeatability and accuracy of a measured result. Experiments prove that: the method is reliable and practical and can meet the requirement of the total iron content in the directly-reduced iron during daily measurement.
Owner:WUKUN STEEL
Method for measuring content of iron element in different valence states in lithium iron phosphate anode material
InactiveCN101470078ASimple methodEasy to operateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical analysis using titrationLithium iron phosphatePotassium
The invention provides a measurement method for the contents of iron elements of different valence states in lithium iron phosphate anode, comprising: dissolving lithium iron phosphate anode sample via acid; adding stannous chloride to reduce ferric iron to ferrous iron; titrating ferrous ion via potassium dischromate, thereby obtaining the total ion weight; under protective gas, reacting lithium iron phosphate anode with ferric chloride, dissolving via acid, titrating ferrous ion via potassium dischromate, thereby obtaining the total weight of ferric iron and ferrous iron; reacting lithium iron phosphate anode with dilute hydrochloric acid, dissolving via acid, and titrating ferrous ion via potassium dischromate, thereby obtaining the content of ferric iron and pure Fe. The measurement method has simple process, simple operation and reliable result, and can provide basis for the quality judgment of LiFePO4 anode.
Owner:湖北盐光能源科技有限公司 +2
Preparation process of radioactive istope gallium-67
InactiveCN1341762ARemove completelyGood removal effectConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsRadioactive sourcesImaging agentIsotope
The preparation process of radioisotope gallium-67 relates to a separation and purification process of radioisotope gallium-67 produced by cyclotron. It is characterized by including the following steps: adding oxidant which does not affect the separation process and H2O2 solution into the concentrated hydrochloric acid in which the zinc target bombarded by proton beam is dissolved so as to make low-valence gallium-67 (67Ga1+, 67Ga2+) ions in the target dissolving solution oxidate into trivalence ions (67Ga3+), then evaporating and drying, adding hydrochloric solution of SnCl2 to make furthersolvation, reducing impurity iron ion (Fe3+) and using cation-exchanginging column to separate and purifying Ga-67. Said invention adopts the addition of two reagents of H2O2 and SnCl2, obtains high recovery rate (95%) of Ga-67 and high quality (impurity iron content is less than 5 microgram / ml-5mCi-Ga-67). It can ensure that the impurity iron content in the tumor imaging agent gallium citrate made up by using said invention is as low as possible.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Preparation method of nano Ag-SnO2 electric contact composite
