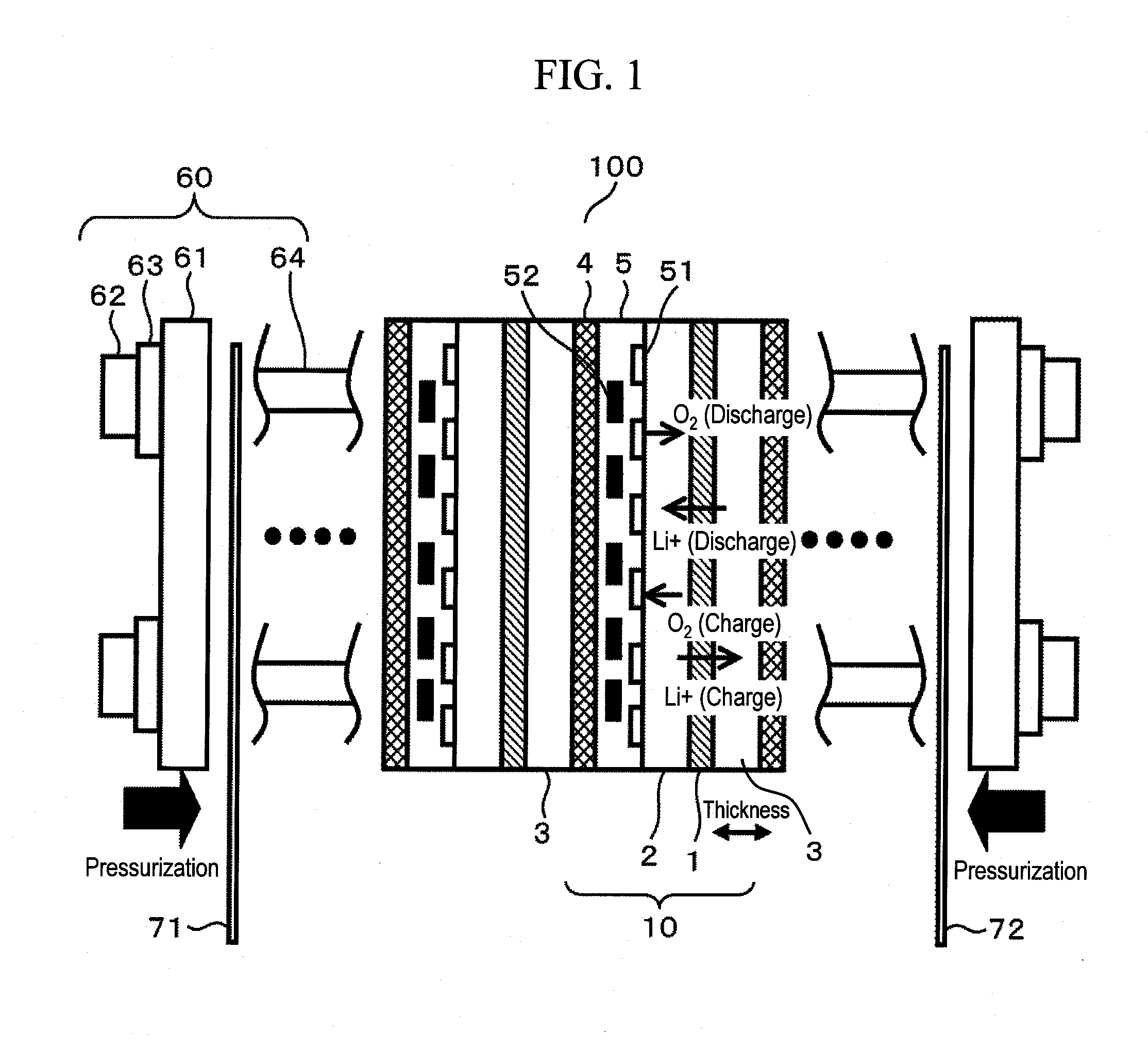
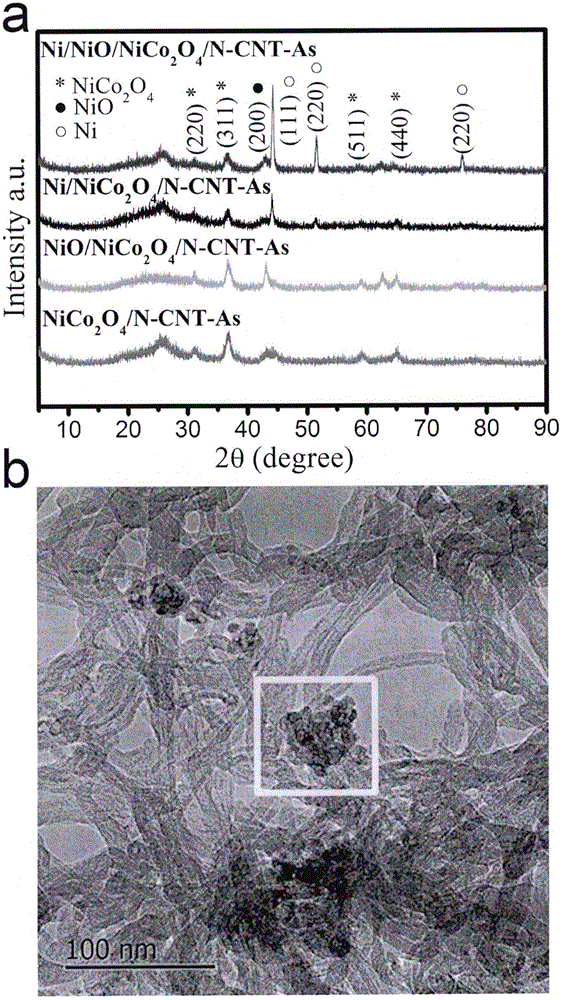
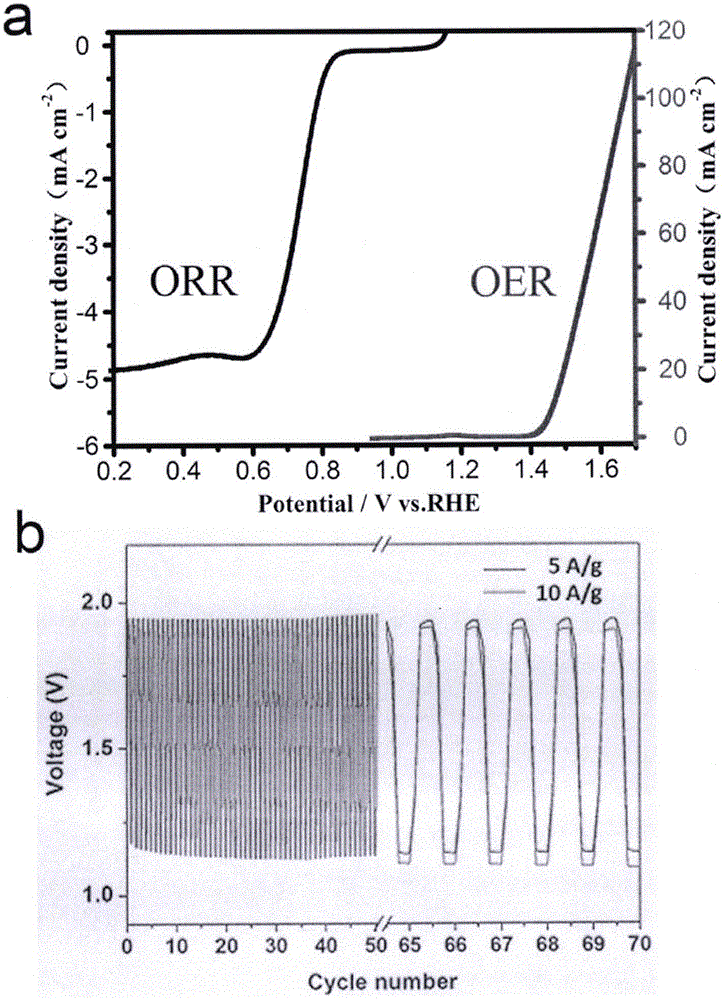
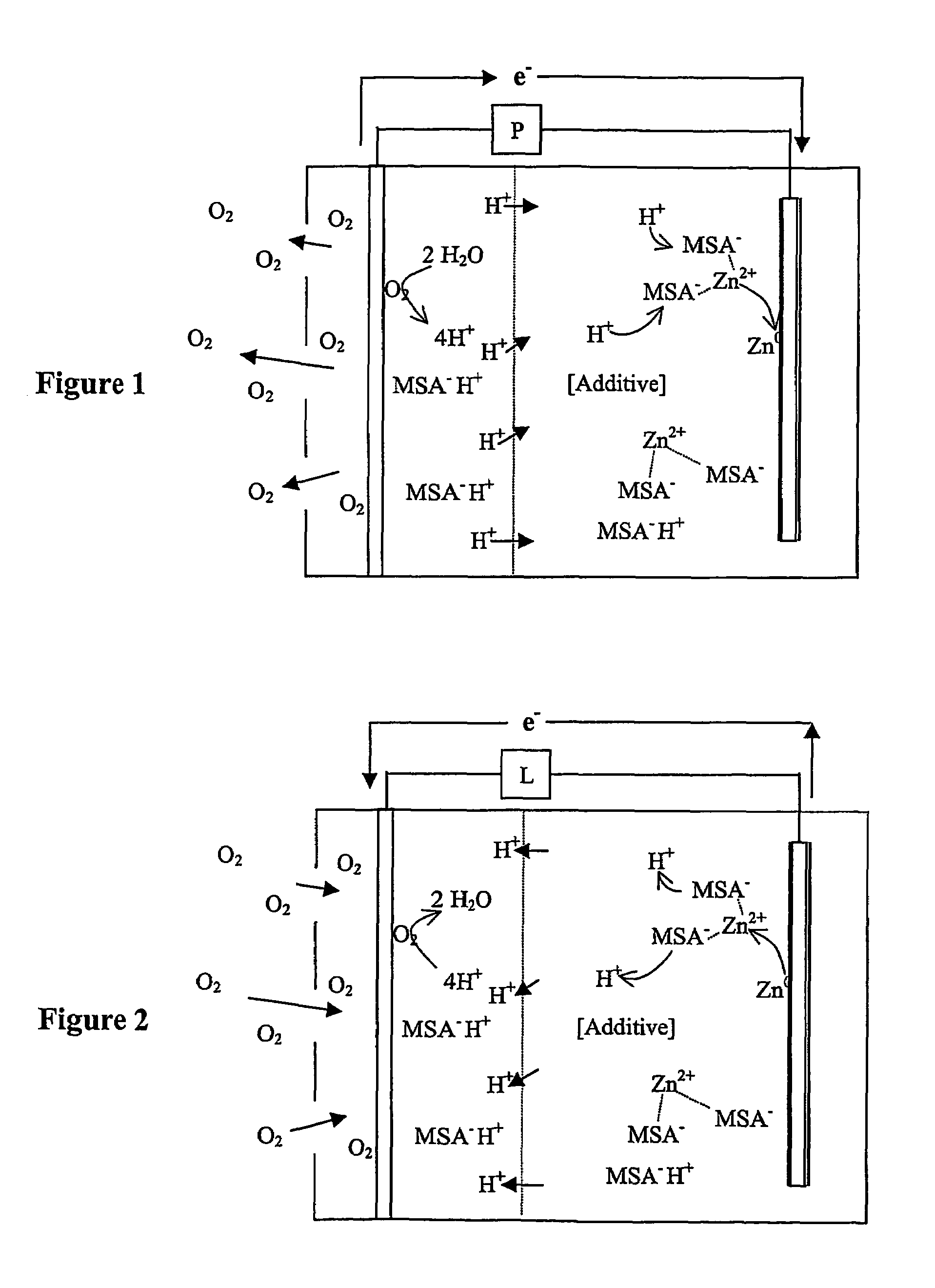
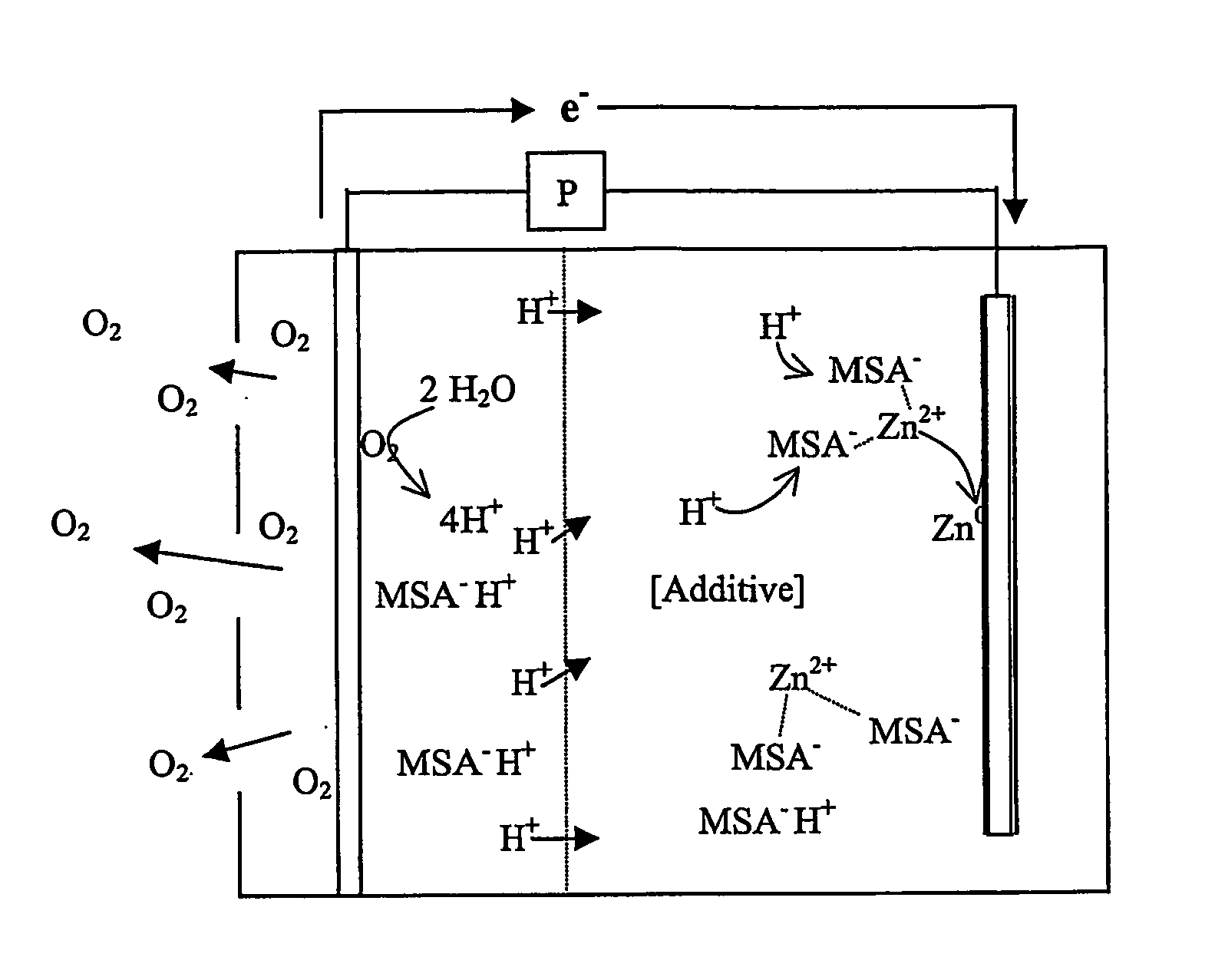
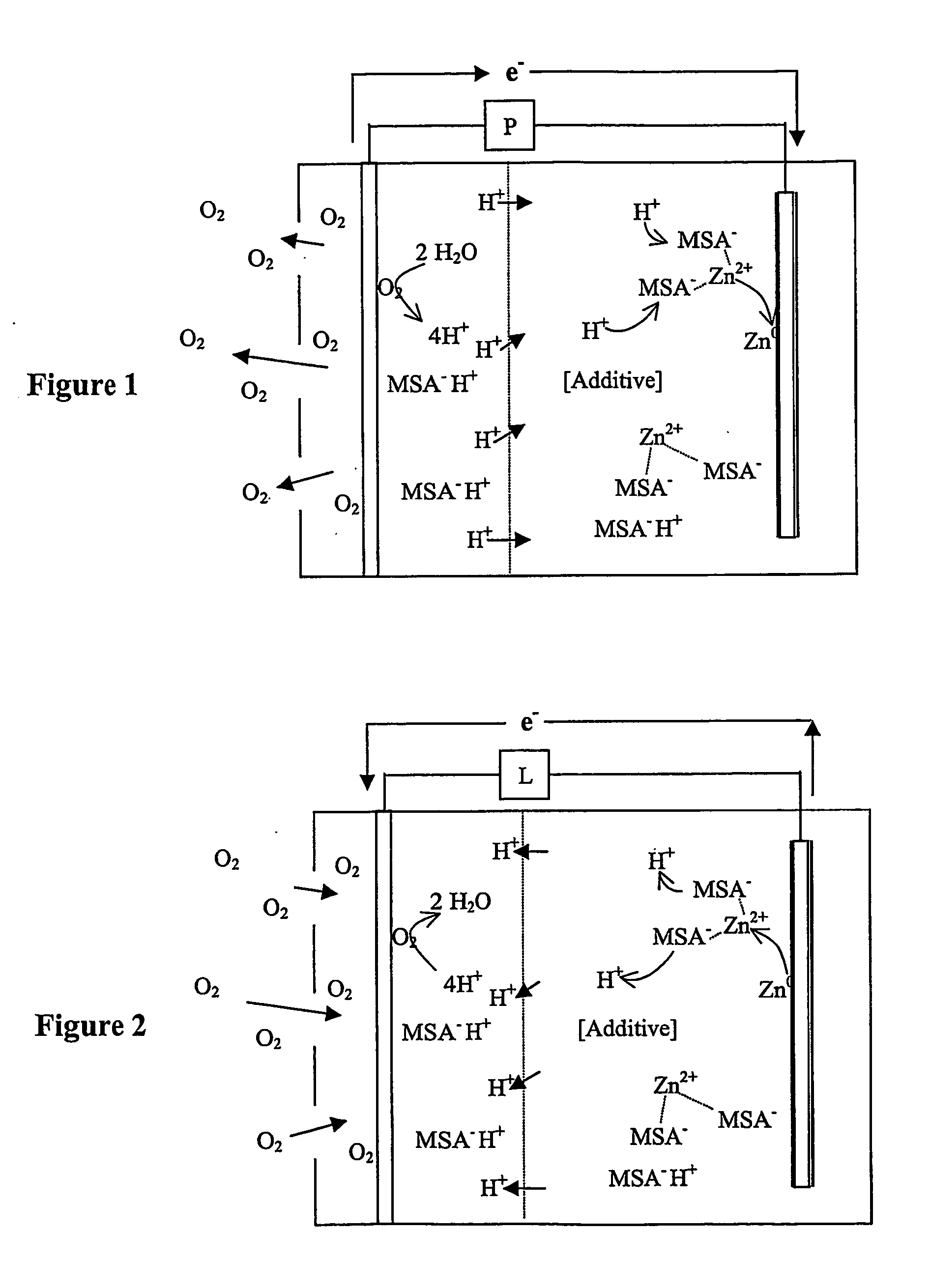
Patents
Literature
574 results about "Zinc–air battery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Zinc–air batteries (non-rechargeable) , and zinc–air fuel cells (mechanically rechargeable) are metal–air batteries powered by oxidizing zinc with oxygen from the air. These batteries have high energy densities and are relatively inexpensive to produce. Sizes range from very small button cells for hearing aids, larger batteries used in film cameras that previously used mercury batteries, to very large batteries used for electric vehicle propulsion.
