Patents
Literature
550 results about "Alloy thin film" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
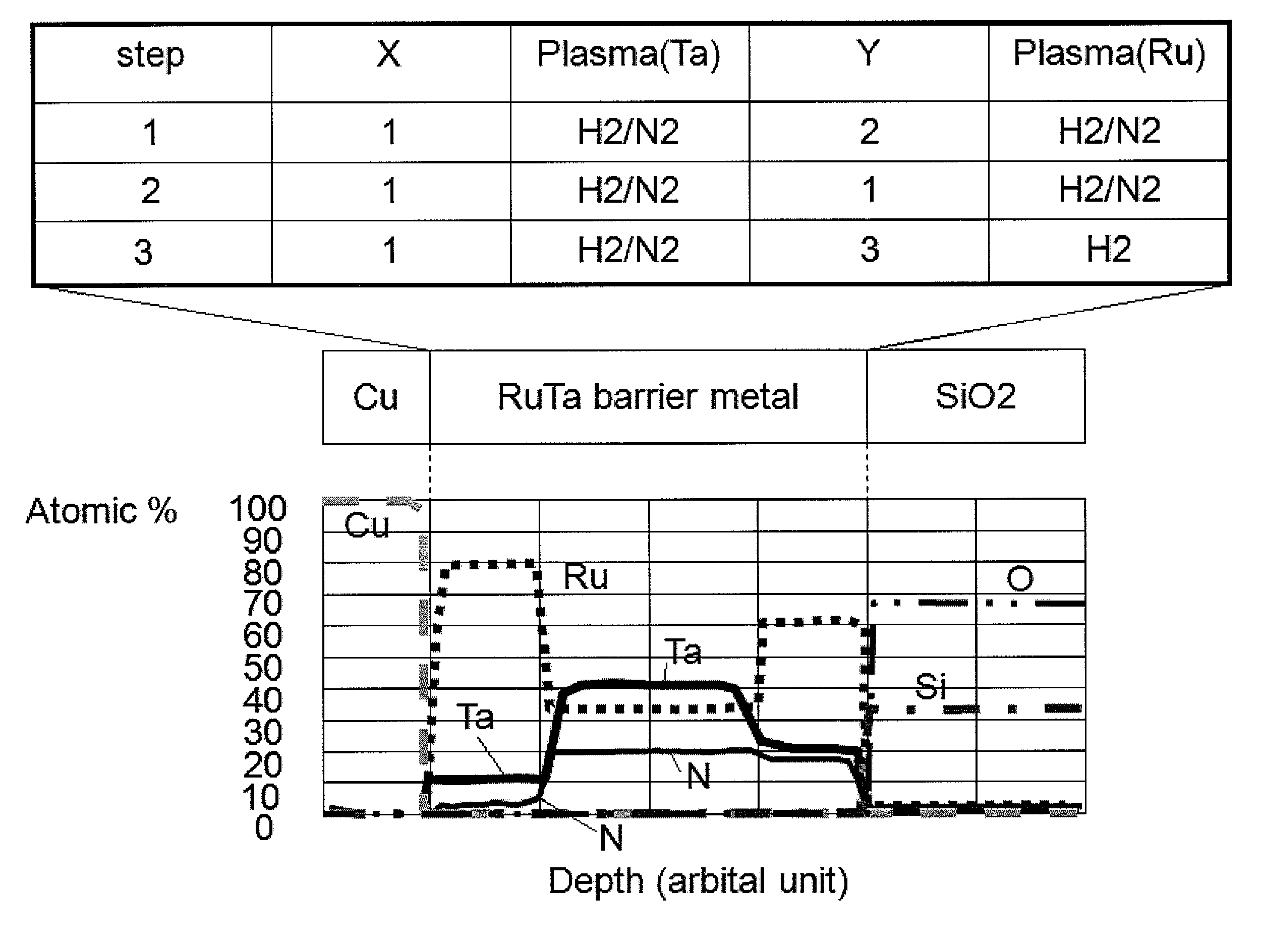
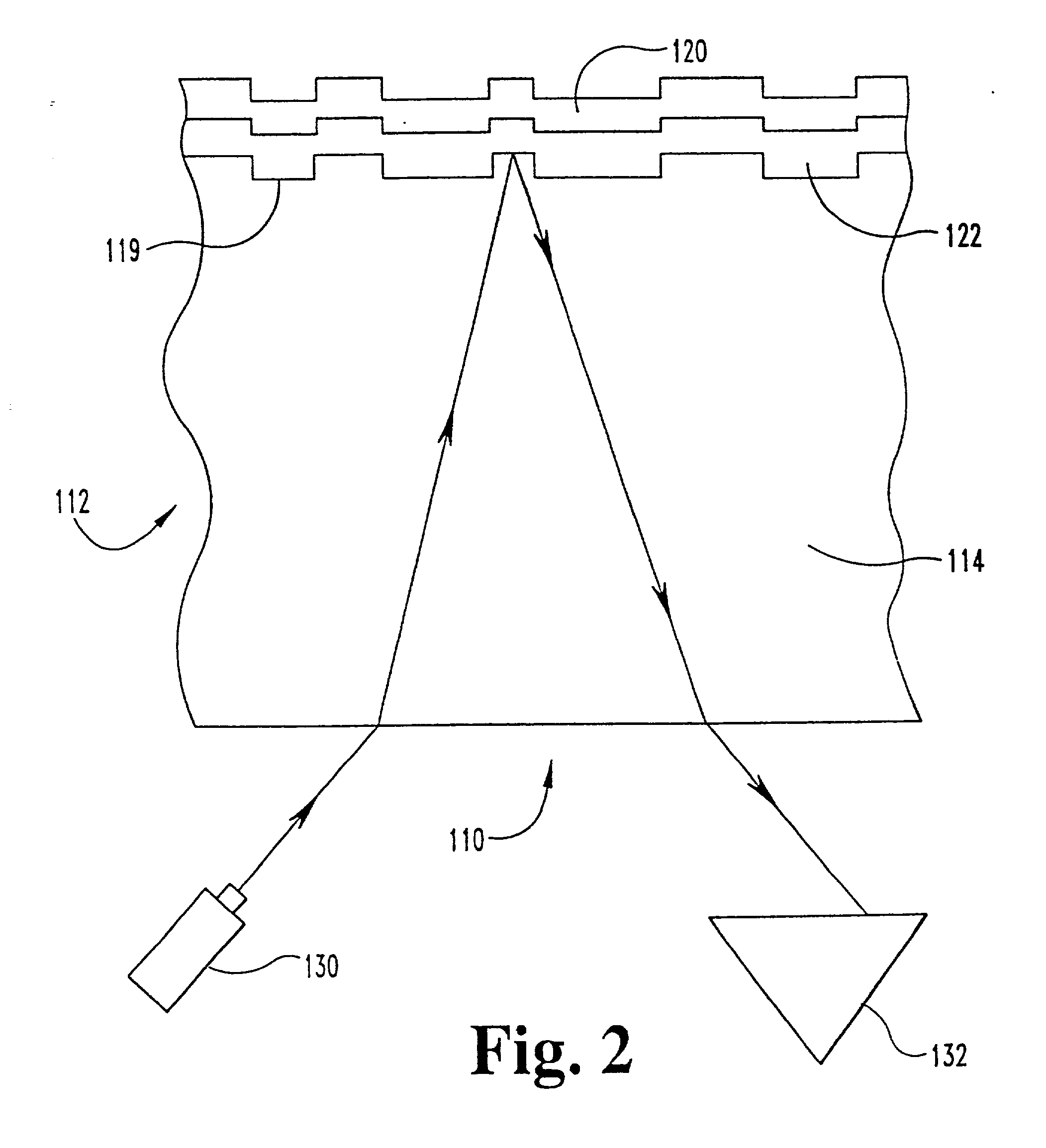
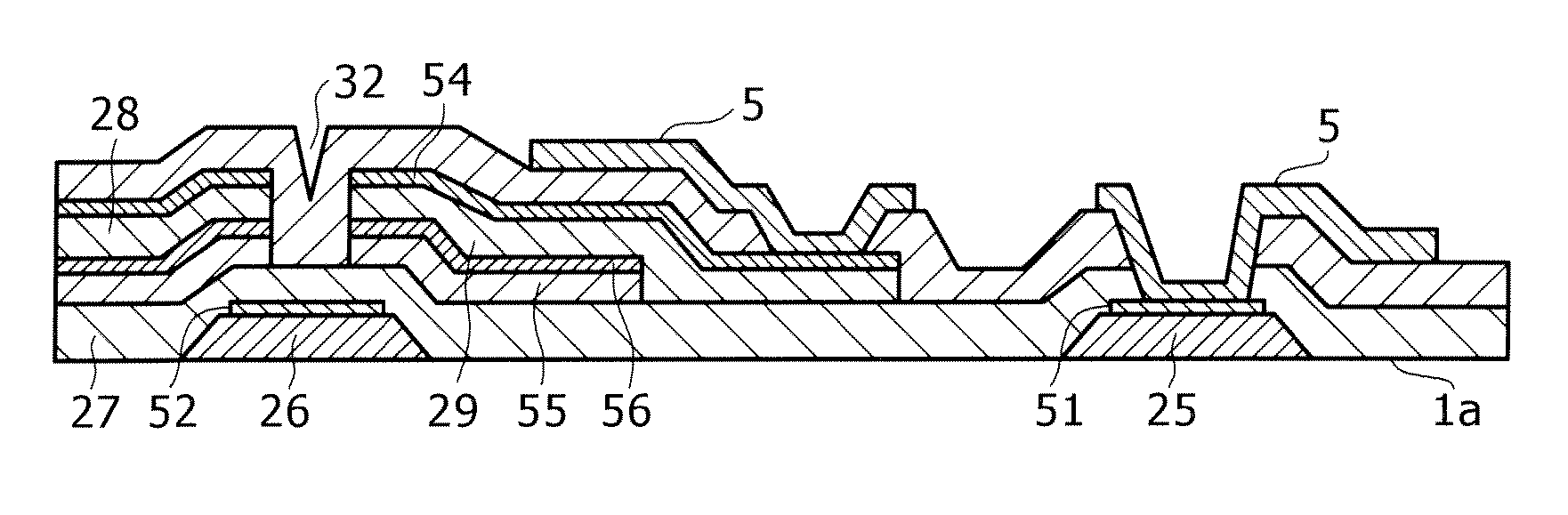
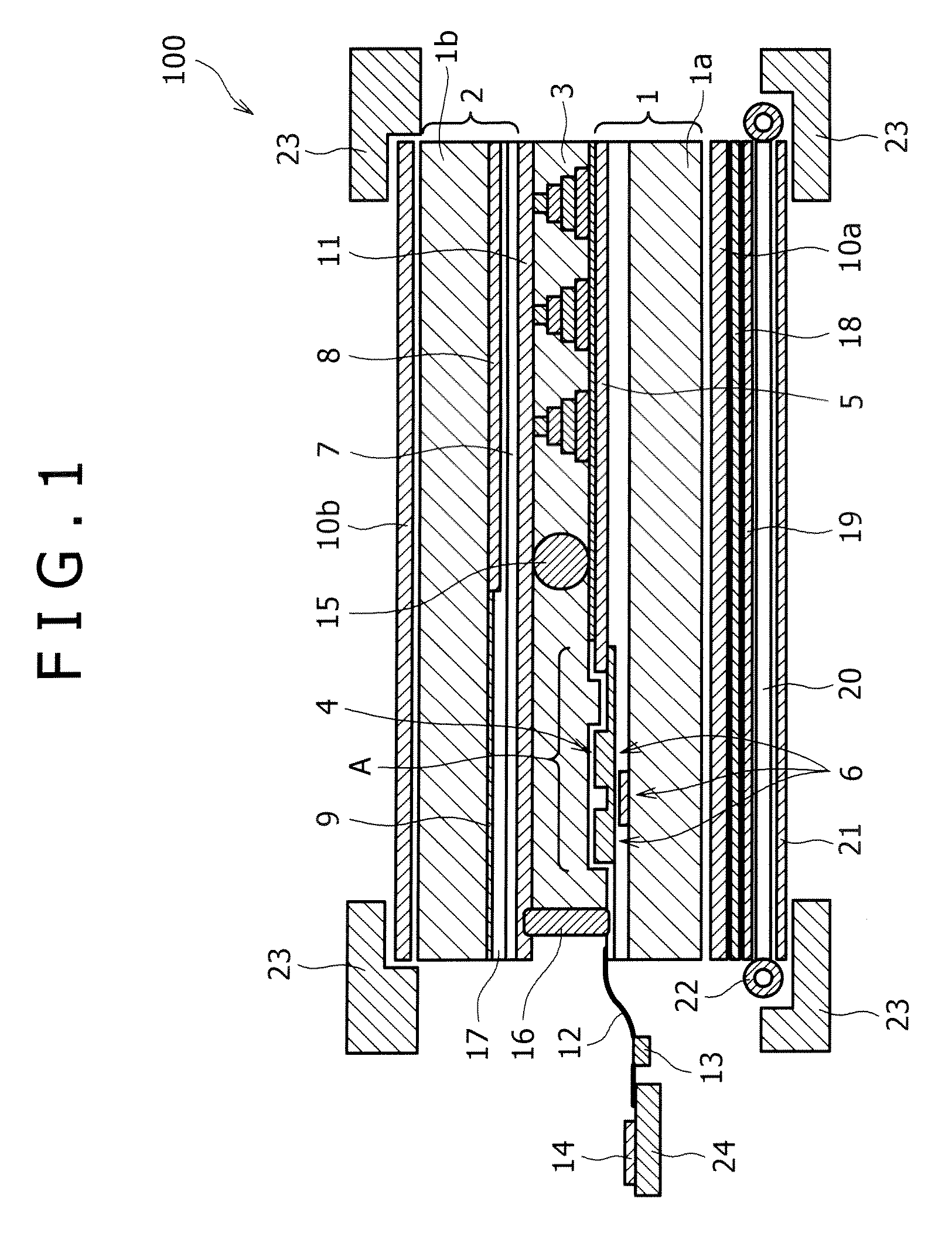
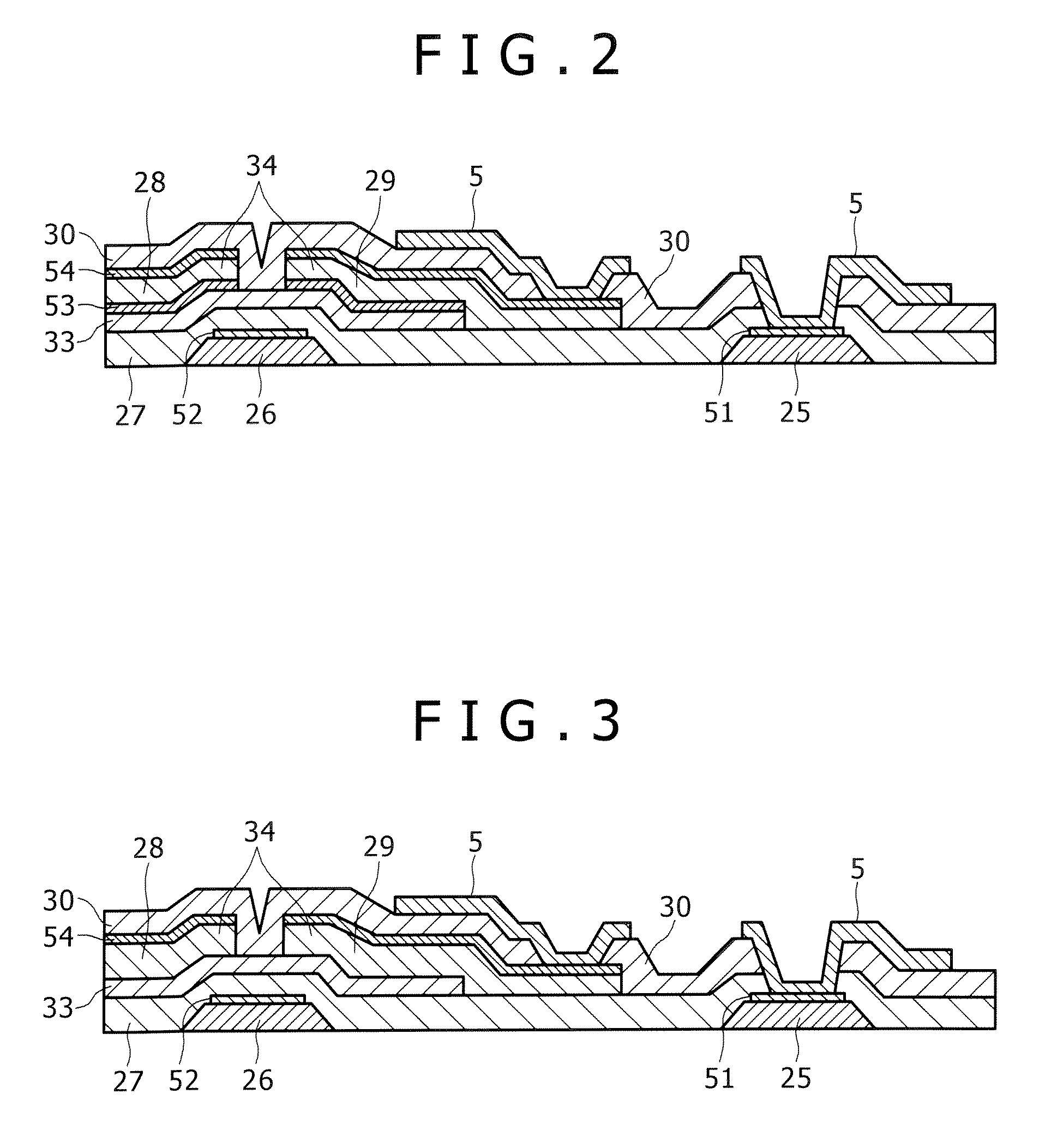
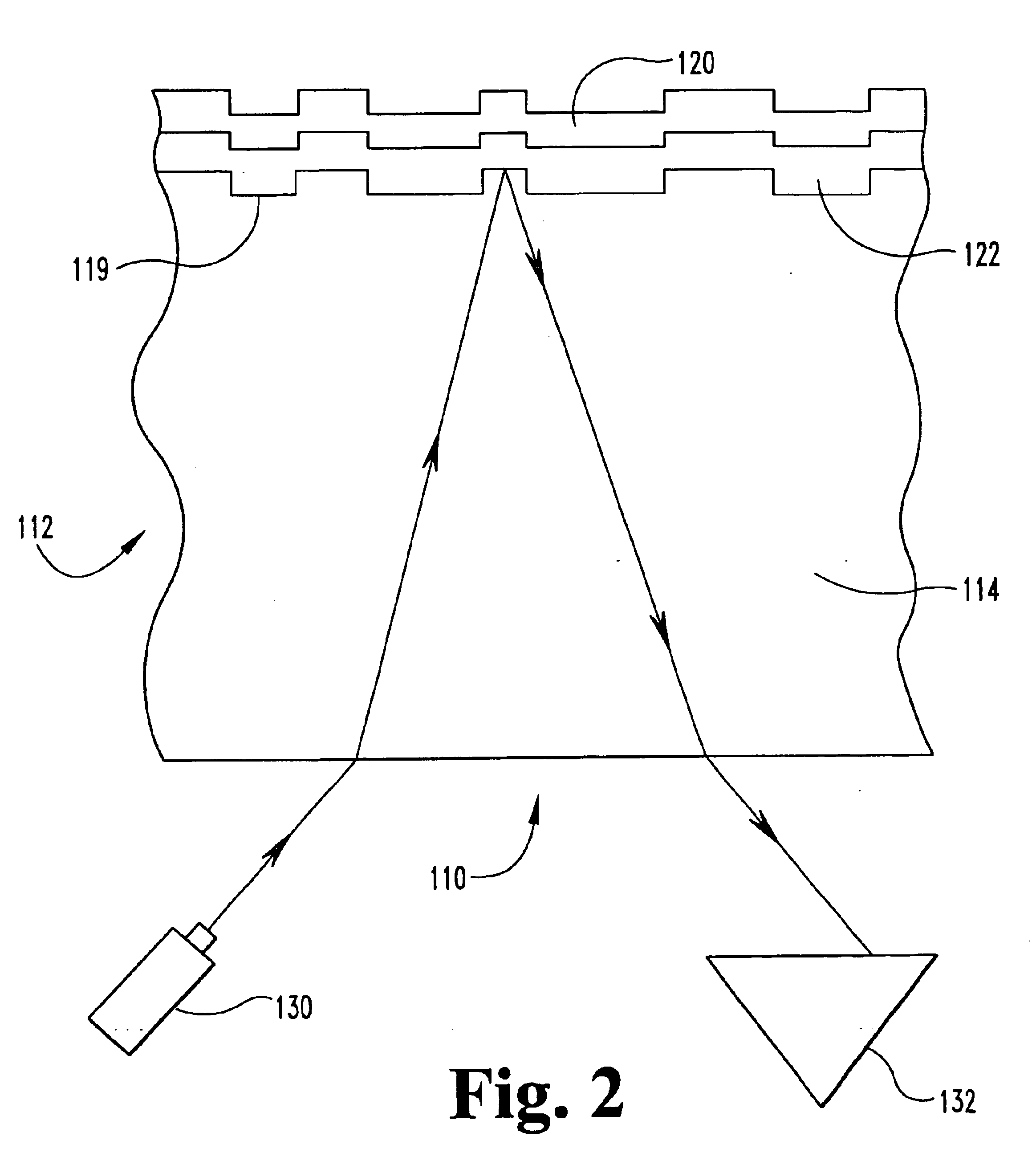
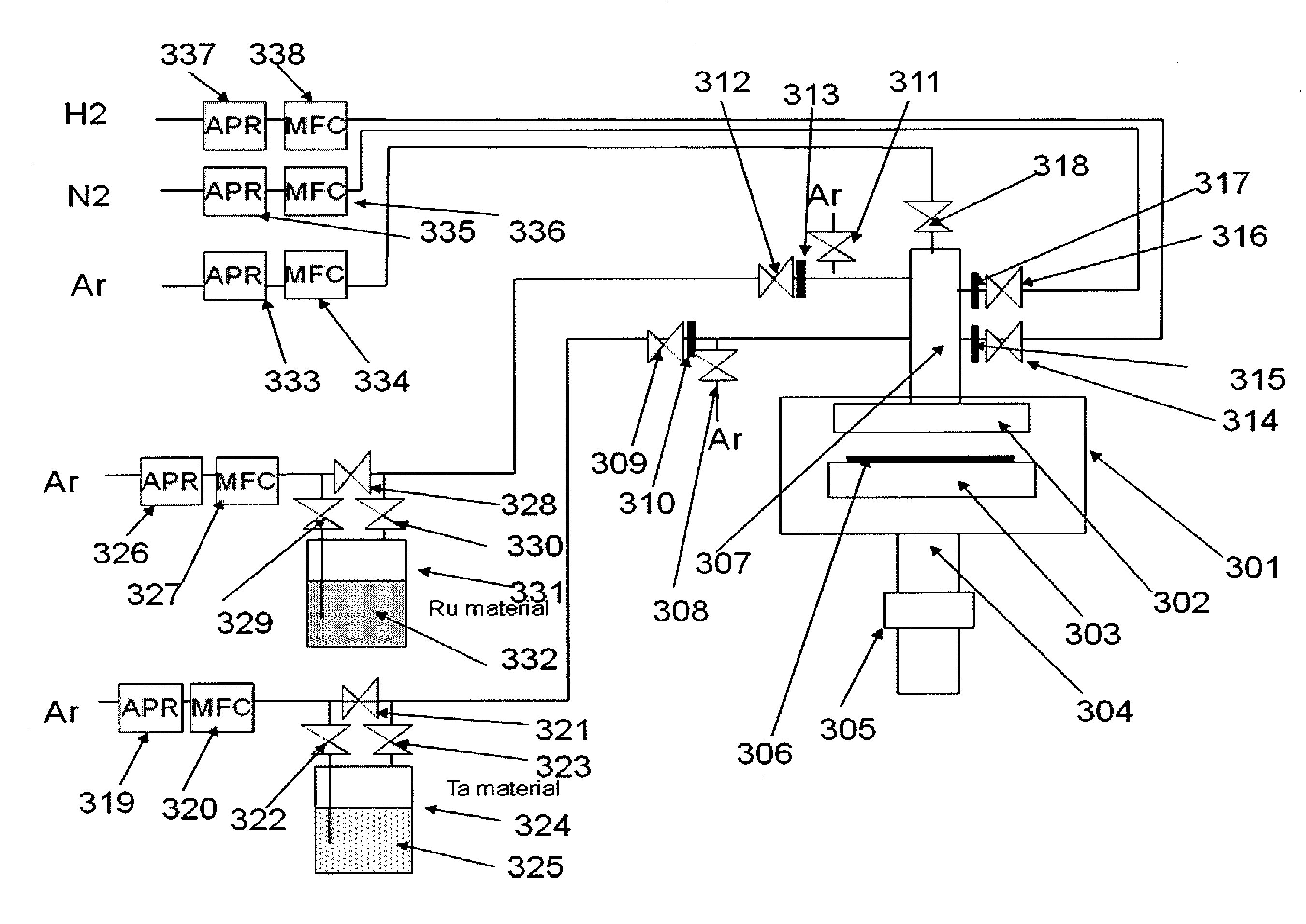
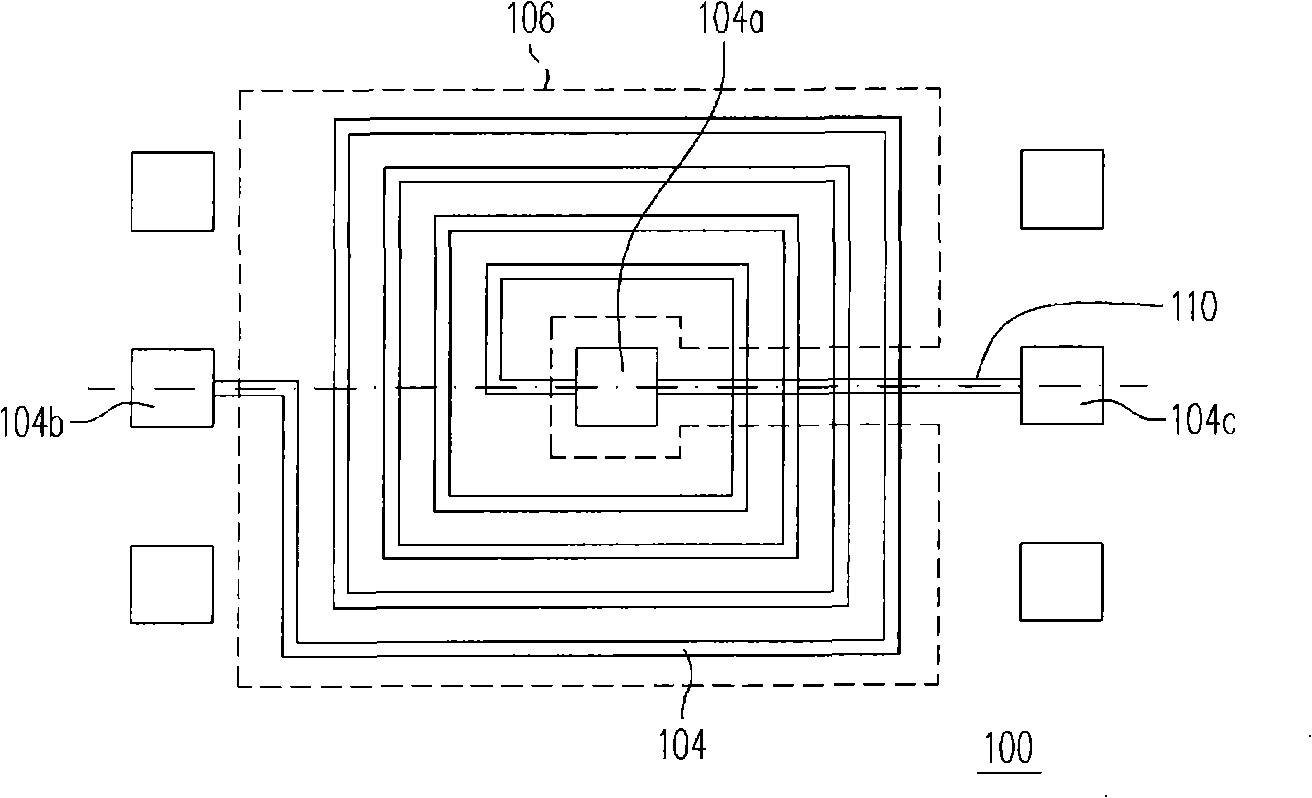
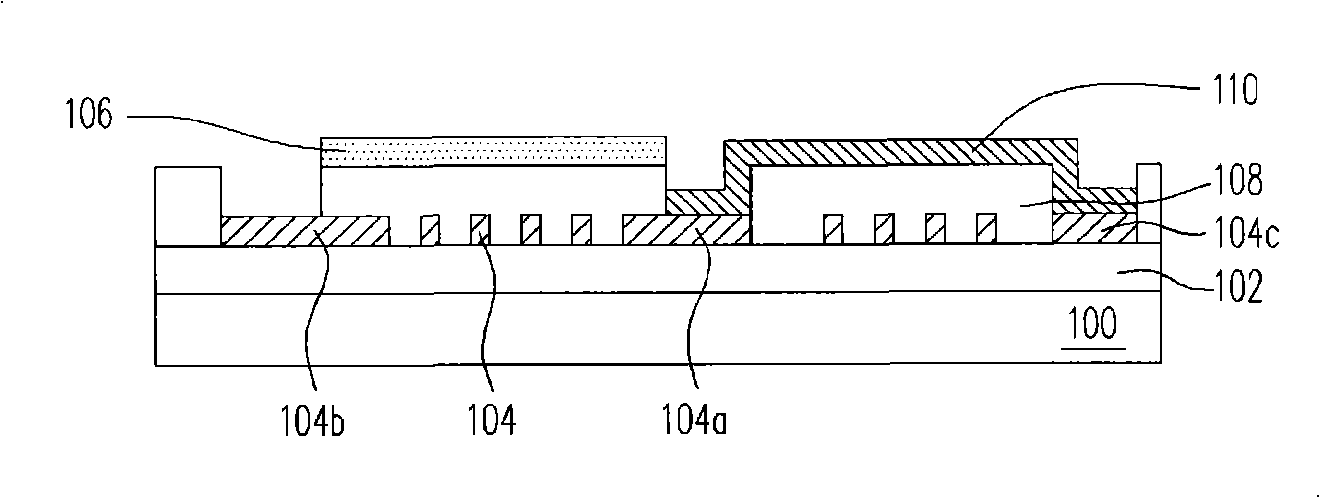
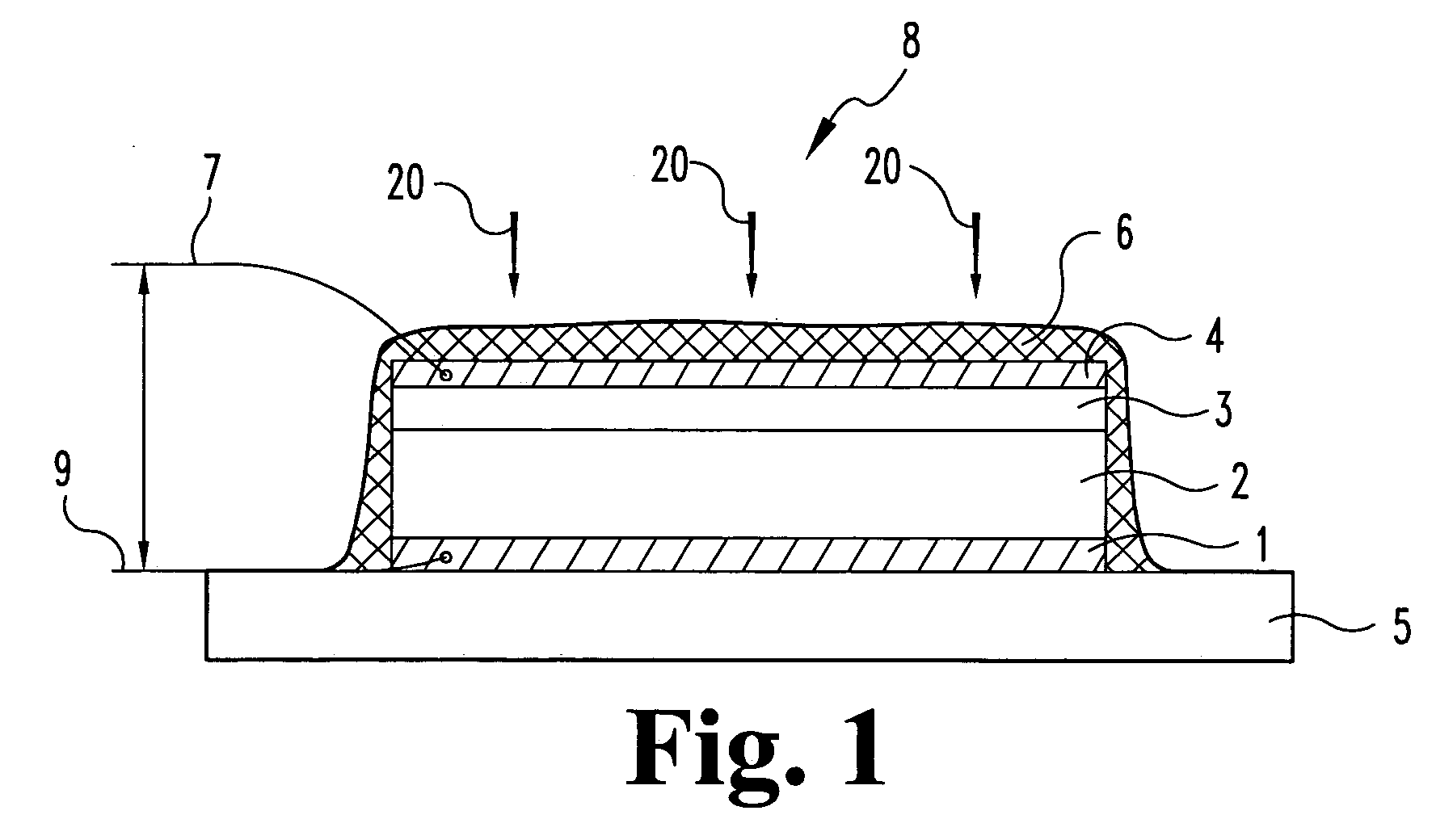
Atomic composition controlled ruthenium alloy film formed by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition
ActiveUS8084104B2Reduce resistanceLow densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSynthetic resin layered productsRutheniumAlloy
A metal film composed of multiple atomic layers continuously formed by atomic layer deposition of Ru and Ta or Ti includes at least a top section and a bottom section, wherein an atomic composition of Ru, Ta or Ti, and N varies in a thickness direction of the metal film. The atomic composition of Ru, Ta or Ti, and N in the top section is represented as Ru(x1)Ta / Ti(y1)N(z1) wherein an atomic ratio of Ru(x1) / (Ta / Ti(y1)) is no less than 15, and z1 is 0.05 or less. The atomic composition of Ru, Ta or Ti, and N in the bottom section is represented as Ru(x2)Ta / Ti(y2)N(z2) wherein an atomic ratio of Ru(x2) / (Ta / Ti(y2)) is more than zero but less than 15, and z2 is 0.10 or greater.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Metal alloys for the reflective or the semi-reflective layer of an optical storage medium
InactiveUS6544616B2Improve reflectivitySimilar sputtering characteristicMagnetic materials for record carriersVacuum evaporation coatingMetal alloyManganese
A silver-based alloy thin film is provided for the highly reflective or semi-reflective coating layer of optical discs. Alloy additions to silver include zinc, aluminum, zinc plus aluminum, manganese, germanium, and copper plus manganese. These alloys have moderate to high reflectivity and reasonable corrosion resistance in the ambient environment.
Owner:TARGET TECH
Metal alloys for the reflective or the semi-reflective layer of an optical storage medium
InactiveUS20020034603A1Improve reflectivitySimilar sputtering characteristicMagnetic materials for record carriersVacuum evaporation coatingManganeseHigh reflectivity
