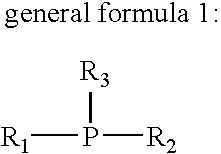
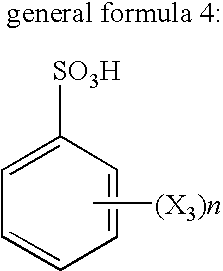
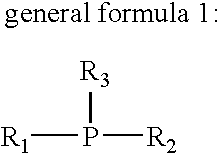
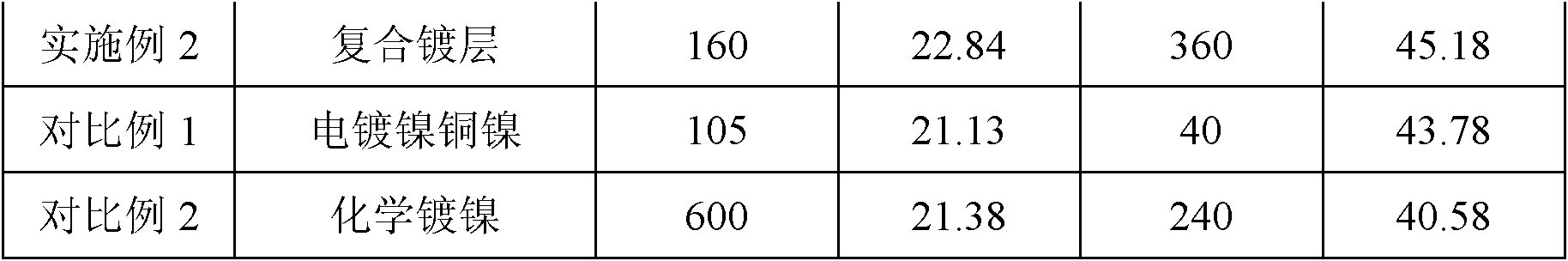Patents
Literature
1728 results about "Electroless nickel plating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
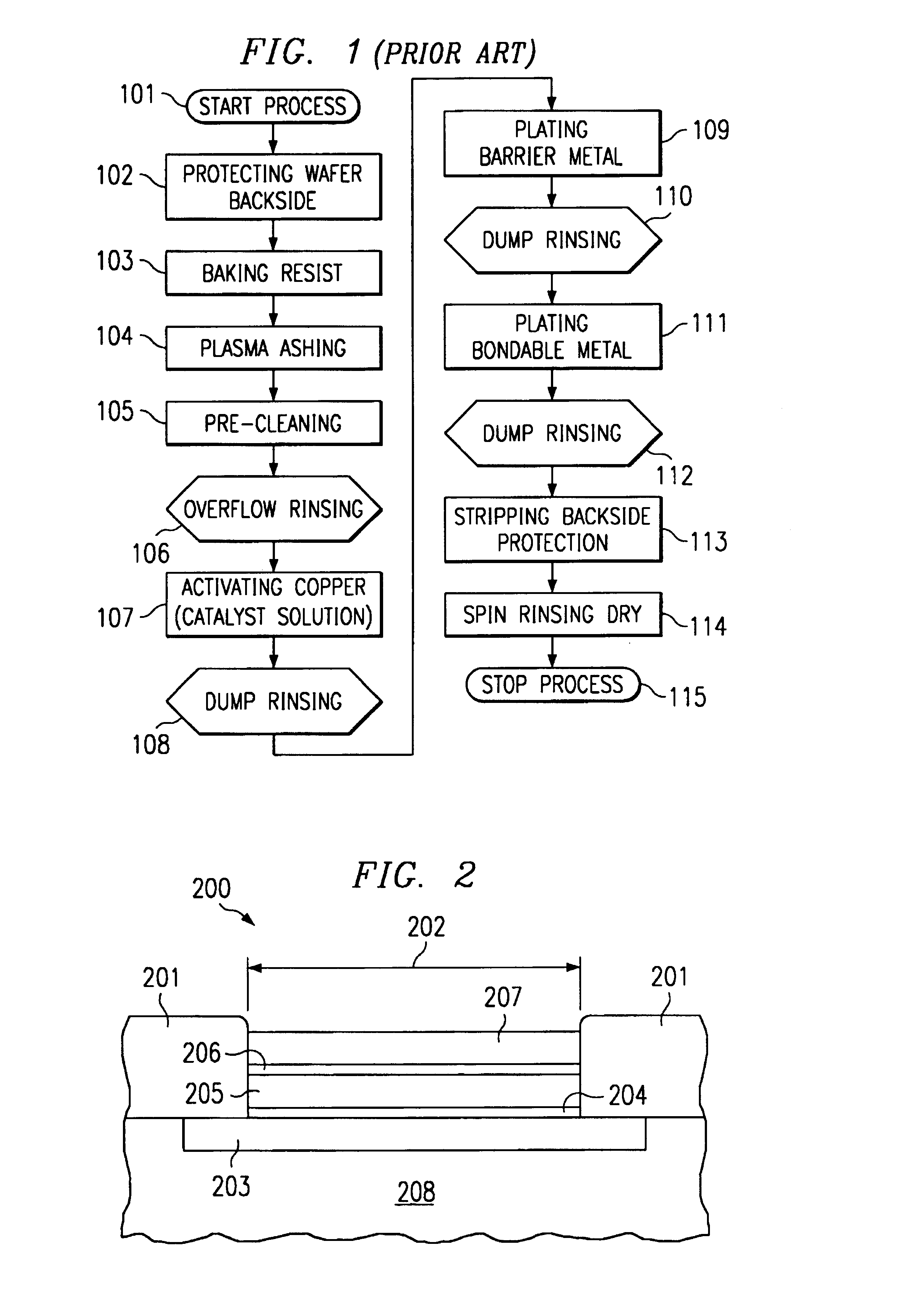
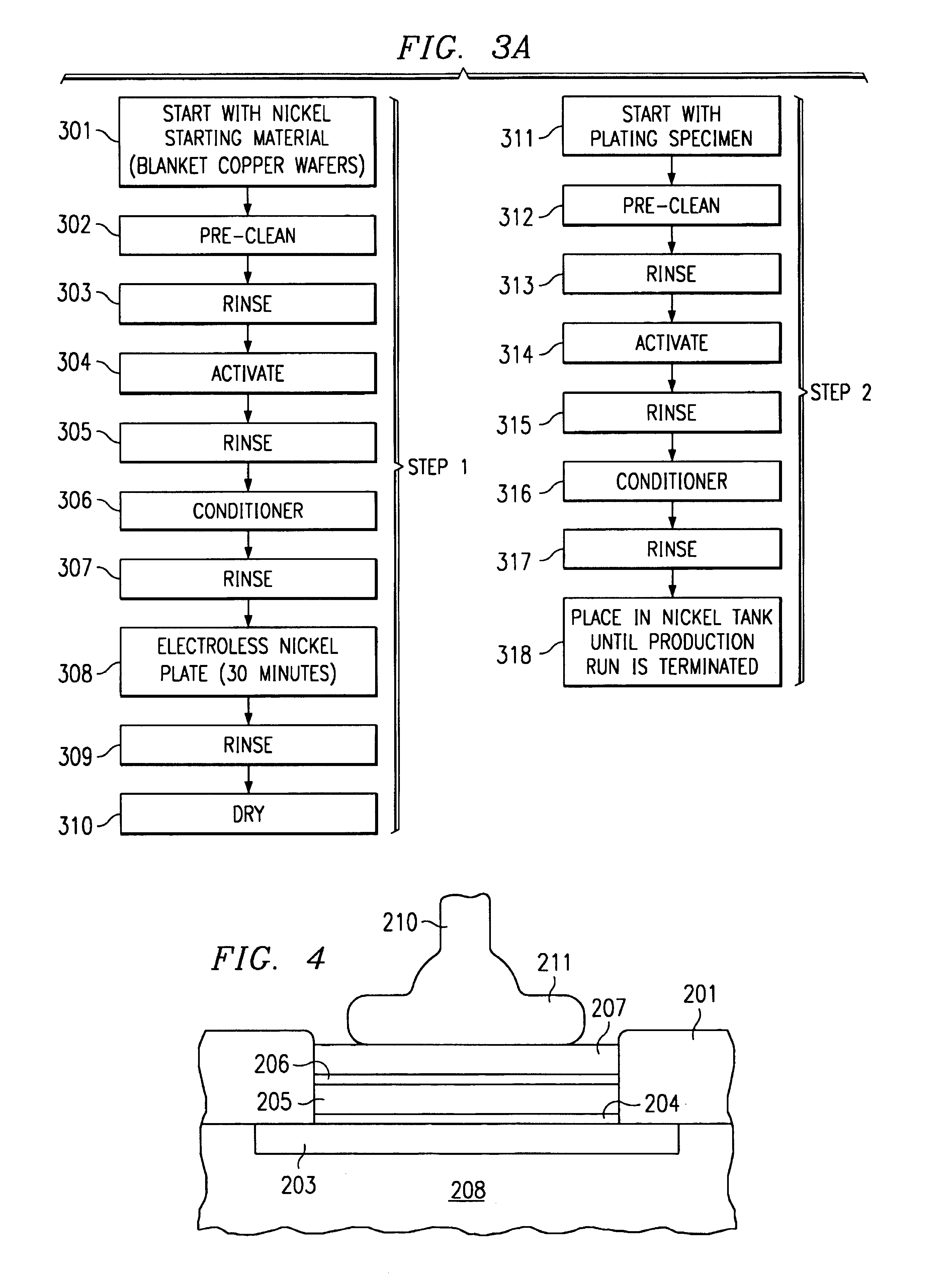
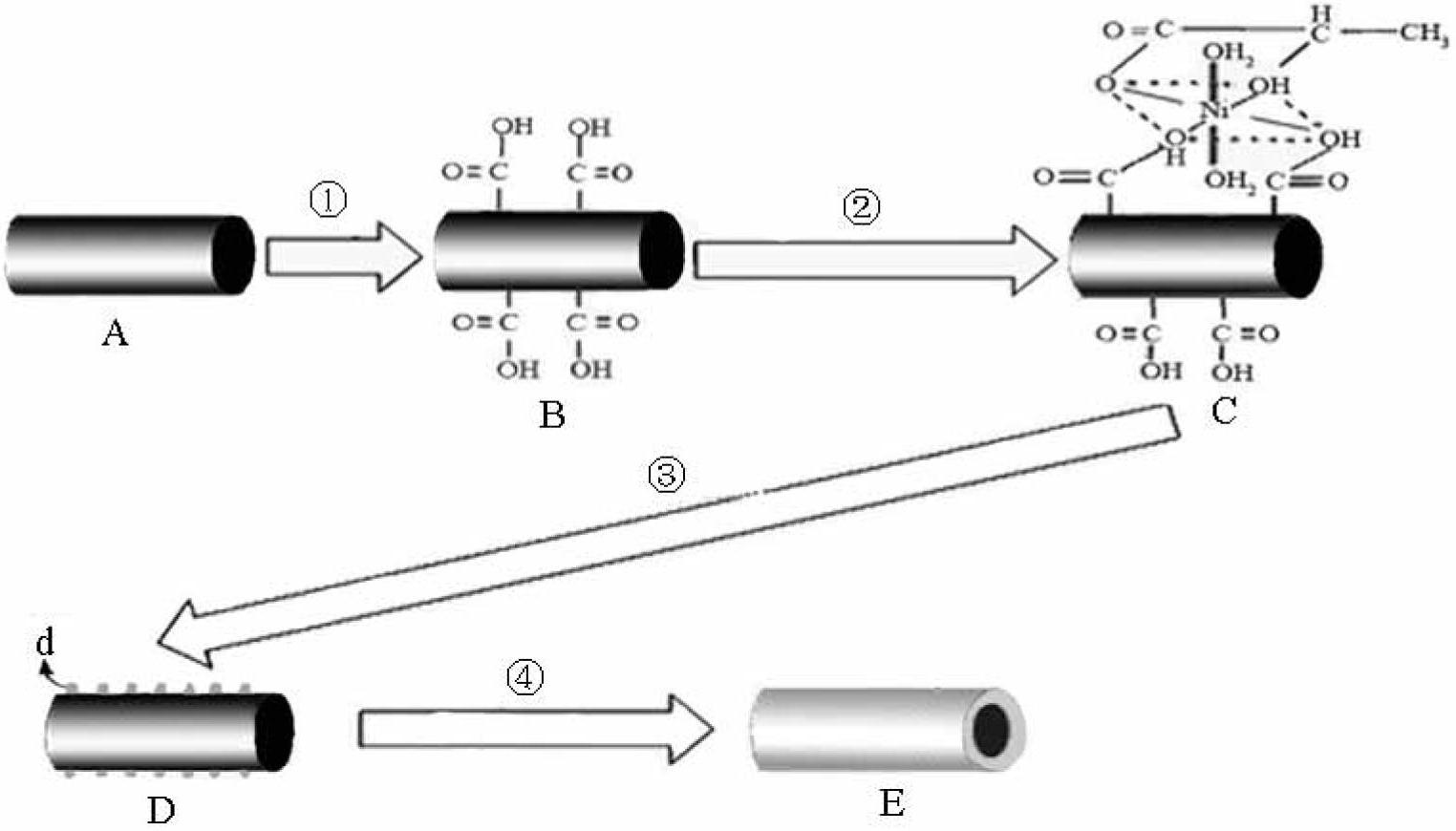
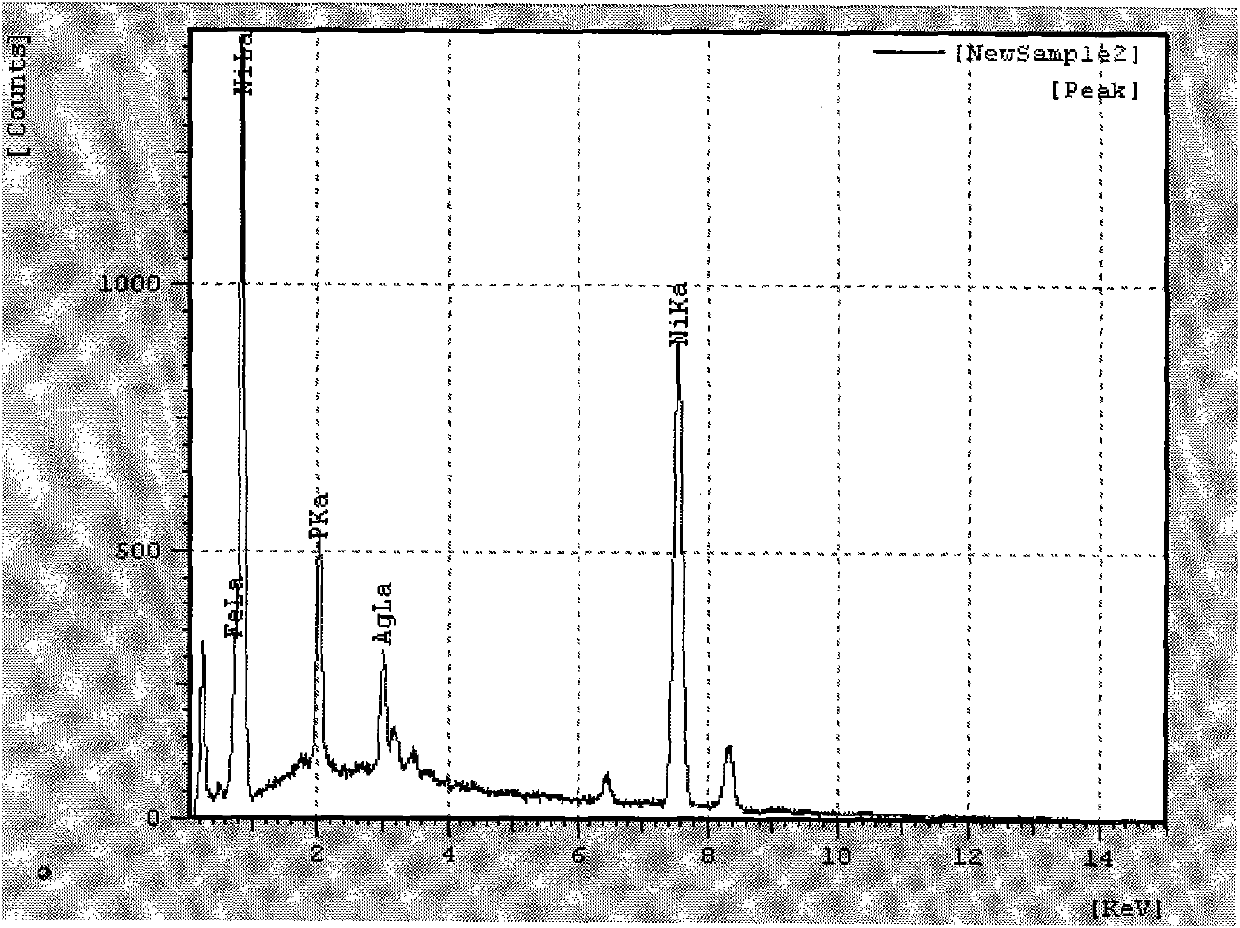
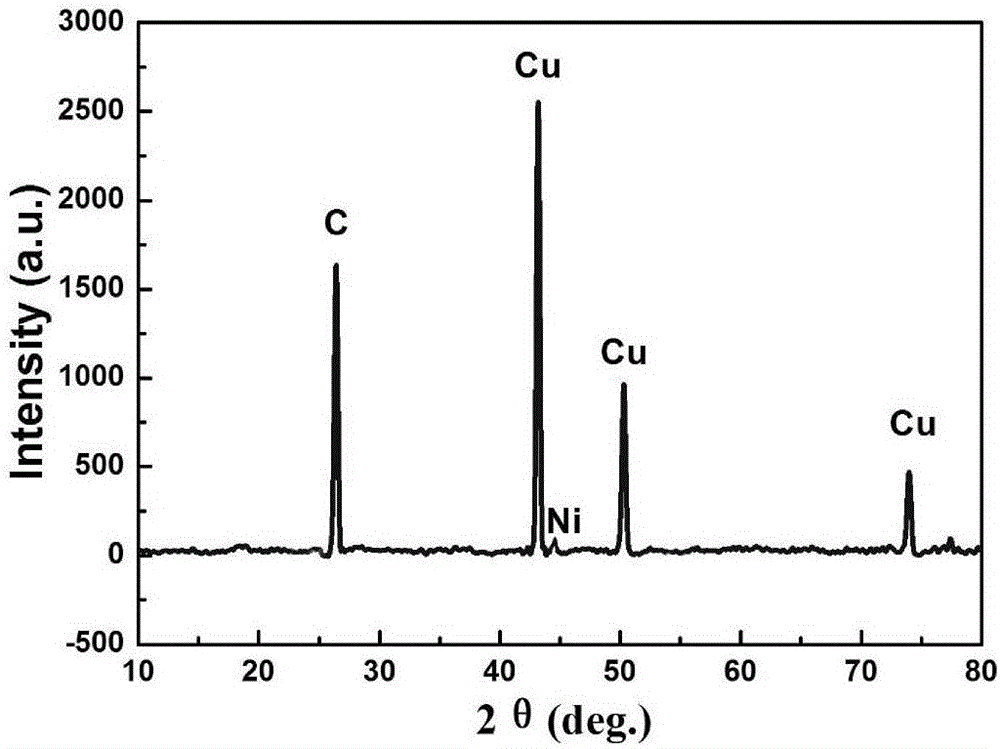
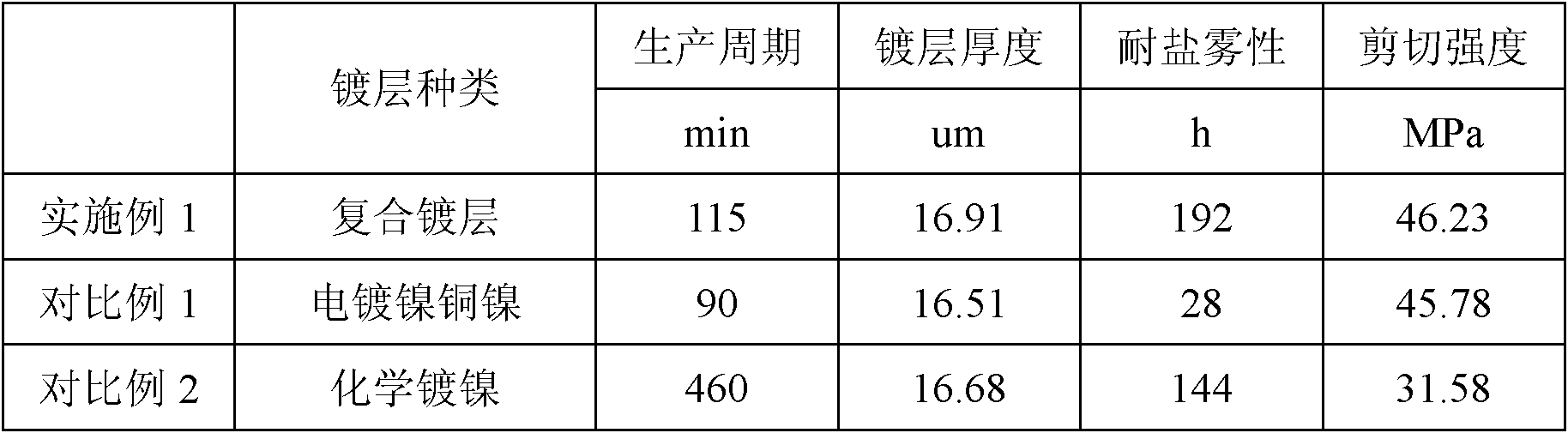
Electroless nickel (EN) plating is an auto-catalytic reaction that deposits an even layer of nickel-phosphorus or nickel-boron alloy on the surface of a solid material, or substrate, like metal or plastic. The process involves dipping the substrate in a bath of plating solution, where a reducing agent, like hydrated sodium hypophosphite (NaPO₂H₂ · H₂O), reacts with the material's ions to deposit the nickel alloy. The metallurgical properties of the alloy depend on the percentage of phosphorus, which can range from 2–5% (low phosphorus) to 11–14% (high phosphorus). Unlike electroplating, it is not necessary to pass an electric current through the plating solution to form a deposit. Electroless plating prevents corrosion and wear, and can be used to manufacture composite coatings by suspending powder in the bath. EN plating creates an even layer regardless of the geometry of the surface – in contrast to electroplating which suffers from flux-density issues as an electromagnetic field will vary due to the surface profile and result in uneven depositions. Depending on the catalyst, EN plating can be applied to non-conductive surfaces.
Organic thin film forming apparatus
InactiveUS20130333619A1Low costEasy to disassembleLiquid surface applicatorsVacuum evaporation coatingElectroless nickelOptoelectronics
An organic thin film forming apparatus that can easily remove an organic thin film adhered to a surface of a deposition preventive plate. The apparatus forms an organic thin film on a substrate disposed on a surface of a substrate stage from an organic gas. An electroless nickel film containing fluorine resin is formed on the surface of a deposition preventive plate. The electroless nickel film containing fluorine resin has mold release characteristics for an organic thin film. Even if the organic thin film adheres, the organic thin film can be easily removed by a method (such as, high pressure cleaning).