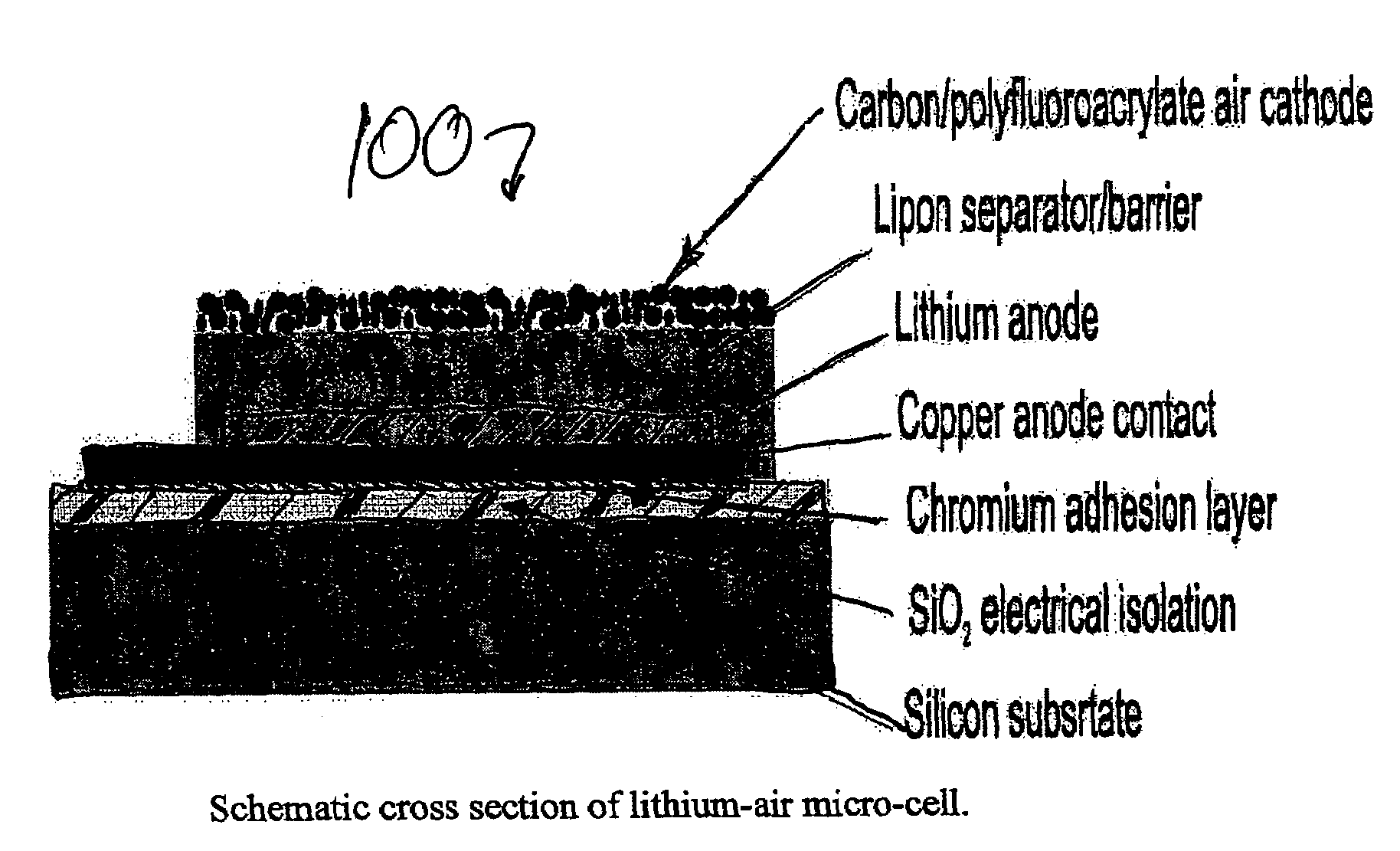
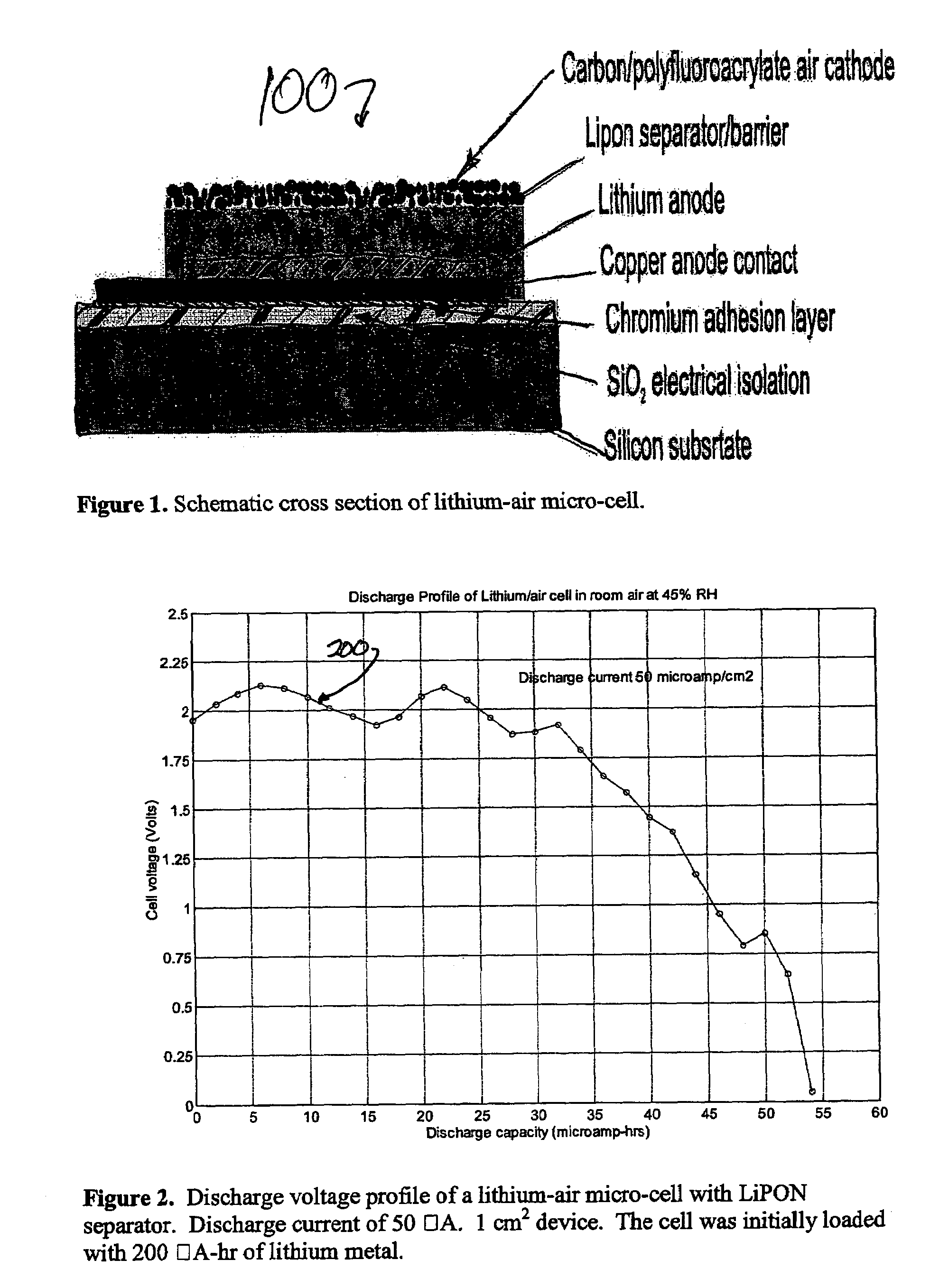
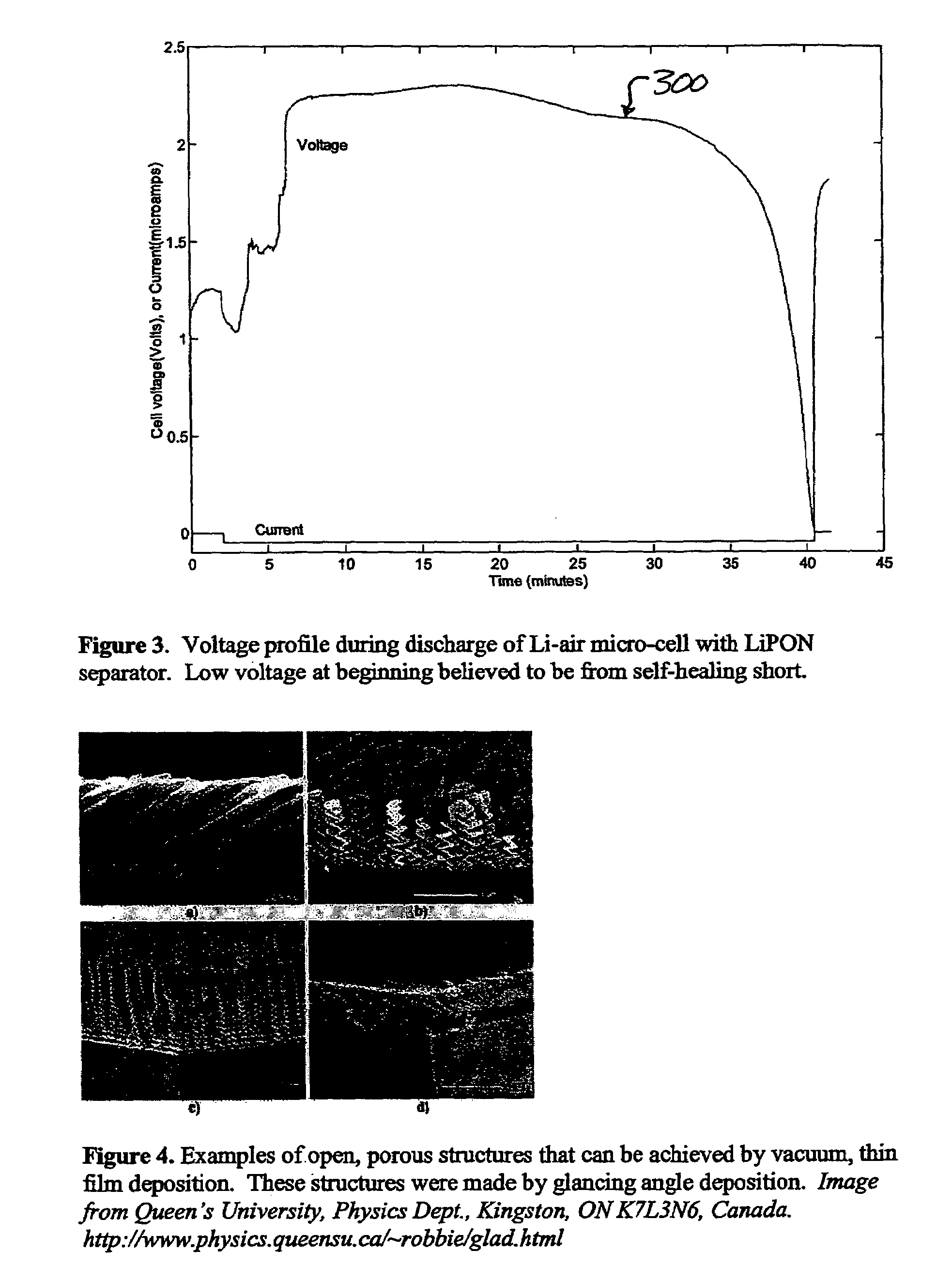
Lithium/air batteries with LiPON as separator and protective barrier and method
A method and apparatus for making lithium / air batteries with LiPON as separator and protective barrier, and the resulting cell(s) and / or battery(s). Some embodiments include an apparatus that includes a lithium anode; a polymer-air cathode; and a LiPON separator between the anode and cathode. In some embodiments, the polymer-air cathode includes a carbon-polyfluoroacrylate material. In some embodiments, the anode overlays a copper anode contact.
Owner:CYMBET CORP
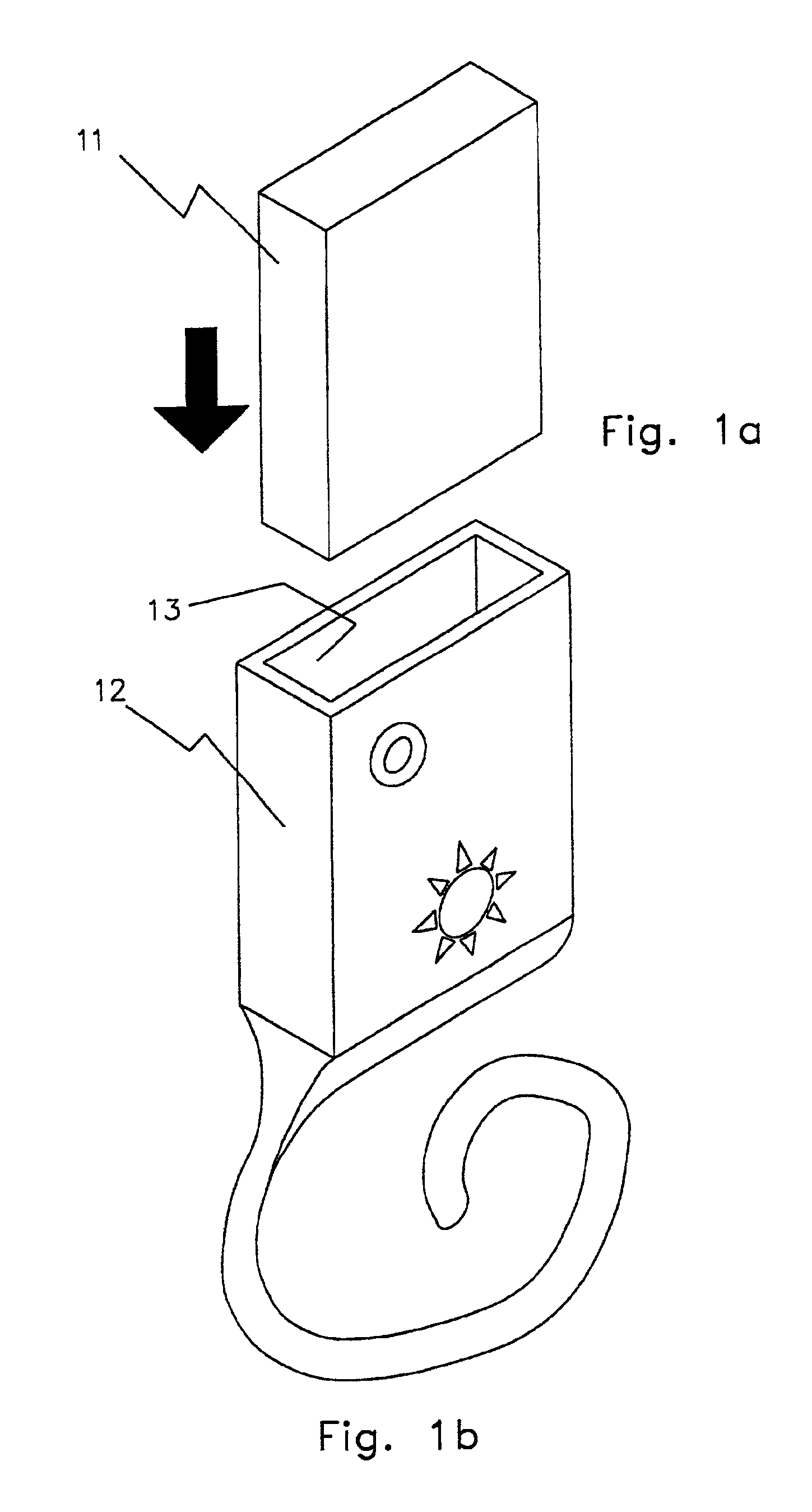
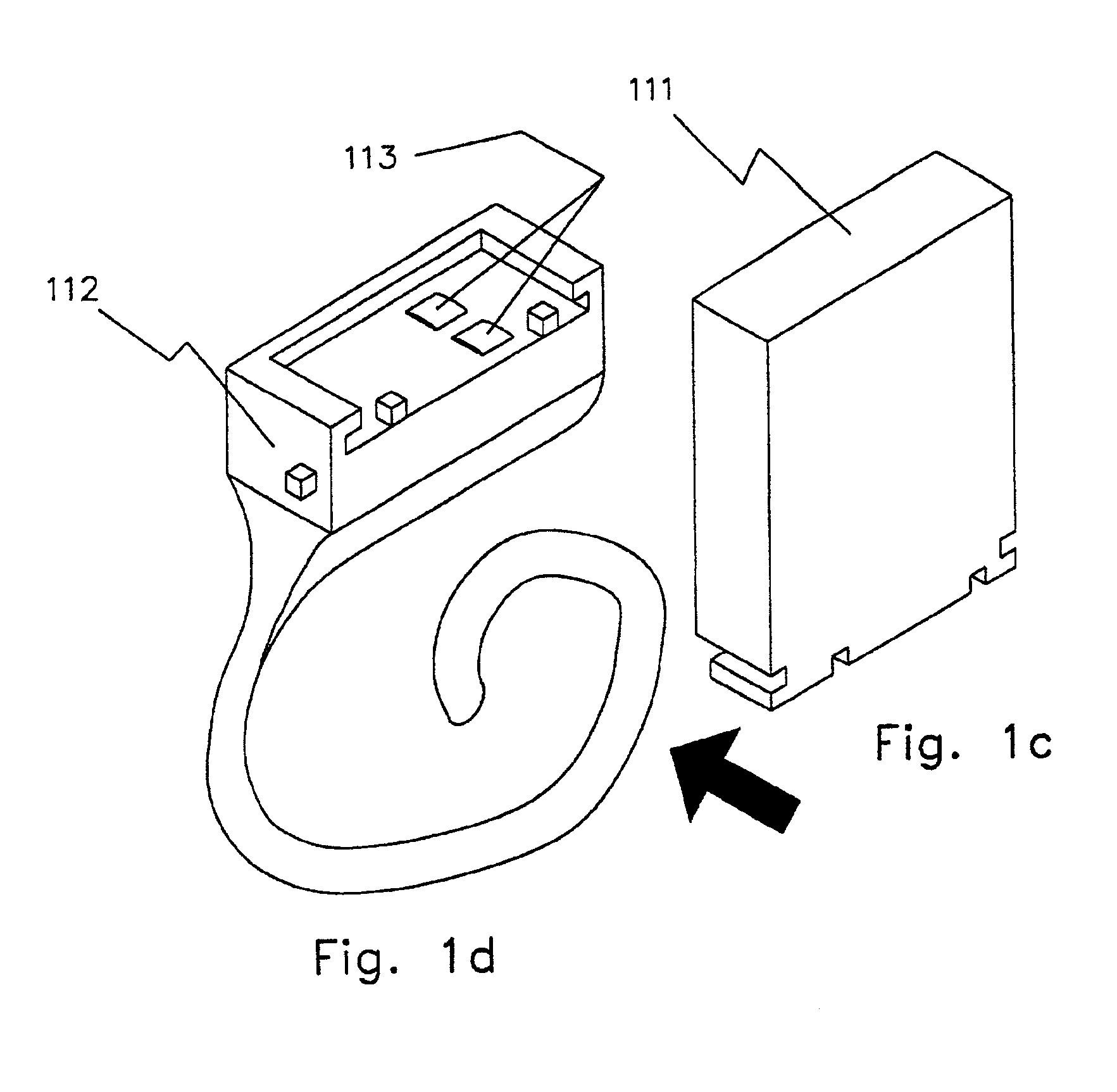
Zinc air battery and its uses
InactiveUS6879855B2Small sizeCheap to makeFuel and primary cellsElectrotherapyArtificial cochlea implantHigh energy
The invention is a method for increasing the airflow to a zinc-air battery such that the energy density is 500 mwh / cc to 1000 mwh / cc. This allows 8 to 16 hours use as a primary (throw-away) battery, with, for example, high-duty cycle, high-drain cochlear implants, and neuromuscular stimulators for nerves, muscles, and both nerves and muscles together. The systems incorporating the high energy density source are also part of the invention, as well as the resulting apparatus of the method. The uses of this inexpensive, i.e., a $1.00 per day, throw-away primary battery are new uses of the modified zinc-air battery and are directed toward helping people hear again, walk again, and regain body functionality which they have otherwise lost permanently.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