A silver-based alloy thin film is provided for the highly reflective or semi-reflective coating layer of optical discs. Alloy additions to silver include zinc, aluminum, zinc plus aluminum, manganese, germanium, and copper plus manganese. These alloys have moderate to high reflectivity and reasonable corrosion resistance in the ambient environment.
Owner:TARGET TECH
Fabrication of interleaved metallic and intermetallic composite laminate materials
InactiveUS7188559B1Well formedLimit cracking and fracturingWeapon componentsDomestic articlesGramComposite laminates
Typically 20–40 films of a tough first metal, normally 0.1–1.0 mm thick films of titanium, nickel, vanadium, and / or steel (iron) and alloys thereof, interleaved with a like number of films of a second metal, normally 0.1–1.0 mm thick films of aluminum or alloys thereof, are pressed together in a stack at less than 6 MPa and normally at various pressures 2–4 MPa while being gradually heated in the presence of atmospheric gases to 600–800° C. over a period of, typically, 10+ hours until the second metal is completely compounded; forming thus a metallic-intermetallic laminate composite material having (i) tough first-metal layers separated by (ii) hard, Vickers microhardness of 400 kg / mm2+, intermetallic regions consisting of an intermetallic compound of the first and the second metals. The resulting composite material is inexpensive, lightweight with a density of typically 3 to 4.5 grams / cubic centimeter, and very hard and very tough to serve as, among other applications, lightweight armor. Upon projectile impact (i) the hard intermetallic, ceramic-like, layers are confined by the tough metal layers while (ii) cracking and fracturing is blunted and channeled in directions orthogonal to the axis of impact.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Copper alloy thin films, copper alloy sputtering targets and flat panel displays
InactiveUS20060091792A1Low resistivityInhibition formationDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesAlloy thin filmFlat panel display
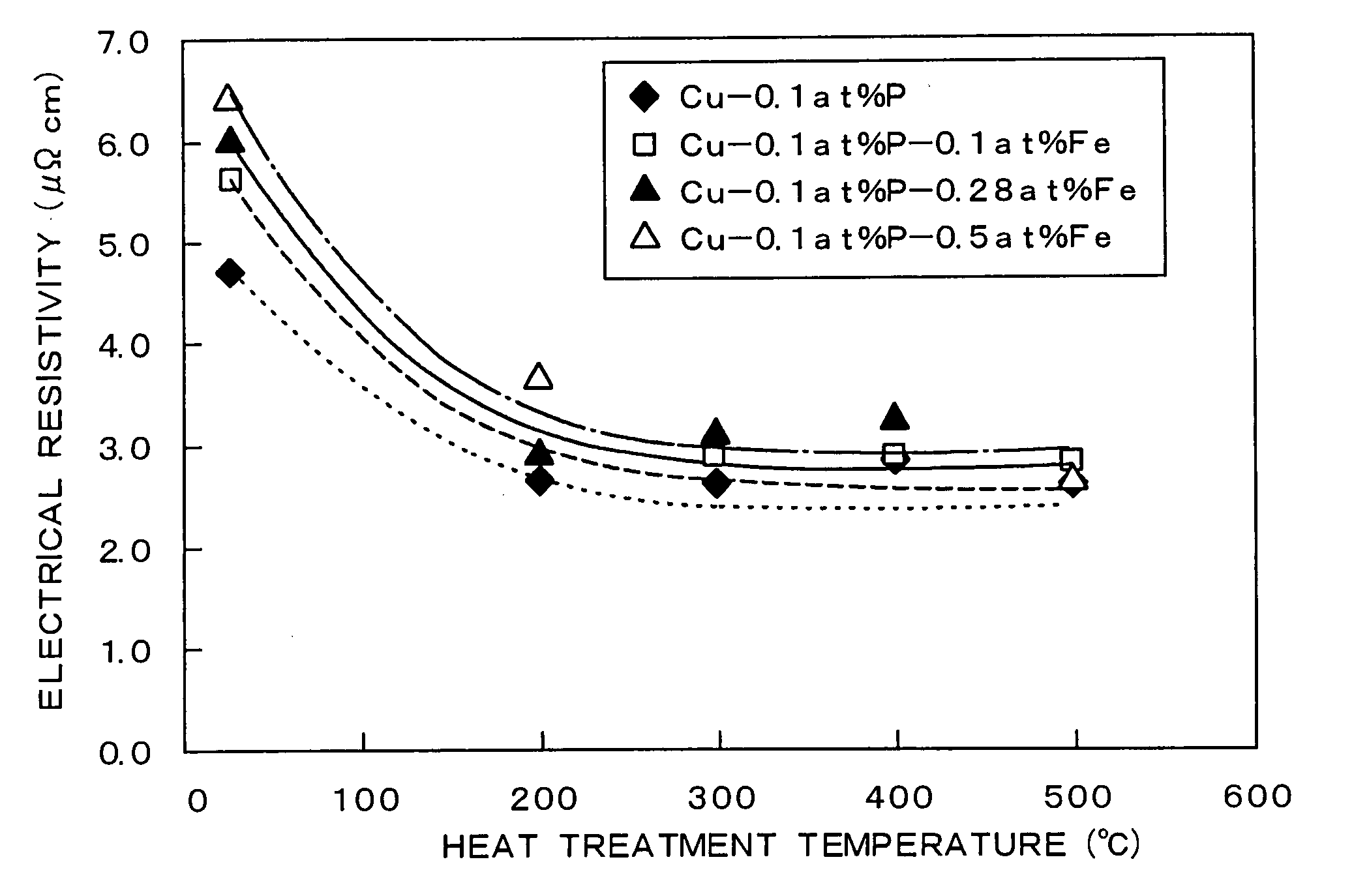
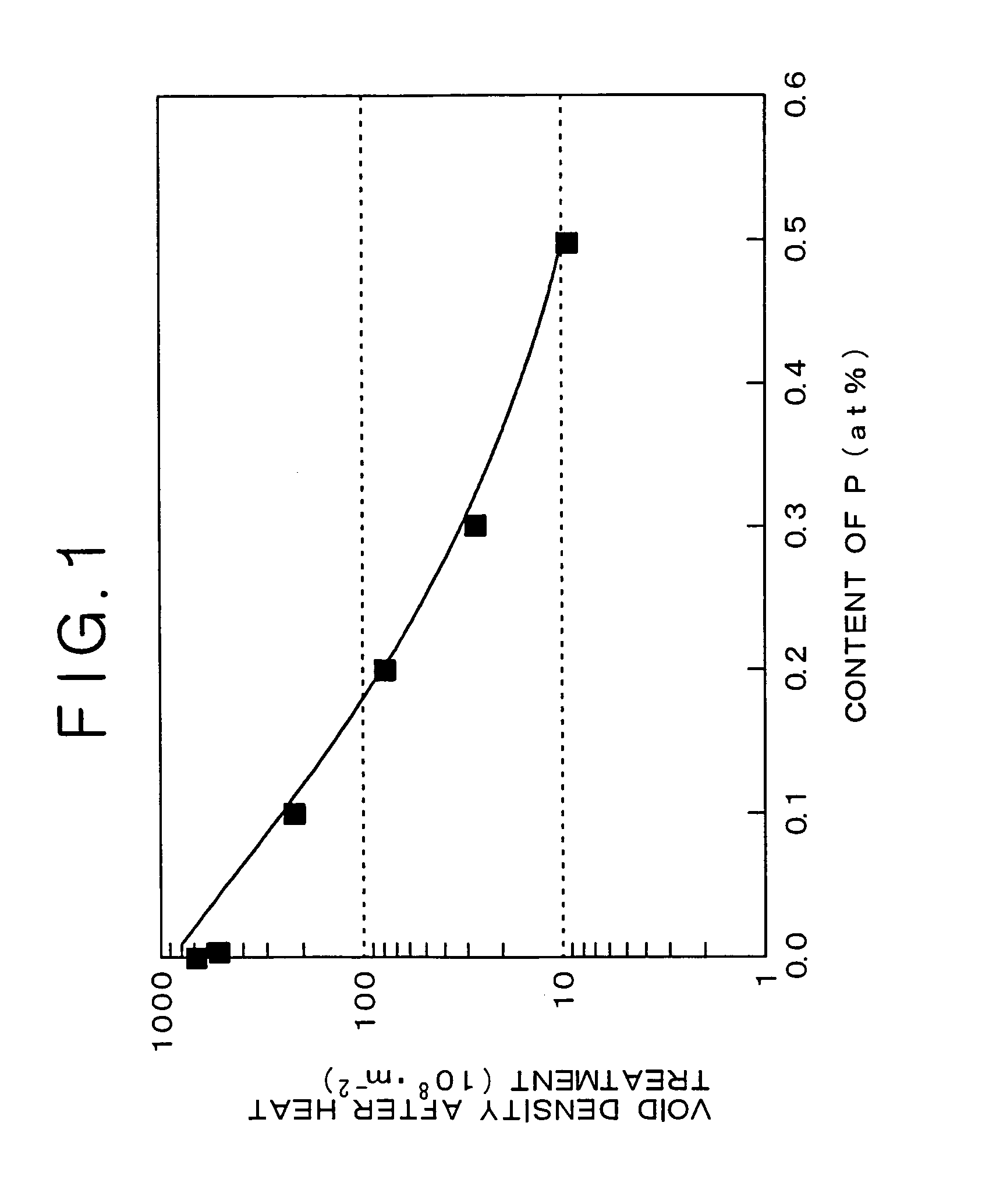
A Cu alloy thin film contains Fe and P with the balance being substantially Cu, in which the contents of Fe and P satisfy all the following conditions (1) to (3), and in which Fe2P is precipitated at grain boundaries of Cu after heat treatment at 200° C. to 500° C. for 1 to 120 minutes: 1.4NFe+8NP<1.3 (1)NFe+48NP>1.0 (2)12NFe+NP>0.5 (3)wherein NFe represents the content of Fe (atomic percent); and NP represents the content of P (atomic percent).