Owner:ULVAC INC
Method to achieve continuous hydrogen saturation in sparingly used electroless nickel plating process
InactiveUS6616967B1Maintain saturationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHydrogenCopper
An improved wire bonding process for copper-metallized integrated circuits is provided by a nickel layer that acts as a barrier against up-diffusing copper. In accordance with the present invention the nickel bath is placed and remains in hydrogen saturation by providing a piece of metal that remains in the nickel plating tank before and during the plating process.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Corrosion-resistant copper bond pad and integrated device
InactiveUS20050001324A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsElectroless nickelAlloy
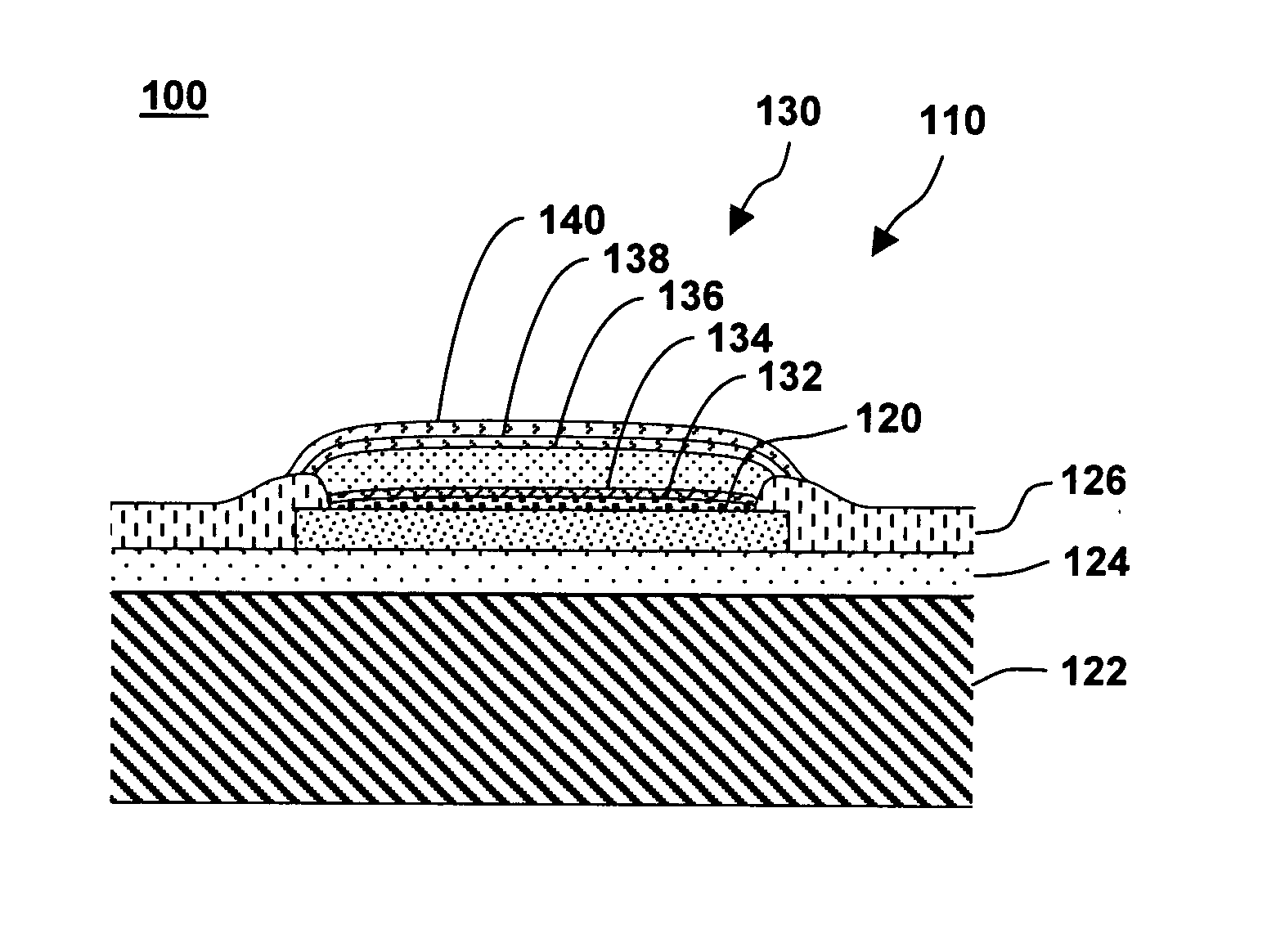
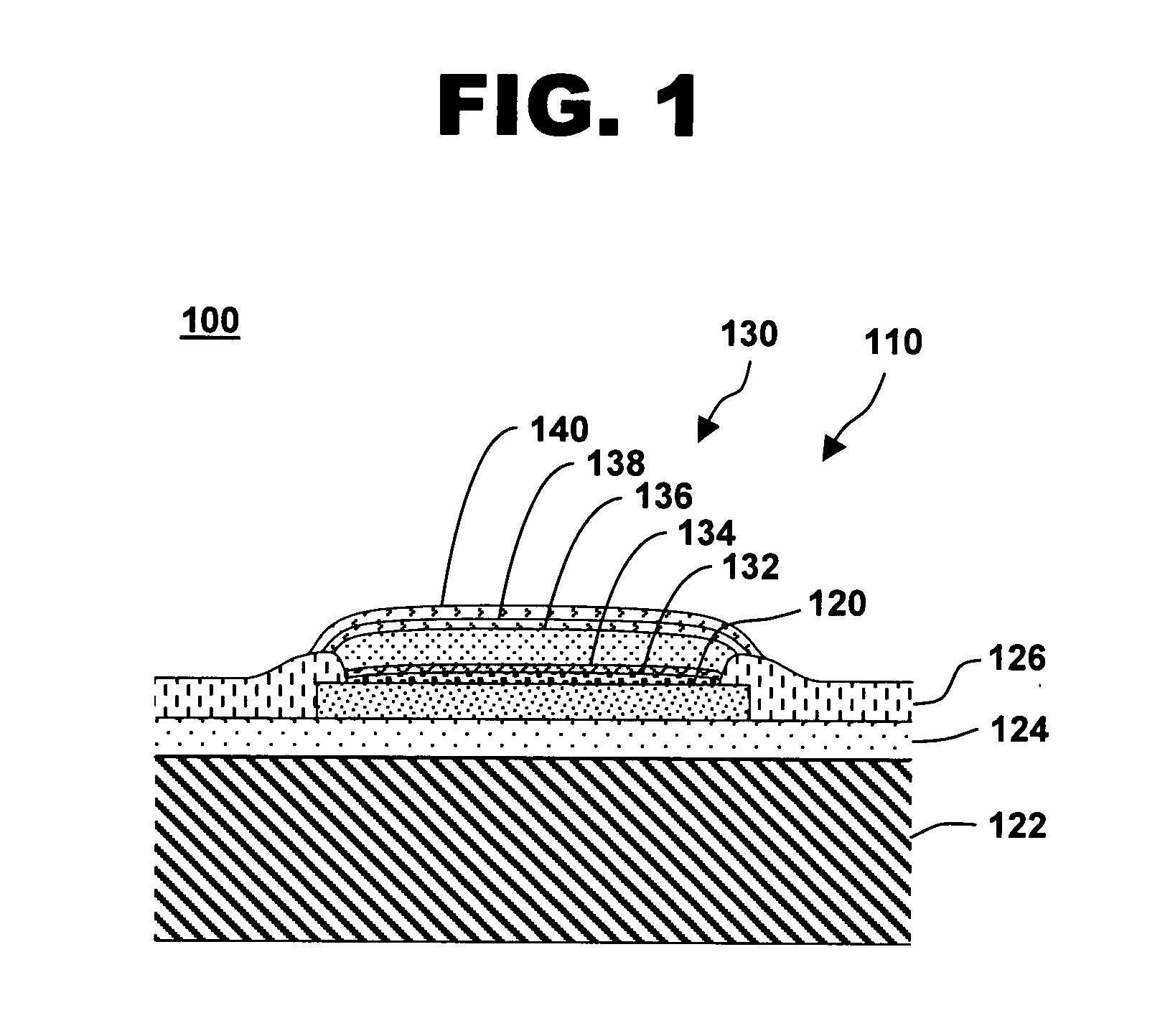
The invention provides an integrated device with corrosion-resistant capped copper bond pads. The capped copper bond pads include at least one copper bond pad on a semiconductor substrate. An activation layer comprising one of immersion palladium, electroless cobalt, or immersion ruthernium is disposed on the copper bond pad. A first intermediate layer of electroless nickel-boron alloy is disposed on the activation layer. A second intermediate layer comprising one of electroless nickel or electroless palladium is disposed on the first intermediate layer, and an immersion gold layer is disposed on the second intermediate layer. A capped copper bond pad and a method of forming the capped copper bond pads are also disclosed.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Method of Chrome Plating Magnesium and Magnesium Alloys
ActiveUS20090317556A1Liquid surface applicatorsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingCopper coatingChrome plating
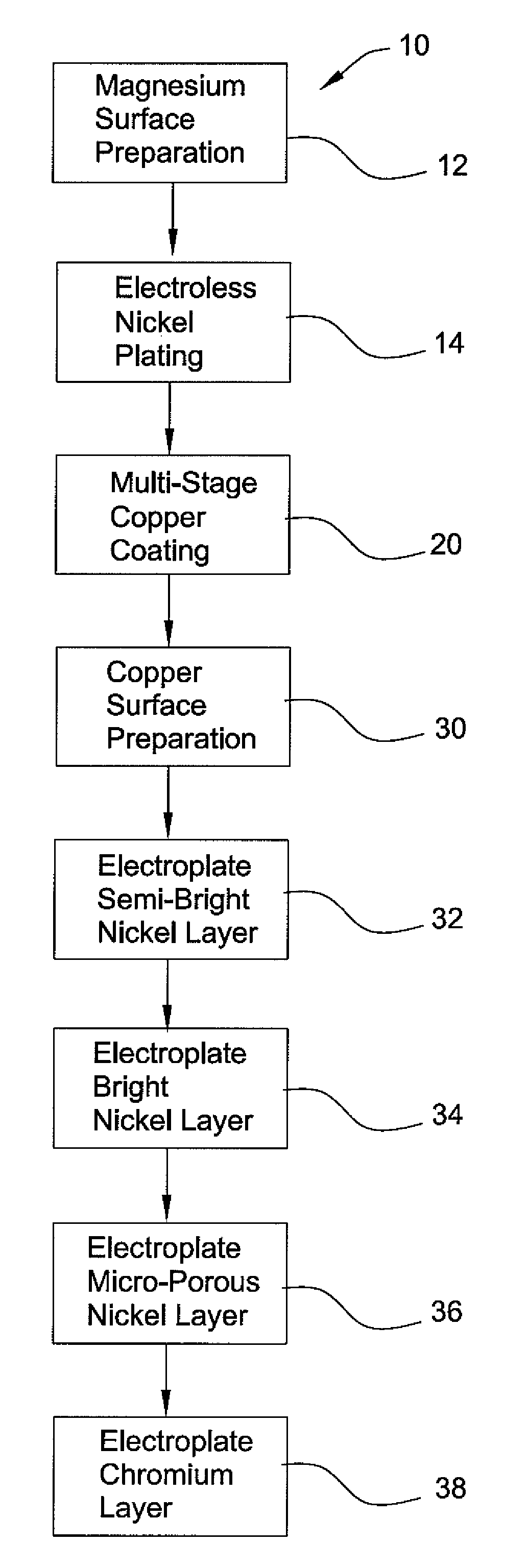
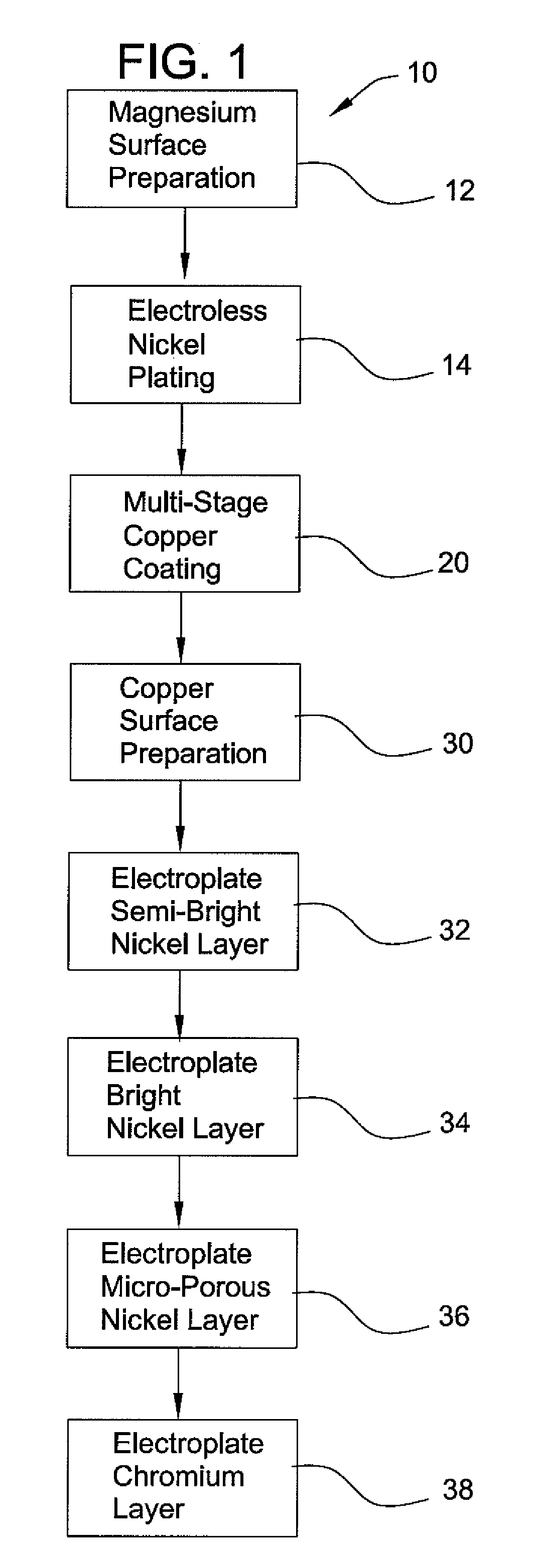
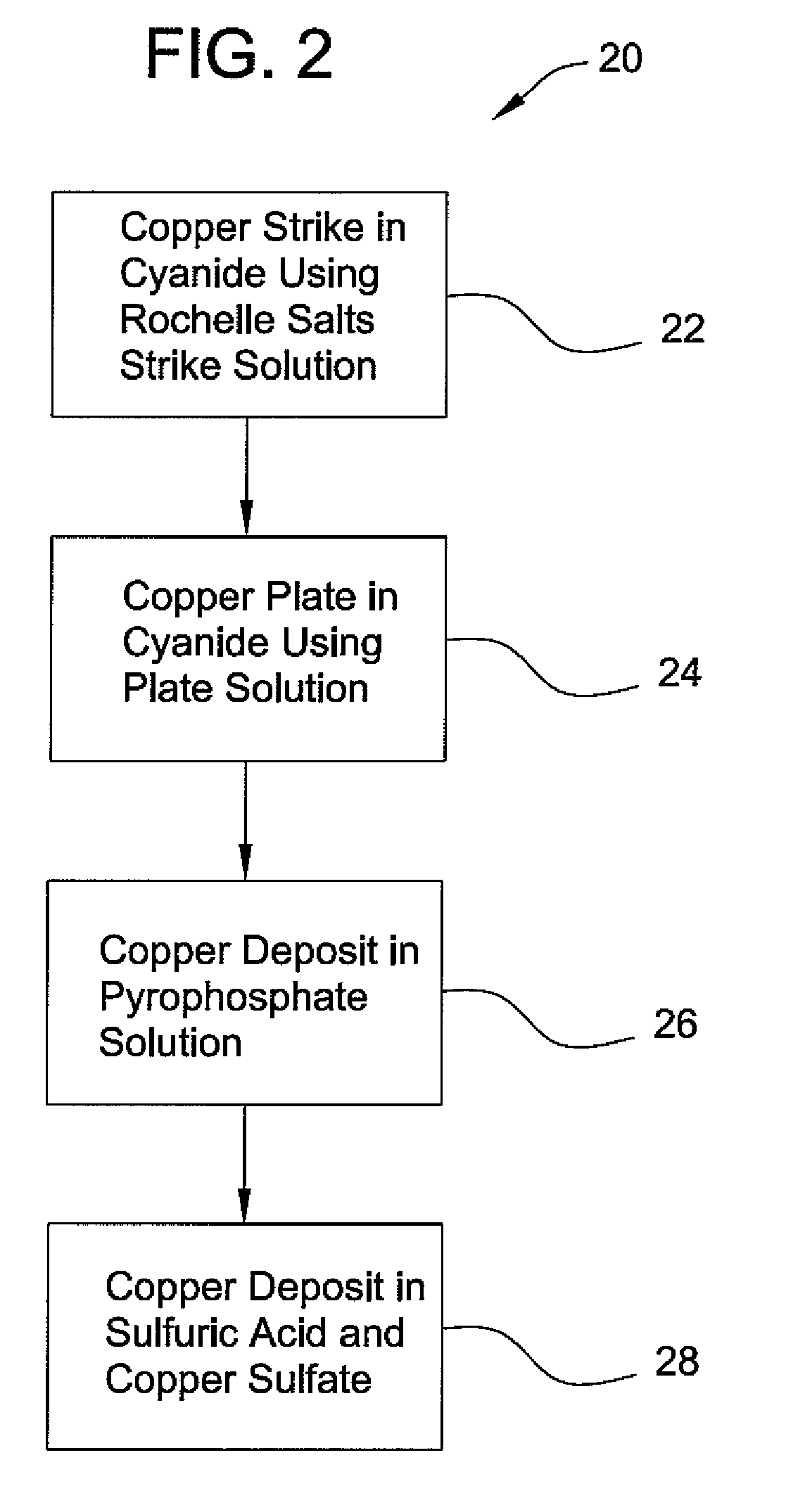
A process for chrome plating magnesium and its alloys. The process uses a combination of electroless nickel plating, a multi-stage copper coating transition system and multiple layers of electrodeposited nickel to form a corrosion resistant system of substantial impermeability and interlayer adherence suitable for direct chromium electroplating.
