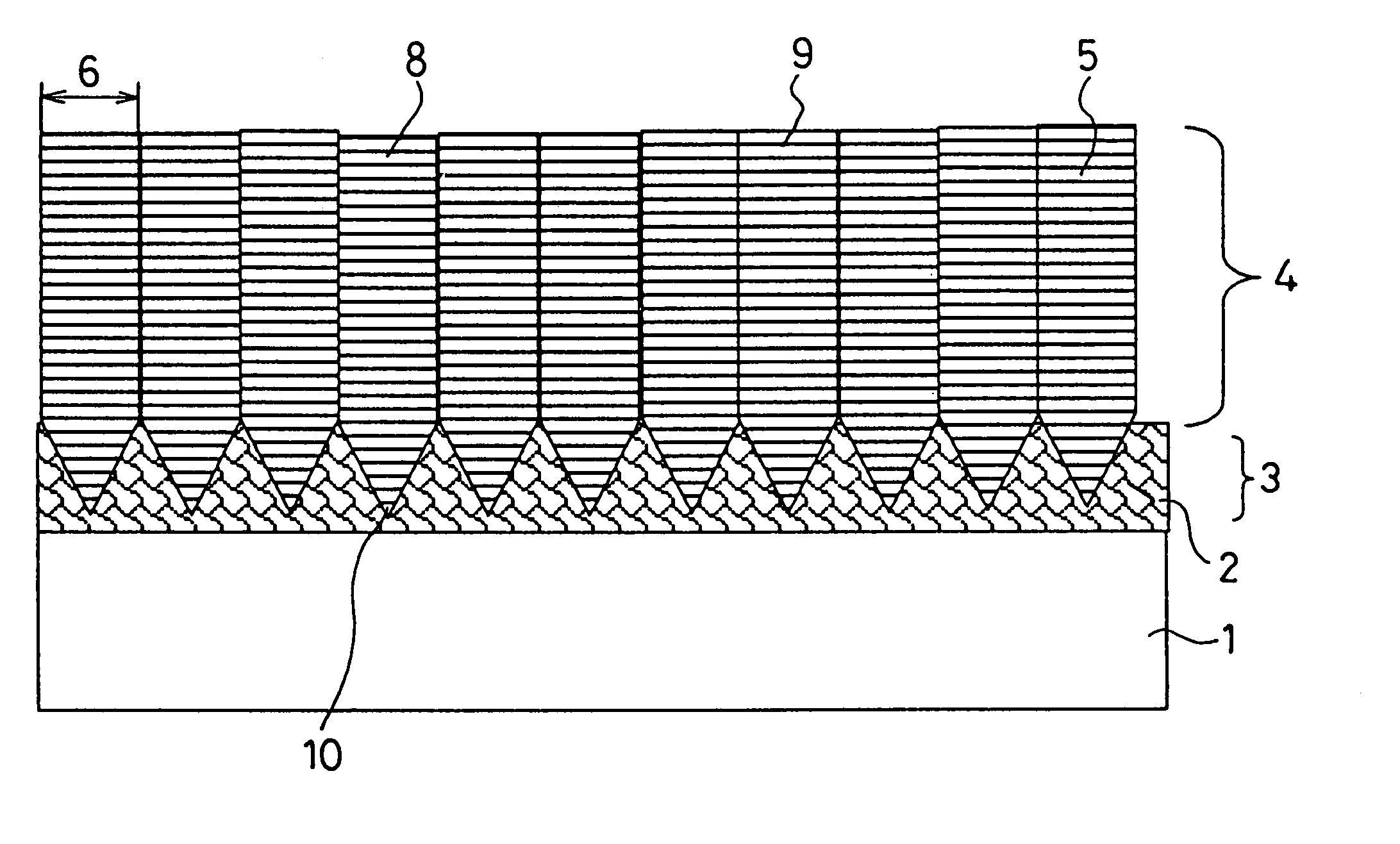
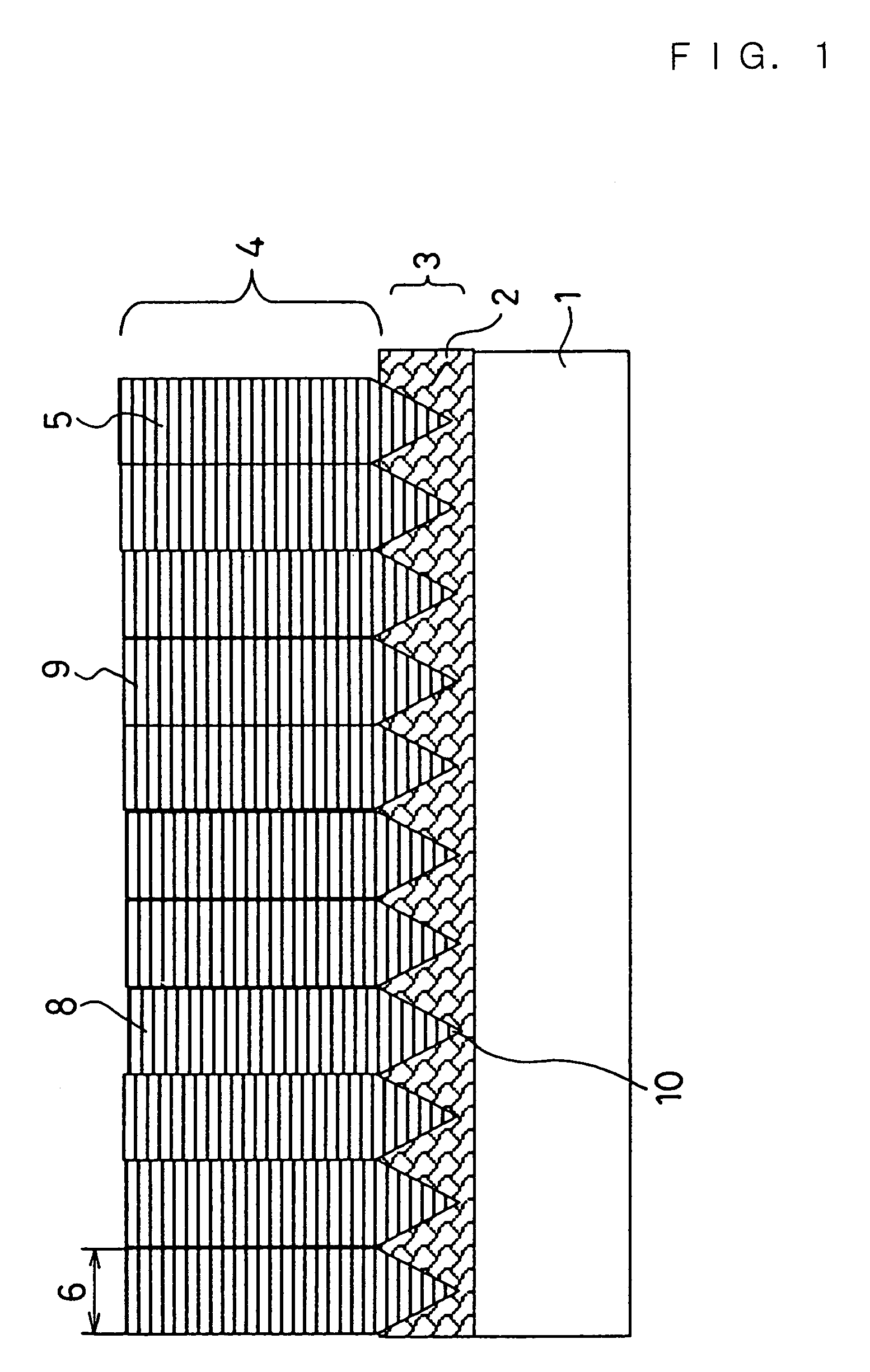
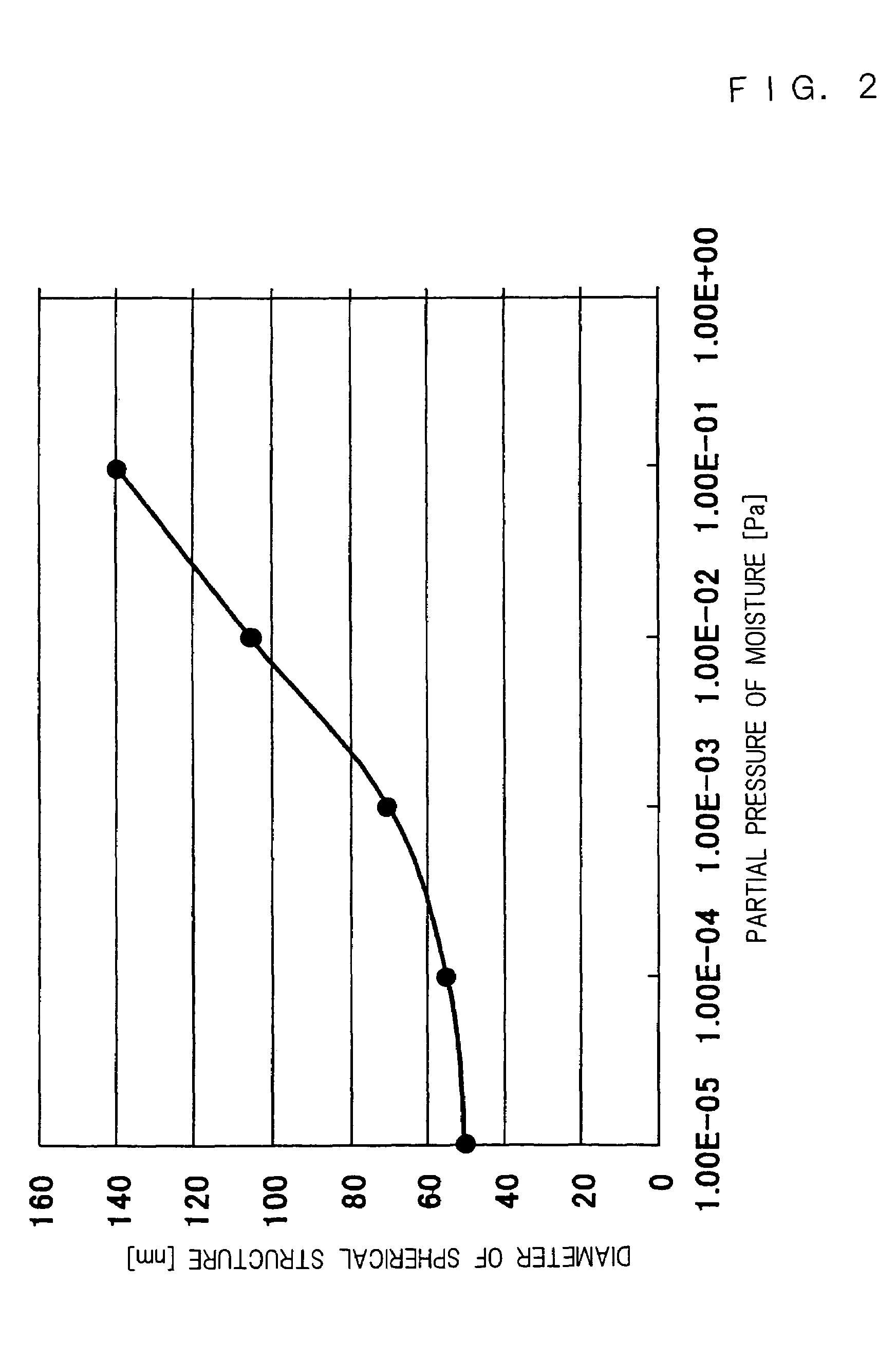
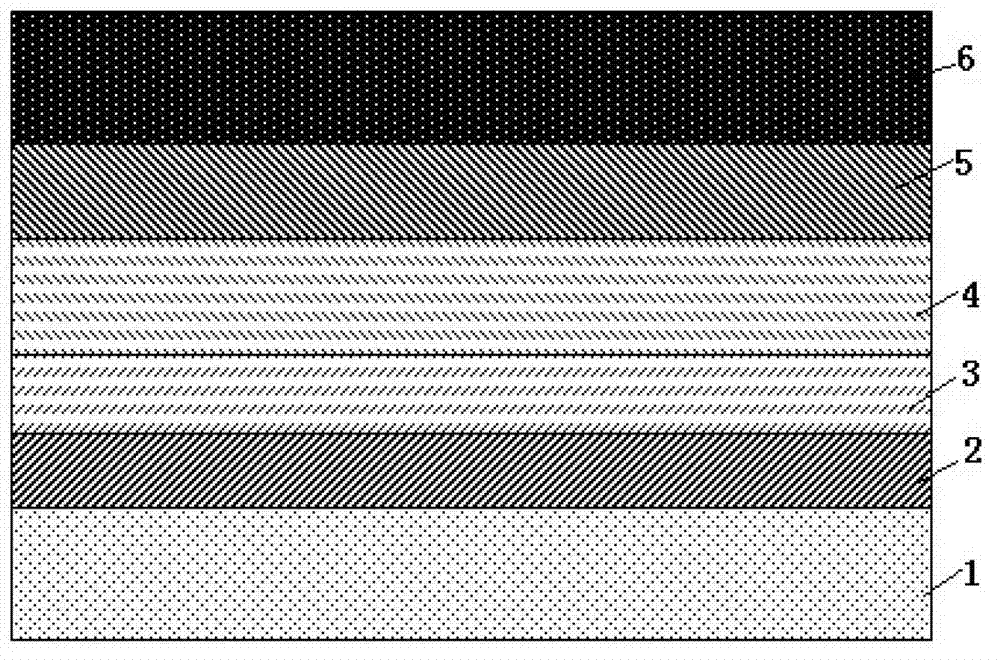
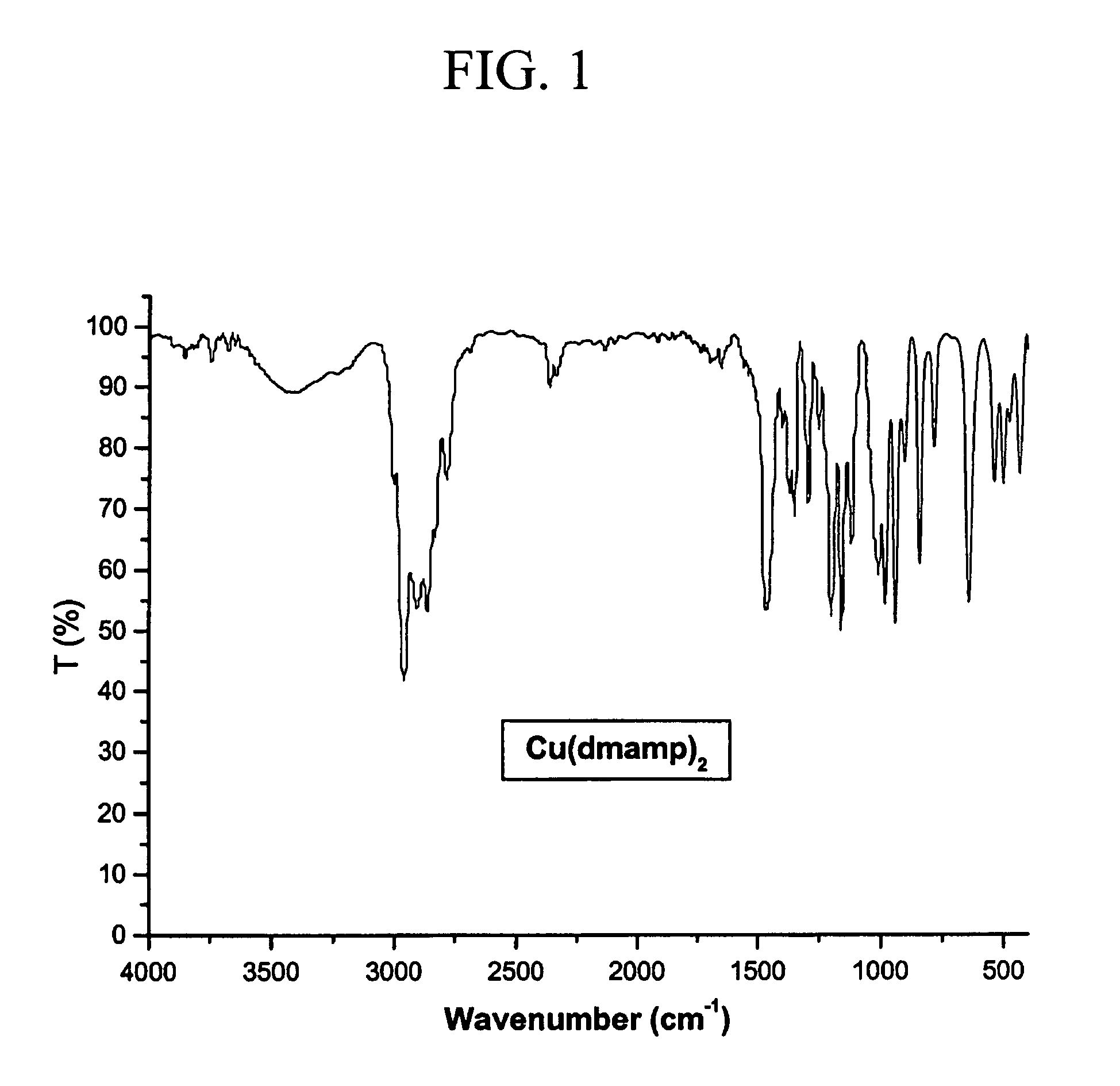
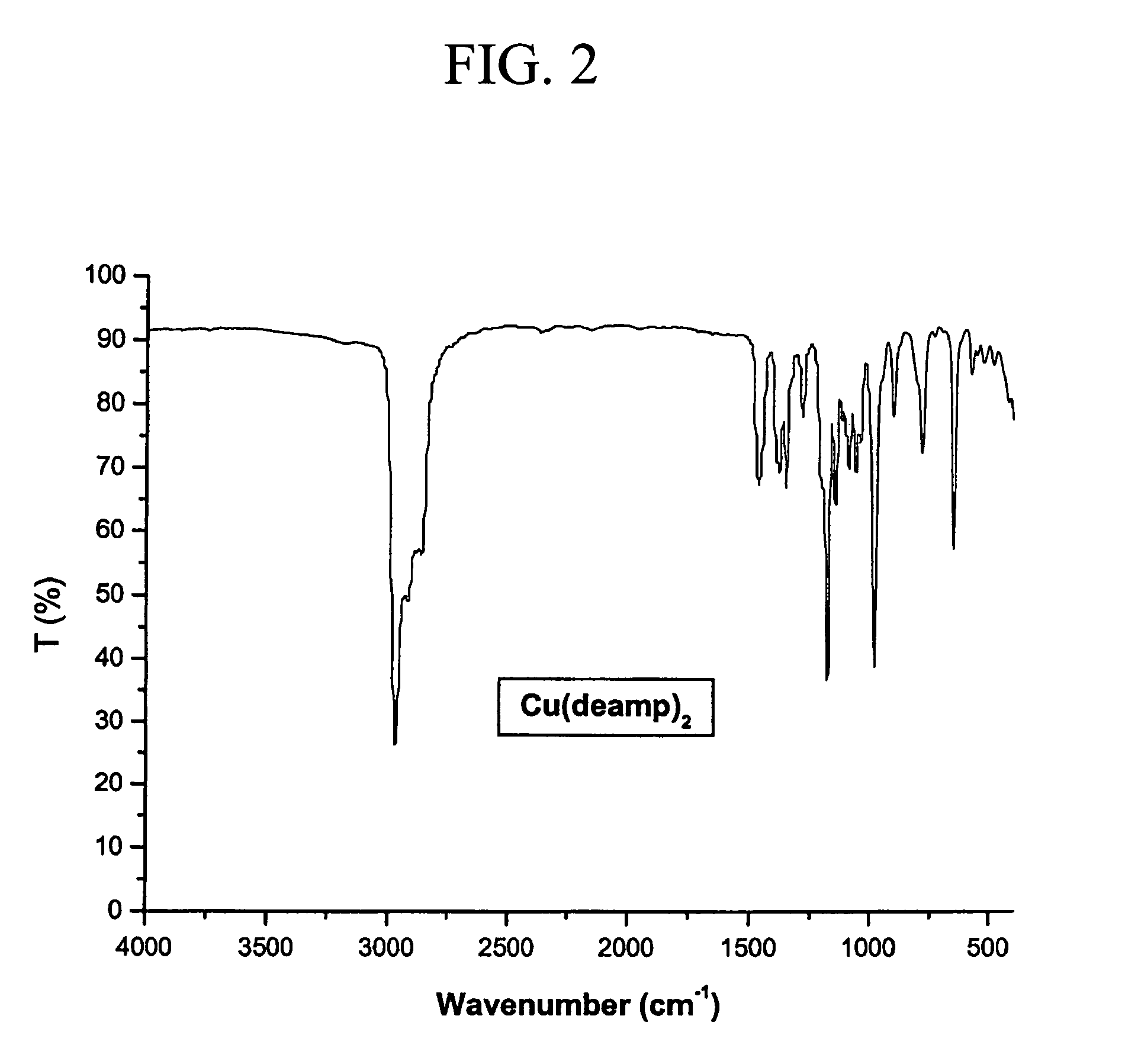
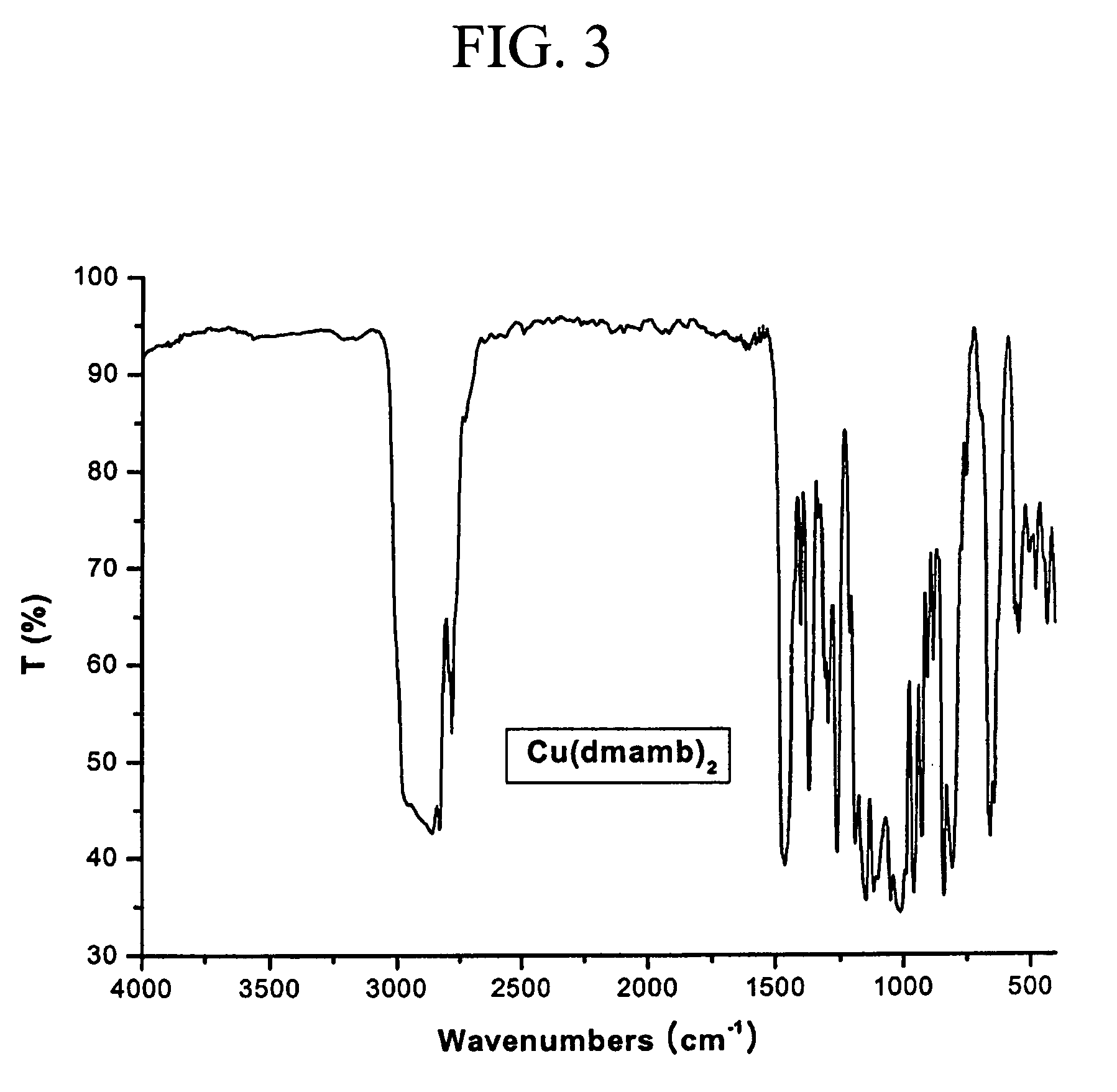
Patents
Literature
255 results about "Copper thin film" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
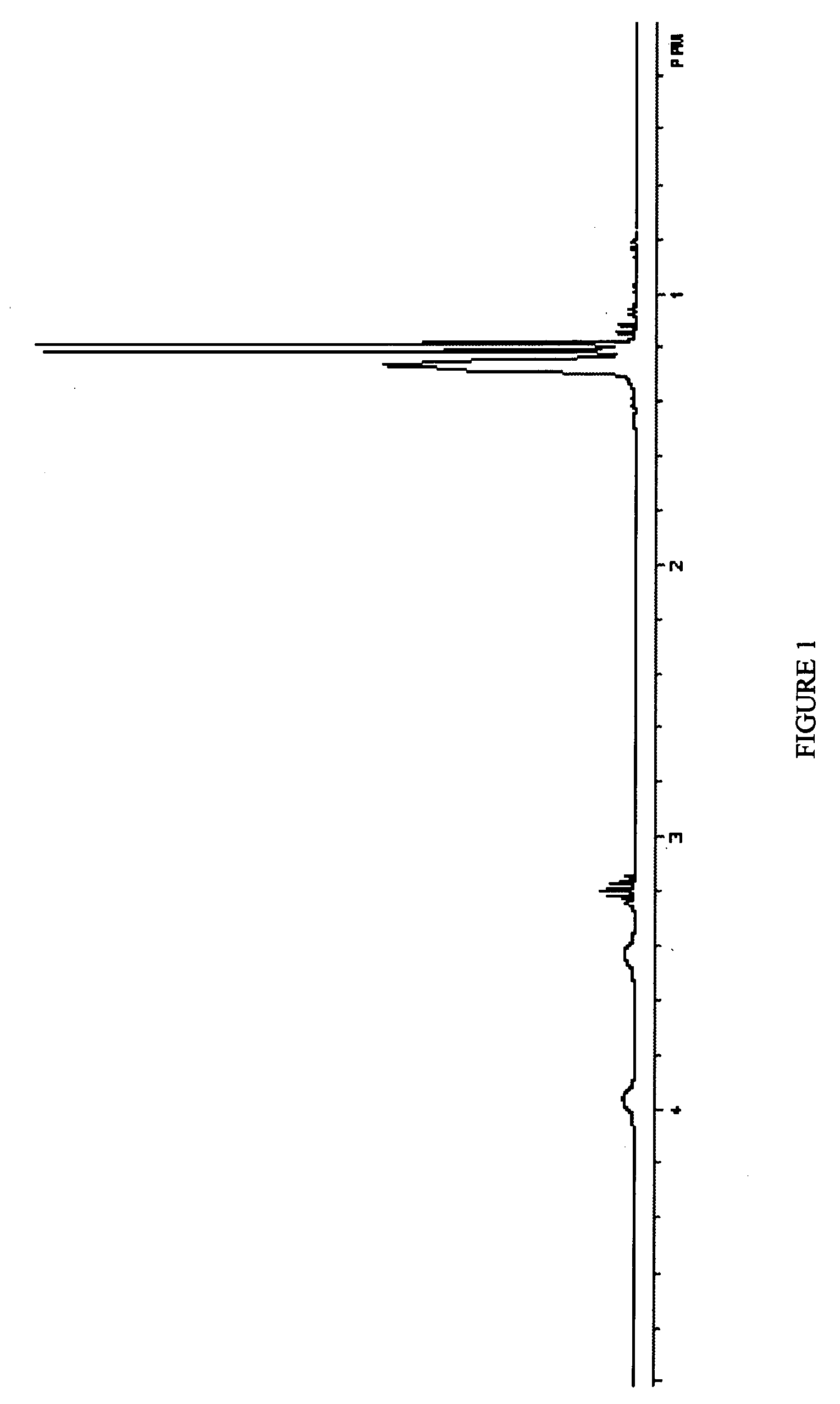
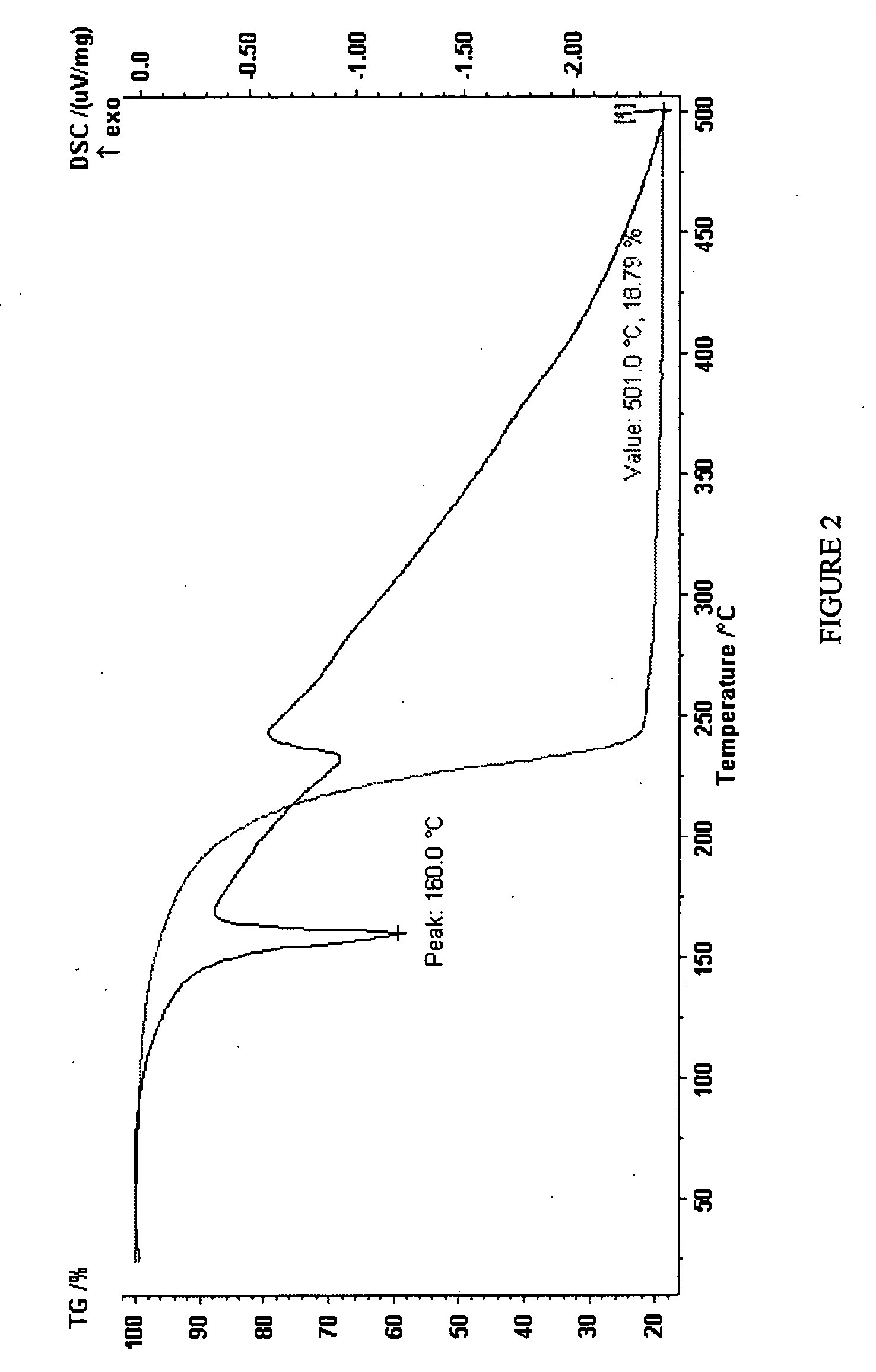