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Metal alloys for the reflective or the semi-reflective layer of an optical storage medium
InactiveUS6764735B2Improve reflectivitySimilar sputtering characteristicPhotomechanical apparatusRecord information storageIridiumHigh reflectivity
Owner:TARGET TECH
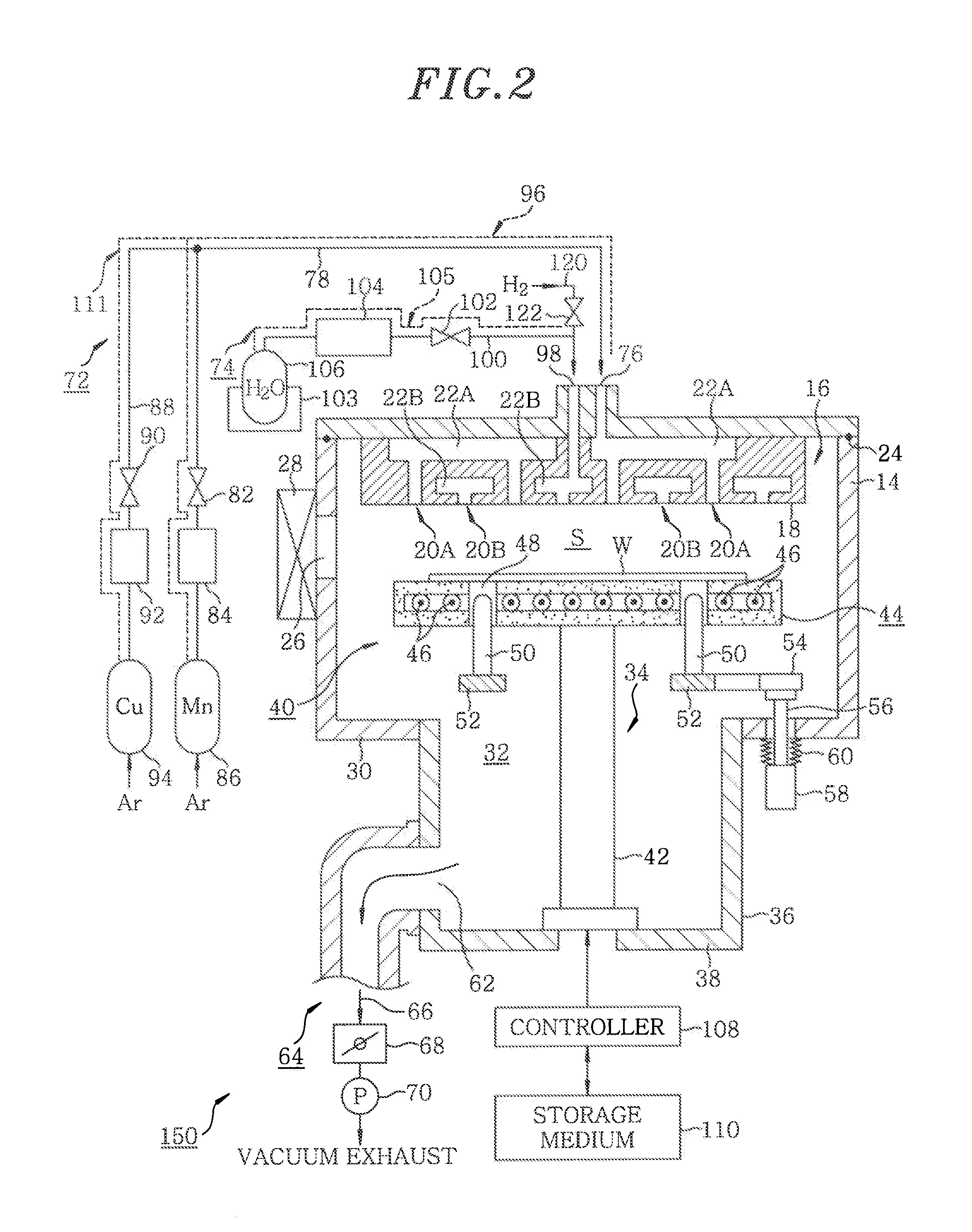
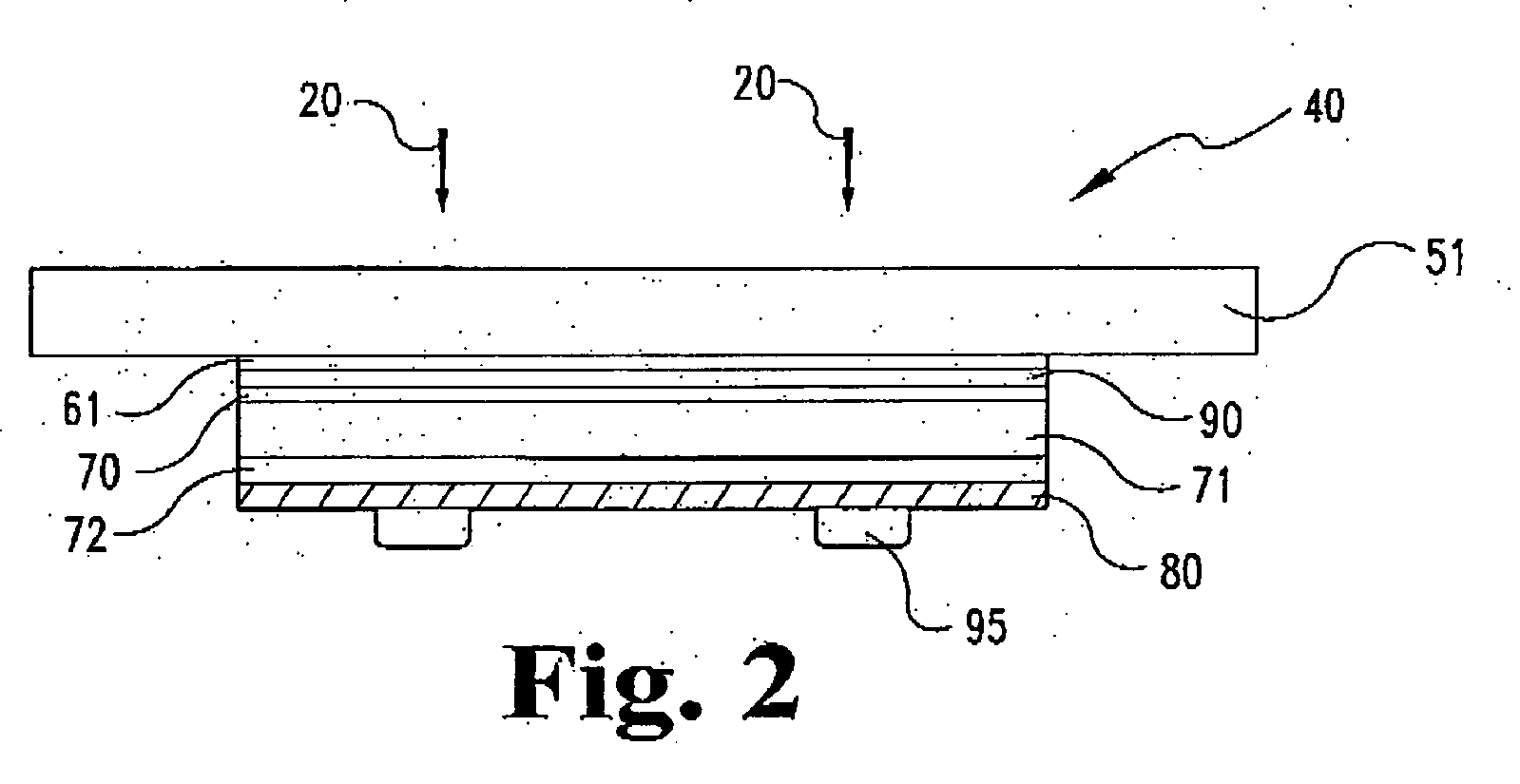
Film forming method and film forming apparatus
InactiveUS20100140802A1Increase coverageReduce installation costsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWater vaporAlloy thin film
On a surface of an object to be treated, a Mn-containing thin film or CuMn-containing alloy thin film is formed by heat treatment (CVD or ALD) by using a Mn-containing source gas (or Mn-containing source gas and a Cu-containing gas) and an oxygen-containing gas (for instance, water vapor) as a processing gas. The Mn-containing thin film or the CuMn-containing alloy thin film can be formed with high step coverage in a fine recess formed on the surface of the object to be treated.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD +1
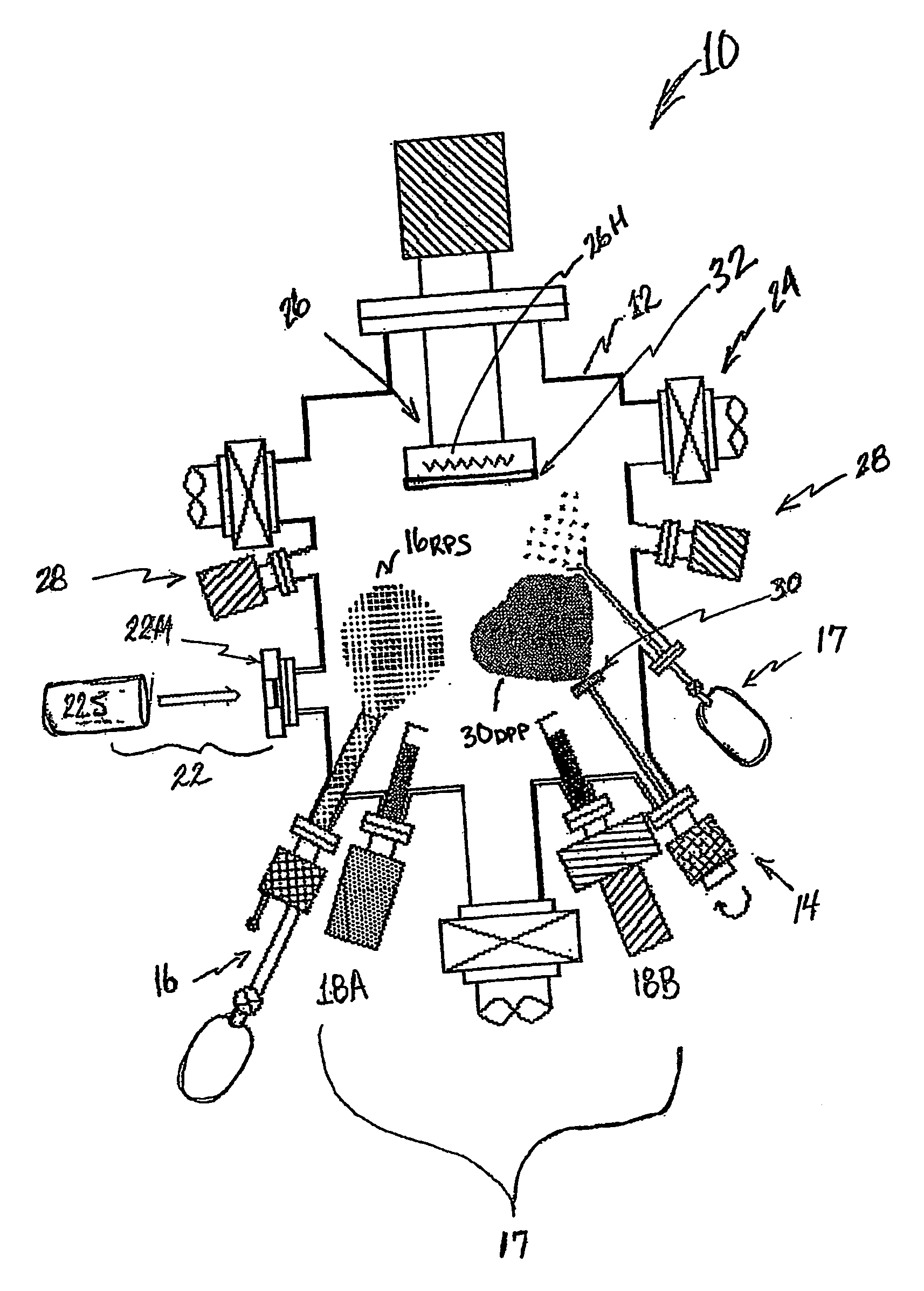
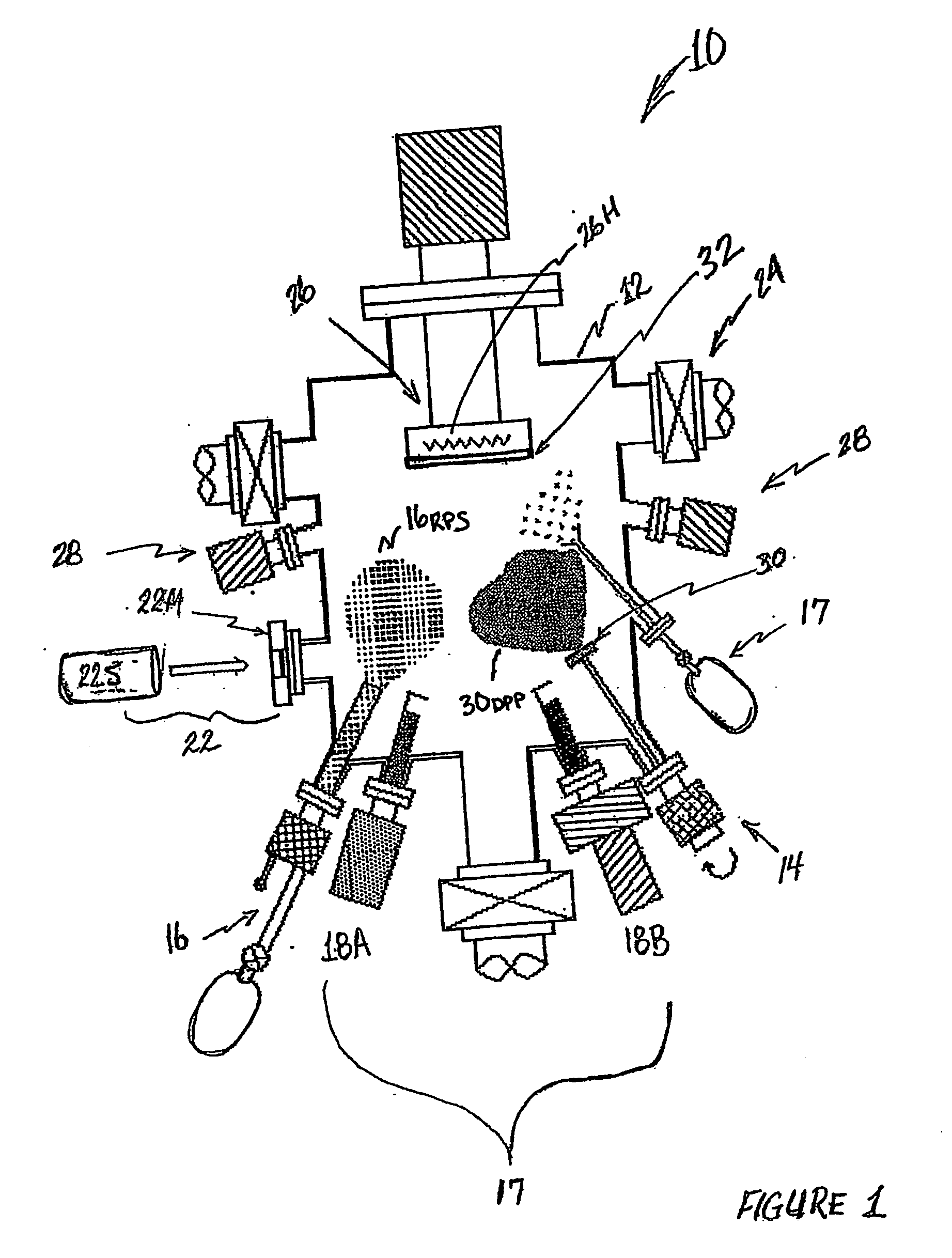
Hybrid beam deposition system and methods for fabricating metal oxide-zno films, p-type zno films, and zno-based II-VI compound semiconductor devices
InactiveUS20060233969A1Increase flux densityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSource materialAlloy thin film
A hybrid beam deposition (HBD) system and methods according to the present invention utilizes a unique combination of pulsed laser deposition (PLD) technique and equipment with equipment and techniques that provide a radical oxygen rf-plasma stream to effectively increase the flux density of available reactive oxygen at a deposition substrate for the effective synthesis of metal oxide thin films. The HBD system and methods of the present invention further integrate molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) and / or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) techniques and equipment in combination with the PLD equipment and technique and the radical oxygen rf-plasma stream to provide elemental source materials for the synthesis of undoped and / or doped metal oxide thin films as well as synthesis of undoped and / or doped metal-based oxide alloy thin films.