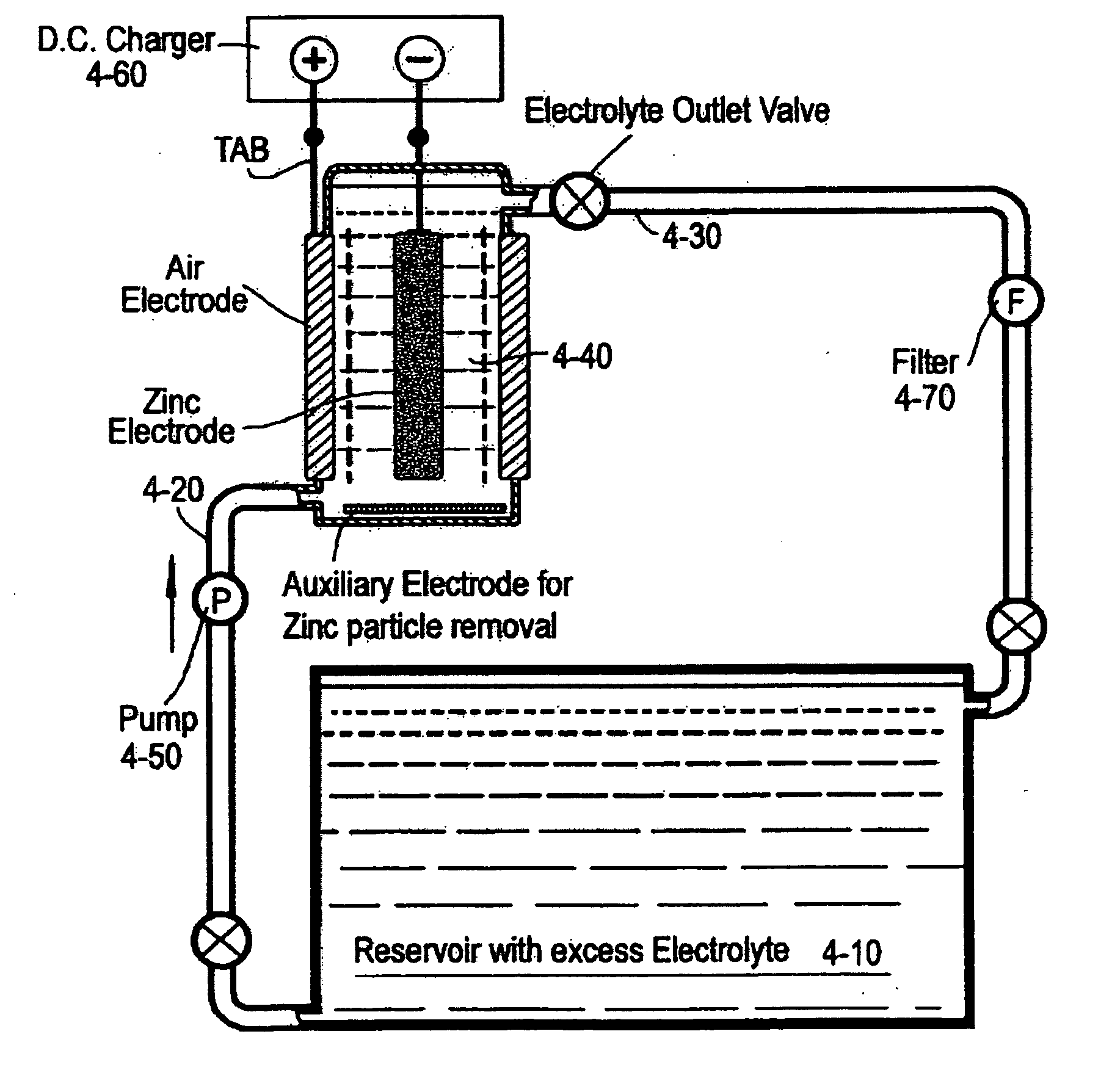
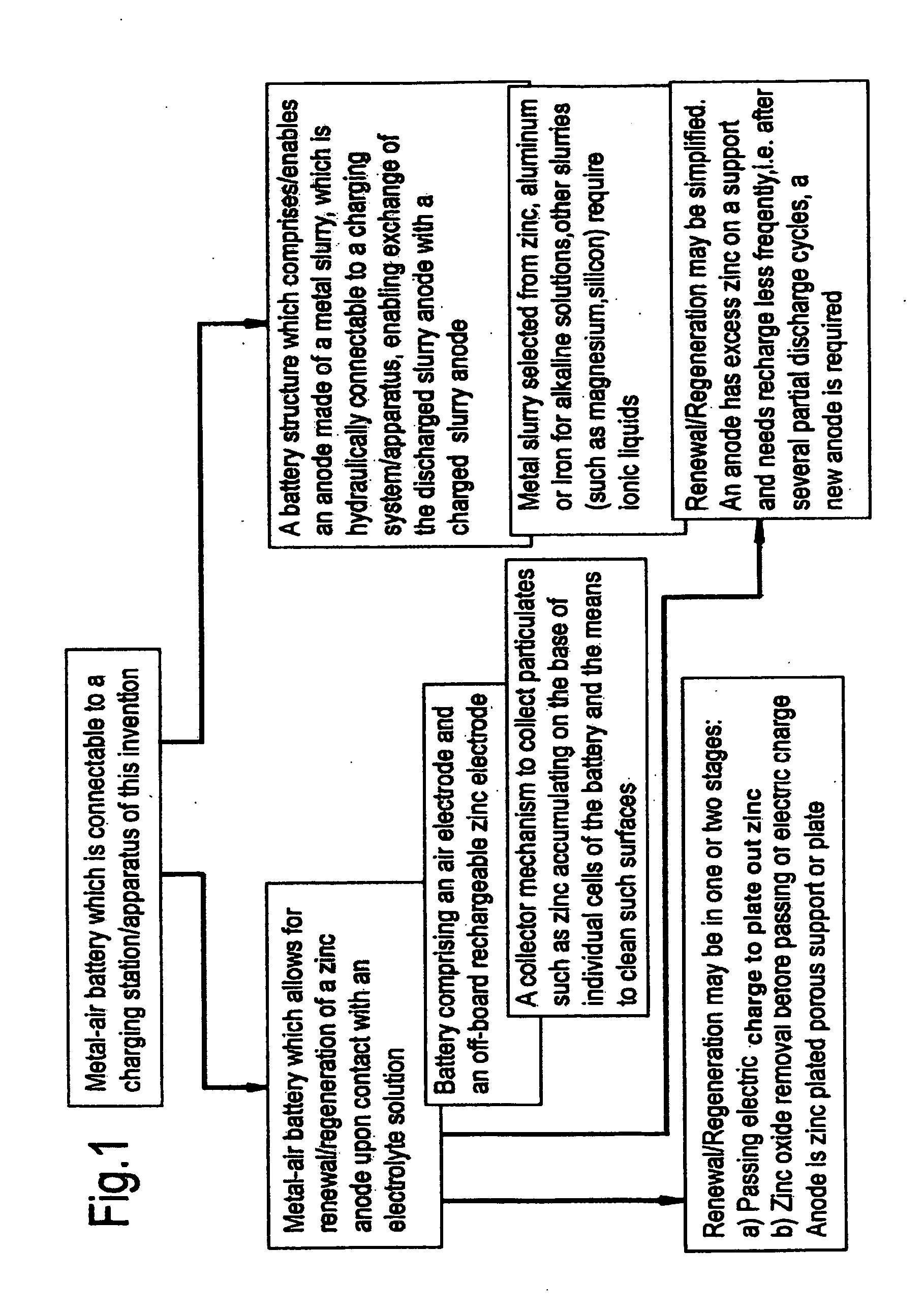
Zinc-Air Battery
ActiveUS20130285597A1Improved energy/volumeImproved energy/weightElectrolyte moving arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsHigh energyEngineering
A zinc-air cell, a battery which is a low weight, low volume, or high energy system, or a combination thereof, and an apparatus for recharging the same are disclosed.
Owner:PHINERGY
Solid porous zinc electrodes and methods of making same
InactiveUS7291186B2Improve conductivityImprove stabilityFuel and primary cellsAlkaline accumulatorsPorosityFiber
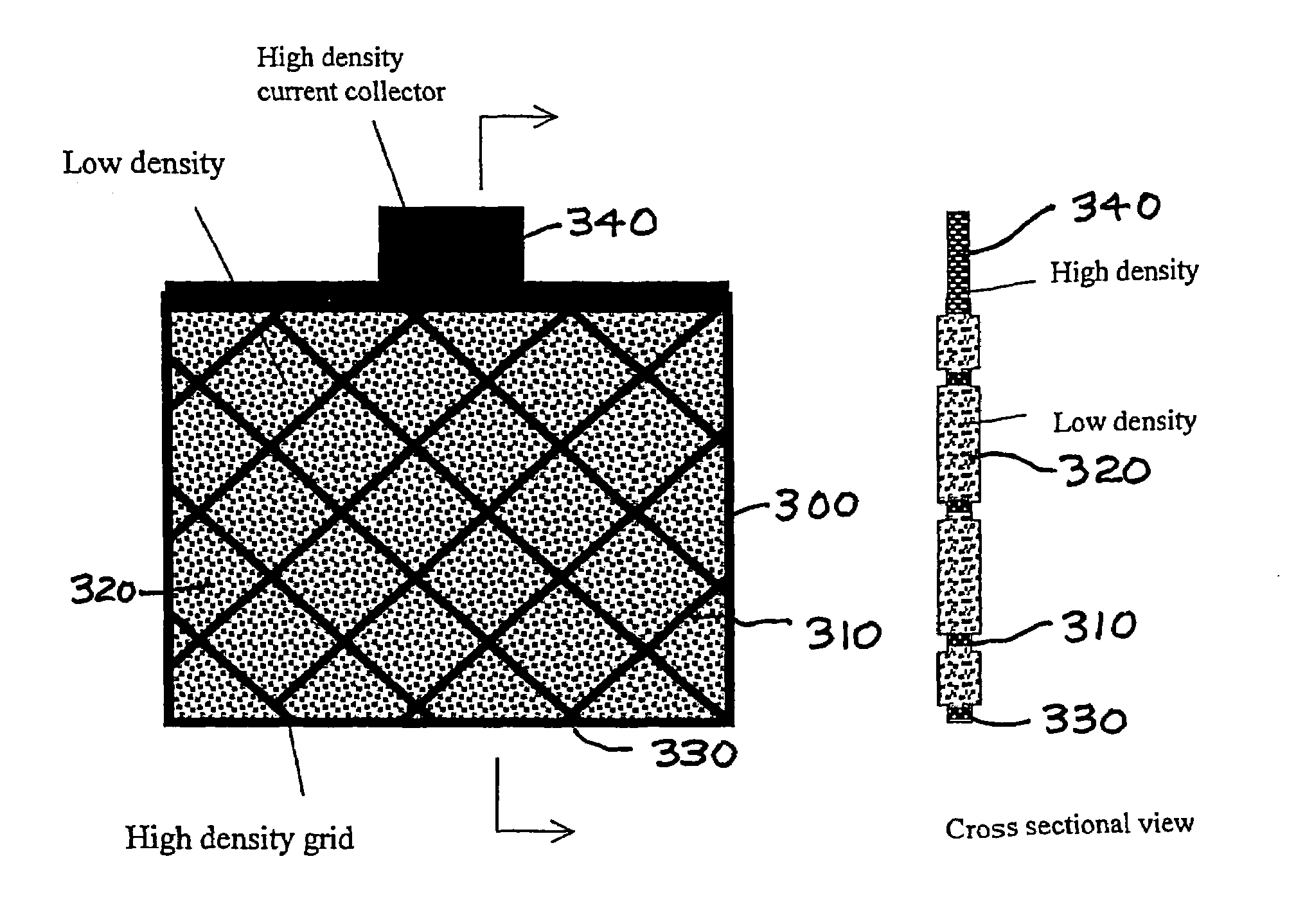
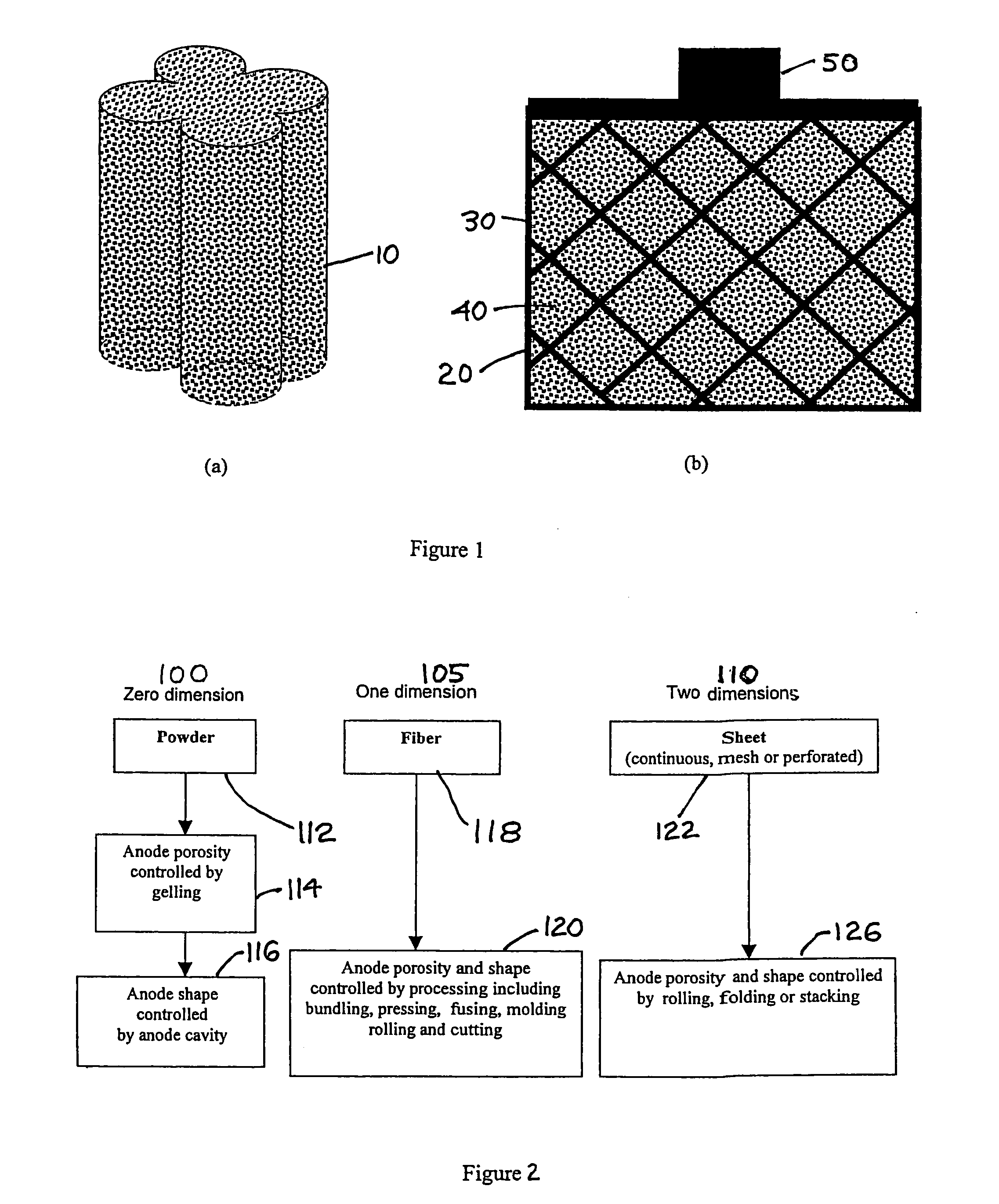
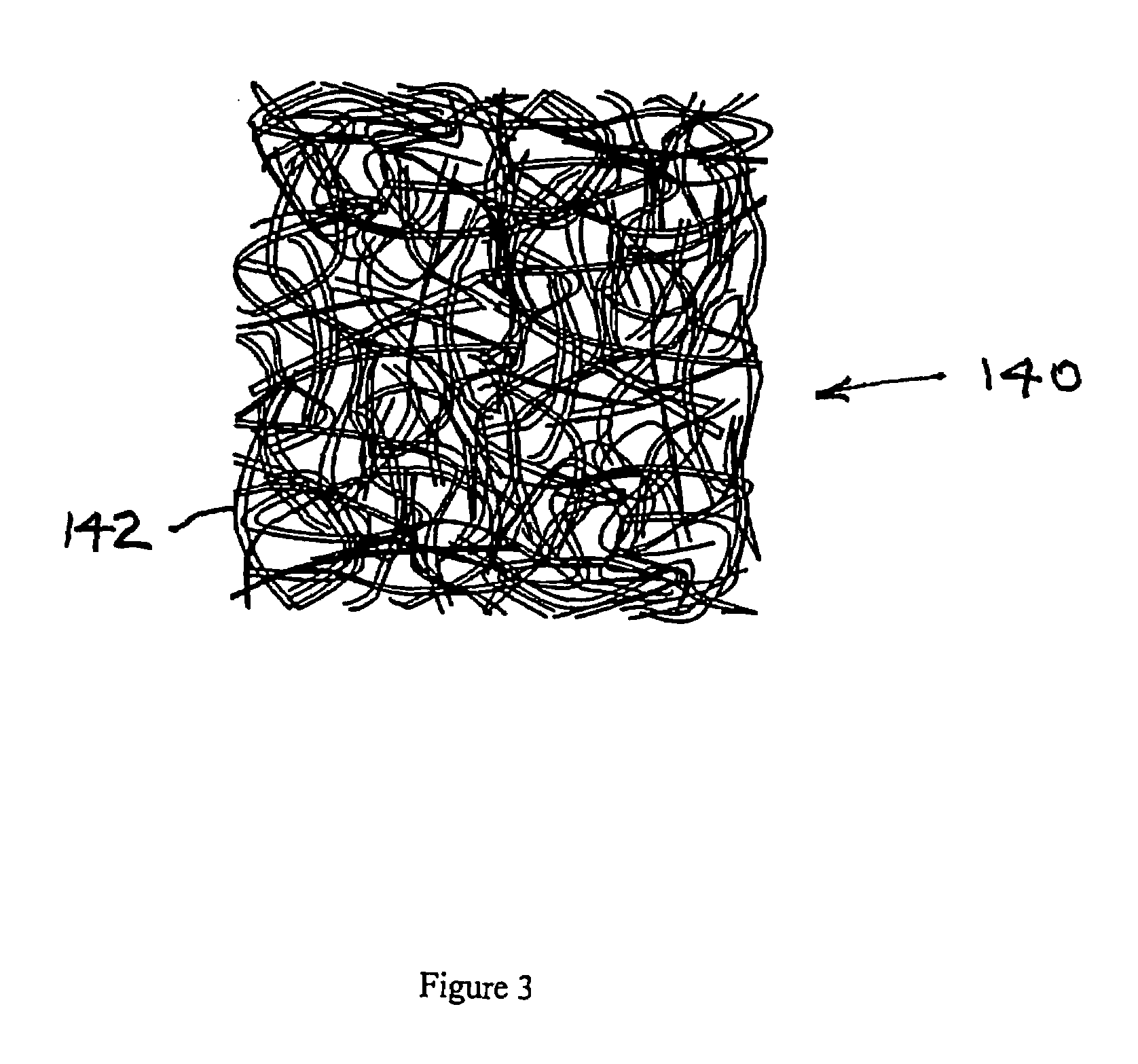
A solid porous zinc electrode for use in alkaline-zinc batteries, zinc-air batteries and fuel cells is provided which comprises specific zinc filaments, fibers, threads or strands compressed into a physically-stable wooly mass to form the electrode with a controlled geometrical shape and porosity distribution. Differential densification incorporates ribs, borders, grids or tabs for good structural integrity, mechanical strength, electrochemical behavior, and electrical conductivity. Pressing in a mold or rolling of a compressed sheet can also provide an anode with a large anode / cathode interface area and a complex geometry. The filaments of controlled dimension and composition are preferably made by spin forming from molten zinc alloys. Such anodes are not susceptible to breakage, have a long storage life and can be used in high rate discharge applications.