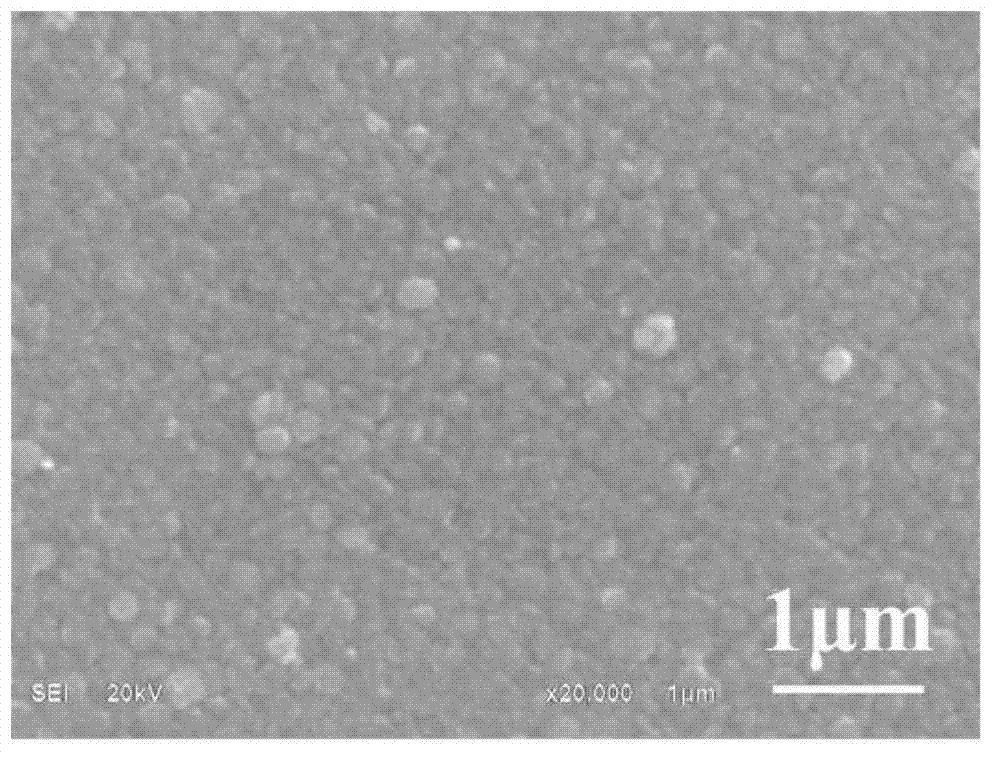
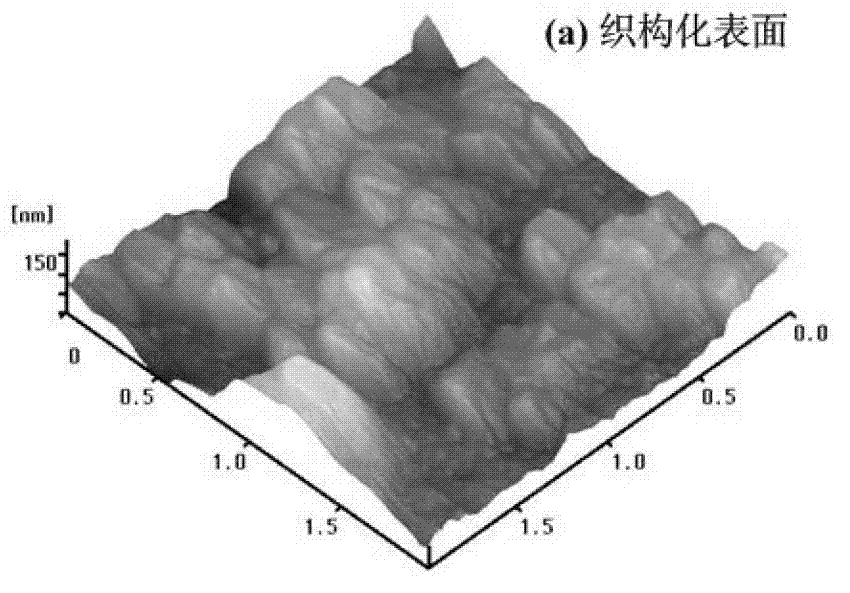
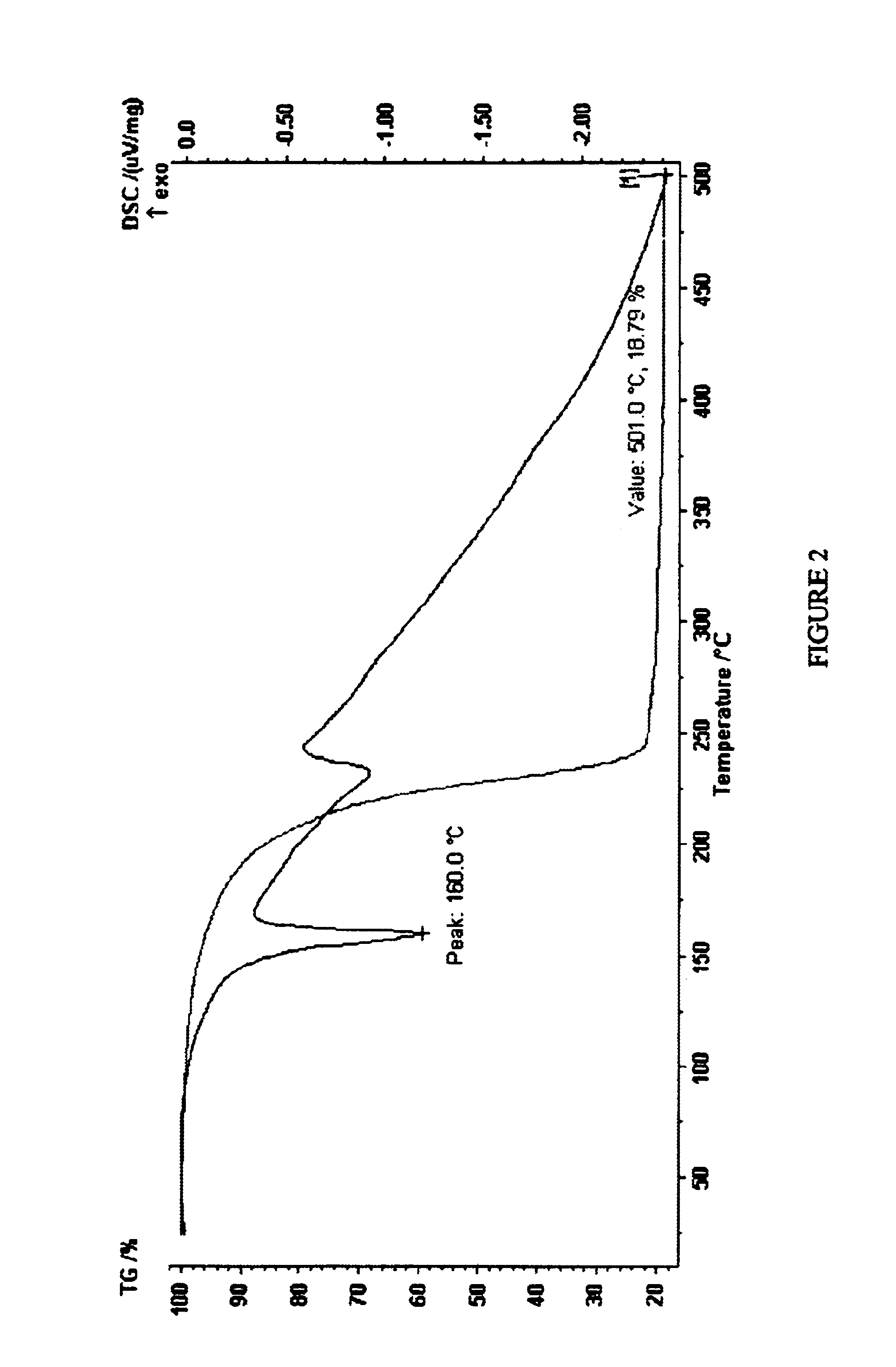
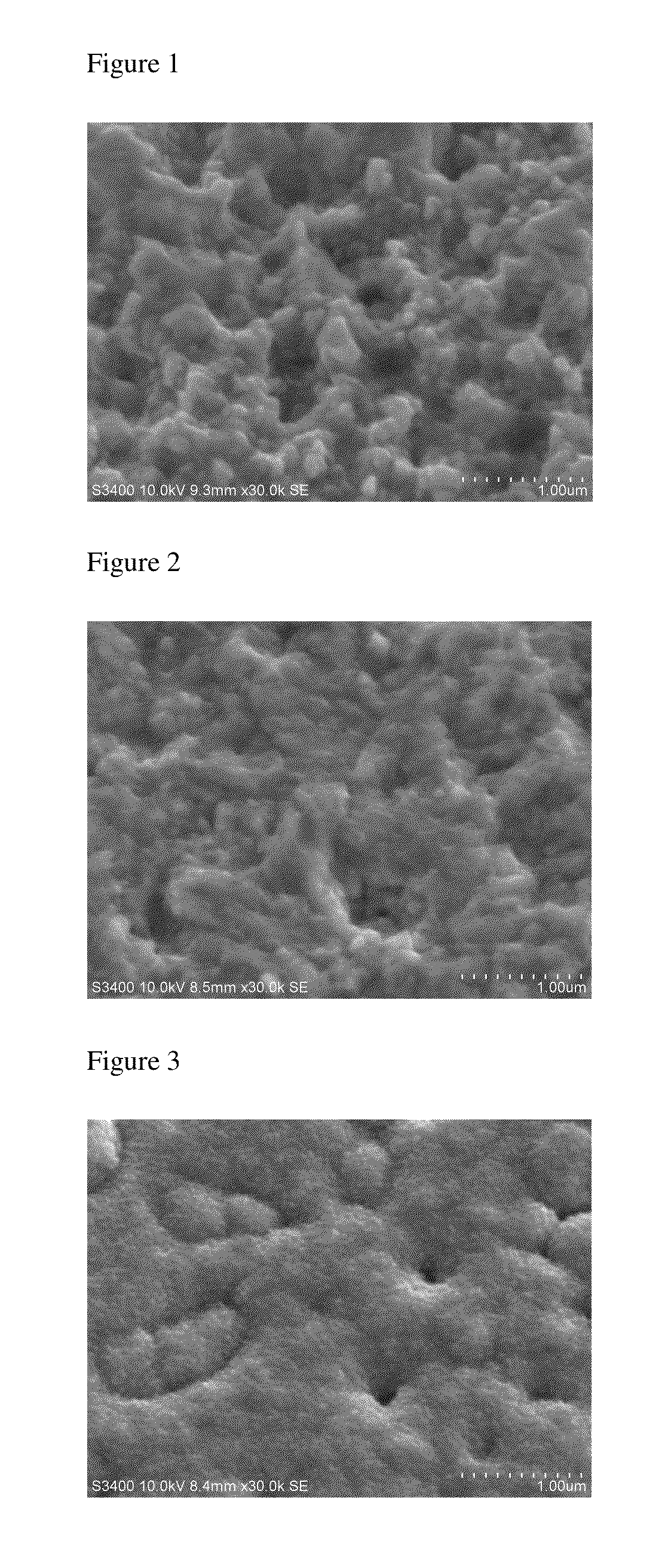
Abstract Copper thin film was deposited on commercial pure aluminium substrate using electron beam deposition route. (SEM), Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM). showed that the coating is made up of crystallites of 15-20 nm size. and found that roughness value was 4.106 nm (Ra value).