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nano Ag-SnO2 electric contact composite, which comprises the steps of: preparing a sol solution by using stannous chloride dehydrate as a raw material, adding a silver nitrate solution, controlling Sn<2+> sol particles and Ag<+> ions in the solution to generate a chemical reaction in situ through regulating a pH value so to prepare Ag-SnO2 intermediate composite particles with the content of SnO2 of 10-90 percent; then mixing the Ag-SnO2 intermediate composite particles with pure silver powder, reducing the SnO2 content to 5-30 percent; and pressing, sintering and thermally extruding to obtain the electric contact composite with nano SnO2 reinforced phase particles in a funicular distribution state in a matrix. Sol and gel are combined to generate the chemical reaction; and by the assistance of ultrasonic waves, the particle diameter (nano level) of the Ag particles and the SnO2 particles in the intermediate particles and the dispersion distribution of the Ag particles and the SnO2 particles are controlled effectively, the compatibility of the matrix and the reinforced phase is improved, and the interface binding strength of the matrix and the reinforced phase is improved.
Owner:WENZHOU HONGFENG ELECTRICAL ALLOY
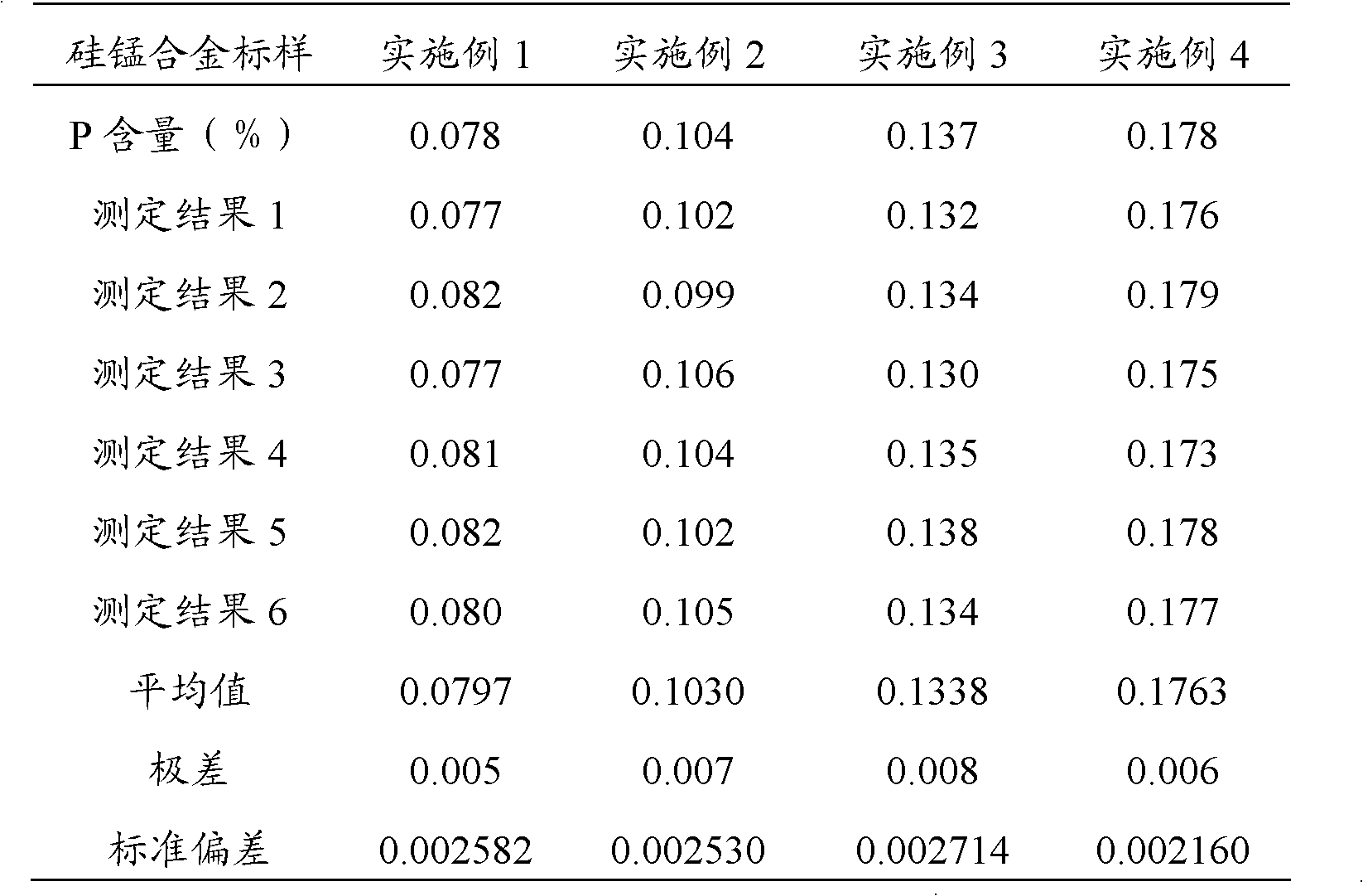
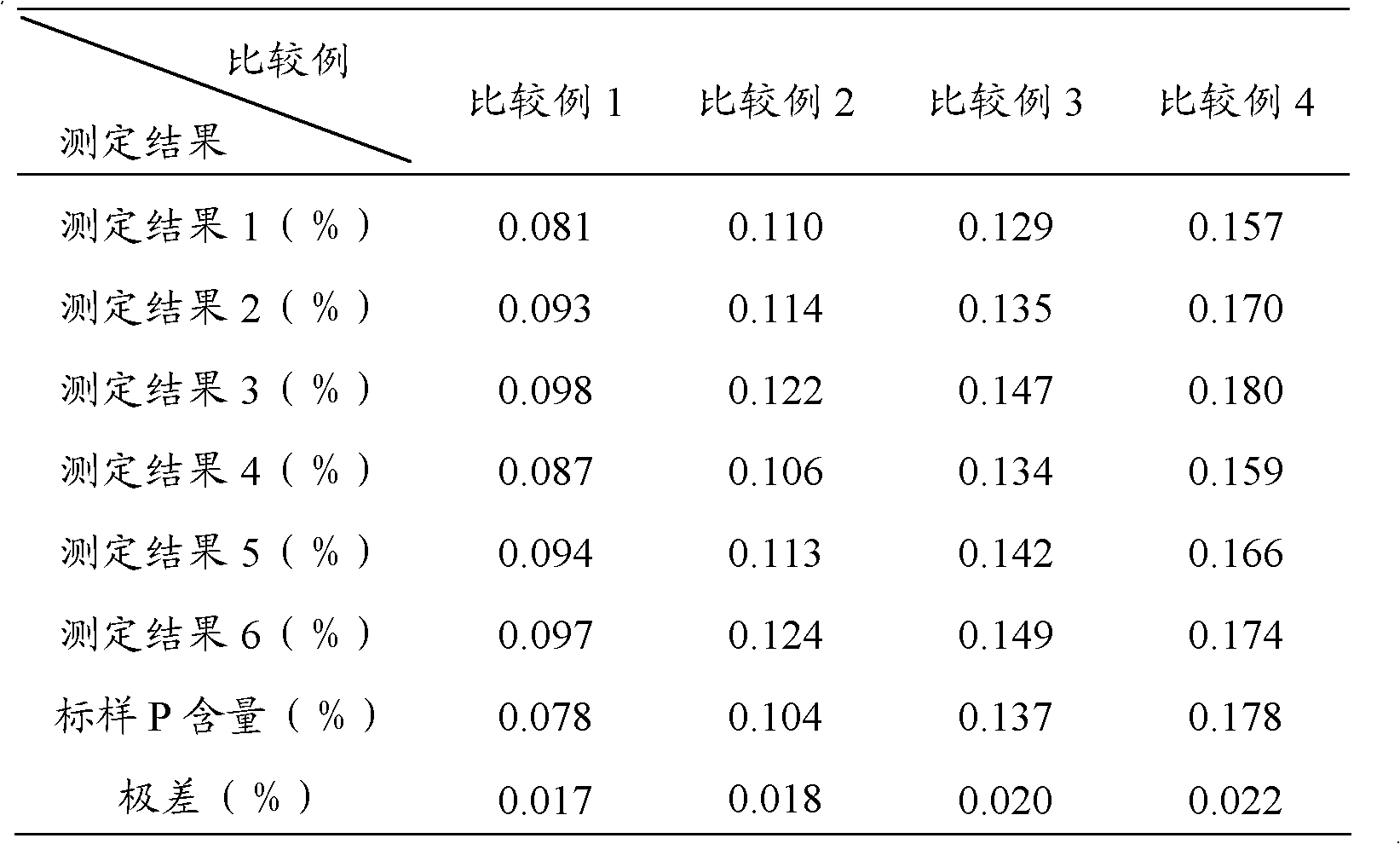
Method for determining phosphorus in silicon-manganese alloy
InactiveCN102539426AShort analysis timeImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFistHeteropoly acid
The invention discloses a method for determining phosphorus in silicon-manganese alloy, which comprises the steps of: dissolving a test sample by using nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid and adding perchloric acid to convert phosphorus in the test sample into orthophosphoric acid to obtain fist mixed solution; adding sodium sulfite into the first mixed solution to reduce manganese in the silicon-manganese alloy to obtain second mixed solution; and adding bismuth nitrate solution, ammonium molybdate solution, potassium sodium tartrate solution, sodium fluoride and stannous chloride into the second mixed solution, wherein ammonium molybdate can convert the orthophosphoric acid in the first mixed solution into phosphorus-molybdenum heteropoly acid, using stannous chloride to reduce the formed phosphorus-molybdenum heteropoly acid into blue phosphomolybdenum blue and finally using a spectrophotometric method to determine the content of the phosphorus. Compared with the prior art, by using the stannous chloride as the reducing agent, since the stannous chloride has the characteristics of high reducing speed, good reducing effect and the like, the analysis time of the determination method is shorter, the accuracy and the stability of the determination result are improved and the method is suitable for field mass production analysis.