Owner:MOXTRONICS
All-solid-state reflection-controllable electrochromic device and optical switchable component using it
InactiveUS7545551B2High light transmittanceShort of areaNon-linear opticsAll solid stateAlloy thin film
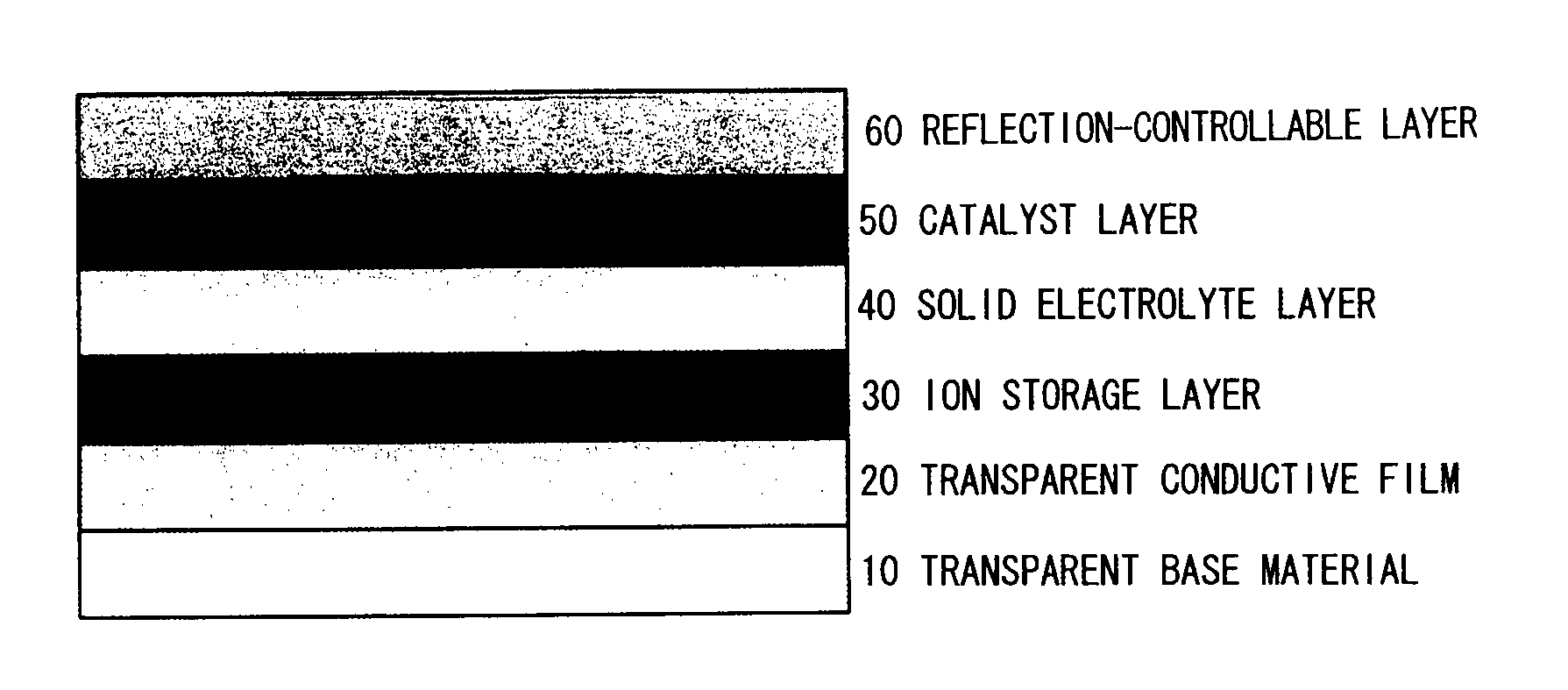
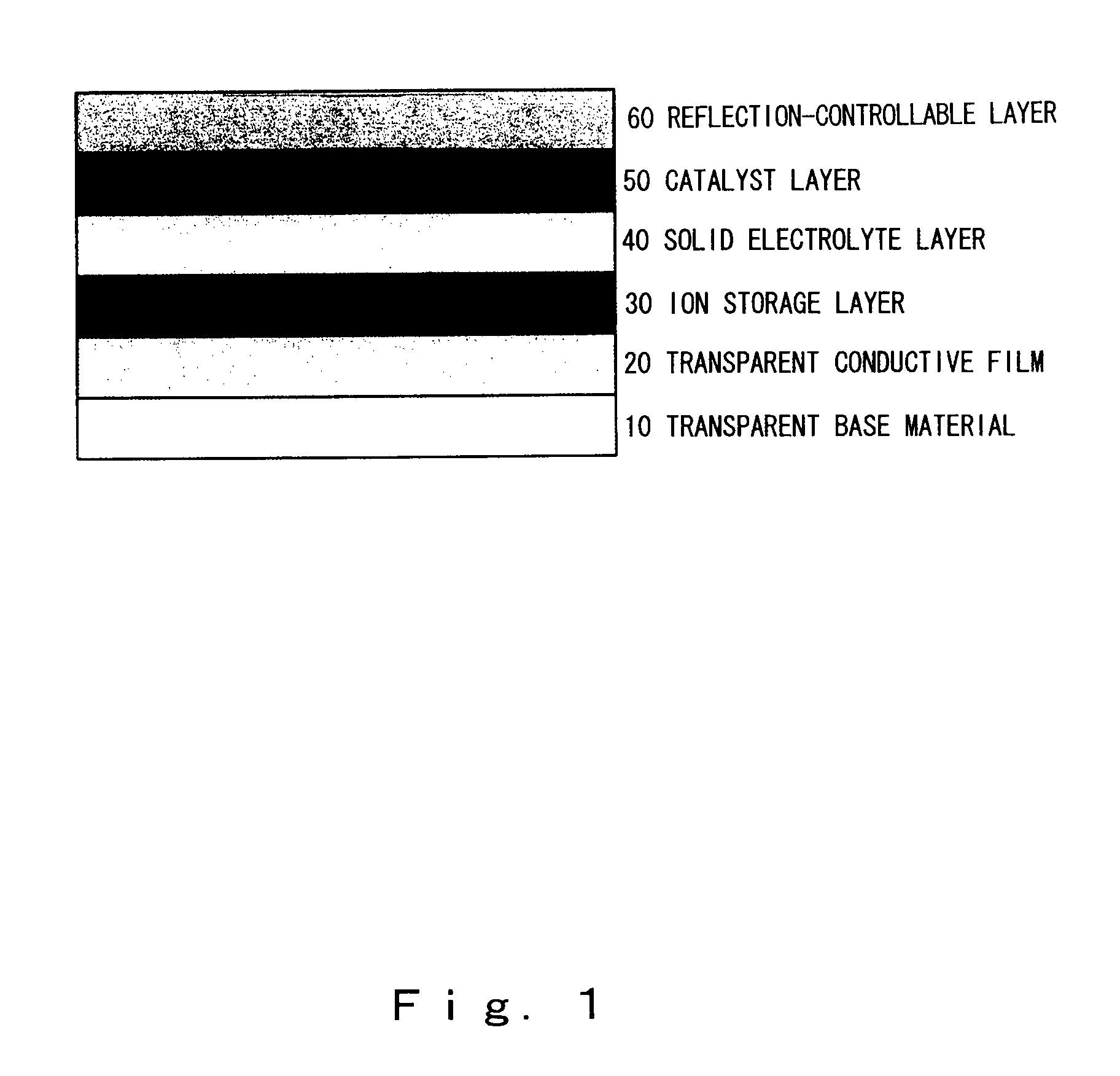
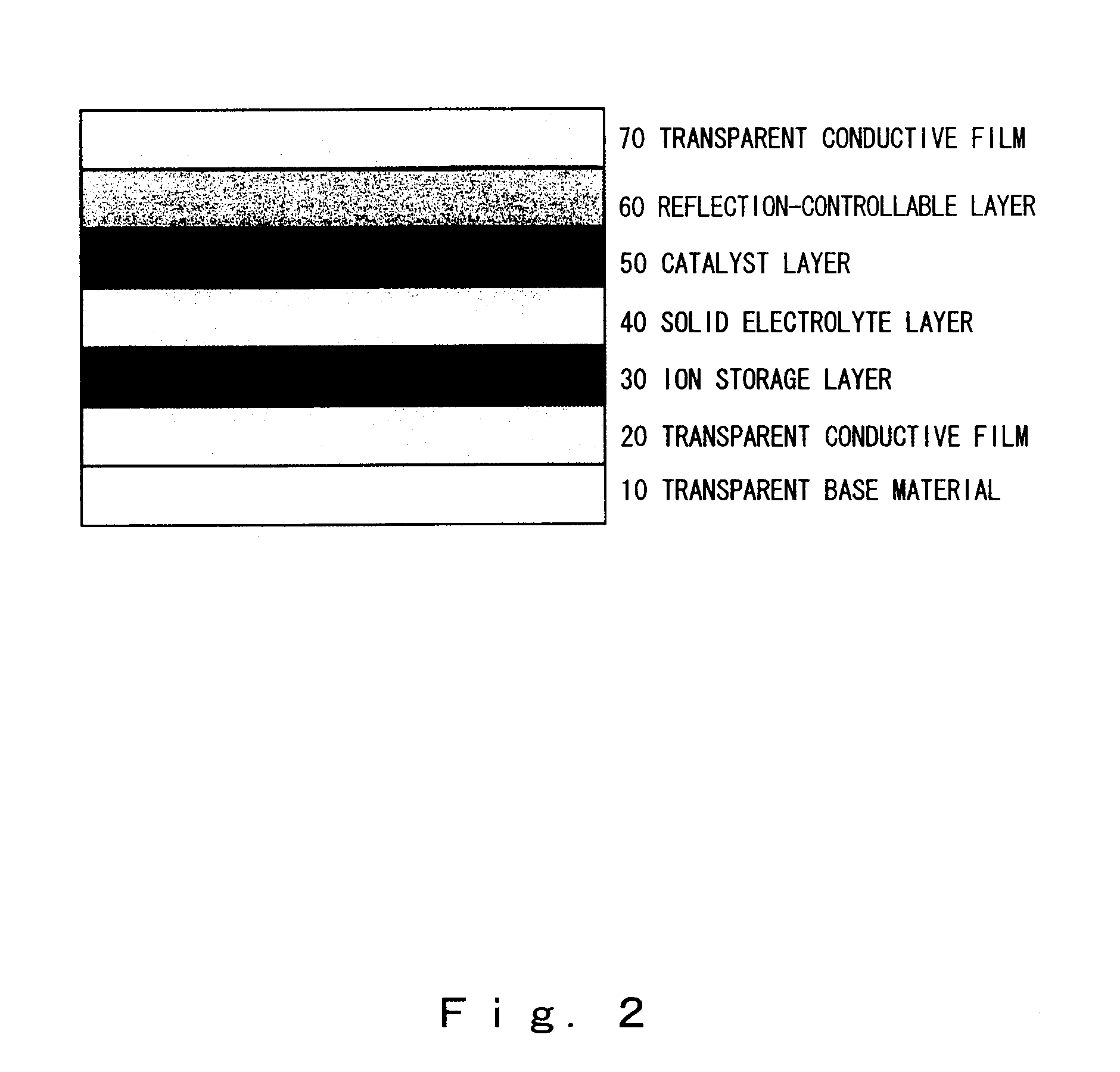
The present invention provides an all-solid-state reflection-controllable electrochromic device and a reflection-controllable member using that device, and the present invention relates to the all-solid-state reflection-controllable electrochromic device, which is a reflection-controllable device in which a multilayer thin film is formed on a transparent base material, wherein, at least a transparent conductive film layer, an ion storage layer, a solid electrolyte layer, a catalyst layer and a reflection-controllable layer using a magnesium-nickel based alloy thin film are formed on the base material; and, a reflection-controllable member incorporating this reflection-controllable electrochromic device, and it is possible to provide a reflection-controllable electrochromic device, having a novel multilayer structure with high transmissivity when transparent and capable of switching in a short period of time over a large surface area, and a reflection-controllable member incorporating this device.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Metal alloys for the reflective or the semi-reflective layer of an optical storage medium
InactiveUS6852384B2Improve reflectivitySimilar sputtering characteristicPhotomechanical apparatusRecord information storageIndiumCadmium Cation
A silver-based alloy thin film is provided for the highly reflective or semi-reflective layer of optical discs. Alloy additions to silver include gold, rhodium, ruthenium, osmium, platinum, palladium, copper, silicon, cadmium, tin, lithium, nickel, cobalt, indium, chromium, antimony, gallium, boron, molybdenum, zirconium, beryllium, titanium, and zinc. These alloys have moderate to high reflectivity and reasonable corrosion resistance in the ambient environment.
Owner:TARGET TECH
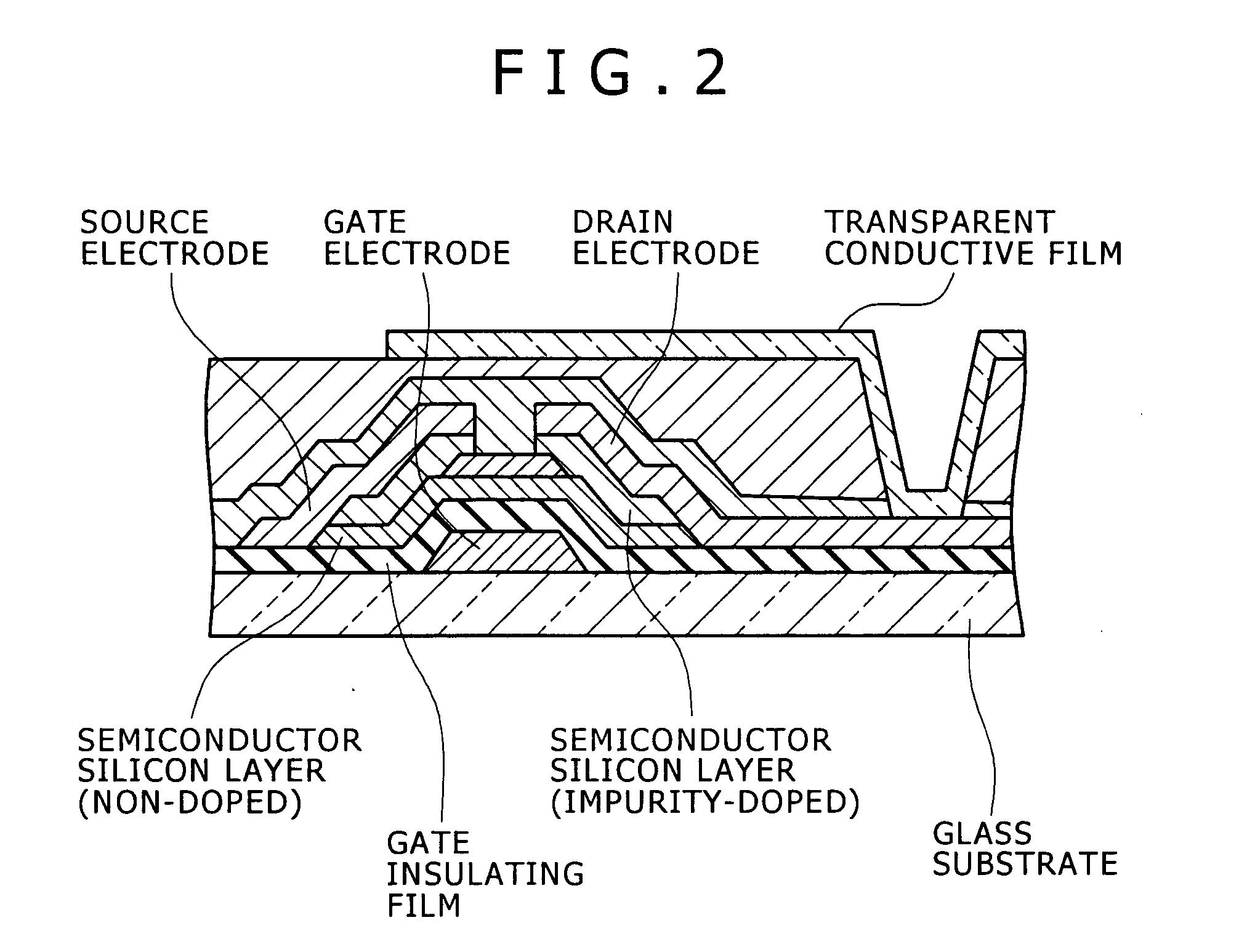
Thin film transistor substrate and display device
InactiveUS20070278497A1Reduce adverse effectsDesired switching performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceAlloy thin film
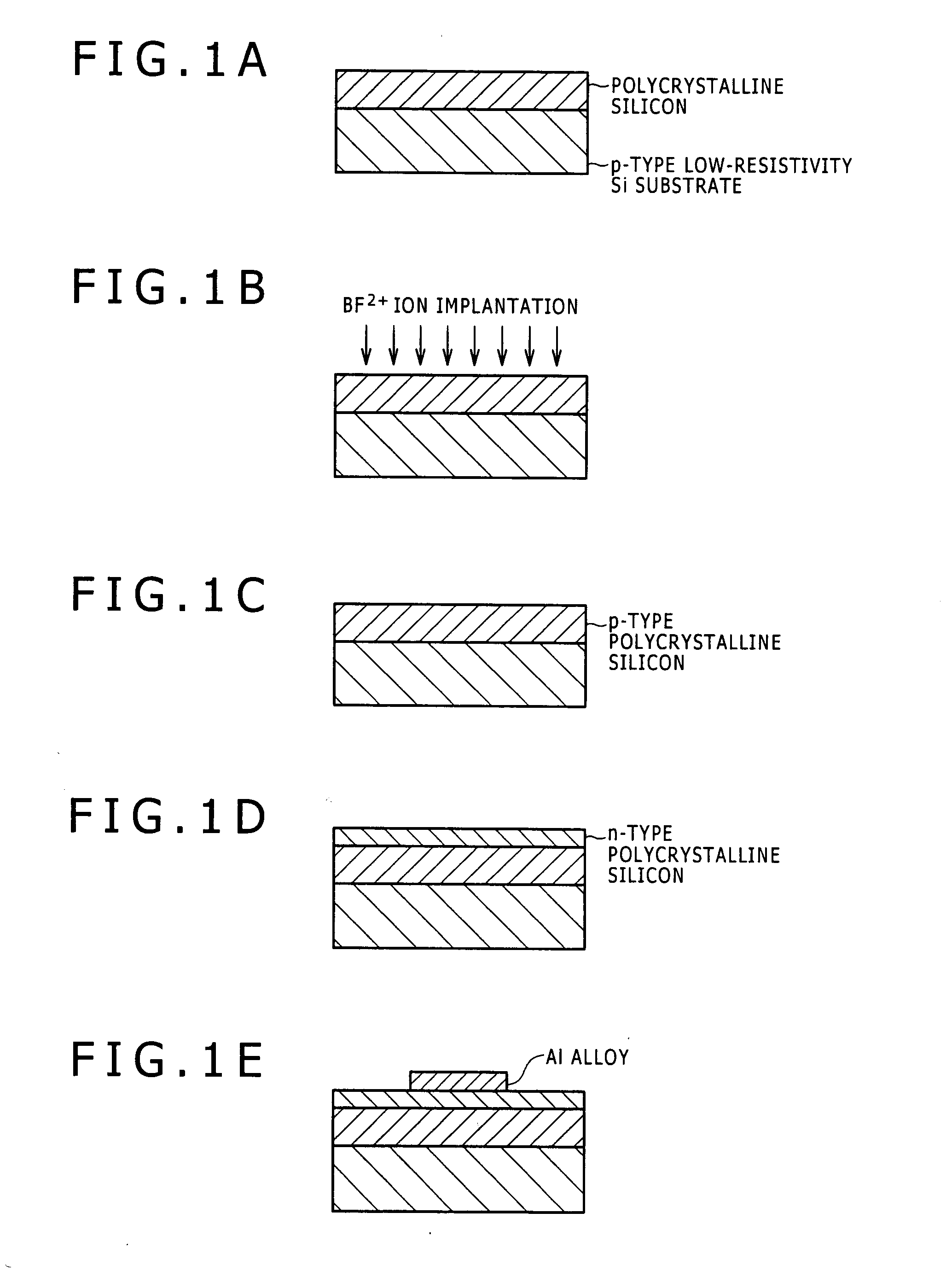
Disclosed are a thin film transistor substrate where barrier metal can be omitted to be formed between a semiconductor layer of a thin film transistor and source and drain electrodes (barrier metal need not be formed between the semiconductor layer of the thin film transistor and the source and drain electrodes), and a display device. (1) A thin film transistor substrate has a semiconductor layer of a thin film transistor, a source electrode, a drain electrode, and a transparent conductive film, wherein the substrate has a structure in which the source and drain electrodes are directly connected to the semiconductor layer of the thin film transistor, and the source and drain electrodes include an Al alloy thin film containing Ni of 0.1 to 6.0 atomic percent, La of 0.1 to 1.0 atomic percent, and Si of 0.1 to 1.5 atomic percent. (2) A display device has the thin film transistor substrate.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Electrode of aluminum-alloy film with low contact resistance, method for production thereof, and display unit
InactiveUS20090001373A1Minimizes number of pixel errorReduce contact resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface roughnessContact resistance
Disclosed herein are an electrode of aluminum alloy film, a method for production thereof, and a display unit provided therewith, said electrode exhibiting a low electric resistance when in contact with a transparent oxide conductive film even though the aluminum alloy contains a less amount of alloying element than usual. The electrode of low contact resistance type is an aluminum alloy film in direct contact with a transparent oxide electrode, wherein said aluminum alloy film contains 0.1-1.0 atom % of metal nobler than aluminum and is in direct contact with a transparent oxide electrode through a surface having surface roughness no smaller than 5 nm in terms of maximum height Rz.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Source/drain electrodes, transistor substrates and manufacture methods, thereof, and display devices
InactiveUS20070040173A1Simple manufacturing processLow resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceAlloy thin film
In a thin-film transistor substrate including a substrate, a thin-film transistor semiconductor layer, a source / drain electrode, and a transparent pixel electrode, the source / drain electrode includes a thin film of an aluminum alloy containing 0.1 to 6 atomic percent of nickel as an alloy element, and the aluminum alloy thin film is directly connected to the thin-film transistor semiconductor layer.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Metal alloys for the reflective or the semi-reflective layer of an optical storage medium
InactiveUS7018696B2Sufficient chemicalSufficient thermalLayered productsVacuum evaporation coatingManganeseHigh reflectivity
A silver-based alloy thin film is provided for the highly reflective or semi-reflective coating layer of optical discs. Elements that can be added to silver to produce useful silver alloys include zinc, aluminum, copper, manganese, germanium, yttrium, bismuth, scandium, and cobalt. These alloys have moderate to high reflectivity and reasonable corrosion resistance in the ambient environment.
Owner:TARGET TECH
Metal alloys for the reflective or the semi-reflective layer of an optical storage medium
InactiveUS6841219B2Improve reflectivitySimilar sputtering characteristicLayered productsPhotomechanical apparatusIndiumCobalt
A silver-based alloy thin film is provided for the highly reflective or semi-reflective layer of optical discs. Alloy additions to silver include gold, rhodium, ruthenium, osmium, platinum, palladium, copper, silicon, cadmium, tin, lithium, nickel, cobalt, indium, chromium, antimony, gallium, boron, molybdenum, zirconium, beryllium, titanium, magnesium, and zinc. These alloys have moderate to high reflective and reasonable corrosion resistance in the ambient environment.