Method for preparing graphite alkyne film
The invention discloses a method for preparing a graphite alkyne film. The method comprises that: a copper sheet or any one substrate the surface of which is covered with a copper film layer is used as a substrate; 6-alkynyl-benzene is subjected to coupling reaction in a solvent under the catalytic action of the copper to obtain the graphite alkyne film on the surface of the substrate. The method for preparing the graphite alkyne film, which is provided by the invention, has simple and convenient process, and can carry out large-scale preparation of the graphite alkyne film on the surface of the copper sheet or the substrate any surface of which is covered with the copper. The electrical conductivity of the graphite alkyne film is 2.516*10-4S / m. The film has uniform surface, can exist stably in the air, is a semiconductor with similar performances with silicon, and has potential application prospect in the fields of catalysis, electron, semiconductor, energy, material and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
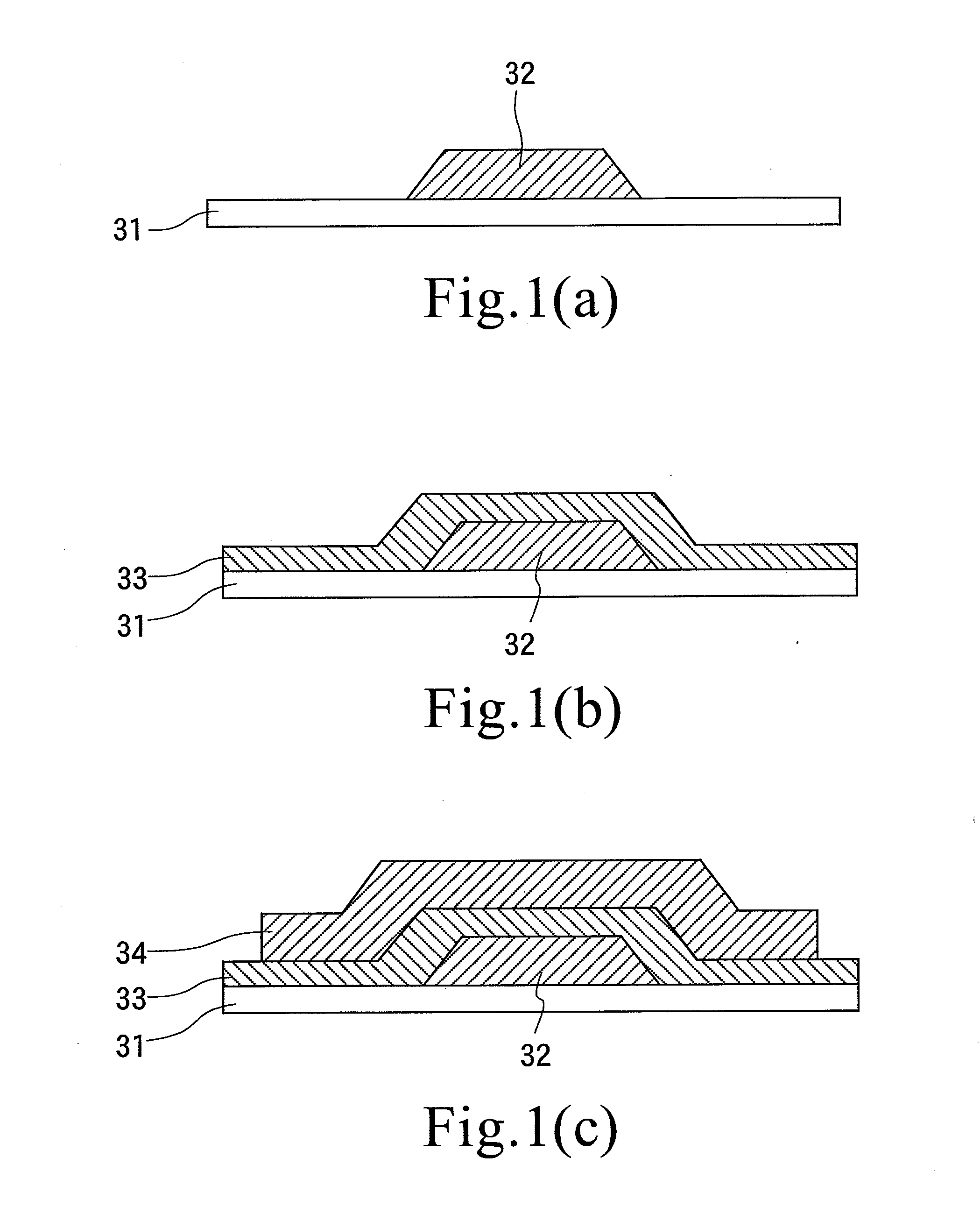
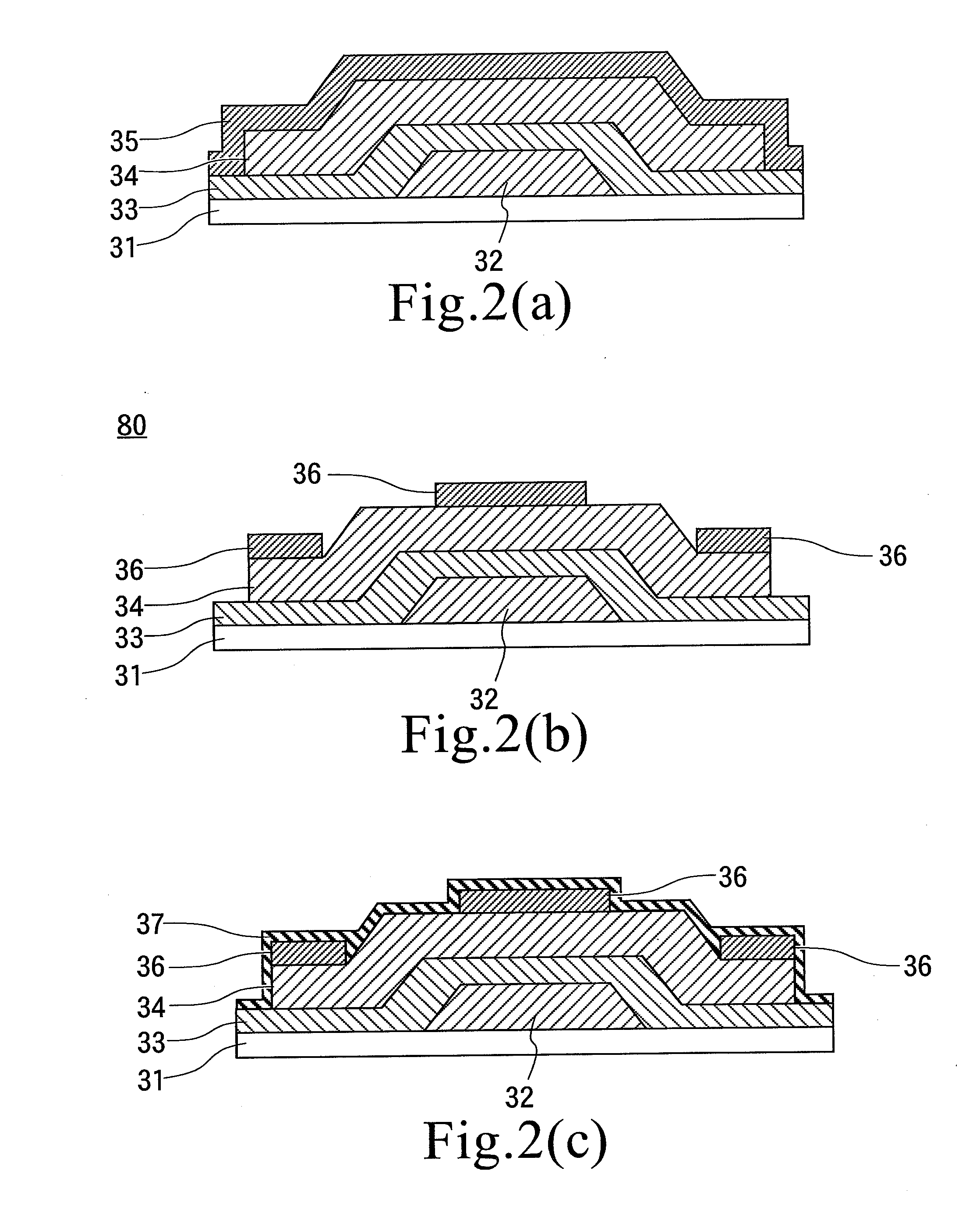
Production method of suspension board with circuit
InactiveUS20050186332A1Preventing deterioration of outward appearance and defectPrevent deterioration of outward appearance and defectFluid-dynamic spacing of headsRecord information storageResistElectrical conductor
In order to provide a new production method of a suspension board with circuit capable of preventing deterioration of the outward appearance and defects in products caused by a metal supporting layer, and further capable of forming an electroless nickel plating layer having an even thickness in a reliable manner, an insulating base layer is first formed on a supporting board, and a chromium thin film and a copper thin film are formed next sequentially on the surface of the supporting board exposed from the insulating base layer and on the entire surface of the insulating base layer. Subsequently, a plating resist is formed in a reversal pattern with respect to the wired circuit pattern on the surface of the copper thin film, and a conductor layer is formed on the surface of the copper thin film exposed from the plating resist by electrolytic plating. The plating resist is removed after an electroless nickel plating layer is formed on the conductor layer. Subsequently, the copper thin film and the chromium thin film are removed sequentially, and an insulating cover layer is formed next.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
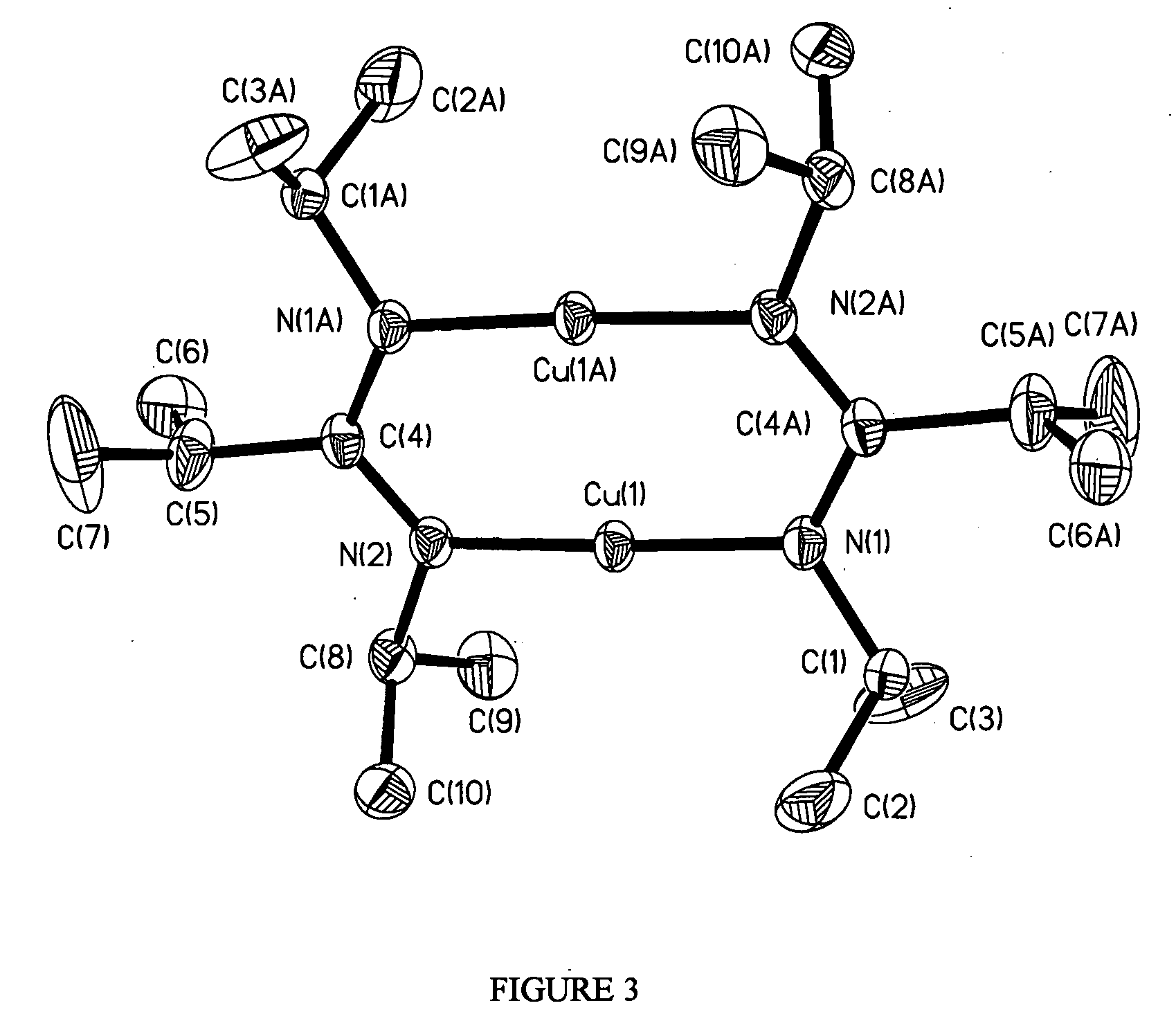
Copper (I) compounds useful as deposition precursors of copper thin films
ActiveUS20050283012A1Group 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesCopper organic compoundsDevice materialPhysical chemistry
Copper (I) amidinate precursors for forming copper thin films in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, and a method of depositing the copper (I) amidinate precursors on substrates using chemical vapor deposition or atomic layer deposition processes.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
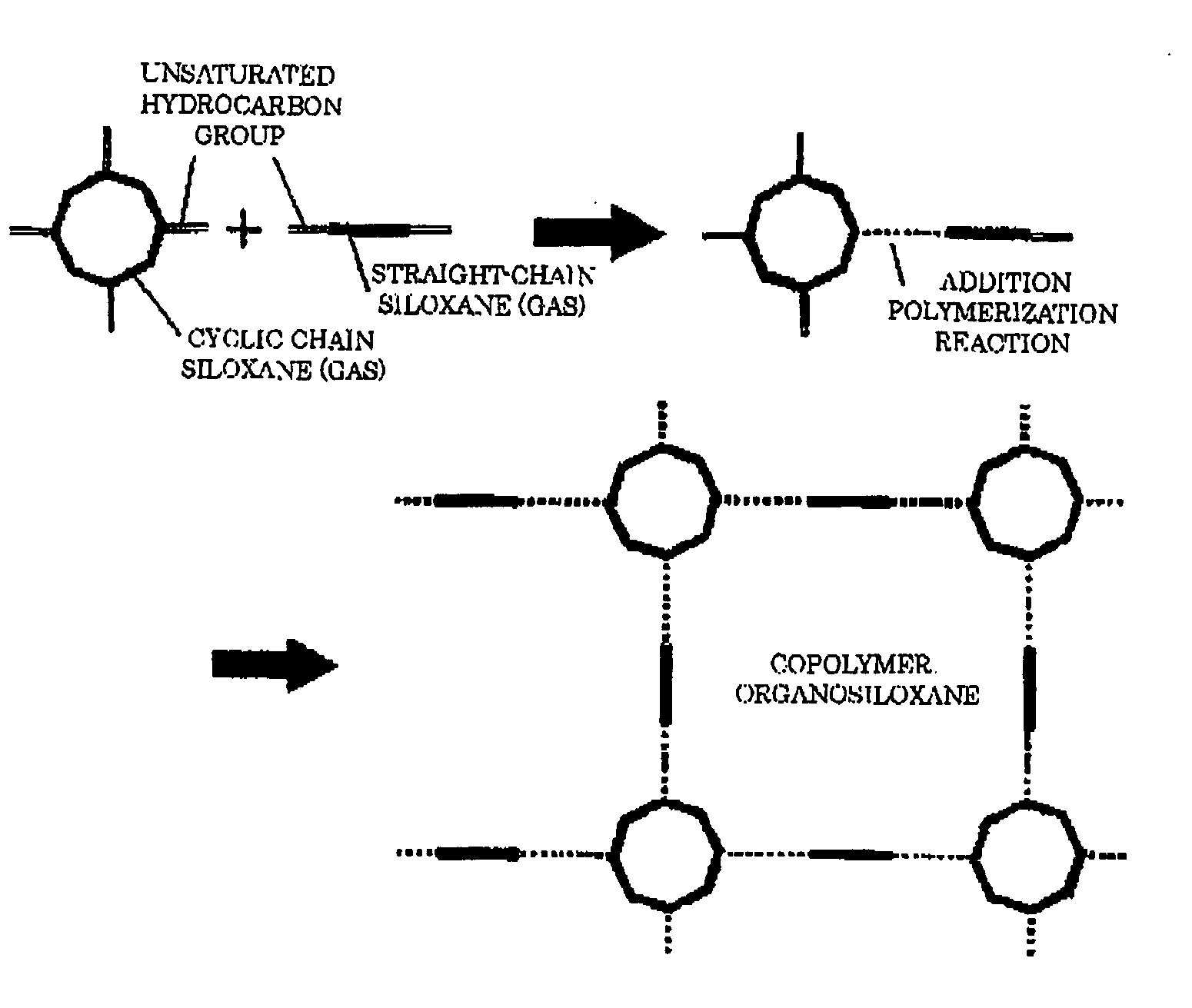
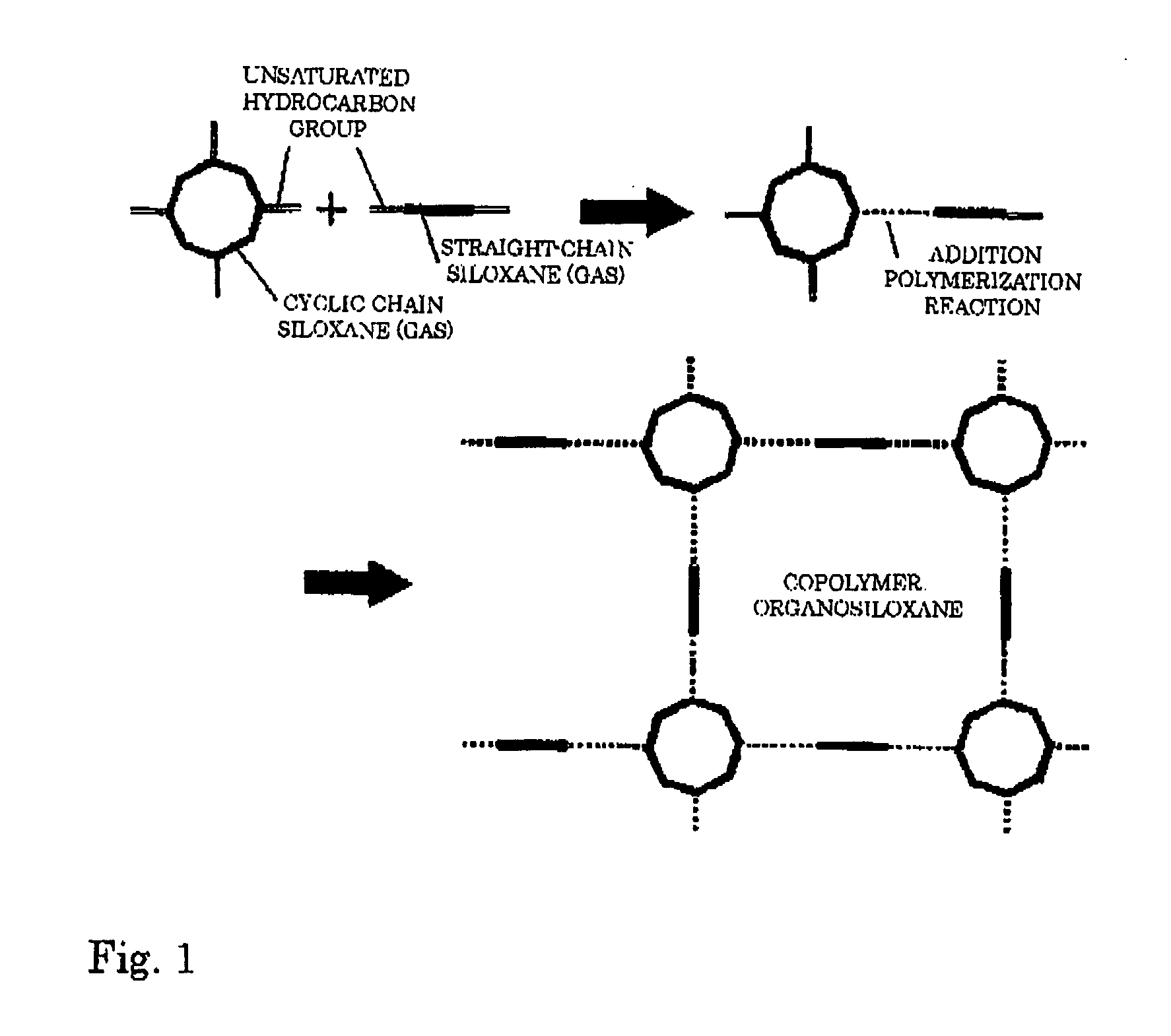
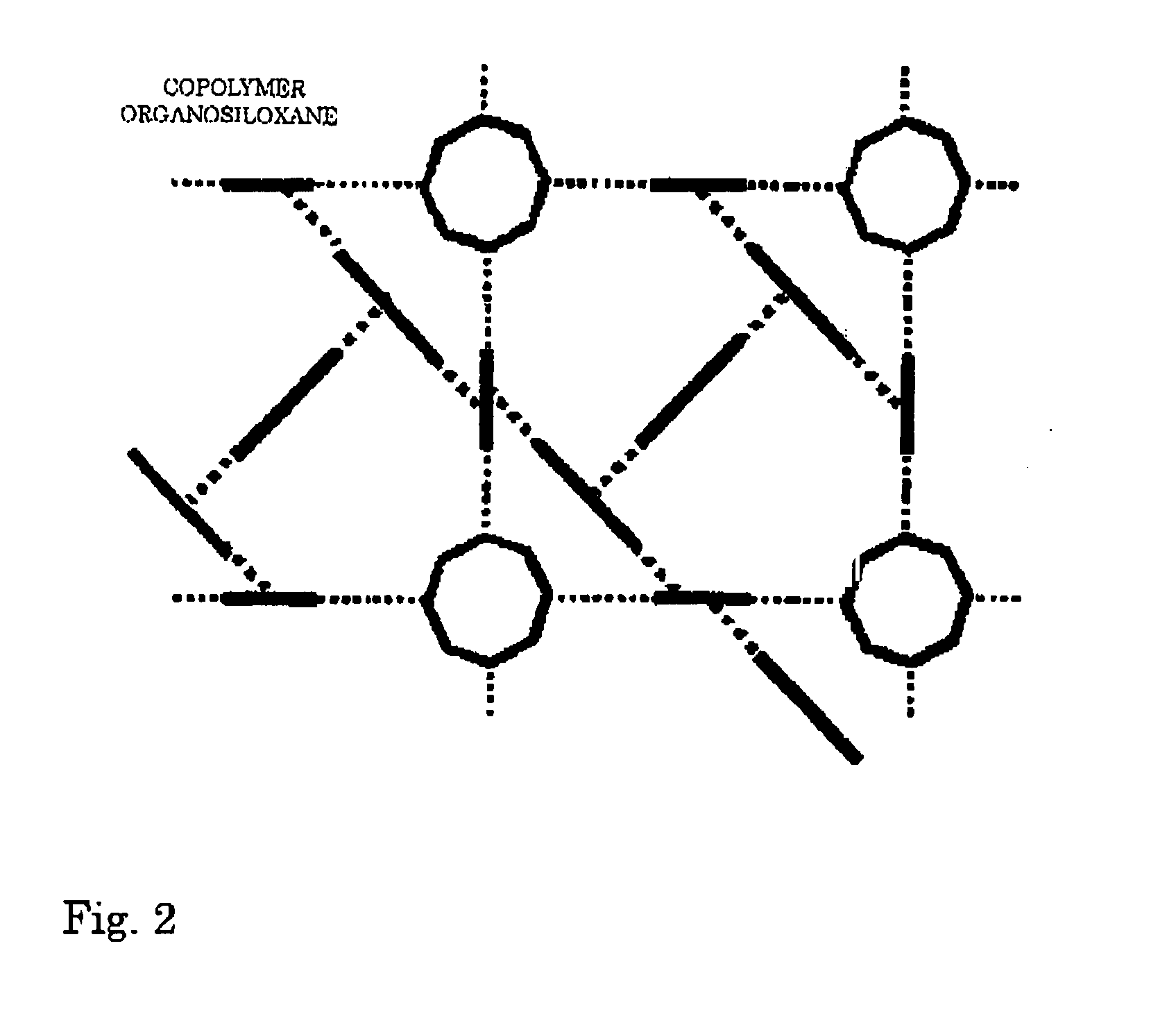
Organic siloxane copolymer film, method and deposition apparatus for producing same, and semiconductor device using such copolymer film
ActiveUS20050267253A1Improve film qualityHigh bridge densityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDielectricCopper-wiring
An insulated organic copolymer is provided, having the excellent mechanical strength and deposition property at an interface contacting the lower base or the upper layer of the inorganic insulation film, and the effective dielectric constant is low as the whole film, which is suitable as the interlayer insulation film that separates the multi-layer copper wirings of the semiconductor device. The organosiloxane copolymer film is obtained by the polymerization of the cyclosiloxane and the straight-chain siloxane as the raw materials by the plasma excitation of both. At the interfaces contacting the inorganic insulation films, the interface layers having a film quality that is intricate and excellent in deposition property are prepared whereby the main component of the film composition is the straight-chain siloxane. The inner section of the copolymer film mixes the cyclosiloxane component having pores surrounded by the cyclosiloxane backbone and the straight-chain siloxane components, has the network structure layer relatively suppressing the density, and has the composition changing in the thickness direction whereby the multi-layer wirings embedding the copper thin film is formed.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Semiconductor wafer cleaning agent and cleaning method
InactiveUS7375066B2Other chemical processesSurface-active detergent compositionsSurface cleaningNitrogen
A semiconductor surface cleaning agent containing a compound the molecule of which has a nitrogen atom having an unshared electron pair and used for cleaning the surface of a semiconductor on which copper wiring is provided, and a method for cleaning the surface of a semiconductor characterized by treating the surface of a semiconductor on which copper wiring is provided with such a cleaning agent. The cleaning agent does not corrode the copper wiring (copper thin film) on the semiconductor and SiO2 of the interlayer insulating film, does not impair the flatness of the surface, and is effective in removing CuO and particles adhering to the surface of the Cu-CMP step.
Owner:FUJIFILM ELECTRONICS MATERIALS US
Copper (i) compounds useful as deposition precursors of copper thin films
ActiveUS20050281952A1Improve adhesionFurnaces without endless coreGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesGas phaseDevice material
Copper (I) amidinate precursors for forming copper thin films in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, and a method of depositing the copper (I) amidinate precursors on substrates using chemical vapor deposition or atomic layer deposition processes.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