Owner:吉林建龙钢铁有限责任公司
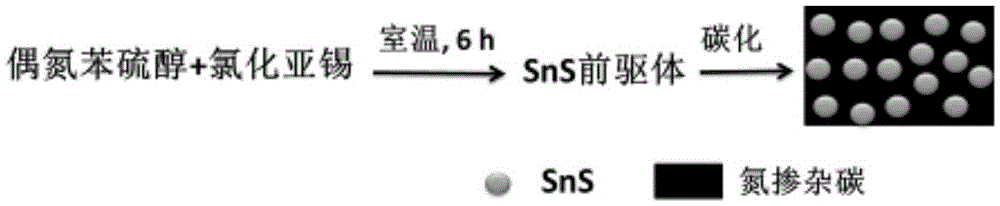
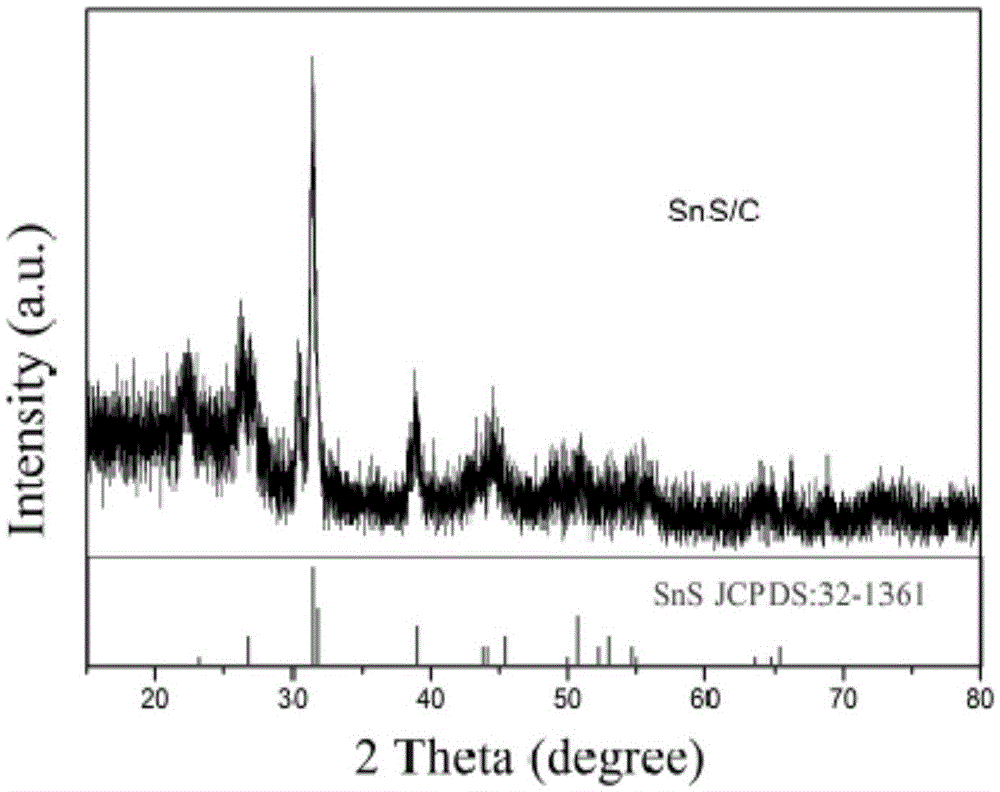
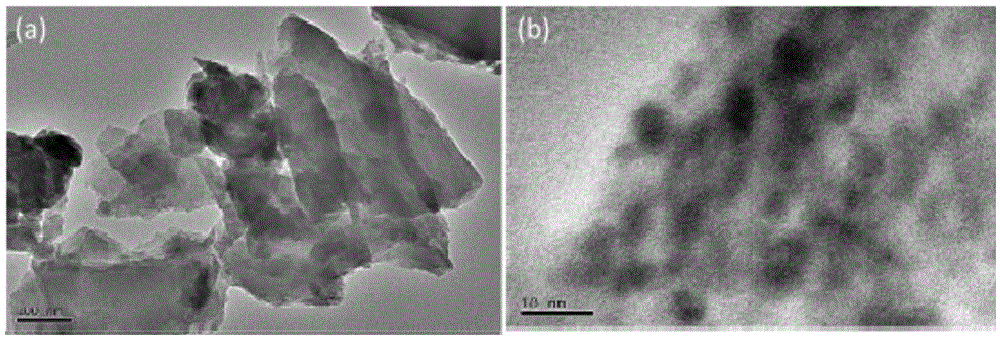
Preparation method of anode material, namely nitrogen-doped SnS/C composite nanomaterial for lithium battery
ActiveCN105552366AImprove conductivityInhibition of volume expansionMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesDischarge efficiencyForced-air
The invention discloses a preparation method of an anode material for a lithium battery. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding azobenzene mercaptan and an acid-binding agent to a toluene solution, mixing the azobenzene mercaptan and the acid-binding agent evenly, adding stannous chloride, and carrying out room-temperature reaction under protection of nitrogen for 6 hours; (2) filtering a reaction liquid, washing a filter cake with absolute ethyl alcohol, and carrying out heat preservation on the filter cake in a forced air oven at 80-120 DEG C for 4-8 hours to obtain a dry SnS precursor; and (3) heating the SnS precursor under protection of an inert atmosphere for burning to prepare the black nitrogen-doped SnS / C composite nanomaterial. The composite material prepared by the method is used as the anode material for the lithium-ion battery, so that SnS volume expansion during charging and discharging can be effectively relieved; and the problems of charge-discharge efficiency reduction and overquick capacity degradation are suppressed.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Nickel based corrosion-resisting alloy dendritic crystal etching agent and preparation method and using method thereof
ActiveCN104634640AImprove corrosion resistanceIncrease contentPreparing sample for investigationCorrosion resistant alloyAlcohol
The invention belongs to the technical field of continuous casting metallographic analysis and in particular relates to a nickel based corrosion-resisting alloy dendritic crystal etching agent and a preparation method and a using method of the nickel based corrosion-resisting alloy dendritic crystal etching agent. The nickel based corrosion-resisting alloy dendritic crystal etching agent is prepared from the following ingredients: 6-18g of stannous chloride, 50-70g of ferric chloride, 50-100ml of hydrochloric acid, 15-30ml of sodium alkyl benzene sulfonate, 10-60ml of absolute ethyl alcohol and 40-300ml of distilled water. The using method comprises the following steps: directly pouring the dendritic crystal etching agent on a sample testing surface for pouring corrosion, when a clear dendritic structure is observed on the testing surface after 15-30s, washing etching liquid with water immediately, washing the testing surface with alcohol, and blow-drying by a blower; and observing the defects of the dendritic structure and the solidification structure of the testing surface of the sample by a stereoptic microscope. The testing steps are simple and convenient, and the detection result on the dendritic crystal corrosion is clear and accurate.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Copper-zinc-tin-sulfur (CZTS) thin film and preparation method and purposes thereof