Owner:TECK METALS
Device for extending zinc-air battery life for intermittent use
InactiveUS20050019634A1SmallIncrease powerFuel and primary cellsFuel cell auxillariesAir volumeHearing aid battery
A device for extending zinc-air battery life for intermittent use with a battery chamber that allows air to flow to the batteries when needed, a battery chamber to completely seal off air flow to the batteries when the device is off, a tension device that enables stacking of zinc-air hearing aid batteries without cutting off air flow between the batteries, a battery chamber with minimal air volume.
Owner:LEGG LARRY K
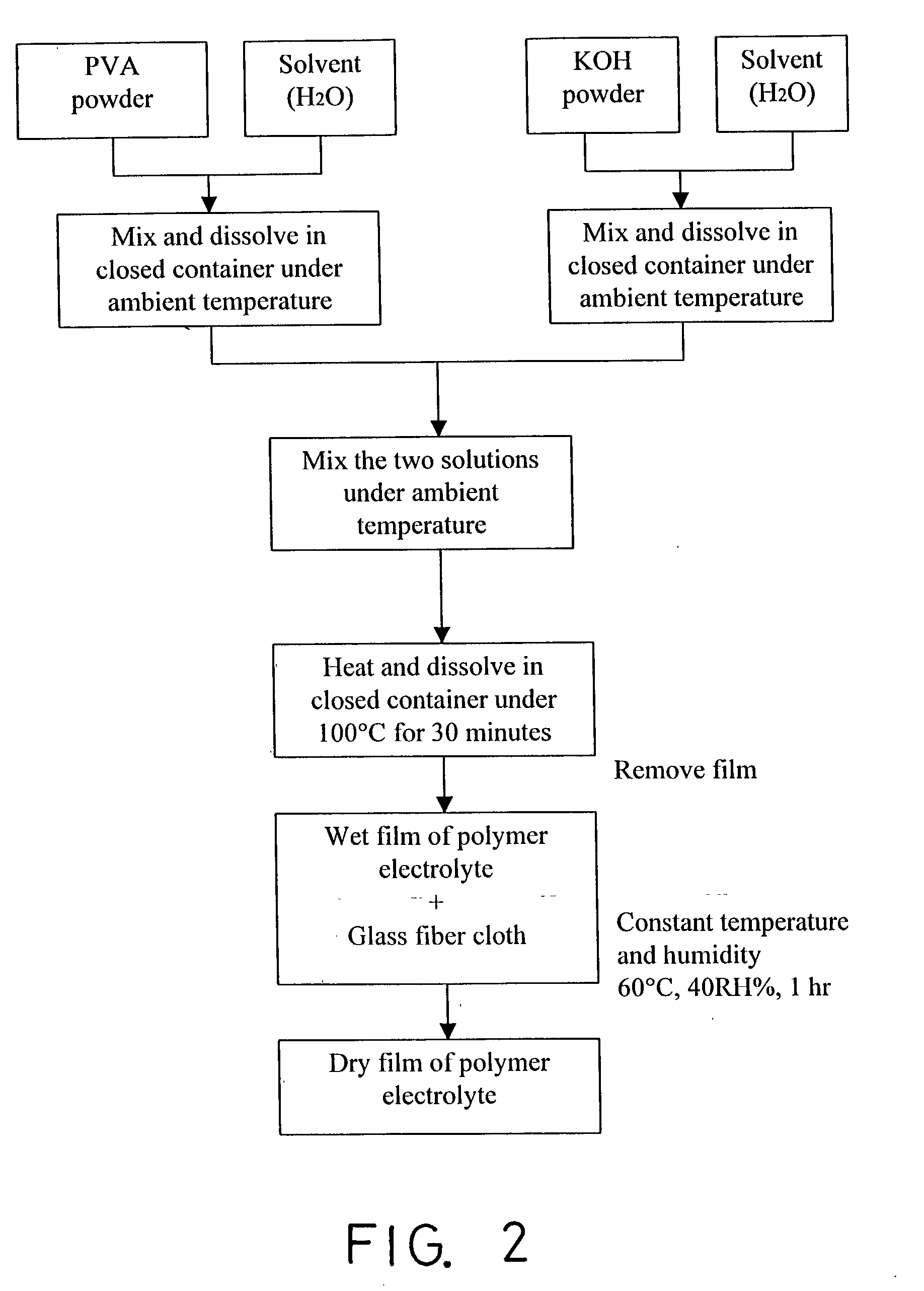
Method for preparing solid-state polymer zinc-air battery
InactiveUS20030228522A1Increase surface areaIncrease motivationFuel and primary cellsAlkaline accumulatorsZinc–air batteryAir cathode
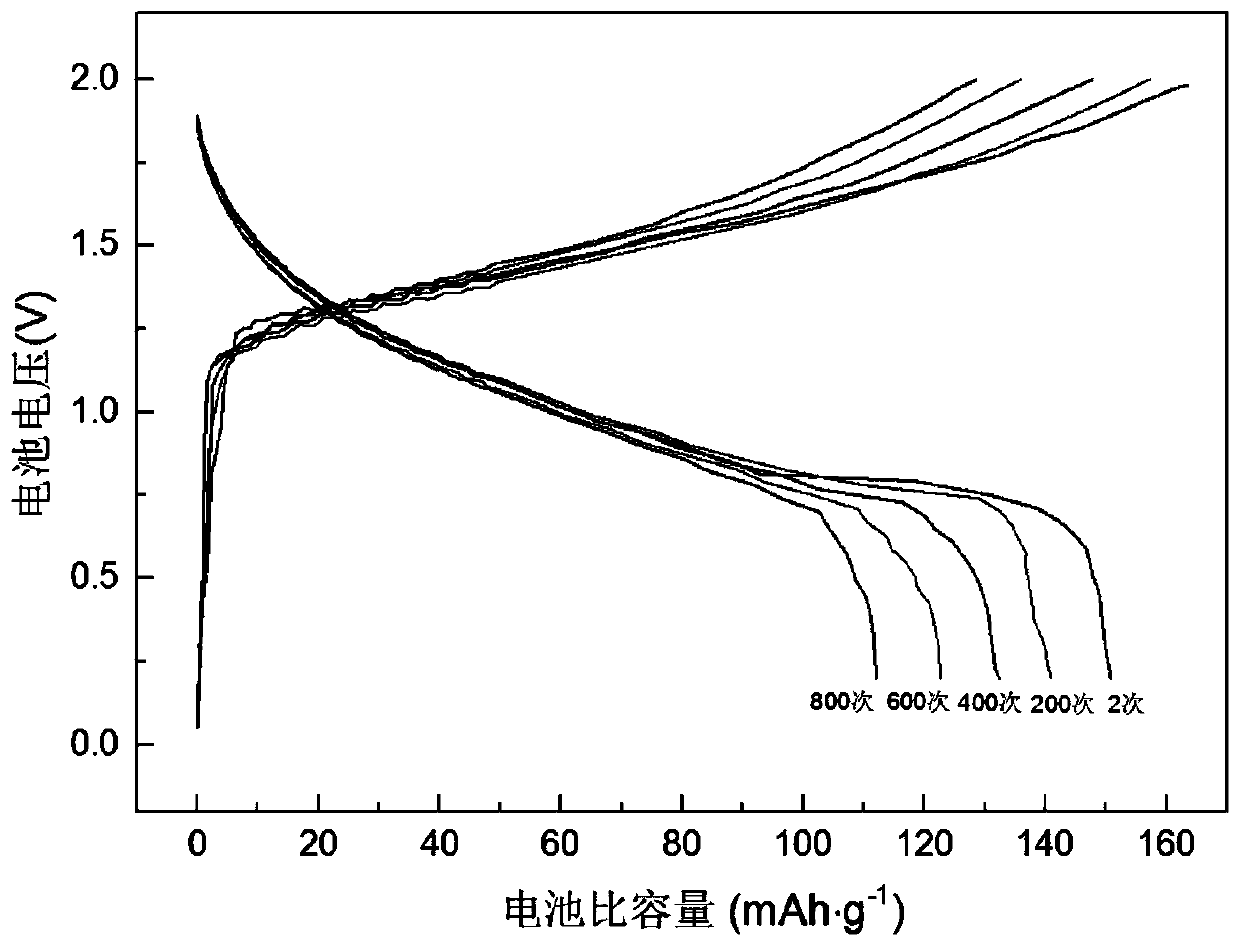
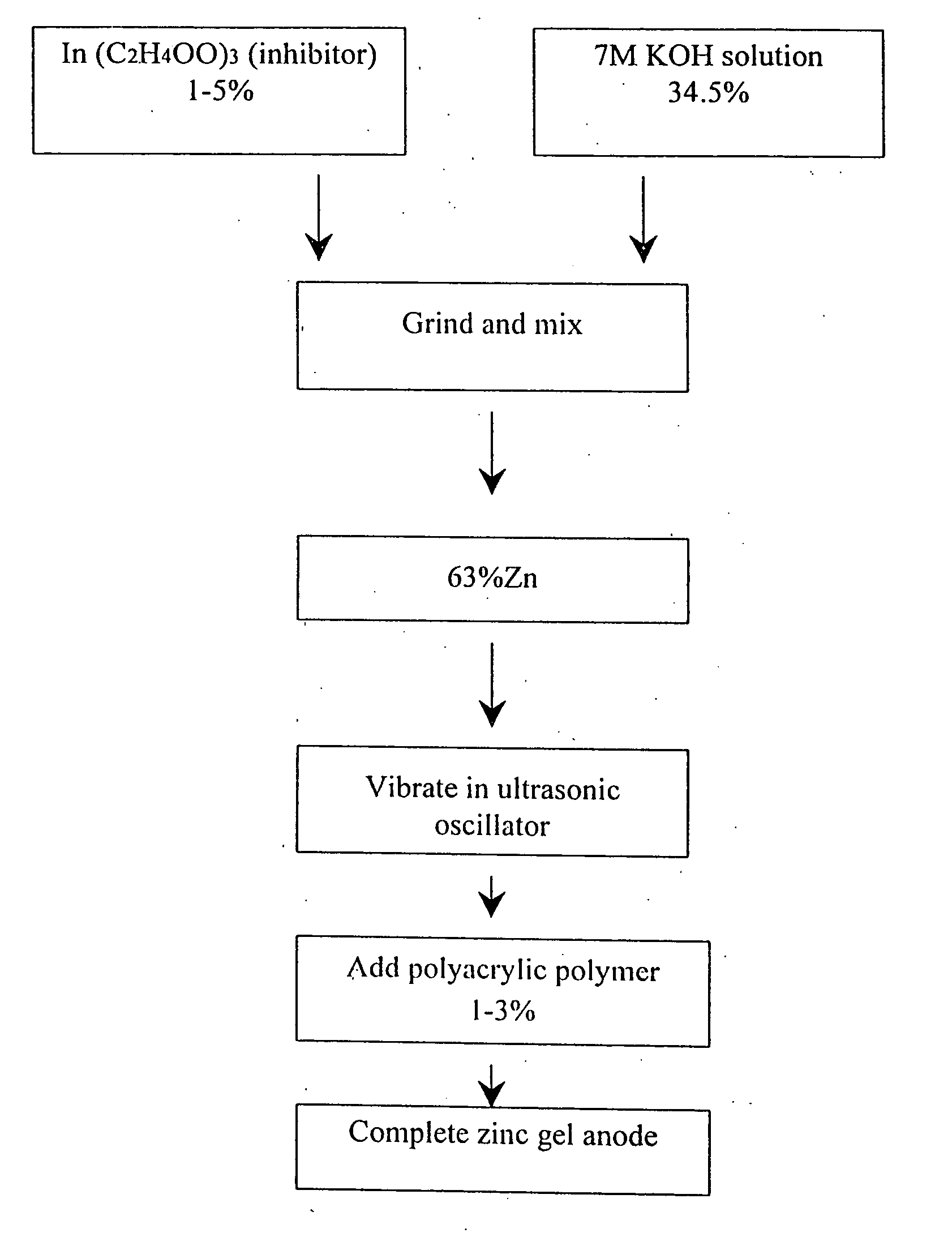
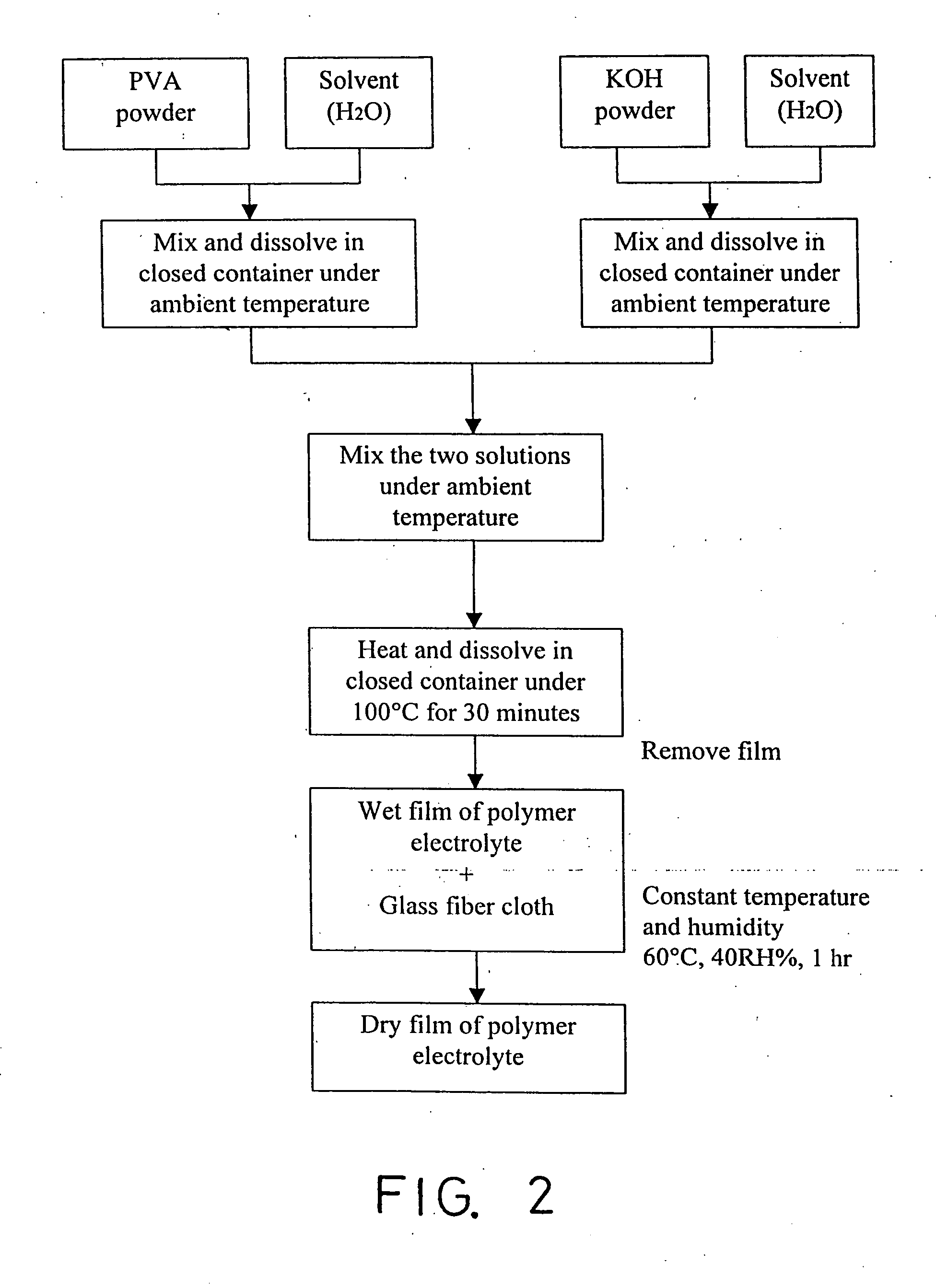
This invention relates to a method for fabricating solid-state alkaline polymer Zn-air battery, which consists of a zinc-gel anode, an air cathode electrode, and alkaline polymer electrolyte. The formulation of said zinc gel anode is similar to that of alkaline Zn-MnO2 battery. The zinc gel anode contains a mixture of electrolytic dendritic zinc powders, KOH electrolyte, gelling agent and small amount of additives. The air cathode electrode is made by carbon gas diffusion electrode, which comprises two layers, namely gas diffusion layer and active layer. The active layer on the electrolyte side uses a high surface area carbon for oxygen reduction reaction and potassium permanganate and MnO2 as catalysts for oxygen reduction. The diffusion layer on the air side has high PTFE content to prevent KOH electrolyte from weeping or climbing. Due to adequate amount of fresh air and oxygen supply, the air cathode electrode can run continuously. Theoretically, the polymer zinc-air battery is an accumulator if the cell has sufficient zinc powder and electrolyte, and the air cathode plays the role of energy transfer.