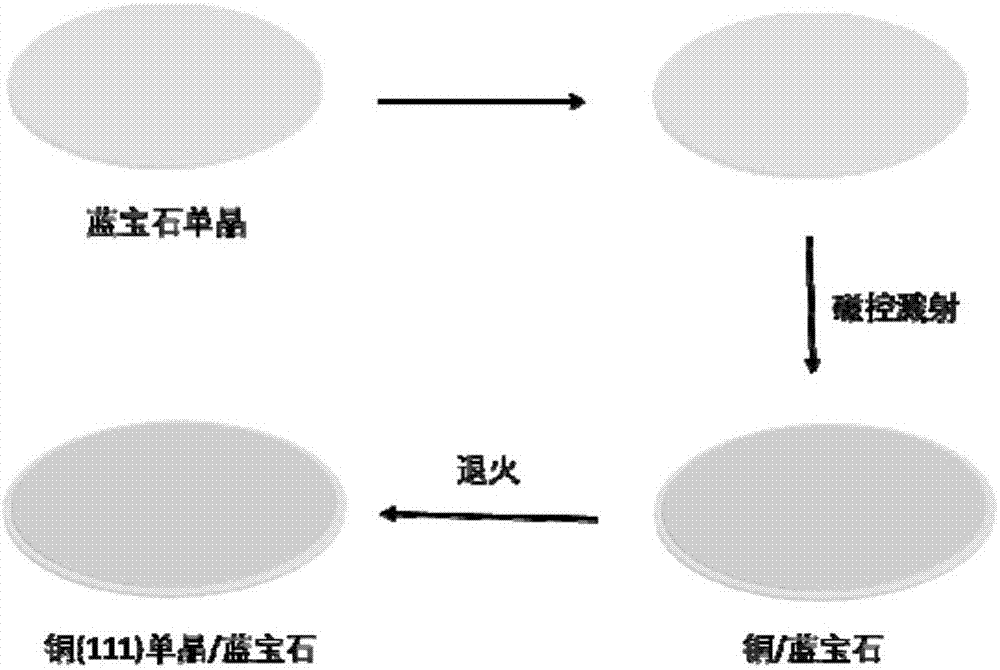
Method for preparing ultra-flat copper monocrystalline film
ActiveCN107354506AFlat surfaceControllable diameterPolycrystalline material growthVacuum evaporation coatingSputteringThin membrane
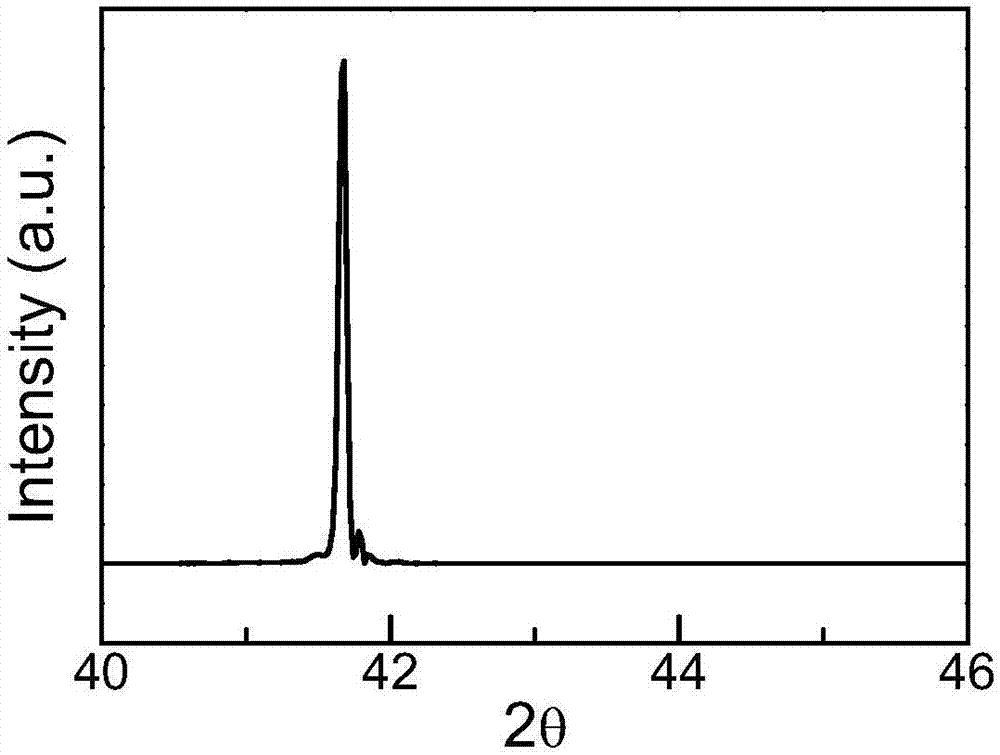
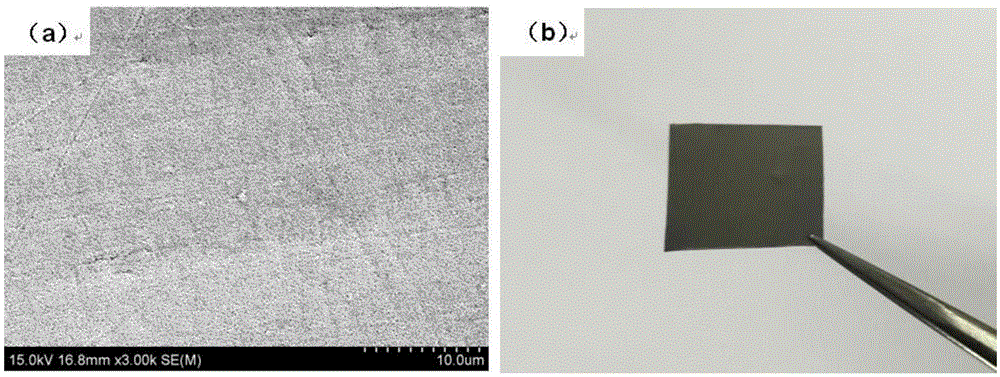
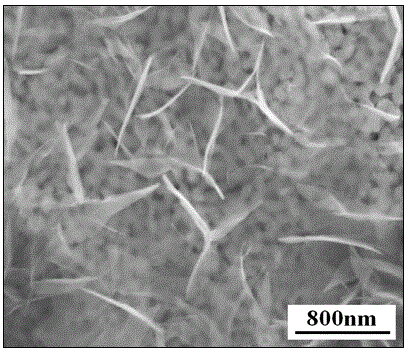
The invention discloses a method for preparing an ultra-flat copper monocrystalline film. The method for preparing the copper monocrystalline film, provided by the invention, comprises the following steps: taking a sapphire monocrystal as a growth substrate, carrying out copper target magnetron sputtering, and carrying out annealing, thereby obtaining the copper monocrystalline film. According to the method, sapphire is adopted as an epitaxial substrate of copper, a magnetron sputtering method is adopted, a copper film with consistent orientation is deposited on the surface of a c-face sapphire substrate, and copper with consistent orientation is aged and grows up during subsequent annealing so as to form a consistent-orientated monocrystalline copper (111) film without in-plane twin crystals. The monocrystalline copper (111) film prepared by the method is extremely flat in surface, controllable in diameter and high in repeatability and has a very extensive application prospect in the fields of communications, electronics, graphene preparation and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for preparing nano porous copper thin film material by magnetron sputtering
ActiveCN105543796AStructural continuityMeet the areaVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingAlloyCopper foil
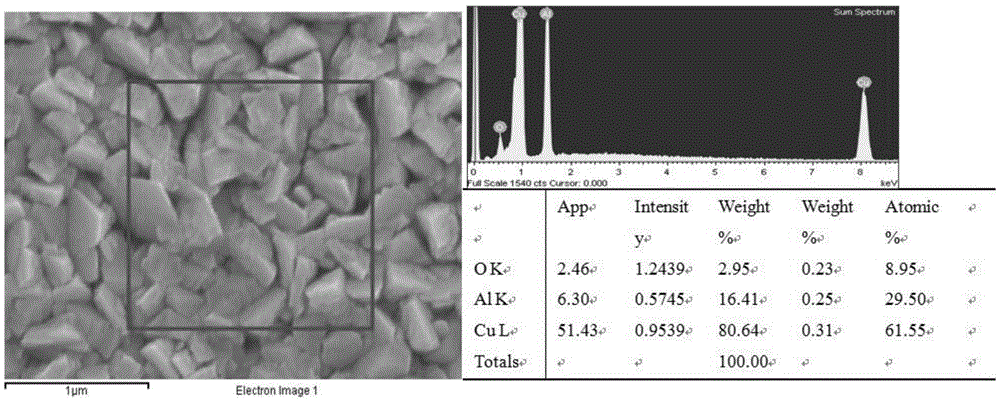
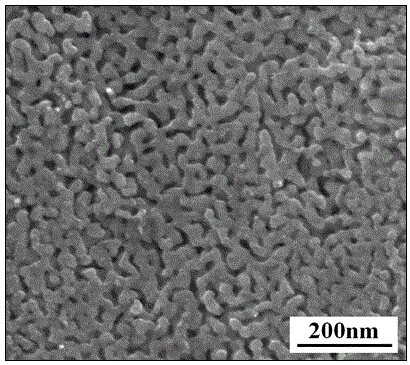
The invention relates to a method for preparing a nano porous copper thin film material by magnetron sputtering. The method takes a commercial copper foil as a base body material and takes high-purity copper target and aluminum target as sputtering materials; magnetron sputtering equipment is a preparation tool; a nano porous copper thin film is obtained by sputtering a copper-aluminum thin film through a glow discharge principle, and dealloying and corroding to remove an active component aluminum after annealing and alloying. The method provided by the invention is a two-step reaction method, the problems in the prior art that steps for carrying out smelting, ball milling and melt spinning on alloy auxiliary materials are complicated and consumed time is long are solved, and steps of a preparation process are simplified; a nano porous structure of nano porous copper is obtained and the size of the thin film is controllable; the obtained structure is better than a nano porous copper powder sample obtained by a traditional method; furthermore, an application range of the nano porous copper is enlarged and the nano porous copper has a commercial prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
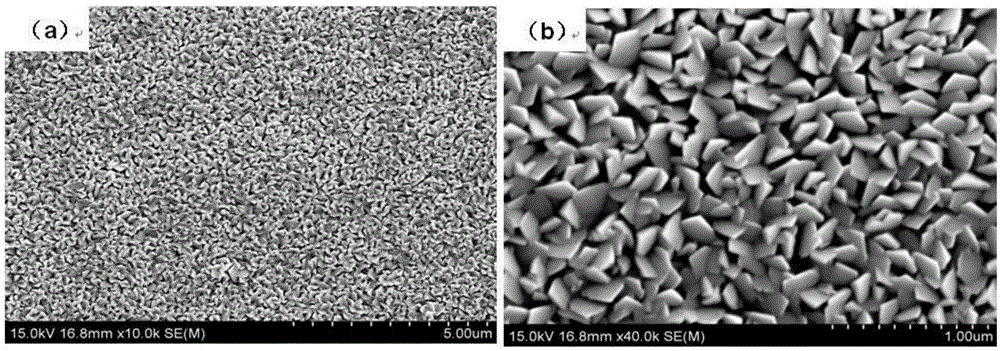
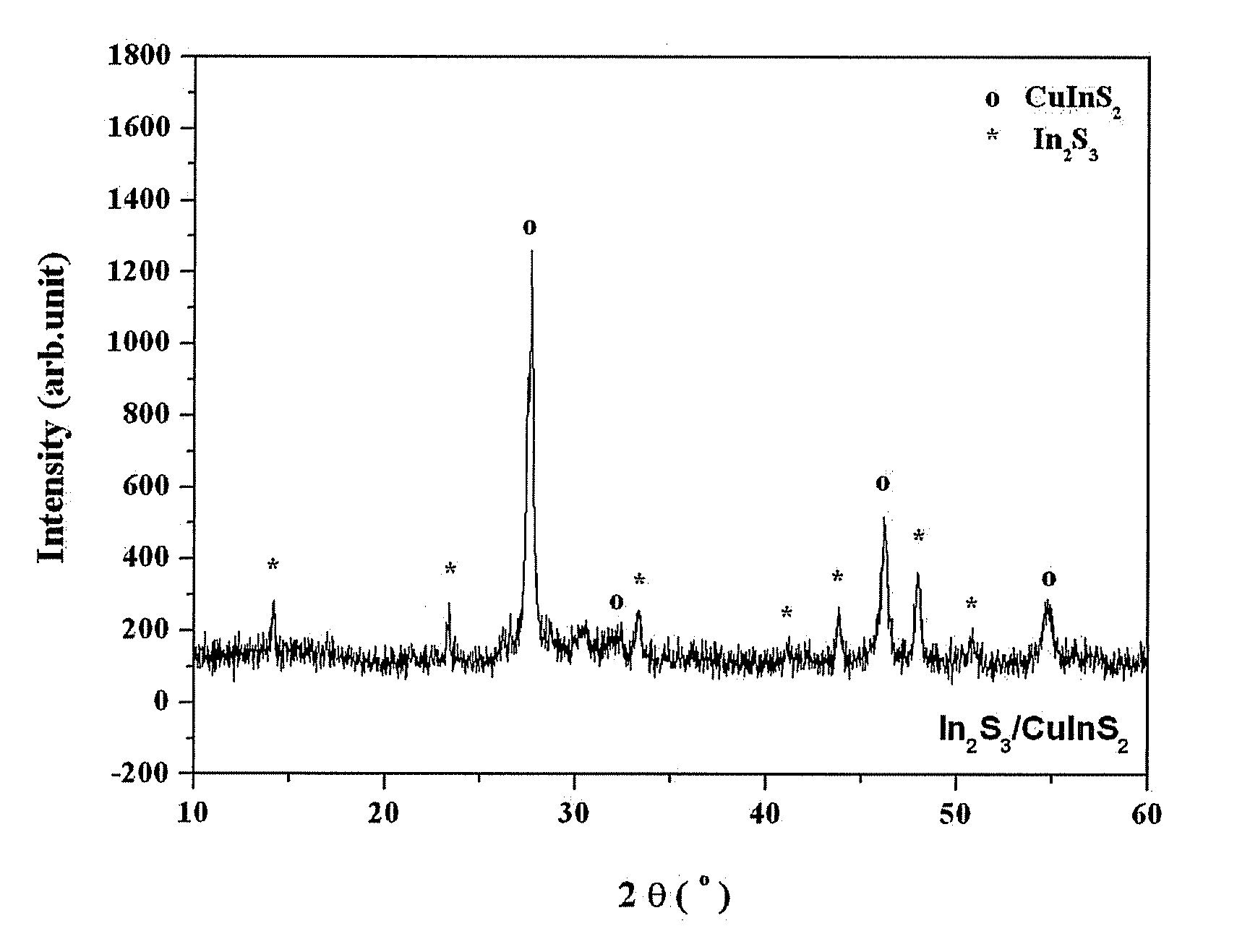
METHOD FOR FABRICATING CuInS2 THIN FILM BY METAL ORGANIC CHEMICAL VAPOR DEPOSITION, CuInS2 THIN FILM FABRICATED BY THE SAME AND METHOD FOR FABRICATING In2S3 THIN FILM THEREFROM
InactiveUS20080012015A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingConstant compositionManufacturing technology
Disclosed is a method for fabricating a CuInS2 thin film by metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). The method comprises fabricating a copper thin film by depositing an asymmetric copper precursor on a substrate by MOCVD and fabricating a CuInS2 thin film by depositing an indium-sulfur-containing precursor on the copper thin film by MOCVD. The method enables fabrication of a CuInS2 thin film with a constant composition even under vacuum as well as an argon (Ar) atmosphere. Disclosed is further a CuInS2 thin film fabricated by the method. Disclosed is further a method for fabricating an In2S3 thin film for a window of a solar cell via deposition of an indium-sulfur-containing precursor on the CuInS2 thin film by MOCVD. Disclosed further is an In2S3 thin film fabricated by the method. The In2S3 thin film is useful for a substitute for CdS conventionally used for windows of solar cells and contributes to simplification in fabrication process of solar cells.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD +2
Flexible printed circuit board and process for producing the same
InactiveUS7282255B2Conductive layers on insulating-supportsSubstation/switching arrangement detailsCrystal structureX-ray
The present invention relates to a flexible printed circuit board which has extremely high adhesion performance and on which very fine circuit patterns can be formed by etching, and to a method for producing the same. In the present invention, in the flexible printed circuit board wherein a copper thin film made of copper or an alloy containing primarily copper is directly formed on at least one side of a plastic film substrate, and copper is formed further on the copper thin film by the electrolytic plating method, the above-mentioned copper thin film has a two-layer structure in which a layer including at least a crystalline structure is formed on the surface side thereof, and the X-ray relative intensity ratio between crystal lattice plane indices (200) / (111) in the above-mentioned crystalline structure is 0.1 or less.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Cadmium telluride thin-film battery and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102779864AShorten the optical pathEnhanced light absorptionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesElectrical batteryPhysics