InactiveCN103943721AEasy to prepareGood compactnessFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIonChemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a copper-zinc-tin-sulfur (CZTS) thin film. The preparation method includes the first step of preparing a precursor solution, dissolving copper chloride, zinc chloride, stannous chloride and thiourea jointly into methyl alcohol or ethyl alcohol and stirring the solution to be clear and transparent, the second step of carrying out ultrasonic cleaning on a substrate FTO in acetone, ethanol and deionized water respectively and sequentially, the third step of coating the precursor solution on the surface of the substrate FTO and then drying the substrate FTO, and the fourth step of placing a sample obtained in the third step into nitrogen or argon for calcining to obtain the CZTS thin film. The preparation method of the CZTS thin film is simple, easy to implement and suitable for mass production; the prepared CZTS thin film is smooth in surface, free of cracks, excellent in performance, good in photoelectrochemical performance, high in chemical stability and capable of being widely applied to the field of production of semiconductor nano-films and photoelectrocatalysis.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Red infrared-penetrating quartz tube and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a red infrared-penetrating quartz tube. Highly-pure arenaceous quartz is used as a basic material in part by weight, and 8-10% of colorant by weight is added, wherein the colorant comprises cuprous oxide (Cu2O), manganese dioxide (MnO2), selenium (Se), cadmium sulfate octahydrate (3Cd2SO4.8H2O), aluminium hydroxide (Al(OH)3), stannous chloride dehydrate (SnCl2.2H2O), samarium chloride (SmCl3) and antimony oxide (Sb2O3). The red infrared-penetrating quartz tube which is formed by drawing by adopting a preparation technique for tube wall integral coloring has favorable uniformity and toughness, strong compression resistance and wide light-absorbing range, has the characteristics of high temperature resistance and stable filtering property, and absorbs visible light and penetrates the near infrared ray of 800-2500nm. The invention has the spectral characteristics of 400nm penetration rate T being less than or equal to 14%, 700nm penetration rate T being less than or equal to 6.0% and 1100nm penetration rate T being more than or equal to 85.0% when the thickness of a sample is 1.0 mm.