Owner:ARLINGTON PLATING
Superficial treatment method of printed wiring board
ActiveCN101525744APrevent oxidationGuaranteed reliabilityLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingCompound (substance)Palladium
The invention discloses a superficial treatment method of printed wiring board, which is dedicated to solving the technical problem of preventing black pad in the process of plating ENIG by chemical means, ensuring reliability of welding and routing process. The method comprises the following steps: chemical Immersion of nickel, chemical immersion of palladium and chemical gilding. Compared with the prior art, chemical immersion of nickel, chemical immersion of palladium and chemical gilding are carried out on the printed wiring board to obtain Ni / Pd gold plating, thus effectively preventing long-term oxidization of palladium surface in the air and ensuring reliability of welding combination and routing combination.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHENGGONG CHEM
Magnesium alloy non cyanogen plating copper chemical plating nickle and its plating process
InactiveCN1598059AImprove bindingUniform coating thicknessSuperimposed coating processCopper platingChemical plating
The invention discloses a method of plating Nickel with magnalium alloy without cyanogen and the plating technique. The direction for the plating solution is: 20 to 80g.dm-3 of copper charred phosphate; one or several of the 60 to 320g.dm-3 of sodium charred phosphate or Potassium charred phosphate or 60 to 250g.dm-3 of sodium citric acid, 5 to 20g.dm-3 of Potassium sodium tartaric acid, 60 to 250g.dm-3 of HEDP and 60 to 250g.dm-3 of amine ethylene; one or several of the 5 to 20g.dm-3 of hydrogen amine di-fluorin or 5 to20 g.dm-3 sodium fluoride or 5 to 20g.dm-3 of Potassium fluoride or 5 to 20g.dm-3 of lithium fluoride. The plating solution chooses the nickel sulfate or alkali type nickel carbonate or nickel acetic acid as the main salt and adds the reducing agent, combination agent and stabilization agent. The plating technique adopts the acid plating copper-plating three nickel-plating chromium. The invention has little pollution to the environment, high binding power and erosion-proof property.
Owner:GCI SCI & TECH +1
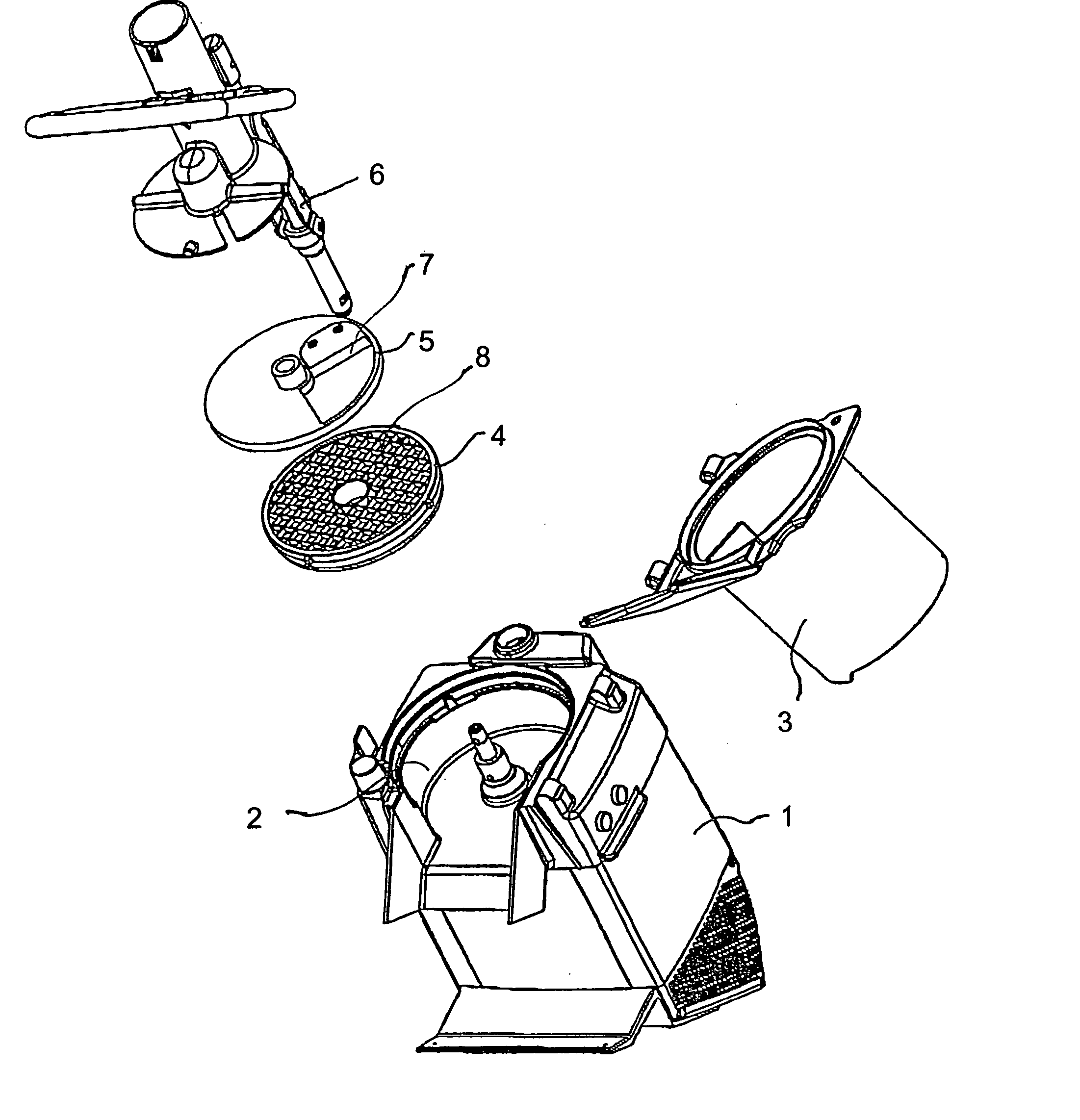
Food processing appliance
A food processing appliance, such as a food slicing or a food dicing machine, that includes aluminum components, such as cutting discs that include knives and / or food dicing gratings, and feeders that come into contact with the food being processed, wherein the aluminum components being made in die cast aluminum. After being cast, cleaned and possibly treated, an aluminum component is tumbled so as to obtain a dense surface. The tumbled component is coated with the aid of a chemical nickel plating process, wherein the chemically applied coating has a thickness exceeding 5 mum.
Owner:HALLDE MASKINER
Preflux, flux, solder paste and method of manufacturing lead-free soldered body
InactiveUS20050217757A1Improve stabilityReduce contentPrinted circuit assemblingWelding/cutting media/materialsThioketoneKetone
There is closed a flux which is designed to be used in a soldering using a lead-free and zinc-free solder containing tin as a major component and not containing lead, the soldering being adapted to be applied to a surface portion which is constituted by a copper-based metal and / or a nickel-based metal (excluding the case where the surface portion is constituted by electroless nickel plating), wherein the flux contains at least one kind of material selected from the group consisting of a copper-based metal, a nickel-based metal, an inorganic salt of copper-based metal and / or a nickel-based metal, an inorganic complex of copper-based metal and / or a nickel-based metal, and an organic complex of copper-based metal and / or a nickel-based metal (a metal complex of an organic compound where atoms of N, O and S in amine (excluding nitrogen-containing hetrocyclic compounds), imine (excluding nitrogen-containing hetrocyclic compounds), oxime, ketone, alkoxy and thioketone are coordinated with a metal). There is also closed a method of manufacturing a lead-free soldered body wherein this flux is employed.
Owner:ESE IND S
Method for plating printed circuit board and printed circuit board manufactured therefrom
InactiveUS20070104929A1Reduce thicknessDecreasing solderabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectroless nickelCrazing
Disclosed herein are a method for plating a printed circuit board and the printed circuit board manufactured therefrom. In the method, a bare soldering or wire bonding portion of a copper (Cu)- or copper alloy layer, is plated with palladium (Pd) or a palladium alloy, and then gold (Au) or a gold alloy is deposited over the palladium or palladium alloy plated layer by an electroless substitution plating process based on ionization tendency. Having superior hardness, ductility and corrosion resistance, palladium is suitable for use between a connector and a substrate and meets requirements for the printed circuit board even when applied to a low thickness, greatly reducing the process time. Accordingly, the problem of black pad, which frequently occur on electroless nickel and electroless gold finish upon surface mount technology, can be perfectly solved. Particularly, fatal bending cracks can be prevented from occurring in the rigid-flexible or flexible printed circuit boards.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD +1
Method for chemically plating nickel on surface of carbon fiber
InactiveCN102644069AEfficient removalImprove hydrophilicityFibre treatmentLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingFiberActivated carbon
The invention relates to a method for chemically plating nickel on the surface of carbon fiber. The invention aims to solve the problem that the existing method for chemically plating the nickel on the surface of the carbon fiber causes environment pollution, is unstable in activation fluid, complex in operation, and low in plating layer bonding intensity. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, firstly, removing glue and oil from the surface of the carbon fiber; 2, soaking in concentrated nitric acid for coarsening, then washing by distilled water under the help of ultrasound, and finally drying into constant weight, so that the cleaned and coarsened carbon fiber can be obtained; 3, firstly, soaking the obtained product in the activation fluid, then washing by distilled water and soaking in sodium borohydride solution to be reduced, and finally rewashing by distilled water, so that the activated carbon fiber can be obtained; and 4, soaking into chemical nickel-plating liquid, withdrawing, and washing by distilled water, and then drying into constant weight, so that the nickel can be chemically plated on the surface of the carbon fiber. The method for is mainly used for chemically plating the nickel on the surface of the carbon fiber.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for processing surface of magnesium alloy
InactiveCN101092694AReduced insulationPrevent breakdownAnodisationLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingMicro arc oxidationChemical plating
This invention discloses a surface treatment method for Mg-based material. The method comprises: (1) performing micro-arc oxidation treatment on Mg or Mg alloy work piece as the anode in a Cl--free alkaline micro-arc oxidation electrolyte; (2) activating; (3) performing preliminary chemical plating of Ni; (4) performing chemical plating of Ni; (5) performing thermal treatment. The micro-arc oxidation treatment comprises: (1) applying a positive pulse with an average current density of 5-20 A / dm2 until the voltage is automatically elevated to a critical value, and applying a constant working voltage of 50-80 V (total time = 5-30 min); (2) applying a positive pulse of 30-300 V and a negative pulse of 0-200 V with an average current density of 0.5-15 A / dm2 (total time = 10-60 min). The activation comprises: (1) performing anode alkaline coarsening treatment for 3-10 min; (2) performing surface activation treatment; (3) performing cathode alkaline electrification reduction activation treatment; (4) performing cathode acidic electrification dispergation activation treatment. The treated Mg alloy work piece has high corrosion resistance of ceramic materials and the properties and touch sense of metal materials.