The invention discloses a perform-optimized cadmium telluride thin-film battery and a manufacturing method for the cadmium telluride thin-film battery, wherein the cadmium telluride thin-film battery comprises a substrate and an epitaxy lamination layer; the epitaxy layer lamination sequentially consists of a conducting layer, a window layer, a light-absorbing layer, a back barrier layer and a back electrode from the bottom up; the window layer is of a textured cadmium sulfide thin-film layer; the light-absorbing layer is of a cadmium telluride thin-film layer, the back barrier layer is of a zinc telluride / copper-doped zinc telluride composite layer or a mercury telluride / copper-doped mercury telluride composite thin-film layer, and the back electrode is of one or more of graphite slurry or graphene slurry thin-film layer or copper thin-film layer, nickel thin-film layer, copper-nickel alloy thin-film layer and molybdenum thin-film layer. According to the cadmium telluride thin-film battery provided by the invention, the window area is textured and an optical path of a light-transmitting area is reduced, and thus a light-absorbing capacity is further improved and the better light-trapping effect is realized.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Resin composition and semiconductor mounting substrate obtained by molding same
InactiveUS20150017450A1Improve flame retardant performanceMaintain good propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsEpoxySilanes
A resin composition which contains at least constituent elements (A)-(E) described below and wherein the epoxy resin (A) contains 80-100% by mass of a bifunctional epoxy resin and component (D) is contained in an amount of 60-85% by mass relative to 100% by mass of the total mass of the resin composition. This resin composition does not substantially contain a solvent and is in a liquid state at room temperature. (A) an epoxy rein (B) an amine-based curing agent (C) an accelerator that has at least one functional group selected from among a dimethylureide group, an imidazole group and a tertiary amino group (D) silica particles (E) a silane coupling agent Provided is a resin composition which has excellent curability at low temperatures and a sufficiently low linear expansion coefficient after curing. This resin composition does not suffer from warping in cases where applied to a copper thin film and molded, and does not suffer from separation or cracks even if a substrate obtained therefrom is bent. Also provided is a semiconductor mounting substrate which is obtained by molding the resin composition.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Copper (I) compounds useful as deposition precursors of copper thin films
ActiveUS7166732B2Furnaces without endless coreGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesGas phaseChemical vapor deposition
Copper (I) amidinate precursors for forming copper thin films in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, and a method of depositing the copper (I) amidinate precursors on substrates using chemical vapor deposition or atomic layer deposition processes.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
Preparation method of three-dimensional micrometer level porous copper thin film
InactiveCN103132111AUniform pore size distributionWide range of aperture adjustmentElectroforming processesPorosityMicrometer
A preparation method of a three-dimensional micrometer level porous copper thin film comprises: a metal substrate is offered and serves as a negative electrode and a red copper sheet is offered and serves as a positive electrode; electroplating liquid is prepared, the content of Cu2+ in the electroplating liquid is 0.08mol / L to 0.2mol / L, the content of H2SO4 is 1.50mol / L to 3.00mol / L, the total content of a surface active agent is 0.5 mmol / L to 4.0mmol / L and the content of Cl- is 1.5mmol / L to 3.0mmol / L; and the three-dimensional porous copper thin film is formed on the metal substrate by using the electroplating liquid, the negative electrode and the positive electrode and adoption of a hydrogen bubble dynamic formwork electrodeposition method. The three-dimensional micrometer level porous copper thin film manufactured through the preparation method is even and small in hole diameter and high in porosity.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Laminated metal thin plate formed by electrodeposition and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20050103637A1Excellent characteristicsGood chemical resistanceBonded abrasive wheelsGrinding devicesMetal sheetChemical resistance
A laminated metal thin plate produced by electrodeposition is composed of a plurality of metal layers provided by at least two kinds of materials different in composition from each other. The laminated metal thin plate includes a first layer excellent in mechanical characteristics and / or chemical resistance and a second layer excellent in electrical characteristics such as electrical conductivity. The first and the second layers are adhered to each other in atomic level directly at their interface, with composition gradient at their interface, or with an adherence buffer layer such as a copper thin film interposed therebetween. The first layer is at first deposited on an electrode substrate. The second layer is deposited on the first layer. Deposition is repeatedly carried out in such a way that the first layers on opposite sides of the second layer are equal in thickness. Finally, the electrode substrate is dissolved and removed.
Owner:YAMASAKI TOHRU +1
Volatile copper aminoalkoxide complex and deposition of copper thin film using same
ActiveUS6982341B1Increase relative volatilityQuality improvementCopper organic compoundsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor depositionMetal
A volatile copper aminoalkoxide complex of formula (I) can form a copper thin film having an improved quality by metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD): wherein, R1, R2, R3 and R4 are each independently C1-4 alkyl optionally carrying one or more fluorine substituents; and m is an integer in the range of 1 to 3.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
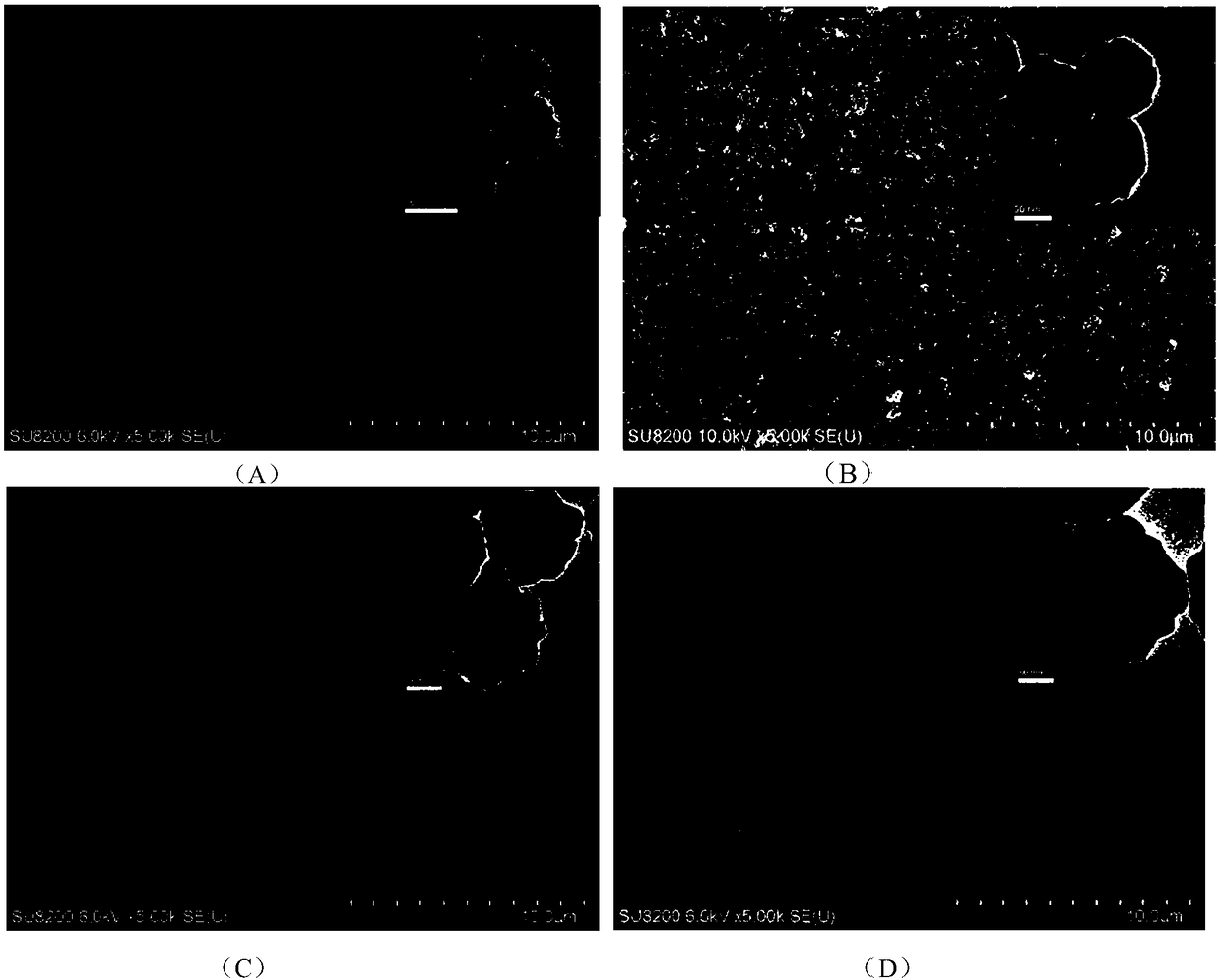
Improved nano porous copper thin film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104789934APrecise thickness controlImprove electrochemical performanceMaterial nanotechnologyVacuum evaporation coatingManganeseAlloy thin film