Owner:MING CHI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Zinc/air cell with improved anode
InactiveUS20050003271A1Eliminate disadvantagesSufficient structural integrityFuel and primary cellsAlkaline accumulatorsSolid massPolyvinyl alcohol
A method of forming an anode comprising zinc for a zinc / air cell. The method involves mixing zinc particles with binders including preferably polyvinylalcohol, surfactant and water to form a wet paste. The wet paste is compacted and molded into the near shape of the cell's anode cavity and then heated to evaporate water. A solid porous zinc mass is formed wherein the zinc particles are held bound within a network with microscopic void spaces between the zinc particles. The solid mass can be inserted into the cell's anode cavity and aqueous alkaline electrolyte, preferably comprising potassium hydroxide, then added. The solid mass absorbs the aqueous electrolyte and expands to fill the anode cavity to form the final fresh anode.
Owner:DURACELL U S OPERATIONS
Rechargeable metal-air redox flow battery combining electrochemical preparation
InactiveCN101714680AImprove power utilization efficiencyIncrease energy densityFuel and primary cellsOxygenZinc–air battery
The invention relates to a rechargeable metal-air redox flow battery compatible with electrochemical preparation. When the battery is charged, electric energy input makes metal ions in the electrolyte flowing through a negative electrode reduced and deposited into metal to prepare for discharge, and the electric energy also makes reductive raw materials in the electrolyte flowing through a positive electrode oxidized into a product required to be synthesized. When the battery is discharged, the positive electrode is introduced with air or oxygen, the air or the oxygen is reduced on the electrode, and the positive electrode and a deposition redox flow metal negative electrode form the metal-air redox flow battery to output electric energy. In each charge and discharge cycle, the accumulation and discharge of the metal-air redox flow battery are carried out, and simultaneously electrooxidation chemical production is carried out so as to achieve the effect that one portion of electric energy is consumed and two functions are realized. The redox flow battery combines two functions of rechargeable metal-air accumulation and electrochemical preparation, realizes the combination of electrosynthesis, a deposition redox flow battery and a rechargeable metal-air battery, achieves the effects of energy conservation and high efficiency, improves the utilization rate of the electric energy and has good application prospect.
Owner:NO 63971 TROOPS PLA
Rechargeable metal-air battery
InactiveUS20110195321A1Reduce contact resistanceImprove battery performanceFuel and primary cellsFuel and secondary cellsElectrical batteryEngineering
The present invention is intended to suppress the increase of contact resistance due to dimensional changes at the time of charge and discharge in a rechargeable metal-air battery, thereby improving battery performance and service life. The rechargeable metal-air battery of the present invention includes a negative electrode for storing and releasing metal ions; a positive electrode using oxygen as an active material; and an electrolyte membrane placed between the negative electrode and the positive electrode, and is characterized in that a flexible dimension-absorbing member is disposed on the negative electrode side, wherein the dimension-absorbing member is an elastic body formed of a substance which changes reversibly.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Preparation method for Ni-Co/carbon nanotube aerogel catalyst of zinc-air battery
ActiveCN105609790AWide variety of sourcesImprove securityCell electrodesPtru catalystZinc–air battery
The invention discloses a preparation method for a Ni-Co / carbon nanotube aerogel catalyst of a zinc-air battery, which is used for the field of the zinc-air battery. In the catalyst, the nanometer Ni-Co / carbon nanotube aerogel dual-functional catalyst is successfully prepared by taking sodium alginate, cobalt chloride hexahydrate, nickel chloride hexahydrate and carbon nanotubes as raw materials. The dual-functional catalyst is endowed with excellent oxygen evolution reaction (OER) and oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalytic performance, the initial potential of OER is early, the current density of the dual-functional catalyst is large, the initial potential of ORR is early, the limiting current density is large, and the stability is high; and moreover, the charging and discharging voltage difference of the zinc-air battery before and after long circulation test is small, and the energy efficiency after long circulation is high. The preparation method has the advantages of simplicity, rapidness in operation, greenness and environment friendliness, the source of sodium alginate is rich, and the obtained dual-functional catalyst is excellent in performance and is the zinc-air battery catalyst having a very good prospect.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Composite nanofibre diaphragm with thermal pore-closing function, preparation method and energy storage device
ActiveCN104485437ALow costEasy to produceHybrid capacitor separatorsCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersPolyesterPolymer
The invention discloses a composite nanofibre diaphragm with a thermal pore-closing function, a preparation method and an energy storage device, and relates to lithium ion batteries, lithium-sulphur batteries, supercapacitors, lead-acid batteries, alkaline batteries, zinc air batteries, sodium-ion batteries and fibre diaphragms thereof. The composite nanofibre diaphragm with the thermal pore-closing function is of a non-woven fabric structure, and formed by mutually crosslinking and compounding fibrillated cellulose nanofibres and at least one low-melting-point polymer nanofibres; the low-melting-point polymer nanofibres are nanofibres containing polyolefin and polyesters. The thickness of the composite nanofibre diaphragm with the thermal pore-closing function can be 10-80 mu m, the pore-closing temperature is 130-170 DEG C, the fibre film does not shrink after pore-closing, and the thermal shrinkage rate in case of heating for 30min at high temperature of 200 DEG C is less than 2%. The composite nanofibre diaphragm is capable of realizing the thermal pore-closing function, thus avoiding the direct contact of the positive electrode and the negative electrode of a battery due to the action of thermal inertia, and remarkably improving the safety of the energy storage devices above-mentioned.
Owner:宁波柔创纳米科技有限公司
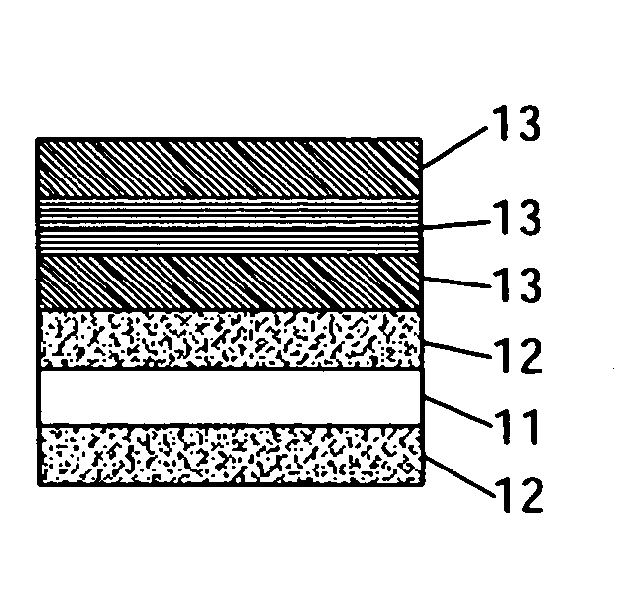
Air cathode having multilayer structure and manufacture method thereof
InactiveUS20080044640A1Reduce processing timeIncrease discharge currentFuel and primary cellsElectrolytic capacitorsSlurryEngineering
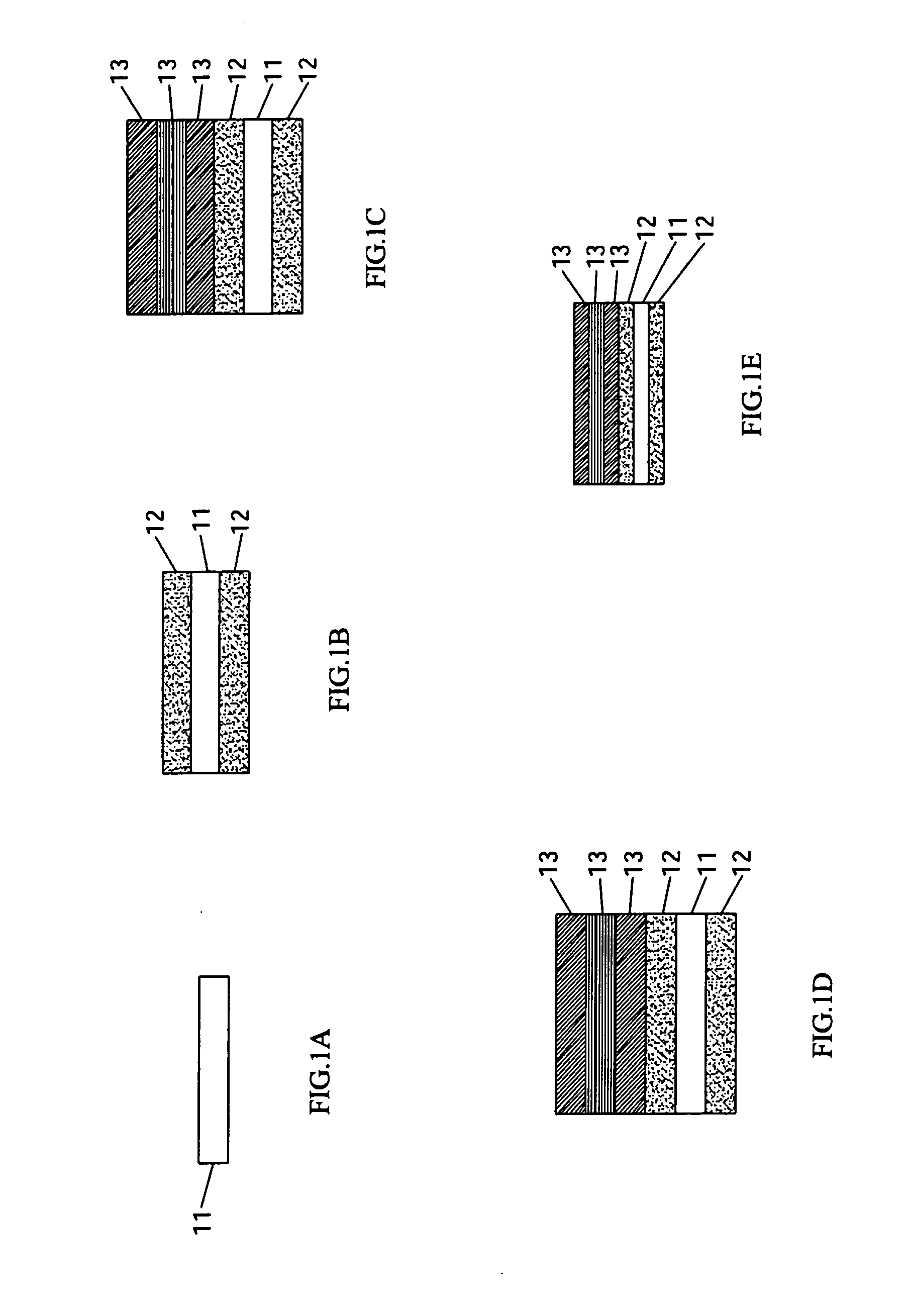
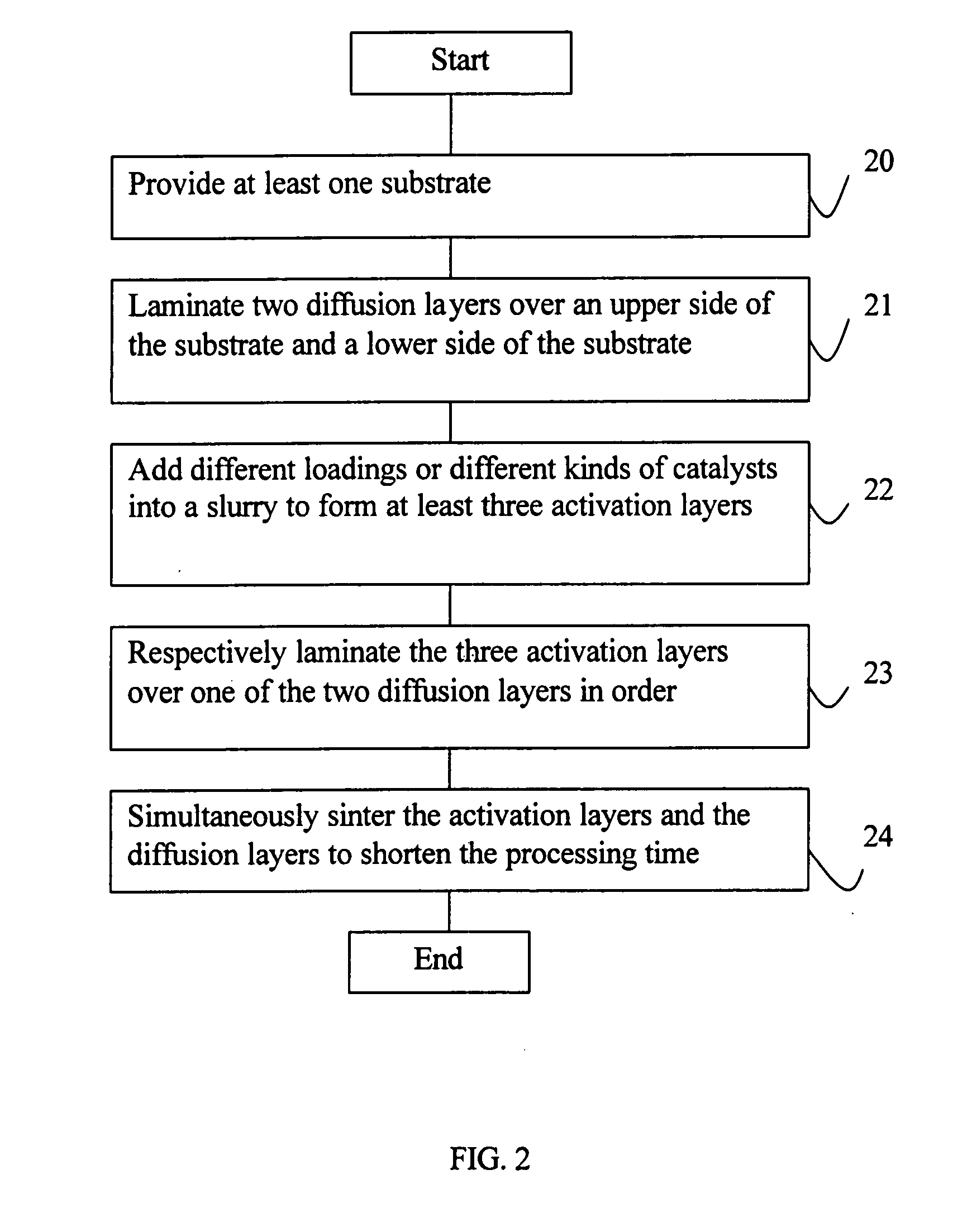
An air cathode having a multilayer structure is composed of at least one substrate, two diffusion layers and three activation layers. The two diffusion layers are laminated over an upper side of the substrate and a lower side of the substrate. The three activation layers are respectively laminated over one of the two diffusion layers in order. Different loadings or different kinds of catalysts are added into a slurry to form the activation layers, and the activation layers and the diffusion layers are made through simultaneous sintering, thereby shortening the processing time. When the air cathode is used as the cathode of the Zinc-Air battery, the electrolyte inside the Zinc-Air battery will not be influenced by the outside air, and the problem of maintaining the water content of the zinc anode of the Zinc-Air battery can be efficiently overcome.
Owner:HIGH TECH BATTERY INC
Gas diffusion electrodes for batteries such as metal-air batteries
InactiveUS20130089795A1Fuel and primary cellsFuel and secondary cellsReactive siteLithium–air battery
The present invention generally relates to batteries and, in particular, to electrodes for use in batteries such as non-aqueous metal-air batteries, for example, lithium-air batteries, as well as in other electrochemical devices. Such devices may exhibit improved performance characteristics (e.g. power, cycle life, capacity, etc.). One aspect of the present invention is generally directed to electrodes for use in such devices containing one or more pores or channels for transport of gas and / or electrolyte therein, e.g., forming an open porous network. In certain embodiments, the electrolyte may be a gel or a polymer. In some embodiments, there may be network of such channels or pores within the electrode such that no active site within the electrode is greater than about 50 micrometers distant from a gas channel. In some embodiments, such systems may be created using electrodes containing gel or electrolyte polymers, and / or by forming electrodes having different wettabilities such that certain regions preferentially attract the electrolyte compared to other regions, thereby causing self-organization of the electrolyte within the electrode. Other aspects of the invention are generally directed to methods of making such batteries or electrochemical devices, methods of using such batteries or electrochemical devices, kits involving such batteries or electrochemical devices, or the like.
