Method for chemically plating nickel on surface of carbon fiber
A surface chemical and electroless nickel plating technology, which is applied in the direction of liquid chemical plating, fiber treatment, metal material coating technology, etc., can solve the problems of low bonding strength of the plating layer, unstable activation solution, complicated operation, etc., and achieve improved hydrophilicity The effect of stability, overcoming instability, and simplifying the operation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
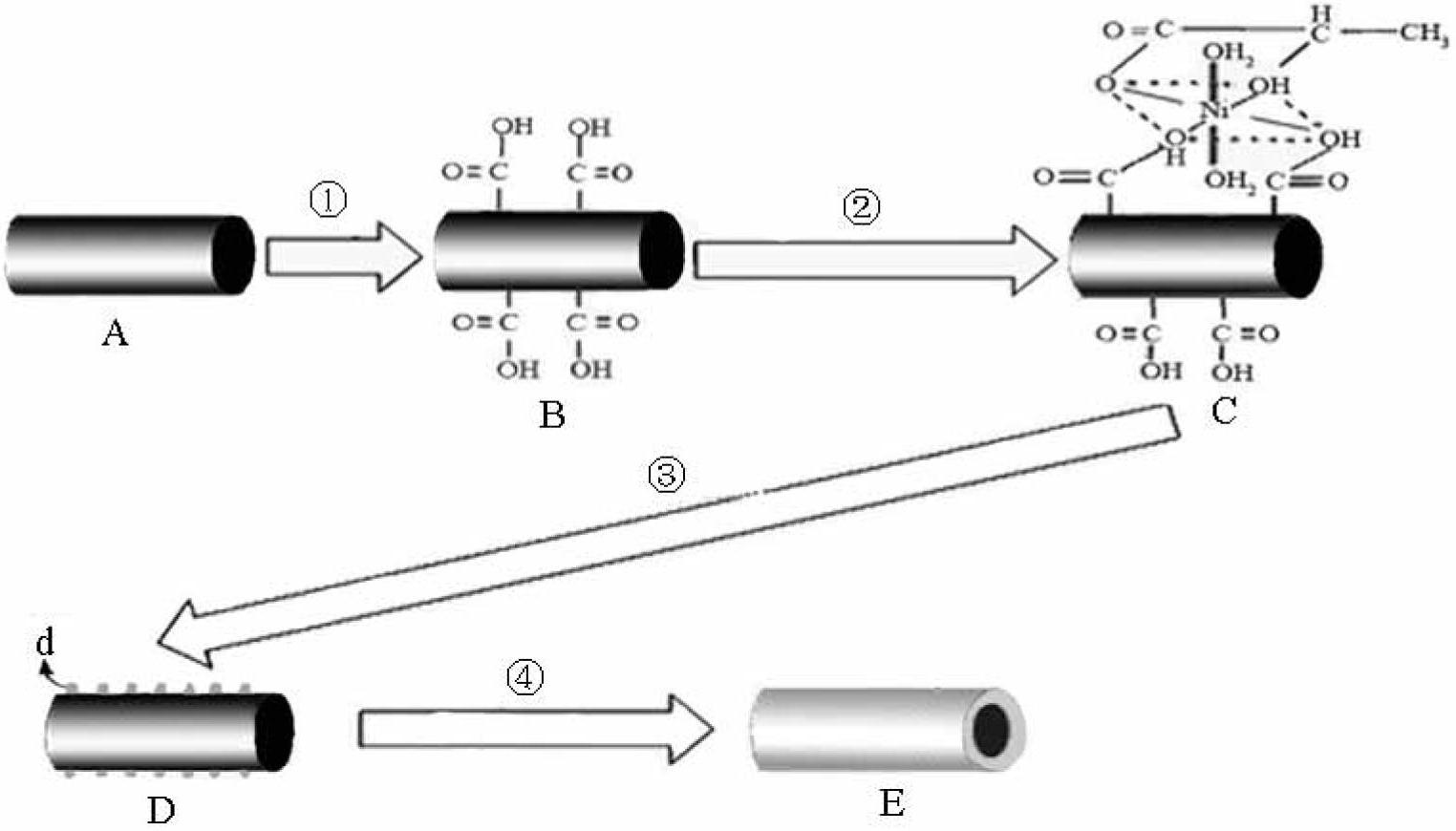
[0010] Specific implementation mode one: this implementation mode is a method for electroless nickel plating on the surface of carbon fiber, specifically completed according to the following steps:
[0011] 1. Surface treatment: ① Degumming: use acetone as solvent, use Soxhlet extraction method to condense and reflux the carbon fiber in a water bath at a temperature of 70℃~80℃ for 12h~48h, and obtain the degummed carbon fiber; ②Degreasing: put The carbon fiber after degumming is placed in a sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 0.8mol / L to 1.2mol / L, then boiled for 10min to 20min at a stirring speed of 40rpm to 130rpm, taken out and placed in a concentration 0.8mol / L ~ 1.2mol / L hydrochloric acid solution, and then boiled for 10min ~ 20min at a stirring speed of 40rpm ~ 130rpm, after taking out, the carbon fiber after surface degreasing is obtained; 2. Coarsening treatment: Immerse the carbon fiber after degreasing the surface in concentrated nitric acid, seal it, a...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0020] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the activation solution described in the step 3 is made of nickel sulfate, sodium acetate, ammonium chloride, sodium hypophosphite, lactic acid, thiourea, ammonia water and Ionized water is mixed; and the concentration of nickel sulfate in the activation solution is 25g / L~35g / L, the concentration of sodium acetate is 15g / L~25g / L, and the concentration of ammonium chloride is 20g / L~30g / L, the concentration of sodium hypophosphite is 25g / L~35g / L, the concentration of lactic acid is 15g / L~20g / L, the concentration of thiourea is 1.5×10 -3 g / L~2.5×10 -3 g / L, the concentration of ammonia water is 45g / L-55g / L; and the pH of the activation solution is 8.0-9.0. Others are the same as the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0021] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the sodium borohydride solution described in step three is formed by mixing sodium borohydride, sodium hydroxide and deionized water; and the The concentration of sodium borohydride in the sodium borohydride solution is 3g / L-4g / L, and the concentration of sodium hydroxide is 8g / L-12g / L. Others are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com