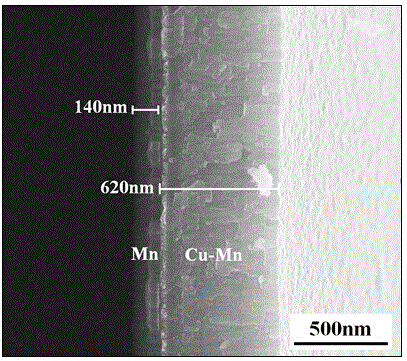
The invention discloses an improved nano porous copper thin film. The surface of nano porous copper is modified by a single layer of graphene. The invention further provides a preparation method of the improved nano porous copper thin film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: placing a target material of manganese and a target material of copper manganese alloy at a target position in the cavity of a magnetic-control sputtering film-preparing instrument; fixing a monocrystalline silicon wafer to a tray right above the target position, vacuumizing, setting sputtering conditions, and opening the target material of pure manganese to start sputtering, so as to prepare a pure-manganese thin film on the silicon wafer; opening the target material of the copper manganese alloy to start sputtering, and forming a layer of copper manganese alloy thin film on the pure-manganese thin film; corroding the copper manganese alloy thin film so as to obtain the nano porous copper thin film; steeping and washing the prepared nano porous copper thin film so as to remove hydrochloric acid residual liquid on the surface; placing the clean nano porous copper thin film in graphene gel for soaking; removing the graphene gel floating on the surface so as to obtain the nano porous copper thin film compounded with the graphene. The nano porous copper thin film disclosed by the invention has the electrochemical cycling properties of high specific capacity and stability.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
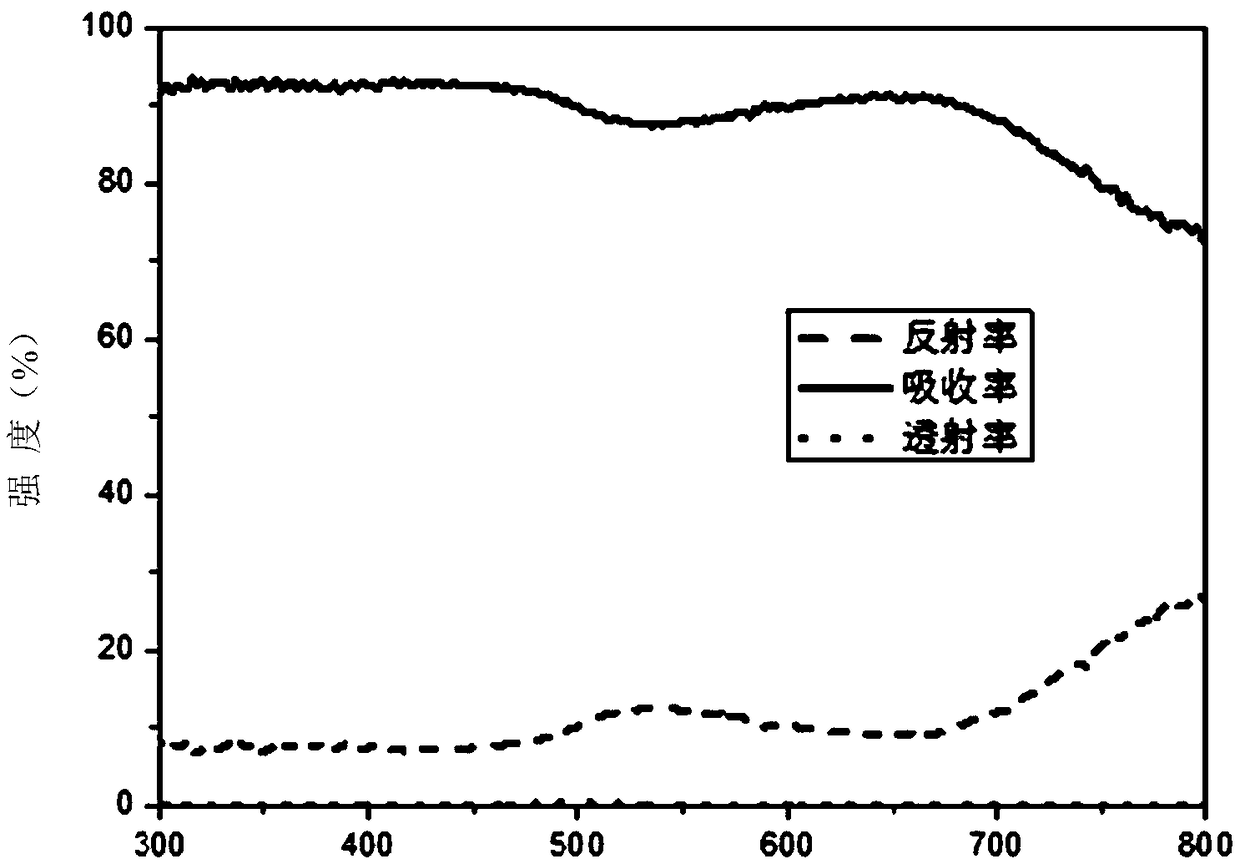
Broadband perfect absorber based on metallic film-core shell plasma structure
The invention provides a broadband perfect absorber based on a metallic film-core shell plasma structure. The broadband perfect absorber comprises a substrate, the broadband perfect absorber is of a multi-layered structure arranged on the substrate, a metallic film layer and a core shell nano-particle film layer are sequentially arranged from the substrate up, the core shell nano-particle film layer is composed of core shell particles with local surface plasma resonance characteristics, and the core shell particles are constituted by taking precious metals as cores and semiconductors as shells. The invention further provides a preparation method of the broadband perfect absorber. The broadband perfect absorber is simple in structure and optional in substrate, the metallic film can be a gold thin film, a silver thin film, a copper thin film and the like, liquid-liquid interface is used for self-assembling into a film, the operation is convenient, the area is controllable, the broadbandperfect absorber is suitable for a plurality of compounds of the precious metals and the semiconductors, and the manufacturing cost is low.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
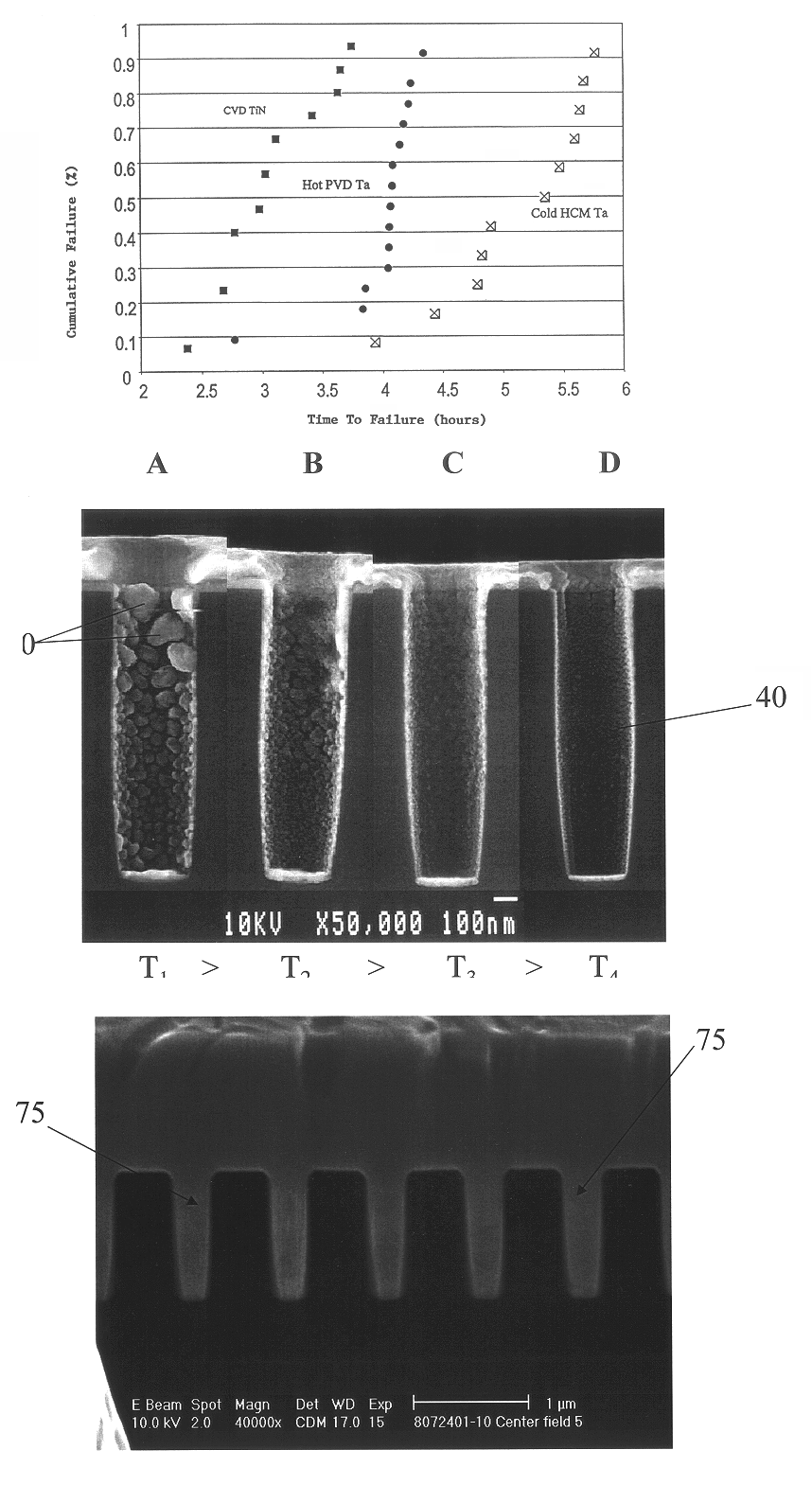
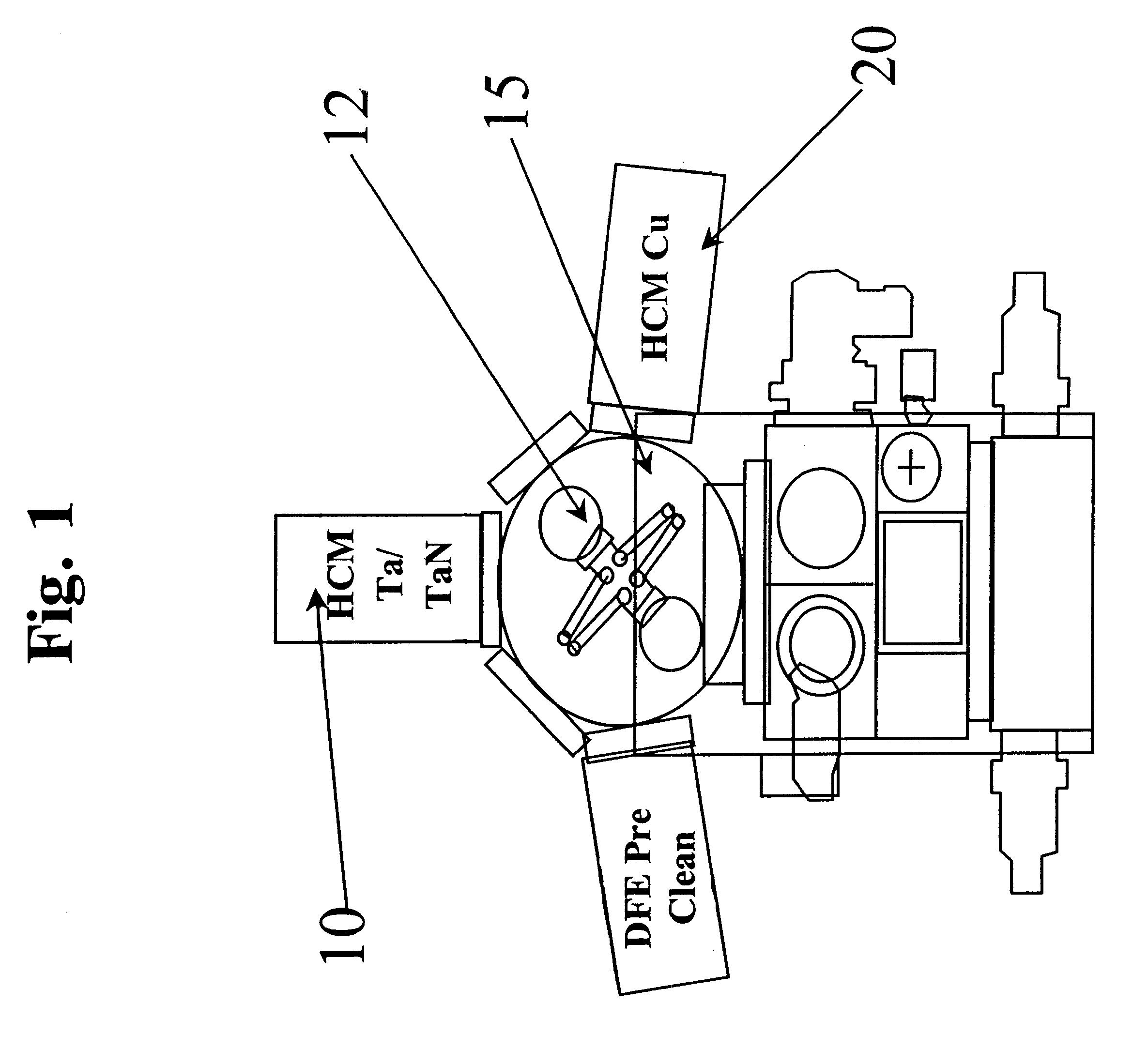
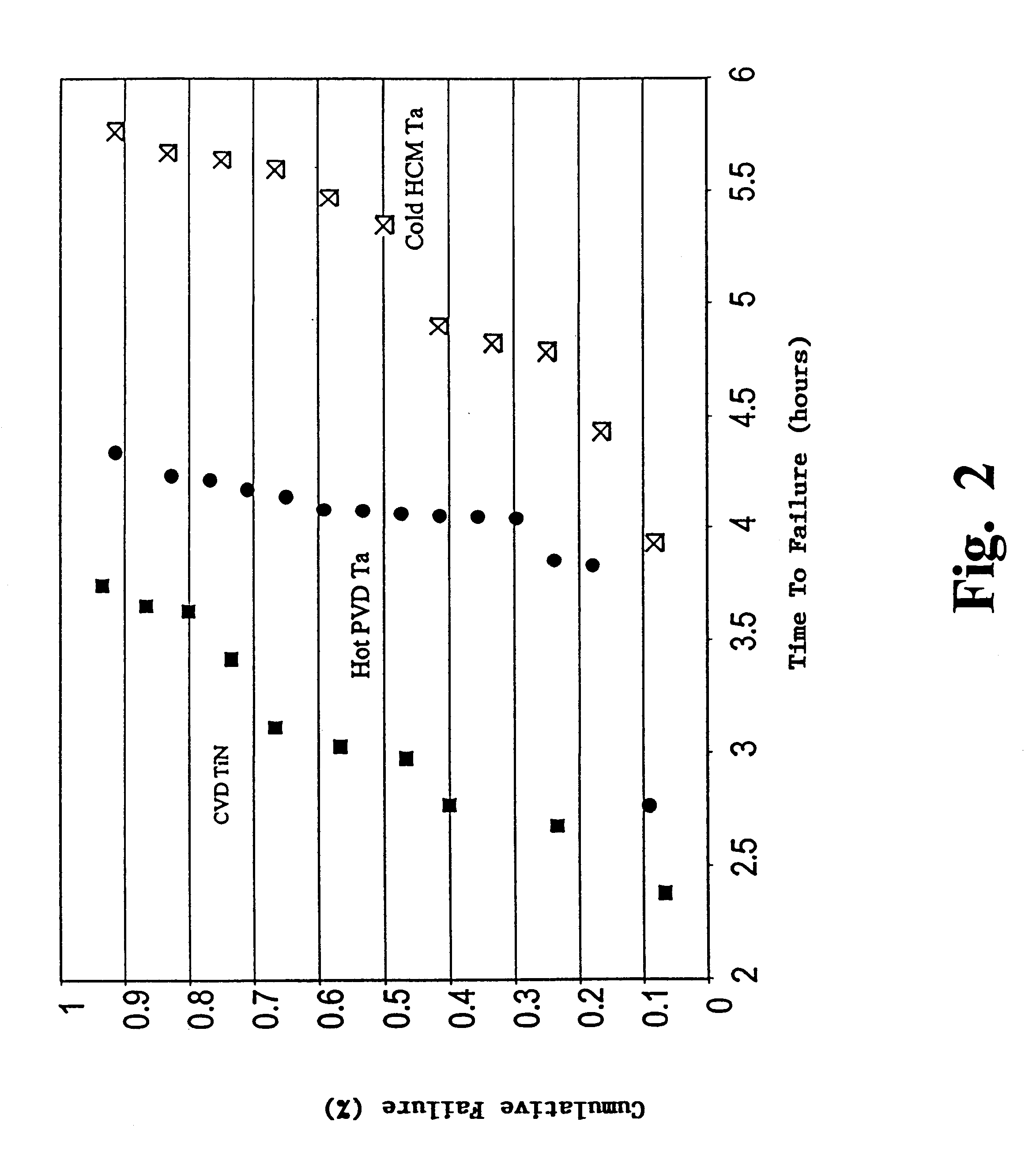
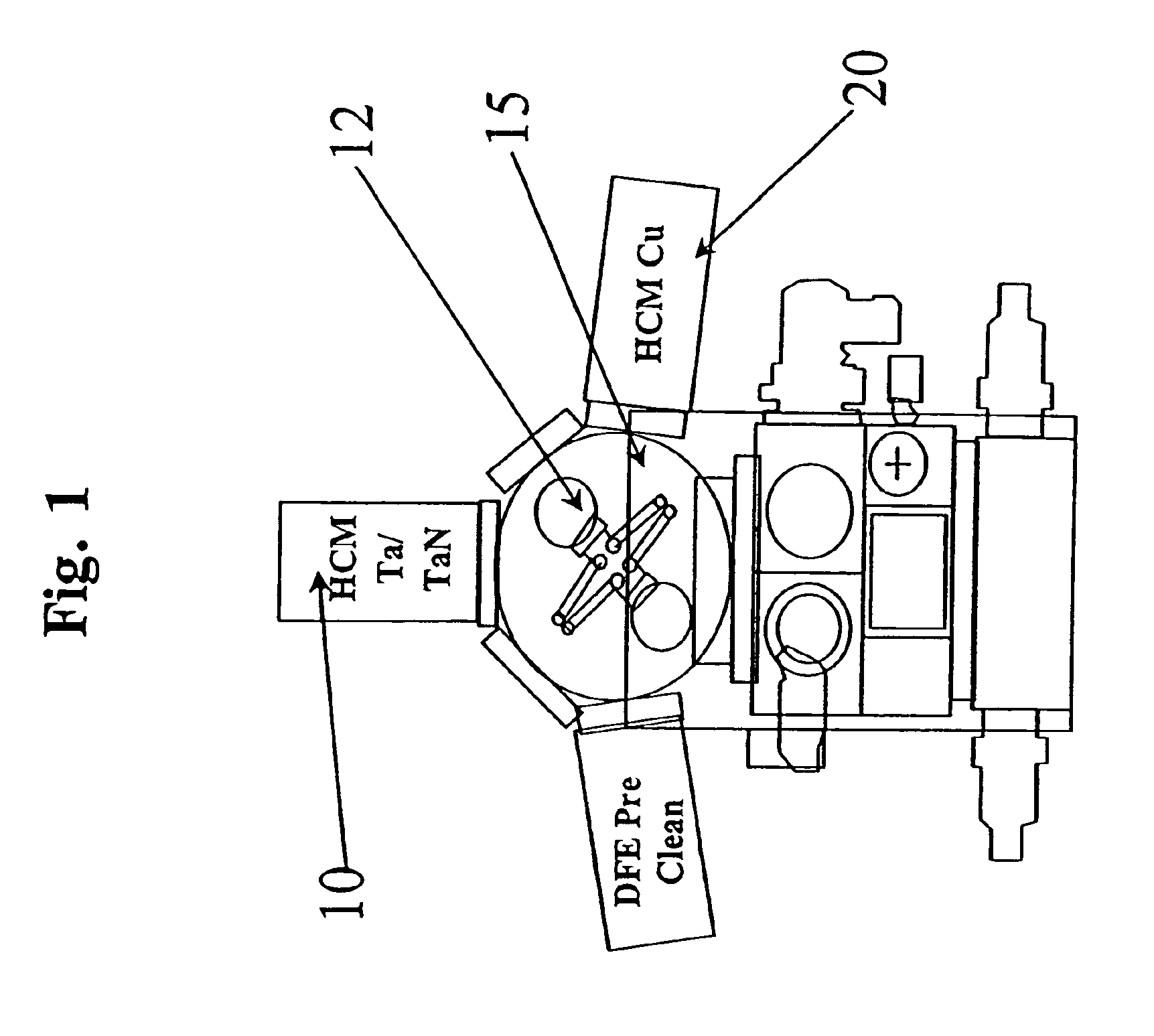
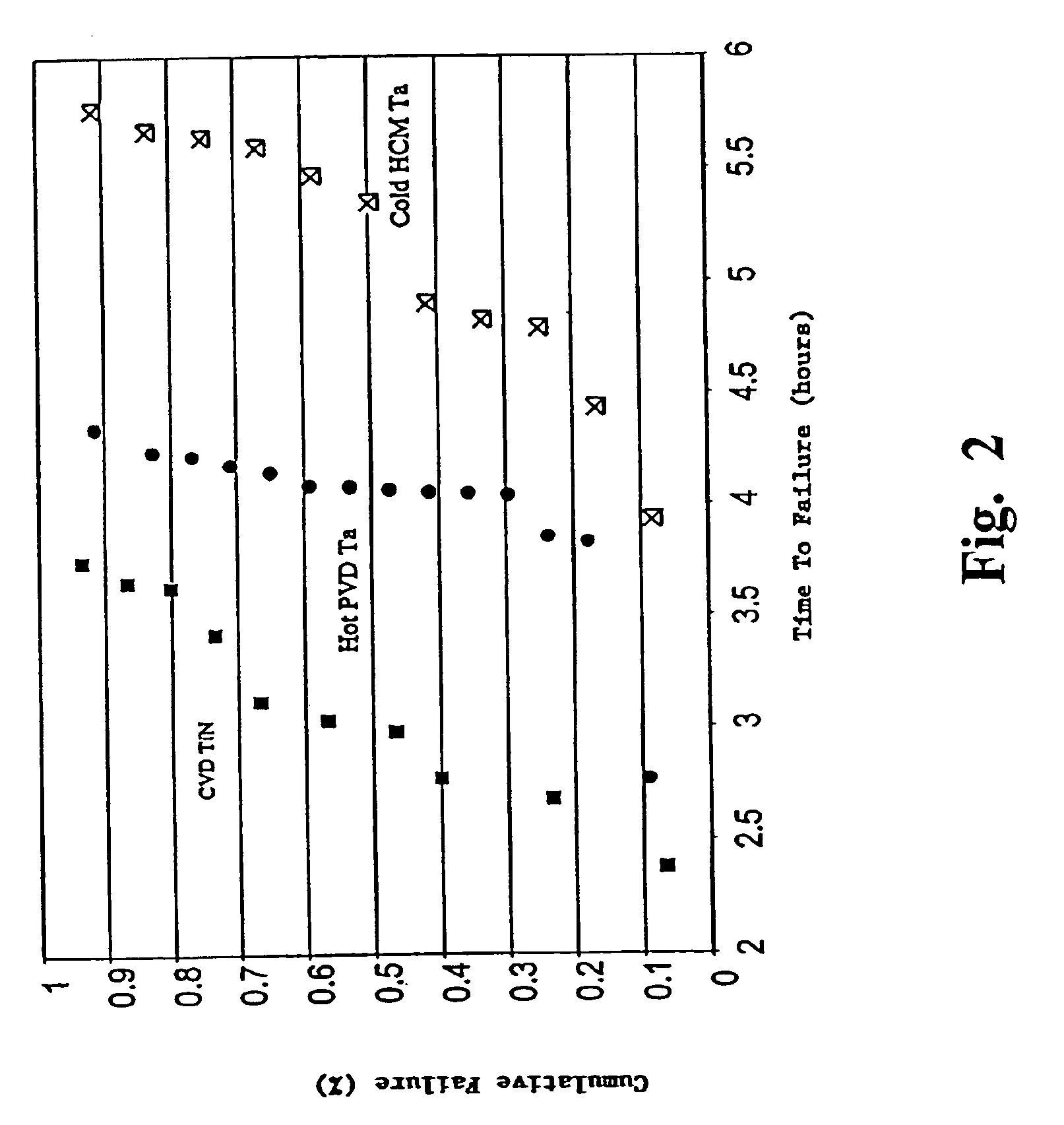
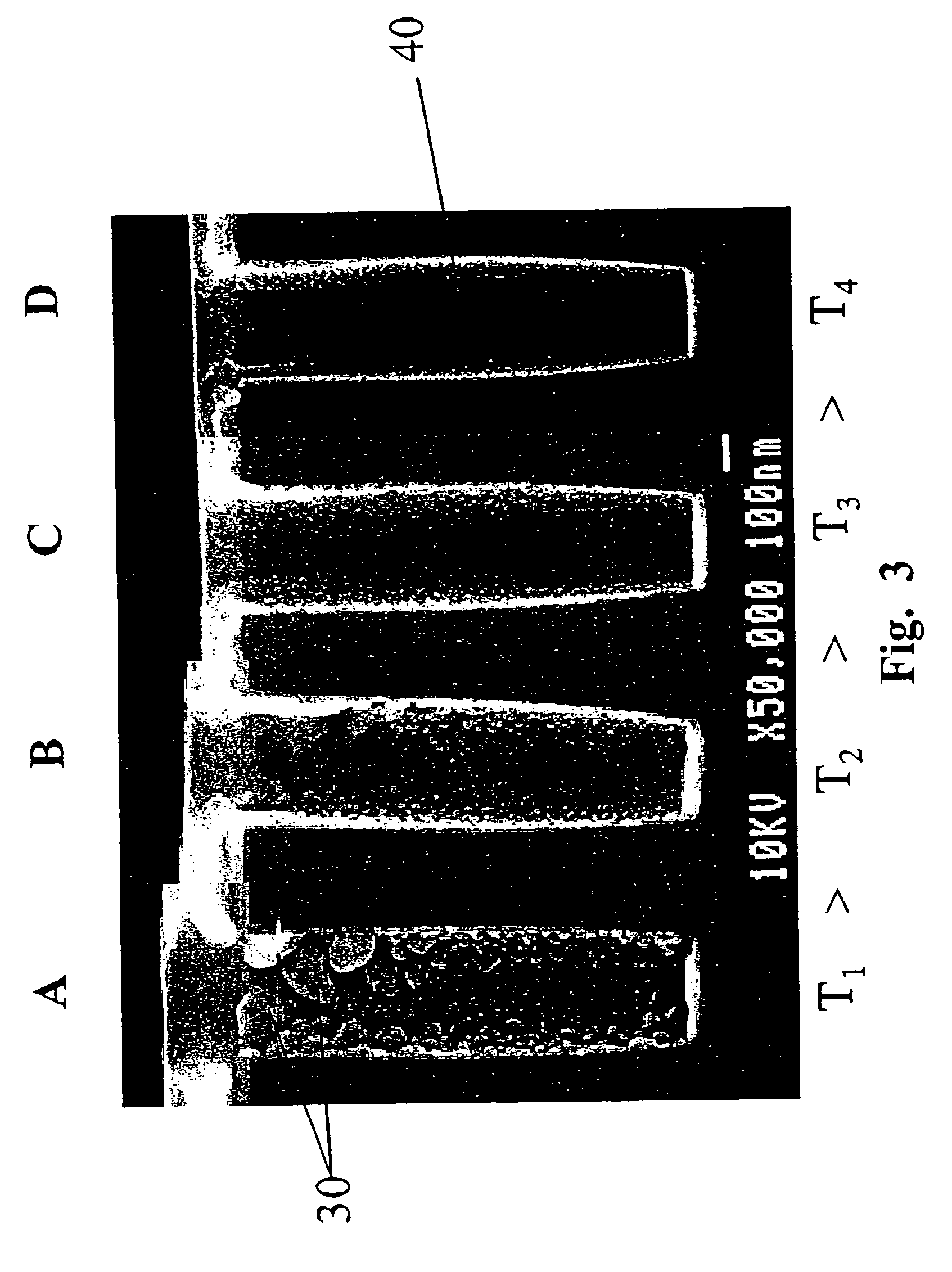
Apparatus and method for depositing superior Ta(N)/copper thin films for barrier and seed applications in semiconductor processing
InactiveUS6541371B1Increase depositionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCopper interconnectTantalum nitride
A method of depositing thin films comprising tantalum, tantalum nitride, and copper for barrier films and seed layers within high aspect ratio openings used for copper interconnects. The barrier films and seed layers are deposited at extremely low temperature conditions wherein the wafer stage temperature of the sputter source is chilled to about -70° C. to about 0° C. Most preferably, the present invention is practiced using a hollow cathode magnetron. The resulting tantalum and / or tantalum nitride barrier films and copper seed layers are superior in surface smoothness, grain size and uniformity such that subsequent filling of the high aspect ratio opening is substantially void-free.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Apparatus and method for depositing superior Ta (N) copper thin films for barrier and seed applications in semiconductor processing
InactiveUS6905959B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCopper interconnectTantalum nitride
A method of depositing thin films comprising tantalum, tantalum nitride, and copper for barrier films and seed layers within high aspect ratio openings used for copper interconnects. The barrier films and seed layers are deposited at extremely low temperature conditions wherein the wafer stage temperature of the sputter source is chilled to about −70° C. to about 0° C. Most preferably, the present invention is practiced using a hollow cathode magnetron. The resulting tantalum and / or tantalum nitride barrier films and copper seed layers are superior in surface smoothness, grain size and uniformity such that subsequent filling of the high aspect ratio opening is substantially void-free.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
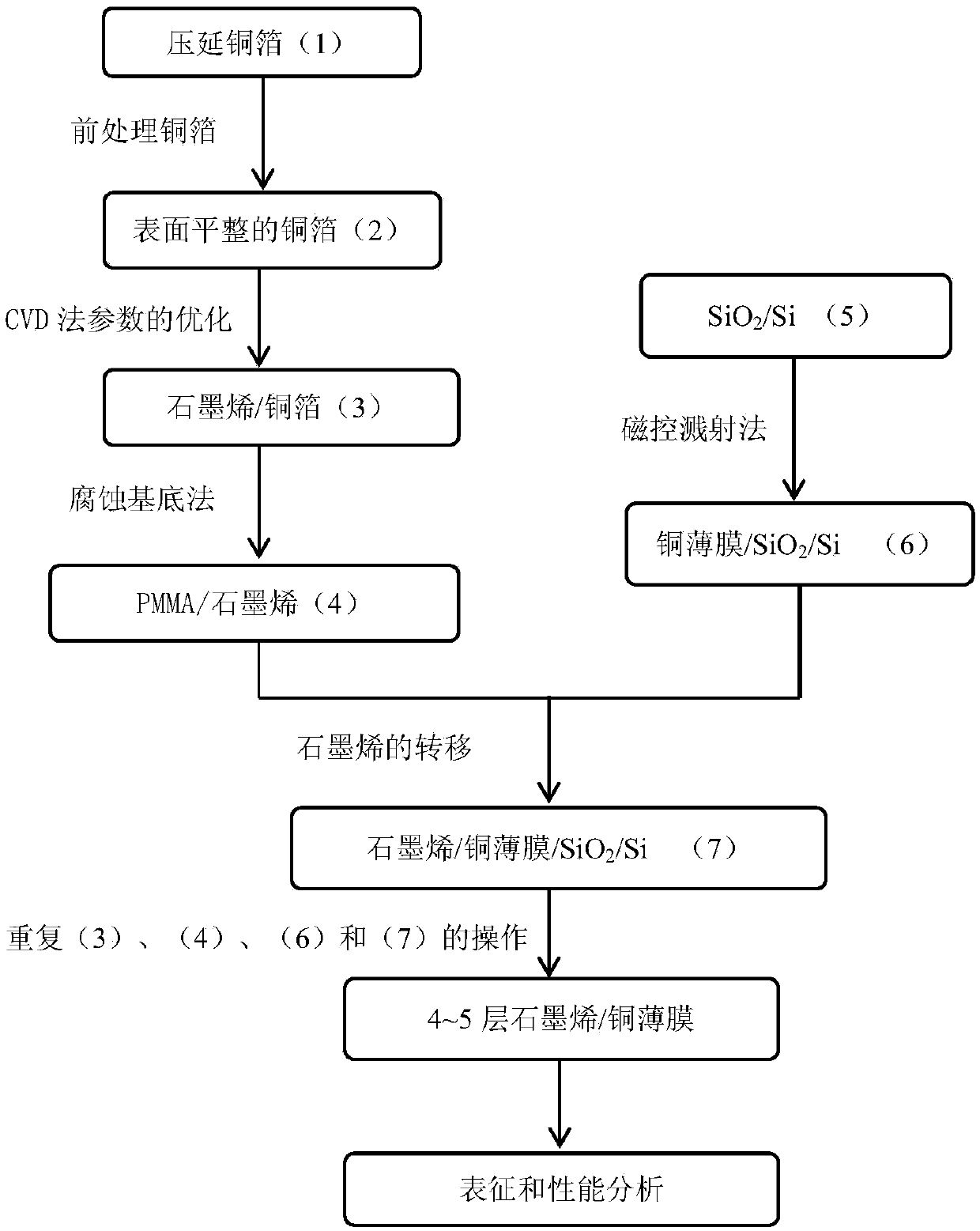
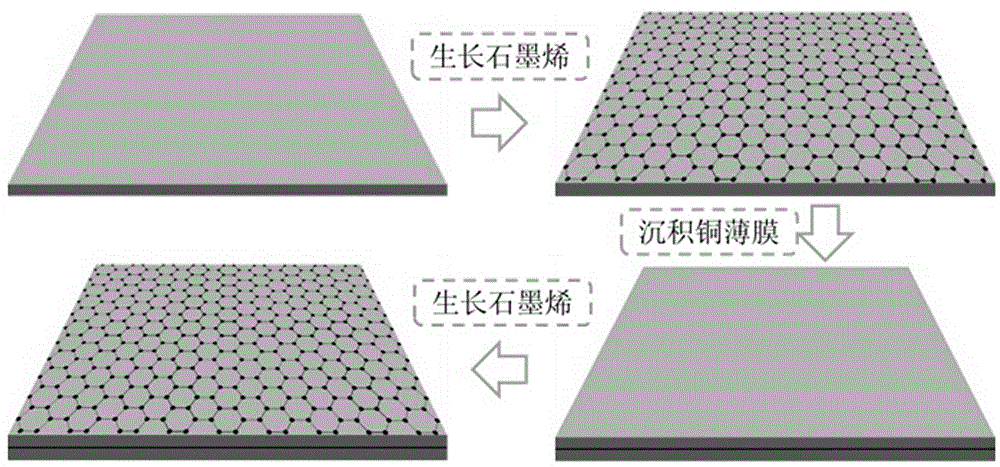
Preparation method of copper/graphene composite material
ActiveCN107697906ASignificant technological progressEasy to prepareVacuum evaporation coatingLaminationSputteringCopper foil