Owner:LIOX POWER
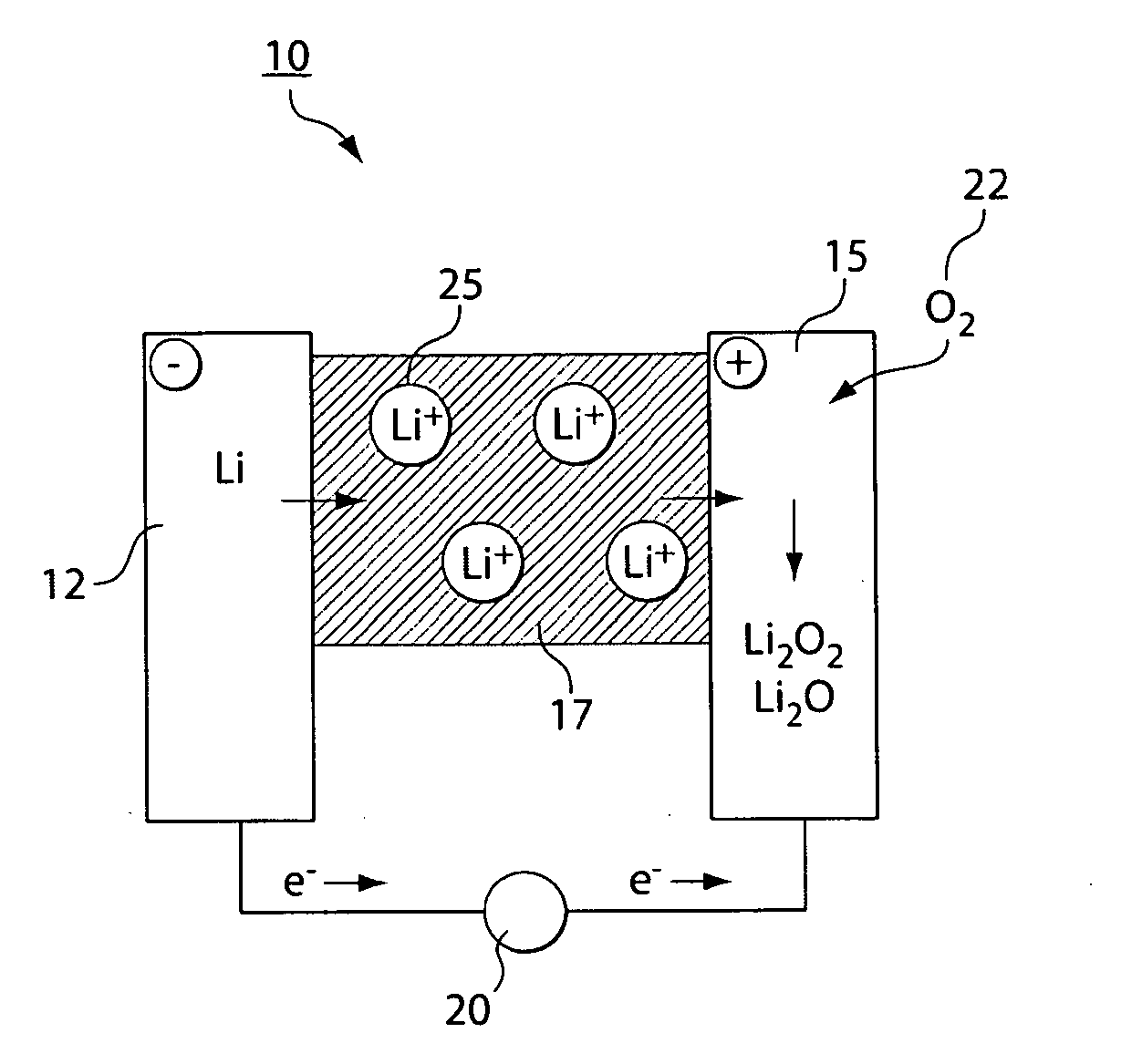
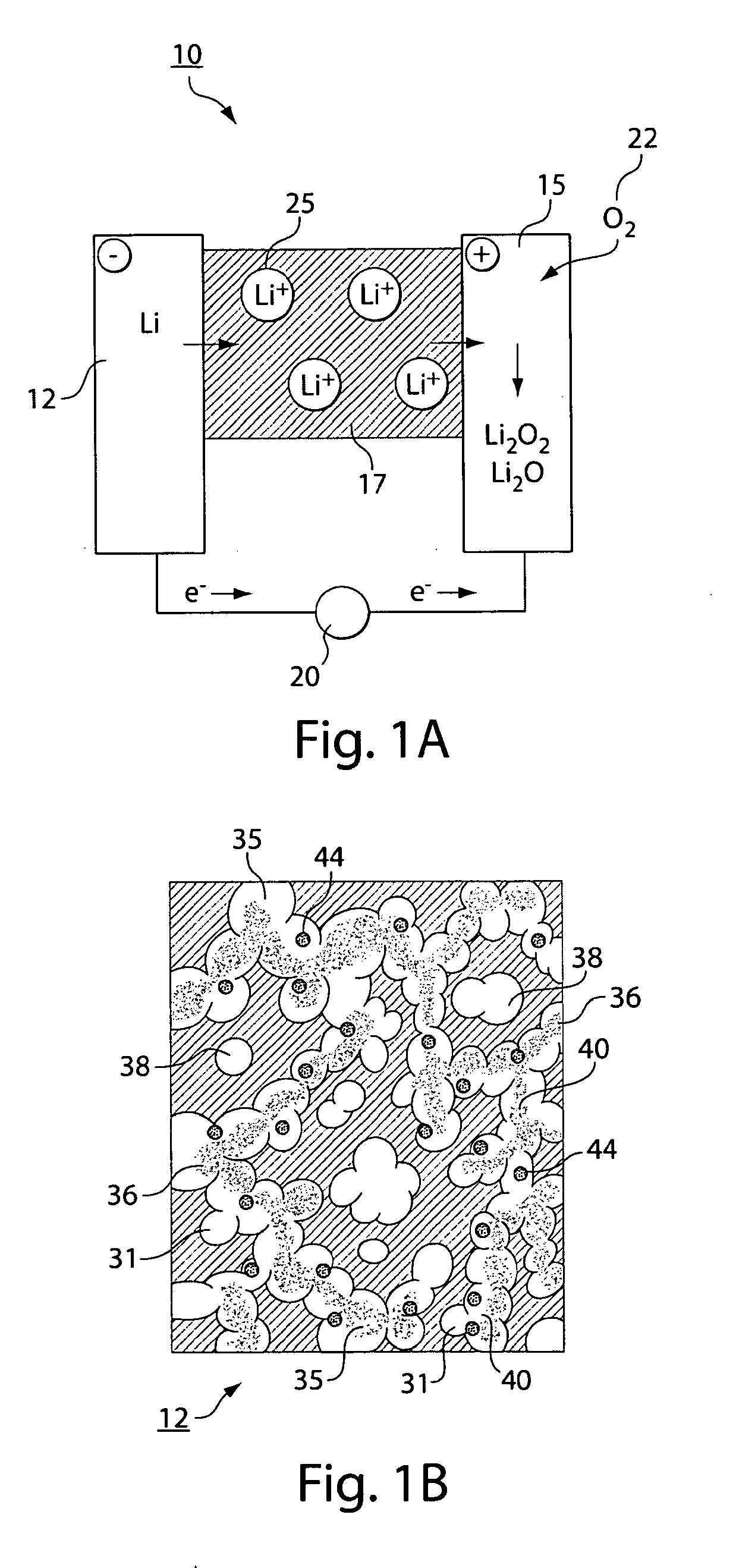
Lithium/air battery
InactiveCN102157763AProtection from erosionReduce corrosionFuel and primary cellsCell electrodesMetallic lithiumElectrochemical window
The invention discloses a lithium / air battery which belongs to the chemical power source field and is designed for solving the technical problem anode metallic lithium corrosion, high possibility of power failure and bad cycle performance of the existing lithium air battery. A shell is divided into an anode room, a buffer room and a cathode room by a solid inorganic electrolyte membrane and a diaphragm. The lithium / air battery uses a hydrophobic ionic liquid as an anode electrolyte, which has the advantages of non-volatile, high conductivity, wide electrochemical window, low melting point and moderate viscosity, and can prevent the metallic lithium from being corroded by water and oxygen. The cathode uses a water base-weak acid-buffer solution with the Ph of not less than 4 and not more than 5 as the electrolyte; compared with a neutral or alkaline electrolyte, the water base-weak acid-buffer solution ensures that the average discharge voltage (0.1-0.2V) can be improved, a discharge plateau can be prolonged, and the corrosion of the strongly alkaline electrolyte to the solid inorganic electrolyte membrane is reduced; and a cathode discharge product is a water-soluble LiOH which cannot deposit on the surface or in the duct of the cathode to cause power failure, and is good in cycle performance.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Preparation method of zinc electrode used for zinc-air battery
InactiveCN102509774AExtended service lifeExtended shelf lifeElectrode manufacturing processesPowder mixtureMass ratio
The invention discloses a preparation method of a zinc electrode of a zinc-air battery. The zinc electrode is obtained by carrying out dry pressing and vacuum drying treatment on active zinc powder used for an alkaline battery; the preparation method specifically comprises the following steps of: 1) uniformly mixing zinc powder and a corrosion inhibitor, and a cohesive material according to the mass ratio of the proportion at 100:(0.5-1.0):(2-10)and dispersing so as to form a zinc powder mixture; 2) pouring the zinc powder mixture into a mould paved with an electrical conduction affluxion body, and preparing the zinc electrode with a mould shape under the pressure of 5-15 MPa in a depressed manner; and 3) putting the zinc electrode of the mould shape into a vacuum drying oven, heating for 30-240 minutes at the temperature of 50-200 DEG C, solidifying and bonding the cohesive material in the zinc electrode to obtain the required zinc electrode. The zinc-air battery using the zinc battery can be stored and the problems such as dehydration moisture absorption, leakage and electrolyte carbonation and the like can not occur, and the service life and storage period of the battery are greatly prolonged.
Owner:BEIJING CHANGLI UNION ENERGY TECH CO
Dry charge type zinc air cell
InactiveCN1617383ASolve the technical problems of self-dischargeImprove performanceFuel and primary cellsZinc–air batteryZinc
This invention relates to a dry charge Zn air battery including an electrolyte solution and an air diffusion electrode as the positive and a Zn electrode as the negative formed by dry-pressing active Zn powder at one run, the battery shell has an injection inlet for injecting electrolyte solution set at outside of the shell to be injected when using, the porous Zn electrode is formed by mixing inhibitor and Zn powder in the quality proportion of 1-5:100, then to mix the pore-former and mixture in the quality ratio of 1-8:100 to be dry-pressed to Zn electrode under 10-20Mpa and heated for 5-40min under 80-300deg.C
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
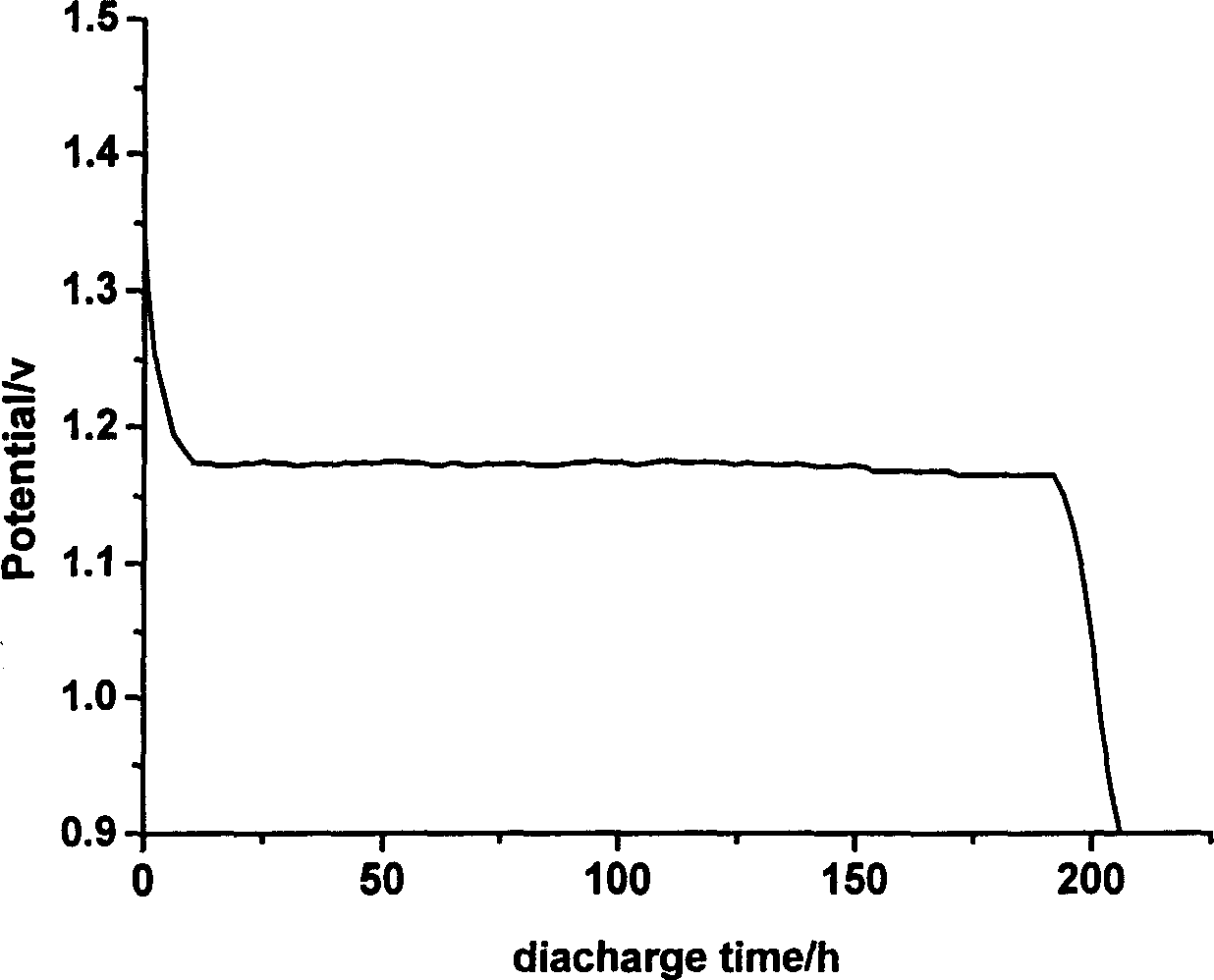
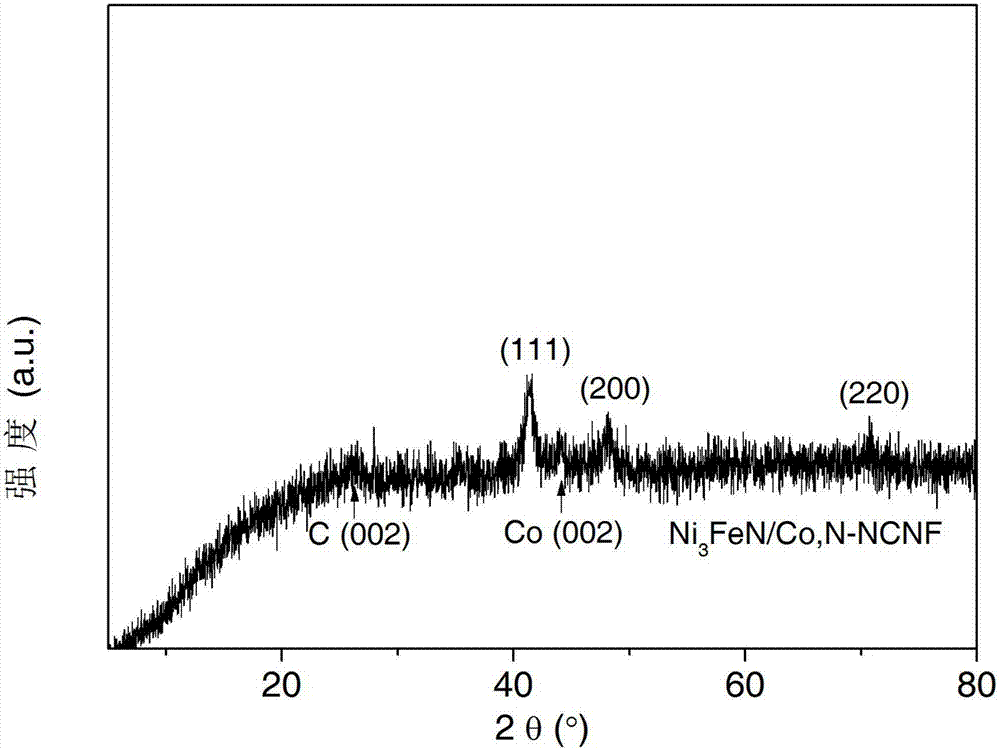
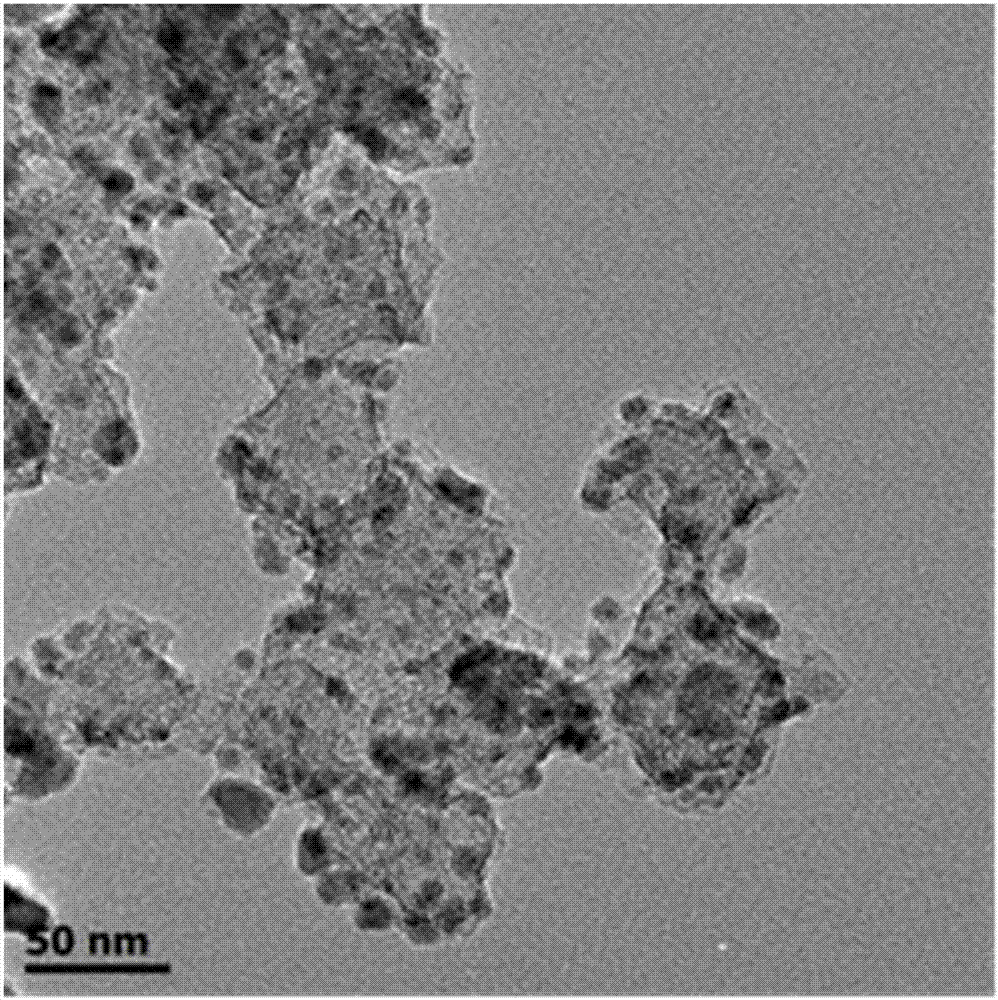
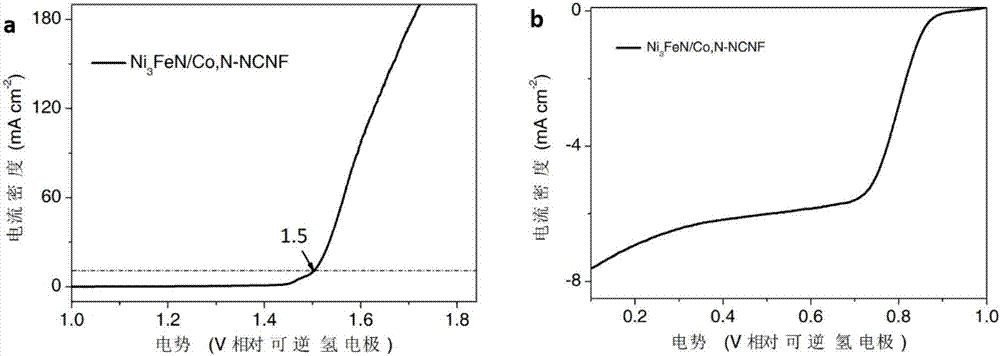
Cobalt/nitrogen-codoped nitrogen-carbon-material-carrier-carried nano nickel iron nitride composite material, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a cobalt / nitrogen-codoped nitrogen-carbon-material-carrier-carried nano nickel iron nitride composite material. The composite material uses a cobalt / nitrogen-codoped nitrogen carbon material as the carrier, and iron nickel nitride nanoparticles are carried in situ on the surface of the cobalt / nitrogen-codoped carbon material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: protecting a zeolite imidazate framework structure material precursor by using silicon dioxide to obtain the high-dispersity carbon-base nanoparticle material, and growing nickel iron hydrotalcite in situ on the carbon material, and calcining to obtain the cobalt / nitrogen-codoped nitrogen-carbon-material-carrier-carried nano nickel iron nitride composite material. The cobalt / nitrogen-codoped nitrogen-carbon-material-carrier-carried nano nickel iron nitride composite material has excellent activity in catalyzing oxygen redox reaction, and can be used as a high-efficiency zinc-air battery negative pole material.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cobalt-nitrogen co-doped carbon nanotube catalyst, preparing method and application
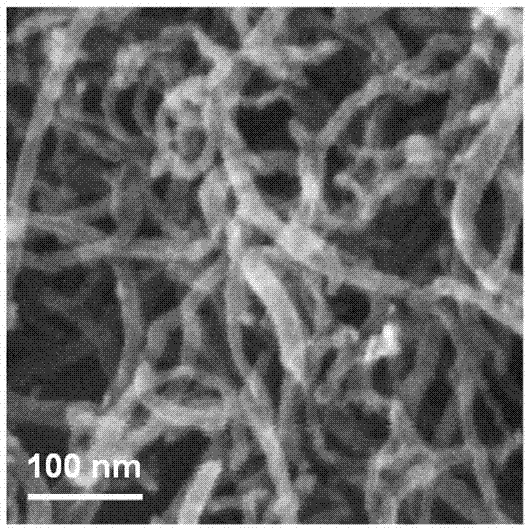
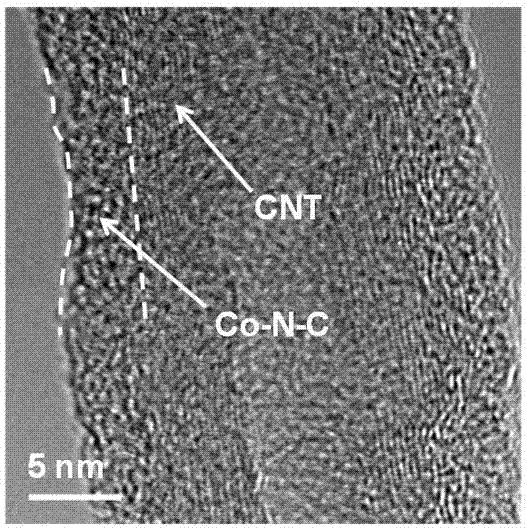
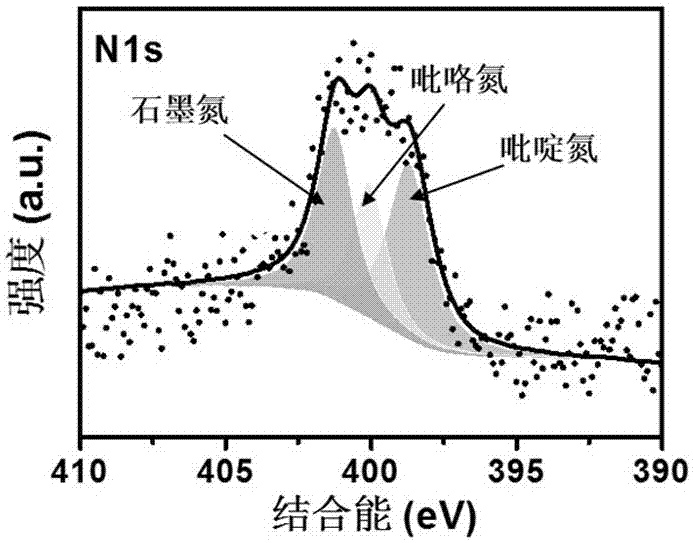
InactiveCN107093748AHigh degree of graphitizationIntegrity guaranteedMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesCarbon nanotubePotassium hydroxide
The invention discloses a cobalt-nitrogen co-doped carbon nanotube catalyst, a preparing method and application. Dopamine on carbon nanotubes are automatically polymerized and forms coordination bonds with cobalt ions, and the product is decomposed at high temperature to obtain the cobalt-nitrogen co-doped carbon nanotube catalyst with the carbon nanotubes as a core and an amorphous carbon layer as a shell structure. The amorphous carbon shell formed by polydopamine derivatization has rich structure defects, which is beneficial for forming cobalt-nitrogen / carbon active sites; as the carbon nanotubes are used as the core, the catalyst is excellent in conductivity and corrosion resistance. The two parts are used for achieving different functions, and efficient electrocatalytic activity is provided for the catalyst. In 1M potassium hydroxide solution, the half-wave potential of the catalyst is about 0.91 V, the content of hydrogen peroxide is smaller than 7%, and the stability is excellent. When the cobalt-nitrogen co-doped carbon nanotube catalyst is applied to a primary zinc-air battery, discharging voltage and currents and power density are remarkably improved, and the stability is good.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Zinc air battery with acid electrolyte
InactiveUS7582385B2Reduce formationBig absorptionFuel and primary cellsFuel and secondary cellsZinc ionZinc–air battery
A zinc air battery, and preferably a secondary zinc air battery has an acid electrolyte in which the anionic form of an acid forms a complex with a zinc ion, and wherein the acid in the electrolyte reduces dendrite formation.