Owner:LIANYUNGANG HONGYANG QUARTZ PROD
Electroless copper plating activating solution and preparation method thereof
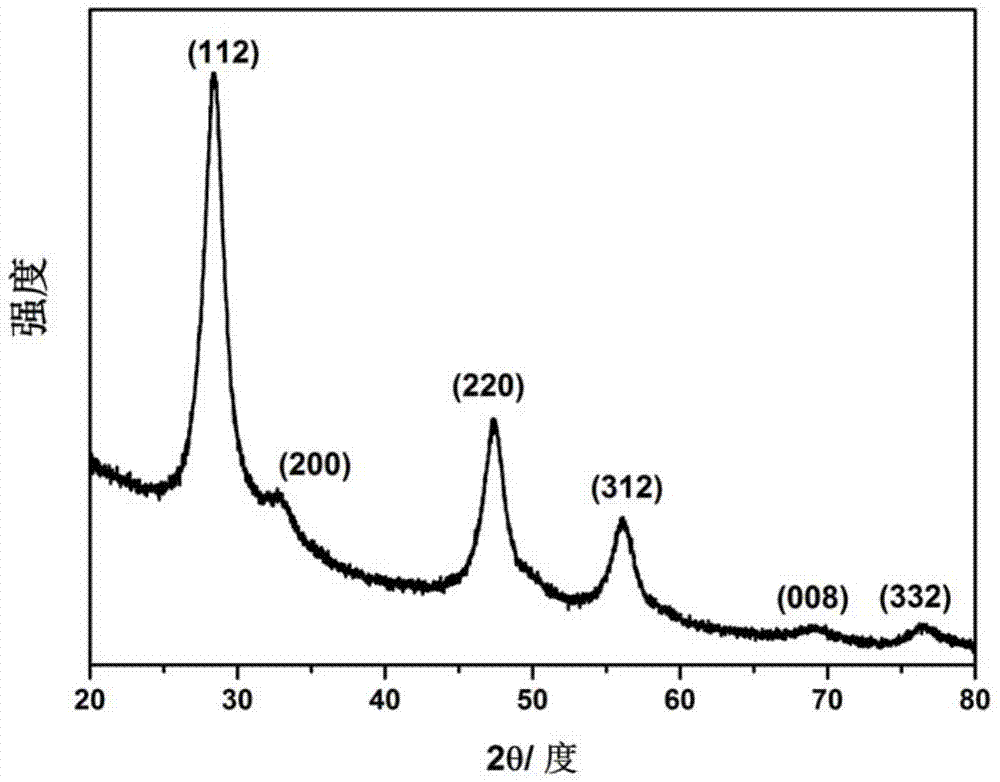
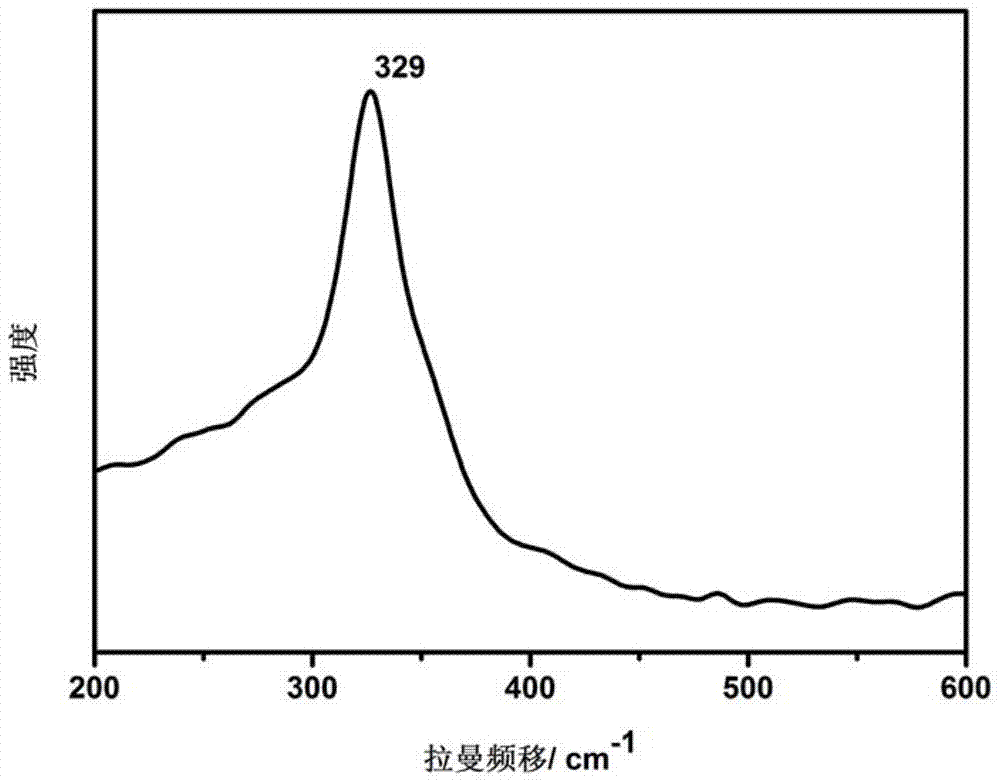
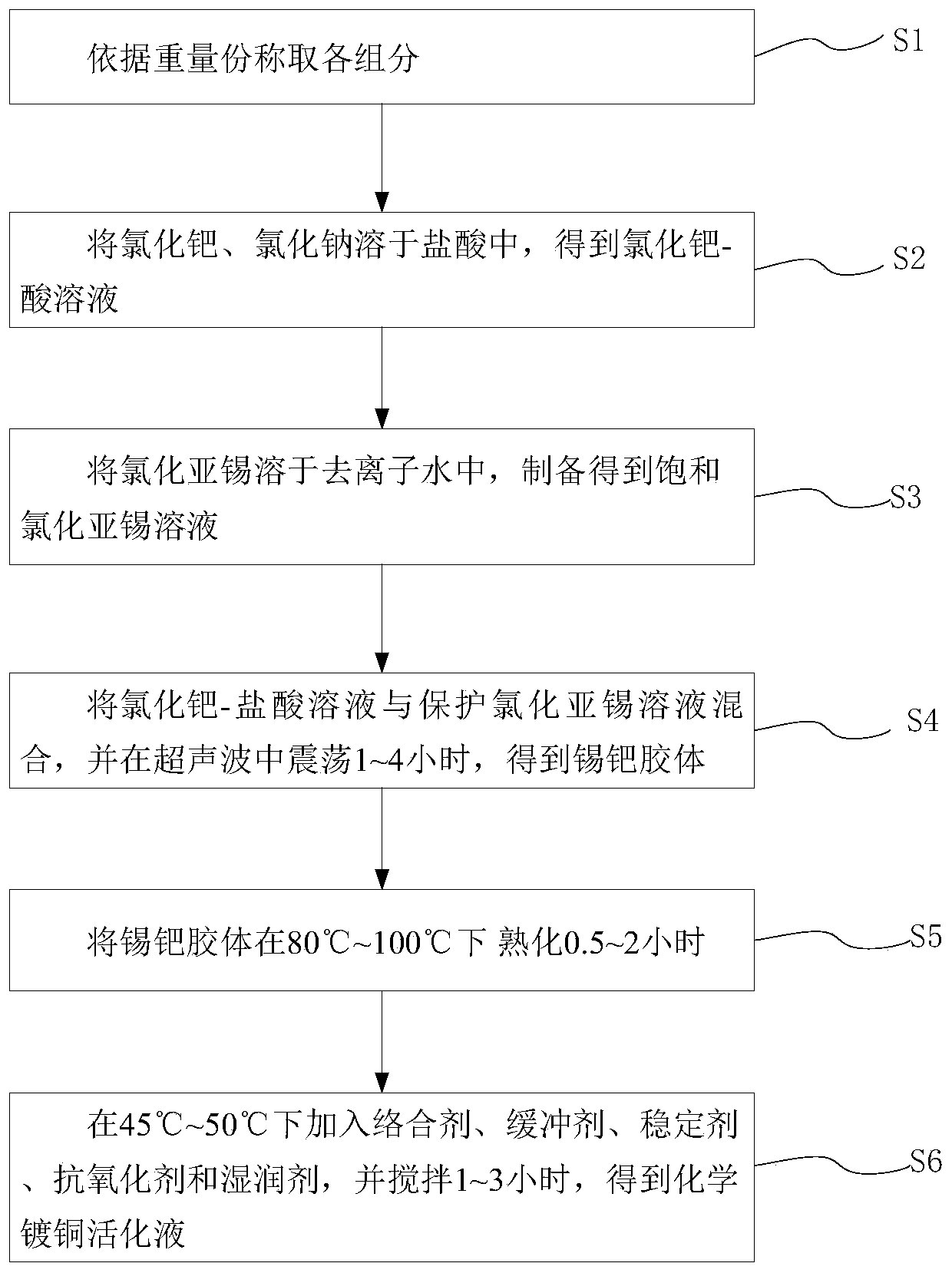
ActiveCN110670050AImprove stabilityStrong complexationLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPropanoic acidDiethylenetriamine
The invention provides an electroless copper plating activating solution and a preparation method thereof. The electroless copper plating activating solution is prepared from, by weight part, 1-10 parts of palladium chloride, 100-400 parts of stannous chloride, 50-200 parts of sodium chloride, 10-100 parts of sodium chloride, 0.1-50 parts of a complexing agent, 1-200 parts of a buffering agent, 0.1-10 parts of a stabilizing agent, 0.05-10 parts of an antioxidant and 0.1-10 parts of a wetting agent. The complexing agent is one or more of ethidene diamine, trimethyl amine, triethylanmine, diethylenetriamine, triethylenetetramine and tetraethylenepentamine. The buffering agent is one or more of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, glycine, propionic acid, malic acid and 2-(cyclohexylamino)ethanesulfonic acid. The electroless copper plating activating solution is high in stability and can adapt to intense circulating stirring in a horizontal electroless copper plating process.