The invention provides a preparation method of a copper / graphene composite material. The preparation method comprises the steps: firstly, preparing a graphene thin film on a rolled copper foil after cleaning and polishing by a chemical vapor deposition method, plating a SiO2 / Si sheet with a layer of copper film with the thickness of 400-700 nm by a magnetron sputtering coater, and preparing a copper film / SiO2 / Si sample; then, transferring the graphene thin film prepared by the chemical vapor deposition method to the surface of the copper film / SiO2 / Si sample by a corrosion substrate method, toprepare a graphene / copper film / SiO2 / Si sample; secondly, carrying out magnetron sputtering of the surface of the graphene thin film / copper film / SiO2 / Si sample with a layer of copper film with the thickness of 450-550 nm, to obtain a copper film / graphene / copper film / SiO2 / Si sample; finally, transferring the graphene thin film prepared by the chemical vapor deposition method to the surface of the composite material; and preparing and transferring graphene and sputtering copper thin films repeatedly, and finally obtaining the nanosandwich composite material with four layers of copper films and three layers of graphene thin films. The preparation method is simple, convenient to operate and low in cost, and has good application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Cuprous oxide solar battery with surface self-texture structure and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102376783ASelf-textured surfaceImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesElectrical batterySolar battery
The invention relates to the technical field of solar batteries, in particular to a cuprous oxide thin film solar battery with a surface self-texture structure; a layer of n-type cuprous oxide thin film is deposited on electrically conductive glass; a layer of p-type cuprous oxide thin film with the shape of a pyramid is deposited on the n-type cuprous oxide thin film; and electrodes are arrangedon the electrically conductive glass and the p-type cuprous oxide thin film. A manufacturing method comprises the following step: when the pH value of the electrolyte is 4-5 and the voltage is from minus 0.01V to 0.1V, the n-type cuprous oxide thin film is deposited on the electrically conductive glass; when the pH value of the electrolyte is 11-12 and the voltage is from minus 0.1 V to minus 0.3V, the p-type cuprous oxide thin film is deposited on the n-type cuprous oxide thin film; and the electrodes are manufactured on the electrically conductive glass and the p-type cuprous oxide thin film. The solar battery of the invention can supply stable constant current output and has higher photoelectricity conversion efficiency; and by adopting the manufacturing method, the rapid low-cost pollution-free mass production of the cuprous oxide solar battery is realized.
Owner:刘畅
Copper-doped perovskite thin film, in-situ preparation method and hole-transport-layer-free solar cell device
ActiveCN106848062ALow costReduce energy consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIodineCopper iodide
The invention relates to a copper-doped perovskite thin film, an in-situ preparation method and a hole-transport-layer-free solar cell device. According to the copper-doped perovskite thin film, copper is doped in perovskite lattices in situ, and content of copper and lead is gradually reduced from the surface to the bottom of the copper-doped perovskite thin film. The in-situ preparation method includes the following steps that 1, a copper thin film is deposited, wherein firstly, the copper thin film is deposited on a substrate material; 2, copper iodide is prepared, wherein the deposited copper thin film reacts with iodine in a closed container, and a copper iodide thin film is obtained; 3, perovskite is prepared, wherein perovskite is prepared on the obtained copper iodide thin film in an in-situ spin-coating mode, and the copper-doped perovskite thin film is prepared in situ through annealing treatment. A solar cell does not need a hole transport layer, the cost is low, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency is high.
Owner:XUCHANG UNIV
Organic solar battery and preparation method thereof
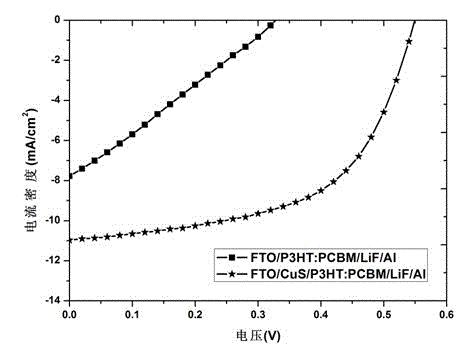
ActiveCN103151463ALow costSimple processFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesOrganic solar cellSolar battery
The invention relates to an organic solar battery and a preparation method thereof, taking CuS as a hole transport layer. The organic solar battery comprises a transparent conductive substrate, a CuS hole transport layer, an organic active layer, an electron transport layer and metal electrodes. The CuS hole transport layer is a thin film formed in a way that a copper thin film is obtained through magnetron sputtering, and then the copper thin film and powdered sulfur are subjected to in-situ hydrothermal growth. The CuS prepared by the magnetron sputtering and a hydrothermal reaction method is used as the hole transport layer of the organic solar battery, and compared with the energy conversion efficiency of an organic inorganic hybridized solar battery without the CuS hole transport layer, the energy conversion efficiency of the organic solar battery with the CuS hole transport layer is generally improved. Compared with a PEDOT:PSS (poly-ethylenedioxythiophene : p-styrene sulfonate) hole transport layer, the CuS avoids the erosion effect on the conductive substrate, and the stability is enhanced. The organic battery photovoltaic feature, taking the CuS as the hole transport layer, can be on a par with the battery property, taking MoO3 as the hole transport layer, and further, the organic solar battery is lower in cost and is more practical.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Flexible printed circuit board and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20050174722A1Conductive layers on insulating-supportsSubstation/switching arrangement detailsLattice planeX-ray
The present invention relates to a flexible printed circuit board which has extremely high adhesion performance and on which very fine circuit patterns can be formed by etching, and to a method for producing the same. In the present invention, in the flexible printed circuit board wherein a copper thin film made of copper or an alloy containing primarily copper is directly formed on at least one side of a plastic film substrate, and copper is formed further on the copper thin film by the electrolytic plating method, the above-mentioned copper thin film has a two-layer structure in which a layer including at least a crystalline structure is formed on the surface side thereof, and the X-ray relative intensity ratio between crystal lattice plane indices (200) / (111) in the above-mentioned crystalline structure is 0.1 or less.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for producing printed-wiring board