Owner:APPLIED INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL
Positive electrode for zinc-air battery and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN1738085AChange structureChange granularityFuel and primary cellsCell electrodesElectrolysisEngineering
The invention relates to a positive electrode of zinc-air battery and its manufacturing method. Said positive electrode comprises a catalytic layer (2) mixed by polytetrafluoroethylene emulsion and the mixture which uses industrial alcohol to infiltrate carrier, conductor, and catalytic agent; a flow collector (3) and a waterproof layer (1), wherein, said catalytic agent is electrolytic manganese dioxide material. Since the conductor selects expansible graphite and the flow collector (3) selects nickel-plated iron net, the surface of material is increased more than 400 % to improve the ability of absorbing oxygen of electrode, and the conductivity of material is increased 40 % to improve the discharging current density and reduce the cost. The electrolytic manganese dioxide is processed into manganese dioxide powder, to change the crystal phase structure and its particle, so the manufacturing process is simplified.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 18 RES INST
Zinc air battery with acid electrolyte
InactiveUS20050208386A1Reduce formationBig absorptionFuel and primary cellsFuel and secondary cellsZinc ionZinc–air battery
A zinc air battery, and preferably a secondary zinc air battery has an acid electrolyte in which the anionic form of an acid forms a complex with a zinc ion, and wherein the acid in the electrolyte reduces dendrite formation.
Owner:APPLIED INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL
Zinc-air cell electro-catalyst and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN1529374AImprove electrocatalytic activityGood chemical stabilityFuel and primary cellsCell electrodesAlkaline earth metalRare earth
The invention relates to electrocatalyst with general expression A1-xBxC1-yDyO3 of zinc air cell, where A is rare earth; B is earthy element; C and D denote different or same transition-metal element; X more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to1, y more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1. Structure of the said electrocatalyst is perovskite typed structure of crystalline state. In the invention, electrocatalyst of metal composite oxides possessing parasite typed structure of crystalline state is synthesized by using sol gel method. Obtained electrocatalyst possessing high electrocatalysis activity for oxygenic deoxidation and oxygenic liberation, good chemical stability and long life is a dual functional electrocatalysis.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
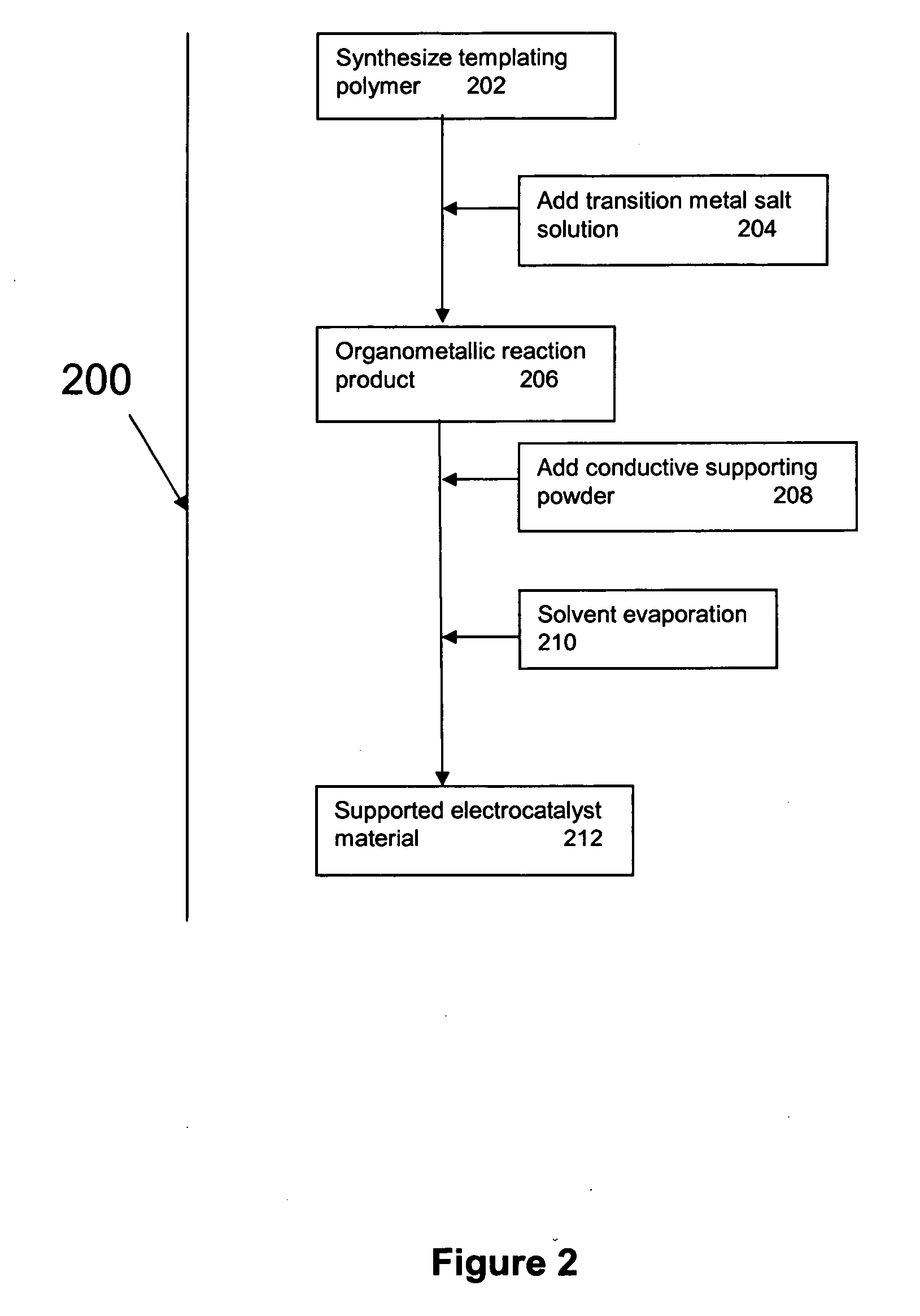
Supported metal electrocatalyst materials and the method for forming the same
InactiveUS20060264325A1High catalytic activityFuel and primary cellsHybrid capacitor electrodesOxygenHydrogen sensor
The present invention discloses a novel process for the fabrication of a class of conductive supported electrocatalysts based on transition metals. The electrocatalysts are formed by pyrolysis of an organometallic polymer complex precursor which is the reaction product of transition metal salts and a templating polymer. The electrocatalysts has enhanced catalytic activity, and are useful in the preparation of supercapacitor and fuel cell electrodes, auto-thermal fuel reformer catalysts, oxygen and hydrogen sensors, zinc-air battery electrode and oxidation catalysts.
Owner:ENERAGE INC
Rechargeable metal hydride air battery
InactiveCN101752628AIncrease usageExtend your lifeFuel and primary cellsElectrode manufacturing processesElectrical batteryElectric vehicle
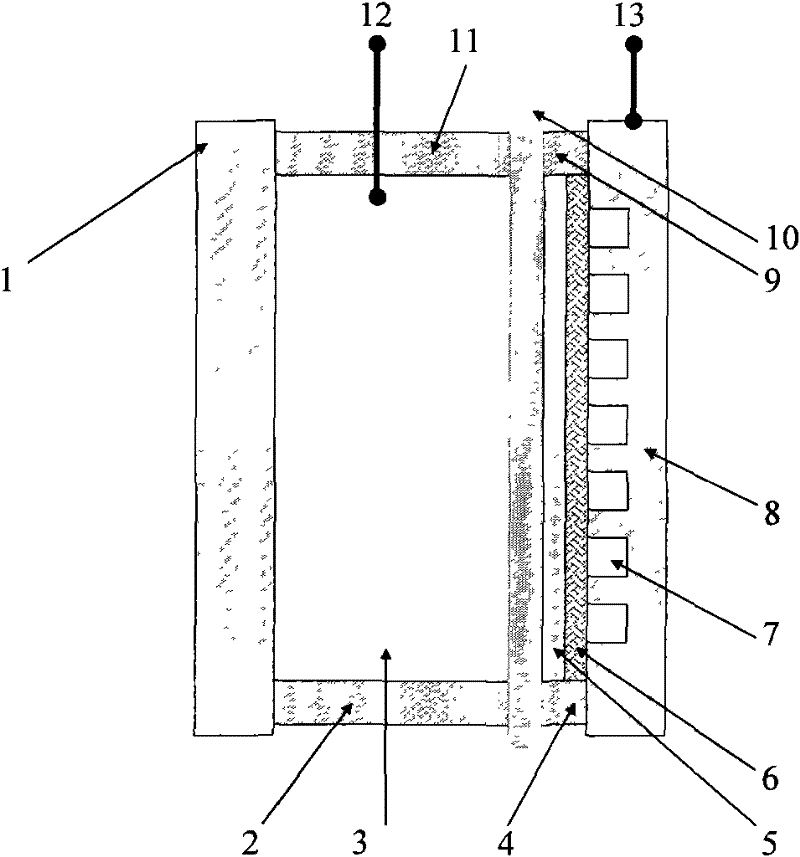
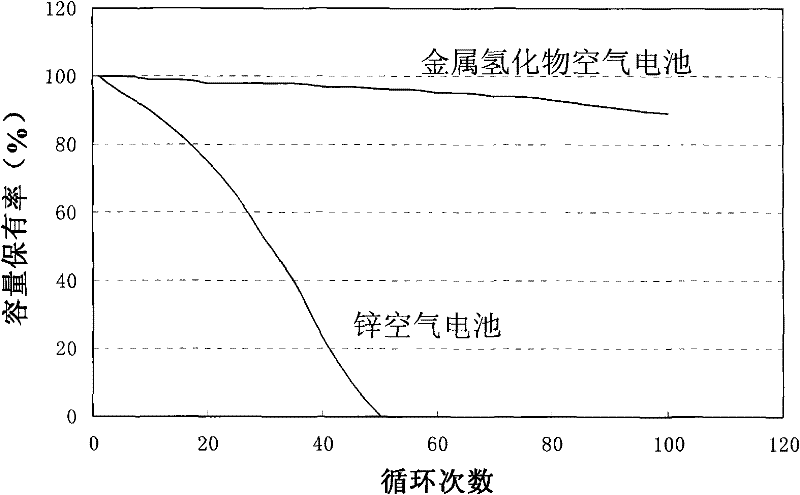
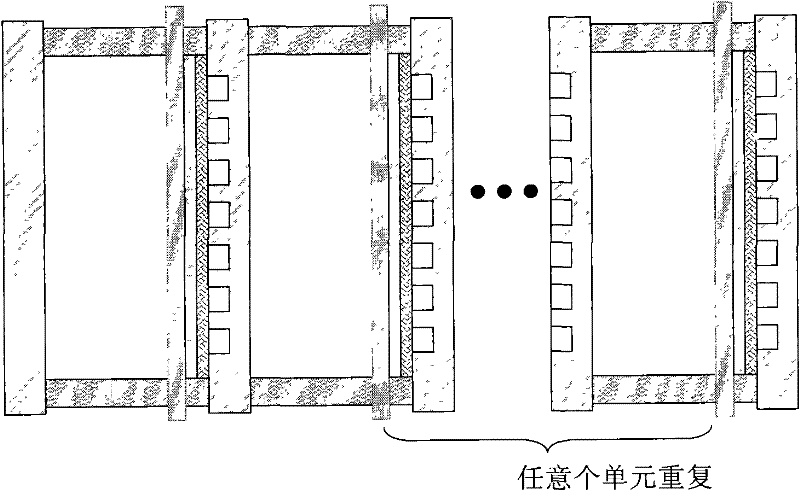
The invention relates to an air battery and aims at providing a rechargeable metal hydride air battery. In the batter, an anion-exchange membrane or polypropylene non-woven fabric can be taken as the diaphragm to separate a cathode and an anode; the transverse structure sequentially comprises a cathode current collection body, a porous cathode, a diaphragm, a carrier and an anode current collection body that are sealed by a sealing ring; the carrier is coated with an anode catalyst, and the anode current collection body is provided with an air channel; an anode terminal of the air battery is led out by the anode current collection body, and a cathode terminal thereof is led out by the cathode current collection body; and the porous cathode is loaded with hydrogen-stored metal as cathode material, and electrolyte solution is absorbed in the porous cathode. The invention can avoid the short circuit of the battery and the deformation of a zinc electrode after recharging for a plurality of times caused by the formation of dendritic crystal as zinc serves as the energy storage medium in a zinc air battery, so as to increase the use times of the air battery and prolong the service life of the air battery. In the invention, single batteries can be connected with each other in series for producing the high-power air battery, so as to meet the requirement as the power supply of an electric vehicle, thereby reducing the air pollution.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Flexible water system zinc ion battery
ActiveCN110190344AAvoid safety hazardsNot easy to decomposeFinal product manufactureSecondary cellsElectrical batteryDynamic balance
The invention discloses a flexible water system zinc ion battery. The flexible water system zinc ion battery comprises a cathode layer, an anode layer, a current collection layer, a diaphragm and an aqueous electrolyte. The current collection layer comprises a breathable layer and a substrate layer, the substrate layer is provided with at least one opening holes. The perforated structure of the breathable layer and the substrate layer solves the problems of gas generation and electrolyte drying in the battery circulation process, so that the internal and external gaseous water of the battery reaches the states of circulation exchange and dynamic balance, and the circulation performance of the battery is greatly improved; and the assembled flexible water system zinc ion battery has the advantages of light weight, thin thickness, low cost, environmental friendliness, high safety, good rate capability, high power density and the like, and the excellent bending performance and flexibilityof the flexible water system zinc ion battery can meet the bending requirements of different angles, so that the flexible water system zinc ion battery is suitable for large-scale application and industrial production in the field of wearable electronic equipment.
Owner:SHENZHEN CITY THROUGH SCI & TECH OF NEW ENERGY CO LTD
Method for preparing solid-state polymer zinc-air battery
InactiveUS20070045106A1Increase surface areaHigh utilization percentFuel and primary cellsElectrodesZinc–air batteryAir cathode
This invention relates to a method for fabricating solid-state alkaline polymer Zn-air battery, which consists of a zinc-gel anode, an air cathode electrode, and alkaline polymer electrolyte. The formulation of said zinc gel anode is similar to that of alkaline Zn—MnO2 battery. The zinc gel anode contains a mixture of electrolytic dendritic zinc powders, KOH electrolyte, gelling agent and small amount of additives. The air cathode electrode is made by carbon gas diffusion electrode, which comprises two layers, namely gas diffusion layer and active layer. The active layer on the electrolyte side uses a high surface area carbon for oxygen reduction reaction and potassium permanganate and MnO2 as catalysts for oxygen reduction. The diffusion layer on the air side has high PTFE content to prevent KOH electrolyte from weeping or climbing. Due to adequate amount of fresh air and oxygen supply, the air cathode electrode can run continuously. Theoretically, the polymer zinc-air battery is an accumulator if the cell has sufficient zinc powder and electrolyte, and the air cathode plays the role of energy transfer.