Owner:李克清 +1
Flux for soldering and circuit board
InactiveUS20060147683A1High bonding strengthSuppress DiffuseBlast furnace componentsBlast furnace detailsSolventCopper complex
A flux contains resin having film forming ability, activator, solvent, and at least one complex selected from silver complex and copper complex. The flux is used when soldering is performed onto a circuit having electroless nickel plating or further having gold plating on the electroless nickel plating. Allowing a barrier layer of silver or copper to deposit on the surfaces of lands suppresses the diffusion of nickel into the melted solder alloy during soldering, and also prevents phosphorous concentration. This improves the bonding strength of soldering and suppresses the reduction deposition of silver and / or copper to portions other than circuit patterns.
Owner:HARIMA CHEM INC
Method for chemical plating metal for non-metal substrate surface and pretreatment system used thereof
InactiveCN1641070ASave resourcesReduce manufacturing costLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingAlkaneCopper plating
The present invention discloses new activating process and activating solution with non-noble metal for chemical plating of metal onto the surface of non-metal base material. The activating solution is alkaline organic metal complex solution comprising water soluble salt of bivalent Ni, Cu or Co ion, organic alkane complexing agent and pH regulator. The new activating process and activating solution of the present invention may be used to replace available process and solution with noble metal for wide use in the chemical plating of metal material onto the surface of non-metal base material, such as chemically plating nickel, chemically plating copper, chemically plating cobalt, etc. The activating solution of the present invention is stable, simple in technological process and low in cost, and the present invention makes it possible to save noble metal resource effectively and is ideal technology to replace available one.
Owner:HUNAN CORUN NEW ENERGY CO LTD
Controlled plating on reactive metals
InactiveUS6503343B1Avoid consumptionInhibited porositySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectroless nickelSolubility
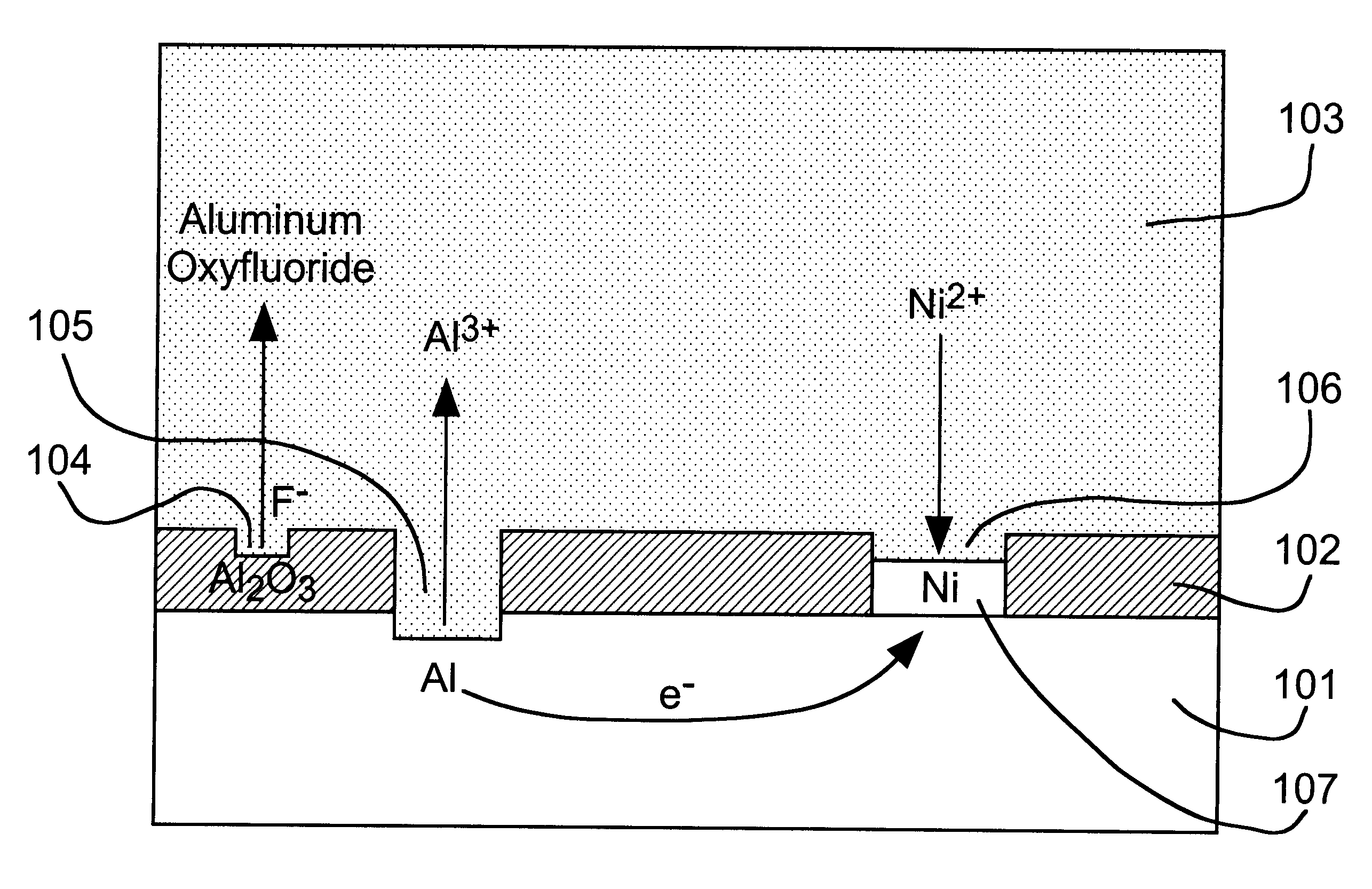
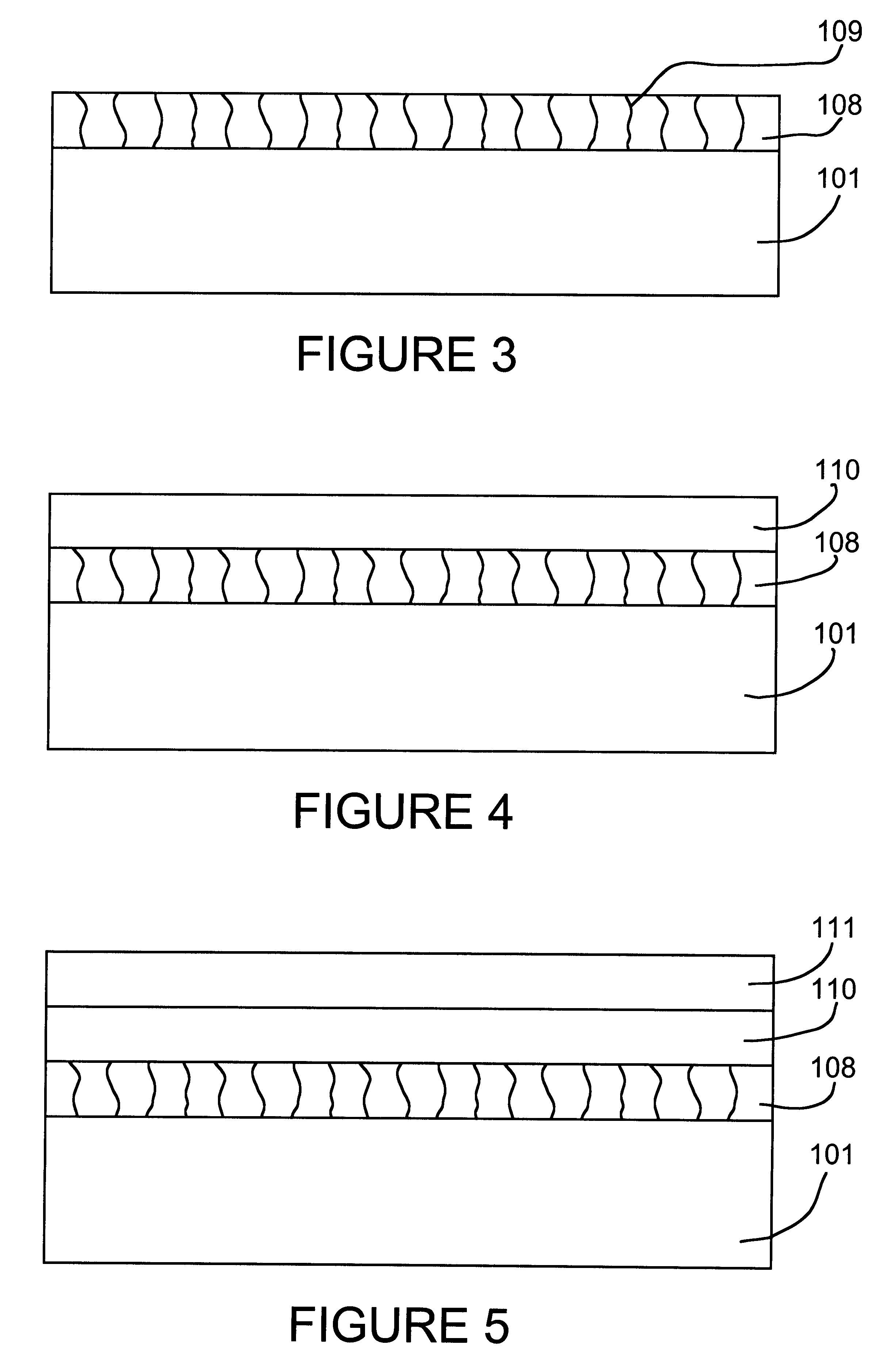
A direct displacement plating process provides a uniform, adherent coating of a relatively stable metal (e.g., nickel) on a highly reactive metal (e.g., aluminum) that is normally covered with a recalcitrant oxide layer. The displacement reaction proceeds, preferably in a nonaqueous solvent, as the oxide layer is dissolved by a fluoride activator. Halide anions are used to provide high solubility, to serve as an anhydrous source of stable metal ions, and to control the rate of the displacement reaction. A low concentration of activator species and little or no solution agitation are used to cause depletion of the activator species within pores in the surface oxide so that attack of the reactive metal substrate is minimized. Used in conjunction with electroless nickel deposition to thicken the displacement coating, this process can be used to render aluminum pads on IC chips solderable without the need for expensive masks and vacuum deposition operations. Such coatings can also be used to preserve or restore wire bondability, or for corrosion protection of aluminum and other reactive structural metals and alloys. A thin layer of immersion gold can be used to protect the thickened coating from oxidation. The solderable aluminum IC chip pads provide the basis for a maskless bumping process for flip chip attachment.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Preparation method of nickel-plated and silver-plated aromatic polyamide conductive fibers
The invention relates to a preparation method of nickel-plated and silver-plated aromatic polyamide conductive fibers, which comprises the following concrete steps of: a. washing and oil removal; b. coarsening: increasing the surface roughness and the surface wettability of fibers; c. sensitizing: soaking the fibers by adopting an aqueous solution formed by stannous chloride and hydrochloric acid; d. activation: soaking the fibers by adopting an aqueous solution formed by palladium chloride and hydrochloric acid; e. chemical nickel plating; f. sensitizing; g. activation; h. chemical silver plating; and i. coating protection. The prepared high performance nickel-plated and silver-plated aromatic polyamide conductive fibers have good electric conductivity, characteristics of heat resistance, flame retardance, light weight and high strength and functions of eliminating static electricity, conducting electricity and transmitting electrical signals. Therefore, the prepared nickel-plated and silver-plated aromatic polyamide conductive fibers can be widely applied to special departments of aviation, space flight, war industry, communication and the like and can also satisfy the clothing and equipment requirements of staffs engaging radars, television relaying and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for performing electroless nickel plating on surface of aluminum nitride ceramic
ActiveCN101962760AHigh bonding strengthImprove high temperature resistanceLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectroless nickelSodium acetate
The invention provides a method for performing electroless nickel plating on the surface of aluminum nitride ceramic, belonging to the ceramic thin-film metallization field. The method comprises the following specific steps: 1) polishing the surface of aluminum nitride with a machinery; coarsening the aluminum nitride substrate with mixed acid or alkali, completely cleaning away the residual acid or alkali; 3) sensitizing the coarsened substrate in stannous chloride solution, activating in palladium chloride solution or performing activation without palladium; 4) weighting a certain amount of nickel sulphate, sodium hypophosphite, sodium citrate, sodium acetate, lactic acid, thiourea and sodium dodecyl sulfate in sequence to prepare a chemical plating solution; and 5) adjusting the pH value of the solution to 4.0-6.0 with acid or alkali, heating the solution to 70-95 DEG C, and placing the prepared substrate in the solution to perform electroless nickel plating. The invention is characterized in that the electroless nickel plating can be performed on the surface of the aluminum nitride ceramic substrate which is difficult to plate; and a certain amount of surfactant is added so that the plating becomes denser and smoother, the binding force between the plating and the substrate is increased, and the solderability of the plating is better.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Chemical nickel-plating method for carbon fiber
InactiveCN102086517ALow costEasy to operateLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingFiberCarbon fibers
The invention discloses a chemical nickel-plating method for carbon fiber, which is designed for overcoming the disadvantages of high cost, a large number of process steps and poor operability existing in the prior art. In the method, a chemical plating process is adopted; and a pre-treatment is performed on a raw material and chemical plating solution is prepared before the chemical plating. The pre-treatment process comprises the steps of: calcining by using a muffle furnace to remove glue; soaking in solution of absolute ethanol to remove oil; performing surface roughening and activating treatment by using solution of sodium hydroxide and solution of silver ammonia; sensitizing by using a sensitizer, namely stannous chloride; and performing surface reduction by using solution of sodium hypophosphite. The chemical plating solution consists of nickel sulfate hexahydrate, sodium hypophosphite, sodium pyrophosphate and sodium citrate. The chemical nickel-plating on the carbon fiber is finished by placing a pre-treatment product of the chemical plating into the chemical plating solution, and reacting, standing, filtering and drying under a chemical plating condition. The method has the characteristics that: the product has a uniform surface, a compact plating layer and uniform particles.