Owner:TARGET TECH
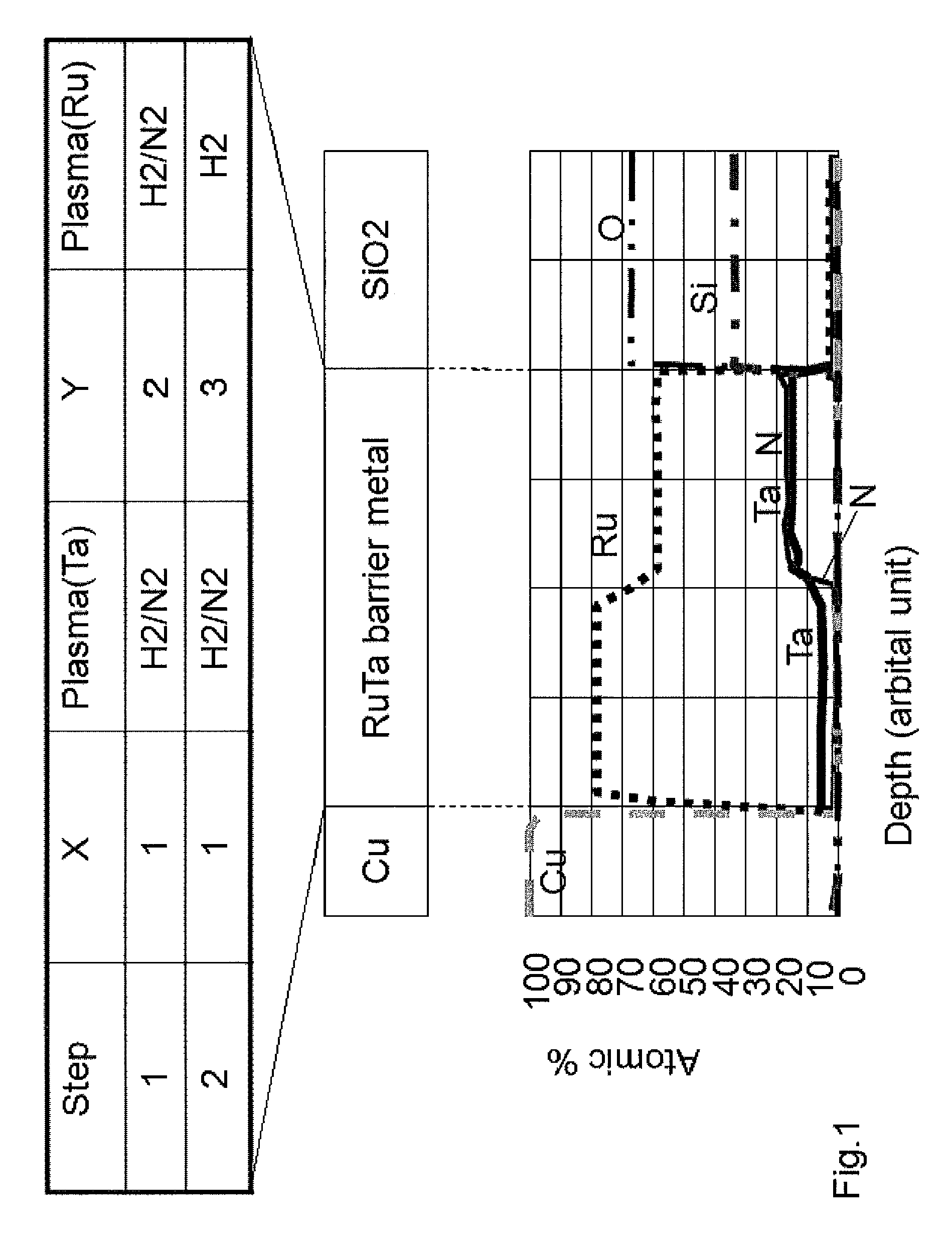
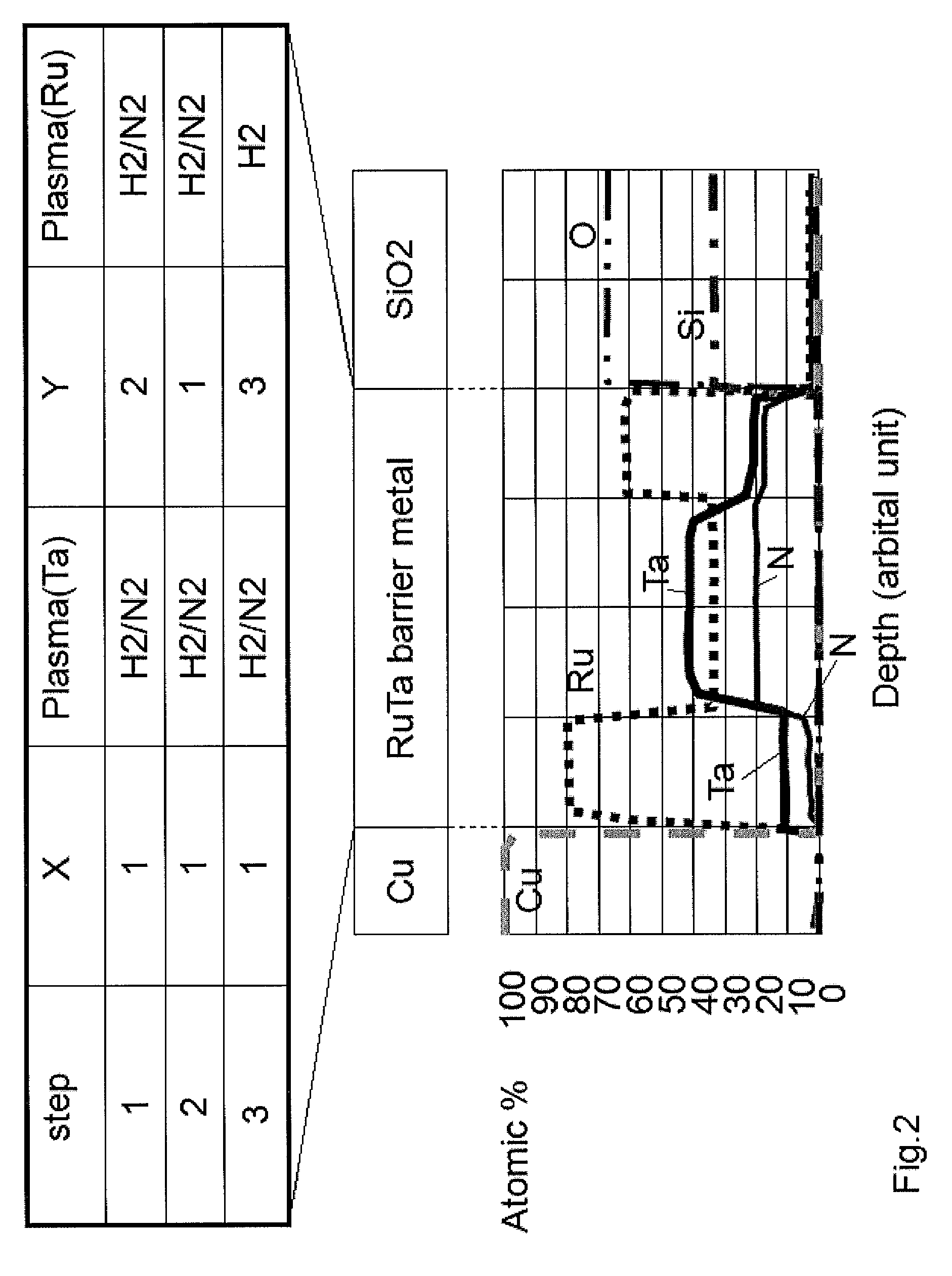
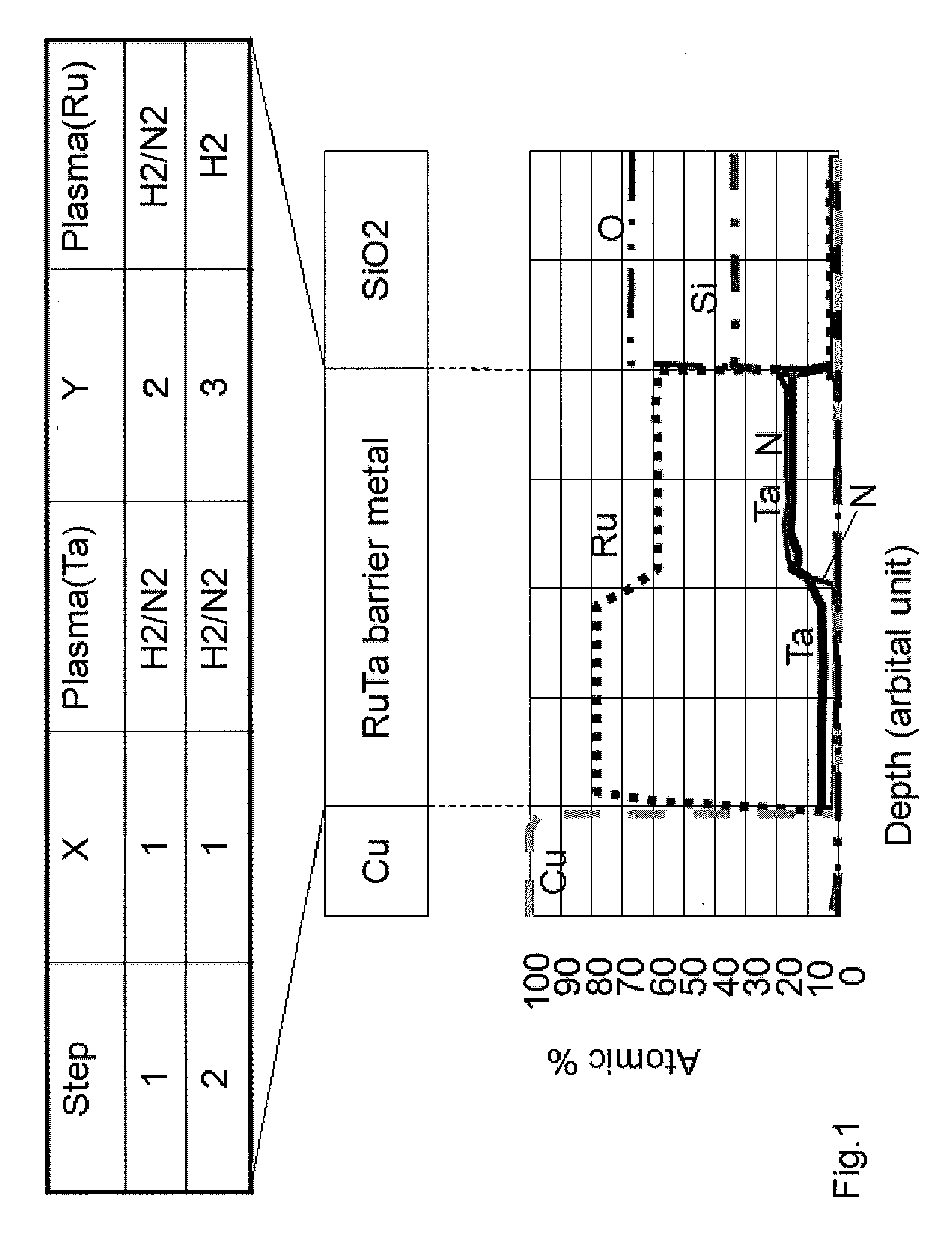
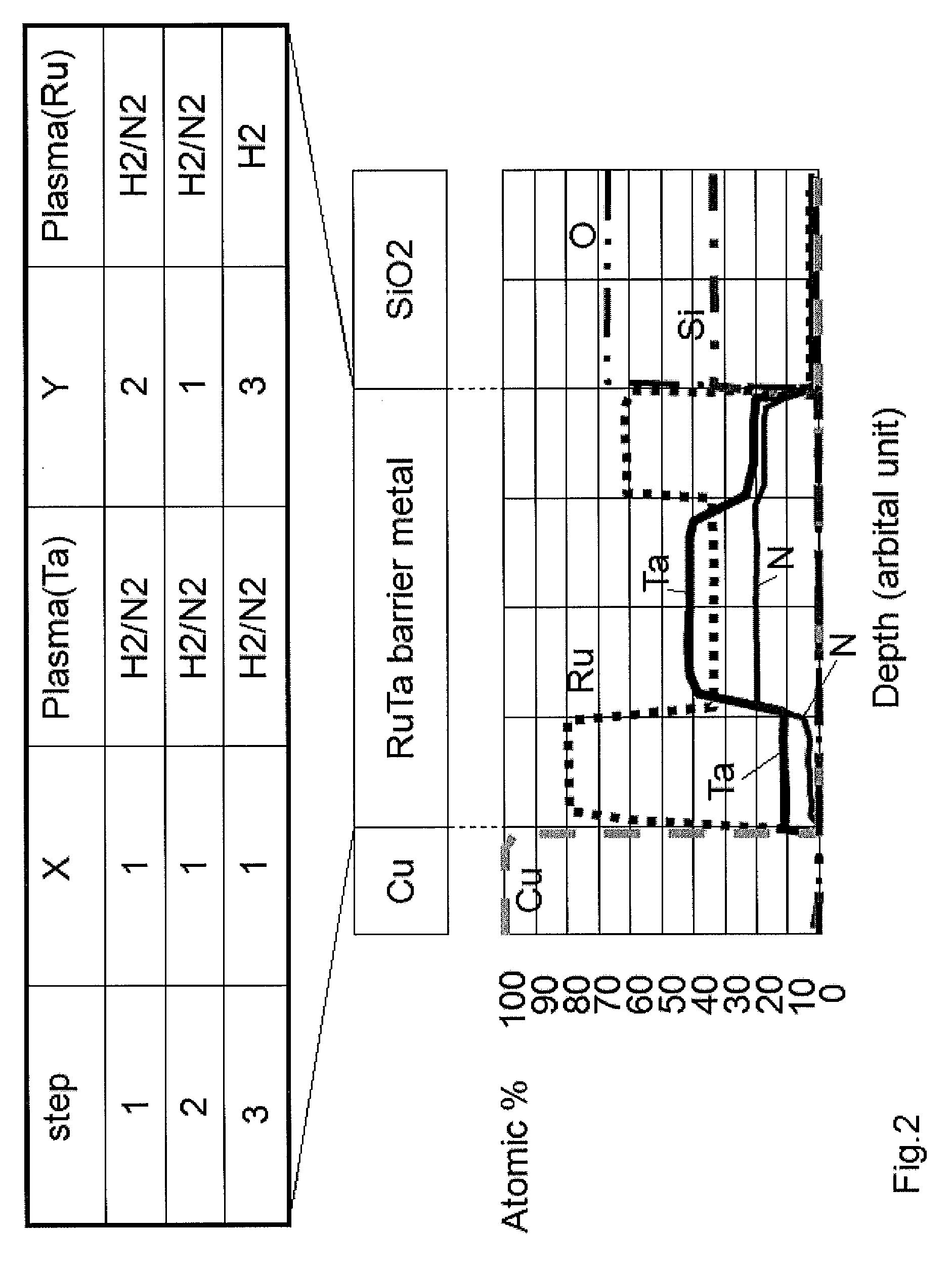
Atomic composition controlled ruthenium alloy film formed by plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition
ActiveUS20100055433A1Increase flow rate ratioLow densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSynthetic resin layered productsAtomic compositionAtomic ratio
A metal film composed of multiple atomic layers continuously formed by atomic layer deposition of Ru and Ta or Ti includes at least a top section and a bottom section, wherein an atomic composition of Ru, Ta or Ti, and N varies in a thickness direction of the metal film. The atomic composition of Ru, Ta or Ti, and N in the top section is represented as Ru(x1)Ta / Ti(y1)N(z1) wherein an atomic ratio of Ru(x1) / (Ta / Ti(y1)) is no less than 15, and z1 is 0.05 or less. The atomic composition of Ru, Ta or Ti, and N in the bottom section is represented as Ru(x2)Ta / Ti(y2)N(z2) wherein an atomic ratio of Ru(x2) / (Ta / Ti(y2)) is more than zero but less than 15, and z2 is 0.10 or greater.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Magnetic recording medium
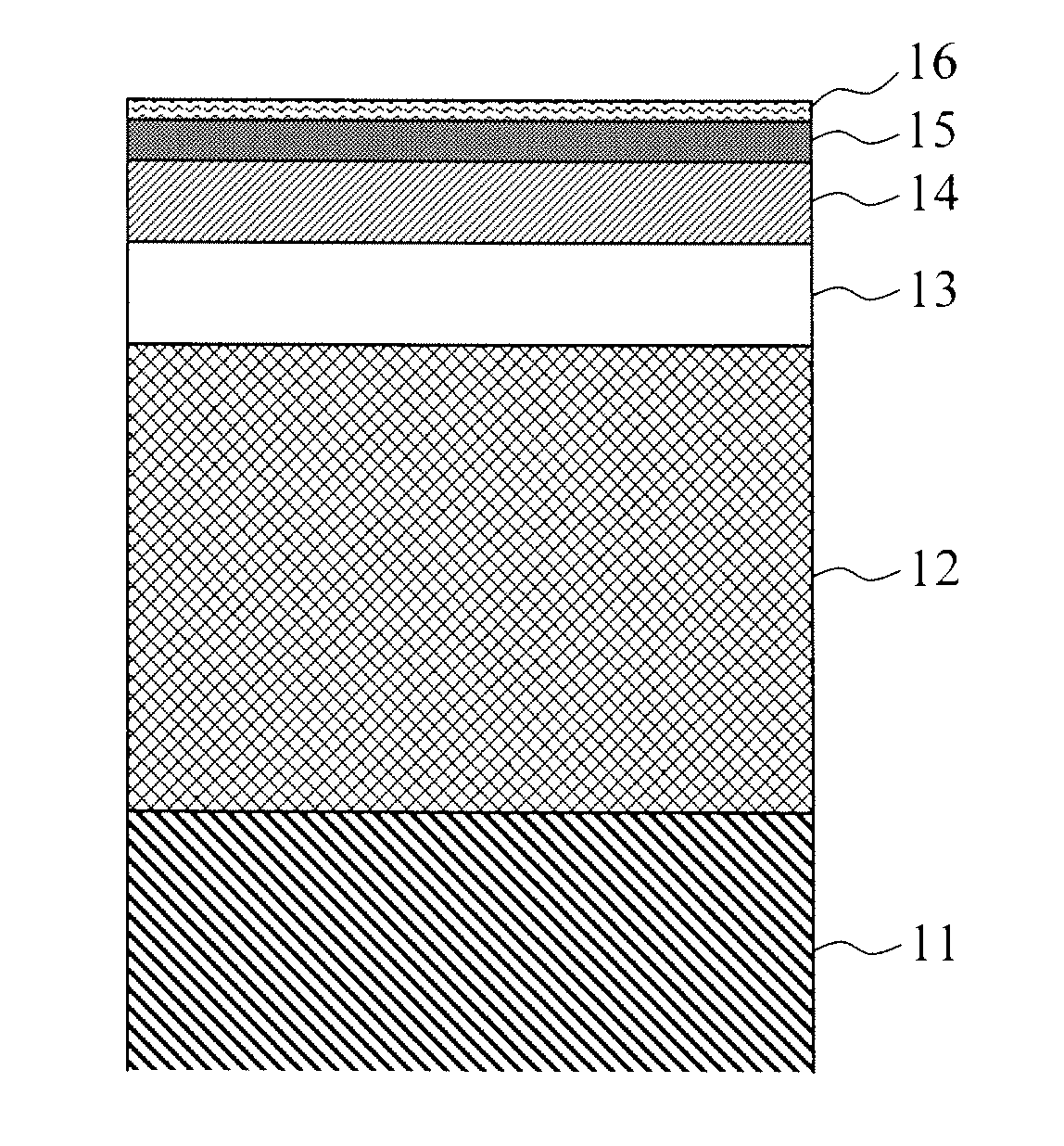
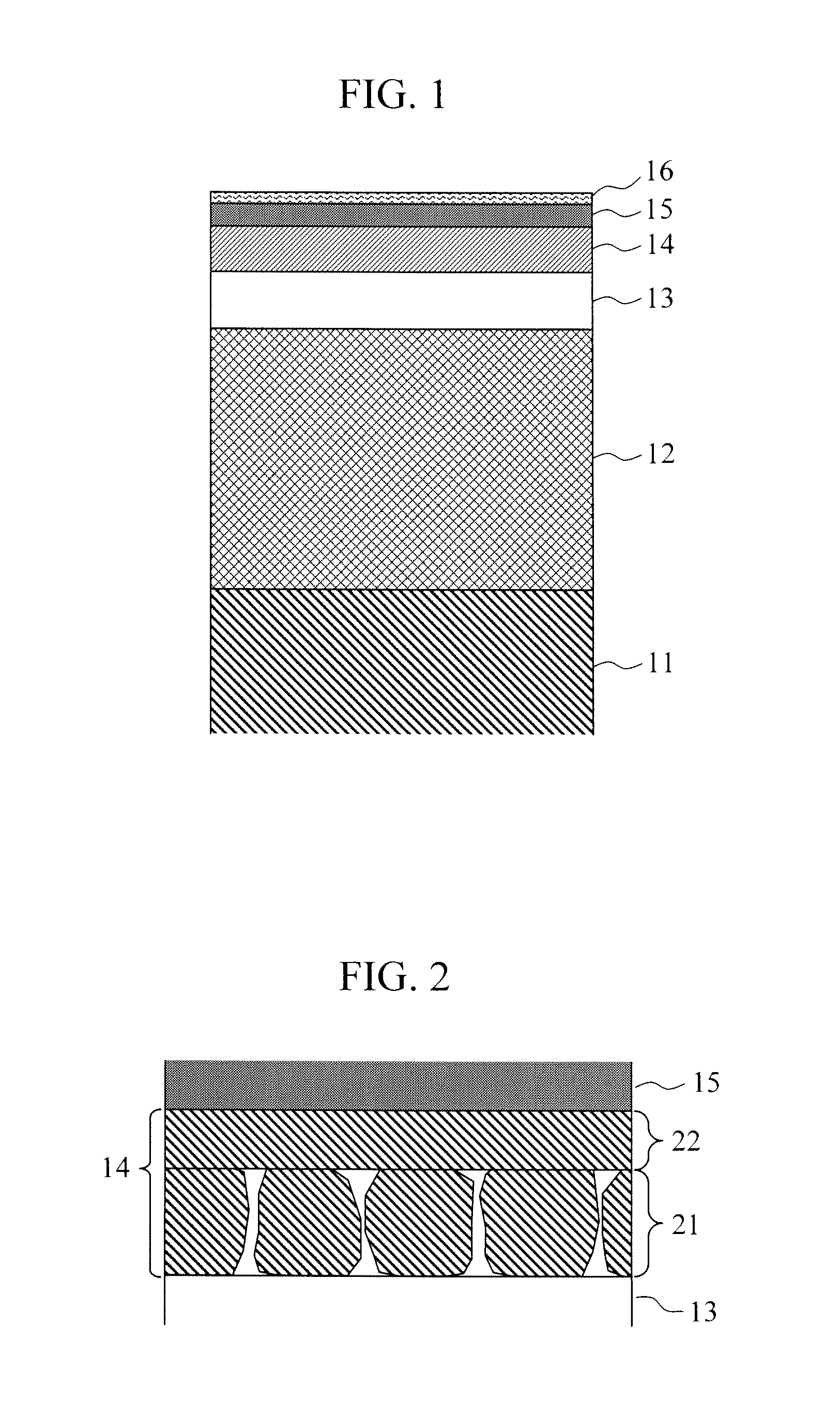
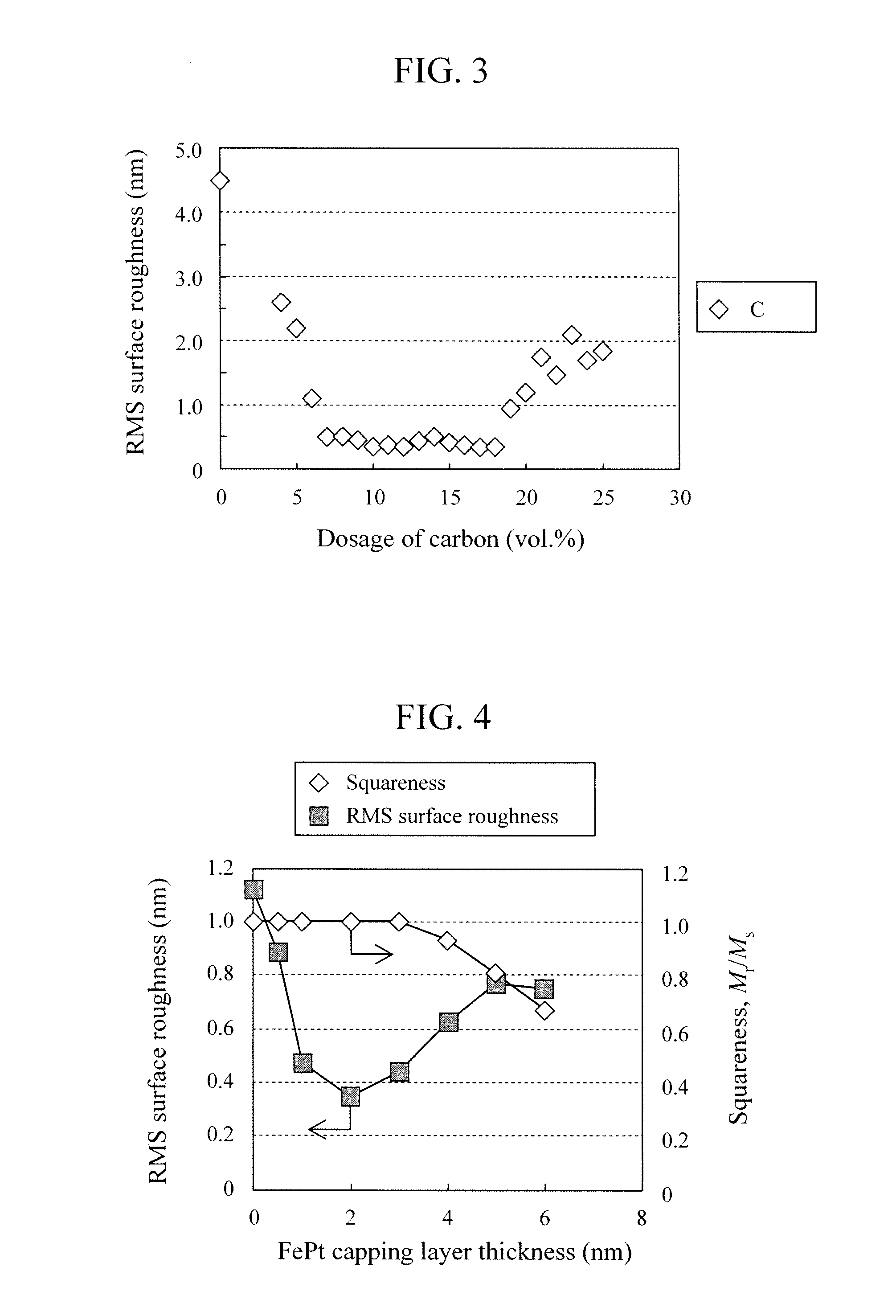
Surface flatness of magnetic recording medium to which a magnetic recording layer made of L10 FePt magnetic alloy thin film, with distance between a magnetic head and a magnetic recording medium sufficiently reduced. The magnetic recording layer includes: magnetic layers containing a magnetic alloy including Fe and Pt as principal materials; and one non-magnetic material selected from carbon, oxide and nitride. The first magnetic layer disposed closer to a substrate has a granular structure in which magnetic alloy grains including FePt alloy as the principal material are separated from grain boundaries including the non-magnetic material as the principal material. The second magnetic layer disposed closer to the surface than the first magnetic layer is fabricated so as to have a homogeneous structure in which an FePt alloy and the non-magnetic material are mixed in a state finer than diameters of the FePt magnetic alloy grains in the first magnetic layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Source/drain electrodes, transistor substrates and manufacture methods, thereof, and display devices
InactiveUS7683370B2Simple manufacturing processLow resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAlloy thin filmDisplay device
In a thin-film transistor substrate including a substrate, a thin-film transistor semiconductor layer, a source / drain electrode, and a transparent pixel electrode, the source / drain electrode includes a thin film of an aluminum alloy containing 0.1 to 6 atomic percent of nickel as an alloy element, and the aluminum alloy thin film is directly connected to the thin-film transistor semiconductor layer.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Metal alloys for the reflective or the semi-reflective layer of an optical storage medium