Owner:SHENZHEN CYPRESS IND DEV CO LTD
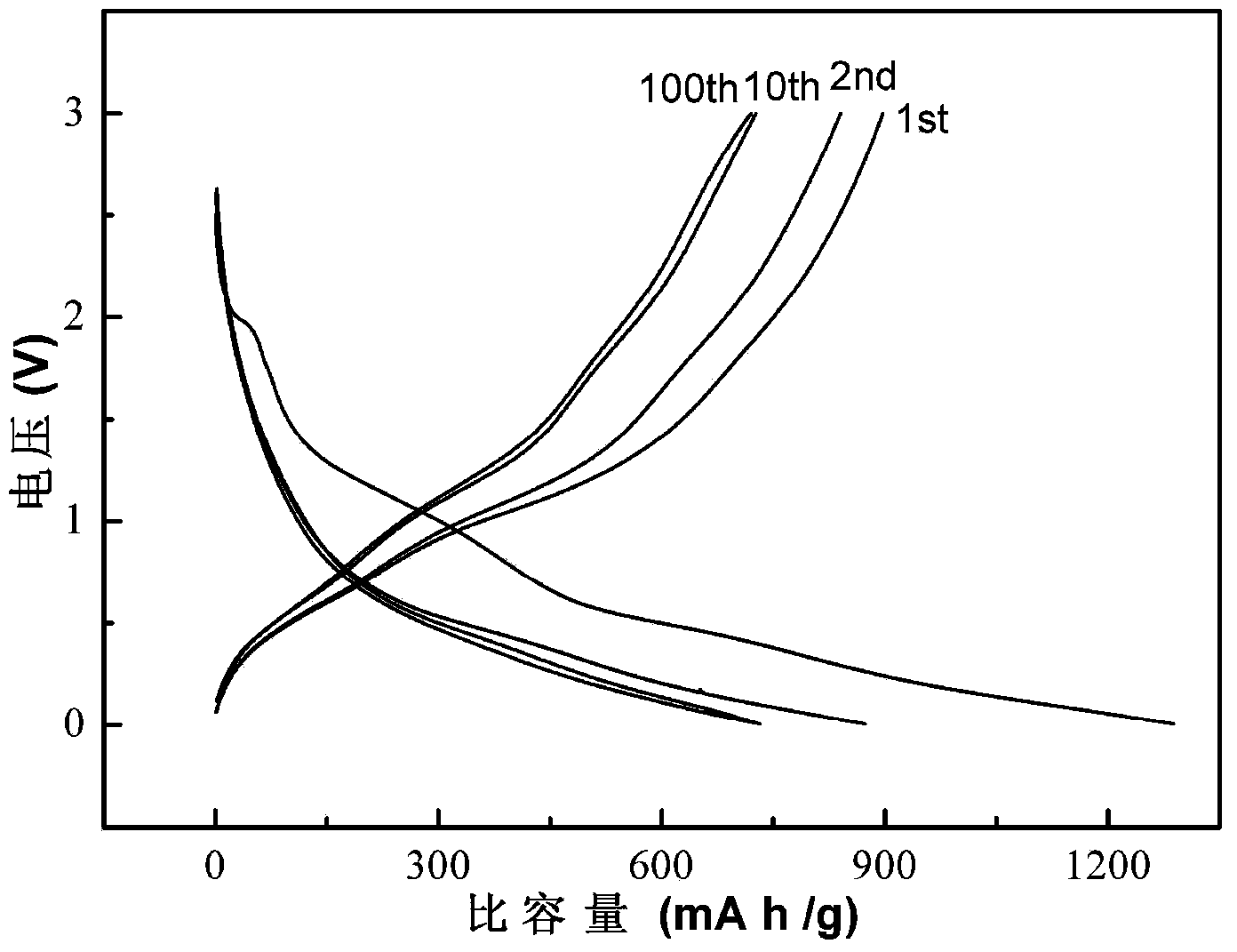
Method for preparing tin-carbon composite material for cathode of lithium ion battery
InactiveCN102227019ARaw materials are easy to getSimple methodCell electrodesCarbon compositesTin(II) chloride
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for preparing zeolite molecular film reactor coating carried noble metal
ActiveCN101147853AComposite catalytic performanceHigh catalytic activityMolecular sieve catalystsNitrogen gasMembrane reactor
The present invention discloses a preparation method of zeolite molecular sieve membrane reactor coated with noble metal. Said preparation method includes the following steps: stainless steel tube treatment, preparing binding agent, preparing coating liquor, utilizing gas auxiliary coating technique to obtain the stainless steel tube coated with zeolite molecular sieve membrane, using tin dichloride, hydrochloric acid and deionized water to prepare sensitizing agent, using palladium chloride or chloroplatinic acid or silver nitrate, hydrochloric acid and deionized water to prepare activating agent, sensitizing and activating the stainless steel tube coated with zeolite molecular sieve membrane, mixing the solution untaining noble metal ions and complexing agent, and using ammonia water and deionized water to regulate pH, injecting plating liquor into the interior of stainless steel tube coated with zeolite molecular sieve membrane, drop-adding reduction agent to make plating, introducing hydrogen gas or nitrogen gas, baking so as to obtain the invented zeolite molecular sieve membrane reactor coated with noble metal.