Owner:沈阳临德陶瓷研发有限公司
Copper-carbon composite material and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN106424713APromotes even distributionImprove performanceTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusFiberCarbon composites
The invention discloses a copper-carbon composite material and a preparing method thereof. Natural flake graphite, colloidal graphite, nano graphite, carbon fiber and the like can be selected as a carbon material in the copper-carbon composite material. The preparing method of the copper-carbon composite material includes the steps that firstly, a chemical nickel plating method is used for preparing a nickel plating carbon material; then a chemical copper plating method is used for plating copper on the nickel plating carbon material; and finally, vacuum semi-solid-state low-pressure sintering is conducted on the copper plating carbon material under the copper melting point temperature, and the copper-carbon composite material is prepared. The copper-carbon composite material and the preparing method thereof have the beneficial effects that a layer of even thin nickel plating layer is formed on the surface of carbon through the nickel plating method so as to reduce the wetting angle of the carbon material, the copper plating layer is formed on the surface of the nickel plating carbon material through the copper plating method so that a three-dimensional copper network can be formed by the material in the sintering process, and the bonding strength of a base body is improved through vacuum semi-solid-state low-pressure sintering. The two phases of the base body and the carbon of the copper-carbon composite material prepared through the method are distributed evenly and are well combined, and the good electricity and mechanical properties and the good frictional wear performance are achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Non-ammonia type plating solution for chemical nickel plating
InactiveCN101314848ANo pollution in the processNo pollutionLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingChemical platingNickel salt
The invention discloses an ammonia-free chemical nickel plating bath which adopts an ammonia-free pH modifying agent to regulate the pH value of the bath. Each liter of the bath contains the components that nickel salt is 24 to 30g, reducing agent is 24 to 33g, buffering agent is 10 to 18g, complexing agent is 20 to 30g, stabilizing agent is 0.5 to 1.5mL, brightener is 1.5 to 3.0mL, and others are water. In the ammonia-free chemical nickel plating bath, the ammonia-free pH modifying agent is selected from one or the mixture of sodium hydroxide, and potassium hydroxide or potassium carbonate. All materials in the ammonia-free chemical nickel plating bath do not contain heavy metal, ammonia water is not utilized to regulate the pH value, the problems of environment pollution, invalidation caused by overlong storing time of the bath, etc. are not caused, and the obtained chemical plating bath is friendly to the environment, in addition, the luminance brightness of the made plating layer can be full-bright. The bath has wide application prospect.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
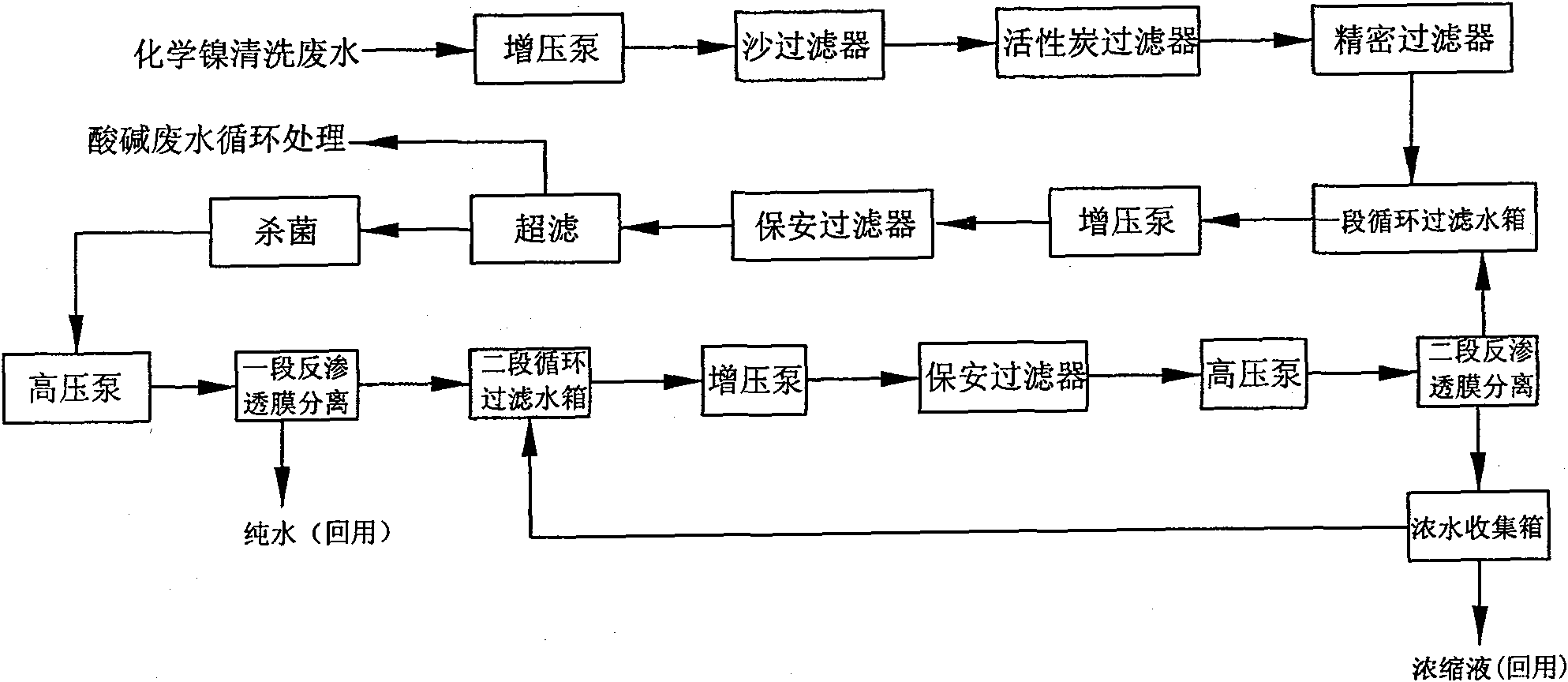
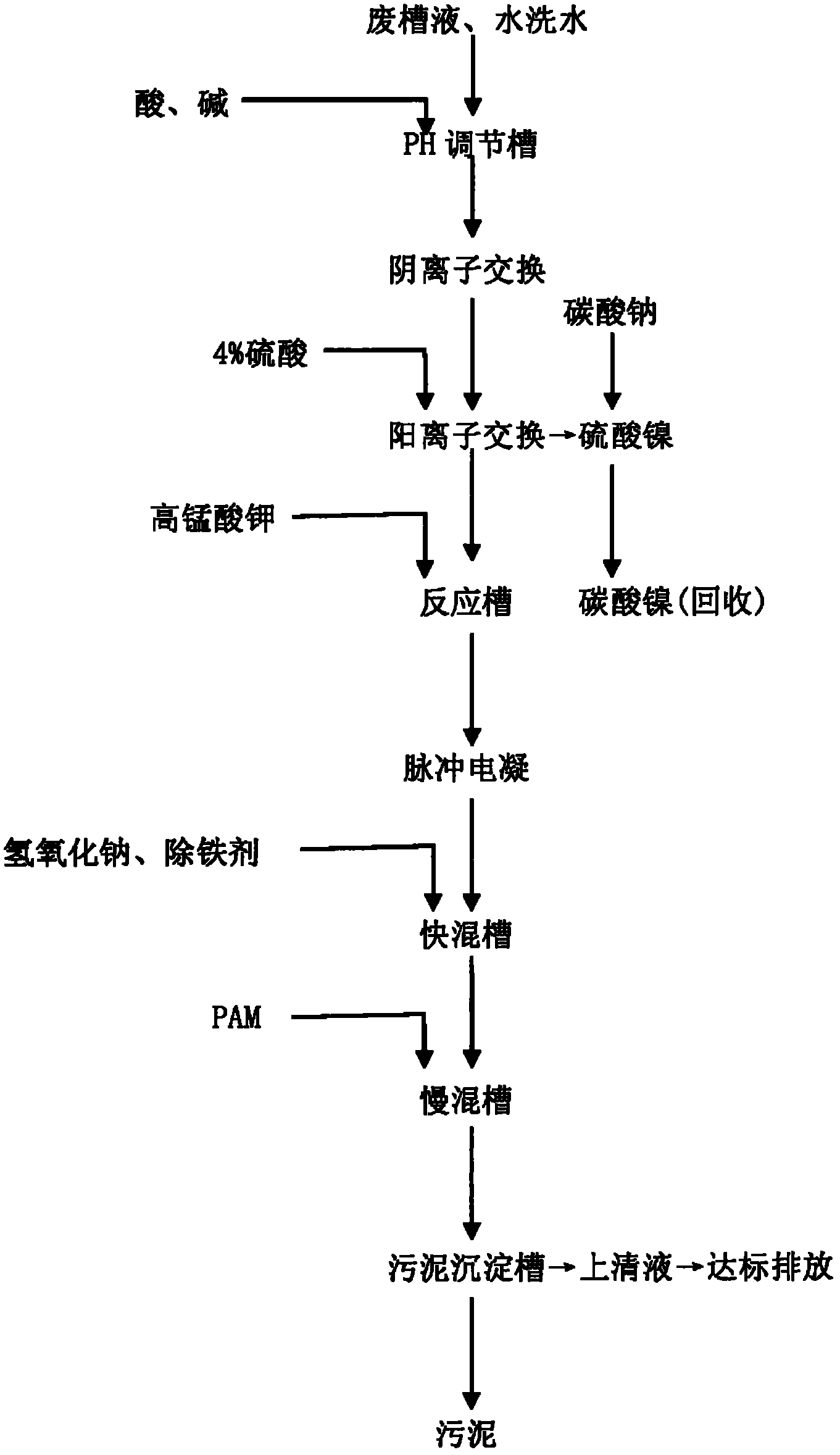
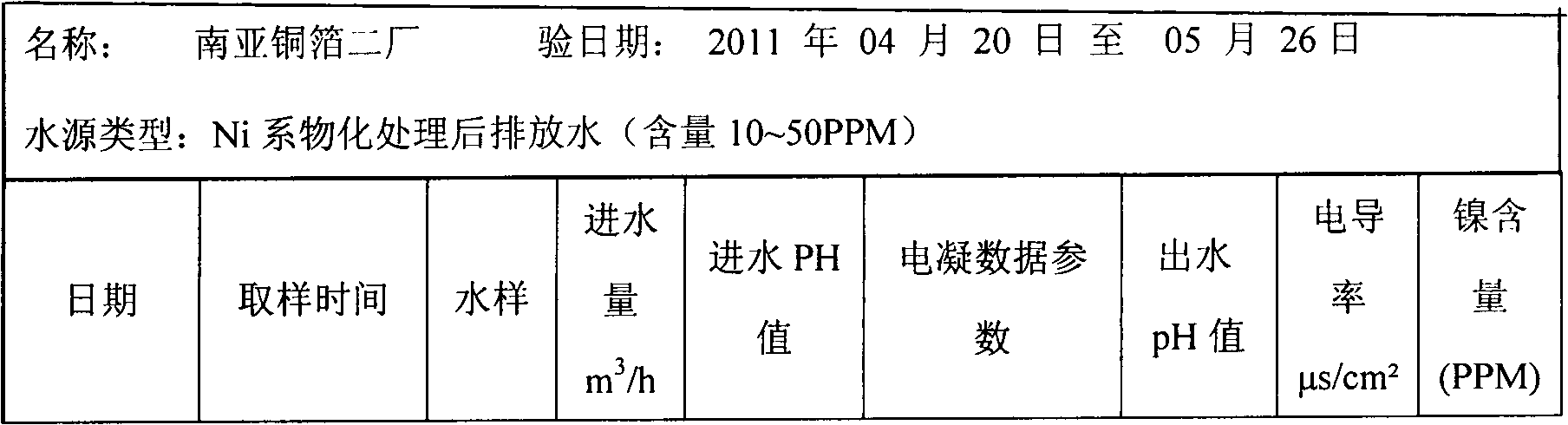
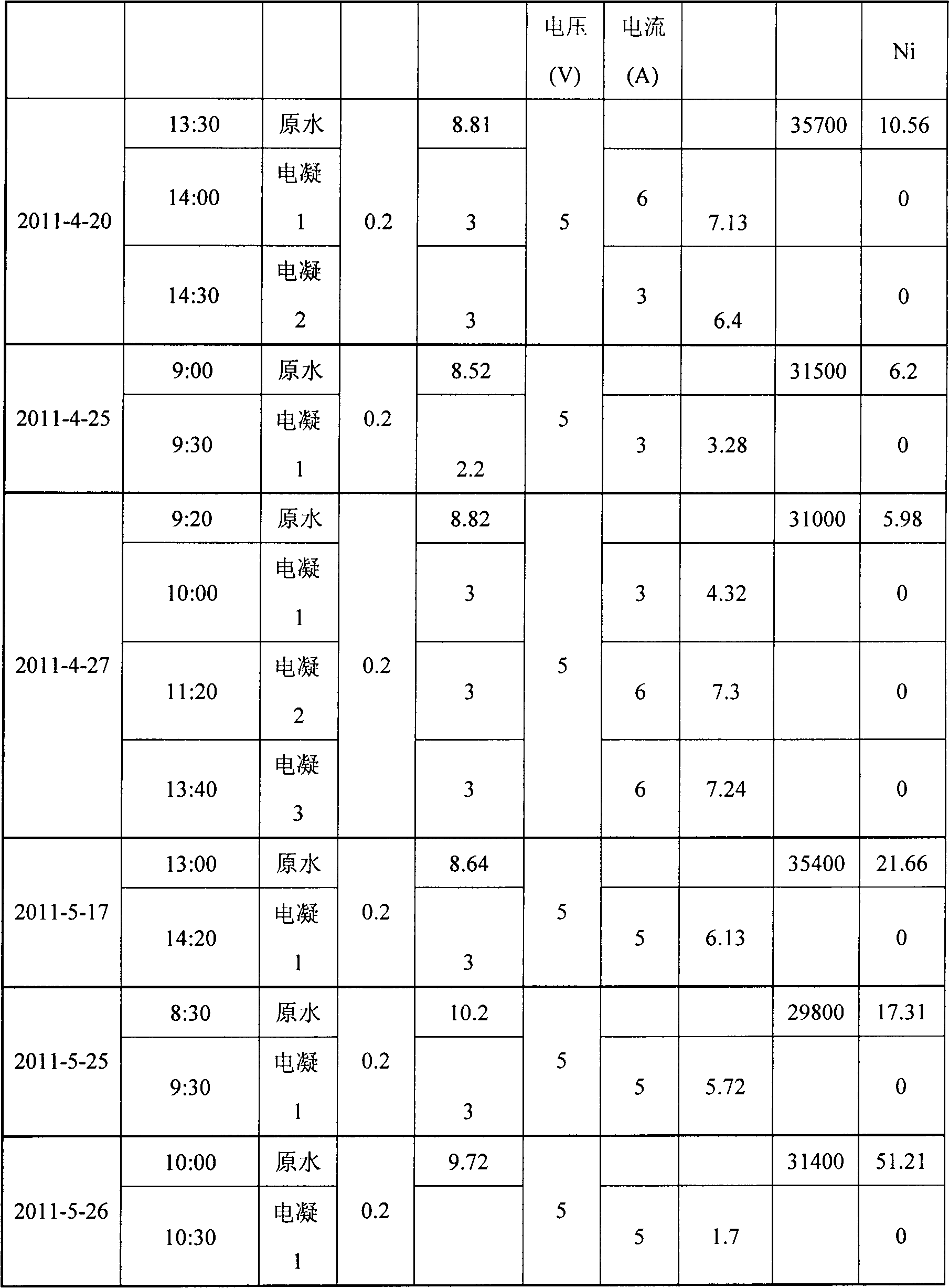
Method for treating complexed chemical nickel electroplating wastewater
InactiveCN103833123AImprove processing efficiencyGood effectWaste water treatment from metallurgical processWater/sewage treatment by oxidationPotassium ferrateAdsorption effect
The invention provides a method for treating complexed chemical nickel electroplating wastewater and aims at the problem in the existing complexed chemical nickel electroplating wastewater treatment processes that the nickel ion removal efficiency is inadequate. The method comprises the main processes of firstly adding calcium hydroxide into the wastewater, adjusting the pH to 8-9 so as to form calcium phosphate precipitates, adding sulfuric acid into a supernatant liquid so as to adjust the pH of the liquid to 4-5, then, adding a potassium ferrate liquid with strong oxidizing power so as to decomplex in a strong oxidizing manner and change complexed nickel ions into free-state nickel ions, then, adding calcium hydroxide, adjusting the pH to 10-11 so as to enable the free-state nickel ions to form precipitates to be removed from the wastewater, enabling trivalent ferric ions with excellent flocculation function generated after oxidation of ferric acid radical ions to have flocculation with hydroxide precipitates with an adsorption effect, and finally, adding polyacrylamide (PAM) to coagulate and precipitate, thereby removing nickel ions from the electroplating wastewater. The method has the advantages that the condition that the nickel ions obtained after the complexed chemical nickel electroplating wastewater is treated reach the national standards can be effectively guaranteed, the treatment efficiency is high, and the requirements on emission are met.
Owner:陈瀚翔
Electroplating and chemical plating composite protecting process for NdFeB permanent magnet and NdFeB permanent magnet with composite protective layer
InactiveCN102108511AImprove corrosion resistanceReduce porosityPermanent magnetsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingChemical platingPre treatment