InactiveUS6905750B2Improve reflectivitySimilar sputtering characteristicLayered productsPhotomechanical apparatusIndiumCadmium Cation
A silver-based alloy thin film is provided for the highly reflective or the semi-reflective layer of optical discs. Alloy additions to silver include gold, rhodium, ruthenium, osmium, platinum, palladium, copper, silicon, cadmium, tin, lithium, nickel, cobalt, manganese, indium, chromium, antimony, gallium, boron, molybdenum, zirconium, beryllium, titanium, aluminum, germanium and zinc. These alloys have moderate to high reflectivity and reasonable corrosion resistance in ambient environments.
Owner:TARGET TECH
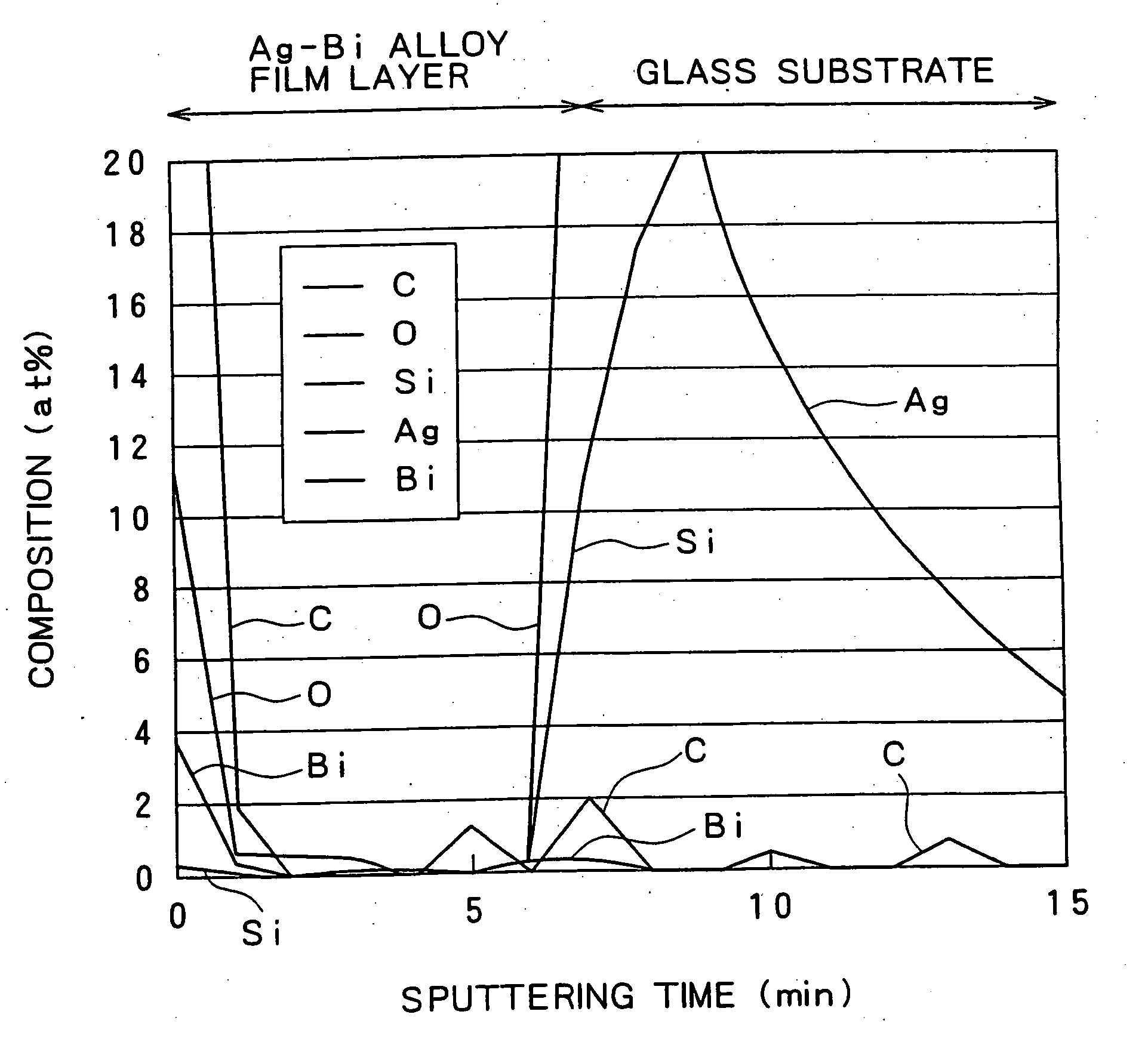
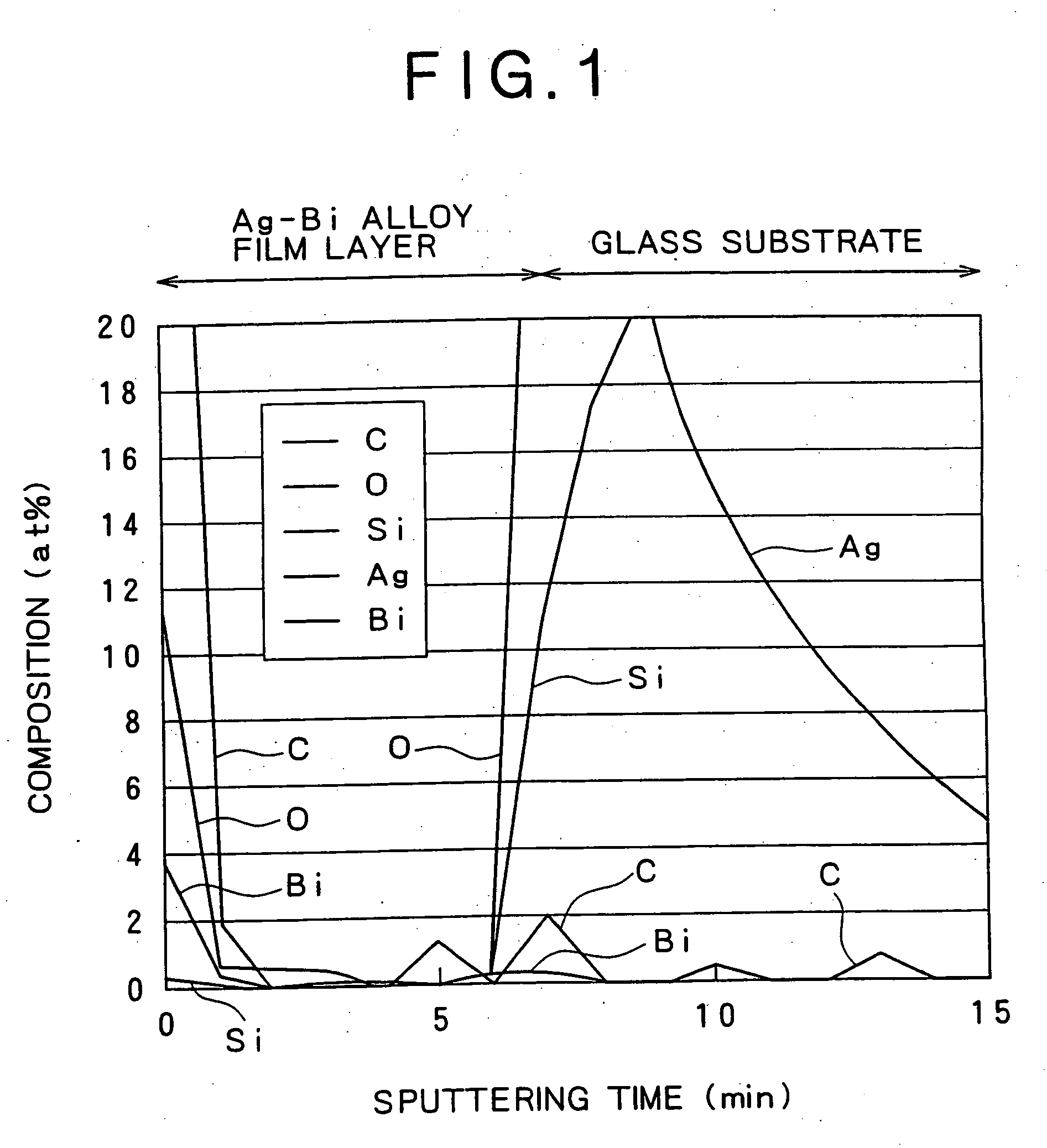
Ag base alloy thin film and sputtering target for forming Ag base alloy thin film
ActiveUS20060104853A1Improve recordEnhance reproduction characteristicSteering ruddersVacuum evaporation coatingOptical reflectionElectrical resistance and conductance
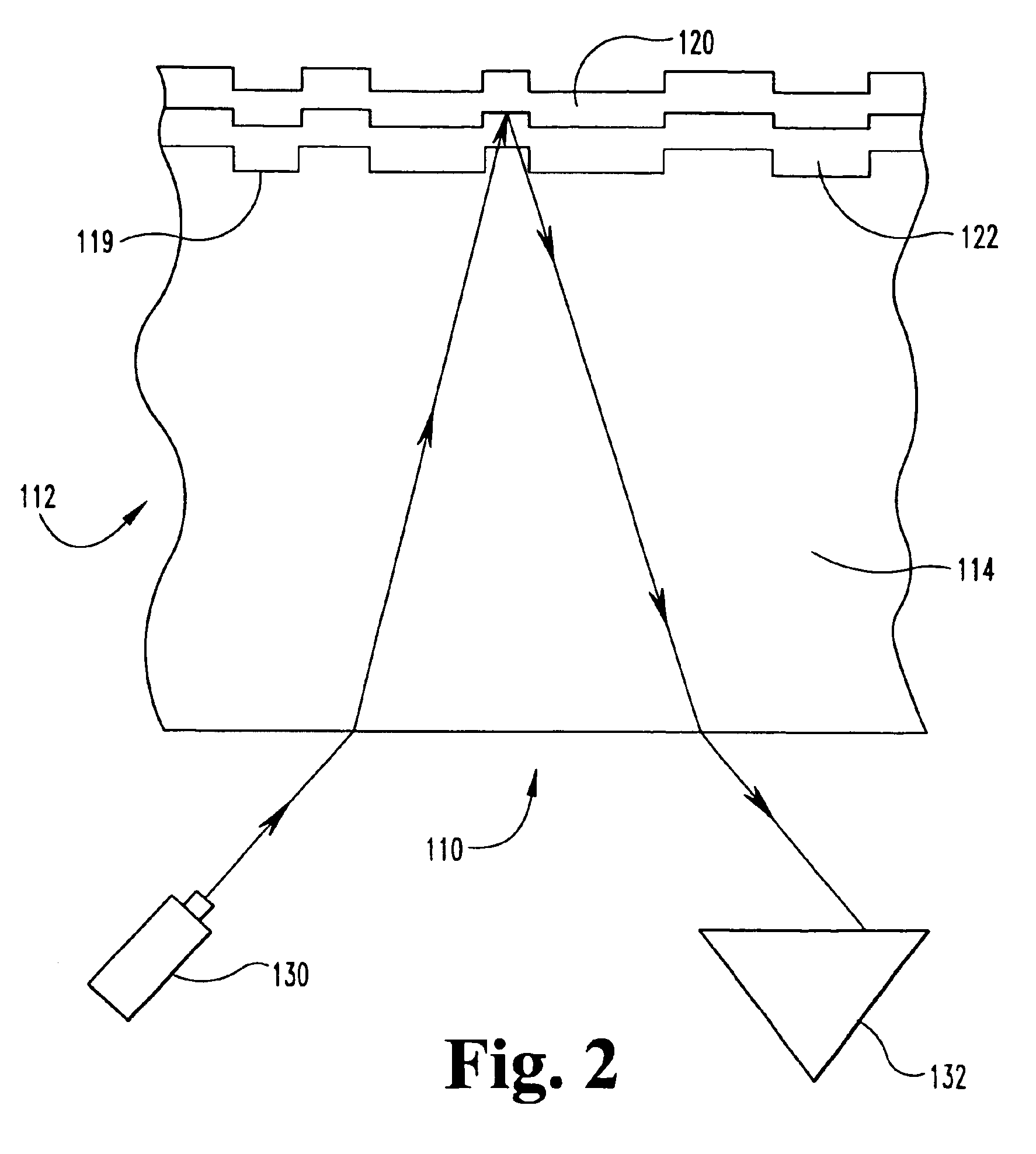
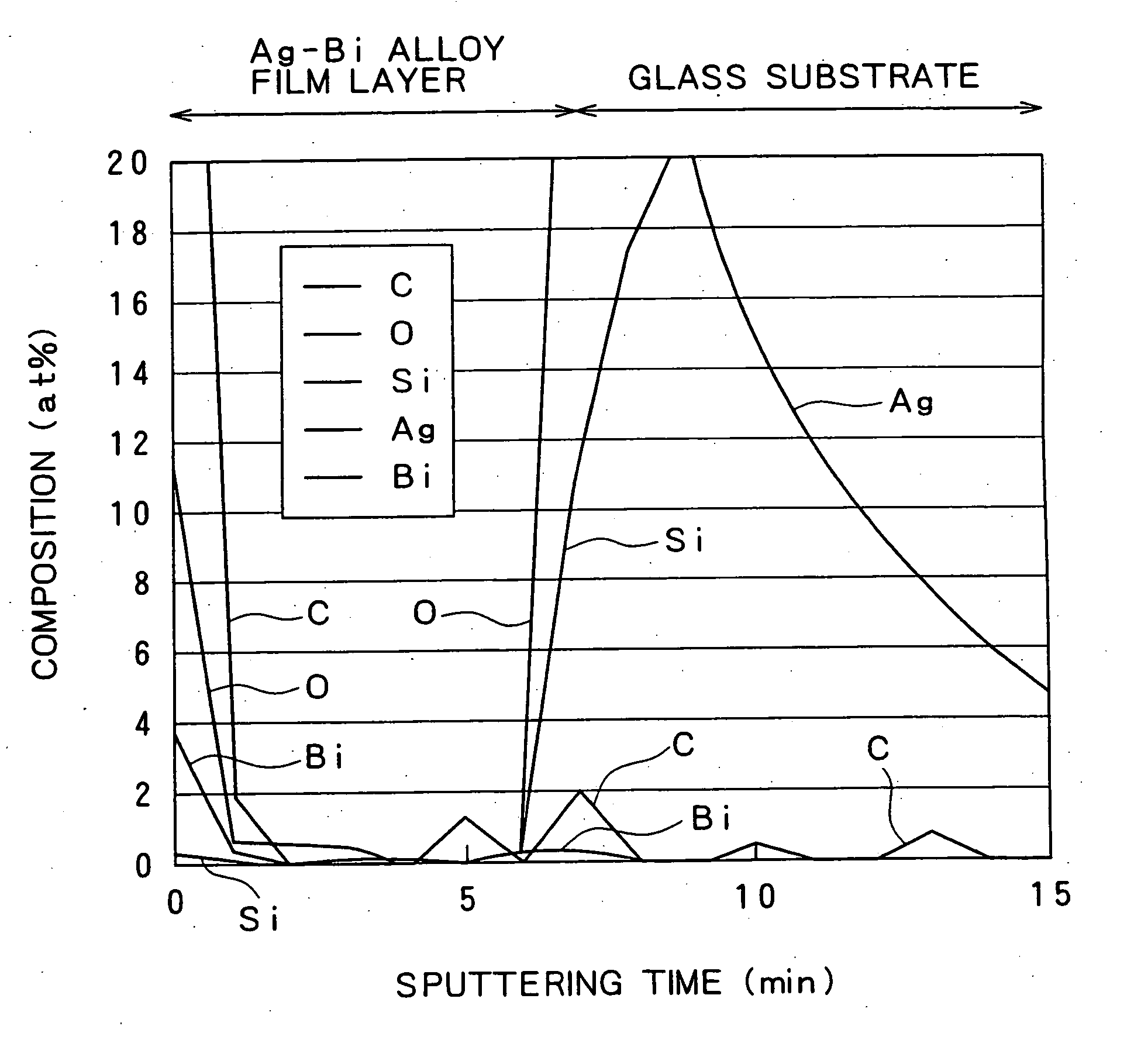
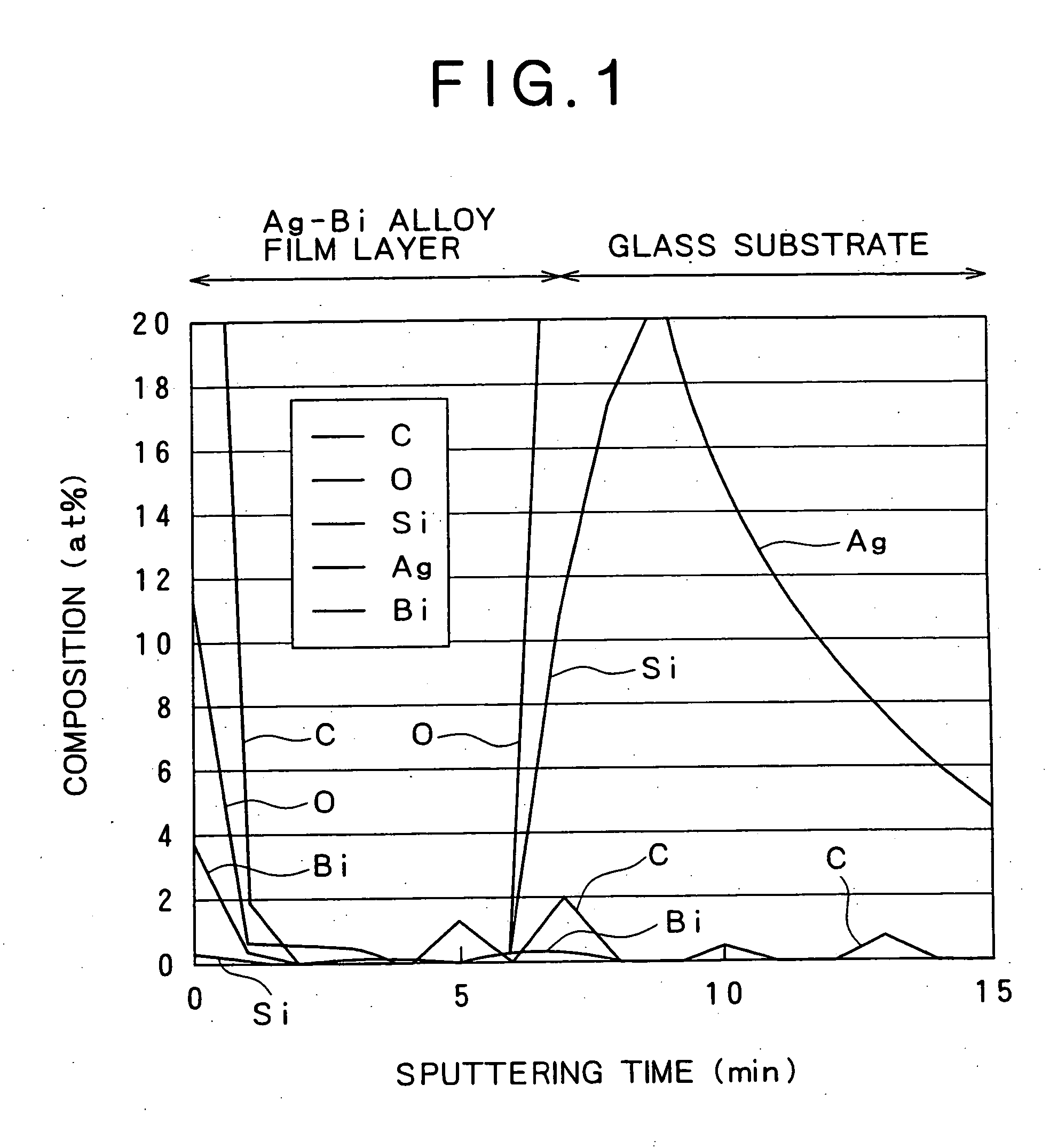
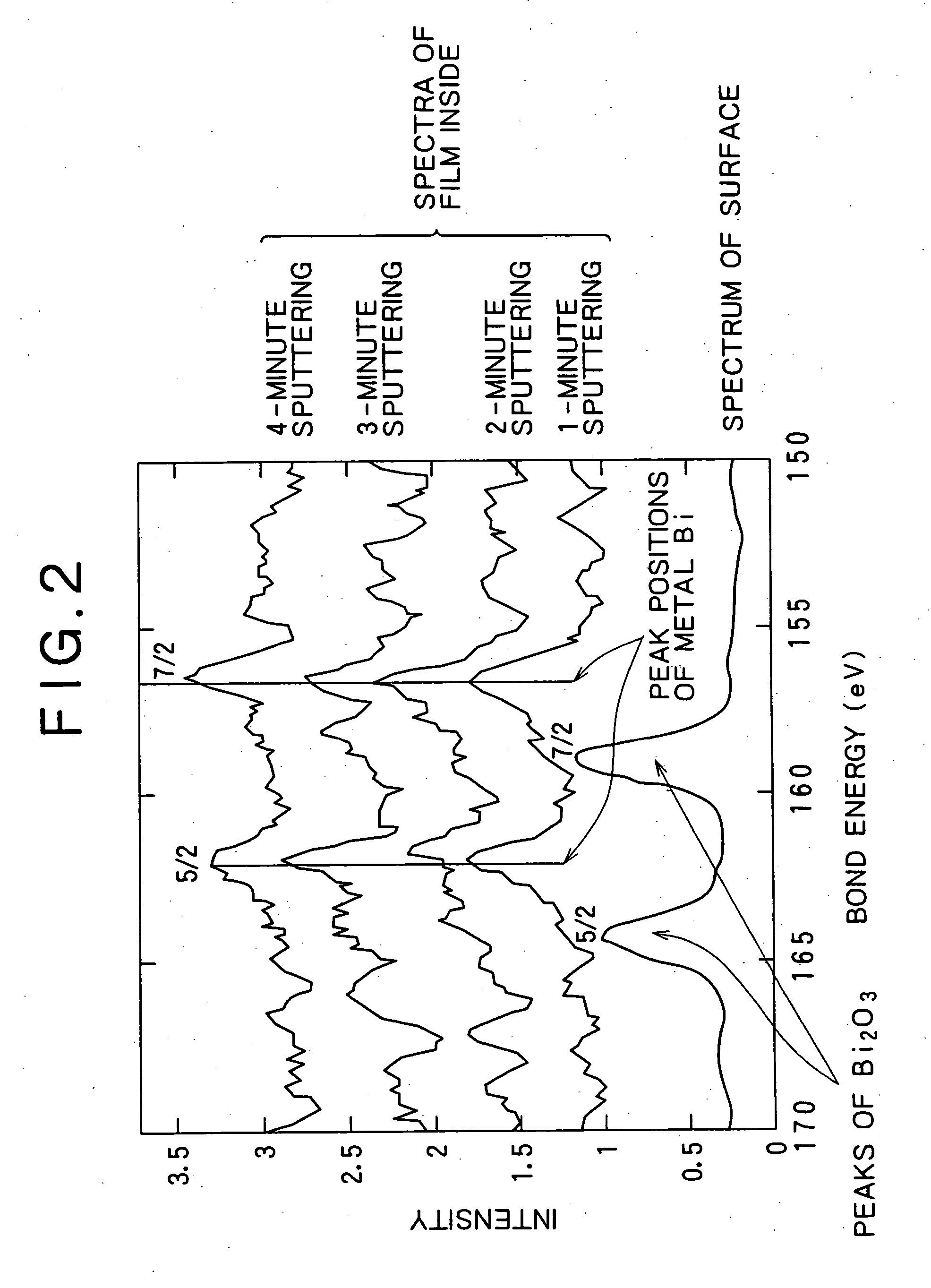
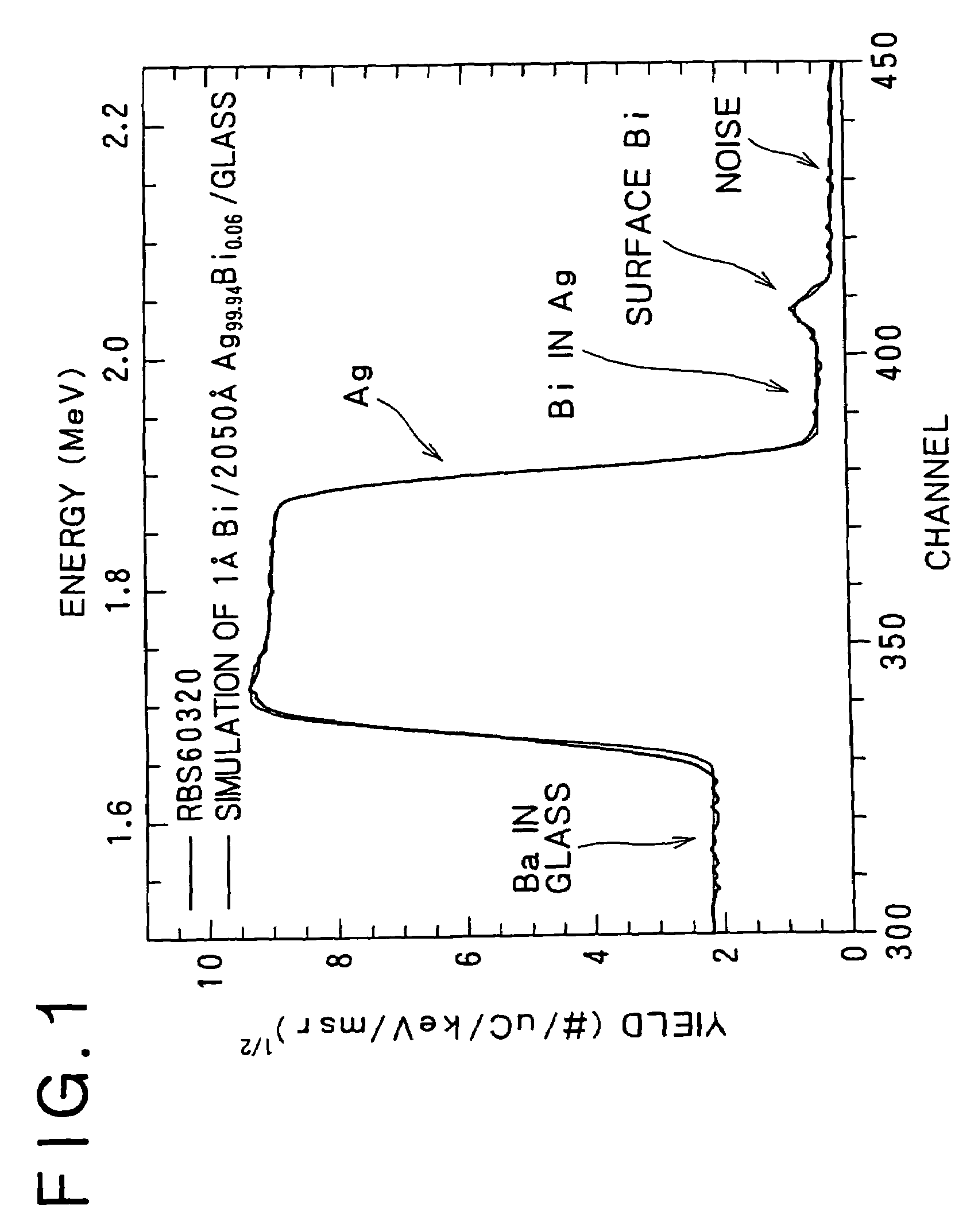
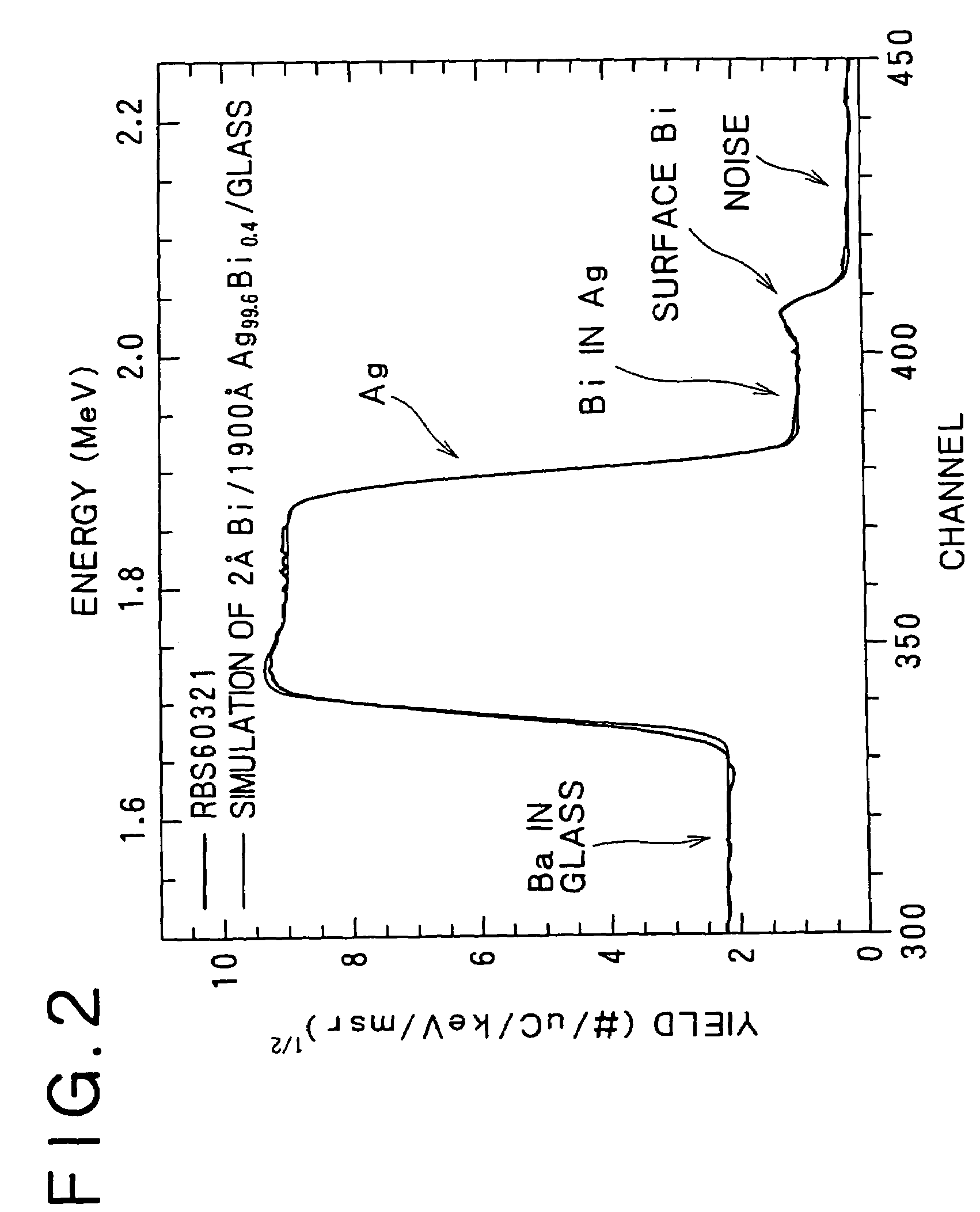
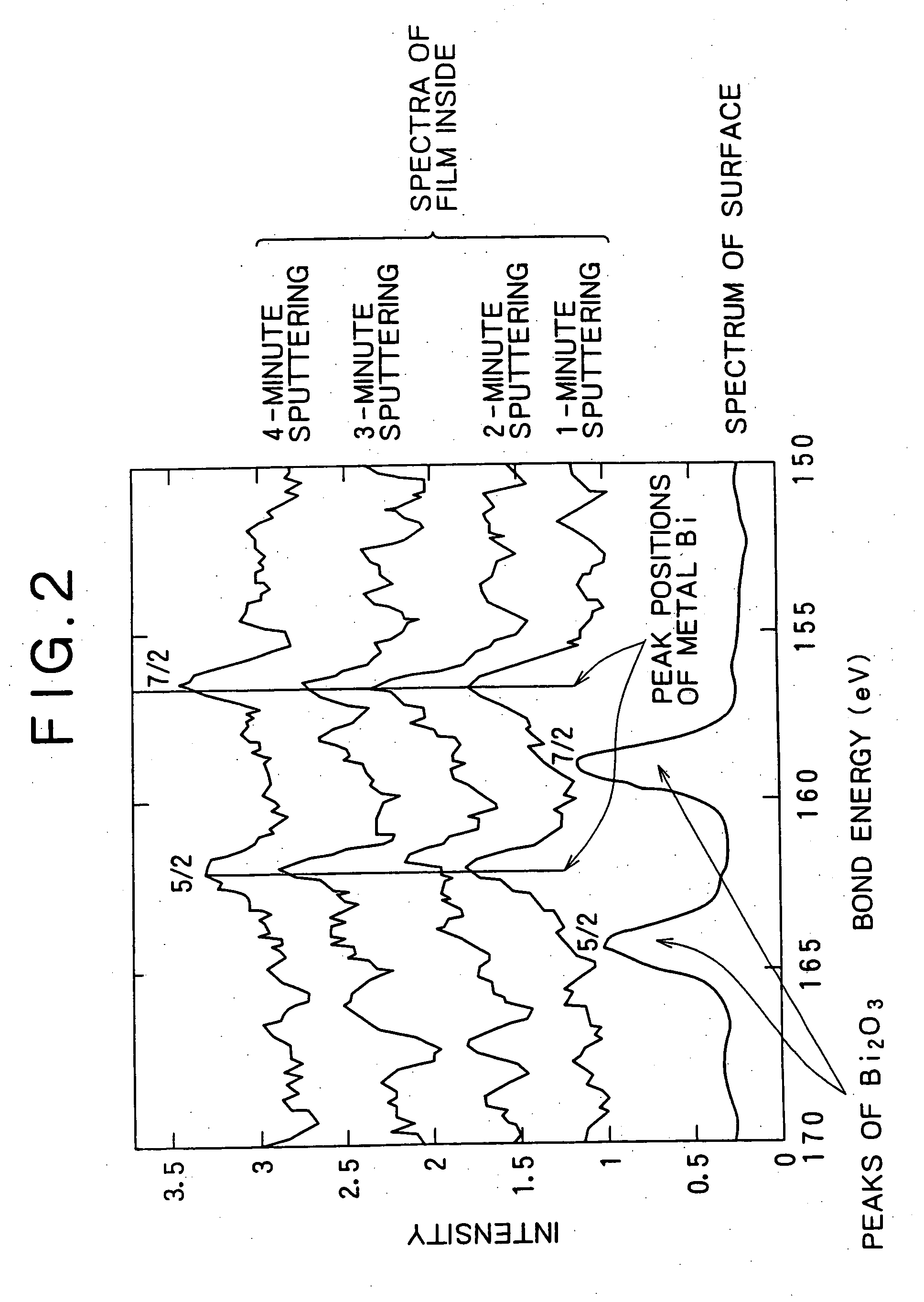
The present invention relates to an Ag alloy film. Particularly, it is preferably used as a reflective film or semi-transmissive reflective film for an optical information recording medium having high thermal conductivity / high reflectance / high durability in the field of optical information recording media, an electromagnetic-shielding film excellent in Ag aggregation resistance, and an optical reflective film on the back of a reflection type liquid crystal display device, or the like. The Ag alloy film of the present invention comprises an Ag base alloy containing Bi and / or Sb in a total amount of 0.005 to 10% (in terms of at %). Further, the present invention relates to a sputtering target used for the deposition of such an Ag alloy film.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Metal alloys for the reflective or the semi-reflective layer of an optical storage medium
InactiveUS20030138591A1Improve reflectivitySimilar sputtering characteristicPhotomechanical apparatusRecord information storageIridiumHigh reflectivity
A silver-based alloy thin film is provided for the highly reflective or semi-reflective layer of optical discs. Alloy additions to silver include gold, palladium, copper, rhodium, ruthenium, osmium, iridium, and platinum. These alloys have moderate to high reflectivity and reasonable corrosion resistance in the ambient environment.
Owner:TARGET TECH
Reflective Ag alloy film for reflectors and reflector provided with the same