Owner:BINHAI IND RES INST OF TIANJIN UNIV CO LTD
Method for rapidly determining content of total iron in vanadium titano-magnetite
InactiveCN104181272AEasy to operateQuick breakdownMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical analysis using titrationMagnetiteRoom temperature
The invention provides a method for rapidly determining the content of total iron in vanadium titano-magnetite. The method comprises the following steps: (1) weighing a to-be-determined vanadium titano-magnetite sample with the weight of M; (2) adding sufficient mineral dissolving solution to dissolve the to-be-determined vanadium titano-magnetite sample in a heating manner; (3) adding dilute hydrochloride acid into a reaction vessel; (4) dropwise adding stannous chloride solution to the reaction vessel until the mixed solution turns pale yellow, reheating the mixed solution to be boiled slightly, and cooling the mixed solution to the room temperature; (5) adding sodium tungstate solution into the reaction vessel, dropwise adding titanium trichloride solution until the mixed solution turns blue, and dropwise adding titanium trichloride solution to be slightly excessive in volume; (6) dropwise adding potassium dichromate solution into the reaction vessel until the mixed solution is colorless, and dropwise adding sodium diphenylaminesulfonate indicator; (7) titrating the mixed solution in the reaction vessel to be purple by adopting potassium dichromate standard titration solution; (8) sampling the solution after being titrated to be purple, and determining the weight percentage of vanadium in the sample; and (9) calculating. The method is easy to operate, high in determination speed, capable of enabling the detection result to be equivalent to that of a national standard method and capable of better meeting the in-situ rapid analysis requirement.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Photosensitive fuel for dye-sensitized solar cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102408744AReduced transition energyImprove absorption ratePorphines/azaporphinesPorphyrinSolar cell
The invention belongs to the technical field of solar cell materials, and particularly relates to a sensitizer for a dye-sensitized solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the photosensitizer provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: taking 5-(4-nitrophenyl)-10,15,20-tris(4-hydroxyphenyl)porphyrin as an initiator; under nitrogen conditions, dissolving the initiator in concentrated hydrochloric acid, and reducing the initiator into 5-(4-aminophenyl)-10,15,20-tris(4-hydroxyphenyl)porphyrin by using stannous chloride; then, dissolving the reduced porphyrin and zinc acetate in an inert organic solvent for coordination; finally, dissolving the generated zinc protoporphyrin and 4-carboxybenzaldehyde in a dichloromethane solvent, and heating and refluxing; and after the reaction is finished, adding petroleum ether or absolute methanol for precipitating products, and recrystallizing to obtain a corresponding product N-(5-p-phenyl)-10,15,20-tris-p-hydroxyphenyl zinc protoporphyrin-p-carboxyl benzimide. The product provided by the invention has the advantages of high molar extinction coefficient, low cost and the like.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Tin dioxide based nano gas sensitive material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1769881AImprove adsorption capacityHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesElemental selenium/telluriumTin dioxidePotassium borohydride
The invention relates to a stannic oxide (SnO2) base nano air-sensitive material and method for making the same which comprises steps of: calculating and getting stannous chloride as mole ratio, proportioning with sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate, potassium borohydride, antimony oxide and ethyl silicate; grinding, drying, prefiring to get stannic oxide nano powder; according to the mole proportion, doping carbon nano tube with the produced stannic oxide nano powder. The inventive method has the advantages of being lower cost than doping noble metallic elements in the stannic oxide (SnO2) base nano air-sensitive material, and of having high sensitivity.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of lithium ion battery cathode material
InactiveCN104659367AHigh specific capacityImprove cycle performanceMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesCarbon coatingSodium-ion battery
The invention belongs to the technical field of lithium ion batteries and particularly relates to a preparation method of a lithium ion battery cathode material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dispersing graphene oxide in deionized water, and then adding hydrochloric acid to uniformly mix; adding stannous chloride and reacting to obtain a graphene-stannic dioxide composite material, then dispersing the composite material in the deionized water, then adding a water soluble macromolecular matter, then converting to a reaction kettle to react, and separating to obtain a reaction product; washing, drying and calcining the reaction product to obtain the graphene-stannic dioxide-carbon nanosheet composite material. Compared with the prior art, SnO2 particles in the composite material prepared by using a hydrothermal carbon coating method are relatively small, and moreover, the structure can alleviate volume expansion of SnO2 and reduce the diffusing distance of lithium ions in the material, so that the lithium storage specific capacity of the material is improved and permeation of the electrolyte is facilitated, and therefore, the electronic conductivity of the material is improved and the rate capability of the material is further improved.
Owner:MCNAIR TECH +1
Stannum copper alloy coating, plating solution prescription and electroplating method
The invention discloses a tin-copper alloy plating layer, a plating liquid prescription and a plating method. The plating layer calculated by weight comprises at least 55 to 60 percent of tin as well as 40 to 45 percent of copper; while the plating liquid prescription mainly includes stannous chloride of 20 to 40g / l and copper pyrophosphate of 10 to 30g / l that are respectively as the main salt of tin and copper. The prescription also includes potassium pyrophosphate of 250 to 350g / l used as a main complexing agent; potassium chloride of 30 to 40g / l used as an auxiliary complexing agent; stannic chloride pentahydrate of 10 to 30g / l to main the stability of the plating liquid; the pH value is controlled between 8.0 to 9.0; a class I additive of 0.5 to 5ml / l and a class II additive of 0.5 to 3ml / l are also added. The scheme can be adopted to lead the plating layer to have the advantages of better heat stability, hard color changing, being more environment protective and being able to avoid the skin from nickel sensitivity.
Owner:RORING IND XIAMEN
Platinum-based catalyst, preparation method and application thereof, and preparation method for propylene
InactiveCN104226307AHigh selectivityImprove stabilityHydrocarbonsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsDehydrogenationHigh activity
The invention discloses a platinum-based catalyst, a preparation method and an application thereof, and a preparation method for propylene. The preparation method of the platinum-based catalyst comprises the following steps of (1) mixing activated aluminium oxide with an auxiliary agent solution uniformly to obtain a mixed solution, vibrating for 1-6 hours under ultrasonic assistant at a temperature of 30-50 DEG C, drying and calcining to obtain a precursor, wherein the auxiliary agent solution is a stannous chloride solution and / or indium nitrate solution and a mass ratio of activated aluminium oxide to the auxiliary agent is (10:1)-(450:1); and (2) mixing the precursor with a chloroplatinic acid solution uniformly, vibrating for 1-6 hours under ultrasonic assistant at a temperature of 30-50 DEG C, drying and calcining, wherein a mass ratio of activated aluminium oxide to chloroplatinic acid is (40:1)-(500:1). The preparation method is simple in process and short in time; the prepared platinum-based catalyst can catalyze propane dehydrogenation to prepare propylene; active components are uniformly dispersed on carrier surfaces; and the prepared platinum-based catalyst has relatively high activity, propylene selectivity and stability.
Owner:SHANGHAI DINGJIDE IND TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com