The invention provides an electroplating and chemical plating composite protecting process for an NdFeB permanent magnet and the NdFeB permanent magnet with a composite protective layer, relating to the surface treatment protecting process for the NdFeB permanent magnet. The invention aims at providing the NdFeB permanent magnet electroplating and chemical plating composite protecting process and the NdFeB permanent magnet with the composite protective layer with high production efficiency and good corrosion resistance. The electroplating and chemical plating composite protecting process for the NdFeB permanent magnet comprises the following steps: (1) pre-treatment: the NdFeB permanent magnet is subjected to oil removal, dust removal and surface activation; (2) electroplating: the surface of the NdFeB permanent magnet is electroplated; (3) transitional treatment: the electroplated NdFeB permanent magnet is subjected to water cleaning and surface activation; (4) chemical plating: nickel is plated chemically outside the electroplating layer of the NdFeB permanent magnet; and (5) post-treatment: the chemically plated NdFeB permanent magnet is subjected to water cleaning, surface adjustment and drying.
Owner:YANTAI ZHENGHAI MAGNETIC MATERIAL CO LTD
Gold-plating method of high silicon-aluminum composite material
ActiveCN103540935AImprove bindingNo foamingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingBinding forceAlkaline etching
The invention relates to a gold-plating method of a high silicon-aluminum composite material. According to a second zinc immersion treatment method of conventional aluminum alloy electroplating, pre-treatment of the method comprises the following six steps: cleaning and oil removing; alkaline etching; bright dipping; primary zinc immersion; zinc annealing; secondary zinc immersion. The gold-plating method subsequently comprises the following steps: I, preplating chemical nickel in a chemical nickel-plating liquid; II, plating nickel for the first time according to a conventional nickel-plating method, wherein the nickel layer is 2-3 microns thick; III, performing aging treatment; IV, performing activating treatment; V, plating nickel for the second time according to a conventional nickel-plating method, wherein the nickel layer is 2-3 microns thick; VI, taking a pure gold plate or a platinum titanium mesh as an anode and the high silicon-aluminum composite material as a cathode according to a conventional pure gold-plating method, wherein the gold layer is 2-3 microns thick; VII, detecting the binding force of the plating layer. The plating layer observed under tenfold amplifying glass is free from peeling and bubbling phenomena and good in binding force. The binding force of the gold-plating plating layer and a high silicon-aluminum base material adopted by the method provided by the invention is firm and reaches the standard of appendix A of GJB1420 General Specification of Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Shell.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
Method for classifying, treating and recycling plating washing water on line
ActiveCN101891323AAvoid cross contaminationStrong targetingWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeCopper platingWater cycling
The invention discloses a method for classifying, treating and recycling plating washing water on line, which comprises the following steps of: removing oil, coarsening, reducing, activating, peptizing, chemically plating nickel, preplating nickel, plating copper, plating nickel and plating chromium in a plating process; and treating water and washing water during production and cleaning. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: preparing pure plating water, circularly processing acid and alkaline waste water, coarsening, circularly treating chromium-plating washing water, circularly treating chemically nickel-plating washing water, circularly treating copper-plating washing water and circularly treating nickel-plating washing water. Waste water in each procedure is directly used beside a tank edge in a closed cycle by an economical and effective means after being treated, no wastewater is discharged, and the cross contamination of different water qualities among the procedures is avoided. The method is a technological innovation for realizing zero emission of plating waste water and plating cleaner production.
Owner:NANJING YUANQUAN TECH CO LTD
Plastic product and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102071411AImprove bindingAchieve selective metallizationPrinted circuit aspectsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingCopper platingElectroplating
The invention provides a plastic product and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1) forming a plastic base, wherein the plastic base contains chemically plated catalysts which are compounds shown in the formula I, II or III; 2) removing the plastics in the selected area on the surface of the plastic base and exposing the chemically plated catalysts in the corresponding area; and 3) chemically plating copper or nickel and continuing chemical plating and / or electroplating at least once to form a metal layer on the surface of the plastic base. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple process, low requirement for energy and low cost. In addition, the chemically plated catalysts are distributed in the plastic base, so the plating layer formed after chemical plating and the plastic base have very high adhesion.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Method for degrading organic pollutant and recycling phosphate in chemical nickel-plating waste liquid
InactiveCN102616961AReduce phosphorus contentRemove completelyPhosphatesWaste water treatment from metallurgical processPhosphorous acidLiquid waste
The invention discloses a method for degrading organic pollutant and recycling phosphate in chemical nickel-plating waste liquid, which belongs to the technical field of environment-friendly waste water treatment and resource recycle. The method conducts oxidation degradation of organic pollutant in waste water through the oxidation technology, simultaneously oxidizes hypophosphorous acid radical and phosphorous acid radical in waste water into orthophosphate radical and recycles phosphate and nickel by enabling the orthophosphate radical and nonmetal or metal ions to be precipitated. The method achieves resource recycle while treating waste water and has good environment benefits and economical benefits and wide application prospect.