ActiveUS7203003B2Improve reflectivityImprove heat resistanceMirrorsVacuum evaporation coatingAlloy thin filmBi layered
A reflective Ag alloy film includes a Ag—Bi alloy thin film, and a Bi layer and / or a Bi oxide layer formed on the surface and / or between the Ag—Bi alloy thin film and another layer formed on the Ag—Bi alloy thin film. The thickness of the Bi layer and / or the Bi oxide layer is 2.0 nm or below. The Ag—Bi alloy thin film of the reflective Ag alloy film has a Bi content in the range of 0.01 to 3.0 at %. A reflector is formed by depositing the Ag—Bi alloy thin film on a base member.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Electrode for lithium secondary battery and lithium secondary battery
InactiveUS20020086215A1Improve featuresModerate pressureElectrode manufacturing processesElectrode carriers/collectorsIndiumSurface roughness
An electrode for a lithium secondary battery in which an alloy thin film containing Sn (tin) and In (indium) is formed on the surface of a current collector having a surface roughness Ra of 0.1 mum or more, and a lithium secondary battery using thereof.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Soft magnetic film inductor and magnetic multi-component alloy thin film
InactiveCN101320617AIncrease disorderHigh nanocrystalline structureInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic layersMaterial DesignHigh entropy alloys
A magnetic complex alloy film is suitable for high frequency operation. This magnetic complex alloy film is used for improving the quality factors of the film inductance under high frequency operation and improving the inductance value. This magnetic complex alloy film achieves that the magnetic complex alloy film still has good soft magnetic property when under high frequency operation mainly through leading the materials design concept of complex high-entropy alloy and utilizing some material properties of the complex high-entropy alloy, such as high randomness, nano microcrystalline structure, low coercive field and high resistivity.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Transparent laminated film and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20110262742A1Prevent peelingReduce internal stressLamination ancillary operationsMagnetic/electric field screeningLight energyUltraviolet
A transparent laminated film is provided with which it is possible to inhibit peeling of thin film layers, even with long-term exposure to sunlight during use and exposure to UV rays during quality evaluation. The film has a thin film layer obtained by lamination of multiple thin films on at least one side of a transparent polymer film. This thin film layer has metal oxide thin films formed by a sol-gel process using light energy during sol-gel hardening and post-oxidation thin films formed by post-oxidation of at least one thin film selected from metal thin film, alloy thin film, and partially oxidized metal oxide thin film.