ActiveUS20150034590A1Improve unevennessReduce the amount of etchingPhotomechanical apparatusLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingResistInsulation layer
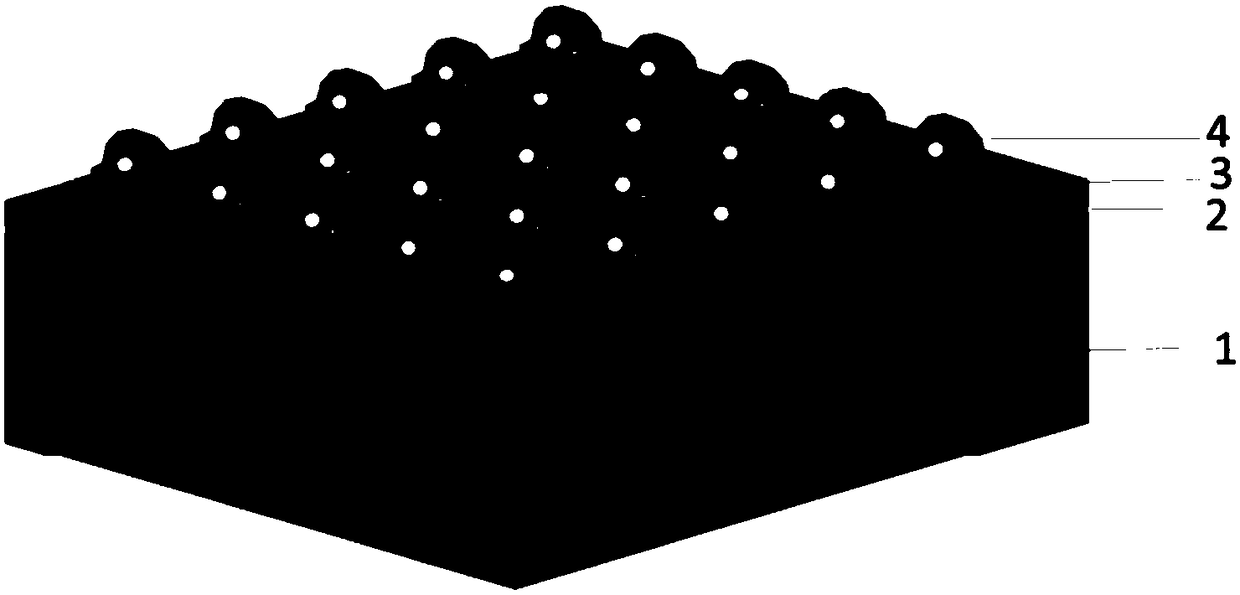
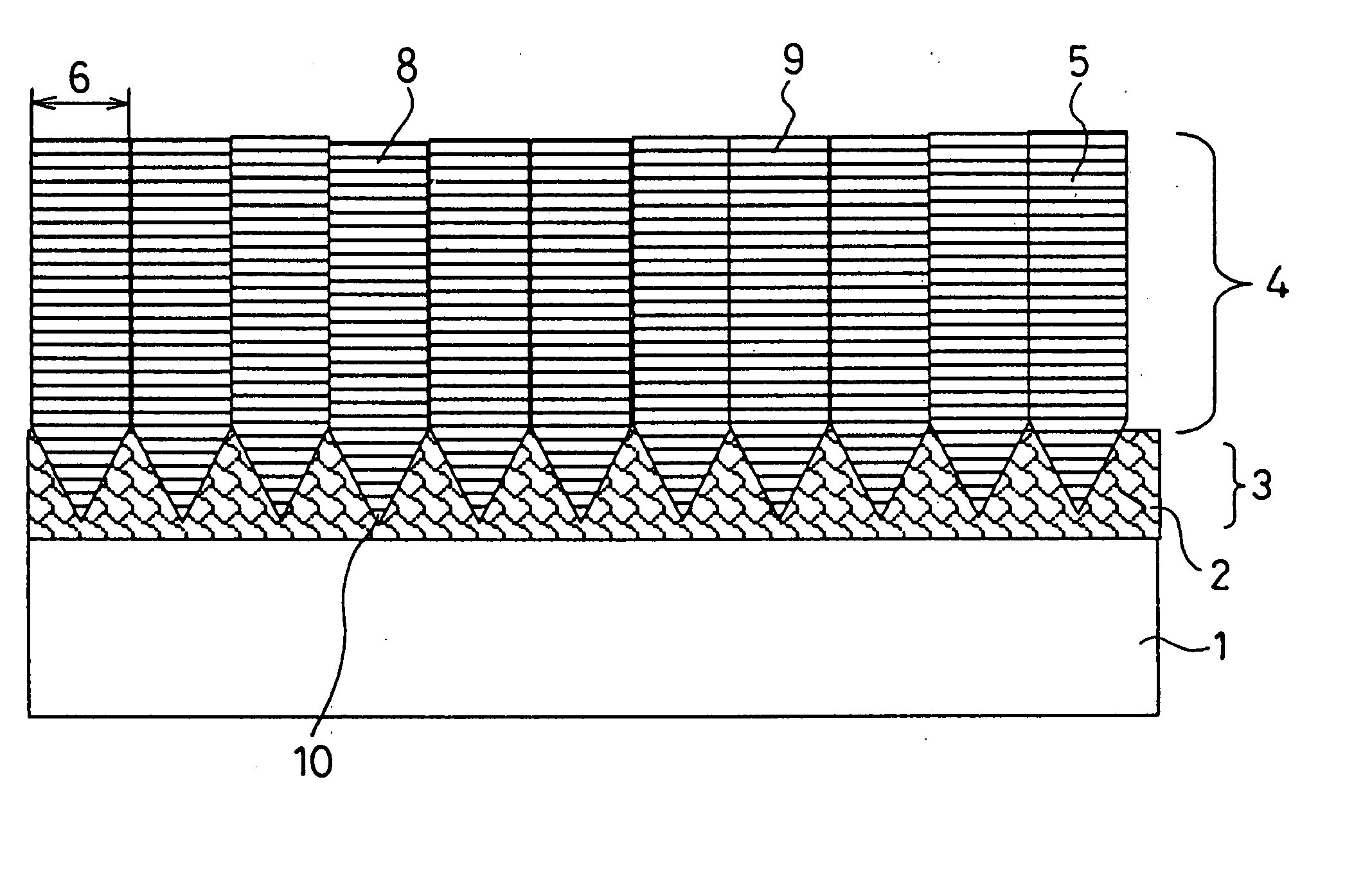
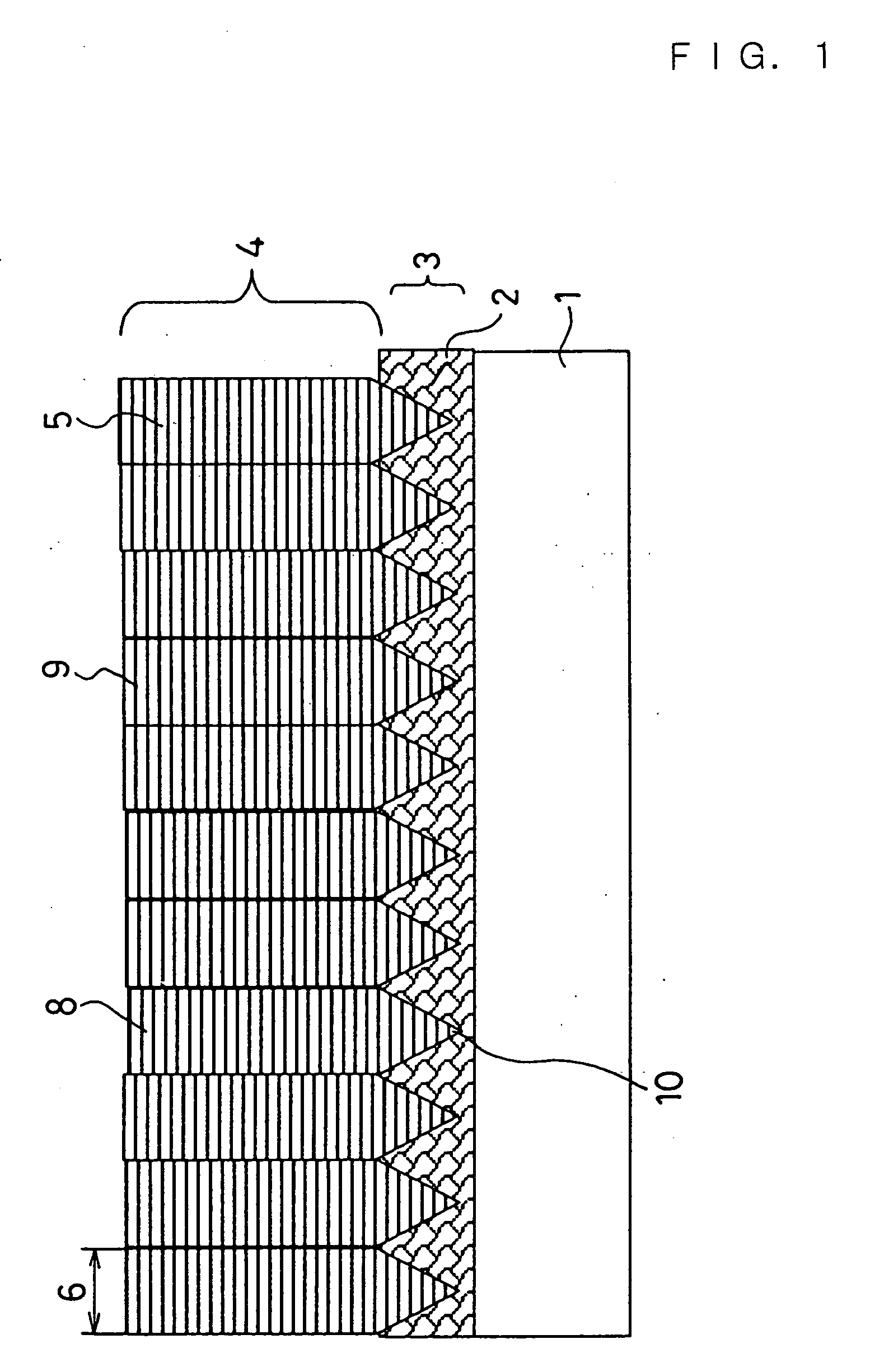
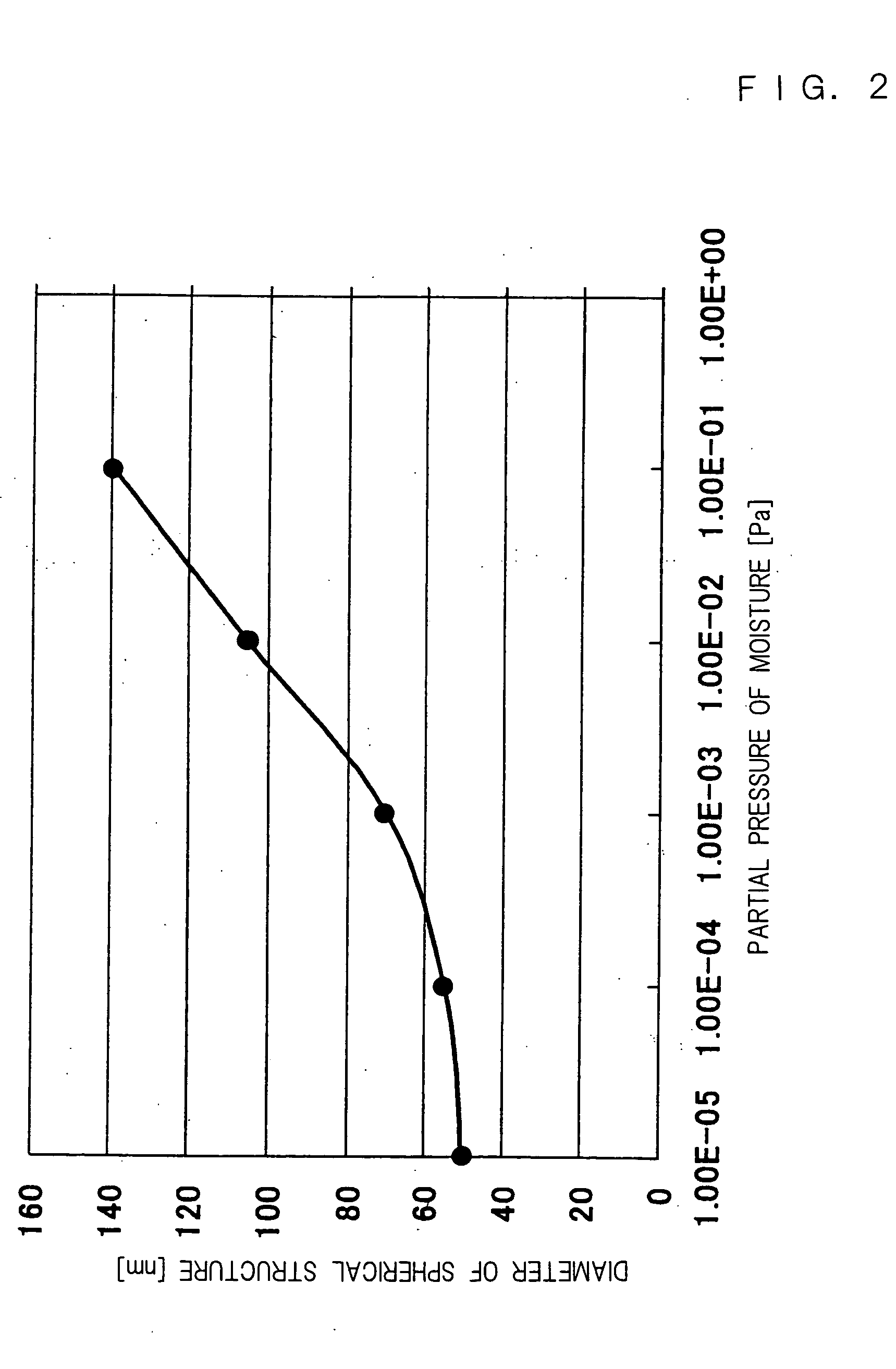
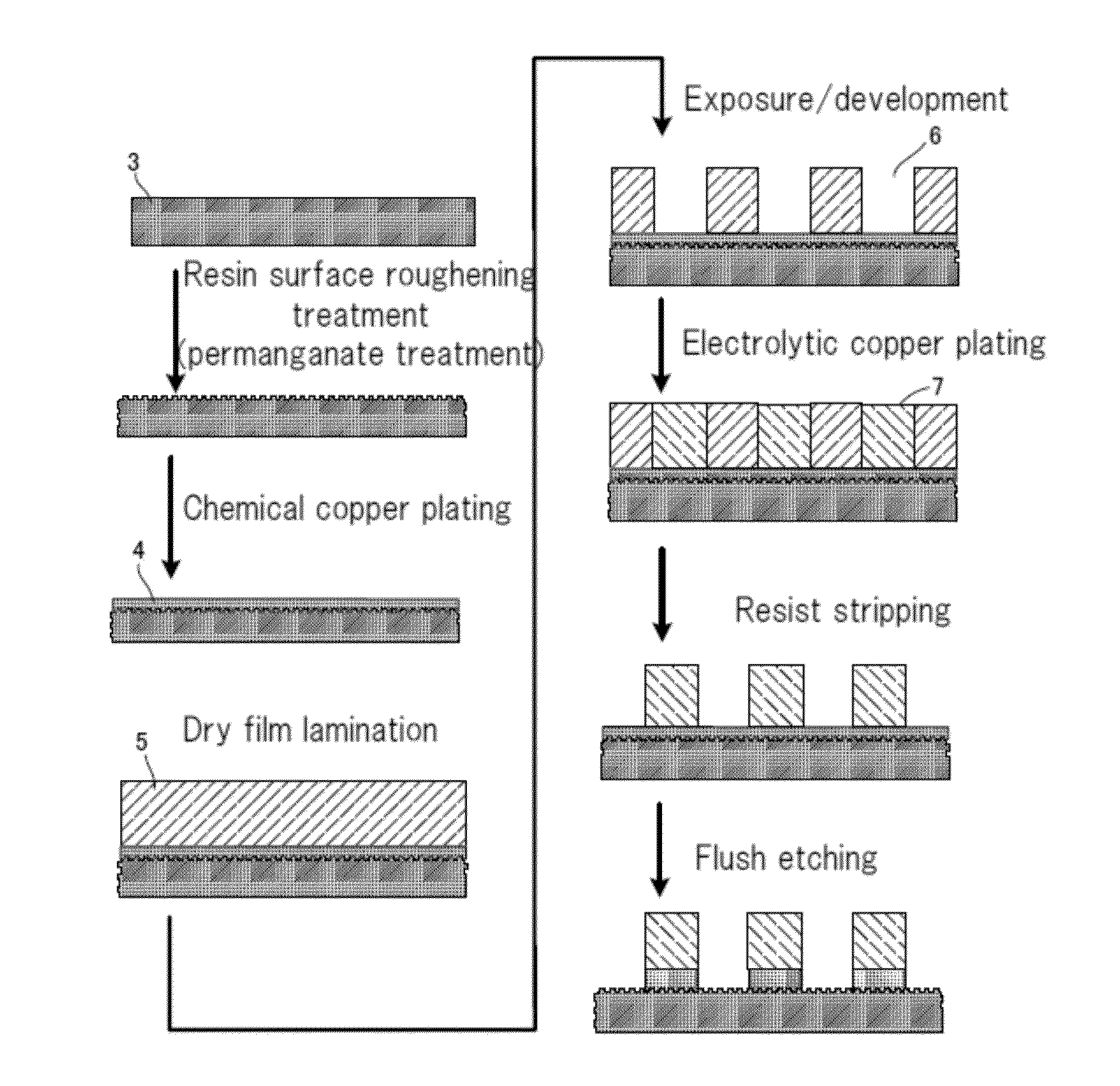
The present invention provides a method for producing a printed-wiring board in a semi-additive process, comprising the steps of: providing a chemical copper plating 4 on an insulation layer 3 or forming a copper thin film on the insulation layer 3 using a sputtering method; subjecting the obtained copper surface 4 to a roughening treatment using an etching solution containing 0.1 to 3% by mass of hydrogen peroxide, 0.3 to 5% by mass of sulfuric acid, 0.1 to 3 ppm of halogen ion and 0.003 to 0.3% by mass of tetrazoles; attaching a dry film resist 5 to the copper surface 4 after the roughening treatment to perform exposure and development and providing an electrolytic copper plating 7 to an opening 6 after the exposure; and subjecting the remaining dry film resist to a stripping treatment using a resist stripping liquid containing 0.5 to 20% by mass of monoethanolamine, 0.2 to 10% by mass of quaternary ammonium hydroxide, 0.01 to 10% by mass of ethylene glycols and 0.01 to 0.5% by mass of azoles.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Nano twin crystal copper thin film material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112779572AHigh strengthImprove ductilityCellsMaterial nanotechnologyCopper interconnectWafering
The invention discloses a nano twin crystal copper thin film material and a preparation method and application thereof. The copper thin film material comprises a nano twin crystallization hierarchical structure, and the thickness ratio of the hierarchical structure in a copper thin film is larger than or equal to 90%. The hierarchical structure is composed of nano twin crystallization columnar crystals and nano twin crystallization equiaxed crystals, the thickness ratio of the nano twin crystallization equiaxed crystals in the hierarchical structure is larger than that of the nano twin crystallization columnar crystals in the hierarchical structure, and the nano twin crystallization equiaxed crystals are randomly distributed in the twin crystal lamellar direction. The nano twin crystal copper thin film material has the characteristics of excellent strength, ductility and mechanical isotropy, and can meet the requirement of a copper interconnection material for mechanical service performance.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for forming a copper thin film
InactiveUS20020157610A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingCopper platingElectroplating
In a method for forming a Cu thin film on a substrate including a Cu-CVD step of forming a first copper film on predetermined surface of a substrate by a CVD process and a plating step of further forming a second copper film on the first copper film by an electrolytic copper plating process using the first copper film as an electrode, a modifying step for modifying the first copper film by exposing it in an active atmosphere is interposed between the Cu-CVD step and the plating step. Thereby, fine voids can be effectively prevented from being formed in the vicinity of the interface between the first copper film and the second copper film.
Owner:ANELVA CORP
Semiconductor device, liquid crystal display device having semiconductor device, and method for producing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20120206685A1Improve adhesionImprove barrier propertiesTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLiquid-crystal displayDevice material
Disclosed is an electrode film which does not exfoliate from, or diffuse into, an oxide semiconductor or an oxide thin film. An electrode layer comprises a highly adhesive barrier film being a Cu—Mg—Al thin film and a copper thin film; and an oxide semiconductor and an oxide thin film contact with the highly adhesive barrier film. With the highly adhesive barrier film having magnesium in a range of at least 0.5 at % but at most 5 at % and aluminum at least 5 at % but at most 15 at % when the total number of atoms of copper, magnesium, and aluminum is 100 at %, the highly adhesive barrier film has both adhesion and barrier properties. The electrode layer is suitable because a source electrode layer and a drain electrode layer contact the oxide semiconductor layer. A stopper layer having an oxide may be provided on a layer under the electrode layer.
Owner:ULVAC INC
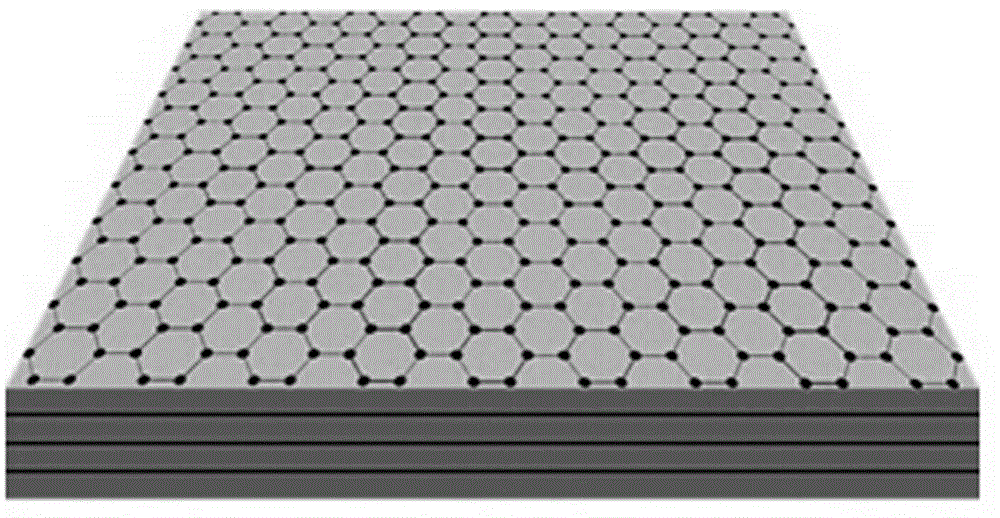
Heat sink material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105984179AImprove machinabilitySolve problems that cannot be directly used for heat sink materialsMetal layered productsThin membraneGraphite
The invention relates to a heat sink material, in particular to a heat sink material applied to micro-nano-scale power devices such as micro-nano optoelectronic devices and a preparation method of the heat sink material. The heat sink material comprises three or more copper film layers and three or more graphene layers, wherein the copper film layers and the graphene layers are combined together in an alternative mode. According to the heat sink material and the preparation method thereof, the multilayer stacking structure of copper / graphene is adopted, and the composite heat sink material with the multi-stacking layers of copper / graphene is obtained by preparing the copper films and graphene alternatively. The superhigh heat conductivity characteristic of graphene is utilized, graphene is directly grown on the copper film layers, the problem that graphene of a planar structure cannot be directly applied to heat sink materials is solved, and high heat conductivity can be achieved; meanwhile, the heat sink material has very high processibility through combination of graphene and copper.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com