Owner:李朝林
Production method of suspension board with circuit
InactiveUS20050186332A1Preventing deterioration of outward appearance and defectPrevent deterioration of outward appearance and defectFluid-dynamic spacing of headsRecord information storageResistElectrical conductor
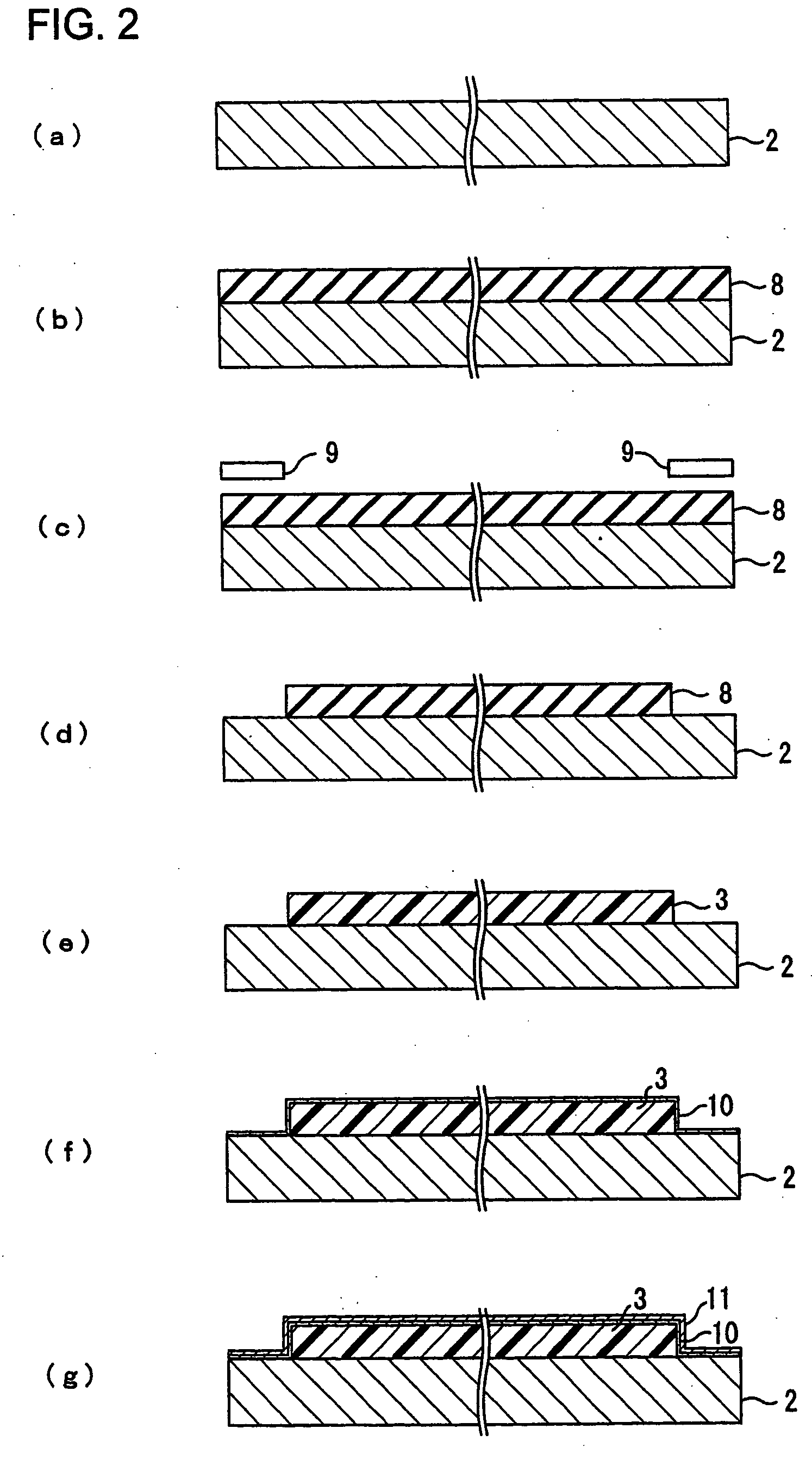
In order to provide a new production method of a suspension board with circuit capable of preventing deterioration of the outward appearance and defects in products caused by a metal supporting layer, and further capable of forming an electroless nickel plating layer having an even thickness in a reliable manner, an insulating base layer is first formed on a supporting board, and a chromium thin film and a copper thin film are formed next sequentially on the surface of the supporting board exposed from the insulating base layer and on the entire surface of the insulating base layer. Subsequently, a plating resist is formed in a reversal pattern with respect to the wired circuit pattern on the surface of the copper thin film, and a conductor layer is formed on the surface of the copper thin film exposed from the plating resist by electrolytic plating. The plating resist is removed after an electroless nickel plating layer is formed on the conductor layer. Subsequently, the copper thin film and the chromium thin film are removed sequentially, and an insulating cover layer is formed next.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
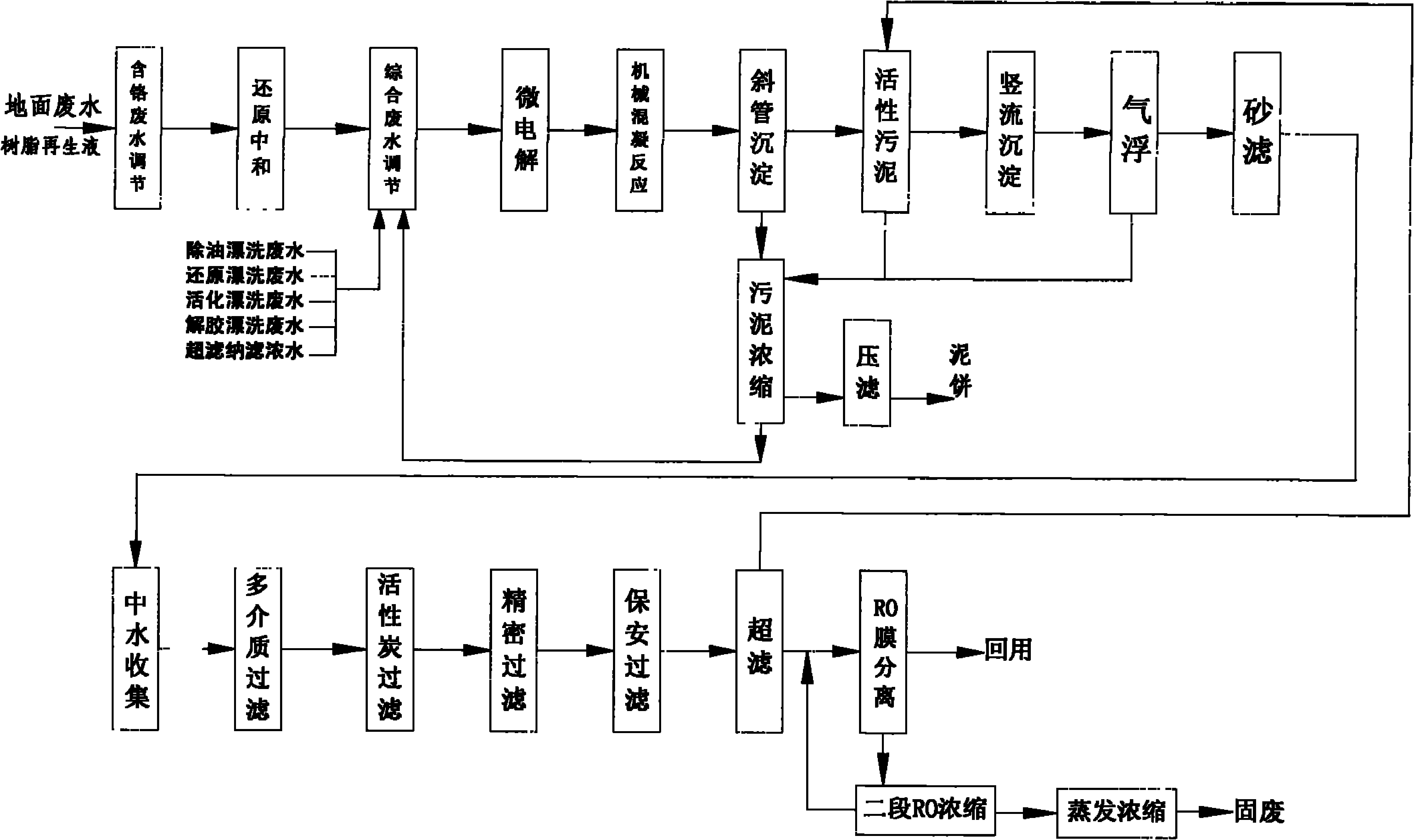
Treatment method of chemical nickel-plating wastewater
ActiveCN102329030AImprove processing economicsAchieve recyclingWaste water treatment from metallurgical processWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangePhosphateIon-exchange resin
The invention discloses a treatment method of chemical nickel-plating wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: (1) treating nickel-plating wastewater with strongly basic anion-exchange resin so as to destabilize nickel complex; (2) adsorbing nickel ions contained in the nickel-plating wastewater with strongly acidic cation-exchange resin; (3) adding a strong oxidant in the nickel-plating wastewater so that hypophosphite, phosphite and macromolecular organic acid complexing agent which are contained in the wastewater are oxidized so as to form phosphate and organic micromolecules;(4) carrying out pulse electrocoagulation on the nickel-plating wastewater so that the phosphate forms iron phosphate to be precipitated and residual nickel ions are oxidized to form oxidized scale precipitate at the same time; and (5) regulating the wastewater to alkalinity so that iron ions in the wastewater are precipitated, successively adding a deironing agent and a flocculant to remove ferrous ions and suspended matters in the wastewater, and directly discharging supernate. According to the invention, the content of the nickel ions in the wastewater treated by the process is far less than 0.1ppm and meets a national primary standard, the recycle of nickel resources can be realized, and the economic benefits of wastewater treatment are improved.
Owner:中新联科环境科技(安徽)有限公司
Plating solution of magnesium alloy nickle sulfate main salt and technology of chemical plating thereof
InactiveCN1598053ALow priceReduce manufacturing costLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingChemical platingThiourea
The invention discloses a plating solution of magnalium alloy Nickel sulfate and its chemical plating technique. The plating solution is made up of: (1) 5 to 40g.dm-3 of Nickel sulfate, (2) 10 to 50g.dm-3 of reducing agent of hypo-phosphite sodium; (3) one or several of the 2.5 to 30g.dm-3of the citric acid or tri-sodium citric acid, 2.5 to 30g.dm-3of the lactic acid, 2.5 to 30g.dm-3of the acetic acid, 2.5 to 30g.dm-3of the malic acid, 2.5 to 30g.dm-3 of the third acid and 2.5 to 30g.dm-3of the buta-acid; (4) one or several of the 5 to 30g.dm-3of Potassium fluoride, 5 to 30g.dm-3of sodium fluoride, 5 to 30g.dm-3of lithium fluoride and 5 to 30g.dm-3of NH4HF2; (5) 0.1 to 3g.dm-3of sulphur carbamide. The plating steps include: washing with ultrasonic->washing with alkali->washing with acid->activation->dipping it in the zinc solution->getting rid of the activation solution->secondary dipping it in the zinc solution->chemical plating->passivation and sealing the holes. The invention is featured by little pollution to the environment, low cost, uniform film and simpel technique.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Chemical palladium plating solution
InactiveCN101709462AReduce utilizationIncrease profitLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingPrinted circuit boardStabilizing Agents
The invention relates to a chemical palladium plating solution, in particular to a chemical palladium plating solution which can directly form a palladium film with good adhesive force on a chemical nickel plating film formed on a printed circuit board (PCB) and does not affect the chemical nickel plating film serving as a base film. The chemical palladium plating solution contains a soluble palladium salt, a first complexing agent, a second complexing agent and a stabilizing agent, wherein the first complexing agent is one out of ammonia and diamine compounds, and the second complexing agent is one or more out of alcohol amine compounds with 2-7 carbon atoms, amine compounds with less than 7 carbon atoms and aminocarboxylic acid compounds. The palladium plating solution has stable pH, stable deposition rate, long bath service life and excellent bath stability, does not generate cracks, and can obtain the palladium plating film with very low phosphorus content and excellent corrosion resistance, solder connectivity and lead weldability.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for performing neutral electronickelling following magnesium alloy chemical nickeling
InactiveCN101560662AImprove bindingHarm reductionLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSuperimposed coating processBiological activationFluoride
The invention discloses a method for performing neutral electronickelling following magnesium alloy chemical nickeling, which comprises the technical steps as follows: (1) surface treatment of magnesium alloy material: performing surface treatment to the magnesium alloy material by adopting the prior art; (2) acid membrane removal: removing the membrane by using fluoride-containing acid solution; (3) alkaline erosion: performing surface erosion by using fluoride-excluding alkaline solution; (4) activation: performing surface activation by using fluoride-containing solution; (5) chemical nickeling; (6) thermal treatment; (7) subsequent neutral nickeling; and (8) regular nickeling. According to the method, neutral electronickelling is performed following magnesium alloy chemical nickeling so that double-layer nickel is covered on the magnesium alloy base material. The method has the advantages of high bonding force, good uniformity and dense property, strong wearing resistance and corrosion resistance, and simple technical process and convenient operation. In the whole process, alkaline-copper electroplating and chromium are not needed, thus reducing harm to environment and human.
Owner:李远发
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com