Owner:MING CHI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
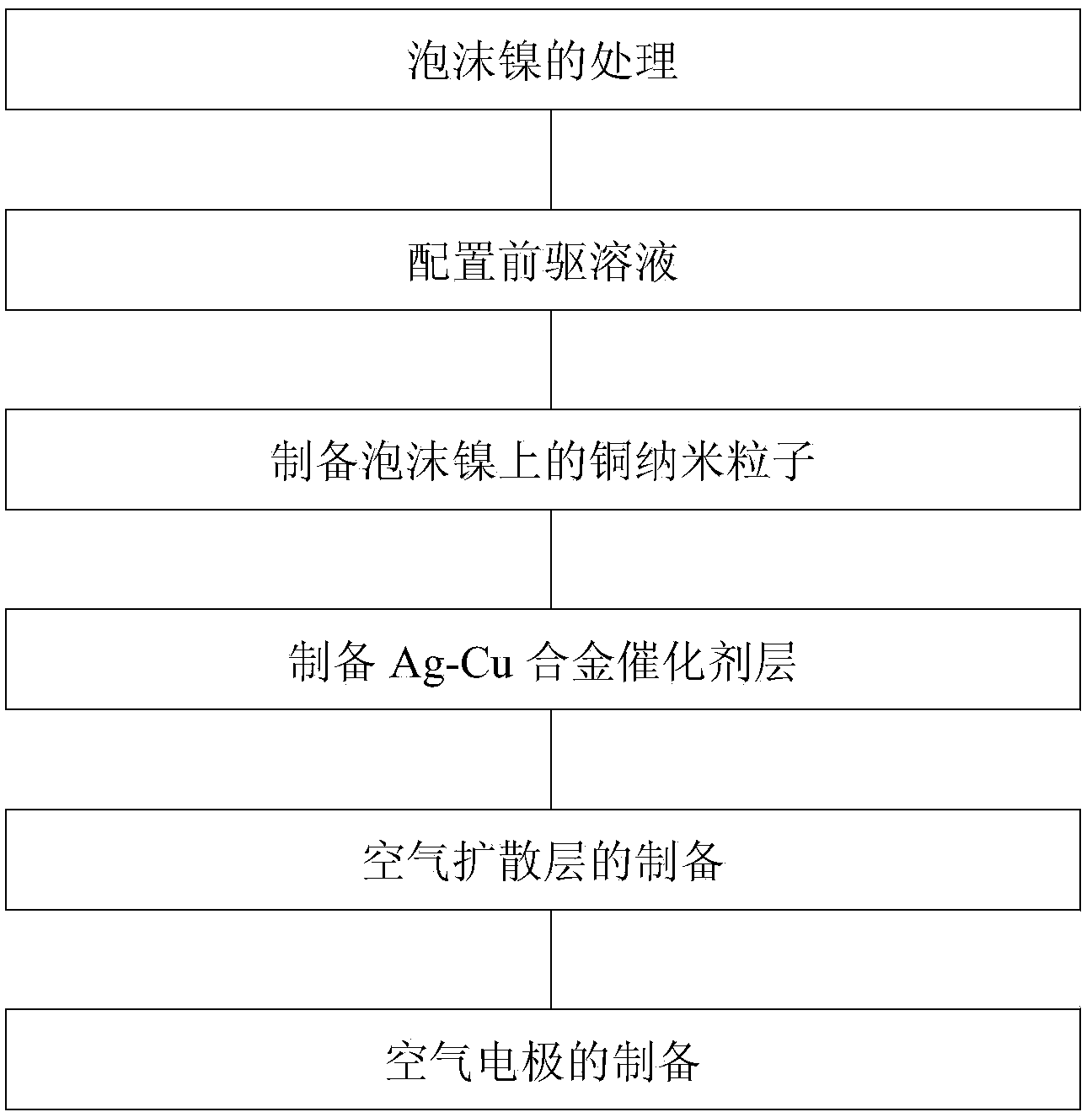
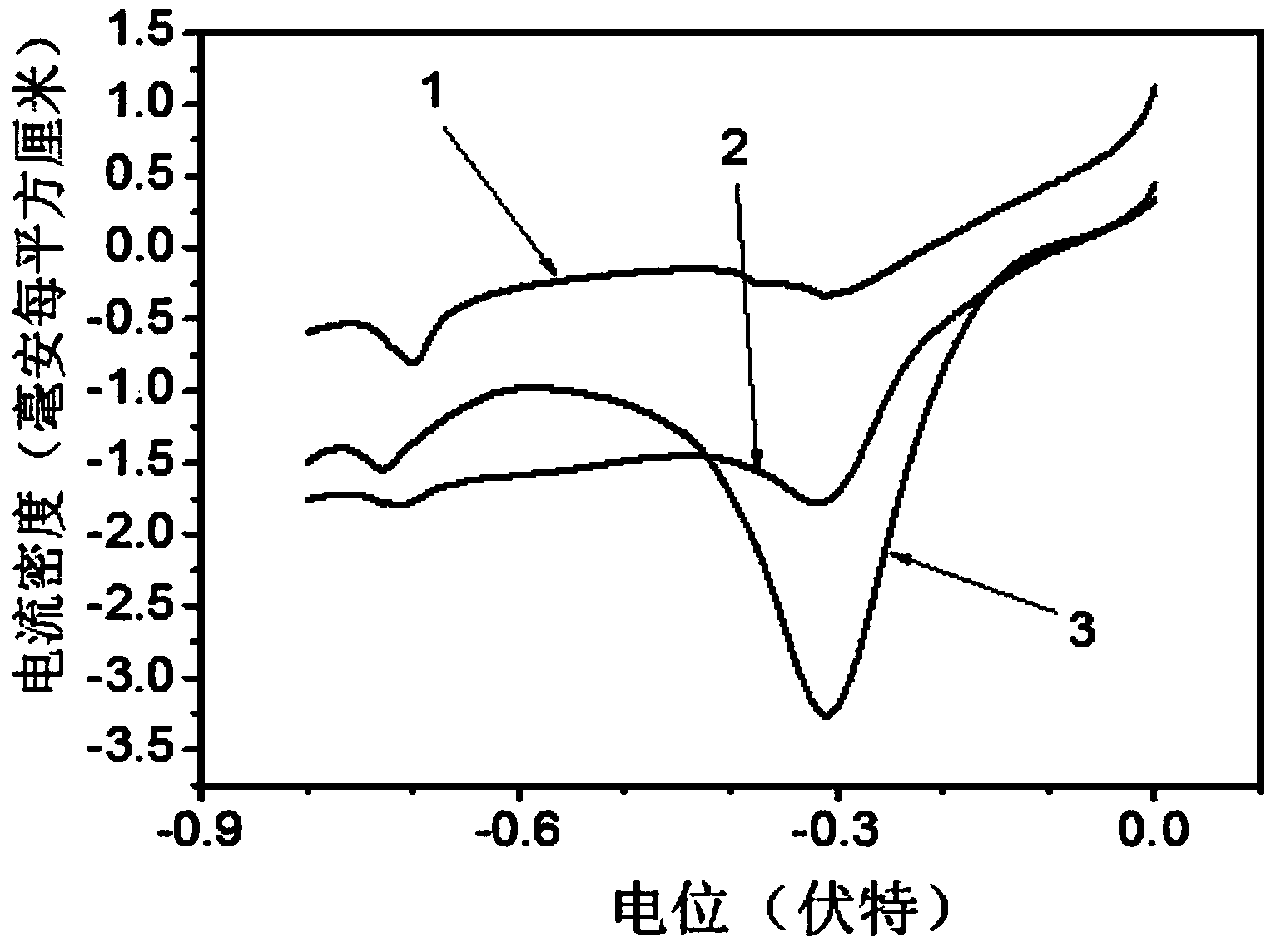
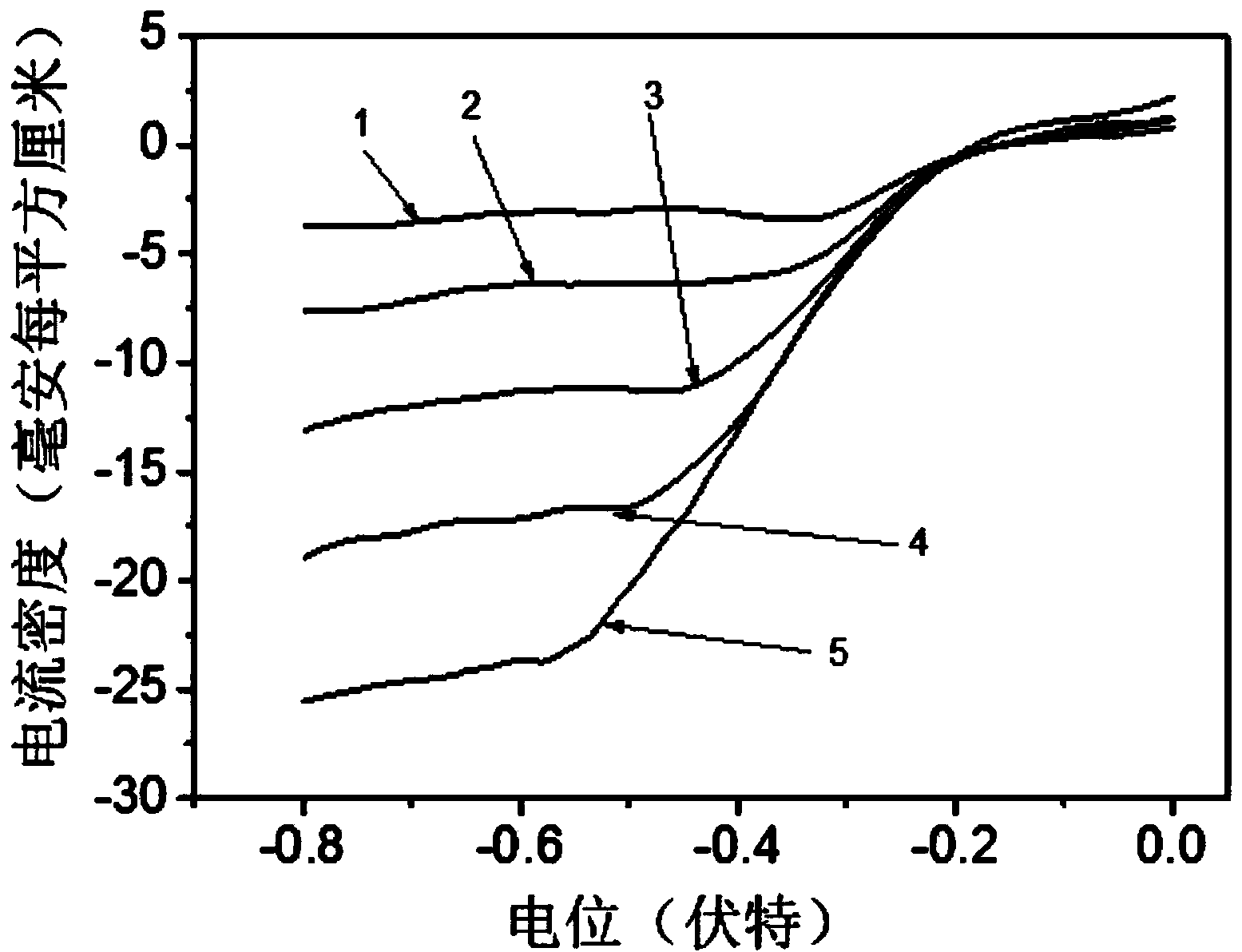
Carbon-free Ag-Cu catalyst layer-based air electrode and its making method
ActiveCN104393307AImprove electrocatalytic activityEnhanced electrocatalytic reduction propertiesCell electrodesCarbon corrosionCopper oxide
The invention relates to a carbon-free Ag-Cu catalyst layer-based air electrode and its making method. The carbon-free Ag-Cu catalyst layer-based air electrode is obtained by depositing Ag-Cu alloy on foamed nickel; the microstructure of the Ag-Cu alloy is dendrite or spherocrystal or lamella crystal; and a Ag, Cu and Cu2O phase exists in the Ag-Cu alloy and is composed of Ag in zero valence state and Cu, and a copper oxide layer is arranged on the surface of the Ag-Cu alloy. The discharge power of the primary zinc air battery of the Ag-Cu catalyst air electrode under 100mA / cm<2> is 79.9-85.8mW.cm<-2>, and the charge and discharge reciprocating efficiency of the secondary zinc air battery of the Ag-Cu catalyst air electrode is greater than 51.8%. The catalyst layer has a very good oxygen reduction electrocatalysis property and overcomes the disadvantages of carbon corrosion and low electrocatalytic activity in the prior art.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Zinc/air cell
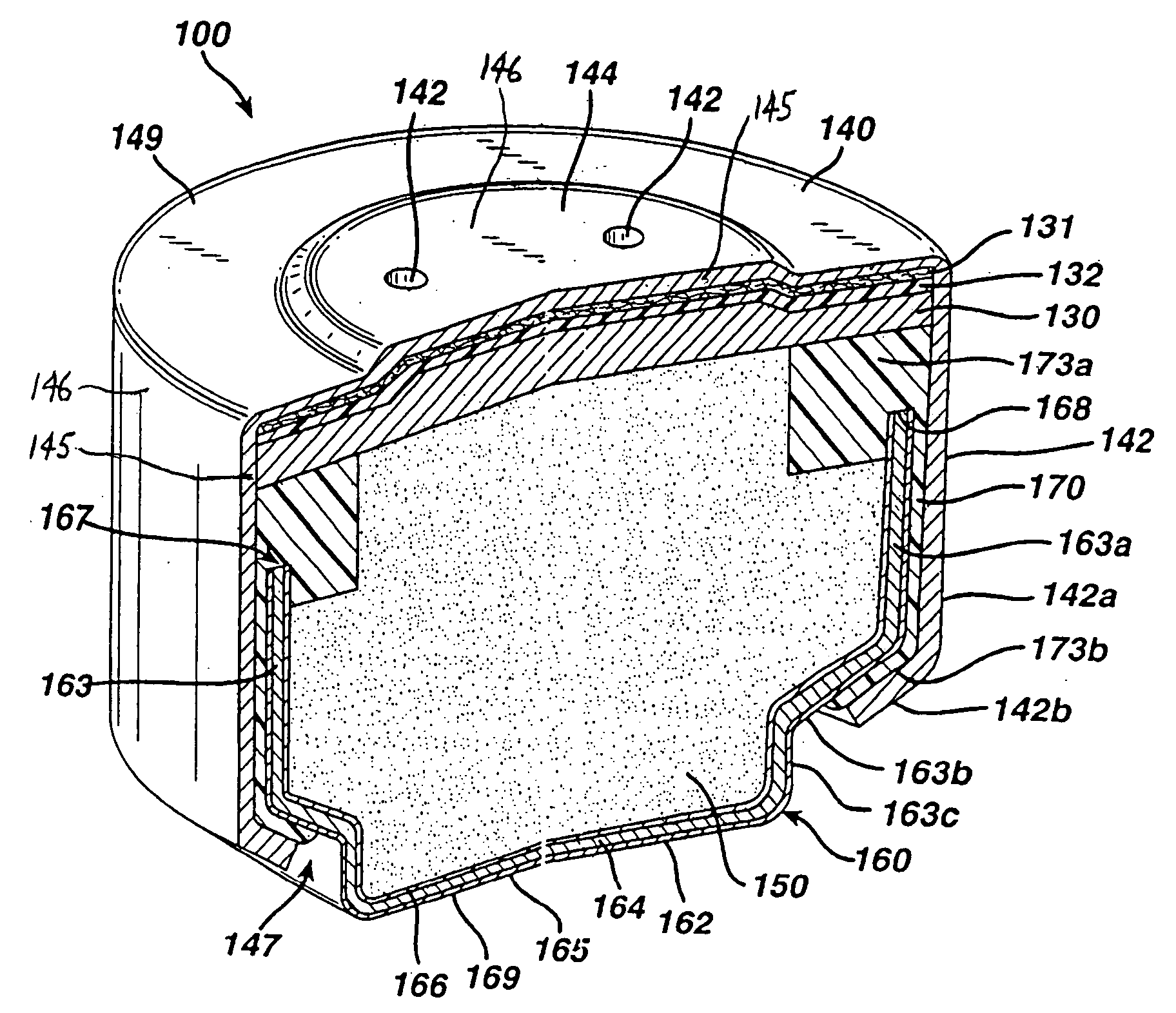
ActiveUS20060115724A1Contact area reliableImprove contact reliabilityFuel and primary cellsJackets/cases materialsHardnessHearing aid
A zinc-air cell with an anode cup comprising anode active material and a cathode cup comprising catalytic or cathode active material wherein the cathode cup comprises an exposed nickel layer which has been softened to improve electrical contact with the device being powered such as a hearing aid. A cathode cup in desired shape and size is formed of a substrate metal such as cold rolled steel or stainless steel. A nickel layer is plated onto the cathode cup substrate metal and is subsequently heat treated resulting in reduction in the surface hardness of the nickel layer. This improves the reliability of the electrical contact between the cathode cup and the corresponding terminal in the hearing aid or other device being powered.
Owner:DURACELL U S OPERATIONS
Carbon-loaded pyridine-nitrogen-modified cobalt-phthalocyanine catalyst, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102489328AHigh activityEffective activation of molecular oxygenCell electrodesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsFuel cellsNitrogen
The invention relates to a carbon-loaded pyridine-nitrogen-modified cobalt-phthalocyanine catalyst, and a preparation method and application thereof. The catalyst comprises a carbon material, pyridine or pyridine derivative and cobalt-phthalocyanine in mass ratio of 1:(0.01-1):(0.01-1). The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) dissolving the carbon material, the pyridine or pyridine derivative and the cobalt-phthalocyanine in a solvent, grinding until methanol is completely volatilized, and drying to obtain catalyst precursor; and (2) performing roasting reduction on the precursor under the protective atmosphere of nitrogen to obtain the carbon-loaded pyridine-nitrogen-modified cobalt-phthalocyanine catalyst. Carbon-loaded nano cobalt-phthalocyanine is modified by pyridine nitrogen, so molecular oxygen can be activated effectively, and electrode activity is greatly improved; and the operation condition and the preparation process are easy, and the catalyst is easy to prepare, is low in cost, and can be used for commercial production of fuel cells and zinc air batteries; and dependence on noble metal Pt is greatly reduced.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Ag / C catalytic agent used for zinc air battery and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103151538AHigh catalytic activity for oxygen reductionImprove stabilityCell electrodesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystElectrical battery
The invention relates to an Ag / C catalytic agent used for a zinc air battery and a preparation method thereof. The Ag / C catalytic agent used for the zinc air battery is made of silver salt and uses polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) as a protective agent. The Ag / C catalytic agent used for the zinc air battery is prepared by deoxidation of the silver salt using NaBH4 as a reducing agent. The mass ratio of the protection agent to the silver salt is 0.1:1-15:1 in a process of preparing the catalytic agent. The mass ratio of the Ag to C in the catalytic agent is 98:2-40:60. When the method is adopted to prepare the Ag / C catalytic agent, process is simple, mass production is available, materials which can pollute the environment are not used in the preparing process, and the environment is protected. The Ag / C catalytic agent prepared with the method is used in the zinc air battery, and performance is excellent.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com