Owner:SUMITOMO RIKO CO LTD
Photo-voltaic cells including solar cells incorporating silver-alloy reflective and/or transparent conductive surfaces
The current invention provides for the manufacture of solar voltaic cells with high sunlight to electricity conversion efficiencies by using improved silver-alloy thin films with a thickness in the range of 30 to 60 as a back reflector / conductor. The back reflector surface may be smooth or roughened depending on the design of the solar voltaic cell and the reflective surface used. Silver-alloy thin film in the thickness range of 3 to 10 nanometers can be used to replace traditional transparent conductor such as indium oxide, indium tin oxide, zinc oxide, tin oxide etc. Elements that can be alloyed with silver to create alloys for use in the invention include, Pd, Cr, Zr, Pt, Au, Cu, Cd, B, In, Zn, Mg, Be, Ni, Ti, Si, Li, Al, Mn, Mo, W, Ga, Ge, Sn, and Sb. These alloys may be present in the silver-alloys in amounts ranging from 0.01 to 10.0 a / o percent. Preferably, elements such as of Cu, In, Zn, Mg, Ni, Ti, Si Al, Mn, Pd, Pt, and Sn are alloyed with silver, these elements are present in the alloy the amounts ranging from 0.05 to 5 a / o percent.
Owner:TARGET TECH
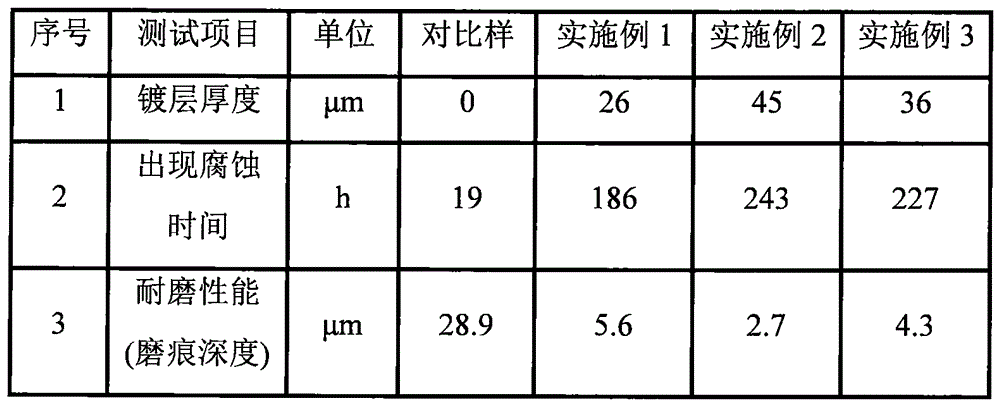
Corrosion-resistant multi-coating neodymium iron boron and preparation process
ActiveCN106710767AAccelerated corrosionImprove wear resistanceMagnetic materialsSuperimposed coating processSingle processDysprosium
The invention provides corrosion-resistant multi-coating neodymium iron boron and a preparation process. The corrosion-resistant multi-coating neodymium iron boron is composed of a neodymium iron boron permanent magnet and multiple coatings arranged on the outer surface of the neodymium iron boron permanent magnet, the multiple coatings sequentially include a nickel-plated layer, a dysprosium-plated aluminum alloy thin film layer and a nickel-chromium composite coating, thickness of the nickel-plated layer is 10-15um, thickness of the dysprosium-plated aluminum alloy thin film layer is 10-20um, and thickness of the nickel-chromium composite coating is 6-10um; modification of the multiple coatings can be realized on the surface of the permanent magnet, binding strength between the coatings and a permanent magnet base is guaranteed, the defect that the coatings are thin and poor in corrosion resistance and wear resistance caused by single process is overcome, and the corrosion-resistant multi-coating neodymium iron boron prepared by the process has high corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
Owner:宁波元辰新材料有限公司
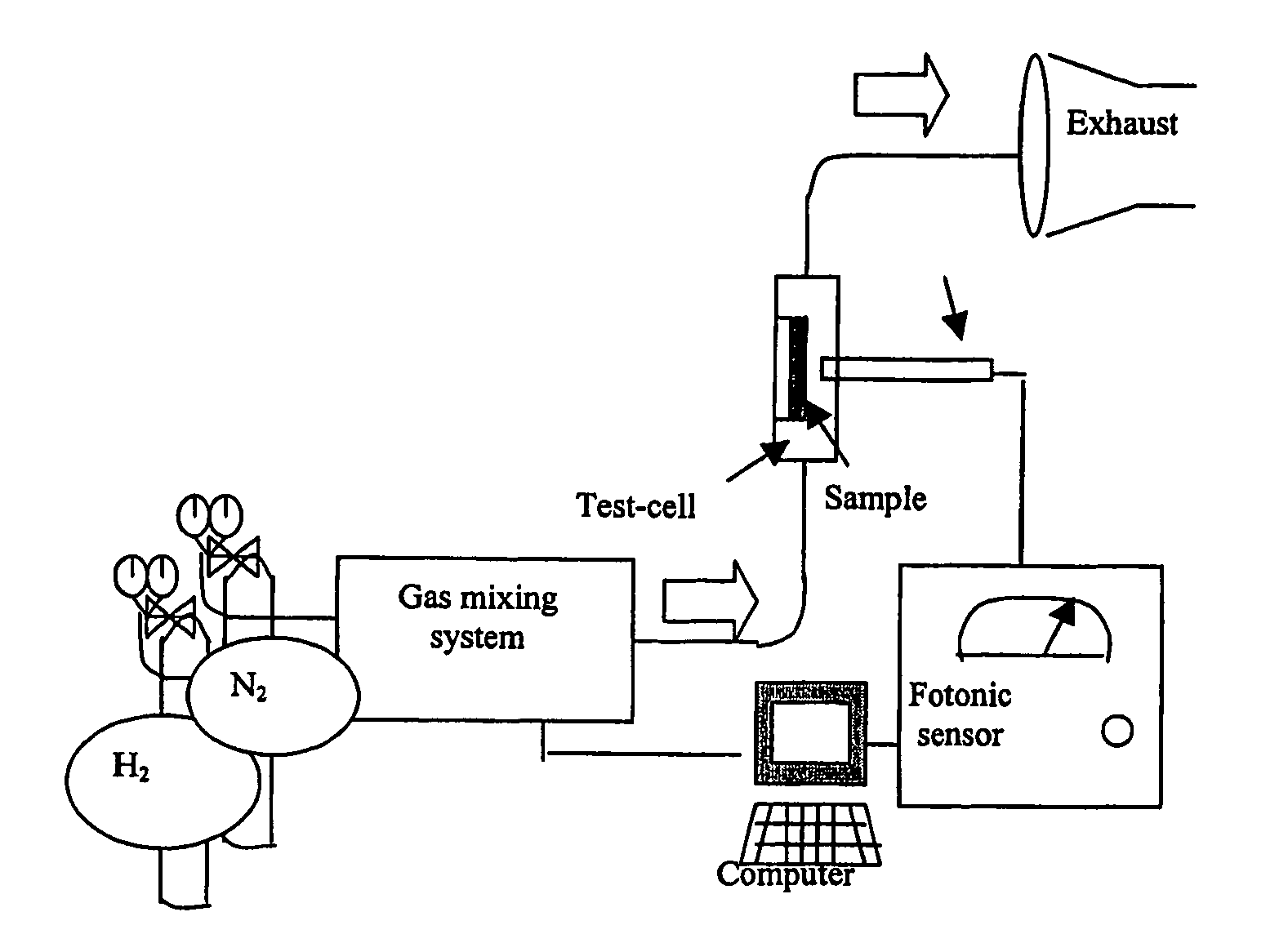
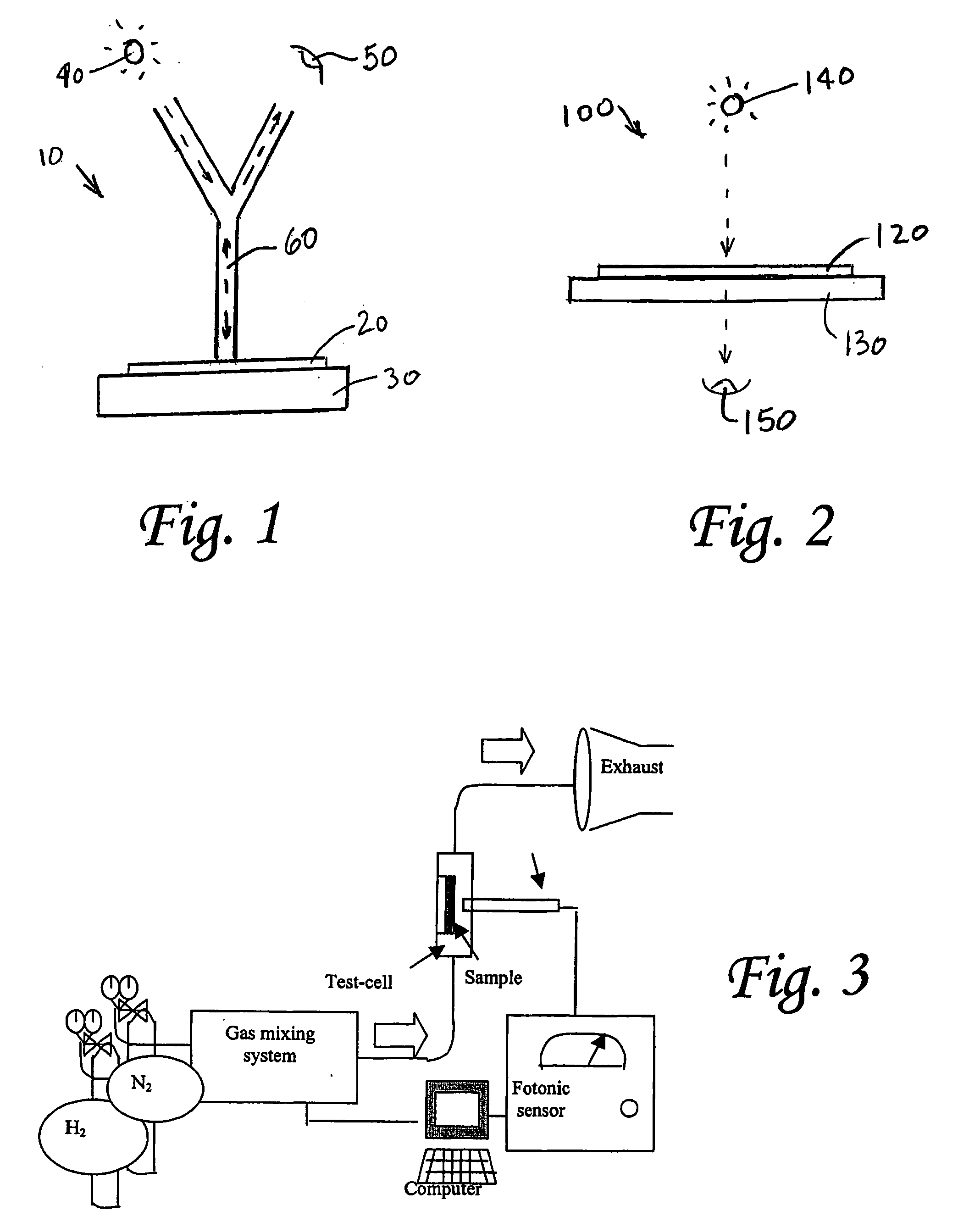
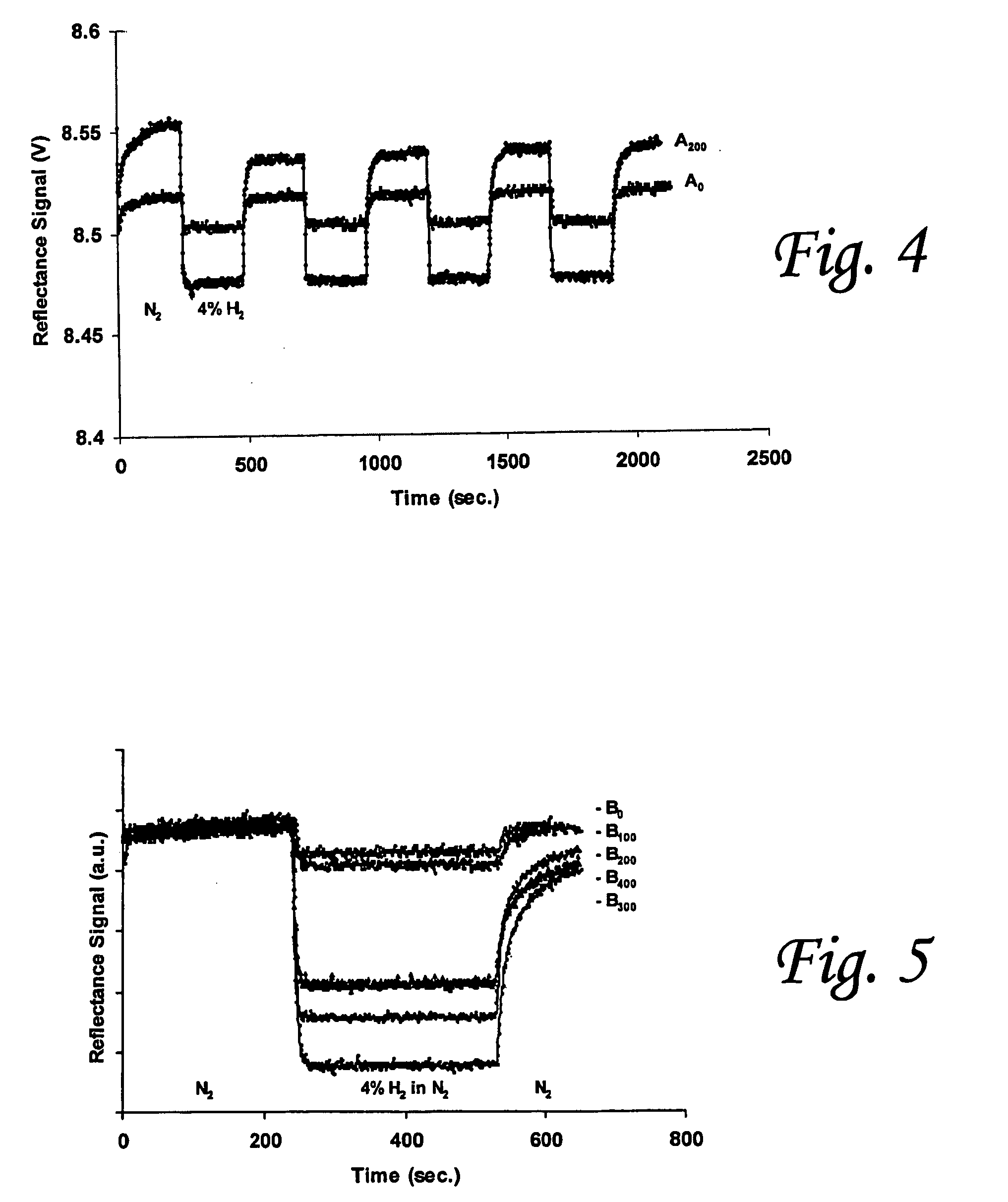
Methods for forming palladium alloy thin films and optical hydrogen sensors employing palladium alloy thin films
InactiveUS20050169807A1Reduce residual stressAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCelsius DegreeAlloy thin film
Methods for forming hydrogen sensing materials include forming a palladium alloy thin film having less than about 83 atomic percent of palladium, and annealing the palladium alloy thin film to relieve residual stress and increase atomic intermixing of the nanorystaline lattice, while maintaining a grain size close to the grain size of the nonannealed palladium alloy thin film. For example, the sensing material may include a palladium-gold alloy thin film having about 60 atomic percent of palladium and about 40 atomic percent of gold. The palladium-gold alloy thin film is then annealed at a temperature of about 200 degrees Celsius for 1 hour. Methods for detecting hydrogen containing gas in which the hydrogen sensing material is maintained in a single phase when exposed to the hydrogen containing gas, and optical hydrogen sensors are also disclosed.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Ag base alloy thin film and sputtering target for forming Ag base alloy thin film
InactiveUS20060154104A1Increased durabilityImprove reliabilitySteering ruddersVacuum evaporation coatingOptical reflectionElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention relates to an Ag alloy film. Particularly, it is preferably used as a reflective film or semi-transmissive reflective film for an optical information recording medium having high thermal conductivity / high reflectance / high durability in the field of optical information recording media, an electromagnetic-shielding film excellent in Ag aggregation resistance, and an optical reflective film on the back of a reflection type liquid crystal display device, or the like. The Ag alloy film of the present invention comprises an Ag base alloy containing Bi and / or Sb in a total amount of 0.005 to 10% (in terms of at %). Further, the present invention relates to a sputtering target used for the deposition of such an Ag alloy film.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
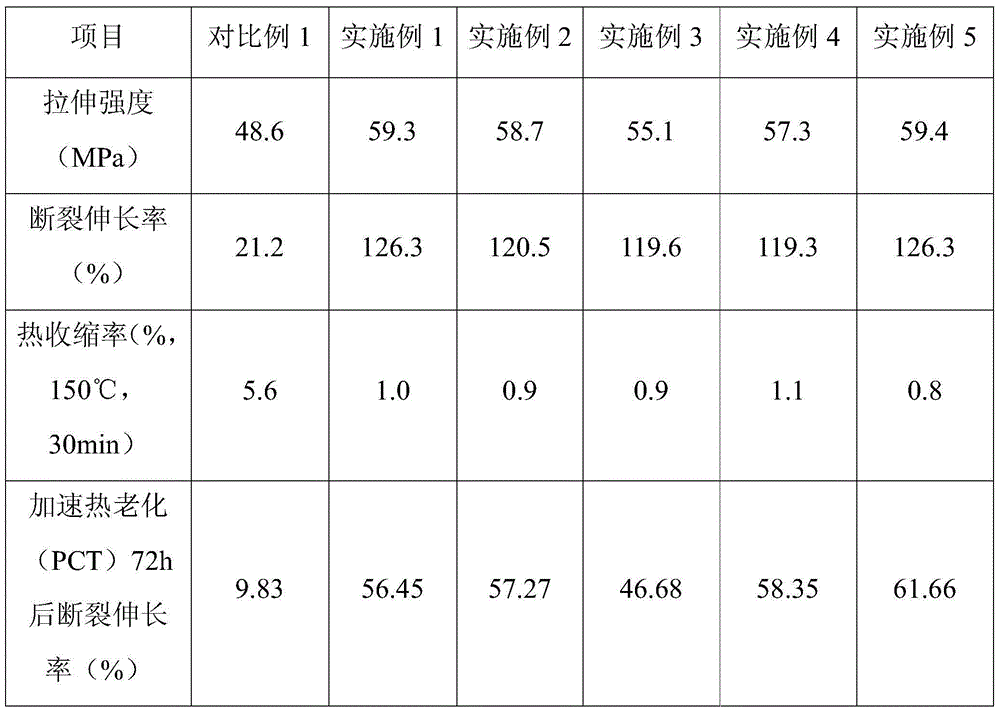
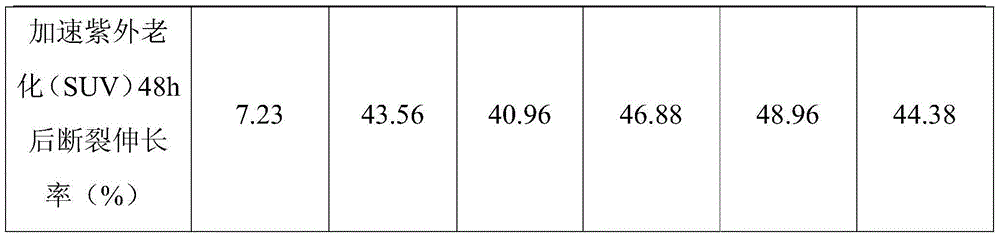
Thermoplastic polyester/polyethylene composition and application thereof
InactiveCN104559080AGood dimensional stabilityImprove hydrolysis resistancePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesThermoplasticWeather resistance
The invention belongs to the technical field of high-polymer composite materials, and relates to a thermoplastic polyester / polyethylene composition and application thereof. The thermoplastic polyester / polyethylene composition is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 20-80 parts of thermoplastic polyester, 20-80 parts of polyethylene, 2-20 parts of solubilizer and 0.1-2 parts of antioxidant, wherein the sum of the thermoplastic polyester and polyethylene is 100 parts. The obtained thermoplastic polyester / polyethylene composition is a uniform-phase composite material, and has favorable properties of the thermoplastic polyester and polyethylene. The polyester / polyethylene alloy material prepared from the thermoplastic polyester / polyethylene composition has the inherent advantages of the PBT (polybutylene terephthalate) and PE (polyethylene), thereby greatly improving the properties of the alloy material and greatly enhancing the dimensional stability and tensile property of the alloy film material; and thus, the alloy material has the advantages of high-temperature resistance, ultraviolet resistance, weather resistance, hydrolysis resistance, low production cost and the like.
Owner:HANGZHOU FUMO NEW MATERIAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com